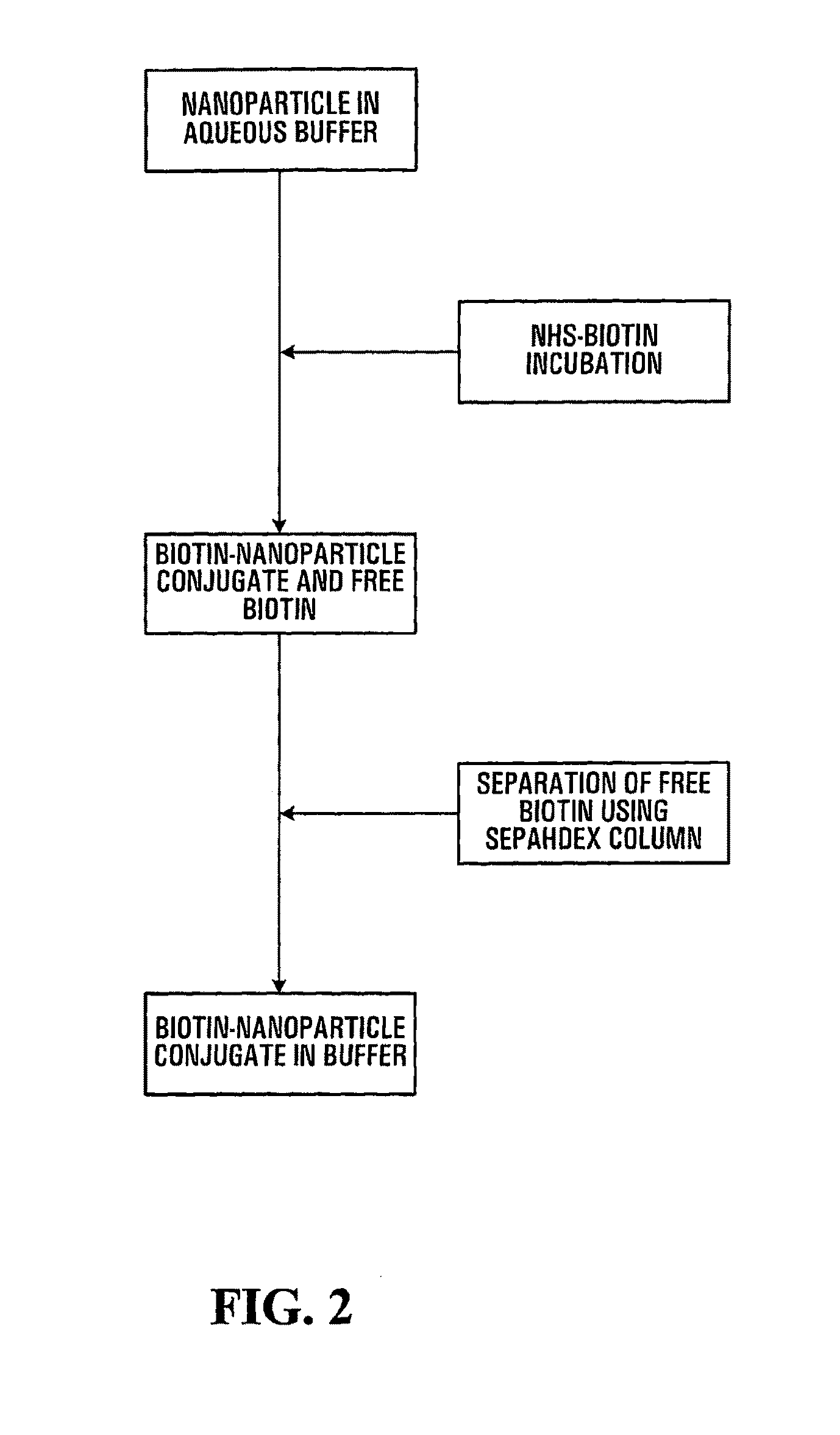
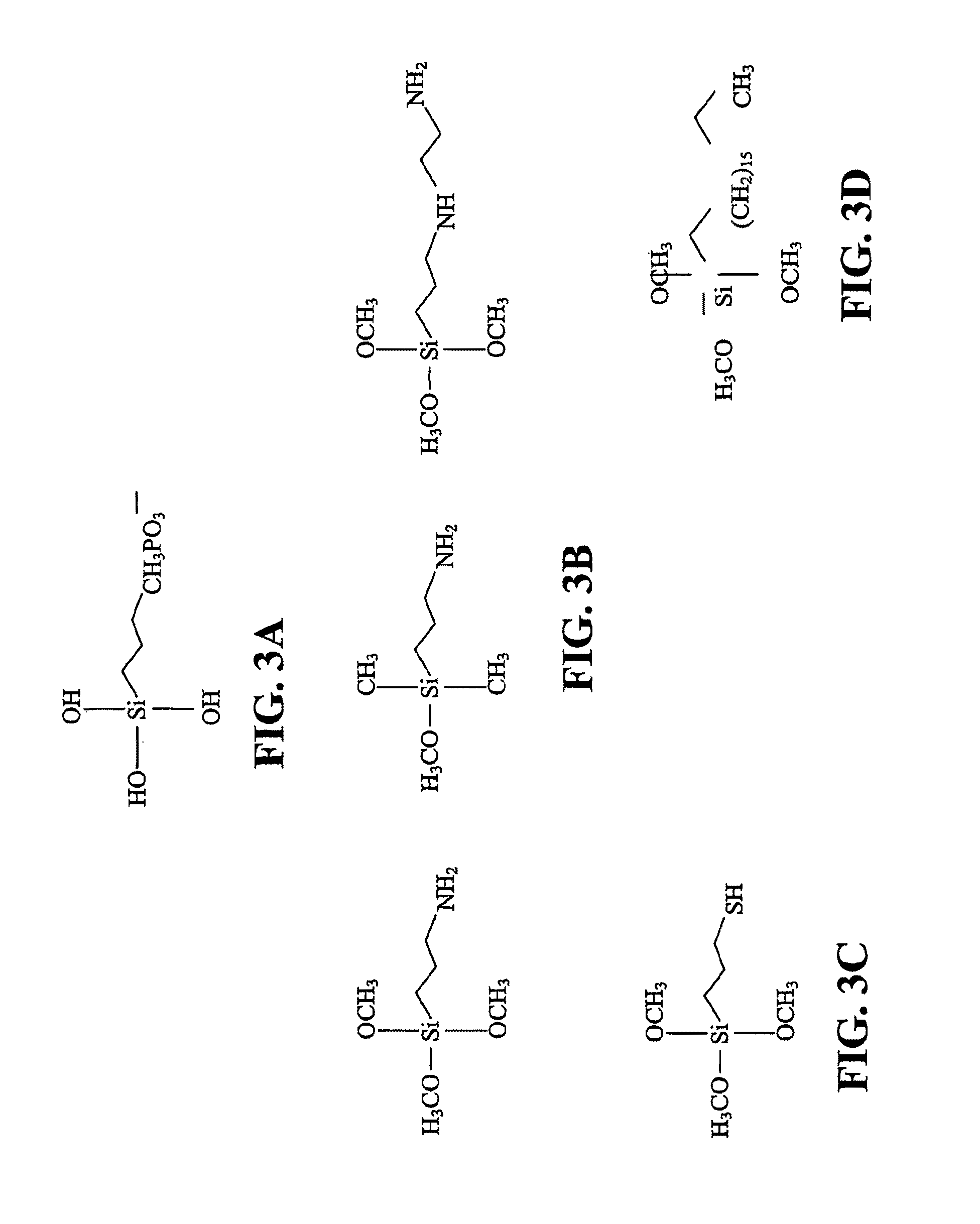
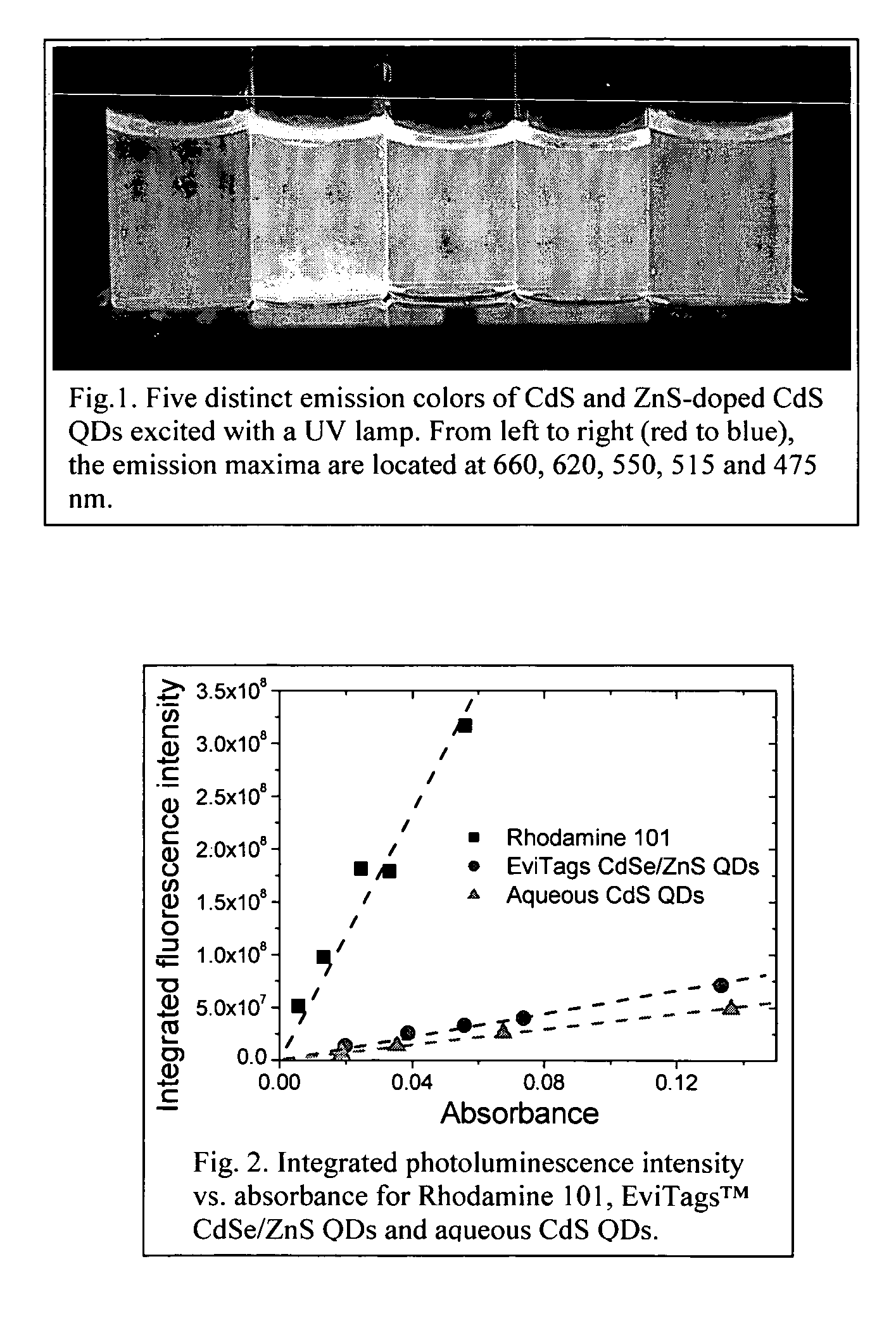
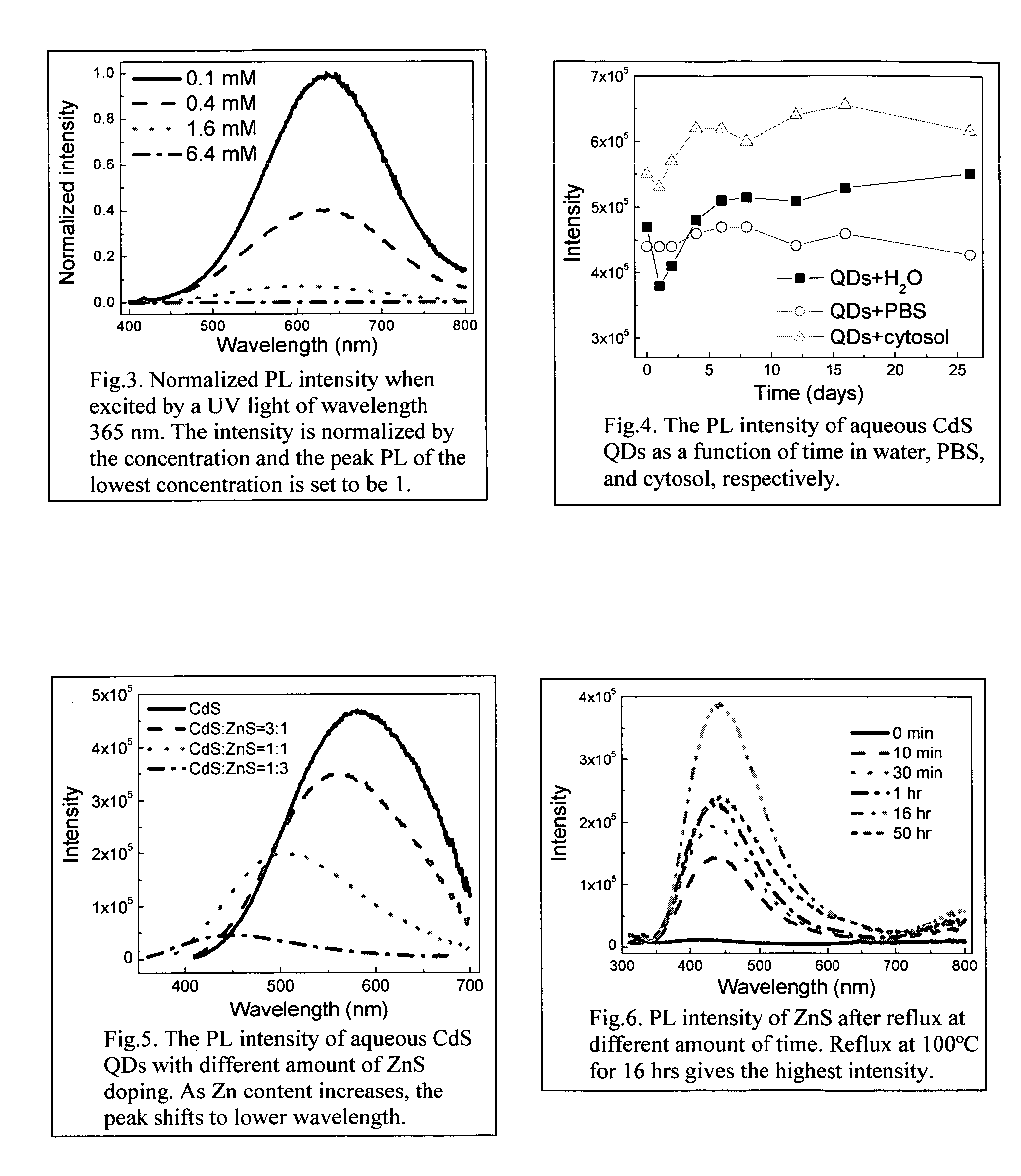
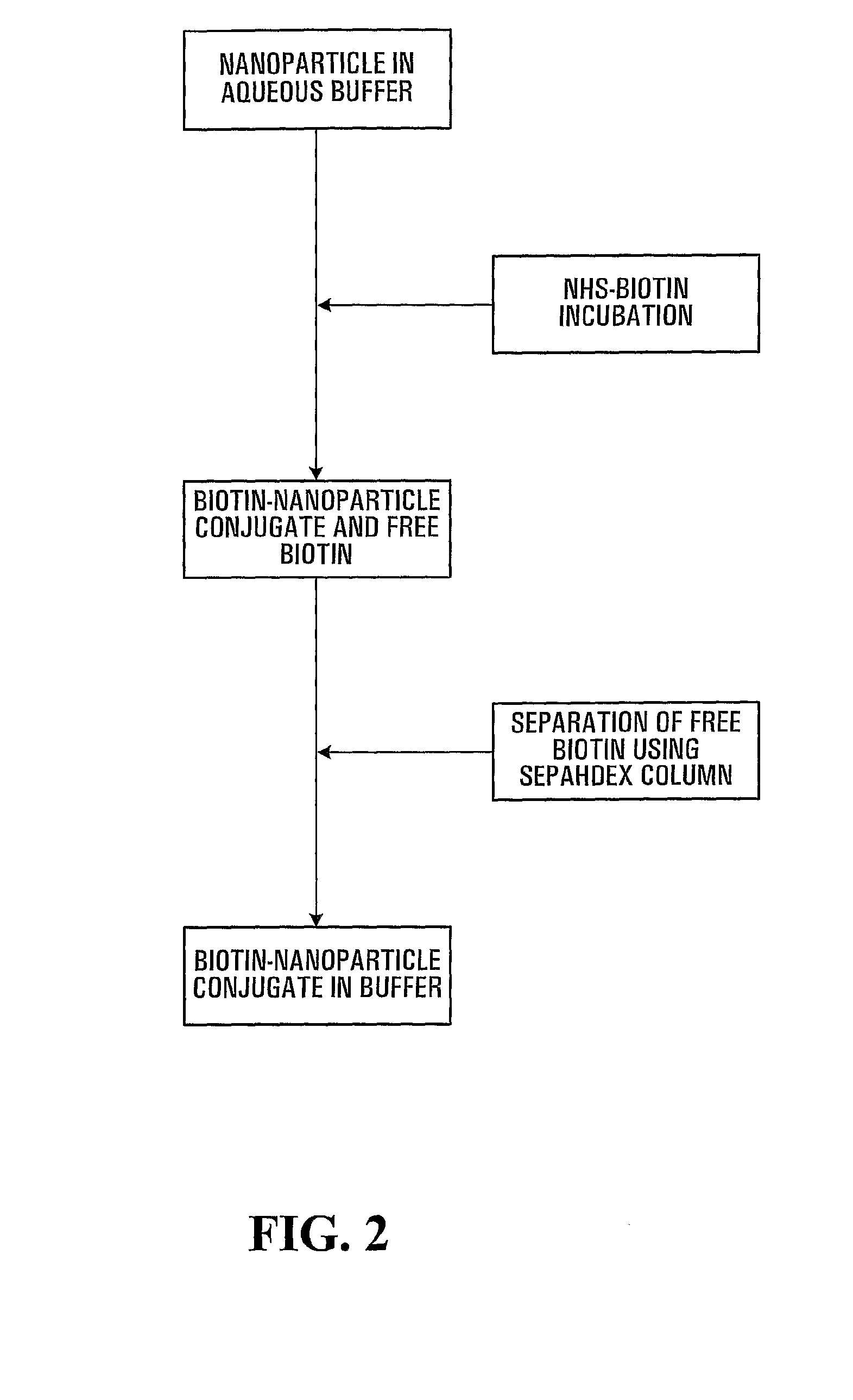
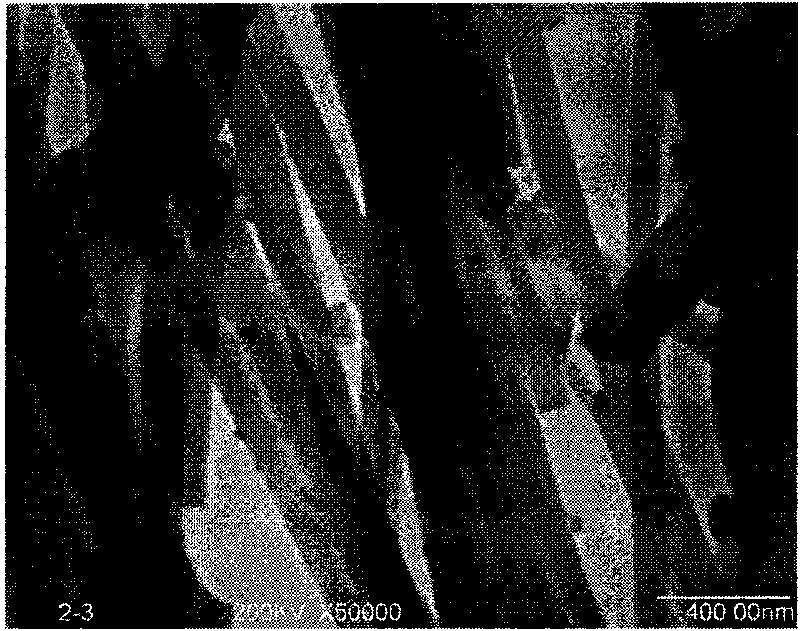Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Bioconjugation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioconjugation is a chemical strategy to form a stable covalent link between two molecules, at least one of which is a biomolecule.
Functionalized chromophoric polymer dots and bioconjugates thereof
ActiveUS20120282632A1Reduces non-specific adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiological testingCombinatorial chemistryIn vivo
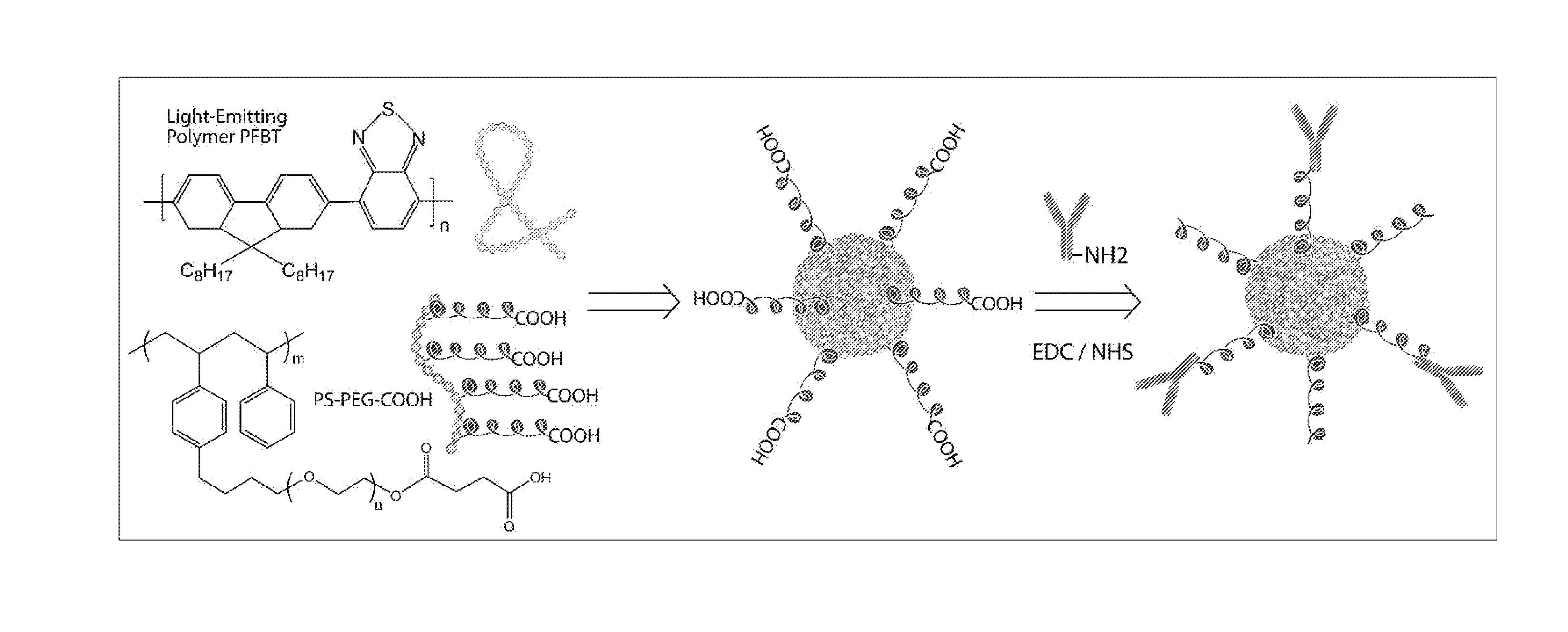
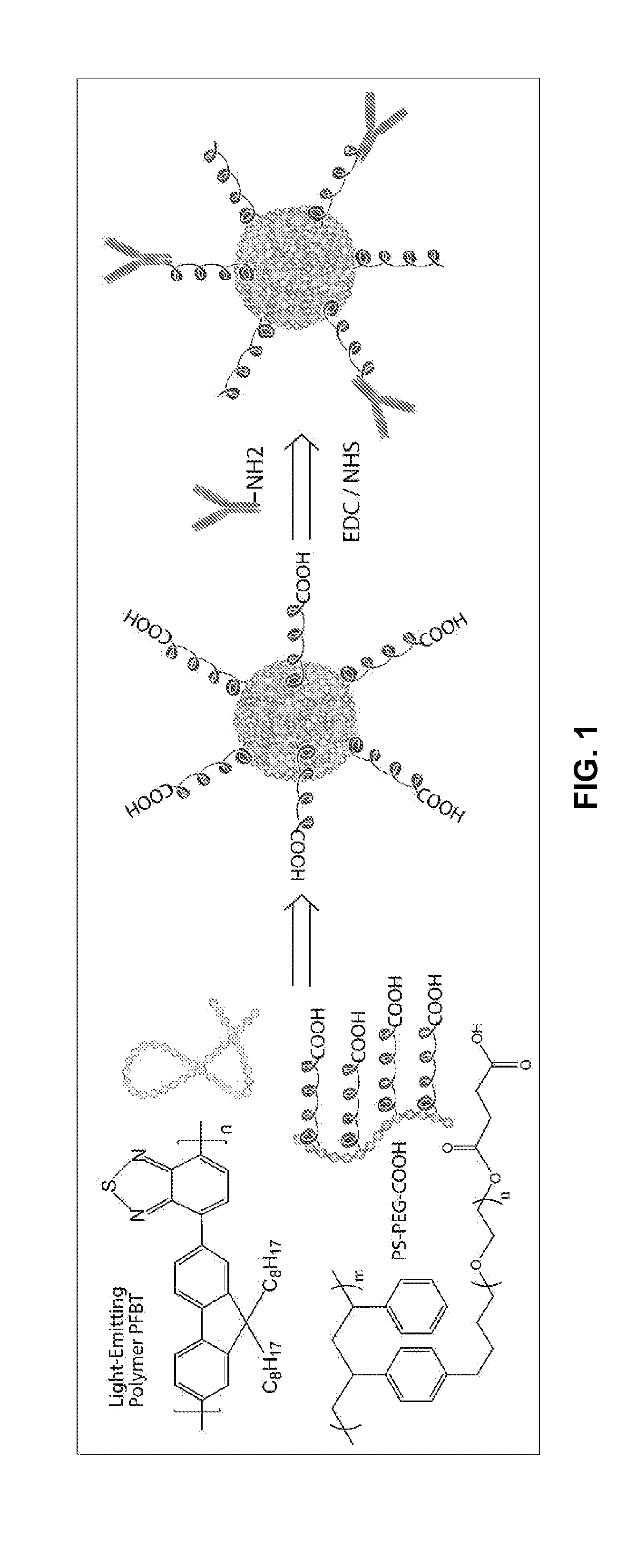
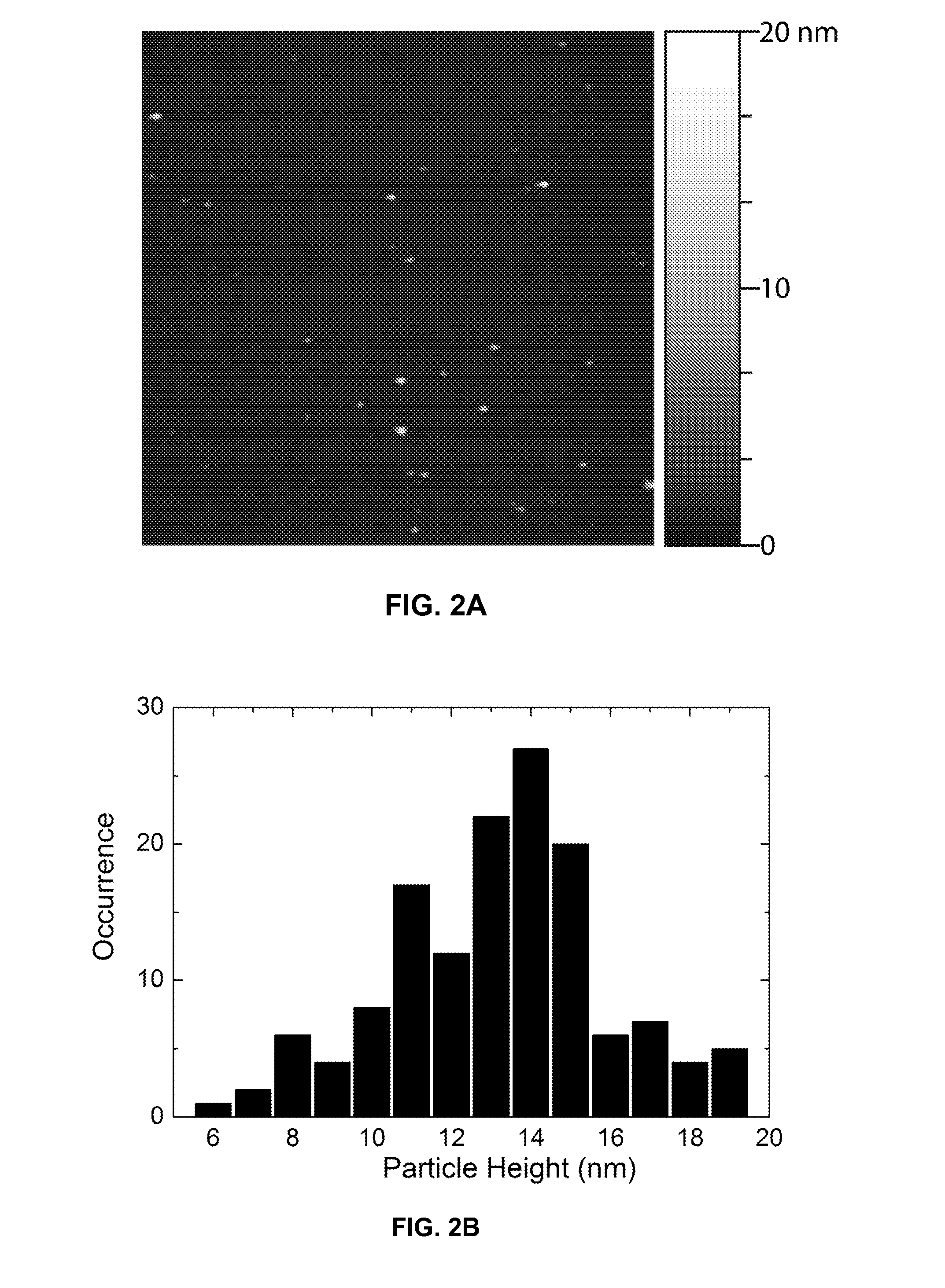
The present invention provides, among other aspects, functionalized chromophoric polymer dots comprising a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic cap, and bioconjugates thereof. Also provided are improved methods for preparing functionalized chromophoric polymer dots. Methods for in vivo imaging and molecular labeling are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Method for Production of Radioisotope Preparations and Their Use in Life Science, Research, Medical Application and Industry
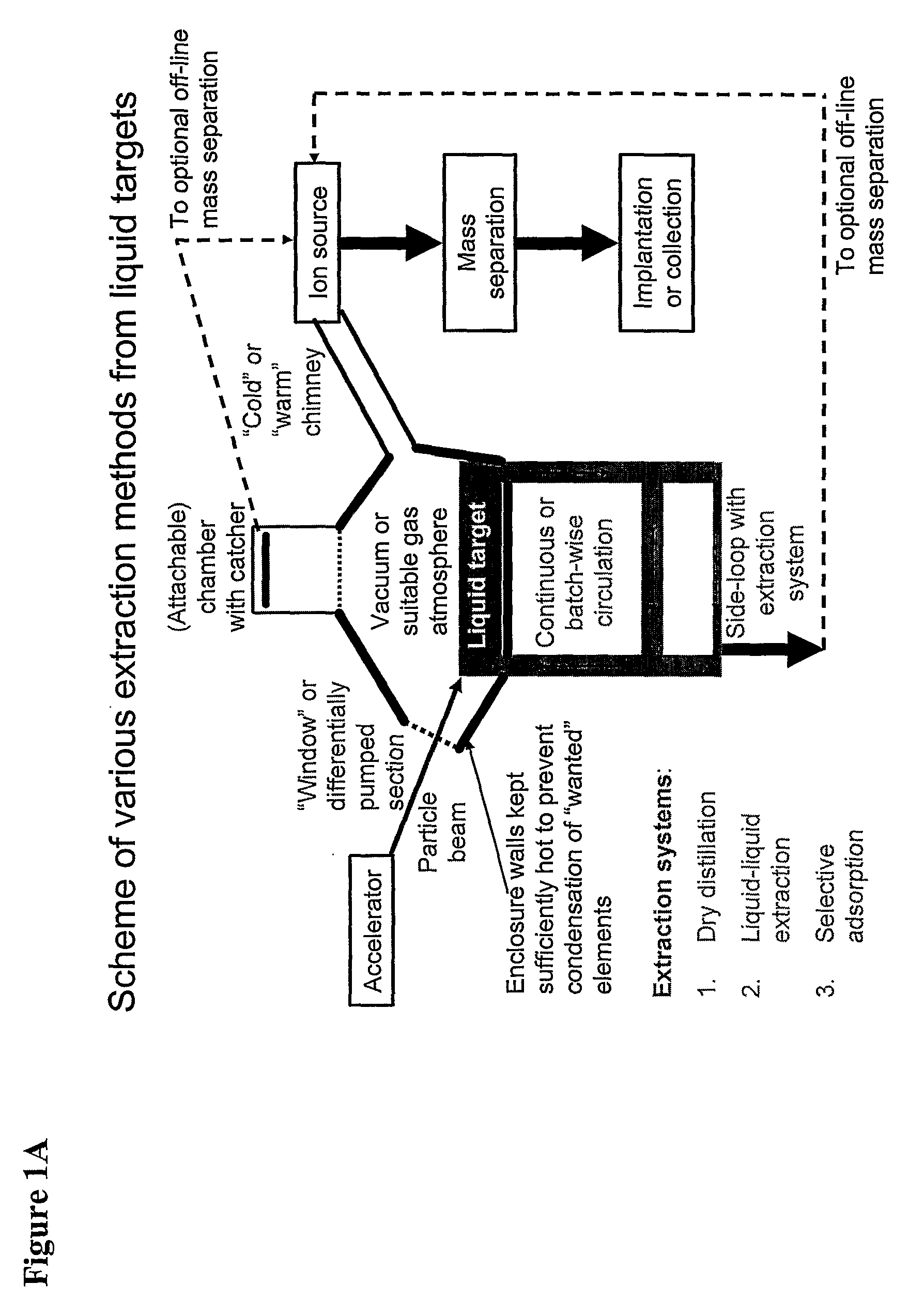
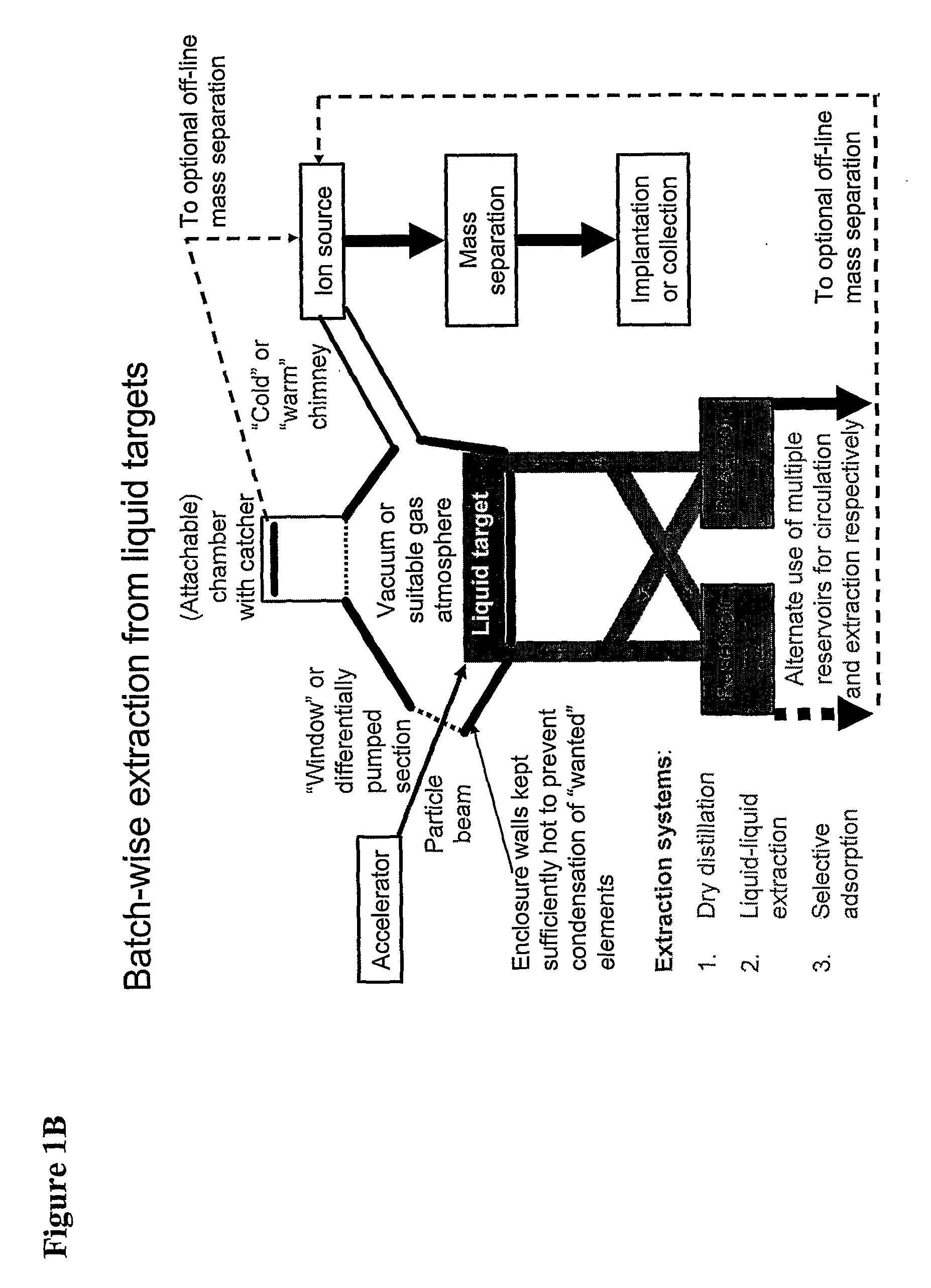
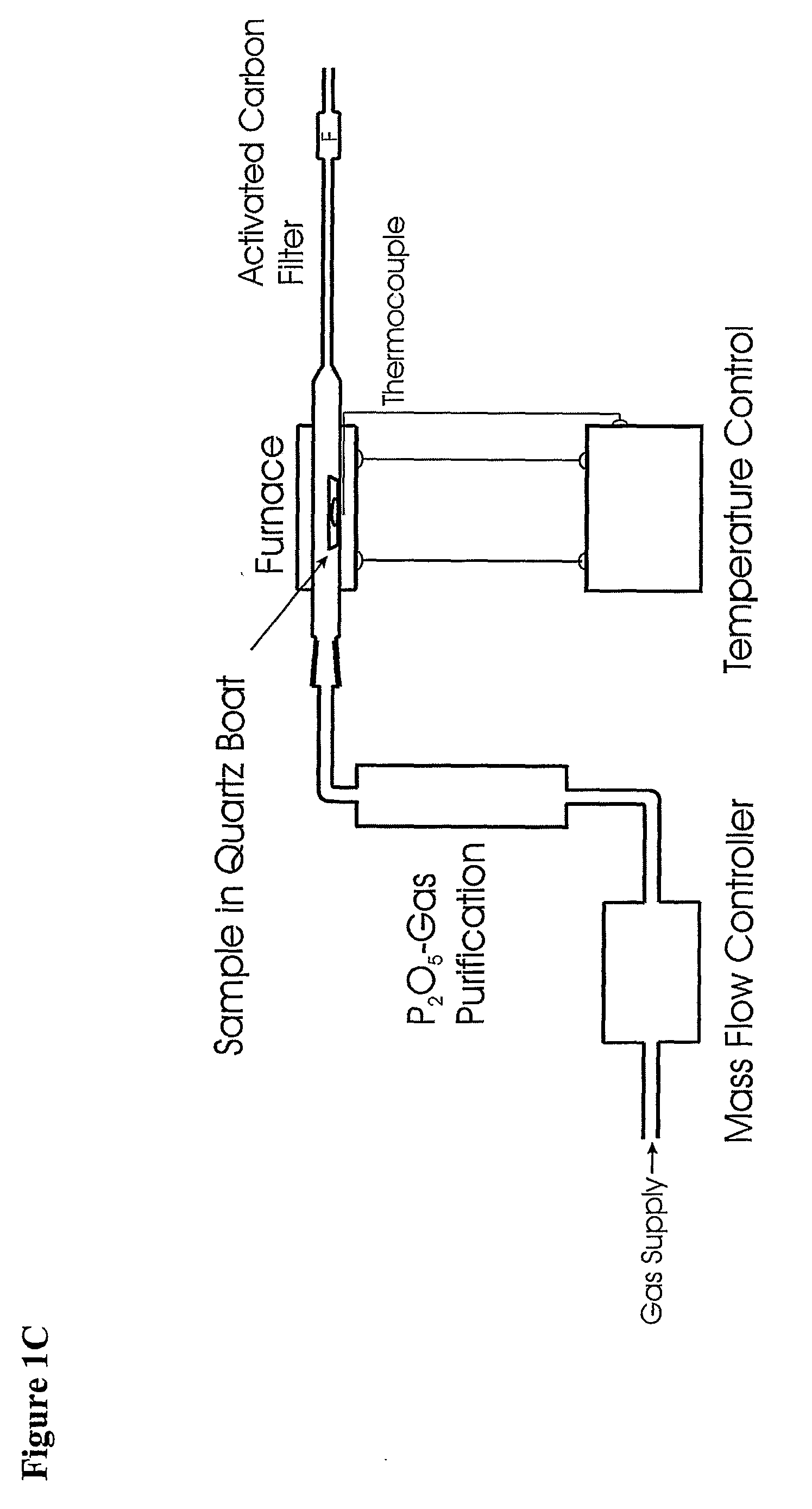
The present invention relates to an universal method for the large scale production of high-purity carrier free or non carrier added radioisotopes by applying a number of “unit operations” which are derived from physics and material science and hitherto not used for isotope production. A required number of said unit operations is combined, selected and optimised individually for each radioisotope production scheme. The use of said unit operations allows a batch wise operation or a fully automated continuous production scheme. The radioisotopes produced by the inventive method are especially suitable for producing radioisotope-labelled bioconjugates as well as particles, in particular nanoparticles and microparticles.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH +1
Fluorescent imaging with substituted cyanine dyes
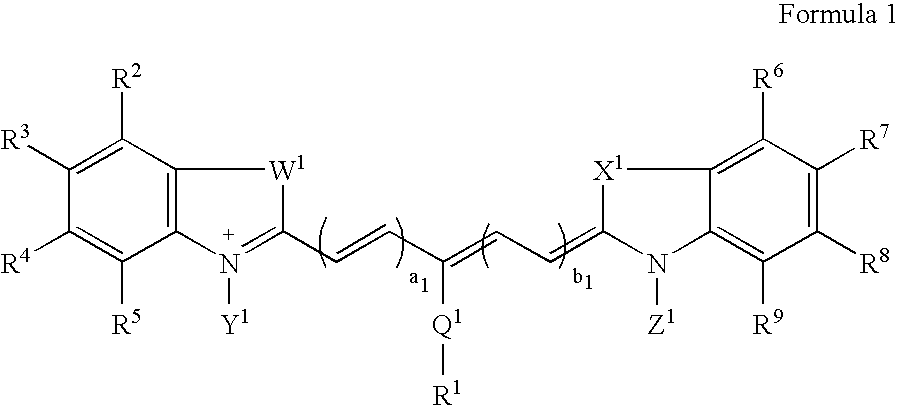
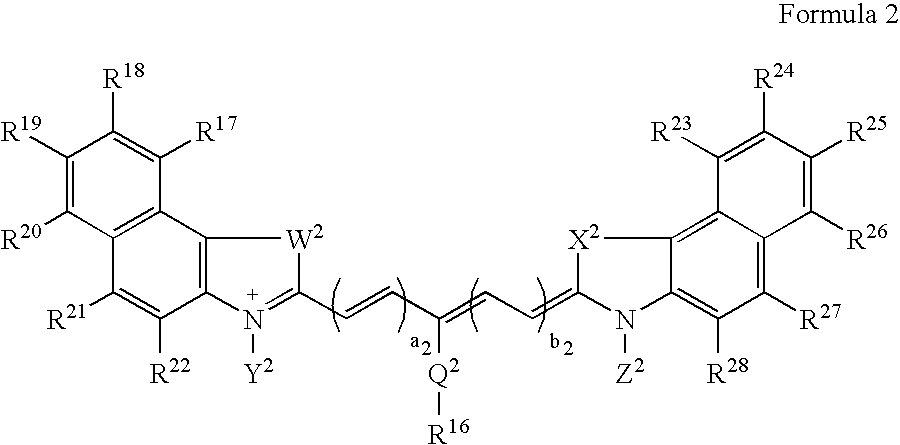
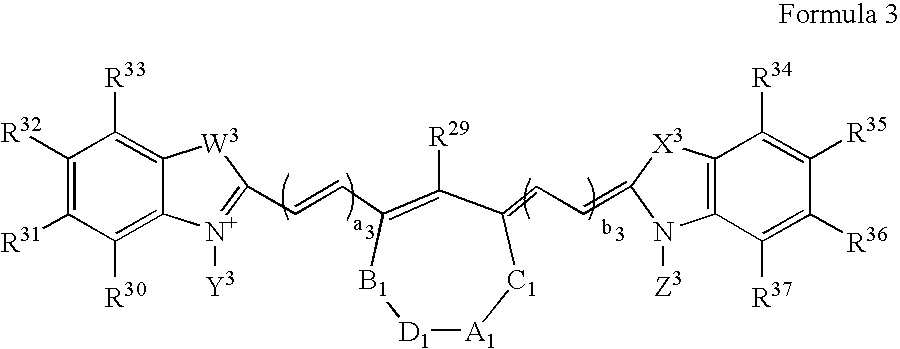
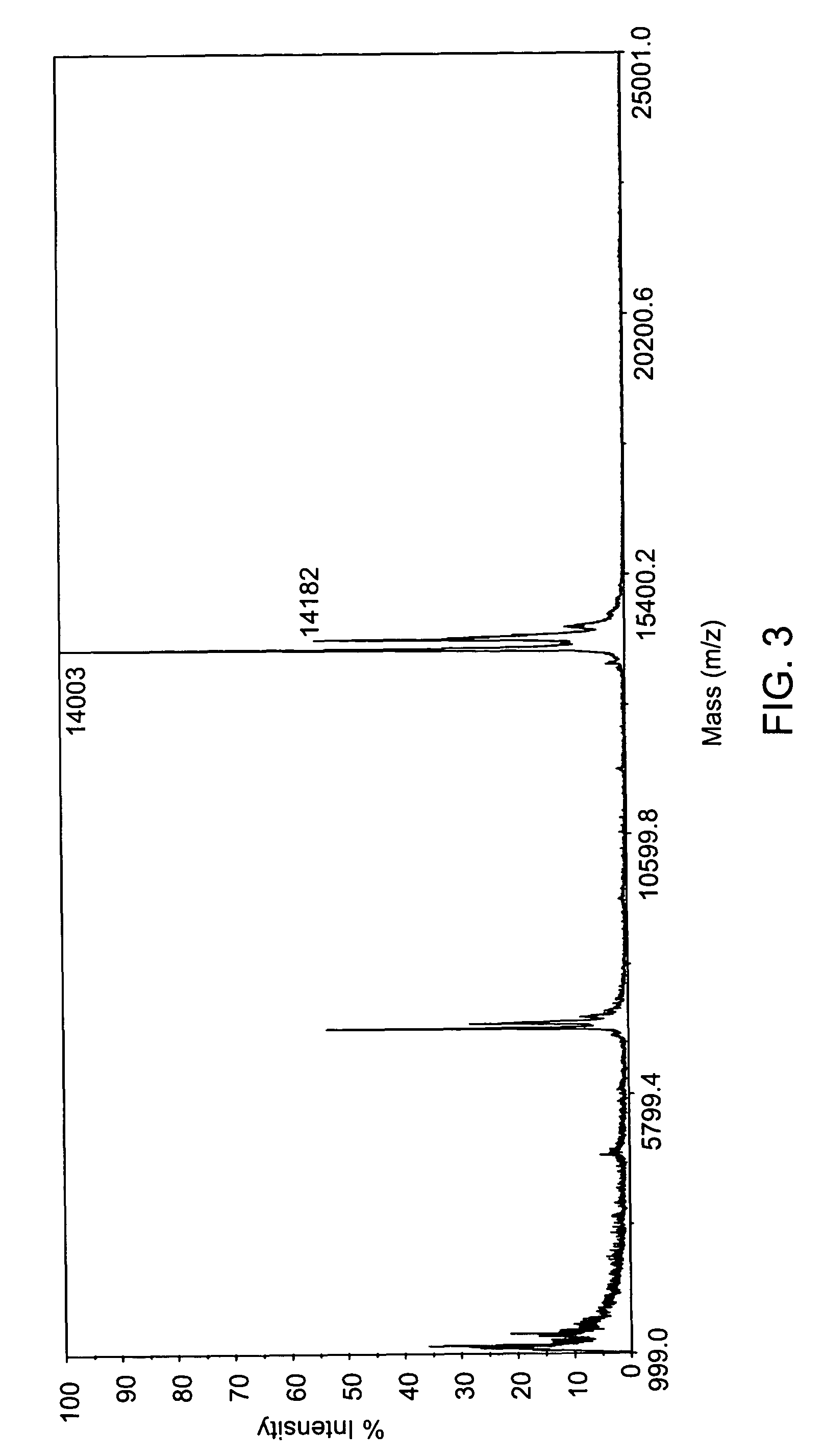
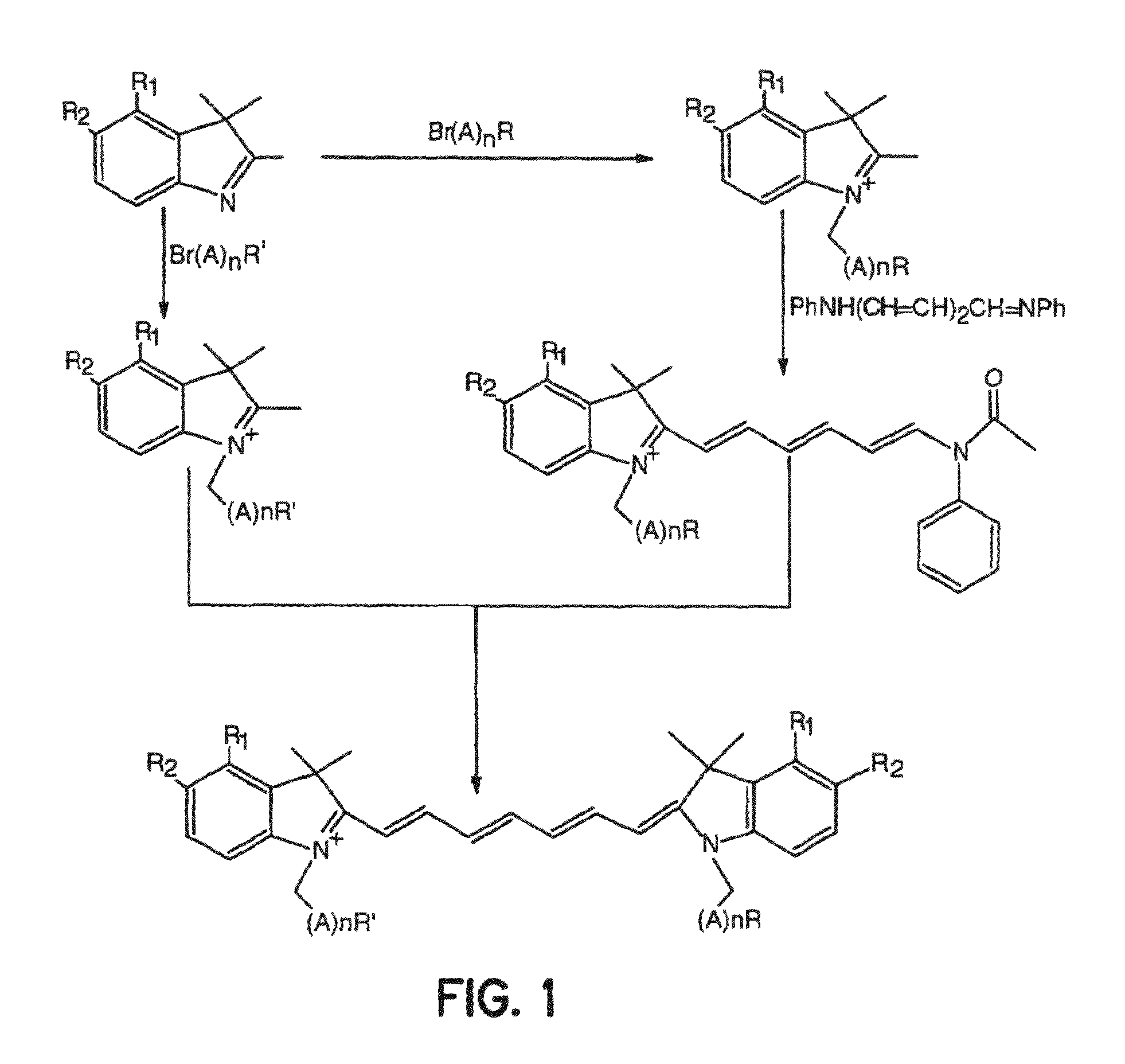
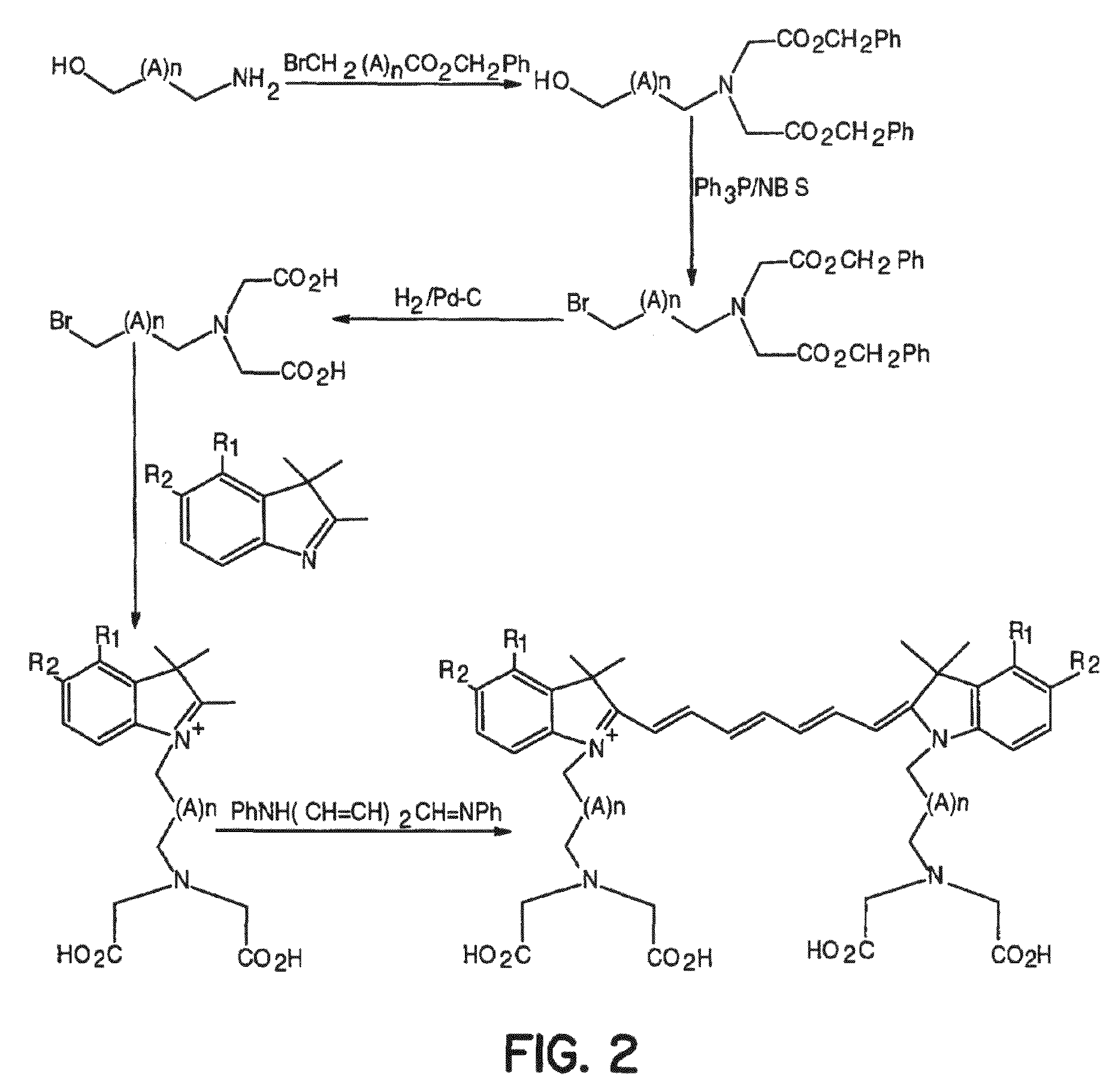
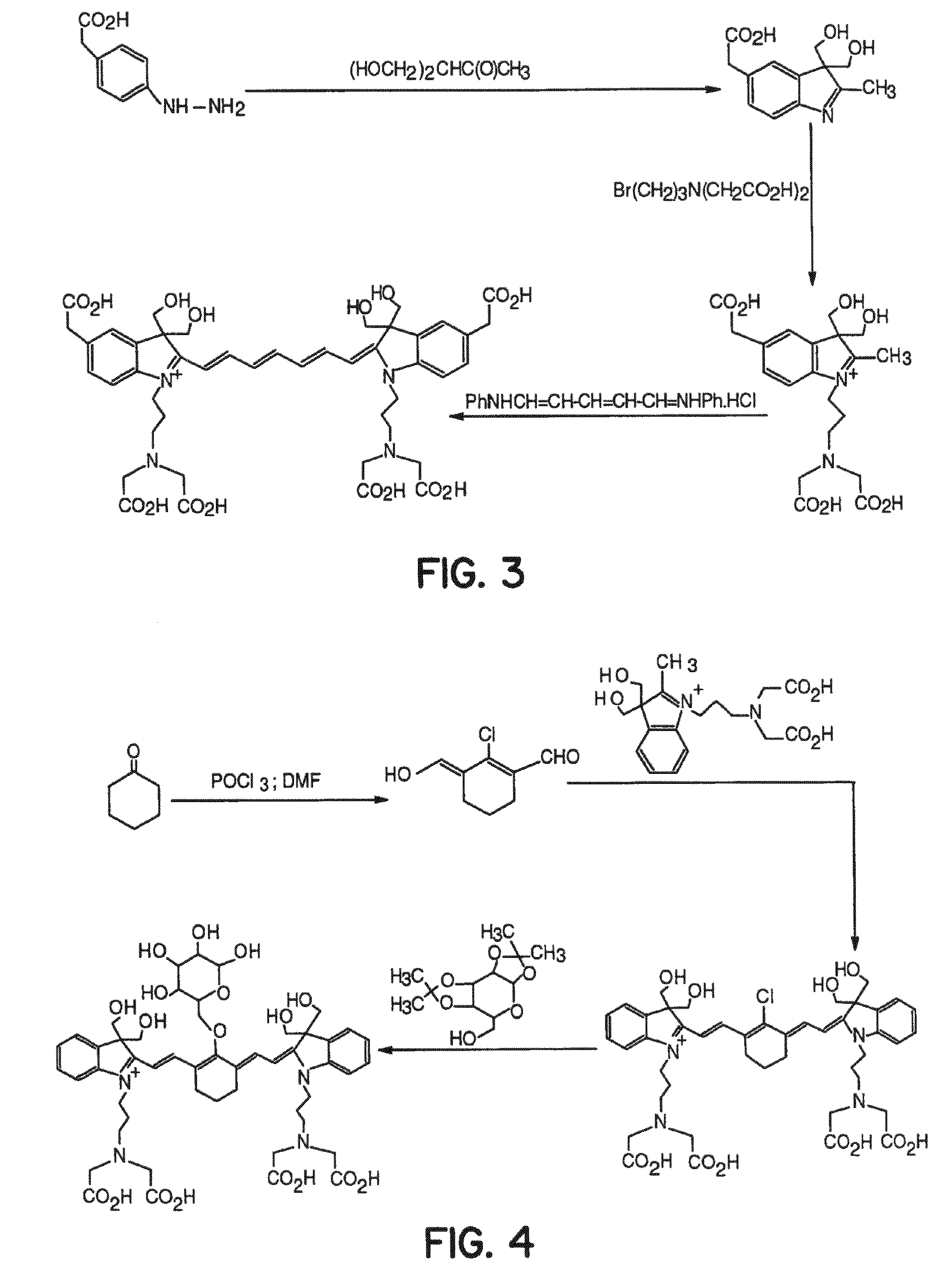
Compounds and methods are disclosed that are useful for noninvasive imaging in the near-infrared spectral range. The cyanine compounds of Formula I are presented:wherein Q is a portion of a polymethine bridge selected from the group consisting of:Also included are bioconjugates of the compounds of Formula I, methods of labeling biomolecules with the compounds, and methods of imaging.
Owner:LI COR
Synthesis of water soluble nanocrystalline quantum dots and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060078490A1Improved emission spectrumAccelerate emissionsMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid immunoglobulinsPhotoluminescenceSynthesis methods
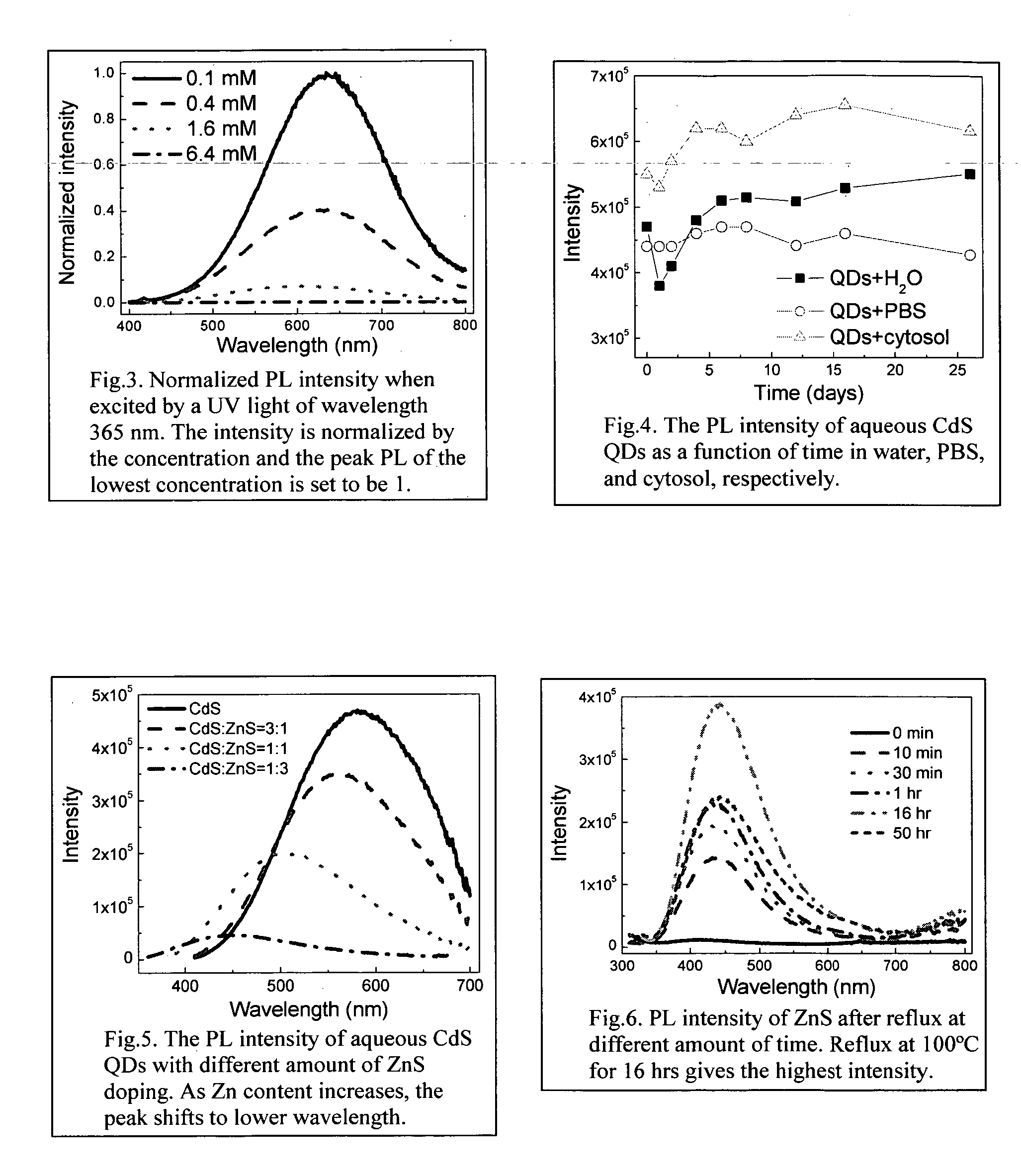
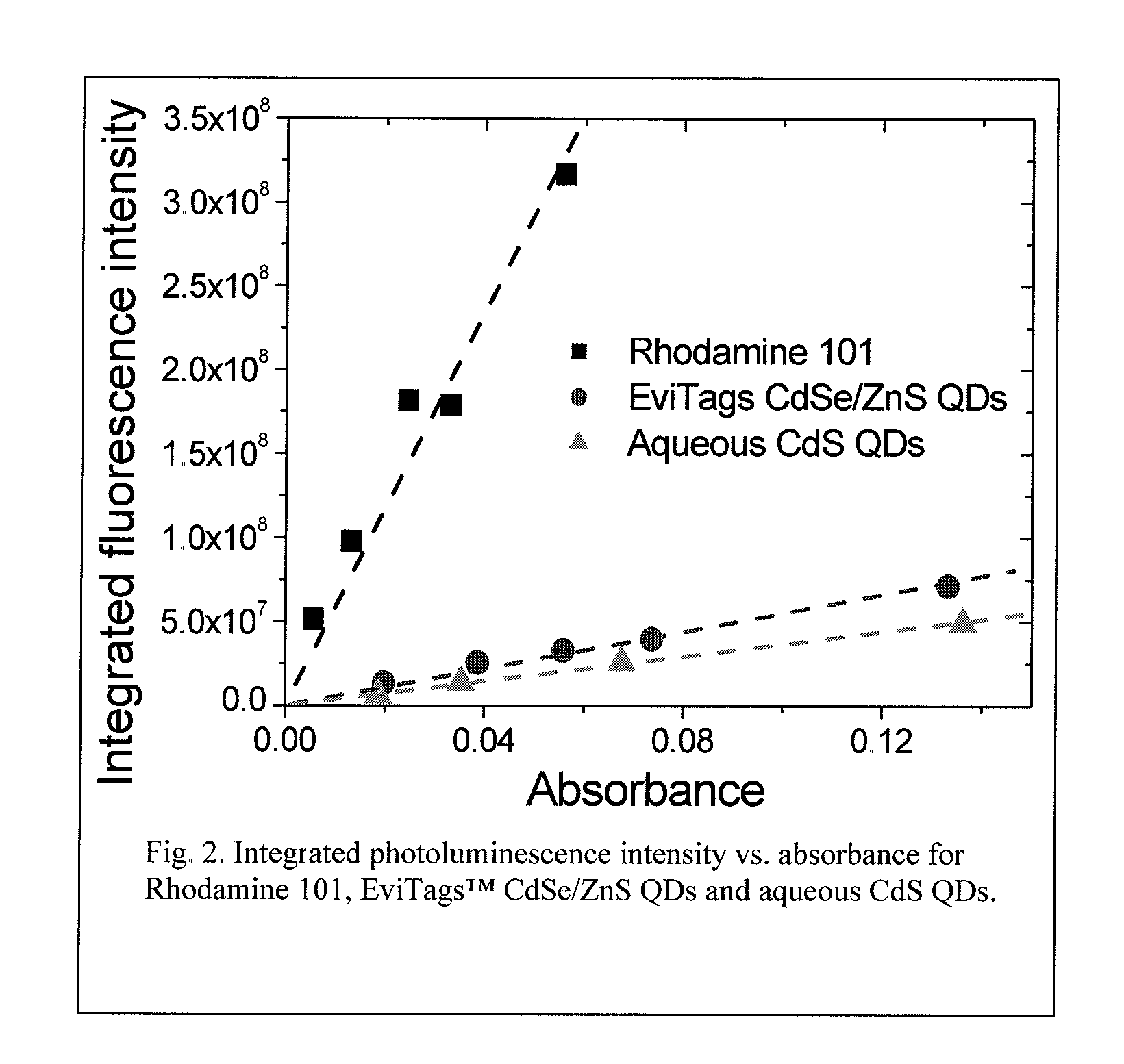
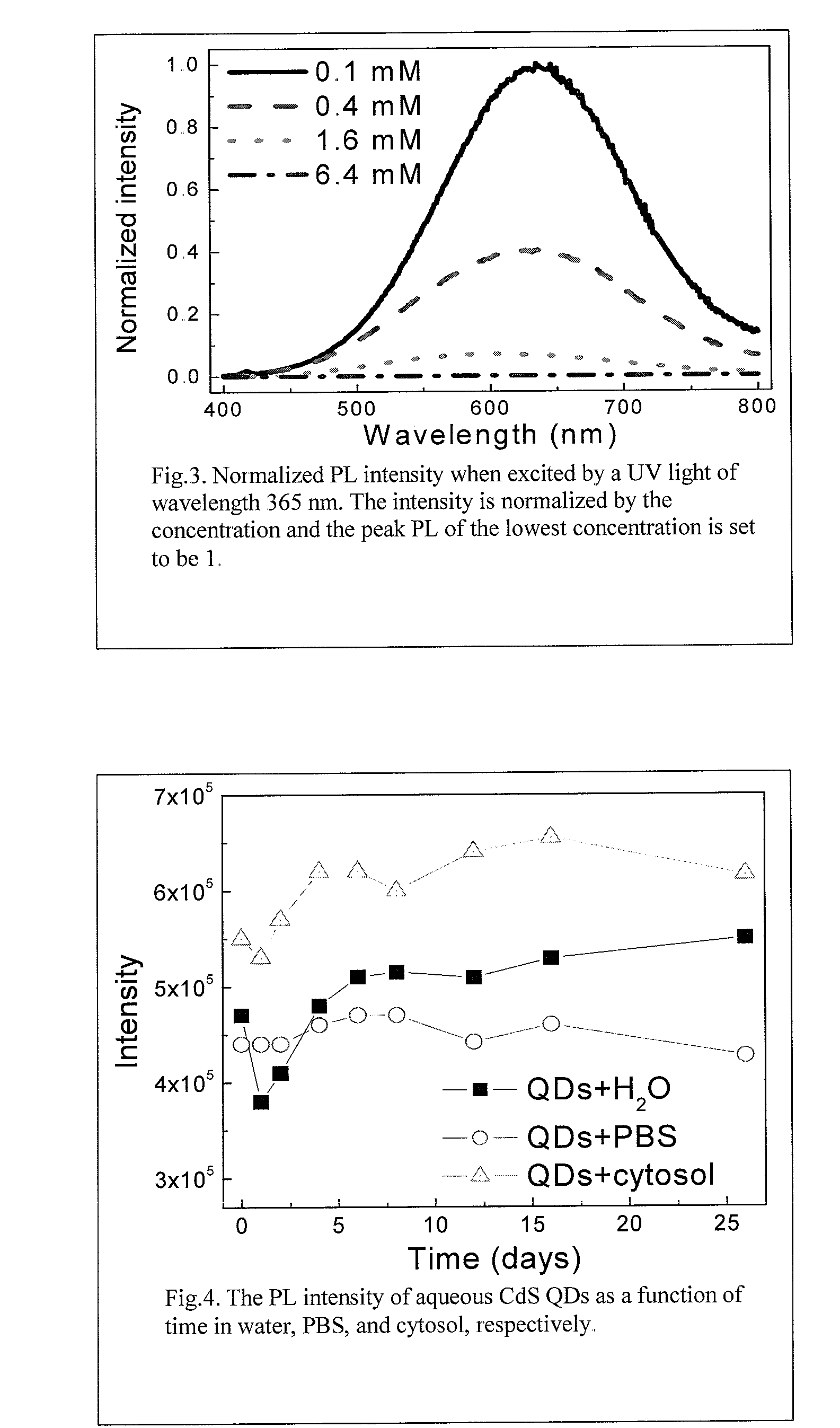
An economic, direct synthetic method for producing water soluble QDs that are ready for bioconjugation is provided. The method can produce aqueous QDs with emission wavelengths varying from 400 nm to 700 nm. Highly luminescent metal sulfide (MS) QDs are produced via an aqueous synthesis route. MS QDs are capped with thiol-containing charged molecules in a single step. The resultant MS QDs exhibit the distinctive excitonic photoluminescence desired of QDs and can be fabricated to avoid undesirable broadband emissions at higher wavelengths. This provides a significant improvement over the present complex and expensive commercial processes for the production of QDs. The aqueous QDs are stable in biological fluids over a long period of time. In addition, nontoxic ZnS QDs have been produced with good photoluminescence properties by refluxing the ZnS QD suspensions over a period of time.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Bioconjugate-nanoparticle probes
The invention provides nanoparticle-bioconjugate probes that are useful for detecting target analytes such as nucleic acids. The probes of the invention are stable towards heat and resistant to displacement by thiol containing compounds such as DTT (dithiothreitol).
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
Synthesis of water soluble non-toxic nanocrystalline quantum dots and uses thereof
An economic, direct synthetic method for producing water soluble ZnS QDs that are ready for bioconjugation is provided. The method can produce aqueous ZnS QDs with emission wavelengths varying from 400 nm to 700 nm. Highly luminescent metal sulfide (MS) QDs are produced via an aqueous synthesis route. MS QDs are capped with thiol-containing charged molecules in a single step. The resultant MS QDs exhibit the distinctive excitonic photoluminescence desired of QDs and can be fabricated to avoid undesirable broadband emissions at higher wavelengths. The aqueous ZnS QDs are stable in biological fluids over a long period of time. In addition, non-toxic ZnS QDs have been produced with good photoluminescence properties.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Engineered Biological Matrices
InactiveUS20070141105A1Improve mobilityPowder deliveryCell culture supports/coatingBoronic acidMatrix strength
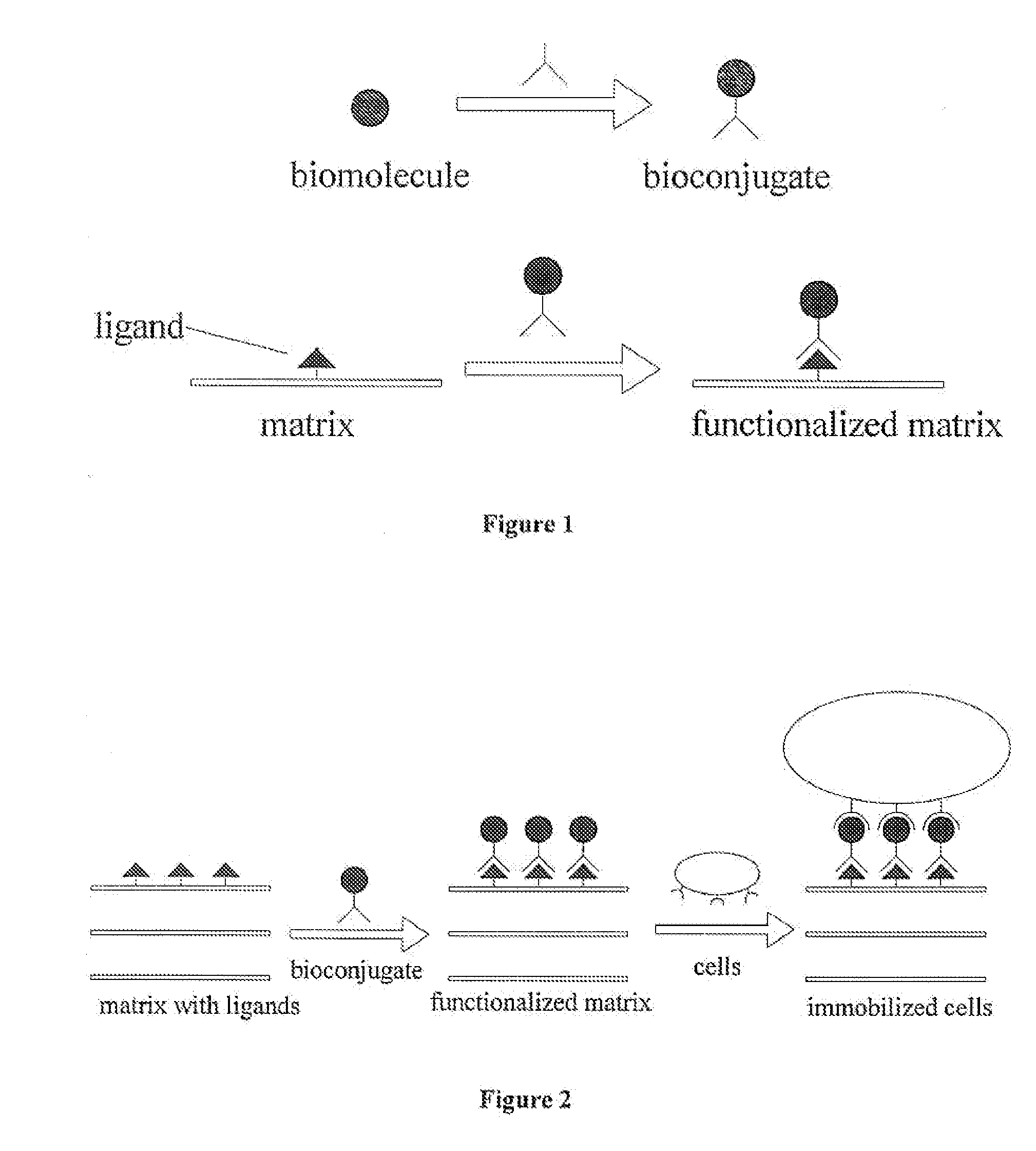
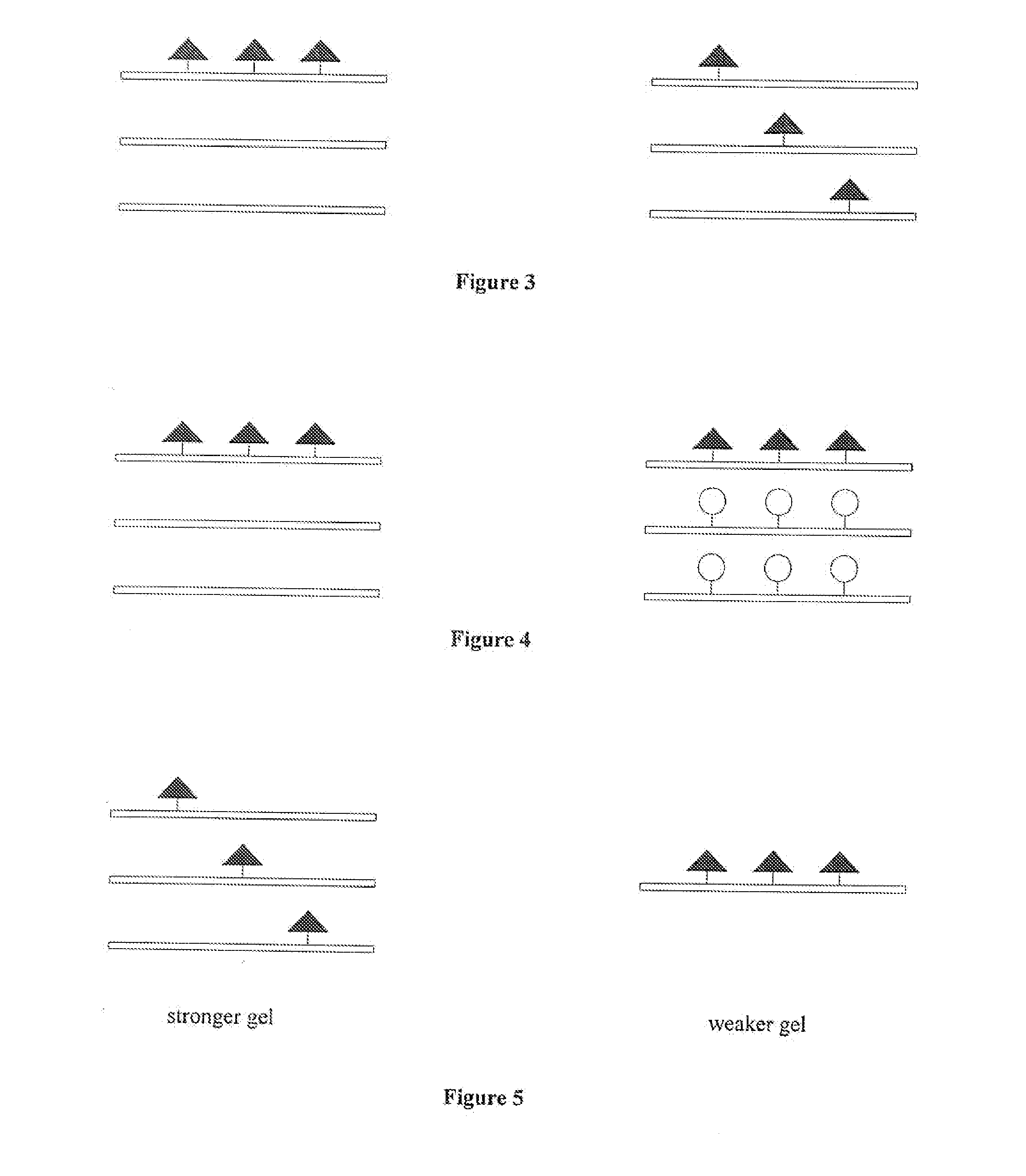
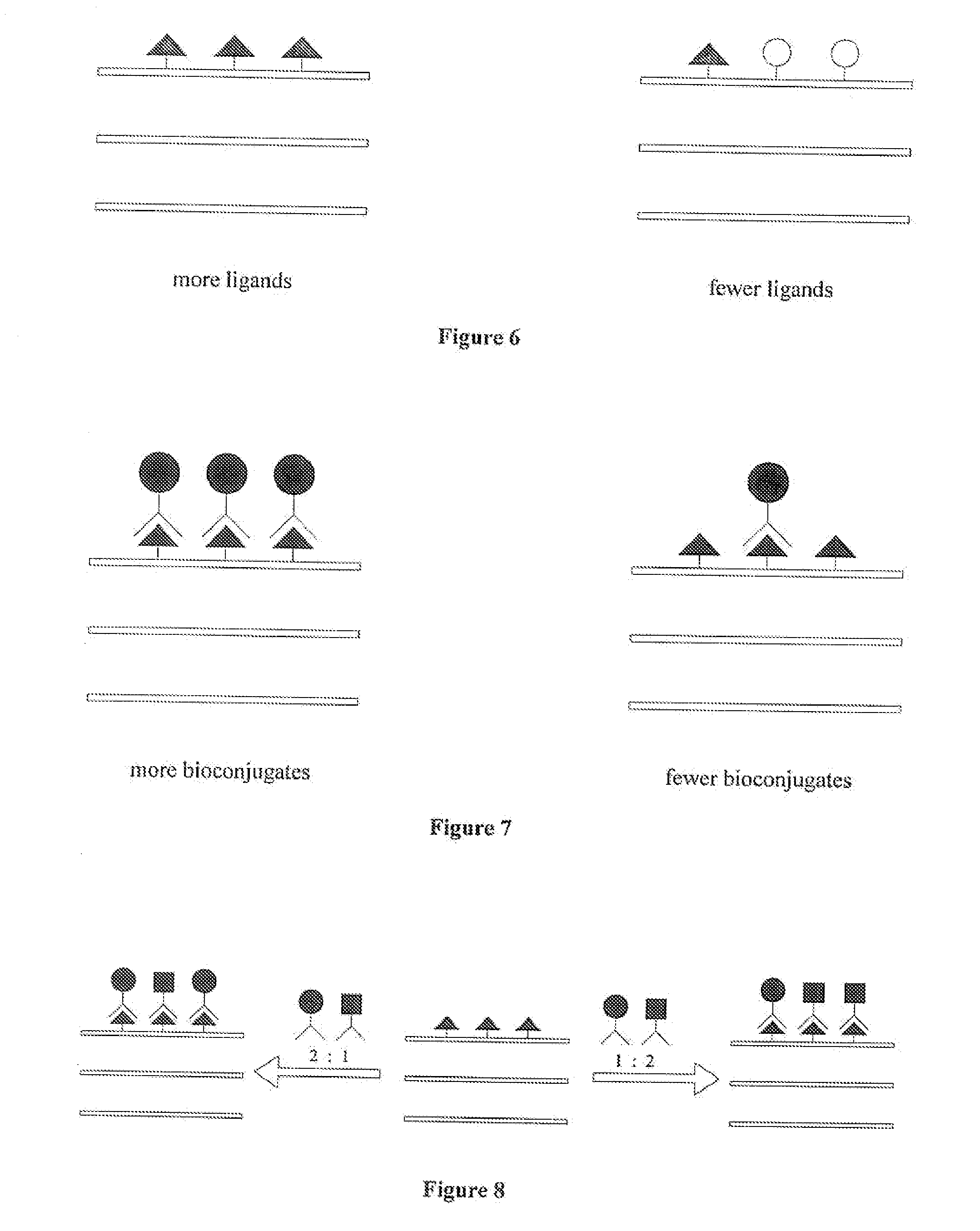
Biocompatible matrices or implants on which one or more specific cell-interactive molecules (“biomolecules”) can be immobilized have been developed. The matrices allow for the independent control of ligand concentration and matrix strength. In one embodiment, the matrix or implant is modified with one or more moieties capable of complexing bioconjugates prepared from one or more biomolecules. Suitable moieties include phenyl boronic acid complexing agents, such as salicylhydroxamic acid, which can complex to one or more biomolecules containing one or more phenyl boronic acid moieties. The biomolecules may be anchored to the matrix via a spacer molecule, which may allow for greater mobility of the biomolecules in aqueous solution. In one embodiment, the matrix is a hydrogel material which has been doubly-derivatized, wherein ligand concentration and matrix strength can be independently controlled. The matrices and implants can be used in vivo and in vitro applications including diagnostics, biosensors, bioprocess engineering, tissue engineering, regeneration and repair, and drug delivery.
Owner:CAMBREX BIO SCI WALKERSVILLE
Receptor-avid exogenous optical contrast and therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20050281741A1Enhance tumor detectionPreserve fluorescence efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesAbnormal tissue growthImaging agent
Cyanine and Indocyanine dye compounds and bioconjugates are disclosed. The present invention includes several cyanine and indocyanine dyes, including bioconjugates of the same, with a variety of bis- and tetrakis (carboxylic acid) homologues. The compounds of the invention may be conjugated to bioactive peptides, carbohydrates, hormones, drugs, or other bioactive agents. The small size of compounds of the invention allows favorable delivery to tumor cells as compared to larger molecular weight imaging agents. Further, use of a biocompatible organic solvent such as dimethylsulfoxide may be said to assist in maintaining the fluorescence of compounds of the invention. The compounds and bioconjugates herein disclosed are useful in a variety of medical applications including, but not limited to, diagnostic imaging and therapy, endoscopic applications for the detection of tumors and other abnormalities, localized therapy, photoacoustic tumor imaging, detection and therapy, and sonofluorescence tumor imaging, detection and therapy.
Owner:MEDIBEACON
Fluorine-labeled compounds
InactiveUS20080139787A1Peptide/protein ingredientsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsBioconjugationAldehyde
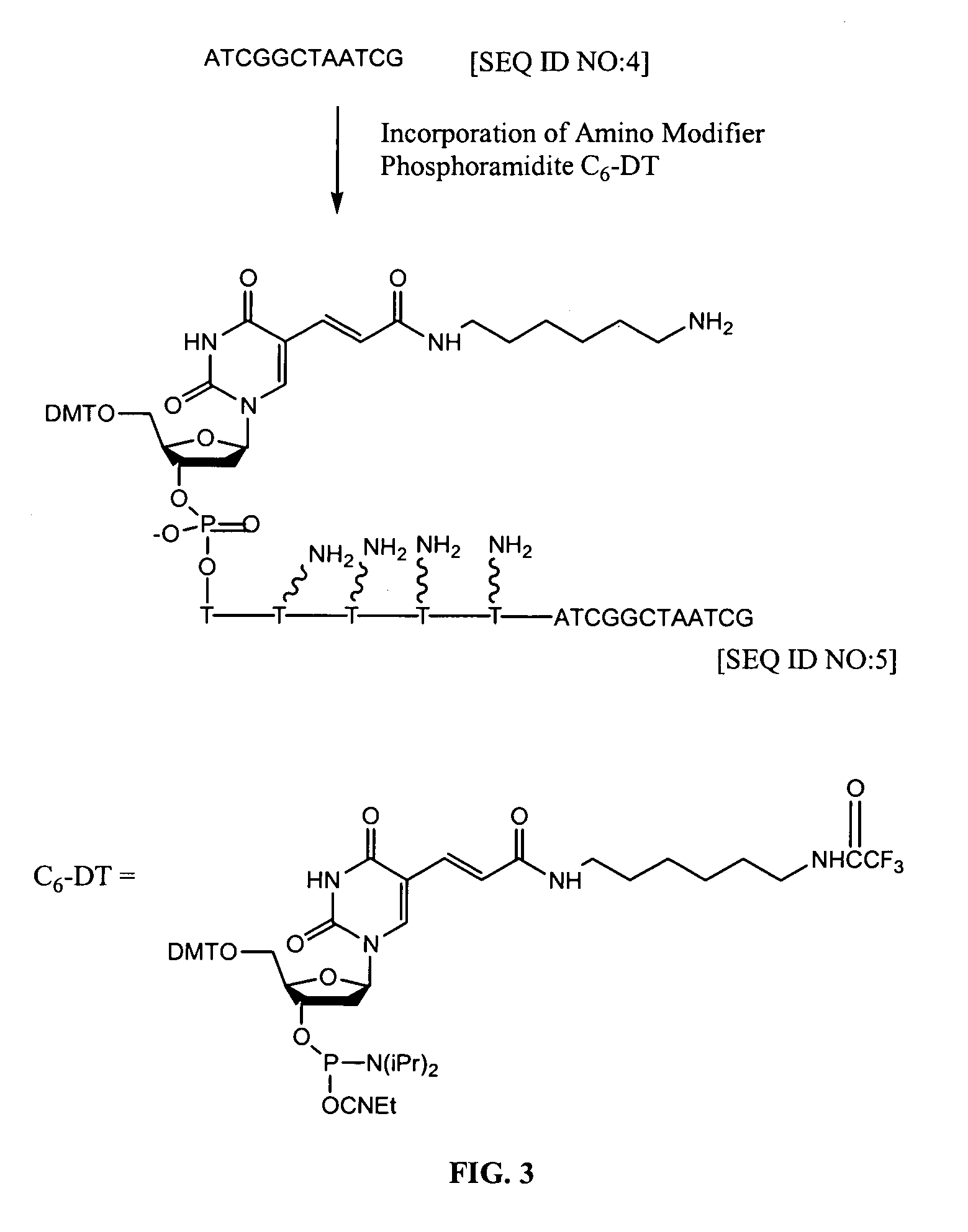
Methods for introducing fluorine atom onto a polypeptide are provided. Also provided are linkers, bioconjugates, and bifunctional compound agents made using the methods, linkers, and bioconjugates. The methods comprise: (i) providing a linker comprising a thiol-reactive terminus and an aldehyde-reactive terminus; (ii) reacting the thiol-reactive terminus of the linker with a polypeptide comprising at least one thiol group or a reactive derivative thereof; and (iii) subsequently reacting the aldehyde-reactive terminus of the linker with a fluorine-substituted aldehyde.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
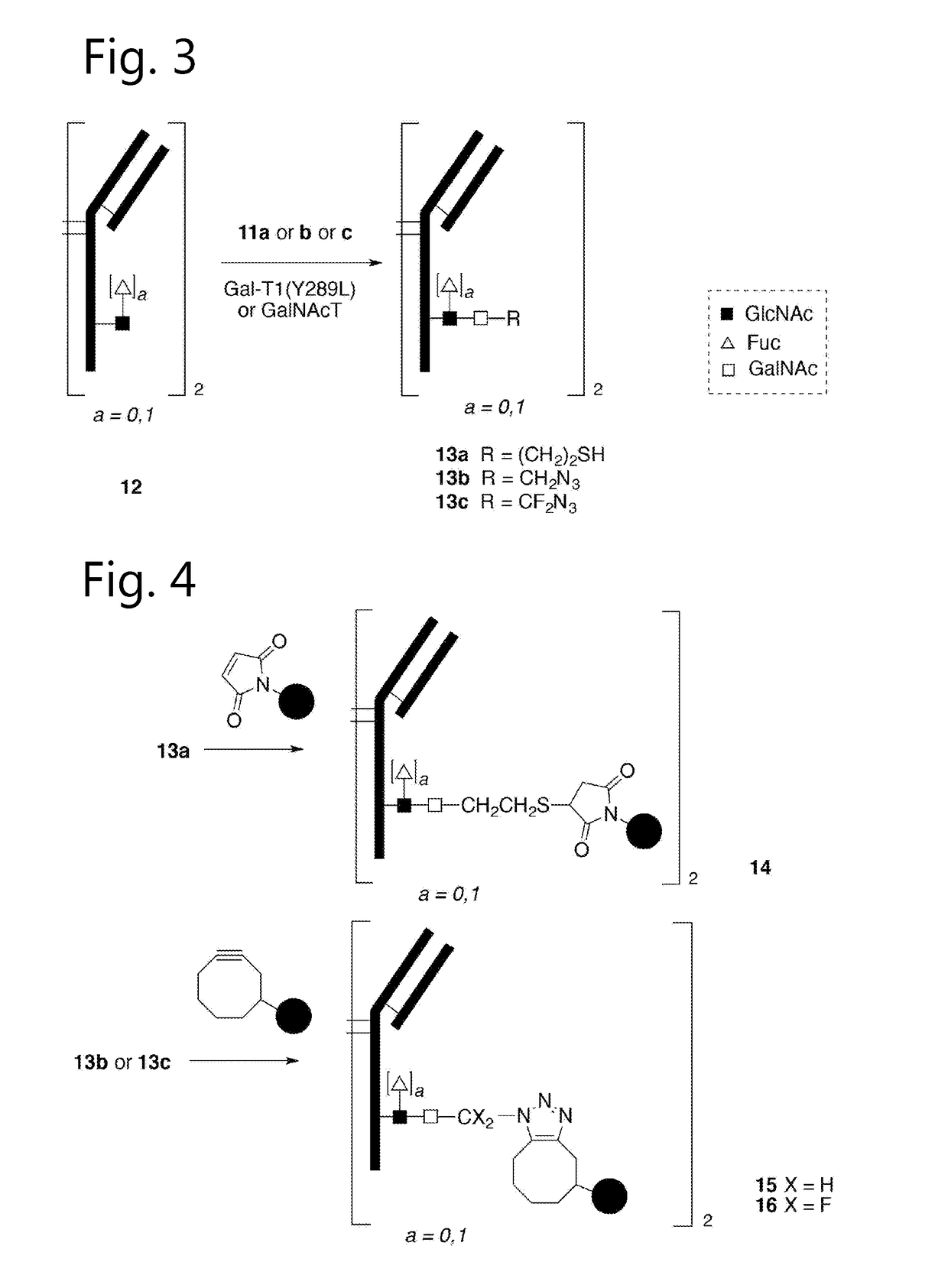
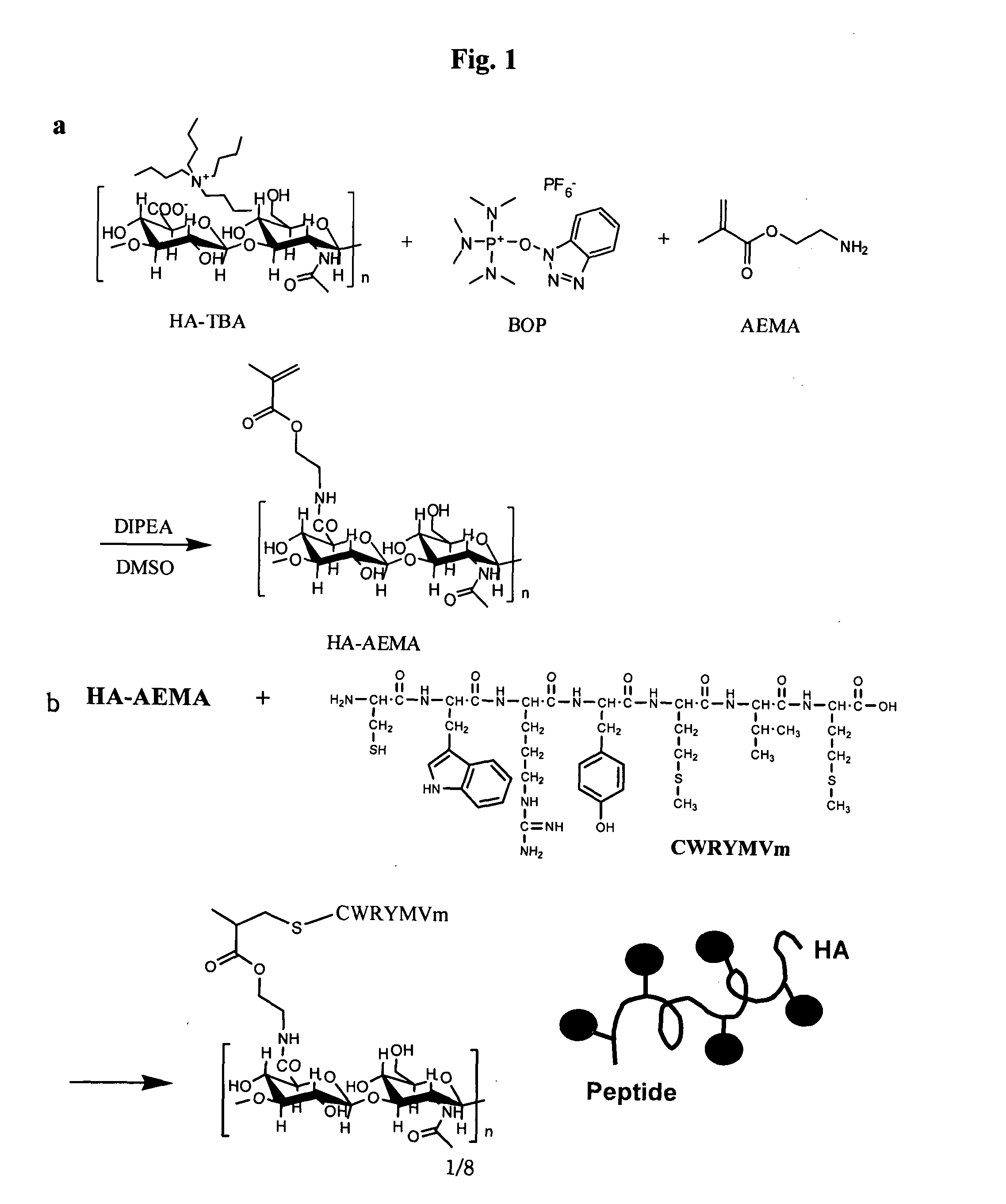
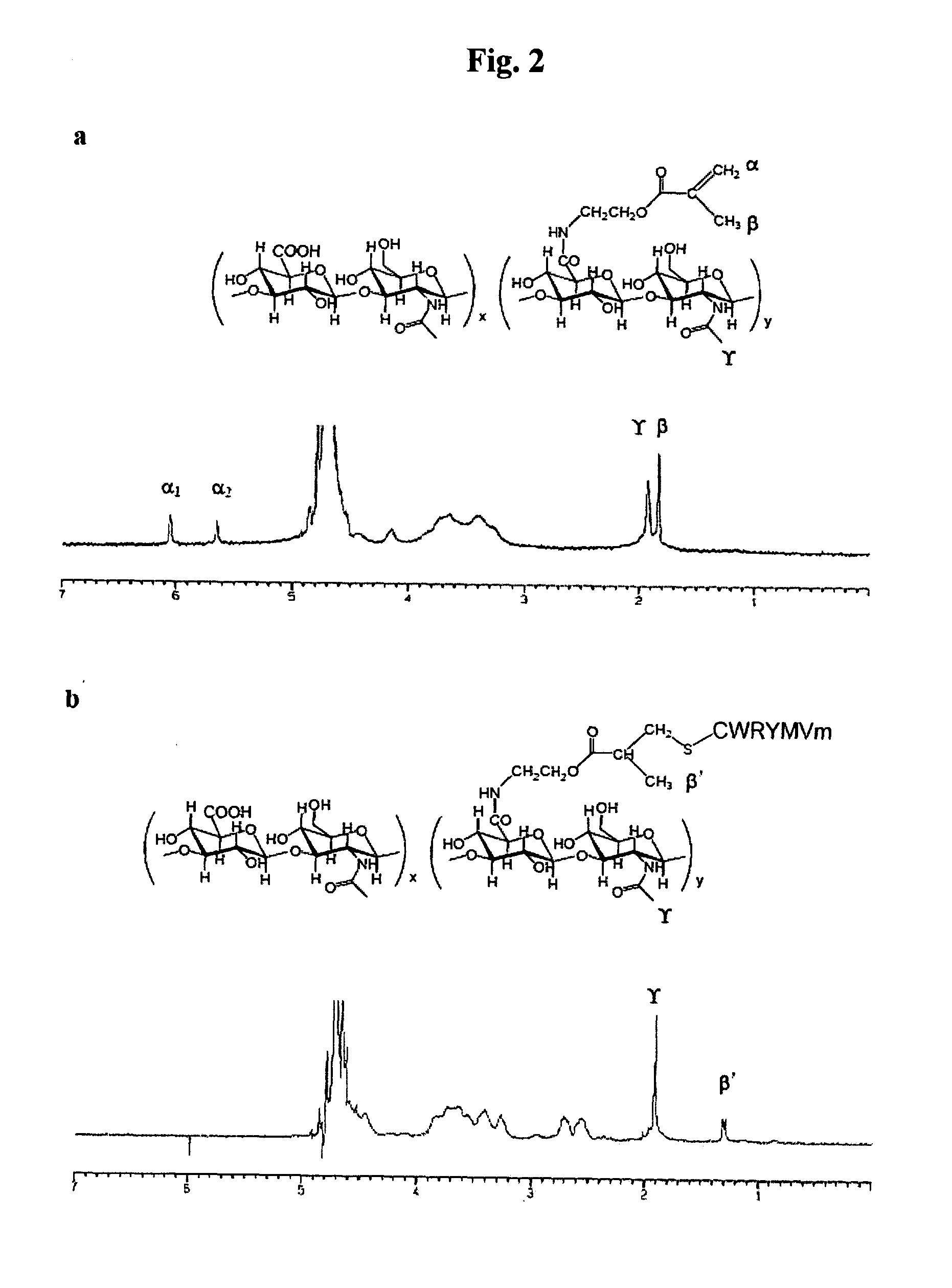
Long acting hyaluronic acid - peptide conjugate
The invention relates to a novel bioconjugation protocol for peptide suitable for in vivo applications. Bioconjugation of the peptide to HA derivative increases its half life in circulation contributing for a high efficacy. More over, conjugate of HA derivative and peptide which is treated with hyaluronidase shows increased bioactivity. And also, in contrast to PEGylation, HA derivative can be conjugated with many numbers of peptide molecules per single HA derivative chain, which enables multiple action of peptide drugs.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Functionalized chromophoric polymer dots and bioconjugates thereof
ActiveUS10191060B2Reduces non-specific adsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiological testingCombinatorial chemistryIn vivo
The present invention provides, among other aspects, functionalized chromophoric polymer dots comprising a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic cap, and bioconjugates thereof. Also provided are improved methods for preparing functionalized chromophoric polymer dots. Methods for in vivo imaging and molecular labeling are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
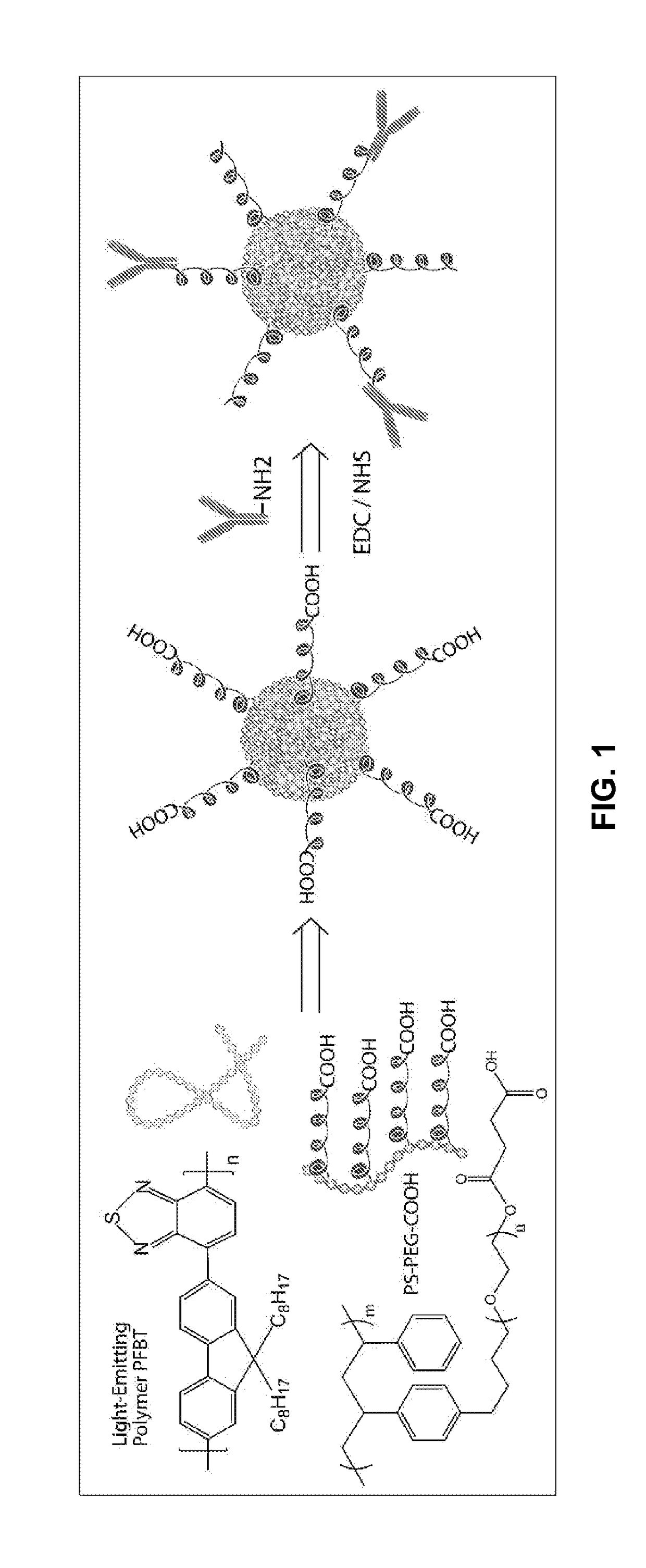
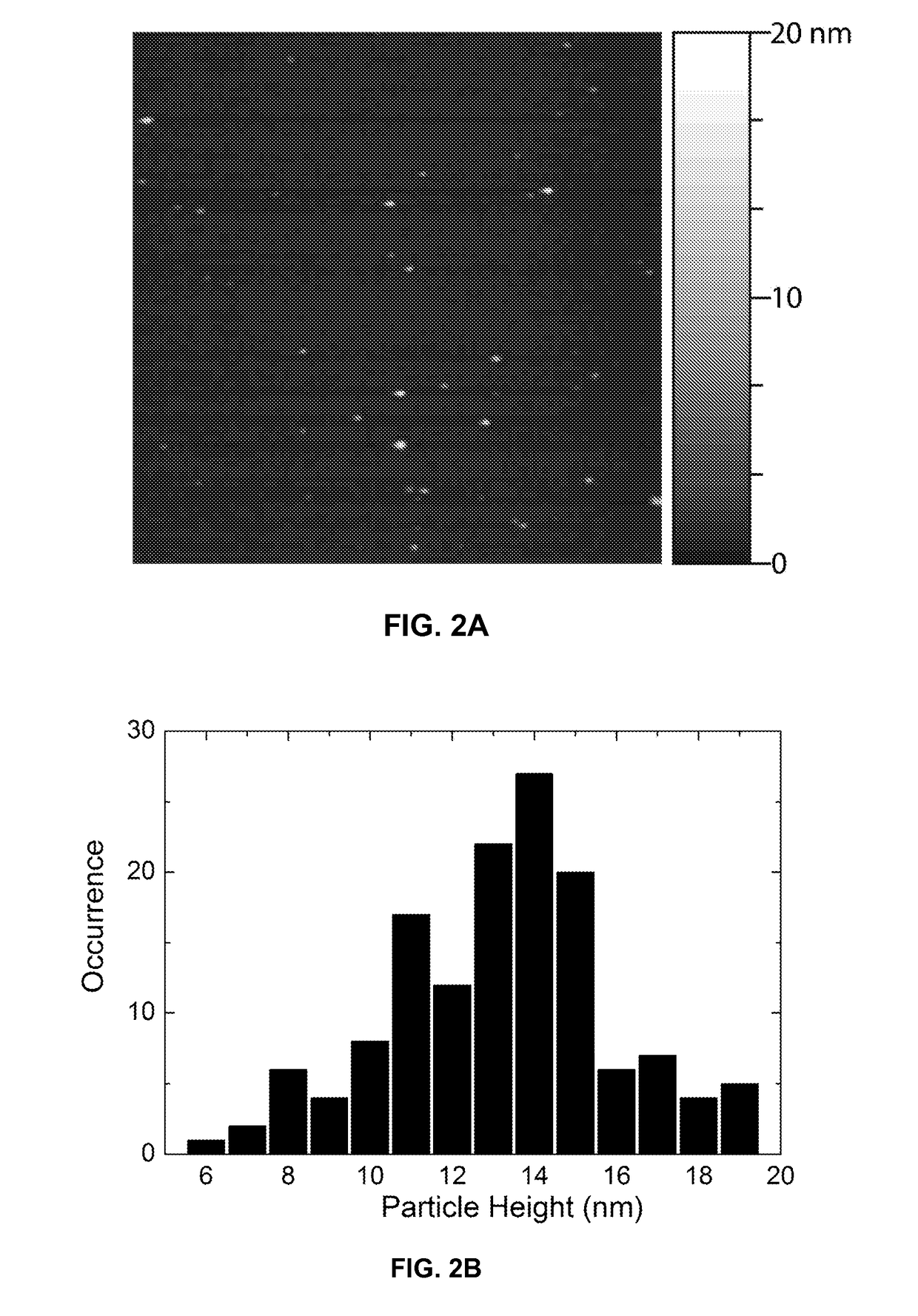
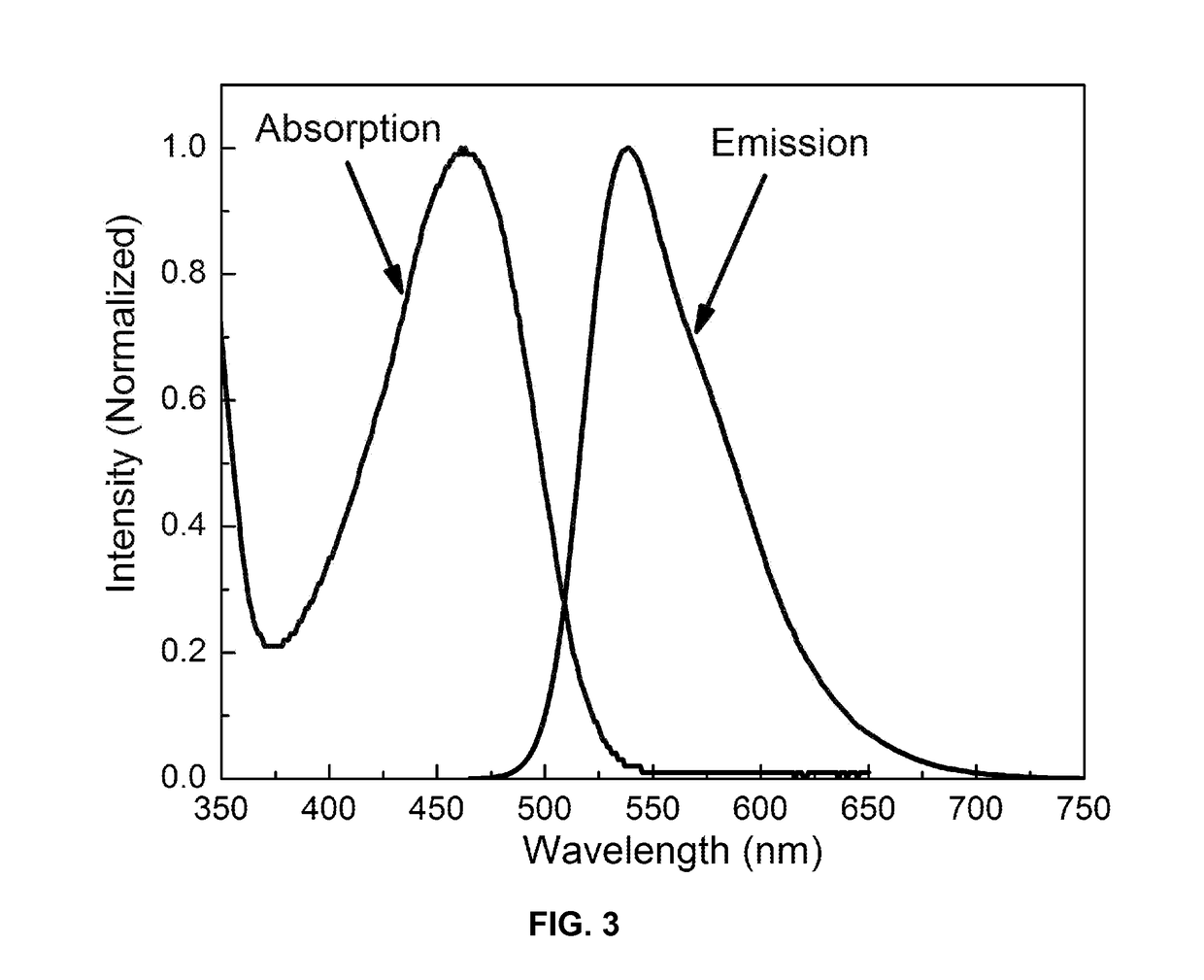
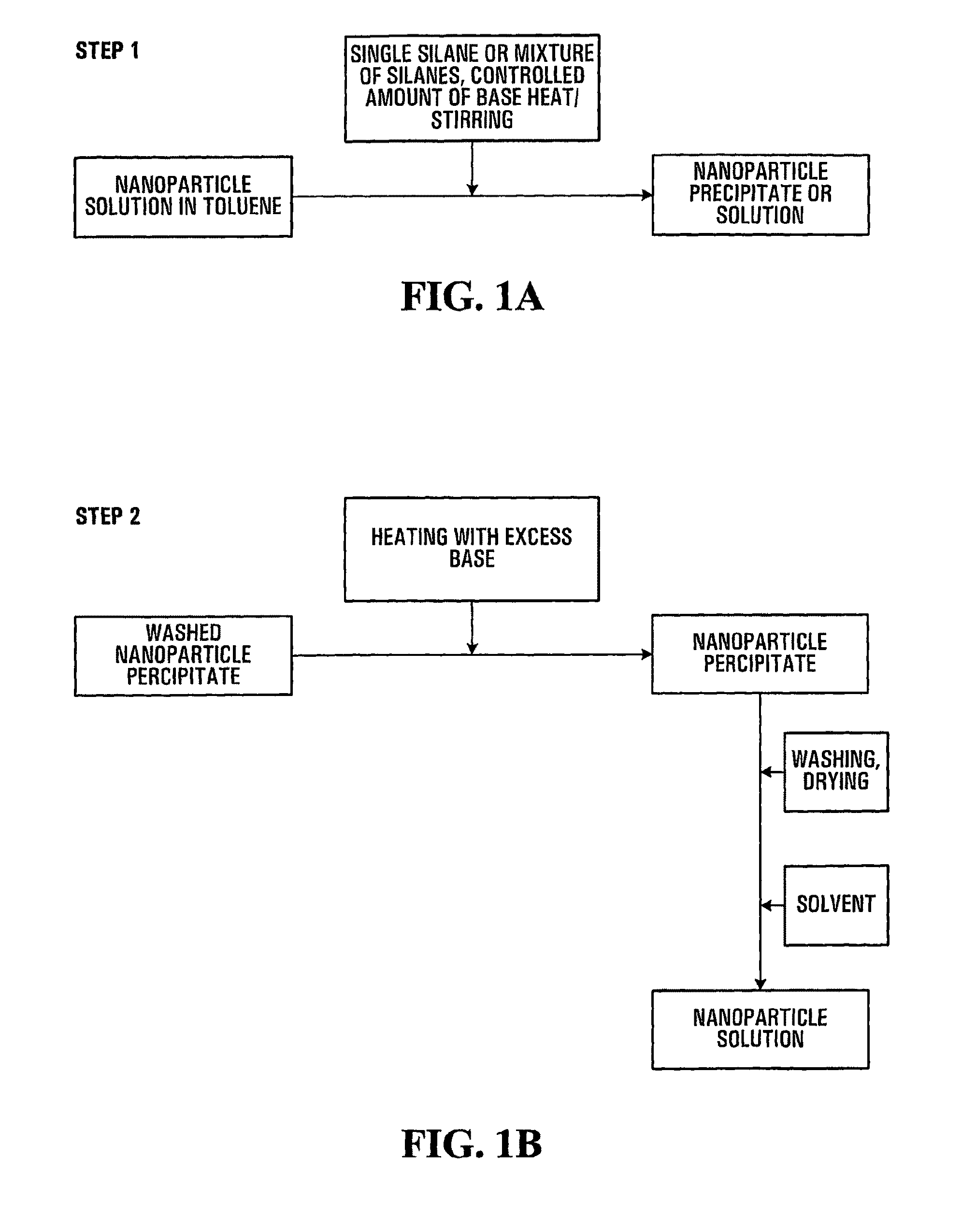
Water-soluble, surface-functionalized nanoparticle for bioconjugation via universal silane coupling
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Synthesis of water soluble nanocrystalline quantum dots and uses thereof
InactiveUS7335345B2Accelerate emissionsMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesPhotoluminescenceMetallic sulfide
An economic, direct synthetic method for producing water soluble QDs that are ready for bioconjugation is provided. The method can produce aqueous QDs with emission wavelengths varying from 400 nm to 700 nm. Highly luminescent metal sulfide (MS) QDs are produced via an aqueous synthesis route. MS QDs are capped with thiol-containing charged molecules in a single step. The resultant MS QDs exhibit the distinctive excitonic photoluminescence desired of QDs and can be fabricated to avoid undesirable broadband emissions at higher wavelengths. This provides a significant improvement over the present complex and expensive commercial processes for the production of QDs. The aqueous QDs are stable in biological fluids over a long period of time. In addition, nontoxic ZnS QDs have been produced with good photoluminescence properties by refluxing the ZnS QD suspensions over a period of time.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Bioconjugates made from recombinant n-glycosylated proteins from procaryotic cells
The present invention is directed to a bioconjugate vaccine, such as an 01-bioconjugate vaccine, comprising: a protein carrier comprising a protein carrier containing at least one consensus sequence, D / E-X—N—Z—S / T, wherein X and Z may be any natural amino acid except proline; at least one antigenic polysaccharide from at least one pathogenic bacterium, linked to the protein carrier; and, optionally, an adjuvant. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a method of producing an O1-bioconjugate in a bioreactor comprising a number steps.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
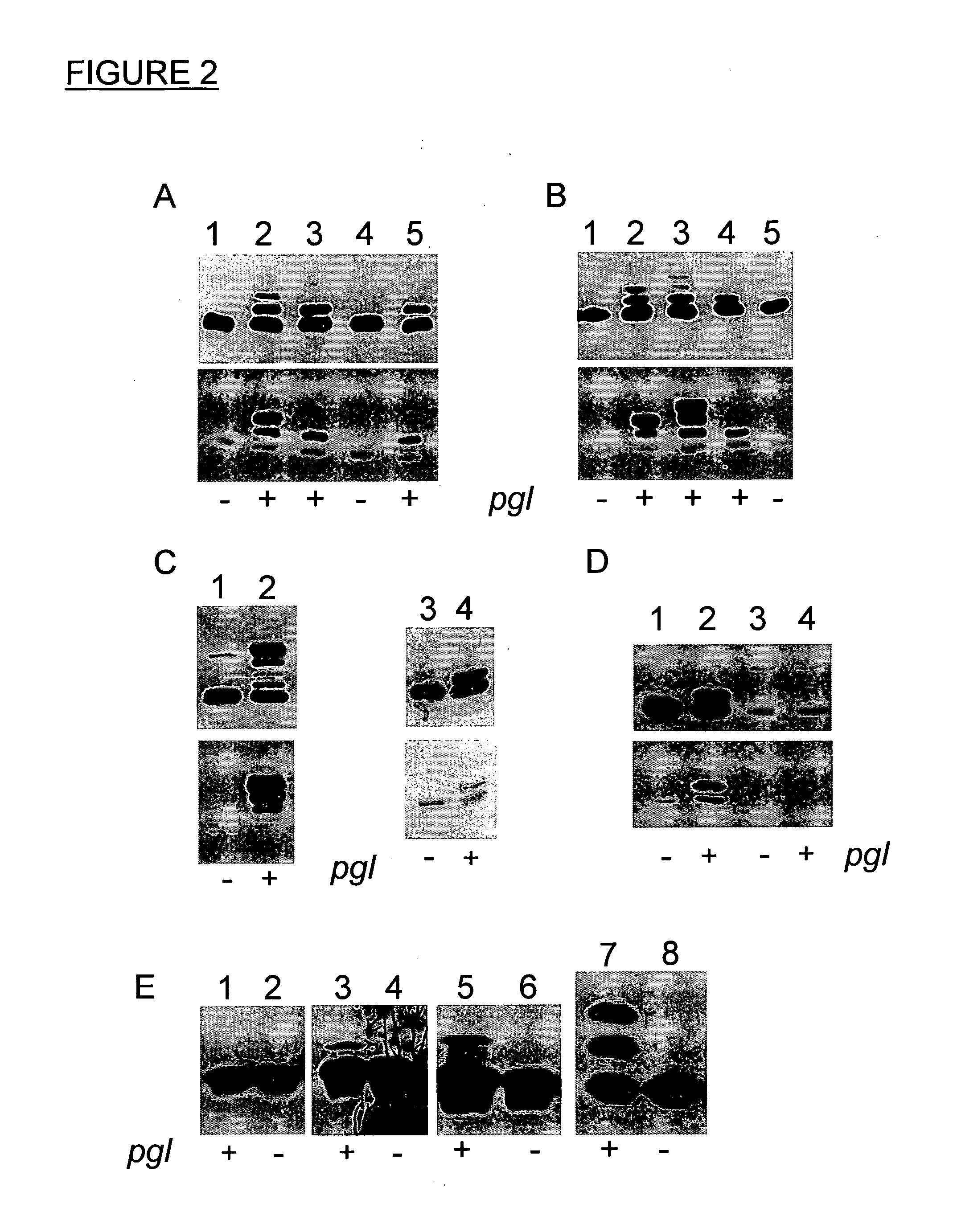
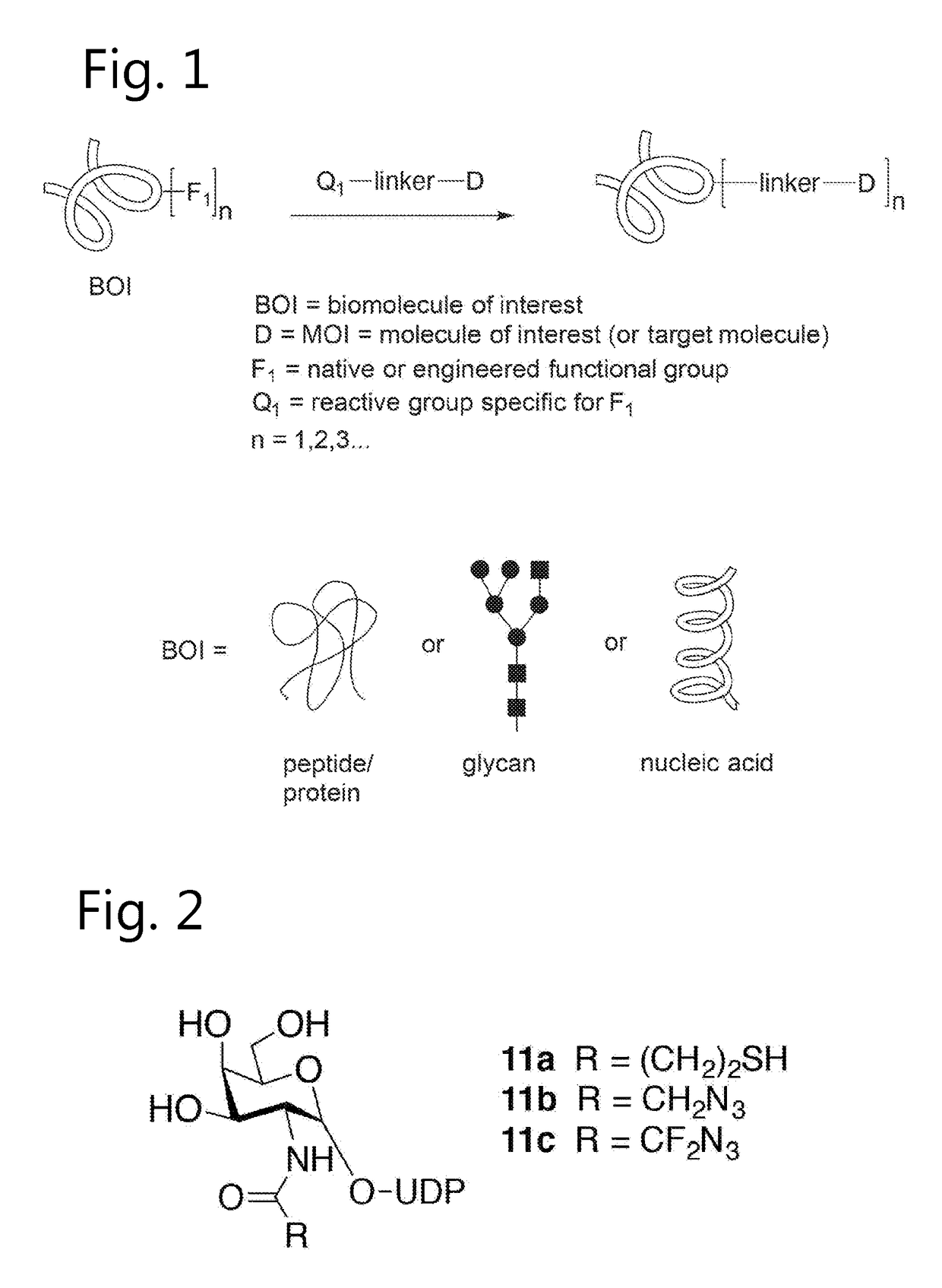
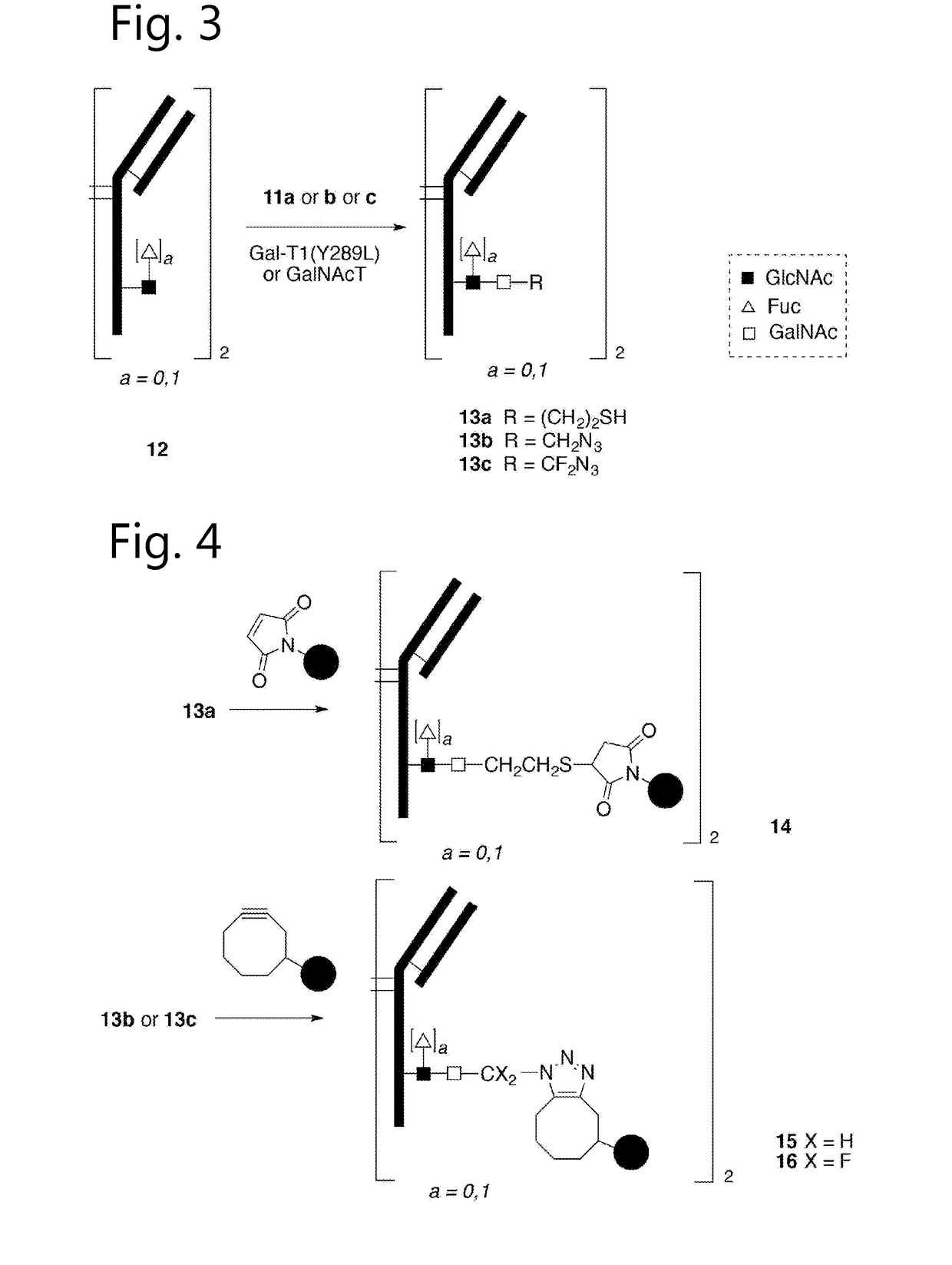
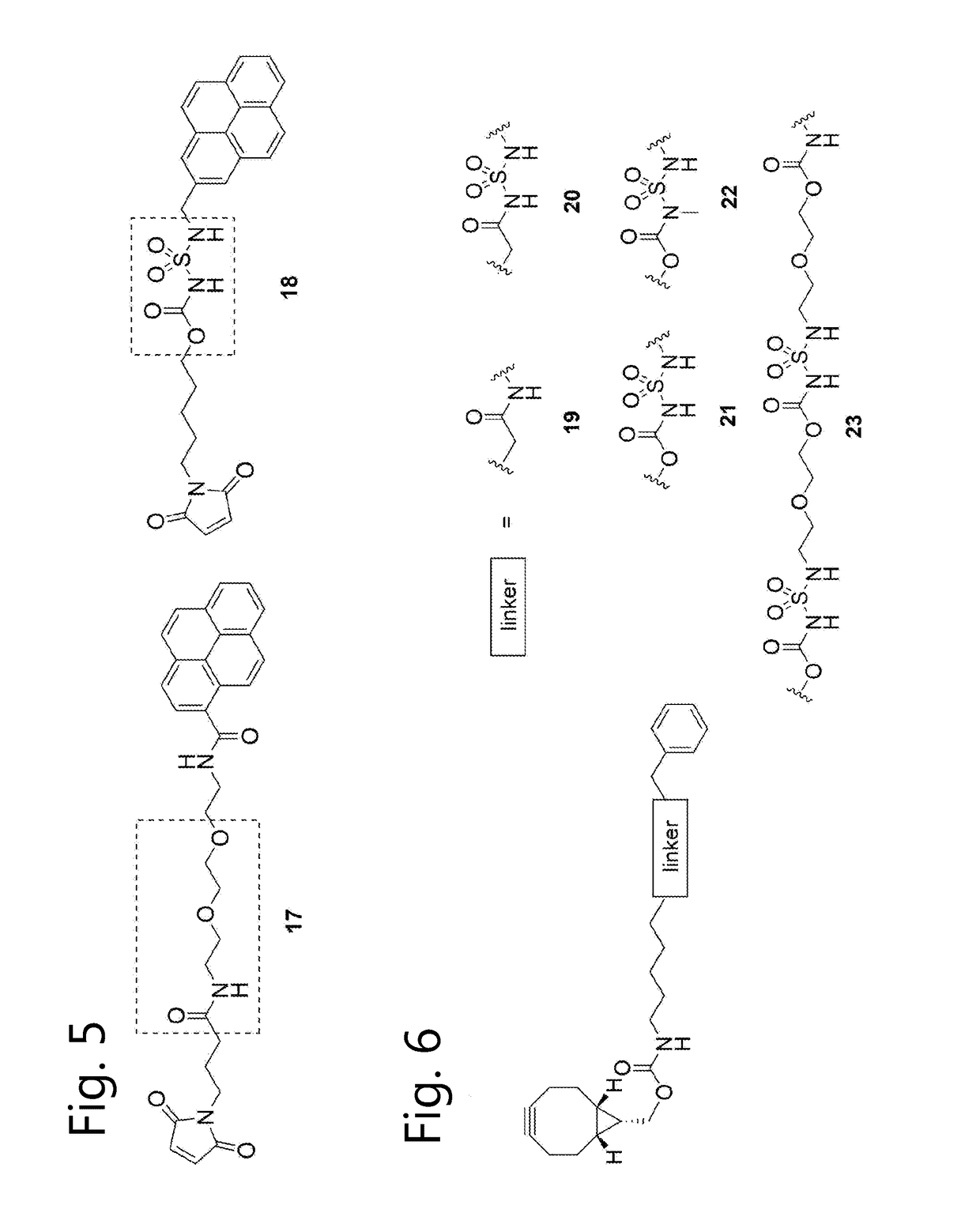
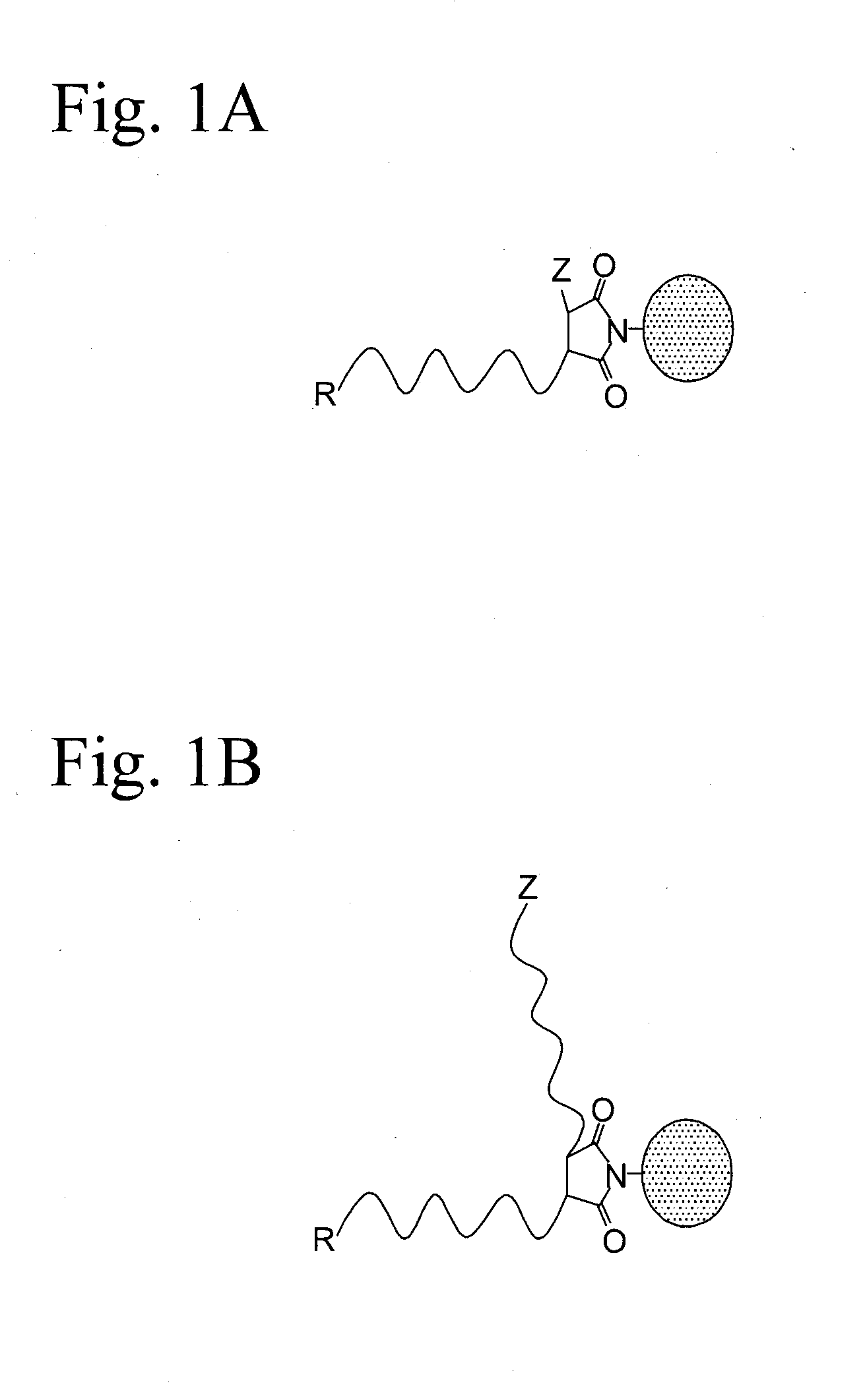
Sulfamide linker, conjugates thereof, and methods of preparation
ActiveUS20170072068A1Improve efficiencyConjugation efficiency of the sulfamide-containing maleimide 18 is higherImmunoglobulinsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical compoundSulfamide
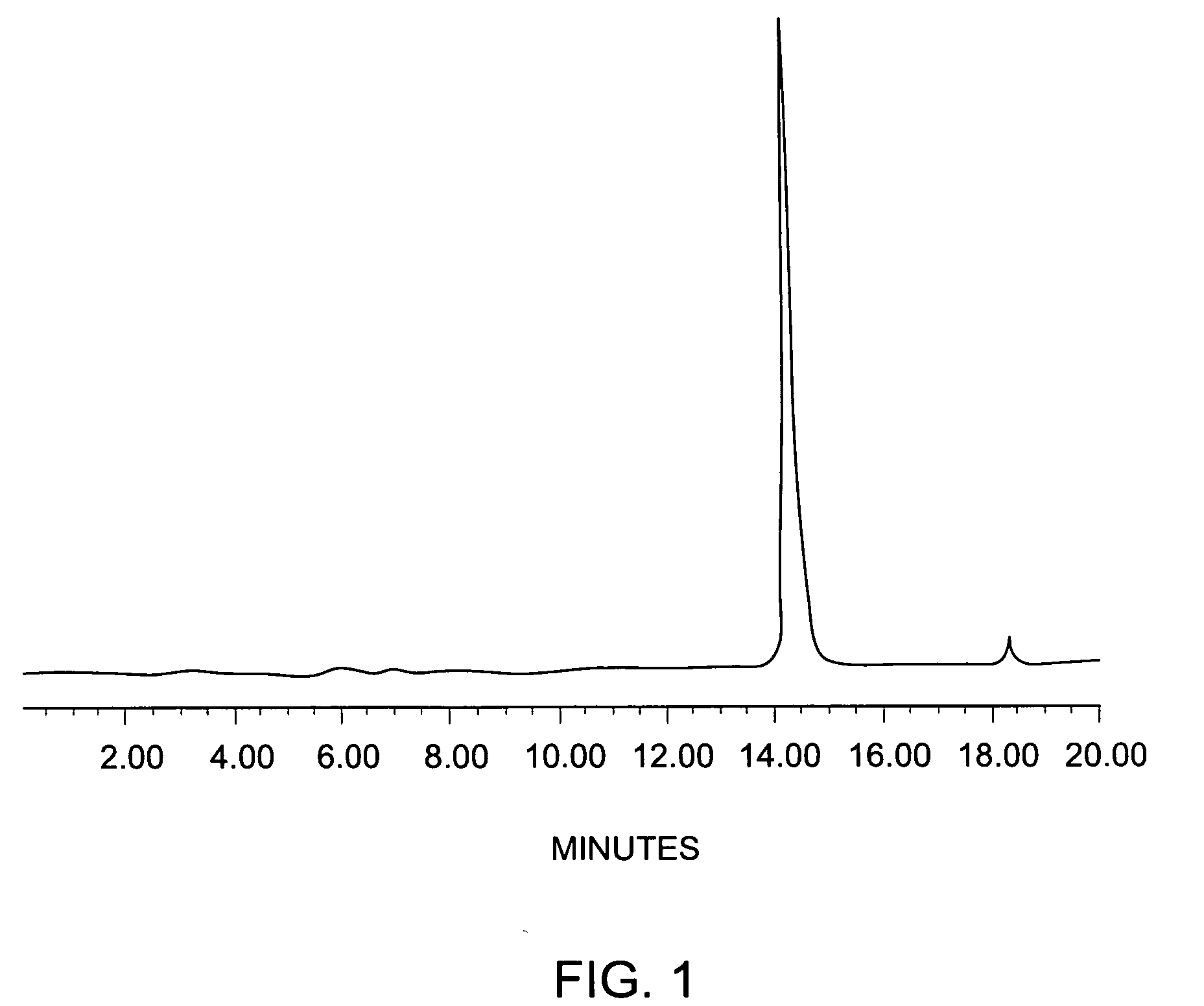
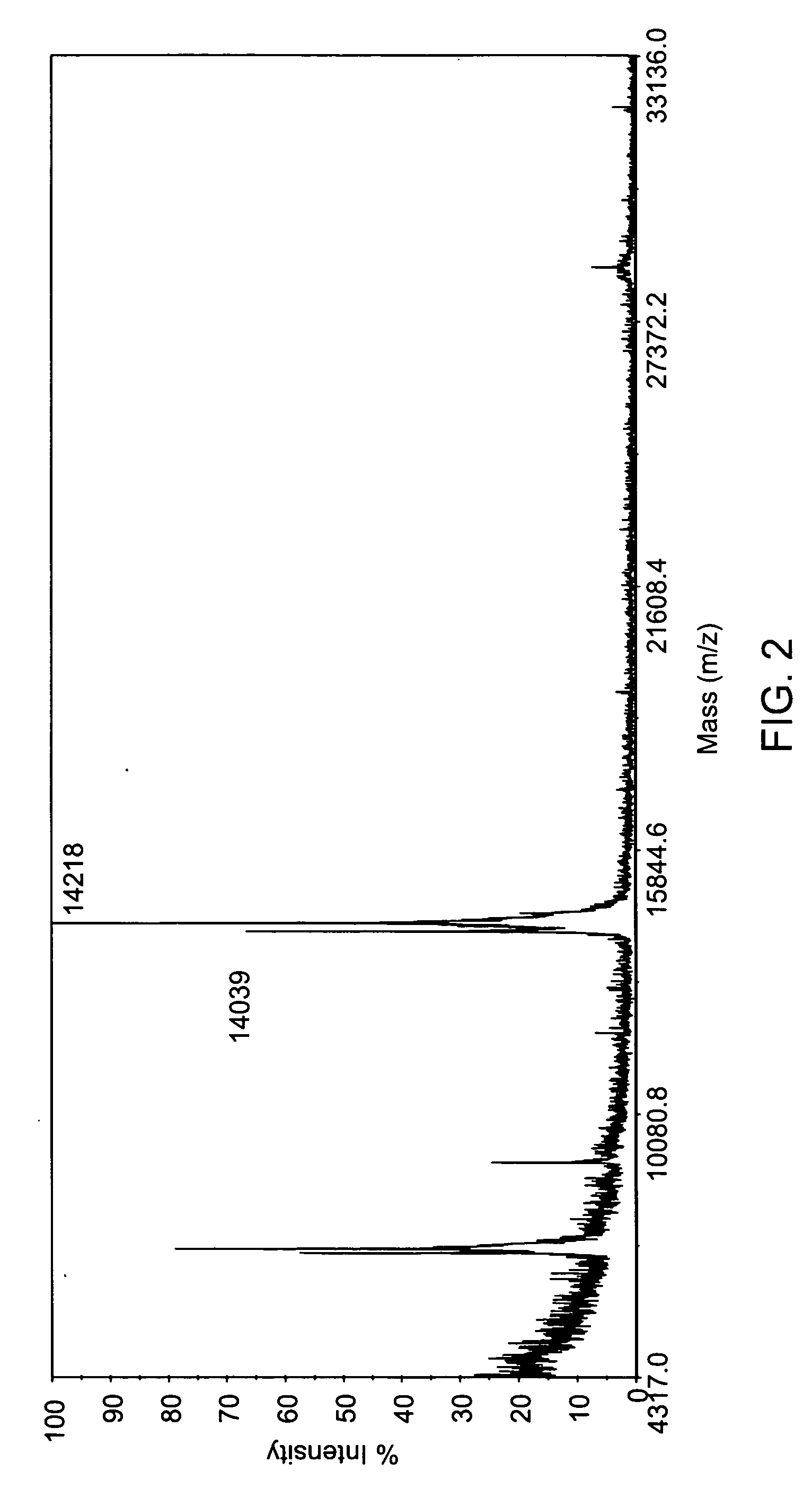
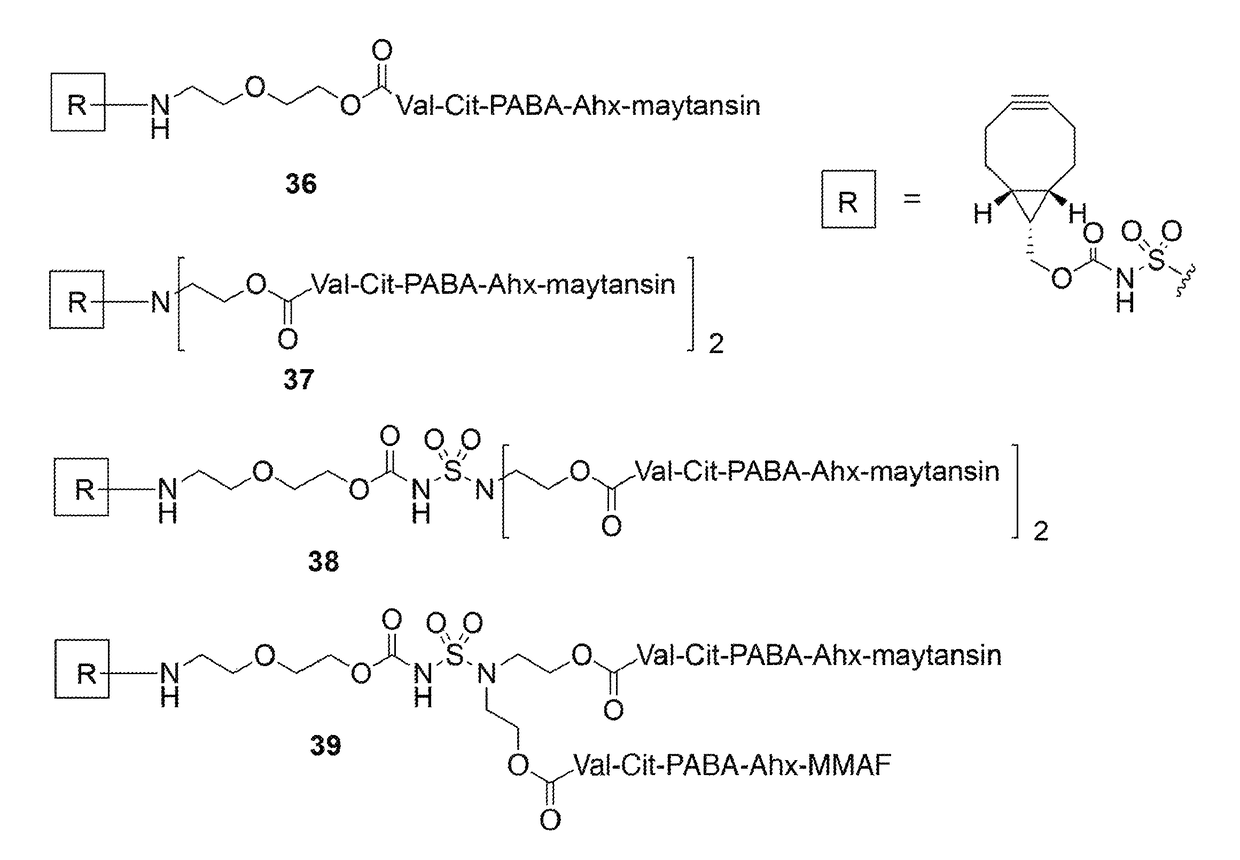
The present invention relates to a compound comprising an alpha-end and an omega-end, the compound comprising on the alpha-end a reactive group Q1 capable of reacting with a functional group F1 present on a biomolecule and on the omega-end a target molecule, the compound further comprising a group according to formula (1) or a salt thereof:Said compound may also be referred to as a linker-conjugate. The invention also relates to a process for the preparation of a bioconjugate, the process comprising the step of reacting a reactive group Q1 of a linker-conjugate according to the invention with a functional group F1 of a biomolecule. The invention further relates to a bioconjugate obtainable by the process according to the invention.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
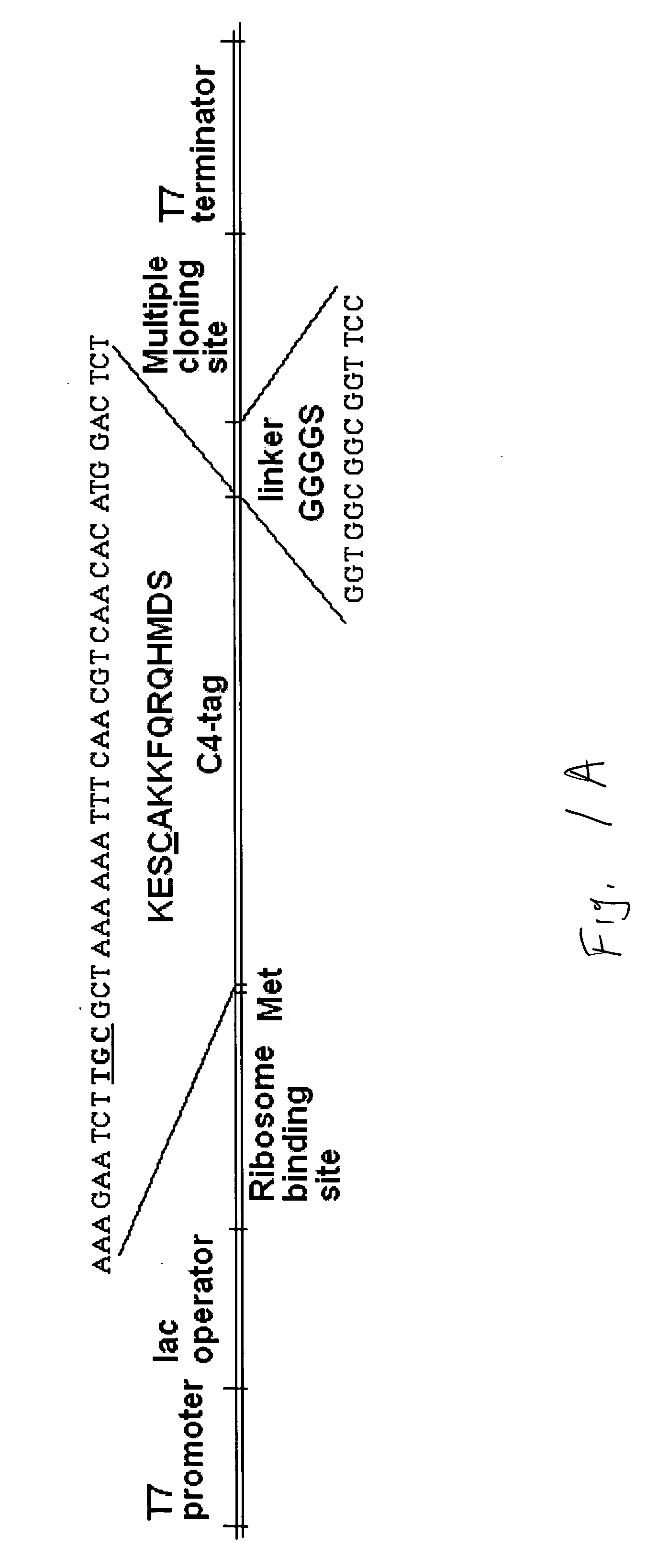
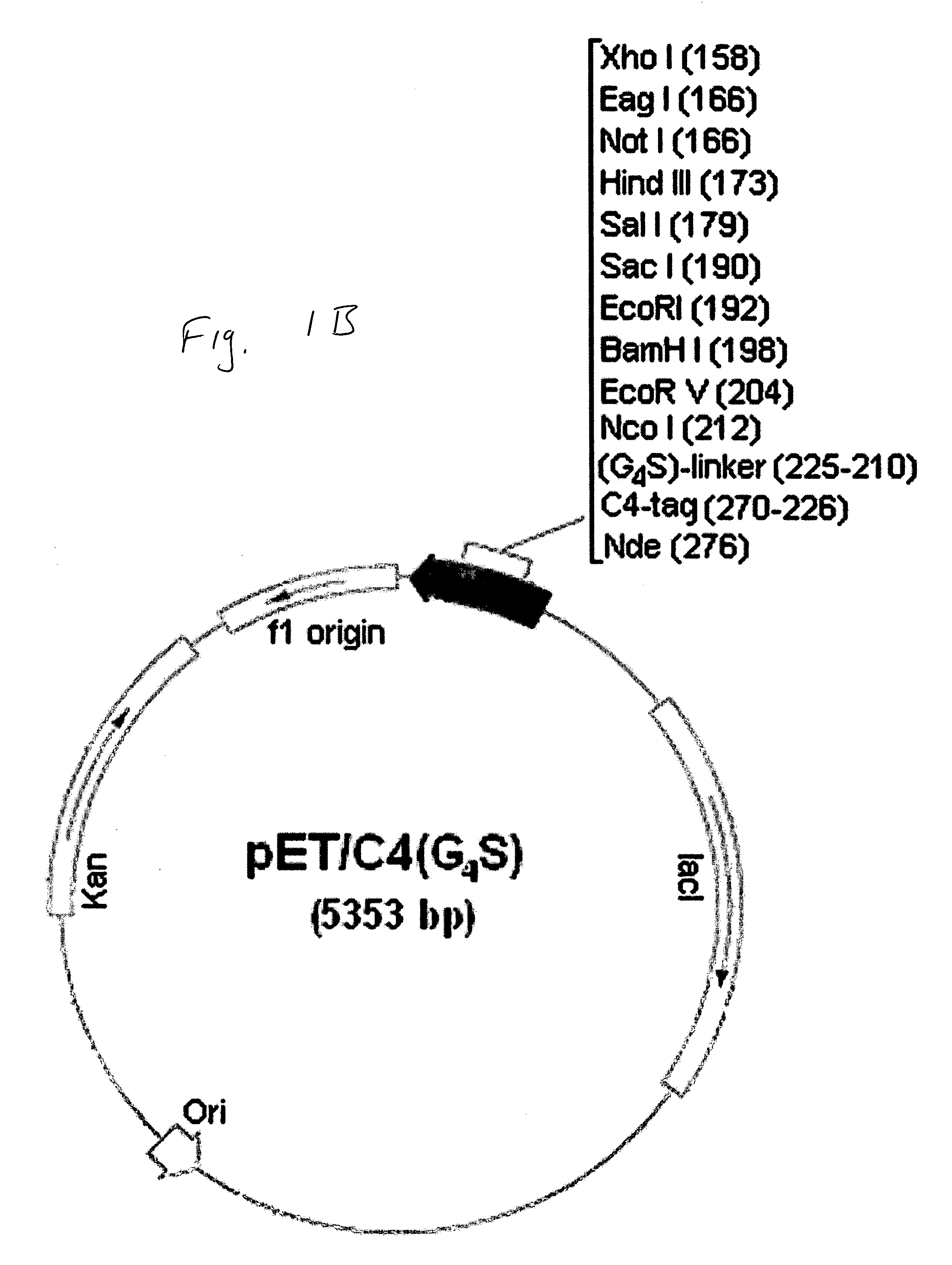
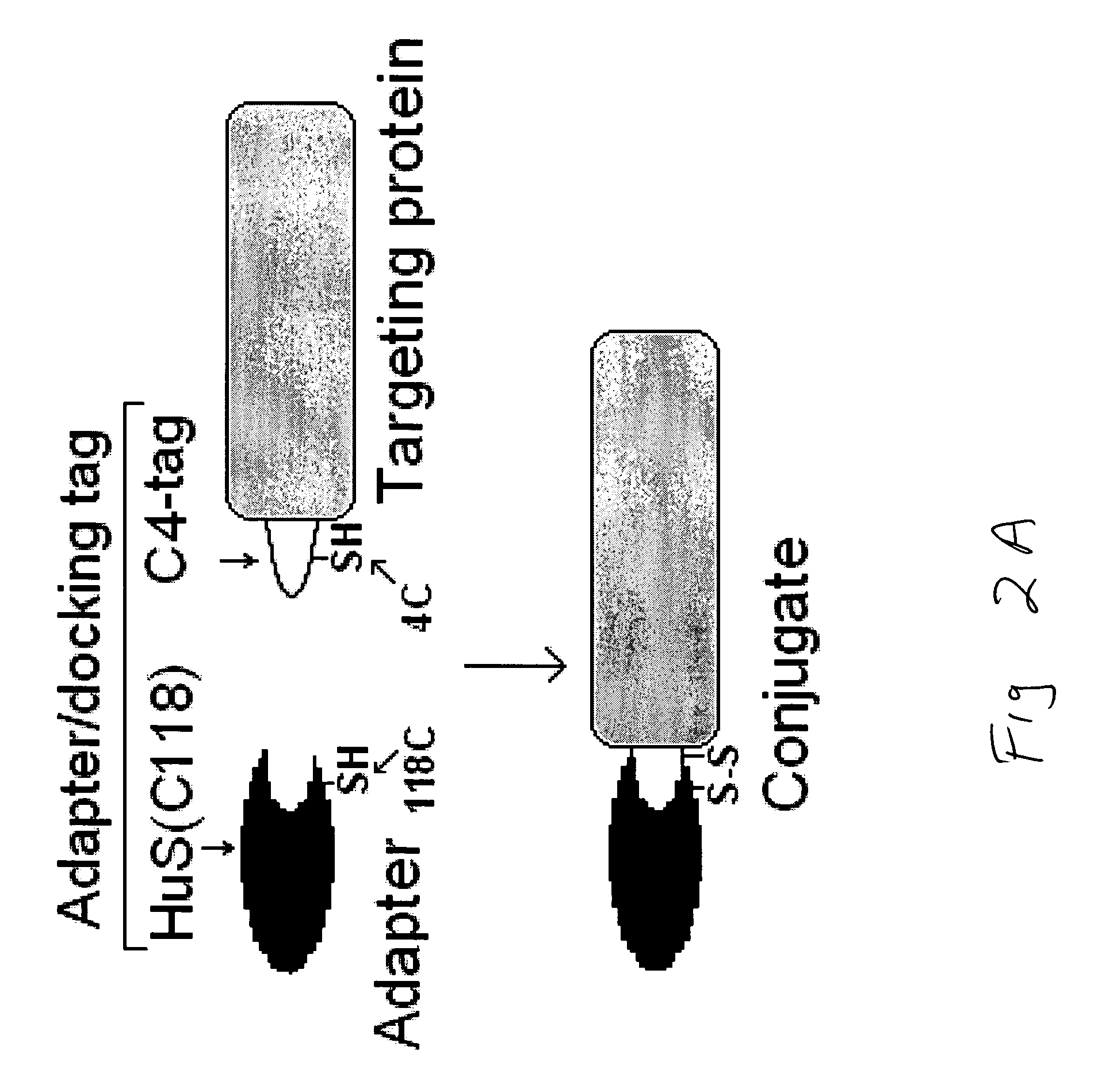
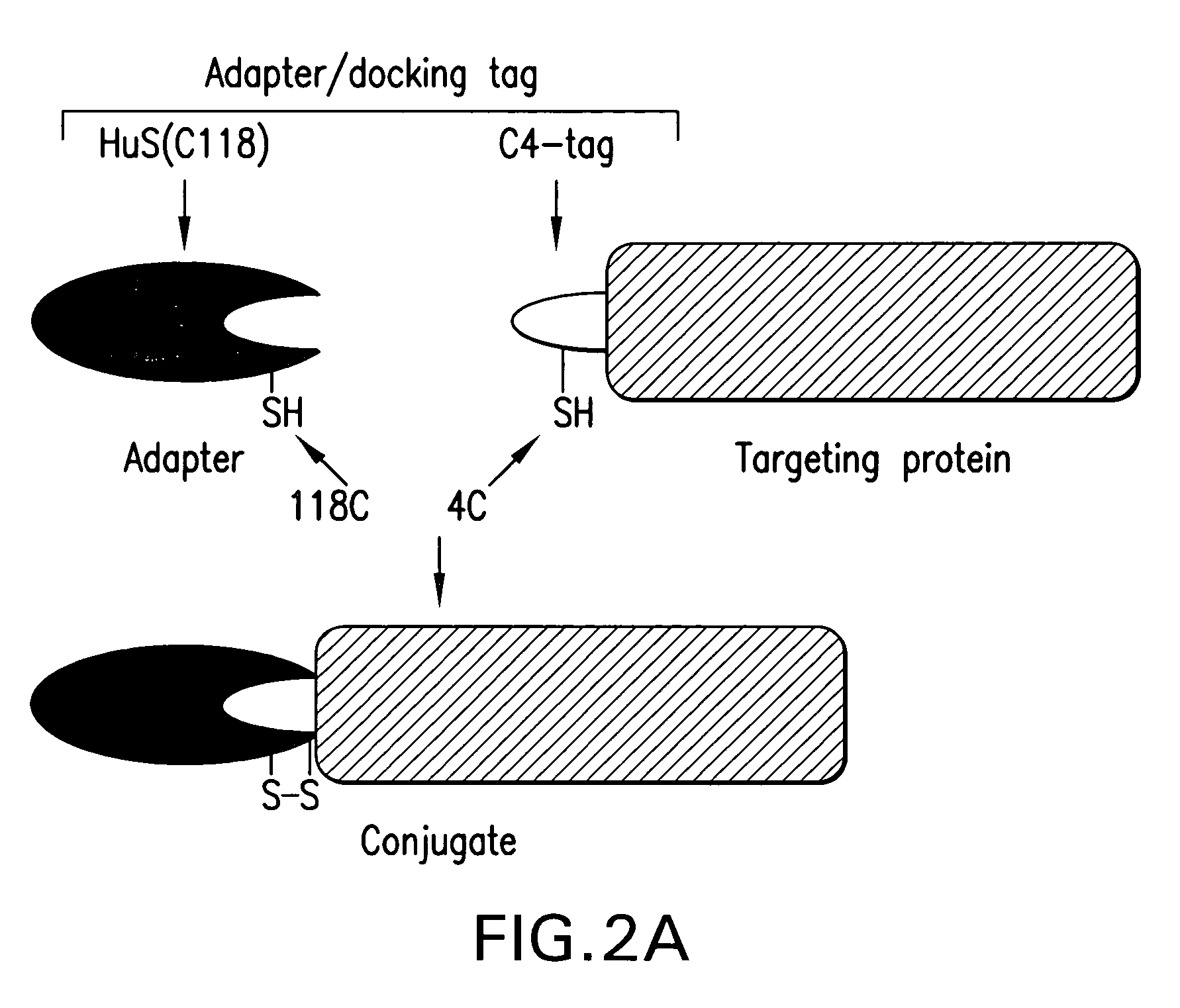
Cysteine-containing peptide tag for site-specific conjugation of proteins
The present invention is directed to a biological conjugate, comprising: (a) a targeting moiety comprising a polypeptide having an amino acid sequence comprising the polypeptide sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 and the polypeptide sequence of a selected targeting protein; and (b) a binding moiety bound to the targeting moiety; the biological conjugate having a covalent bond between the thiol group of SEQ ID NO:2 and a functional group in the binding moiety. The present invention is directed to a biological conjugate, comprising: (a) a targeting moiety comprising a polypeptide having an amino acid sequence comprising the polypeptide sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 and the polypeptide sequence of a selected targeting protein; and (b) a binding moiety that comprises an adapter protein, the adapter protein having a thiol group; the biological conjugate having a disulfide bond between the thiol group of SEQ ID NO:2 and the thiol group of the adapter protein. The present invention is also directed to biological sequences employed in the above biological conjugates, as well as pharmaceutical preparations and methods using the above biological conjugates.
Owner:SIBTECH
Omega-functionalized polymers, junction-functionalized block copolymers, polymer bioconjugates, and radical chain extension polymerization
InactiveUS20110305660A1Maximal diversitySpecial deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer scienceBioconjugation
Polymeric compounds having spatially controlled bioconjugation sites are described. Functionalization is achieved by selective co-terminal chain extension of polymer chains by radical polymerization, such as reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization.
Owner:GENEVANT SCI GMBH +1
Fluorine-labeled compounds
InactiveUS7902332B2Peptide/protein ingredientsIsotope introduction to peptides/proteinsBioconjugationThiol group
Methods for introducing fluorine atom onto a polypeptide are provided. Also provided are linkers, bioconjugates, and bifunctional compound agents made using the methods, linkers, and bioconjugates. The methods comprise: (i) providing a linker comprising a thiol-reactive terminus and an aldehyde-reactive terminus; (ii) reacting the thiol-reactive terminus of the linker with a polypeptide comprising at least one thiol group or a reactive derivative thereof; and (iii) subsequently reacting the aldehyde-reactive terminus of the linker with a fluorine-substituted aldehyde.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Receptor-avid exogenous optical contrast and therapeutic agents
Cyanine and indocyanine dye compounds and bioconjugates are disclosed. The present invention includes several cyanine and indocyanine dyes, including bioconjugates of the same, with a variety of bis- and tetrakis (carboxylic acid) homologues. The compounds of the invention may be conjugated to bioactive peptides, carbohydrates, hormones, drugs, or other bioactive agents. The small size of compounds of the invention allows favorable delivery to tumor cells as compared to larger molecular weight imaging agents. Further, use of a biocompatible organic solvent such as dimethylsulfoxide may be said to assist in maintaining the fluorescence of compounds of the invention. The compounds and bioconjugates herein disclosed are useful in a variety of medical applications including, but not limited to, diagnostic imaging and therapy, endoscopic applications for the detection of tumors and other abnormalities, localized therapy, photoacoustic tumor imaging, detection and therapy, and sonofluorescence tumor imaging, detection and therapy.
Owner:MEDIBEACON
Biological activated carbon nano-fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101736441AGood bone conductionImprove osteogenic abilityFilament/thread formingProsthesisFiberCarbon nanofiber
The invention provides biological activated carbon nano-fiber and a preparation method thereof. An electrospinning process and high-temperature sintering are adopted to generate calcium phosphate nano-particles with biological activity in situ in carbon nano-fiber, wherein the diameter of the carbon nano-fiber is between 50 and 500nm; the particle size of nanometer calcium phosphate is between 10 and 100nm; and the weight percentage is between 1 and 10 percent. The method has a simple process; and the highly dispersed calcium phosphate nano-particles strengthen the bioconjugation between the carbon nano-fiber and bone tissue, and obviously improve the induced osteogenesis ability of the carbon nano-fiber.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Use of isocyanate linkers to make hydrolyzable active agent biopolymer conjugates
The invention provides bioconjugates of the formula: in which A is an active agent comprising an active hydroxy or amino functionality and B is a biopolymer comprising an active hydroxy or amino functionality, and X1 and X2 are independently N or O, and R is substituted alkyl or unsubstituted alkyl or unsubstituted or substituted heteroalkyl from 1 to about 30 atoms in length. The biopolymer may for instance be a transport protein or an antibody directed to a transport protein (e.g., a p97 protein or antibody thereto). The active agent may be a therapeutic agent such as a chemotherapeutic agent or an antineoplastic agent or an enzyme. The bioconjugates find therapeutic usages according to the therapeutic indications of the active agent. Methods of making the bioconjugates and bifunctional isocyanate cross linking reagents of use in making such bioconjugates are provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
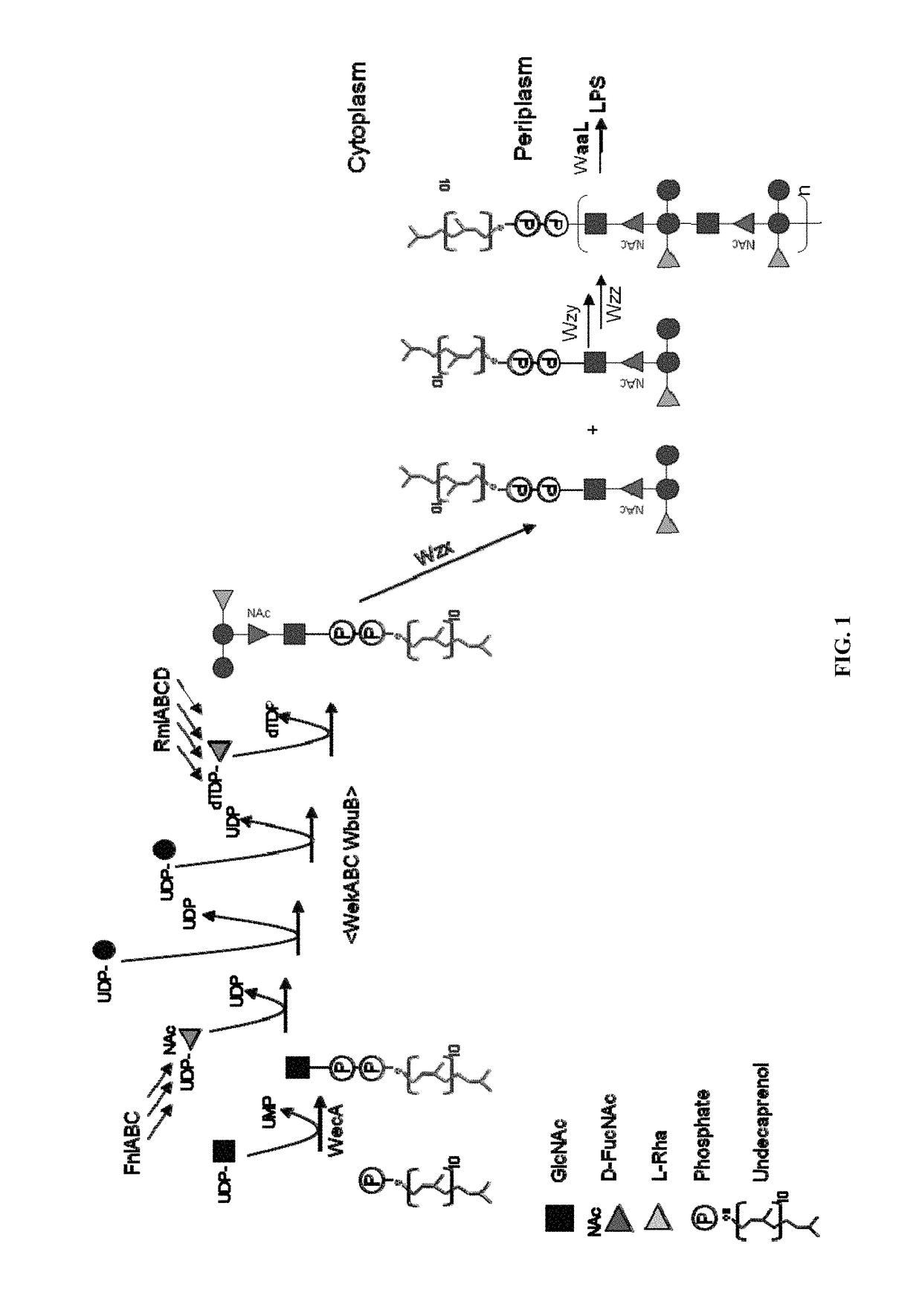
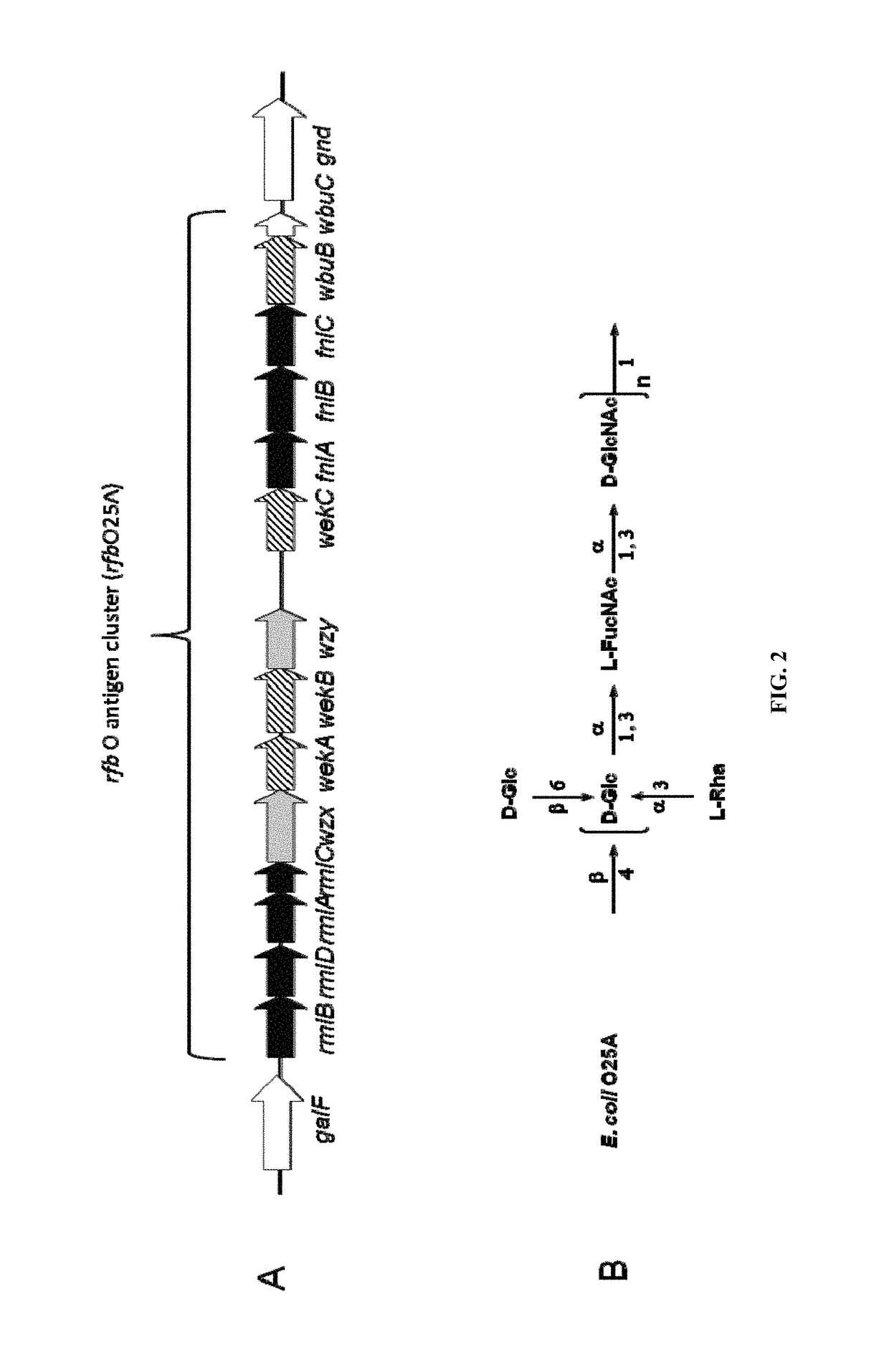
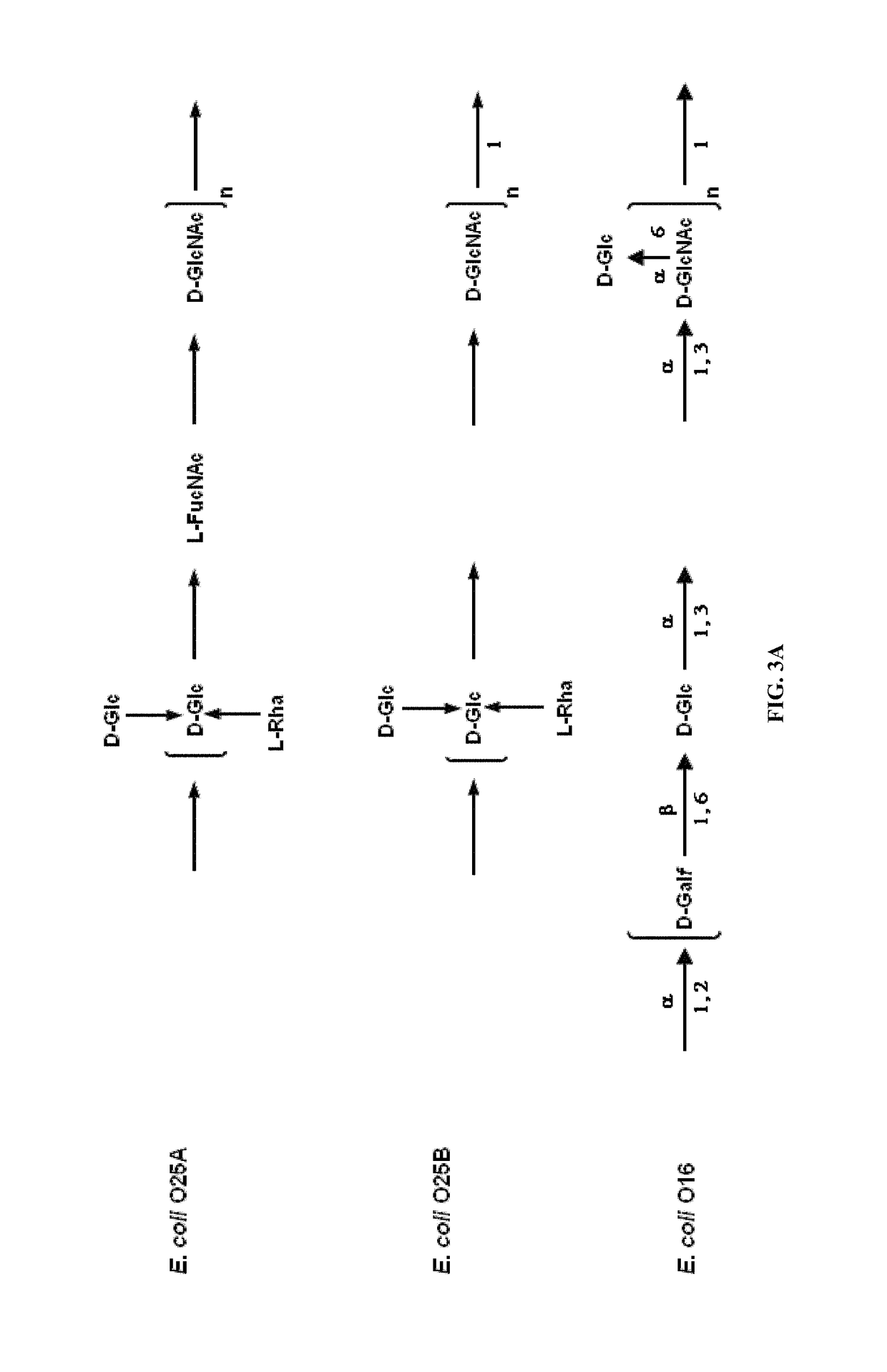
Novel polysaccharide and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150238588A1Reduce severityInhibit progressAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical drugCarrier protein
Provided herein is a novel E. coli O polysaccharide, O25B. Also provided herein are prokaryotic host cells comprising enzymes (e.g., glycosyltransferases) used in O25B production. The host cells provided herein produce O25B bioconjugates, wherein said bioconjugates comprise O25B linked to a carrier protein. Further provided herein are compositions, e.g., pharmaceutical compositions, comprising O25B and / or bioconjugates comprising O25B. Such compositions can be used as vaccines against infection with ExPEC, and may further comprise one or more additional bioconjugates.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
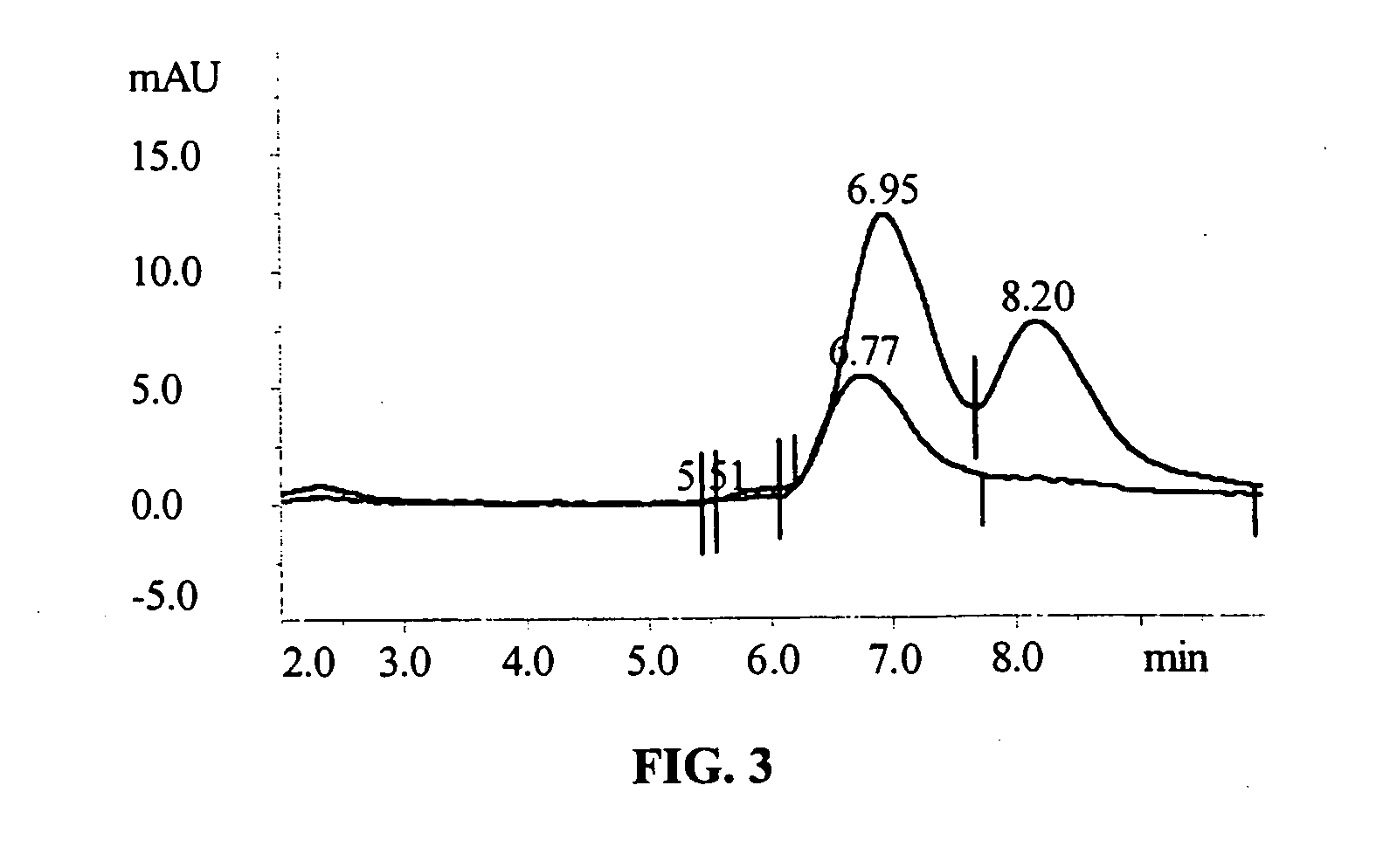
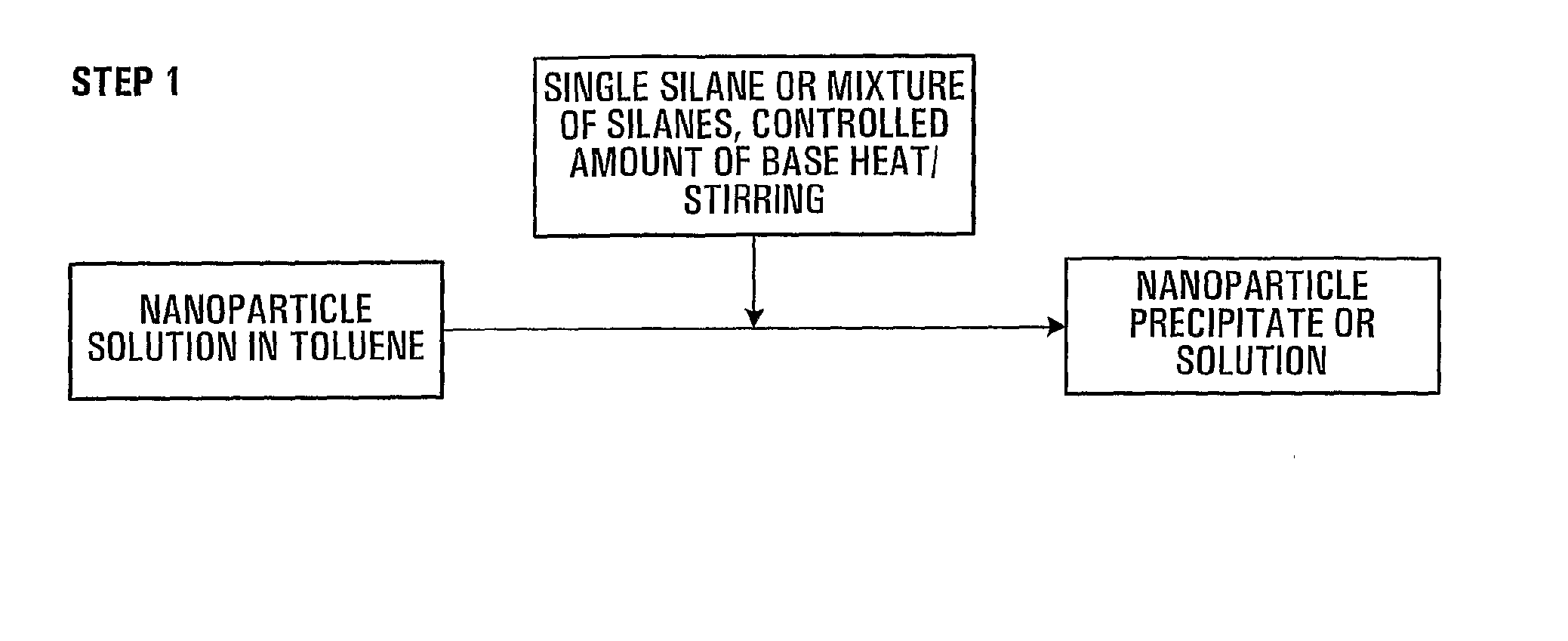
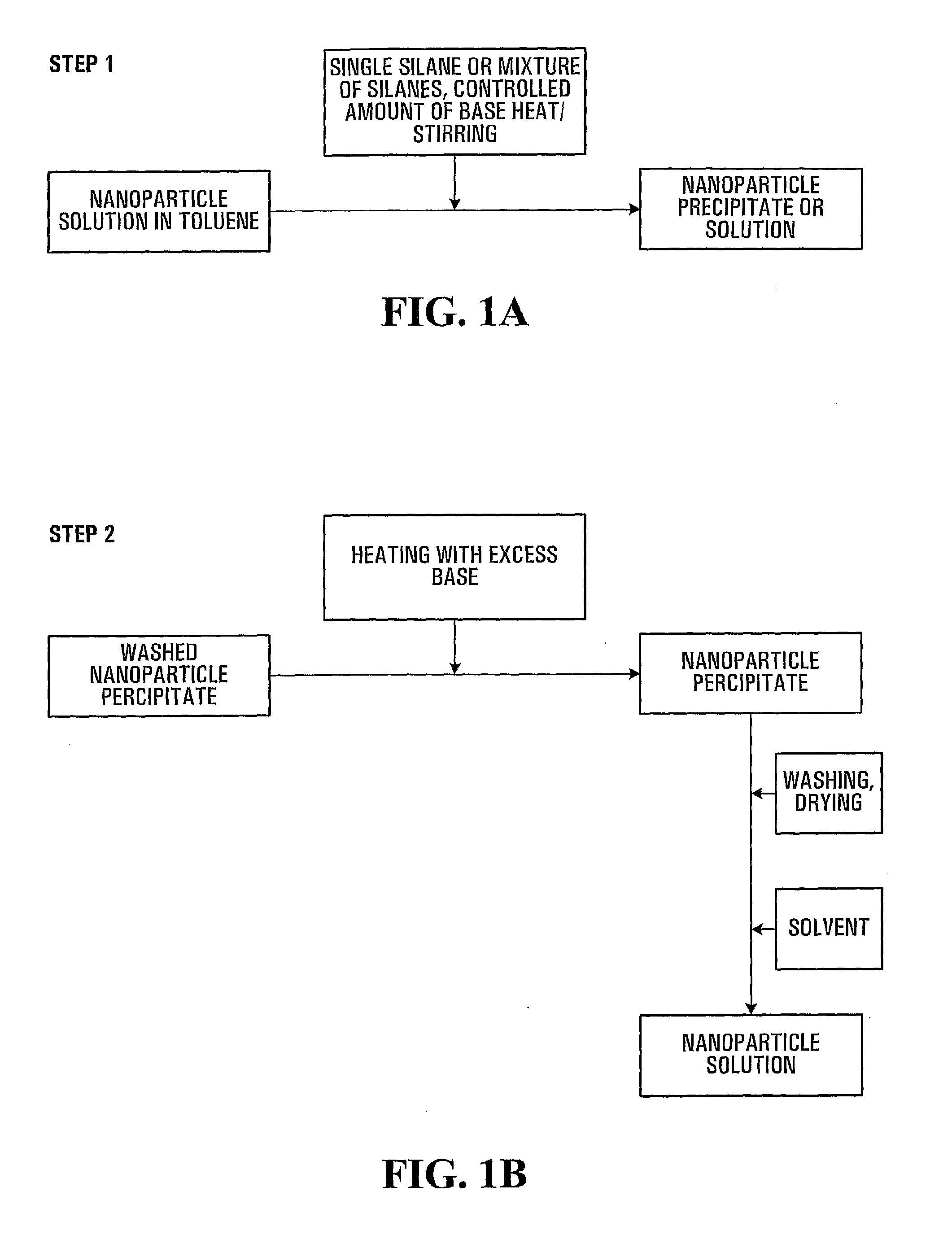
Water-Soluble, Surface-Functionalized Nanoparticle for Bioconjugation Via Universal Silane Coupling
The invention provides a process for the preparation of a surface-functionalized nanoparticle comprising: (a) reacting a nanoparticle with a functionalized silane and a base in a substantially non-aqueous solvent to obtain a partially conjugated silanated nanoparticle, wherein the functionalized silane and the base are present in relative amounts such that said functionalized silane undergoes substantially only a single hydrolysis reaction; (b) reacting the partially conjugated silanated nanoparticle formed in step (a) with a base in a solvent in which the partially conjugated silanated nanoparticle is substantially insoluble and in which the base is substantially soluble. The invention also provides a surface-functionalized nanoparticle prepared therefrom and a bioconjugate comprising said a surface-functionalized nanoparticle.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
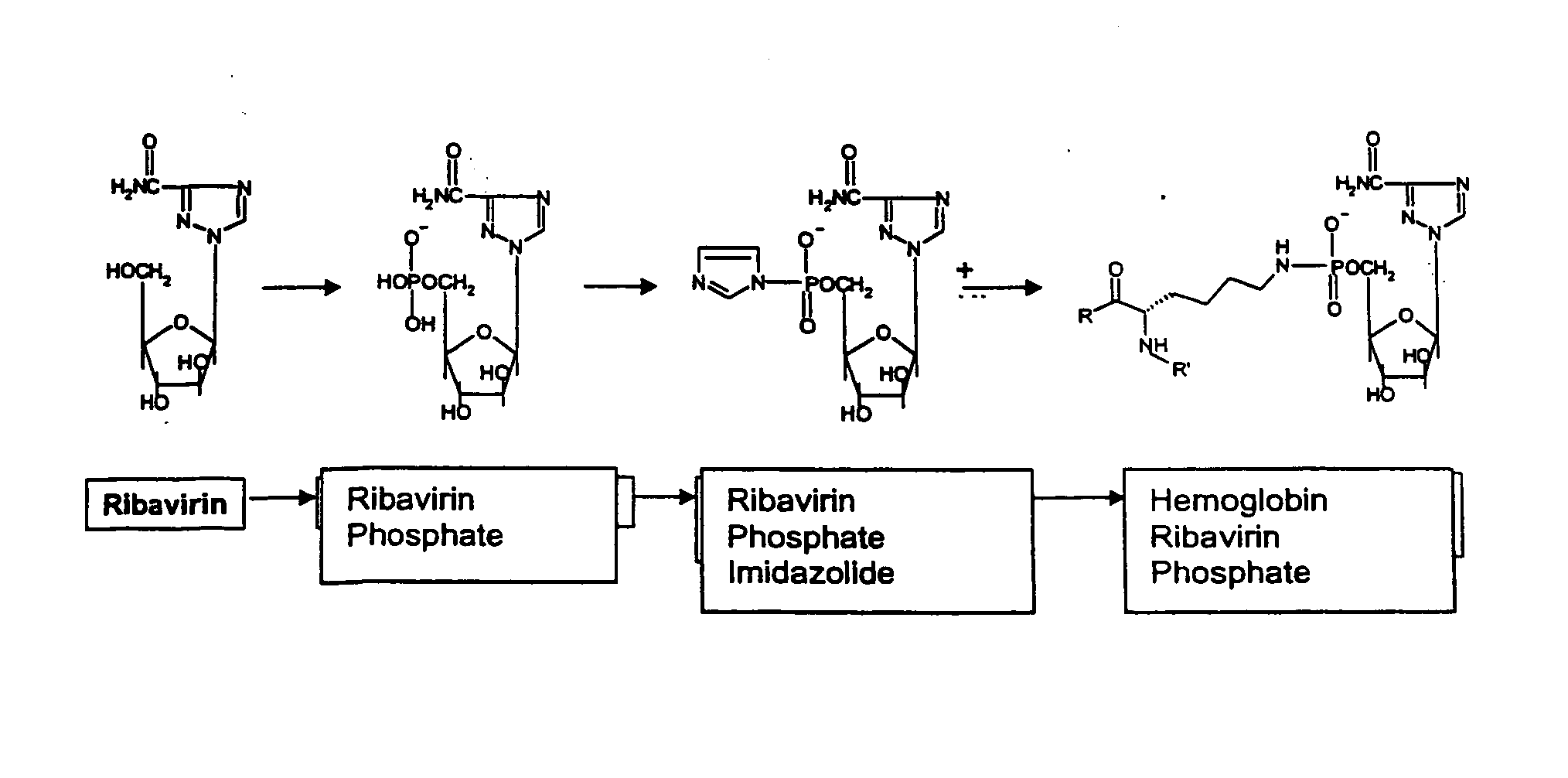
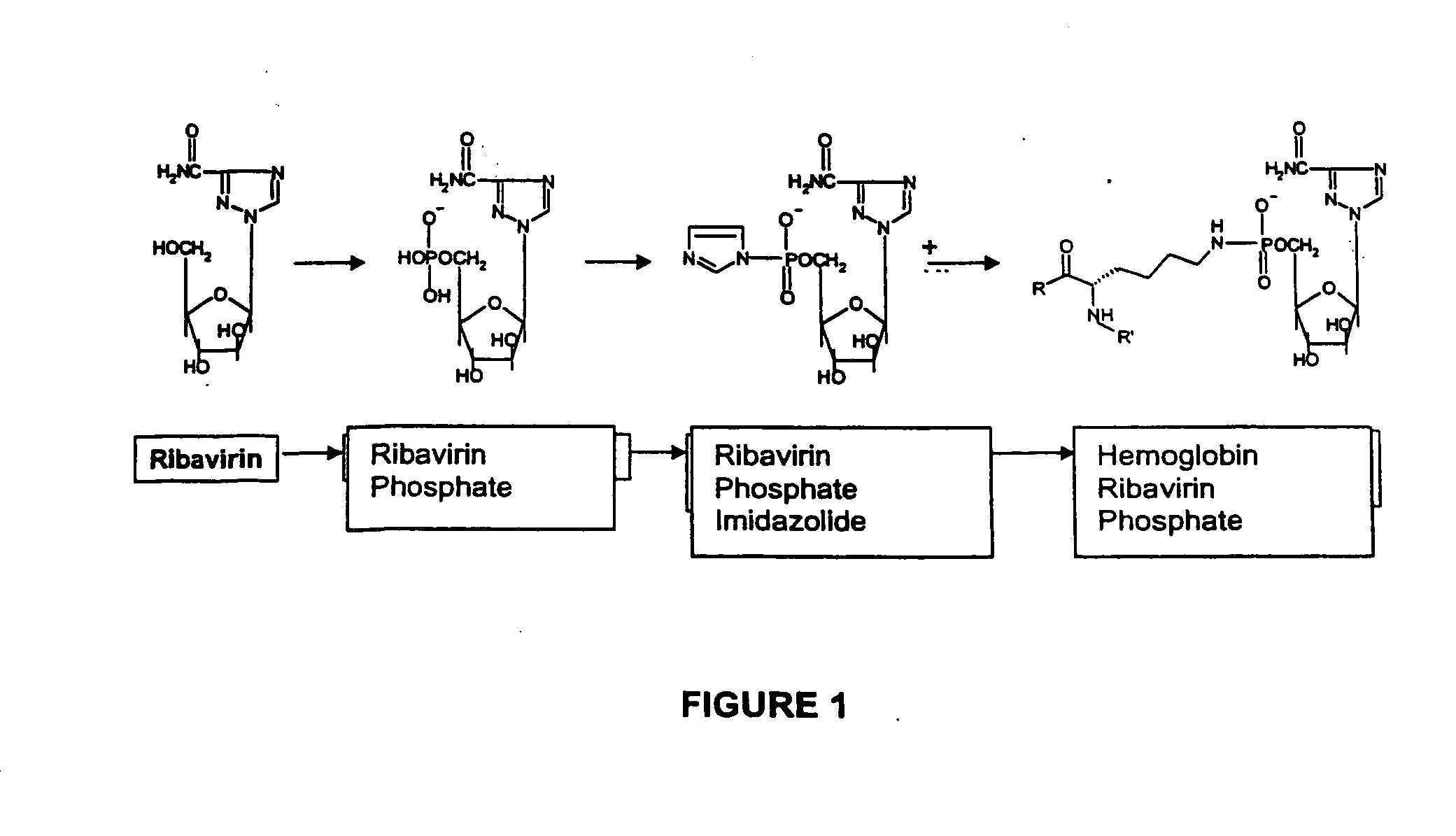
Targeted delivery of antiviral compounds through hemoglobin bioconjugates
InactiveUS20050059576A1Simple methodBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCompound (substance)Viral infection
This invention relates to targeted delivery of anti-viral compounds through protein bioconjugation. More particularly, it relates to an anti-viral compound conjugated to a protein, such as hemoglobin and to a method of treating a viral infection using said conjugate. The invention also provides a method of targeted drug delivery of an anti-viral nucleoside analogue to macrophages, cells comprising a hemoglobin receptor and to CD163 bearing cells.
Owner:ADAMSON J GORDON +3
Polysaccharide and uses thereof
ActiveUS9700612B2Reduce severityInhibit progressAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier proteinPolysaccharide
Provided herein is a novel E. coli O polysaccharide, O25B. Also provided herein are prokaryotic host cells comprising enzymes (e.g., glycosyltransferases) used in O25B production. The host cells provided herein produce O25B bioconjugates, wherein said bioconjugates comprise O25B linked to a carrier protein. Further provided herein are compositions, e.g., pharmaceutical compositions, comprising O25B and / or bioconjugates comprising O25B. Such compositions can be used as vaccines against infection with ExPEC, and may further comprise one or more additional bioconjugates.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Conjugate conjugated from polyethylene glycol and curcumin derivative
InactiveCN101524546AKetone active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityHydrogen
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and more particularly relates to conjugate conjugated from polyethylene glycol and curcumin derivative as shown in formula 1 and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from nitro, amidogen, bi-low alkyl amidogen and low alkoxy; R3 and R4 are independently selected from halogen, nitro and hydrogen; R5 is low alkyl or hydrogen; R6 is hydrogen or low alkyl that can be substituted by low alkyl, nitro, hydroxide radical or sulfhydryl which are randomly selected; and n is 1 or 2. The conjugate has good water solubility, overcomes the disadvantages of poor water solubility, low bioavailability, and the like, existing in curcumin, and has low preparation cost and better antitumor activity. In addition, the invention also relates to the pharmaceutical composition, the preparation method and the application as medicament of the conjugate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
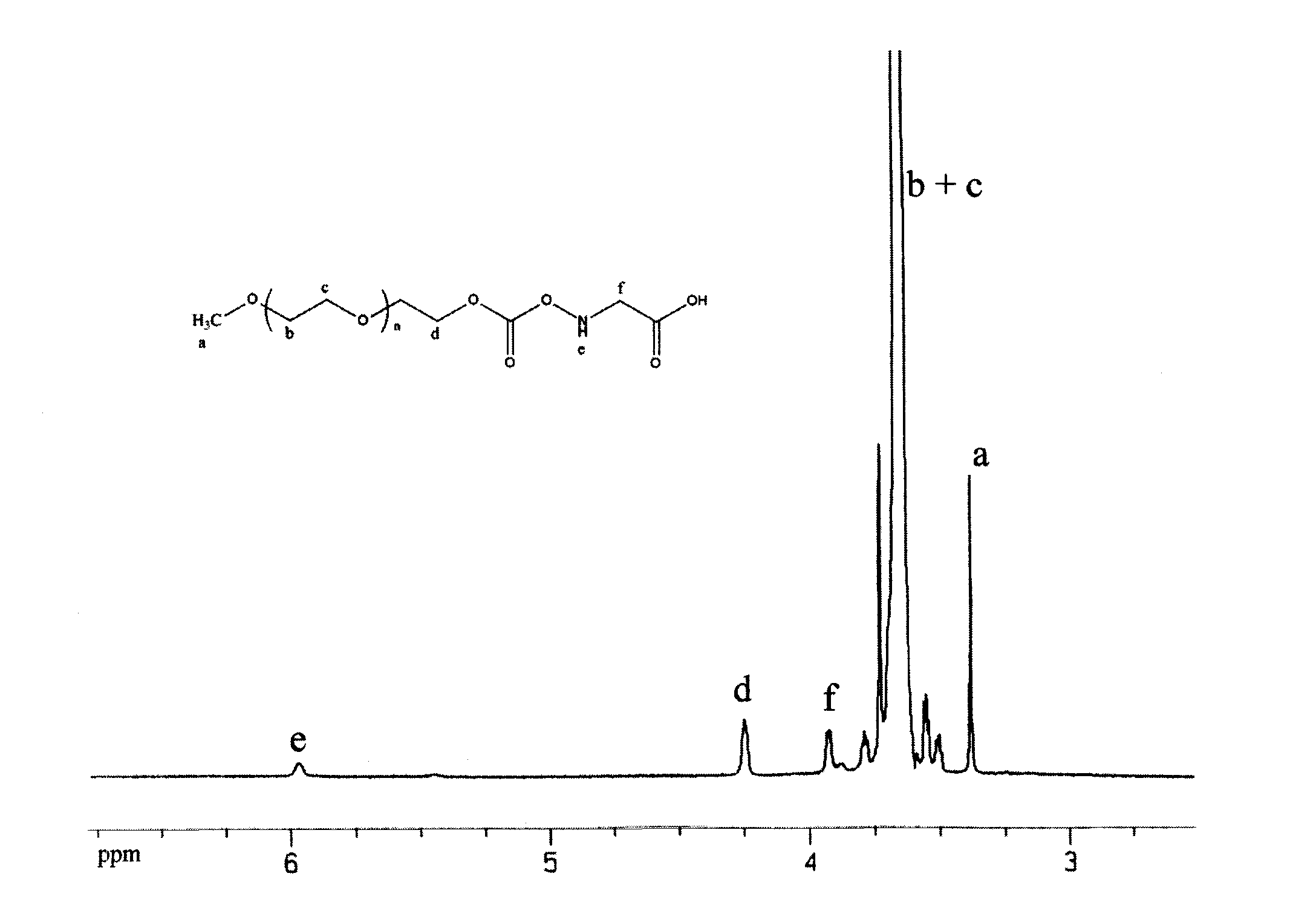
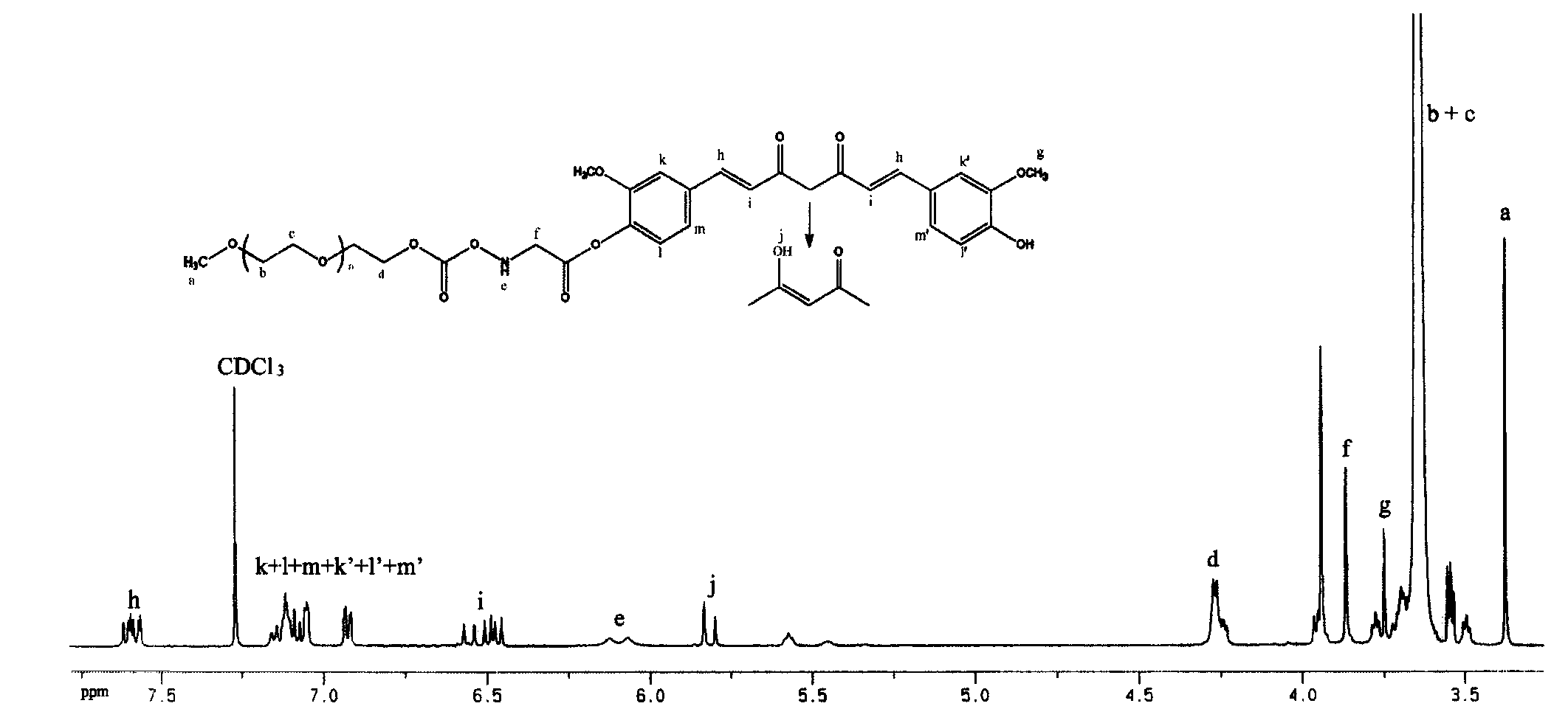
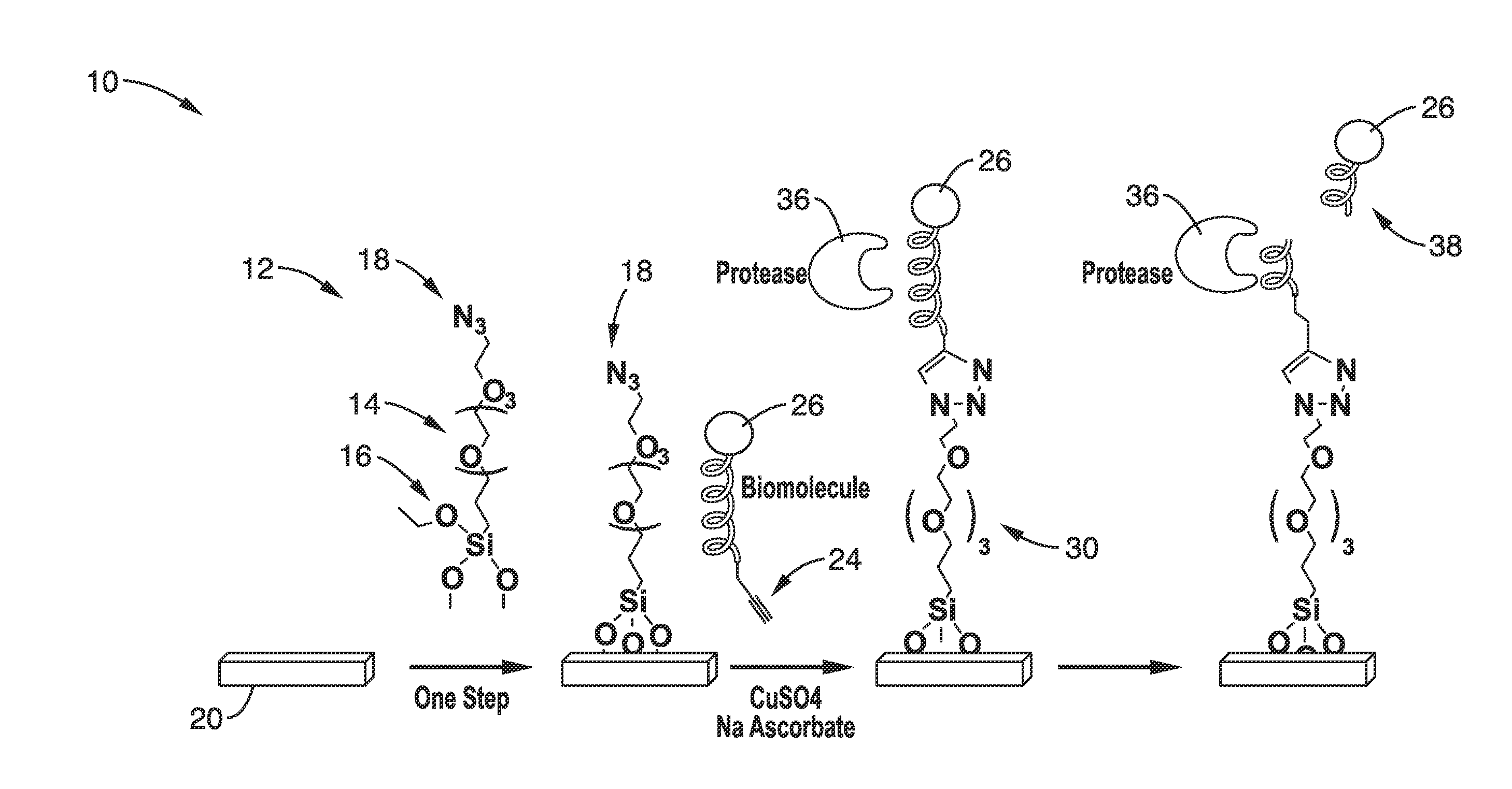
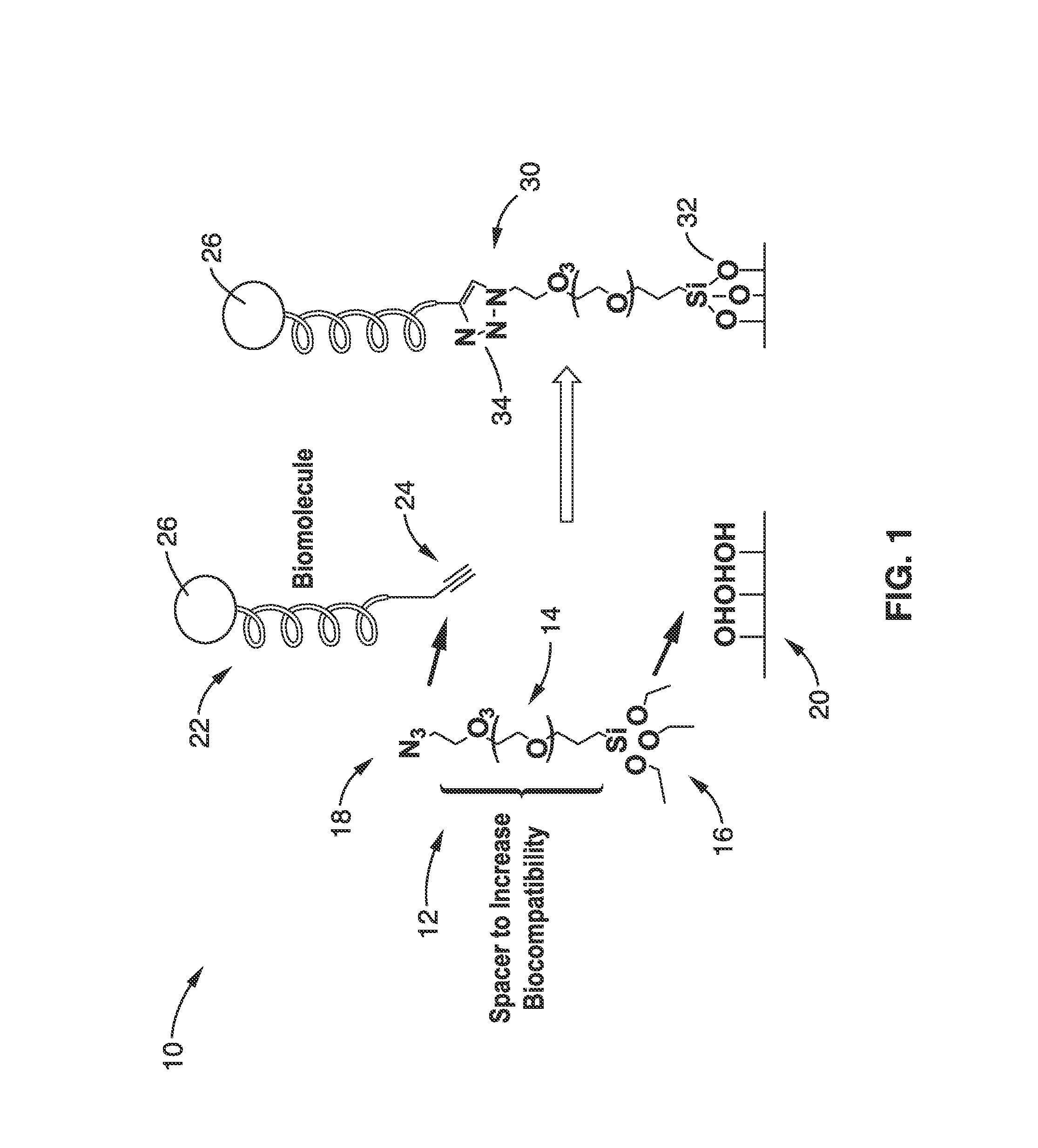
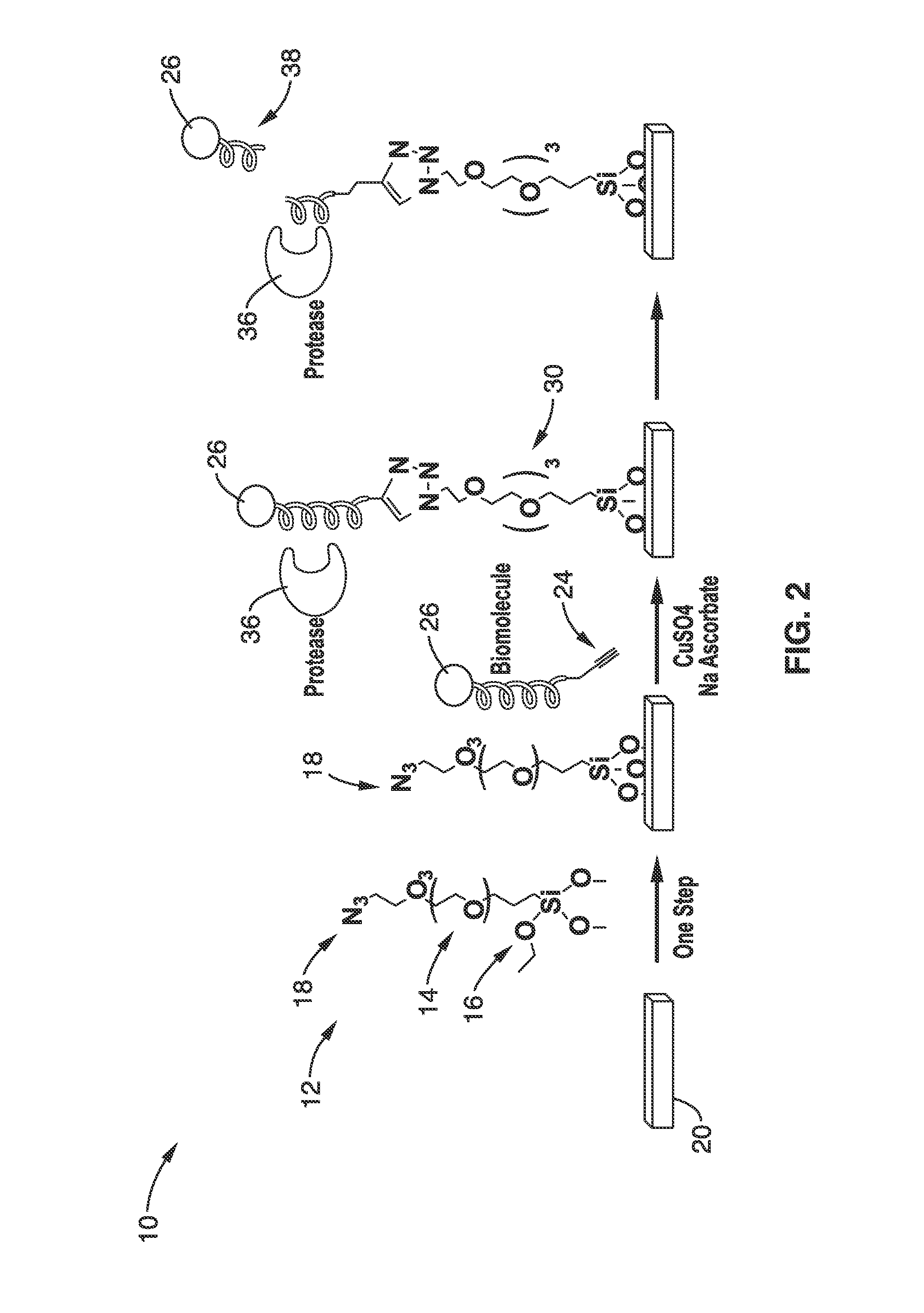
Bioconjugation using bifunctional linkers
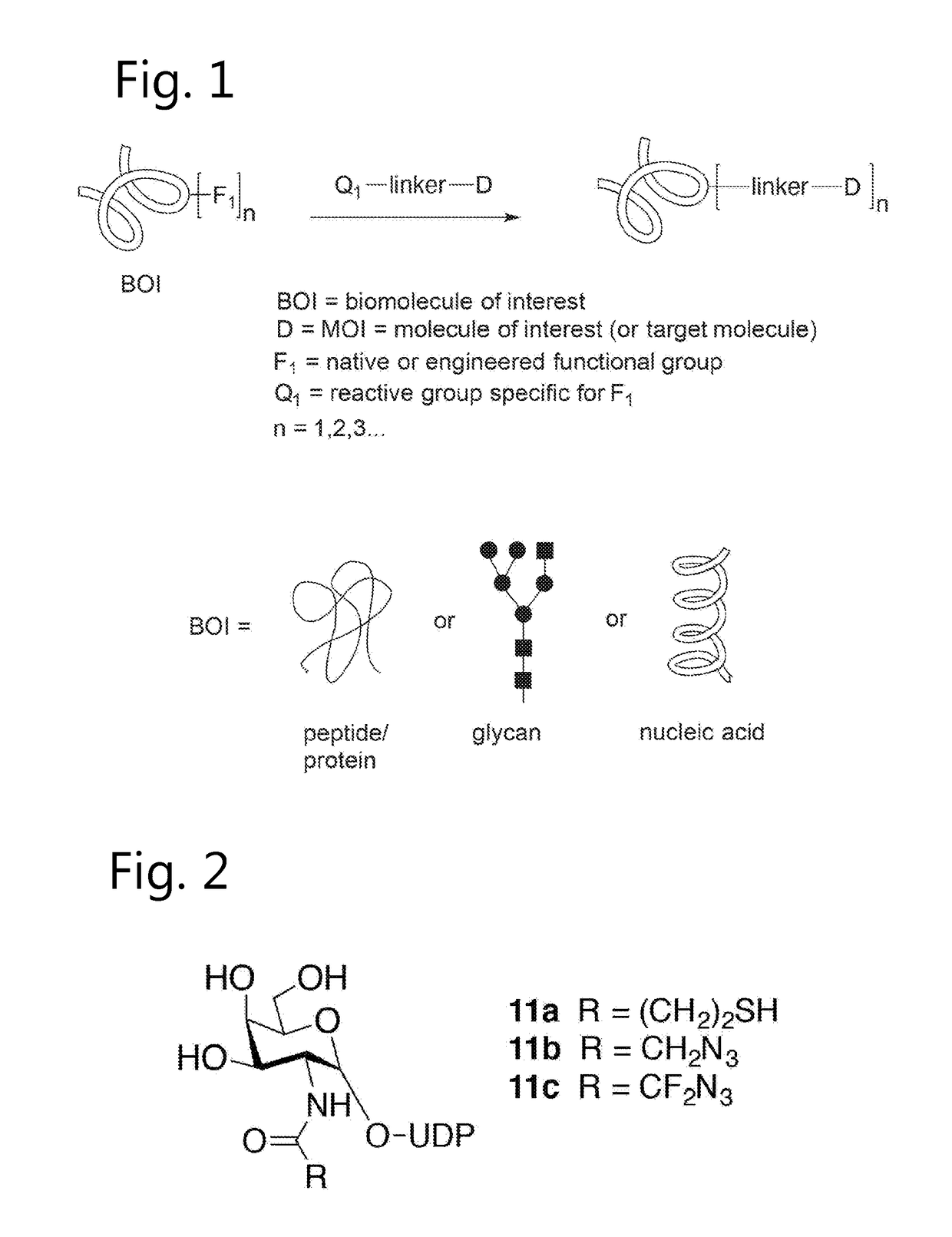
InactiveUS20130338044A1Rapidly achieve high yieldHigh densityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSugar derivativesSilanesClick chemistry
A bifunctional linker and method of use is provided that has a spacer molecule with a functional group on one end configured to couple to the surface of a substrate and a function group on the other end that is configured couple to a biomolecule and methods of use. The preferred bifunctional linker has a poly(ethylene glycol) spacer ranging from 3 to 20 ethylene glycol units that has a silane functional group to react with a substrate and an azide functional group that can couple to a biomolecule that includes an alkyne group. The preferred linker can produce an azide-derivatized glass surface in one step and the azide functional group of the spacer can in sequence conjugate with a biomolecule using click chemistry, which can be conducted at low temperature and in aqueous solution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
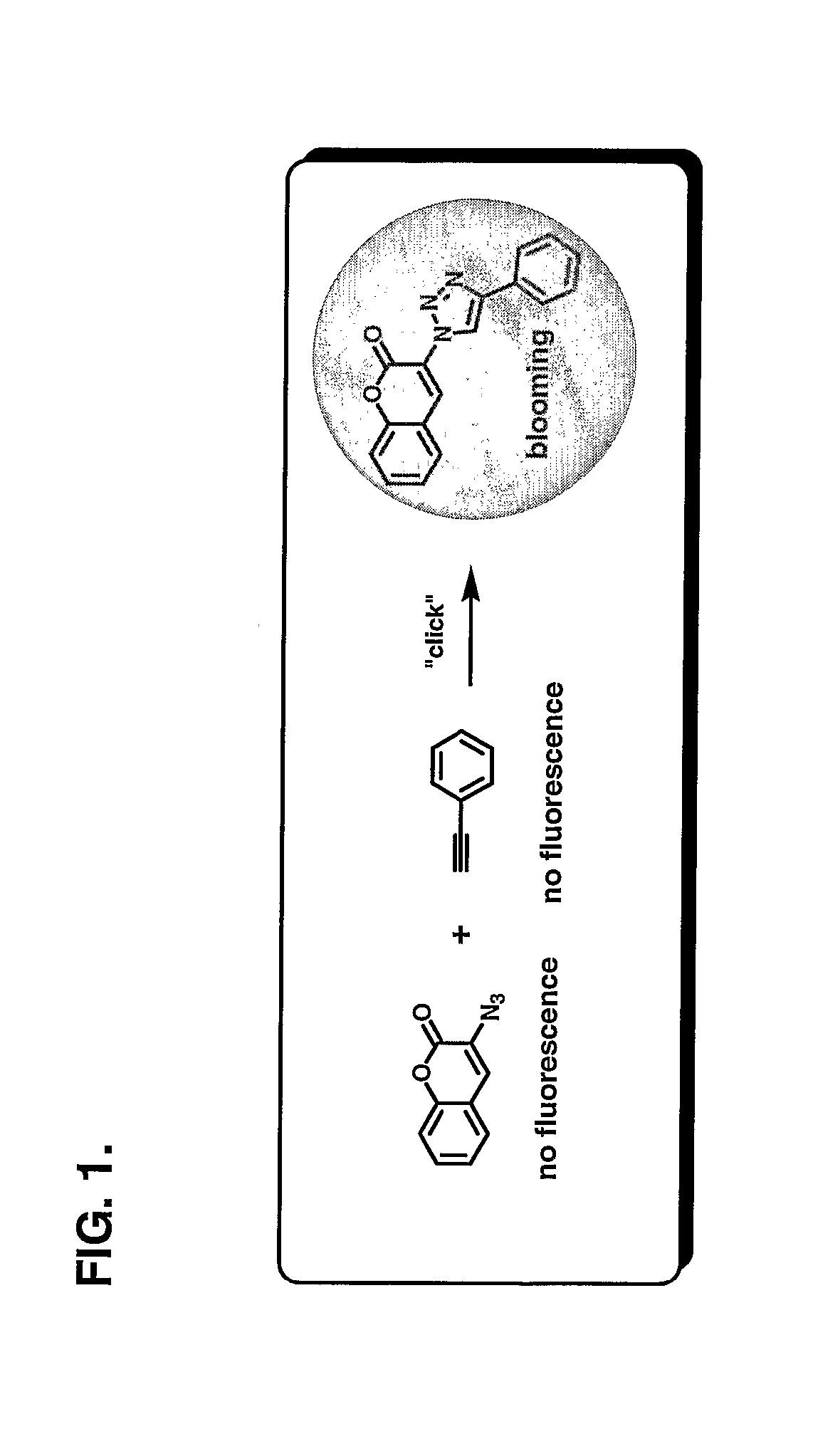
Chemoselective Fluorgenic Molecular Linkers and Methods for Their Preparation and Use
ActiveUS20070224695A1Easy to useEasy to distinguishBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceChemical compound
The present invention describes a bioconjugation strategy and compounds that are useful therein in which a fluorescent signal is produced when two molecular or supramolecular entities are linked by chemoselective combination of one linker having an azido or halide substituent group with another linker having a cyano or an alkyne substituent group. A kit is also provided.
Owner:SOUTH CAROLINA UNIV OF
Cysteine-containing peptide tag for site-specific conjugation of proteins
The present invention is directed to a biological conjugate, comprising: (a) a targeting moiety comprising a polypeptide having an amino acid sequence comprising the polypeptide sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 and the polypeptide sequence of a selected targeting protein; and (b) a binding moiety bound to the targeting moiety; the biological conjugate having a covalent bond between the thiol group of SEQ ID NO:2 and a functional group in the binding moiety. The present invention is directed to a biological conjugate, comprising: (a) a targeting moiety comprising a polypeptide having an amino acid sequence comprising the polypeptide sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 and the polypeptide sequence of a selected targeting protein; and (b) a binding moiety that comprises an adapter protein, the adapter protein having a thiol group; the biological conjugate having a disulfide bond between the thiol group of SEQ ID NO:2 and the thiol group of the adapter protein. The present invention is also directed to biological sequences employed in the above biological conjugates, as well as pharmaceutical preparations and methods using the above biological conjugates.
Owner:SIBTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com