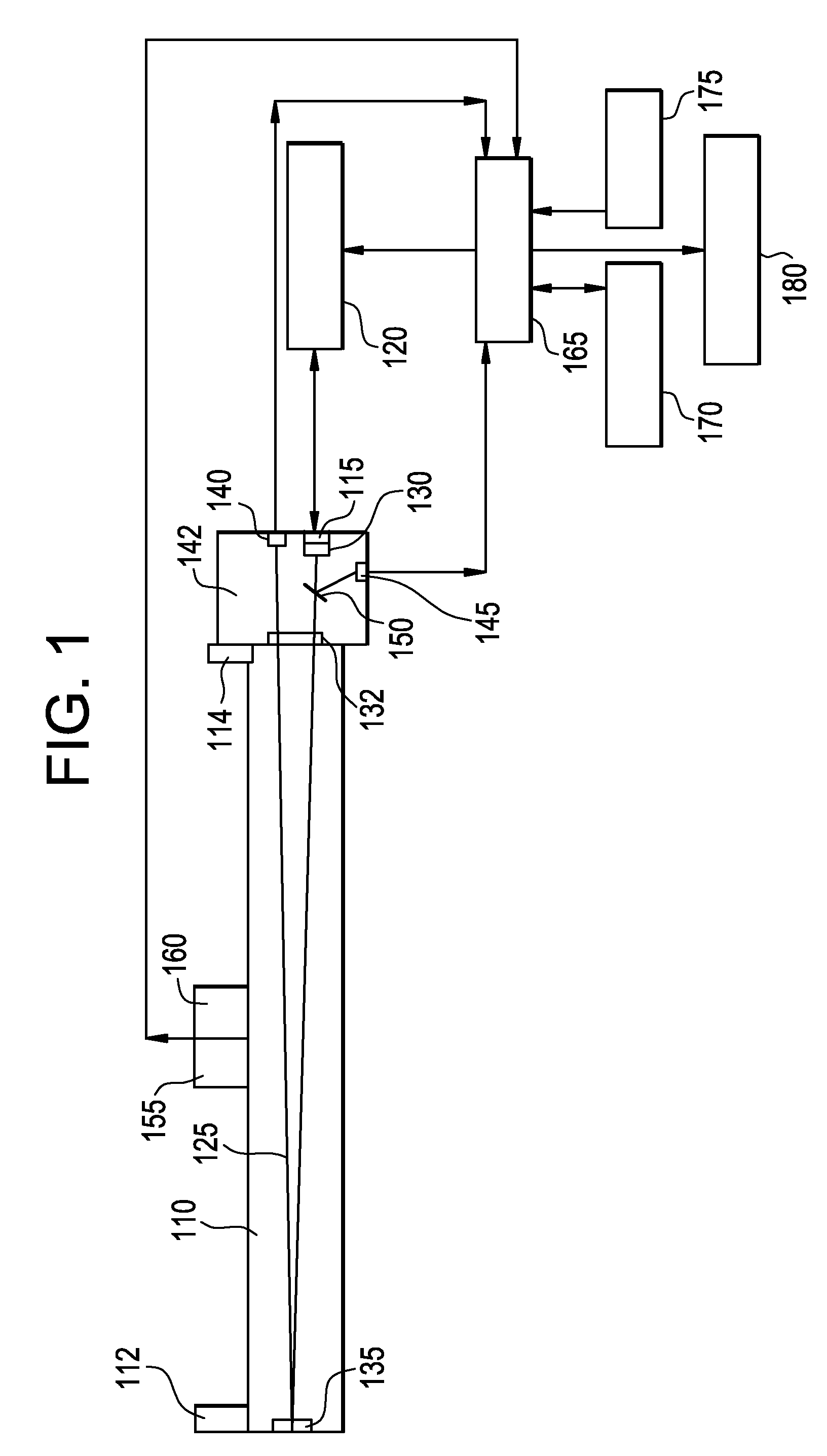
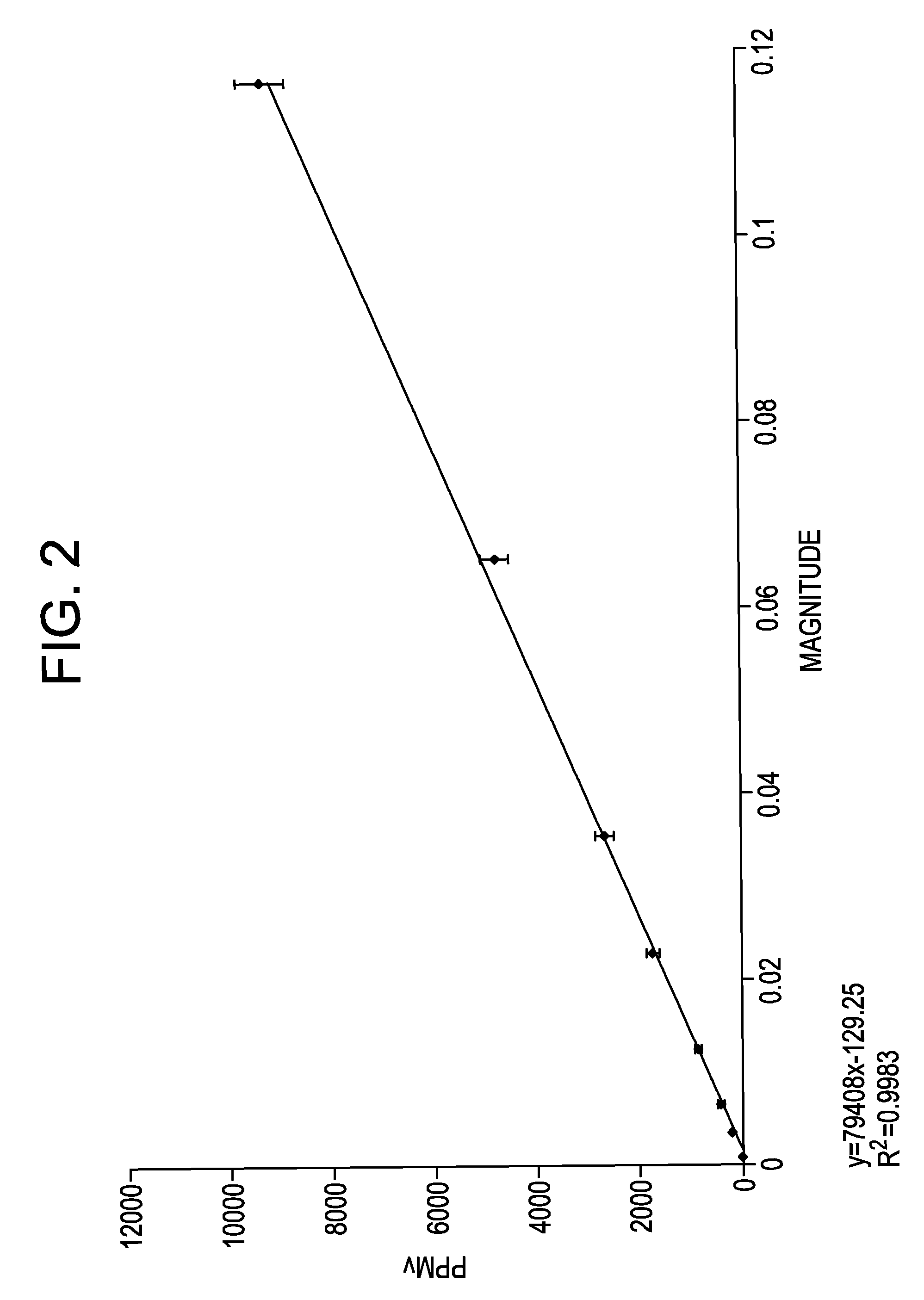
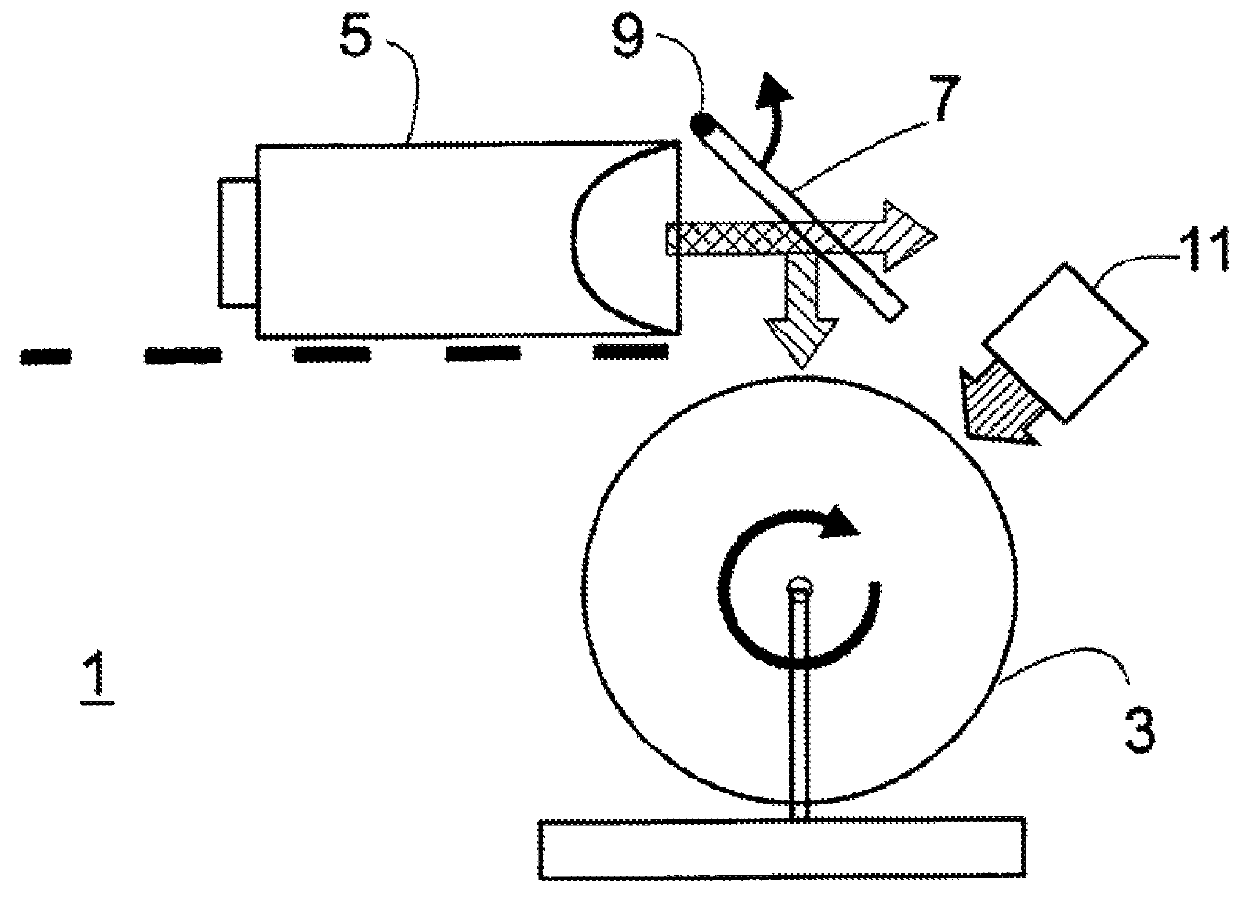
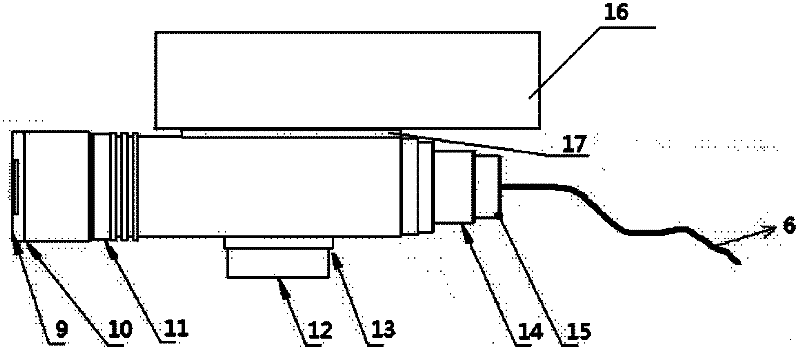
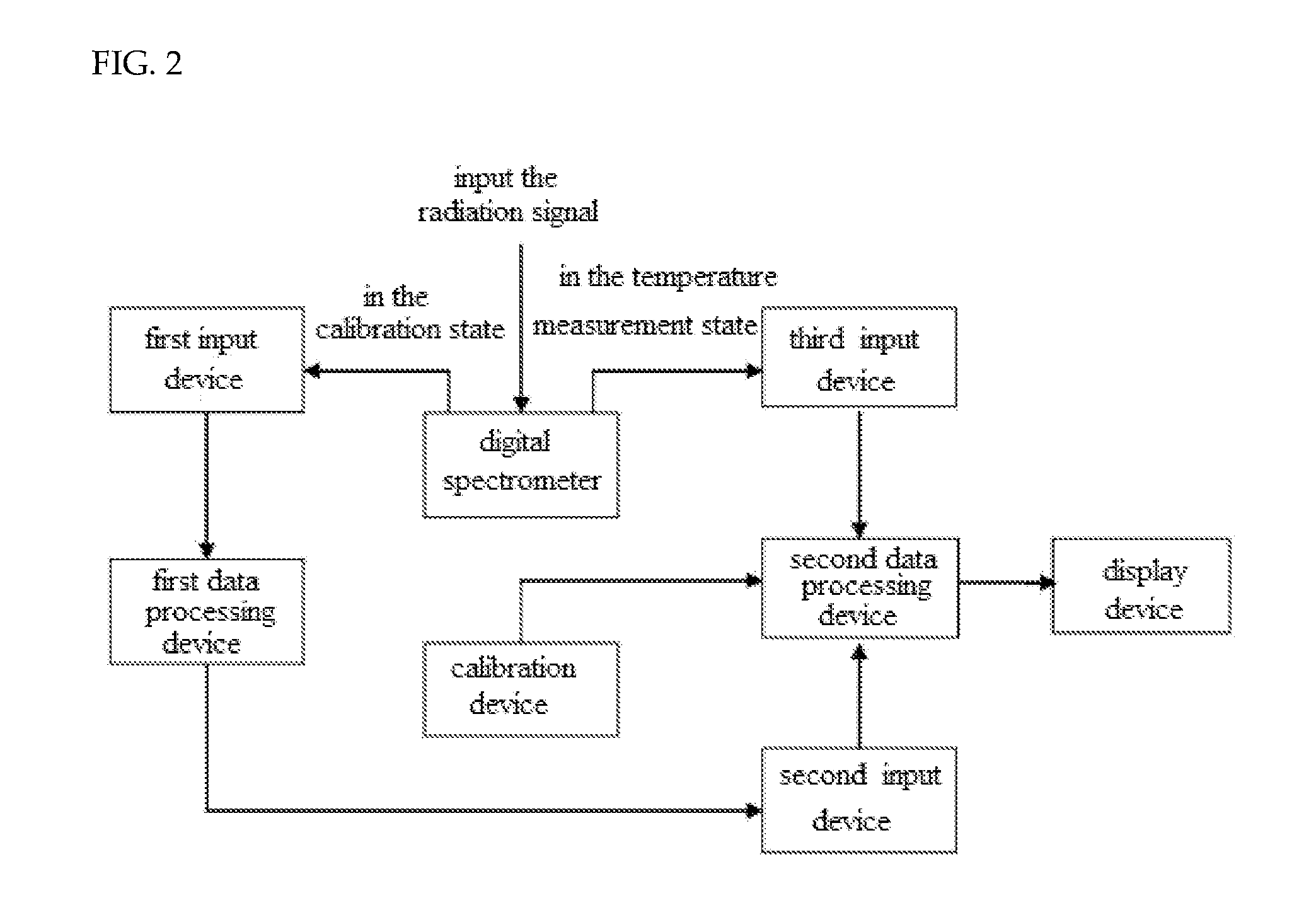
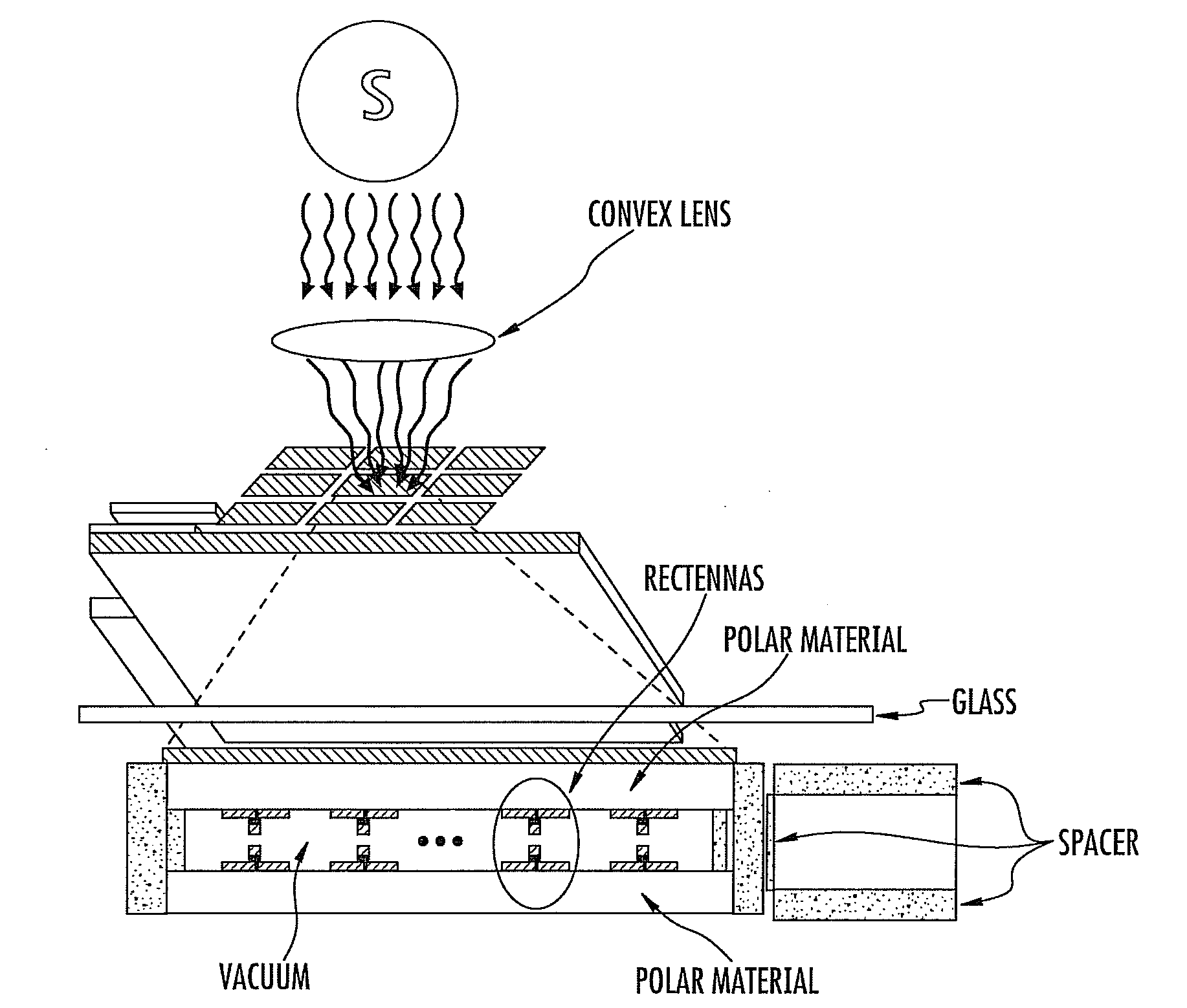
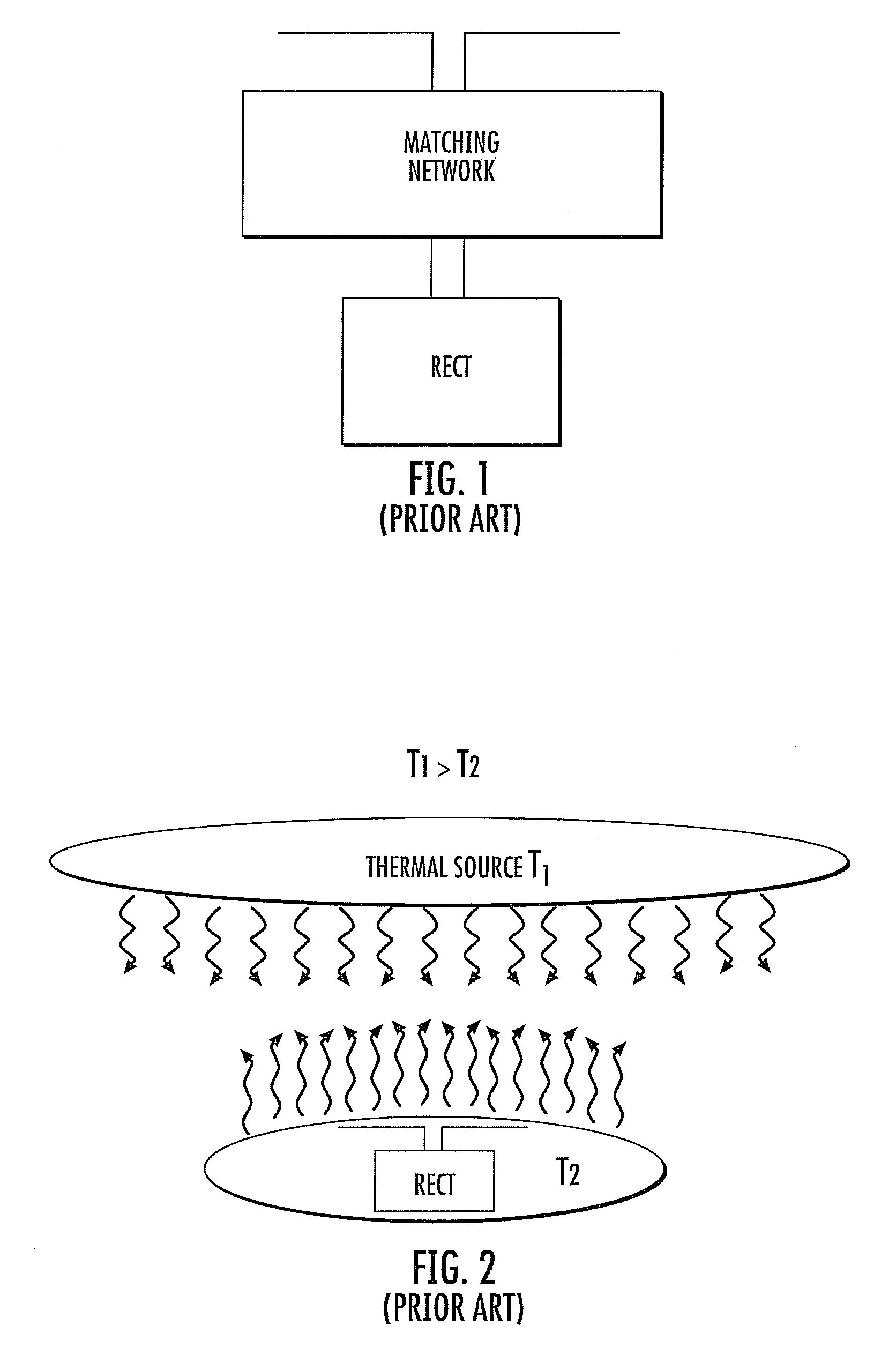
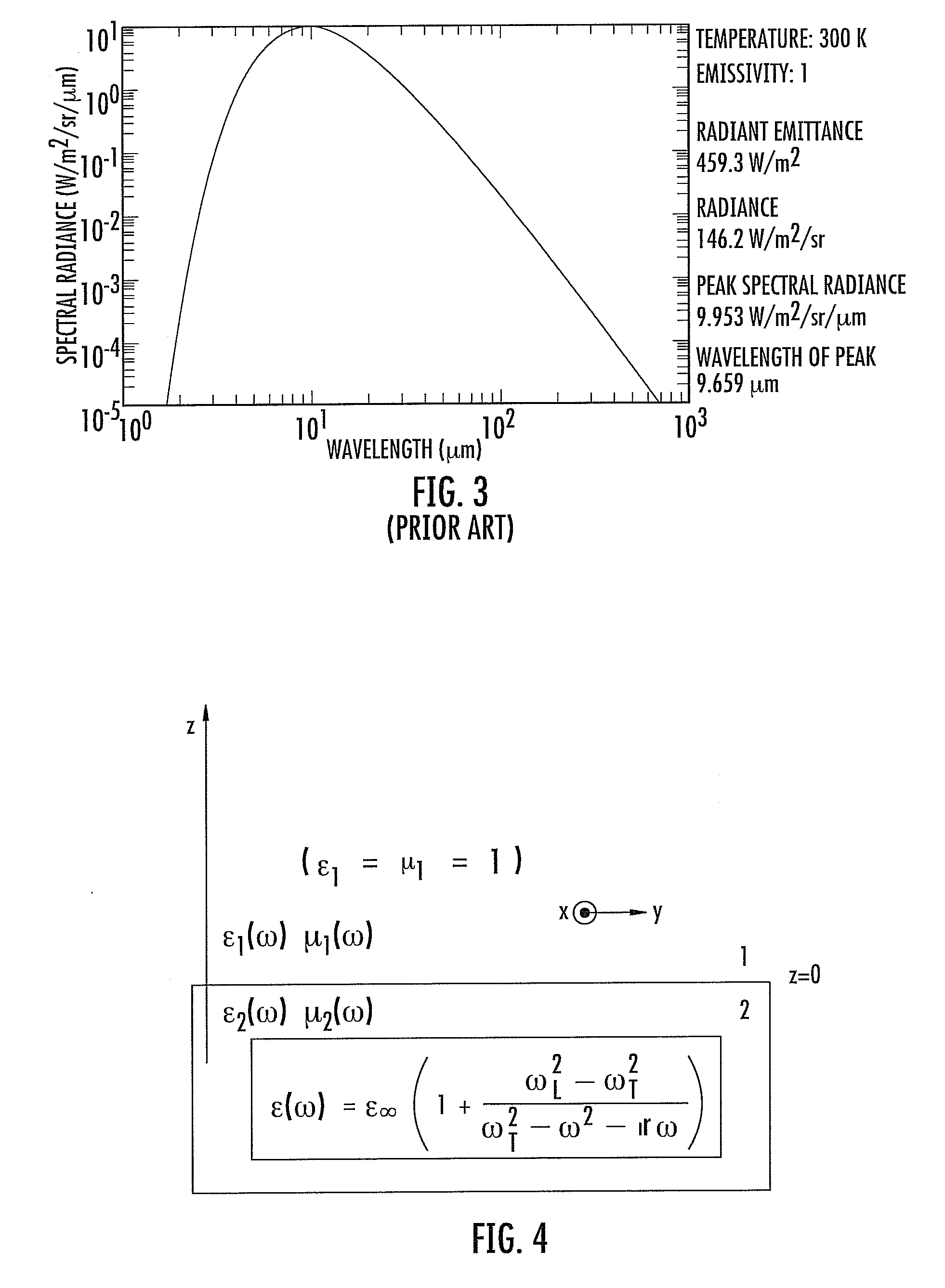
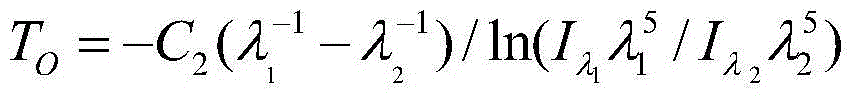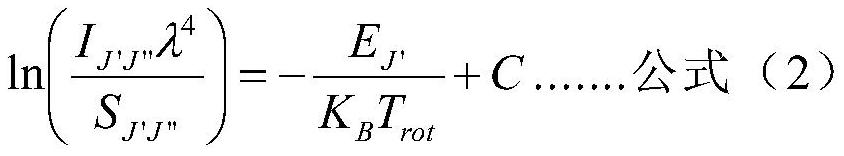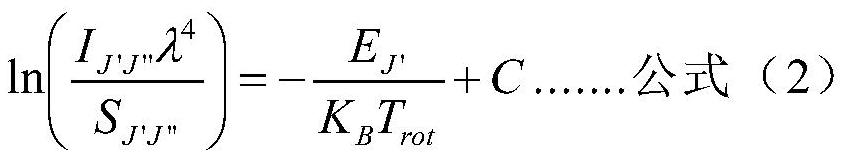Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Monochromatic radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, monochromatic light is electromagnetic radiation of a single frequency. In the physical sense, no source of electromagnetic radiation is purely monochromatic, since that would require a wave of infinite duration as a consequence of the Fourier transform's localization property (cf. spectral coherence).
Method and apparatus of sterilization using monochromatic UV radiation source
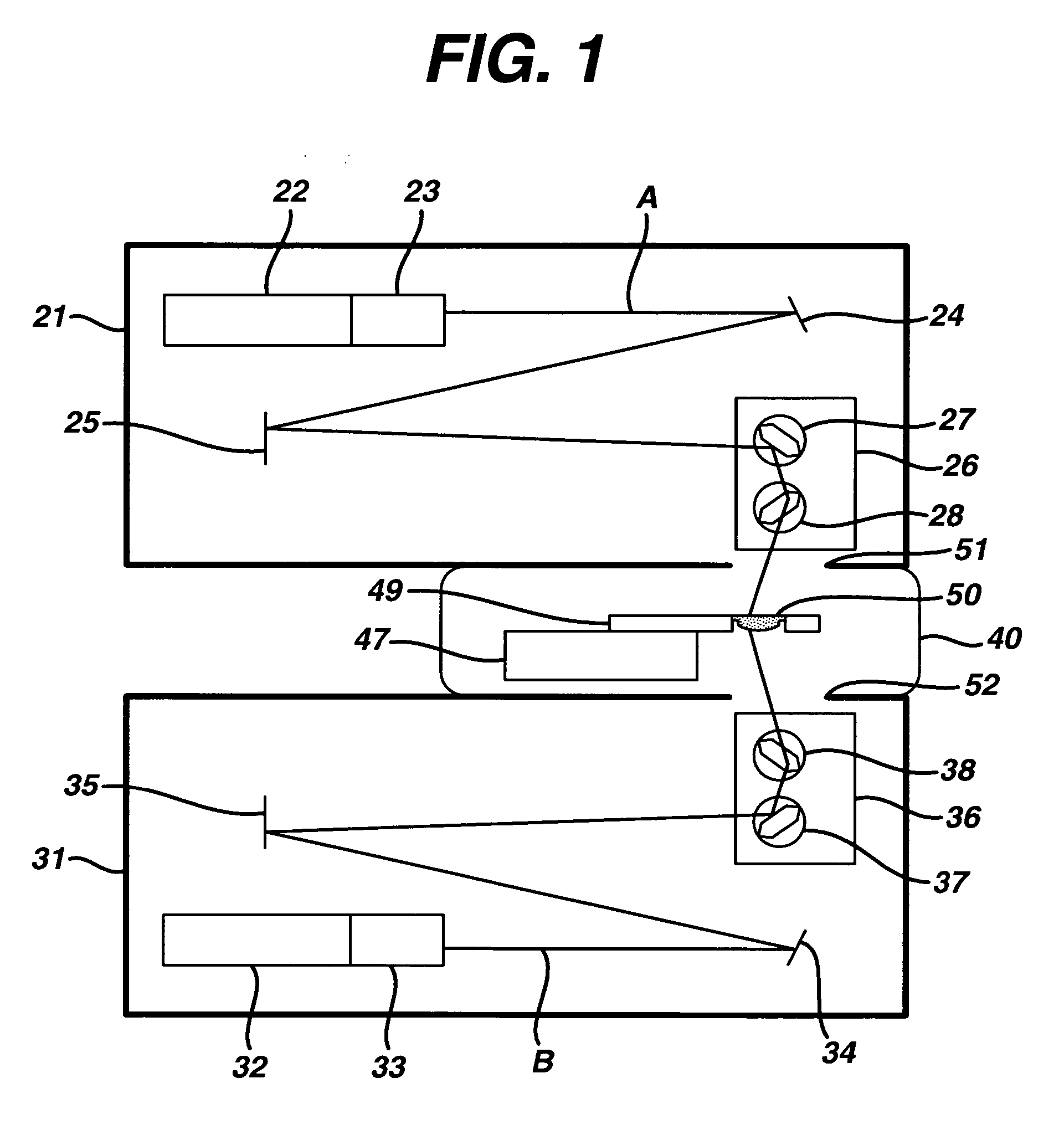
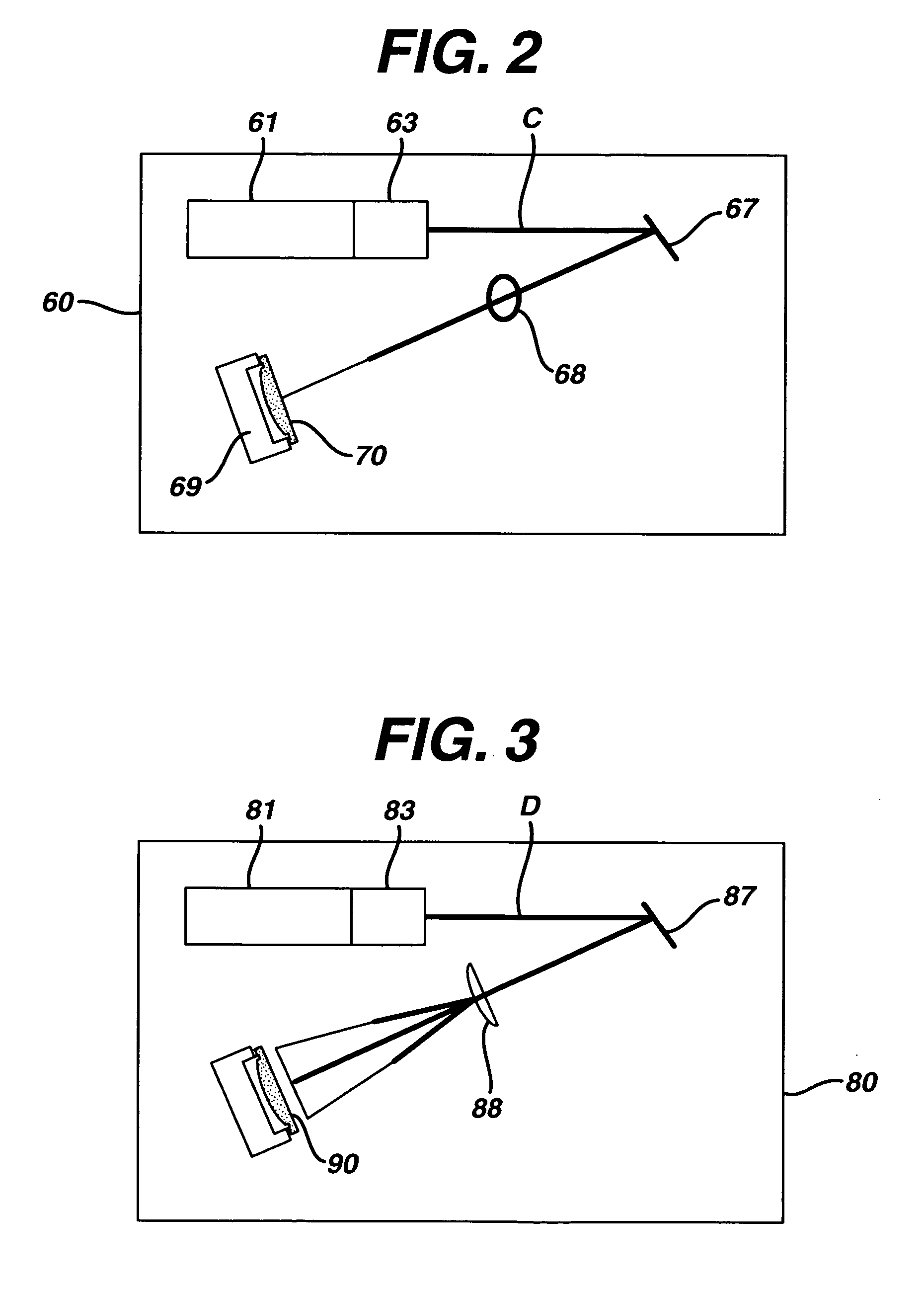
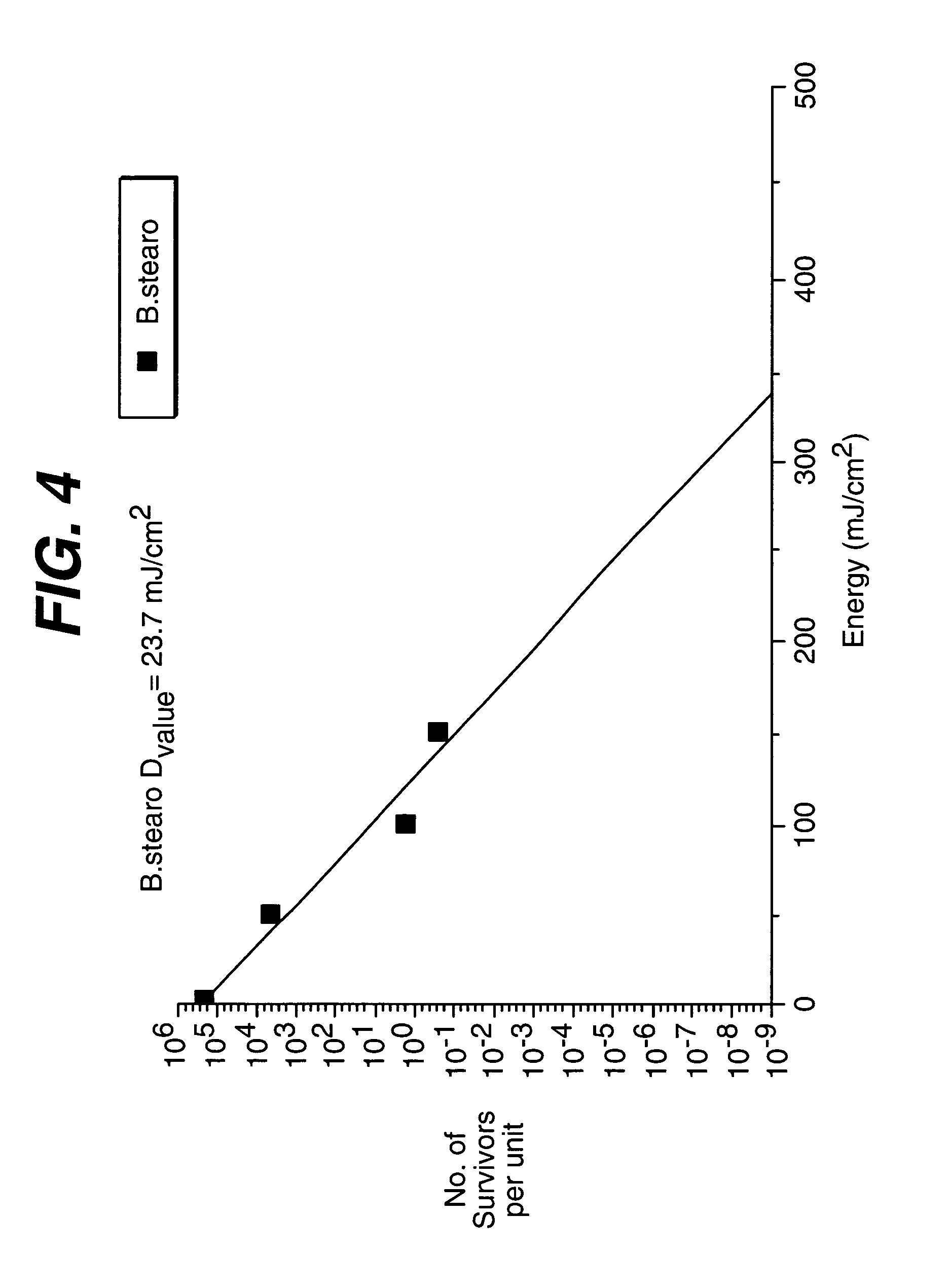
This invention provides a process of sterilizing a medical device, and preferably the contents of a sealed container which comprises said medical device, comprising the step of exposing said medical device to monochromatic ultraviolet radiation whereby the Dvalue of Bacillus stearothermophilus (ATCC 7953) is at least 23.7 mJ / cm2 monochromatic ultraviolet radiation at 257 nm to the spore. Further, this invention provides a process of sterilizing a medical device comprising the step of subjecting said medical device to monochromatic ultraviolet radiation wherein the minimum total energy density of said monochromatic ultraviolet radiation at 257 nm which reaches the microorganisms present on said medical device is at least 284 mJ / cm2. This invention further provides an apparatus for delivering UV radiation to a medical device for sterilization comprising a laser and a scanner for the laser such that at least 284 mJ / cm2 at 257 nm is applied to a treatment area for said medical device. This invention provides a process and apparatus in which sterilization can be achieved in less than 20 seconds, preferably less than 15 seconds, more preferably in less than 5 seconds. The process and apparatus are efficient and continuous.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
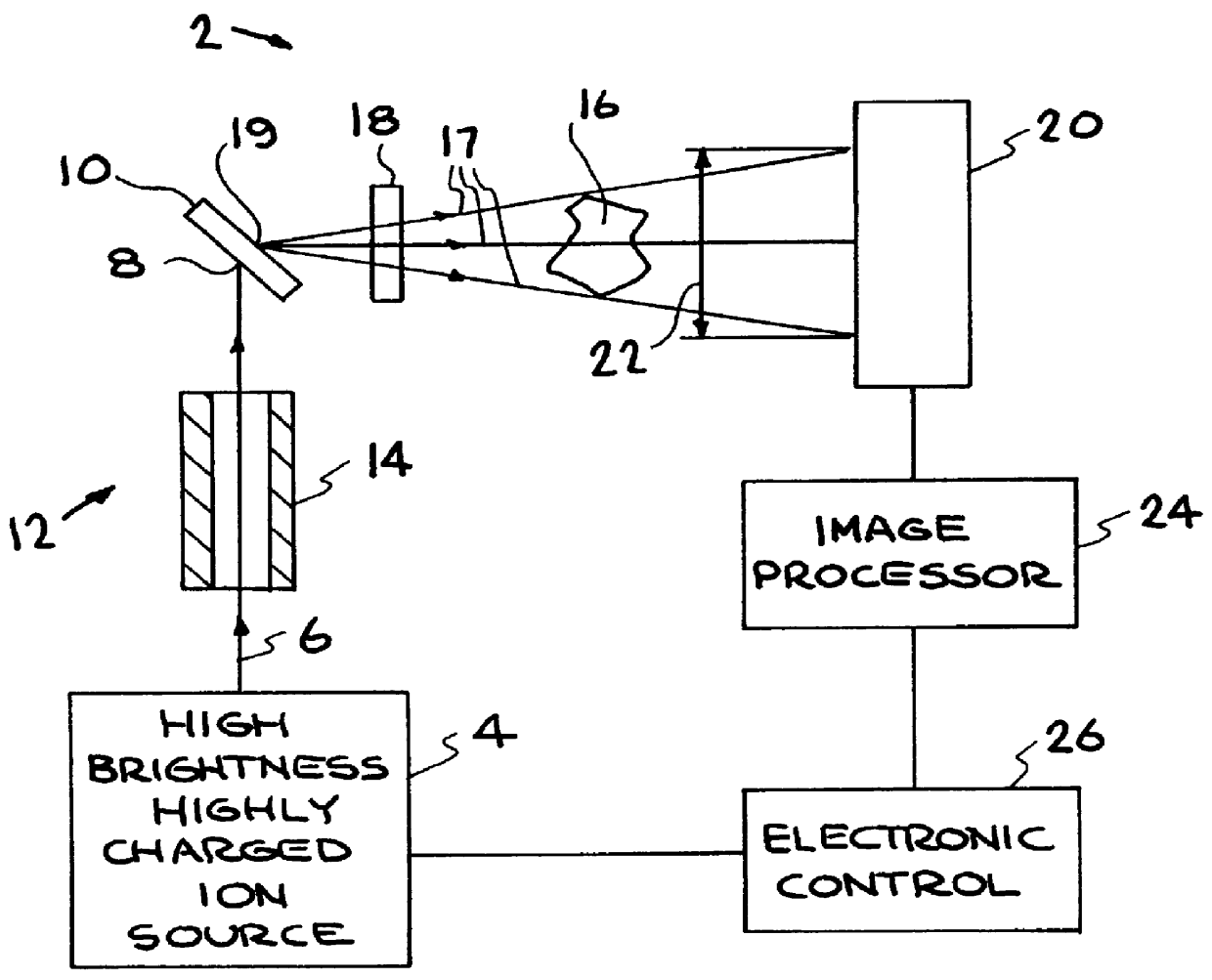
X-ray radiography with highly charged ions
An extremely small (1-250 micron FWHM) beam of slow highly charged ions deexciting on an x-ray production target generates x-ray monochromatic radiation that is passed through a specimen and detected for imaging. The resolution of the x-ray radiograms is improved and such detection is achieved with relatively low dosages of radiation passing through the specimen. An apparatus containing an electron beam ion trap (and modifications thereof) equipped with a focusing column serves as a source of ions that generate radiation projected onto an image detector. Electronic and other detectors are able to detect an increased amount of radiation per pixel than achieved by previous methods and apparati.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Optical filtering device
An optical filtering device incorporates first and second prisms, the latter prism counteracting the angular dispersion of the former prism. A spatial light modulator provides a positionally variable optical stop located to block radiation within a wavelength interval and received from a location within a scene. Unobscured radiation from that and other scene locations passes to a camera, which produces an image on a display. Opaque pixels in the stop are positioned to block unwanted light sources. The invention attenuates potentially dazzling monochromatic radiation while retaining radiation at other wavelengths for imaging purposes.
Owner:THE SEC OF STATE FOR DEFENCE IN HER BRITANNIC MAJESTYS GOVERNMENT OF THE UK OF GREAT BRITAIN & NORTHERN IRELAND
Wavelength-modulation spectroscopy method and apparatus
In one embodiment of the spectroscopy method, the method comprises the steps of modulating the wavelength of a monochromatic radiation at a modulation amplitude and a modulation frequency; determining a first variable representative of an absorbance of an analyte in a sample; and demodulating by phase-sensitive detection the first variable at a harmonic of the modulation frequency to produce a harmonic spectrum of the analyte. In one embodiment of the spectroscopy apparatus, the apparatus comprises a laser diode integrated with a first photodetector configured to detect an intensity of a backward emission from the laser diode and act as a reference detector; a second photodetector configured to detect an intensity of laser radiation exiting a sample; and electronic circuitry coupled to the laser diode and the photodetectors, configured to acquire and process spectra of the sample. In another embodiment, the spectroscopy apparatus comprises a beam splitter configured to split the laser radiation into a first radiation portion and a second radiation portion and a first photodetector configured to detect the intensity of the first radiation portion.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE SENSING
Scatter attenuation tomography using a monochromatic radiation source
InactiveUS8842808B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionVoxelTomographic image
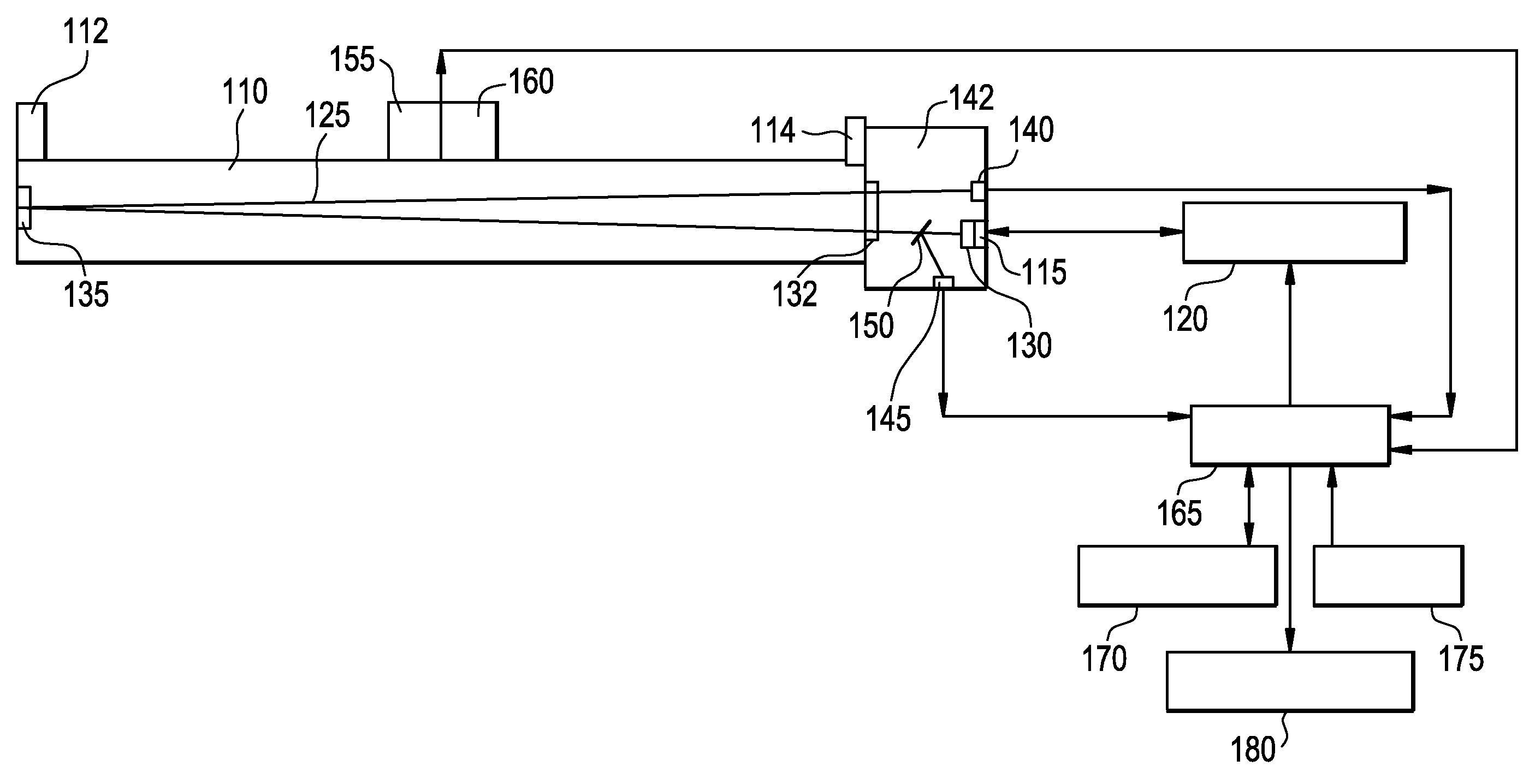
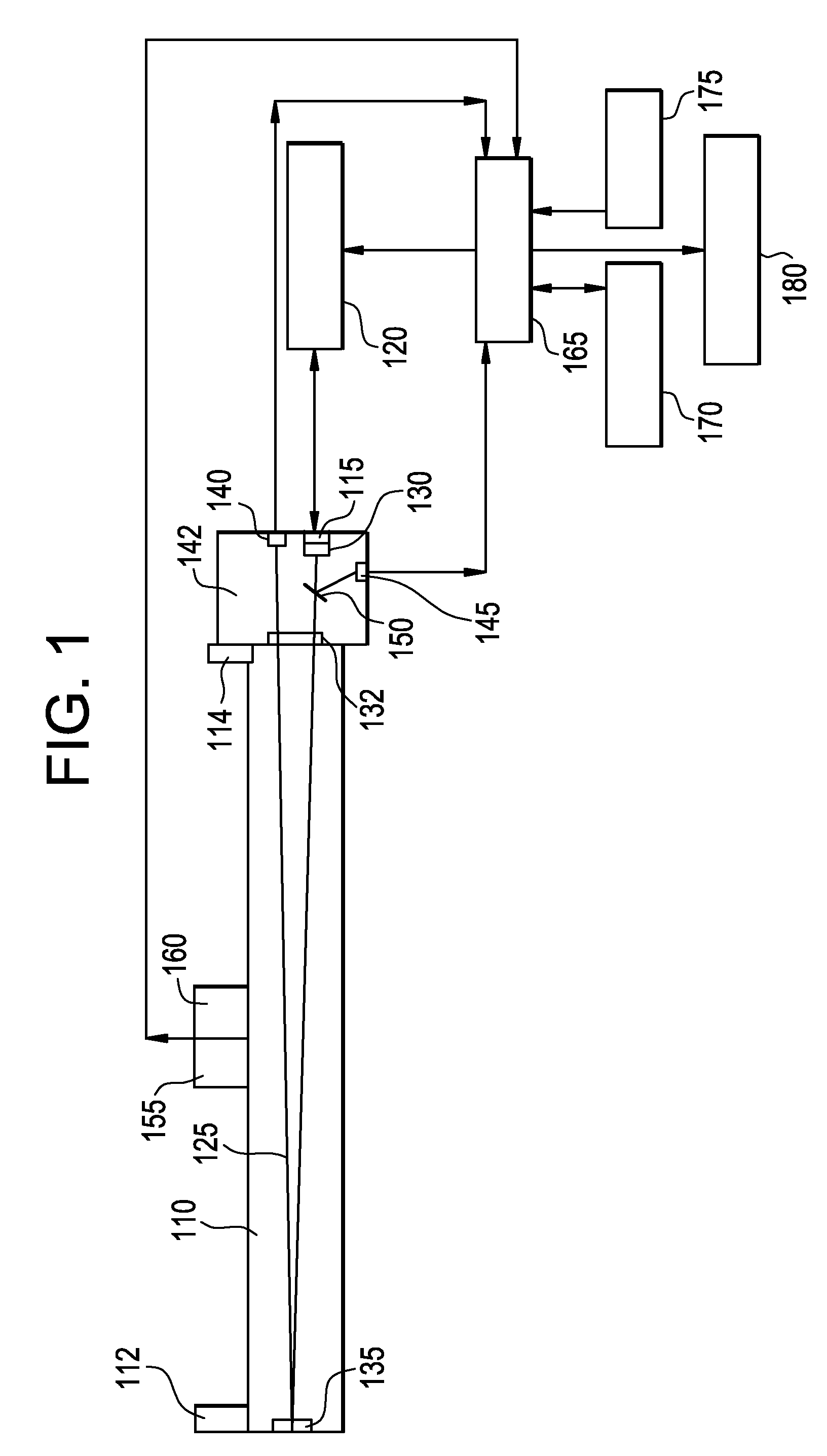
A system and methods for characterizing an inspected object on the basis of attenuation between identified regions of scattering and a plurality of detectors. An incident beam of substantially monochromatic penetrating radiation is generated by a source, which may be a radioactive source. The incident beam is characterized by a propagation axis and a source energy. Radiation scattered by the object is detected by means of a plurality of detector elements disposed about the beam of penetrating radiation, each detector element generating a detector signal characterizing a detected energy of scattered radiation. The detector signal provides for determining a displacement for each scattering point of the object relative to a fiducial position on the propagation axis of the incident beam, based upon the detected energy of the scattered radiation. By calculating the attenuation of penetrating radiation between pairs of scattering voxels, a tomographic image is obtained characterizing the three-dimensional distribution of attenuation in the object of one or more energies of penetrating radiation, and thus of material characteristics.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
Method and system for determining atmospheric profiles using a physical retrieval algorithm
ActiveUS7558673B1Indication of weather conditions using multiple variablesThermometerFrequency spectrumNoise level
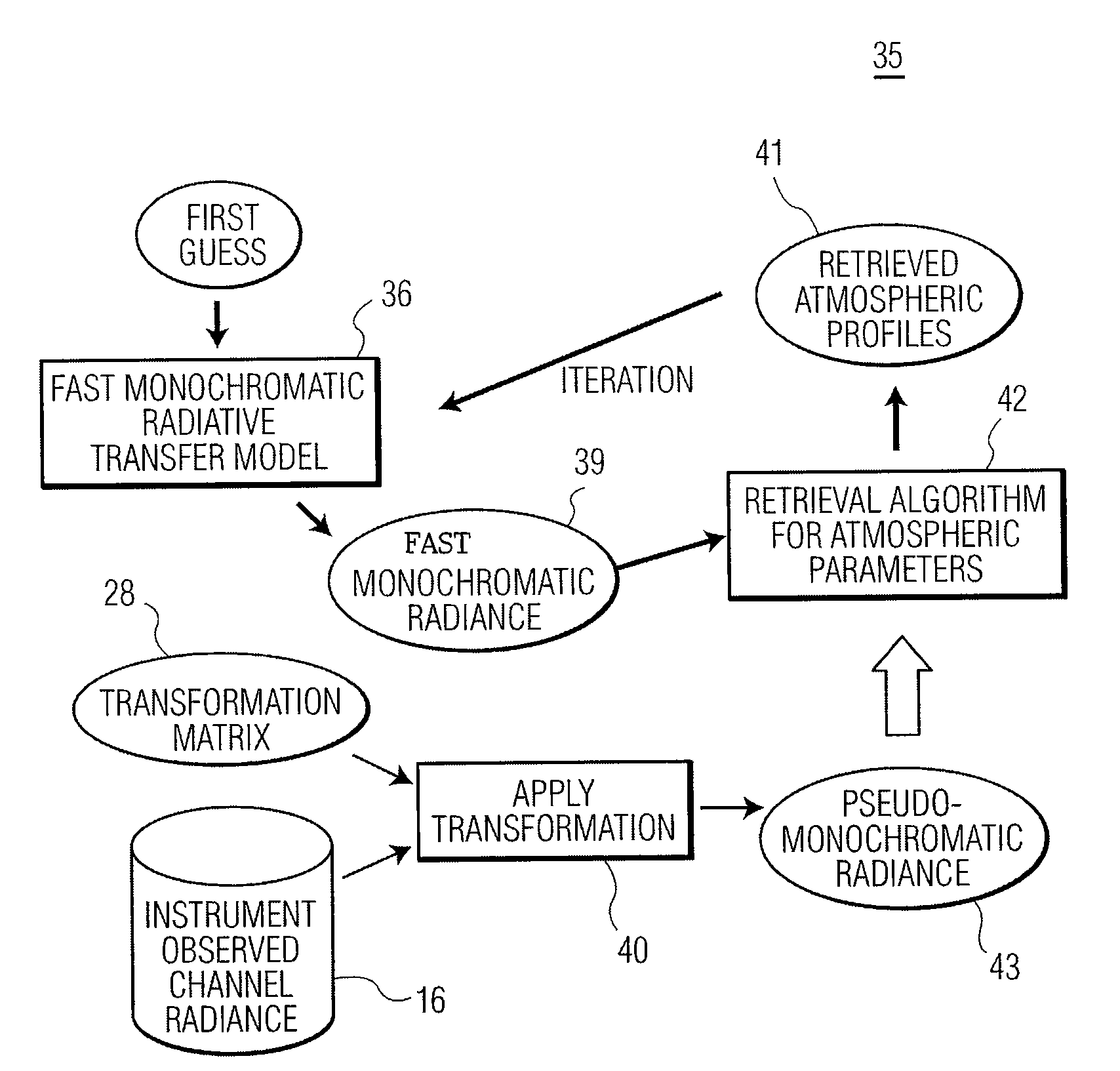
The present invention provides a new approach for processing hyper-spectral radiance data. It uses a transformation matrix to convert an instrument radiance spectrum into a pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum. The pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum is produced by an empirical transform of the instrument channel spectrum to a monochromatic equivalent spectrum (i.e., a pseudo-monochromatic spectrum). Eigenvector regression is used to produce the empirical transformation. Although the transformation does not produce the monochromatic radiance spectrum without error, the transformation error is generally well below nominal instrument noise levels for most spectral channels. The reduction in instrument noise results from a noise filtering effect of the eigenvector transformation. One of the advantages of the present invention is that it eliminates the need to build different fast radiative transfer models (RTMs) for different observing instruments, since the retrieval of geophysical parameters is based on an inversion of the monochromatic radiative transfer model. Although a different transformation matrix is required for different instrument spectral channel characteristics, the production of this transformation matrix is straightforward and simpler than the production of an accurate channel radiance fast model.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Spectral imaging of biofilms
ActiveUS20070109535A1Reduce distractionsDetailed analysisRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringBiofilmMicroorganism
A spectroscopic method and system to identify a biofilm of a microorganism. A sample containing a sample microorganism is irradiated with substantially monochromatic radiation. A Raman data set is obtained based on radiation scattered from the irradiated sample. A database is searched in accordance with the Raman data set in order to identify a known Raman data set from the database. The database contains a plurality of known Raman data sets where each known Raman data set is associated with a known sessile form of a corresponding known microorganism. A sessile form of the sample microorganism is identified based on the known Raman data set identified by the searching.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
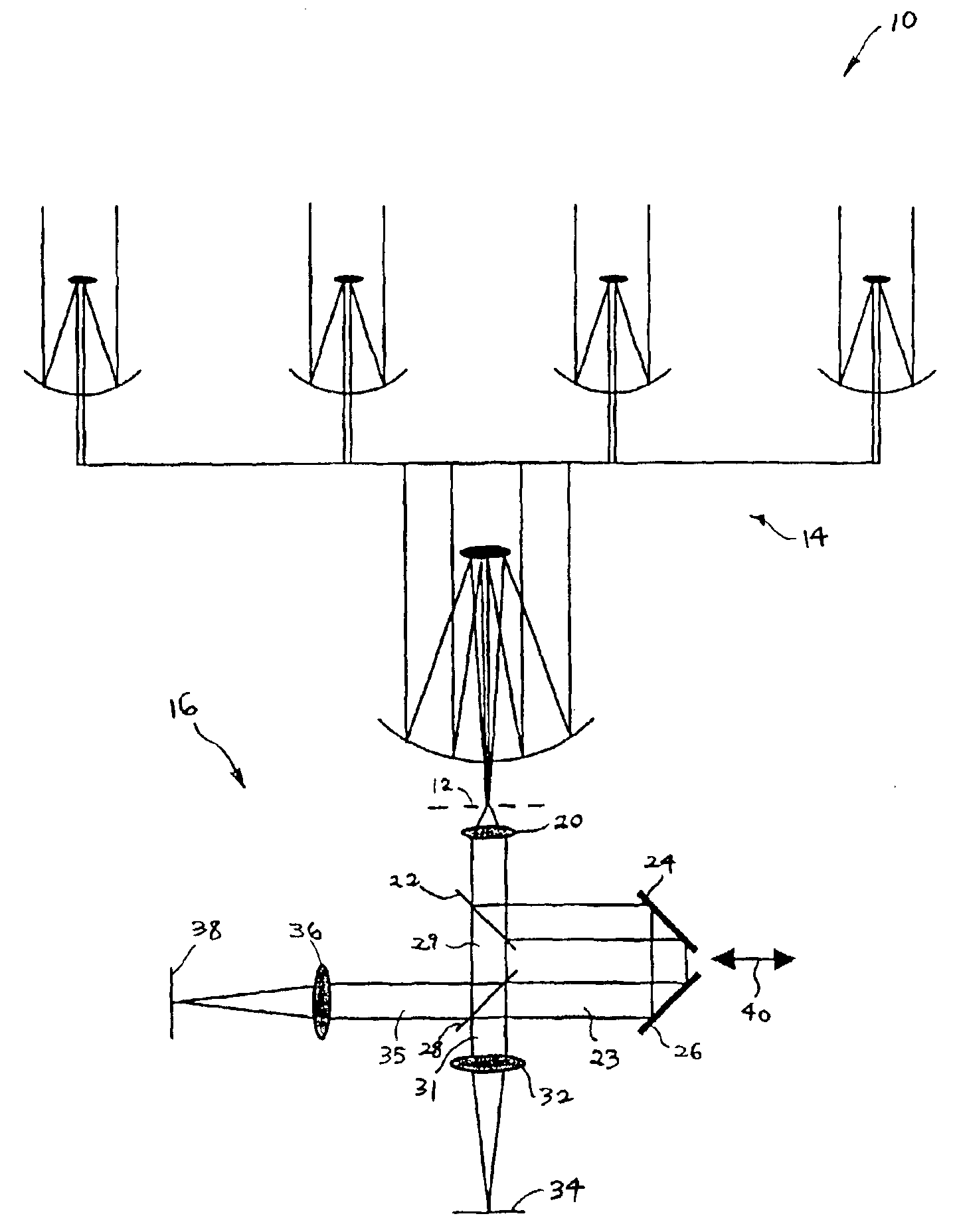
Method and apparatus for three dimensional imaging using infrared radiation
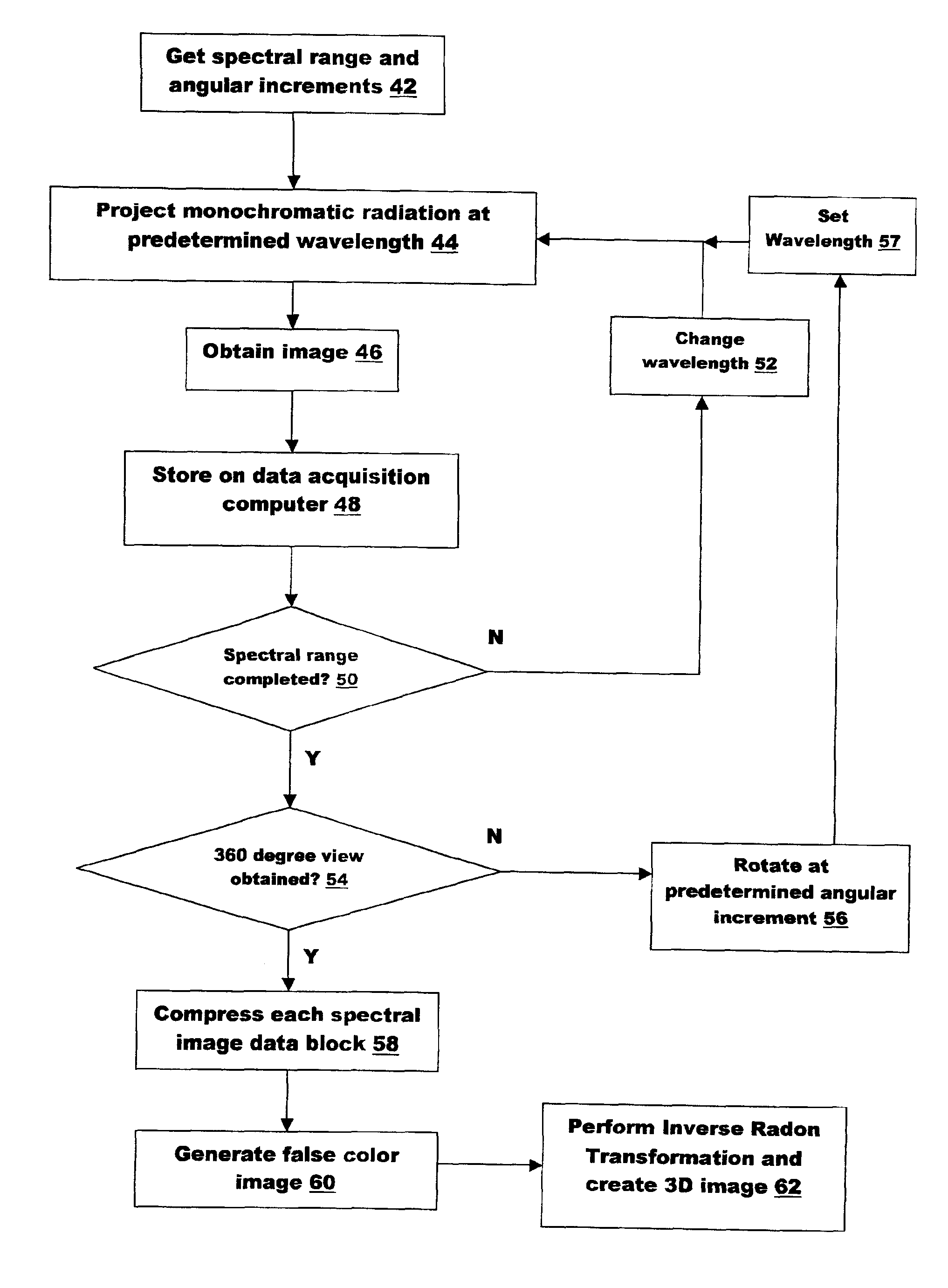
An infrared three-dimensional imaging system and method in which an object is irradiated by monochromatic radiation in the near-infrared or mid-infrared region of the spectrum. A spectral image is captured for each wavelength in a spectral range by a radiation detector to create a spectral image data block that is stored on a data storage device. The object is rotated by some predetermined angular increment until a complete three hundred and sixty degree view is obtained so that a spectral image data block is created for each angular position. Each spectral image data block is compressed to its most relevant spectral information and used to re-create a three dimensional image by a known computerized tomography algorithm.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
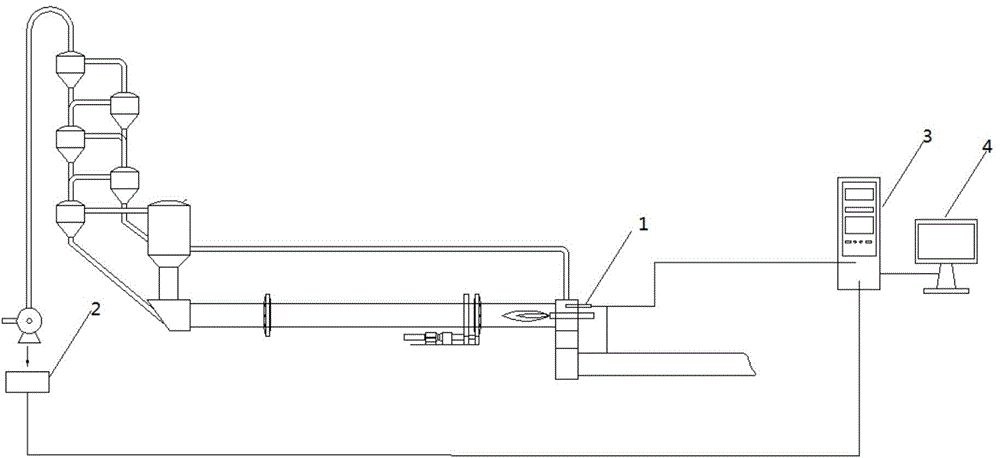
Method for measuring temperature of rotary cement kiln and method and device for online detection of temperature field of rotary cement kiln
ActiveCN103557965AAccurately obtainedRelatively small error in temperature measurementThermometer applicationsHeating powerHeat power
The invention discloses a method for measuring the temperature of a rotary cement kiln and a method and device for online detection of the temperature field of the rotary cement kiln. The method for measuring the temperature of the rotary cement kiln comprises the steps that an offline calibration portion establishes a mapping relational table of gas phase each-component gas-solid absorption coefficient correction coefficients and the temperature by considering gas-solid two-phase radiation characteristics inside the rotary cement kiln; an online detection portion selects one set of gas-solid absorption coefficient correction coefficients from the mapping relational table obtained by the offline calibration portion by testing monochrome radiation intensity and gas phase component molar volume quotients, so that the calculated theoretical monochrome radiation intensity and the detected actual monochrome radiation intensity are closest, and the corresponding temperature is the temperature to be measured. The invention further discloses the method and device for online detection of the temperature field of the rotary cement kiln by applying the method for measuring the temperature. According to the method for measuring the temperature of the rotary cement kiln and the method and device for online detection of the temperature field of the rotary cement kiln, the measuring result is accurate, the temperature field inside the rotary cement kiln can be globally analyzed, excessive temperature of materials of a burning zone and deteriorating combustion conditions are avoided, and heating-power-type NOx emission caused by the excessively-high temperature is reduced.
Owner:北京汉能清源科技有限公司
Dynamic coherent nuller
ActiveUS6882427B1Reduce eliminateSimple configurationOptical measurementsUsing optical meansNullerLight beam
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a nuller that is used to significantly reduce or eliminate a monochromatic radiation signal within a polychromatic object field. In one embodiment, a method of nulling a coherent light from a light beam having the coherent light and an incoherent light comprises collimating the light beam having the coherent light and the incoherent light, and destructively interfering the coherent light to null the coherent light with no destructive interference of the incoherent light so as to project the incoherent light without the coherent light.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
RAW image radiation temperature measuring apparatus and method
ActiveCN104180908ALarge dynamic response rangeAccurate calculationTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryRgb imageImage detection
The invention discloses a RAW image radiation temperature measuring method. The method comprises the following steps: a CCD camera outputting image data in a RAW format, and storing the data as a true color RGB image after linearity interpolation; arranging the exposure time of the CCD camera through RAW image gray scale signals obtained from the image data in the RAW format; and extracting a spectral color value of each channel from the true color RGB image; obtaining image detection data from ratios of the spectral color values to the exposure time; taking a conversion proportion coefficient, calibrated through a black-body furnace, between the image detection data and incident radiation intensity, as a calibration constant; through the CCD camera, continuously acquiring radiation images, and extracting spectral color signals and exposure time signals of any two channels in pixels R, G or B; and performing correction through the calibration constant to form correspondingly extracted monochromatic radiation intensity signals under the condition of two primary wavelengths, and according to a colorimetric temperature measurement principle, obtaining an image temperature and a radiation ratio. The temperature measuring apparatus provided by the invention comprises the CCD camera, a stiff rod endoscope, a network switch and a background server.
Owner:HUANENG POWER INTERNATIONAL +1
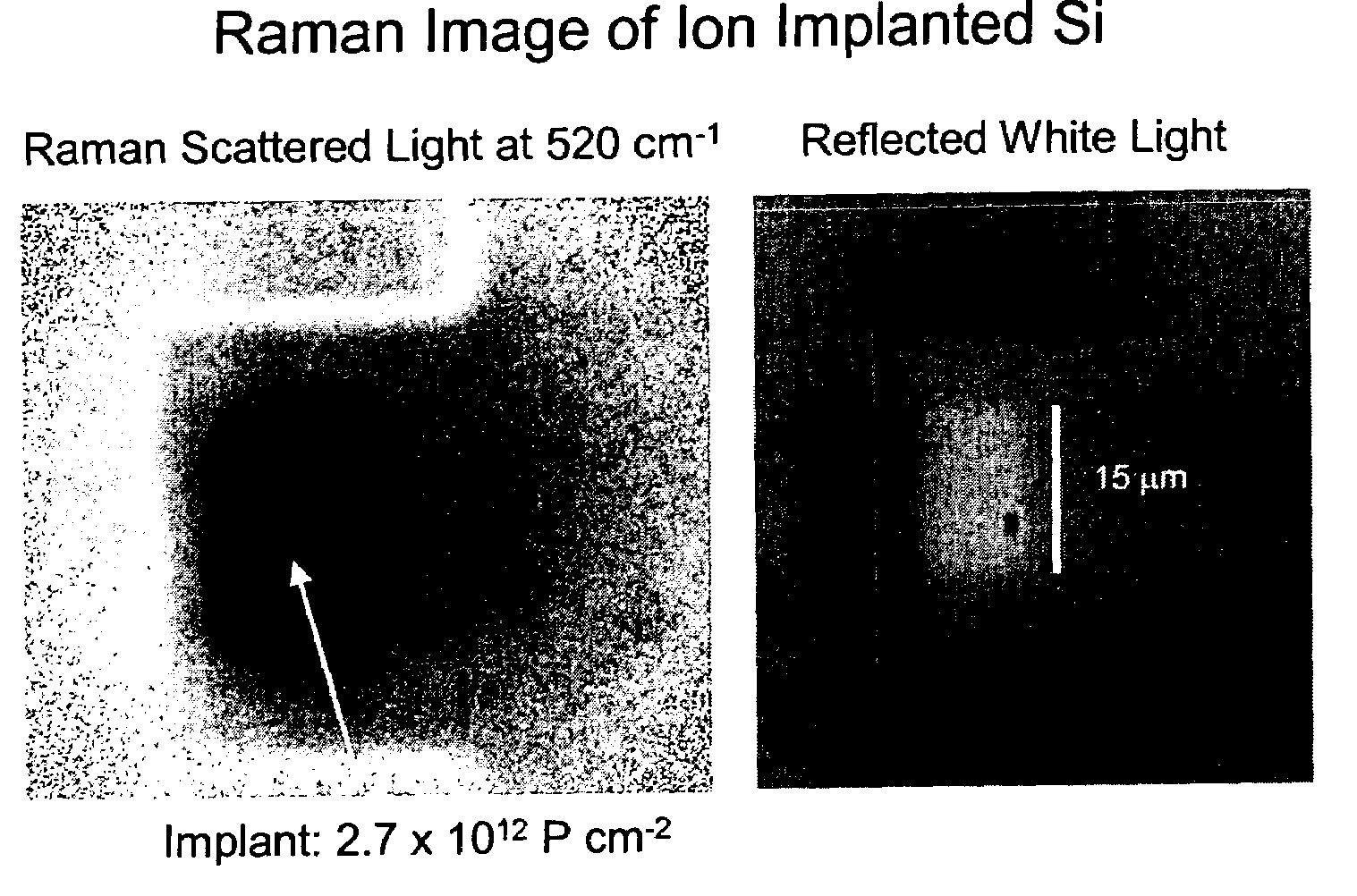
Method for Raman imaging of semiconductor materials
InactiveUS7123358B2Material becomes quickHigh spatialImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryRaman imagingSemiconductor materials
An ion implanted semiconductor surface is illuminated with a flood illumination of monochromatic radiation, and an image of the surface is taken using light which has been Raman scattered. The illumination and imaging system are calibrated by flood illuminating a uniformly Raman scattering surface.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Method for measuring temperature distribution of inner walls of sealed cavity metalware
InactiveCN104101432ATroubleshooting Emissivity ProblemsSolve problemsRadiation pyrometryMeasurement pointWavelength
The invention discloses a method for measuring temperature distribution of inner walls of a sealed cavity metalware. The method includes the following steps that (1) an infrared charge coupled device (CCD) camera and a spectrograph are calibrated through a blackbody furnace to establish a corresponding relation between a spectral signal and a radiation intensity signal; (2) radiation spectral signals of a metal surface in different wave lengths are received by the spectrograph, and reference point temperature and radiancy can be calculated according to calibration data; (3) infrared radiation images of the metal surface are filmed by the infrared CCD camera, and according to a monochromatic radiation intensity ratio between each pixel point and a reference point, the temperature distribution images of the metal surface are obtained by calculation, and the actual temperature distribution of the metal surface can be obtained. Radiation energy information of a radiation source in multiple bands can be obtained through the spectrograph, changing curves of the temperature and the radiancy of the radiation source with the change of wave lengths can be obtained by calculation, multi-point radiation energy information of surfaces of the radiation source can be captured by the infrared CCD camera, a measurement point of the spectrograph is used as the reference point, and thereby, accurate measurement of temperature distribution of the surfaces of the radiation source can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA HUANENG GRP CO LTD +1
System for continuously generating polychromatic light by means of doped microstructured optical fibre
InactiveUS8643940B2Less powerfulIncrease generationLaser using scattering effectsLight demodulationOptical pumpingLength wave
A system for generating polychromatic light, which includes: an optical pumping device suitable for continuously or quasi-continuously emitting a monochromatic or quasi-monochromatic radiation according to a pumping wavelength; a device for guiding light arranged such as to emit polychromatic radiation continuously or quasi continuously, at the output thereof, and a device for coupling between the pumping and coupling device. In the system, the guiding device, includes a microstructured optical fiber in which the core is at least partially doped with a material having a high intrinsic non-linear response, and the geometry of the optical fiber and the doping rate of the core thereof are predetermined such as to adapt the zero dispersion length of the optical fiber to the pumping wavelength.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Device for and Method of Measurement of Chemical Agents Quantity in Gas Medium
InactiveUS20080225285A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsMeasurement deviceProduct gas
Measurement device for chemical agents quantity contained in a gas medium having a source of monochromatic radiation with a wavelength which changes in accordance with time law that is supplied through an optical brancher to an optical modulator, and then into a gas medium to be measured and further into a photoreceiver, whose signal is supplied into a computing block, while another part of the radiation from the optical brancher is supplied into a gas correlating filter, and the radiation which passed through the gas correlating filter is supplied to the auxiliary photoreceivers, whose signal is supplied to the solving block of standard comparison for controlling the optical modulator and the computing block, so that on the photoreceiver, a radiation is supplied only from spectral lines or bands of radiation of the chemical agents to be measured, and signals from a part of spectral radiation in spectral lines and bands which coincide with a spectral lines of bands of absorption of foreign gasses are filtered out.
Owner:SERGEEVICH MOCHKIN V
Spectral imaging of biofilms
ActiveUS7450228B2Reduce distractionsDetailed analysisRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMicroorganismBiofilm
A spectroscopic method and system to identify a biofilm of a microorganism. A sample containing a sample microorganism is irradiated with substantially monochromatic radiation. A Raman data set is obtained based on radiation scattered from the irradiated sample. A database is searched in accordance with the Raman data set in order to identify a known Raman data set from the database. The database contains a plurality of known Raman data sets where each known Raman data set is associated with a known sessile form of a corresponding known microorganism. A sessile form of the sample microorganism is identified based on the known Raman data set identified by the searching.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Diagnostic method of atmospheric pressure inductively coupled plasma temperature field
ActiveCN112763480AOvercome the problem that the temperature field distribution of atmospheric pressure inductively coupled plasma cannot be obtainedOvercome the problem of temperature field distributionAnalysis by thermal excitationOptical spectrometerPlasma diagnostics
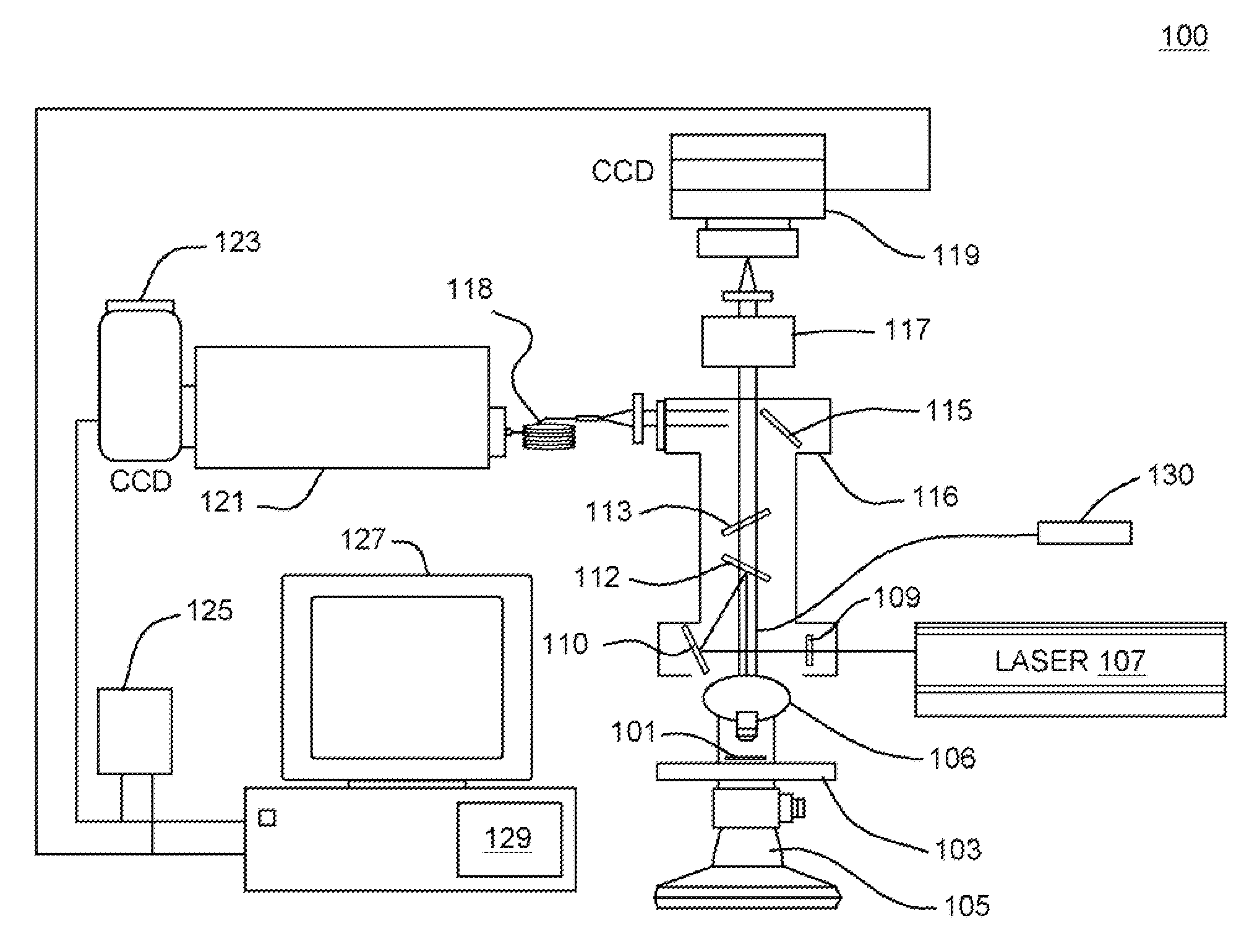
The invention discloses a diagnostic method of an atmospheric pressure inductively coupled plasma temperature field, and belongs to the field of plasma diagnosis science and technology. The method includes the steps of: acquiring radiation intensity of local points in plasma and a monochromatic grayscale image of a plurality of rotating spectral lines in the whole plasma radiation light, and acquiring a quantitative relational expression between gray values and radiation intensity by utilizing a one-to-one mapping relation between the radiation intensity of the local points and the gray values in the monochromatic grayscale image, further acquiring monochromatic radiation images of a plurality of rotation spectral lines in the plasma radiation light, acquiring molecular rotation temperature, namely gas temperature, of a point by using a Boltzmann slope method for a plurality of monochromatic radiation images of each point, and finally acquiring gas temperature field distribution of the plasma for other points accordingly. According to the method, the problem that the atmospheric pressure inductively coupled plasma temperature field distribution cannot be obtained by the current plasma diagnosis means is solved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
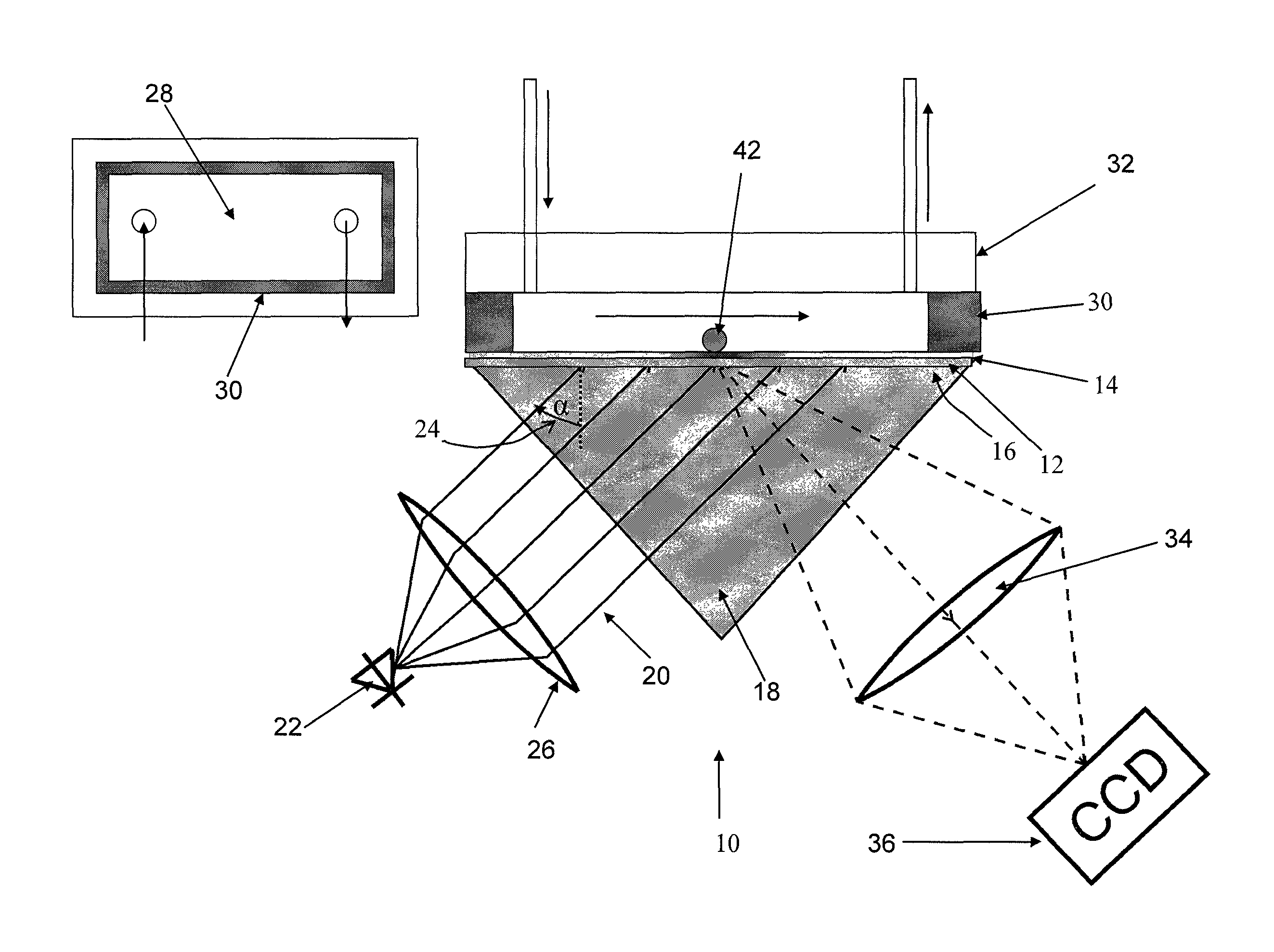
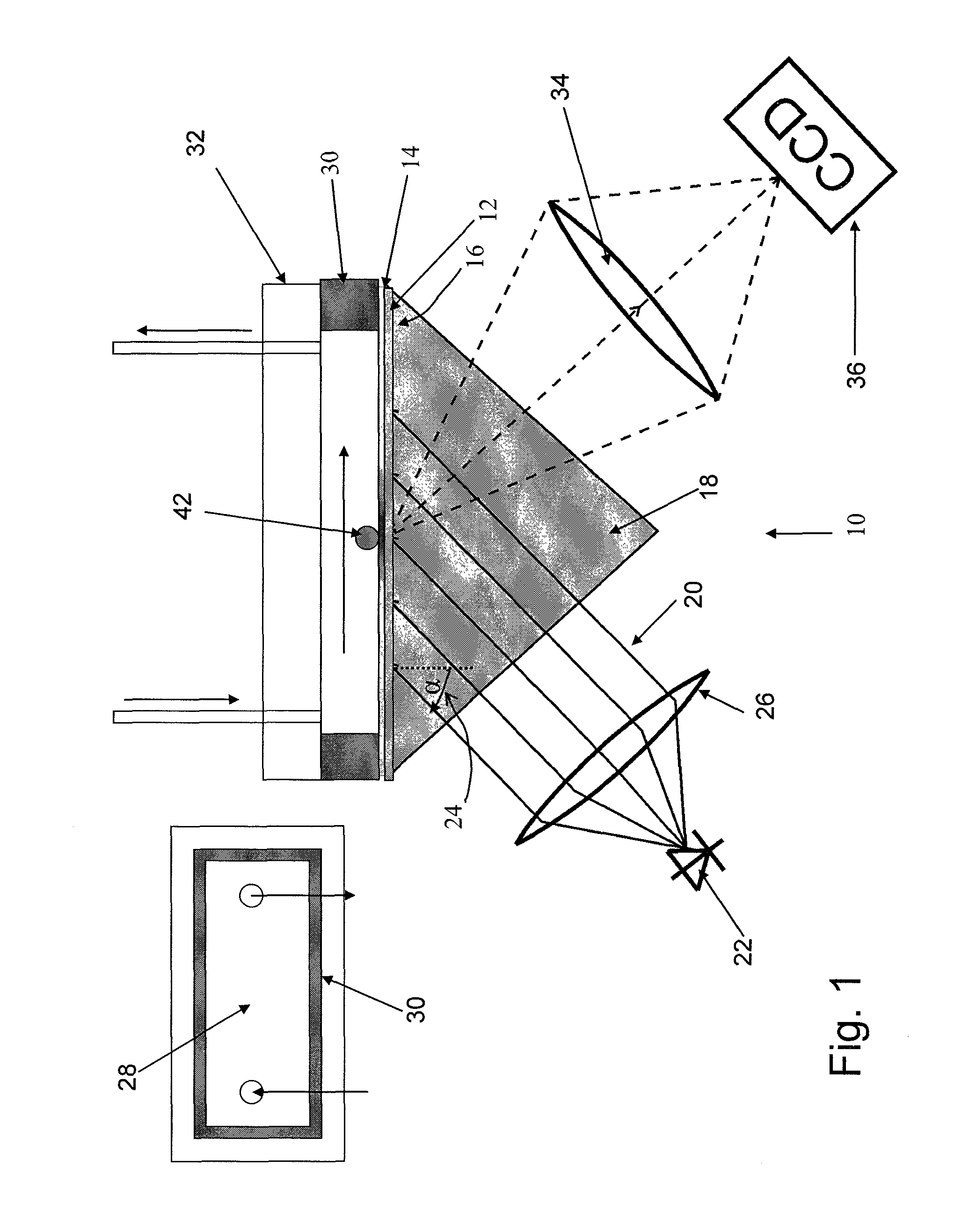
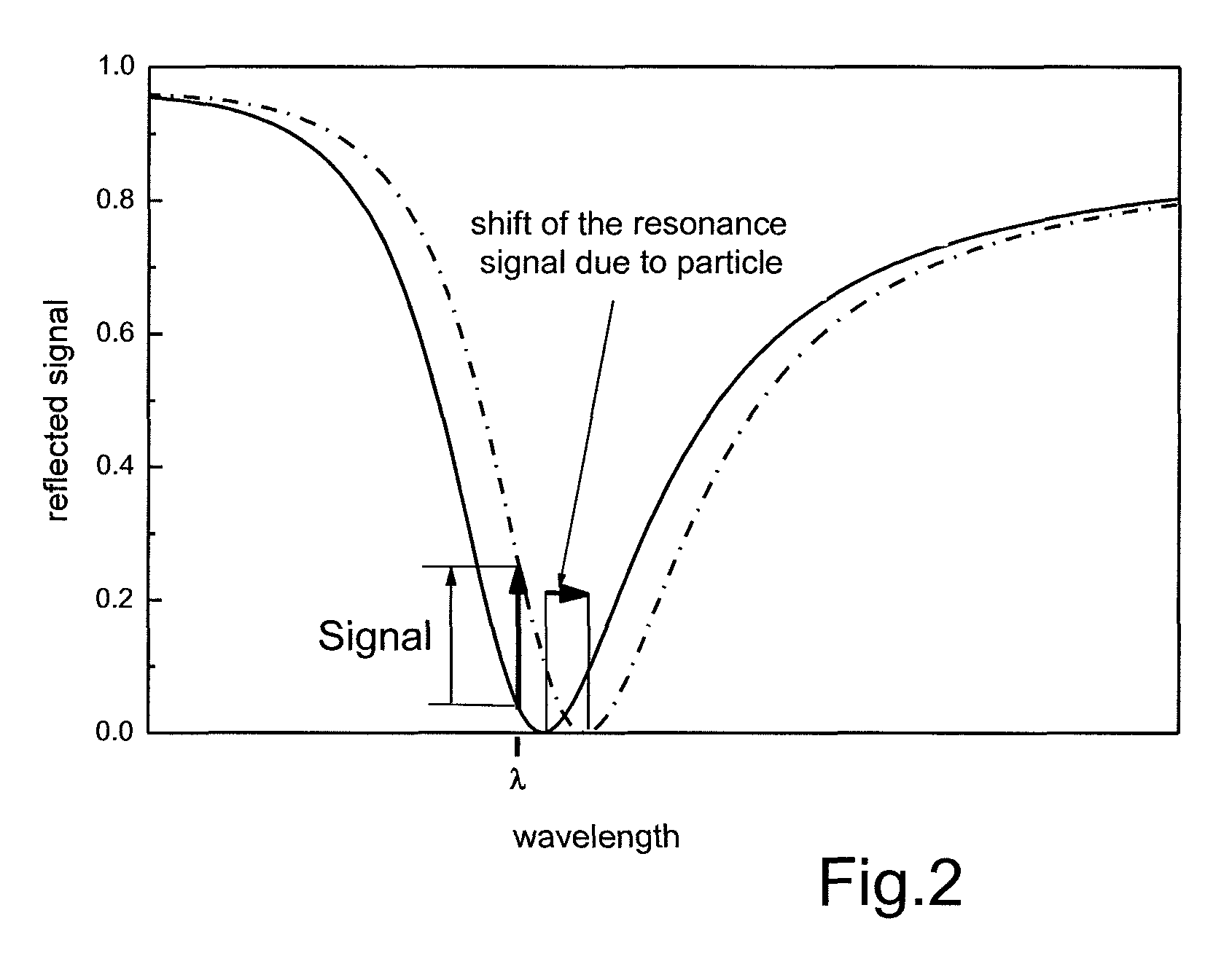
Method for high-resolution detection of nanoparticles on two-dimensional detector surfaces
ActiveUS8587786B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurface plasmon resonance spectroscopyTwo dimensional detector
The invention relates to a surface plasmon resonance spectrometer comprising a radiation source that emits substantially monochromatic radiation, a sensor surface, an optical arrangement for lighting the sensor surface by the radiation emitted from the radiation source such that surface plasmons can be created in the sensor surface, a detector having a plurality of image elements and observation optics for depicting the radiation reflected by the sensor surface on the detector, characterized in that the resolution capability of the observation optics and of the detector is larger than the resolution that can be obtained by the deflection-limited radiation source.
Owner:LEIBNIZ INST FUER ANALYTISCHE WISSENSCHAFTEN ISAS EV
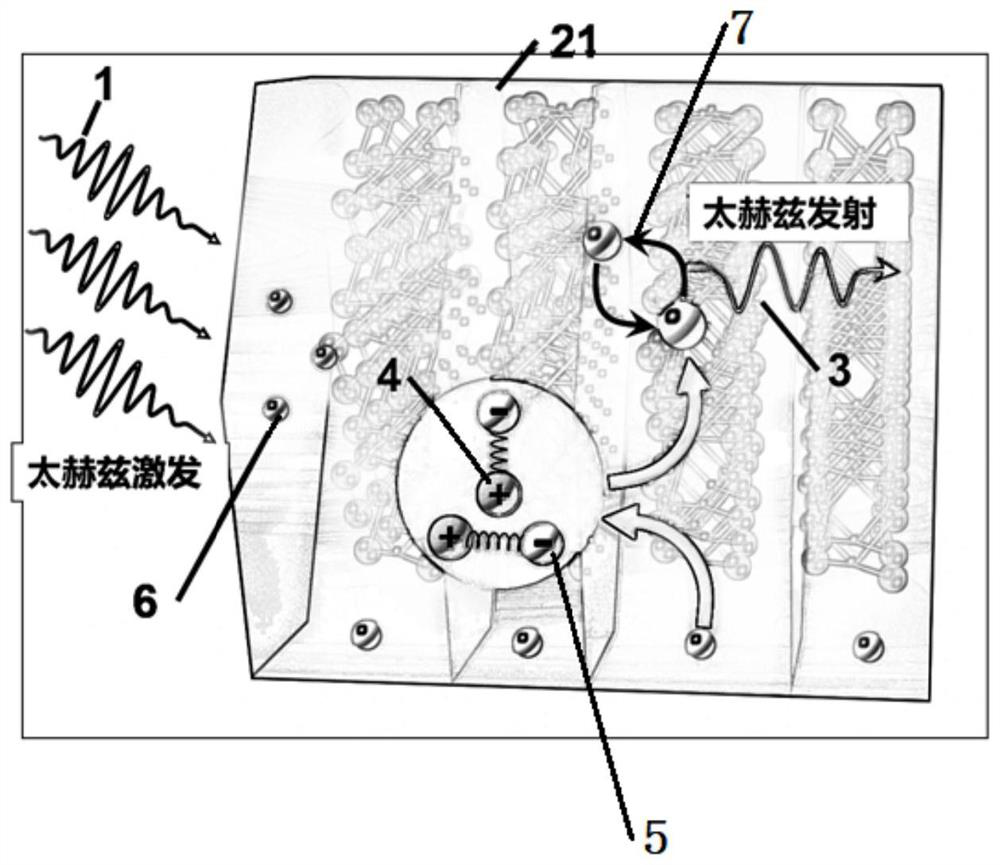
Terahertz generator based on two-dimensional material phonon mode
ActiveCN113178766AReduce absorptionAdjust the transmission frequencySolid masersTemperature controlTerahertz pulse
The invention discloses a terahertz generator based on a two-dimensional material phonon mode. The terahertz generator comprises a low-energy broadband terahertz pulse generation device, a terahertz monochromatic radiation generator and a temperature control device used for controlling the temperature of the terahertz monochromatic radiation generator. The terahertz monochromatic radiation generator comprises a two-dimensional material layer and a high-transmission substrate, the two-dimensional material layer is loaded on the high-transmission substrate, broadband terahertz pulses emitted by the low-energy broadband terahertz pulse generation device sequentially pass through the two-dimensional material layer and the high-transmission substrate to output monochromatic terahertz radiation, and the efficient monochromatic terahertz radiation is achieved at the emitting end through the two-dimensional material layer of the terahertz generator.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System for Continuously Generating Polychromatic Light By Means of Doped Microstructured Optical Fibre
InactiveUS20120268807A1Less powerfulIncrease generationLight demodulationNon-linear opticsOptical pumpingLength wave
A system for generating polychromatic light, which includes: an optical pumping device suitable for continuously or quasi-continuously emitting a monochromatic or quasi-monochromatic radiation according to a pumping wavelength; a device for guiding light arranged such as to emit polychromatic radiation continuously or quasi continuously, at the output thereof, and a device for coupling between the pumping and coupling device. In the system, the guiding device, includes a microstructured optical fiber in which the core is at least partially doped with a material having a high intrinsic non-linear response, and the geometry of the optical fiber and the doping rate of the core thereof are predetermined such as to adapt the zero dispersion length of the optical fiber to the pumping wavelength.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
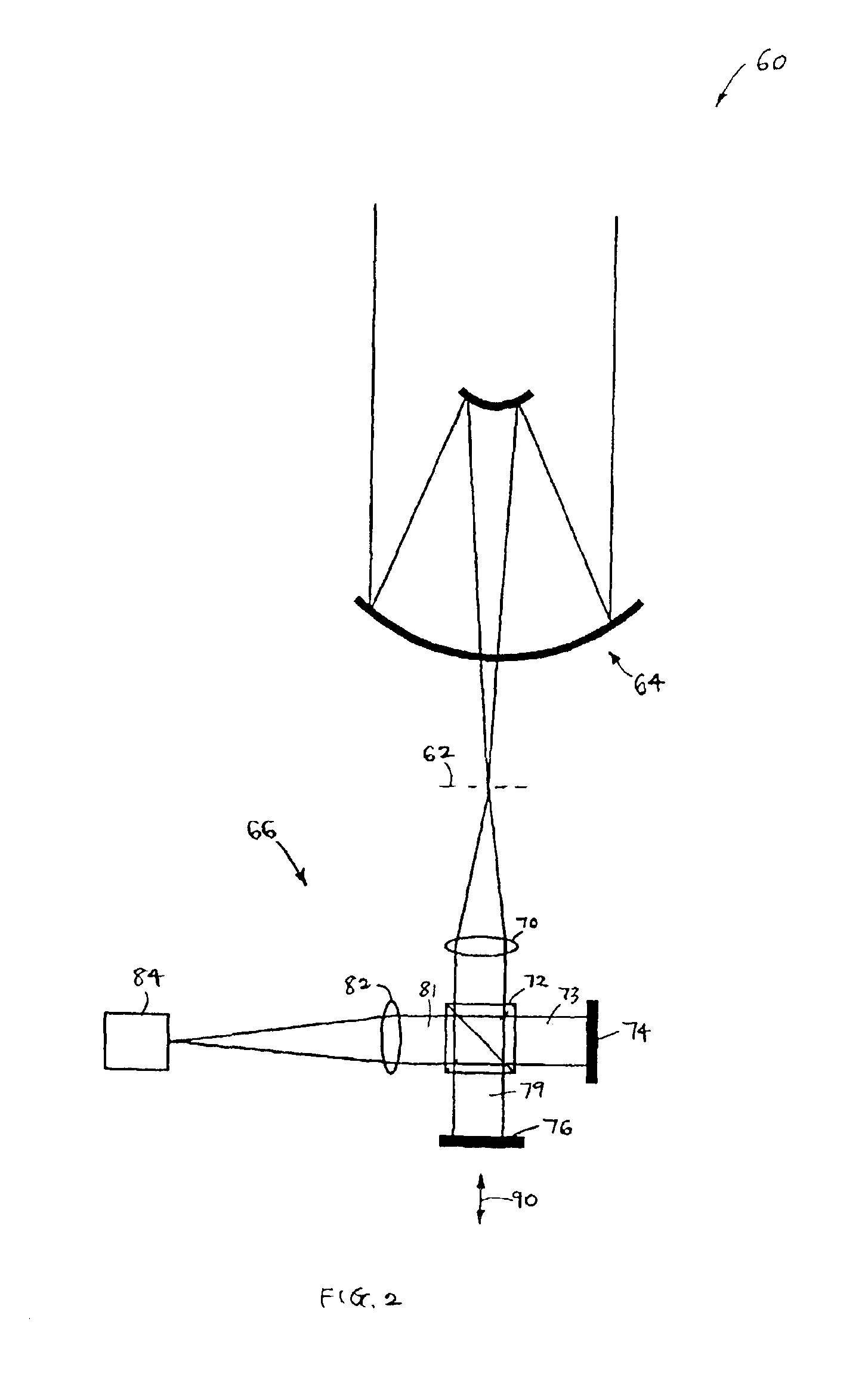
Single particle caloric absorption spectrometer
A single particle caloric absorption spectrometer for directly measuring the absorption spectra in situ of individual aerosol type particles comprises a differential arrangement of two identical electrodynamic traps (separated by a series of pneumatic valves) capable of suspending a charged particle in free-space in a non-intrusive manner in one of the traps; a source of monochromatic radiation, e.g., a laser, which is split and directed equally through transmission windows into the traps; and, a high precision capacitance manometer capable of detecting the pressure differential between the traps. After a particle has been trapped in one of the traps and the traps have been sealed from the atmosphere and from each other by the pneumatic vales, the radiation source is turned on and is evenly split / directed into both trap volumes via an appropriate beam splitter and transmission windows. This results in identical illumination of both the target and reference trap regions. A certain fraction of energy will be absorbed by the particle resulting in its heating. The heat generated within the particle is rapidly transferred to the surrounding air resulting in a net change in pressure between the target and reference traps. This change in pressure is recorded by the capacitance manometer and is shown to be proportional to the actual absorption cross section of the particle. The wavelength of the laser is then shifted slightly and the measurement is repeated until the desired spectra are completely recorded.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Wavelength-modulation spectroscopy method and apparatus
In one embodiment of the spectroscopy method, the method comprises the steps of modulating the wavelength of a monochromatic radiation at a modulation amplitude and a modulation frequency; determining a first variable representative of an absorbance of an analyte in a sample; and demodulating by phase-sensitive detection the first variable at a harmonic of the modulation frequency to produce a harmonic spectrum of the analyte. In one embodiment of the spectroscopy apparatus, the apparatus comprises a laser diode integrated with a first photodetector configured to detect an intensity of a backward emission from the laser diode and act as a reference detector; a second photodetector configured to detect an intensity of laser radiation exiting a sample; and electronic circuitry coupled to the laser diode and the photodetectors, configured to acquire and process spectra of the sample. In another embodiment, the spectroscopy apparatus comprises a beam splitter configured to split the laser radiation into a first radiation portion and a second radiation portion and a first photodetector configured to detect the intensity of the first radiation portion.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE SENSING
UV irradiation apparatus with an additional monochromatic radiation source
InactiveUS9994952B2Good resistance against micro-scratchingImprove brittlenessVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesOptoelectronicsIrradiation
Owner:OERLIKON SURFACE SOLUTIONS AG PFAFFIKON
Spectrometer-component-based non-contact engine exhaust flame monitoring device
InactiveCN102564768AJudgment of wear and tearJudging the working statusInternal-combustion engine testingAnalysis by material excitationGratingComputer module
The invention provides a spectrometer-component-based non-contact engine exhaust flame monitoring device. The device can monitor the health state of an engine under the condition that the normal work of the engine is not affected. The working principle of the device is that: a pre-optical system acquires the complex radiation in exhaust flame of the engine, the complex radiation is transmitted into a spectrometer component through an optical fiber and is decomposed into monochromatic radiation through a grating in the spectrometer component, and an analog signal is converted into a digital signal by using a charge coupled device (CCD) detector; data processed by using the spectrometer component pass through a high-speed universal serial bus 2 (USB2), are transferred into a network module, are output through a network cable port, and are transmitted into a computer through a router; and the computer receives the spectral data and can judge the wear condition of the engine by comparing spectra and theoretical spectra of target elements to judge the existence of metals in the exhaust flame of the engine.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Stabilized lidar system and method for stabilization
ActiveUS20200033459A1Low costReduced assembly effortLaser detailsWave based measurement systemsErbium lasersWavelength
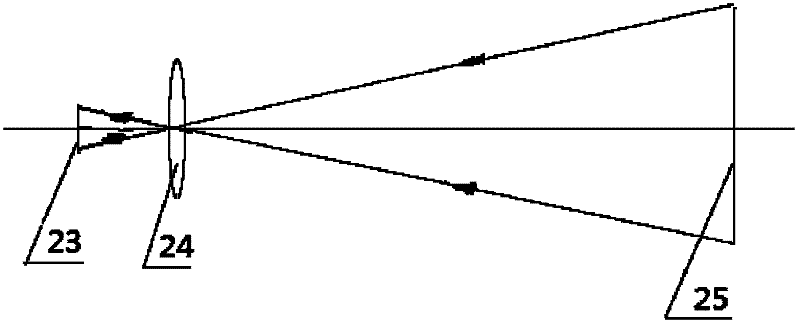
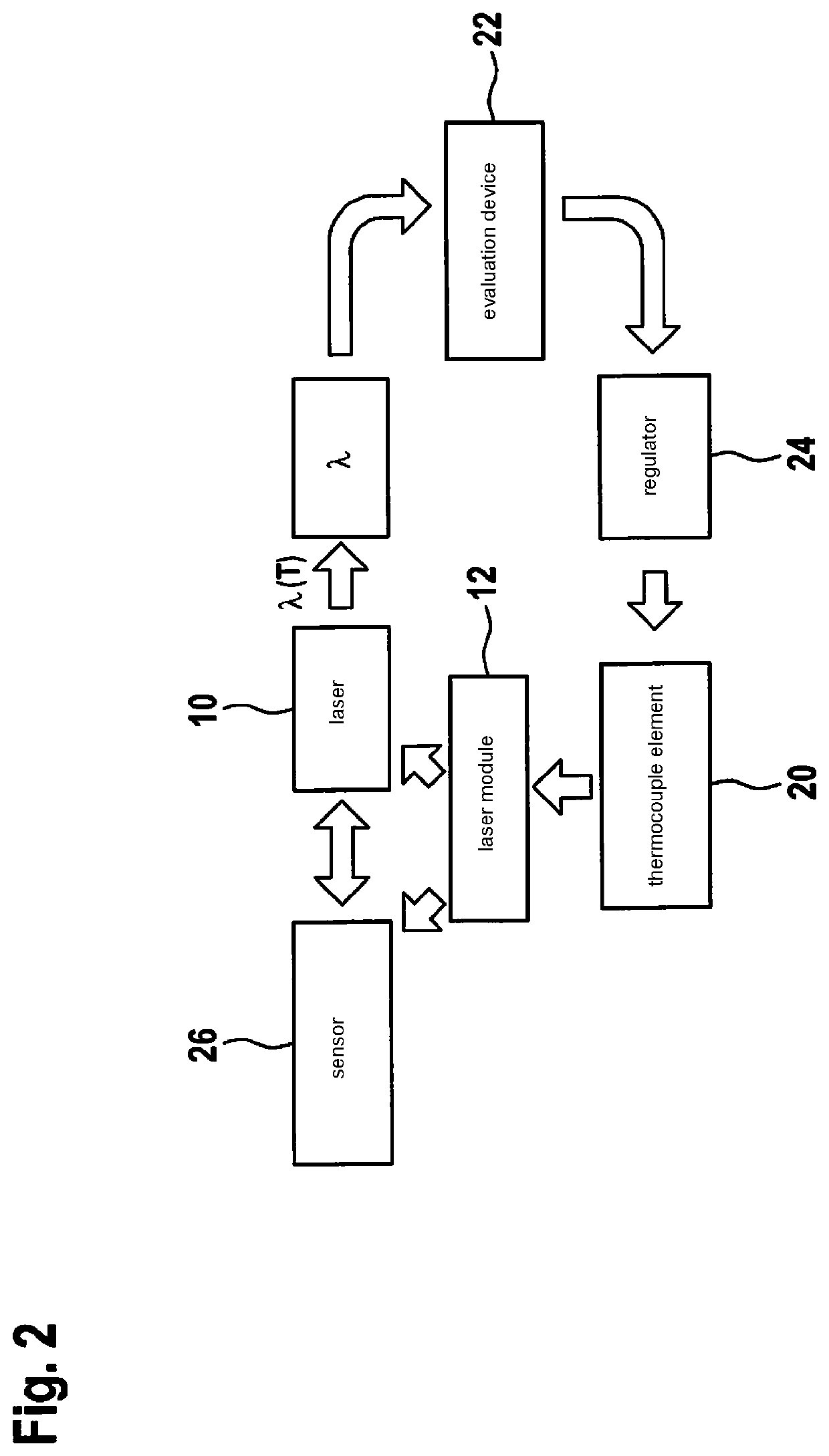
A stabilized LiDAR system and a method for stabilization. The LiDAR system includes a laser, the laser being designed for emission of monochromatic LiDAR radiation within a wavelength working range; a thermocouple element configured to set the working temperature of the laser; a means for evaluation, designed to determine, from the radiation emitted by the laser, a measure for the deviation from an actual wavelength of the radiation to a setpoint wavelength within the wavelength working range of the laser; and a means for regulation, designed to control the thermocouple element on the basis of the measure of deviation determined by the means for evaluation, in such a way that the working temperature of the laser is set to a value, at which the emitted monochromatic LiDAR radiation corresponds to the setpoint radiation.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Spectroscopy-based real-time control for microwave-assisted chemistry
InactiveUS7141769B2Dielectric heating circuitsAnalysis by electrical excitationChemical synthesisSpectroscopy
The invention is an instrument and method for microwave-assisted chemical synthesis. The instrument includes a source of microwave radiation for applying microwave energy to a sample, a microwave cavity in wave communication with the source for holding the sample during the application of microwave energy, and a substantially monochromatic radiation source in electromagnetic communication with the cavity for applying substantially monochromatic light to the sample. The instrument further includes a detector positioned to detect Raman scattering of light from the monochromatic source by the sample, and a controller in signal communication with the microwave energy source and the Raman scattering detector for moderating the application of microwave energy to the sample based upon the detected Raman scattering.
Owner:CEM CORP
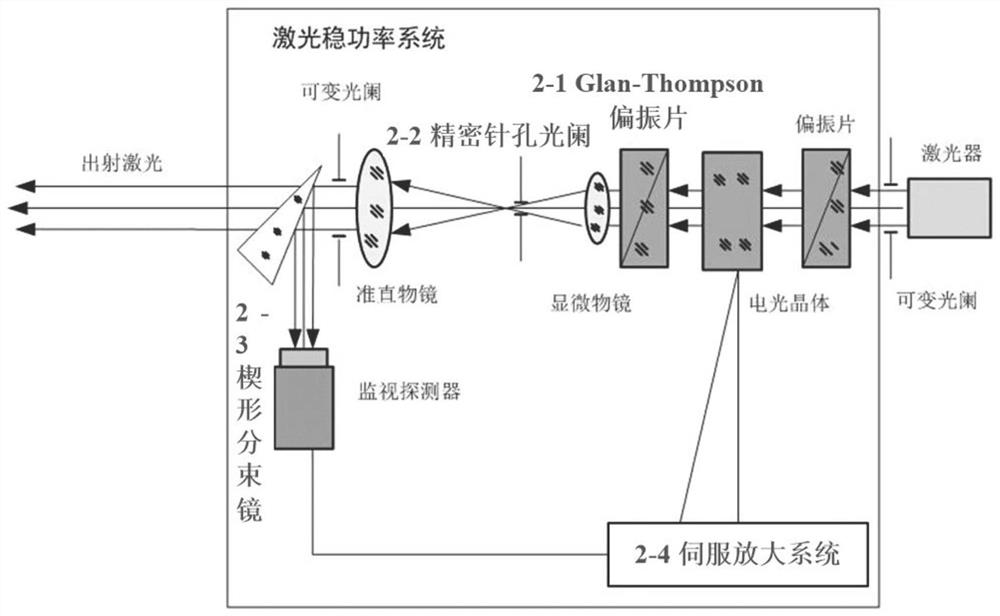
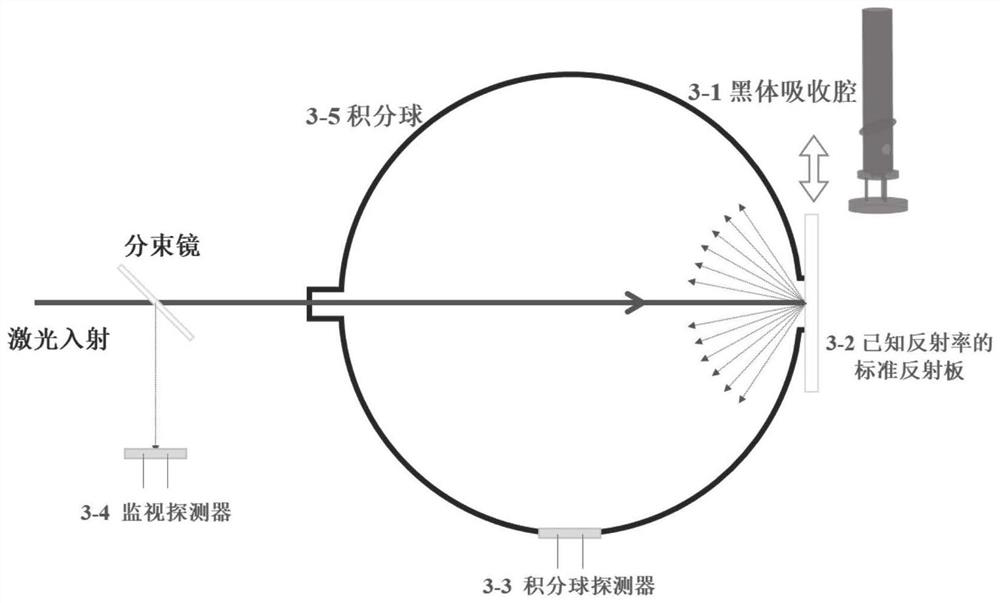
Method for measuring actual temperature of flame by using all information of radiation spectrum and measurement system thereof
ActiveUS20170045398A1Strong anti-environmental interference abilitySimple divisionSensing radiation from gases/flamesRadianceData transmission
The present invention discloses a method for measuring an actual temperature of a flame by using all information of a radiation spectrum and a measurement system thereof. The method includes: conducting more theoretical data processing by using energy level structure correction, wherein all information of the radiation spectrum can be used; and by way of a keyboard input manner or a data transmission input manner, acquiring an energy level structure correction parameter, and finally acquiring a more accurate actual temperature value of a measured flame. The method effectively overcomes a defect that the true temperature of the flame can be obtained by only conducting radiance correction through data processing with great calculations when adpted multi-spectral temperature measurement method. In the existing multi-spectral temperature measurement method at present, only information of several monochromatic radiation capacities in the radiation spectrum can be used; and in the method, information of all the monochromatic radiation capacities, thousands of monochromatic radiation capacities in general, in the radiation spectrum can be used.
Owner:TIANJIN YITONG TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION ELECTRIC TECH
Device for transforming electromagnetic ir energy from spatially incoherent, low-power density, broad-band radiation in spatially coherent, high-power density, quasi-monochromatic radiation
InactiveUS20120076162A1High sensitivityIncrease power generationPhotovoltaicsLaser cooling arrangementsEnergy exchangeHigh power density
A device to be positioned between a heat source and a heat sink may transform infrared electromagnetic (IR-EM) energy exchanged therebetween from a first form to a second form. The device may include a pair of layers facing each other and having dielectric material with molecular excitability characteristics to produce the second form of IR-EM energy. The pair of layers may define a gap therebetween. The device may include a conversion circuit configured to convert the second form of IR-EM energy into electrical energy.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Calibration method for blackbody cavity absorption coefficient under variable temperature condition
PendingCN114279562ARealize full temperature range calibrationSolving Drift check puzzlesRadiation pyrometryPhotometryBlackbody cavityPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention belongs to the field of optical metrology testing, and discloses a blackbody cavity absorption coefficient calibration method under a variable temperature condition, which comprises the following steps of: generating uniform monochromatic radiation by using a high-stability radiation source in combination with a stable power instrument, receiving the monochromatic radiation by a blackbody cavity to be tested, and measuring the absorption coefficient of the blackbody cavity by adding an inverted photoelectric detector in front of a Brewster window. And the reflected light beam intensity is calibrated, so that the full-temperature-section calibration of the blackbody cavity absorption coefficient is realized. According to the method, aiming at the verification problem of blackbody cavity absorption coefficient drift caused by current temperature fluctuation, a variable-temperature cavity-detector integrated test means is innovatively introduced, the measurement of the full-band absorption coefficient of the cavity in a variable-temperature environment is realized, and the method has the characteristics of small size, high calibration accuracy and wide application prospect.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Method for measuring actual temperature of flame by using all information of radiation spectrum and measurement system thereof
ActiveUS11359967B2Improve temperature measurement accuracyReduce calculationSensing radiation from gases/flamesRadianceData transmission
Owner:TIANJIN YITONG TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION ELECTRIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com