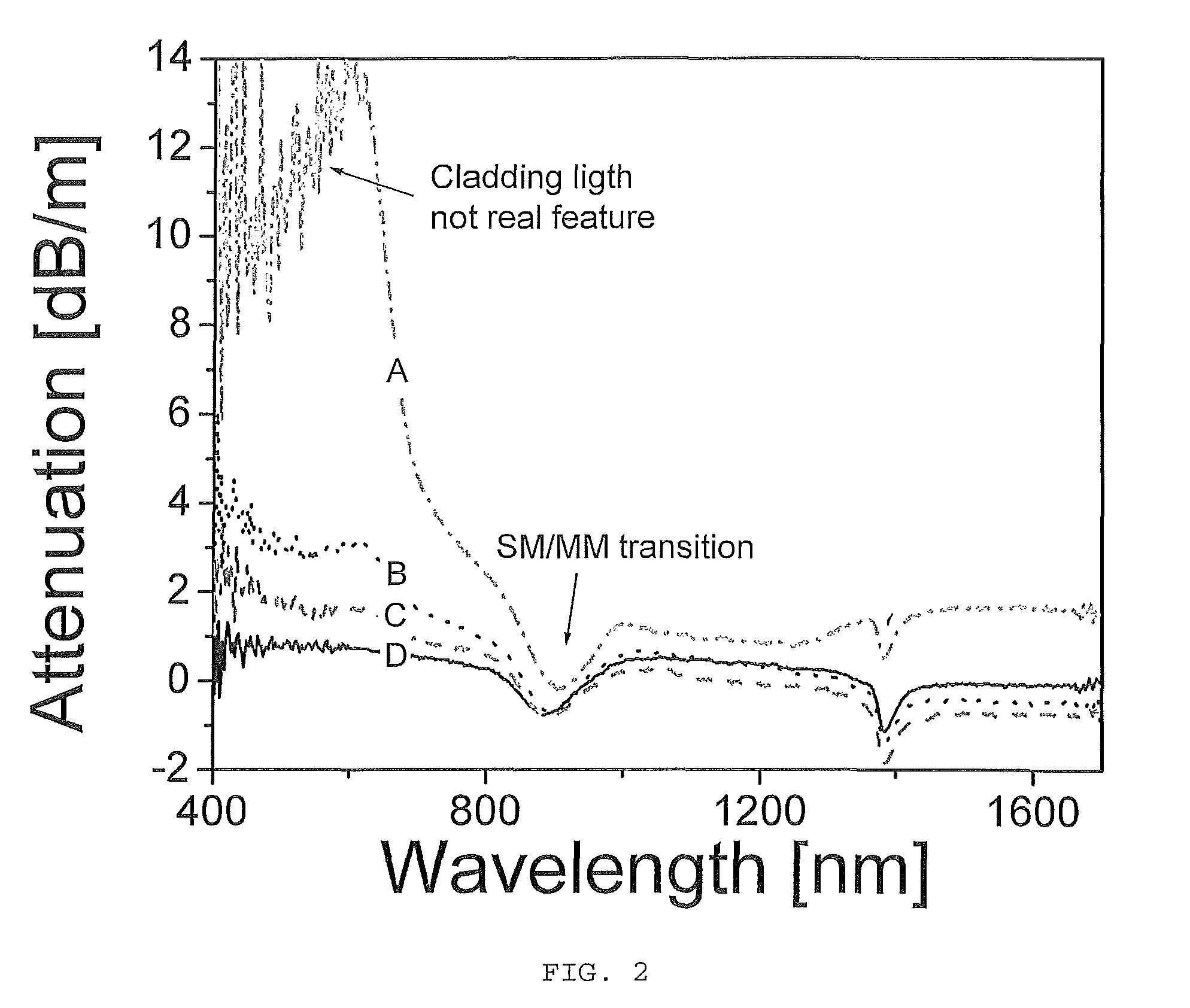
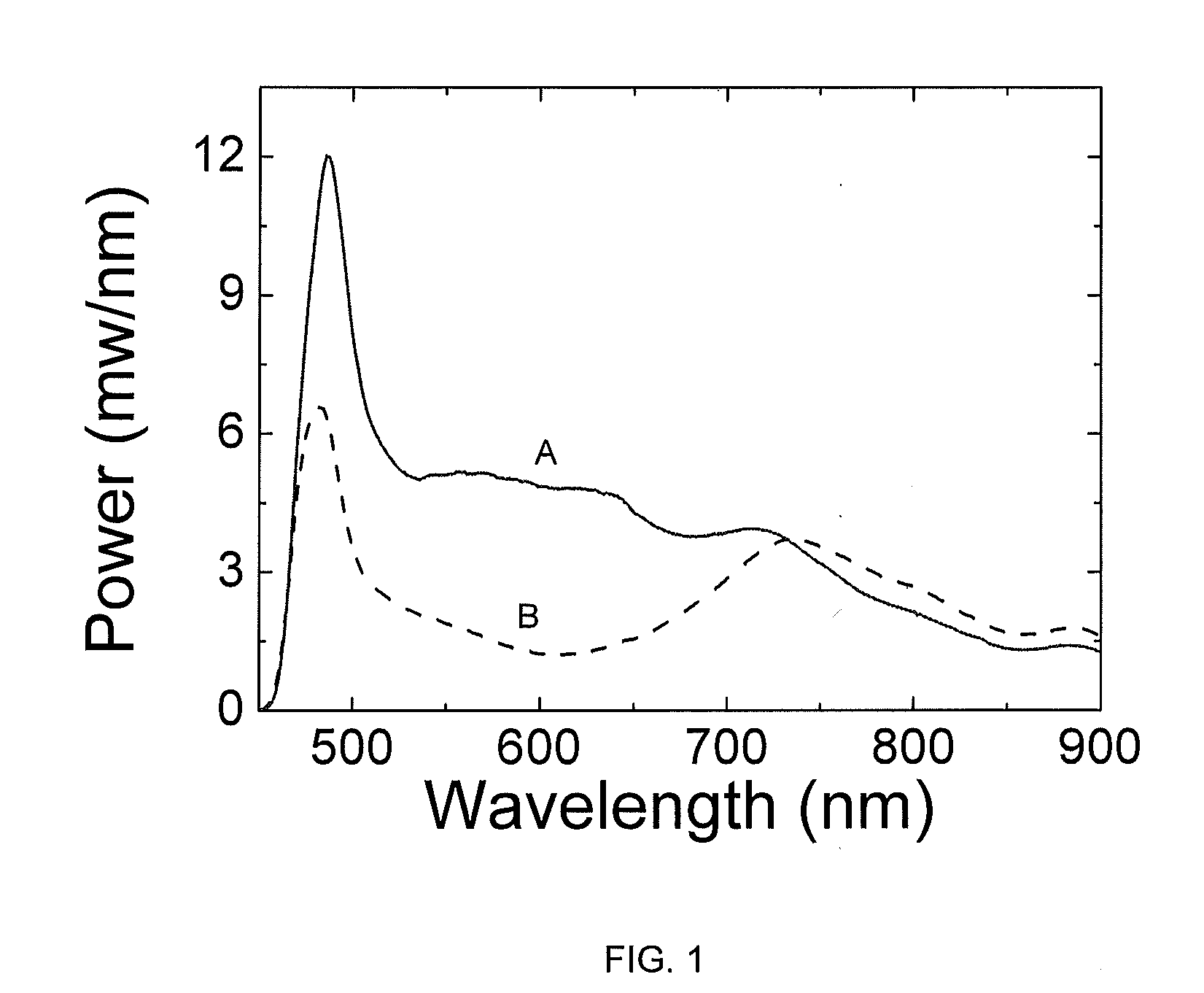
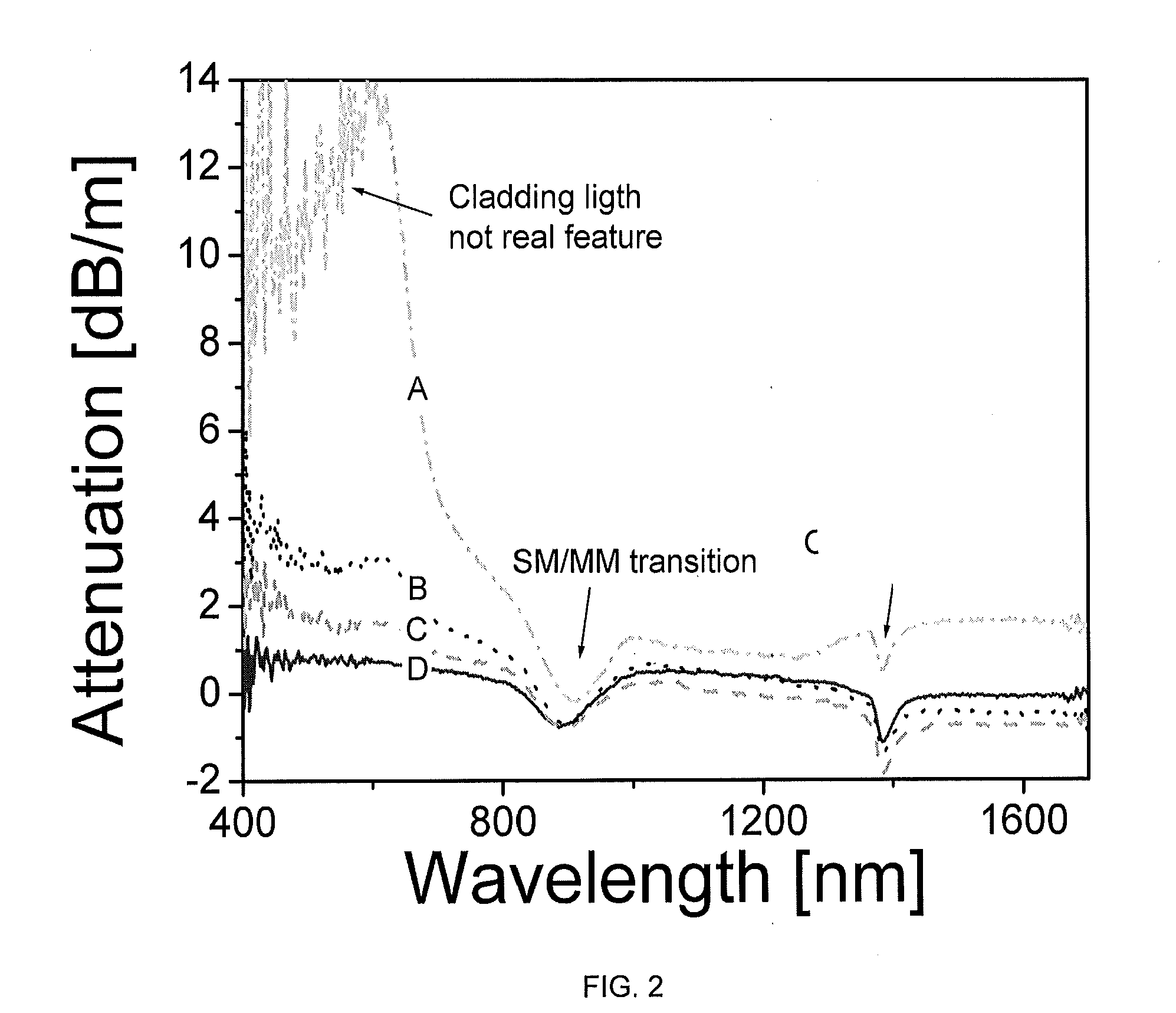
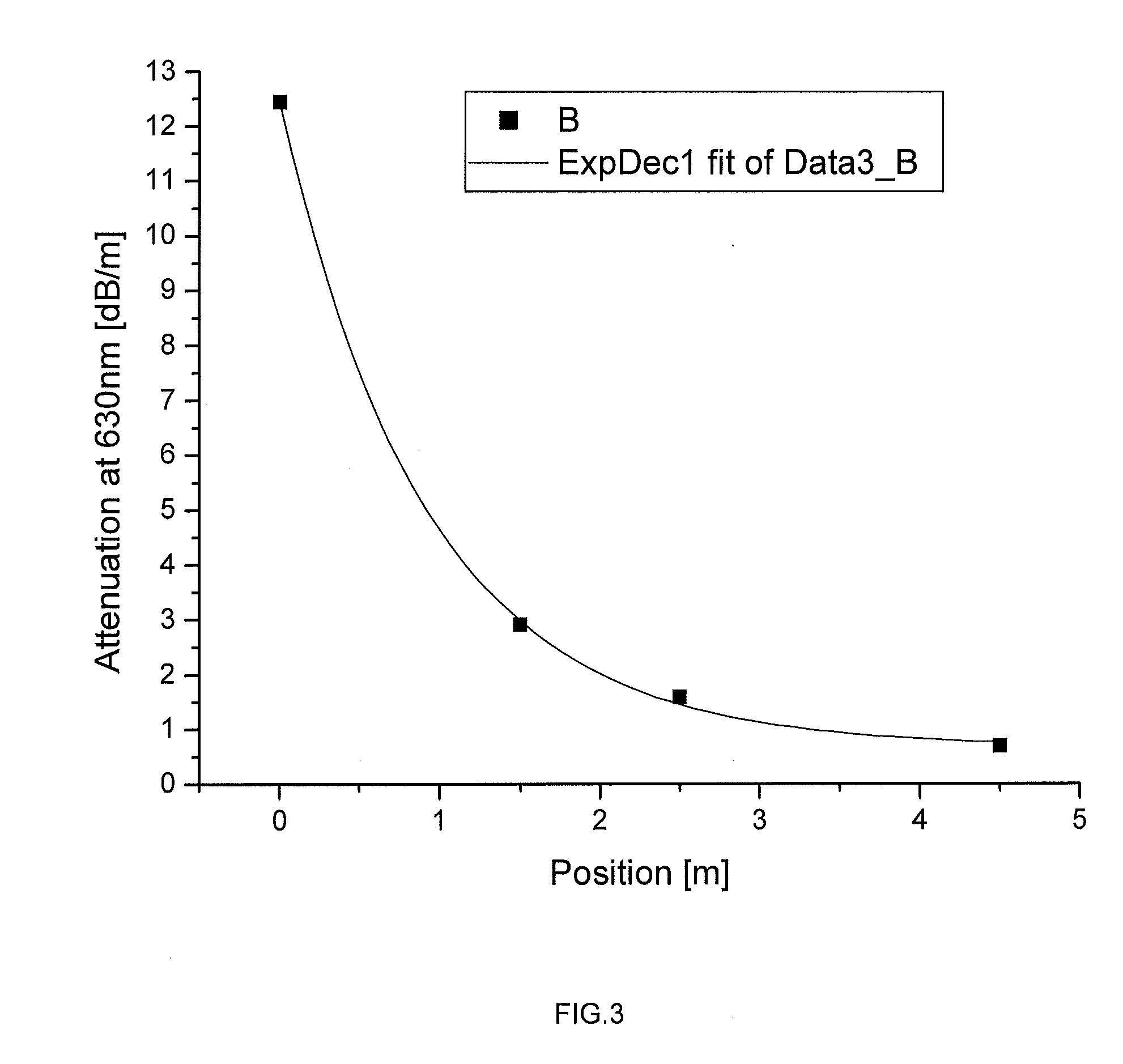
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Microstructured optical fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
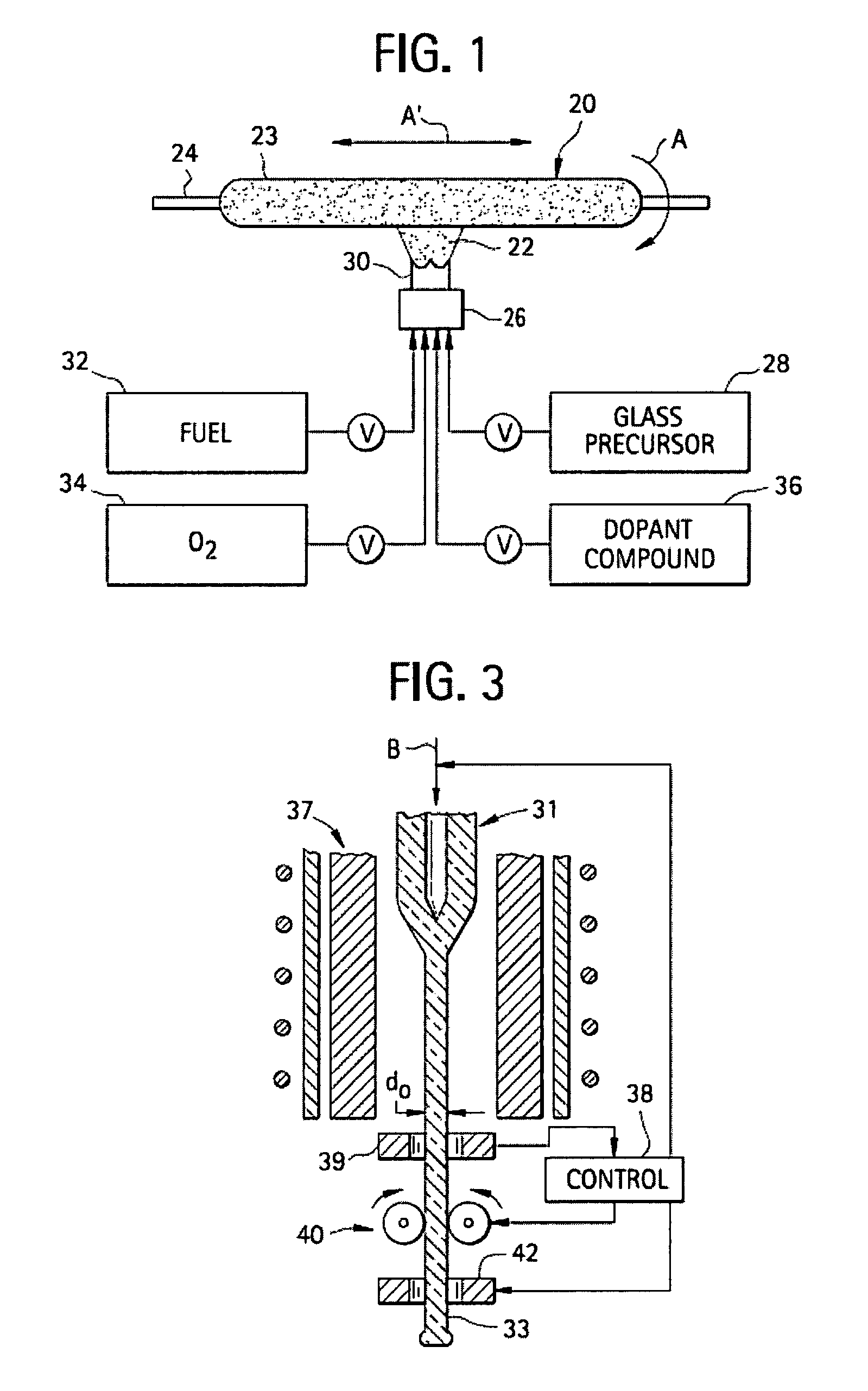
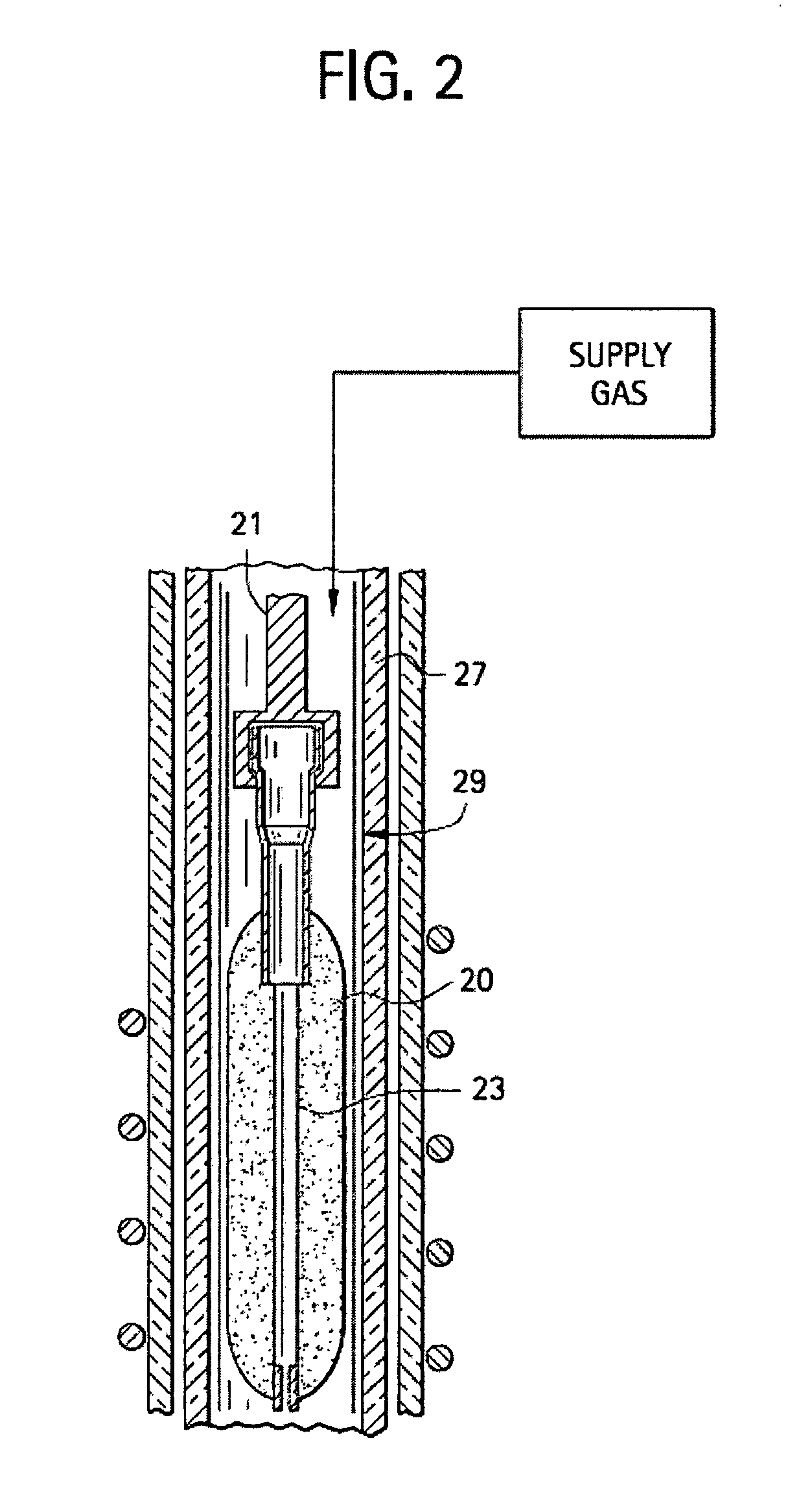
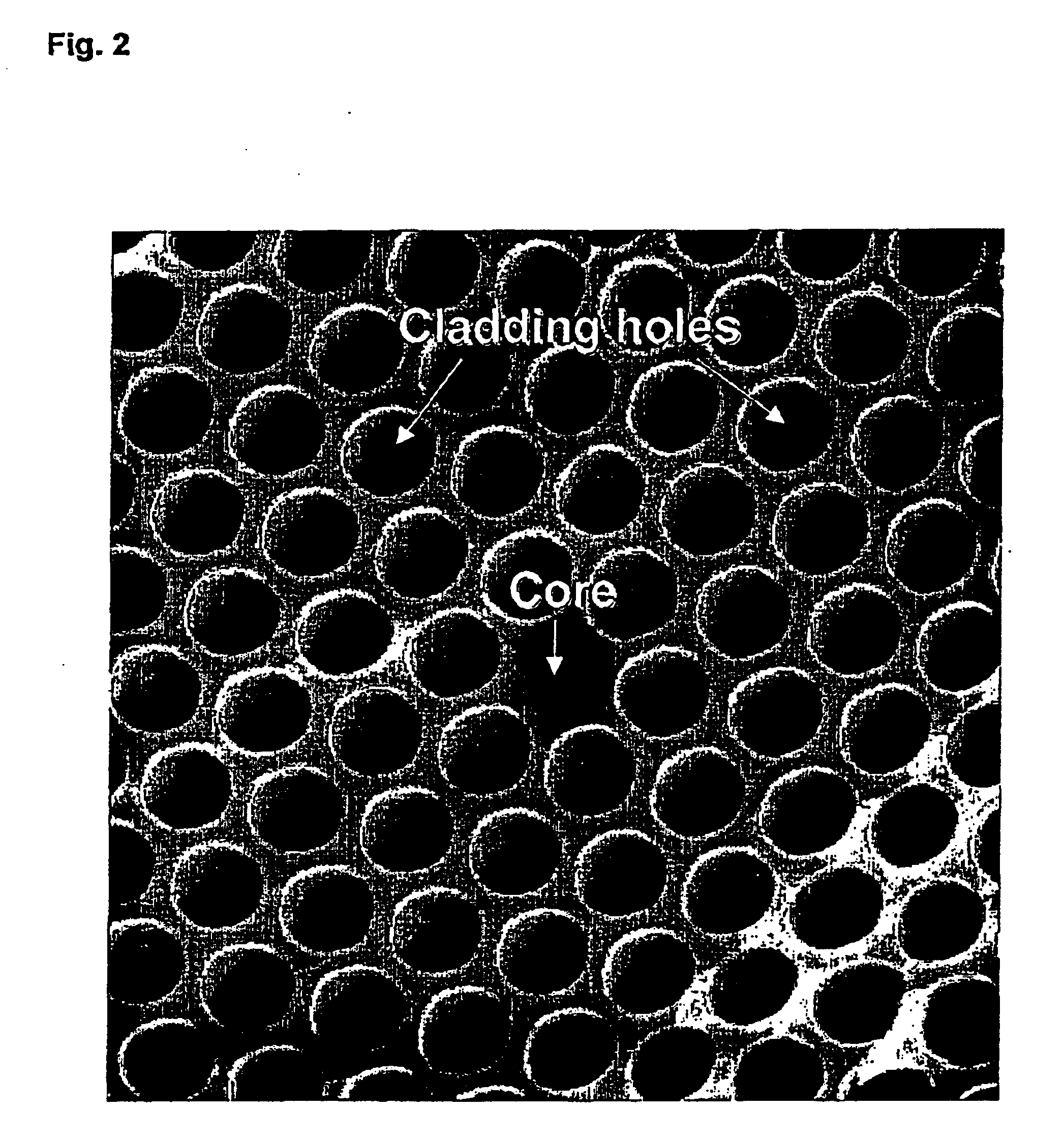
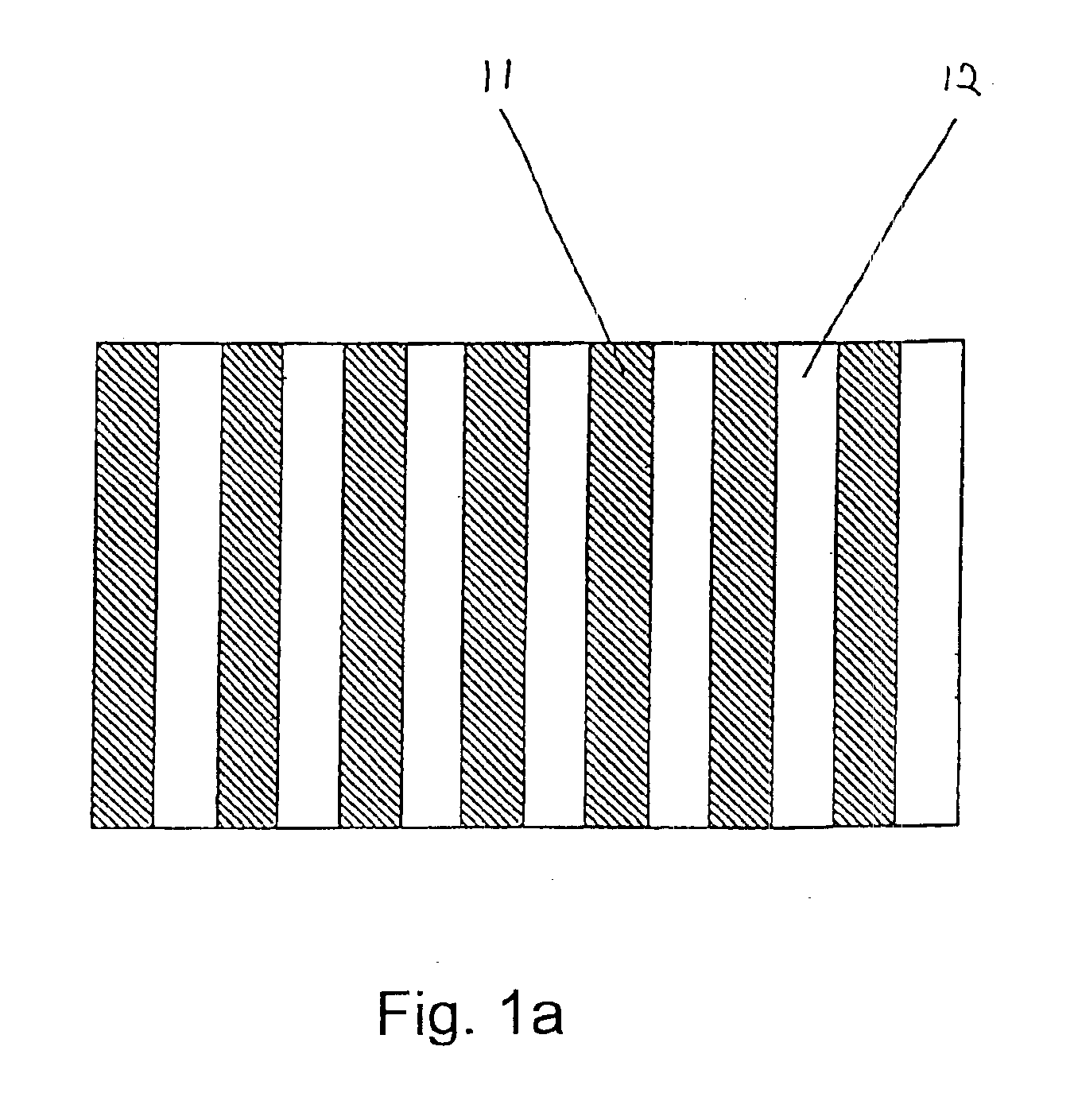
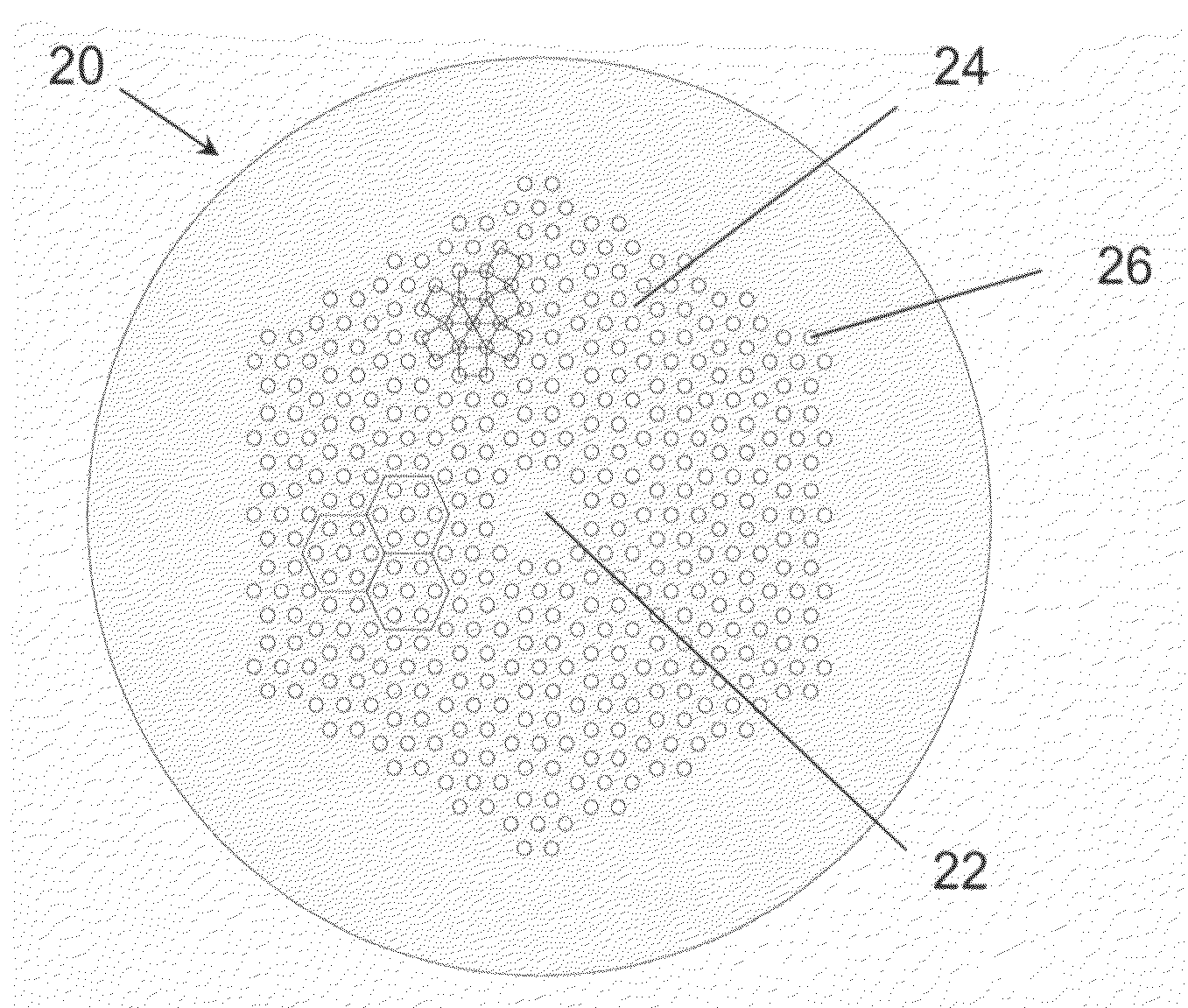
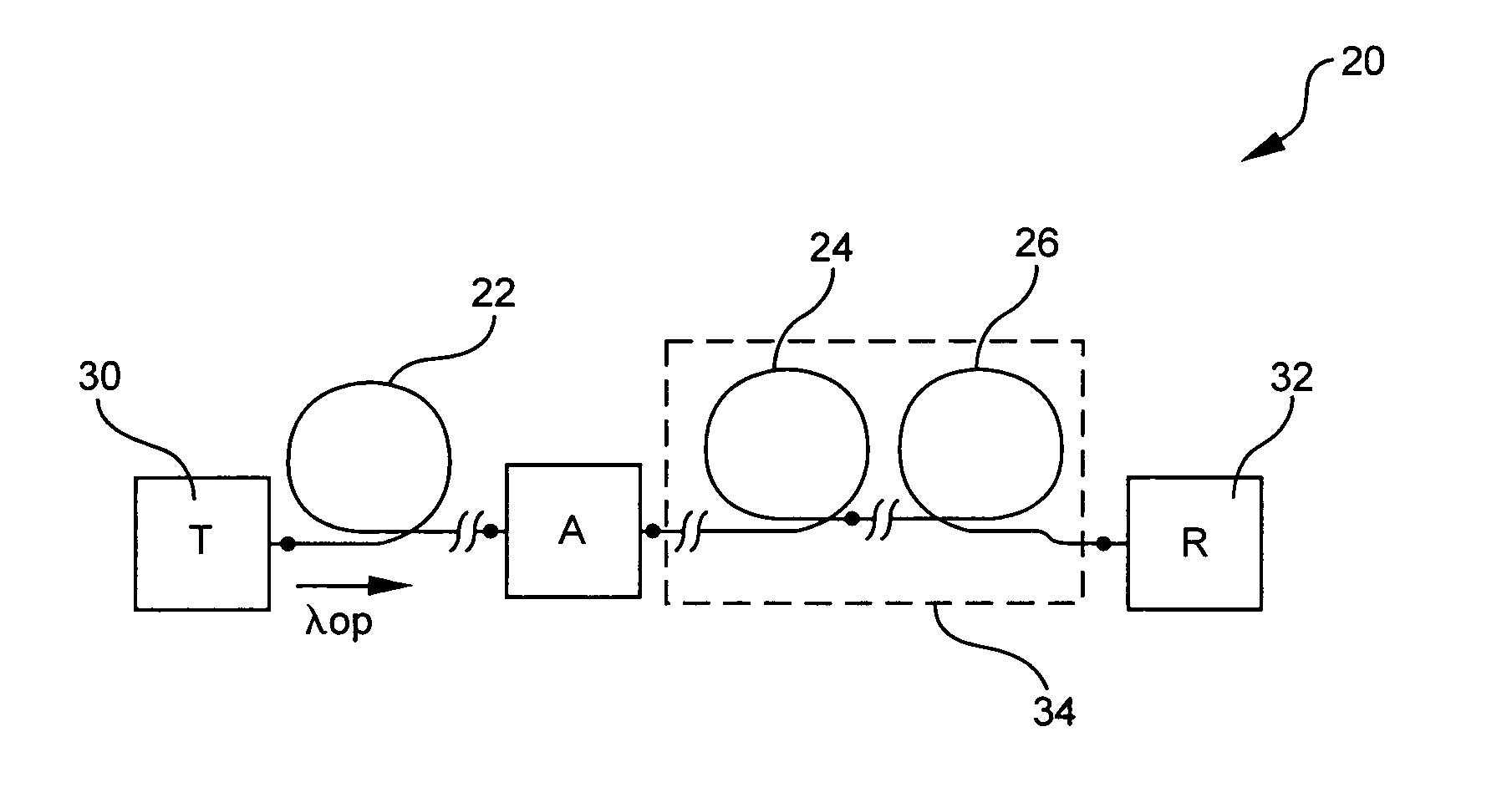
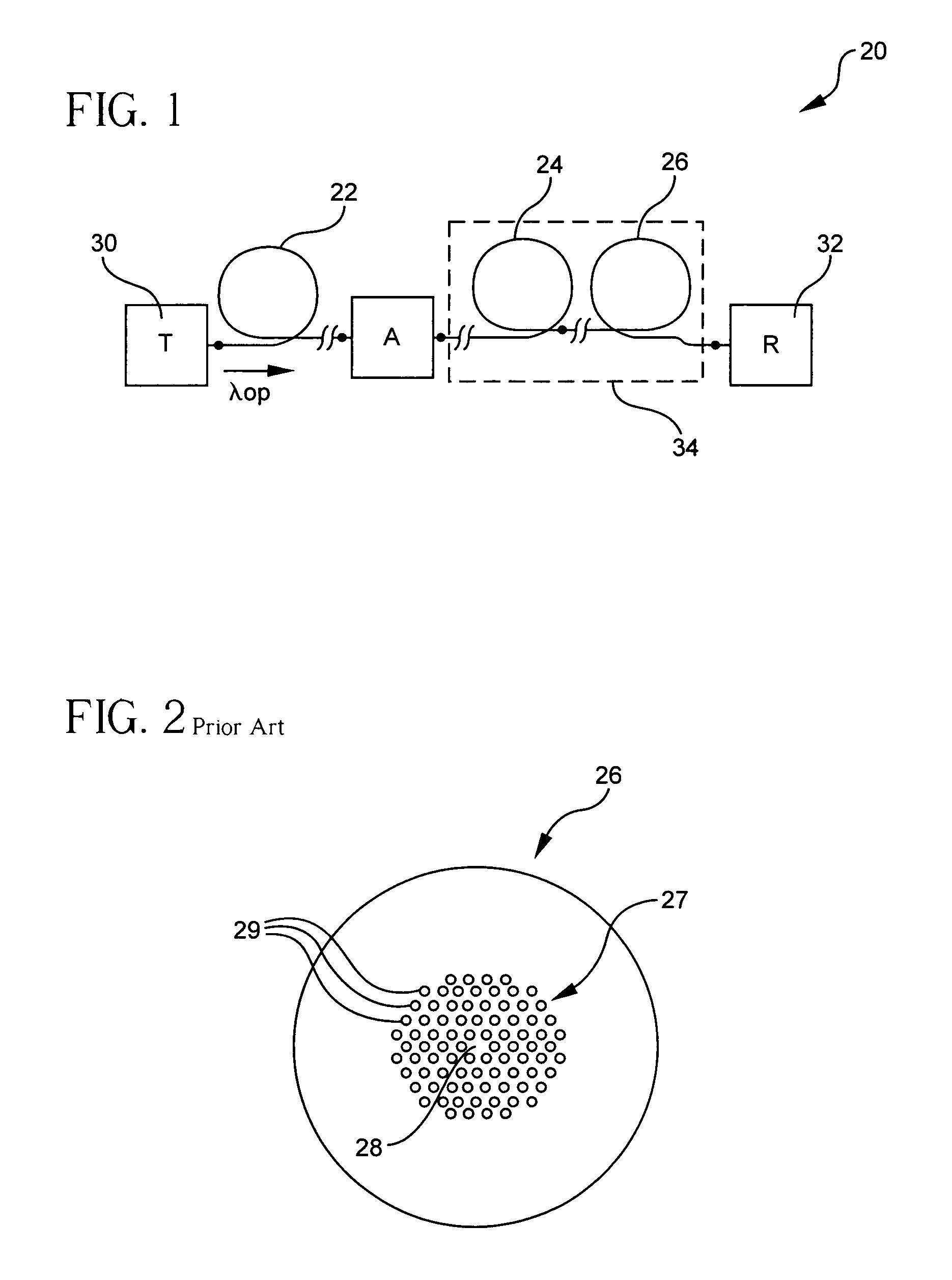
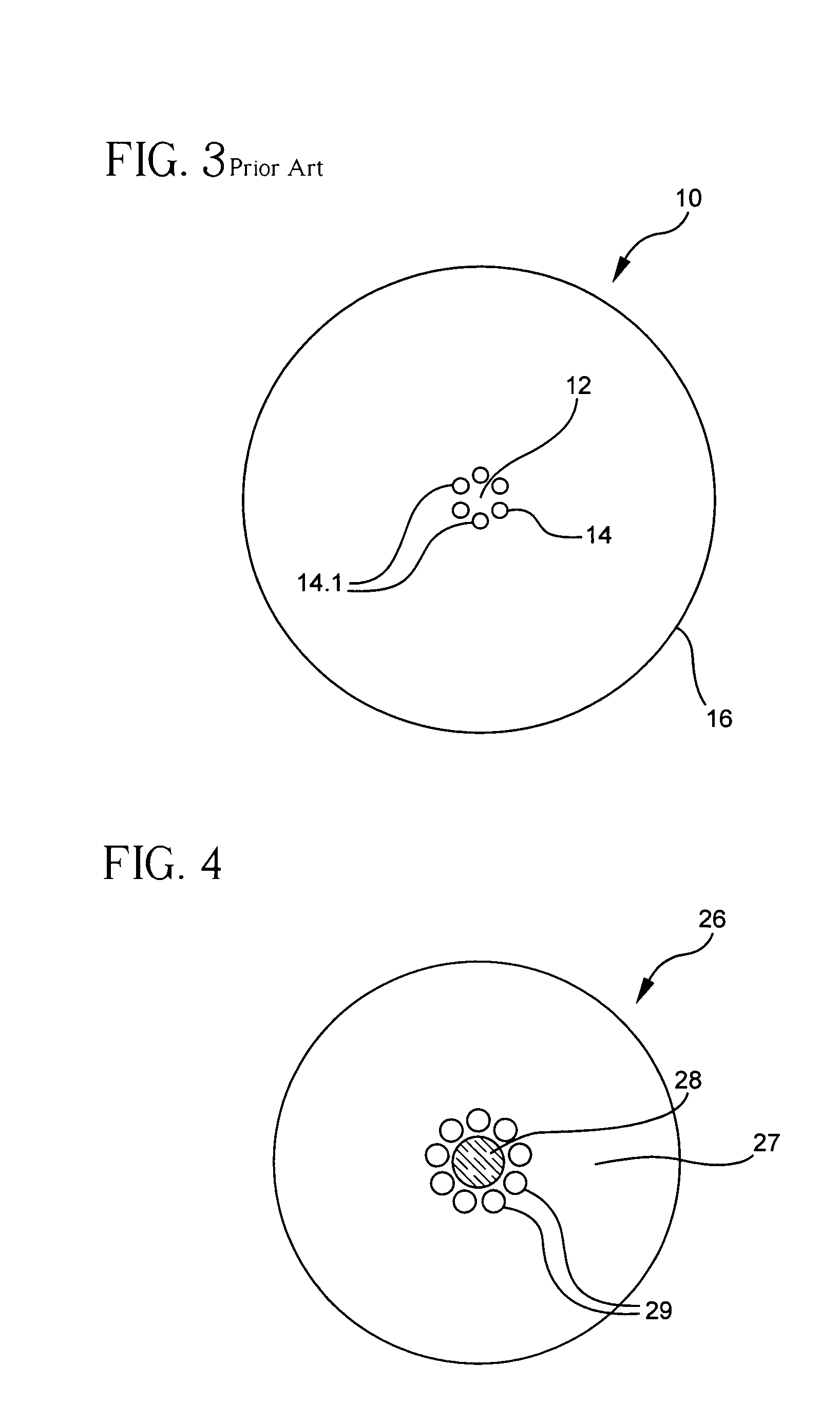
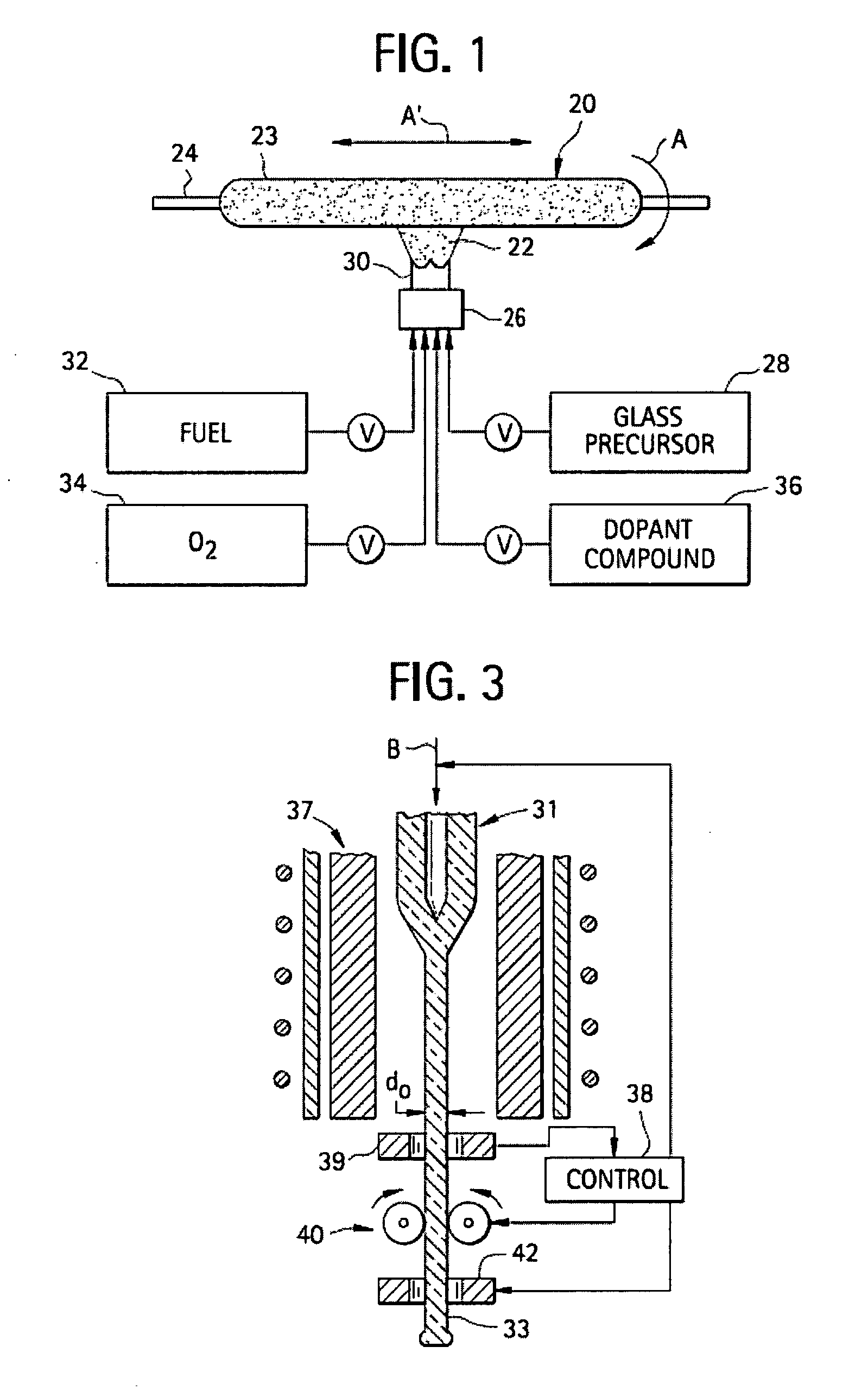
Microstructured optical fibers (MOF) are optical fiber waveguides where guiding is obtained through manipulation of waveguide structure rather than its index of refraction. In conventional optical fibers, light is guided through the effect of total internal reflection. The guiding occurs within a core of refractive index higher than refractive index of the surrounding material (cladding). The index change is obtained through different doping of the core and the cladding or through the use of different materials. In microstructured fibers, a completely different approach is applied. Fiber is built of one material (usually silica) and light guiding is obtained through the presence of air holes in the area surrounding the solid core. The holes are often arranged in the regular pattern in two dimensional arrays, however other patterns of holes exist, including non-periodic ones. While periodic arrangement of the holes would justify the use of term "photonic crystal fiber", the term is reserved for those fibers where propagation occurs within a photonic defect or due to photonic bandgap effect. As such, photonic crystal fibers may be considered a subgroup of microstructured optical fibers.
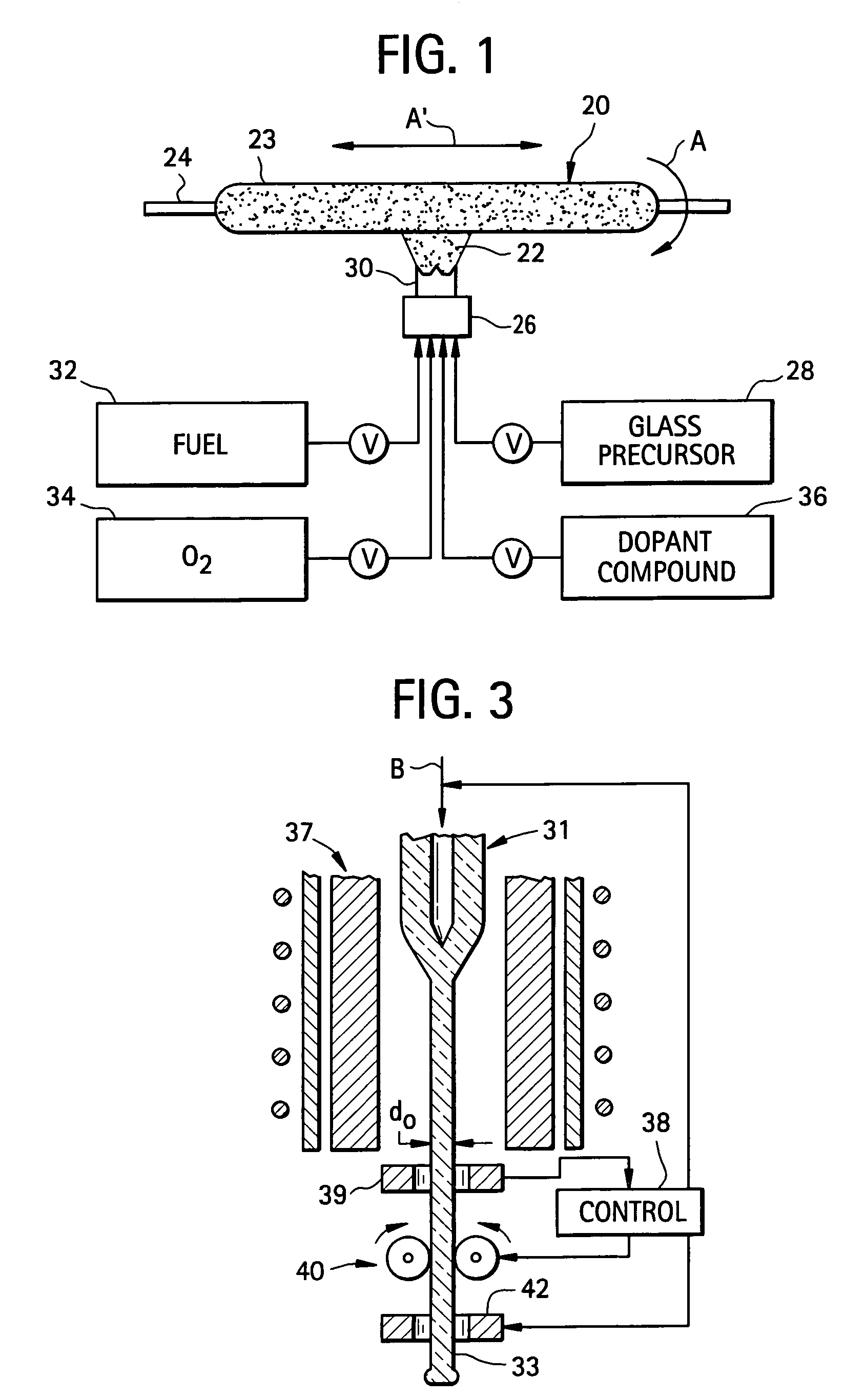
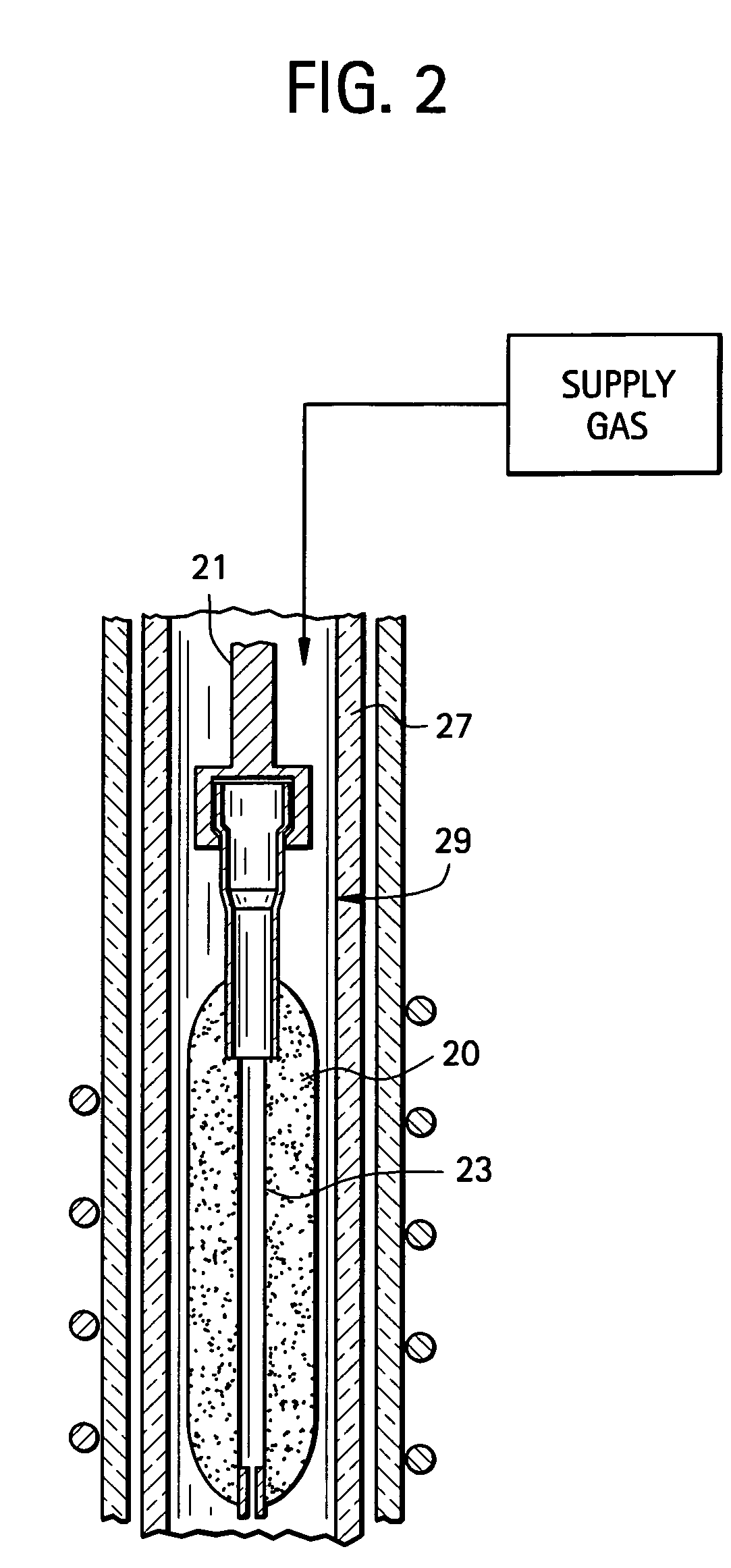
Microstructured optical fibers and methods
InactiveUS7450806B2Improve bending performanceLower refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingNitrogenNitrogen gas
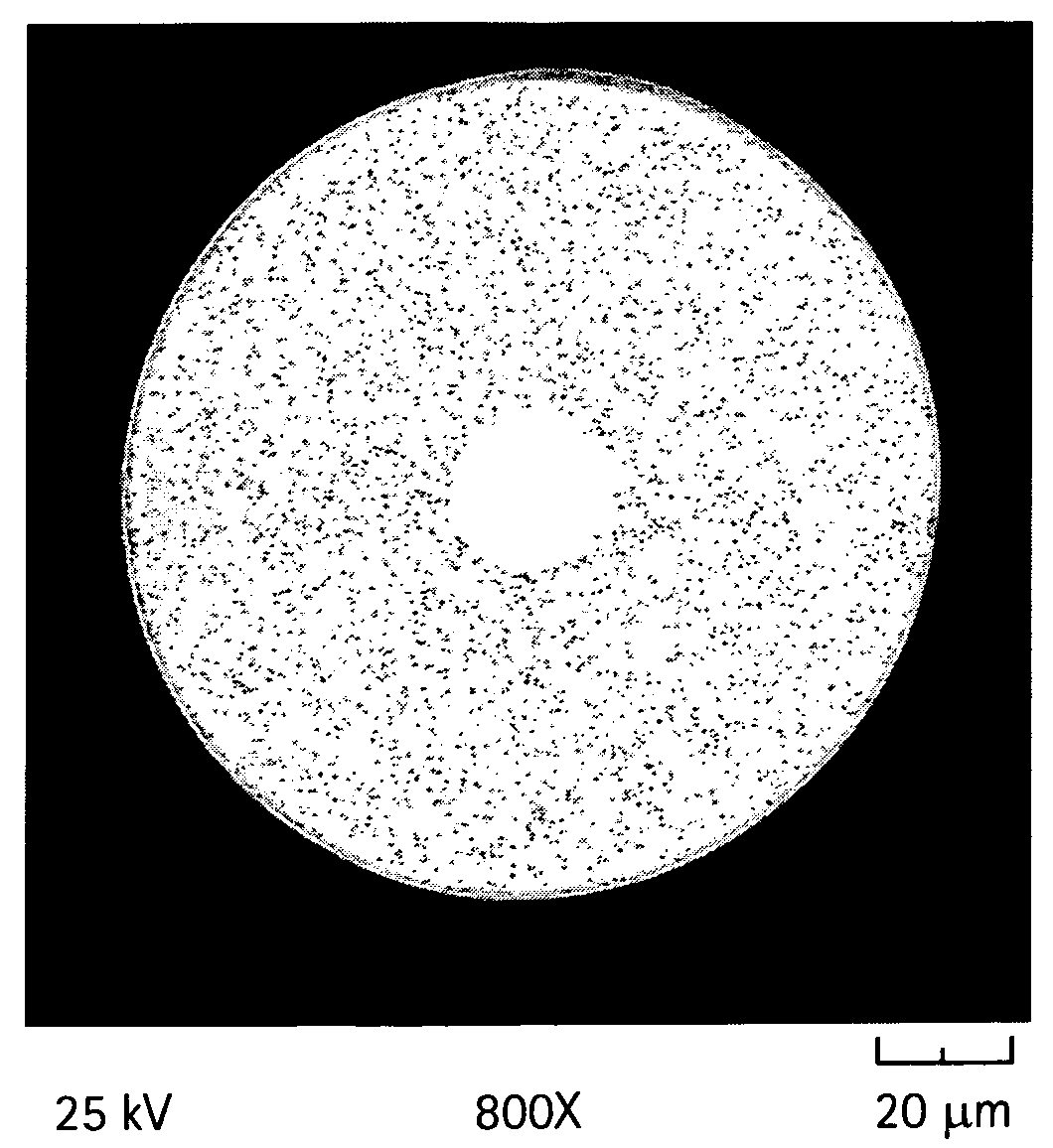
Microstructured optical fiber and method of making. Glass soot is deposited and then consolidated under conditions which are effective to trap a portion of the consolidation gases in the glass to thereby produce a non-periodic array of voids which may then be used to form a void containing cladding region in an optical fiber. Preferred void producing consolidation gases include nitrogen, argon, CO2, oxygen, chlorine, CF4, CO, SO2 and mixtures thereof.
Owner:CORNING INC
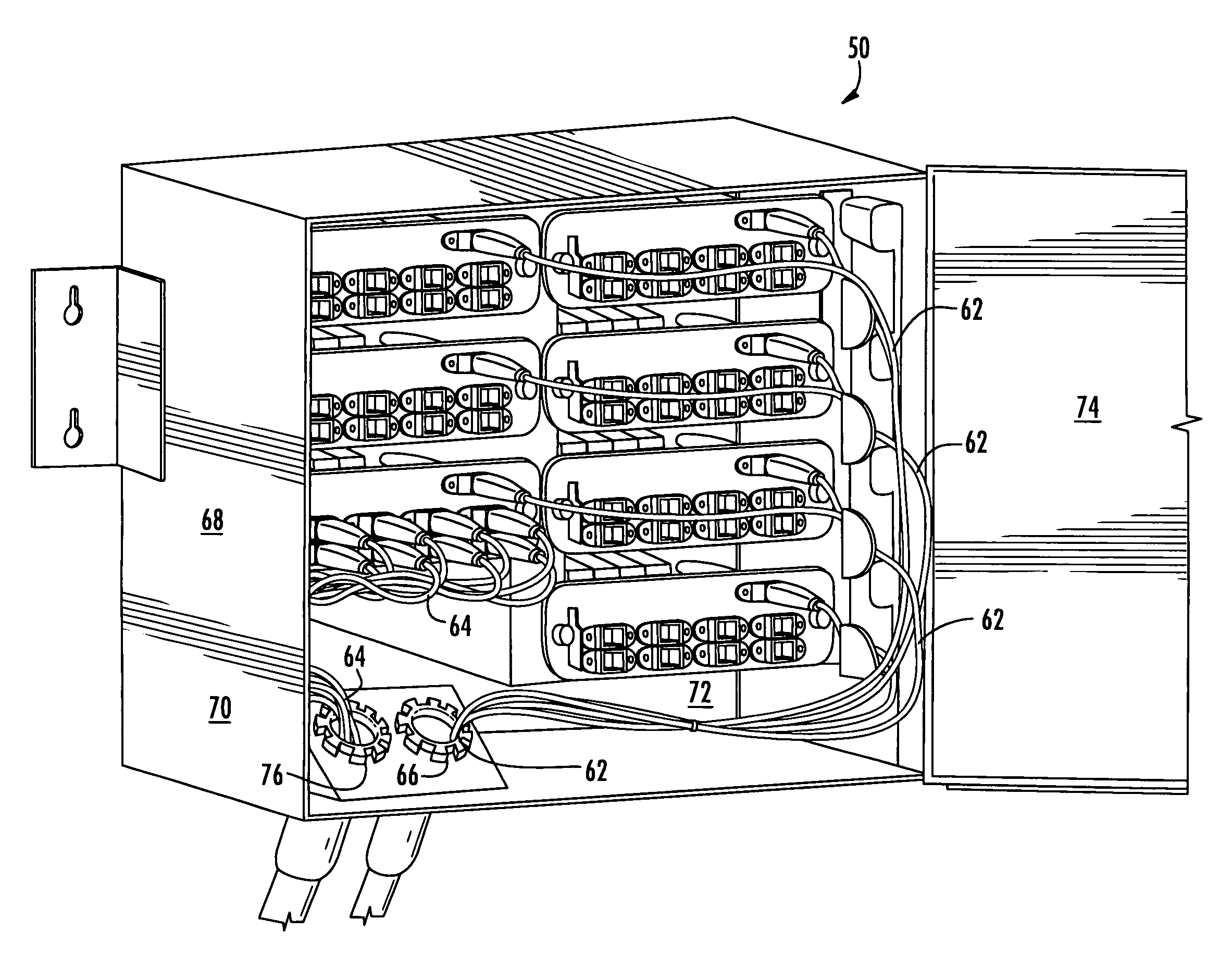
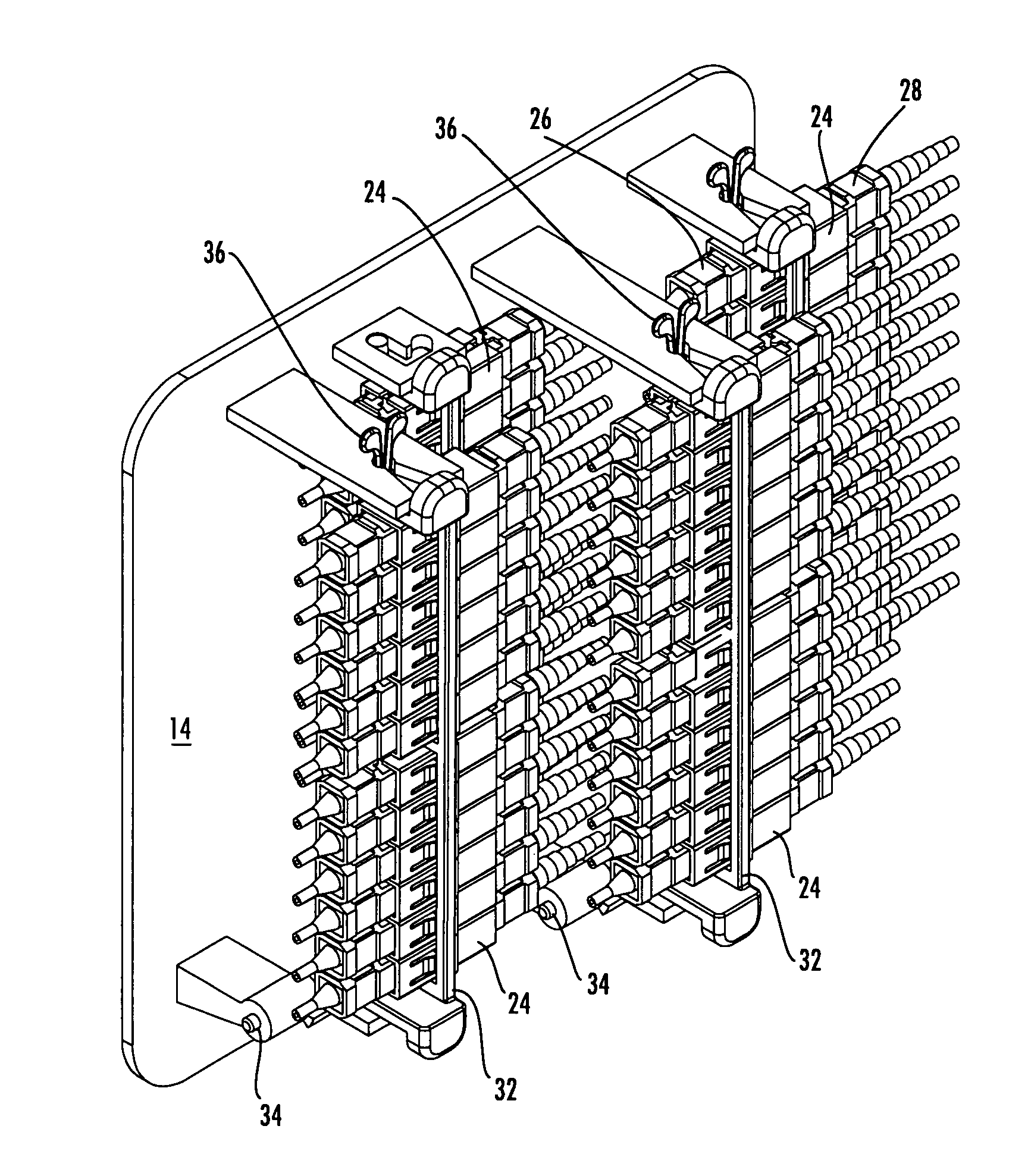
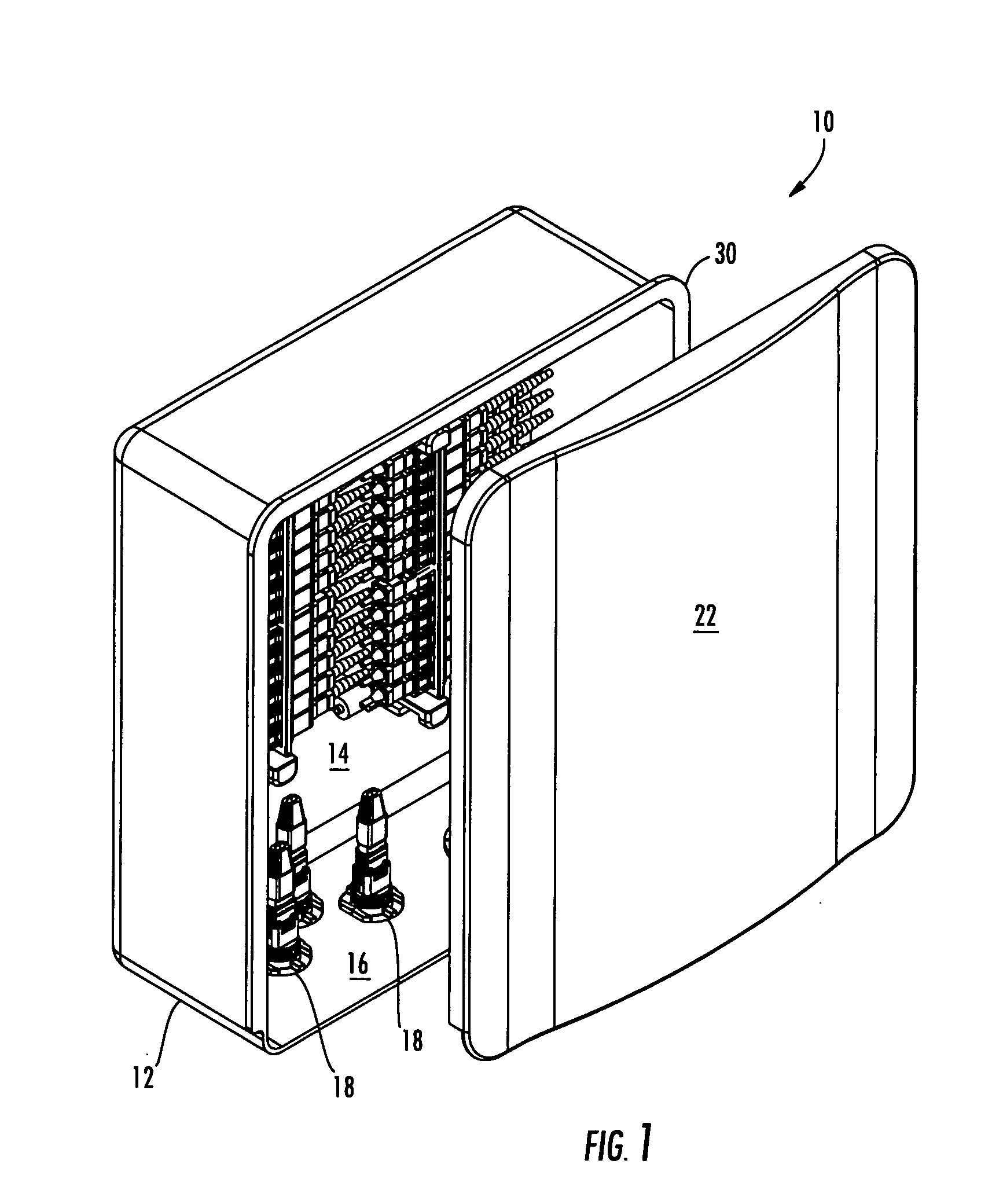
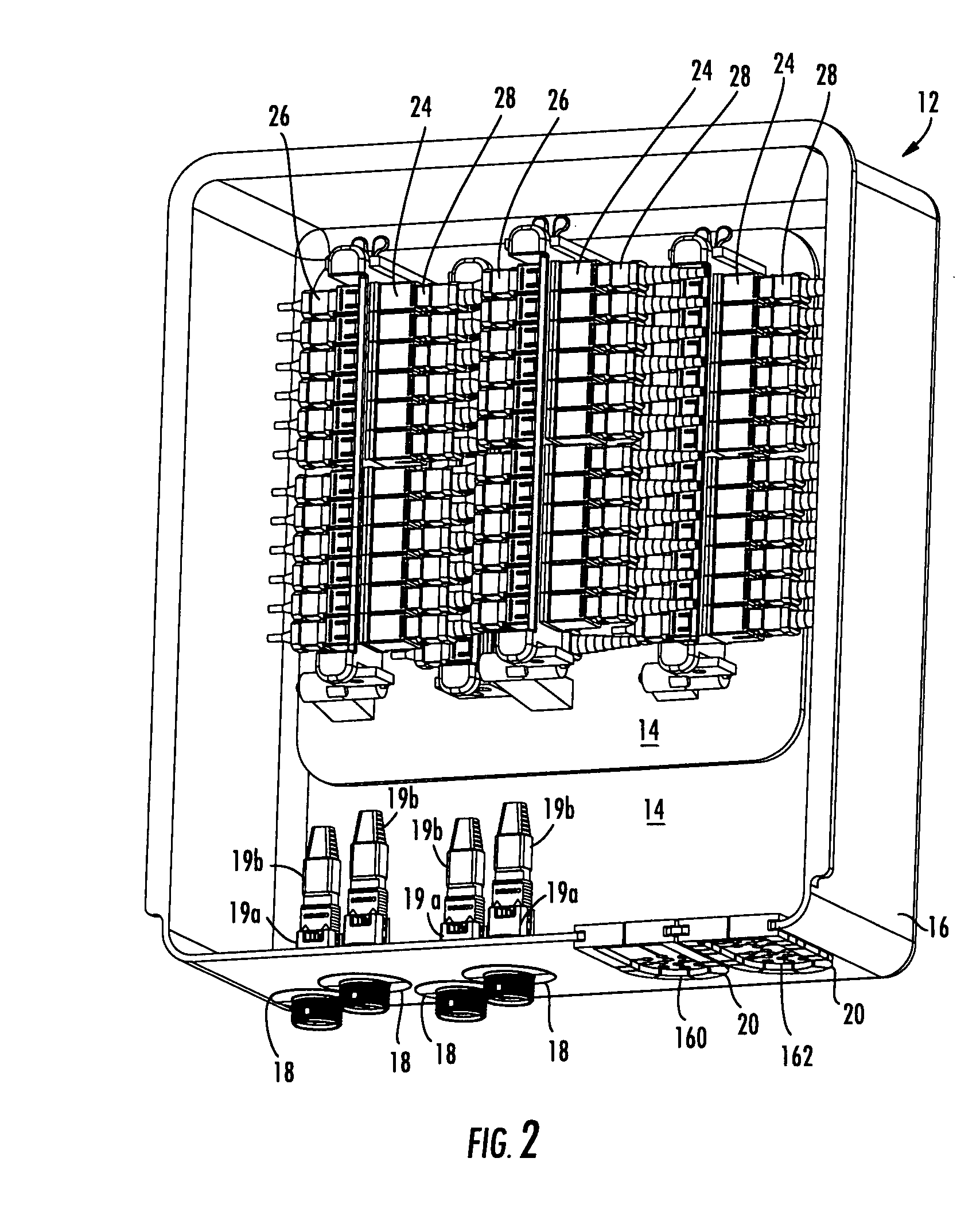
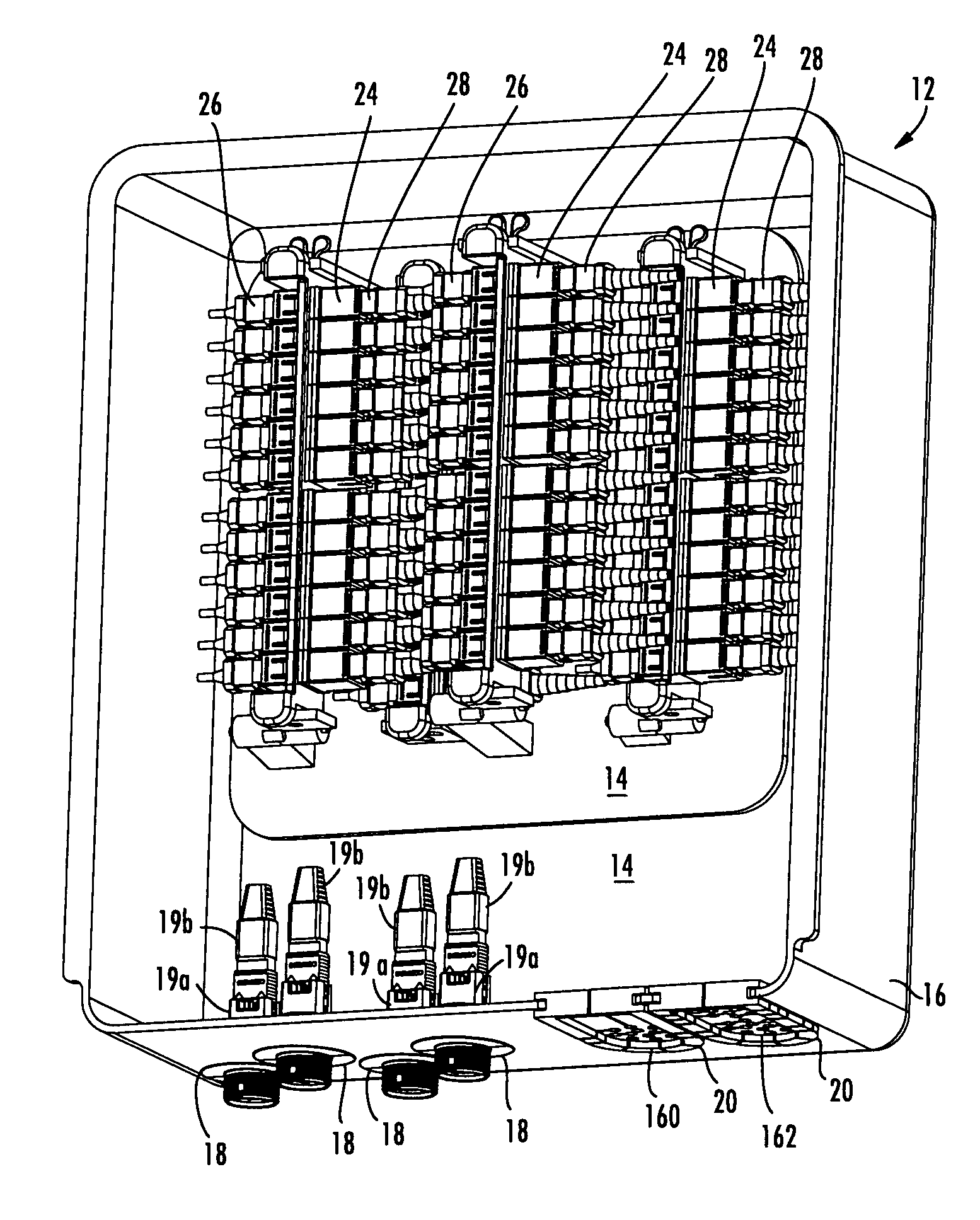
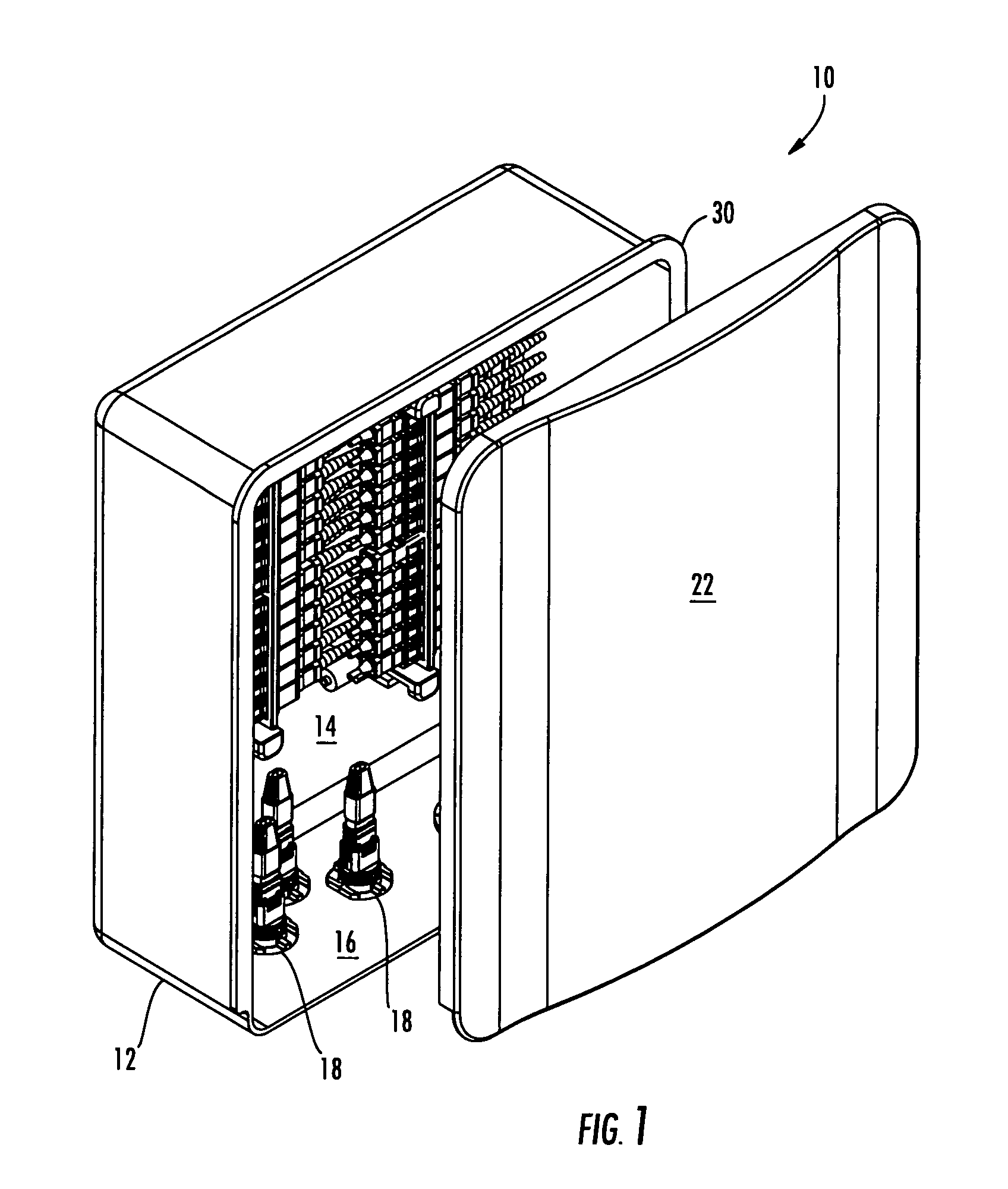
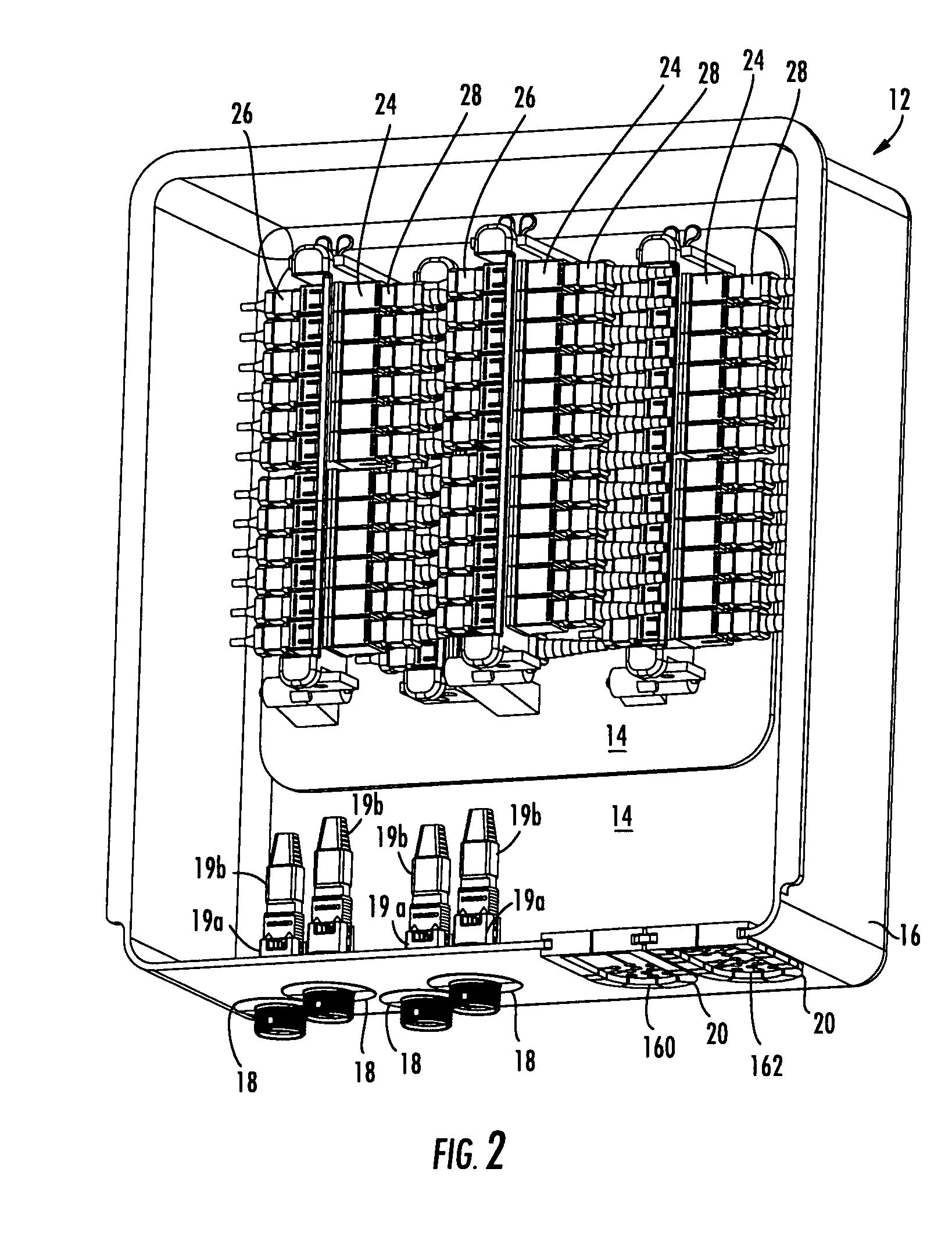
High density fiber optic hardware
There is provided fiber optic hardware and hardware components adapted to provide a desired amount of fiber optic connectivity and / or functionality for a desired amount of volume, materials, etc. The fiber optic hardware components include, but are not limited to multiports, local convergence points (LCPs), particularly LCPs for multiple dwelling units or similar applications, network interface devices, equipment frames, and fiber distribution hubs. Certain fiber optic hardware components are adapted to accommodate microstructured optical fiber or other bend performance optical fiber.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Fiber optic drop terminals for multiple dwelling units
InactiveUS20080205843A1Small “ footprint ”Convenient and secure accessCoupling light guidesSelection arrangementsFiberEngineering
There is provided fiber drop terminals (“FDTs”) and related equipment for providing selective connections between optical fibers of distribution cables and optical fibers of drop cables, such as in multiple dwelling units. The FDTs require relatively little area and / or volume while providing convenient connectivity for a relatively large number of optical connections. The FDTs include adapters for optically connecting the connectors, and the adapters of some FDTs are adapted to rotate, move, or otherwise be removed to provide convenient access for technicians. Some FDTs and the related equipment are adapted for use with microstructured optical fiber having preferred bend characteristics.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
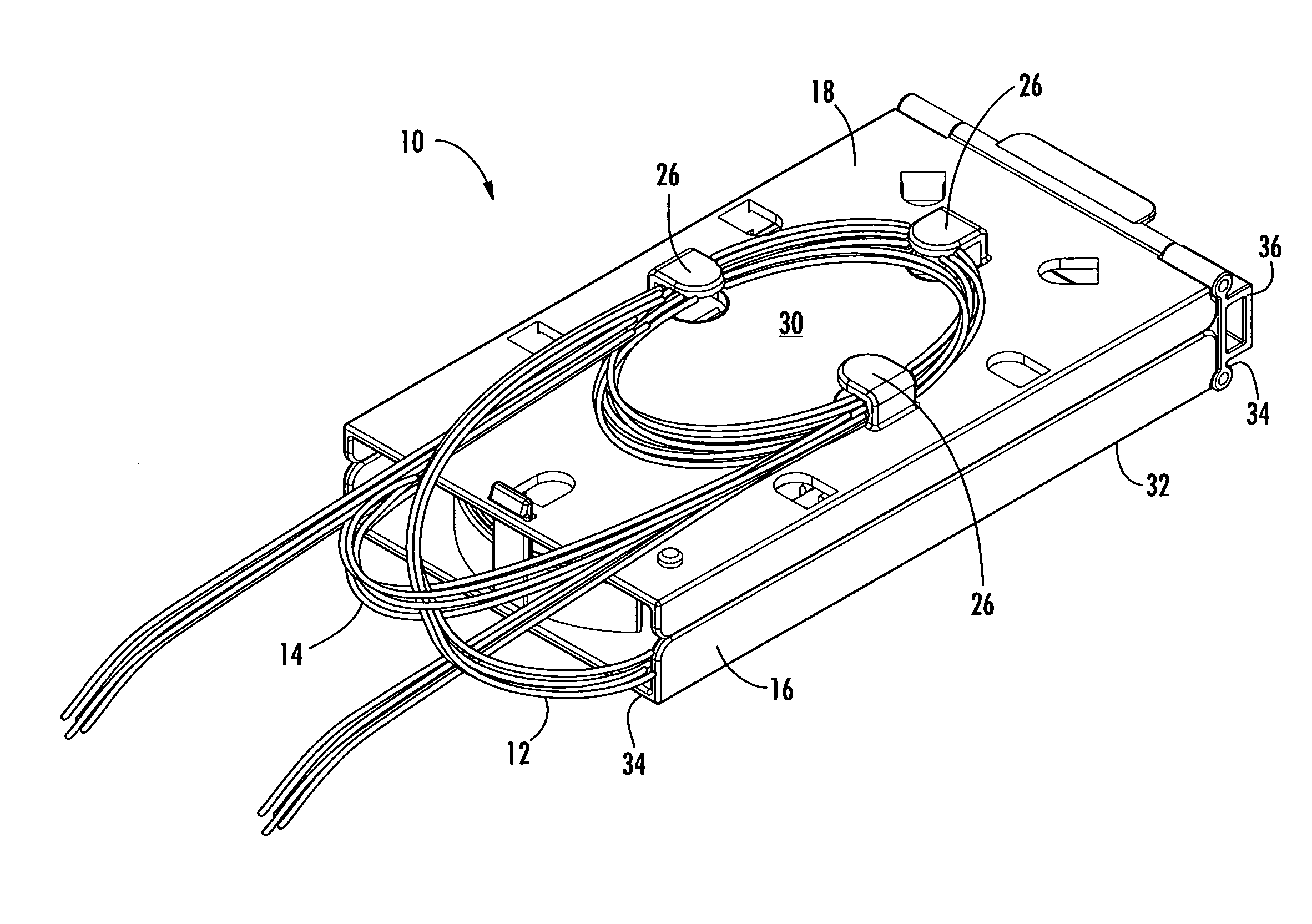
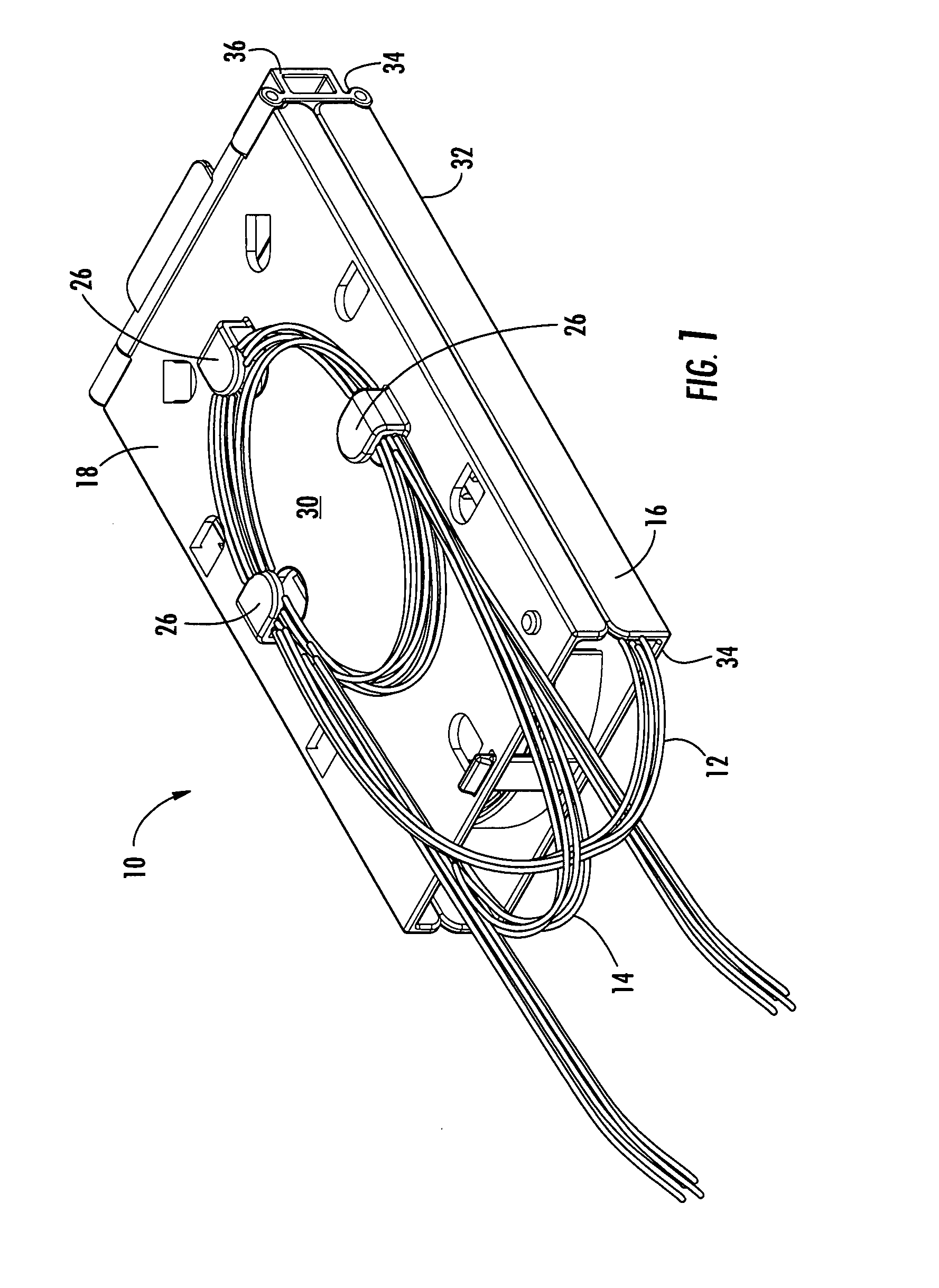
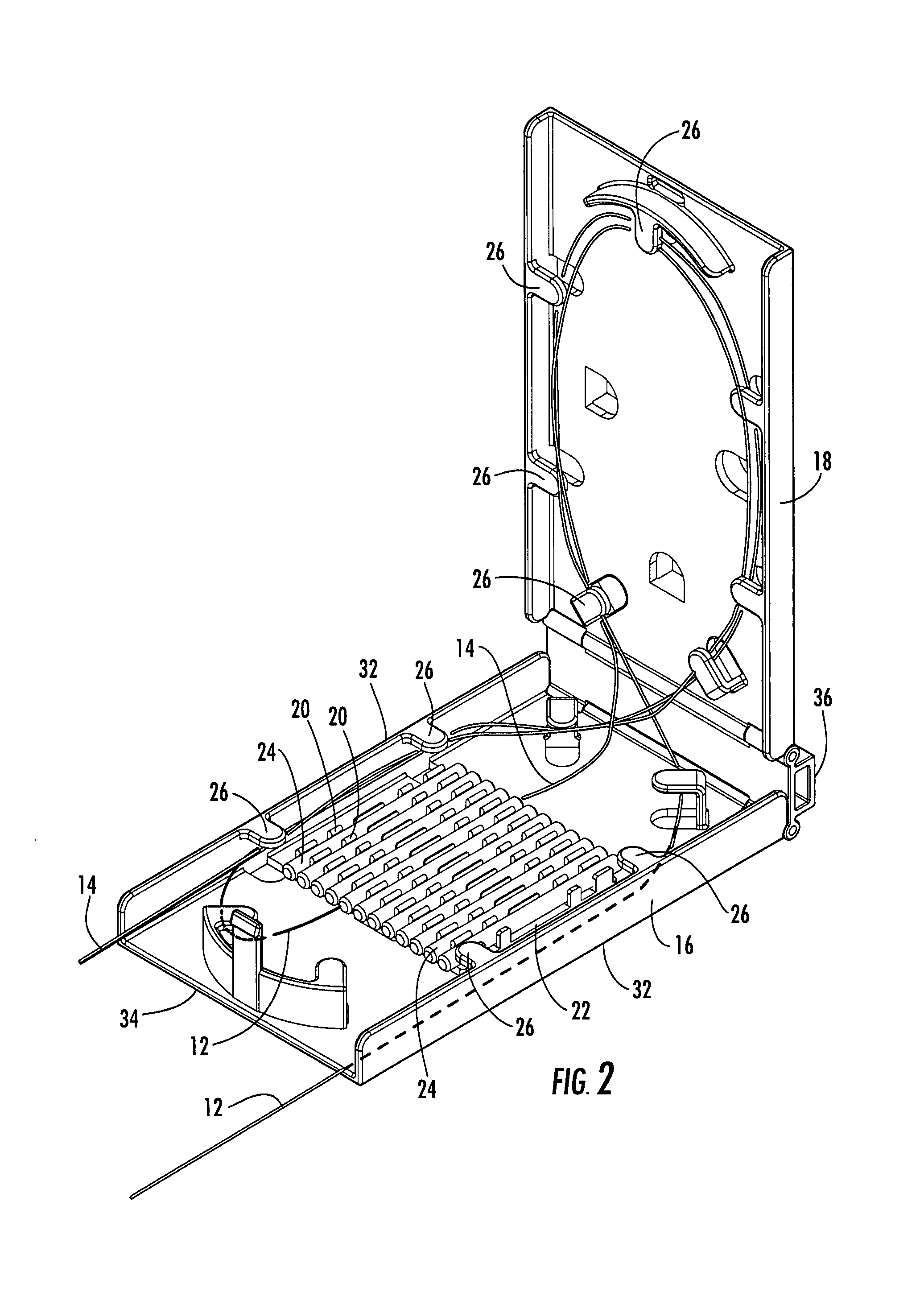
Fiber optic splice trays
InactiveUS20080205844A1SmallFunction increaseElectrically conductive connectionsCable junctionsFiberOptical fiber connector
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Fiber optic drop terminals for multiple dwelling units
InactiveUS7499622B2Small “ footprint ”Convenient and secure accessOptical light guidesSelection arrangementsFiberEngineering
There is provided fiber drop terminals (“FDTs”) and related equipment for providing selective connections between optical fibers of distribution cables and optical fibers of drop cables, such as in multiple dwelling units. The FDTs require relatively little area and / or volume while providing convenient connectivity for a relatively large number of optical connections. The FDTs include adapters for optically connecting the connectors, and the adapters of some FDTs are adapted to rotate, move, or otherwise be removed to provide convenient access for technicians. Some FDTs and the related equipment are adapted for use with microstructured optical fiber having preferred bend characteristics.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
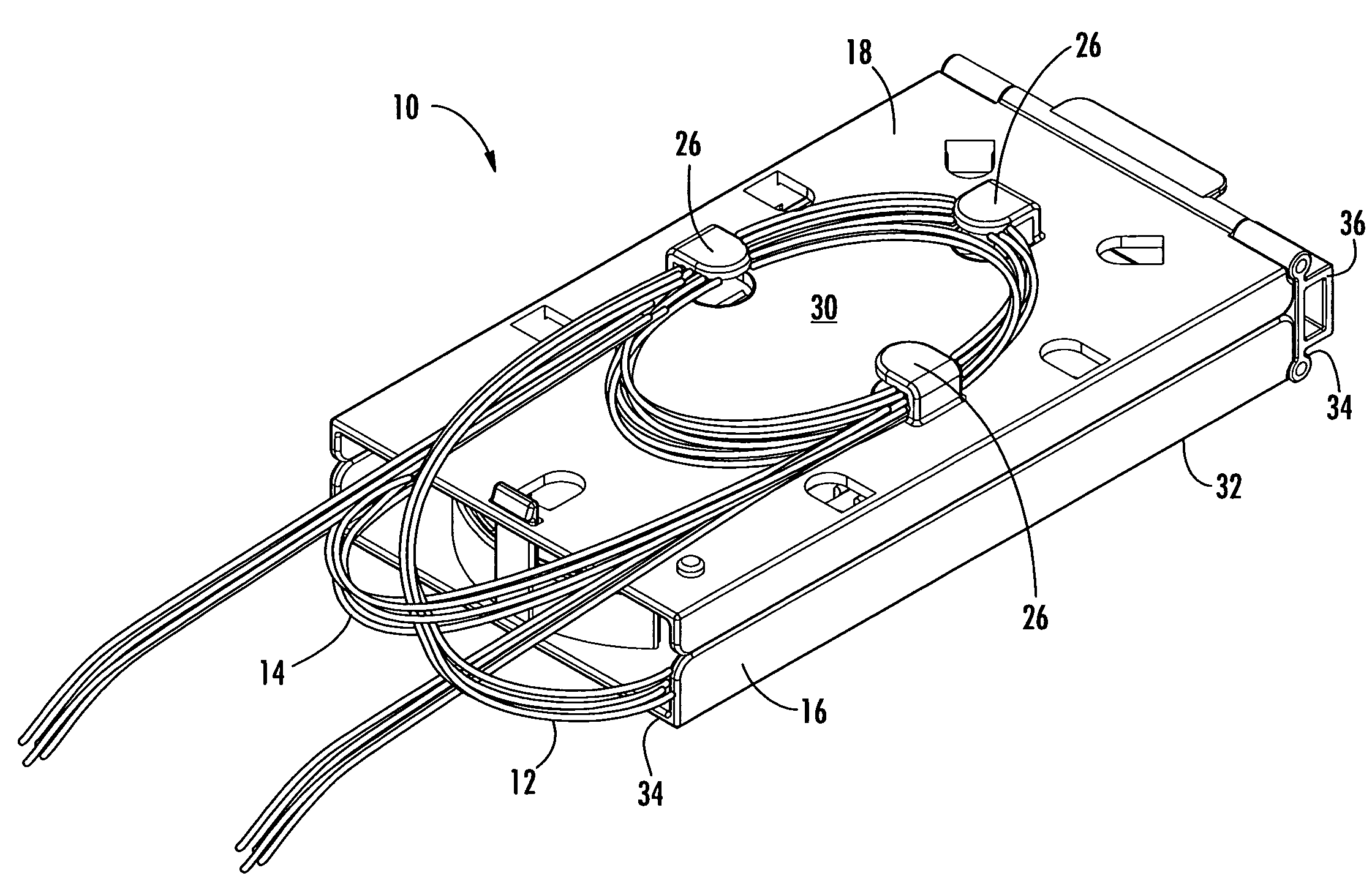
Fiber optic splice trays
InactiveUS7822310B2Reduce areaFunction increaseElectrically conductive connectionsCable junctionsFiberOptical fiber connector
There is provided splice trays and splice assemblies that provide convenient access to optical fiber slack within a relatively small area or volume. Some splice trays are adapted for use with microstructured optical fibers to further reduce the size of the splice tray or splice assembly. Some splice trays provide fiber routing devices on the cover of the splice tray. The fiber routing device may be positioned on an inside surface of the cover and / or on an outside surface of the cover. The splice trays and / or splice assemblies may be used with or as fiber drop terminals used within multiple dwelling units.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
High density fiber optic hardware
InactiveUS20080145013A1More freedomImprove connectivityOptical waveguide light guideFiberHigh density
There is provided fiber optic hardware and hardware components adapted to provide a desired amount of fiber optic connectivity and / or functionality for a desired amount of volume, materials, etc. The fiber optic hardware components include, but are not limited to multiports, local convergence points (LCPs), particularly LCPs for multiple dwelling units or similar applications, network interface devices, equipment frames, and fiber distribution hubs. Certain fiber optic hardware components are adapted to accommodate microstructured optical fiber or other bend performance optical fiber.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
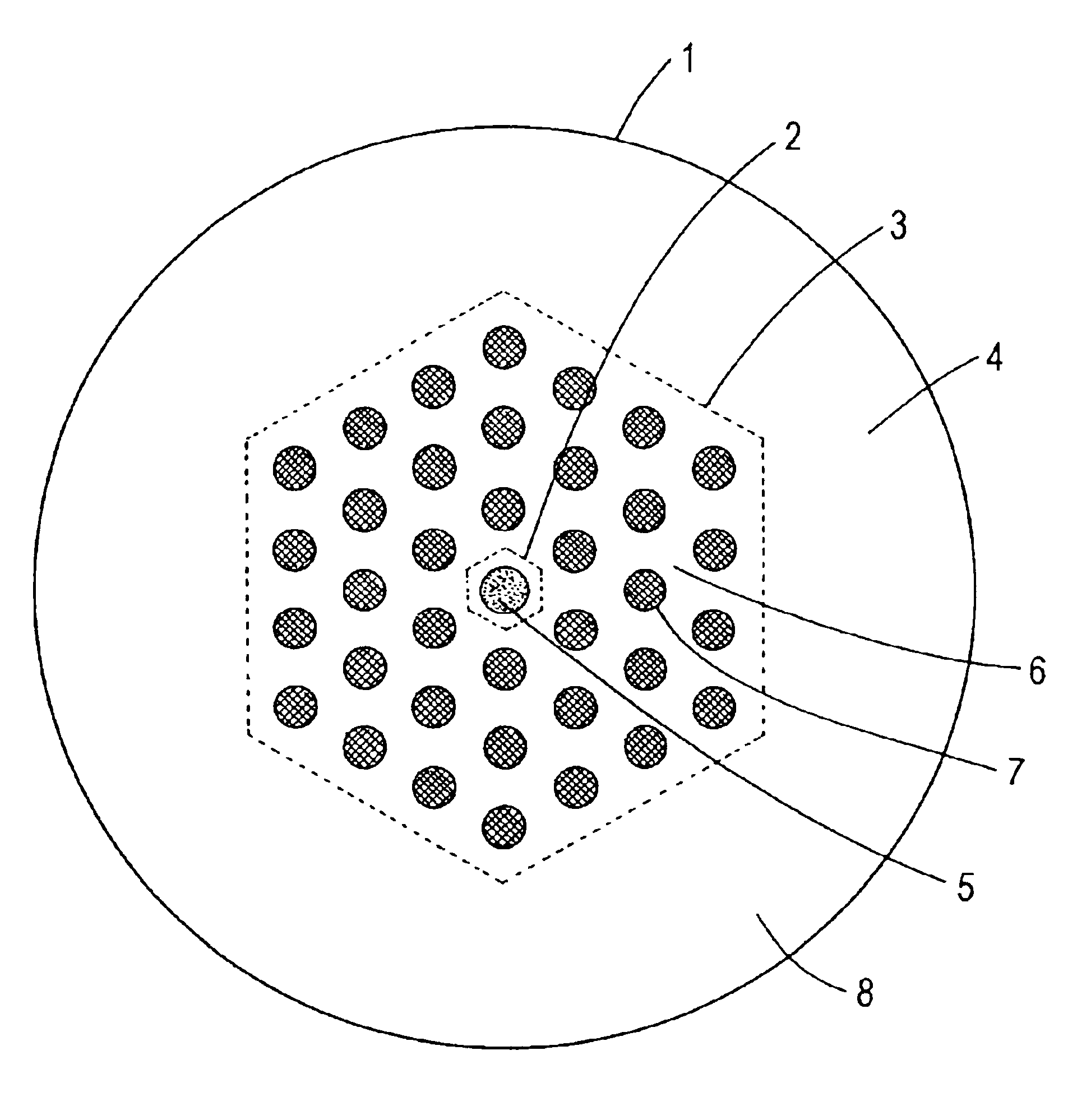
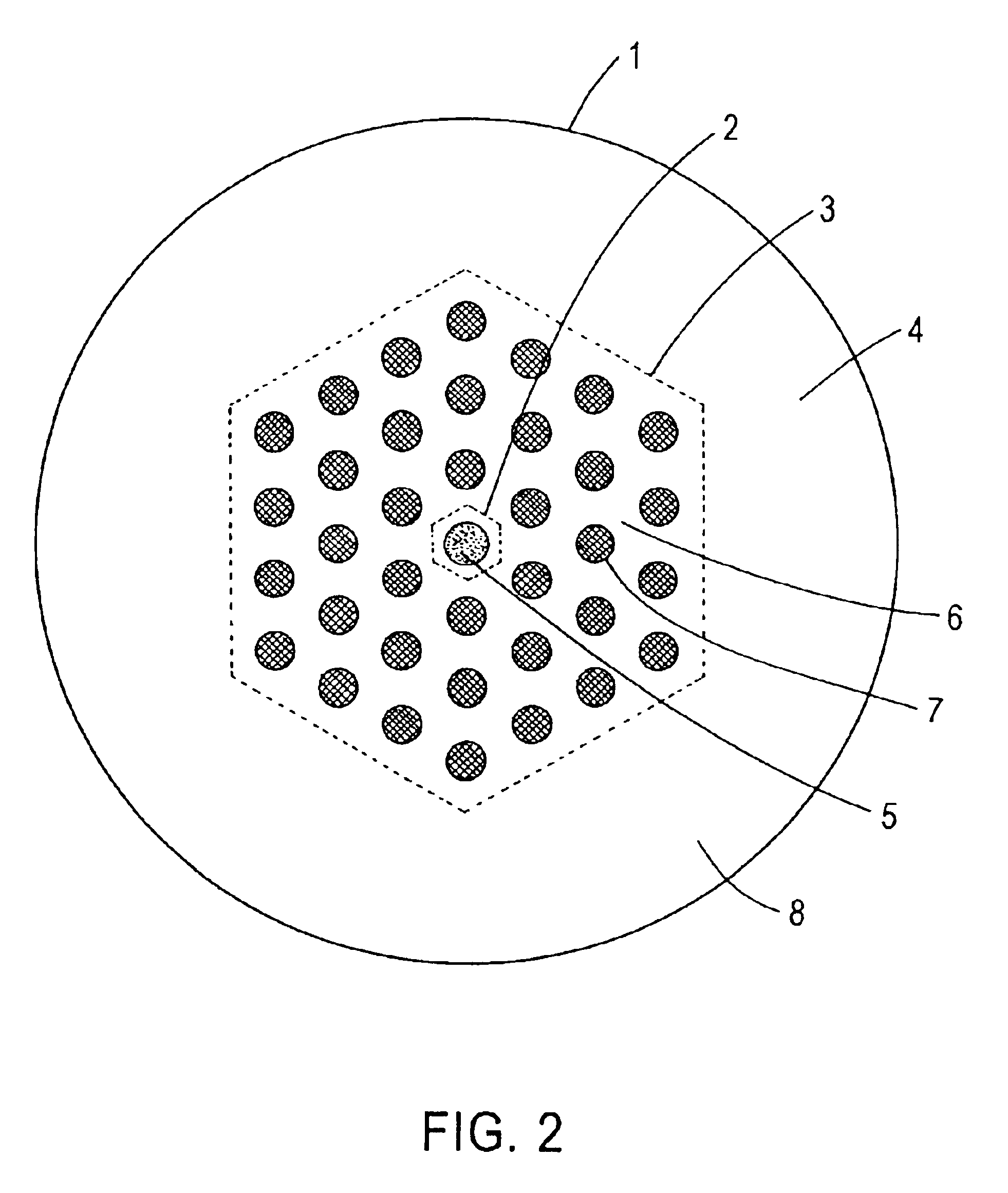
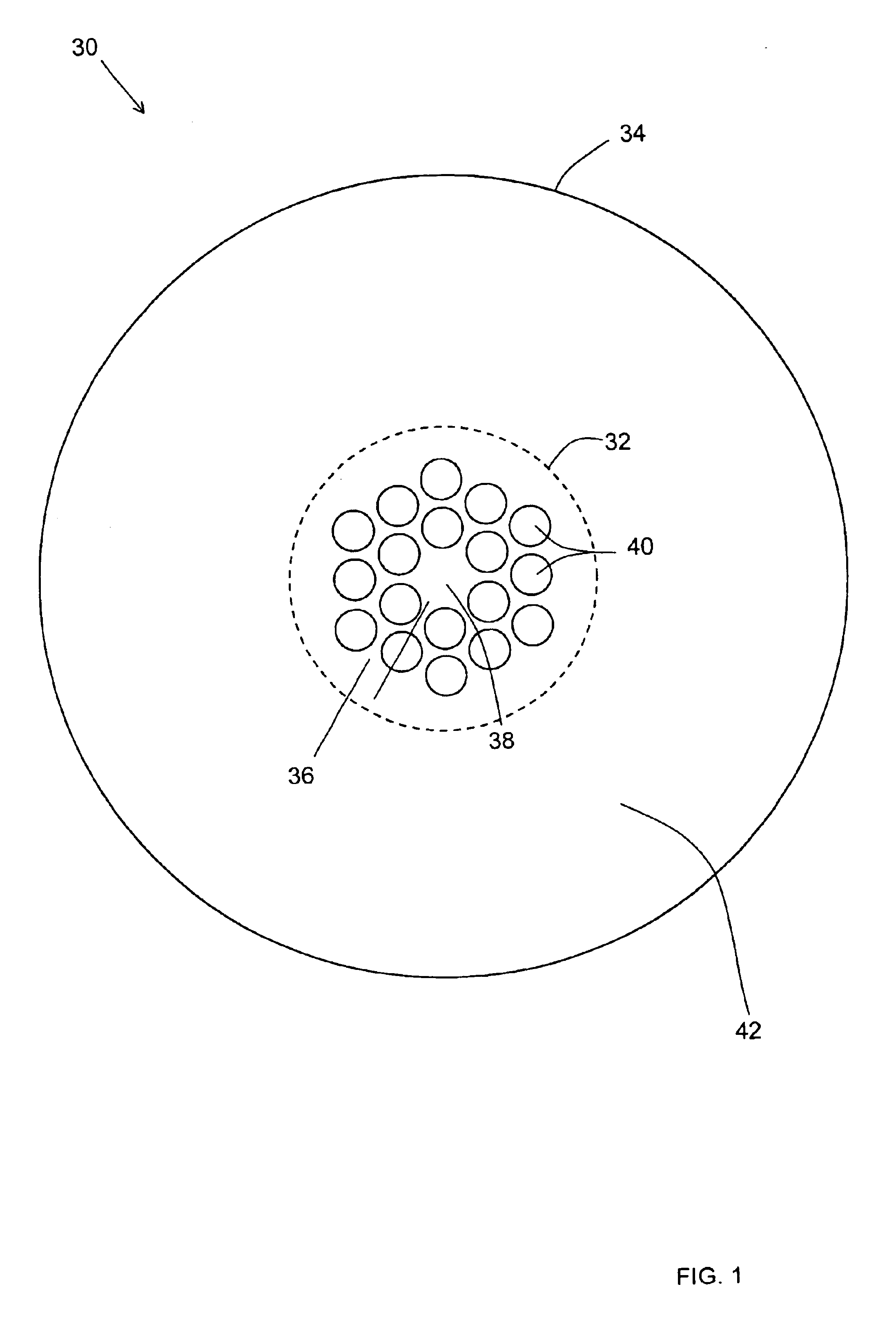
Microstructured optical fiber
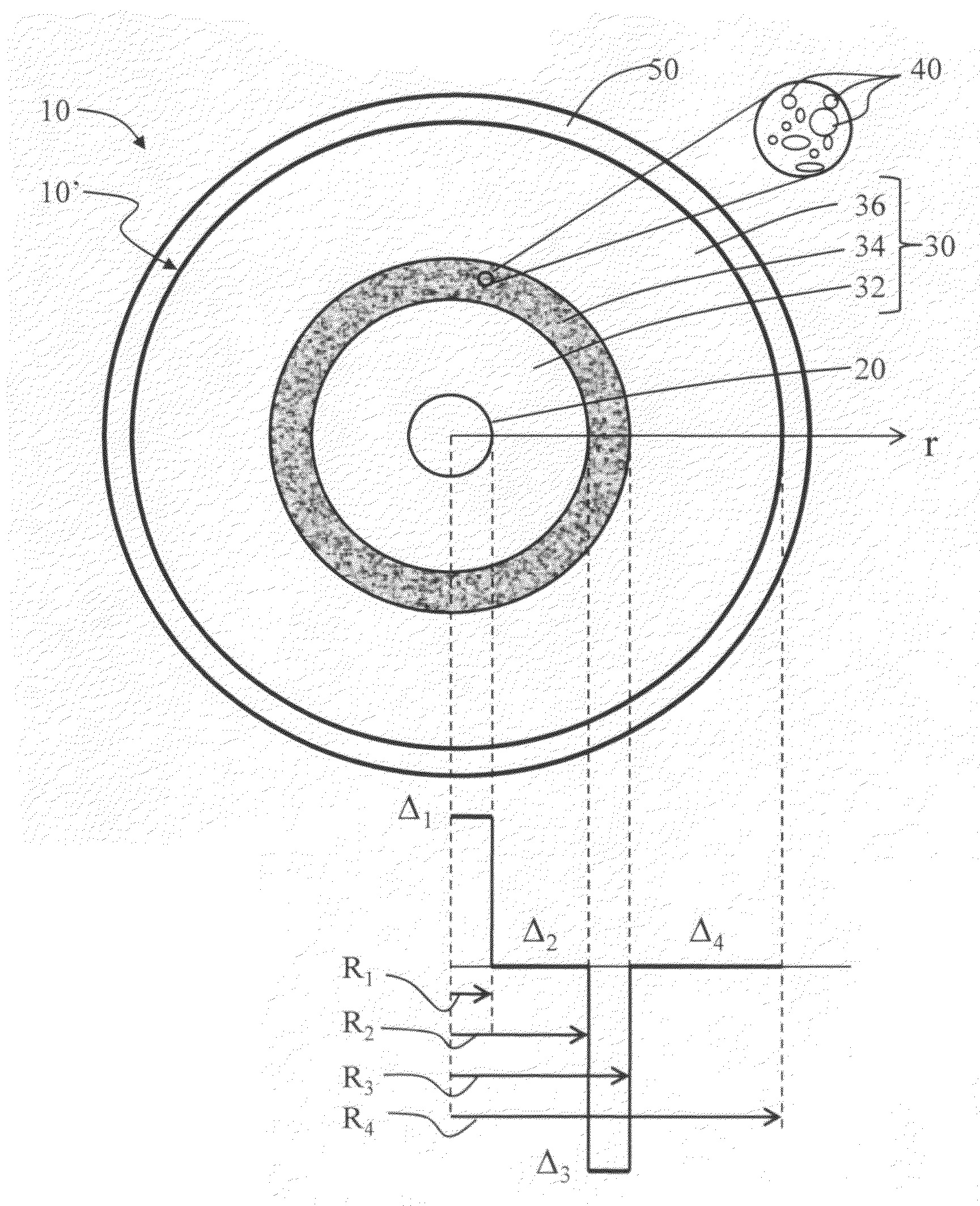
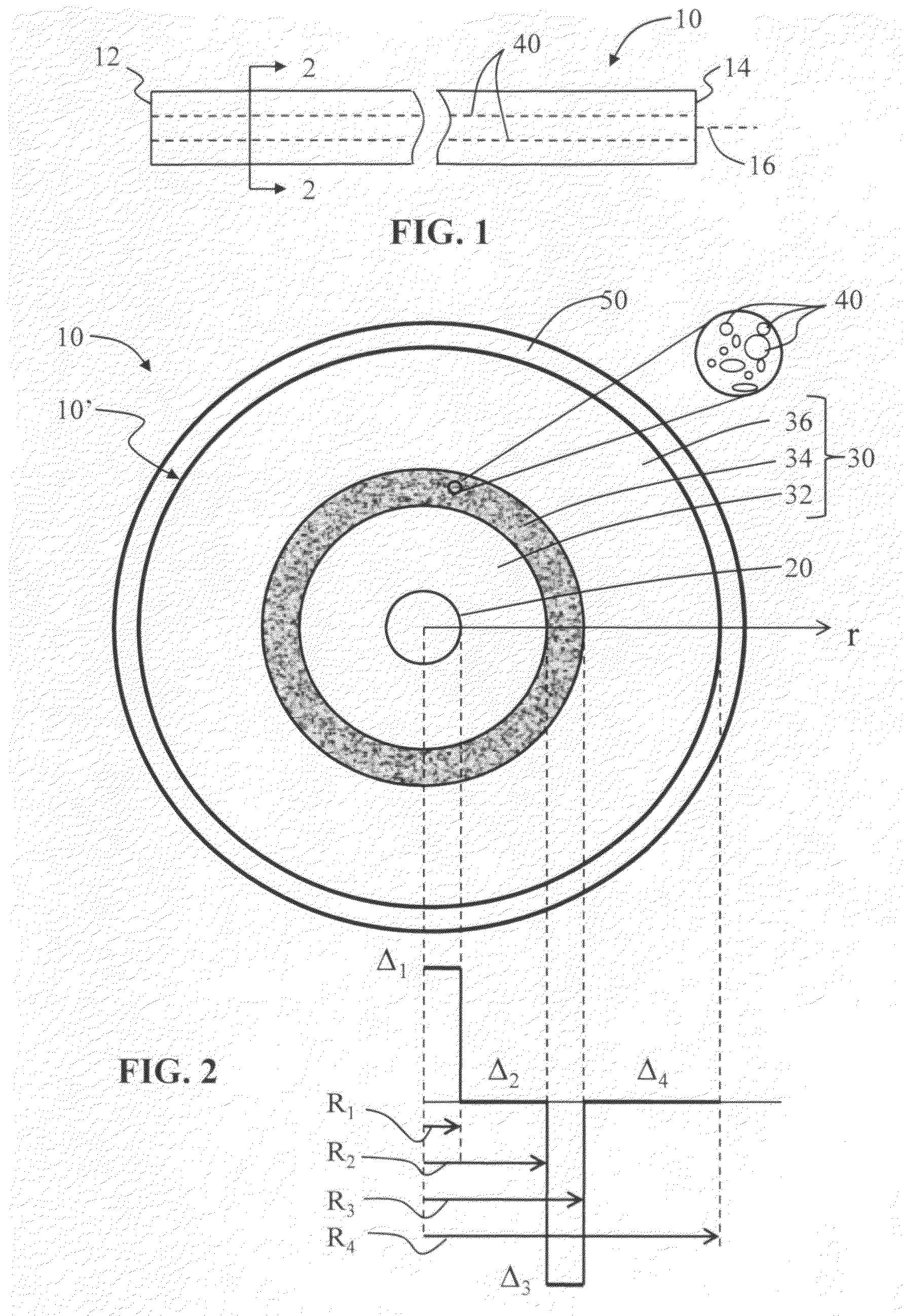
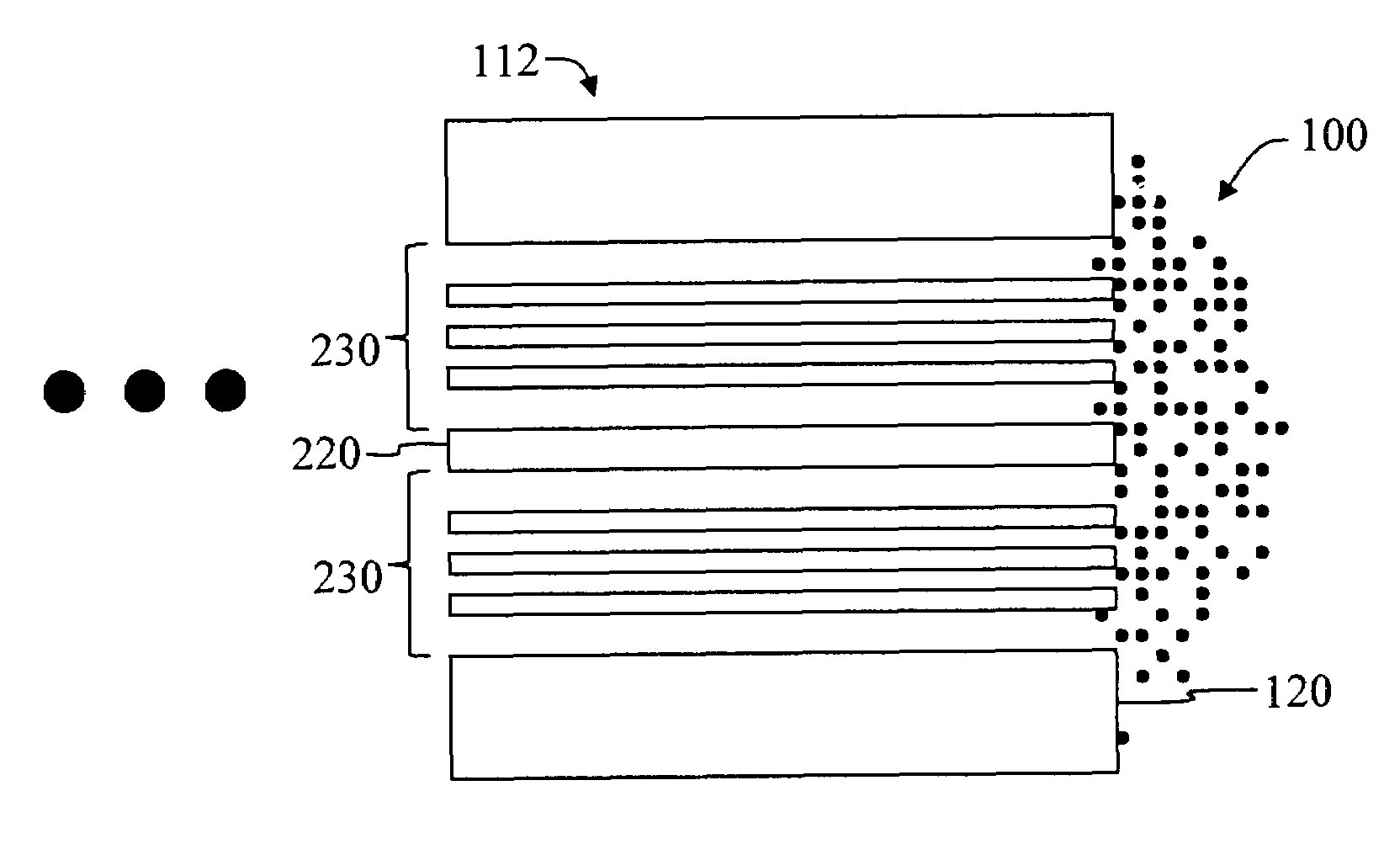
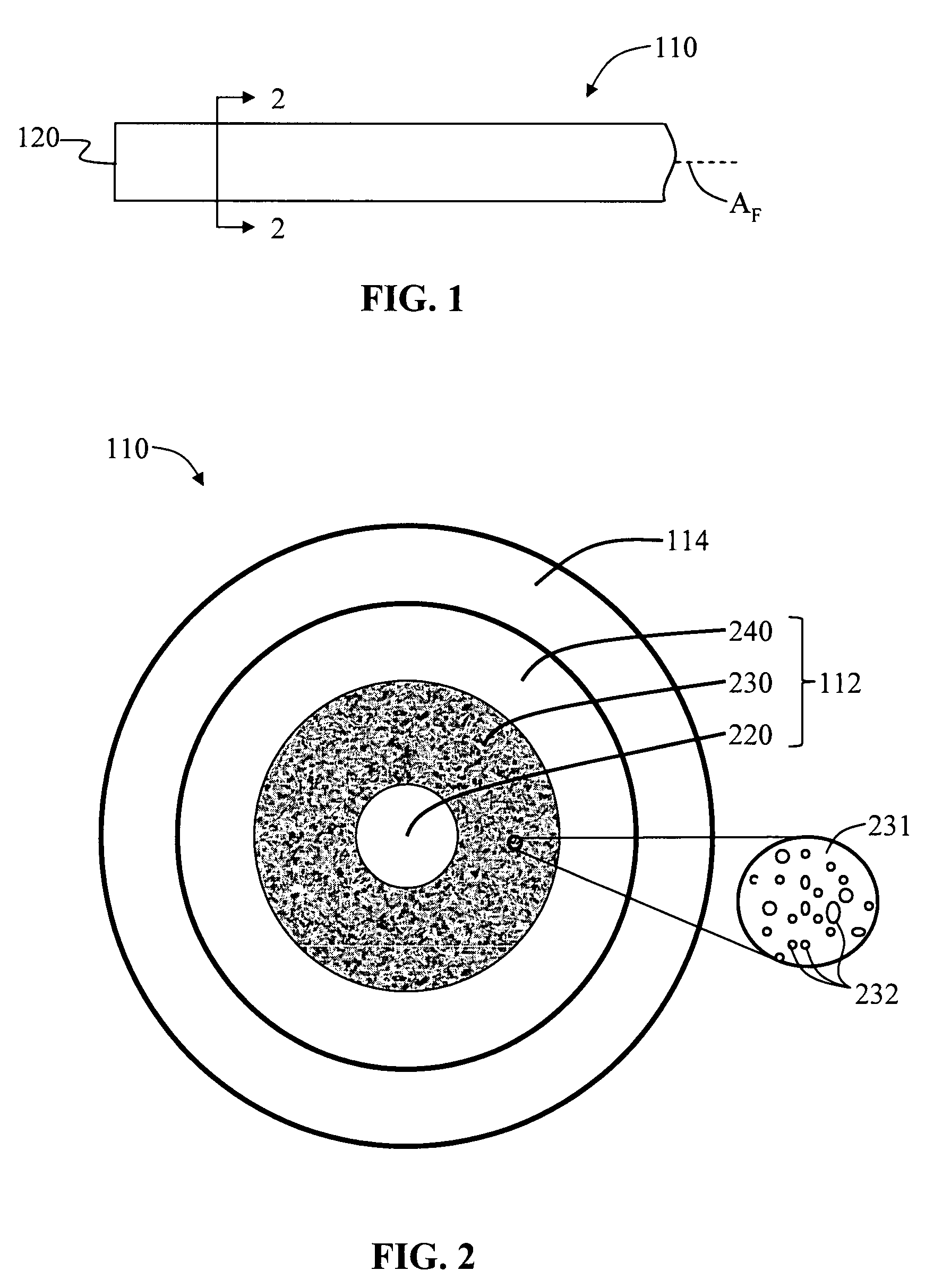
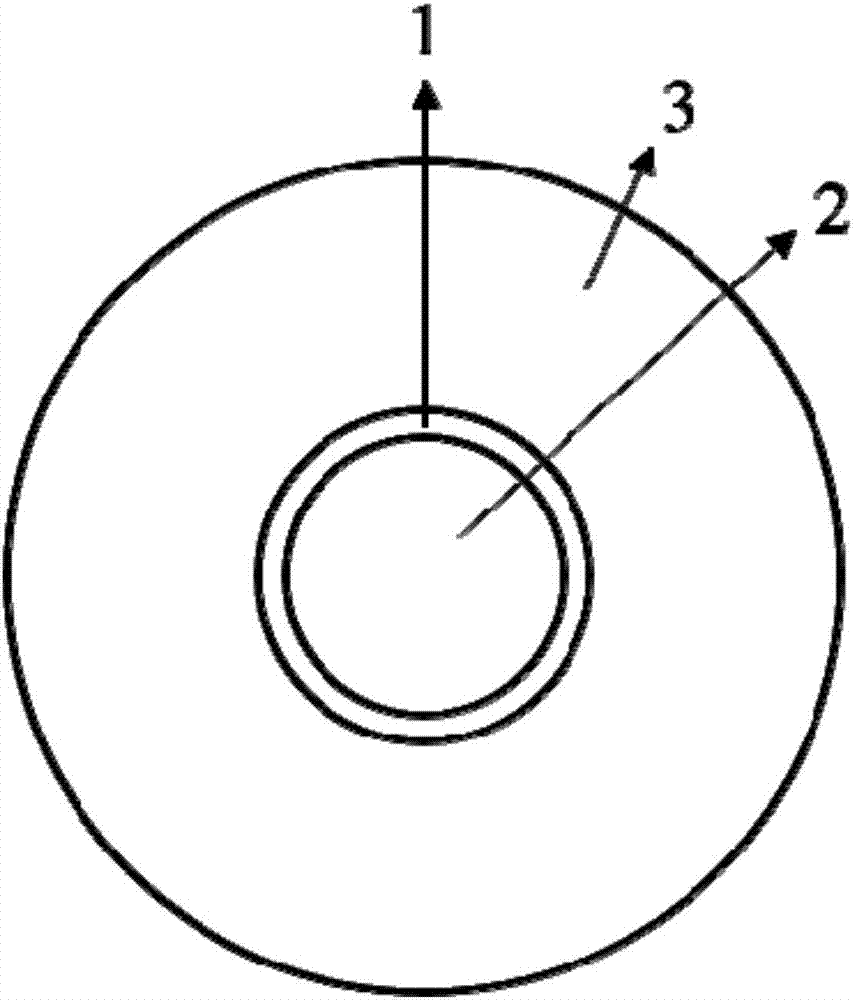
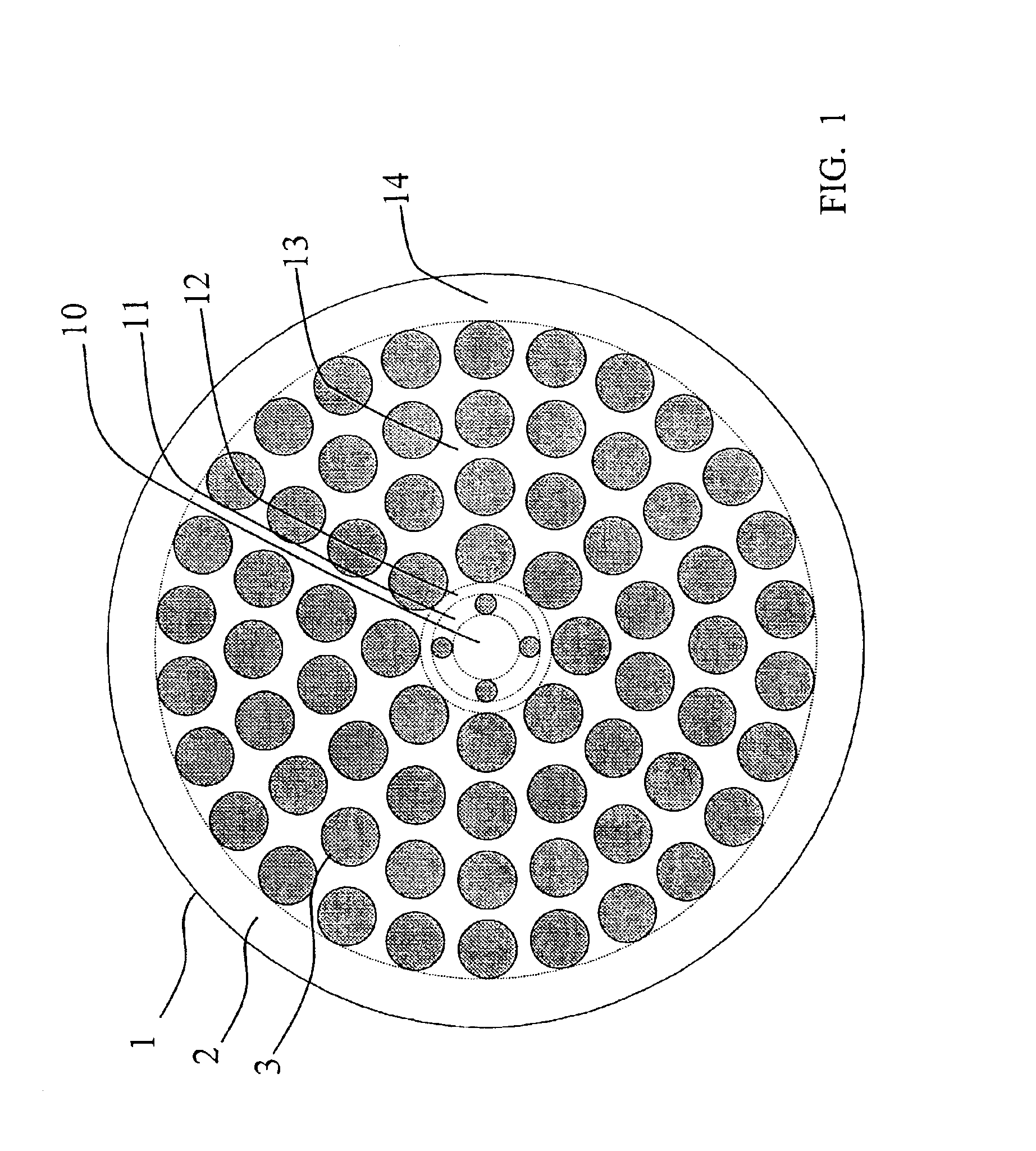
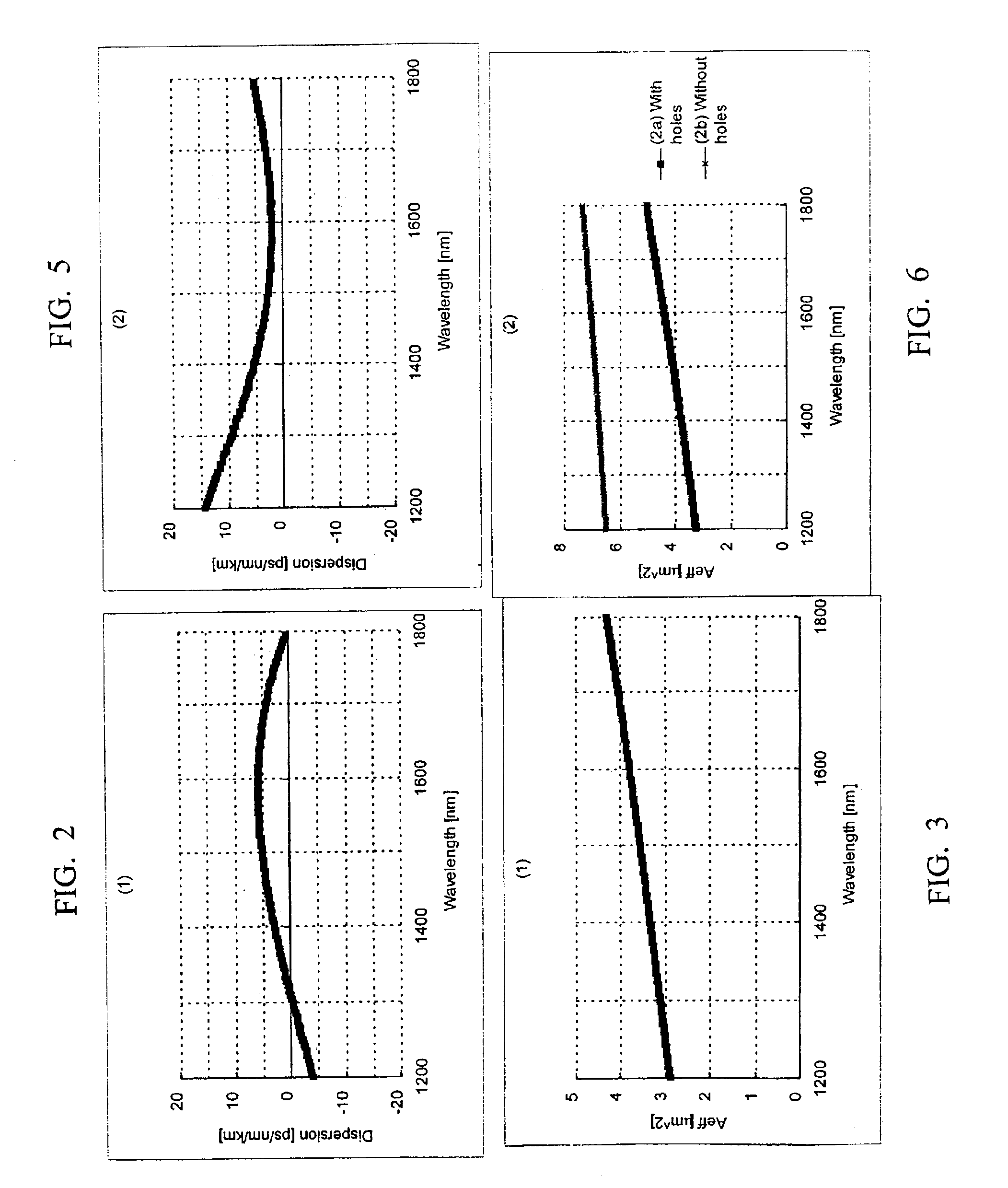
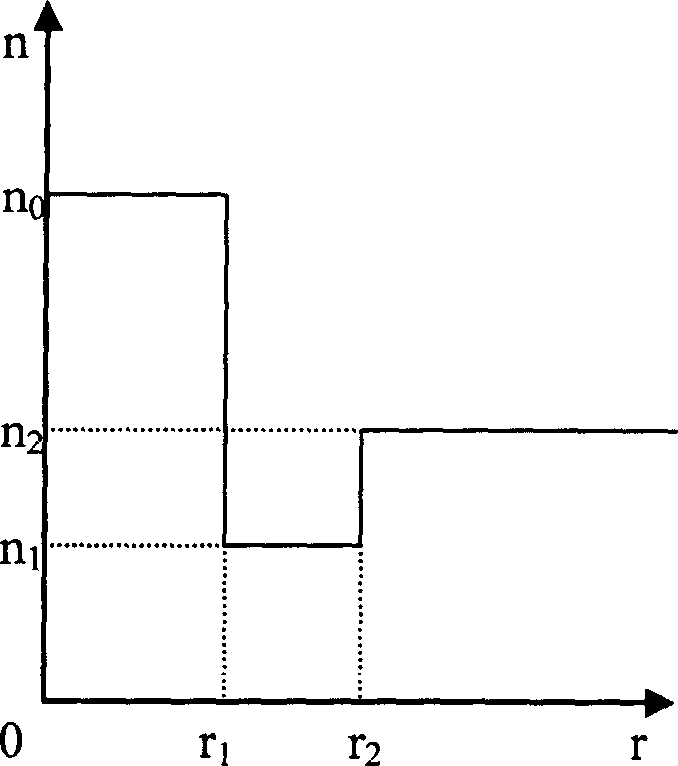
An optical fiber suitable for use in a single fiber or multifiber optical connector or array is structured with a core region and a cladding region surrounding the core region, and exhibits a bending loss of a fundamental mode of the fiber at a wavelength λ is lower than 0.1 dB / m at a diameter of 15 mm, a mode-field diameter of the fundamental mode at an end of the fiber at the wavelength λ is between 8.0 μm and 50 λ, and a bending loss of a first higher-order mode at the wavelength λ is higher than 1 dB / m at a diameter of 30 mm. The fiber may be multistructured, wherein the cladding region comprises a main medium and a plurality of sub medium regions therein to form a spatially uniform average refractive index.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Microstructured transmission optical fiber
InactiveUS7505660B2Improve bending abilityReduce decreaseGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Microstructured optical fiber for single-moded transmission of optical signals, the optical fiber including a core region and a cladding region, the cladding region including an annular hole-containing region that contains non-periodically disposed holes. The optical fiber provides single mode transmission and low bend loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
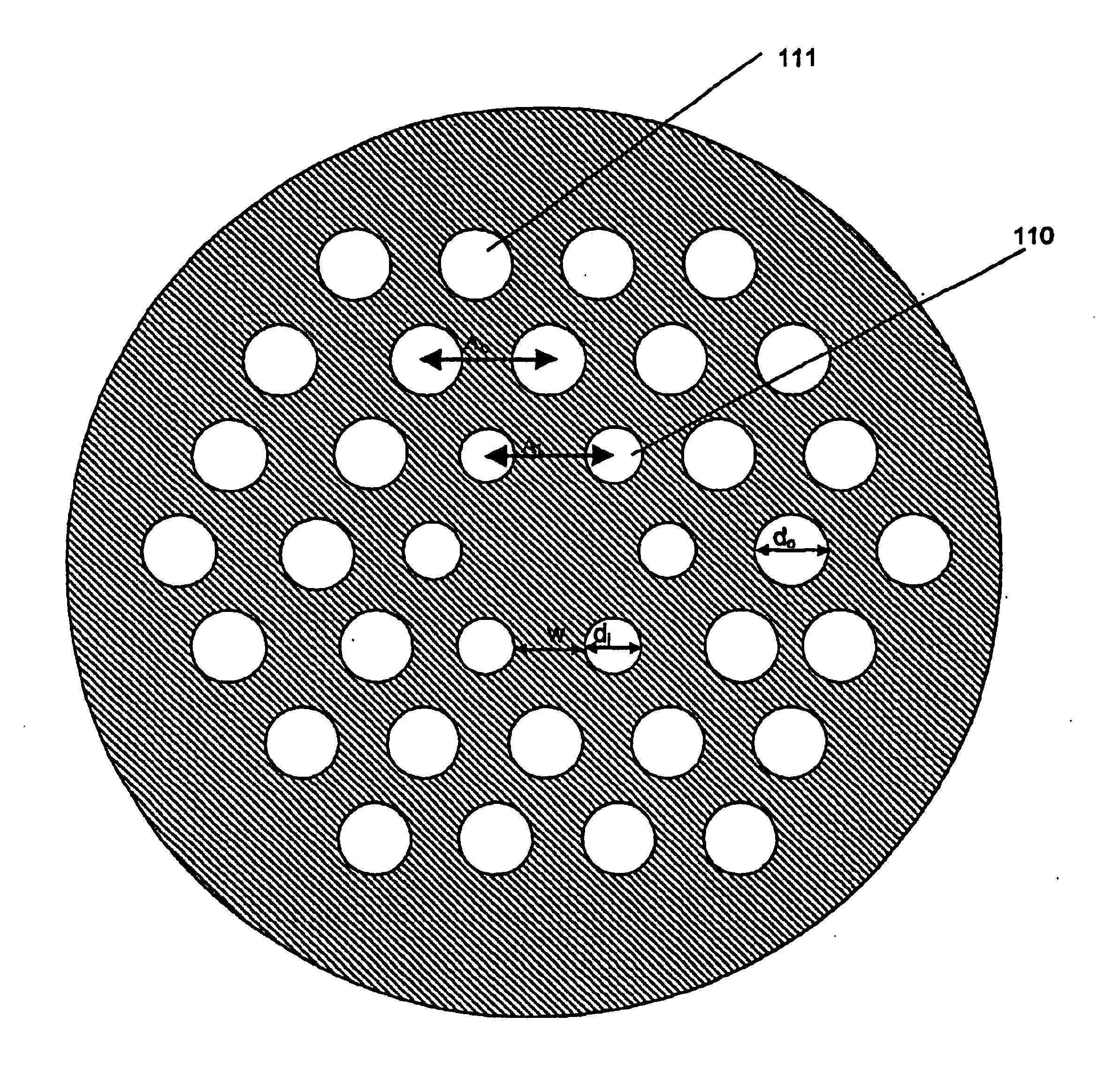
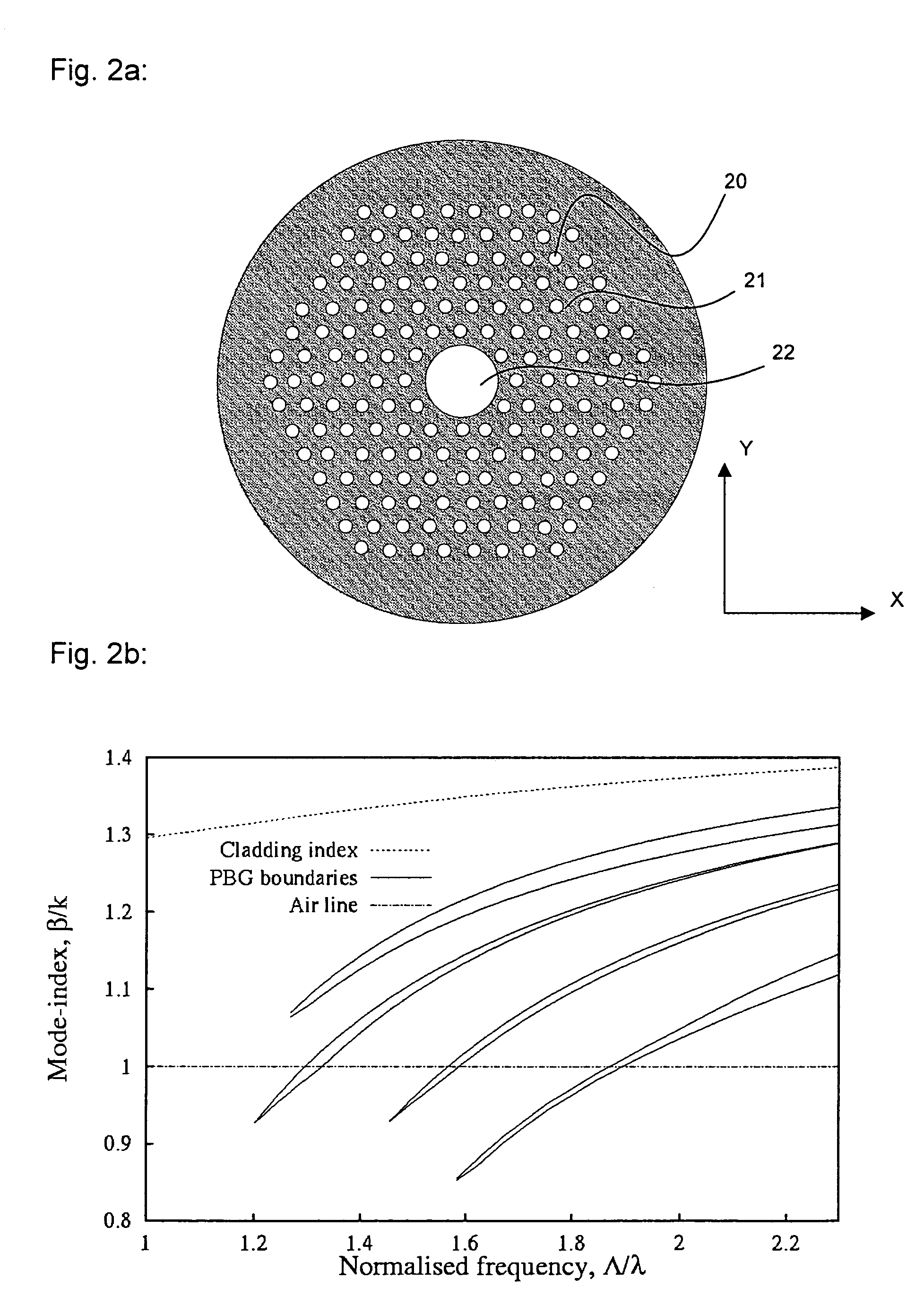
Optical fibres with special bending and dispersion properties
InactiveUS6856742B2Improve the cutoff effectGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationEngineeringEquilateral polygon
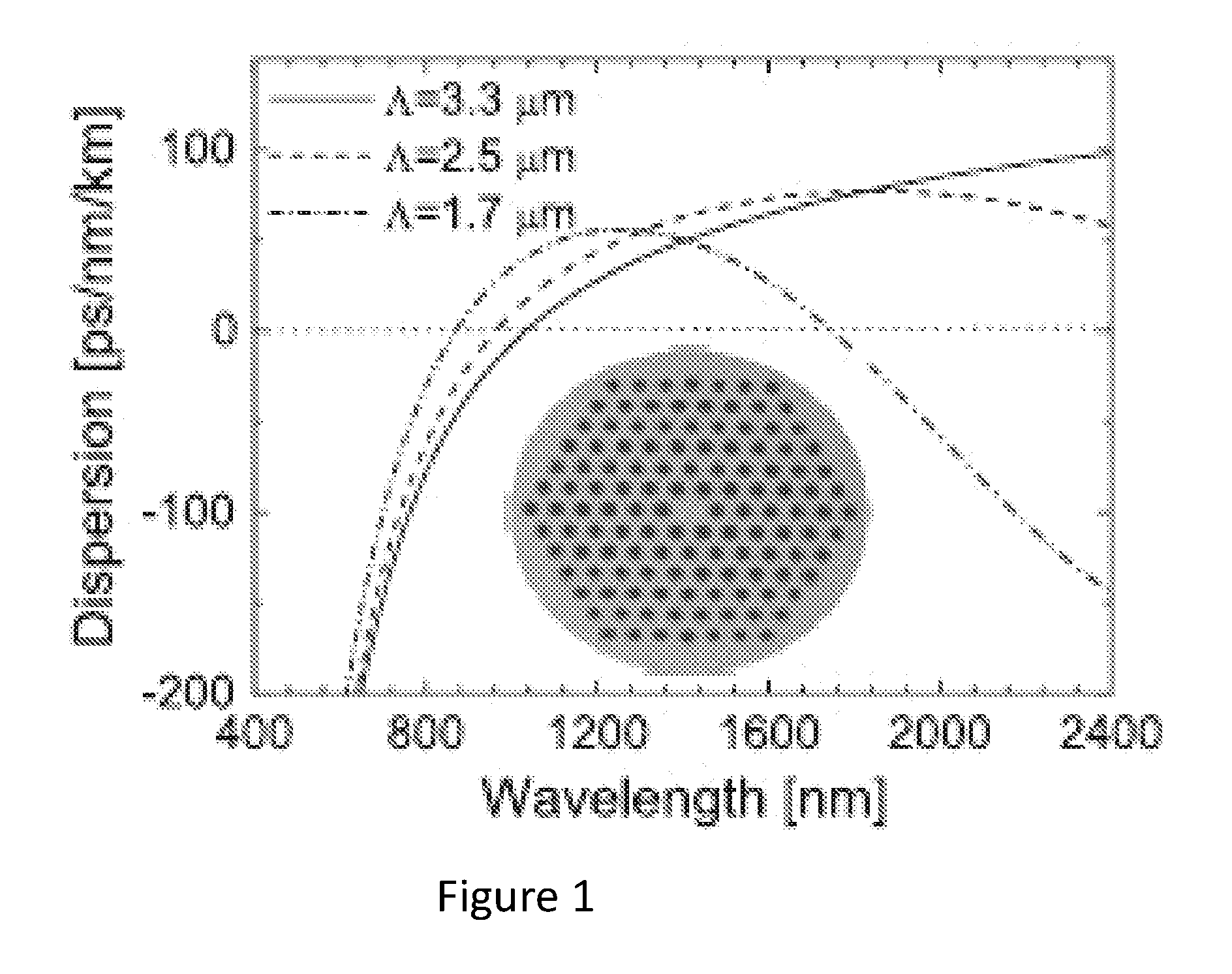
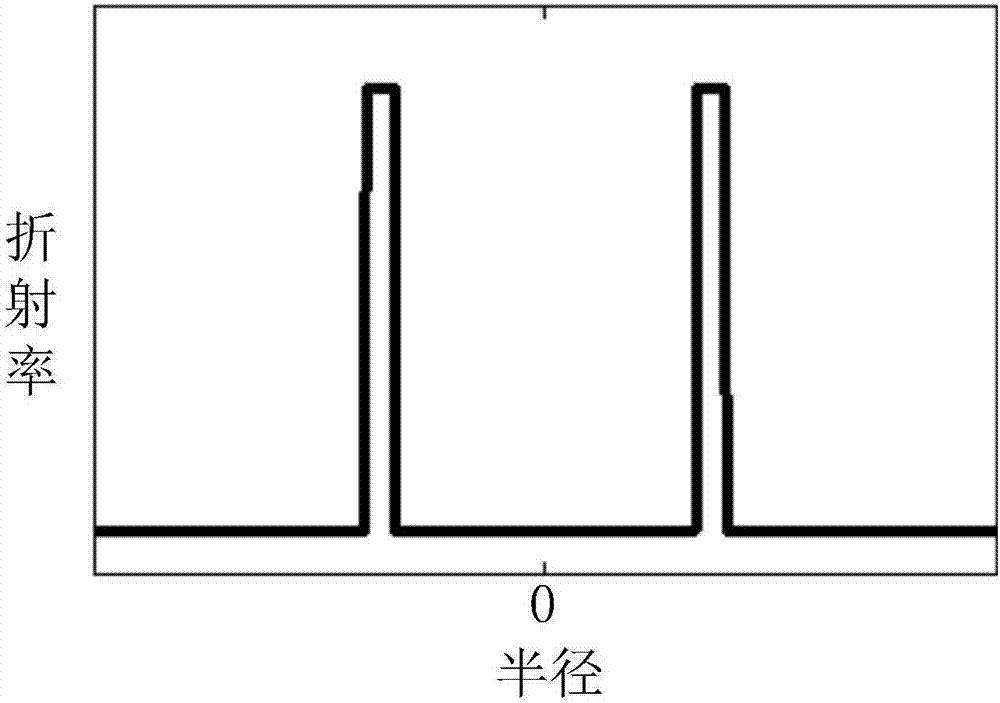
A microstructured optical fiber having a specially designed cladding to provide single mode waveguidance and low sensitivity to bending losses. In one aspect the optical fiber has an inner and an outer cladding each comprising elongated features. The inner cladding features have normalized dimensions in the range from 0.35 to 0.50 and the outer cladding features have normalized dimensions in the range from 0.5 to 0.9, where the normalization factor is a typical feature spacing. The fiber is further characterized by a feature spacing of the inner cladding larger than 2.0 micron. In a second aspect, the fiber has a special non-circular and non-equilateral-polygonial outer cross-sectional shape to mechanically ensure bending in predetermined directions that are favourable with respect to low bending losses. The present invention provides fibers, which are less sensitive to macro-bending losses than presently known single-mode fibers with similar sized mode areas, and provides robust, single-mode, large-mode area fibers for long-distance optical transmission and fibers with special dispersion properties.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Micro-structured optical fiber
InactiveUS6892018B2Reduce coupling lossGood dispersionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusPhotonic bandgapLight guide
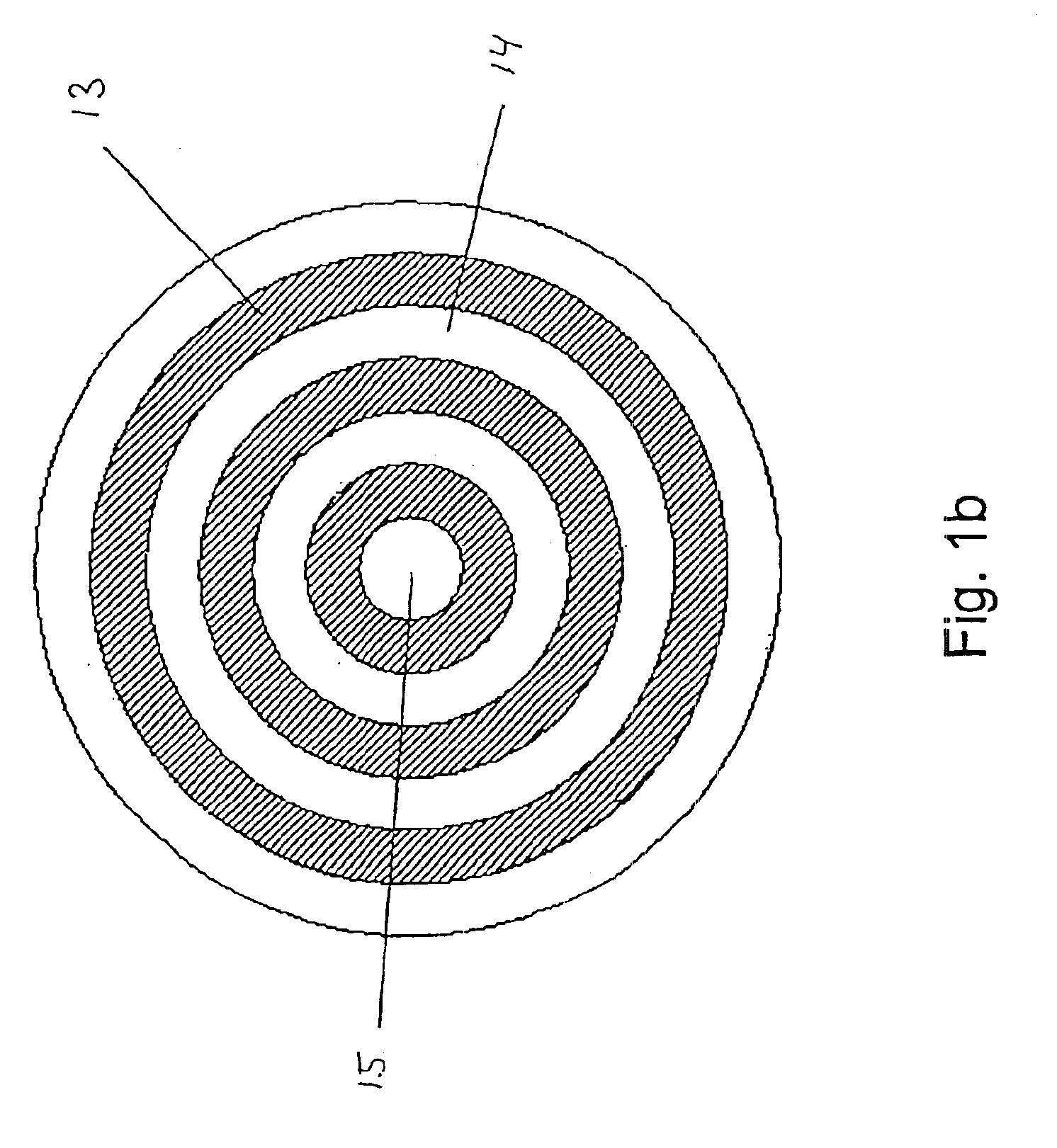
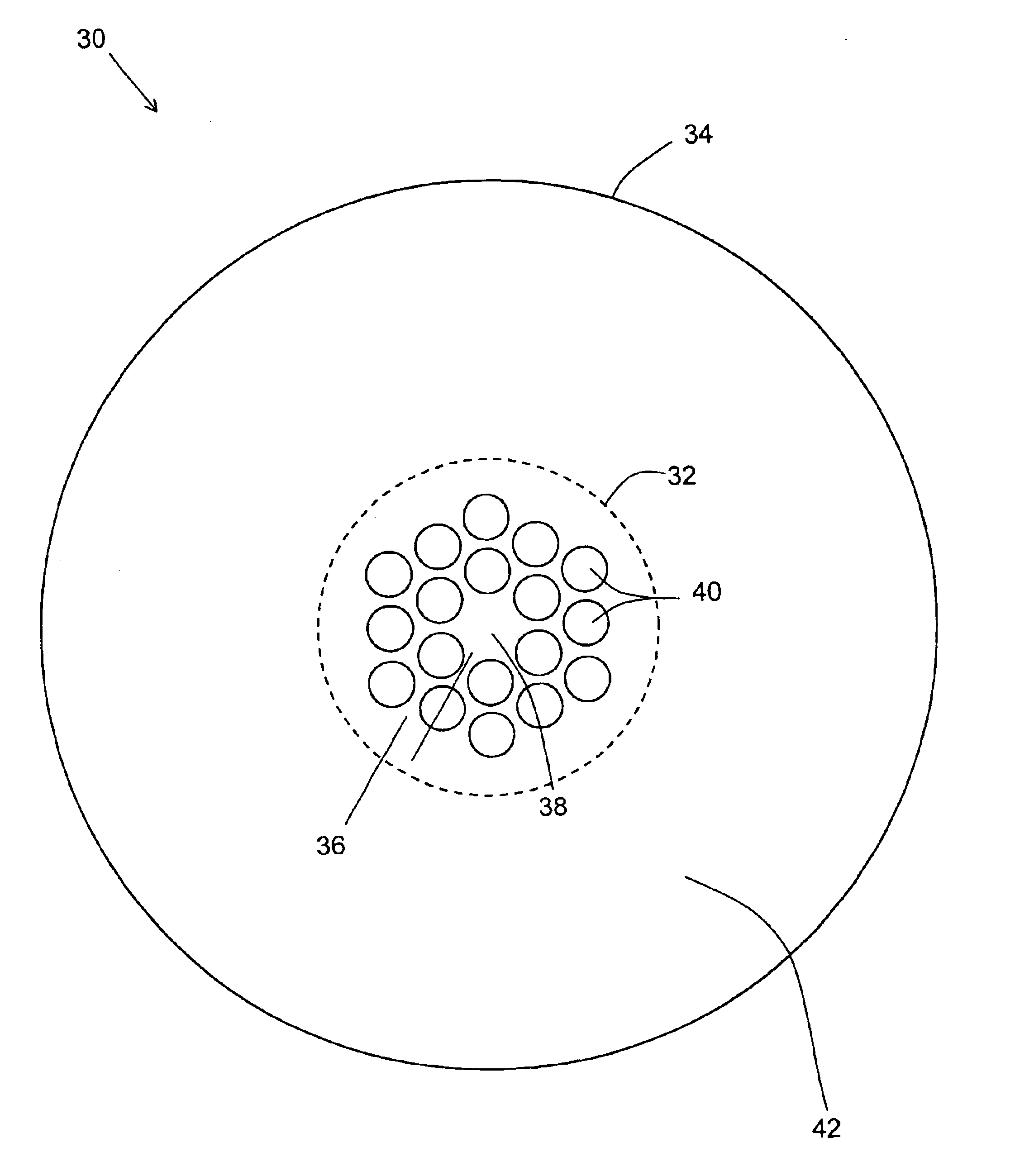
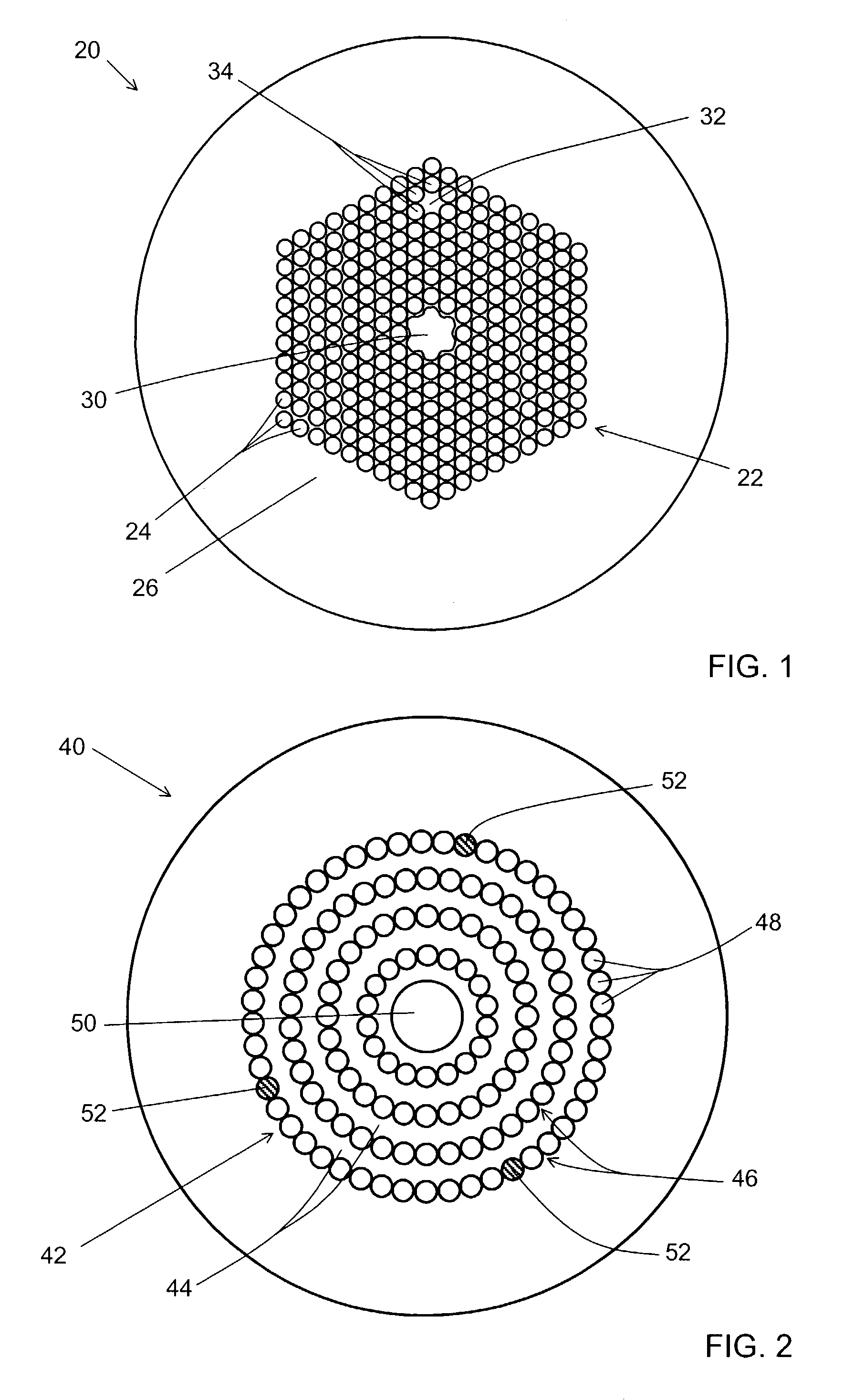
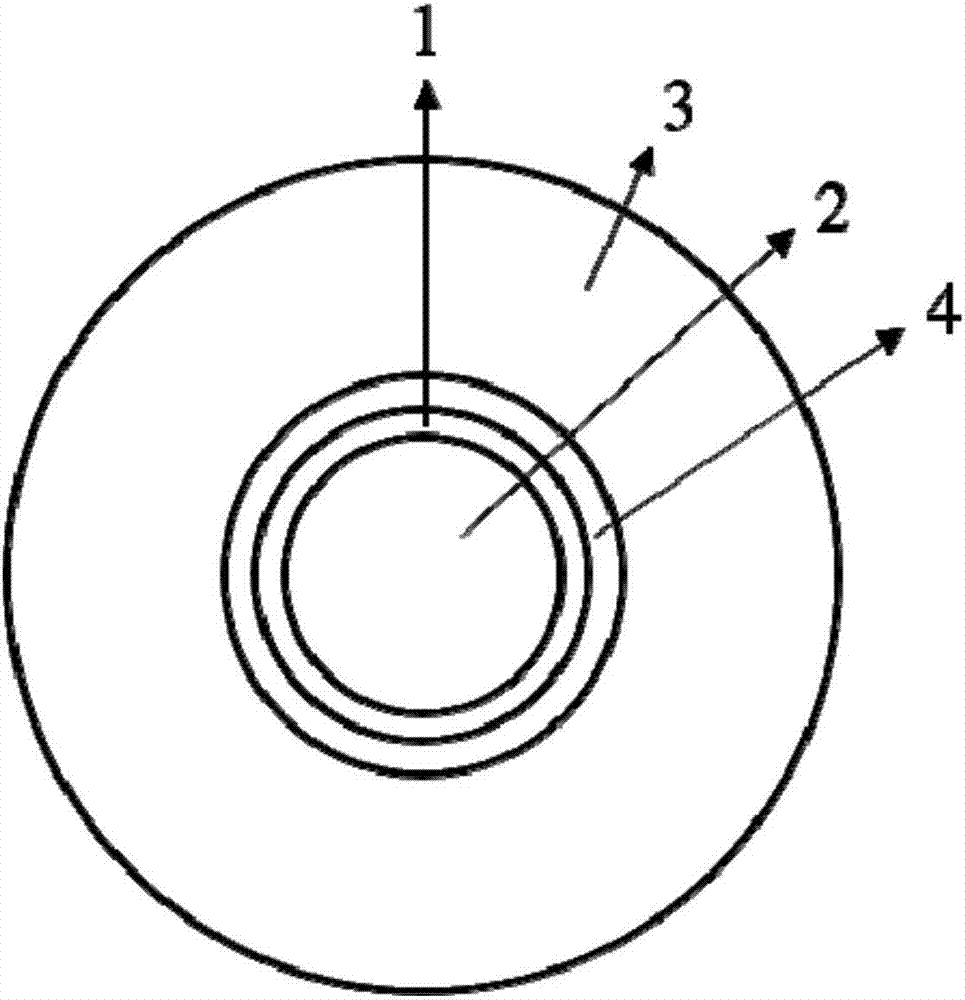
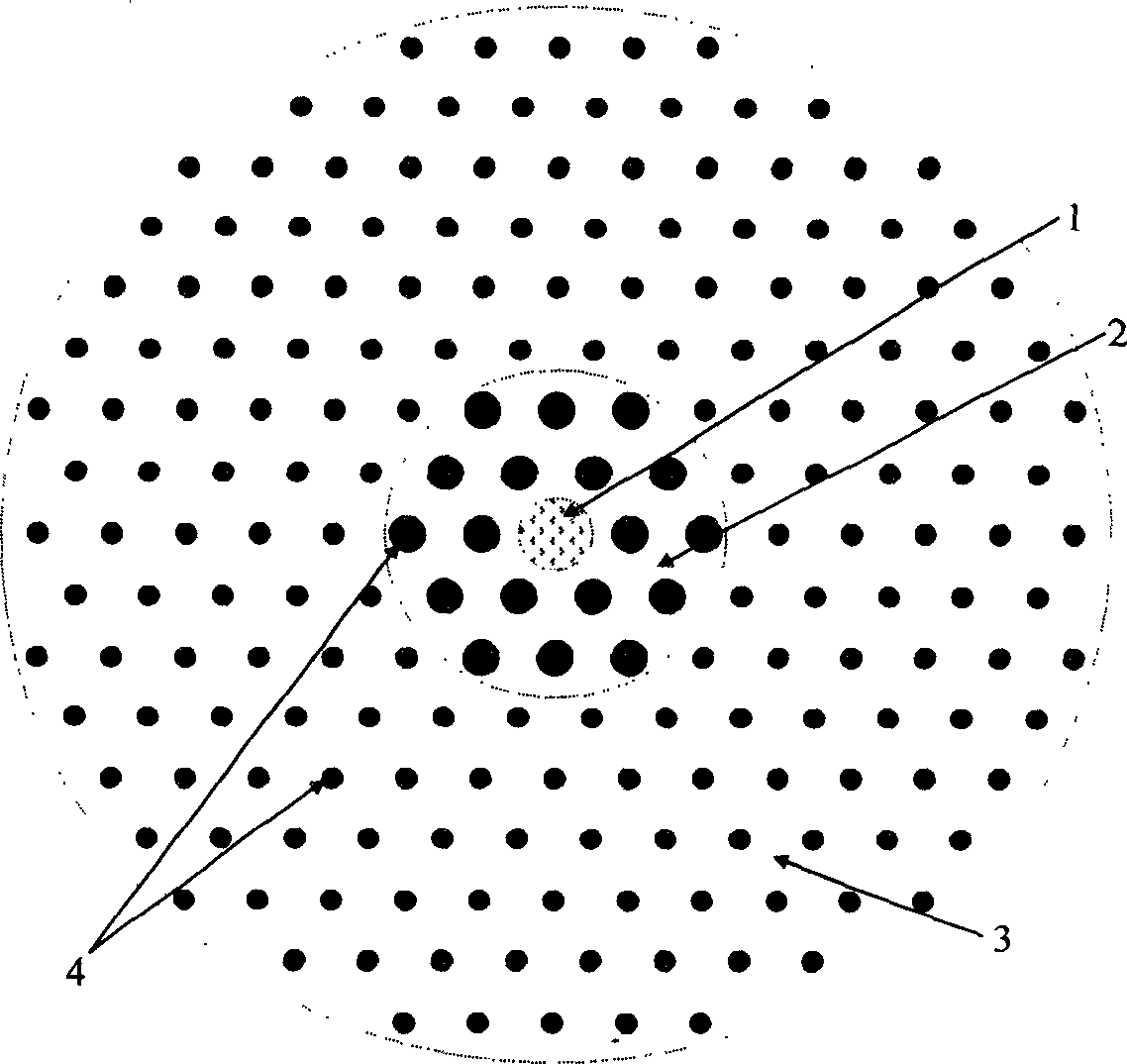
A microstructured fiber having a cladding comprising a number of elongated features that are arranged to provide concentric circular or polygonial regions surrounding the fiber core. The cladding comprises a plurality of concentric cladding regions, at least some of which comprising cladding features. Cladding regions comprising cladding features of a relatively low index type are arranged alternatingly with cladding regions of a relatively high index type. The cladding features are arranged in a non-periodic manner when viewed in a cross section of the fiber. The cladding enables waveguidance by photonic bandgap effects in the fiber core. An optical fiber of this type may be used for light guidance in hollow core fibers for high power transmission. The special cladding structure may also provide strong positive or negative dispersion of light guided through the fiber-making the fiber useful for telecommunication applications.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
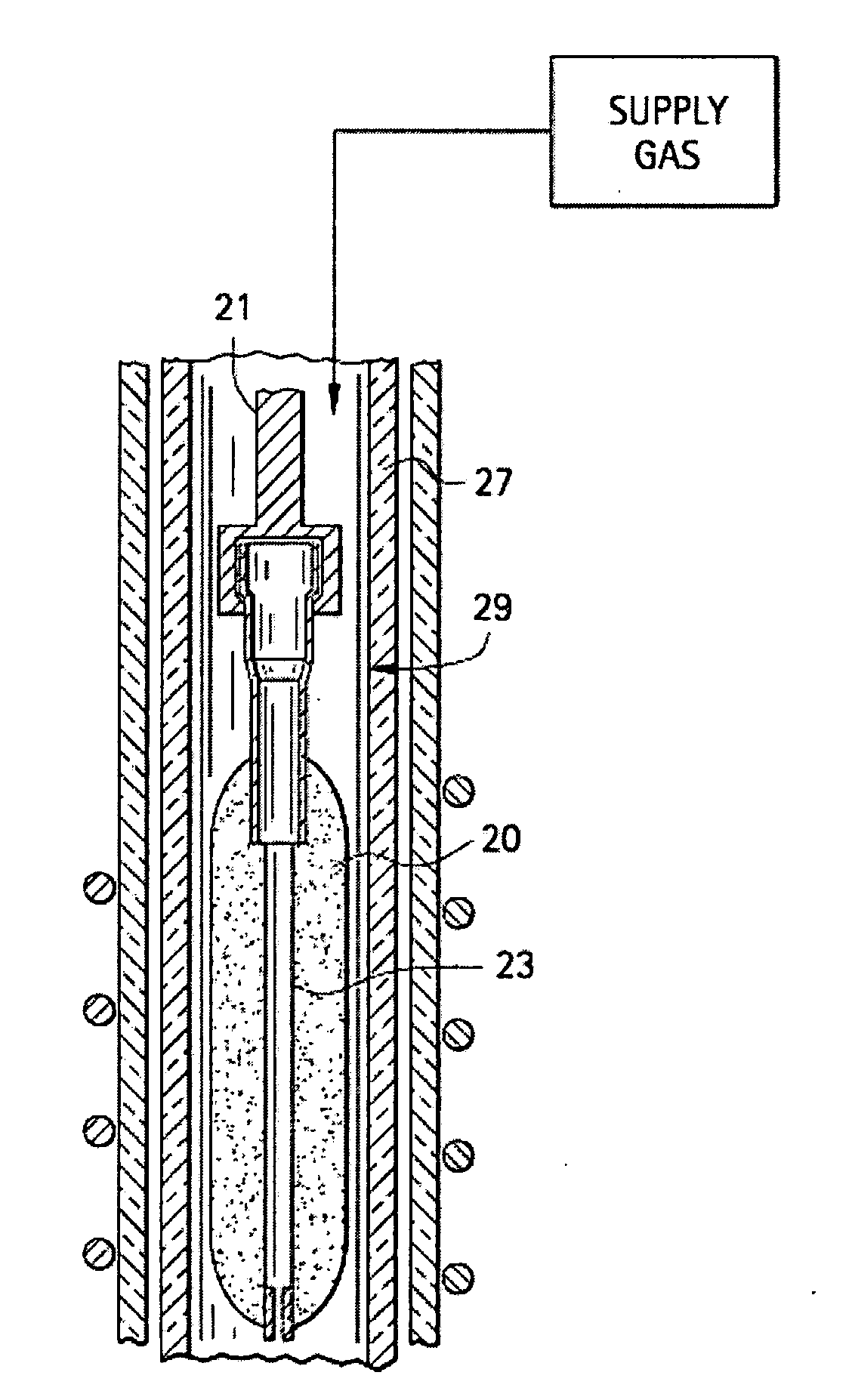
Systems and methods for collapsing air lines in nanostructured optical fibers
InactiveUS20090199597A1Heating evenlyGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesLine tubingMid infrared
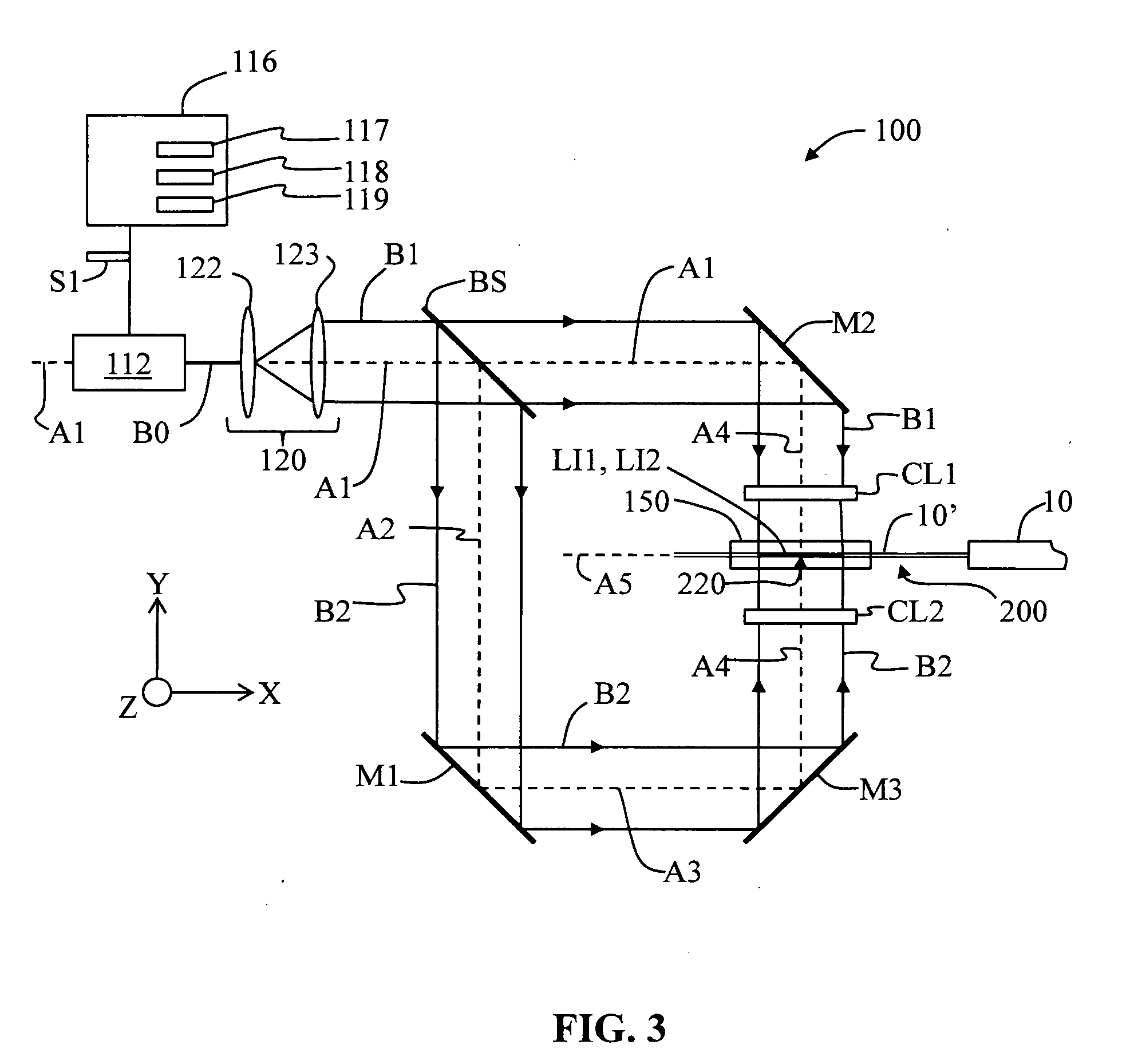
Systems and methods of collapsing the air lines in the air line-containing region of a nanostructure optical fiber are disclosed. One method includes initiating irradiation of a portion of the nanostructure optical fiber from essentially opposite directions with at least first and second laser beams having substantially equal power and essentially the same mid-infrared wavelength. The method includes continuing the irradiation for an irradiation time t1 so as to bring the optical fiber portion to a softening temperature TS at which the air lines in the optical fiber portion collapse into the adjacent cladding. Exemplary optical systems for carrying out the air- line-collapsing methods of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Microstructured optical fibers and preforms and methods for fabricating microstructured optical fibers
InactiveUS6847771B2Good optical performanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical fiber cableMaterials science
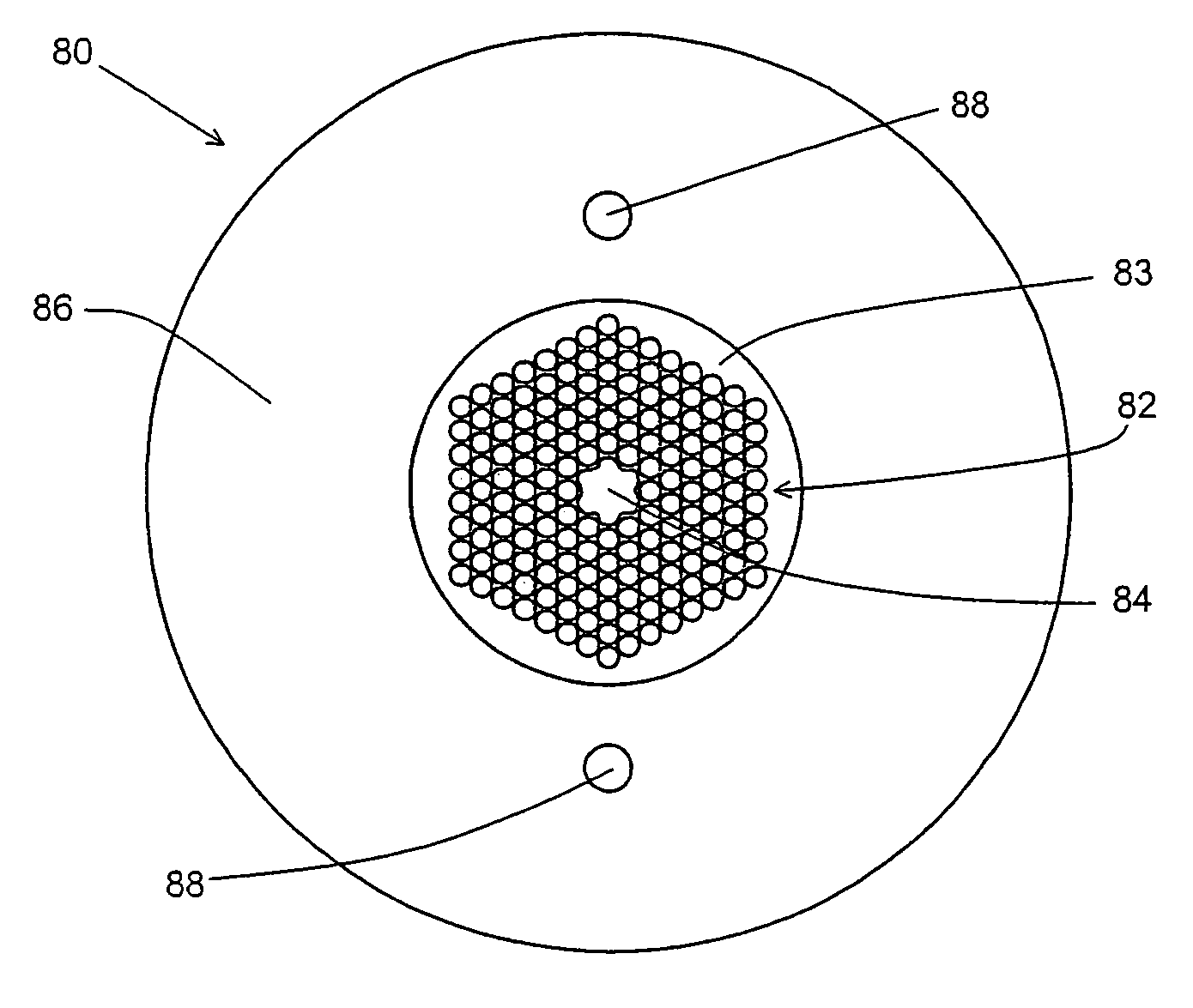
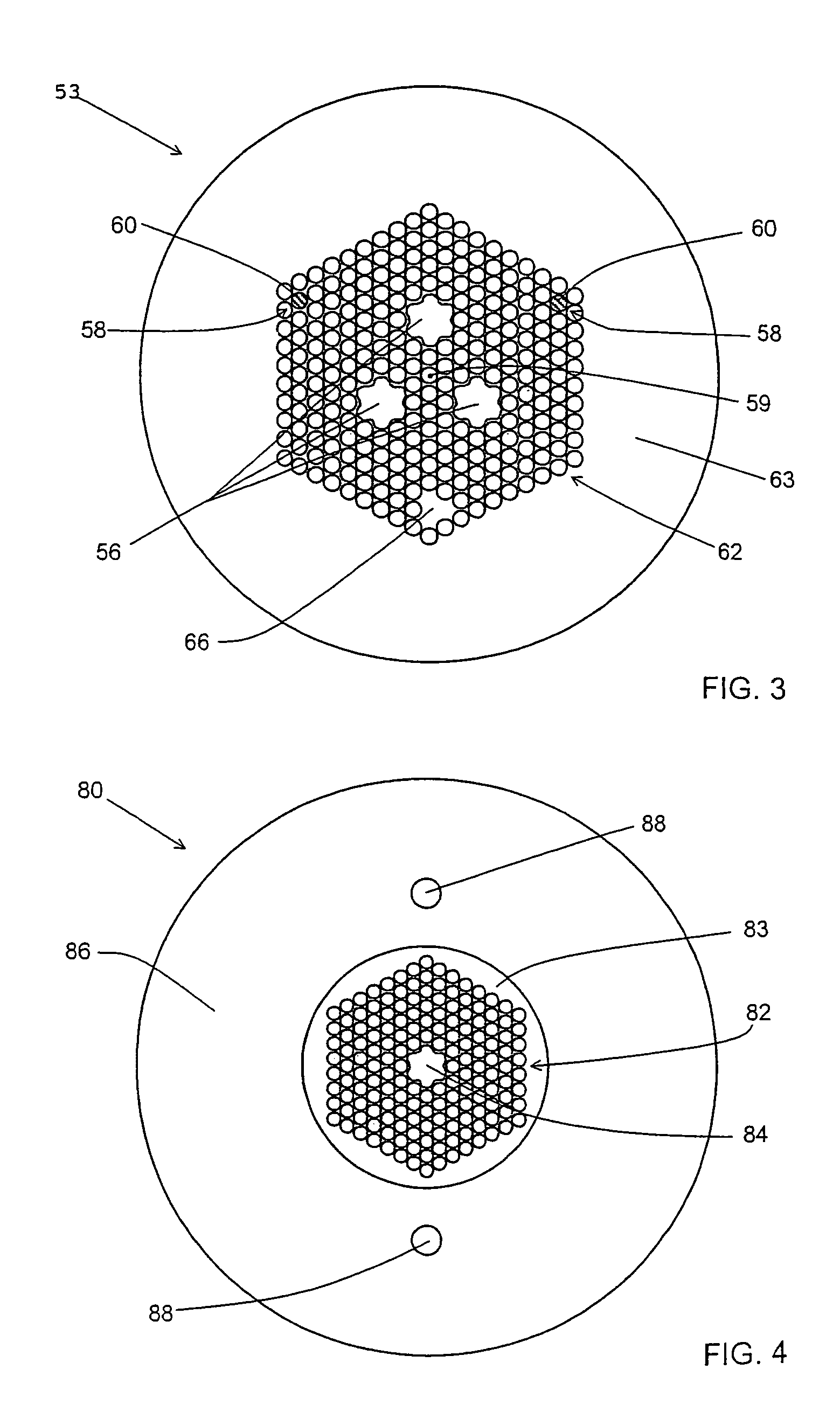
A microstructured optical fiber is described. The microstructured optical fiber comprises an inner region and an outer region. The inner region includes an inner material and a plurality of holes formed in the inner material. The outer region surrounds the inner region, and includes an outer material. The softening point temperature of the inner material is greater than the softening point temperature of the outer material by at least about 50° C. Microstructured optical fiber preforms and methods for making the microstructured optical fibers are also described. The microstructured optical fiber may be made to have substantially undistorted holes in the inner region.
Owner:CORNING INC
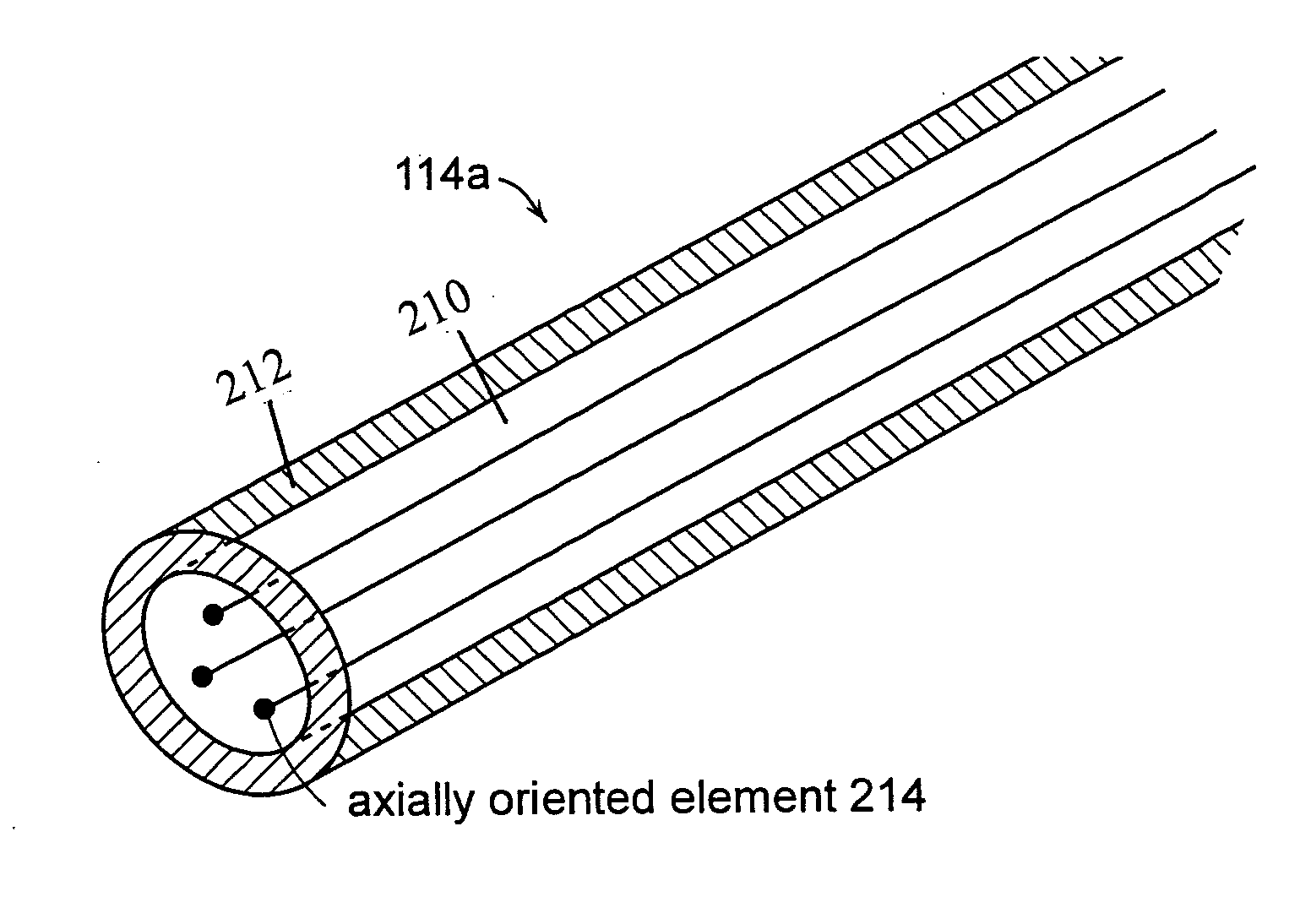
Large mode-area microstructure optical fiber
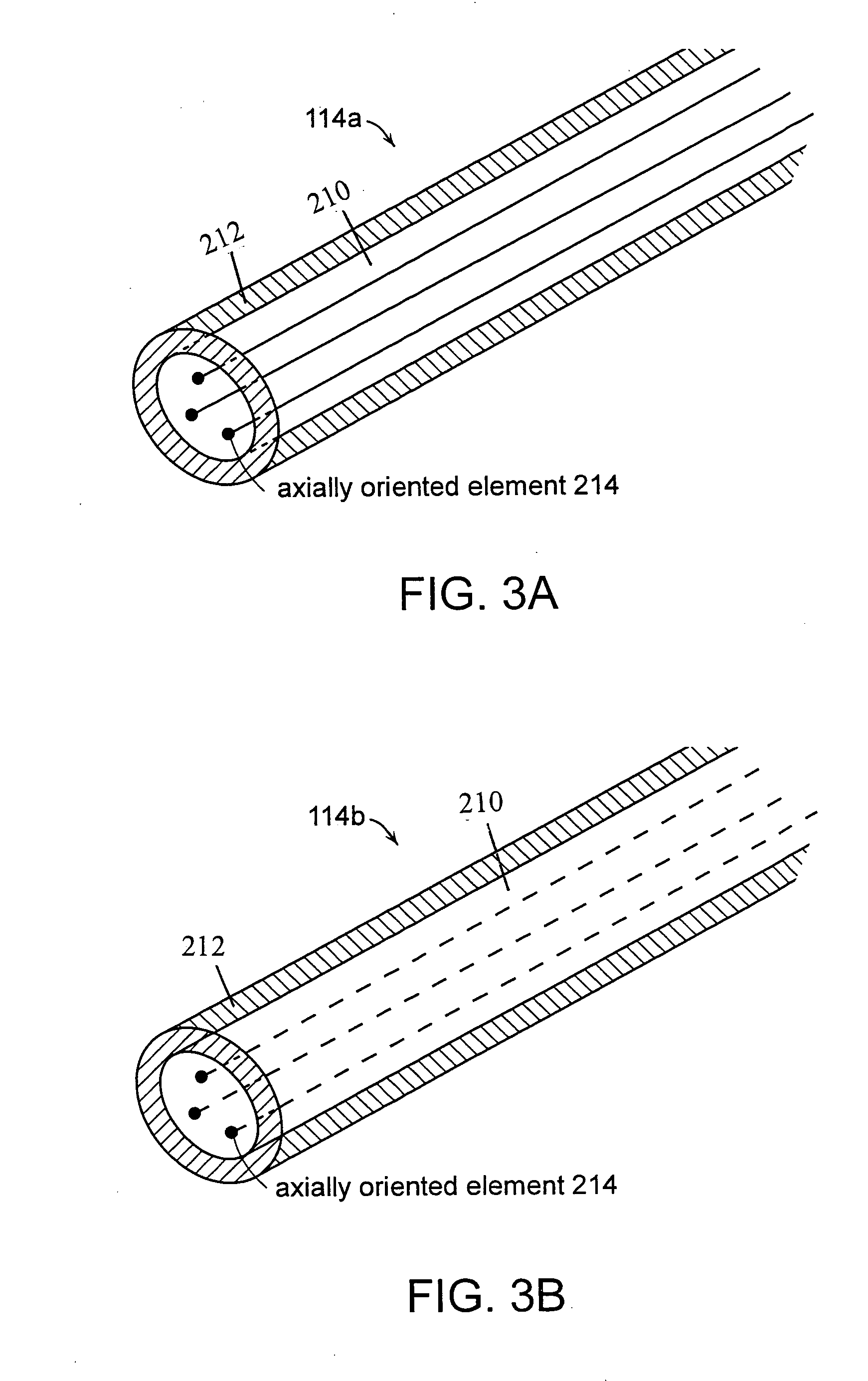
InactiveUS20060204190A1Alter waveguide mode propertyImprove discriminationCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexLight beam
A large mode-area microstructured optical fiber includes a core, at least one axially oriented element disposed in the core, and a cladding about the core. The axially oriented element has a refractive index less than a refractive index of the core. The axially oriented element(s) defines sectional regions in the core. The sectional regions defined by the axially oriented element(s) can discriminate between symmetric and antisymmeteric modes of an optical beam that propagates through the optical fiber.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
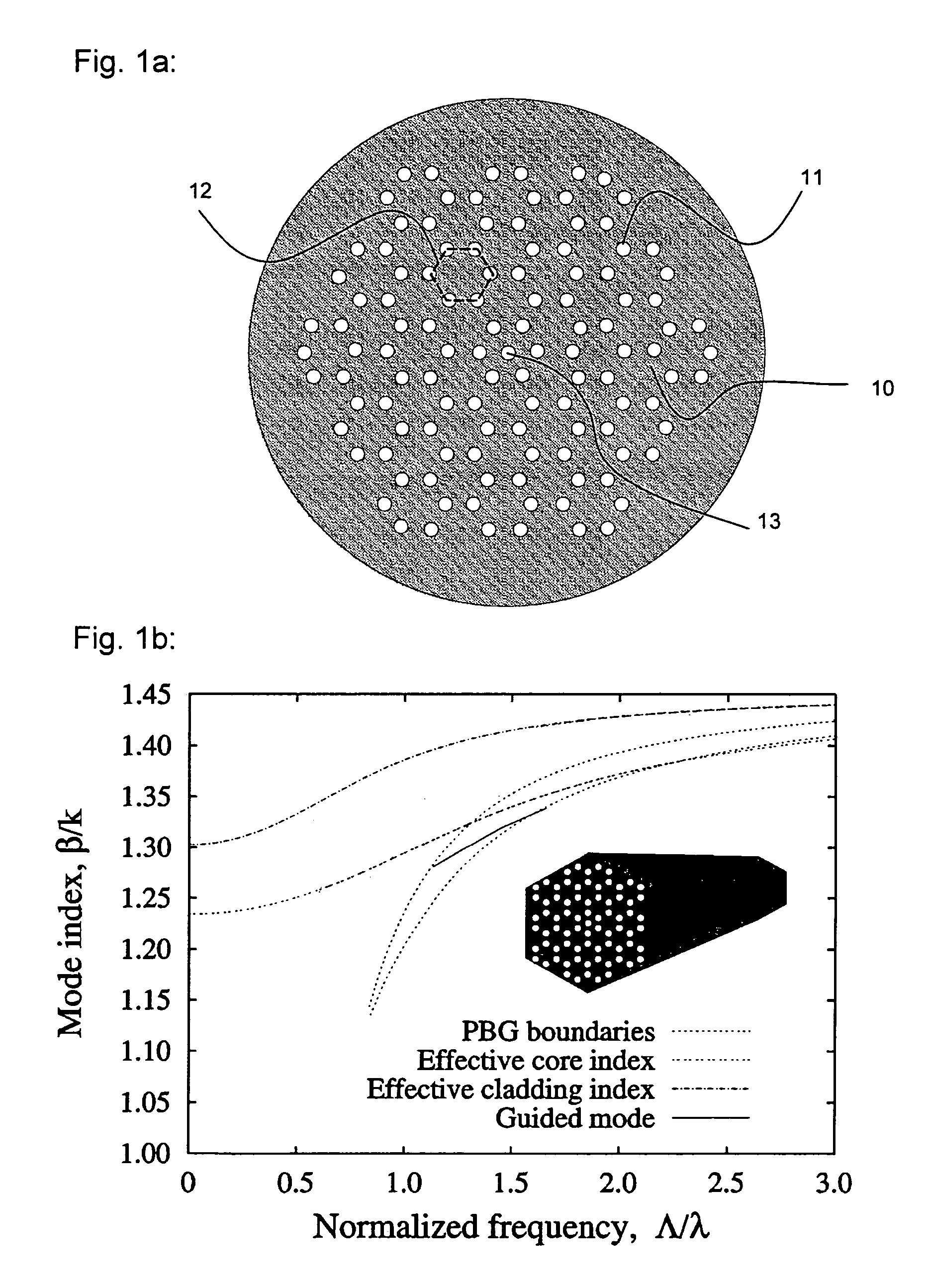
Photonic bandgap fibre, and use thereof
InactiveUS7349611B2Increase the number ofIncrease flexibilityGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingPhotonic bandgapEffective refractive index
A mircrostructured optical fiber that guides light in a core region, where the fiber has a cladding region that includes a background material and a number of cladding features or elements that are elongated in the longitudinal direction of the fiber and have a higher refractive index than the cladding background material. The core region has a lower effective refractive index than the cladding, and the fiber may guide light in the core by photonic bandgap effects.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Index-matching gel for nanostructure optical fibers and mechanical splice assembly and connector using same
A polymer based index-matching gel for use with nanostructure optical fibers is disclosed. The index-matching gel has a viscosity η at 25° C. of 3 Pa-s≦η≦100 Pa-s, which prevents the index-matching gel from wicking into the voids and down the nanostructure optical fiber to a depth where the fiber performance and / or device performance is compromised. The gel is suitable for use when mechanically splicing optical fibers when at least one of the optical fibers is a nanostructure optical fiber. The gel is also suitable for use in fiber optic connectors wherein at least one of the optical fibers constituting the connection is a nanostructure optical fiber.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Microstructured optical fibers for gas sensing systems
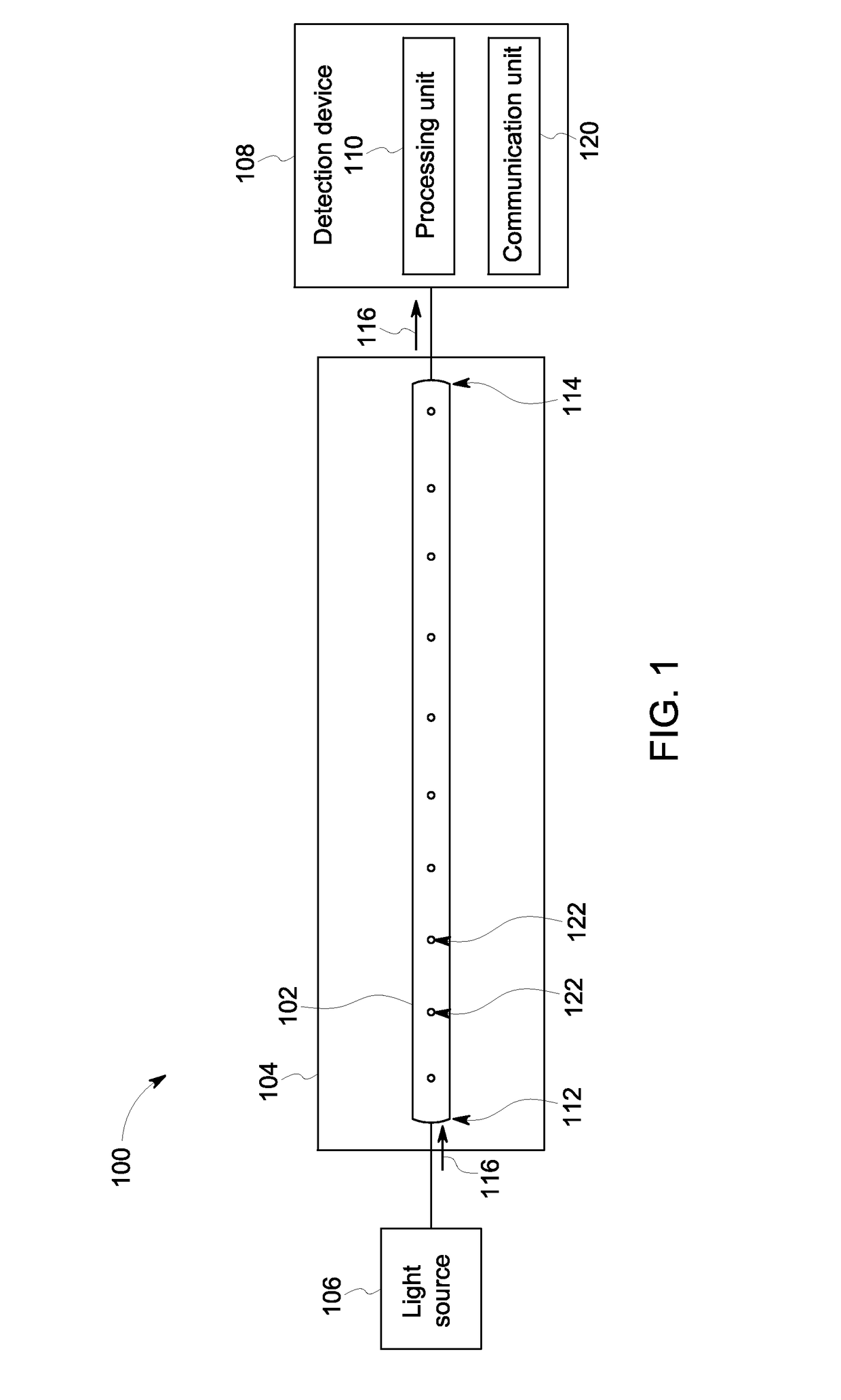
Microstructured optical fiber (MOF) includes a cladding extending a length between first and second ends. The cladding includes an inner porous microstructure that at least partially surrounds a hollow core. A perimeter contour of the hollow core has a non-uniform radial distance from a center axis of the cladding such that first segments of the cladding along the perimeter contour have a shorter radial distance from the center axis relative to second segments of the cladding along the perimeter contour. The cladding receives and propagates light energy through the hollow core, and the inner porous microstructure substantially confines the light energy within the hollow core. The cladding defines at least one port hole that extends radially from an exterior surface of the cladding to the hollow core. Each port hole penetrates the perimeter contour of the hollow core through one of the second segments of the cladding.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES OILFIELD OPERATIONS LLC
Multiple core microstructured optical fibers and methods using said fibers
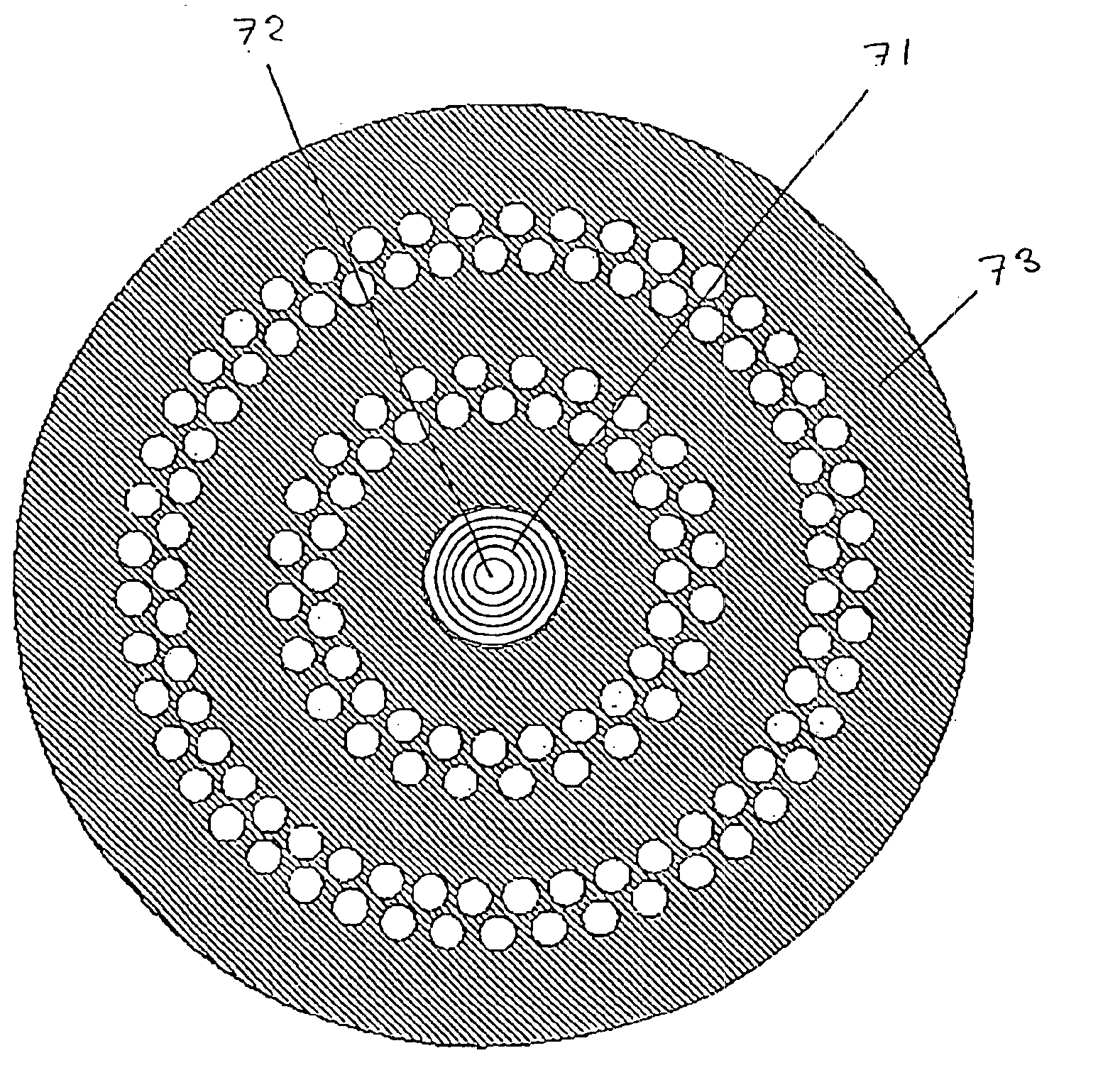
The present invention relates to a microstructured optical fiber including a photonic band gap-guided core; and at least one index-guided core. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a microstructured optical fiber including a set of main cores; a microstructured region surrounding the set of main cores; and at least alignment core, the alignment cores having substantially different optical propagation properties than the main cores. The present invention also includes methods for coupling, monitoring, and locating discontinuities in the fibers of the present invention.
Owner:CORNING INC
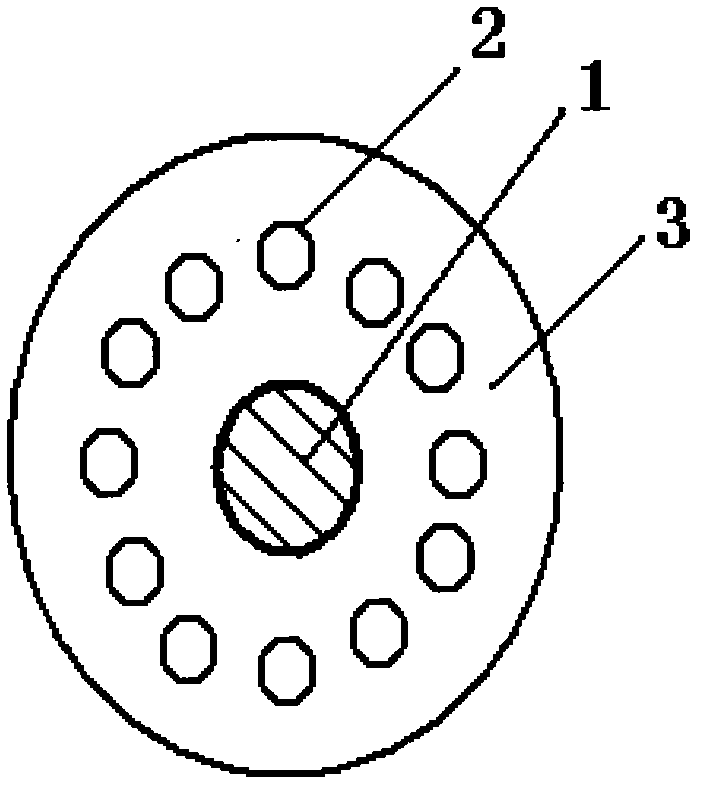
Bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber and production method thereof
ActiveCN102354019AOvercoming Polarization Mode Dispersion Characteristic ProblemOvercomes ineffective bending lossCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringTower
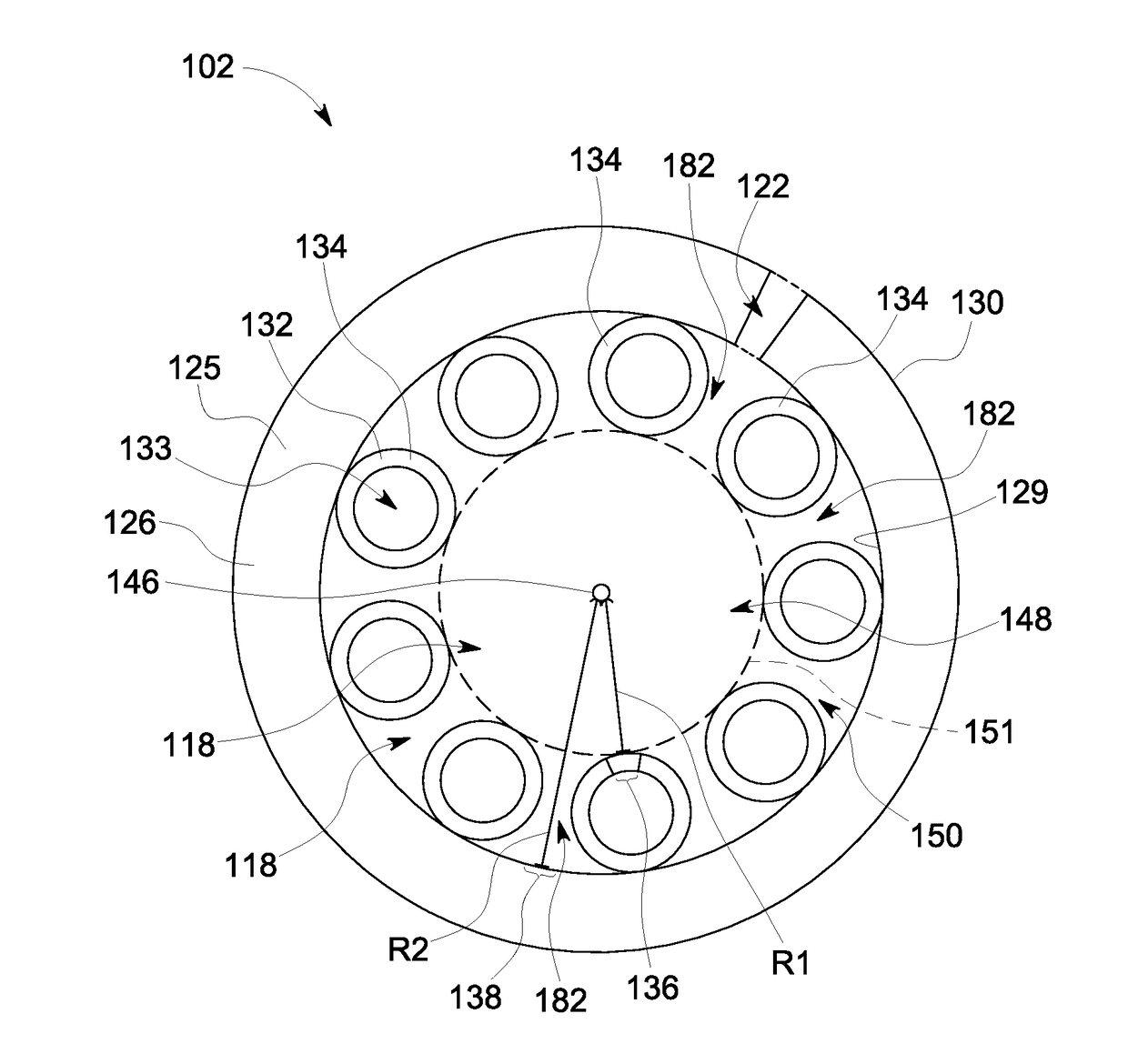
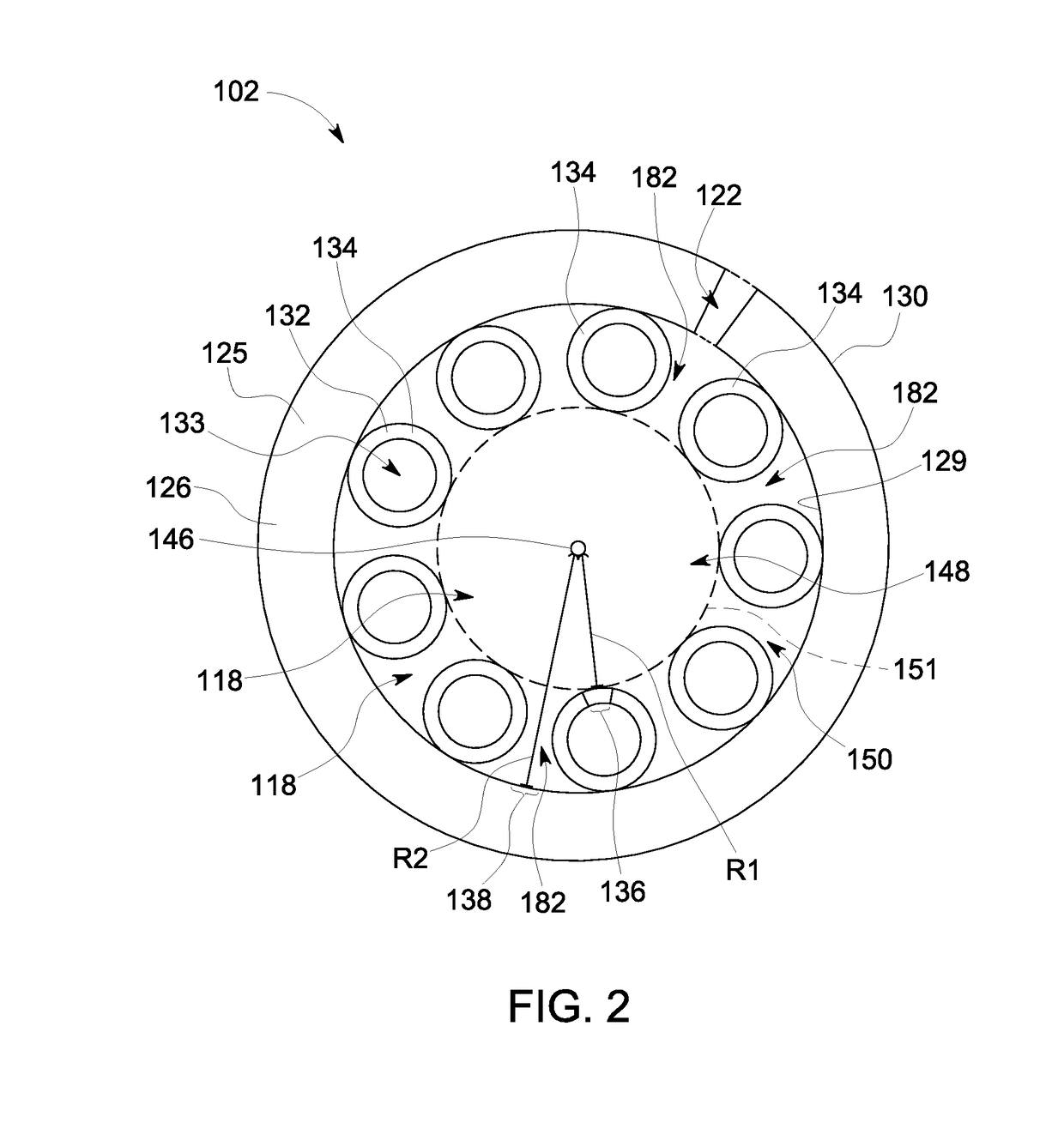
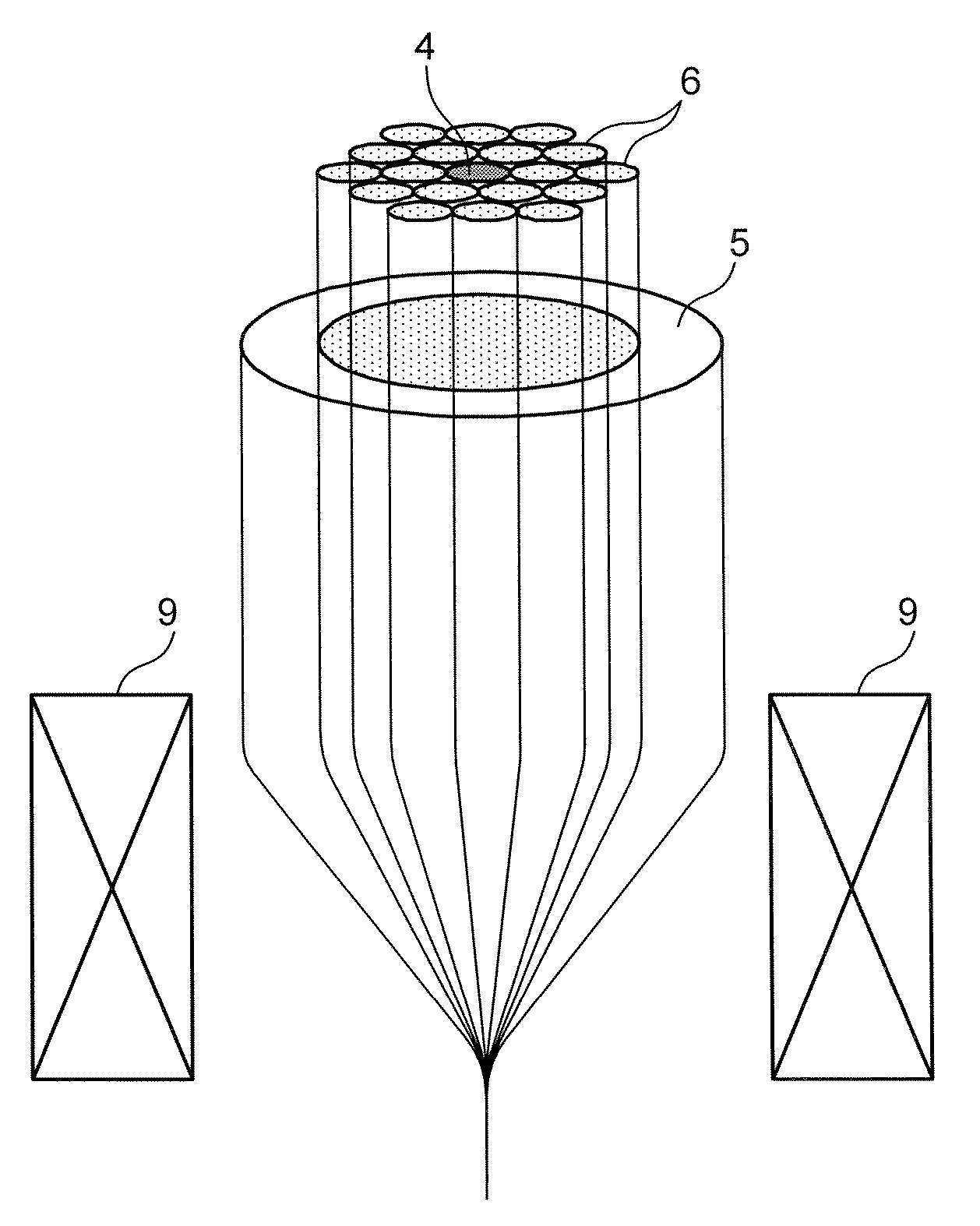
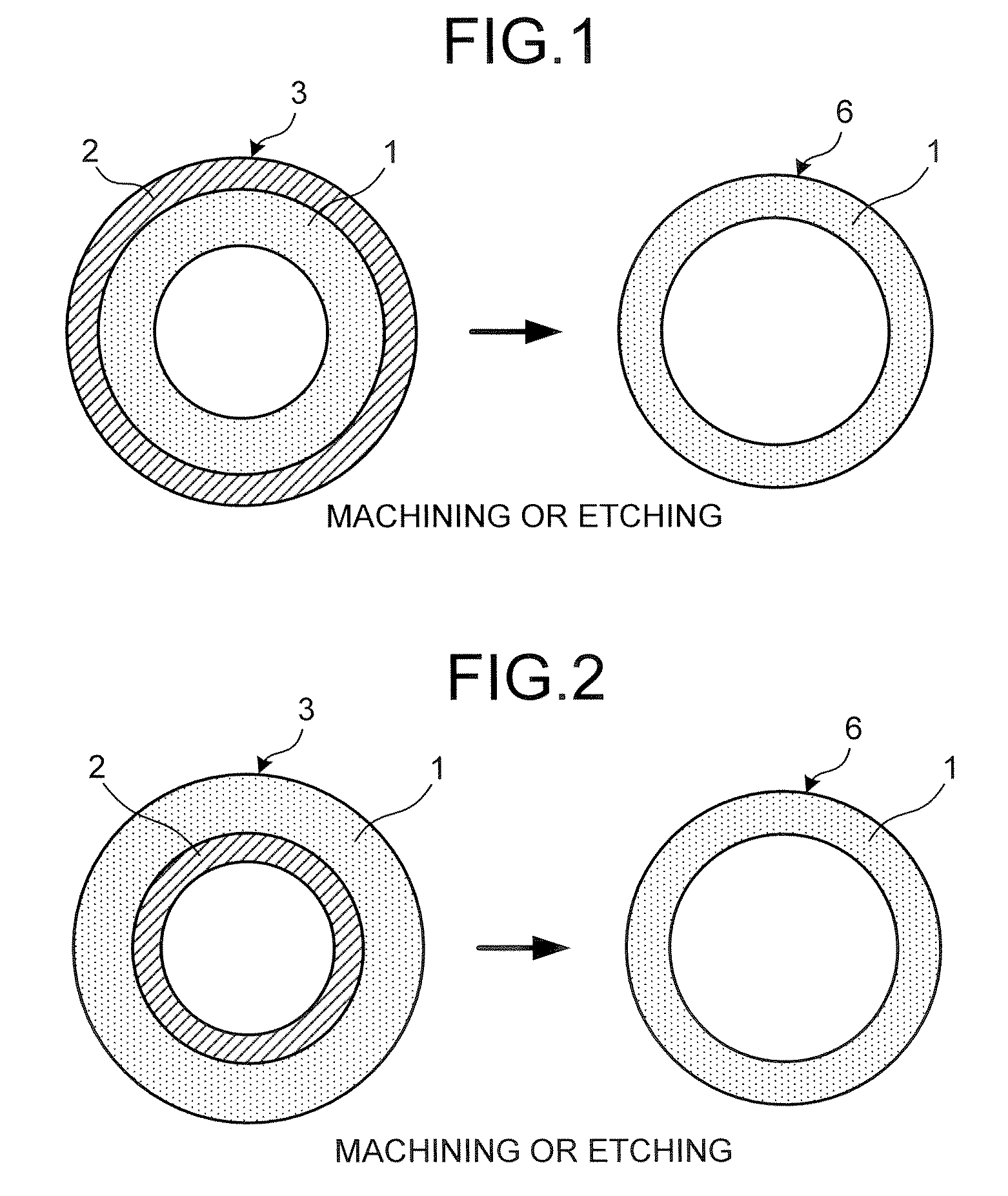
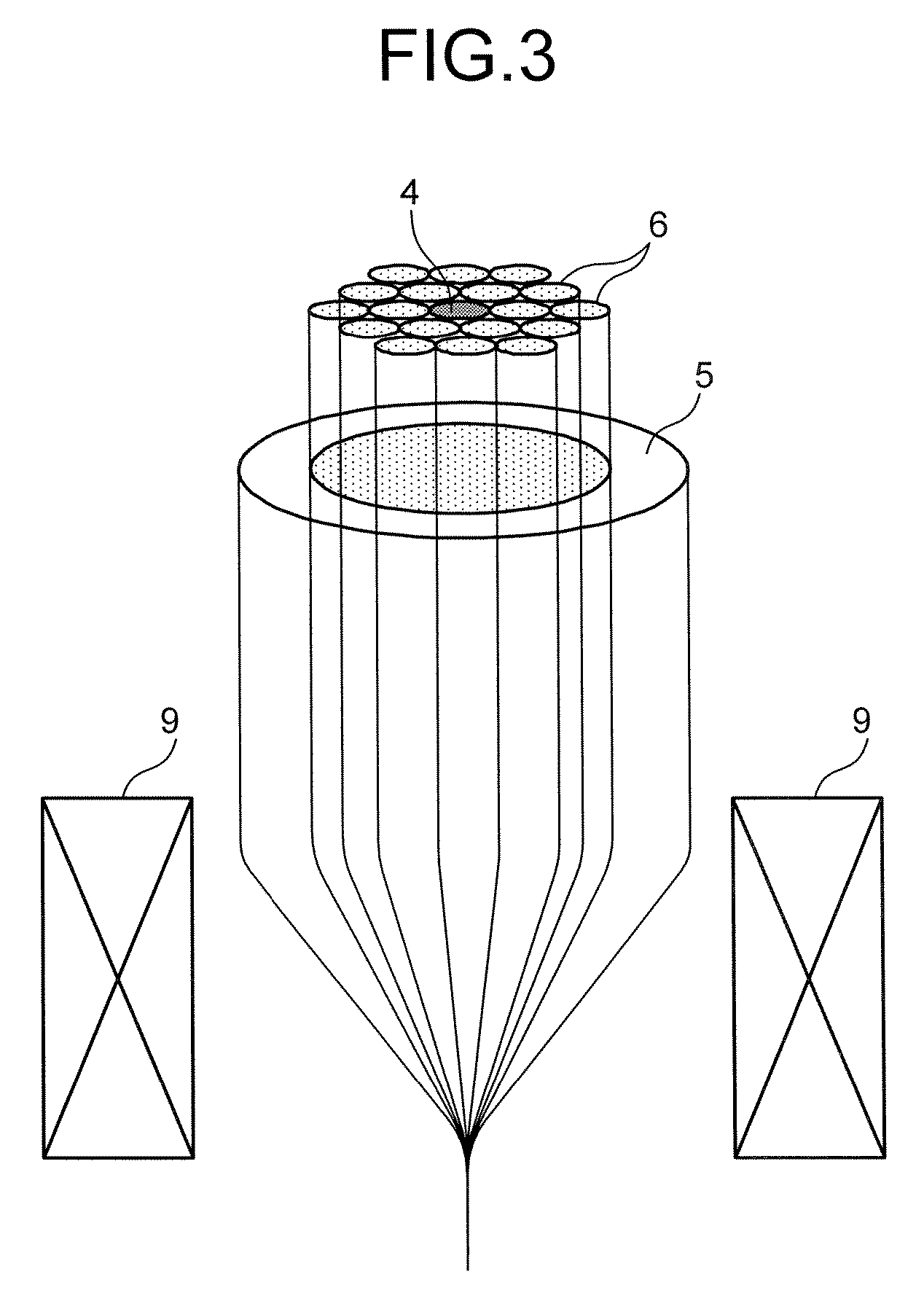
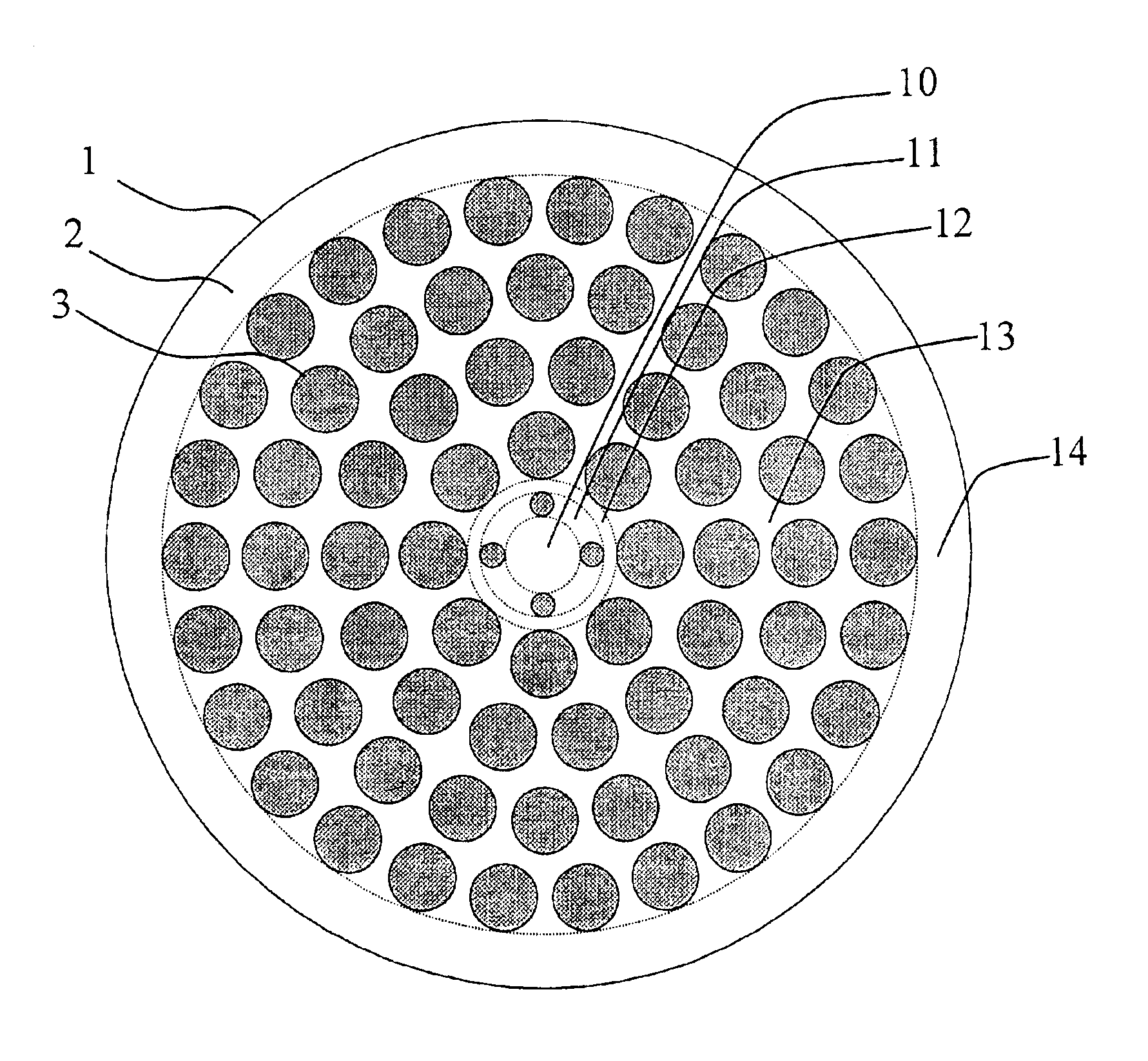
The invention discloses a bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber and a production method thereof. The bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber comprises a germanium-doped fiber core and a quartz covering layer which covers the periphery of the fiber core; and 12 air holes are uniformly distributed on the surrounding of the fiber core. The production method comprises the following steps of: utilizing rod making equipment to prepare the germanium-doped fiber core; uniformly arraying 12 quartz pipes in a circumferential direction of the surrounding of the fiber core; fixing the tail ends of the 12 quartz pipes to form an integrated rod combining the bunched fiber cores and the quartz pipes; covering a quartz sleeve on the periphery of the integrated rod to form a bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber prefabricated rod; and utilizing an optical fiber drawing tower to draw the bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber prefabricated rod into the bent non-sensitive micro-structured optical fiber. According to the production method provided by the invention, the problem of bad bending loss effects caused by the asymmetry of micro-pores in the actualproduction process can be effectively solved and better characteristics such as small bending radius and low loss can be provided.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
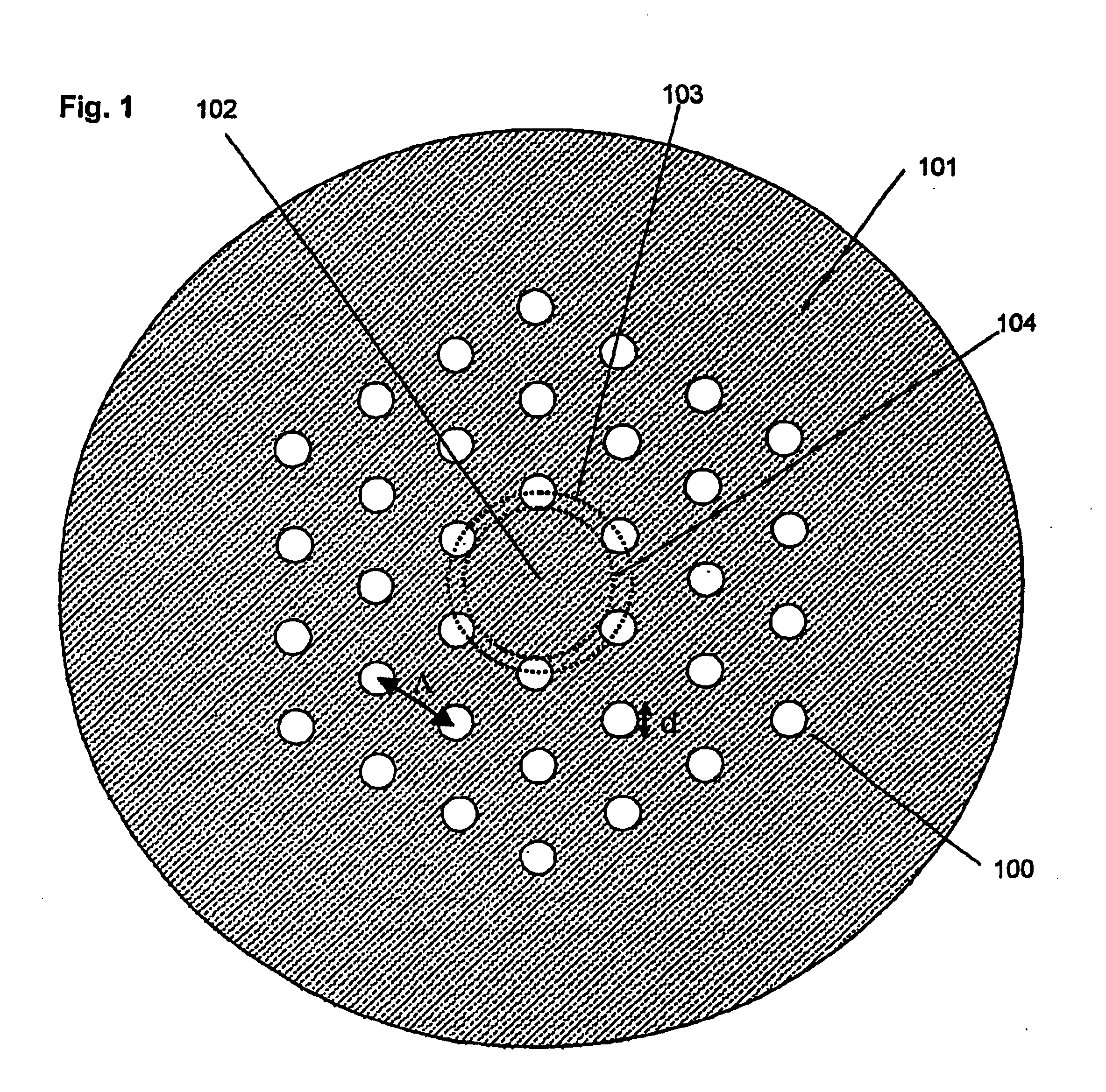
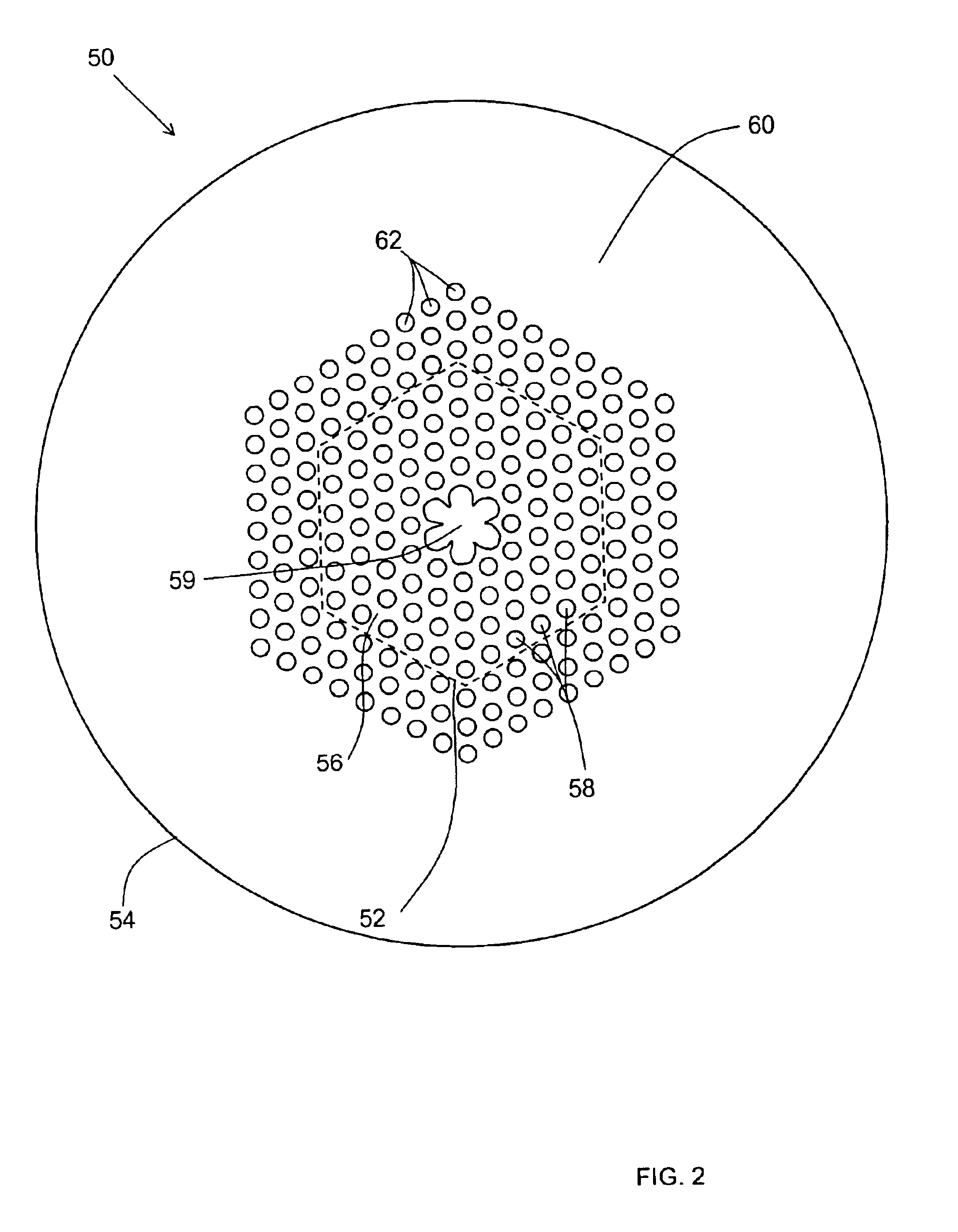
Archimedean-lattice microstructured optical fiber
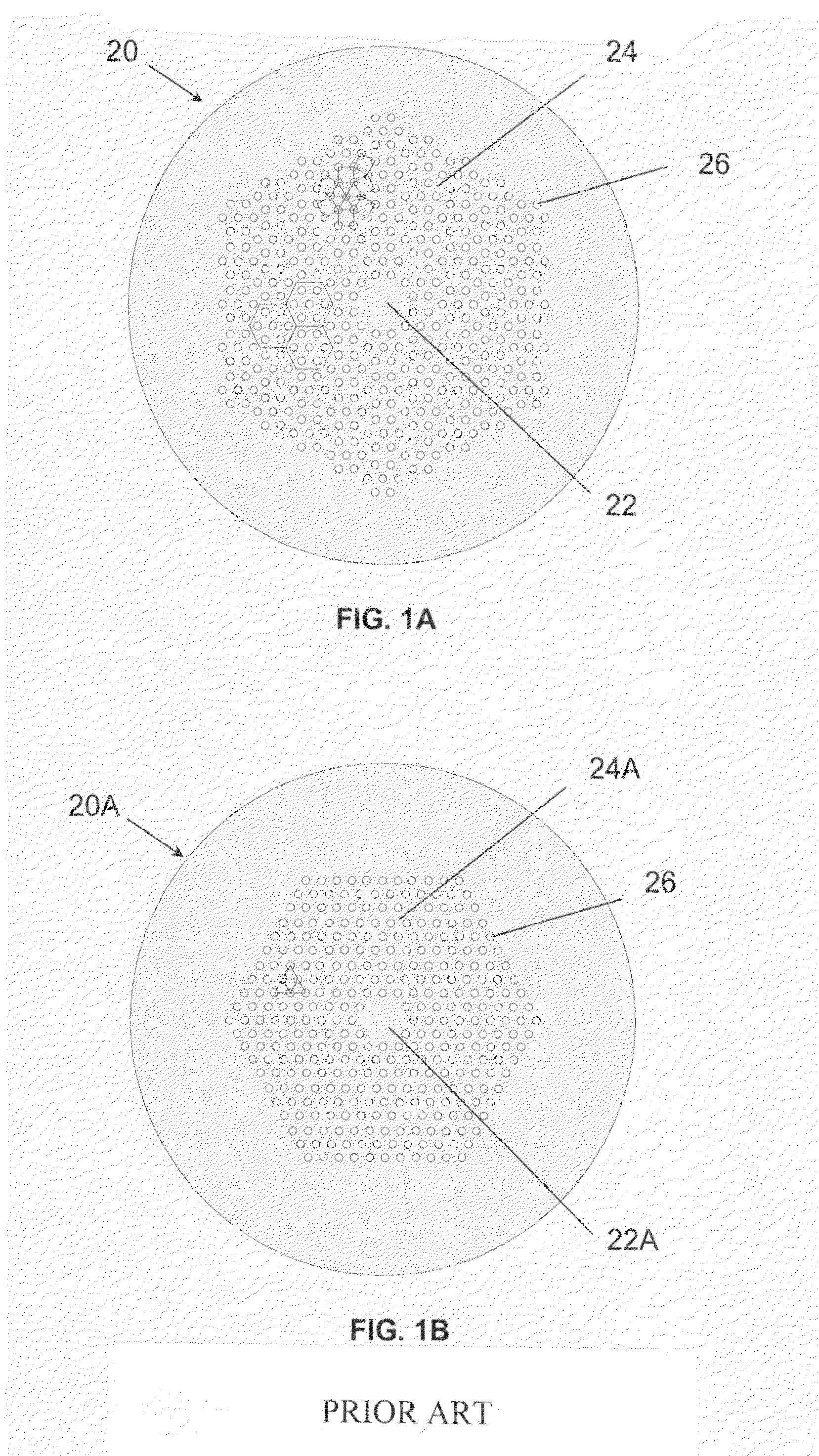
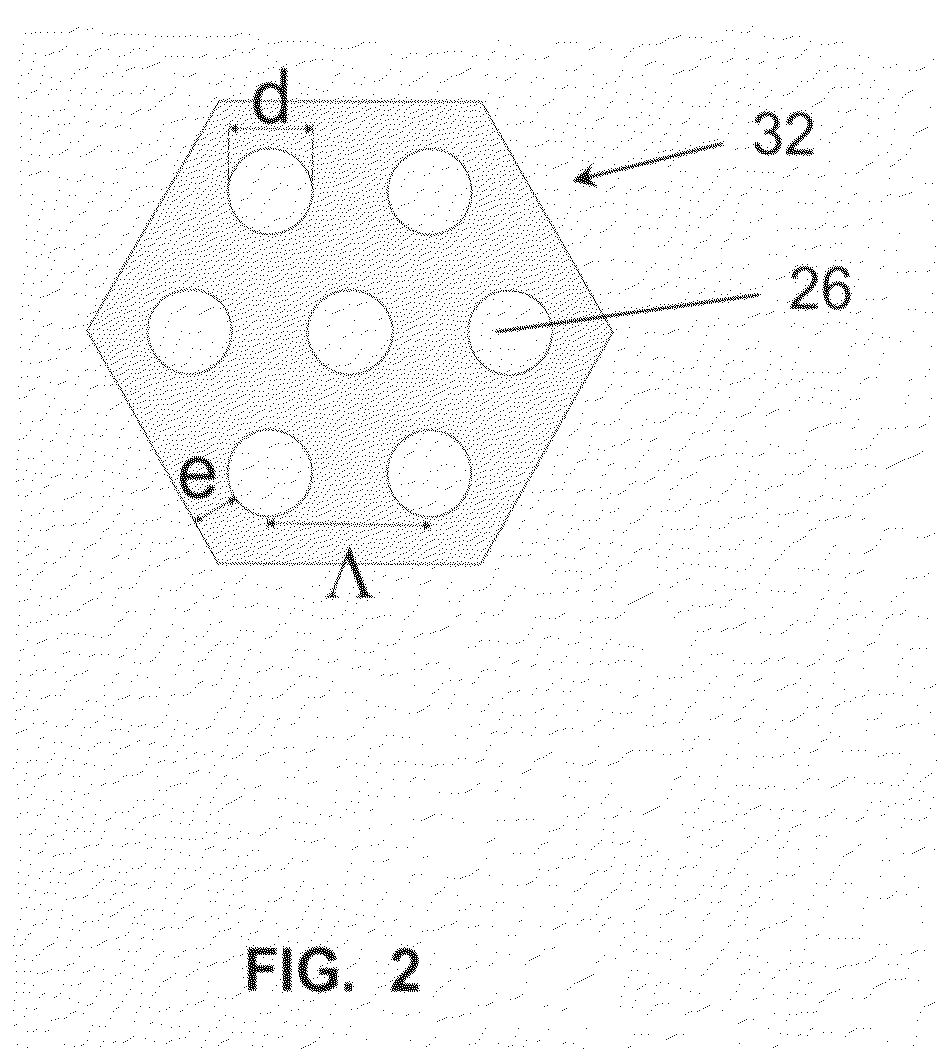
A microstructured optical fiber exhibiting enhanced circularity of the guided light mode is provided. The microstructured optical fiber includes a light-guiding core and a primary cladding surrounding the core wherein the primary cladding has a plurality of holes arranged in hexagonal unit cells defining an Archimedean-like lattice. Preferably, the core is defined by a break in a center of the Archimedean-like lattice, the break being characterised by an absence of at least one of the unit cells. Also preferably, each of the unit cells has seven holes arranged in a centred hexagon. A method of making the microstructured optical fiber is also provided. The method includes fabricating a fiber preform by stacking a plurality of canes around a rod, each cane having a number of holes arranged in a unit cell defining an Archimedean-like lattice, and drawing said fiber preform into the microstructured optical fiber.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Lifetime extending and performance improvements of micro-structured fibers via high temperature loading
The disclosure relates to an optical fiber including a core and a cladding having a core material and a cladding material, respectively, wherein the fiber is a non-linear microstructured optical fiber, the microstructured optical fiber being obtainable by a method including loading the core material and optionally the cladding material with hydrogen and / or deuterium whereby the lifetime of the fiber may be extended in high pulse applications.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Lifetime extending and performance improvements of optical fibers via loading
ActiveUS20110116283A1Degradation is eliminated and reducedExtended service lifeCosmonautic condition simulationsCladded optical fibreFiberHydrogen
The invention relates to an optical fiber comprising a core and a cladding comprising a core material and a cladding material, respectively, wherein said fiber is a non-linear microstructured optical fiber, said microstructured optical fiber being obtainable by a method comprising loading with hydrogen and / or deuterium and optionally anneal and / or irradiation hereby the lifetime of the fiber may be extended in high power applications.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Dispersion compensated optical fiber transmission system and module including micro-structured optical fiber
InactiveUS6993228B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical fiber transmission
Disclosed is an optical transmission system and module which includes a negative dispersion, dispersion compensating optical fiber coupled to a micro-structured optical fiber (such as band gap fiber, photonic crystal fiber or holey fiber) for compensating for the accumulated dispersion in a transmission fiber. The optical transmission system and module in accordance with the invention provides substantially equal compensation of total dispersion over an operating wavelength band, reduced overall system length, and lower insertion loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
Microstructured transmission optical fiber
InactiveUS20080131066A1Improve bending abilityReduce decreaseGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Microstructured optical fiber for single-moded transmission of optical signals, the optical fiber including a core region and a cladding region, the cladding region including an annular hole-containing region that contains non-periodically disposed holes. The optical fiber provides single mode transmission and low bend loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
Functional material filled micro-structure optical fiber based tunable dual-channel grating filter
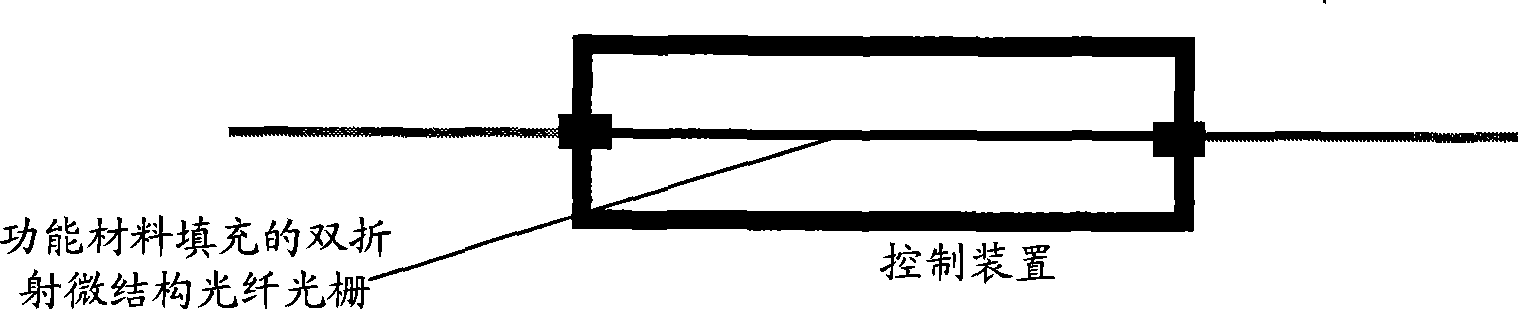
InactiveCN101520555AImplementation is flexibleThere are various ways to realizeCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideMicro structureGrating
The invention discloses a functional material filled micro-structure optical fiber based tunable dual-channel grating filter which comprises a birefringent micro-structure optical fiber grating filled with functional material and a control device, wherein the birefringent micro-structure optical fiber grating filled with the functional material is positioned in the control device, and the control device is used for generating, loading and regulating electric field, temperature, optical field, magnetic field or sound field which can change the refractive index of the functional material in the birefringent optical fiber. Compared with the prior art, the filter has the advantages of flexible realization way, varied tuning mode, wide tuning range, and can realize the electric tuning. The invention can be widely applied to the fields of tunable lasers, optical fiber sensors, and the like, is suitable for large-scale popularization and application and has great significance of production practice.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Microstructured optical fiber, supercontinuum light source comprising microstructured optical fiber and use of such light source
ActiveUS20160170136A1Quality improvementReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreFiberOptical fiber cable
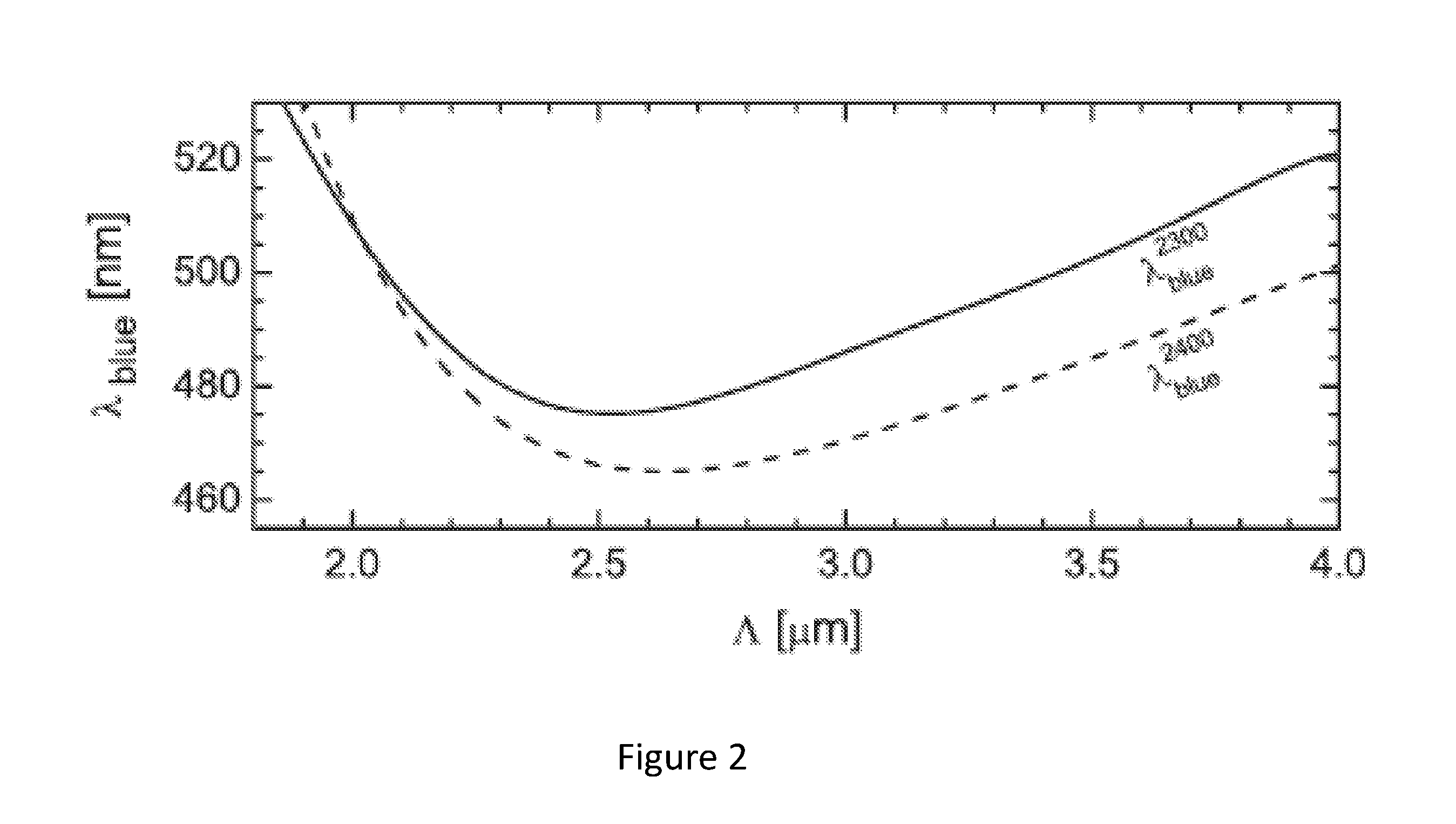
The invention relates to a microstructured optical fiber for generating incoherent supercontinuum light upon feeding of pump light. The microstructured optical fiber has a first section and a second section. A cross-section through the second section perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the fiber has a second relative size of microstructure elements and preferably a second pitch that is smaller than a blue edge pitch for the second relative size of microstructure elements. The invention also relates to an incoherent supercontinuum source comprising a microstructured optical fiber according to the invention.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Weak-guide annular-structure optical fiber
ActiveCN106950644AReduce complexityGuaranteed numberOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideDigital signal processingFiber
The invention discloses a weak-guide annular-structure optical fiber. The weak-guide annular-structure optical fiber comprises an annular fiber core, a central zone and a cladding. The annular fiber core has step or gradient type refractive index distribution, and an auxiliary low-refractive-index annular groove can be disposed in an inner or outer side. A refractive index difference between the annular fiber core and the clapping / central zone does not exceed 1%. A refractive index difference between the annular groove and the clapping / central zone does not exceed -1%. The weak-guide annular-structure optical fiber only supports a multichannel radial first-order mode and is divided into different mode groups. The other mode groups except for the two front mode groups have large refractive index differences. The front two mode groups can be combined and then be multiplexed through a 6*6 Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) digital signal processing assist, the other mode groups are multiplexed through a 4*4 MIMO-DSP assist in each mode group, i.e., inter-mode-group low-crosstalk multiplexing and small-scale MIMO-DSP assist multiplexing in mode groups are combined. Expandability is possessed. A mode base can be a linear polarization / optical vortex / intrinsic mode. And, the weak-guide annular-structure optical fiber has a C+L waveband broadband characteristic and is compatible with existing mature optical fiber technology, the communication capacity can be effectively improved through a combination with wavelength division multiplexing, and loss can be reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method of manufacturing microstructured optical fiber
InactiveUS20060213230A1Solve problemsGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesSilicon dioxideMaterials science
A silica material having a higher purity than a cylindrical preform formed of a silica material is deposited on at least one of an inner side and an outer side of the preform to fabricate a cylindrical intermediate member. A part of the cylindrical intermediate member including at least a part of the preform is removed to fabricate a high-purity silica tube. A plurality of the high-purity silica tubes is bundled with a core rod arranged at a center axis of a bundle of the high-purity silica tubes, and the bundle of the high-purity silica tubes with the core rod arranged at the center axis is drawn to obtain a microstructured optical fiber.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Microstructured optical fiber and optical module
ActiveUS6915053B2Reduce the effective areaIncreasing effective core areaGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical ModuleEngineering
A microstructured optical fiber is structured with a core region and a plurality of cladding regions surrounding the core region. Chromatic dispersion is relatively flat over a broad wavelength range with a small effective area, without need for air holes that are unacceptably small. An enlarged effective core area is obtained by selectively closing the holes in the innermost cladding, which holes are smaller and easier to close than the holes in other regions.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Microstructured optical fiber with long wave cut-off function and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1844962AFlexible designRefractive Index ControlGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberRare earth ions
The invention relates to a micro optical fiber, especially providing a micro optical fiber with stop function on long wavelength, which can be used in optical fiber laser, optical fiber amplifier, and optical fiber filter. It is formed by core fiber, reflective index concave layer and coat. Wherein, the reflective index concave layer is between the core fiber and the coat; the reflective index concave layer and the coat have some arranged holes, via whose shape, size, and distribution, to control the average effective reflective index, to make the reflective index of concave layer lower than the reflective indexes of core fiber and coat. Compared to common optical fiber, the invention can control reflective index more accurately and easily, while it has large long wavelength loss and small short wavelength loss, to be used as optical filter. The core filter is doped with rare earth ion; the low reflective index layer can make the light emitted by doped optical fiber excurse to short wavelength, to prepare special optical fiber powered device.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com