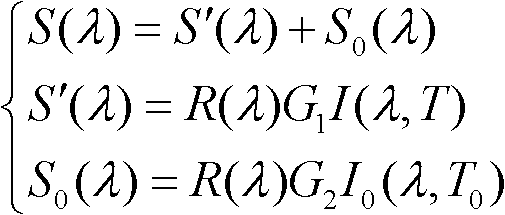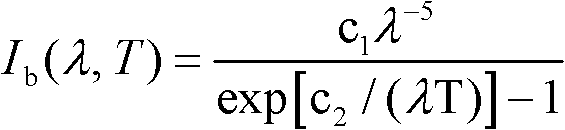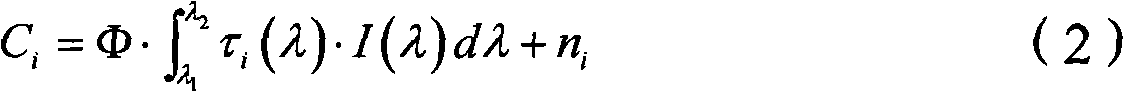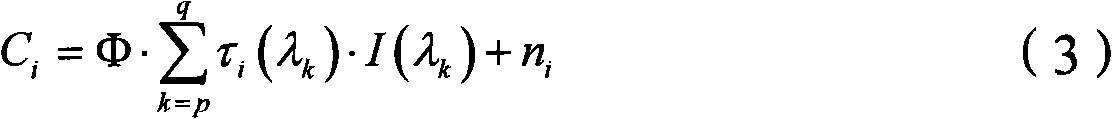Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Spectral radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
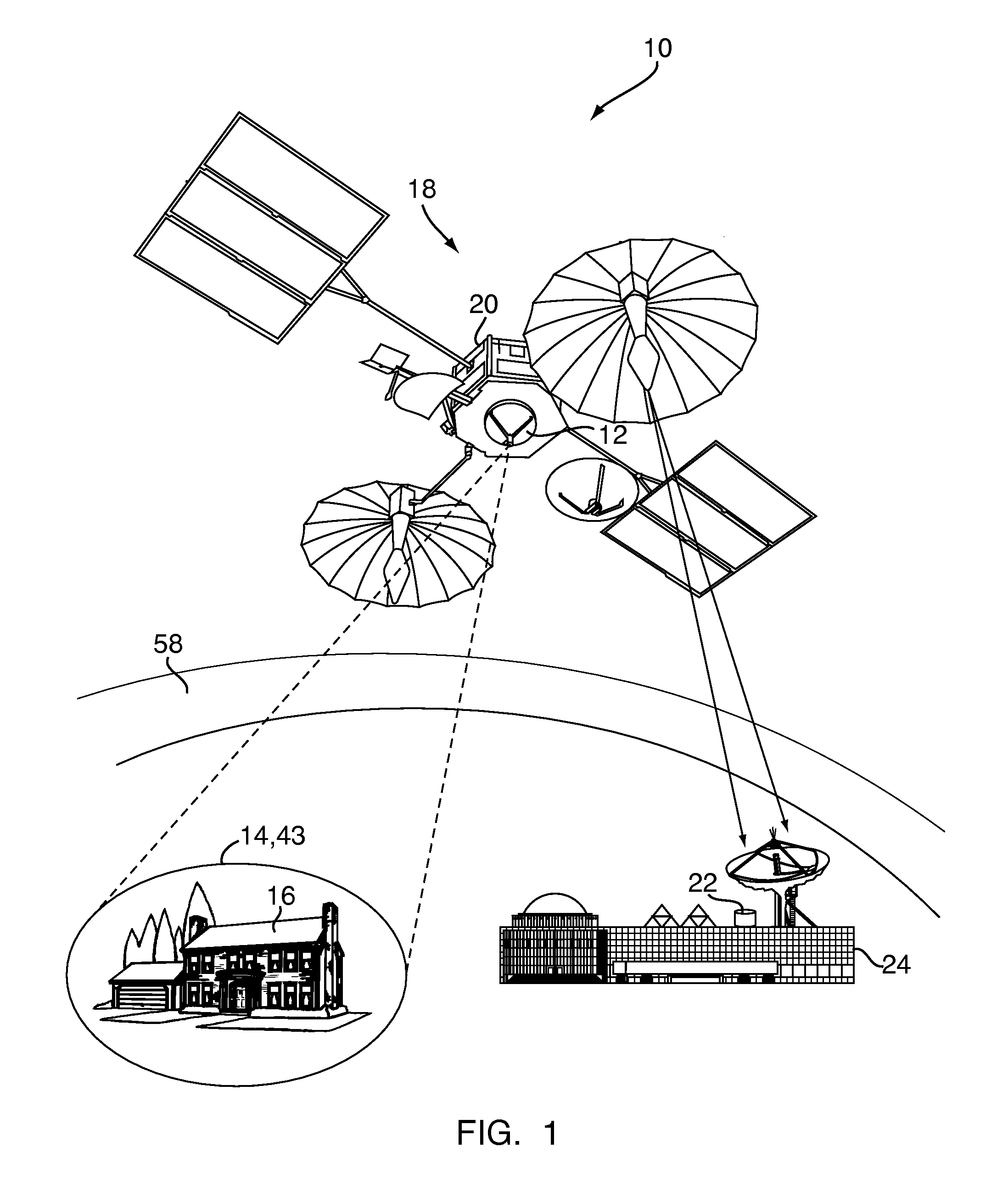
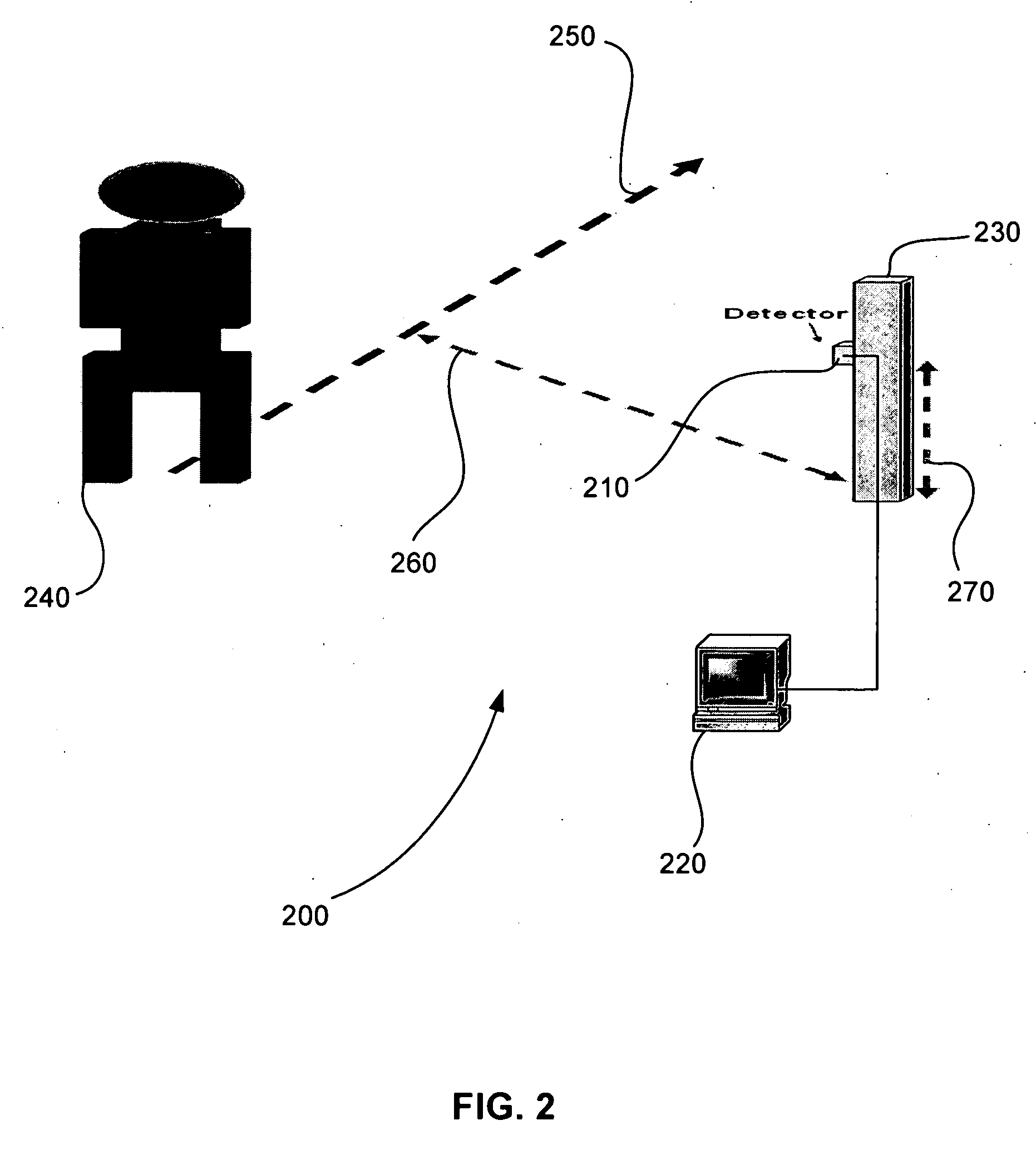
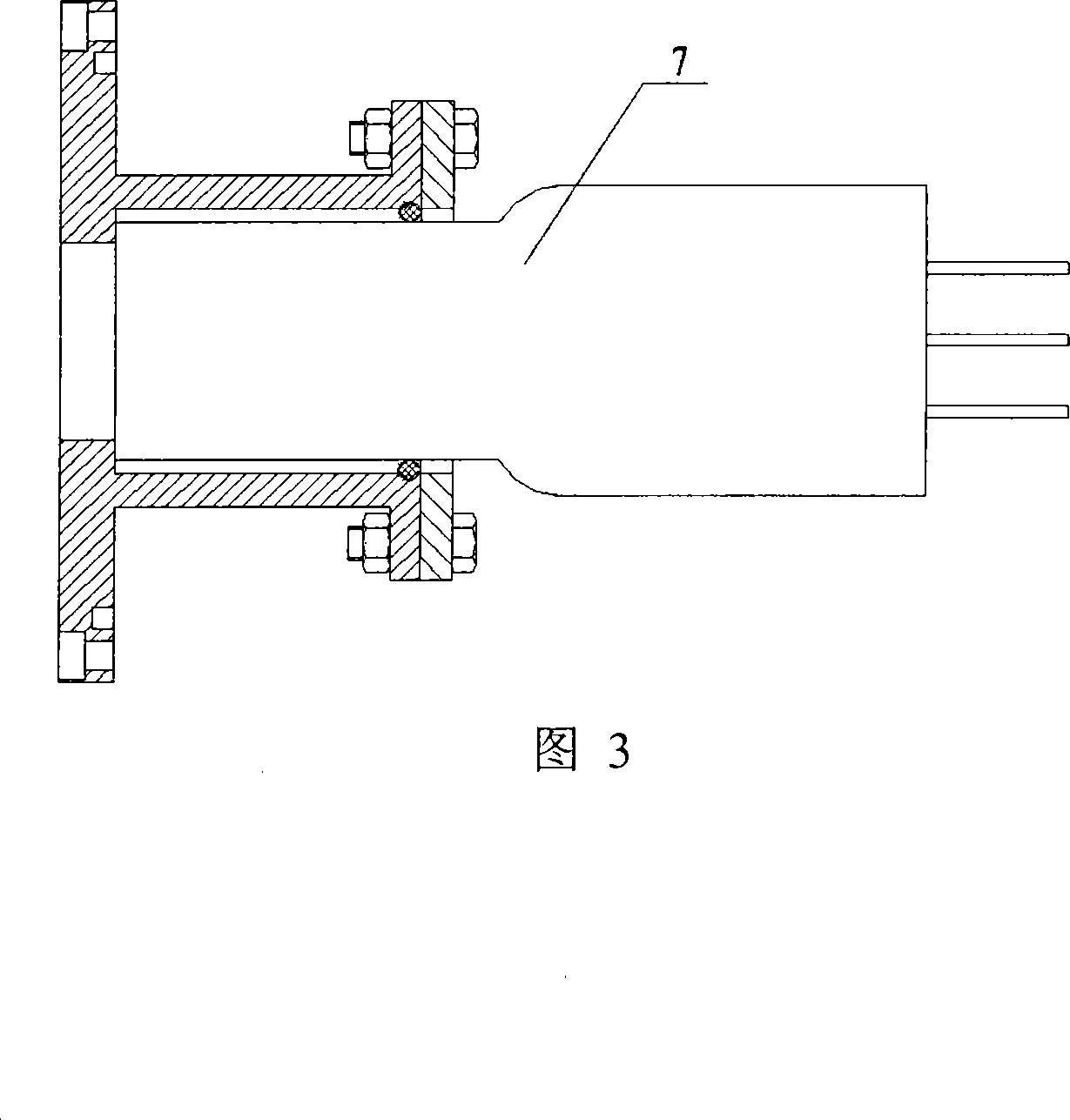
Sensor system for identifying and tracking movements of multiple sources
ActiveUS7351975B2Improves collection efficiency and spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensing radiation from moving bodiesVisibilityFresnel lens
A system identifies a human being from the movement of the human being. The system includes a dual element pyroeleetric detector, a Fresnel lens array, and a processor. The dual element pyroelectric detector detects radiation from the human being as the human being moves over time. The Fresnel lens array is located between the dual element pyroelectric detector and the human being. The Fresnel lens array improves collection efficiency and spatial resolution of the dual element pyroelectric detector. The Fresnel lens array includes a mask. The mask provides at least one zone of visibility. The processor is coupled to the dual element pyroelectric detector, the processor converts the detected radiation to a spectral radiation signature. The processor compares the spectral radiation signature to at least a second spectral radiation signature to identify the human being.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
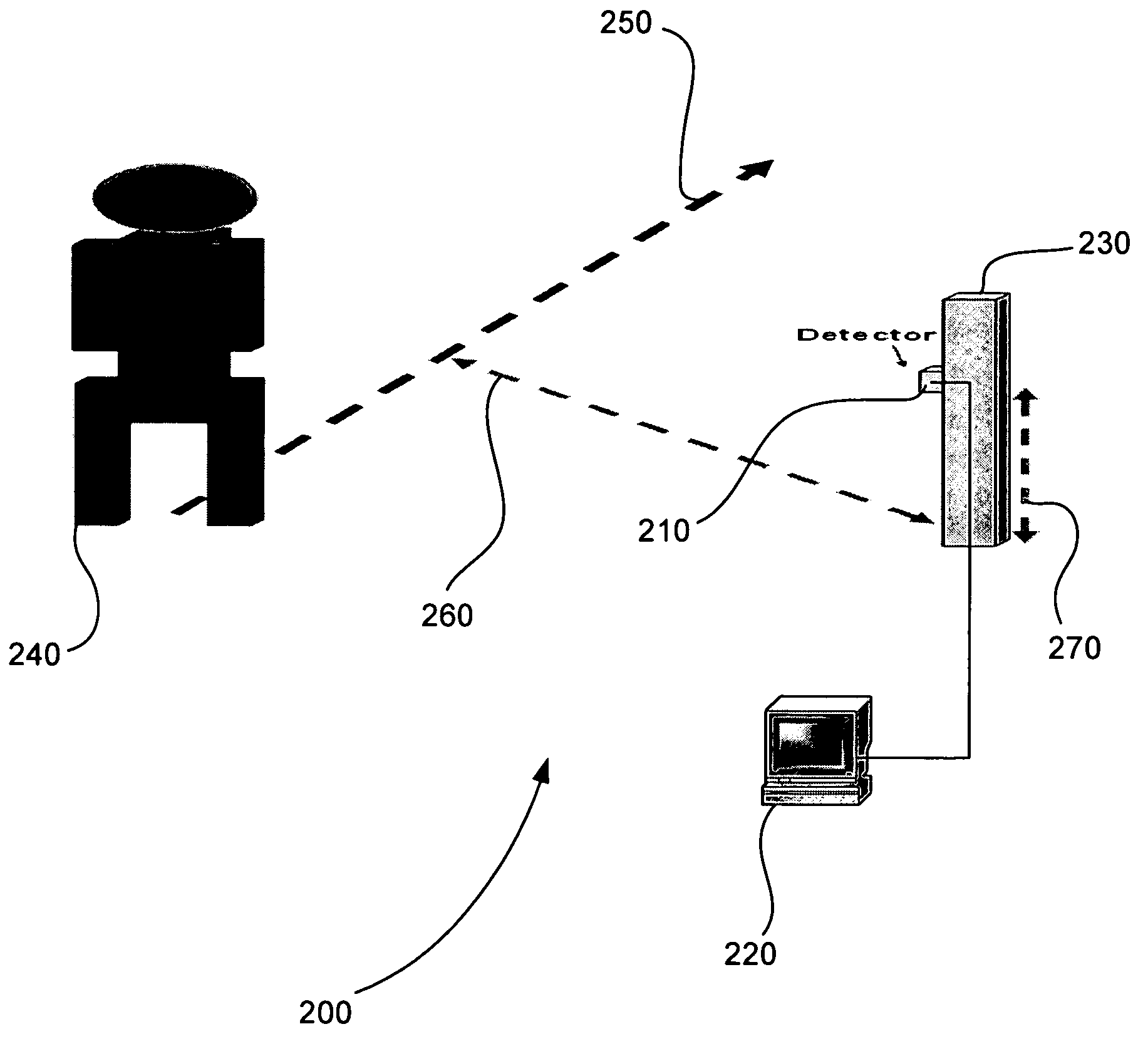
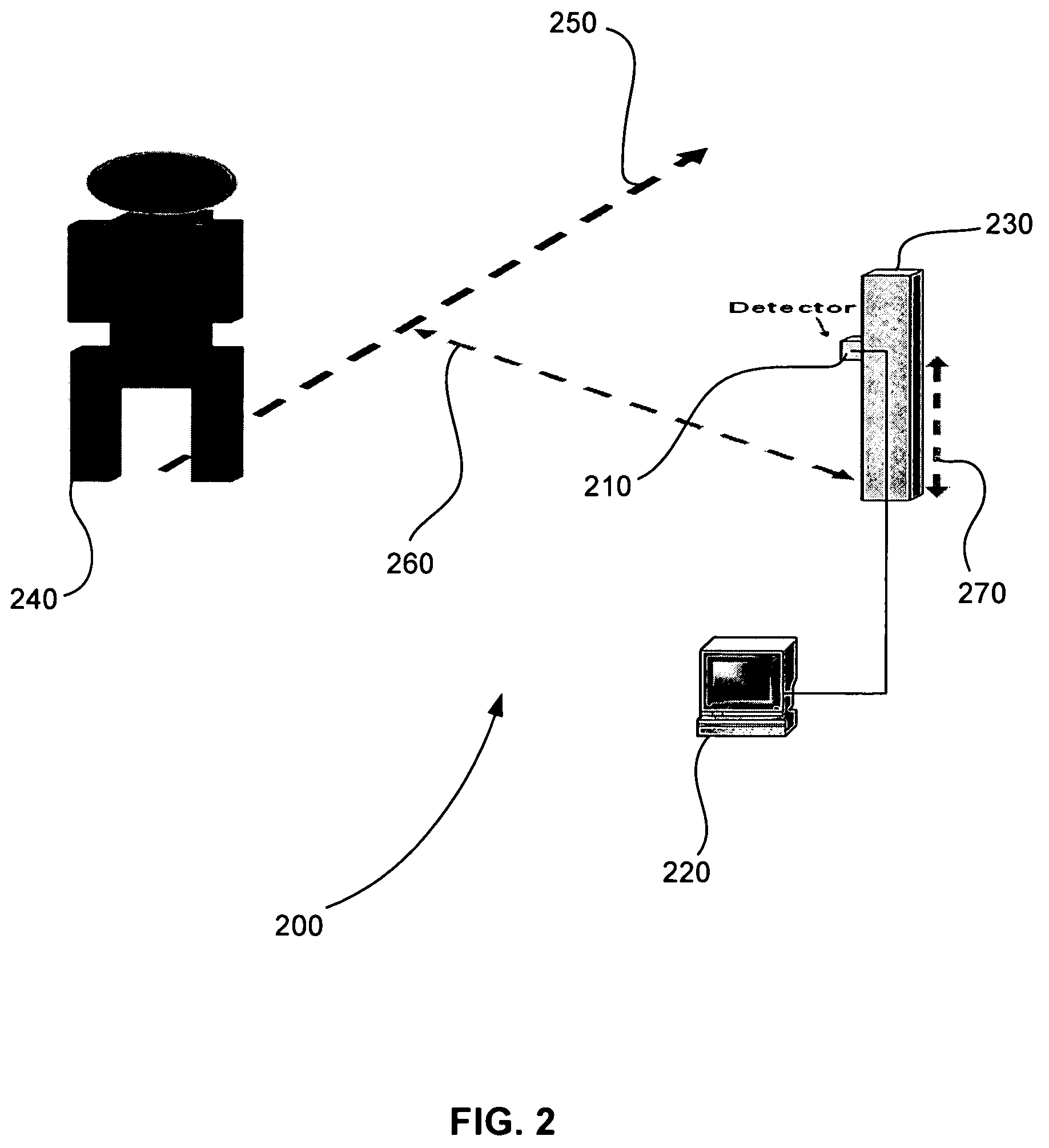
System and method for assessing a condition of property
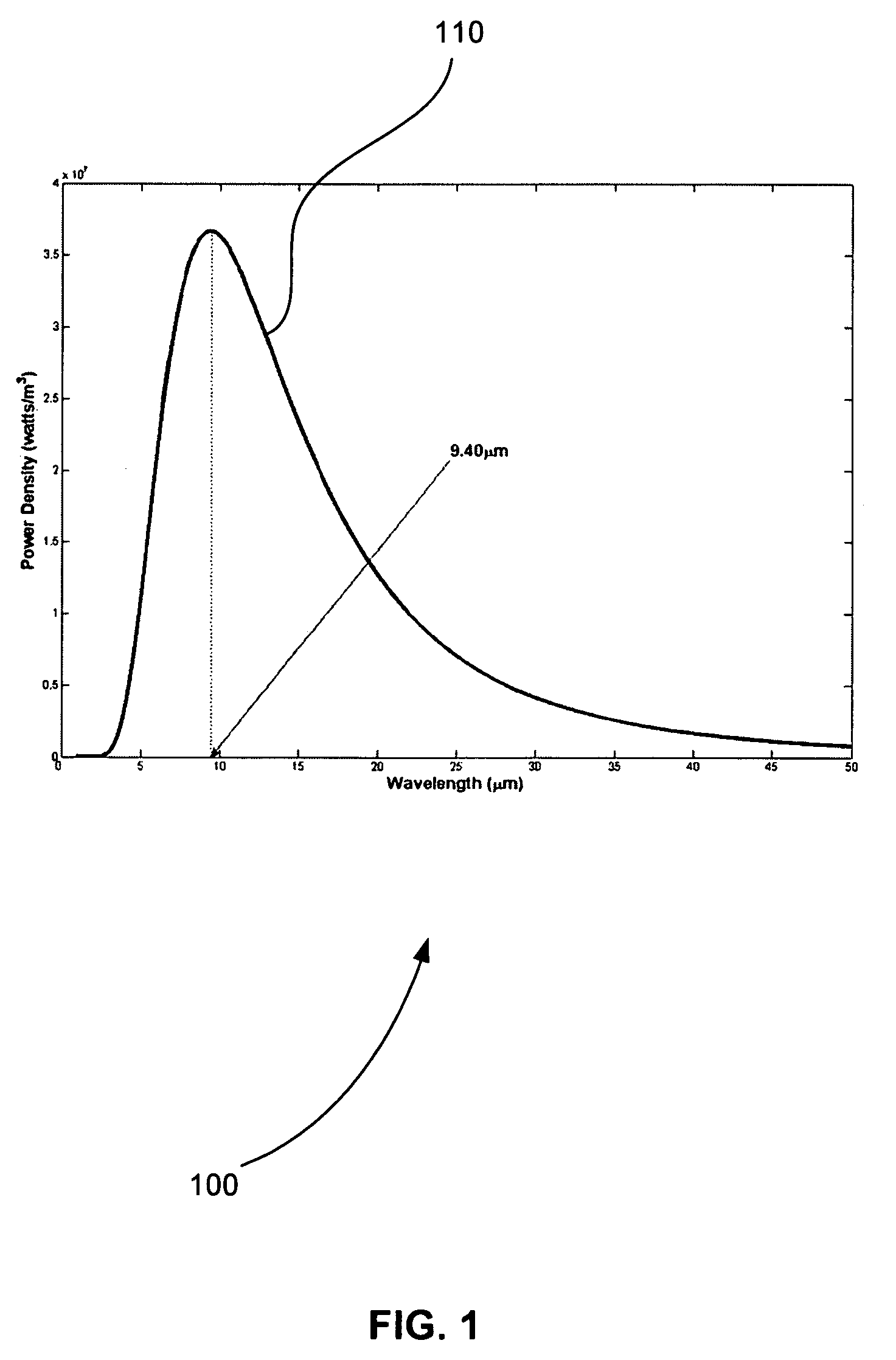
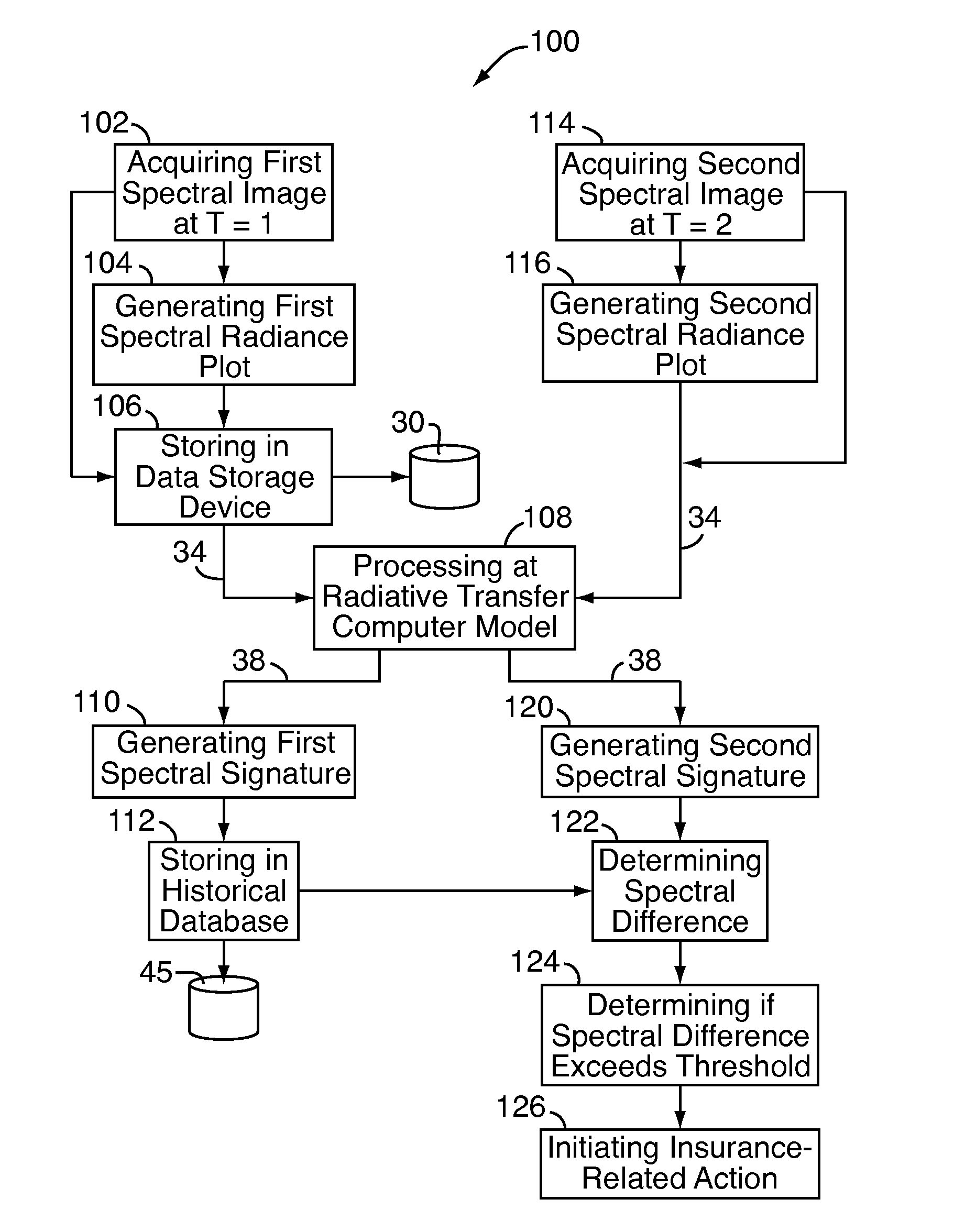
A system and method for assessing a condition of property for insurance purposes includes a sensor for acquiring a spectral image. In a preferred embodiment, the spectral image is post-processed to generate at least one spectral radiance plot, the plot used as input to a radiative transfer computer model. The output of the model establishes a spectral signature for the property. Over a period of time, spectral signatures can be compared to generate a spectral difference, the difference attributed to a change in the condition of the property, such as a fire or flood. In response to the change, an insurance company initiates an insurance-related action such as processing a claim.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
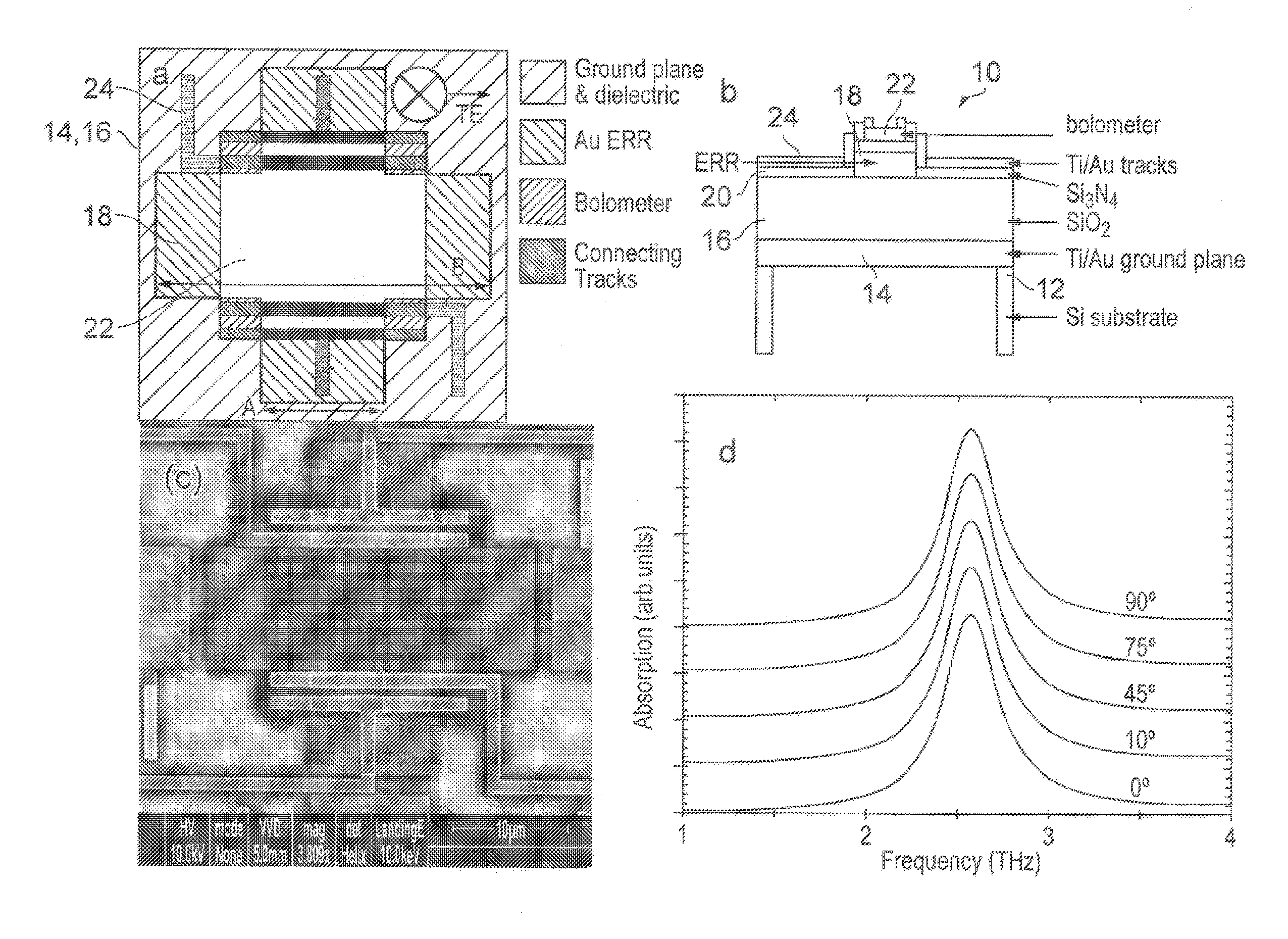
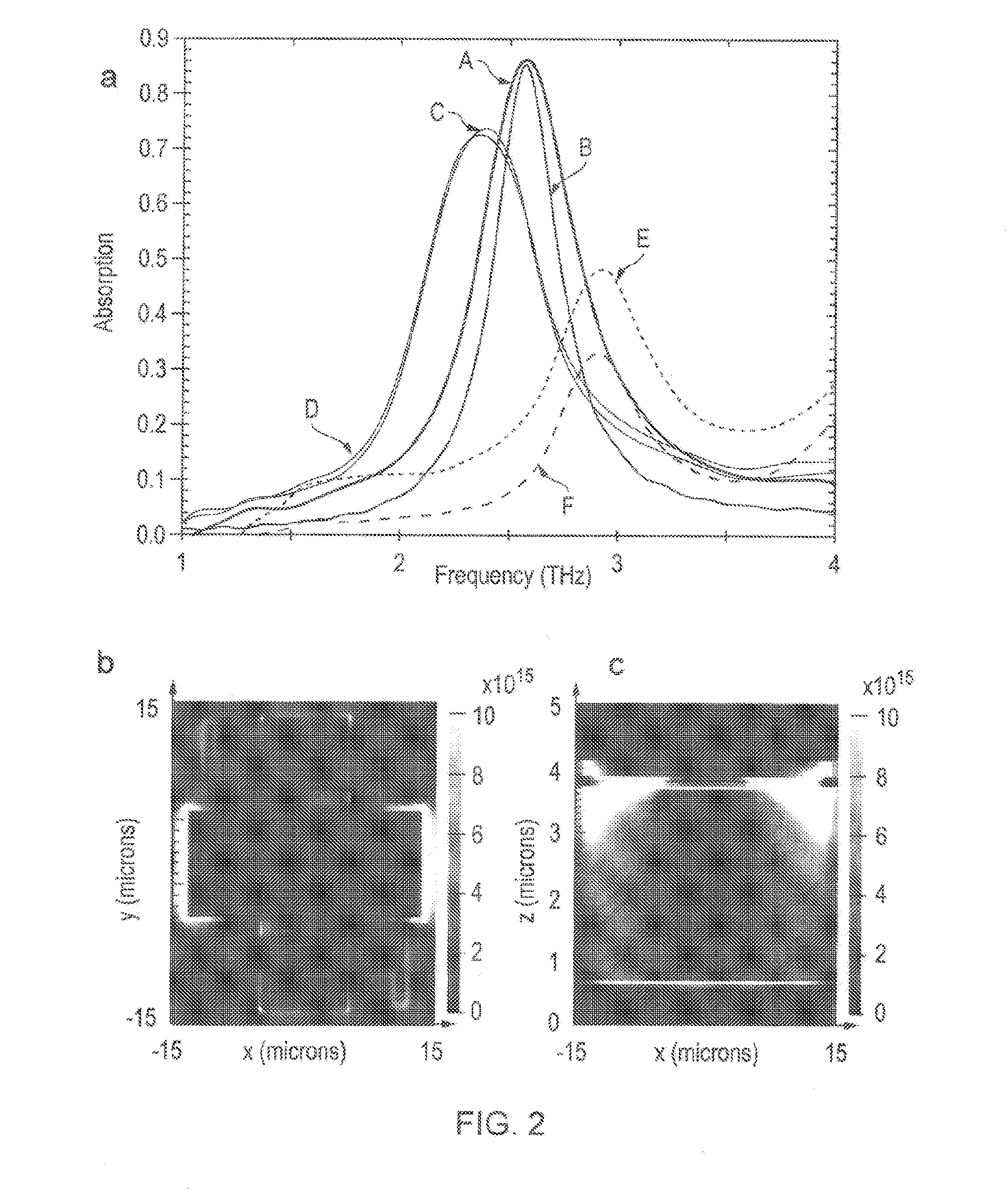
Terahertz radiation detector, focal plane array incorporating terahertz detector, multispectral metamaterial absorber, and combined optical filter and terahertz absorber
InactiveUS20150276489A1Partly effectiveMinimised and possibly eliminatedMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsOptical radiationInformation density
The invention provides a detector comprising a metamaterial absorber and a micro-bolometer arranged to detect terahertz (THz) radiation. The metamaterial absorber can absorb multiple frequency bands, from the infrared and the THz regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The detector is scalable to be suitable for use in a focal plane array.The invention also provides a hybrid of a plasmonic filter, e.g. for optical radiation, and a metamaterial absorber for terahertz (and / or infrared) radiation, to create a single material capable of absorbing narrow band terahertz radiation and filtering radiation in another part of the spectrum, e.g. optical radiation. Such material has great potential in future imaging technology where hybridisation can maximise the spectral information density of an optical system.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
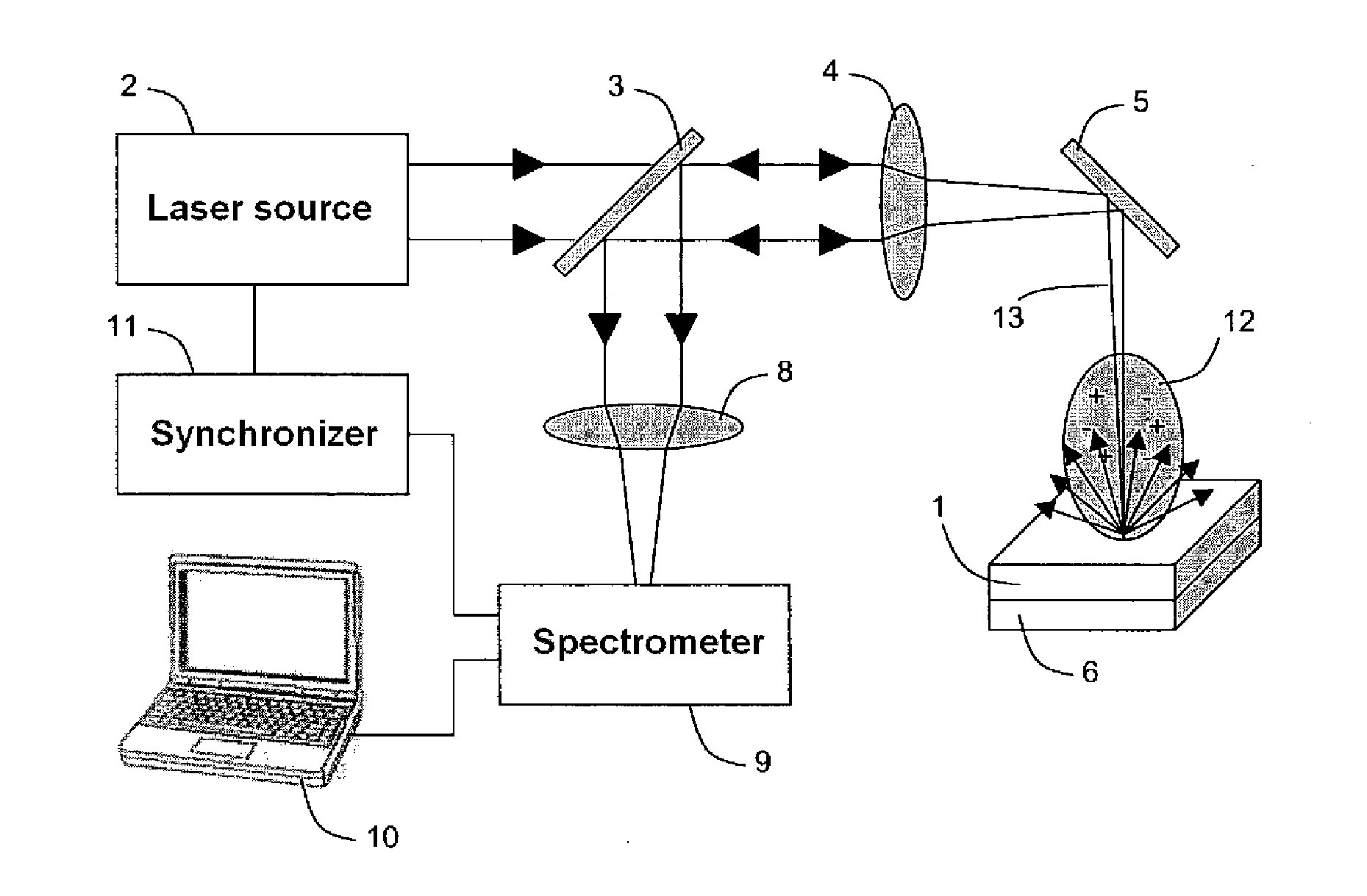
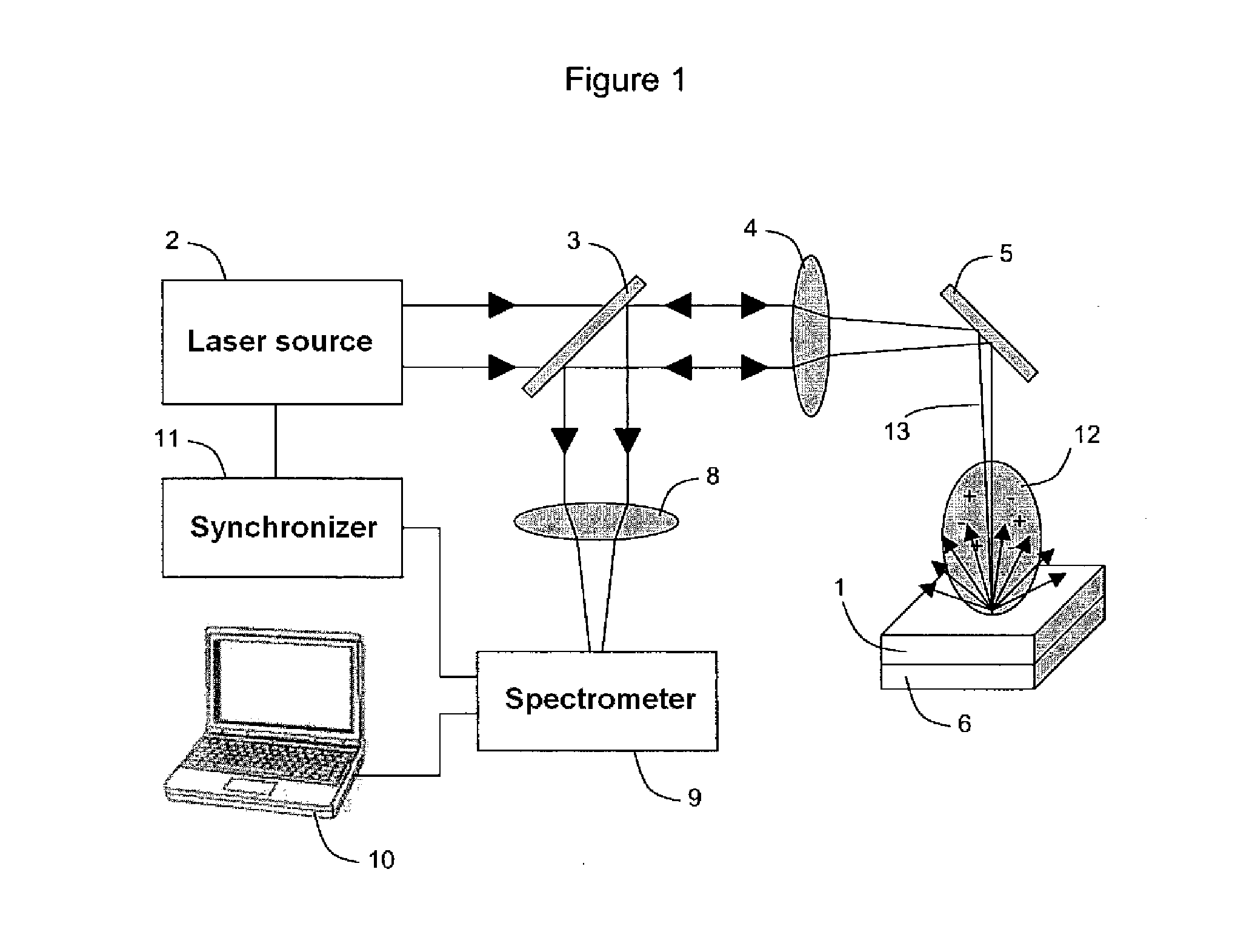
System and method for quantitative analysis of the elemental composition of a material by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
ActiveUS20120029836A1Quick calculationShort calculation timeEmission spectroscopyAnalysis by thermal excitationElemental compositionChemical composition
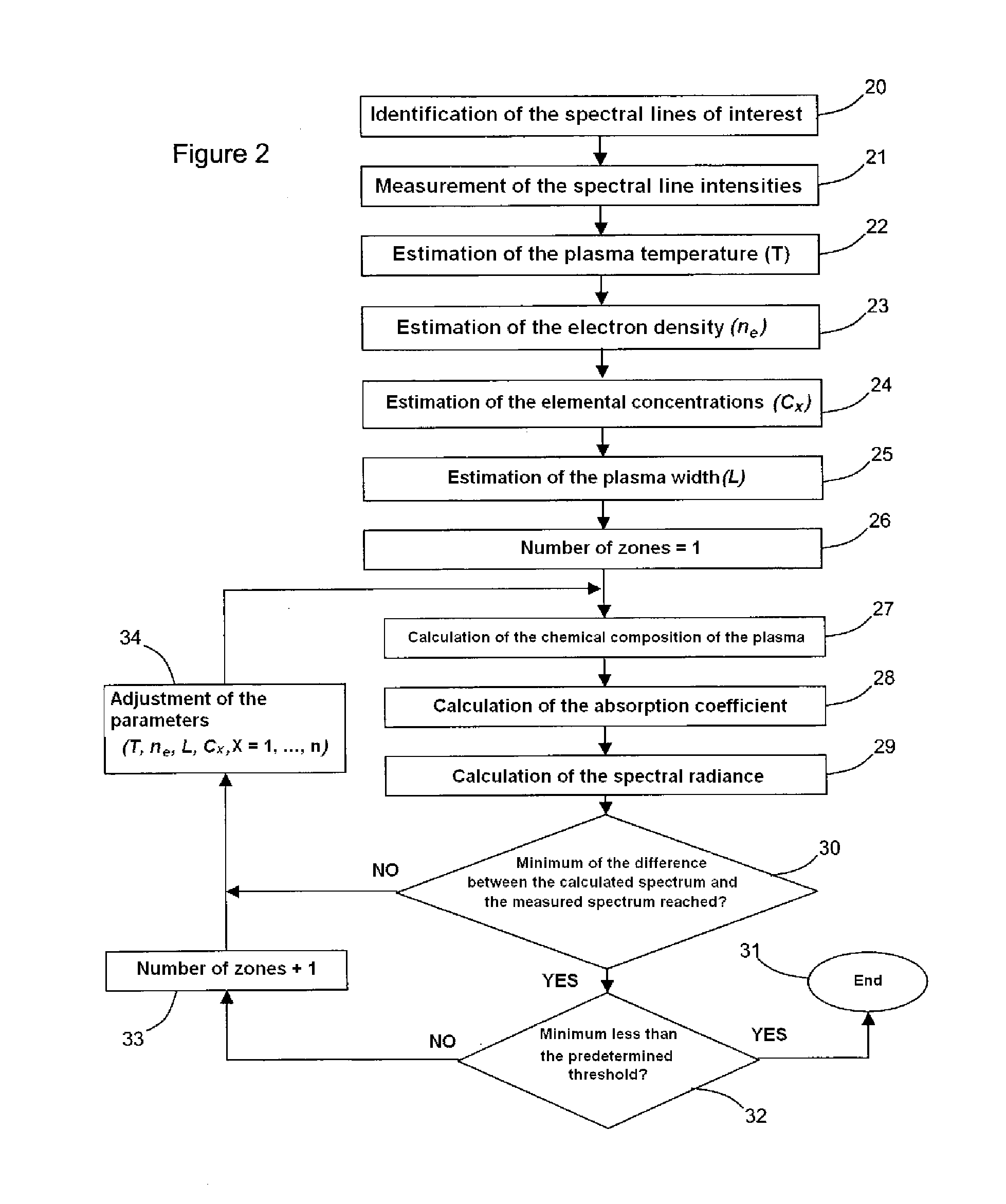
A system and method for measuring elemental concentrations of a material from a sample containing several elements by LIBS analysis. The material is heated to generate plasma and its chemical composition is determined from spectral analysis of its radiation. The spectral lines of interest are identified among those emitted by the constituents of each element composing sample. The intensities of the spectral lined identified are measured. From an estimate of temperature, electron density and relative concentration values, the chemical composition of the plasma is calculated. The absorption coefficient according to wavelength is calculated for the spectral zones of the lines of interest. From an estimate of the plasma width, the spectral radiance of the plasma is calculated for the same spectral zones and then a comparison of the intensity and shape of the spectrum thus calculated with those of the spectrum measured is performed. These calculations and this comparison are repeated iteratively in order to adjust the temperature, electron density, relative values of the elemental concentrations and width of the plasma.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Energy method-based high-temperature radiation rate measuring device of semi-transparent material and revising method for deducting background radiation
ActiveCN102564610AAccurate calculation of high temperature spectral transmittanceEasy to measureRadiation pyrometryMaterial thermal analysisSpectrum analyzerHorizontal axis
The invention provides an energy method-based high-temperature radiation rate measuring device of a semi-transparent material and a revising method for deducting background radiation, relating to a high-temperature normal spectral radiation rate revising and testing method of the semi-transparent material and belonging to the technical field of high-temperature material physical property measurement. The energy method-based high-temperature radiation rate measuring device of the semi-transparent material and the revising method for deducting the background radiation solve the problems of high construction cost, low temperature heating upper limit and lower testing precision of the traditional test system. The high-temperature radiation rate measuring device comprises a Fourier infrared spectrum analyzer, a reference blackbody furnace, a rotatable reflection mirror, a heating furnace, a heater, a temperature collecting device, a temperature routing inspection operation instrument, an incidence light source, a data processing system, a diaphragm and a semi-transparent test piece; the heating furnace is internally provided with a light-transmitting opening, a fixing device of the semi-transparent test piece, and the temperature collecting device; the central axis of a light-emitting opening of the incidence light source, the central axis of the light-transmitting opening of the heating furnace, the mirror surface of the rotatable reflection mirror and the central axis of the light outlet opening of the reference blackbody furnace are collinear with a horizontal axis. The energy method-based high-temperature radiation rate measuring device of the semi-transparent material and the revising method for deducting the background radiation, disclosed by the invention, are used for measuring the high-temperature spectral normal radiation rate of the surface of the semi-transparent material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sensor system for identifiying and tracking movements of multiple sources
ActiveUS20070023662A1Improve collection efficiencyImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensing radiation from moving bodiesVisibilityFresnel lens
One embodiment of the present invention is a system for identifying a human being from movement of the human being. The system includes a dual element pyroelectric detector, a Fresnel lens array, and a processor. The dual element pyroelectric detector detects radiation from the human being as the human being moves over time. The Fresnel lens array is located between the dual element pyroelectric detector and the human being. The Fresnel lens array improves collection efficiency and spatial resolution of the dual element pyroelectric detector. The Fresnel lens array includes a mask. The mask provides at least one zone of visibility. The processor is coupled to the dual element pyroelectric detector, the processor converts the detected radiation to a spectral radiation signature. The processor compares the spectral radiation signature to at least a second spectral radiation signature to identify the human being.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
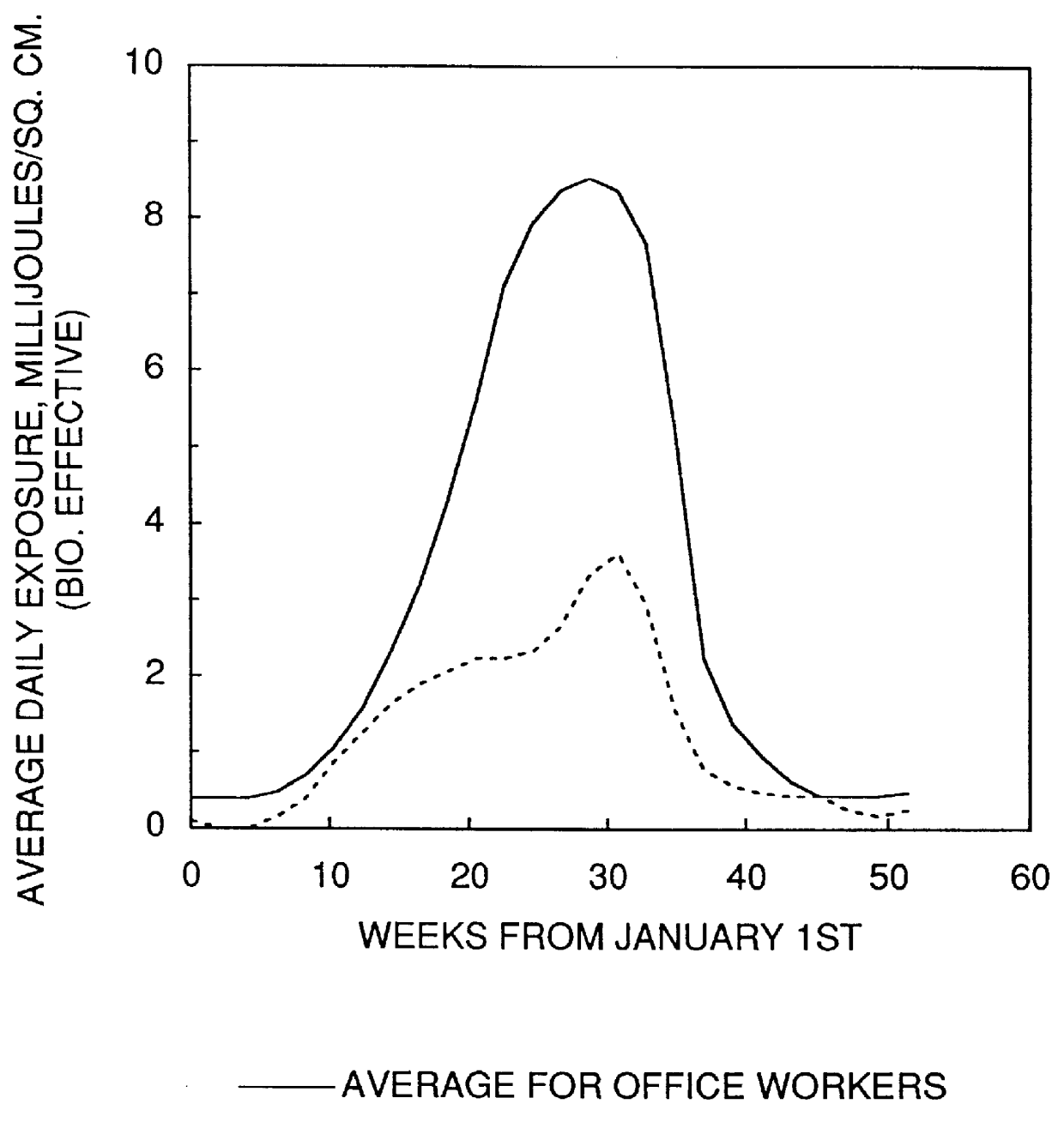
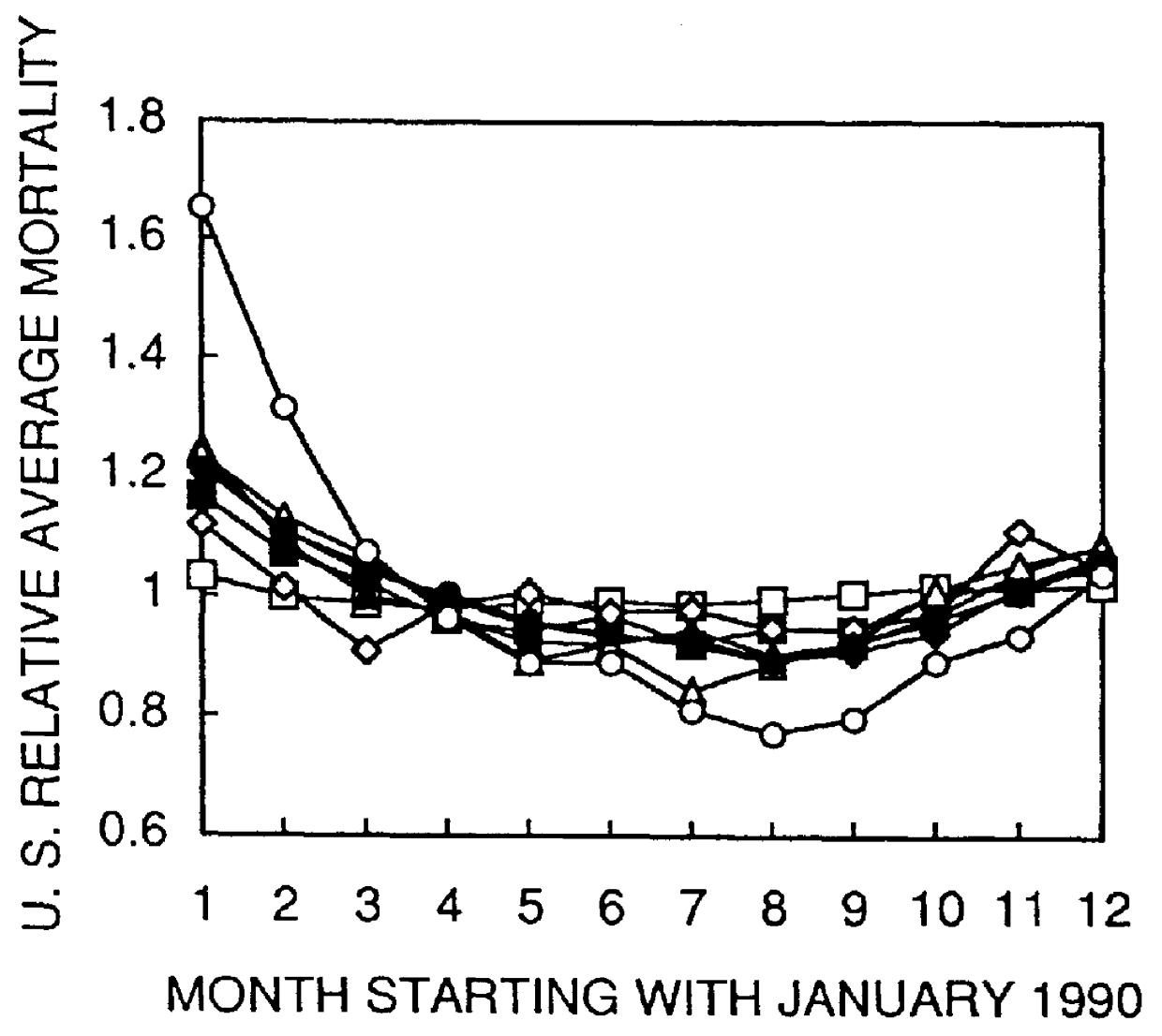
Skin light exposure control methods
A method to improve the probability for good health and decrese the risk of cancer and disease comprising: controlling the indoor spectral radiation environment partial body exposure in an amount above 0.06 MED, but not exceeding 0.2 MED per day by irradiating the body with an artificial light source.
Owner:CHUBB CHARLES R +1
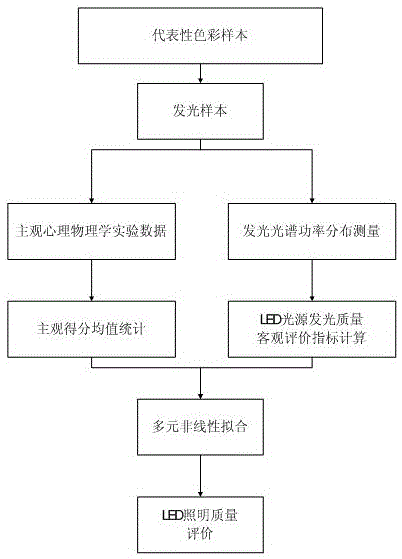
LED lighting quality evaluation method based on objective and subjective experiment data and system
InactiveCN105136432AGuaranteed to be scientificGuarantee the accuracy of evaluationTesting optical propertiesSpectroradiometerEffect light
The invention provides an LED lighting quality evaluation method based on objective and subjective experiment data and a system. The method comprises the steps that subjective experiment data acquired from a preset LED lighting evaluation angle for light emitting samples are input; the subjective score mean of each group of light emitting sample is counted; for each group of light emitting sample, a spectroradiometer is used to measure spectral power distribution; data in a visible wavelength range are intercepted; objective evaluation indicators are calculated; a multiple nonlinear fitting method is used to construct an association model between the subjective score mean and a corresponding objective evaluation indicator under different light emitting sample conditions; for a light emitting sample to be evaluated, the spectroradiometer is used to measure the spectral power distribution; the data in the visible wavelength range are intercepted; the objective evaluation indicator is calculated; a corresponding score estimation value is acquired based on the association model; and the lighting quality of a light source is characterized. The LED lighting quality evaluation method provided by the invention has the advantages of flexible and targeted use, accurate evaluation and easy implementation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Spectrometric using broadband filters with overlapping spectral ranges
InactiveUS20040149915A1Prevent reversalGood choiceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBroadbandWavelength range
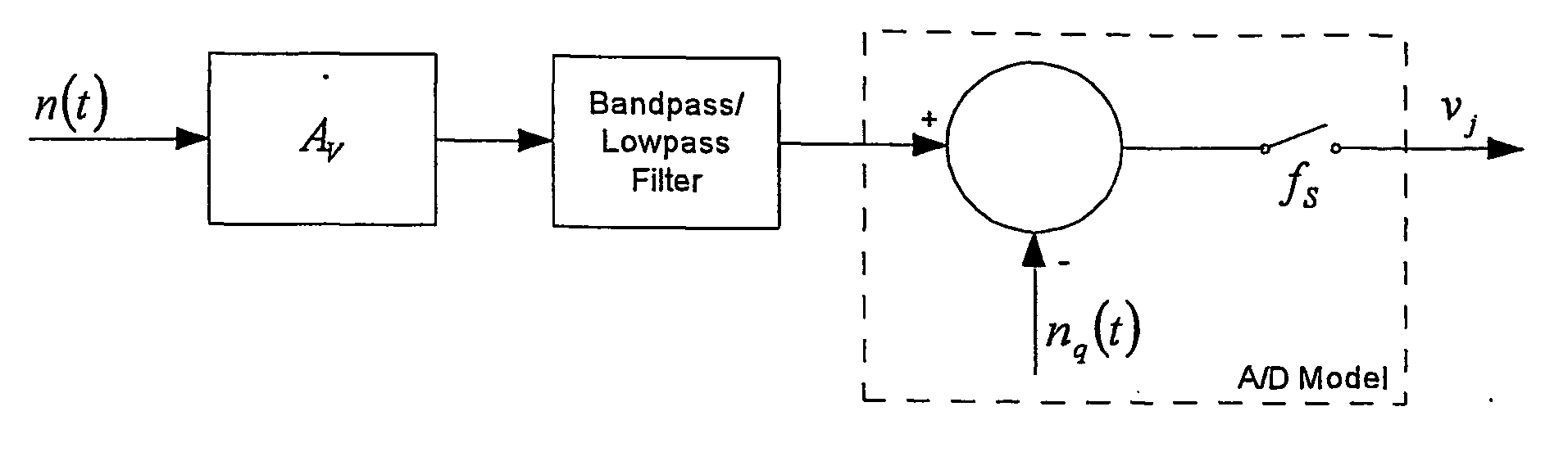
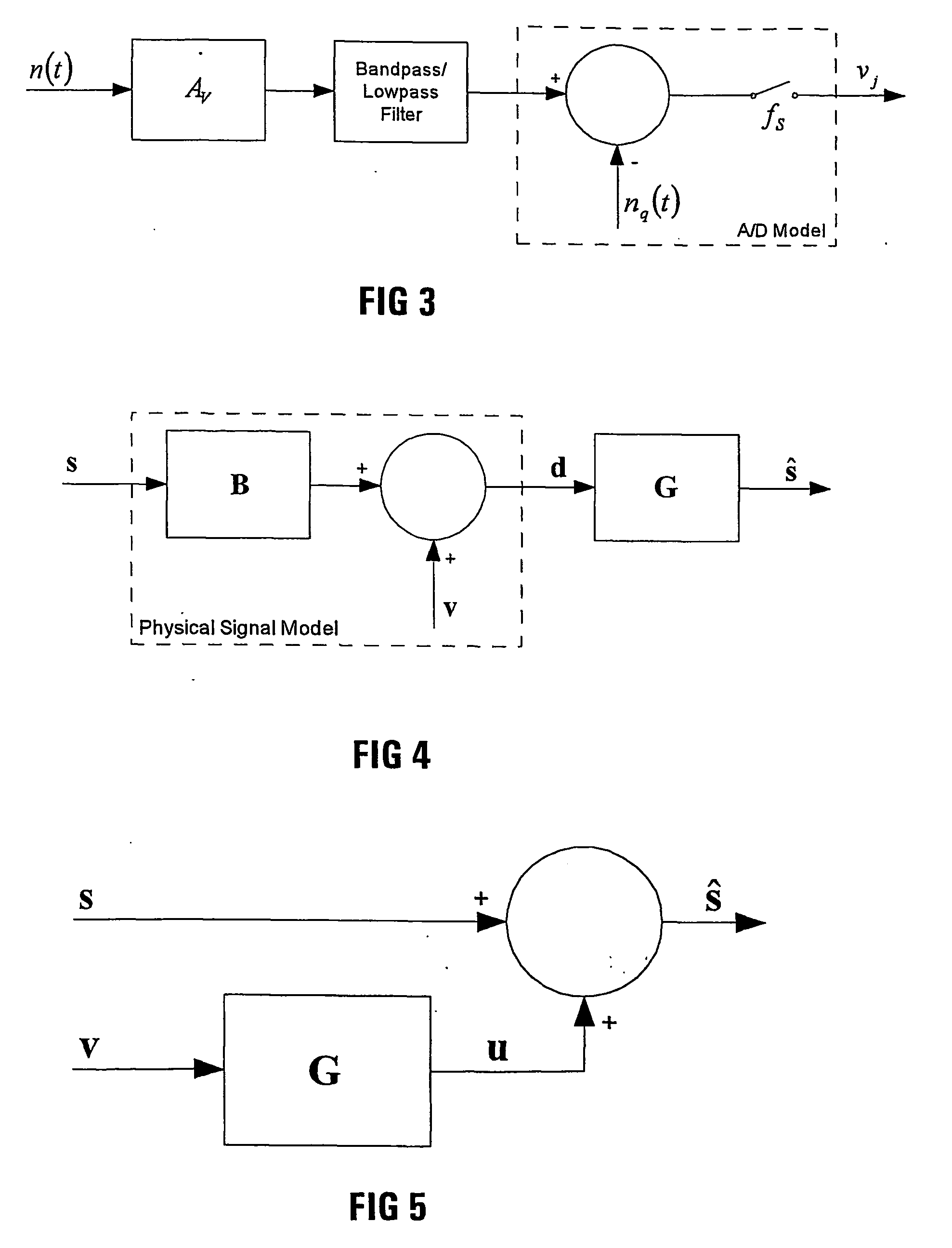
The invention provides a spectrometer (10) which includes a filter arrangement (16,18), in addition to any option filters (20) for limiting an operational wavelength range of the spectrometer, the filter arrangement (16,18) comprising a plurality of broadband optical filters or broadband optical filter areas each of known transmission and being located or selectively locatable in a path of collected incident spectral radiation (44). The spectrometer further includes at least one detector (24) arranged to measure the spectral radiation passing through at least one of the broadband filters located in the path of collected incident spectral radiation, and signal-processing means (34) for recovering the spectrum of the collected spectral radiation from measurements by the detector (24).
Owner:CSIR
Ultraviolet vacuum ultraviolet spectroscopy radiation transfer characteristic test device
The invention relates to a testing technique for testing transmission characteristics of spectral radiation, particularly to a testing device for testing transmission characteristics of ultraviolet-vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiation. The testing device comprises a monochrometer, a standard light source, a vacuum container, a photomultiplier tube disposed in the vacuum container and fixed at one side of a rotary table, a cryogenic pump and a molecular pump respectively communicated with the cavity of the vacuum container via two gate valves, a dry vacuum pump communicated with the cavity pipeline of the vacuum container, and a cryogenic unit communicated with the vacuum container via a pipeline, wherein a flange interface is provided at one end of the vacuum container and used for alternatively connecting with the monochrometer or standard light source; the movement platform capable of performing translational movement with respect to the vertical direction of the axial line of the interface is disposed in the vacuum container, and the rotary table is disposed on the movement platform. The invention can be used for high-precision calibration of the spectral radiation brightness and the spectral irradiance responsibility of the entire machine of an ultraviolet spectra remote sensing instrument; and can be used for testing the spectral responsibility of an ultraviolet detector and testing the spectral transmission characteristics of an ultraviolet optical element.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
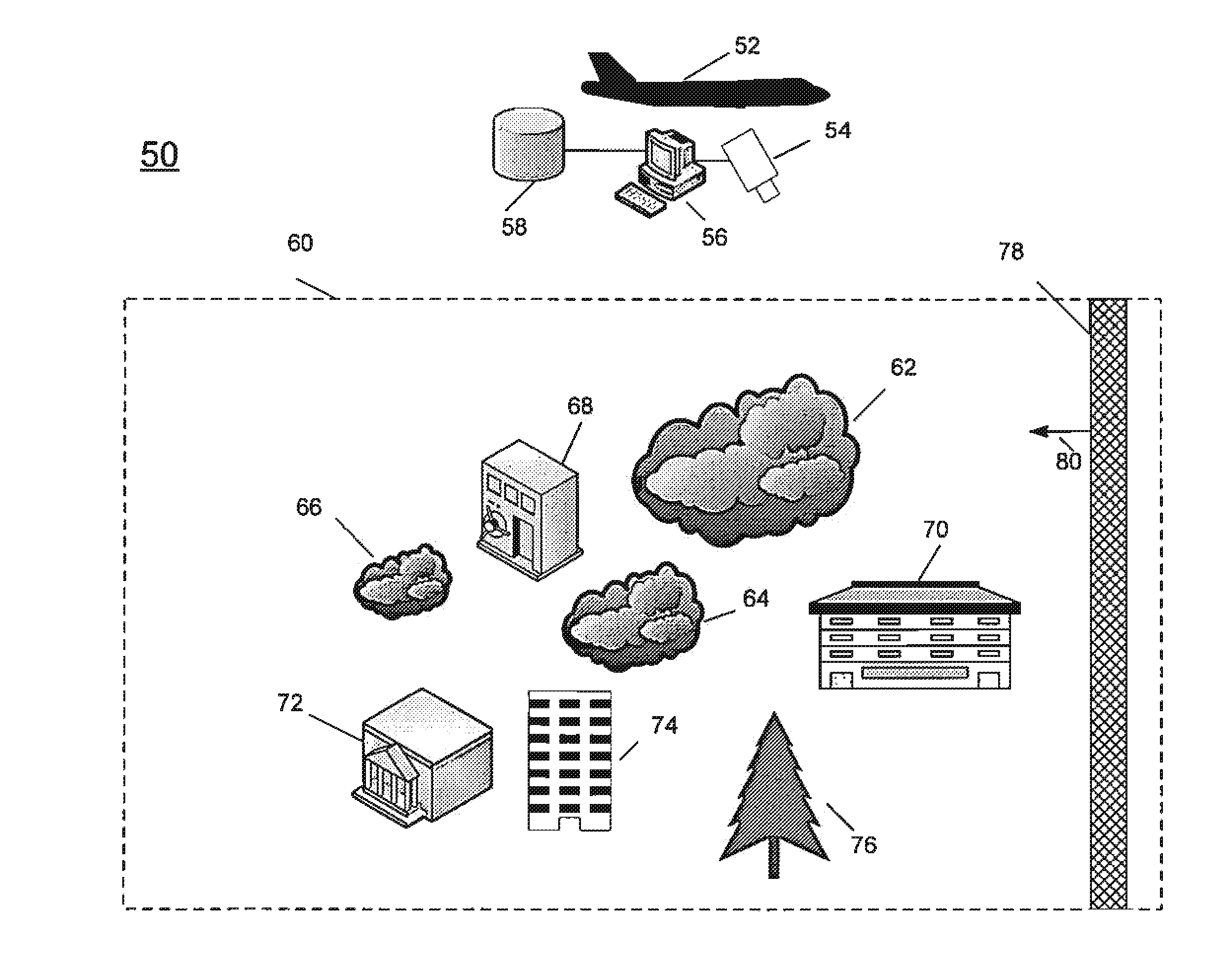
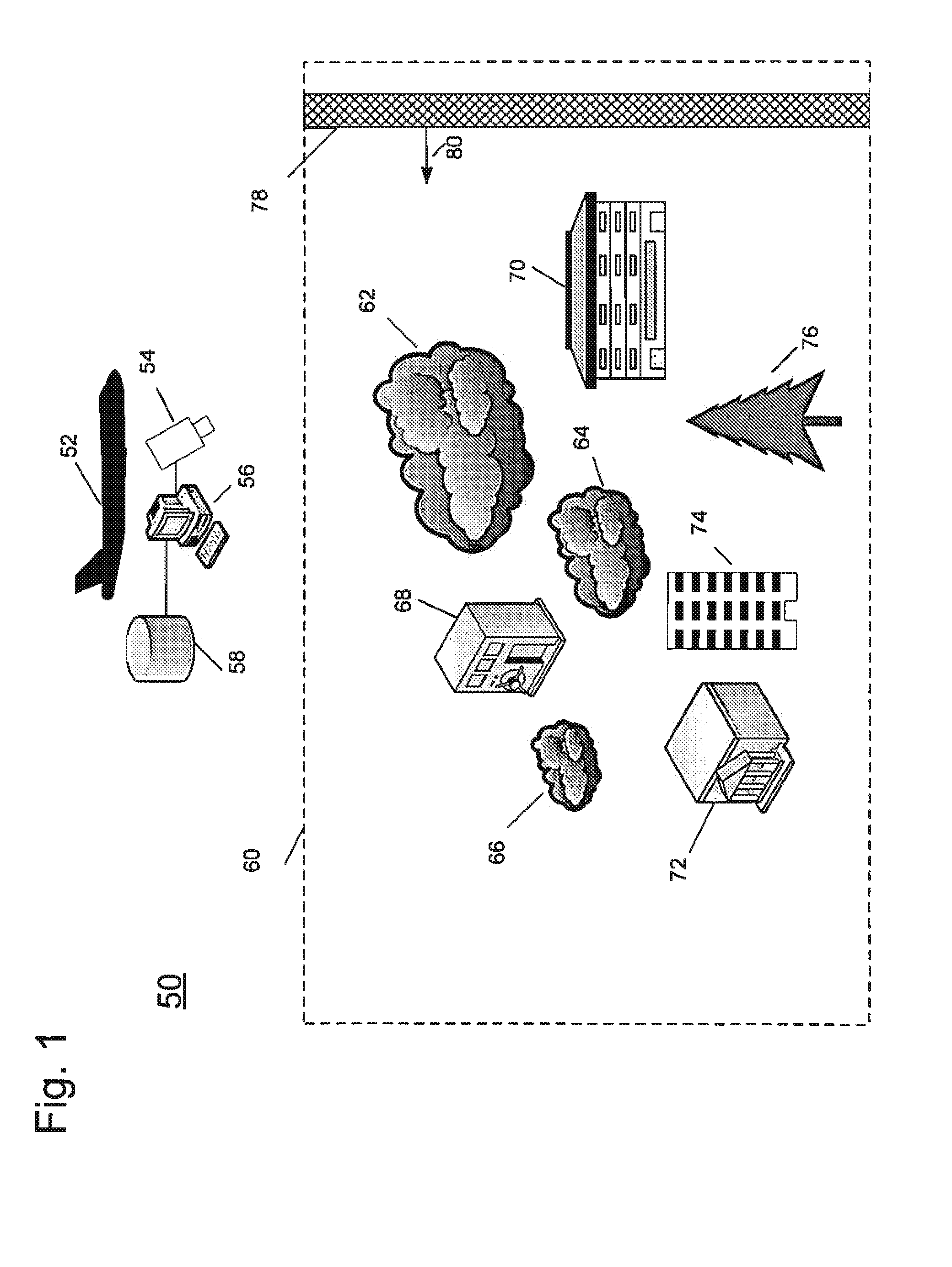
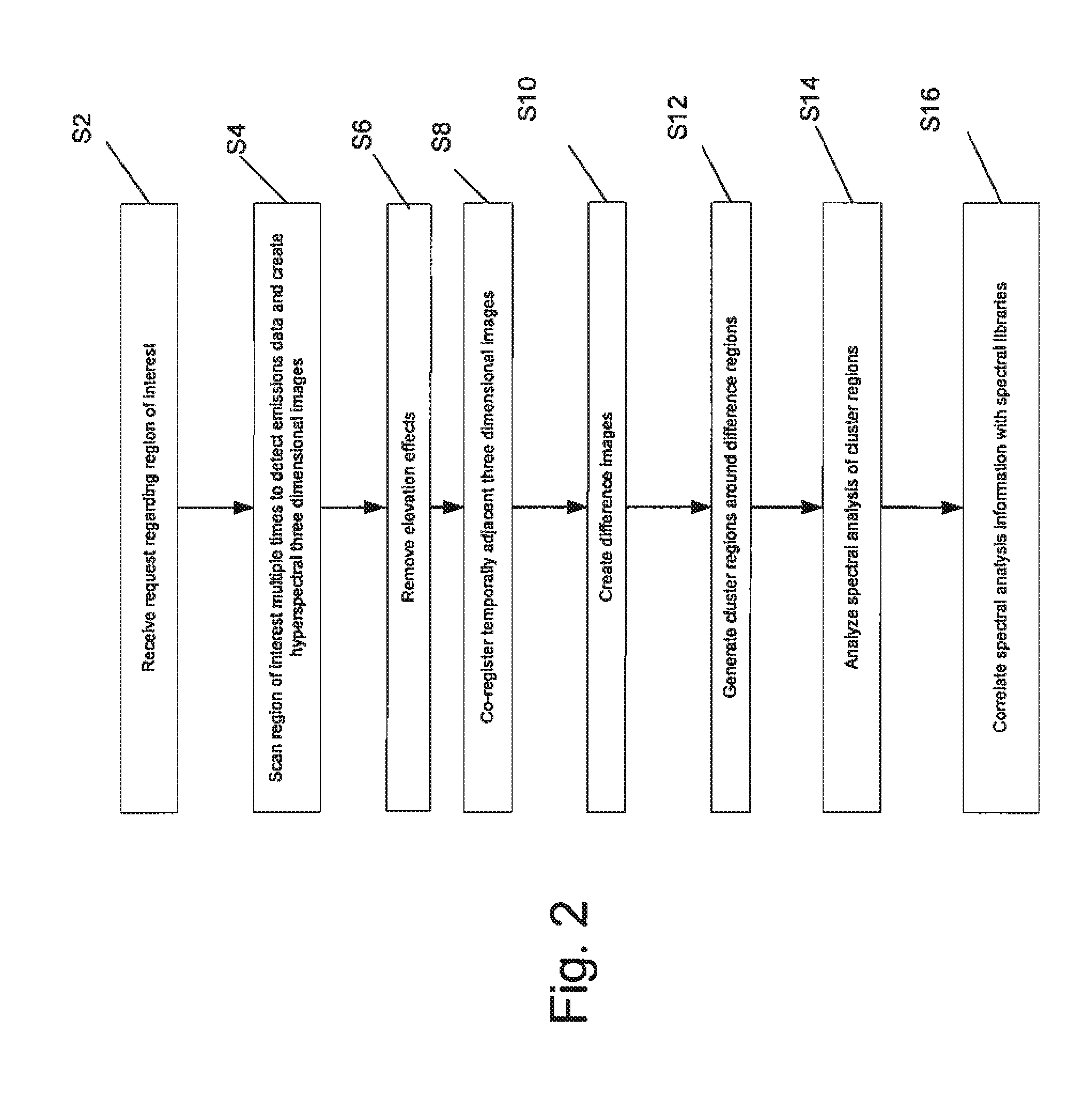
System and method for detecting, tracking and identifying a gas plume
A system and method for detecting, tracking and identifying a gas plume. The system comprises a processor and a detector in communication with the processor. The detector is effective to detect spectral radiance from a region of interest to detect first and second detected spectral radiance data with a known time difference. A database is in communication with the processor, the database includes a library. The processor is effective to create at least a first image and a second image from the first and second detected spectral radiance data and co-register the first and second images to produce a first co-registered image and a second co-registered image. The processor is further effective to subtract the first co-registered image from the second co-registered image to produce a difference image and generate a cluster region around a difference region in the difference image. The processor is further effective to analyze the spectral radiance from the cluster region to produce a spectral characteristic curve; and correlate the spectral characteristic curve against the library to identify the gas plume.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Laser heating device and laser heating method
InactiveCN101107501AAvoid burnsStable temperature controlLaser detailsPhotometryInfraredLaser heating
A laser heating device and a laser heating method enabling soldering that does not burn the periphery and resin bonding that does not burn resin by detecting a temperature change when solder or resin at a processing point is melted and an abnormal heating that may indicate a possible burn occurrence. An IR sensor (9) generates a signal based on the integrated value of the spectral radiation luminance of an IR ray radiated from solder to be heated. Prior to an actual soldering, a relational expression between the calibration values of an output signal from the IR sensor (9) and an actual master solder measuring temperature is determined in advance. At an actual soldering, an IR ray radiated from solder (3) is received by the IR sensor (9) and the temperature of the solder (3) is calculated based on an output signal from the IR sensor (9) and the above relational expression.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
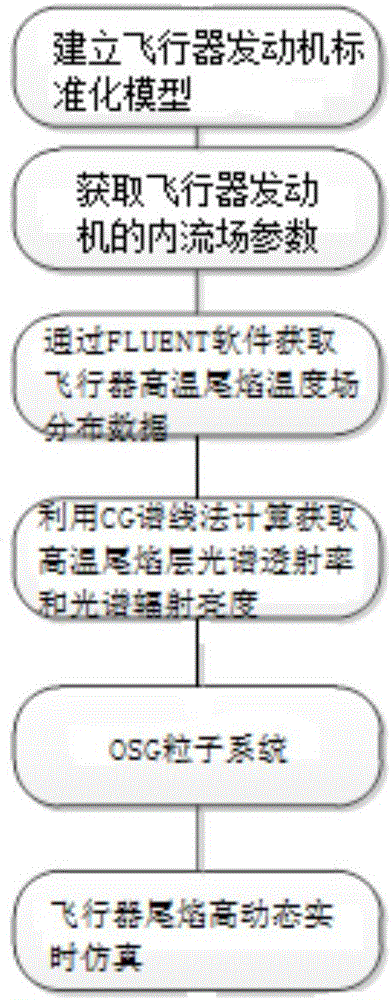
Fast calculation and dynamic simulation method of aircraft tail flame infrared radiation
InactiveCN106599400ARealize dynamic real-time simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsReal-time simulationSpectral transmittance
The present invention discloses a fast calculation and dynamic simulation method of aircraft tail flame infrared radiation. The method comprises a first step of building a standard model of an aircraft engine, and acquiring an internal flow field parameter of the aircraft engine; a second step of inputting the internal flow field parameter acquired in the first step into FLUENT software, and acquiring high temperature tail flame temperature field distribution data of the aircraft by using the FLUENT software; a third step of calculating to acquire a layer spectral transmittance and a layer spectral radiation brightness of high temperature tail flame by using a CG spectral method according to the high temperature tail flame temperature field distribution data obtained in the second step; and a forth step of assigning the layer spectral transmittance and the layer spectral radiation brightness of the high temperature tail flame acquired in the third step to an OSG particle system, and realizing high dynamic real-time simulation of the aircraft tail flame by using the OSG particle system. Through adoption of the method, problems in the prior art that simulation has high calculation difficulty, poor real-time performance and cannot be applied to dynamic simulation are solved.
Owner:西安天圆光电科技有限公司
Method for calibrating a spectroradiometer
ActiveCN107209059AGuaranteed synchronicityStable and transportableRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectroradiometerUsability
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a spectroradiometer (1), comprising the following method steps: capture of light measurement data by the measurement of the radiation of at least one standard light source (4) using the spectroradiometer (1) that is to be calibrated; derivation of calibrated data from the light measurement data by the comparison of the captured light measurement data with known data of the standard light source (4); and calibration of the spectroradiometer (1) according to the calibration data. The aim of the invention is to provide a reliable and practical method for calibrating the spectroradiometer (1). In particular, the synchronism of spectroradiometers (1) situated in different locations (9, 10, 11) is to be produced simply and reliably. To achieve this aim, the validity, i.e. the usability, of the standard light source for the calibration is checked by a comparison of the light measurement data of the standard light source (4) with light measurement data of one or more additional standard light sources (4) of the same type, the validity of the standard light source (4) being established if the deviations of the light measurement data of the standard light sources (4) from one another lie below predefined limit values, and / or the standard light source (4) is measured using two or more standard spectroradiometers (1') of the same type or of different types, the validity of the standard light source (4) being established if the deviations of the light measurement data from one another, said data being captured using the different standard spectroradiometers (1'), lie below predefined limit values.
Owner:仪器系统有限公司
Method for manufacturing organic light emitting element, and organic light emitting element
ActiveUS20160020429A1Solve low luminous efficiencyIncreased durabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic electrodePhoto irradiation
A method of manufacturing an organic light emitting element equipped with a transparent substrate, an internal light extracting layer, and a transparent metal electrode includes: forming the internal light extracting layer on the transparent substrate, and forming the transparent metal electrode on the internal light extracting layer. The step of forming the internal light extracting layer includes: applying a coating solution onto the transparent substrate into a predetermined pattern, the coating solution containing a light scattering particle having an average particle size of 0.2 μm or more and less than 1 μm and a refractive index of 1.7 or more and less than 3.0 and a hydroxy-containing solvent, and drying the applied patterned coating solution through irradiation with infrared light having a proportion of 5% or less of a spectral radiance at a wavelength of 5.8 μm to a spectral radiance at a wavelength of 3.0 μm.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
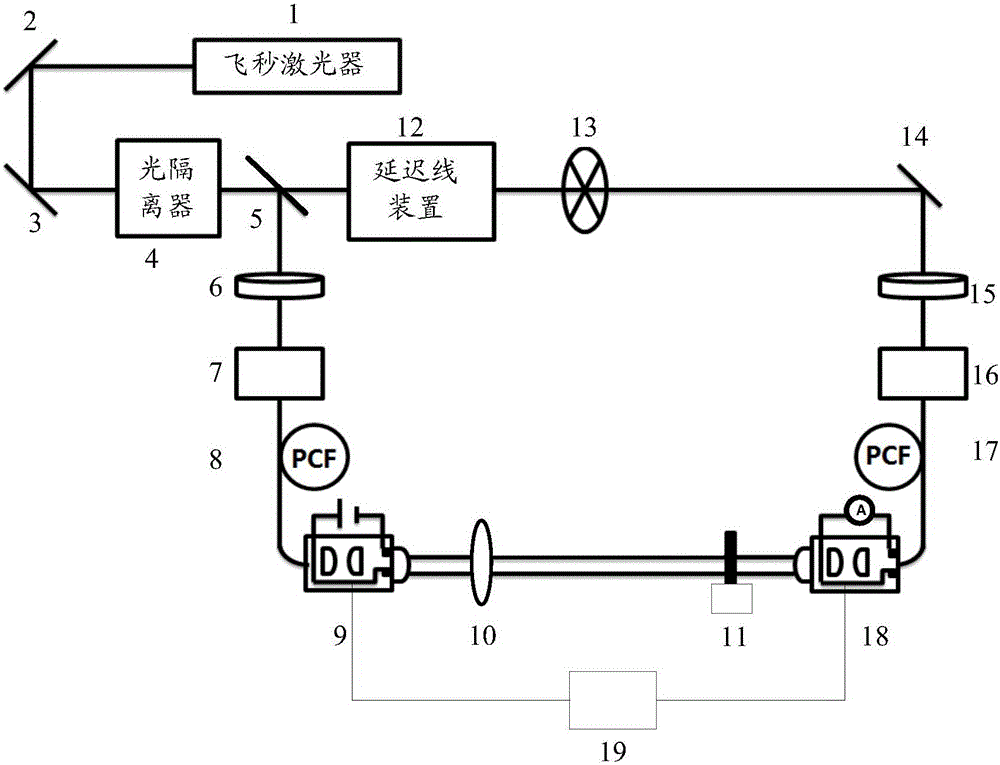
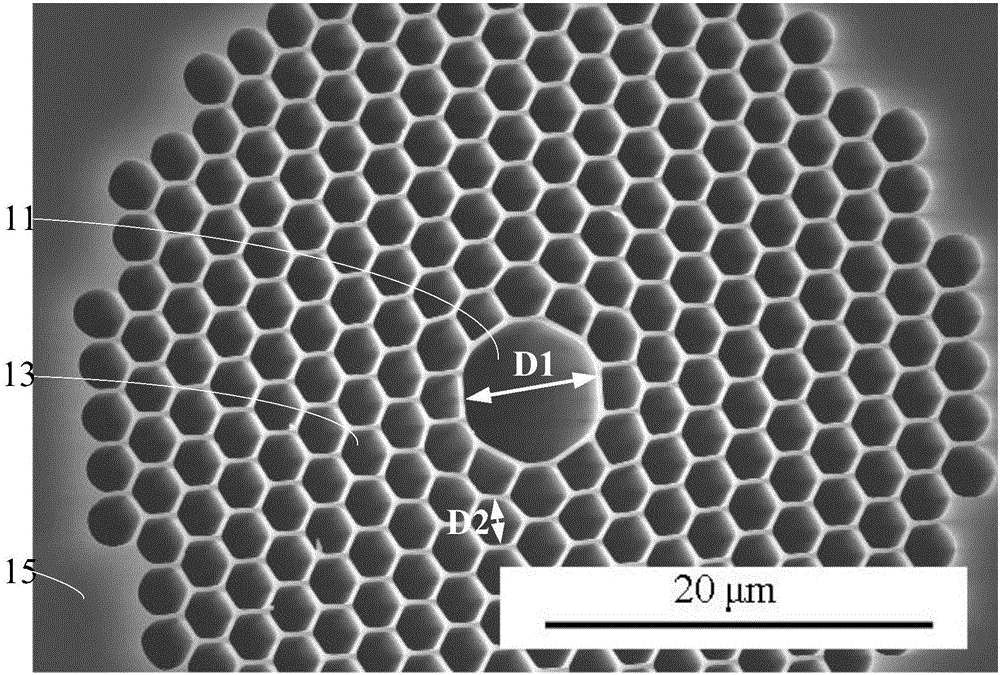
Terahertz time domain spectral radiation and detecting device
InactiveCN105737984AHigh energyAvoid inconvenienceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterFiber chromatic dispersion
The invention relates to a terahertz time domain spectral radiation and detecting device. In the terahertz time domain spectral radiation and detecting device, femto second laser which is emitted from a femto second laser device is divided into pump light and probe light. Furthermore the pump light and the probe light are transmitted in a hollow photonic crystal fiber. In the terahertz time domain spectral radiation and detecting device, through reasonably selecting central wavelength of a pulse which is output from the femto second laser device, a two-order fiber dispersion which is generated in transmission of a laser pulse in the hollow photonic crystal fiber is a negative value, and the two-order fiber dispersion is neutralized with a positive dispersion which is generated by an optical isolator, a beam splitter, etc. The terahertz time domain spectral radiation and detecting device prevents inconvenience and cost of grating or a pair of prisms for compensating the dispersion. Secondly, because the pulse is basically transmitted in the hollow photonic crystal fiber, the energy of the pulse with pulse width of dozens of femto seconds can reach several hundreds of nanojoules. Furthermore pulse width increase because of self phase modulation is prevented. A high-energy laser pulse is supplied for a terahertz radiation device and a detecting device.
Owner:CHINA COMM TECH CO LTD +1
Method and device for calibrating vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometers
ActiveCN106885632AGuaranteed accuracyImplement calibration workSpectrum investigationSpace environmentIlluminance
The invention relates to a method and a device for calibrating vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometers. The method comprises spectral radiant luminance responsivity calibration, spectral radiant irradiance responsivity calibration and / or wavelength accuracy calibration, which are conducted in an oil-free vacuum chamber. The device comprises a spectral radiant luminance responsivity calibration mechanism, a spectral radiant irradiance responsivity calibration mechanism, and a wavelength accuracy calibration mechanism. There is no calibration device suitable for vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometers in our country at present. By using the method and the device for calibrating vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometers of the invention, the multiple parameters of a vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometer can be calibrated in a ground laboratory before emission, and therefore, the accuracy of data acquired by the vacuum ultraviolet spectral radiometer is guaranteed. The method and the device are of great significance to the acquisition of spectral information of the sun, the earth surface and other sun-earth space environments.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENXING METROLOGY & TEST INST
Imaging spectrometer radiation parameter and imaging parameter calibration device and method
ActiveCN109387284AImprove calibration accuracyMany calibration parametersSpectrum investigationRadiometerVisible near infrared
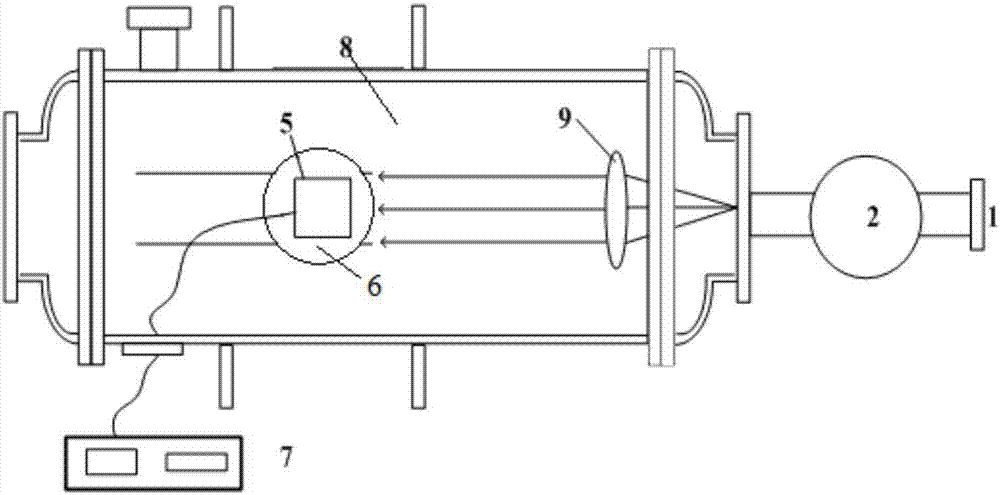
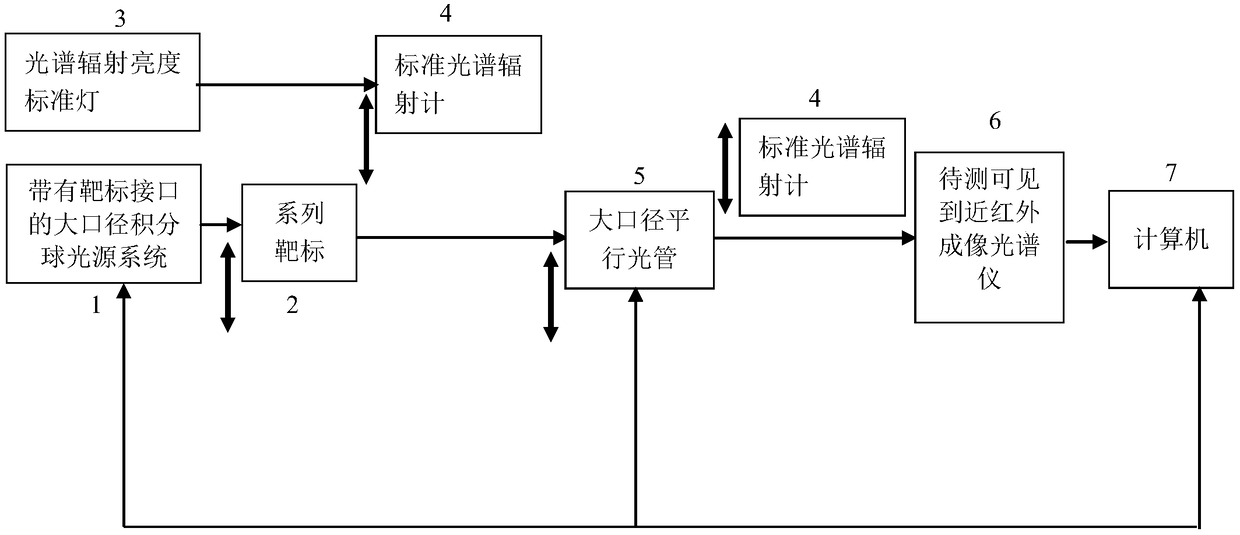
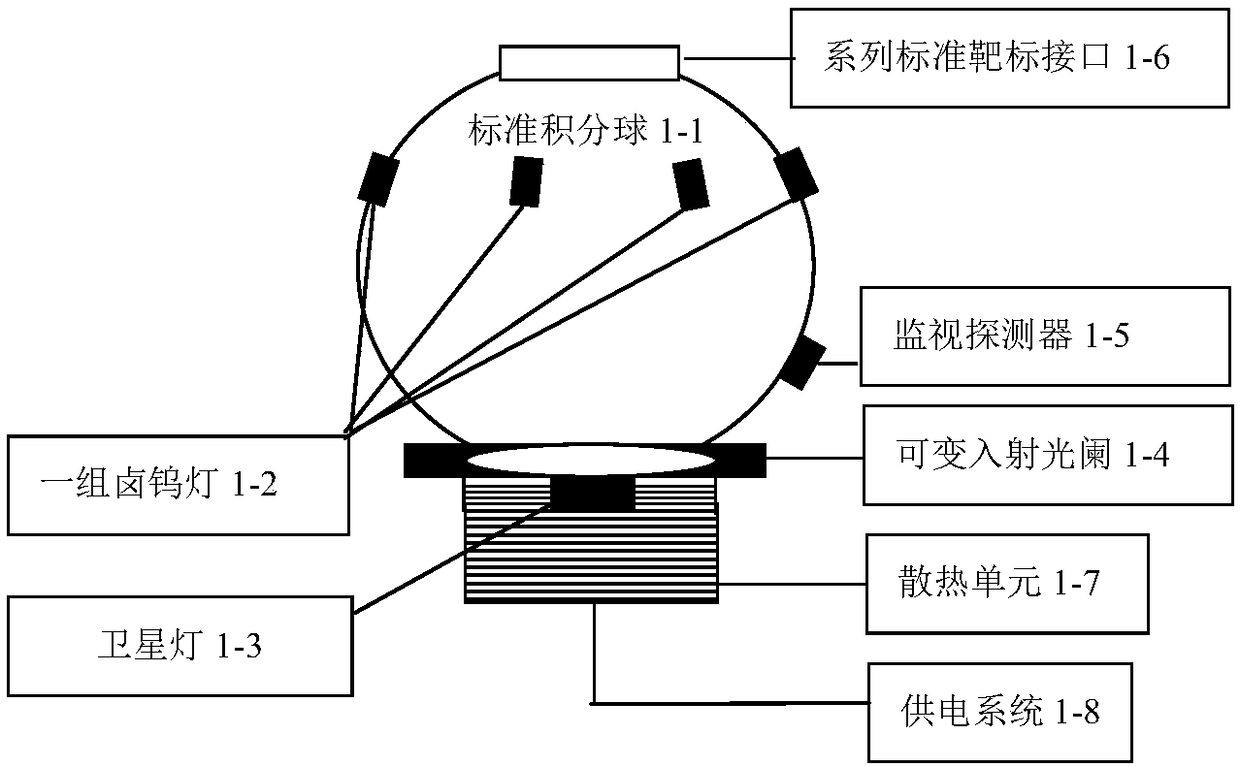
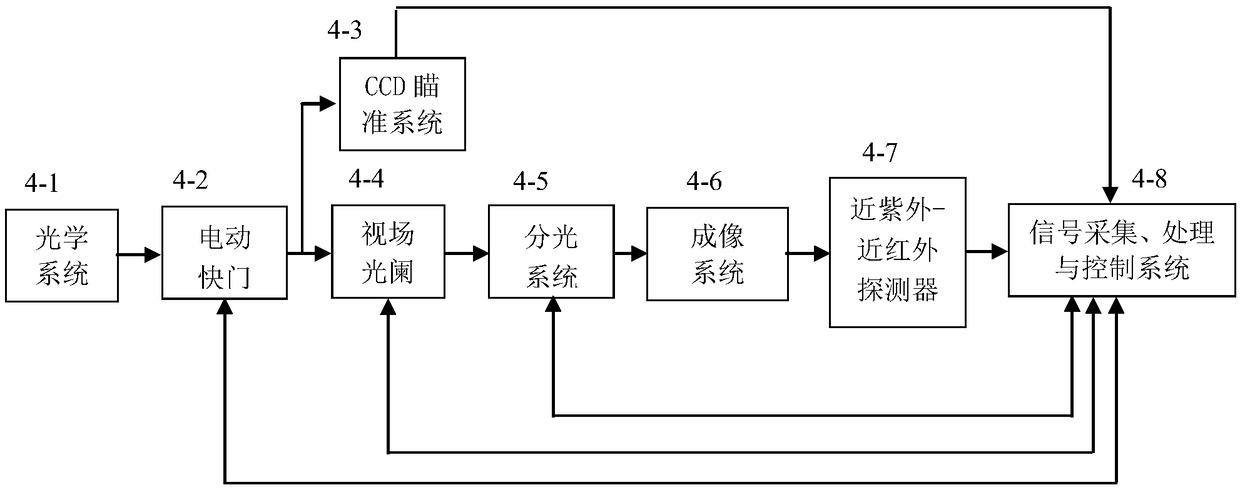
The invention provides a visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer radiation parameter and imaging parameter calibration device and method. The calibration device and method use a high-stability large-caliber standard integrating sphere light source with a target interface to be combined with a large-caliber collimator to form collimation radiation which is received by a measured visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer. A standard spectroradiometer calibrated by a spectral radiance standard lamp calibrates the spectral radiance of the exit of the integrating sphere light source and the collimation radiation respectively, so as to achieve full-band radiance high-accuracy calibration of the visible near-infrared imaging spectrometer of a camera system and a telescope system. The measuredvisible near-infrared imaging spectrometer is used to image a series of standard targets mounted on the target interface of the large-caliber standard integrating sphere light source, so as to realize imaging parameter calibration of the measured imaging spectrometer.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
Calibration method and system for relative spectral-response characteristic of CCD imaging device
InactiveCN101294867ACalibration method is simpleThe calibration method is validSpectrum investigationTesting optical propertiesRadiative transferSpectral response
The invention relates to a method for calibrating the relative spectral response characteristic of a CCD imaging device. The method comprises the following steps: A. taking a light source with known spectral radiation distribution as a measurement object, utilizing the CCD imaging device to be calibrated for the imaging of the measurement object, and acquiring and analyzing the image to obtain a measured value; B. changing the spectral radiation flux entering the CCD imaging device through adjusting the thermodynamic temperature of the light source and / or adopting a color filter; C. constructing an equation set of mathematical physics for describing the corresponding relation between the measured value and the relative spectral response characteristic according to the known equation of mathematical physics of radiative transfer of the CCD imaging device; D. taking the measured value of the CCD imaging device under different spectral radiation flux as known quantity and solving the equation of mathematical physics, so as to calibrate the relative spectral response characteristic of the CCD imaging device. The invention further discloses a system for calibrating the relative spectral response characteristic of the CCD imaging device. The method is simple and efficient, and can avoid the introduction of instrument measurement transfer errors.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Real-time online monitoring method of temperature of molten steel in RH refining furnace
InactiveCN104215334ASolving the Difficulties in Real-time On-line Monitoring of Refining TemperatureOvercoming hysteresisRadiation pyrometrySteelmakingOptimal control
The invention discloses a real-time online monitoring method of temperature of molten steel in an RH refining furnace. An infrared detector arranged at the top of the RH refining furnace is used to acquire infrared thermograms of the molten steel, slag, a wall and scale in a target area, to be measured, in the RH refining furnace; through theoretical analysis on radiation features of the molten steel, the slag, the wall and the scale, the interior conditions of the RH refining furnace and wave characteristic of the molten steel, the infrared thermograms are processed by fuzzy C-means clustering and threshold segmentation, the infrared thermogram of the target molten steel is determined, a target positive radiation area is determined, average grey level of the target positive radiation area is calculated and converted into infrared spectral radiation intensity of the target molten steel, and the temperature of the molten steel is calculated by a molten steel temperature measuring principle model and an iterative inversion algorithm. The method has the advantages that the temperature of the molten steel can be measured continuously in real time, resource waste is greatly decreased, labor intensity is greatly decreased for workers, production guidance and implementation of optimal control are favored, and scientific steelmaking and precision steelmaking are achieved.
Owner:HEFEI RUISHI MEASUREMENT & CONTROL ENG TECH
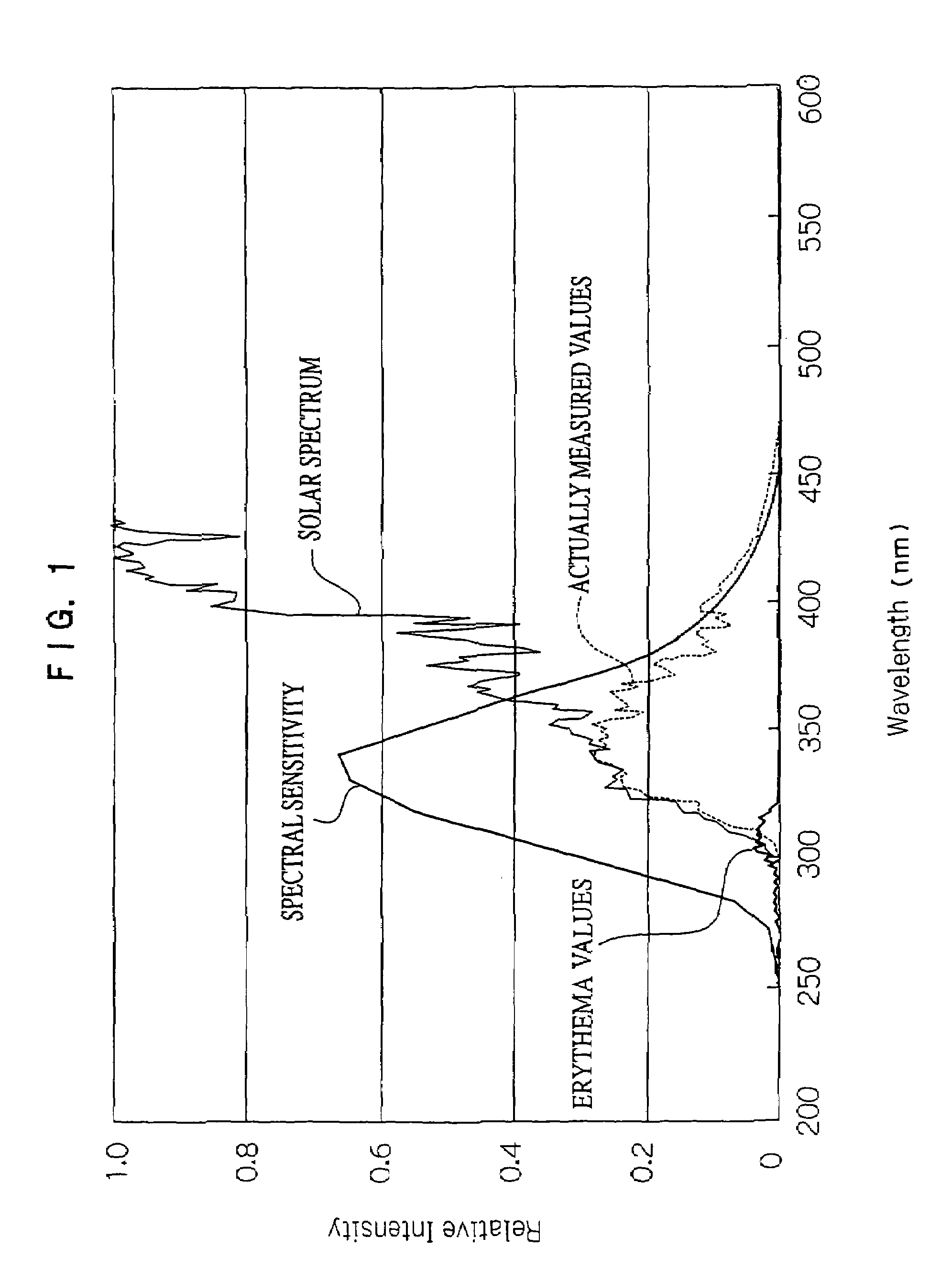
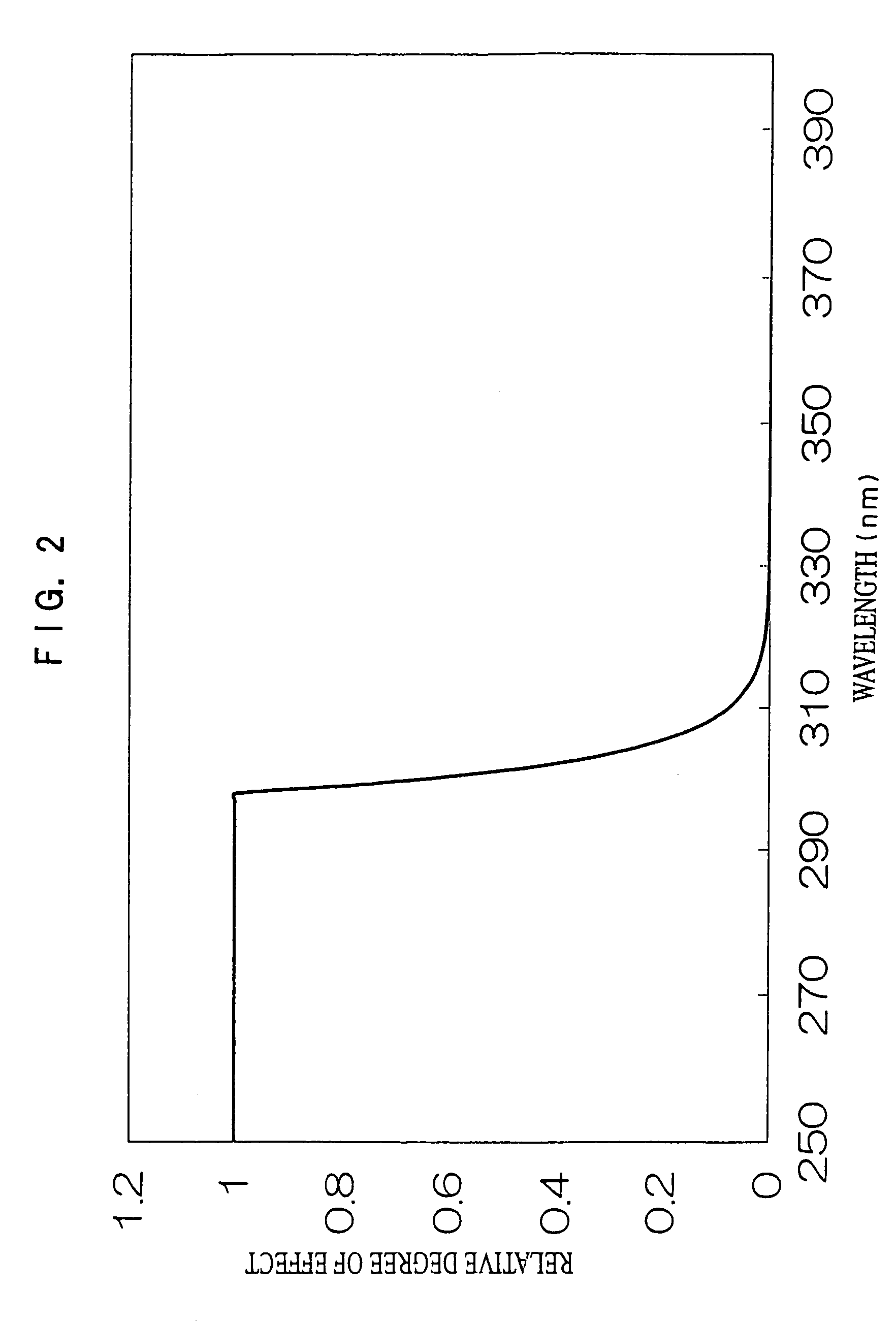
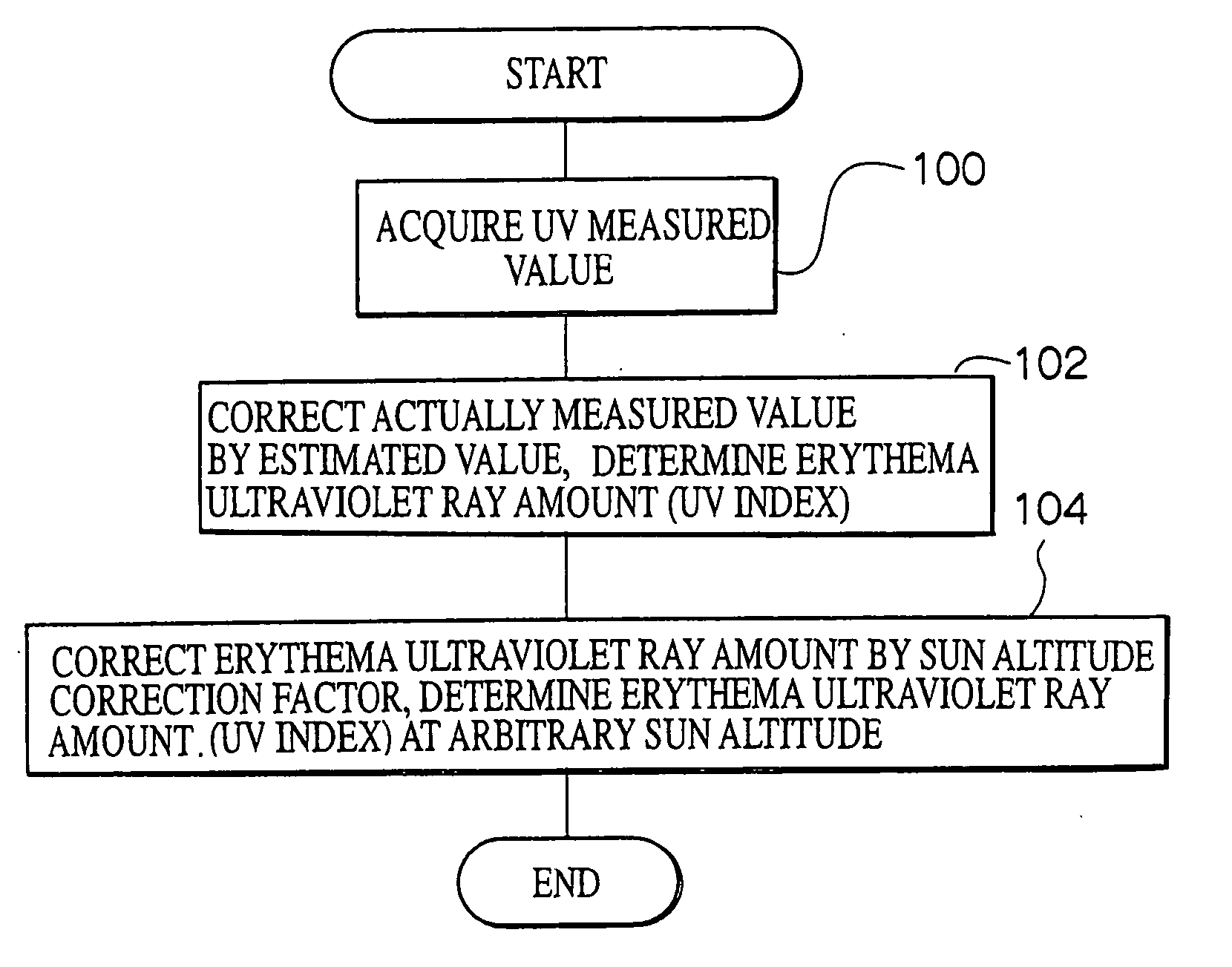
Ultraviolet ray measuring method and ultraviolet ray measuring device
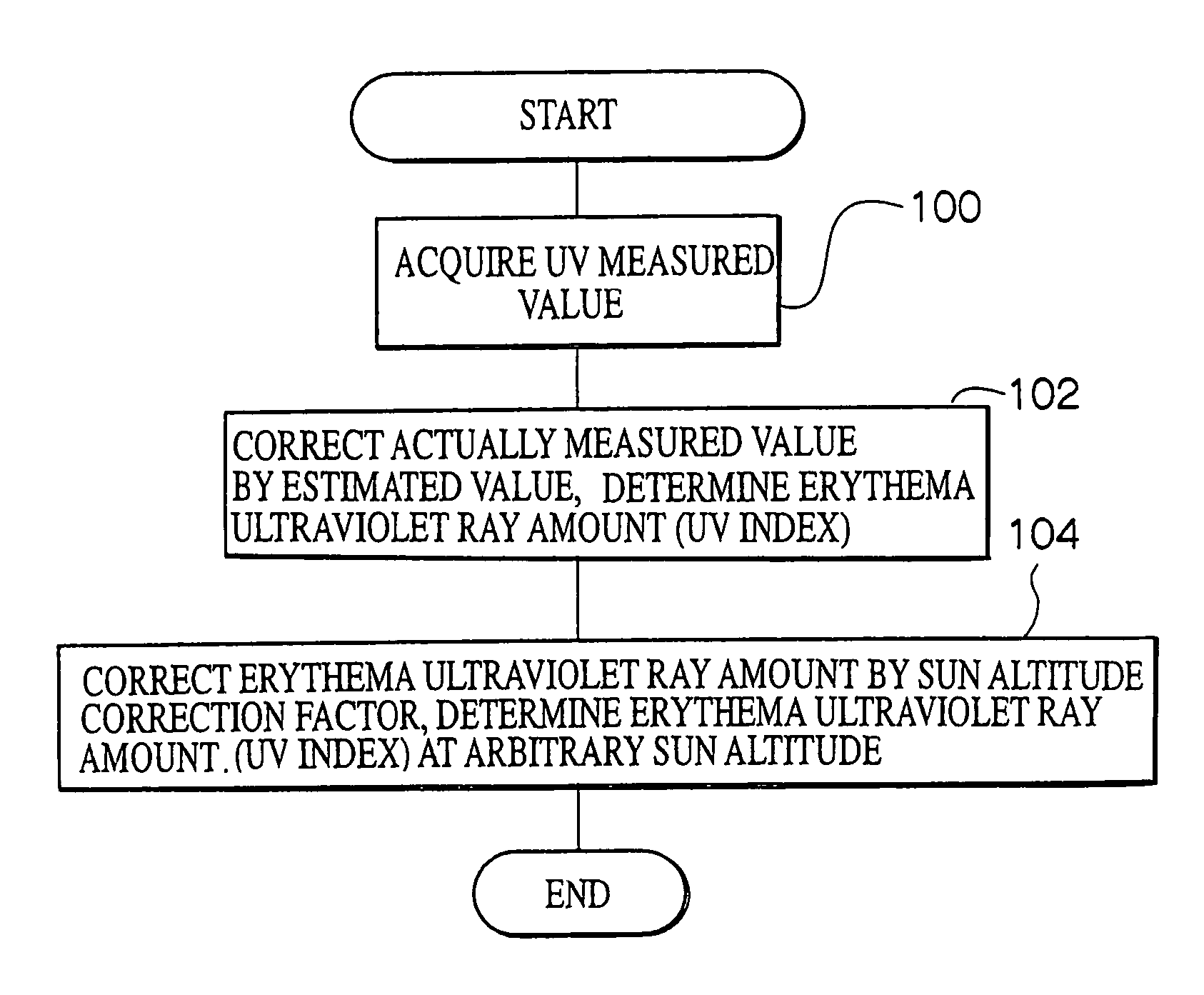
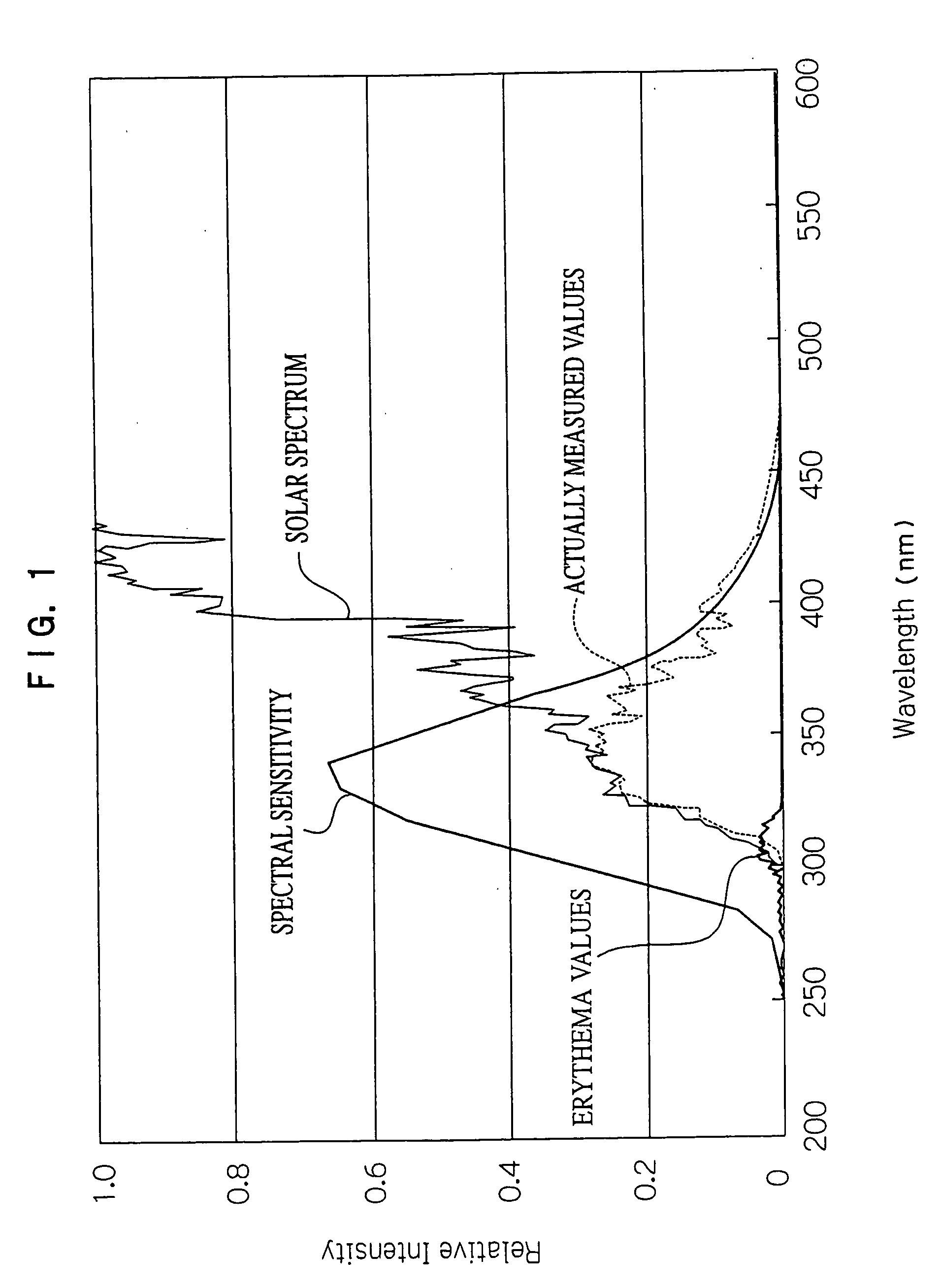
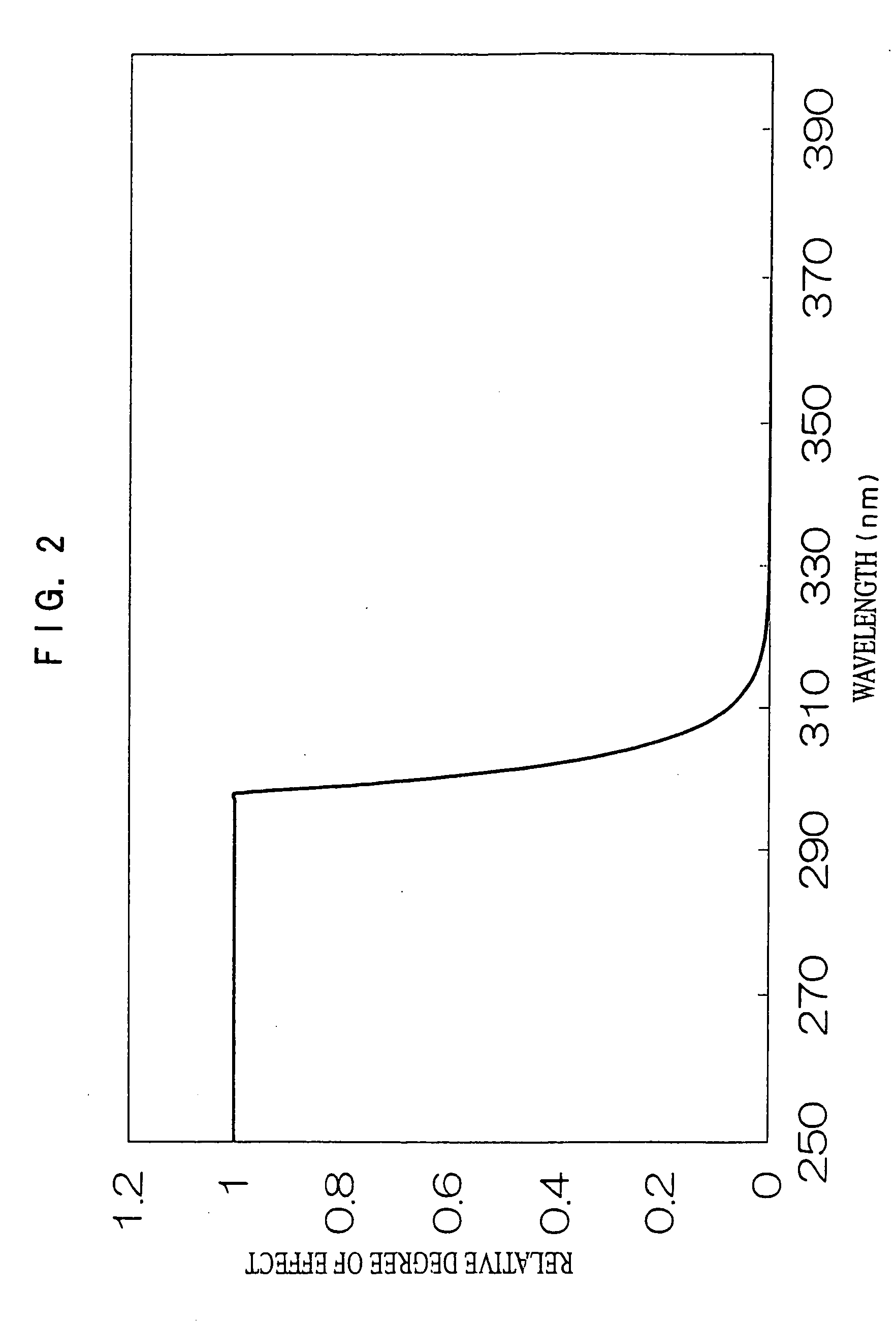
InactiveUS7148489B2Easily and conveniently measureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry for measuring UV lightUltravioletSpectral sensitivity
An ultraviolet ray measuring method using an ultraviolet ray receiving element having a specific spectral sensitivity. The method includes: estimating an estimated value of an entire region from the spectral sensitivity of the ultraviolet ray receiving element and a solar spectral radiation spectrum; estimating an estimated value of a specific region from a specific action curve and the spectral sensitivity and the solar spectral radiation spectrum; and determining specific ultraviolet ray information by, on the basis of the estimated value of the entire region and the estimated value of the specific region, correcting an actually measured value which is measured by the ultraviolet ray receiving element. Further, specific ultraviolet information, which is obtained on the basis of sun altitude information, is also corrected.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
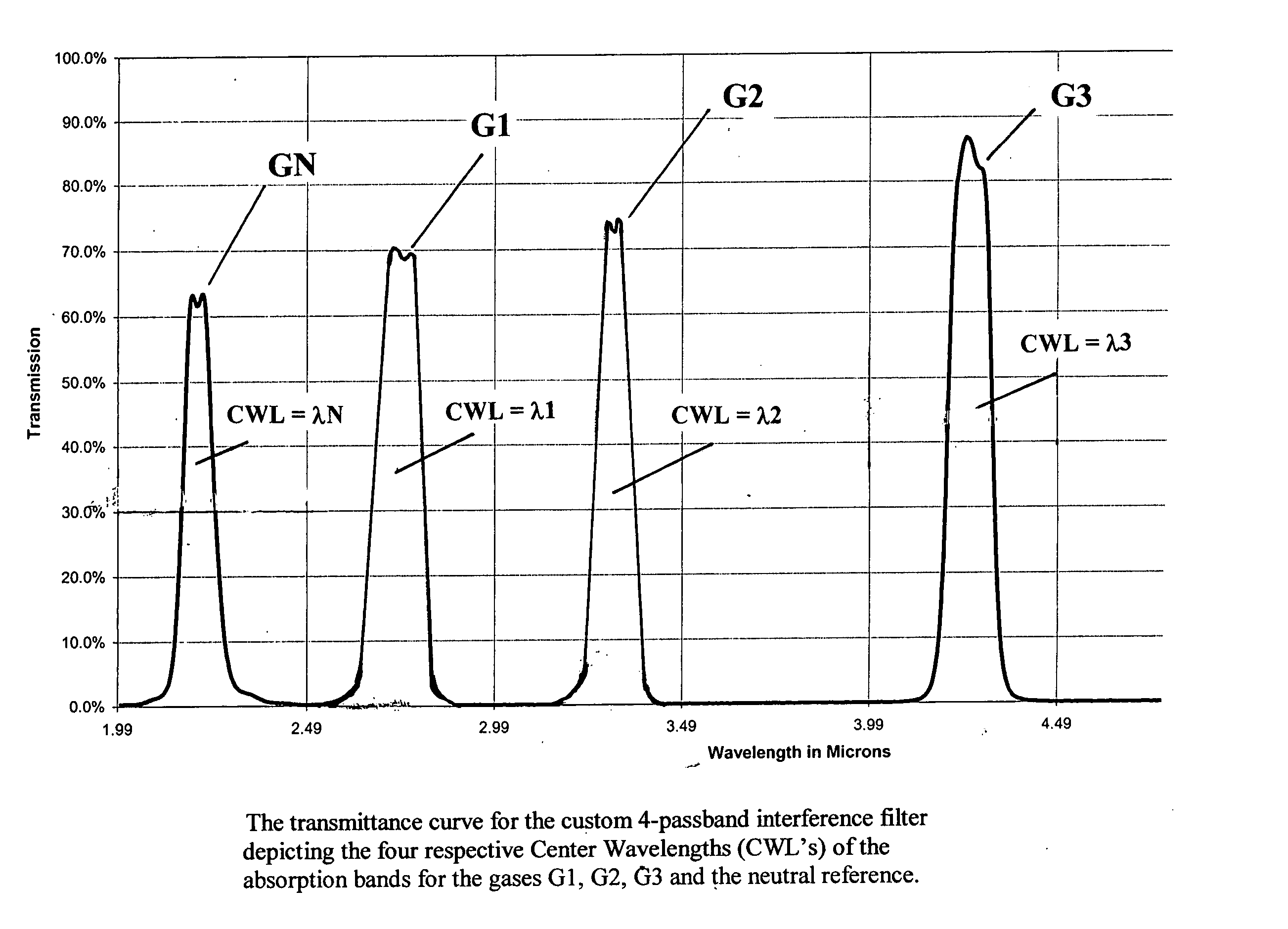
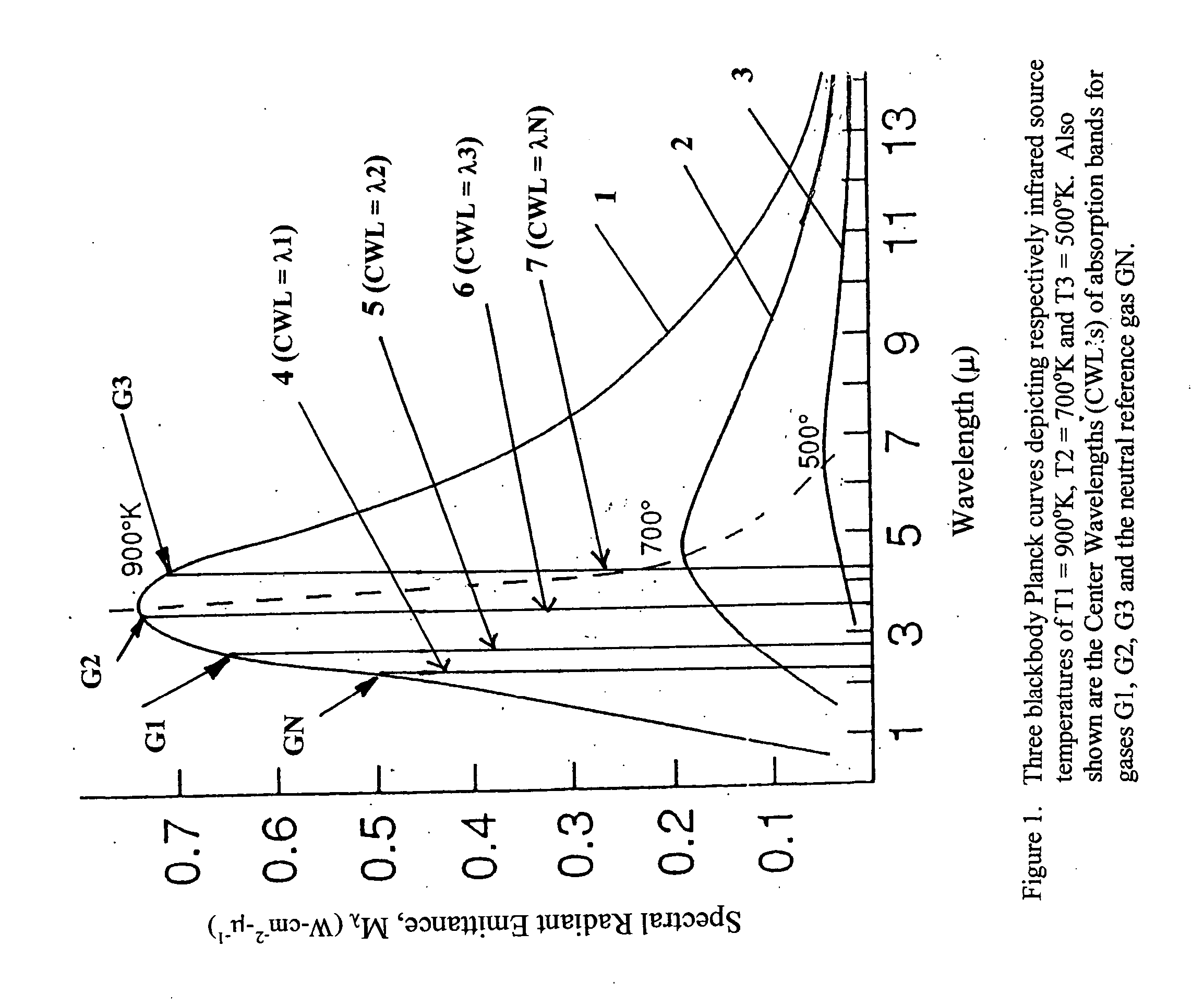
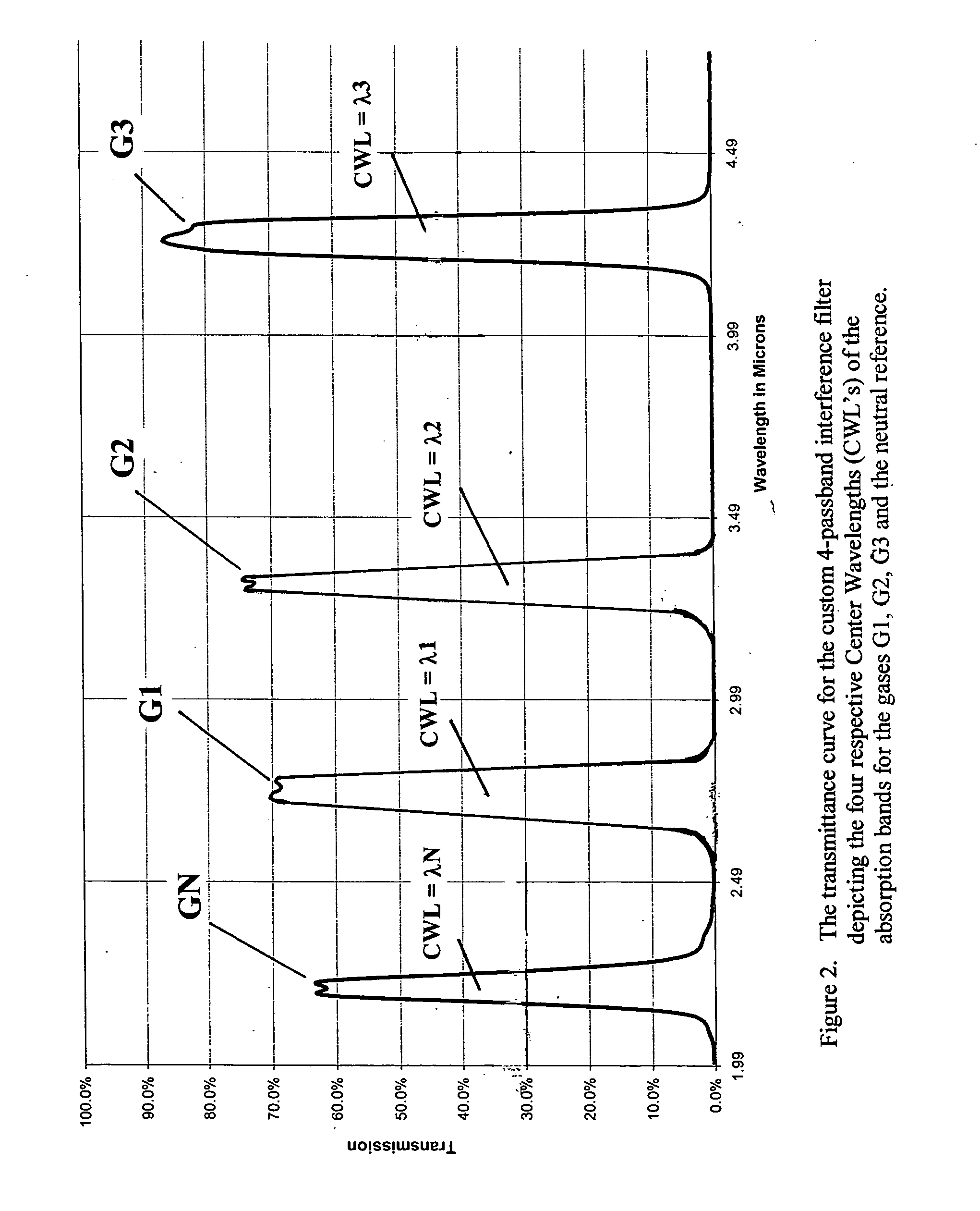
Simple multi-channel NDIR gas sensors
Concentrations of N gas species can be detected from a single beam NDIR gas sensor having a differential infrared source and an (N+1)-passband filter (having a neutral passband and N absorption passbands for N gases) mounted at a single infrared detector by driving the infrared source with N input power levels to render the source into emitting at N distinct temperatures whose radiation outputs are characterized by N corresponding Planck curves which are dependent only upon the respective source temperatures and which link a Spectral Radiant Emittance MsubLamba with wavelength, measuring N detector outputs at the single infrared detector and detecting the concentrations of N different gas species, each of the N gas species having its own unique infrared absorption passband, by (a) setting up N causality relationship equations linking outputs of the detector respectively for N different source temperatures and a set of relevant parameters of the sensor components, (b) determining the values of all of the parameters for the N equations utilizing appropriate boundary conditions except the N concentrations for the respective N gas species, and (c) solving for the N gas concentrations with the measured N detector outputs, there being N equations and N unknowns, when N is an integer of 2 or more.
Owner:AIRWARE INC
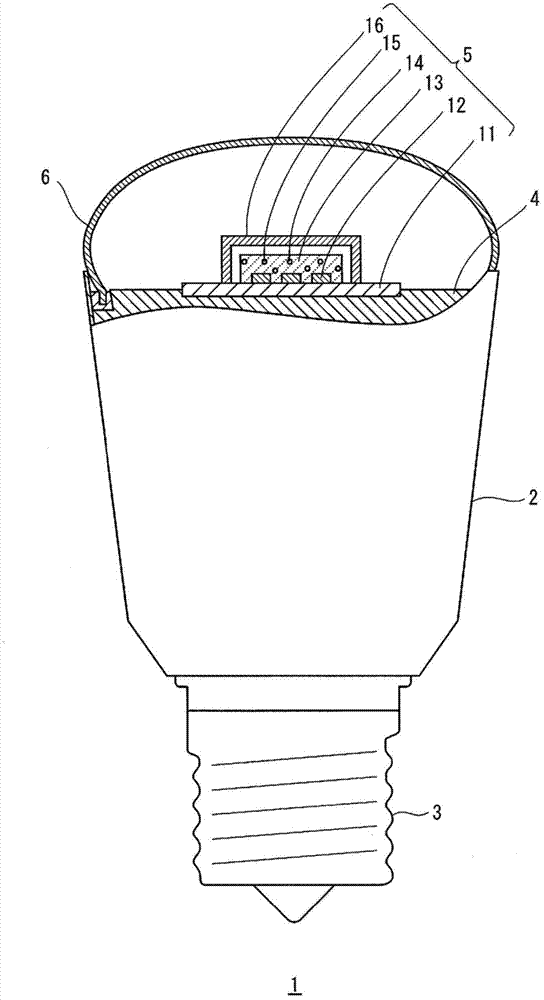
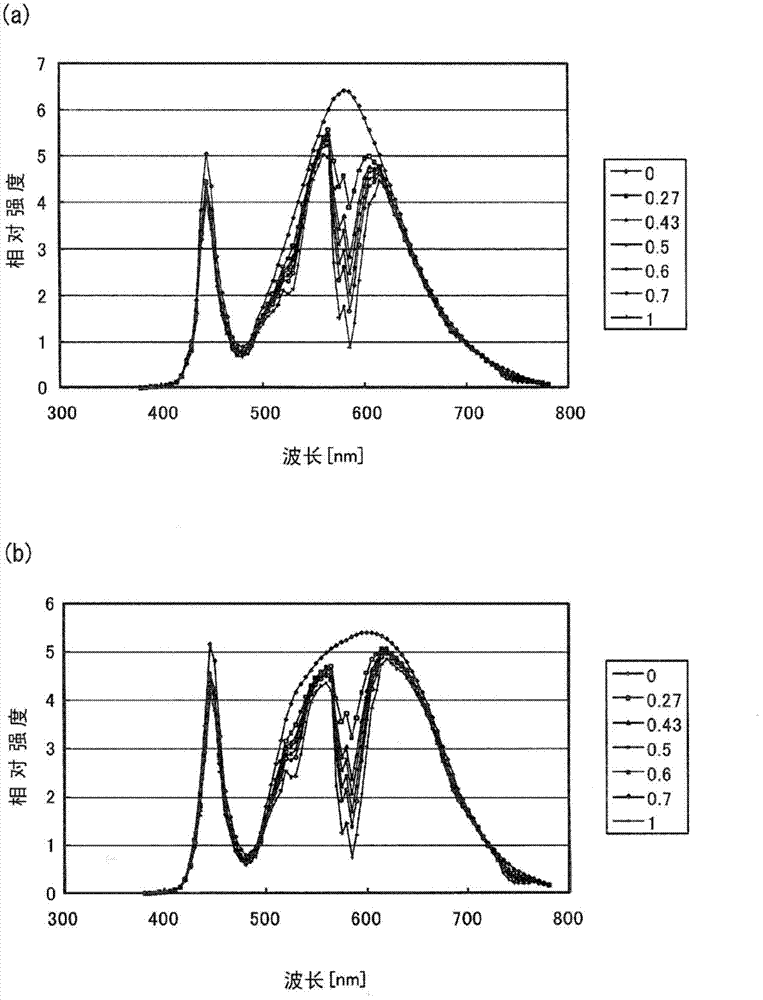
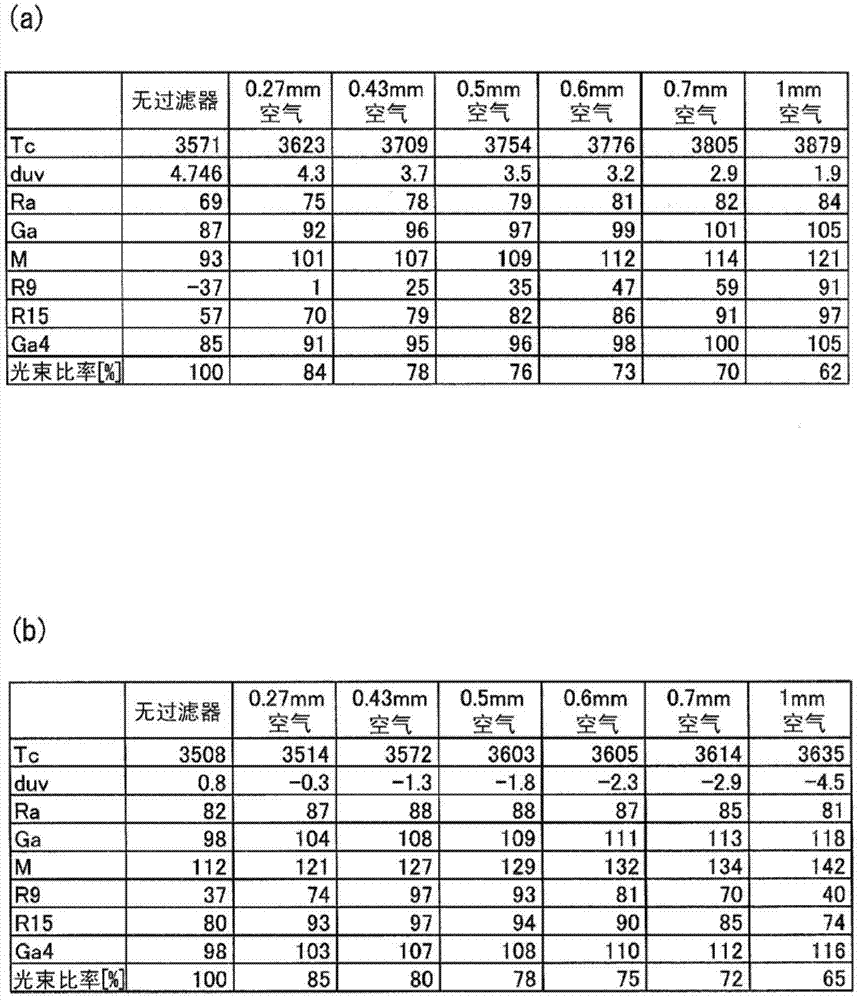
LED lamp, LED illumination device, and LED module
ActiveCN102782396ADecreased spectral radiation intensityPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesPhosphorBright red color
Disclosed is an LED lamp which is capable of having a bright red color look natural. Specifically disclosed is an LED lamp (1) which comprises: an LED module (5) comprising a blue LED (12) that has a main emission peak within the wavelength range of 440-460 nm, a green or yellow phosphor (14) that is excited by the light emitted from the blue LED (12), and a red phosphor (15) that is excited by the light emitted from the blue LED (12) and / or the green or yellow phosphor (14); and a filter (16) that reduces the spectral radiation intensity of at least a part of the wavelength range of 570-590 nm among the light emitted from the LED module (5).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
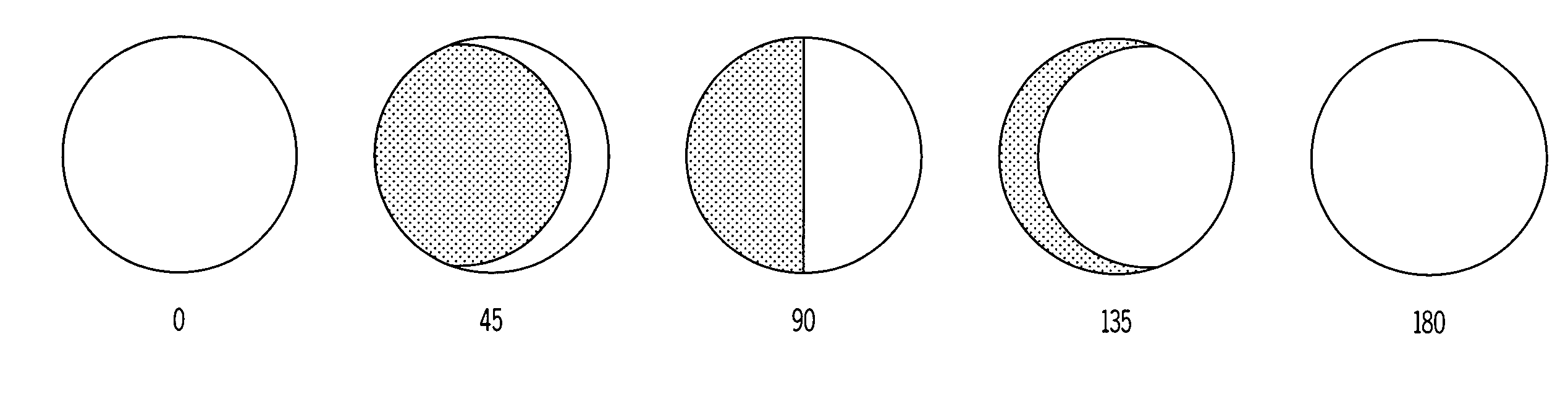
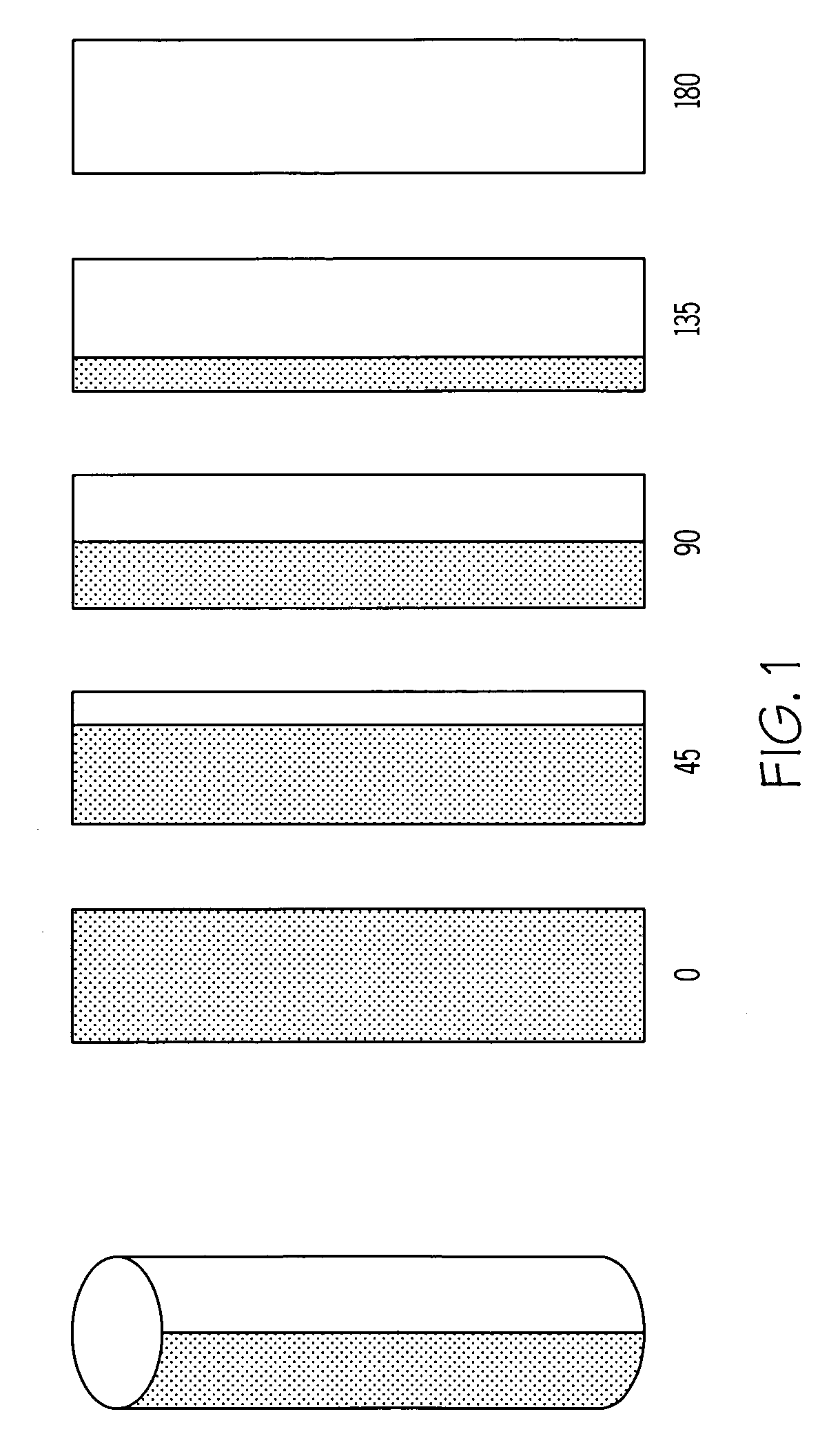
Variable emittance surfaces
Designs for constructing a surface with variable emittance are described. This is achieved by making a surface where the emissivity varies on a scale smaller than the resolution of a thermal imager viewing the surface. One design utilizes many cylindrical surfaces with their axis parallel and their surfaces nearly in contact. Individual cylinders have the property that when rotated to zero degrees they show a surface with an emissivity of one and when rotated to 180 degrees display a surface with an emissivity of zero. At intermediate angles of rotation a sensor that could resolve individual cylinders would see alternate lines with high and low emittance but a sensor unable to resolve individual cylinders sees a surface with an emittance that depends on the angle the cylinders are rotated. Variable emittance surfaces are expected to be useful for controlling target signature and for making spectral reflectivity measurements using a hyper-spectral radiometer.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY DEPT OF THE
Sprouted beans and preparation method thereof, and processed foodstuff with sprouted bean as raw material
InactiveCN103211176AReduce churnGood transferabilityCheese manufactureCultivating equipmentsFood materialSprouting
The invention relates to sprouted beans and a preparation method thereof. Existing sprouted bean products cannot satisfy market requirements and expectations. According to the invention, beans are processed with the methods such as impregnating, sprouting, freezing, and the like, such that frozen sprouted beans with sprout lengths from 1mm to bean length are obtained; specific spectral radiation and nutrition enhancing treatments are carried out according to different requirements, such that sprouted beans suitable for different populations and with good nutritional and dietotherapy values are obtained. The beans include soybeans, black beans, mung beans, chickpeas, coffee beans, and the like. The sprouted beans can be eaten as bean foods, and can be used as raw materials of various processed bean foodstuffs and applied in processed foodstuffs and health-care foodstuffs.
Owner:赵钧永
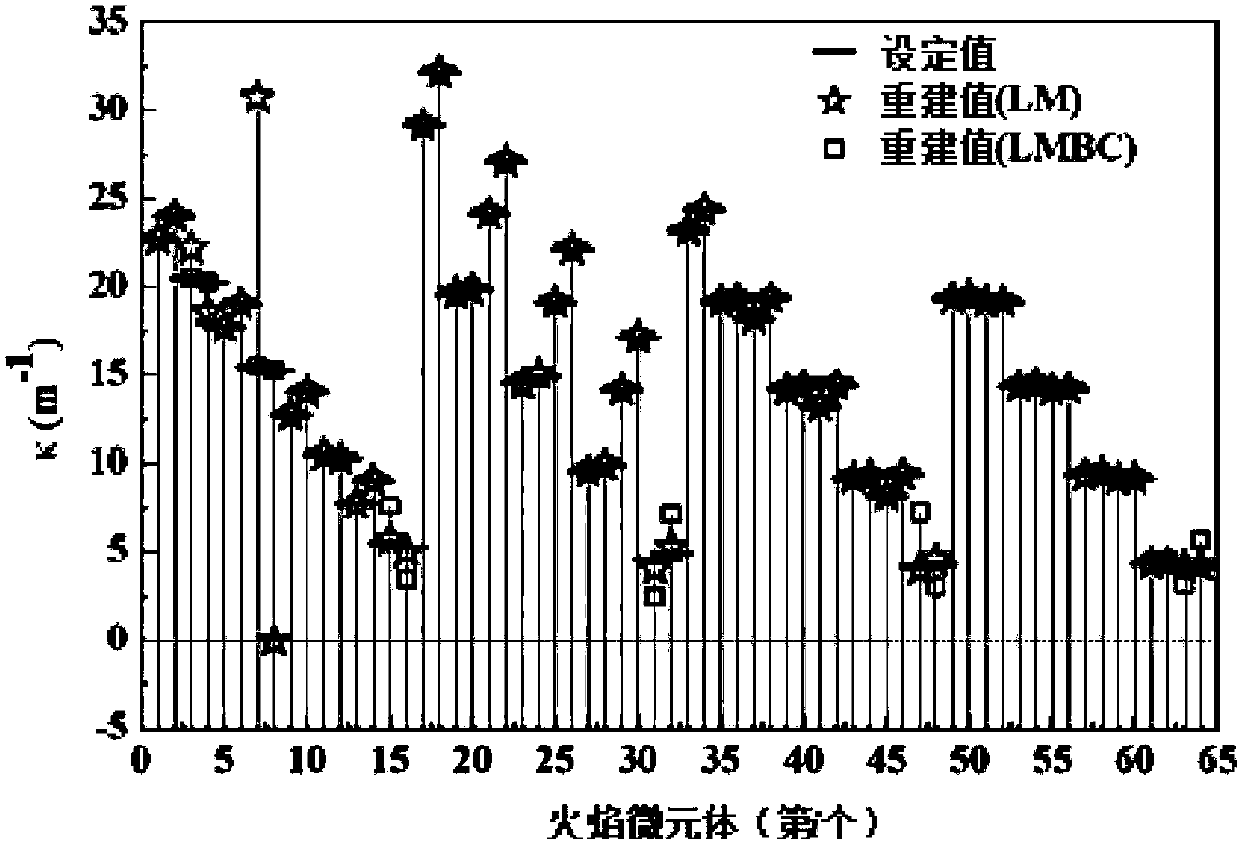
Flame three-dimensional temperature distribution reconstruction method based on bi-spectral radiation information
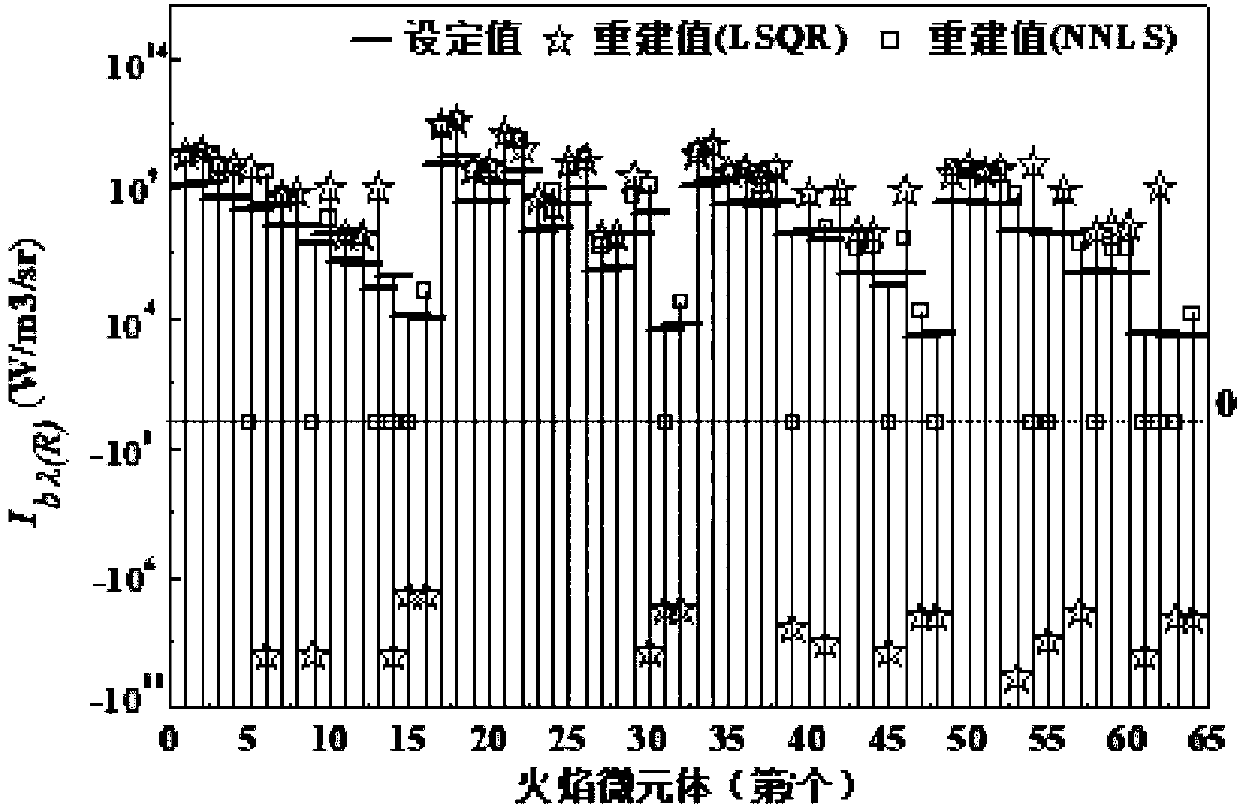
ActiveCN108225577AGuaranteed reasonablenessImprove accuracySensing radiation from gases/flamesPyrometry for temperature profileReconstruction methodReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses a flame three-dimensional temperature distribution reconstruction method based on bi-spectral radiation information. The flame three-dimensional temperature distribution reconstruction method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) dividing a flame microelement according to acquired flame bi-spectral radiation information and establishing a flame radiation transfer equation; 2) setting a target function, iteratively updating a flame absorption coefficient according to a reconstruction algorithm and reconstructing a flame three-dimensional temperature field. The flame three-dimensional temperature distribution reconstruction method based on the bi-spectral radiation information, disclosed by the invention, has the benefits that in the iterative solution process of the algorithm, a non-negative least squares algorithm is used, so that the non-negativity of the spectral radiation intensity of each of parts of flame can be guaranteed; the absorption coefficient of each of the parts of the updated flame is also mapped to a set interval, so that the non-negativity of the absorption coefficient is guaranteed; the algorithm has stronger robustness, isindependent of an initial value and can still maintain higher accuracy and better convergence under the situations that inputted data is larger in error, and a random numerical value is set without providing a priori iterative initial value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
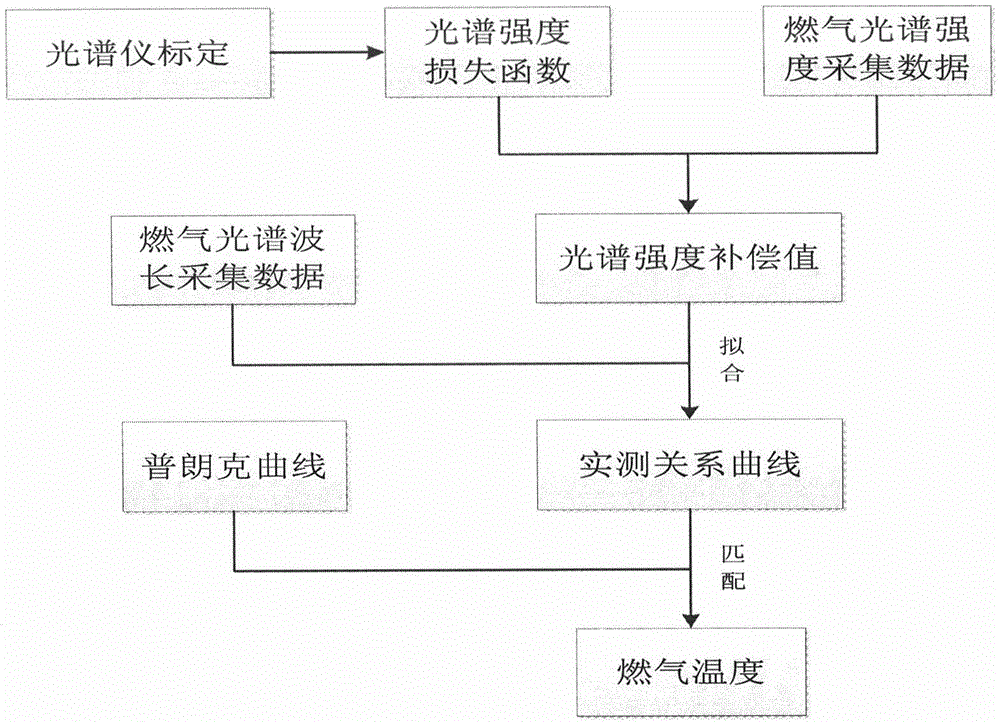
Rocket engine gas temperature testing method in consideration of multi-wavelength spectral radiation
InactiveCN104864977AHigh precisionAccurate calculationThermometers using physical/chemical changesMultiwavelength spectroscopyPlanck's law
The invention discloses a rocket engine gas temperature testing method in consideration of multi-wavelength spectral radiation. On the basis of the Planck's law, through acquiring gas radiation spectrum wavelengths and corresponding spectral radiation intensity data, an actually-measured relationship curve between the gas spectrum wavelength and the spectrum intensity is matched with a Planck curve at different temperatures, and according to a matching degree, the actual temperature of the rocket engine gas is determined. The temperature capable of being tested can be as high as 5000K, which is far beyond a temperature measurement range of a thermocouple, and the method of the invention is more applicable to high-temperature measurement of the rocket engine gas. Hundreds of wavelengths and corresponding spectral radiation intensity data can be acquired, precision of fitting the wavelengths and the spectral radiation intensity data is improved, and the anti-interference ability is strong. Compared with a dual-wavelength temperature measurement method and an eight-wavelength spectrometer temperature measurement method, the gas temperature can be calculated more accurately, and applicability is stronger.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Ultraviolet ray measuring method and ultraviolet ray measuring device
InactiveUS20060076501A1Easily and conveniently measureMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry for measuring UV lightUltravioletSpectral sensitivity
An ultraviolet ray measuring method using an ultraviolet ray receiving element having a specific spectral sensitivity. The method includes: estimating an estimated value of an entire region from the spectral sensitivity of the ultraviolet ray receiving element and a solar spectral radiation spectrum; estimating an estimated value of a specific region from a specific action curve and the spectral sensitivity and the solar spectral radiation spectrum; and determining specific ultraviolet ray information by, on the basis of the estimated value of the entire region and the estimated value of the specific region, correcting an actually measured value which is measured by the ultraviolet ray receiving element. Further, specific ultraviolet information, which is obtained on the basis of sun altitude information, is also corrected.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
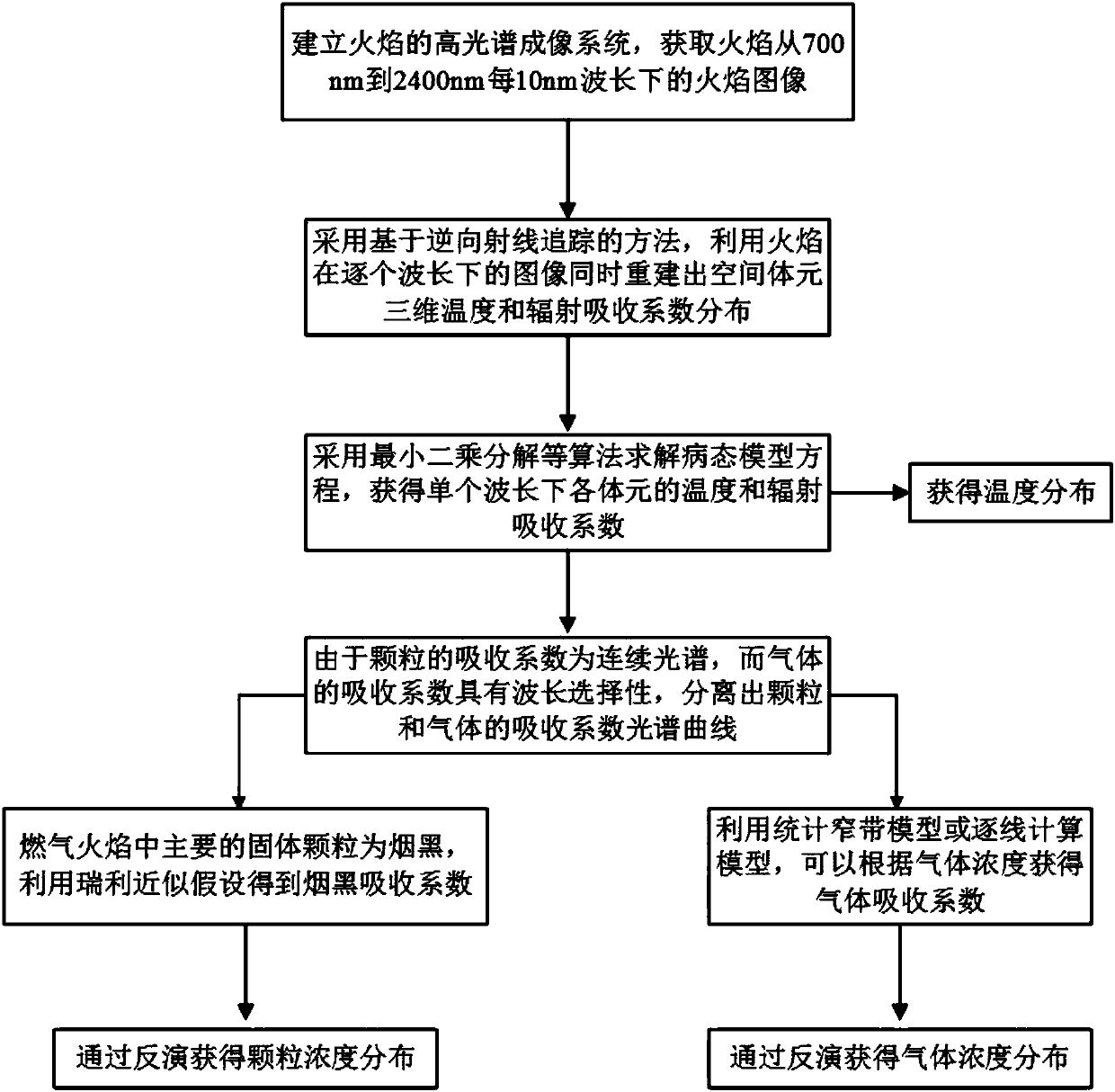
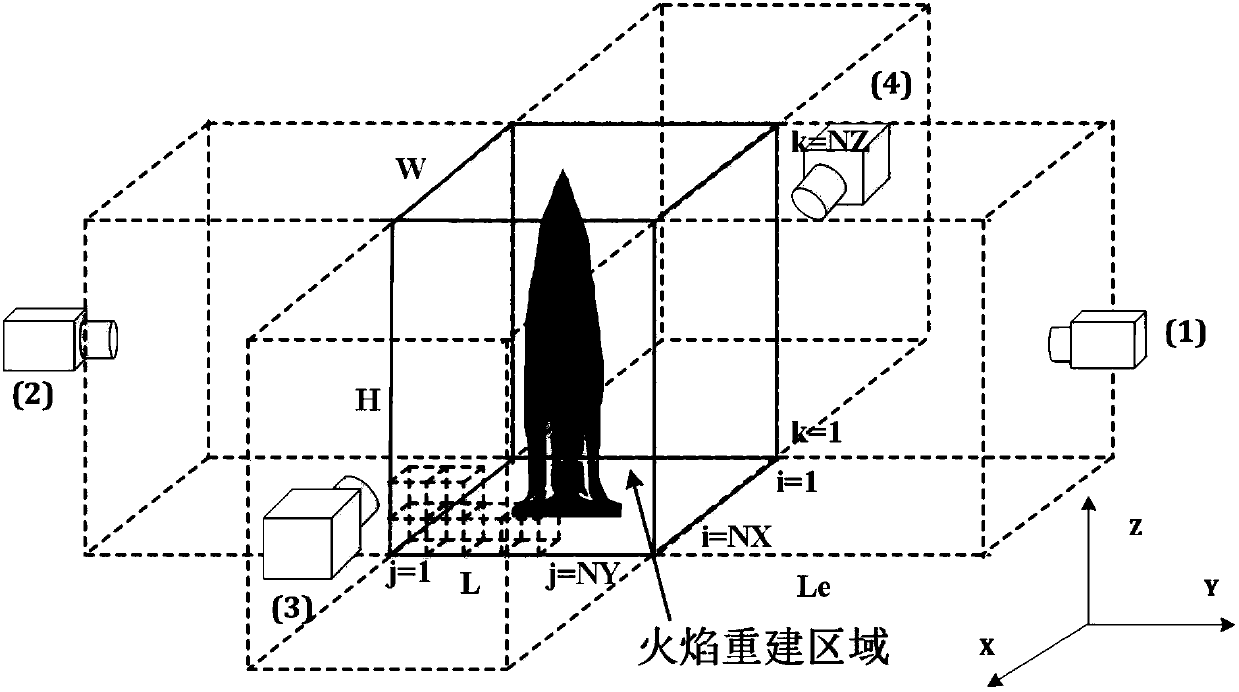
Flame temperature field particle gas concentration field measurement method based on hyperspectral image
ActiveCN108169148AHigh resolutionShort calculation timeColor/spectral properties measurementsRadiation transferGas concentration
The invention relates to a combustion process measurement technology and provides a flame temperature field particle gas concentration field measurement method based on a hyperspectral image. The method comprises building a hyperspectral flame imaging system, acquiring spatial and spectral radiation image information of flame, building a model and an algorithm according to a flame radiation transfer process and a reverse ray tracing process, calculating a flame temperature, a particle concentration and a gas concentration through the hyperspectral image of flame, and simultaneously reconstructing a flame three-dimensional temperature field, a particle concentration field and a gas concentration field. Compared with the traditional colorful camera, the measurement method can acquire the spatial and spectral projection data of flame and rebuild the mold through a reverse ray tracing method, has short calculation time, realizes online real-time monitoring of flame and has the characteristics of more flame measurement parameters, simple device, short treatment process and real-time online monitoring of flame state change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com