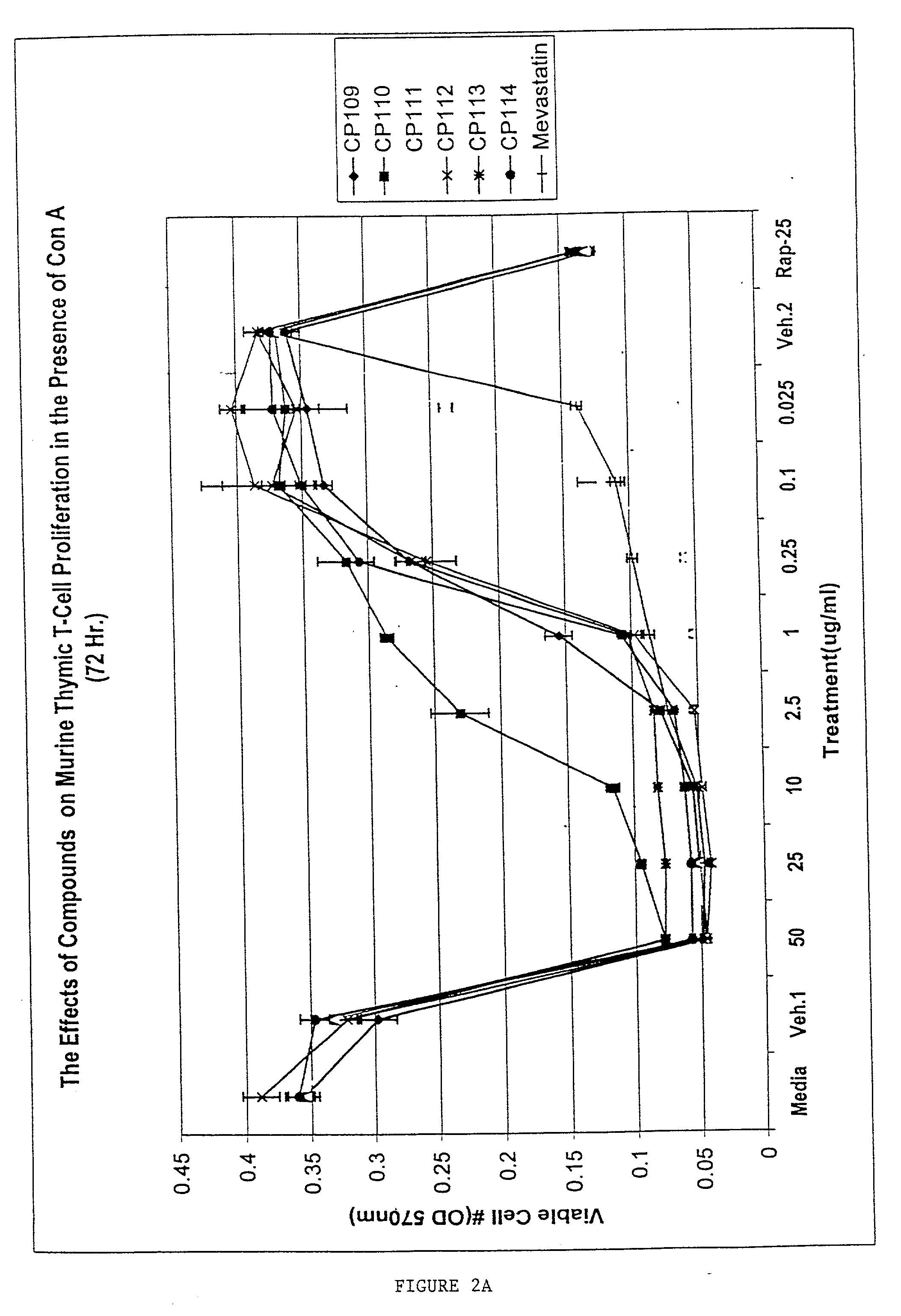
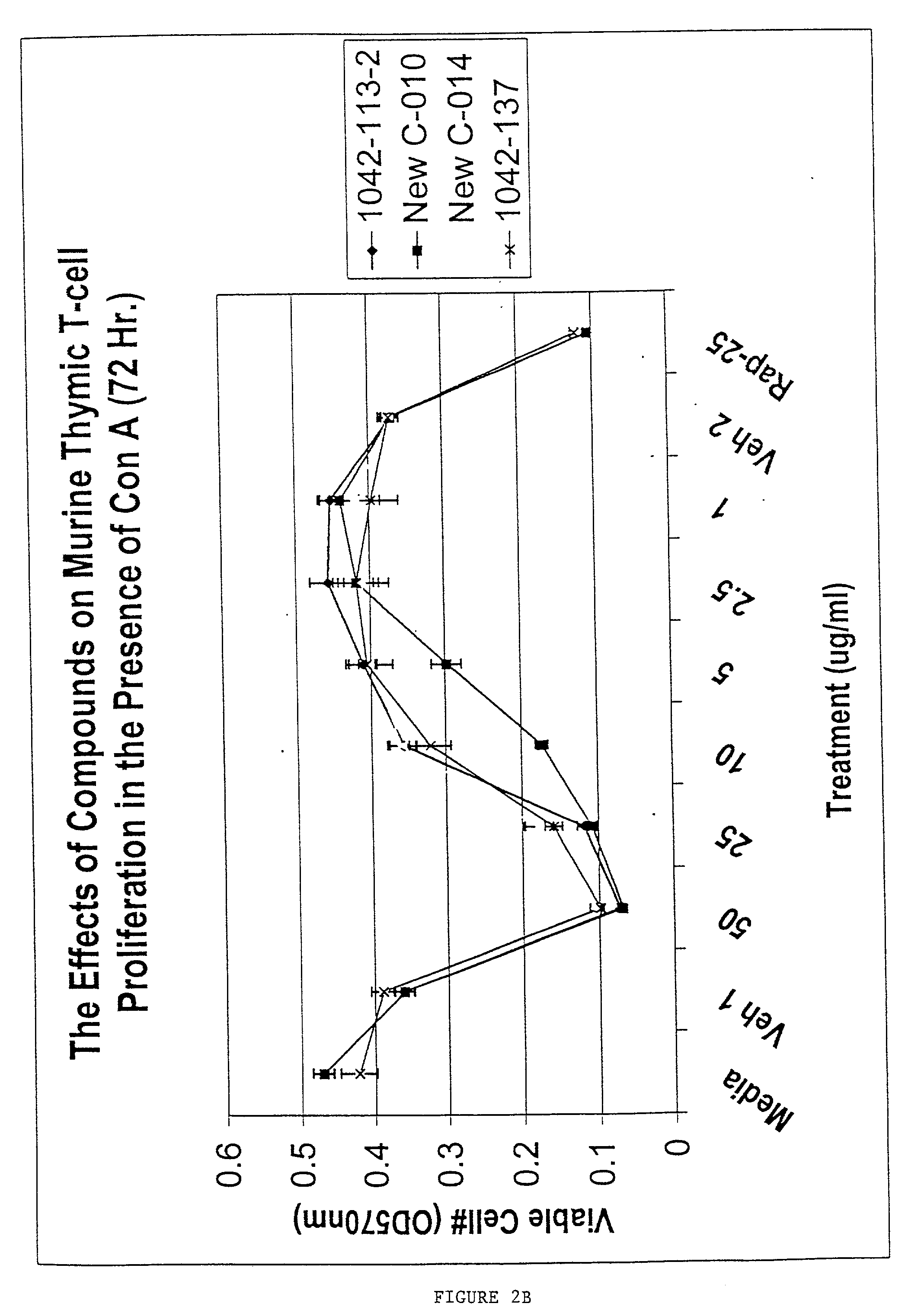
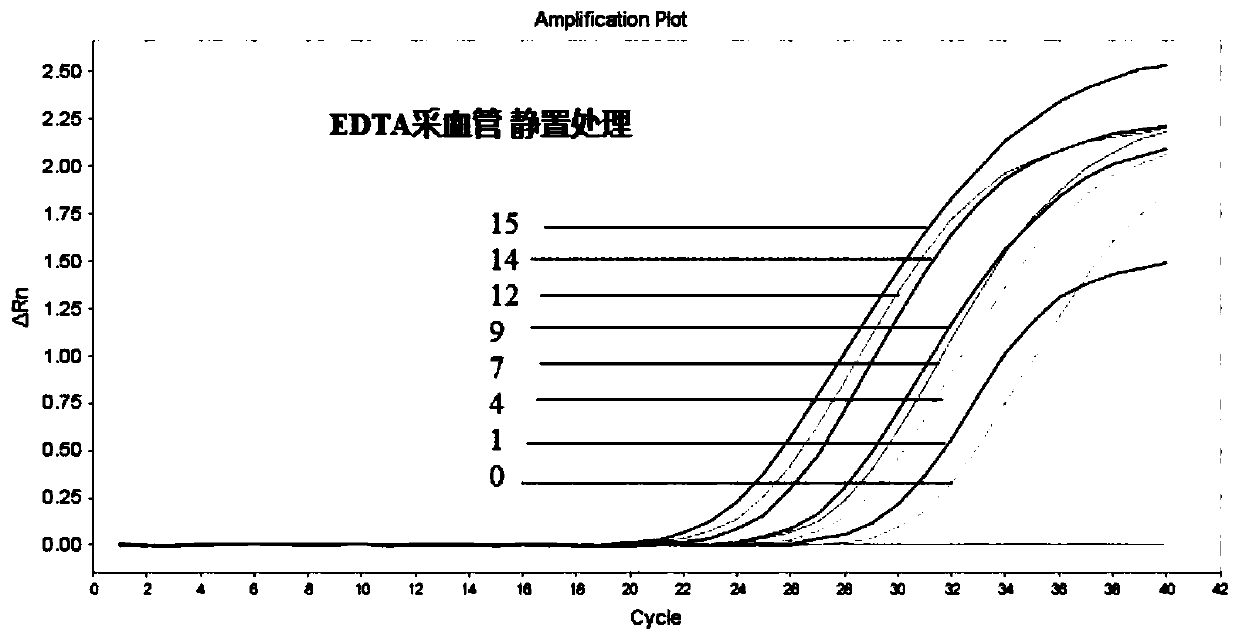
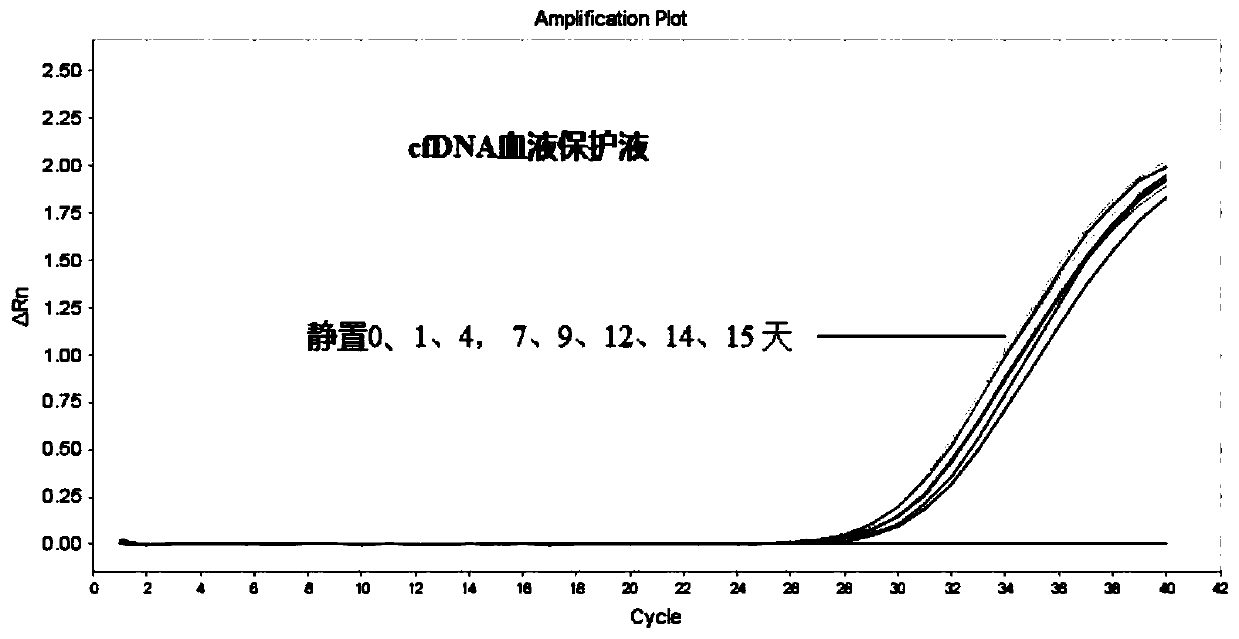
Patents
Literature
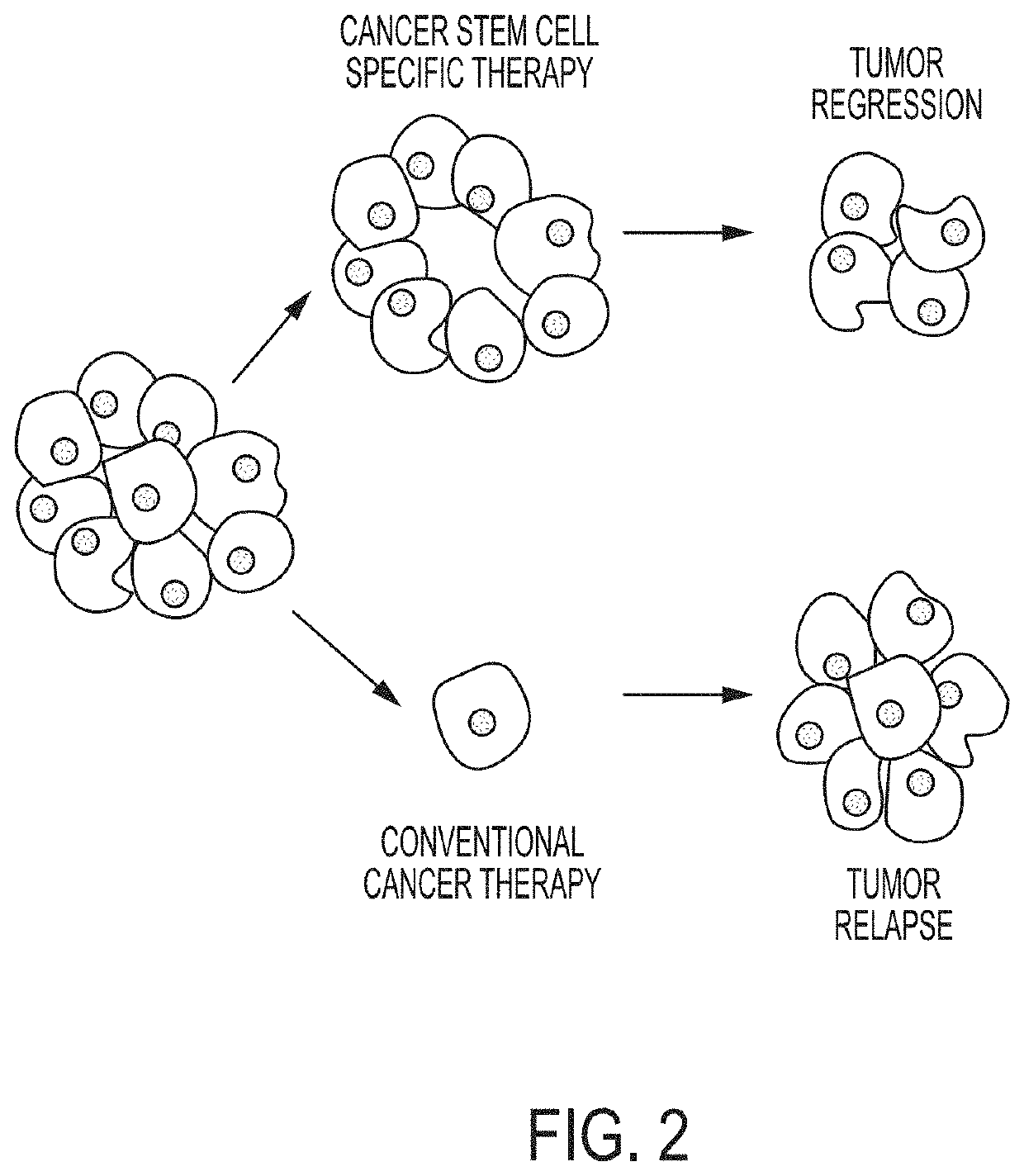
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Metabolic Inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metabolic inhibition technique. a virus neutralization test in tissue culture in which phenol-red indicator is used to detect the acid metabolic products of actively metabolizing cells or the lack of metabolism when cells are infected and destroyed by the virus.
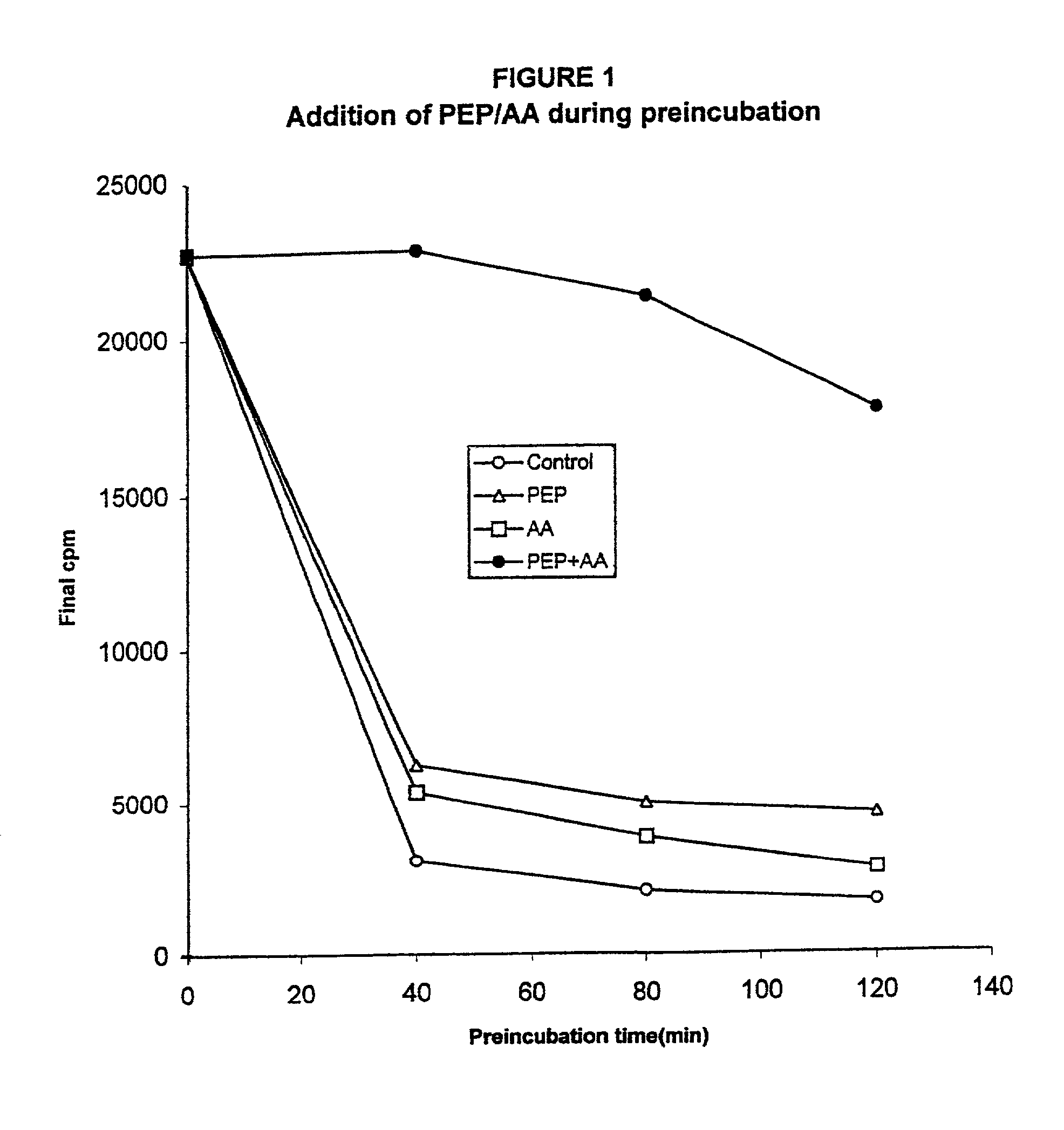
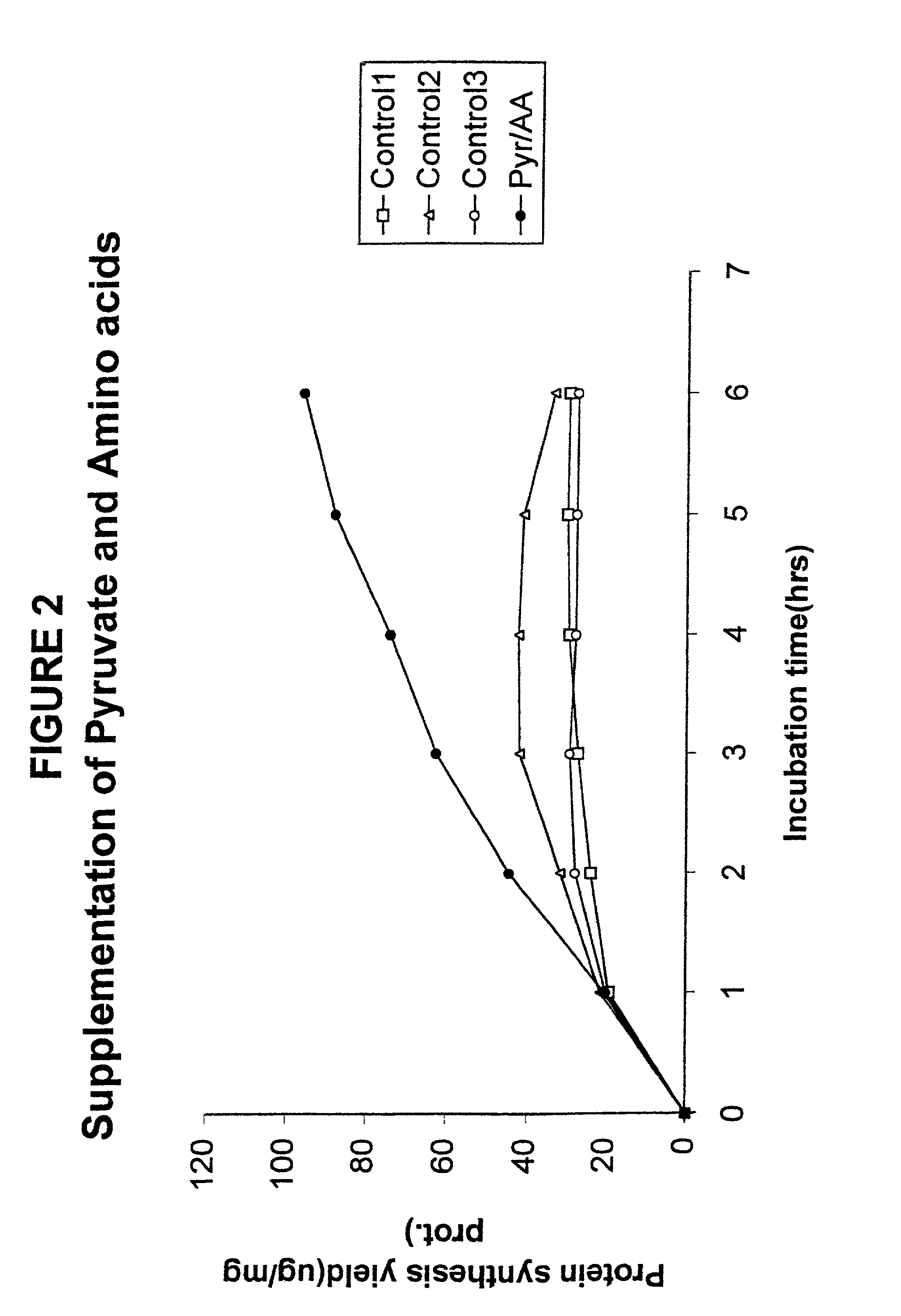
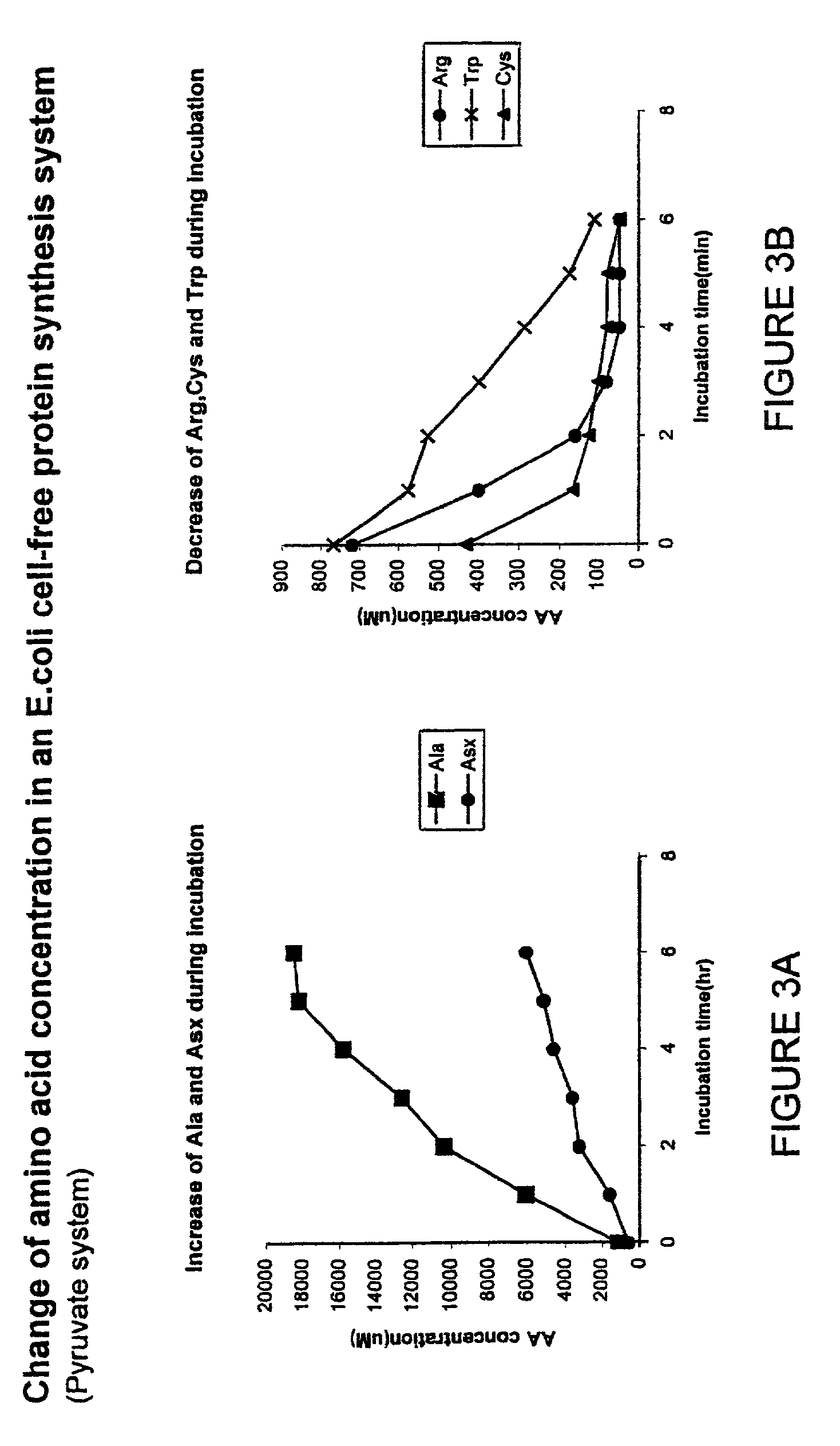
In vitro synthesis of polypeptides by optimizing amino acid metabolism
InactiveUS6994986B2Increasing protein synthesisDecrease and eliminate enzyme activityBacteriaTumor necrosis factorHigh-energy phosphateHomeostatic system
Compositions and methods are provided for the enhanced in vitro synthesis of polypeptides. In order to improve the performance of in vitro protein synthesis reactions, metabolic inhibitors, or manipulation of a source organism, is used to diminish or avoid the action of enzymes responsible for undesirable amino acids production or depletion. A homeostatic system may be used for production of ATP, where the required high energy phosphate bonds are generated in situ, e.g. through coupling with an oxidation reaction. The homeostatic energy source will typically lack high energy phosphate bonds itself, and will therefore utilize free phosphate in the reaction mix during generation of ATP. The homeostatic energy source is provided in combination with an enzyme that catalyzes the creation of high energy phosphate bonds and with an enzyme that can use that high energy phosphate bond to regenerate ATP.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Inhibition of biogenic sulfide production via biocide and metabolic inhibitor combination
ActiveUS20050238729A1Inhibit productionInhibit sulfide productionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSulfide productionSulfate-reducing bacteria
Biogenic sulfide production is synergistically inhibited by treating sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) with a biocide and a metabolic inhibitor. The biocide directly kills a first portion of the SRB. The metabolic inhibitor inhibits sulfate-reducing growth of a second portion of the SRB without directly killing the second portion of the SRB. The treatment of SRB with both a biocide and a metabolic inhibitor provides effective biogenic sulfide inhibition at significantly lower concentrations than would be required if the biocide or metabolic inhibitor was used alone.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
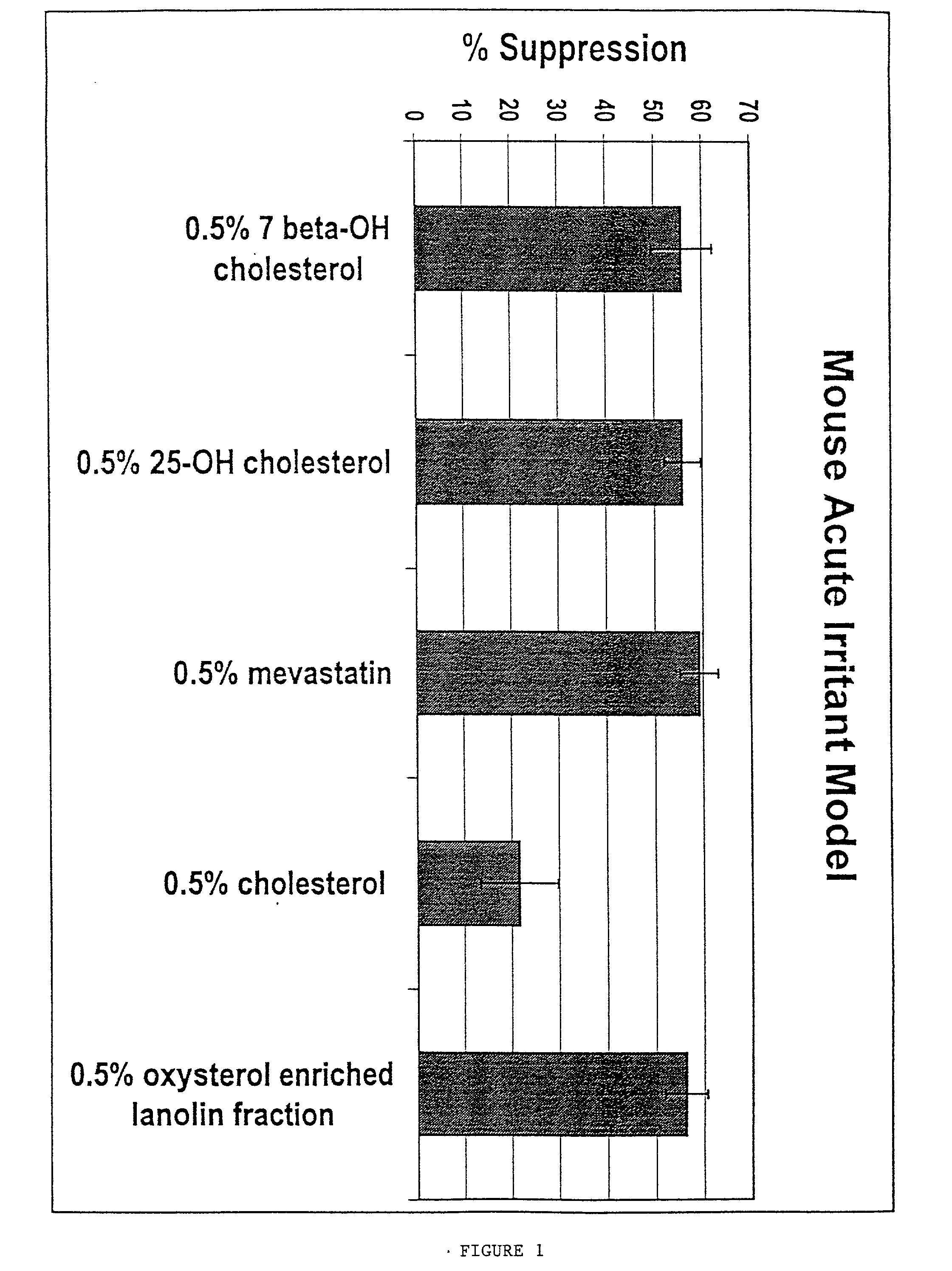
Treatment of hyperproliferative, inflammatory and related mucocutaneous disorders using inhibitors of mevalonate synthesis and metabolism
InactiveUS20020010128A1Inhibit cell proliferationInhibit expressionCosmetic preparationsBiocideSquamous CarcinomasAntiinflammatory drug
The present invention provides methods for treating a variety of hyperproliferative and inflammatory mucocutaneous disorders, including, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, as well as skin irritation and disorders associated with skin aging and skin photodamage using inhibitors of cholesterol metabolism. The present invention further relates to the discovery that the combined use of several inhibitors of cholesterol metabolism produces synergistic effects. Furthermore, the present invention is directed to the use of inhibitors of cholesterol metabolism as excipients to enhance the effects of antiinflammatory drugs.
Owner:CELLEGY PHARMACEUTICALS INC
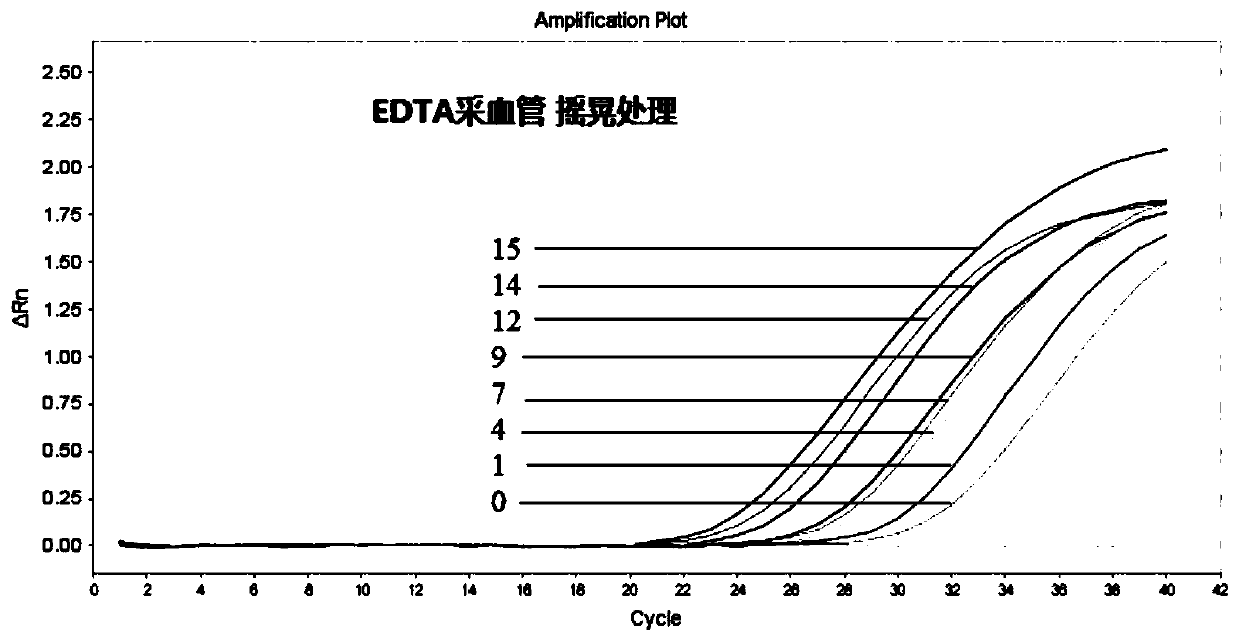
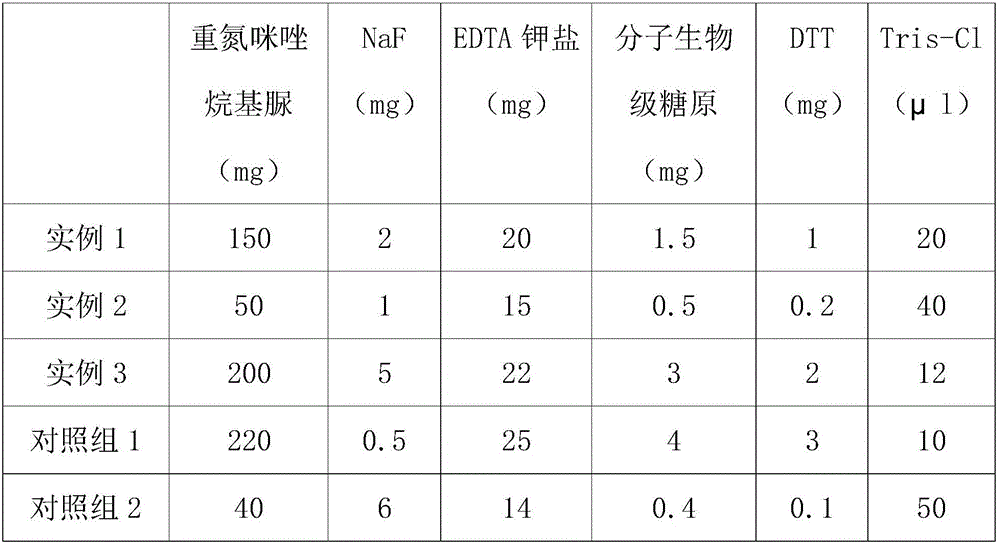
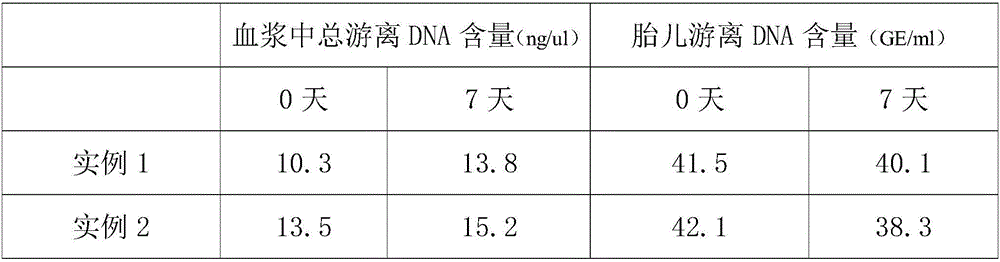
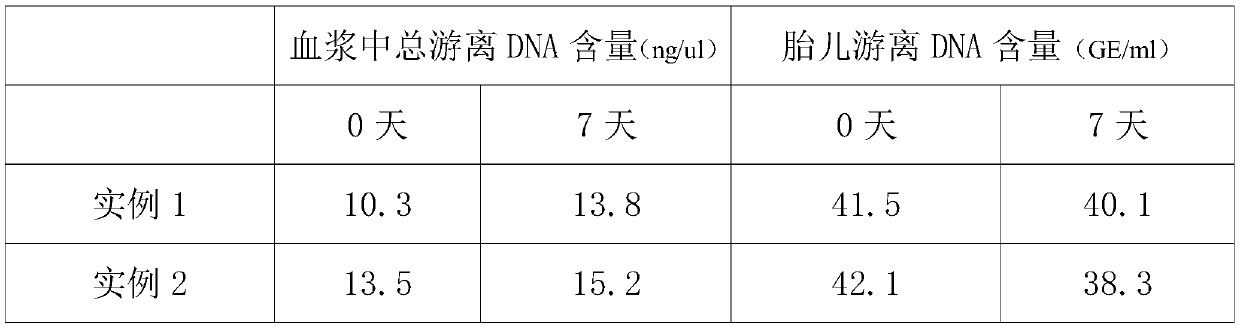
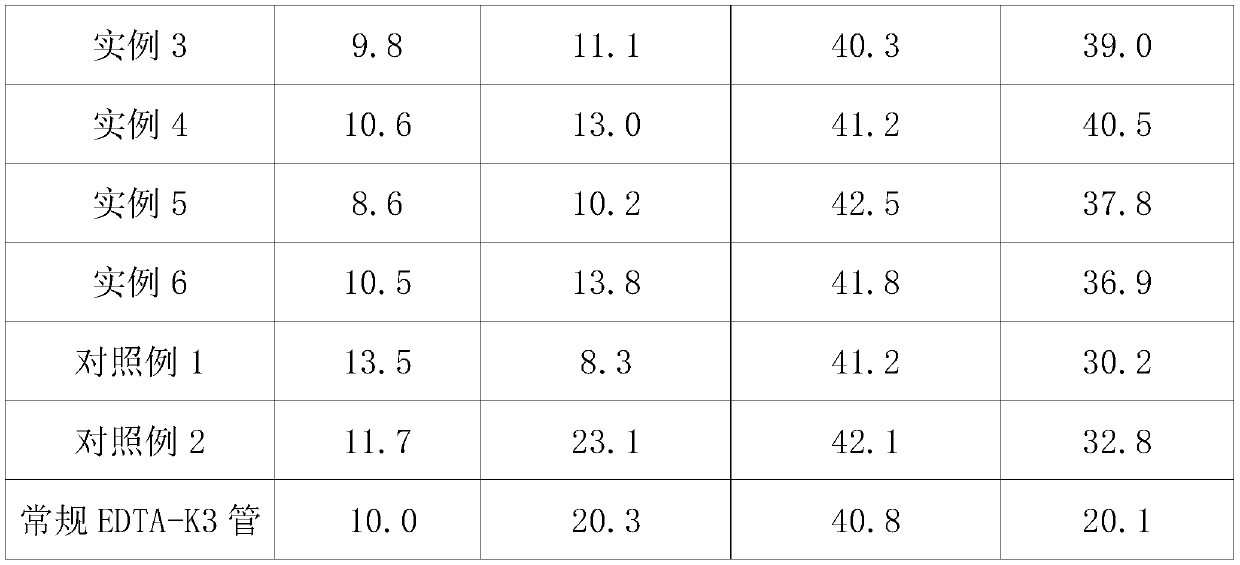
Blood protection solution for preserving cfDNAs (cell-free DNAs) in whole blood at room temperature
InactiveCN109730053AAvoid pollutionReduce testing costsDead animal preservationCell freeWhite blood cell
The invention discloses a blood protection solution for preserving cfDNAs (cell-free DNAs) in whole blood at room temperature. The blood protection solution comprises anticoagulants, preservatives, nuclease inhibitors, metabolic inhibitors, cell stabilizers and membrane stabilizers. The blood protection solution has the advantages that by a blood cfDNA preservative, the nuclease activity can be inhibited, and the cfDNAs in the blood can be protected; white blood cells are stabilized, breakage of the white blood cells is prevented, and the cfDNAs are prevented from being contaminated by cell genomes; peripheral blood can be stored at the room temperature for 14 days and transported at the room temperature for at least 14 days, during which no obvious change occurs, so that the storage timeof blood samples at the room temperature is effectively prolonged, great assistance is brought to long-distance transport of the blood samples, the detection cost of the cfDNAs is saved, and application and promotion of cfDNA-related detection techniques are facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA +1
Preservative for fetus free DNA in peripheral blood of pregnant woman and vacuum blood sampling tube composed of preservative
ActiveCN106244535AInhibition releaseInhibition-mediated degradationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsObstetricsIn vitro test
The invention discloses a preservative for fetus free DNA in peripheral blood of pregnant woman and a vacuum blood sampling tube composed of the preservative. The problems of short storage time and easiness in degrading of the fetus free DNA in plasma caused by the shortage of mature collecting and storing technique for the in vitro test of the fetus free DNA in peripheral blood of pregnant woman are solved. The preservative provided by the invention comprises a cell stabilizing agent, an anti-coagulant agent, a buffering solution, a metabolic inhibitor and a DNA enzyme inhibitor. The preservative can stabilize the karyocyte of the peripheral blood of pregnant woman, can prevent the cell chromosome DNA from being released, can restrain DNA enzyme degradation and is beneficial to the stability of fetus free DNA.
Owner:CHENGDU RICH SCI IND
Inhibition of biogenic sulfide production via biocide and metabolic inhibitor combination
ActiveUS7833551B2Inhibit productionInhibition productionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSulfide productionSulfate-reducing bacteria
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Method for performing mixed fermentation on lactobacillus acidophilus and clostridium butyricum as well as fermentation equipment thereof
InactiveCN108004191AGrowth inhibitionRelease the ability to grow and reproduceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFacultative anaerobic organismOrganism
The invention relates to the field of biology and provides a method for performing mixed fermentation on lactobacillus acidophilus and clostridium butyricum. The method comprises the following steps:inoculating the lactobacillus acidophilus on an unsterilized solid culture medium to perform fermentation, and then inoculating clostridium butyricum liquid to perform fermentation. The synergistic inhibition effect on infectious microbes by the lactobacillus acidophilus and the clostridium butyricum can be utilized, the growth of the infectious microbes can be effectively inhibited and the infectious microbes in the production process can be effectively controlled; furthermore, under the condition of not sterilizing the raw materials, the lactobacillus acidophilus and the clostridium butyricum are fermented, so that the cost is reduced and the practicability is high. In addition, the invention also provides fermentation equipment. The fermentation equipment can be applied to solid fermentation production of anaerobic bacteria or facultative anaerobic bacteria such as the clostridium butyricum and the lactobacillus acidophilus; and the fermentation equipment discharges volatile metabolic products such as hydrogen and carbon dioxide to the external air through a gas outlet pipe, relieves metabolic inhibition, and can release viable bacteria to improve the growth and reproduction capacity and increase the number of the fermented viable bacteria.
Owner:湖北华扬科技发展有限公司
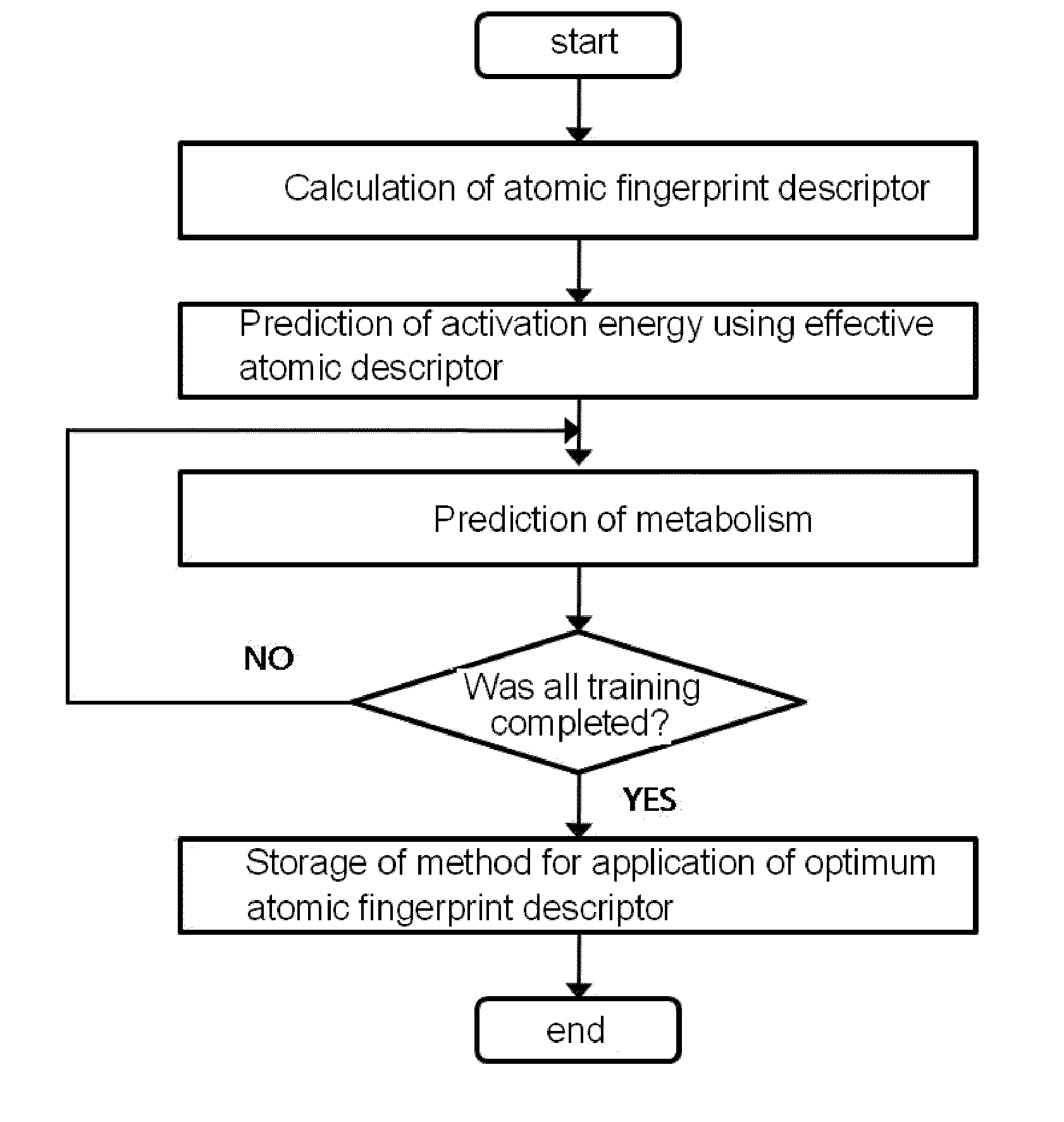
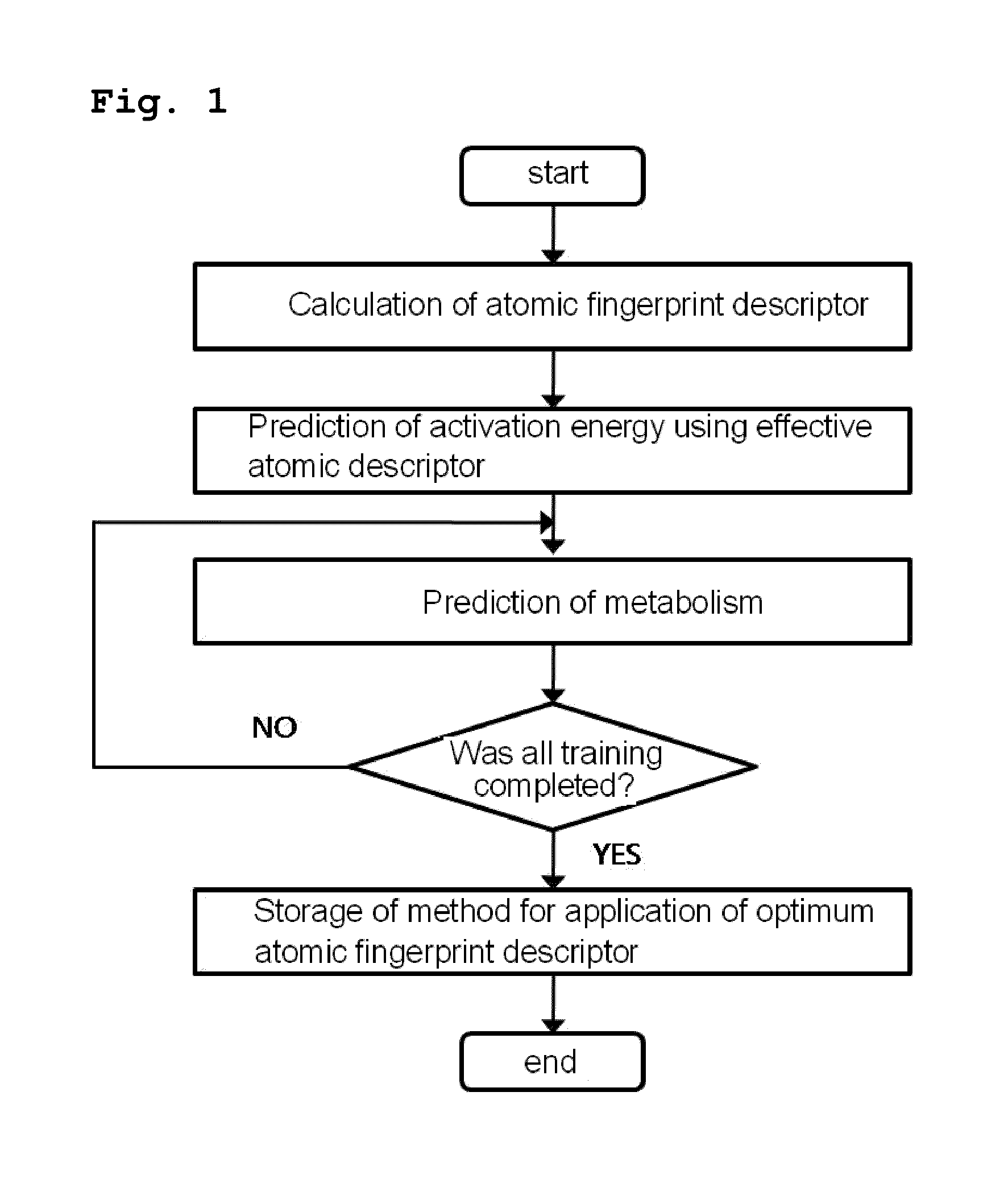
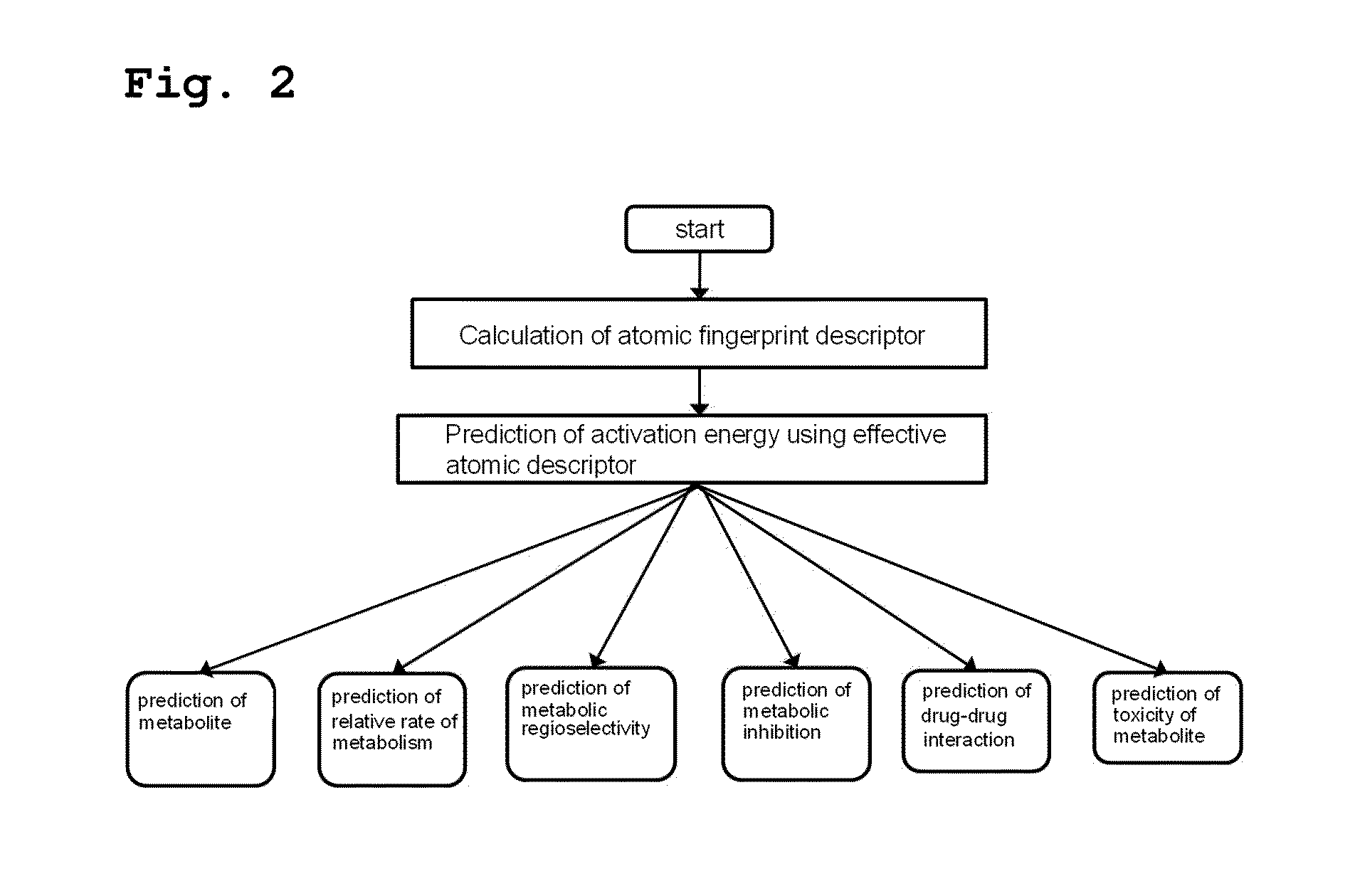
Method for predicting activation energy using an atomic fingerprint descriptor or an atomic descriptor
InactiveUS20110213558A1The process is fast and accurateChemical property predictionMolecular designMetaboliteChemical reaction
The present invention provides a method for constructing a database of atomic fingerprint descriptors. The invention provides a method for predicting activation energy using an atomic fingerprint descriptor and an atomic descriptor, the method comprising the steps of: (i) calculating the atomic fingerprint descriptor of a substrate; (ii) comparing the calculated atomic fingerprint descriptor with the constructed atomic fingerprint descriptor database to select an atomic position where cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism occurs; and (iii) predicting activation energy for the selected atomic position using an atomic descriptor. Also, the invention provides a method of predicting the activation energy of CYP450-mediated phase I metabolism using effective atomic descriptors. Specifically, the invention provides a method of predicting the activation energy either for cytochrome P450-mediated hydrogen abstraction or for tetrahedral intermediate formation in cytochrome P450-aromatic hydroxylation using equations including effective atomic descriptors. The method of the invention can rapidly predict activation energy for phase I metabolites at a practical level without having to perform a docking experiment between any additional CYP450 and the substrate, or a quantum mechanical calculation, thereby making it easier to develop new drugs using a computer. Also, the present invention may propose a strategy for increasing the bioavailability of drugs through the avoidance of metabolites based on the possibility of drug metabolism. Furthermore, the method of the present invention proposes new empirical approaches which can also be easily applied to activation energies for various chemical reactions, and makes it possible to explain physical and chemical factors that determine activation energy. In addition, through the prediction of activation energy according to the present invention, it is possible to predict i) metabolic products, ii) the relative rate of metabolism, iii) metabolic regioselectivity, iv) metabolic inhibition, v) drug-drug interactions, and vi) the toxicity of a metabolite.
Owner:BIOINFORMATICS & MOLECULAR DESIGN RES CENT
Method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria
ActiveCN110607337AReduce metabolic inhibitionReduce competitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteElectron transfer
The invention relates to a method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria, in particular to a method for realizinghigh-efficiency hydrogen production by utilizing syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria and inter-specific electron transfer, and belongs tothe technical field of hydrogen production by fermentation. The method aims to solve problems that the existing anaerobic biological hydrogen production process is inhibited by bacterial metabolism,substrate is not completely utilized, and then hydrogen production efficiency is influenced. According to the method, Ethanoligenens harbinense W1 and Geobacteria PCA are co-cultured, terminal metabolites such as acetic acid and ethanol produced by the hydrogen-producing bacteria in the fermentation system are consumed by the electroactive bacteria, so that metabolic inhibition among the bacteriain a closed fermentation system is reduced, and continuous and efficient hydrogen production is promoted. In addition, glucose can be used as a carbon source in the method, and the glucose only can beutilized only by the fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria, so that substrate competition is reduced, and the produced hydrogen has higher yield and higher purity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
High Density Growth of T7 Expression Strains with Auto-Induction Option
ActiveUS20070224682A1Promoting auto-inductionIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationMetaboliteVitamin B12
Disclosed is a method for promoting auto-induction of transcription of cloned DNA in cultures of bacterial cells grown batchwise, the transcription being under the control of a promoter whose activity can be induced by an exogenous inducer whose ability to induce said promoter is dependent on the metabolic state of said bacterial cells. Initially, a culture media is provided which includes: i) an inducer that causes induction of transcription from said promoter in said bacterial cells; and ii) a metabolite that prevents induction by said inducer, the concentration of said metabolite being adjusted so as to substantially preclude induction by said inducer in the early stages of growth of the bacterial culture; but such that said metabolite is depleted to a level that allows induction by said inducer at a later stage of growth. The culture medium is inoculated with a bacterial inoculum, the inoculum comprising bacterial cells containing cloned DNA, the transcription of which is induced by said inducer. The culture is then incubated under conditions appropriate for growth of the bacterial cells. Also disclosed is a method for improving the production of a selenomethionine-containing protein or polypeptide in a bacterial cell, the protein or polypeptide being produced by recombinant DNA techniques, the bacterial cell encoding a vitamin B12-dependent homocysteine methylase. The method for improving the production of this protein or polypeptide includes culturing the bacterial cell in a culture medium containing vitamin B12. Finally, disclosed is a method for suppressing transcription of cloned DNA in cultures of bacterial cells grown batchwise, said transcription being under the control of a promoter whose activity can be induced by an exogenous inducer whose ability to induce said promoter is dependent on the metabolic state of said bacterial cells. This aspect includes the steps of: a) providing a culture medium comprising a carbon source whose uptake and metabolism by said bacterial cells suppresses induction of transcription from said promoter; b) inoculating the culture medium with a bacterial inoculum, the inoculum comprising bacterial cells containing cloned DNA, the transcription of which is suppressed by the carbon source; and c) incubating the culture of step b), with shaking, under conditions appropriate for growth of the bacterial cells.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Inhibitor for tumor cell abnormal lipid metabolism by using plant cyclopeptides as effective component and application thereof
ActiveCN107970432AWide variety of sourcesThe extraction process is matureSaccharide peptide ingredientsPeptidesProstate cancerOncology
The invention discloses an inhibitor for tumor cell abnormal lipid metabolism by using plant cyclopeptides as an effective component and application thereof in preparation of a medicine for inhibitingthe tumor cell abnormal lipid metabolism, particularly preparation of medicine for treating and preventing related cancers with abnormal lipid metabolism, such as liver cancer, colon cancer, rectum cancer and prostatic cancer. The inhibitor for tumor cell abnormal lipid metabolism has the advantages that the tumor cell abnormal lipid metabolism can be effectively inhibited, the source of the effective component, namely the plant cyclopeptides, is wide, the extracting technology is mature, the preparation type and the medicine usage type are diversified, and the clinical application prospect is broad.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Composition and method for preserving nucleic acid in urine
PendingCN111334560AImprove stabilityInhibition releaseMicrobiological testing/measurementNuclease inhibitorClinical diagnosis
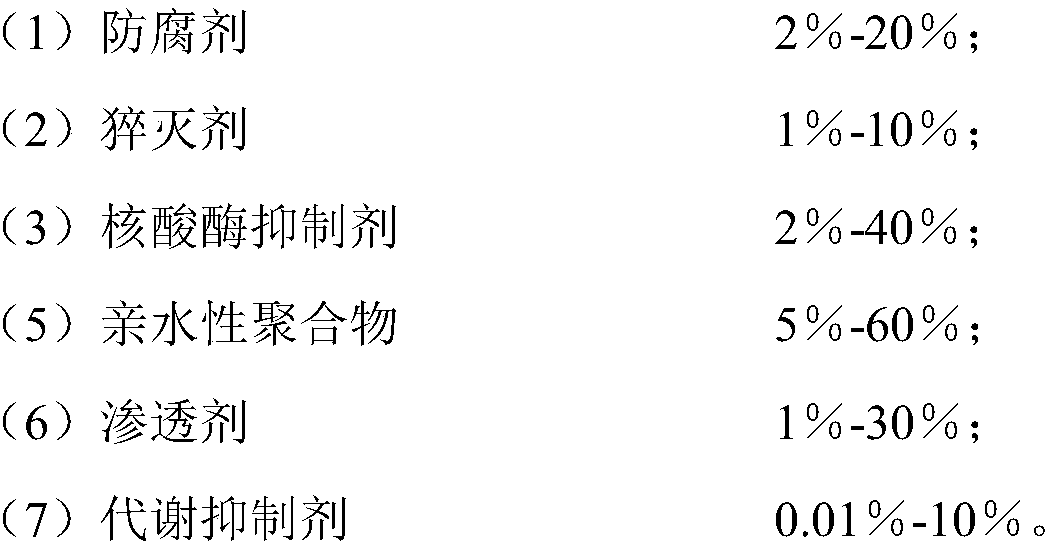
The invention provides a composition and method for preserving nucleic acid in urine. The composition provided by the invention contains the following components in percentage by weight: 2%-20% of a preservative, 1%-10% of a quenching agent, 2%-40% of a nuclease inhibitor, 5%-60% of a hydrophilic polymer, 1%-30% of a penetrating agent and 0.01%-10% of a metabolic inhibitor. The composition is capable of improving the stability of free nucleic acids in a biological sample and preventing release of nucleic acids in a karyocyte genome, and the separated free nucleic acids are widely suitable formass clinical diagnosis, development and application.
Owner:合肥铼科生物科技有限公司
Compositions for Treating and/or Preventing Cancer
InactiveUS20200237711A1Increase blood concentrationHigh anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFuranCancer prevention
The present disclosure provides pharmaceutical compositions, combinations, and uses thereof for treating and / or preventing cancer. For example, a pharmaceutical composition of the present disclosure can also include 2-acetylnaphtho[2,3-b]furan-4,9-dione, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of any of the foregoing, or a pharmaceutically acceptable solvate of any of the foregoing; and at least one excipient independently being a binder, a disintegrant, a lubricant, a surfactant, one other excipient, or a combination thereof. For example, a combination of the present disclosure can include 2-acetylnaphtho[2,3 b]furan-4,9-dione, a prodrug thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of any of the foregoing, or a pharmaceutically acceptable solvate of any of the foregoing; and at least one second agent independently being; a metabolic inhibitor, a transporter inhibitor, a NSAID, or a combination thereof.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA ONCOLOGY INC
Preservative for fetal cell-free dna in peripheral blood of pregnant women and vacuum blood collection tubes composed of it
ActiveCN106244535BInhibition releaseInhibition-mediated degradationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood Collection TubeObstetrics
Owner:CHENGDU RICH SCI IND
Compositions And Methods For Enhancing Immunotherapy
PendingUS20210187023A1Improve usabilityImprove the environmentImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsTumor responseNutrition
The present invention provides, in some embodiments, methods of promoting an immune response in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to a subject a population of immune cells that express an exogenous enzyme that facilitates immune cell function in a nutrient-poor environment. Other embodiments of the invention include methods of promoting an immune response to a tumor in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of an agent that provides a one-carbon unit (e.g., formate) and an agent that promotes an anti-tumor response, and methods of promoting an immune response to a tumor in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to a subject an effective amount of an agent that inhibits consumption of metabolic fuels by tumor cells. The invention also provides, in other embodiments, compositions comprising an ex vivo population of immune cells expressing an exogenous enzyme that enhances immune cell function in nutrient poor environments, and compositions comprising a nucleic acid expression construct encoding an inhibitor of glucose metabolism, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Immune stimulation/metabolic inhibition as antitumor therapy
InactiveUS20150037357A1Organic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthImmune Stimulation
Owner:NOVARX
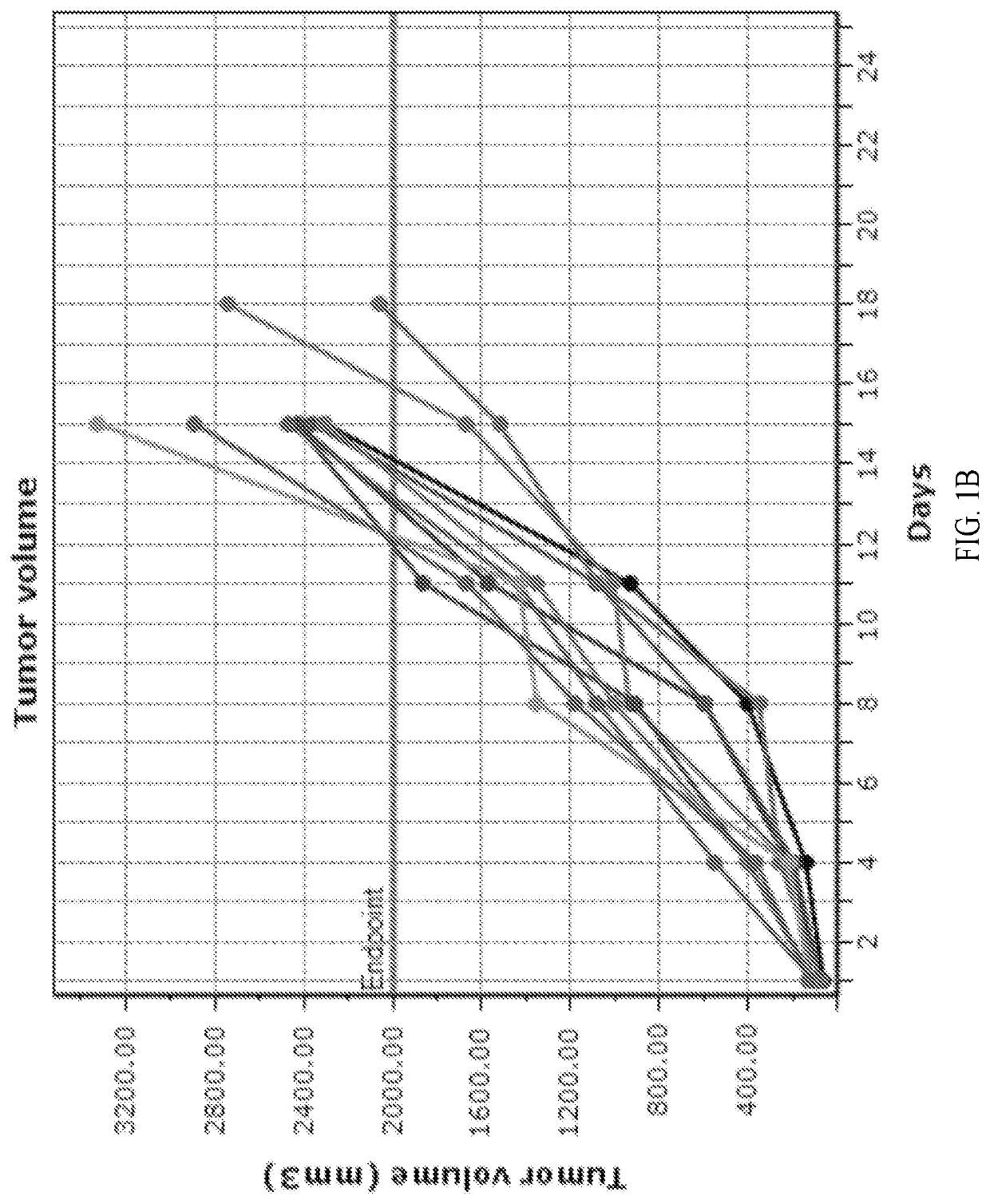
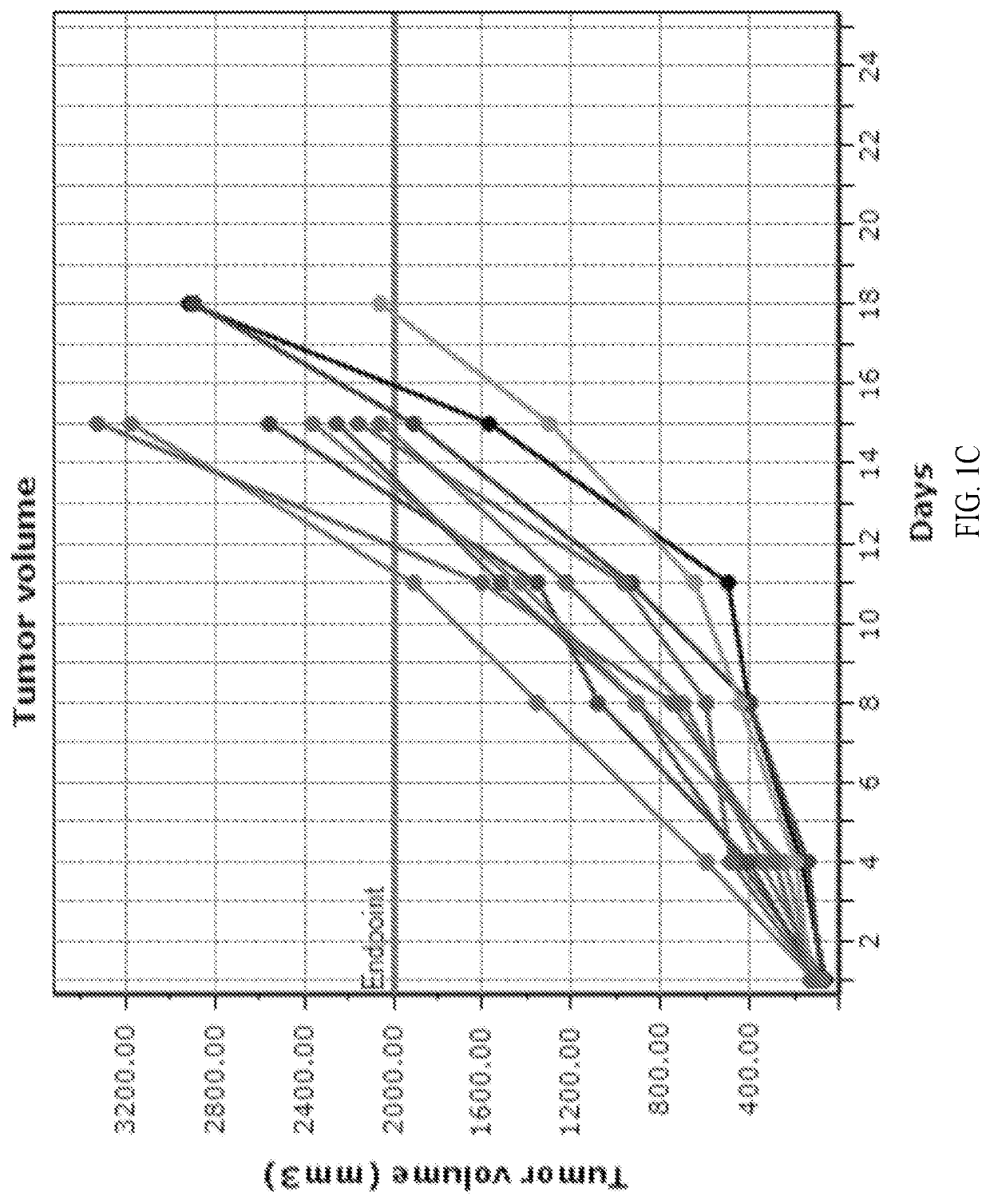
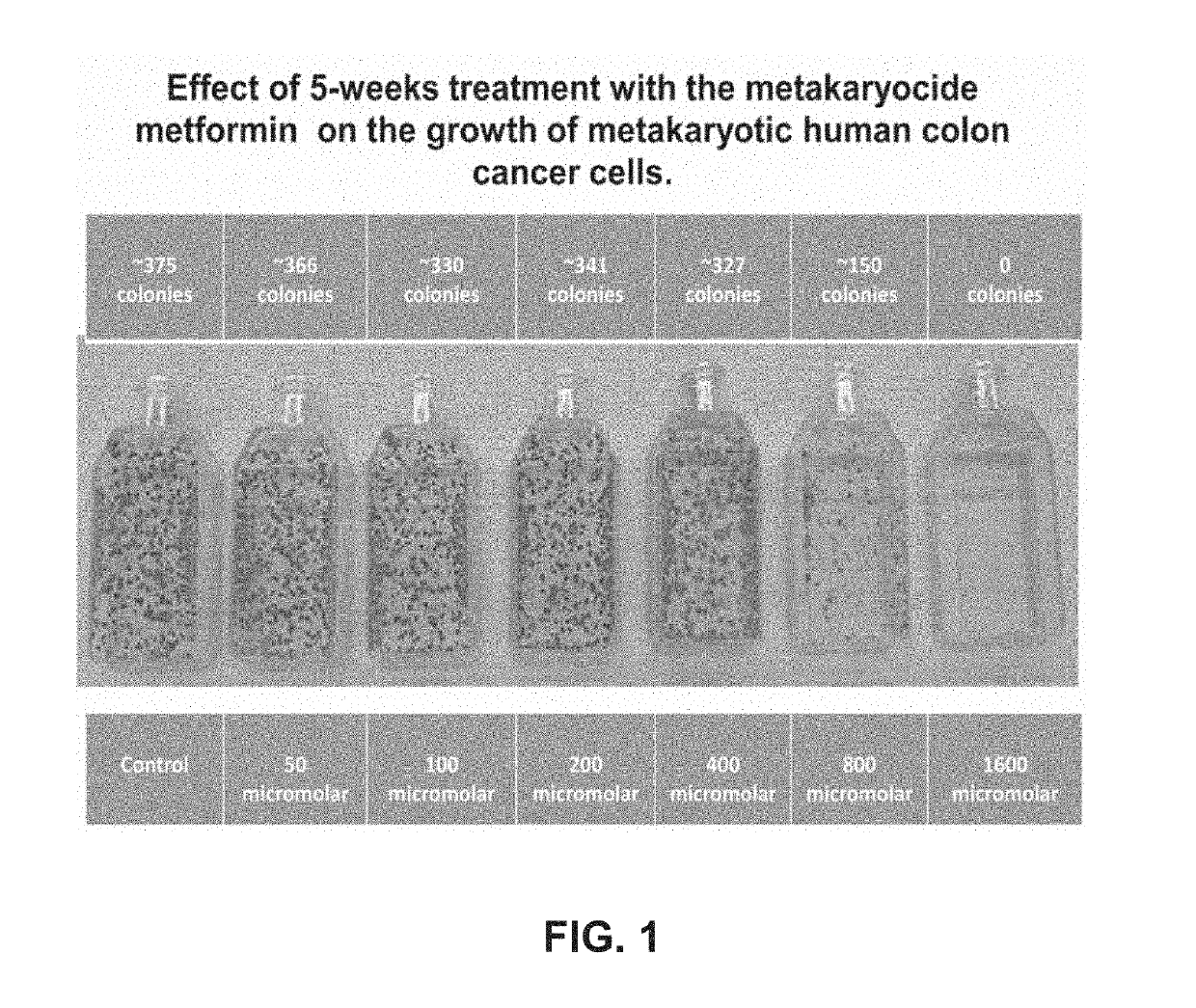
Metakaryocidal treatments
ActiveUS10314851B2Decreased likelihood)Tetracycline active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMedicineCell growth
The invention provides, inter alia, methods of treating a disorder characterized by excessive metakaryotic stem cell growth by a combination metakaryocidal therapy. Also encompassed by the present invention are preventative methods comprising the administration of a metakaryocidal or metakayrostatic therapeutic agent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Coronavirus sample preservation solution and application thereof
PendingCN112662731AAvoid degradationGrowth inhibitionMicrobiological testing/measurementCell membraneEnzyme inhibitor
The invention relates to a coronavirus sample preservation solution and application thereof. The coronavirus sample preservation solution comprises a cell preserving fluid, a cell membrane protective agent, an RNA enzyme inhibitor, a virus metabolism inhibitor, a virus inactivator and a bacteriostatic agent, wherein the virus inactivator is sodium caprylate, and the bacteriostatic agent is Funme polypeptide. The bacteriostatic agent in the preservation solution selects biological Funme polypeptide, growth of various microorganisms can be inhibited in a broad spectrum, nucleic acid detection of coronaviruses is not interfered, the selected virus inactivator does not influence detection of new coronavirus amplification reagents produced by any manufacturer, and RNA in a sample cannot be degraded by RNA enzyme in the preservation and transportation process through the RNA enzyme inhibitor. According to the preservation solution, collected coronavirus samples are comprehensively protected from all links, the samples are kept in an original state in the preservation and transportation process, the originality of the samples can still be kept after the samples are preserved for 5 days at the temperature of 2-8 DEG C, and detection results consistent with those of the original samples are obtained.
Owner:杭州金域医学检验所有限公司
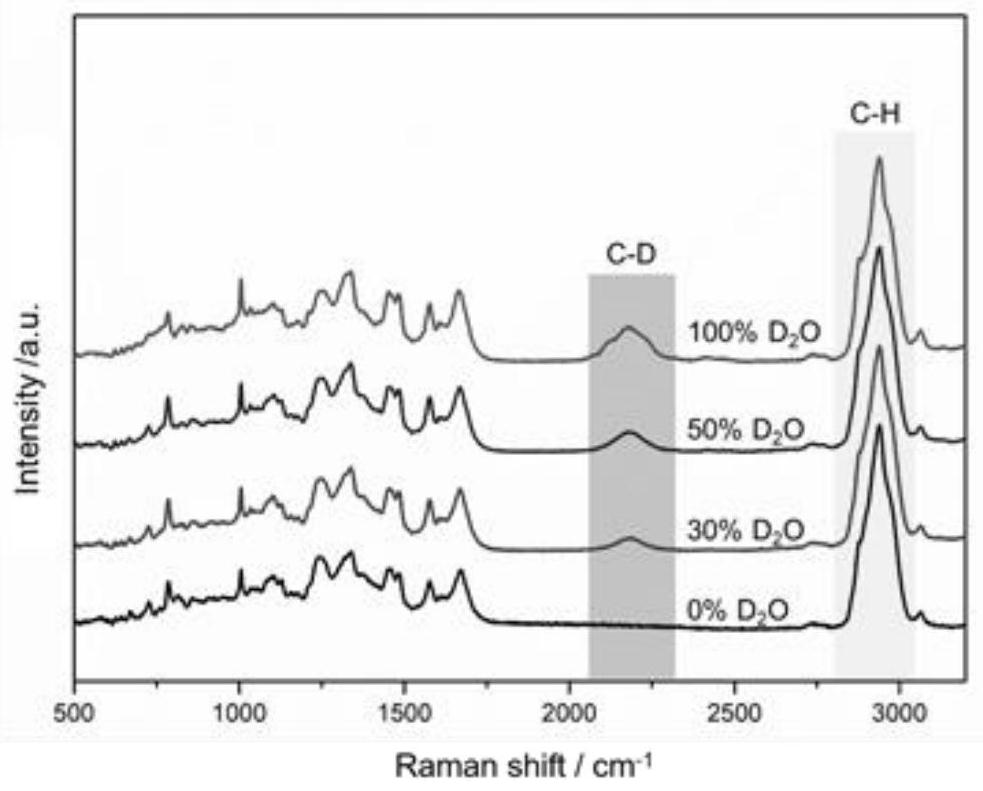
Kit for tigecycline drug sensitivity detection and method for tigecycline drug sensitivity detection by using same
ActiveCN113981036ARapid and accurate tigecycline susceptibility resultsFast and accurate drug susceptibility resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringDrug susceptibility/resistanceTigecycline
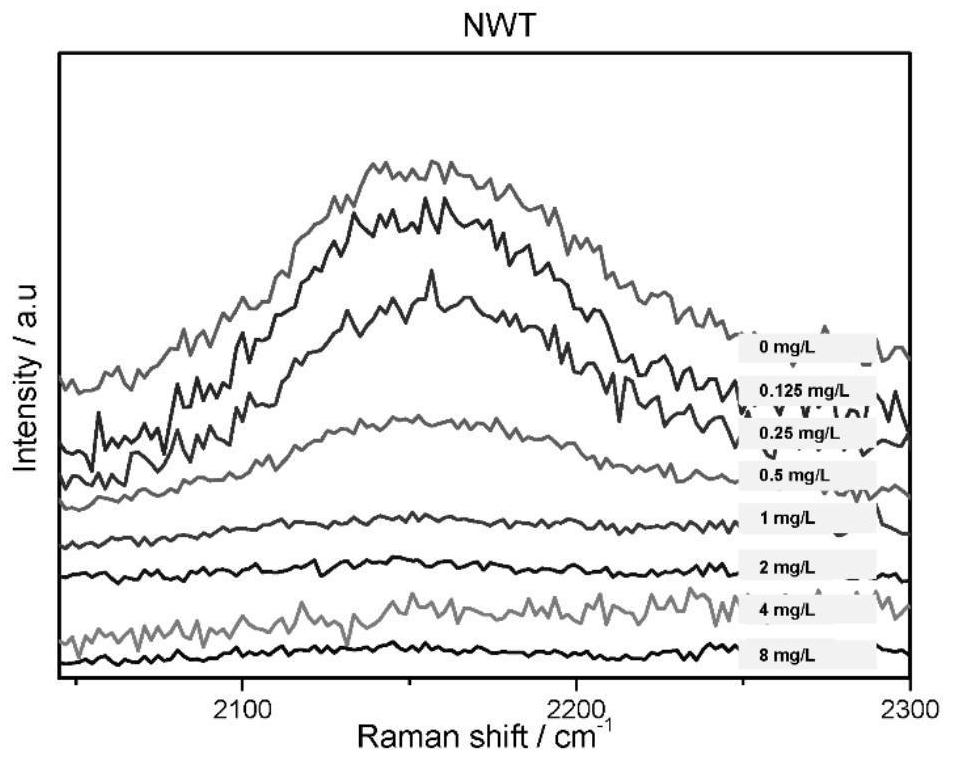
The invention discloses a kit for tigecycline drug sensitivity detection and a method for tigecycline drug sensitivity detection by using the same. The kit comprises a tigecycline drug sensitive plate and incubation liquid. The tigecycline drug sensitive plate comprises a drug sensitive plate body, and the plate holes of the drug sensitive plate body are coated with tigecycline powder. The tigecycline drug sensitivity detection method comprises the following steps of: inoculating a to-be-detected strain suspension into a tigecycline drug sensitivity plate, incubating, adding heavy water into the tigecycline drug sensitivity plate, continuing to incubate for a period of time, sampling at different time points, and carrying out Raman detection; calculating data in a spectrum obtained by Raman detection of the sample to obtain the minimum inhibitory concentration eMIC-MA in the drug concentration under the condition that the metabolic inhibition level of the sample is greater than or equal to 0.8 after continuous incubation for a period of time; and judging the drug sensitivity of the to-be-detected strain tigecycline according to a result judgment standard formulated by the American Food and Drug Administration and the European Drug Sensitivity Test Committee according to the numerical value of eMIC-MA. According to the method, the tigecycline drug sensitivity result can be quickly and accurately obtained.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Blood collection tube containing free desoxyribonucleic acid stabilizer
PendingCN114107005APrevent or slow down degradationEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNABlood plasma
The invention discloses a blood collection tube containing a free desoxyribonucleic acid stabilizer, the blood collection tube comprises a stabilizer, a tube body and a sealing plug, the stabilizer comprises a preservative, an anticoagulant, a metabolic inhibitor, an enzyme inhibitor and a buffer substance, and the tube body of the blood collection tube is made of quartz, PET plastic and other materials. And the sealing rubber plug is made of a polypropylene material. The stabilizer in the blood collection tube can effectively prevent genomic DNA in cells from being released into plasma, can stably preserve free DNA in blood at normal temperature, effectively prolongs the storage time of blood samples at room temperature, has no influence on subsequent detection results, can be used for various medical biological monitoring institutions such as laboratories and hospitals, and has wide application prospects. Good use values and application prospects are realized.
Owner:河南驼人医疗器械研究院有限公司
Plasma preservation solution, blood collection tube and application of plasma preservation solution and blood collection tube in ctDNA detection
InactiveCN114480640AEffective preservationAvoid degradationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnticoagulant AgentCell membrane
The invention relates to a plasma preservation solution, a blood collection tube and application of the blood collection tube in ctDNA detection, and belongs to the technical field of liquid biopsy. Comprising 50 to 200 mg / ml of an anticoagulant, 50 to 300 mg / ml of a preservative, 10 to 100 mg / ml of an aldehyde quenching agent, 10 to 80 mg / ml of a cell membrane protective agent, 2 to 35 mg / ml of a metabolic inhibitor, 5 to 50 mg / ml of a free radical trapping agent and water. The plasma preserving fluid provided by the invention can effectively preserve a blood sampling sample, is especially suitable for a sample treatment process of ctDNA detection, and has the advantages of long storage time and avoidance of ctDNA degradation.
Owner:南京兔牙医疗器械有限公司
Application of improved atmt in constructing Trichoderma dark green t23△crel
ActiveCN105368866BRepress transcriptionInhibition of secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTrichoderma sp.
The invention discloses an application of improved ATMT (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation) to construction of trichoderma atroviride T23 deltaCrel. The application is characterized in that the genomic DNA of trichoderma atroviride T23 is taken as a template, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is carried out on the Crel gene sequence, and thus upstream and downstream flanking sequences of the Crel gene are obtained; then leading in respectively to knock out upstream and downstream of plasmid pC1300qh, so as to form recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel; converting escherichia coli competence of the recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, performing verification, screening positive clone, extracting recombinant plasmid pC1300qh-deltaCrel, leading in agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL1, and carrying out improved ATMT. By using the improved ATMT technique, a trichoderma atroviride carbon metabolism inhibiting factor CRE1-knocked-out mutant strain is successfully constructed; the T23 deltaCrel bacterial strain has the functions of promoting secretion and activity of degrading enzyme of cell walls of trichoderma spp., and indirectly improving the function of trichoderma spp. to antagonize pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
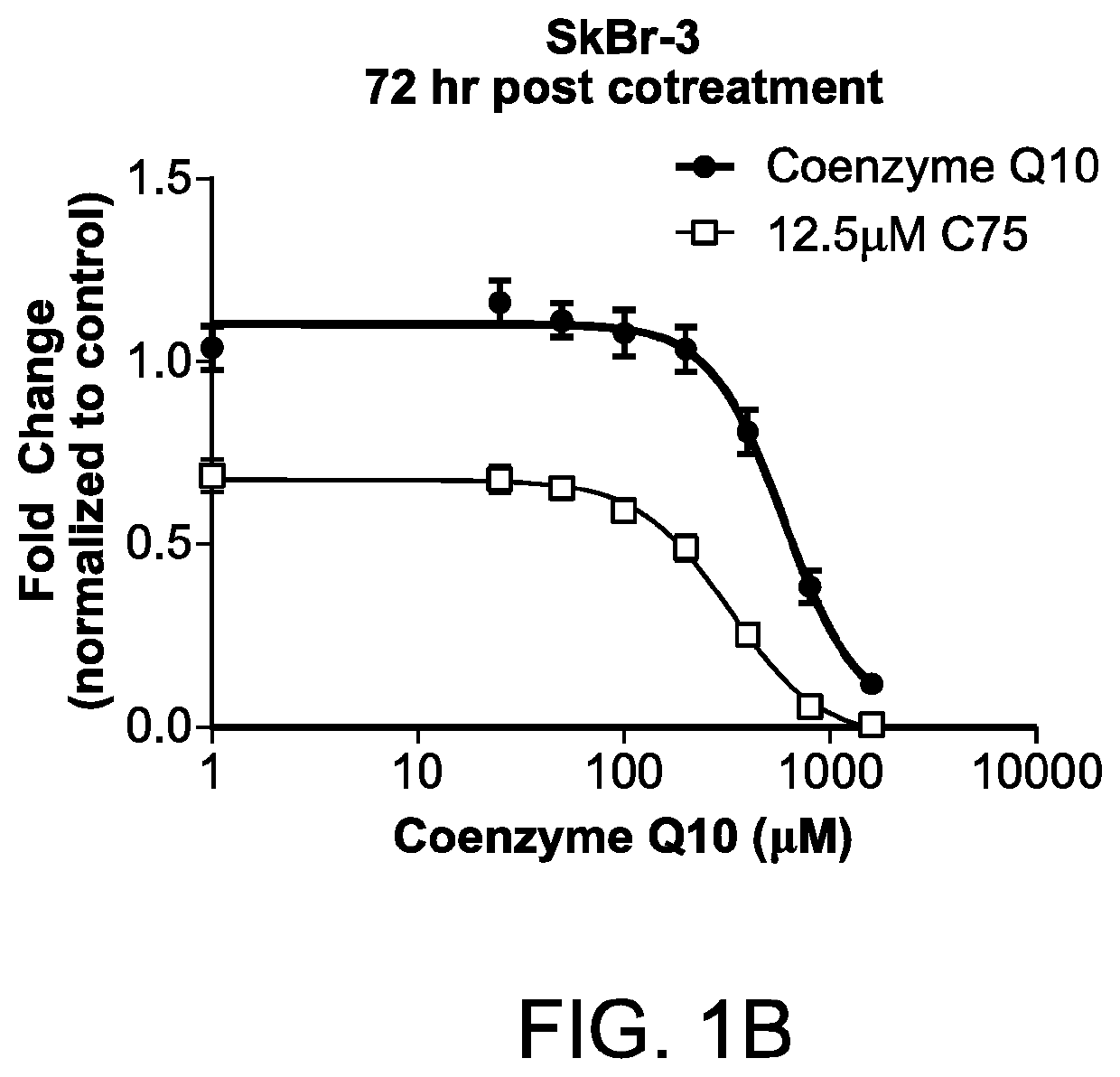
Methods for the treatment of cancer using coenzyme q10 and fatty acid metabolism inhibitors
InactiveUS20200330400A1Promote degradationHigh activityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipidomeTrimetazidine
Presented herein are methods for the treatment of oncological disorders by the co-administration of CoQ10 compositions and at least one fatty acid metabolism inhibitor. In one embodiment, the CoQ10 compositions are lipid-containing compositions. The fatty acid metabolism inhibitor may be an inhibitor of fatty acid synthesis, storage, transport or degradation. The fatty acid metabolism inhibitor may also be a modulator of fatty acid structure, for example a fatty acid desaturase or elongase. The fatty acid inhibitor may inhibit any molecule involved in fatty acid metabolism, such as fatty acid synthase (FASN), carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT-1), long-chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, or stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1). In embodiments, the fatty acid metabolism inhibitor may be C75, Etomoxir, trimetazidine or A939572.
Owner:BERG
Application of CAI (Carboxyamidotriazole) and glutamate uptake and metabolic inhibitors in resisting tumor
ActiveCN109674789AFavorable Treatment StrategiesInhibition of energy metabolismOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsGlutamate uptakeGlutamate dehydrogenase 1
The invention relates to application of CAI (Carboxyamidotriazole) and glutamate uptake and metabolic inhibitors in resisting tumor. Specifically, the invention relates to the application of the CAI and a combination of one or multiple glutamate uptake and metabolic inhibitors in preparing an anti-tumor drug for mammals. Particularly, the invention relates to the application of the CAI and a combination of an amino acid transporter inhibitor, a glutamate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitor and a glutaminase inhibitor in preparing the anti-tumor drug for the mammals.
Owner:GUANGDONG YINZHU PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Methods for determining the metabolic status of lymphomas
ActiveUS10947598B2The process is simple and convenientOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationGlyceraldehyde
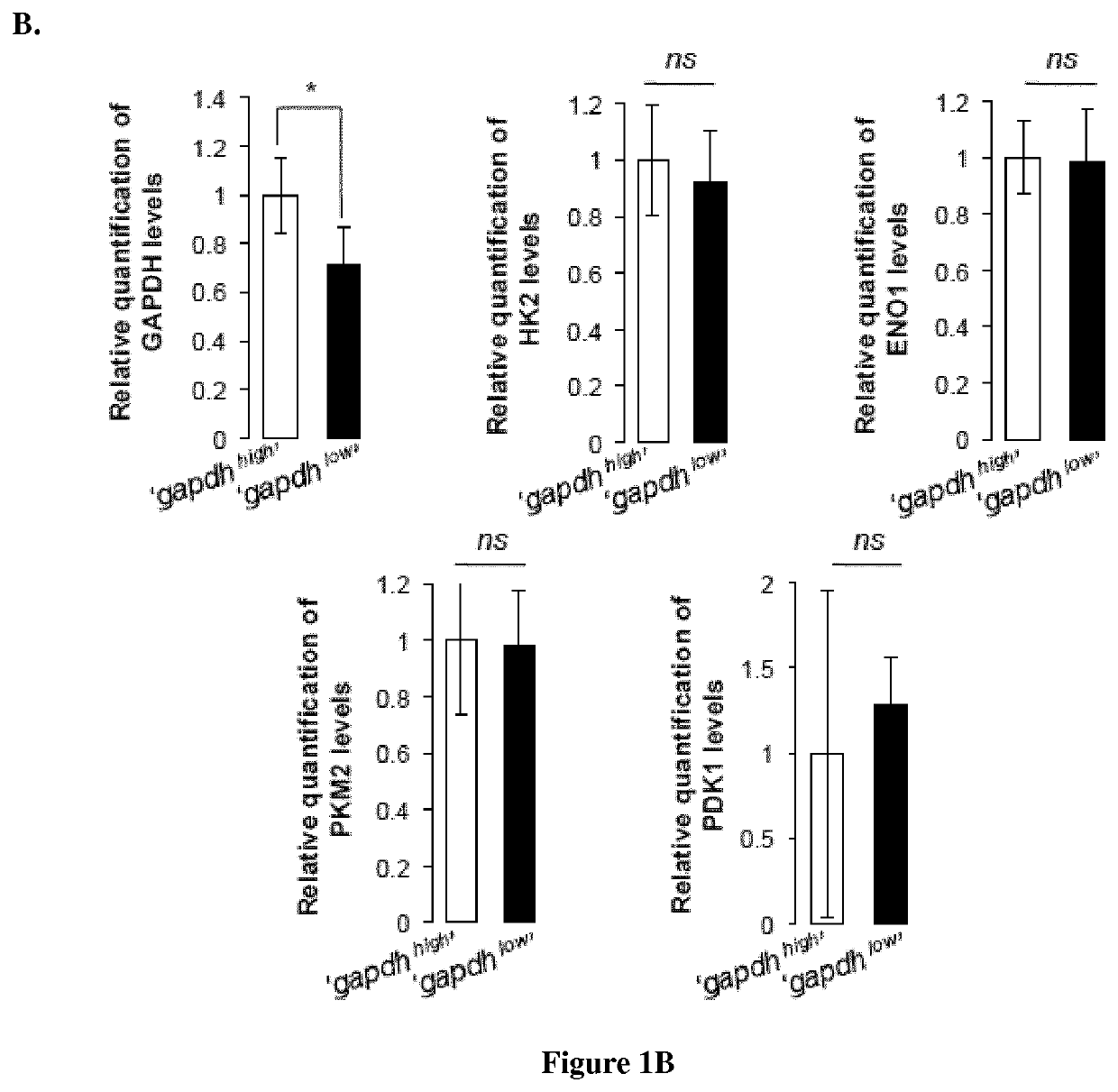
Provided is an in vitro method for determining the metabolic status of a lymphoma comprising a step of determining the level of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression in lymphoma cells, wherein a low level of GAPDH expression is indicative of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) status. Also provided is an in vitro method for predicting the responsiveness of a patient afflicted with a lymphoma to a treatment with a metabolic inhibitor selected from the group consisting of mitochondrial metabolic inhibitors and glutamine metabolism inhibitors comprising a step of determining the level of GAPDH expression in lymphoma cells obtained from said patient, wherein a low level of GAPDH expression is predictive of a response to a treatment with a metabolic inhibitor.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Application of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) in aspects of regulating tumor metabolism and inhibiting tumor growth
ActiveCN111568891APrevent proliferationLower metabolismOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersTumour metabolismTumor therapy
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and medicine, and particularly relates to an application of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) in the aspects of regulating tumor metabolism and inhibiting tumor growth. The application of the DMF as a small-molecule inhibitor in the aspect of regulating the tumor metabolism so as to inhibit the tumor growth is discovered for the first time; the DMF can inhibit proliferation of various tumor cells in vitro and reduce metabolism of the tumor cells, and has a certain inhibiting effect on occurrence and development of tumors in vivo; and by inhibiting thetumor metabolism, the tumor acidic microenvironment is improved, the inhibition on the T cell functions is reduced, the T cell reactivity is improved, the immunotherapy efficiency is enhanced, and a new target and a new idea are provided for tumor treatment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating cancer
ActiveUS20220064177A1Balance will shiftImprove throughputOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsBlastomaGlioblastoma
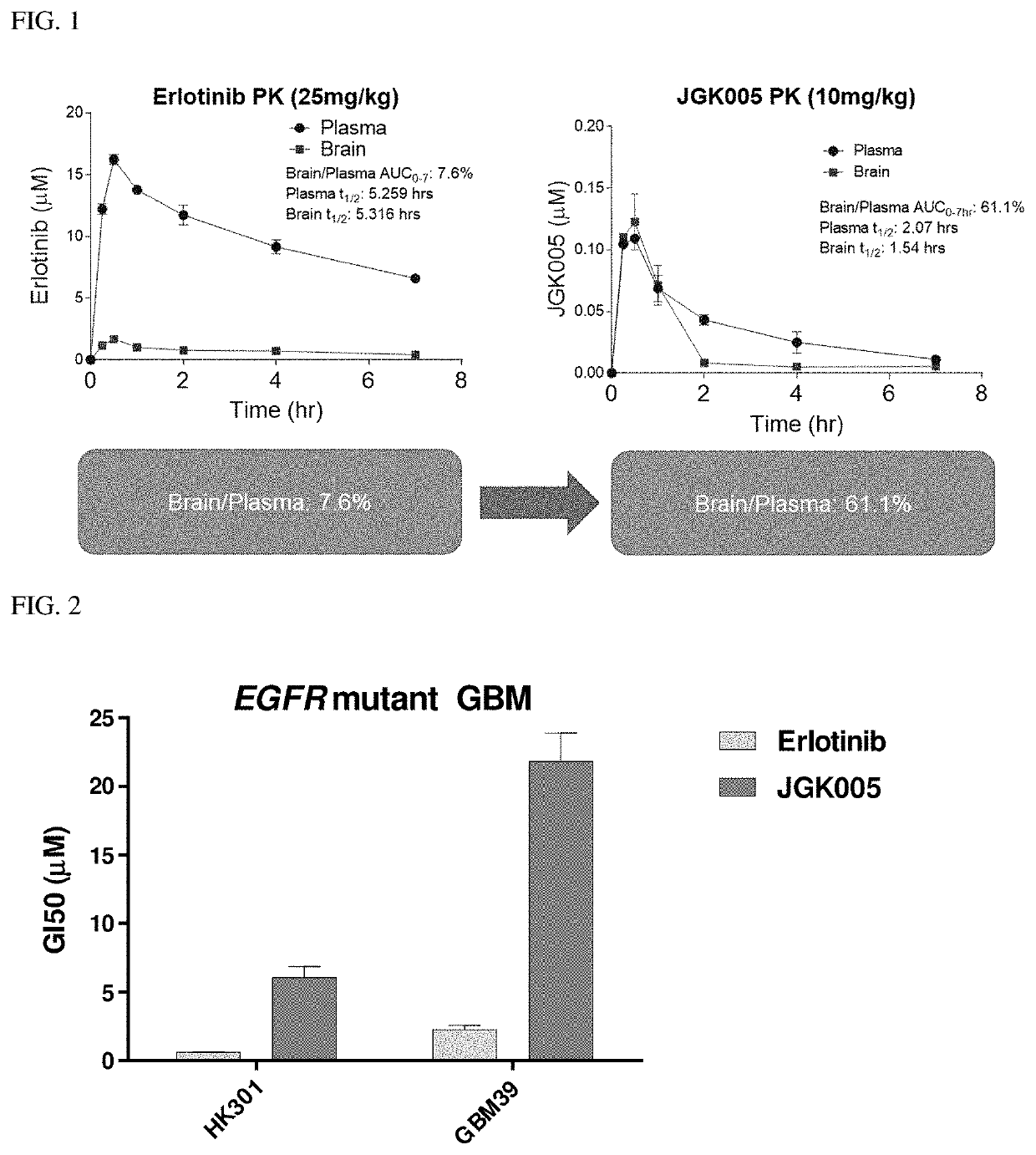
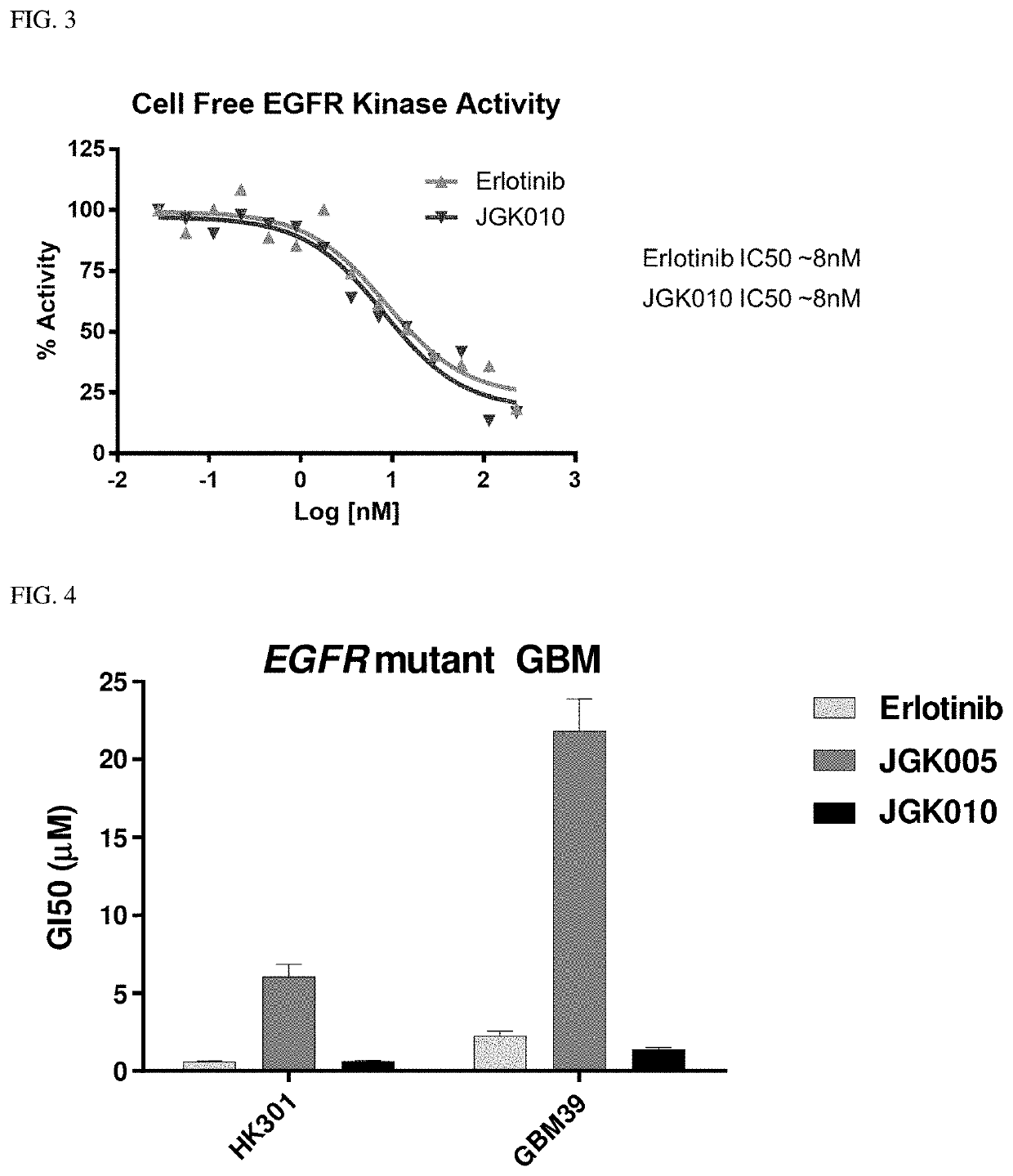
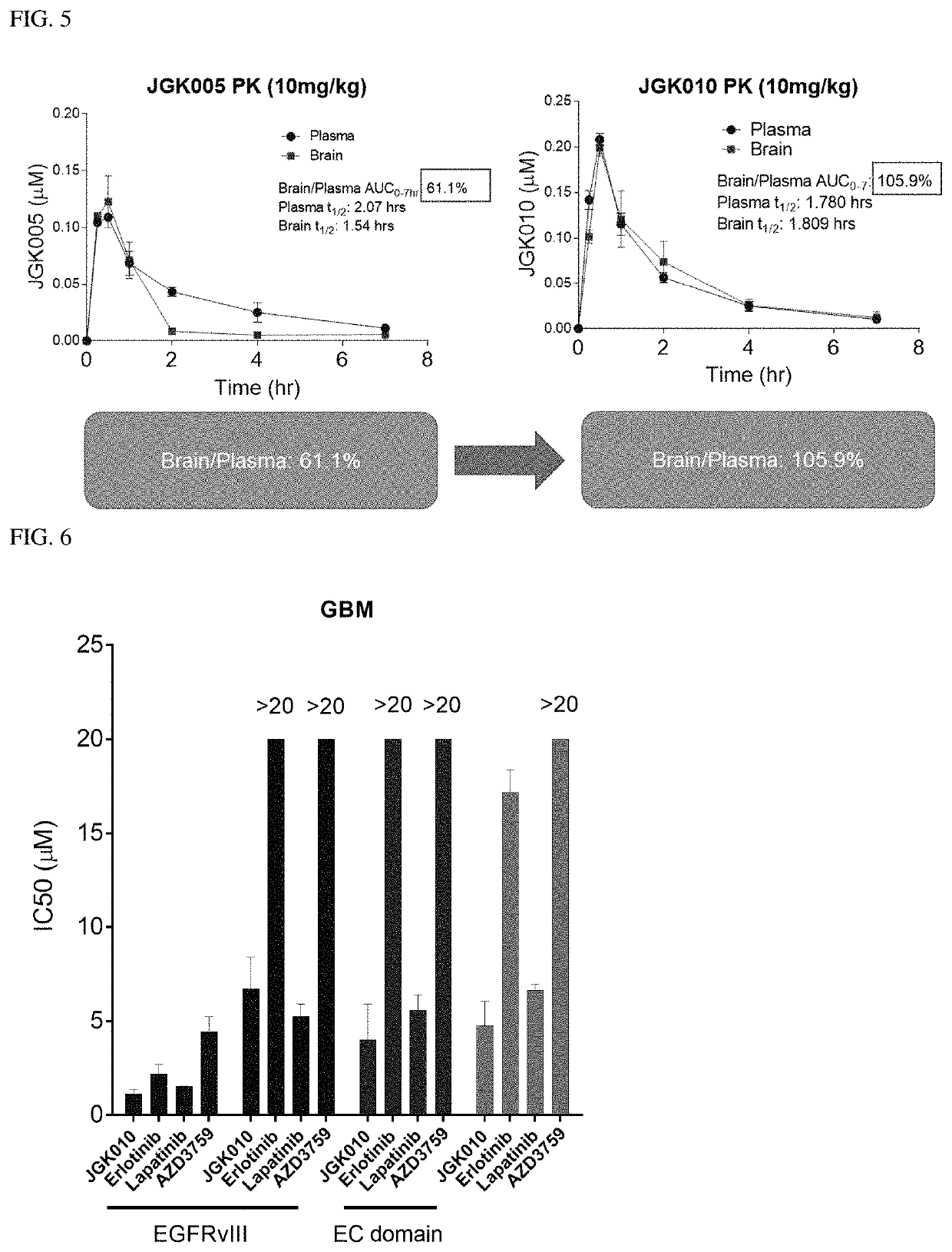
The present disclosure relates to compounds that are capable of penetrating the blood brain barrier to modulate the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase. The disclosure further relates to methods of treating glioblastoma and other EGFR-mediated cancers, such as those that have been determined to have altered glucose metabolism in the presence of inhibitors. The present disclosure also provides methods of administering to a subject a glucose metabolism inhibitor and a cytoplasmic p53 stabilizer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-methionine at high yield as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN112779200AIncrease productionStrengthen internal transportationBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliLarge intestine
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Inhibitors of HSV nucleotidyl transferases and uses therefor
ActiveUS10463664B2Organic chemistryHydroxy compound active ingredientsNucleic acid metabolismTreatment use
The present invention involves identification of inhibitors of herpesvirus nucleic acid metabolism. Also provided are methods of treatment using agents identified.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacteria with high production of l-methionine and its construction and application
ActiveCN112779200BIncrease productionStrengthen internal transportationBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliLarge intestine
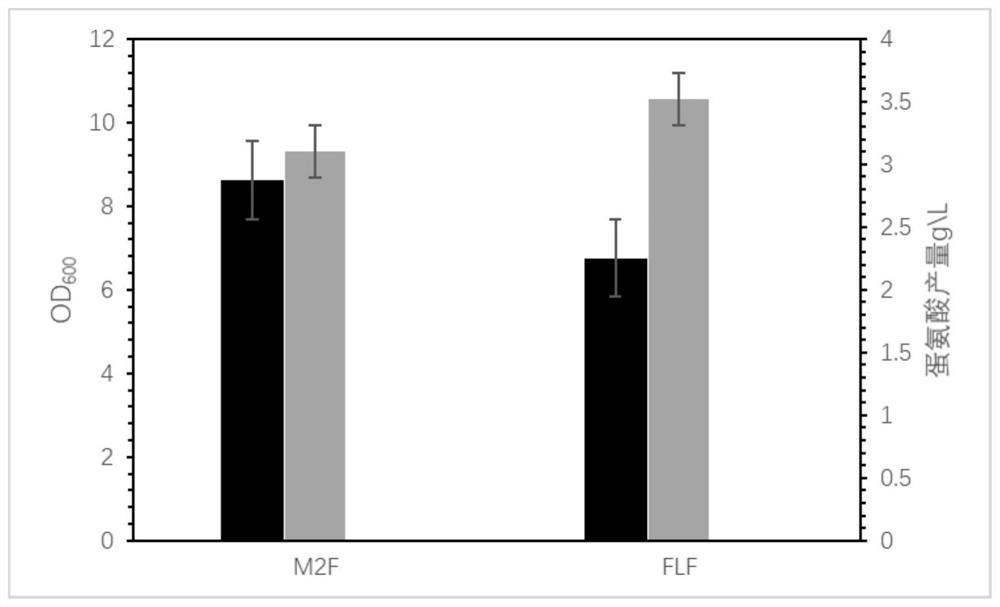
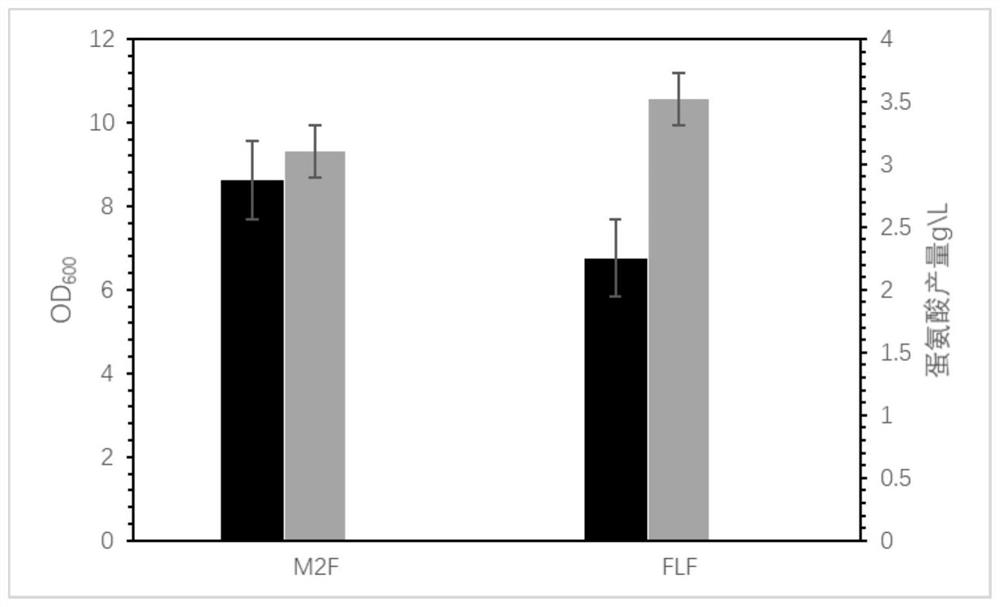
The present invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium with high L-methionine production and a construction method and application thereof. The invention transforms the L-methionine synthesis network of Escherichia coli, and enhances the utilization of methylenetetrahydrofolate by Escherichia coli by strengthening metF and GCV in the one-carbon module of the L-methionine synthesis pathway of Escherichia coli Ability; by replacing the original promoters of fliY and malY with the Trc promoter derived from pTrc99A, the cysteine / cystine transport pathway and the cysteine utilization pathway are enhanced, and the cysteine production in E. coli is relieved. The resulting metabolic inhibition; by knocking out the glyA of E. coli itself and introducing the glyA derived from Arthrobacter sp.FB24 to overexpress on the plasmid, the restriction of serine hydroxymethyltransferase in the large intestine itself is relieved, and finally high-yielding bacteria containing the plasmid are obtained. , the L-methionine yield increased from 2.8g / L to 3.83g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com