Method for predicting activation energy using an atomic fingerprint descriptor or an atomic descriptor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Database of Atomic Fingerprint Descriptors
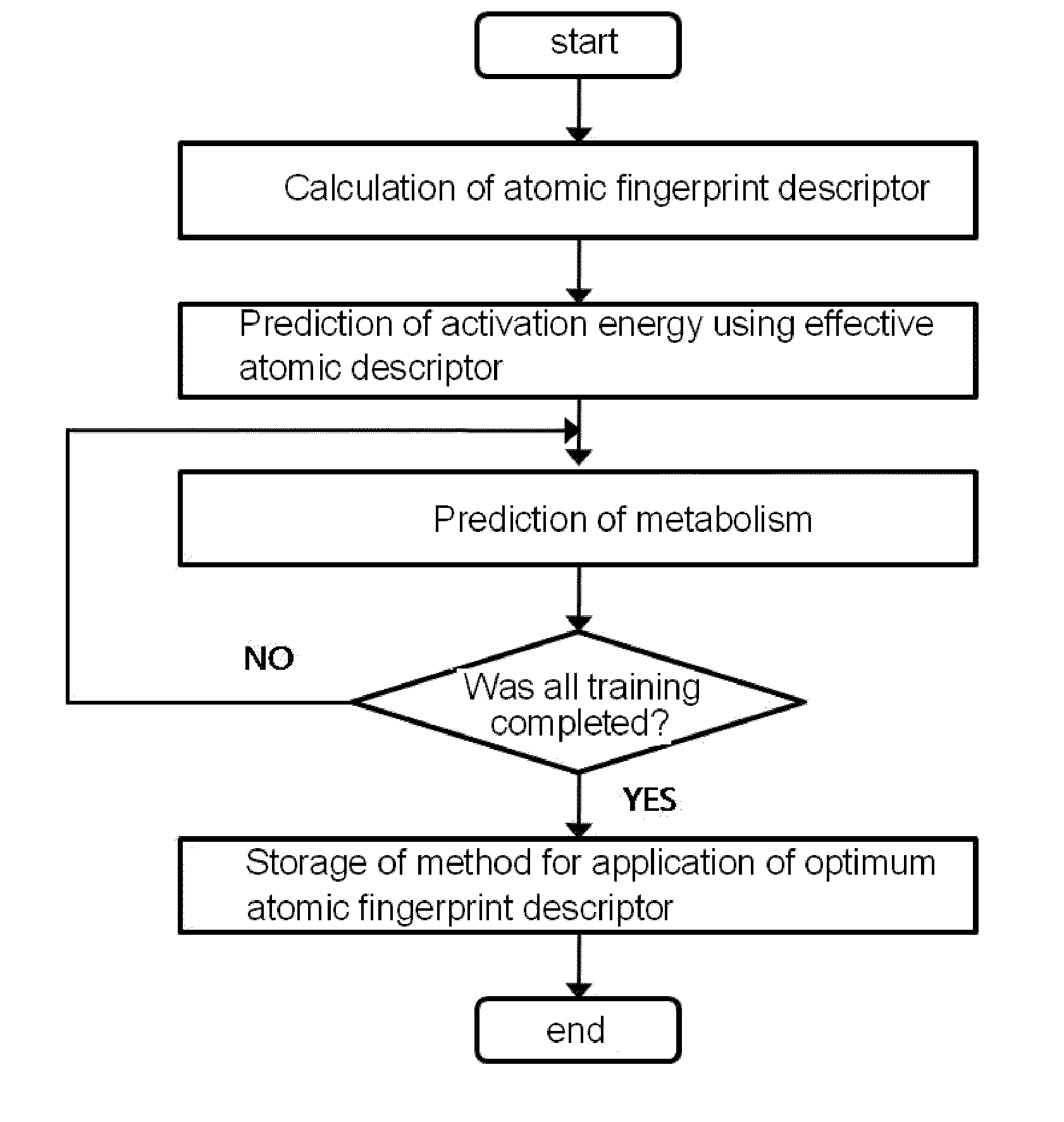
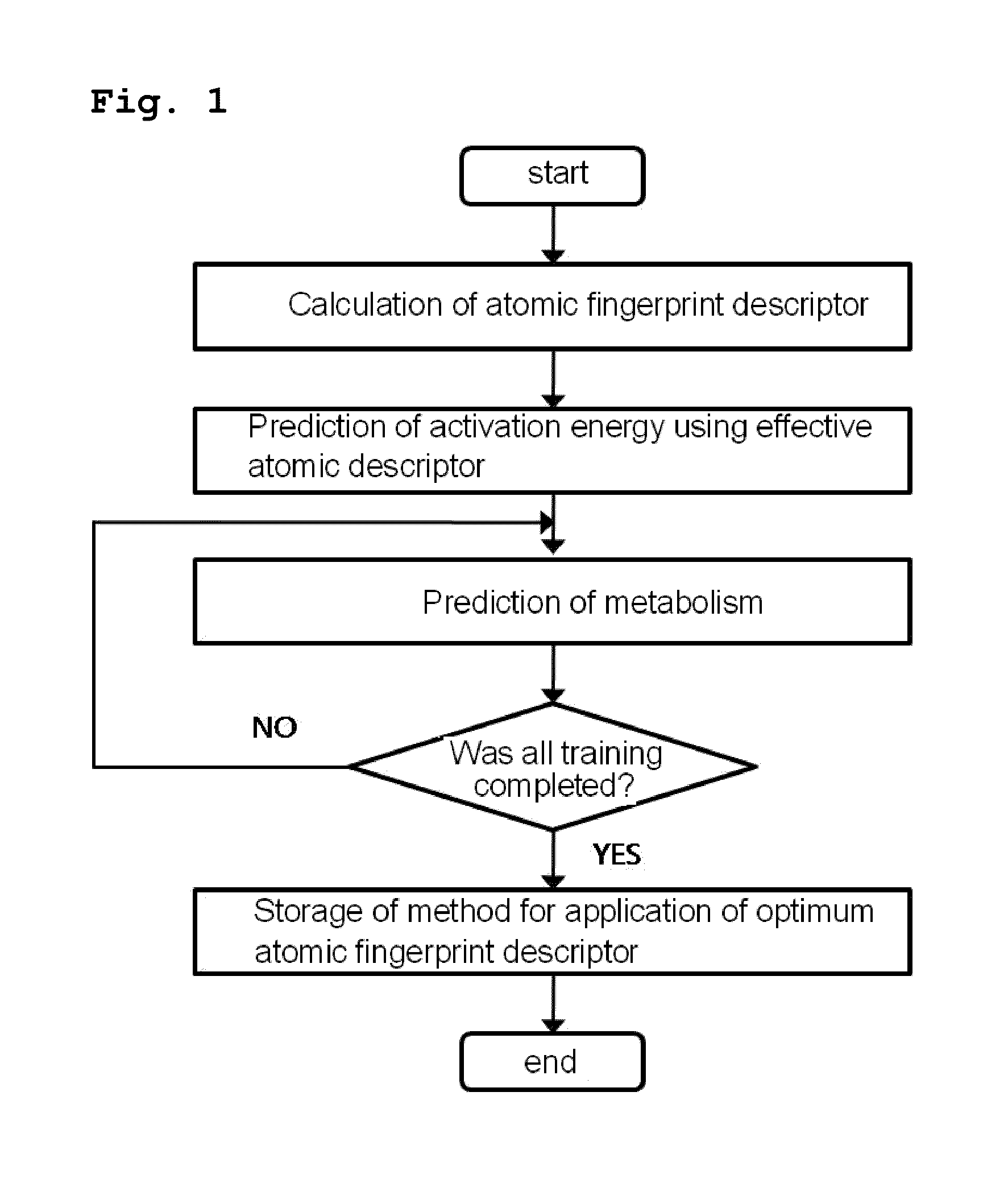
[0073]As shown in FIG. 1, the present inventors constructed a database of atomic fingerprint descriptors through a training method comprising the following steps (see FIG. 1):
[0074](i) calculating the atomic fingerprint descriptor of a substrate, which is represented by the following equation 1;
[0075](ii) predicting activation energy for an atomic position using an atomic descriptor;
[0076](iii) predicting cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism using the predicted activation energy; and
[0077](iv) comparing the predicted metabolism with experimental metabolism and storing whether the predicted metabolism occurs:
Xabc [Equation 1]
wherein X is the chemical symbol of an atom; a is a bond order that indicates the number of atoms bonded; b is a ring indicator that indicates whether the atom is part of a ring; and c is an aromatic indicator that indicates whether the atom is an aromatic atom.
[0078]Using the above-constructed database of...
example 2
Prediction of Metabolite of 2-Methoxyamphetamine Using the Prediction Method of the Present Invention
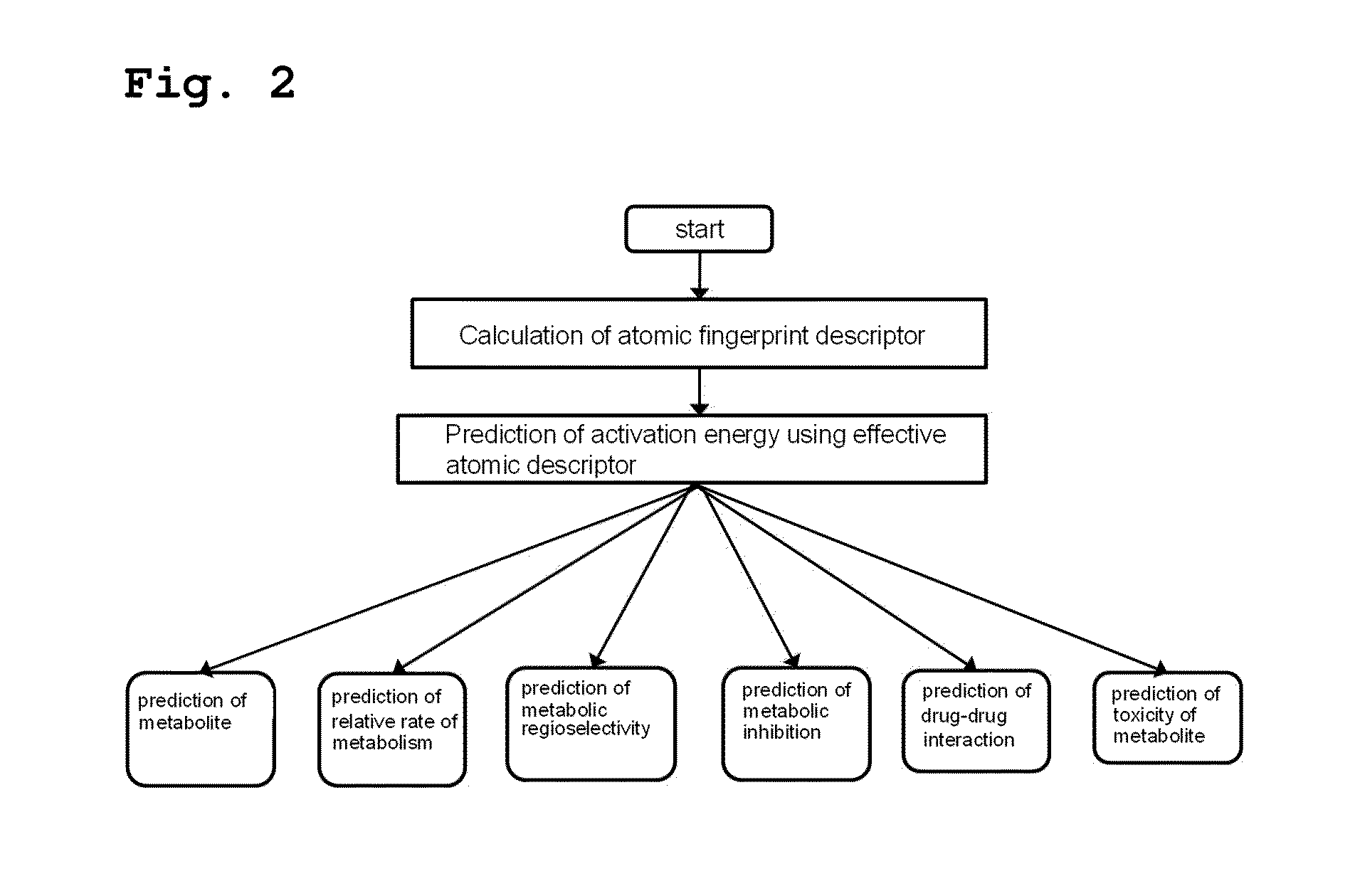
[0080]As shown in FIG. 2, the present inventors predicted activation energy using a method comprising the following steps (see FIG. 2):
[0081](i) calculating the atomic fingerprint descriptor of a substrate, which is represented by the following formula 1;
[0082](ii) comparing the calculated atomic fingerprint descriptor with the data, constructed by the method of Example 1, to select an atomic position where cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism can occur; and
[0083](iii) predicting activation energy for the selected atomic position using an atomic descriptor:
Xabc [Equation 1]
wherein X is the chemical symbol of an atom; a is a bond order that indicates the number of atoms bonded; b is a ring indicator that indicates whether the atom is part of a ring; and c is an aromatic indicator that indicates whether the atom is an aromatic atom.
[0084]After predicting the activation energy of 2-meth...
example 3
Prediction of Metabolite Using Only Reactivity Prediction Model
[0089]A metabolite was predicted only with a reactivity prediction model without considering the binding possibility of a substrate. When analysis was carried out using a method of selecting two positions having the highest possibility, a predictability of about 62-70% was generally shown.
TABLE 4Results of metabolite prediction carried outusing only reactivity prediction modelNaNcbNc / N (%)CYP1A214410170.1CYP2C91198369.7CYP2D61469162.3CYP3A419612865.3aNumber of substrates used in training;bNumber of substrates that accurately reproduced an experimentally known metabolism.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com