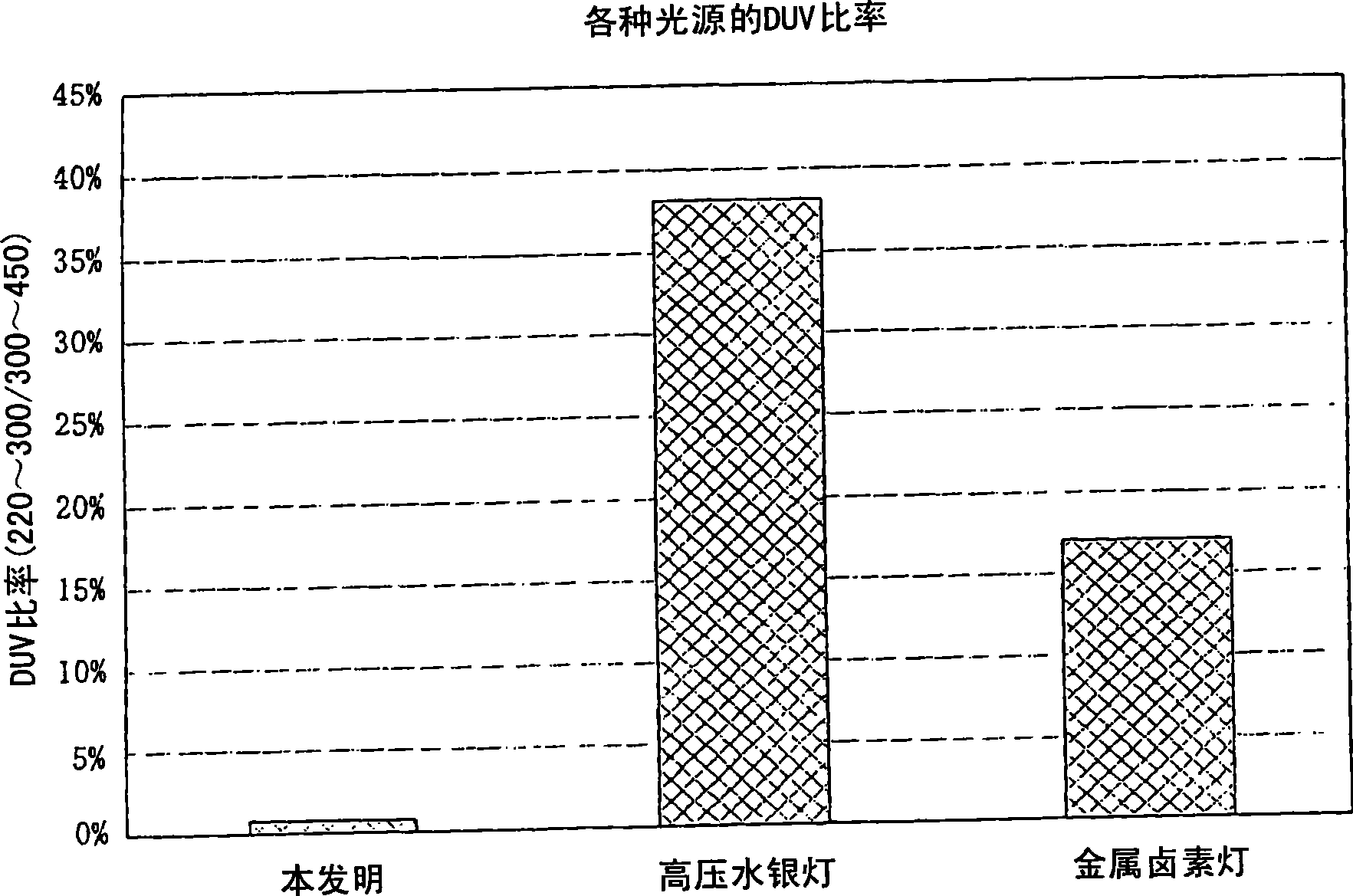
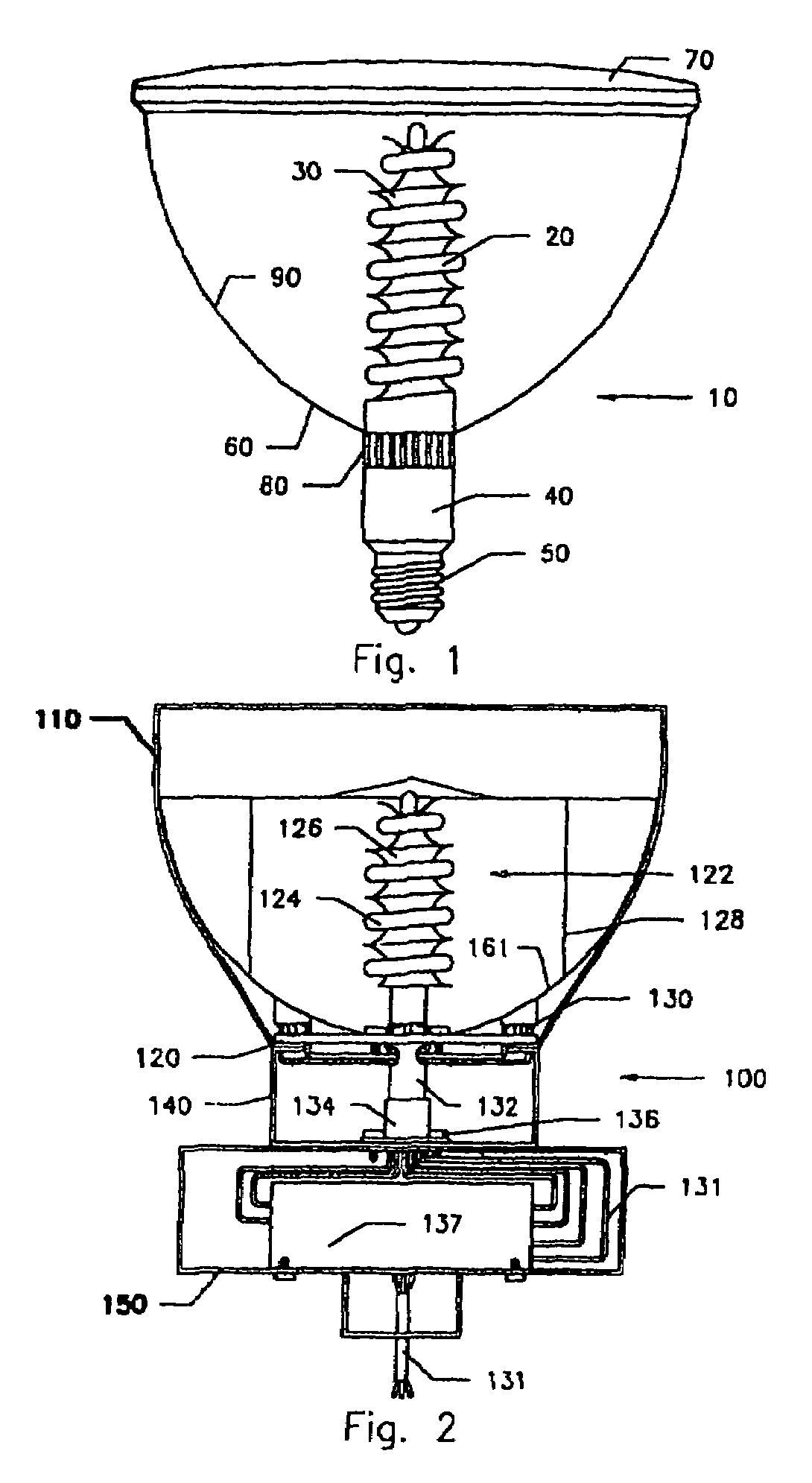
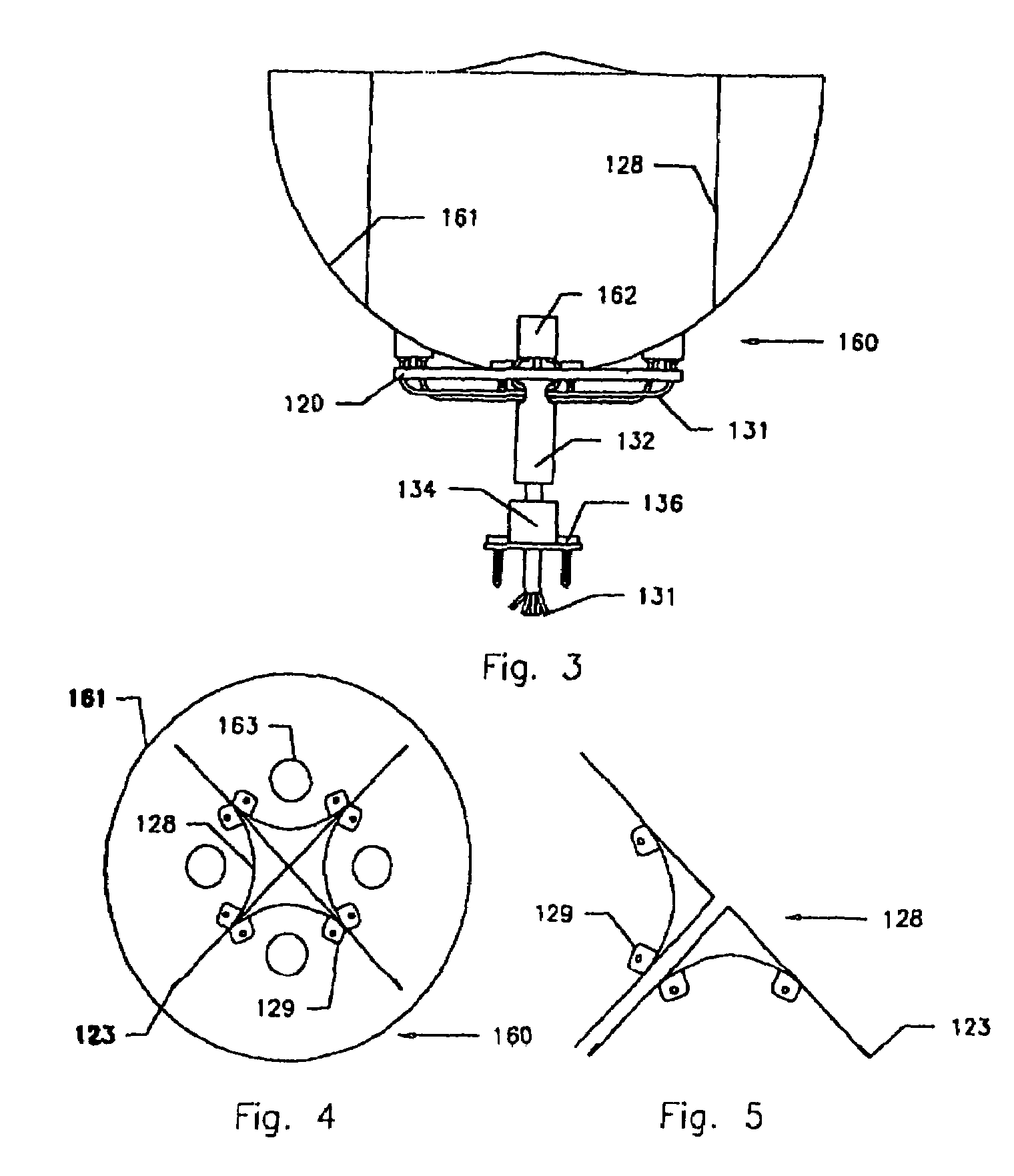
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Mercury-vapor lamp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
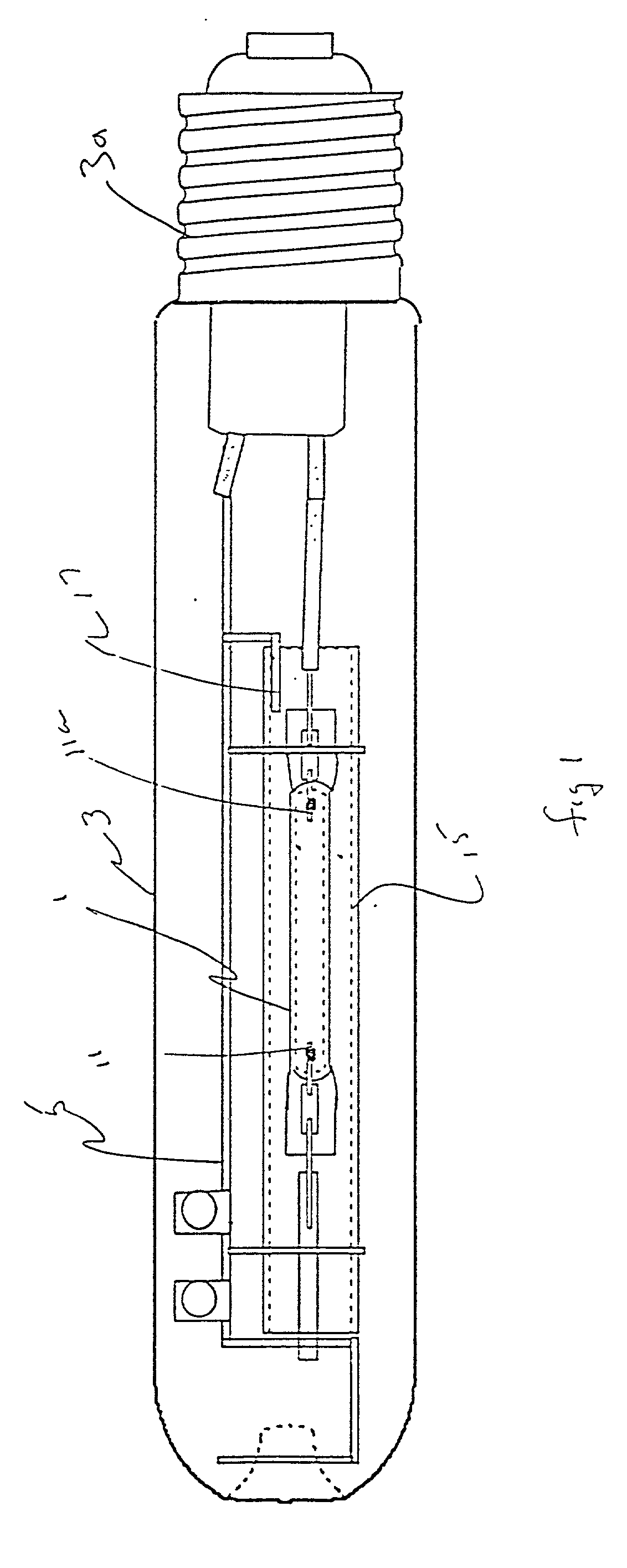
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger borosilicate glass bulb. The outer bulb may be clear or coated with a phosphor; in either case, the outer bulb provides thermal insulation, protection from the ultraviolet radiation the light produces, and a convenient mounting for the fused quartz arc tube.
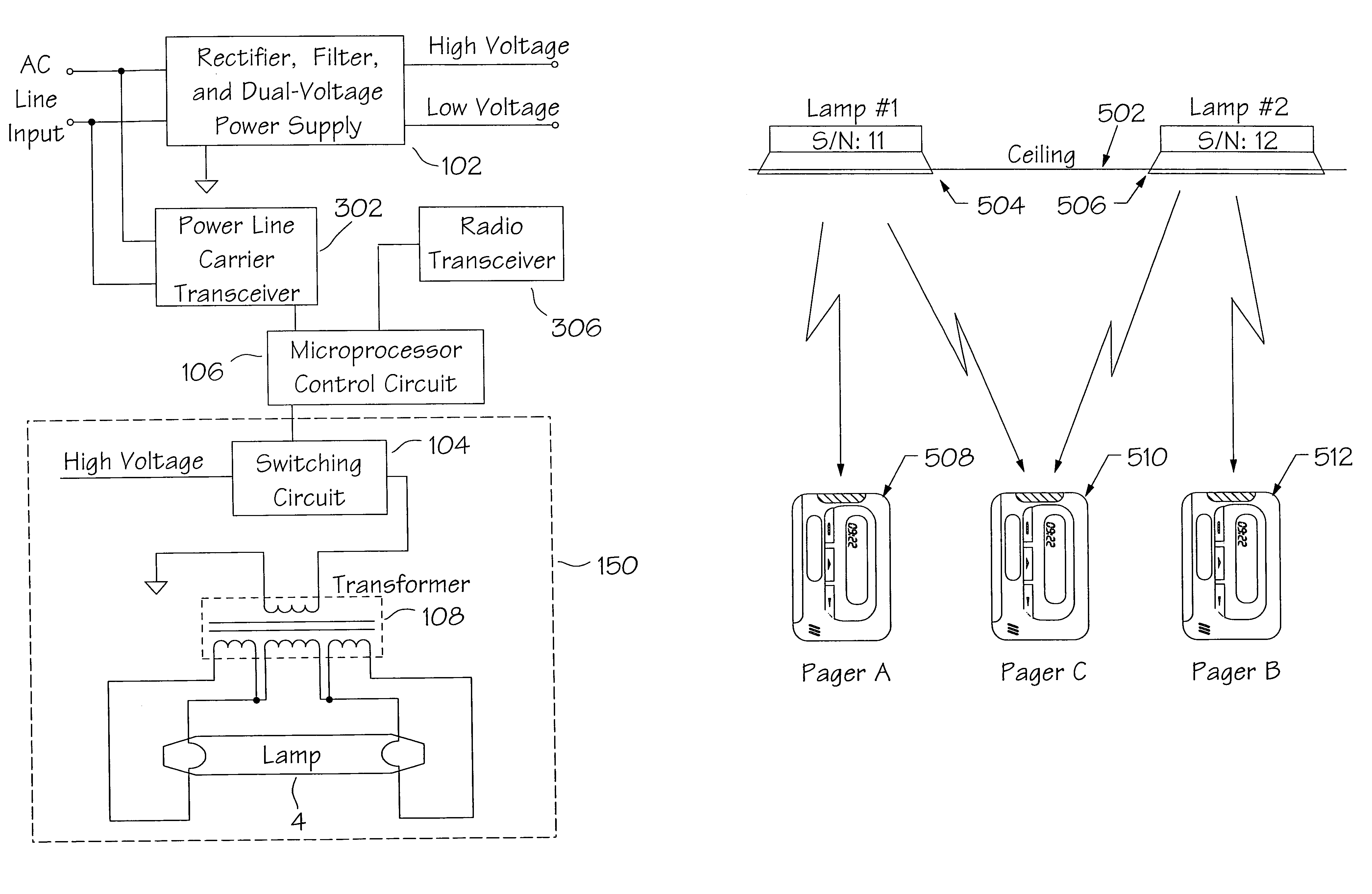
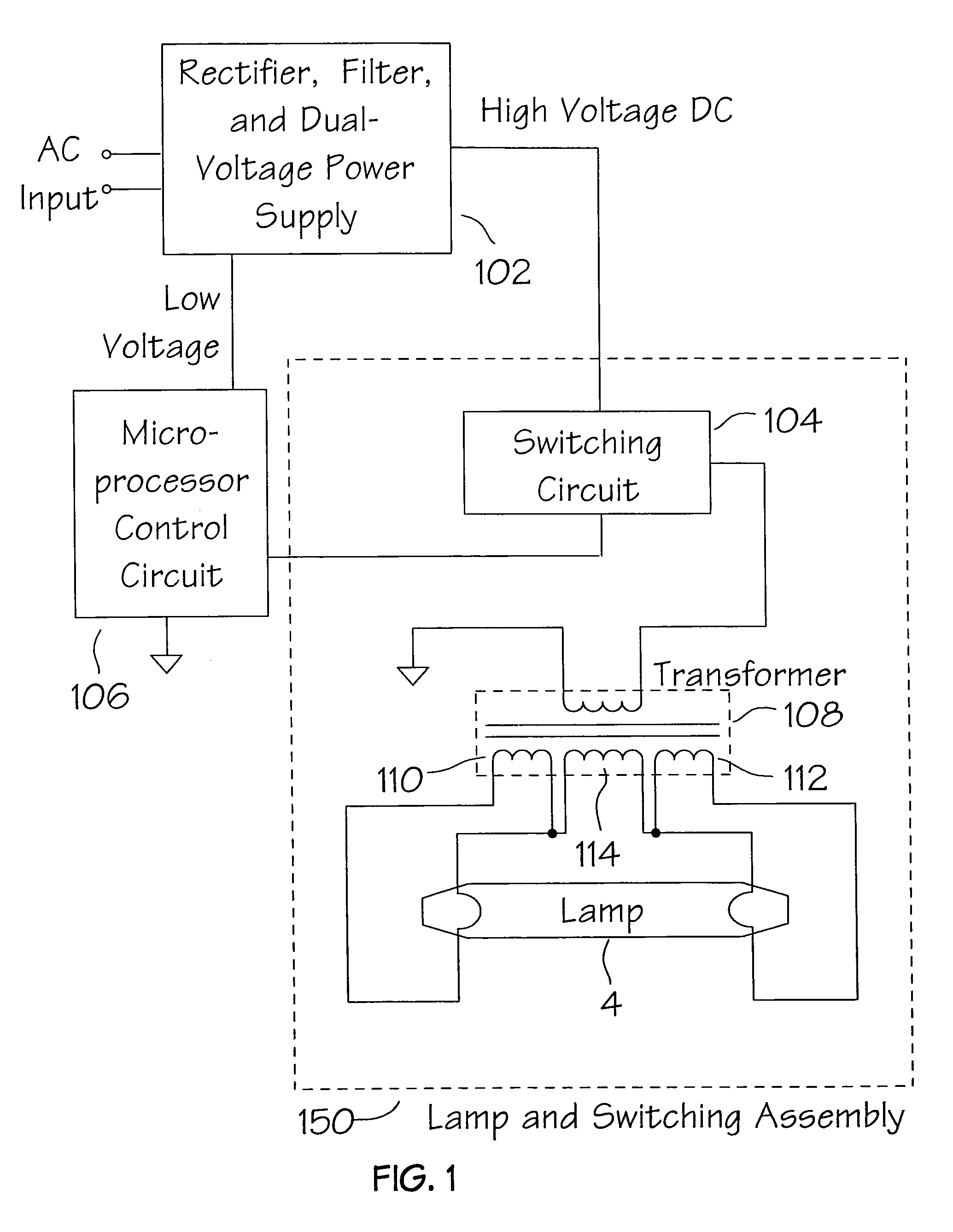
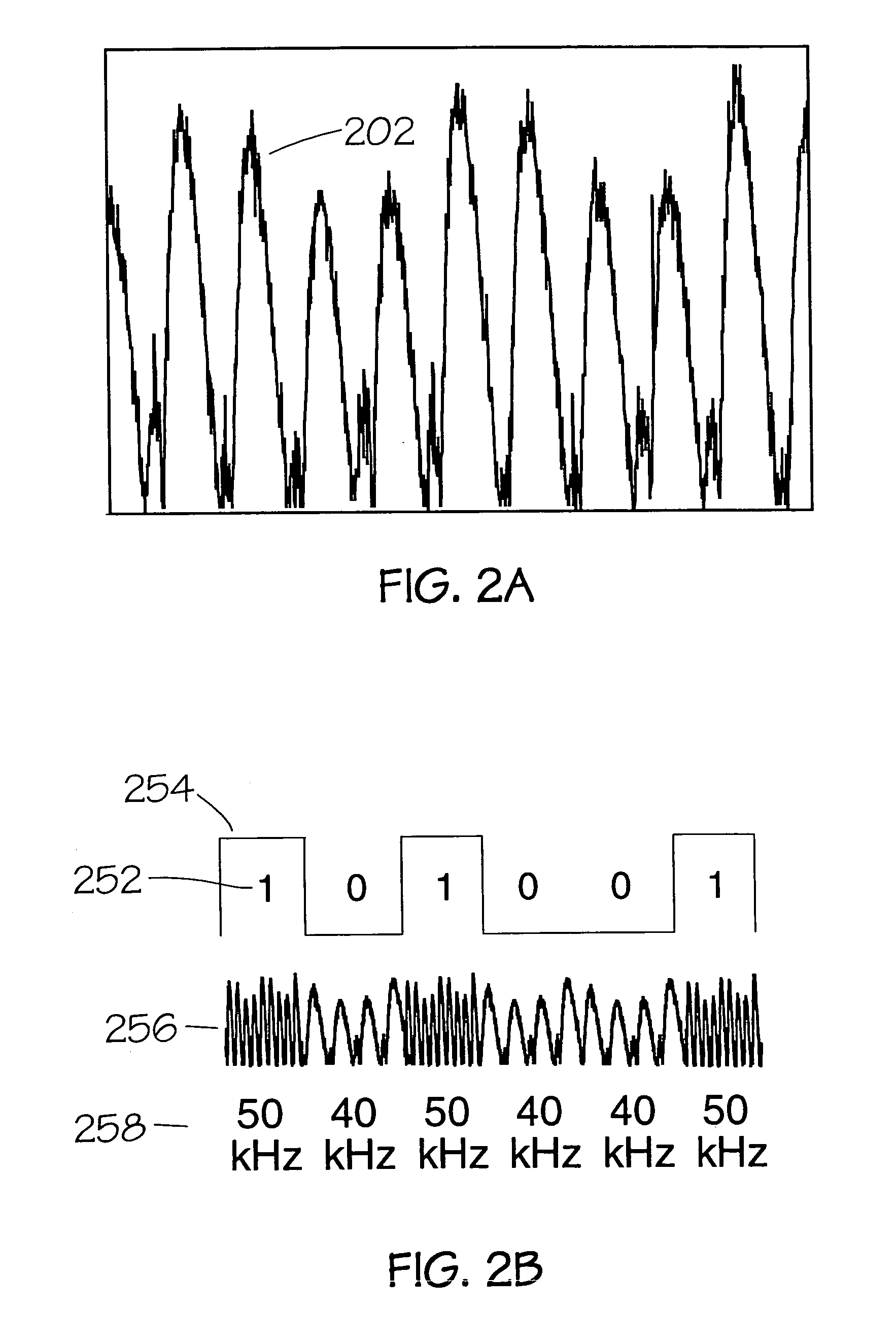
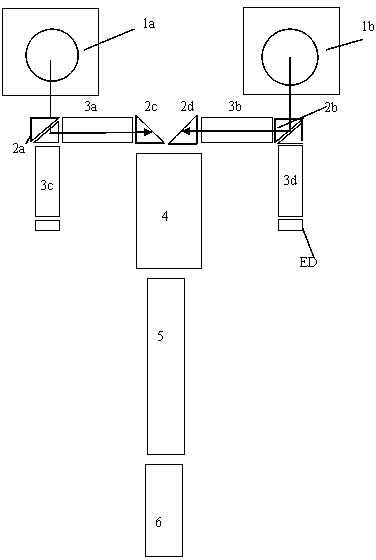
Method and apparatus for the zonal transmission of data using building lighting fixtures
This invention relates to the zonal transmission of data by the modulation of the light output of arc lamps or discharge lamps; including the visible or invisible light output of fluorescent lamps, mercury vapor lamps, high or low-pressure sodium lamps, metal-halide based lamps, or other arc or discharge lamps. The method results in an easily installed, easily maintained, and economical to purchase, optical-wave communications system which exploits the existing infrastructure of a building or facility to facilitate the transmission of data in individual zones; thereby facilitating the transmission of wide-area as well as zonal-specific data to compatible receivers, and further facilitating the determination of location of remote devices or users, and the delivery or exchange of information or data, utilizing limited range transmission techniques.
Owner:CONVERGENCE WIRELESS A CALIFORNIA CORP
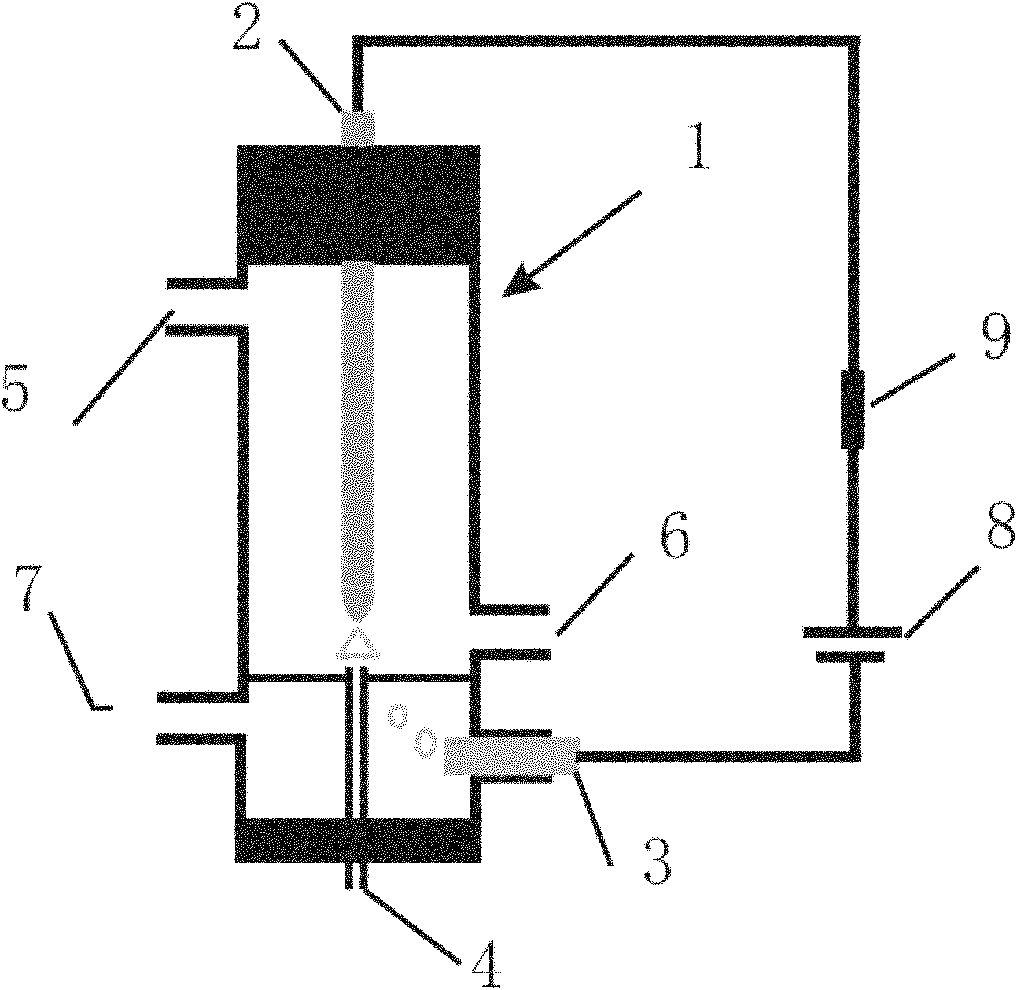
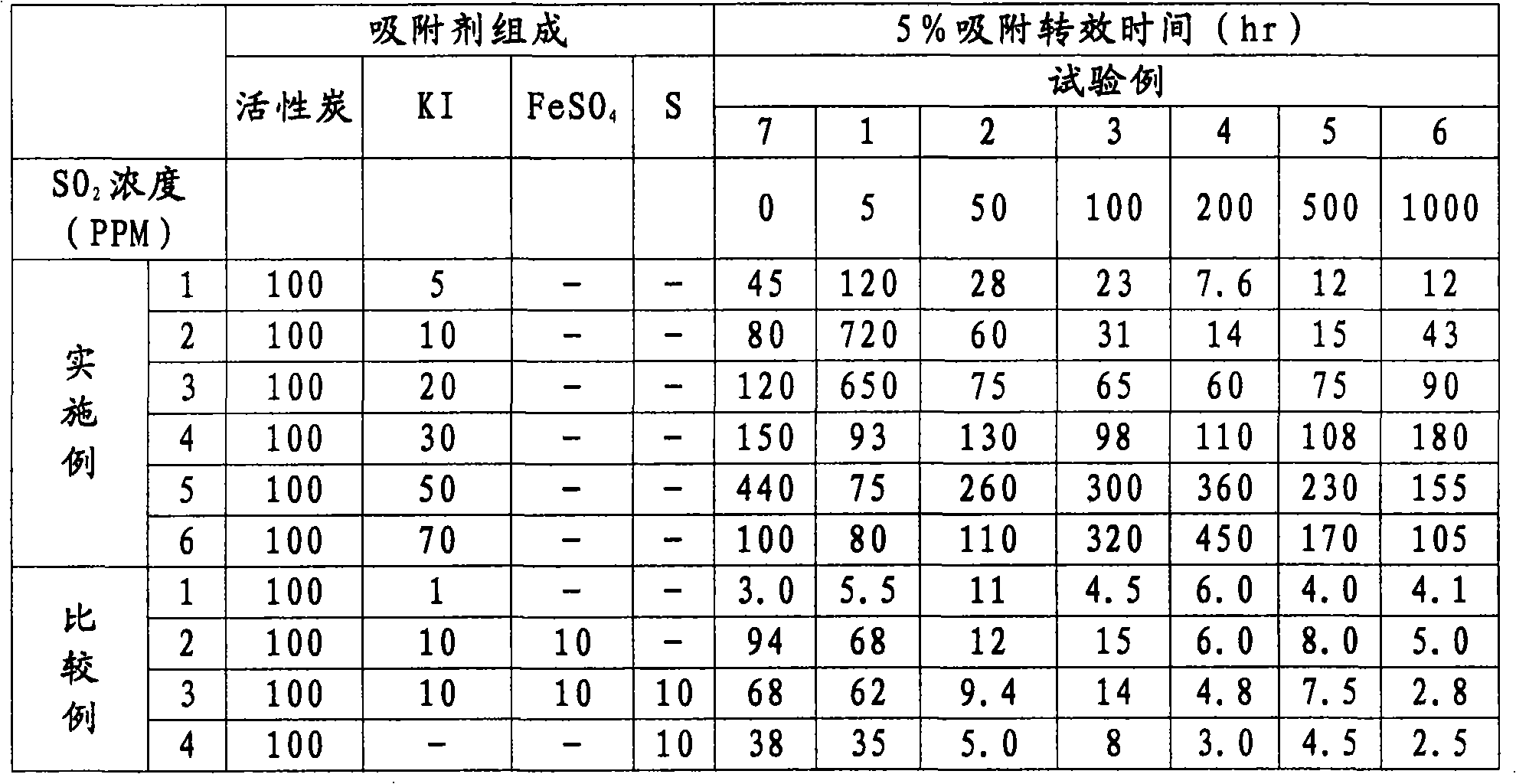
Method for removing mercury vapor in gas
When sulfur oxides are present in mercury vapor-containing gas, the adsorption of mercury vapor by activated carbon is inhibited. Therefore, there has been demand for development of a method for effective adsorption removal of mercury vapor even in the coexistence of sulfur oxides.Efficient and long-term removal of mercury vapor was made successful by contacting an activated carbon adsorbent consisting of 100 parts by weight of activated carbon impregnated with 5 to 70 parts by weight of only an alkali metal halide, with mercury vapor in sulfur oxide-containing gas.
Owner:JAPAN ENVIROCHEM
Method and apparatus for the zonal transmission of data using building lighting fixtures
InactiveUS20050231128A1Electric light circuit arrangementClose-range type systemsEffect lightEngineering
This invention relates to the zonal transmission of data by the modulation of the light output of arc lamps or discharge lamps; including the visible or invisible light output of fluorescent lamps, mercury vapor lamps, high or low-pressure sodium lamps, metal-halide based lamps, or other arc or discharge lamps. The method results in an easily installed, easily maintained, and economical to purchase, optical-wave communications system which exploits the existing infrastructure of a building or facility to facilitate the transmission of data in individual zones; thereby facilitating the transmission of wide-area as well as zonal-specific data to compatible receivers, and further facilitating the determination of location of remote devices or users, and the delivery or exchange of information or data, utilizing limited range transmission techniques.
Owner:CONVERGENCE WIRELESS A CALIFORNIA CORP
Air sterilization apparatus
InactiveUS20070101867A1Improve reflectivityCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesEngineering
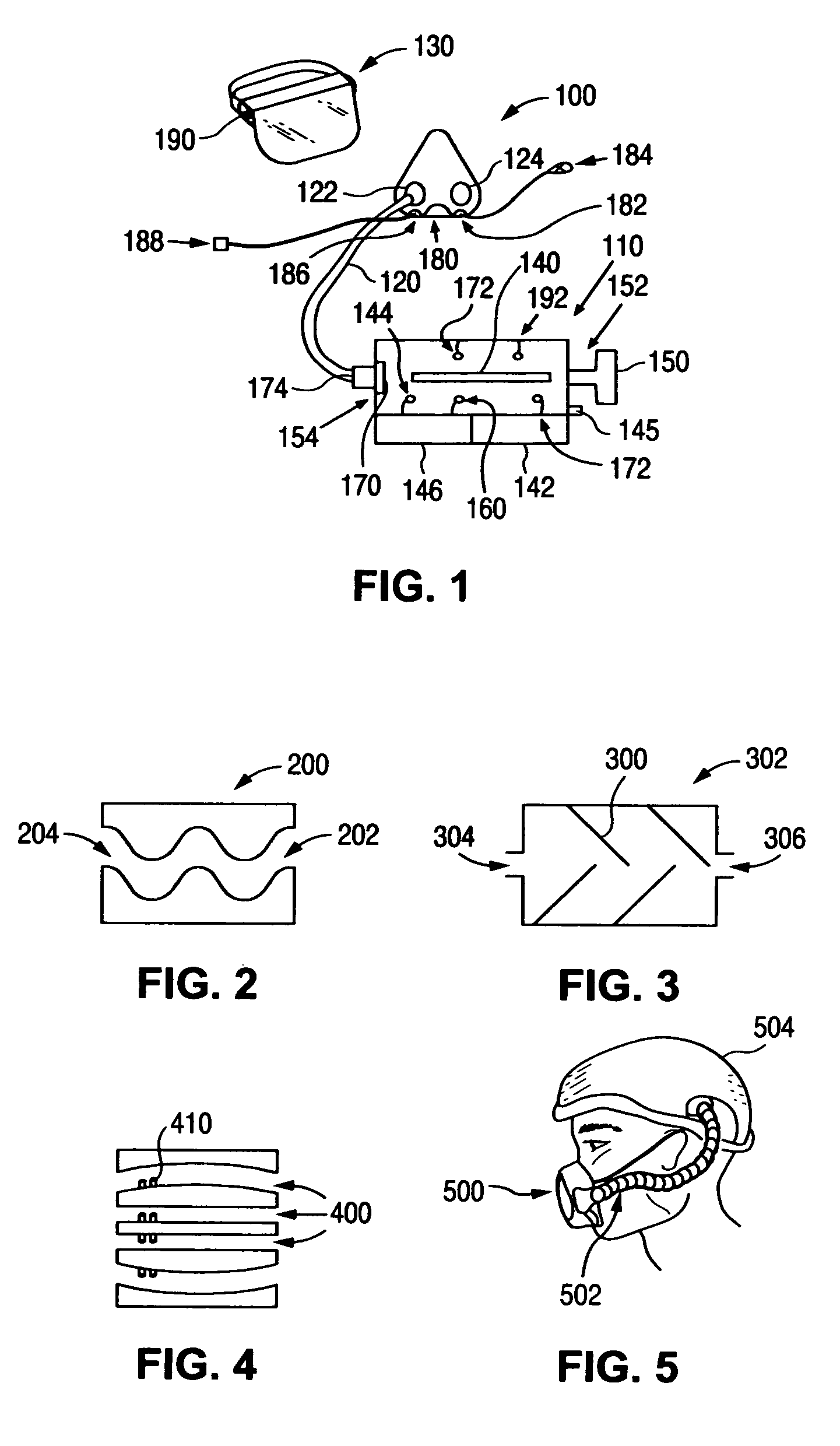
A portable sterilization apparatus that includes a face mask connected to a kill chamber having an ultraviolet source to destroy biological contaminants such as viruses, bacteria and fungi in air supplied to the mask, further includes a disposable particle filter in the kill chamber for filtering out particulates prior to irradiating the air with UV light, and in the case of a mercury vapor lamp UV source, a quartz sleeve surrounding the lamp. Valves are included in the face mask to limit carbon dioxide exhalation back into the kill chamber and to facilitate exhalation of air to the atmosphere.
Owner:NEXT SAFETY INC
Method and apparatus for highly efficient removal of water organisms by utilizing photoelectric Fenton reaction
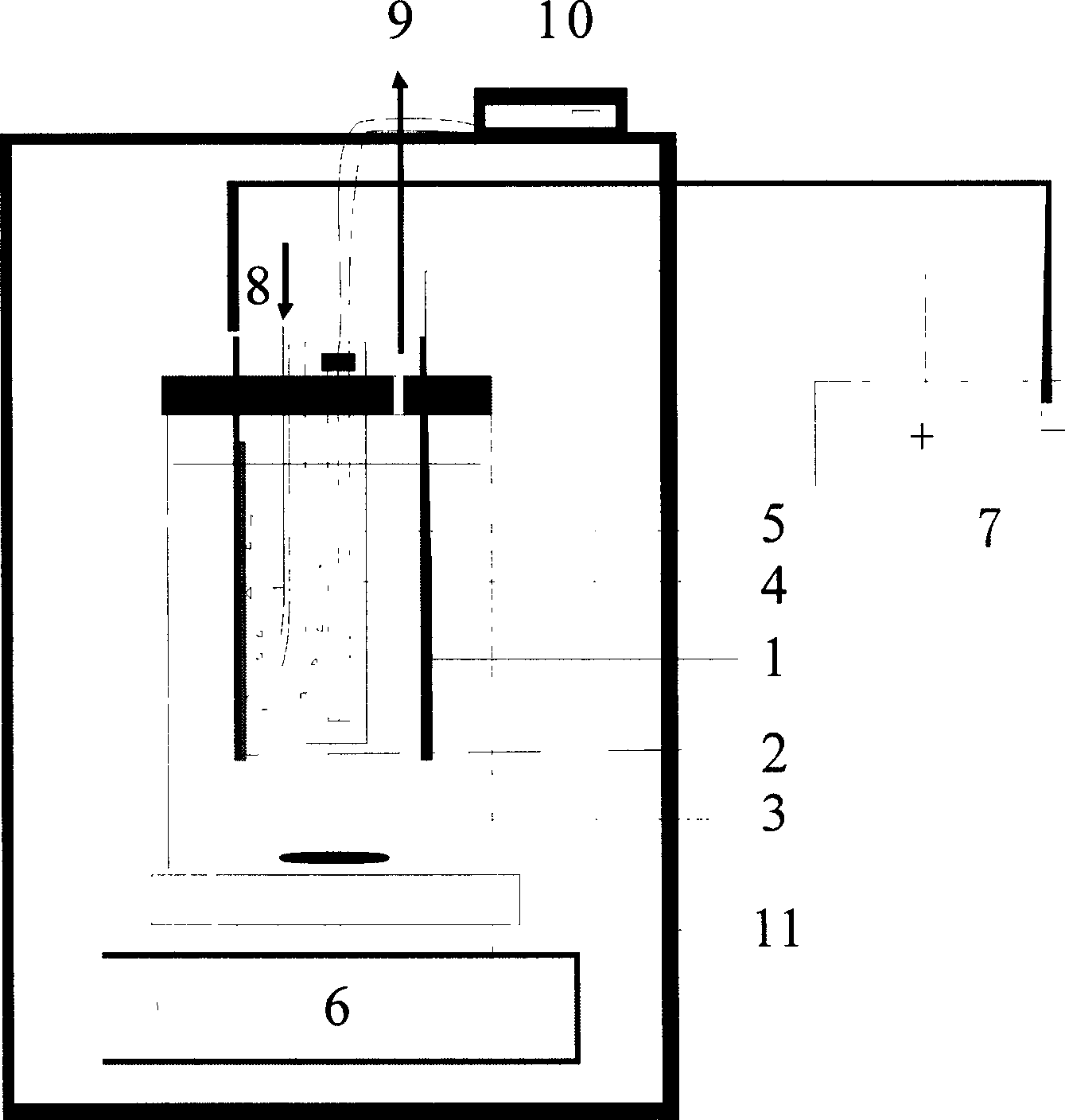
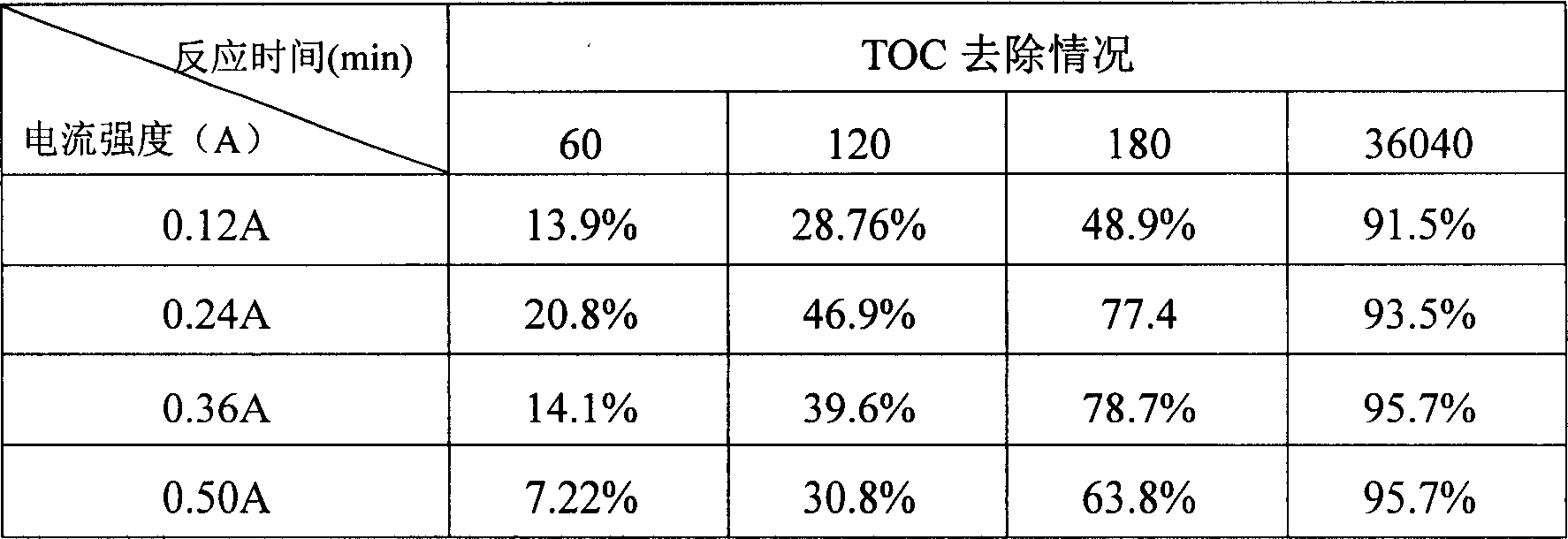
The invention provides a photoelectrical FenDun method for removing the non-degradable organic substance in water, which combines photochemistry reaction and electrical FenDun reaction to co-treat the organic substance effectively with multiple actions. The invention also provides a device applying the photoelectrical FenDUN reaction to remove organic substance in water, which comprises: the reactor employing shape stable electrode (DSA) as anode, employing activated charcoal as cathode, putting the low pressure mercury vapor lamp closed in the quartz glass tube vertically between the anode and cathode and venting a certain quantity of oxygen to the cathode surface, adding marginal ferrous salt into the organic wastewater with pH being about 3 as catalyst and importing current flow for electrolysis to remove pollutant. The invention oxides and degrades organic substance by using the hydroxyl free radical generated by photochemical reaction and electrical FenDun reaction, the hydroxyl free radical possesses strong oxidability which can oxide organic substance without selection, and is characterized by the complete, fast and effective oxidation and no secondary pollution.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing yield of natural cordyceps sinensis
The invention provides a method for increasing the yield of natural cordyceps sinensis. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting a base for increasing the yield of natural cordyceps sinensis; (2) placing a trapping lamp; (3) preparing trapping liquid; (4) screening and preparing culture medium of hepialidae hirsutella sinensis and paecilomyces hepialid; and (5) controlling yield increase conditions. According to the method, at the adult stage, a high pressure mercury vapor lamp is used for trapping, so the imagoes of hepialus armoricanus around the lamp fly to the base, and the egg-laying amount is increased; ethanol, vinegar and sugar solution are sprayed on meadows beneficial to larva growth, so the larvae gather together; and the hepialidae hirsutella sinensis and the liquefied paecilomyces hepialid are sprayed on the gathering area of larvae to raise the infection rate of the larvae of hepialus armoricanus, so the aim of increasing the yield of cordyceps sinensis is achieved and the industrialized production is realized.
Owner:瓜州亿得生物科技有限公司
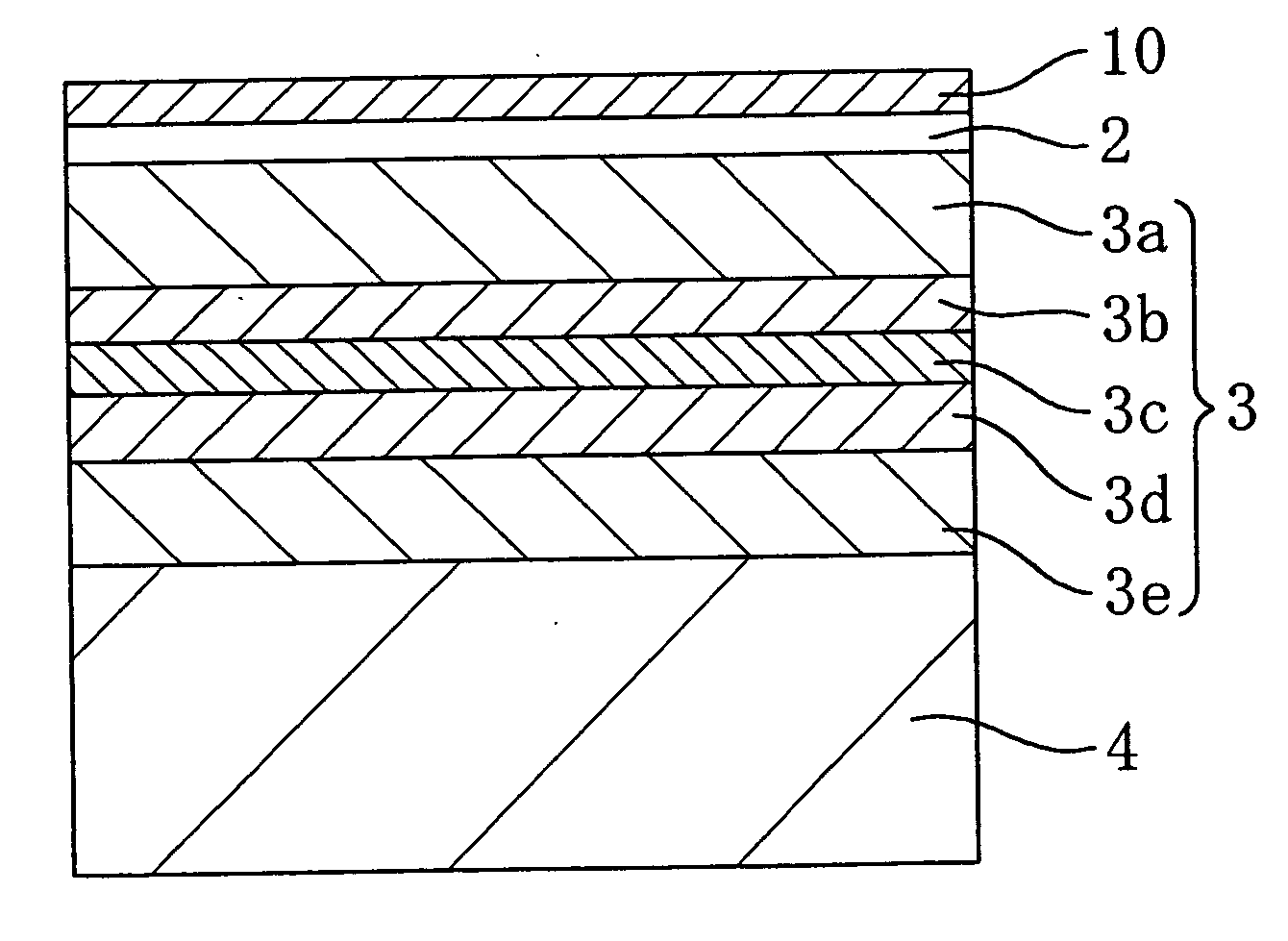
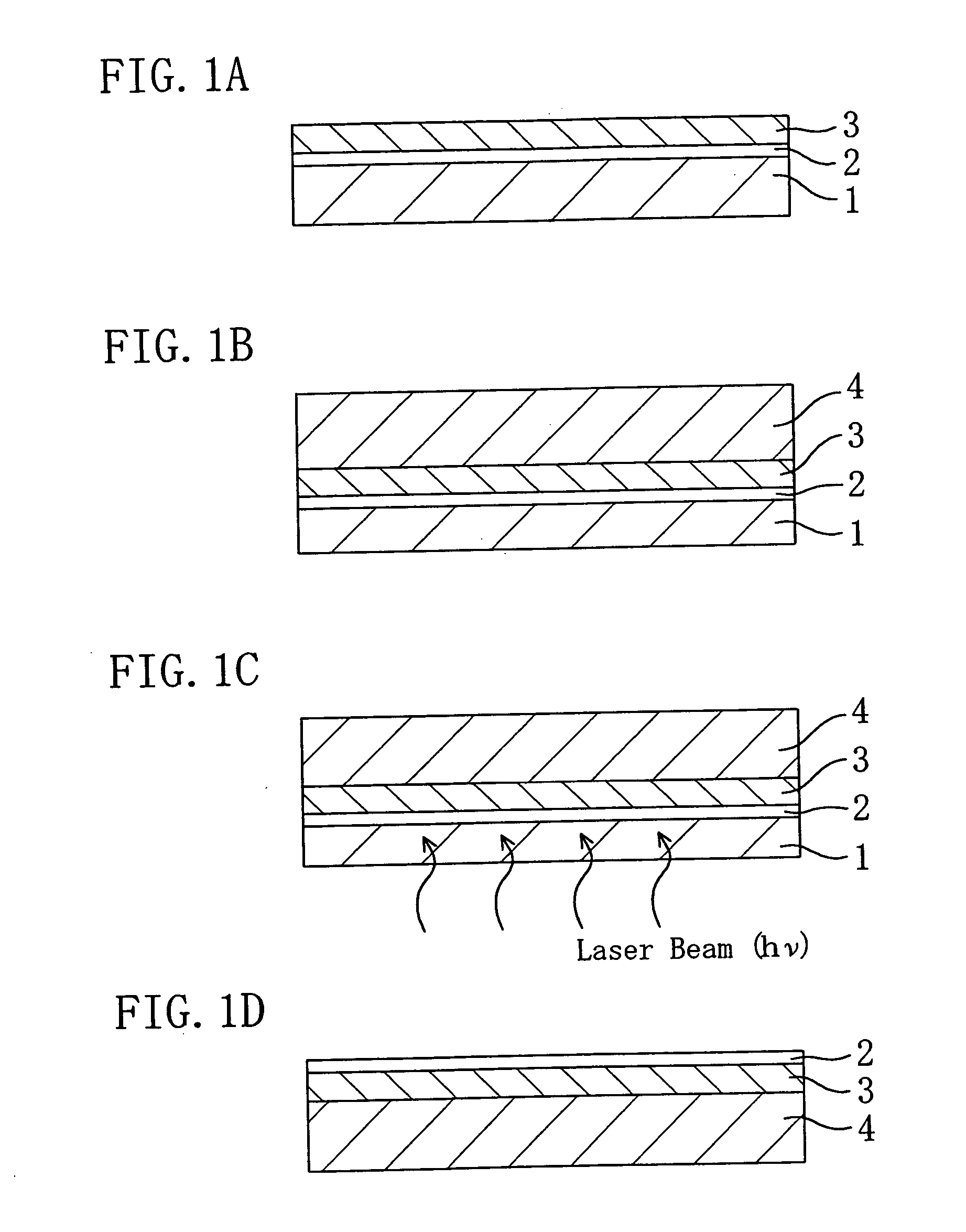
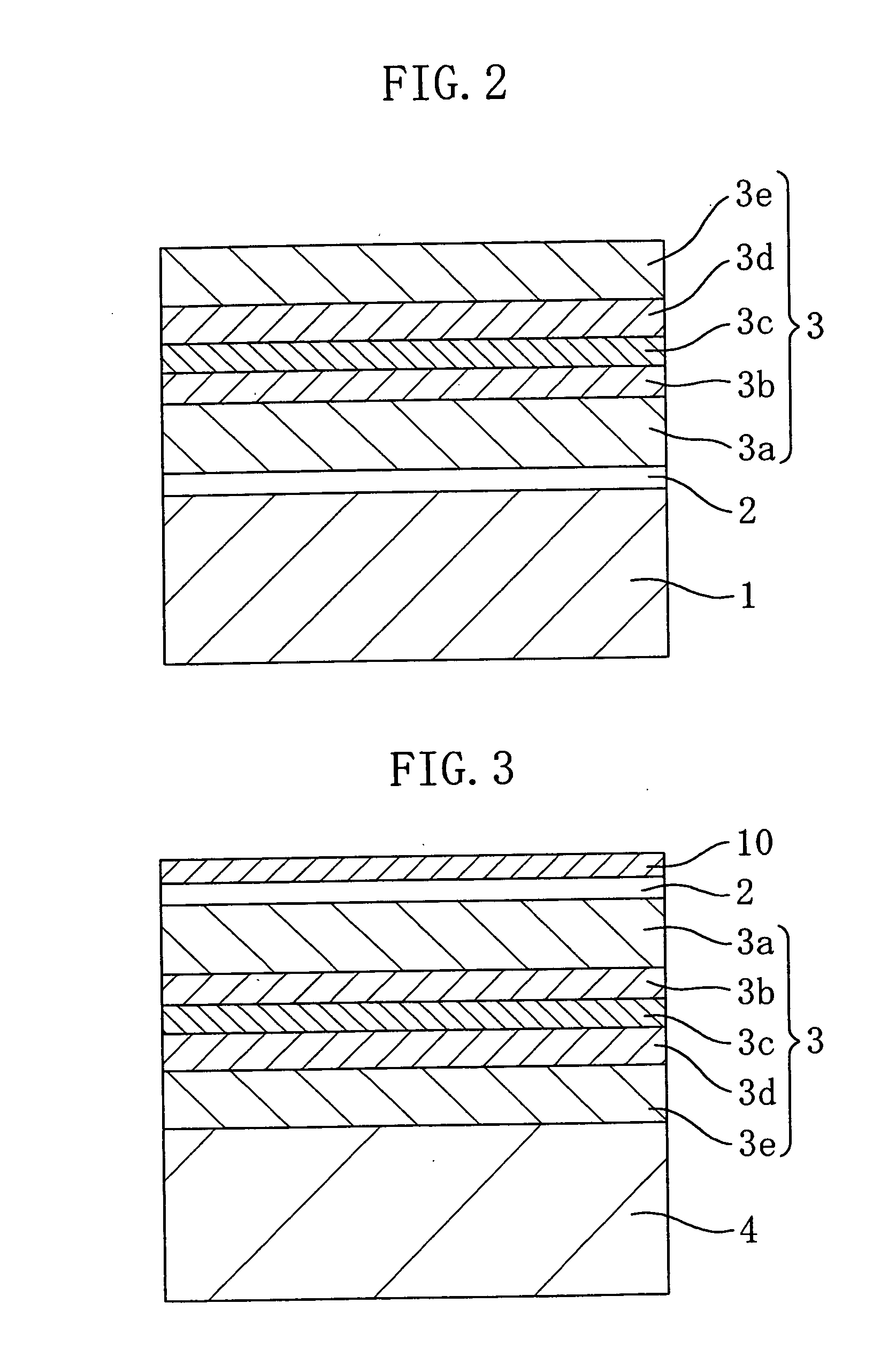
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050199901A1Reduce in quantityPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsDevice materialSingle crystal substrate
A spacer layer is formed on a single-crystal substrate and an epitaxially grown layer composed of a group III-V compound semiconductor layer containing a nitride or the like is further formed on the spacer layer. The epitaxially grown layer is adhered to a recipient substrate. The back surface of the single-crystal substrate is irradiated with a light beam such as a laser beam or a bright line spectrum from a mercury vapor lamp such that the epitaxially grown layer and the single-crystal substrate are separated from each other. Since the forbidden band of the spacer layer is smaller than that of the single-crystal substrate, it is possible to separate the thin semiconductor layer from the substrate by decomposing or fusing the spacer layer, while suppressing the occurrence of a crystal defect or a crack in the epitaxially grown layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
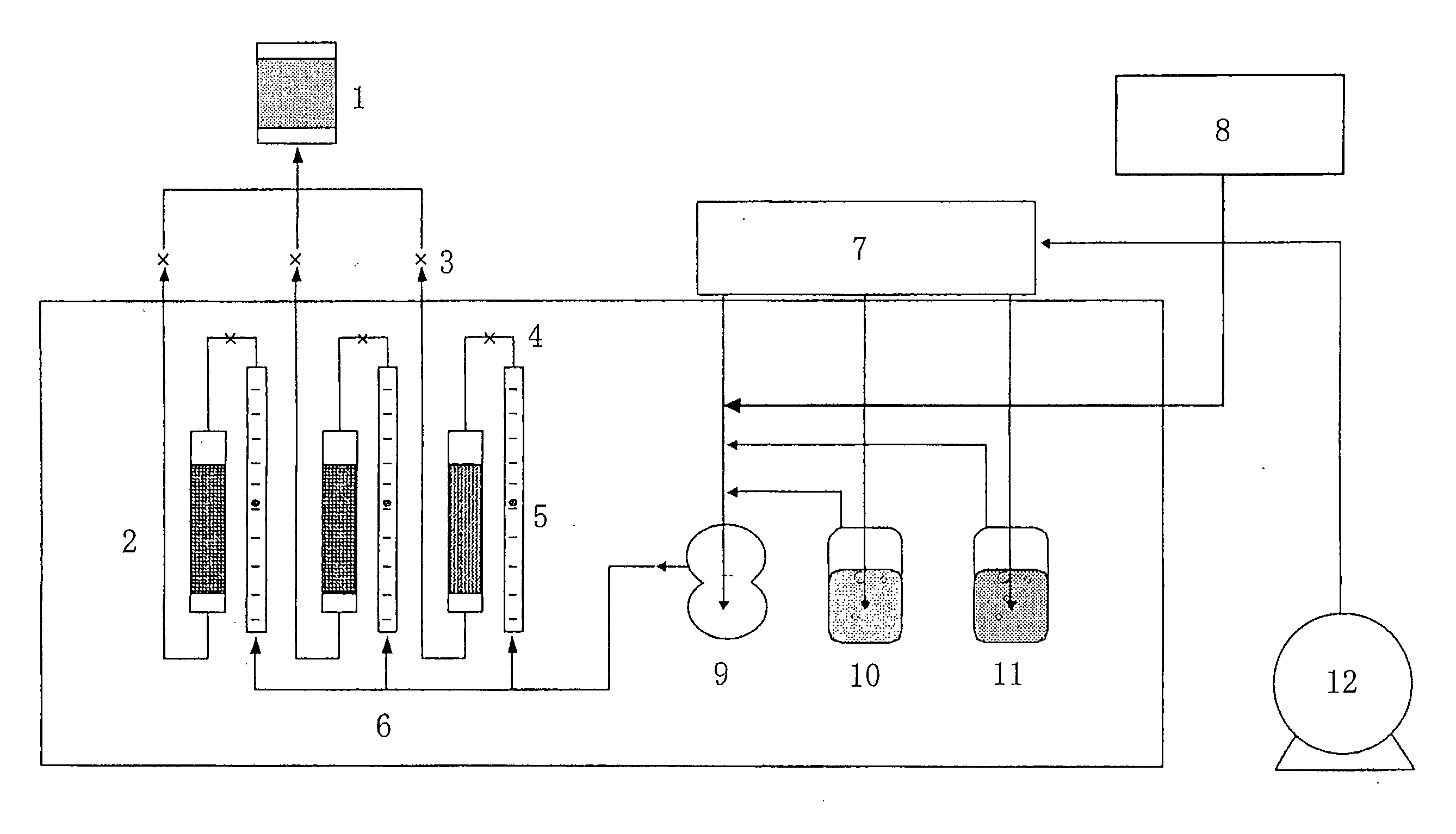
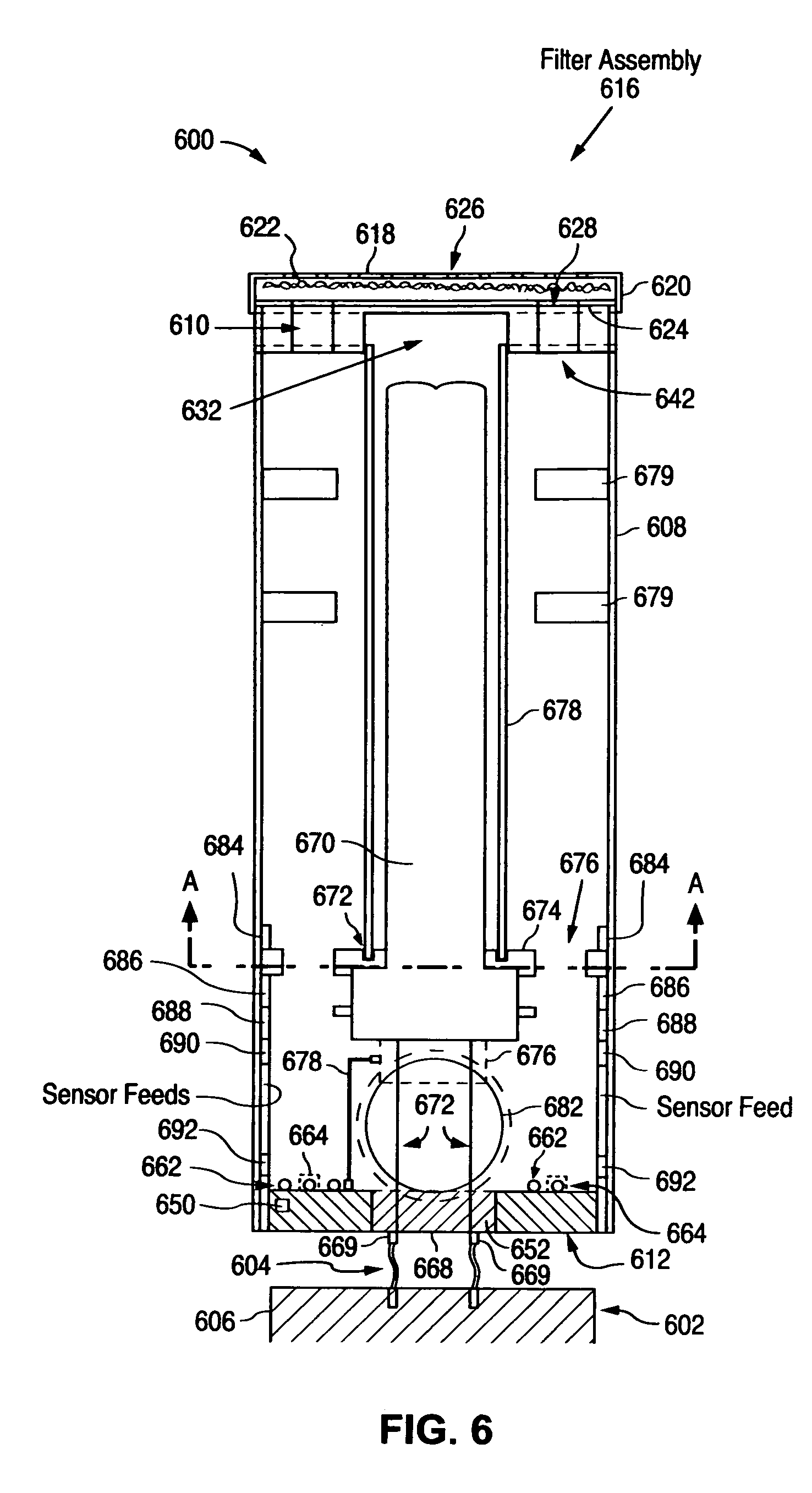
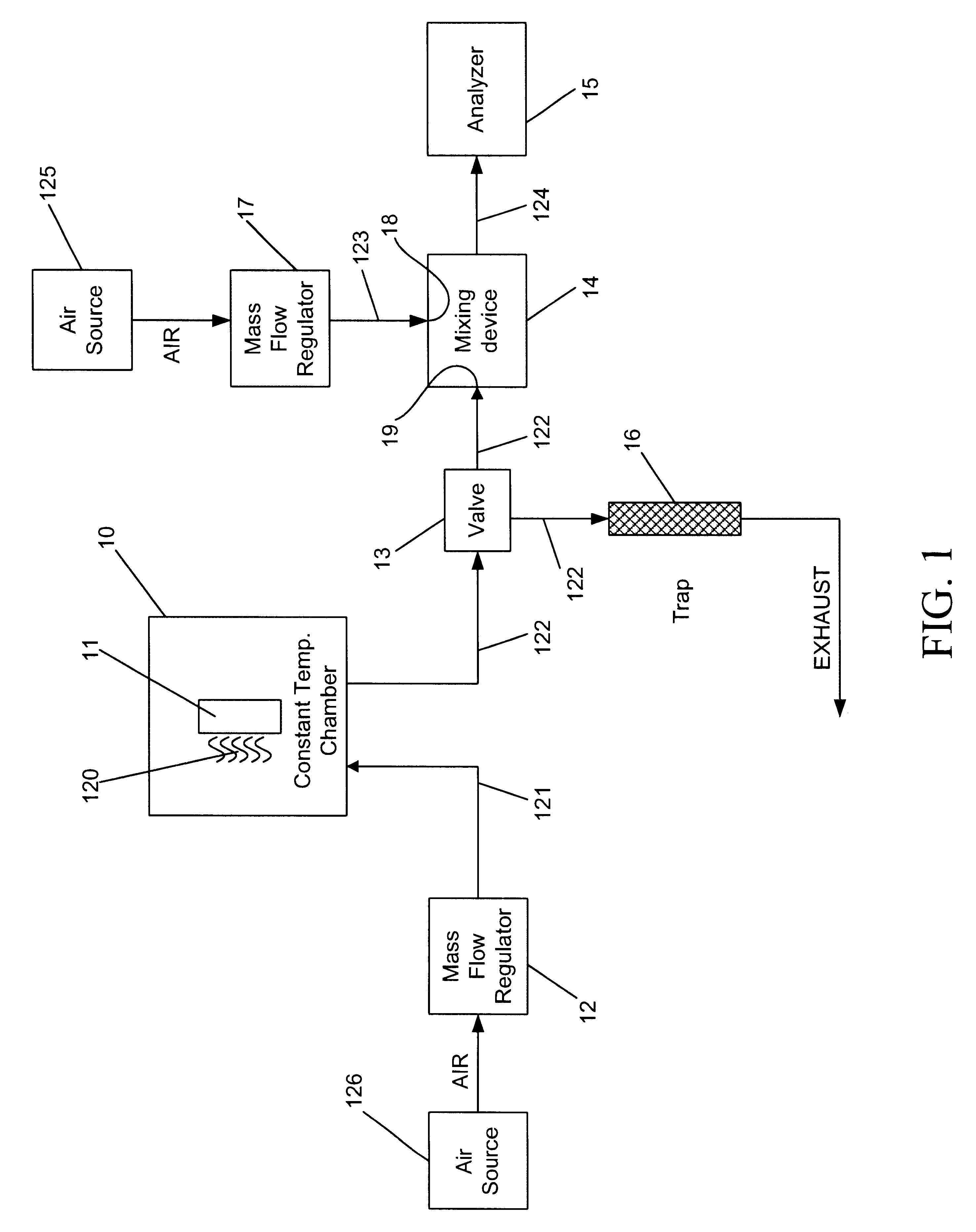
Calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry
InactiveUS6690462B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLinear relationshipOptical emission spectrometry
The disclosed invention relates to a calibration method, system and apparatus for a multimetals continuous emissions monitor system (hereinafter "multimetals CEMS"). More specifically, this invention relates to a calibration scheme for continuous monitoring of mercury emissions from stationary sources by plasma emission spectrometry. A source of mercury vapor, preferably a mercury permeation tube, entrains mercury vapor into a constant flow of carrier air. The carrier air mixes with a constant flow of diluent air in an aerosol mixer. The mixer is operably coupled to the analyzer. A gaseous mixture having a calibration mercury concentration flows from the mixer into the analyzer at a constant rate. A graph having coordinates of analyzer signal intensity and mercury concentration is used to plot the calibration scheme. A first signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to the calibration mercury concentration is used for the first plot on the graph. A second signal intensity generated by the analyzer in response to a blank having zero mercury concentration is used as the second plot on the graph. A linear relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration on the graph is established from the first plot and the second plot. The slope intercept and slope are used to create a mathematical relationship between the analyzer signal intensity and the mercury concentration. This enables the analyzer to be calibrated by inserting a known mercury concentration into the analyzer and adjusting the signal intensity to conform to the signal intensity calculated from the graph or mathematical relationship.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
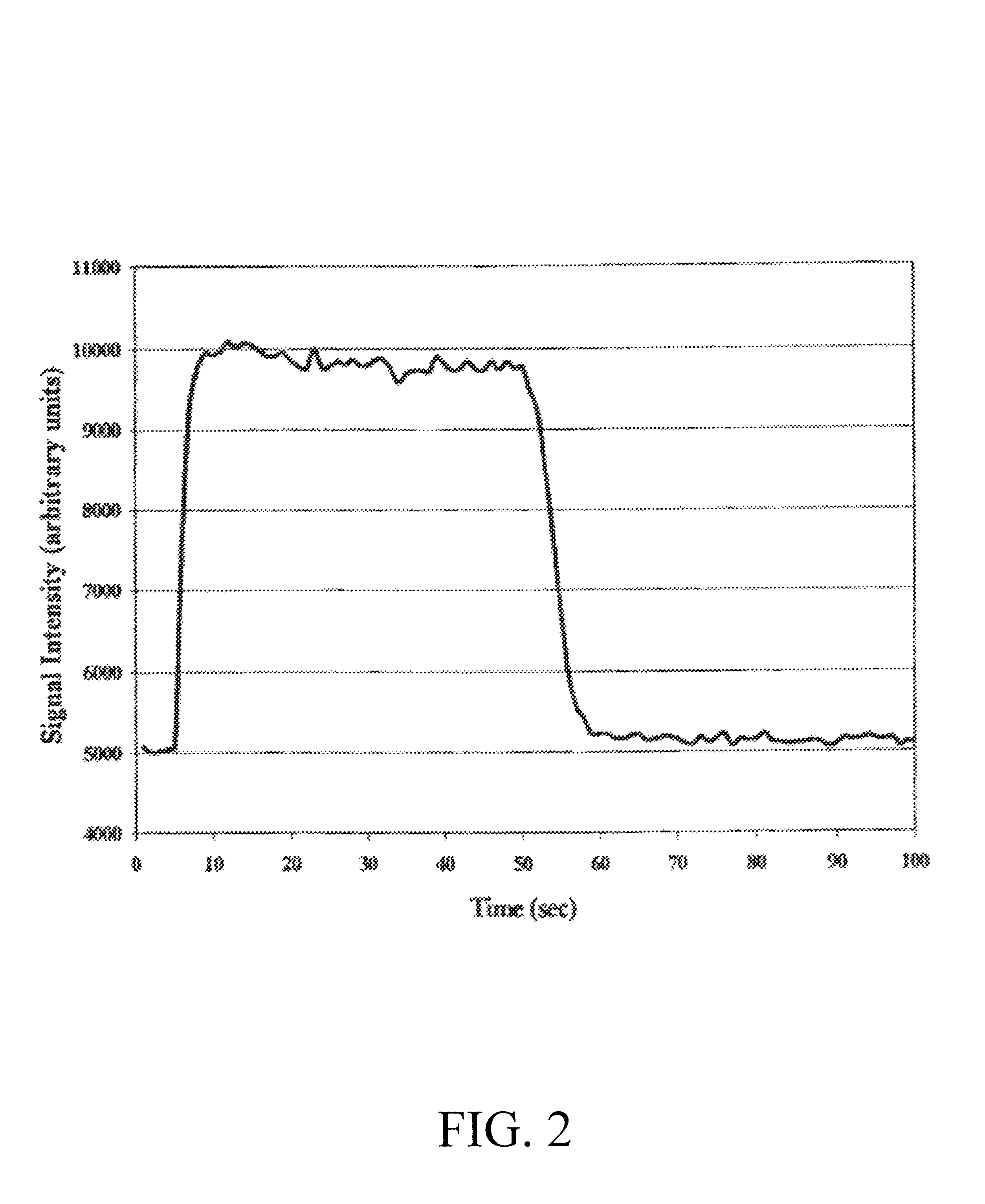
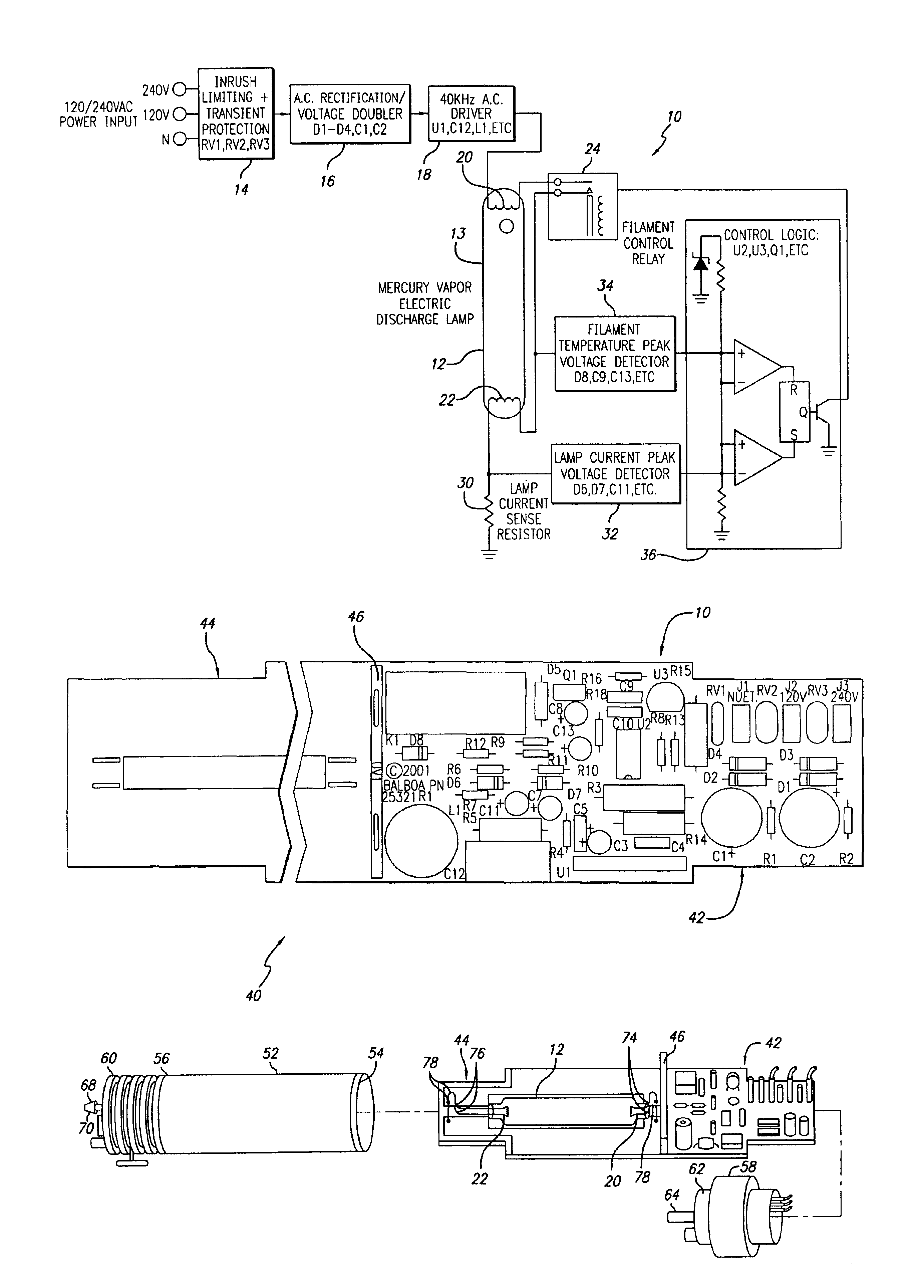
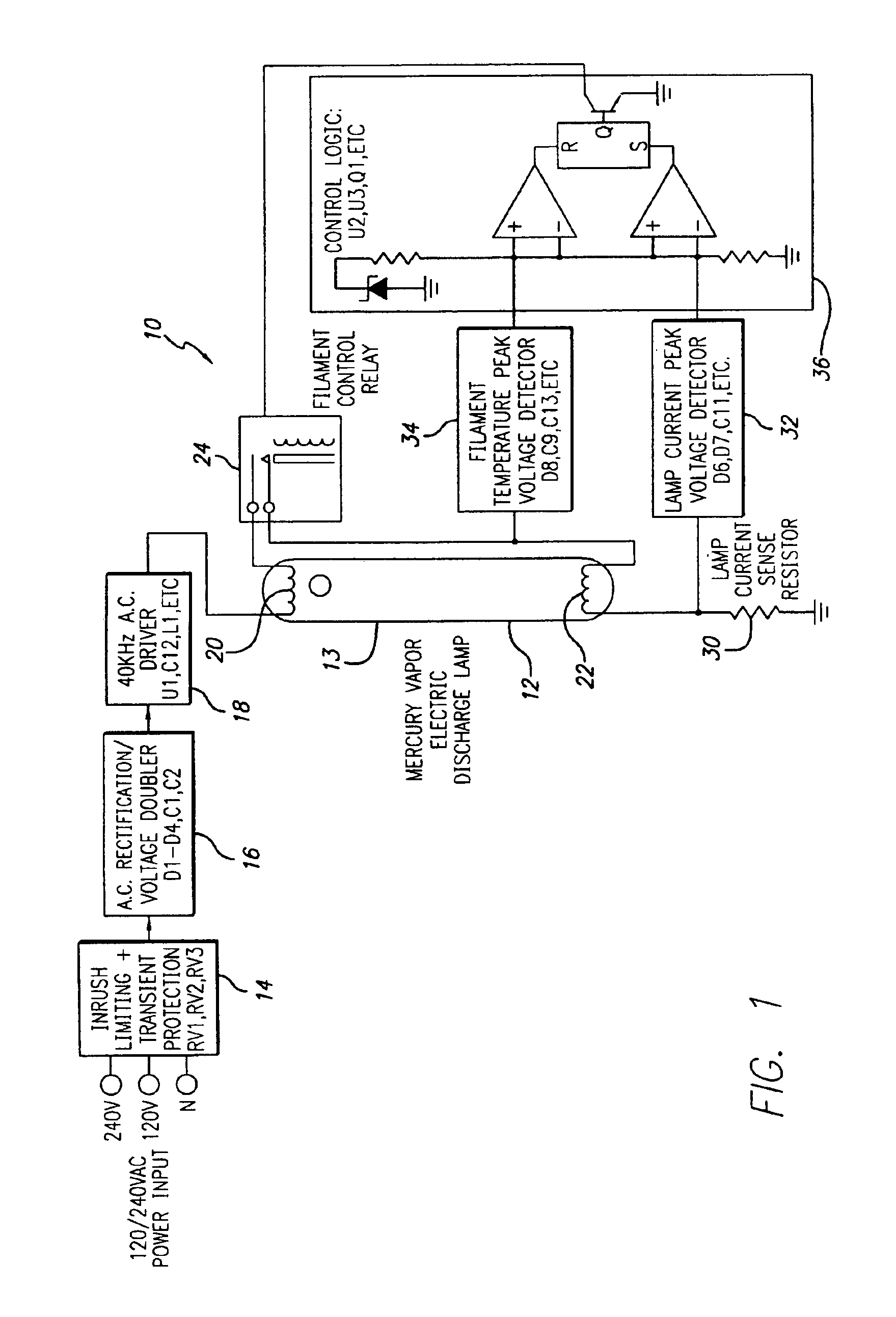
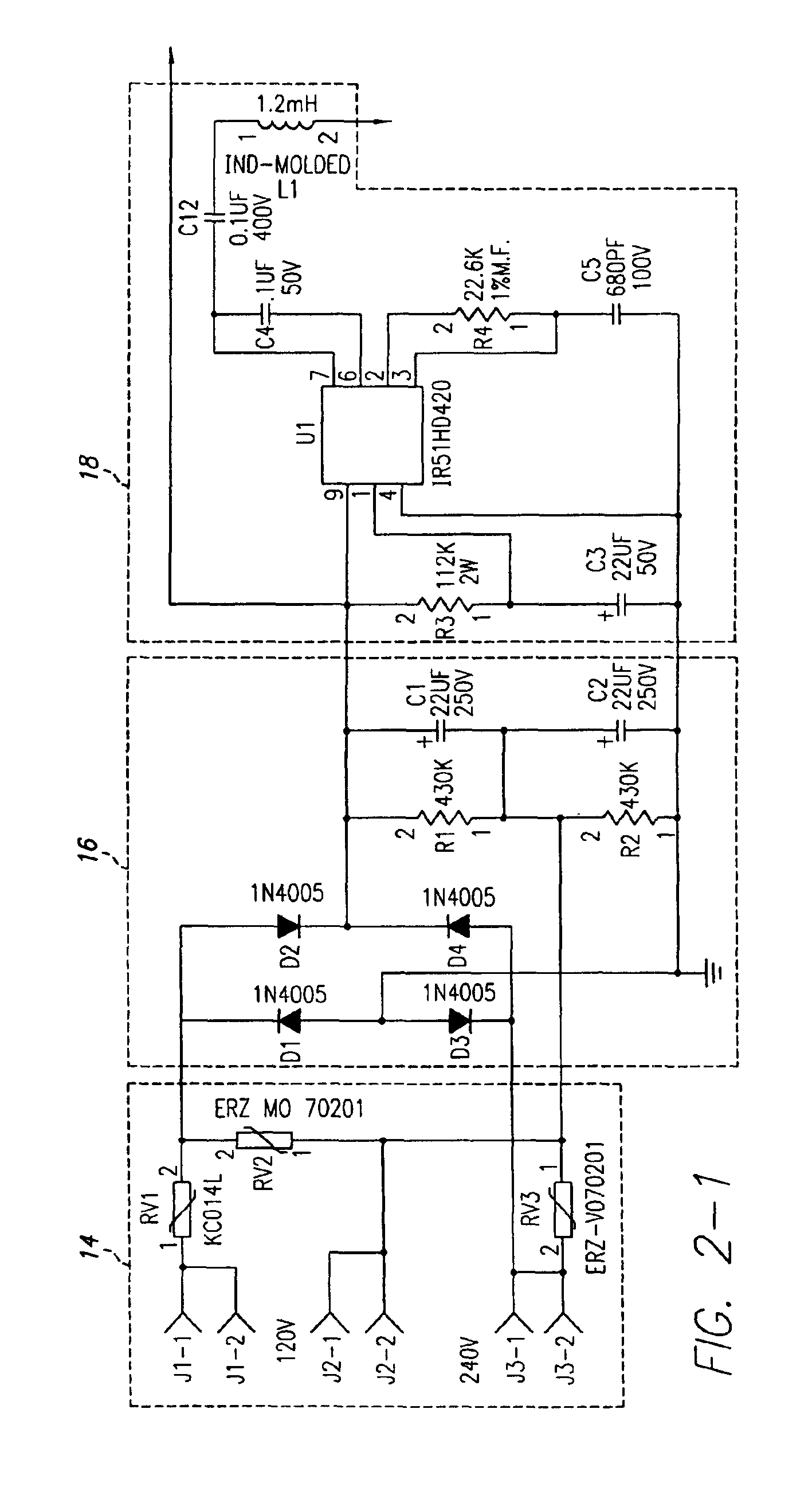
Ozone generator having a mercury lamp with a filament temperature detective circuit
InactiveUS6888324B1Reliable startReduce the starting voltageElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectricityEngineering
An ozone generator including an electric starting circuit for measuring the temperature of at least one filament and further including a mercury vapor lamp. In one aspect, the oxone generator includes and outlet spout which injects ozone into a body of water. The electric starting circuit accepts voltages from about 100 to 270 volts and frequencies as low as 45 hertz.
Owner:DYMAS FUNDING COMPANY
Solar simulator using a combination of mercury and halogen lamps
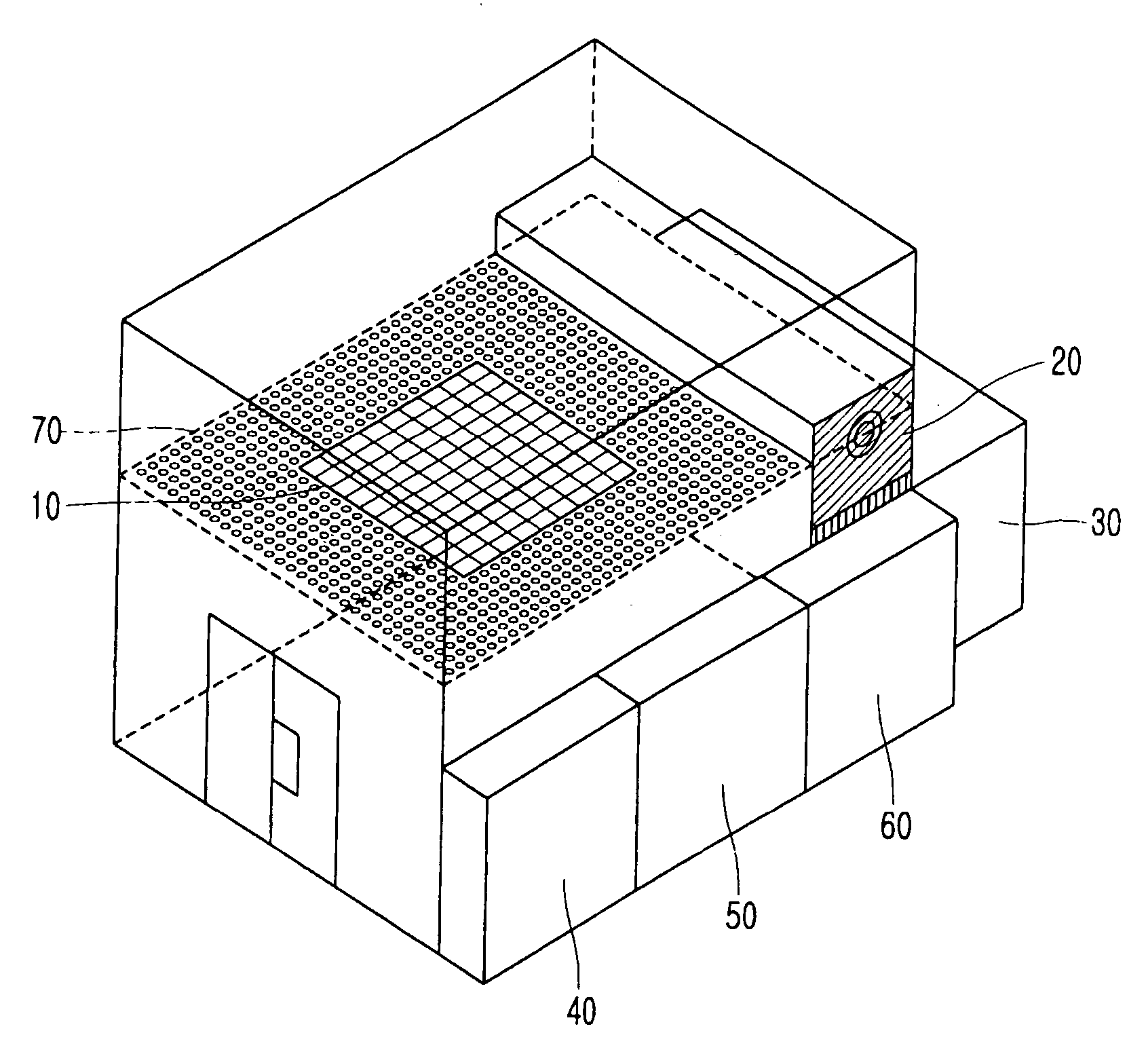
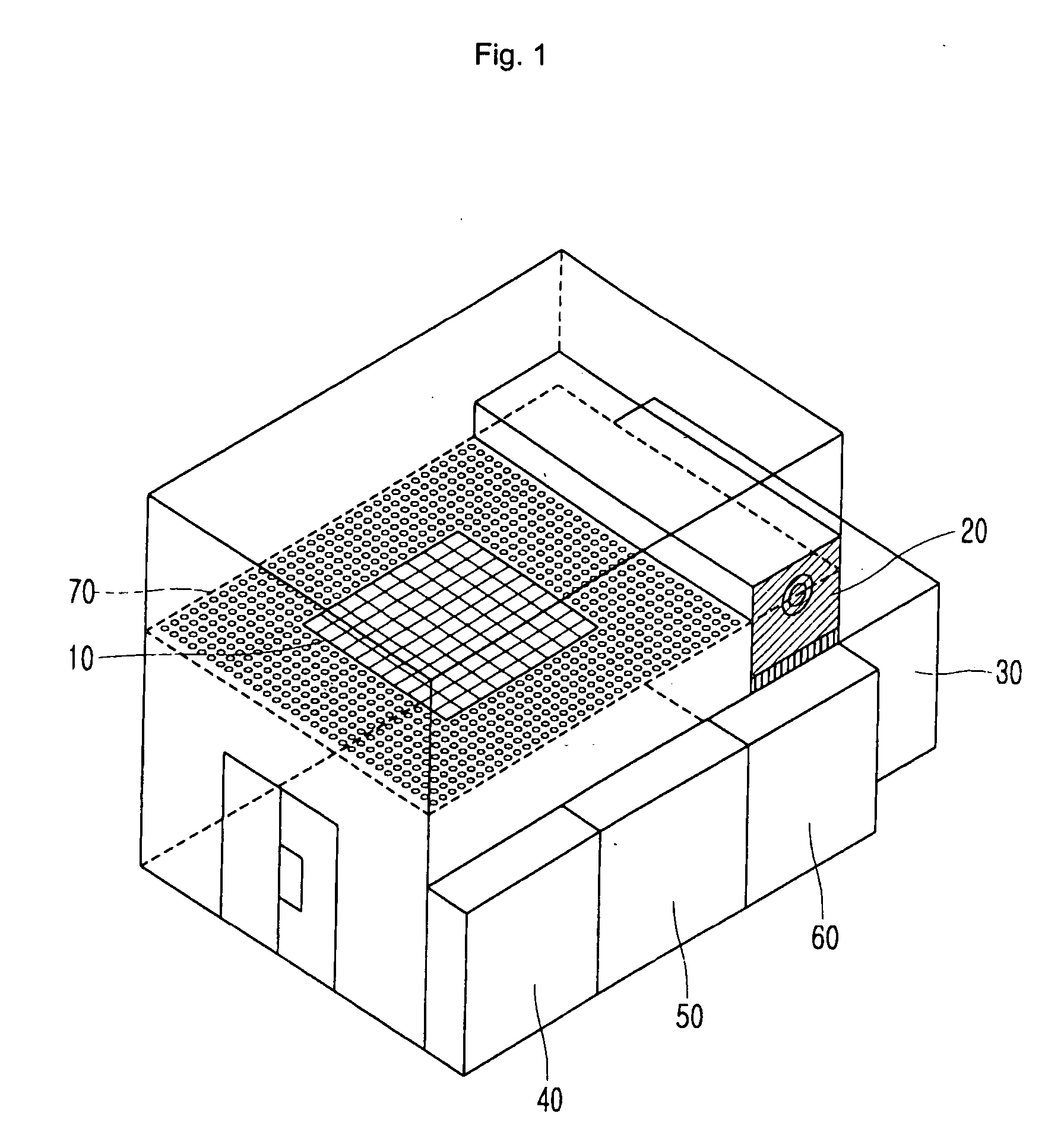
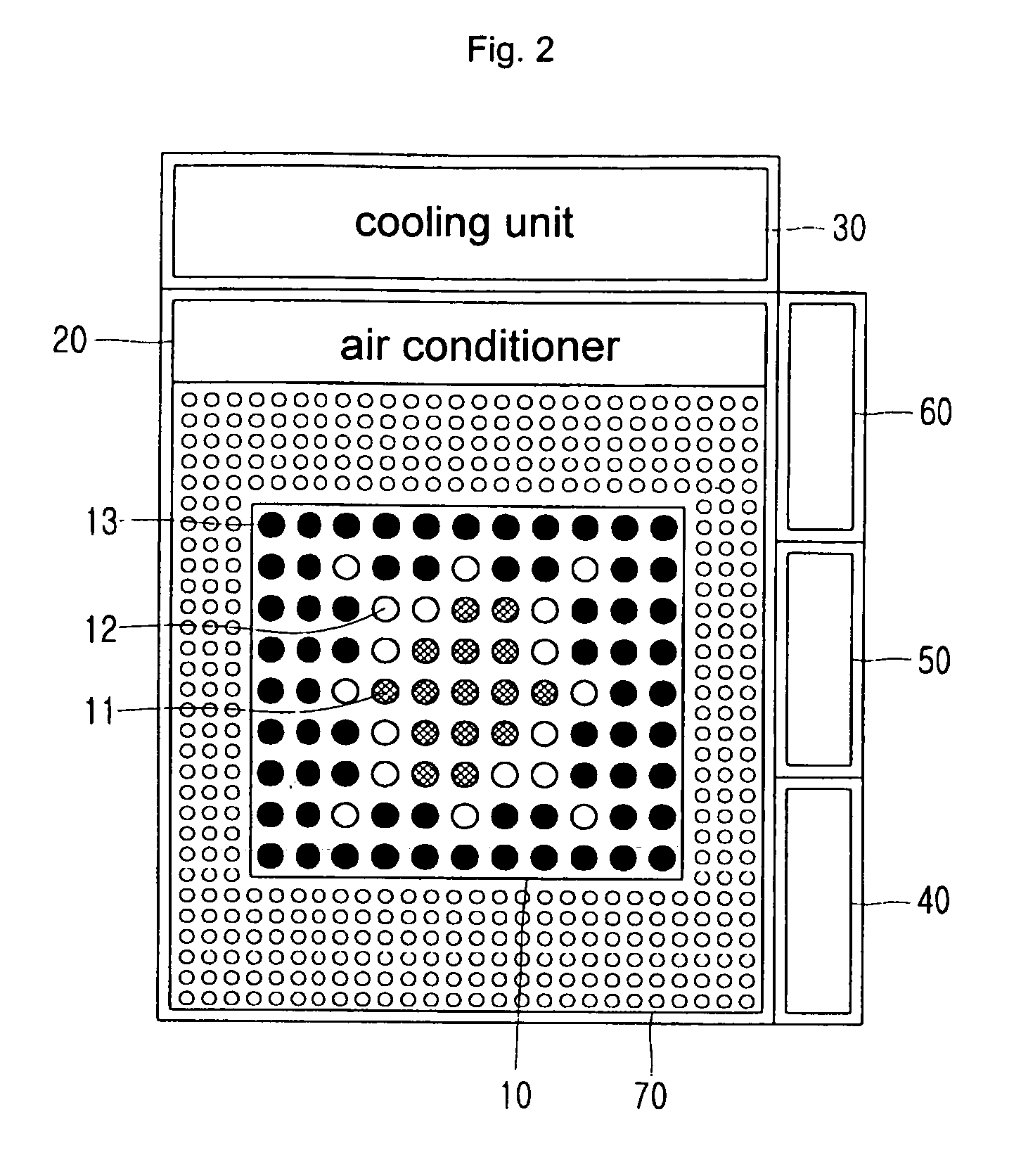
A solar simulator combines mercury lamps and halogen lamps, to improve upon conventional solar simulators using halogen and infrared lamps which cannot recreate an environment close to that under real sunlight, and upon solar simulators using expensive and fragile metal halide lamps and arc xenon lamps. An environment recreation laboratory for solar simulation includes a lamp bank mounted at an upper portion thereof and including a plurality of halogen lamps, halogen filter lamps being halogen lamps provided with an infrared filter, respectively, and mercury lamps. A temperature control unit includes a cooling unit that discharges air to cool the lamp bank, and an air conditioner that distributes the air discharged by the cooling unit. An electrical panel controls operations of the lamp bank and the temperature control unit, such that an environment within the environment recreation laboratory may very closely simulate the environment under real sunlight.
Owner:AGENCY FOR DEFENSE DEV
Single-phase rare earth vanadium phosphate white fluorescent powder for mercury lamp and preparation method thereof
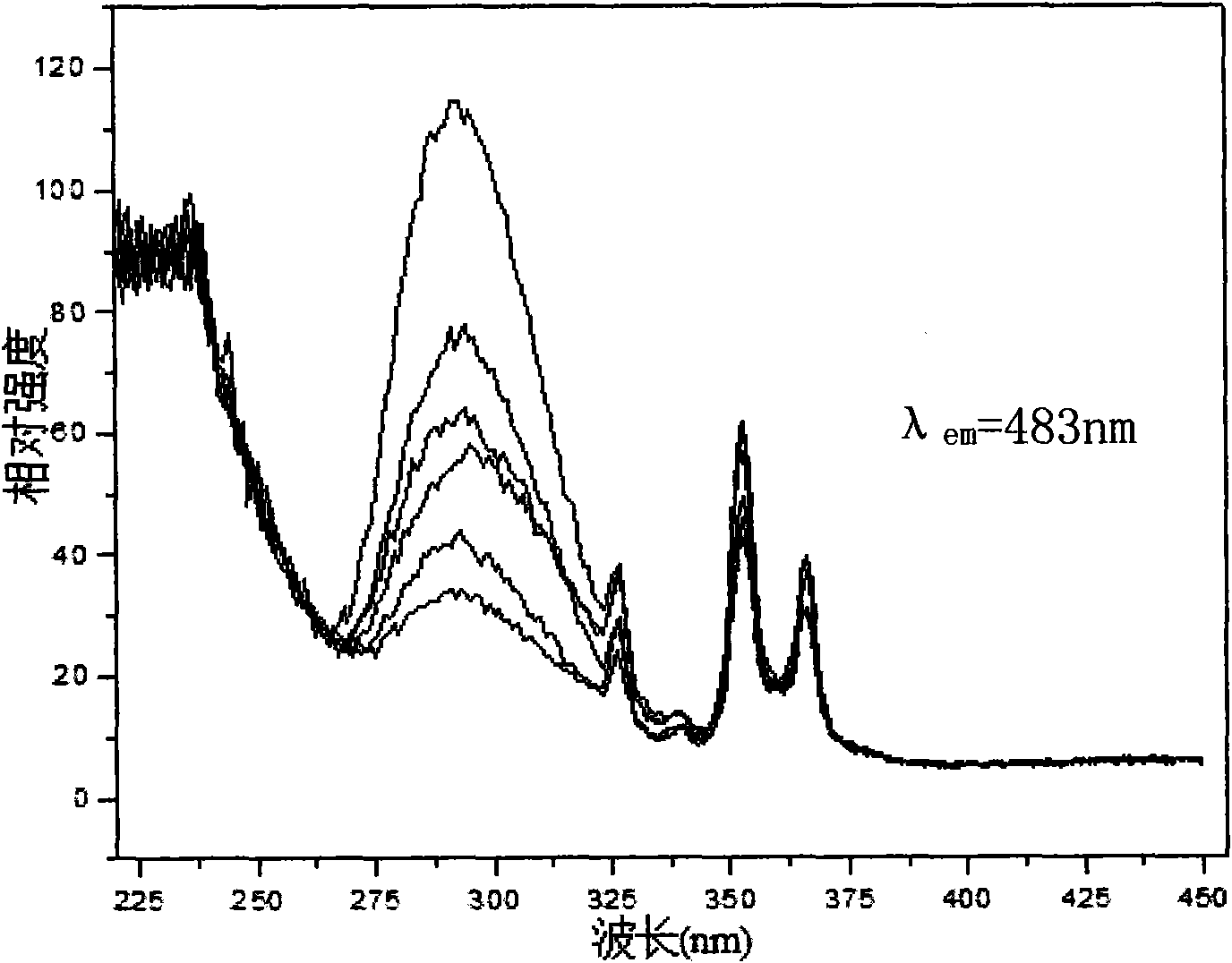
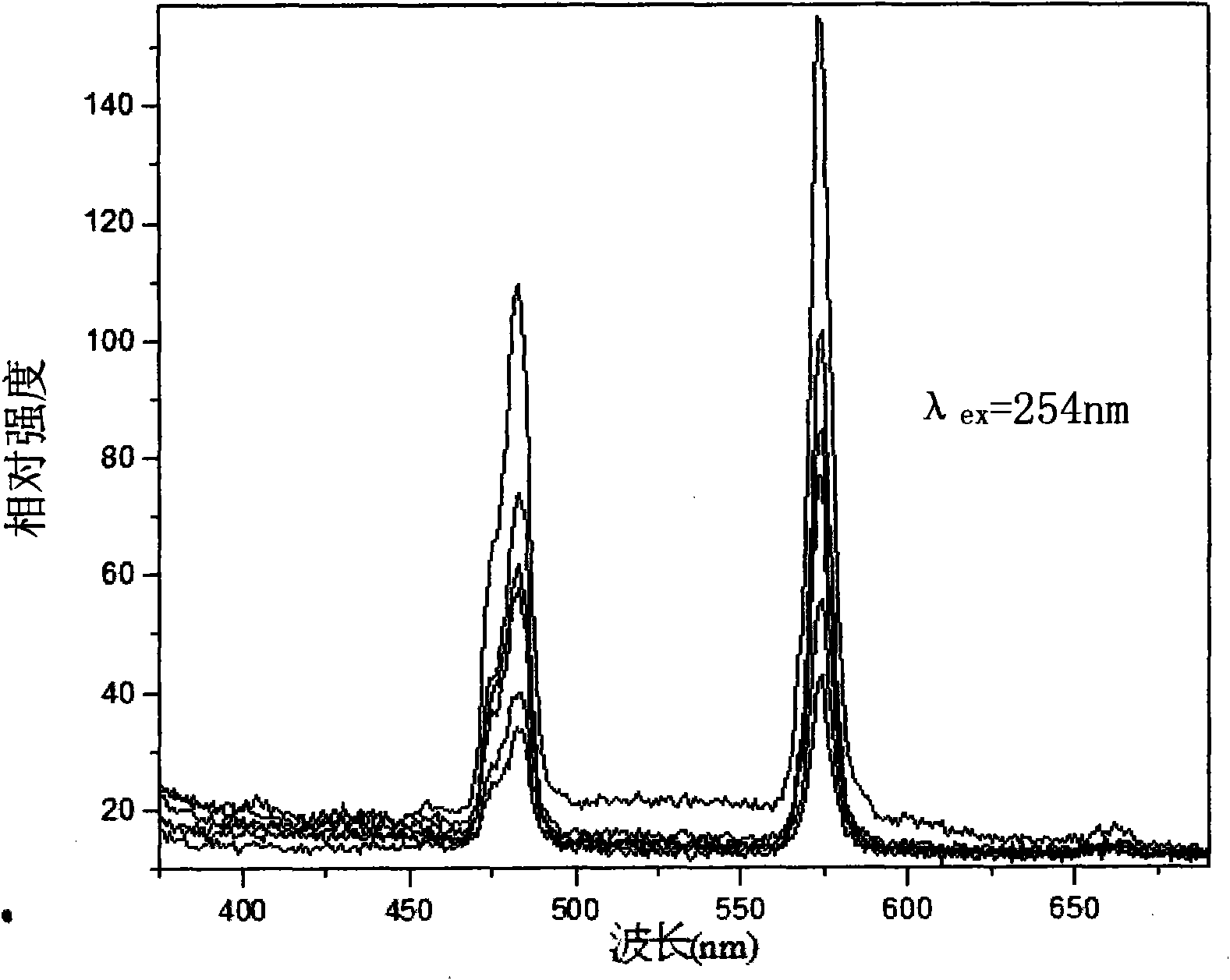
InactiveCN101974334AGood chemical stabilityImprove thermal stabilityGas discharge lamp usageLuminescent compositionsAlkaline earth metalLuminous intensity
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Printer
InactiveCN101367293AAvoid deformationAvoid reflectionsTypewritersHigh-pressure discharge lampsNoble gasHalogen
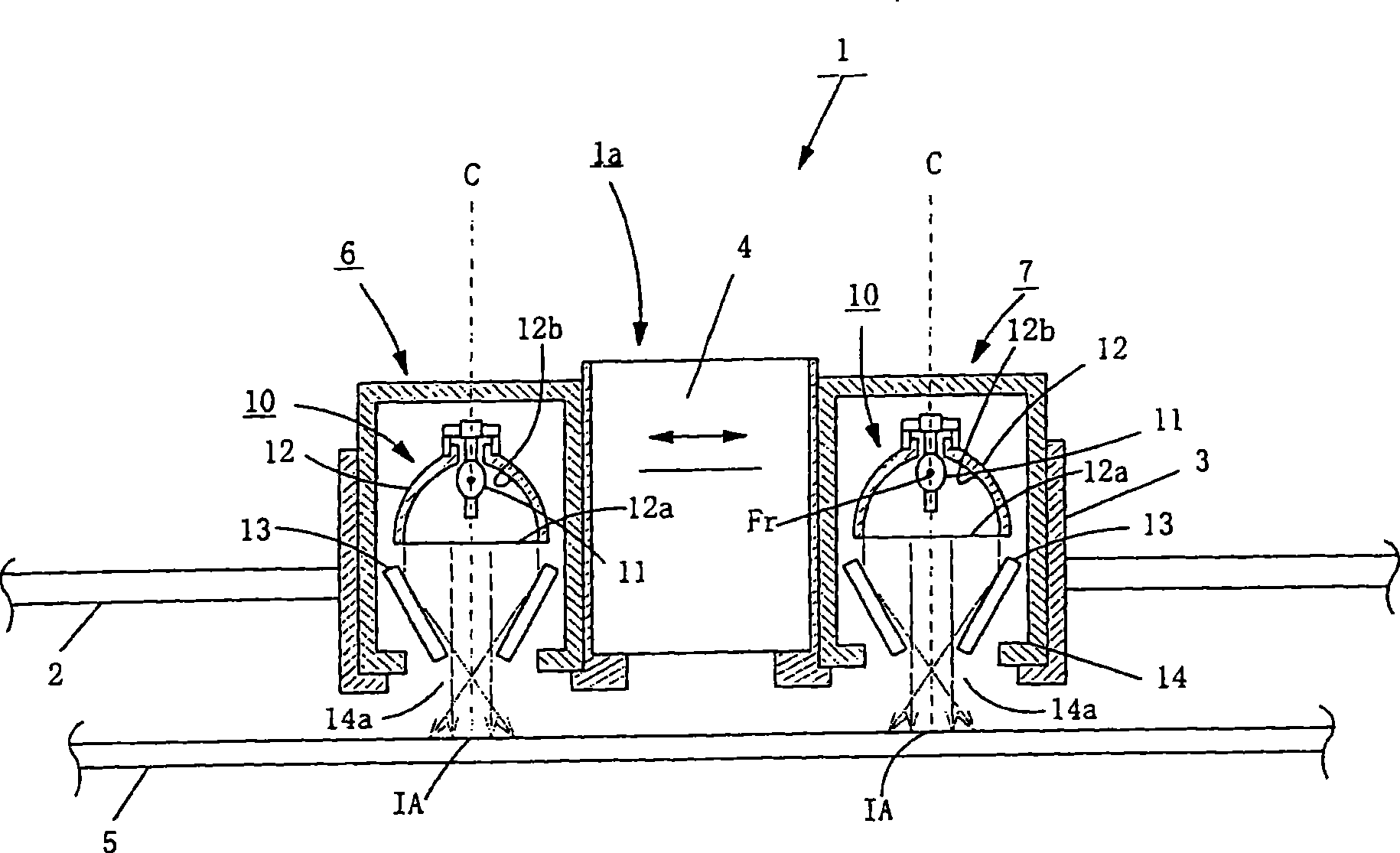
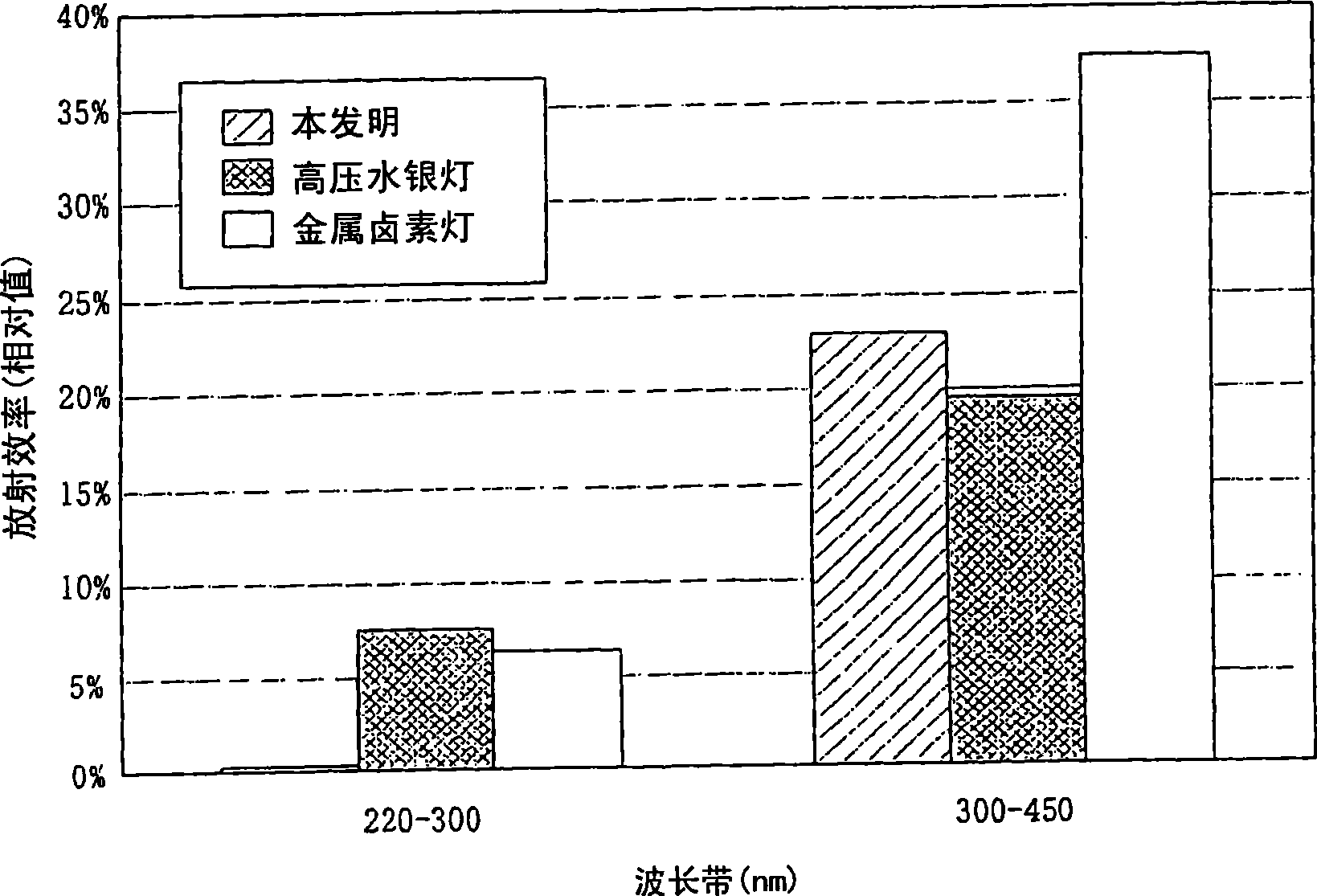
The present invention relates to a printer, which uses a lamp with wavelength of below 300nm without almost emitting light as a light source, even though the electric force of the lamp is increased, any substrates will not distort due to being heated. An electric discharge lamp is a short arc type extra-high-pressure mercury vapor lamp in which a pair of electrodes is provided in an electric discharge container, wherein mercury of 0. 08-0. 30 mg / mm3, rare gas, and halogen are enclosed in the electric discharge container and a distance between electrodes is 0. 5-2. 0 mm, and the lamp contains a plurality of light of wavelength of 300 to 400 nm, but almost contains the light with wavelength below 300 nm. The electric discharge lamp extends along an optical axis of a reflector with a revolution paraboloid shape reflecting face wherein the pair of the electrodes are arranged so that a straight line formed by connecting the pair of electrodes, and the lights emitted from the lamp become parallel lights, wherein part of the lights are emitted from a light-emitting outlet directly, and the other part are emitted from the light-emitting outlet after the reflection of the reflector. A linear illumination area IA is formed on the substrate.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Ink system for cure under low-energy conditions
UV-curable ink formulations are provided that are capable of being cured under low-energy conditions, such as with a conventional mercury vapor lamp operating at half or less of the lamp's nominal wattage. Methods for forming a printed ink image on a substrate using the ink are also provided, which permit maintenance of relatively high line speeds while consuming less energy due to the use of lower-wattage lamp settings.
Owner:DONALD D SLOAN TRUSTEE OF THE DONALD D SLOAN TRUST AND HIS SUCCESSORS UNDER THE FIFTEENTH AMENDMENT TO & COMPLETE RESTATEMENT OF THE DONALD D SLOAN TRUST DATED DECEMBER 17 2013
Man-machine coexisting ultraviolet lamp tube irradiation system for space upper-layer air sterilization
ActiveCN111282012AGood collimationIncrease powerLavatory sanitoryLight therapyMan machineEngineering
The invention discloses a man-machine coexisting ultraviolet lamp tube irradiation system for space upper layer air sterilization, which is characterized by comprising sterilization equipment arrangedon a closed or semi-closed space wall body, the sterilization equipment comprises a mercury lamp tube and an irradiation angle controller, and the mercury lamp tube is arranged in a parabolic reflecting lampshade; the irradiation angle controller drives the reflecting lampshade to rotate so as to adjust the irradiation angle of the mercury lamp tube. According to the sterilization equipment, theradiation angle is easy to adjust so as to provide radiation fields suitable for various ceiling heights, and the sterilization equipment can be suitable for places with high floor heights, such as fitness places, stadiums or indoor performance places. And the system can also be used for rooms with relatively low ceilings, such as elevators, public transport means, rooms, office buildings, halls and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Double-mercury lamp spliced exposure system for lithography equipment
ActiveCN103543609AImplement working mode switchingIncrease illuminationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLithographic artistCoupling
The invention discloses a double-mercury lamp spliced exposure system for lithography equipment. The double-mercury lamp spliced exposure system comprises a first light source and a second light source used for simultaneously or respectively providing illuminating beams; a first dodging component and a second dodging component which respectively correspond to the first light source and the second light source, a coupling lens group used for improving the illumination uniformity of the exposure system, and an illuminating and dodging component used for dodging emergent light of the coupling lens group to illuminate an illumination surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
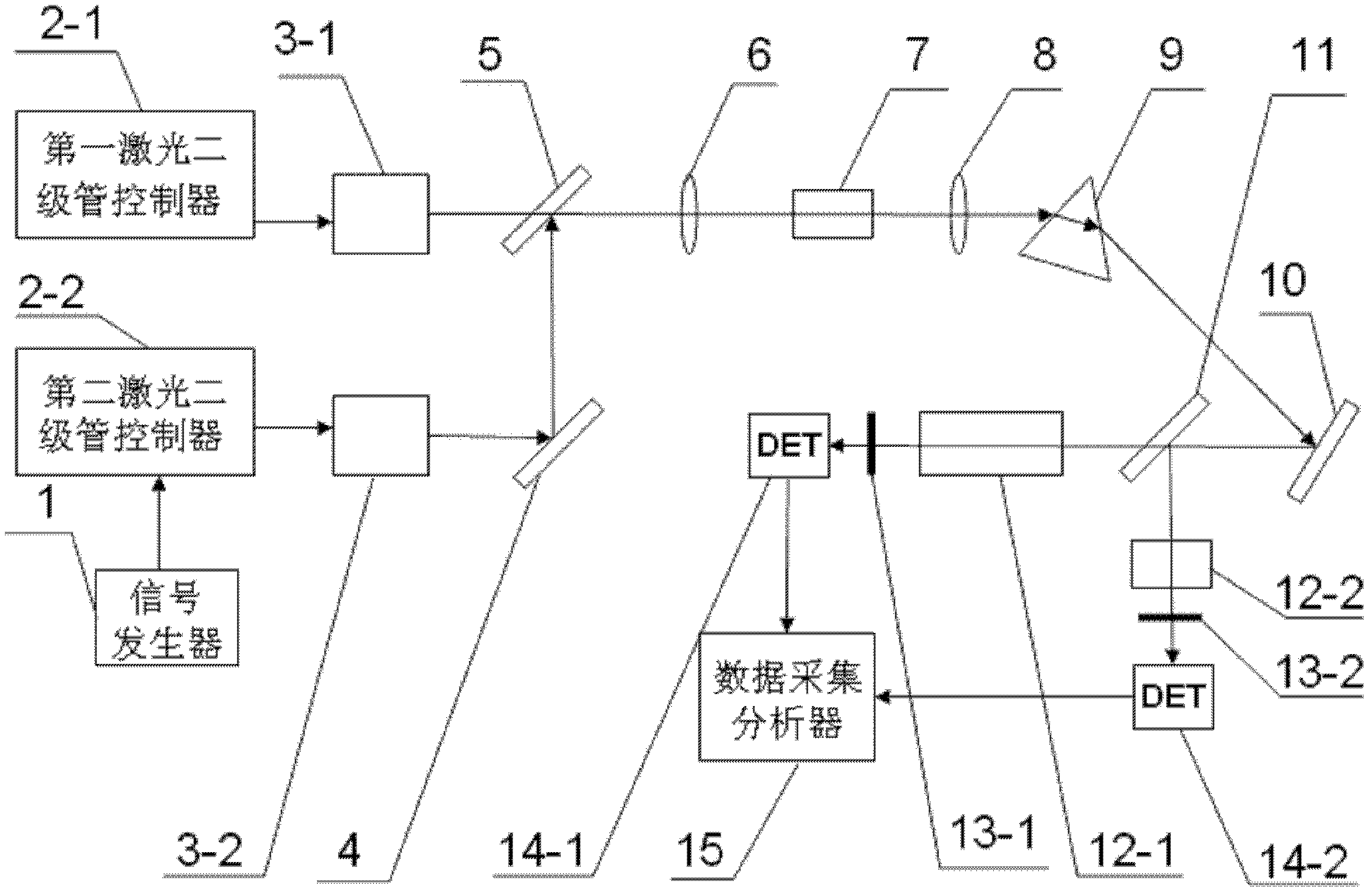
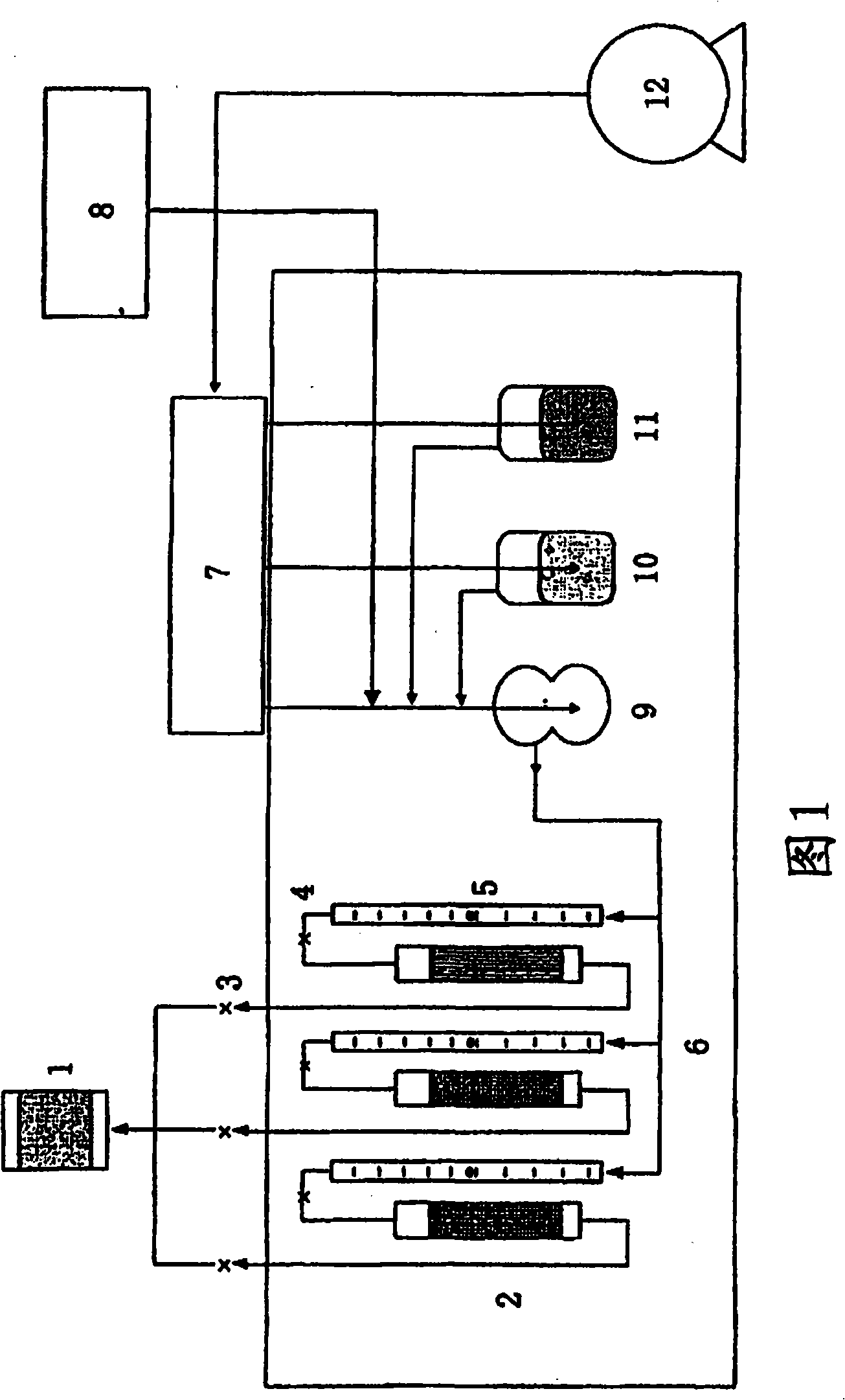
Mercury vapor continuous monitoring device and monitoring method based on diode laser
ActiveCN102590097ASimple structureRealize continuous effective monitoringInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsBeam splitterData acquisition
The invention provides a mercury vapor continuous monitoring device and monitoring method based on diode laser, belonging to the technical field of mercury vapor monitoring. The invention enables the problems that a conventional mercury vapor measuring system has a complex structure and real-time monitoring of mercury emission in conventional mercury vapor measuring is poor to be overcome. The monitoring device comprises a signal generator, a first laser diode controller, a second laser diode controller, a first laser diode, a second laser diode, a first reflector, a dichroic beam combiner, afirst convex lens, BBO crystals, a second convex lens, a beam splitter prism, a second reflector, a spectroscope, a sample cell, a reference cell, a first optical filter, a second optical filter, a first detector, a second detector and a data acquisition analyzer. According to the monitoring method, diode laser absorption spectroscopy is used to realize continuous monitoring of the concentration of mercury vapor, and spectral information of reference gas is utilized to realize selective identification and quantitative detection of gaseous elemental mercury, thereby eliminating interference brought by gas like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. The monitoring device and the monitoring method provided in the invention are used for on-line monitoring of mercury vapor.
Owner:SUZHOU RUILAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO LTD
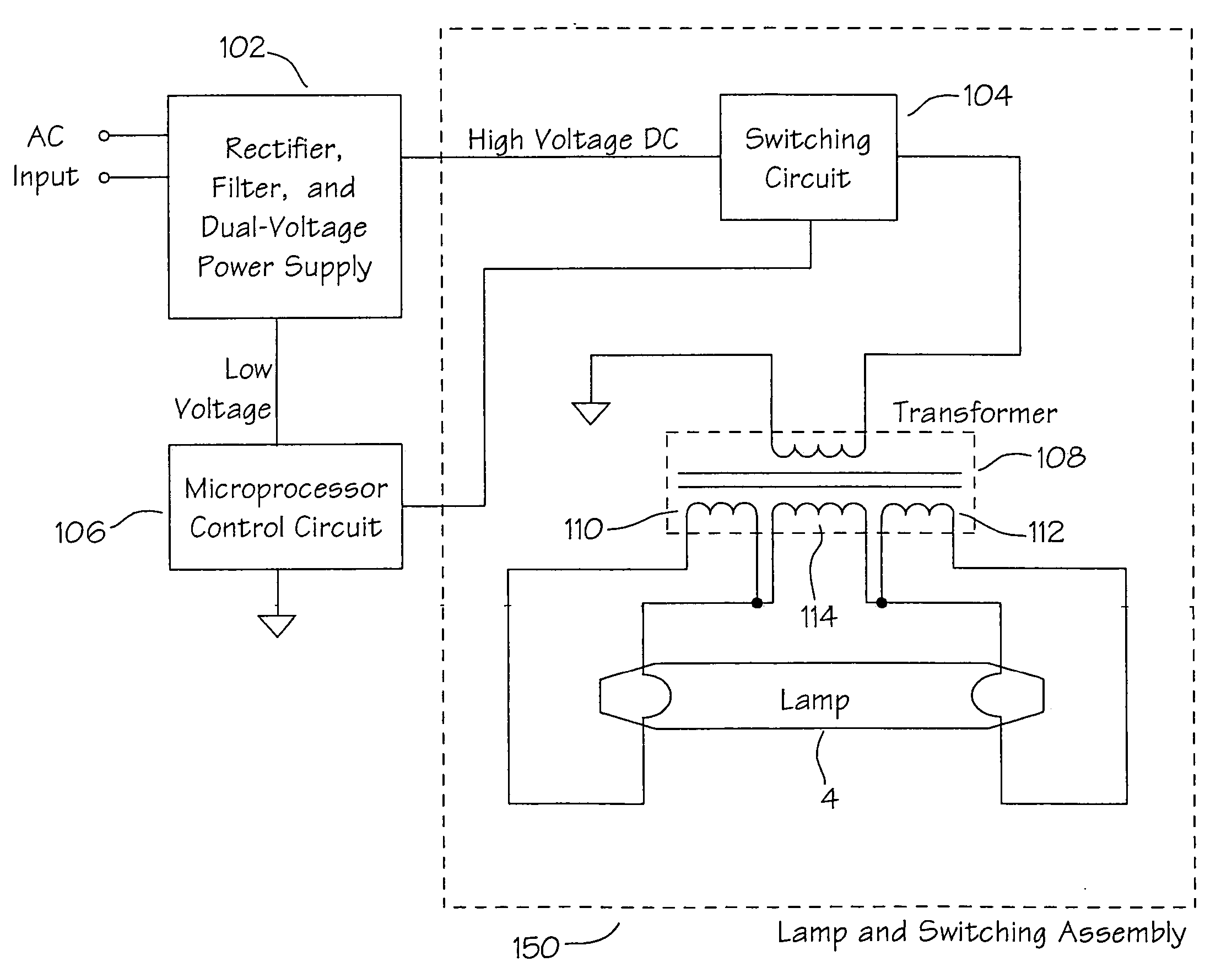
Lighting apparatus
InactiveUS7178944B2Heat dissipationEasy to controlIncadescent body mountings/supportIncadescent screens/filtersLight equipmentHigh intensity
The present invention comprises a method of enhancing illumination by a variety of lamp types through the use of reflective technologies, for example, replacement of expensive high intensity density or mercury vapor lamps with low wattage flourescent tubes having at least one and in some cases, up to three reflective surfaces for focusing otherwise lost light toward a target illumination area. Further, the placement of light sources at the focal point of said reflective surfaces aids in optimizing the amount of light focused in a desired direction.
Owner:WALTON RANDAL D
Mercury morphological analysis method based on liquid cathode discharge and mercury vapor generating device
InactiveCN102033103AAchieve steamEfficient separationComponent separationAnalysis by electrical excitationFluorescenceINTRODUCTION device
The invention discloses a mercury morphological analysis method based on liquid cathode discharge and a mercury vapor generating device. The method comprises: a mercury-containing sample solution is introduced into a chromatographic column of a liquid chromatograph; a discharge medium carrier flow passes through a sample introduction device and is introduced into a sample introduction capillary tube of a discharge pool with the effluence of the chromatographic column through a tee joint; by taking a metal electrode as an anode, and graphite, platinum or a stainless steel material as a cathode, liquid cathode discharging is carried out to generate vapor which is carried by a carrier gas into a gas-liquid separator; and finally the separated gas is detected by an atomic fluorescence spectrometer to obtain the morphology of mercury. Through the method provided by the invention, organic mercury and inorganic mercury in an object to be detected are effectively separated and detected; and the method has the advantages of small volume, low energy consumption, high mercury vapor generation efficiency and low matrix interference, is simple in operation and can be used for analyzing the morphology of mercury in a biological sample.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method for removing mercury vapor in gas
InactiveCN101310826AHigh removal rateLasting effectGas treatmentOther chemical processesActivated carbonMercury-vapor lamp
If oxysulfide is present in the gas including mercury vapor, the adsorption of active carbon on the mercury vapor is baffled. Therefore, it can be hoped that a method is provided, wherein mercury vapor can be effectively adsorbed even if oxysulfide coexists. According to the invention, the mercury vapor of the gas including oxysulfide is contacted with an active carbon adsorbent made by attaching5-70 amounts by weight of alkali halide in 100 amounts by weight of active carbon, thereby effectively removing mercury vapor for a long time.
Owner:OSAKA GAS CHEM KK
Photochemical synthesis preparation method for vitamin D2
ActiveCN1765883ARealize industrial productionEasy to produceOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisVitamina D2
The invention relates to preparation method for vitamin D2 by actinochemical way, which comprises: preparing photoreaction liquid with ergosterin and ethanol, irradiating with ultraviolet ray from low-pressure mercury vapor lamp to obtain the D2 coarse product; after chromatography, esterification and hydrolysis, drying to obtain the product. This invention realizes the industrial product with simple process and low cost.
Owner:SICHUAN NEIJIANG HUIXIN PHARMA
Method for simply preparing N-type graphene field-effect tube
The invention discloses a method for simply preparing an N-type graphene field-effect tube. According to the method, oxidized graphene prepared by virtue of chemical oxidation is used as a raw material, an oxidized graphene sheet is used for forming a film on a substrate by spin coating, and then nitrogen doped graphene is obtained by virtue of illumination. A fluorinated graphene film can be illuminated at a regional position capable of being selected by laser light with the energy of 65-75mJ / cm<2> or a mercury vapor lamp in an atmosphere of NH3 gas of which the flow is 10-30torr, the illumination time is 5-60 minutes, and reduction and doping of nitrogen atoms are realized during illumination. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient to operate, low in cost and capable of realizing mass preparation, and the content of doped nitrogen, the conductivity of graphene and band gaps can be regulated and controlled and an effect of the N-type graphene field-effect tube can be realized by virtue of illumination time and intensity and the concentration of doped fluoride.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
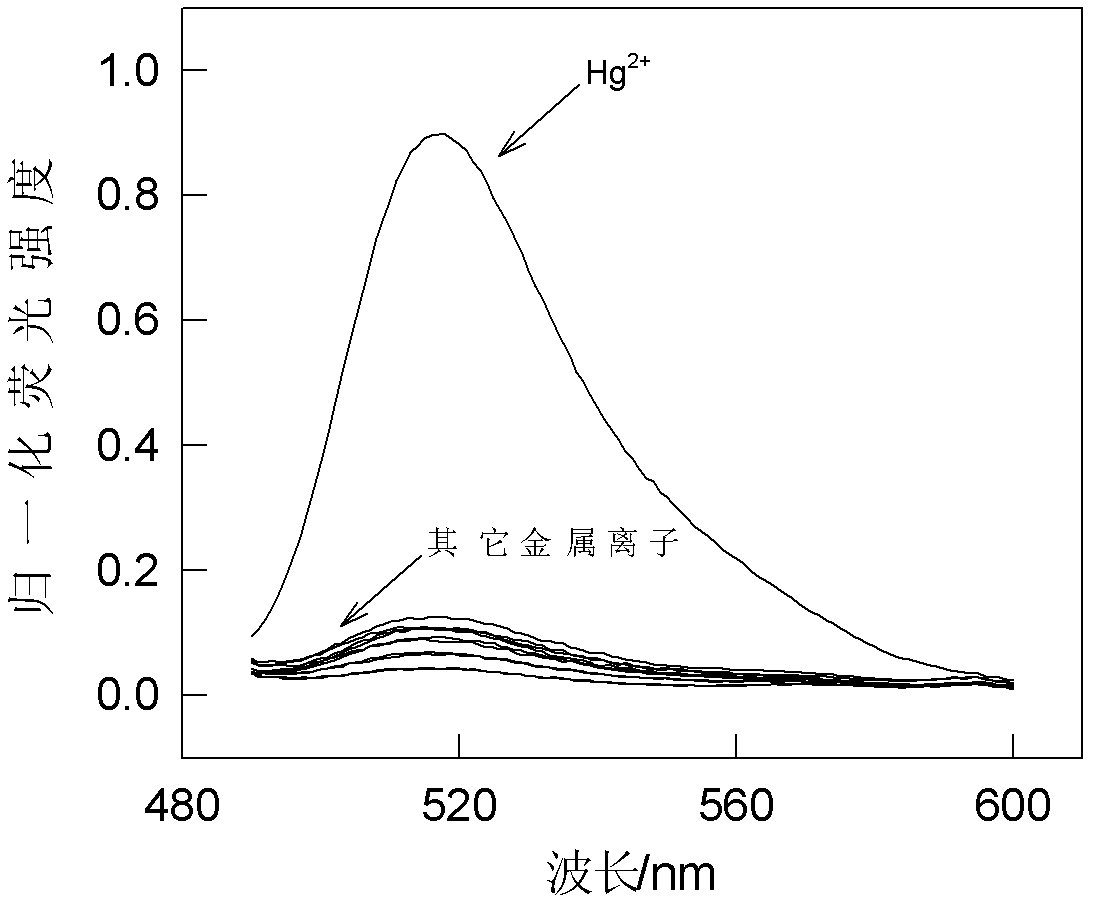
Detection method of mercury element
The invention belongs to the field of nanotechnology and analysis and provides a detection method of mercury element based on interference of silver nanoparticle formation. The method comprises the following steps of: adding fluorescein (FAM) labeled DNA into PBS buffer, mixing by vortexing; adding a silver nitrate solution into the above solution, mixing by vortexing, standing still to make silver ions act fully with DNA and to be adsorbed onto DNA; adding sodium borohydride into the above solution, reducing silver ions on DNA to form silver nanoparticles and quenching the fluorescence of fluorescein. According to the method, mercury ions are infused into the solution to act for a period of time before adding sodium borohydride, and then the silver and mercury ions generate dissociative silver amalgam under the reduction of sodium borohydride so as to reserve the fluorescence of fluorescein. Therefore, the method can be used to detect mercury ions and also can be used to detect mercury vapor simultaneously. The method for the detection of mercury element (ions and vapor) has advantages of simple operation, economy and practicality, high specificity, high sensitivity, great innovation and application prospect in other targets.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
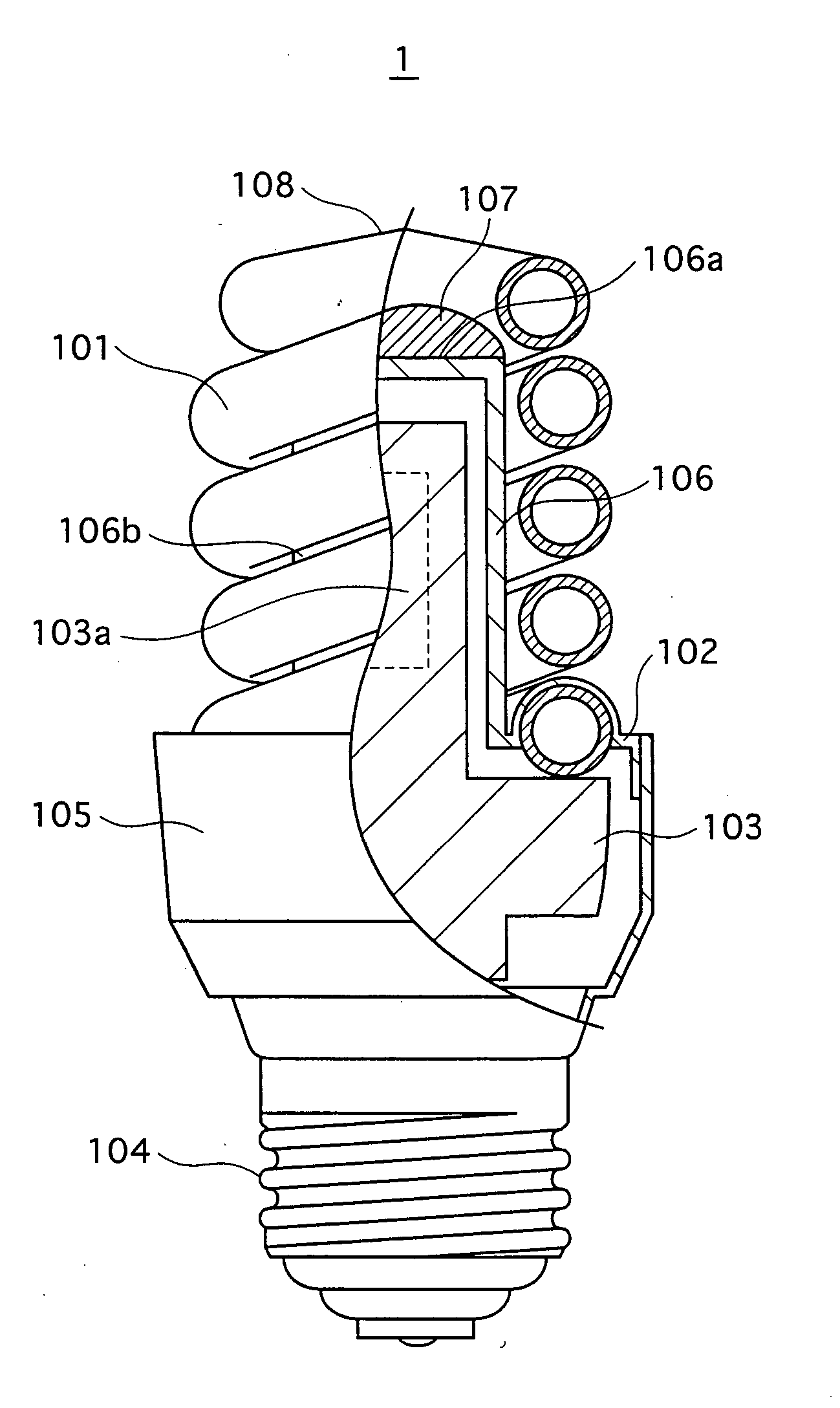
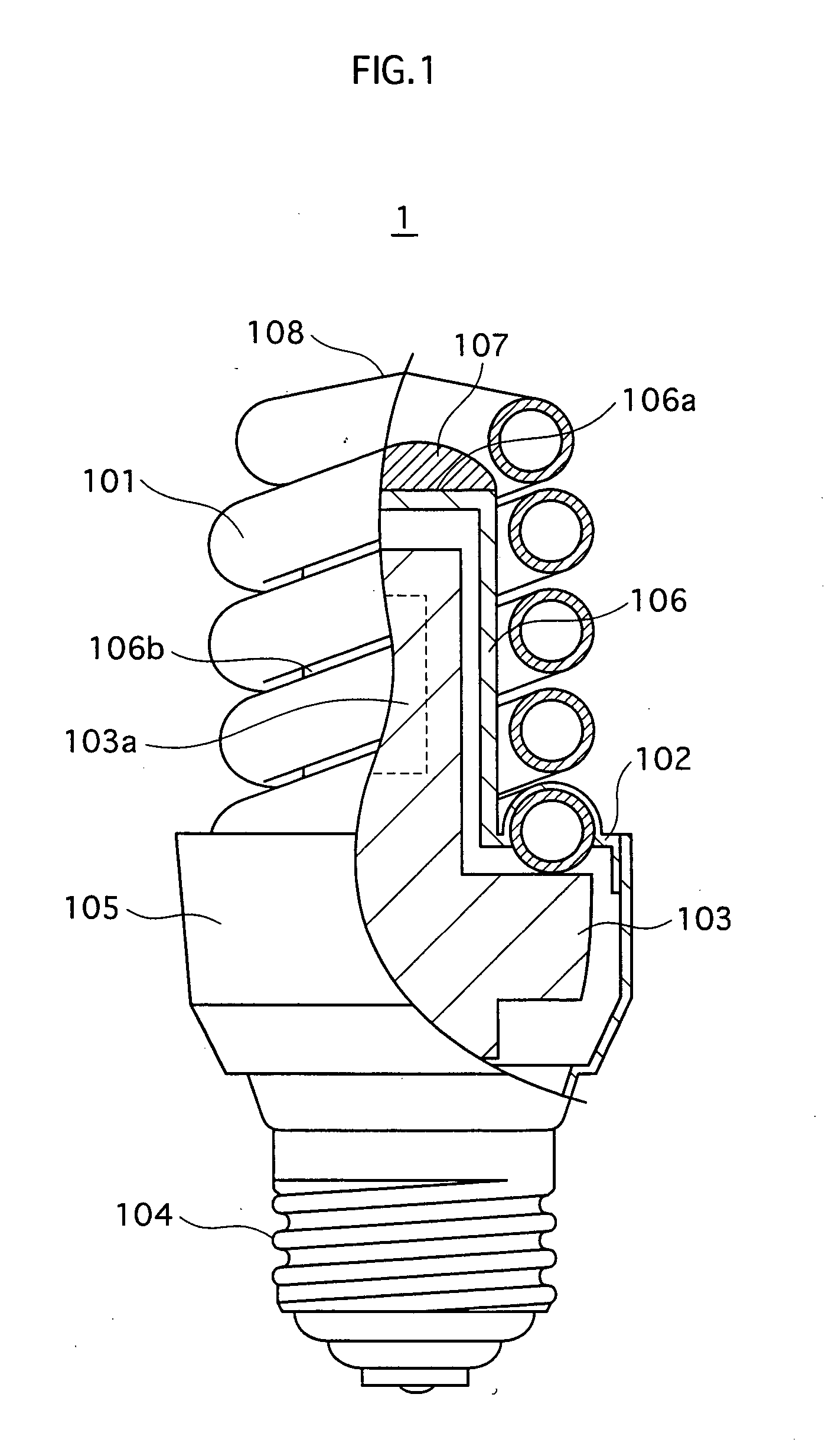
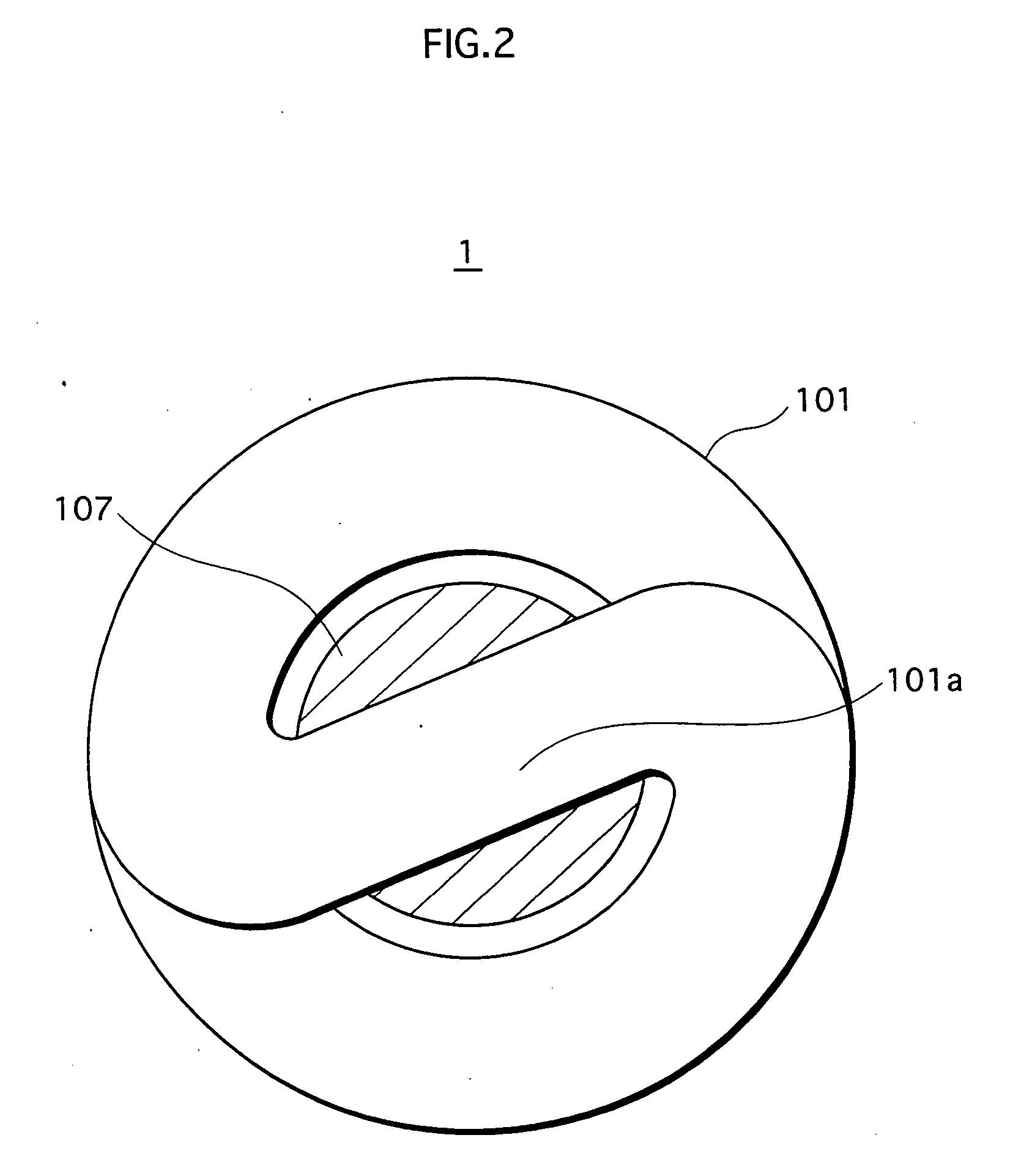
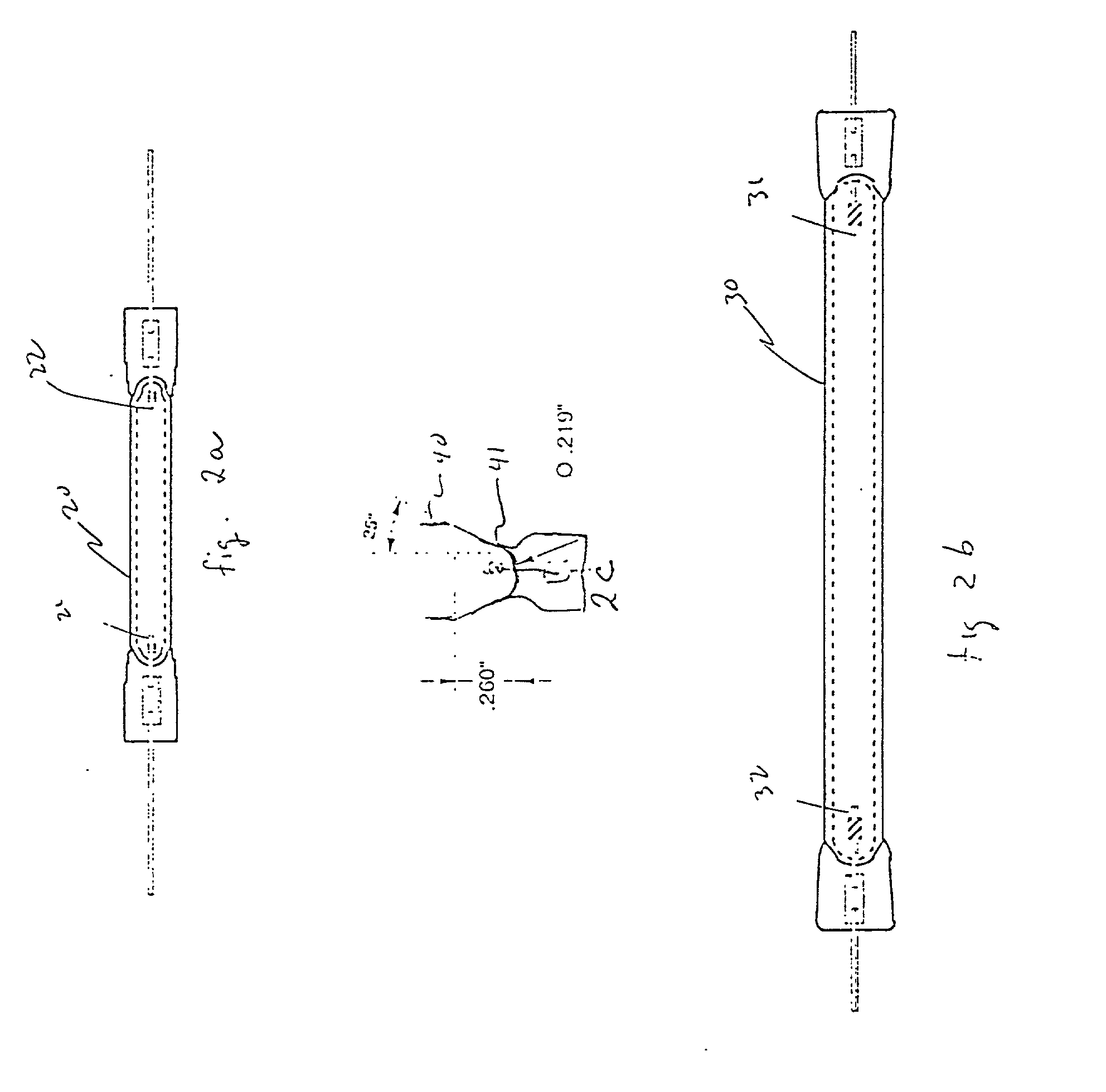
Low-pressure mercury vapor lamp
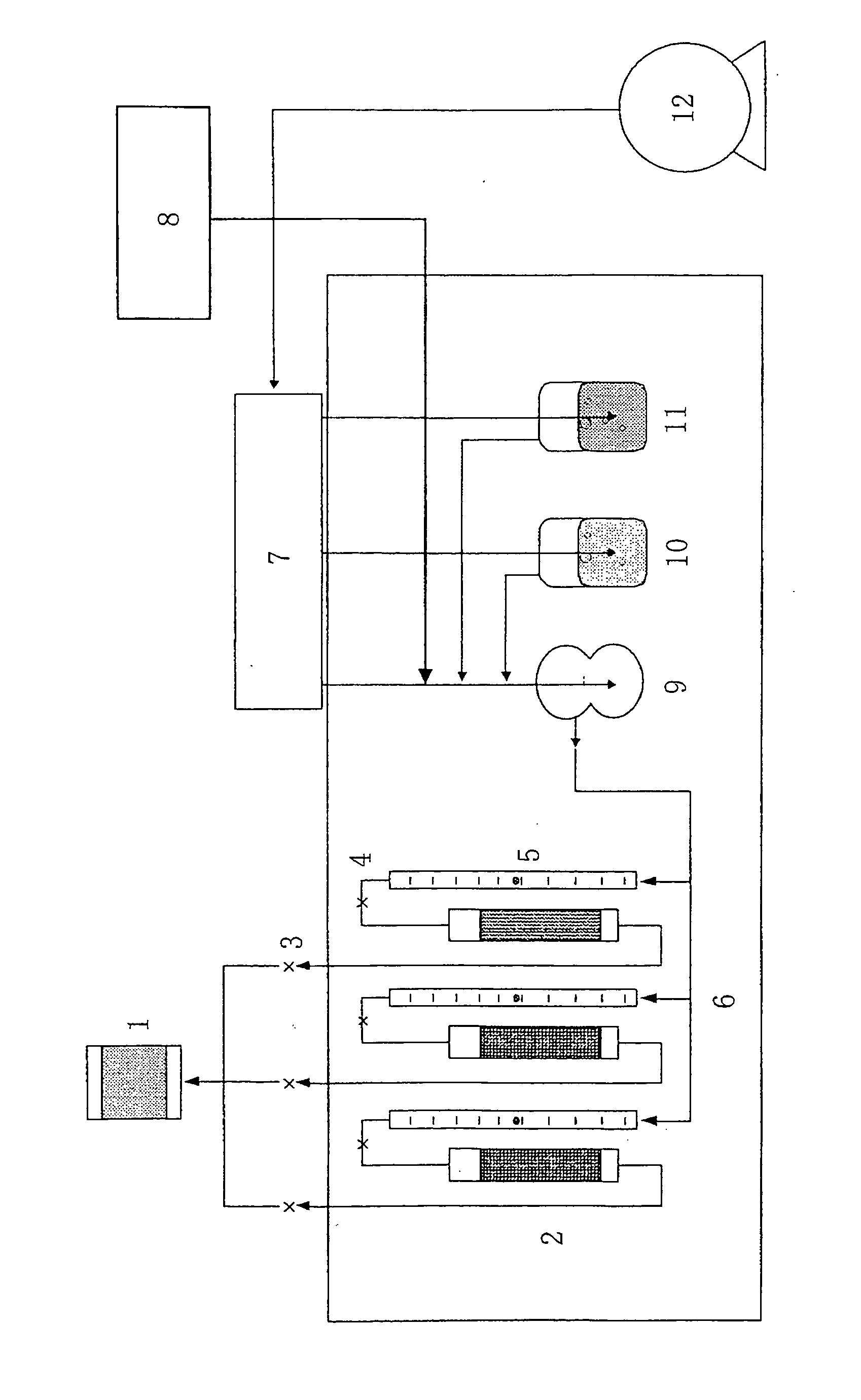
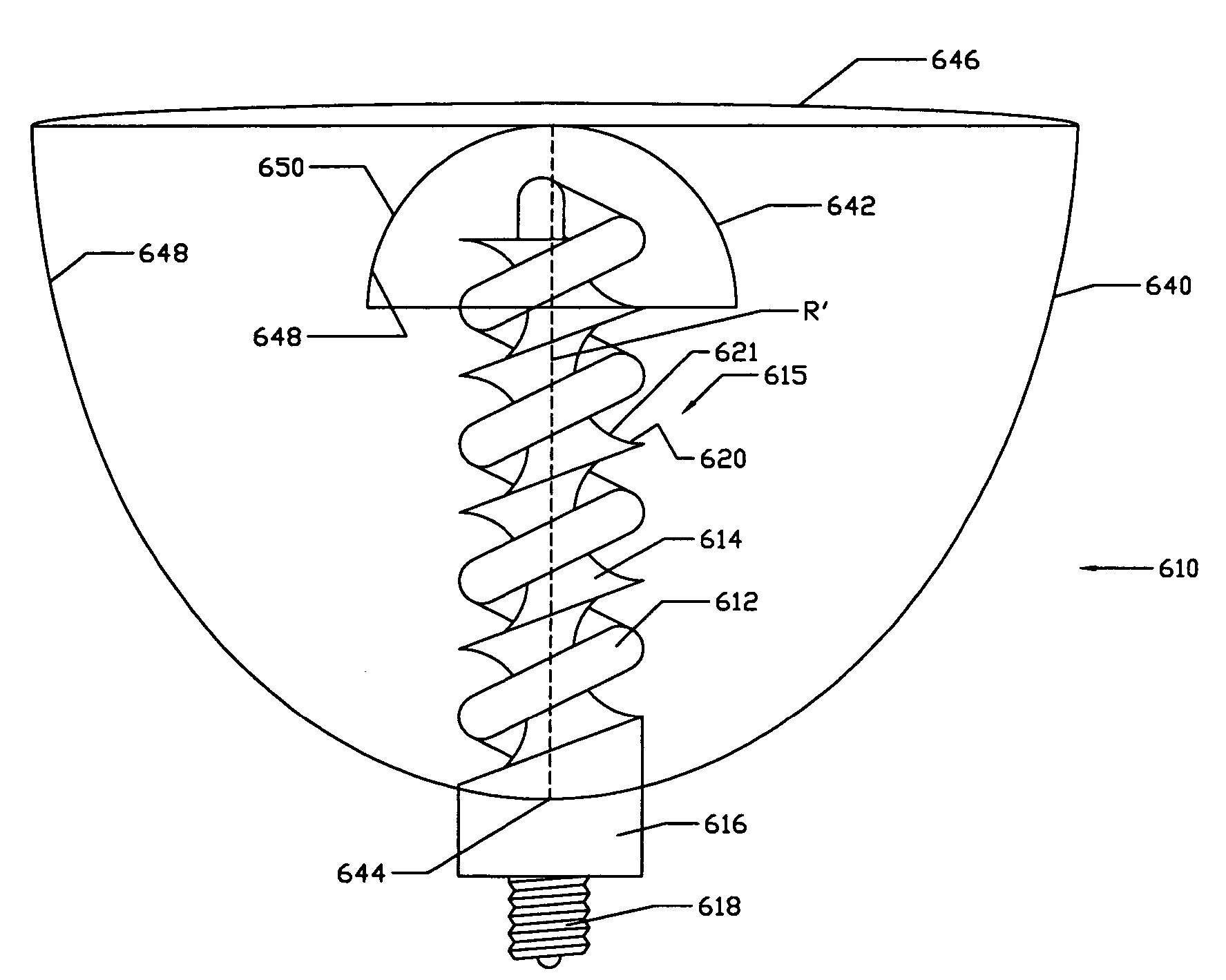
InactiveUS20050206292A1Small sizeLoss of productivityElongate light sourcesElectric circuit arrangementsEngineeringSilicone adhesive
A compact self-ballasted fluorescent lamp includes a double-spiral arc tube and a holder. The holder has a tubular protrusion which is surrounded by the arc tube, at a center of its main surface. A closed end of the protrusion and a part of the arc tube facing the end of the protrusion are bonded together using a silicone adhesive. A part of a vertical printed circuit board that is used as a lighting circuit is housed within the protrusion.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
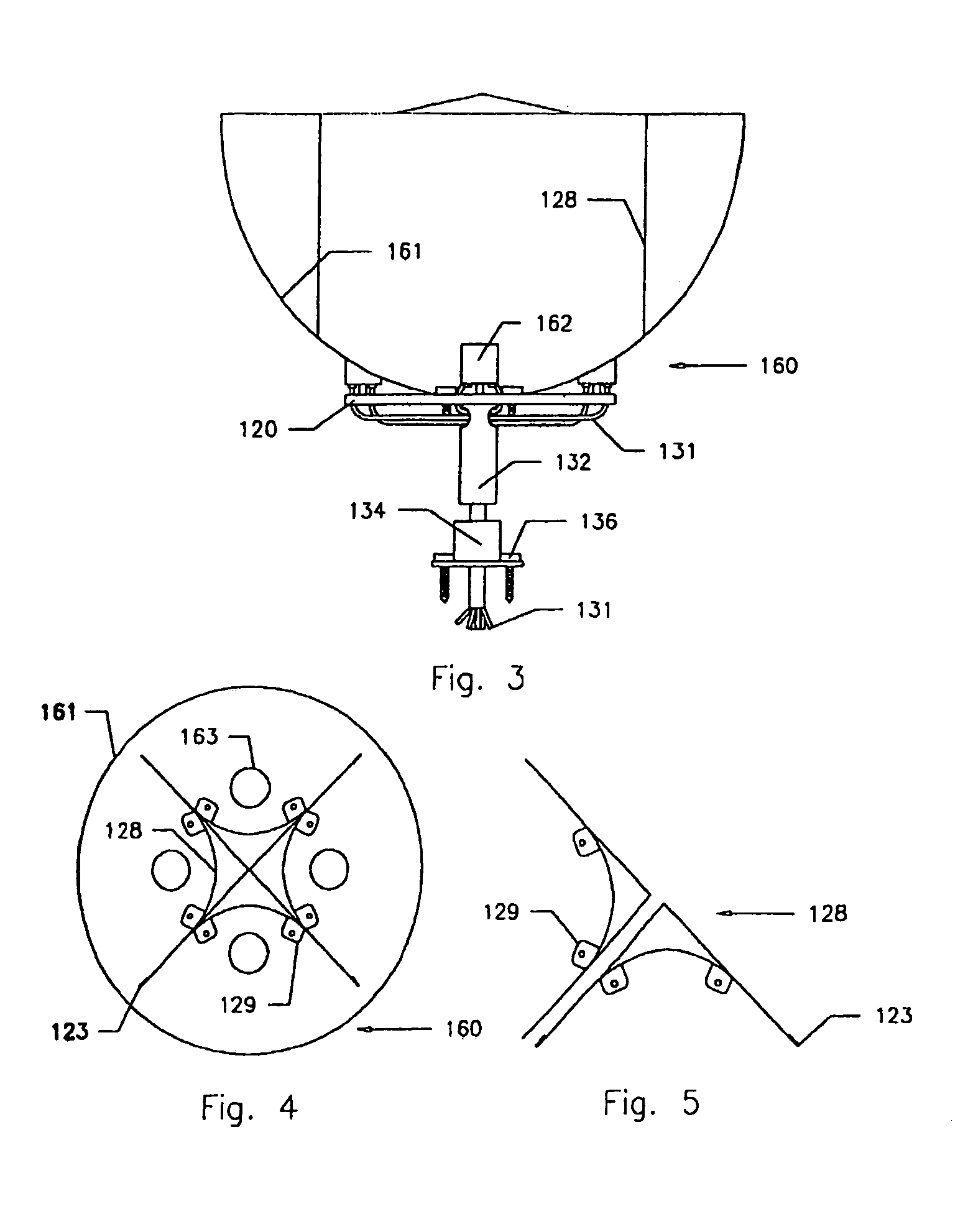
Photolithographic illumination device using mercury lamp light source
InactiveCN102221785APromote conversionConversion not requiredPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLight energyPupil
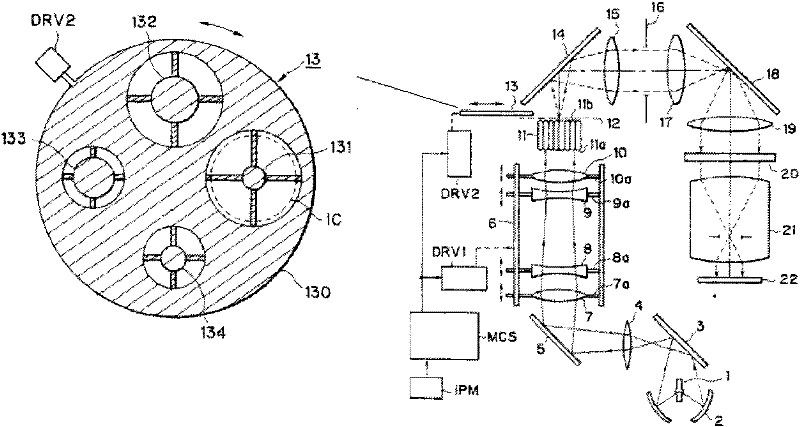
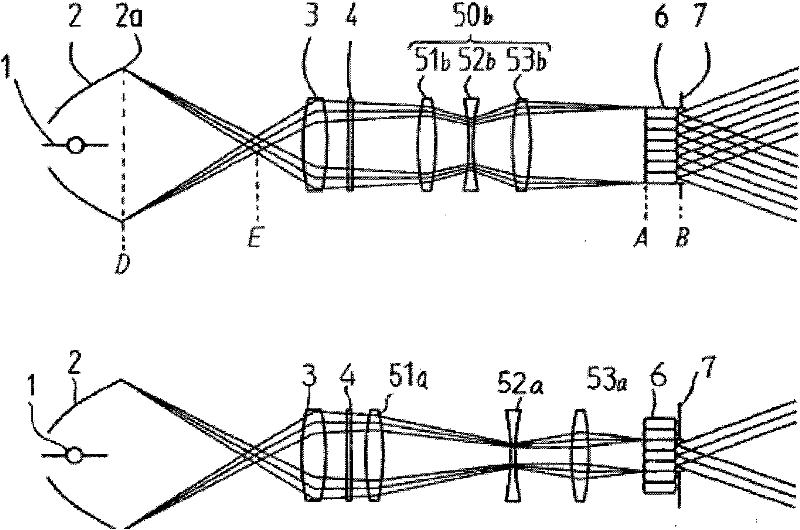
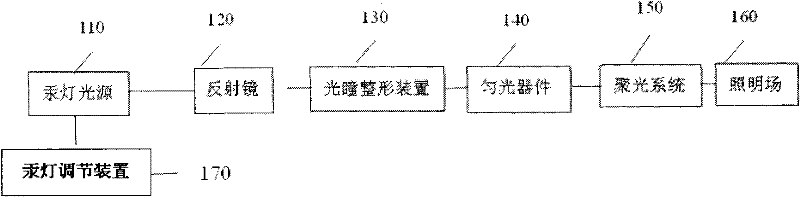
The invention discloses a photolithographic illumination device using a mercury lamp light source. The photolithographic illumination device comprises the mercury lamp light source, a reflective bowl, a pupil reshaping device, a dodging device, a condensation system and a mercury lamp position adjusting device, wherein the reflective bowl is used for converging light energy of a mercury lamp; the pupil reshaping device is used for generating continuous and variable pupils and converting illumination modes; the dodging device is used for acquiring better illumination uniformity; and the mercury lamp position adjusting device is used for changing coherence factors of rays emitted by the mercury lamp light source by moving the position of the mercury lamp to acquire a required illumination field. Through the illumination device provided by the invention, the illumination modes and the illumination coherence factors can be simply converted by using fewer elements, and the elements do not need to be changed.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
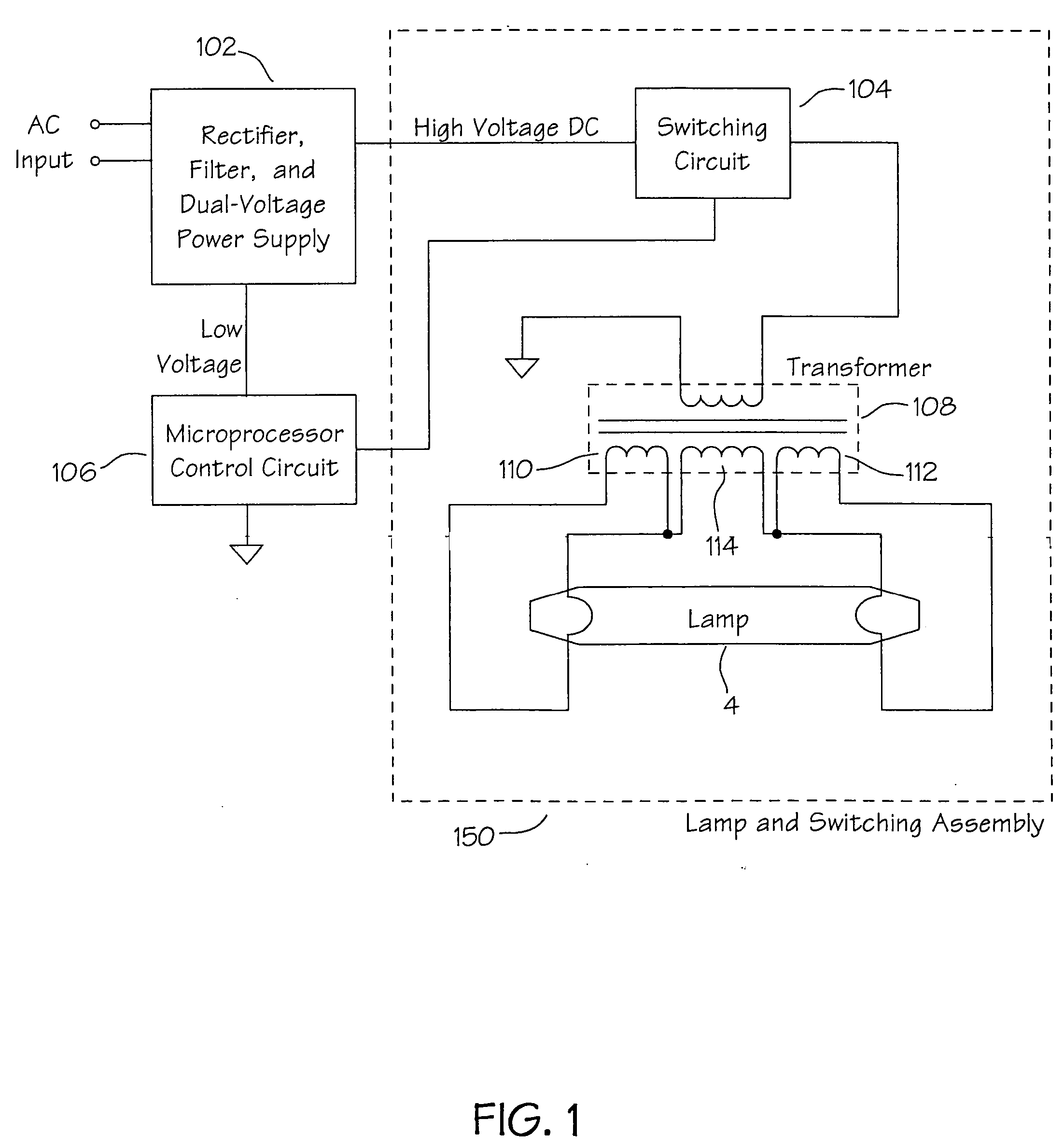
Lighting apparatus
InactiveUS7390106B2Low costIncrease light intensityIncadescent body mountings/supportElectric discharge tubesLight equipmentFluorescence
The present invention comprises a method of enhancing illumination by a variety of lamp types through the use of reflective technologies, for example, replacement of expensive high intensity density of mercury vapor lamps with low wattage fluorescent tubes having at least one and in some cases, up to three reflective surfaces for focusing otherwise lost light toward a target illumination area. Further, the placement of light sources at the focal point of said reflective surfaces aids in optimizing the amount of light focused in a desired direction.
Owner:WALTON RANDAL D
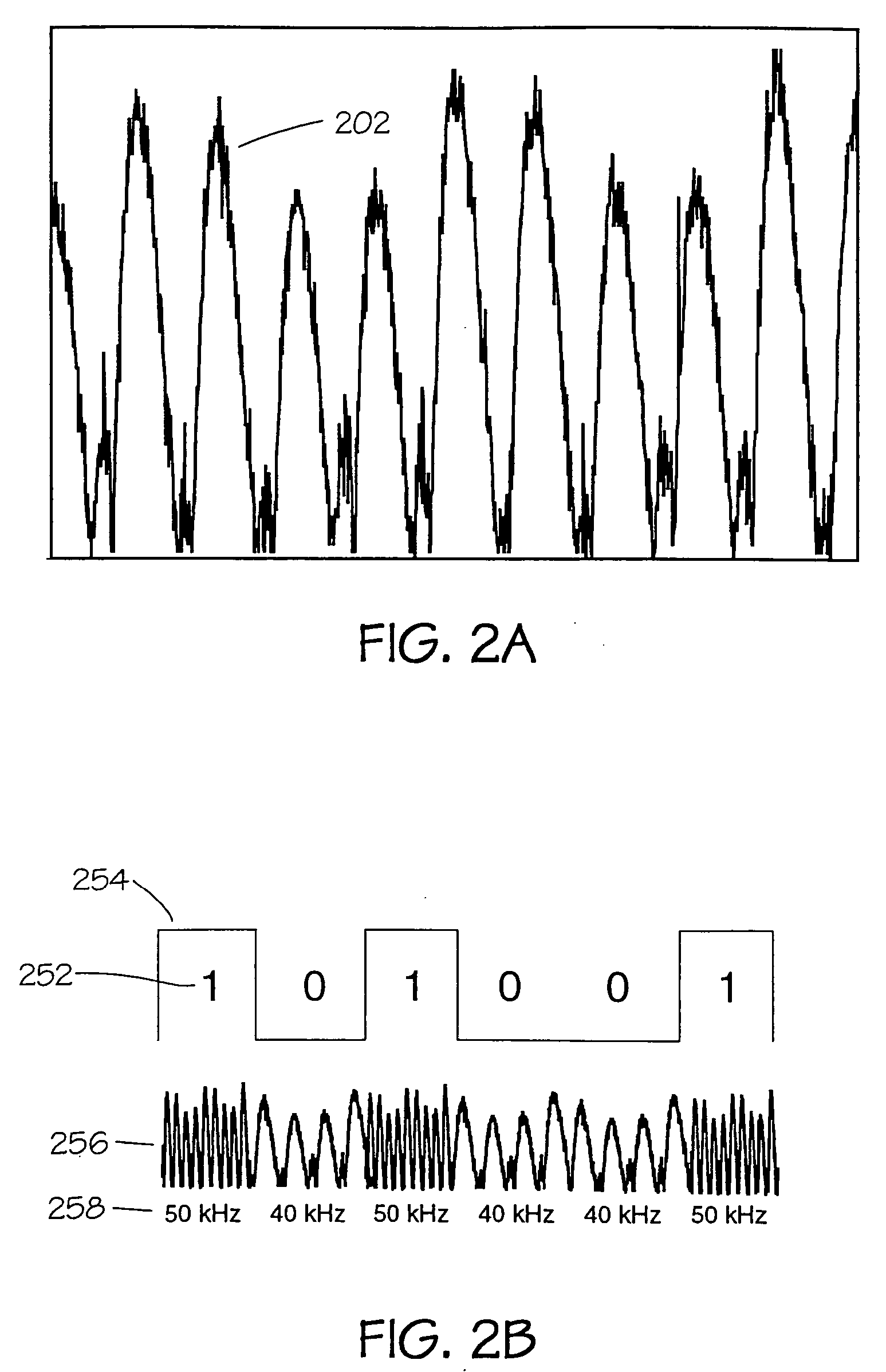
Method of disinfection and lighting by using LEDs and LED device thereof
InactiveUS9144617B2Easy to operateHigh safety factorRadiation pyrometryLight source combinationsEffect lightUltraviolet
A method of disinfection and lighting by using LEDs and an LED device thereof are provided. Two kinds of LEDs, i.e., the lighting LEDs, and the UV-LEDs, are fixed on a circuit board evenly and mixedly in a certain way, and a separator is also provided on the circuit board. Meanwhile, a controlling circuit module having a function of mode switching controls the UV-LEDs and the lighting LEDs, in such a manner that the functions of UV-LED disinfection and LED lighting are combined well in a same device. The method replaces a conventional method of sterilization and disinfection using ultraviolet (UV) rays emitted by a low pressure mercury vapor lamp. After being treated with light distribution by the separator, directionality of light emitted by the LED is stronger, and the LED is easier to operate.
Owner:GUANGDONG LIGHT COLLECTION TECH COMPANY
Lighting apparatus
InactiveUS20070041200A1Less wattage consumedIncrease foot candleIncadescent body mountings/supportElectric discharge tubesLight equipmentHigh intensity
The present invention comprises a method of enhancing illumination by a variety of lamp types through the use of reflective technologies, for example, replacement of expensive high intensity density of mercury vapor lamps with low wattage fluorescent tubes having at least one and in some cases, up to three reflective surfaces for focusing otherwise lost light toward a target illumination area. Further, the placement of light sources at the focal point of said reflective surfaces aids in optimizing the amount of light focused in a desired direction.
Owner:WALTON RANDAL D
Mercury lamp, lamp unit, method for producing mercury lamp and electric lamp
InactiveUS6844679B1Luminance can be restrainedAvoid darkeningIncandescent lamp energy savingTube/lamp factory adjustmentHalogenElectric light
The present invention provides a high-pressure discharge lamp 100 including a luminous bulb 10 enclosing at least a rare gas and halogen in the bulb and made substantially of quartz glass; and an electrode 12 made substantially of tungsten and disposed in the luminous bulb. The mole number of the halogen is larger than the sum of the total mole number of metal elements (except the tungsten element and the mercury element) that have the property of bonding to the halogen and are present in the luminous bulb 10 and the mole number of the tungsten present in the luminous bulb by evaporation from the electrode 12 during lamp operation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Low mercury metal halide lamp
InactiveUS20030020409A1Reducing mercury dosageLess HgSolid cathode detailsControl by magnetic circuit reluctanceNoble gasIodide
A metal halide lamp of about 90% reduced mercury content with performance (efficacy, CCT, CRI) equivalent to a standard commercial metal halide lamp. The lamp comprises an arc shaped tube disposed within an outer jacket and including a fill of a metal halide and not more then about 2.7 mg mercury / cc of arc tube. The arc tube has an inner diameter to arc gap ratio of between about 0.10 and 0.16 and the wall loading of the reduced mercury lamp being equivalent to a standard metal halide lamp of about 20 W / cm2. The metal halide comprises Na and / or Sc iodides of various ratios depending on the color temperature desired, and a rare gas such as Xe, Kr, Ar in pressures of 10-300 torr dependent on the power loading and desired operating voltage of the lamp.
Owner:KELLY TIMOTHY LEE +3
Photoinitiator and ink
An ink jet ink that includes a photopolymerizable material, a pigment, and a liquid blend of (a) oligo [2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-[4-(1-methylvinyl)phenyl]propanone](b) 4-methylbenzophenonone (c) 2,4,6-trimethylbenzophenone (d) 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyldiphenylphosphine oxide, (e) phenyl-bis-(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide, and (f) 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenylpropanone can be cured by either a xenon flash lamp or a mercury vapor lamp, with excellent adhesion over vinyl substrates.
Owner:SCHOEN CATHERINE A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com