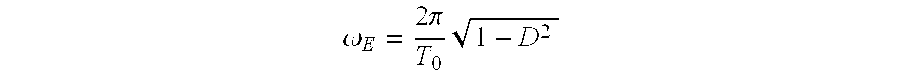Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78results about "Control by magnetic circuit reluctance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
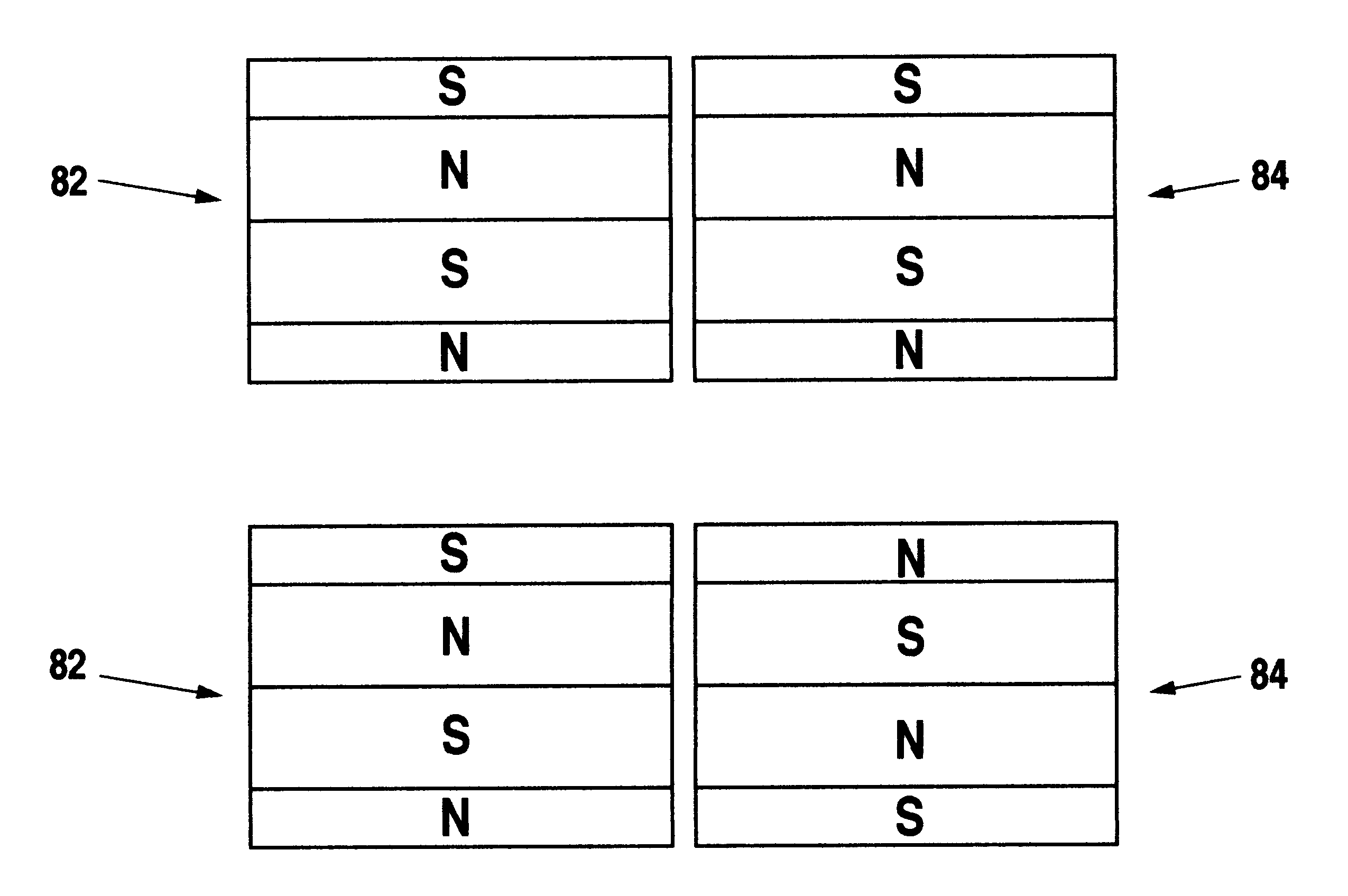
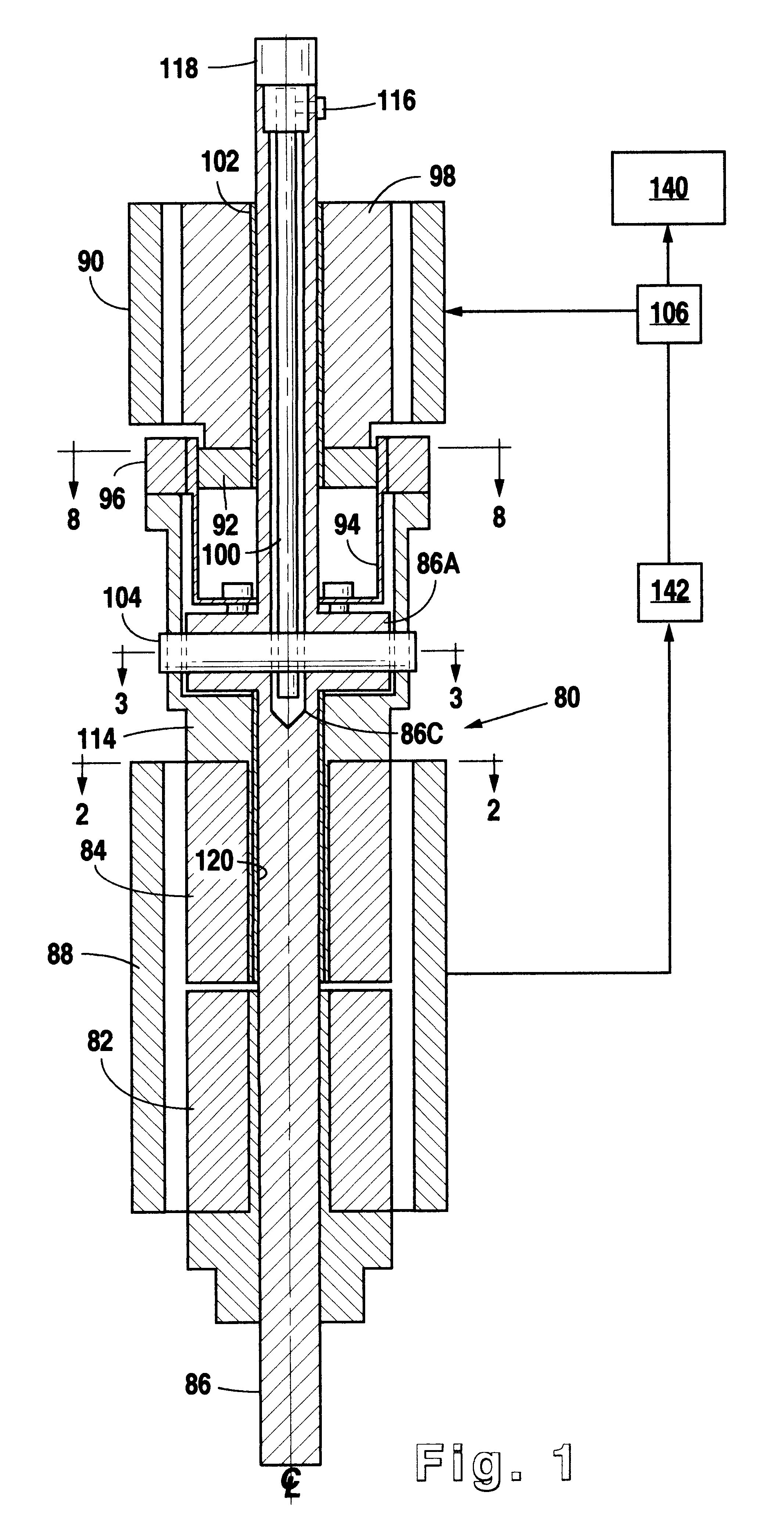
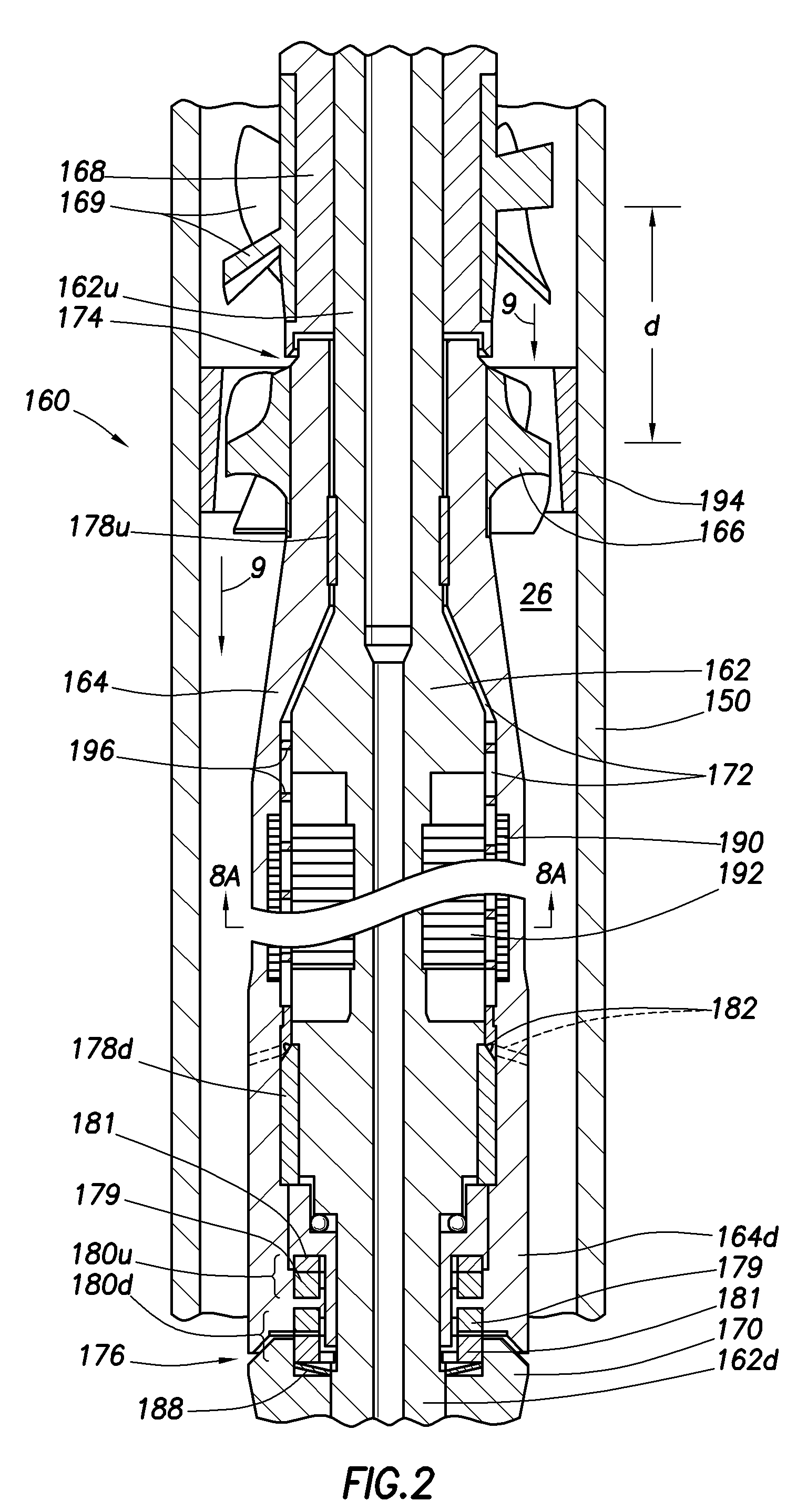
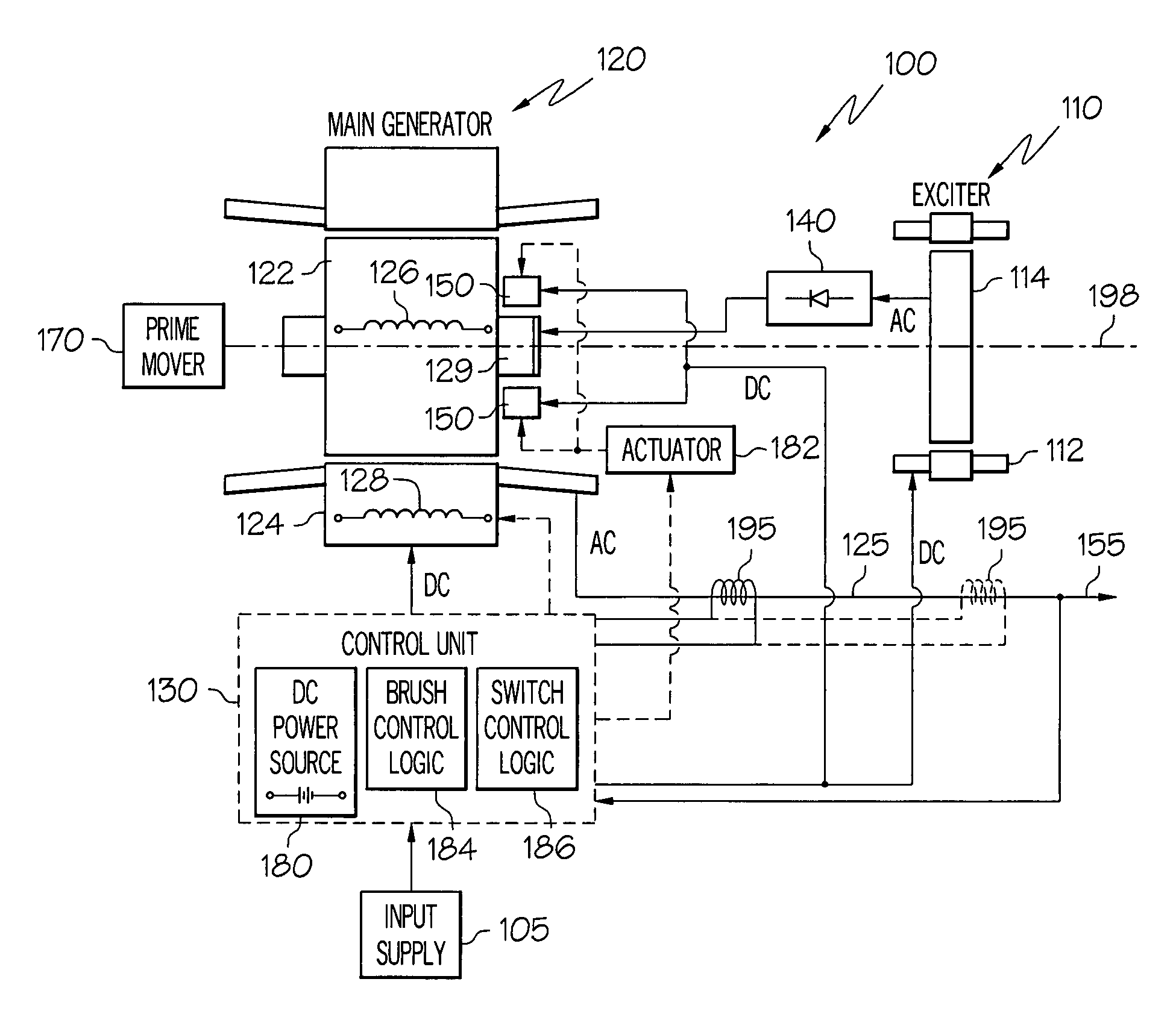
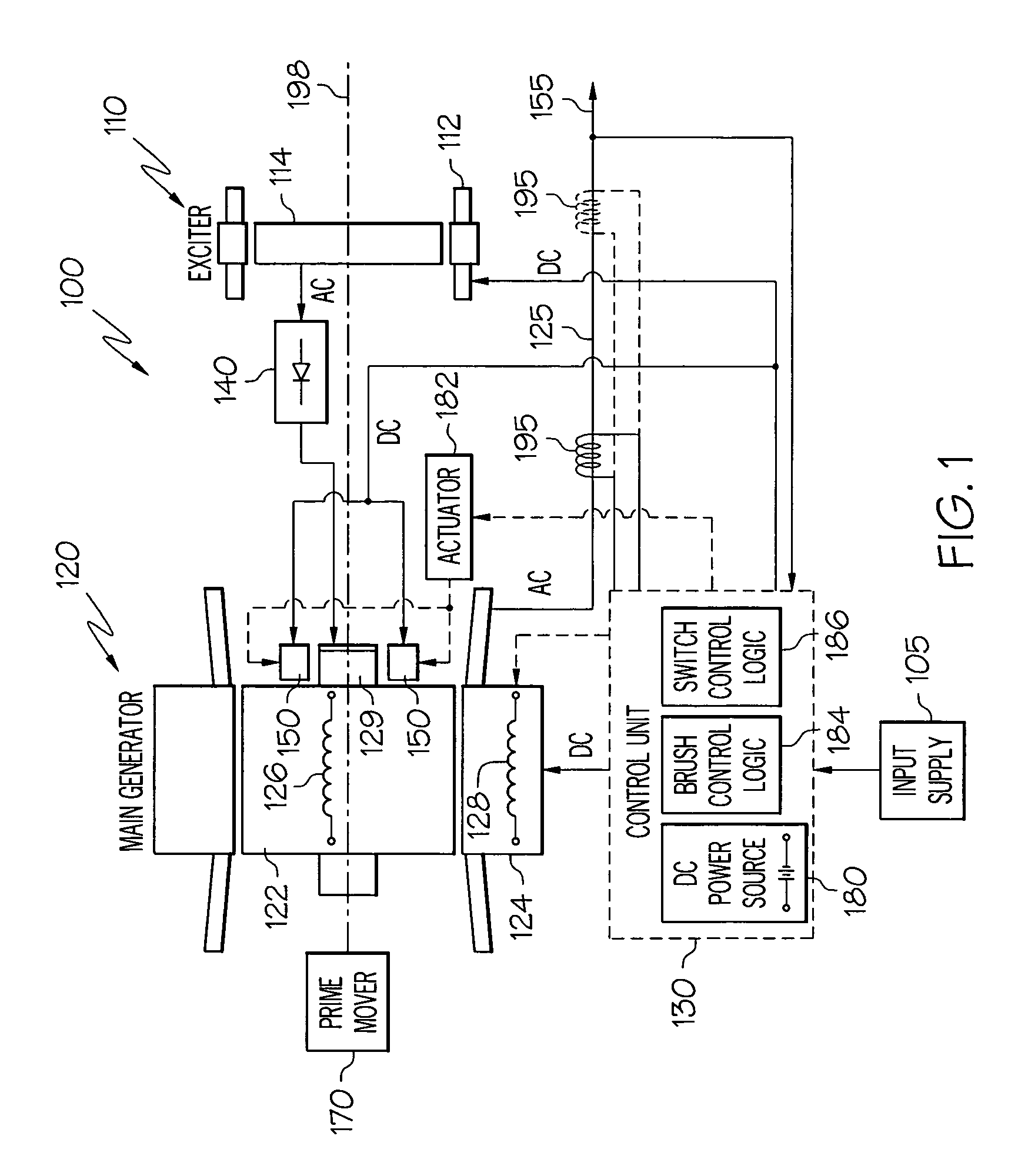
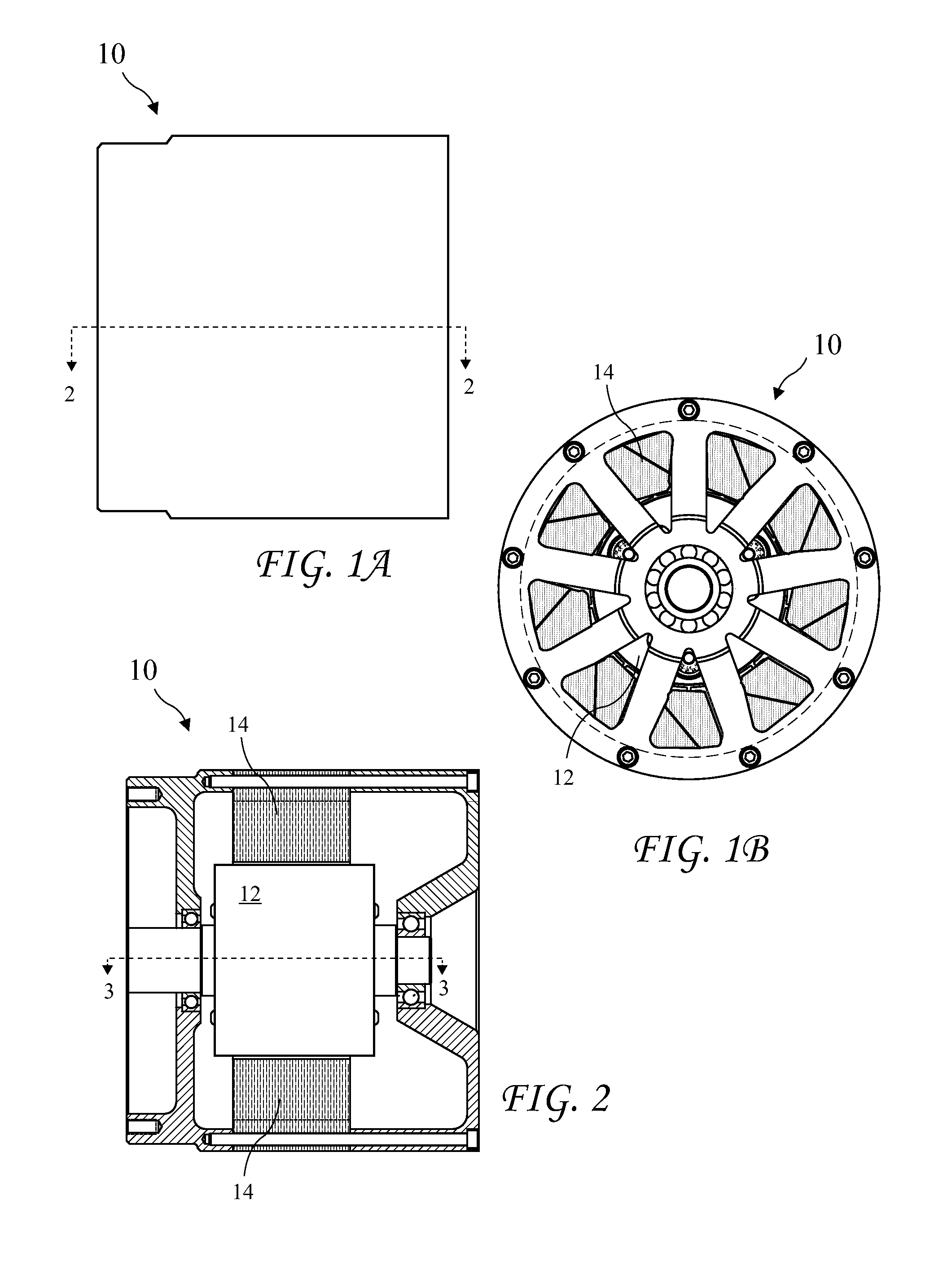
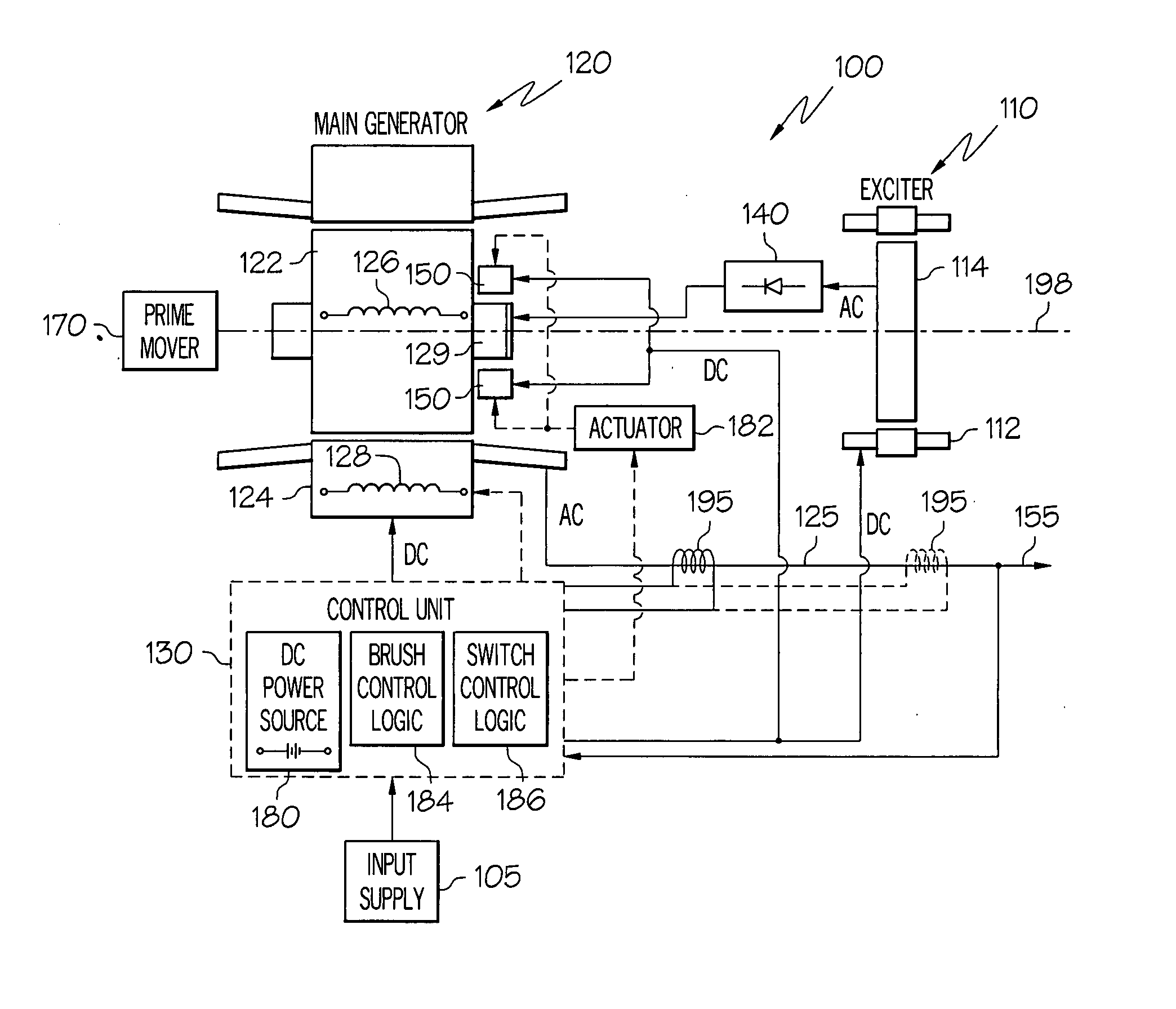
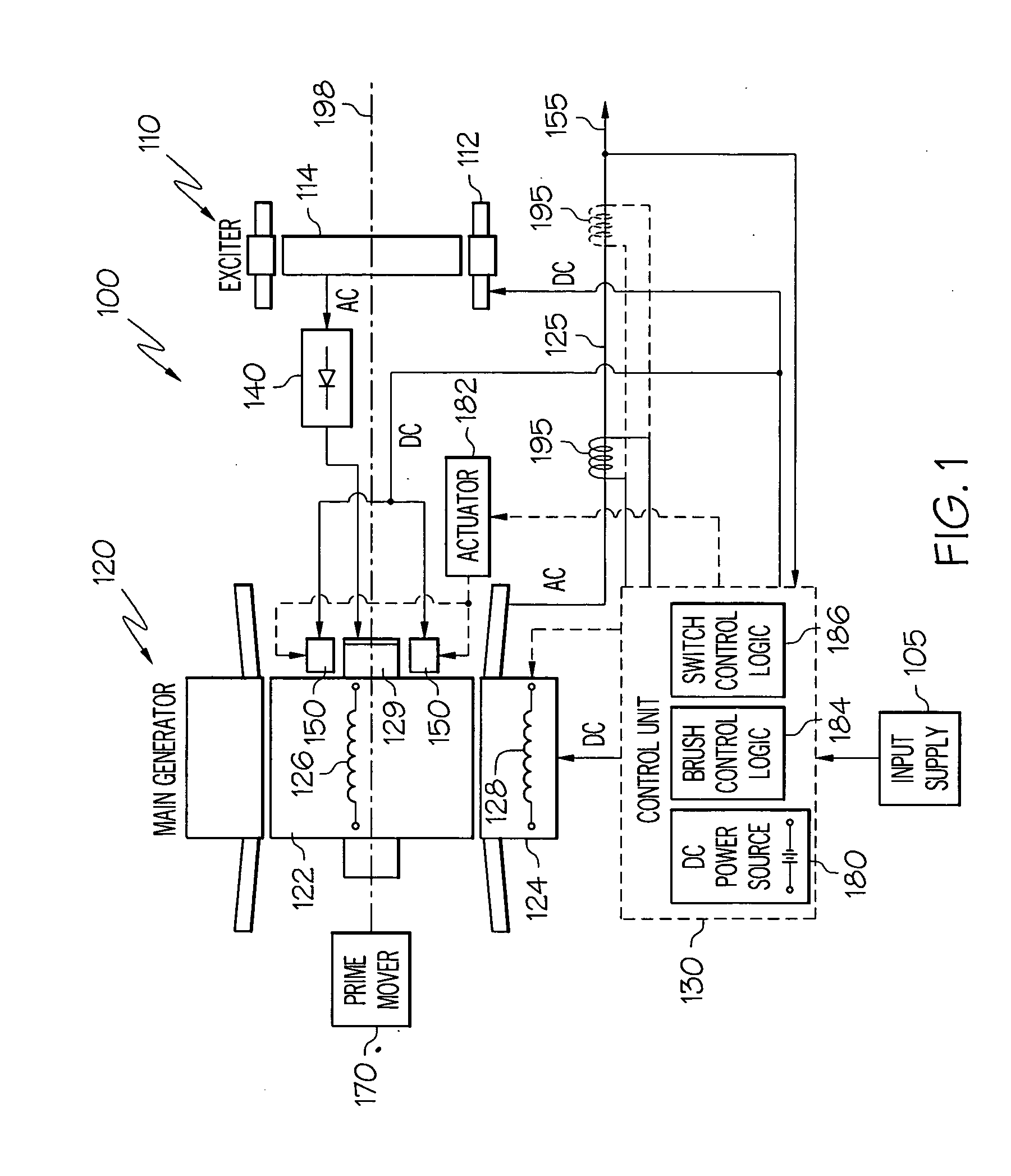
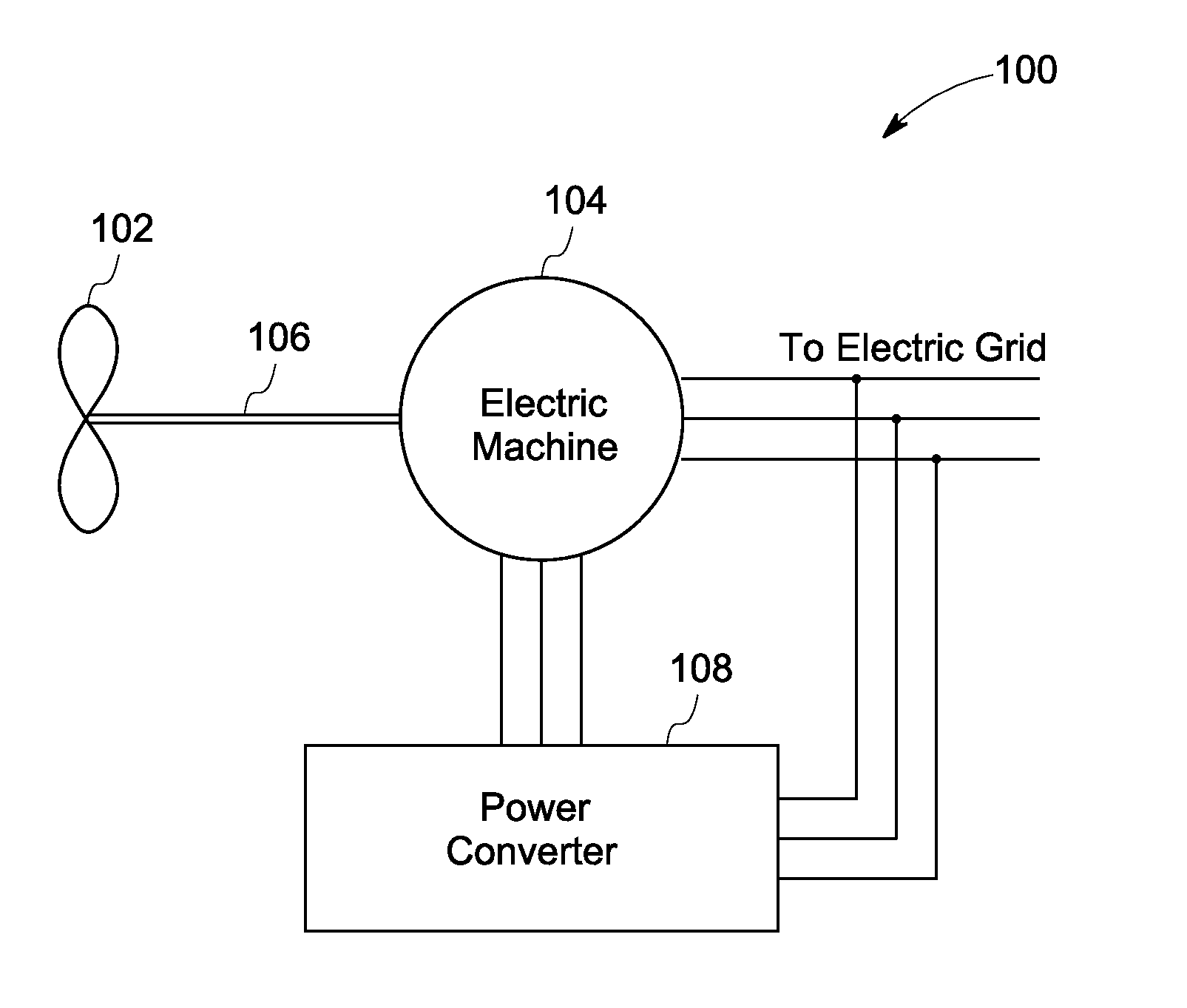
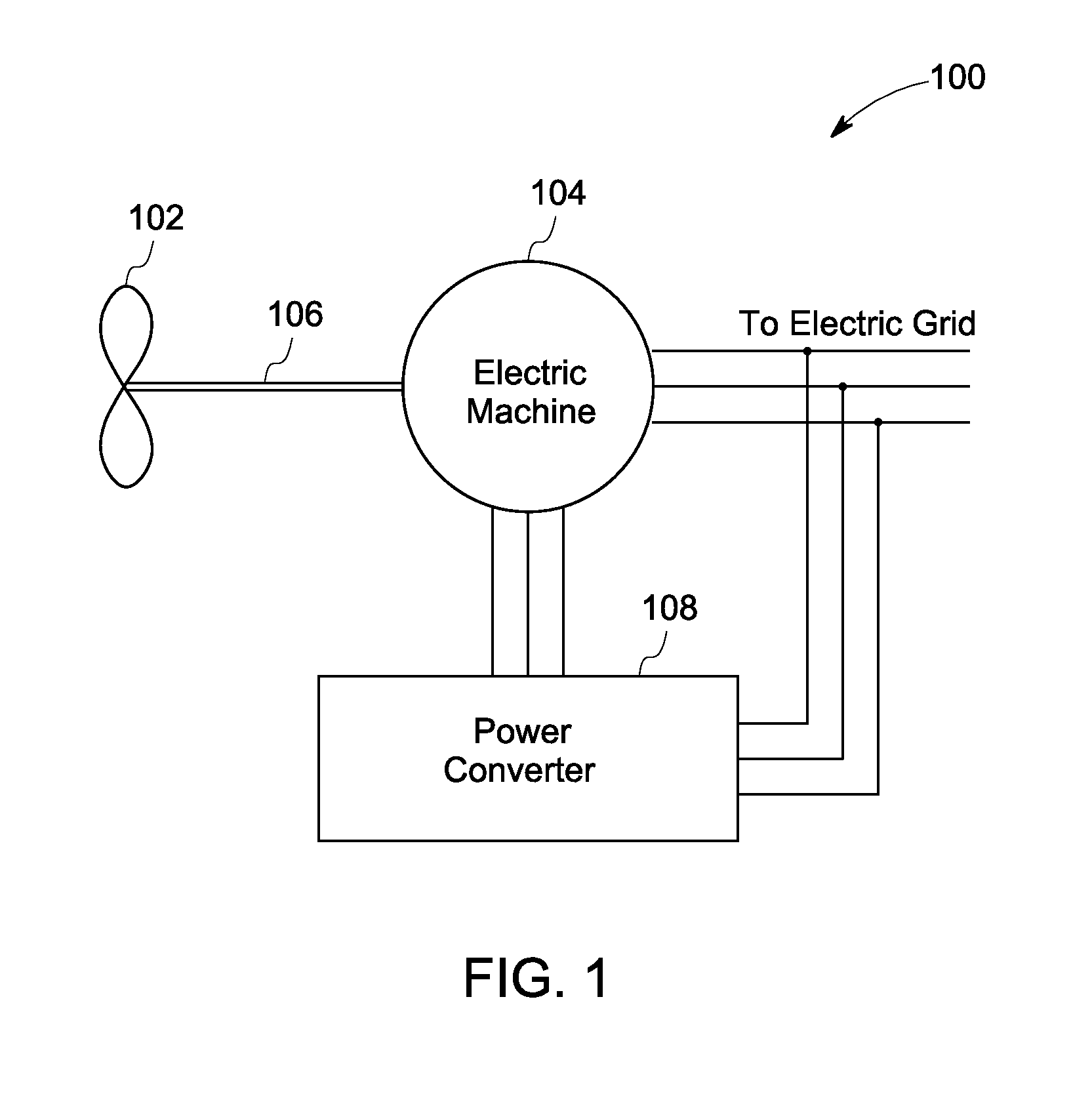
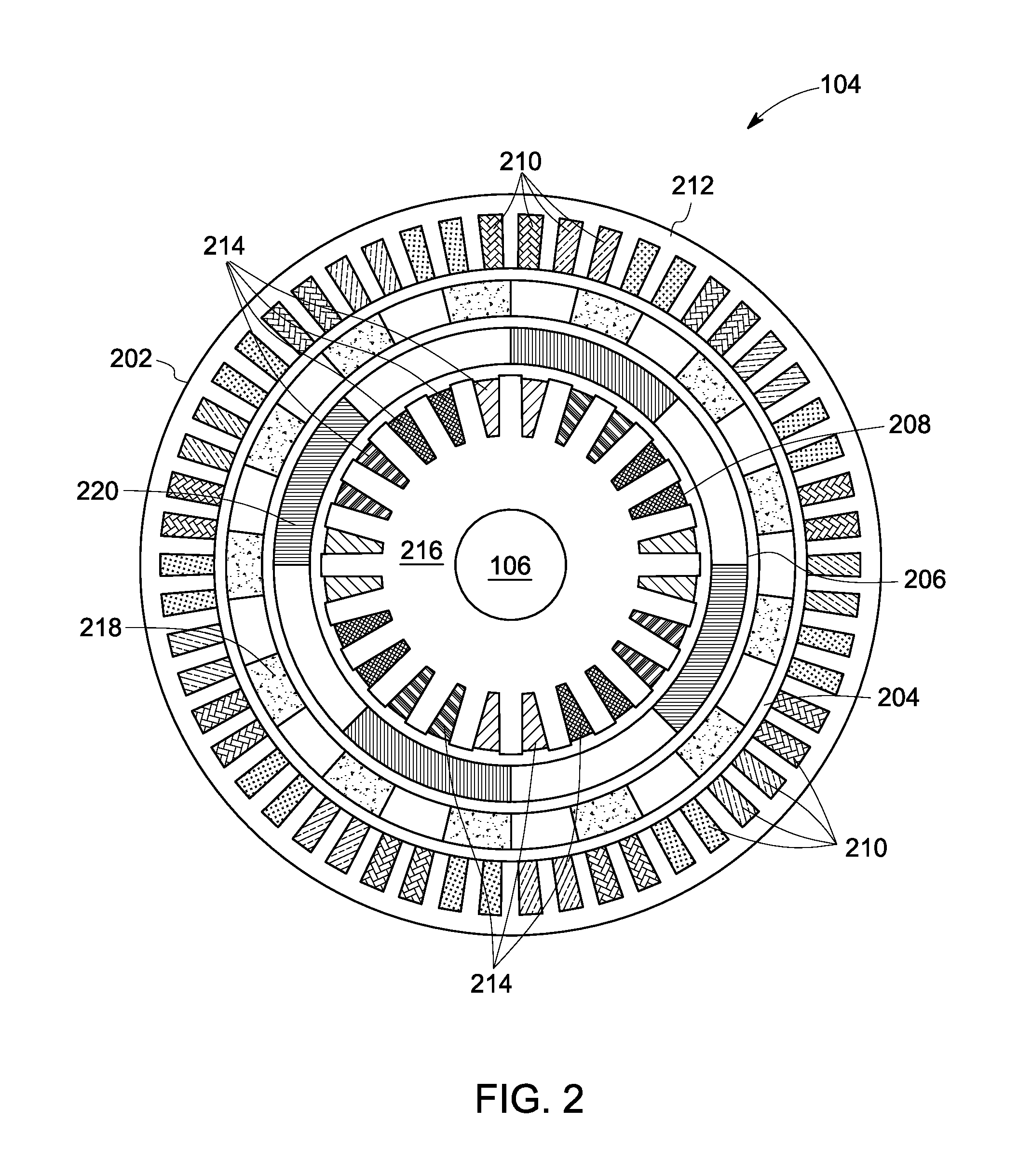
Variable output rotary power generator
The present invention is directed to a downhole apparatus for quickly generating and regulating variable output electric power by varying the alignment of a pair of axially adjacent permanent magnets rotating within an armature having electrically conductive windings. Each of the permanent magnets comprises a plurality of permanent magnetic segments having circumferentially alternating magnetizations. One of the permanent magnets is fixed to the drive shaft, and the other permanent magnet is movably mounted on the drive shaft to enable the alignment or misalignment, as desired, of the magnetizations of the respective magnetic segments on the pair of permanent magnets. When the magnetizations are completely aligned, the maximum electrical power is generated in the windings of the main armature; conversely, when the magnetizations are completely misaligned, zero electrical power is generated. Thus, the output power is regulated by varying the alignment of the pair of permanent magnets, which is accomplished with a drag torque generator which creates a drag torque that is transmitted to the movable permanent magnet by a torque converter.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Apparatus and method for generating electrical power in a borehole
ActiveUS7133325B2Reduce the possibilityRemove heatElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsImpellerAlternator
An apparatus and related method generate electrical power in a tubular housing, such as a drill collar, disposed in a borehole when drilling fluid flows through the tubular housing. The apparatus includes a stator adapted for being secured within the tubular housing against rotation relative to the tubular housing, a tubular rotor rotatably carried about the stator, and an impeller peripherally affixed to the rotor. The stator has an array of conductive windings therein, and is preferably an alternator stator. The rotor has an array of magnets therein, and is preferably an alternator rotor. Accordingly, drilling fluid flowing through the tubular housing when the apparatus is disposed therein engages the impeller and induces rotation of the rotor about the stator to generate electrical power.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Halbach array generator/motor having an automatically regulated output voltage and mechanical power output
A motor / generator having its stationary portion, i.e., the stator, positioned concentrically within its rotatable element, i.e., the rotor, along its axis of rotation. The rotor includes a Halbach array. The stator windings are switched or commutated to provide a DC motor / generator much the same as in a conventional DC motor / generator. The voltage and power are automatically regulated by using centrifugal force to change the diameter of the rotor, and thereby vary the radial gap in between the stator and the rotating Halbach array, as a function of the angular velocity of the rotor.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Apparatus and method for generating electrical power in a borehole
ActiveUS20050200210A1Narrowing range of outputEasily damagedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsImpellerAlternator
An apparatus and related method generate electrical power in a tubular housing, such as a drill collar, disposed in a borehole when drilling fluid flows through the tubular housing. The apparatus includes a stator adapted for being secured within the tubular housing against rotation relative to the tubular housing, a tubular rotor rotatably carried about the stator, and an impeller peripherally affixed to the rotor. The stator has an array of conductive windings therein, and is preferably an alternator stator. The rotor has an array of magnets therein, and is preferably an alternator rotor. Accordingly, drilling fluid flowing through the tubular housing when the apparatus is disposed therein engages the impeller and induces rotation of the rotor about the stator to generate electrical power.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Permanent Magnet Motor with Field Weakening
InactiveUS20120126740A1Reduce field strengthField strength is alteredTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlConstant powerPermanent magnet motor
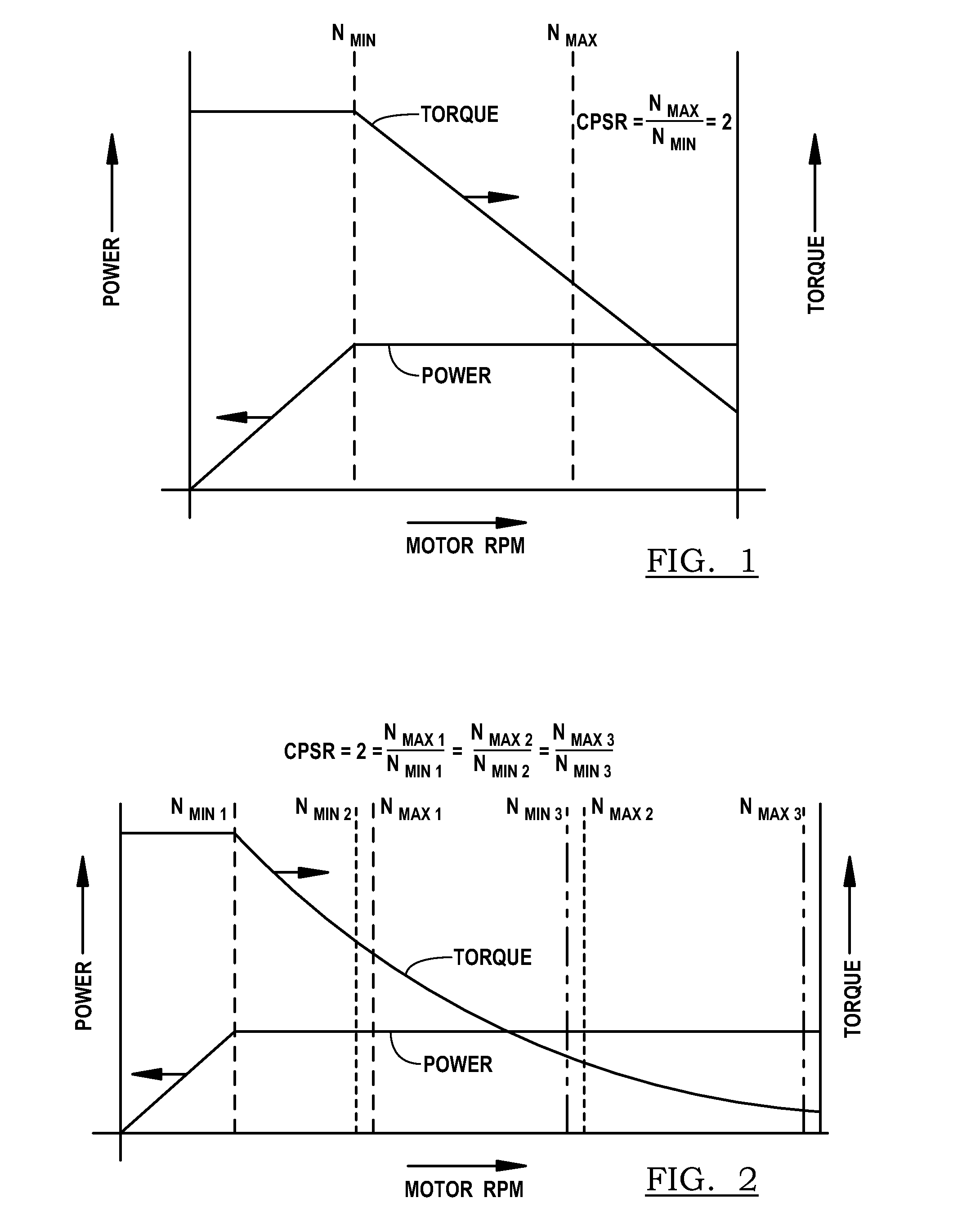
A permanent-magnet electrical machine is disclosed in which the rotor has a fixed back iron and movable back iron segments. When the movable back iron segments are in a first position, such as in contact with the fixed back iron, the field strength is high. When the movable back iron segments are in a second position in which the movable back iron segments are displaced away from the fixed back iron, the field strength is low. The ability to weaken the field strength causes the constant-power, speed ratio to be increased and thereby increases the utility of the motor for applications in which a wide speed range is desired. The disclosure applies to both permanent-magnet motors and generators. In an alternative embodiment, the stator ring is provided with a fixed portion and at least one movable stator segment.
Owner:CURRENT MOTOR
Controller of permanent magnet generator
InactiveUS7554303B1Increasing and decreasing flowReduce magnetic forceAC motor controlElectric motor controlLow speedPower switching
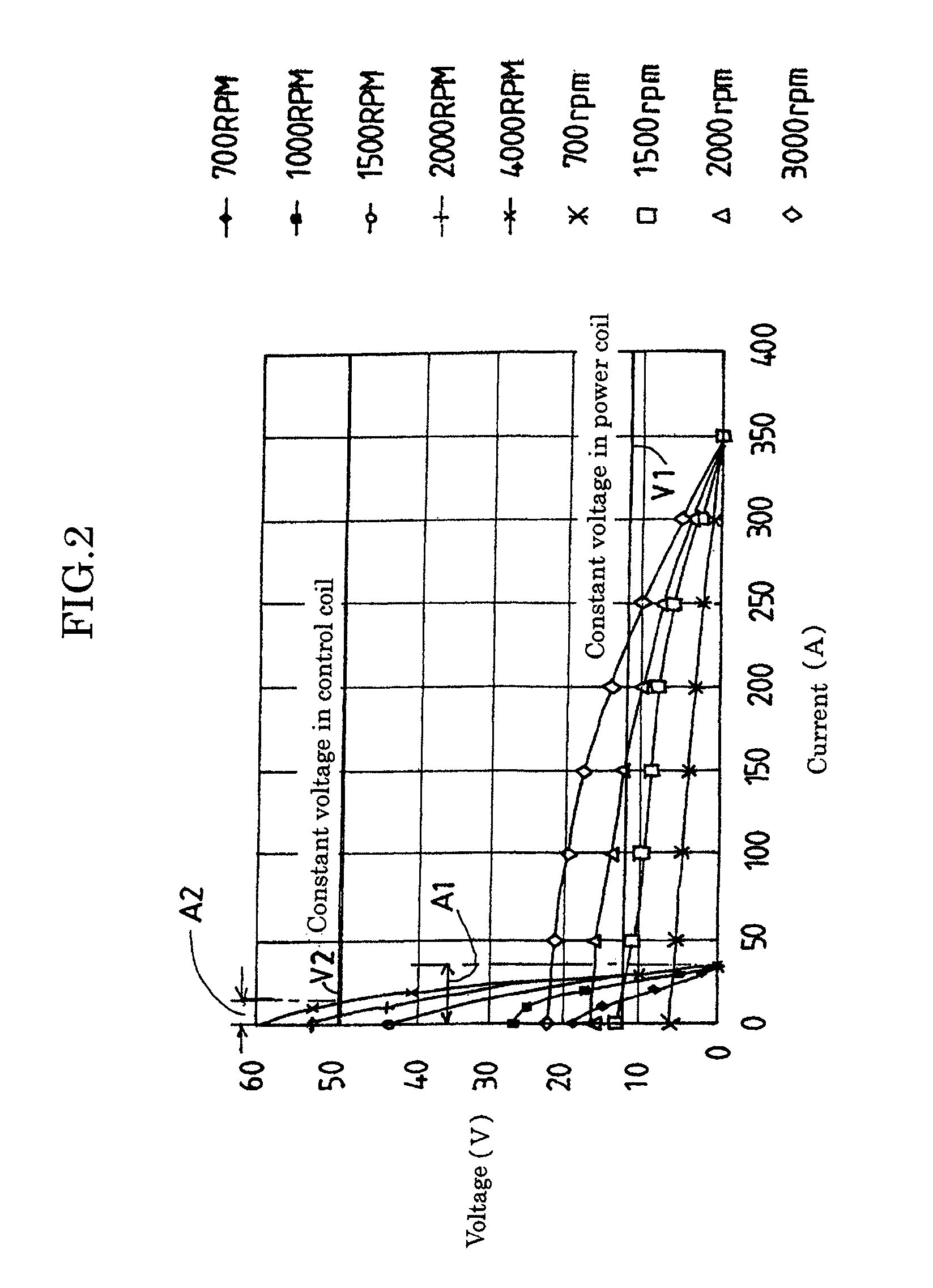
The controller of permanent magnet generator controls the current by using control switch which is installed in between power coil and control coil and switches on and off in switches in order to generate two different voltage and increase the power at very low speed condition of generator. The controller controls the voltage of power coil constantly by adjusting current of flowing in the control switch which the voltage is sensed on the load voltage sensor and the controller control the voltage constantly at very small speed by using power switches furthermore, the controller controls the two kind of voltage in power coils constantly by using control switch and switches in case of the generator having different kind of voltages.
Owner:KAWAMURA MEGUMI +1
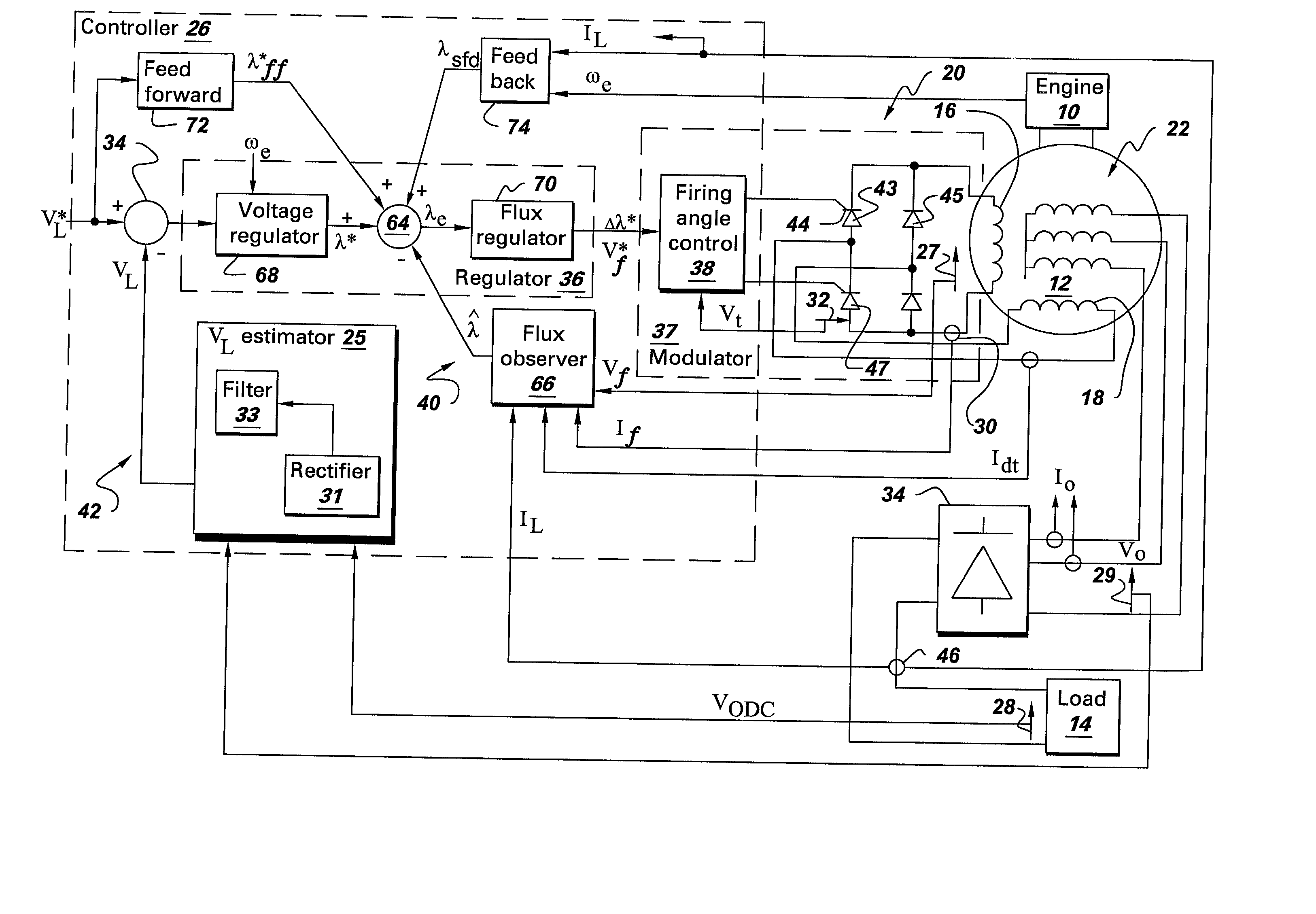
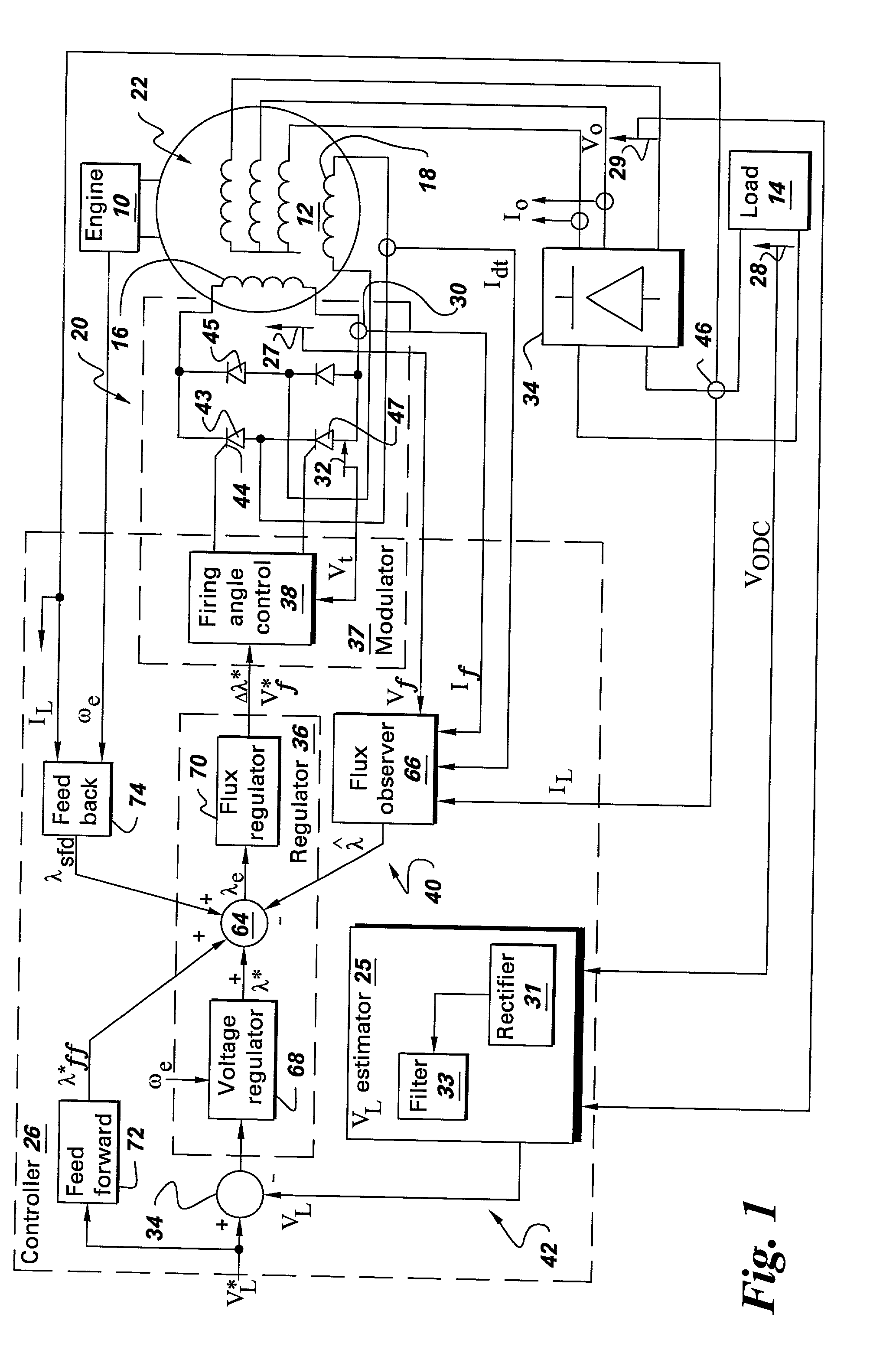
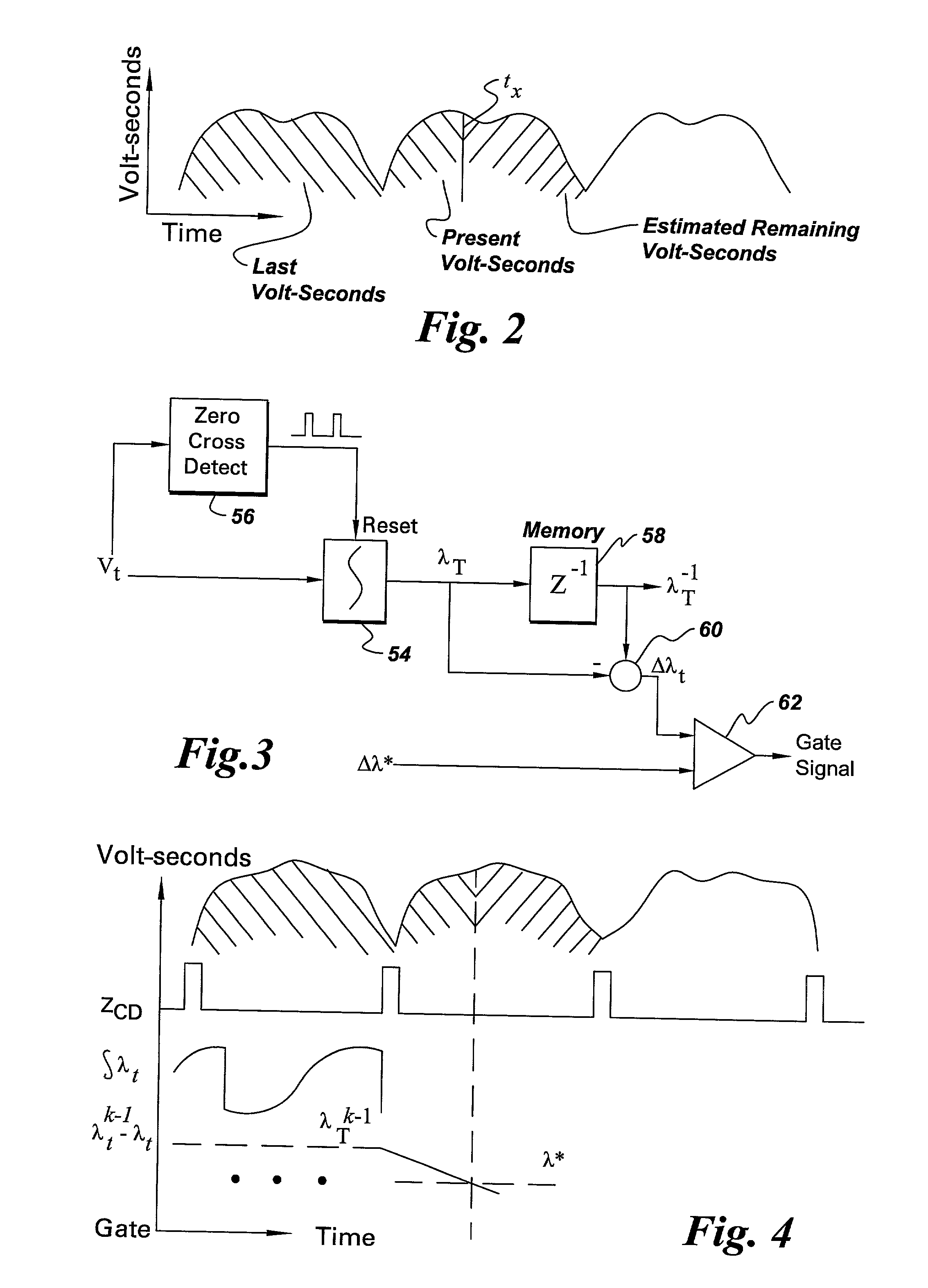
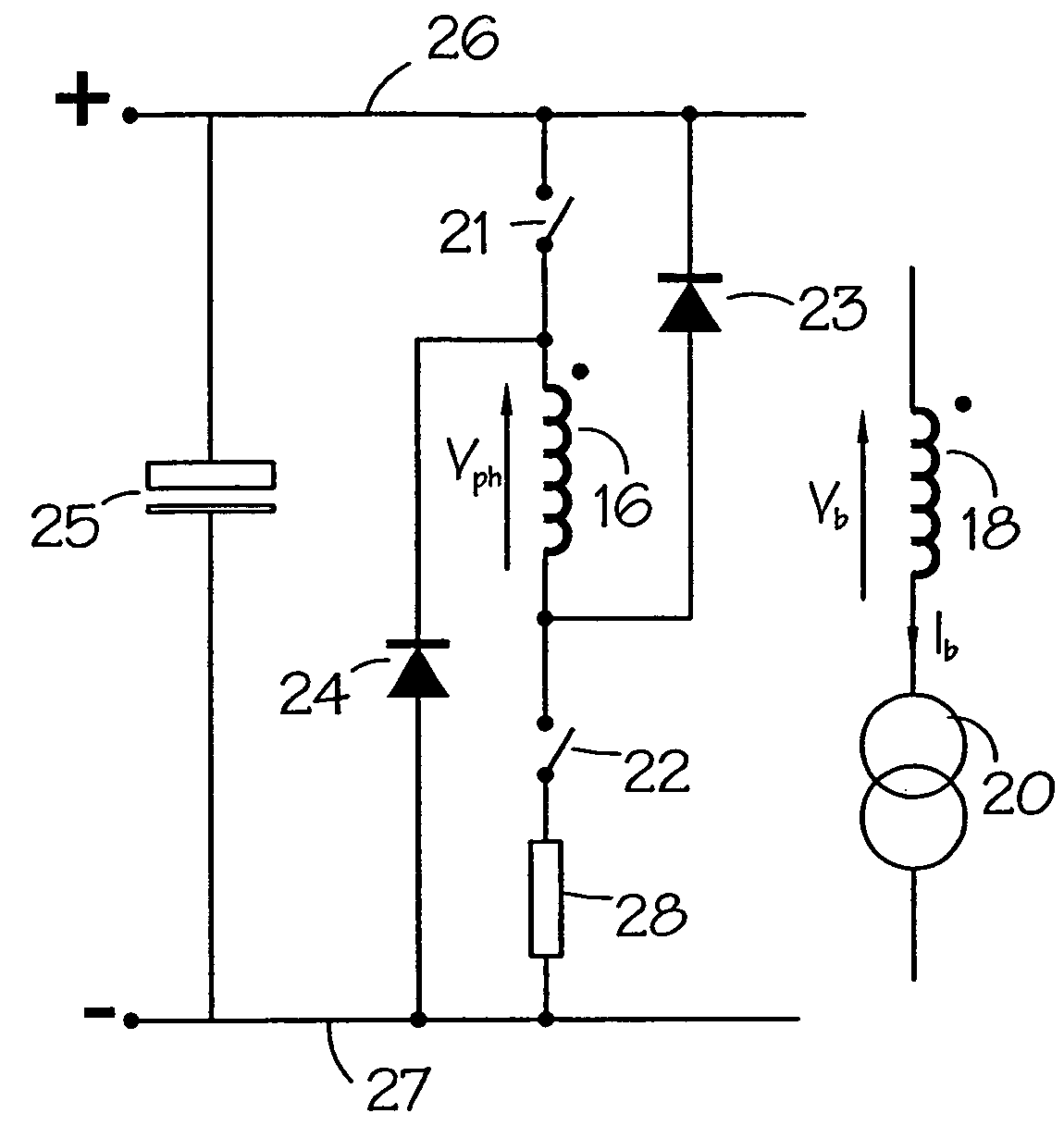
Wound field synchronous machine control system and method
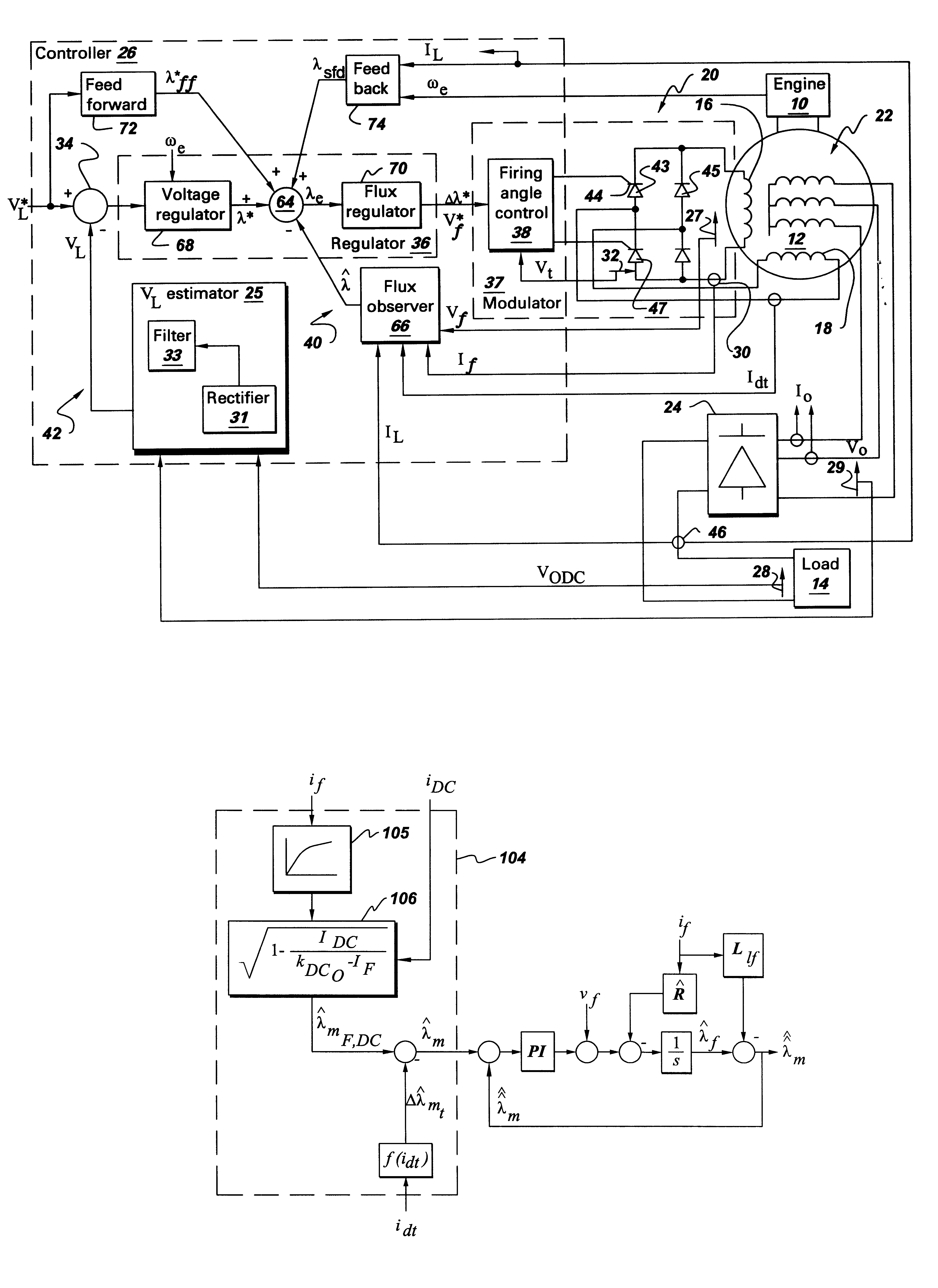
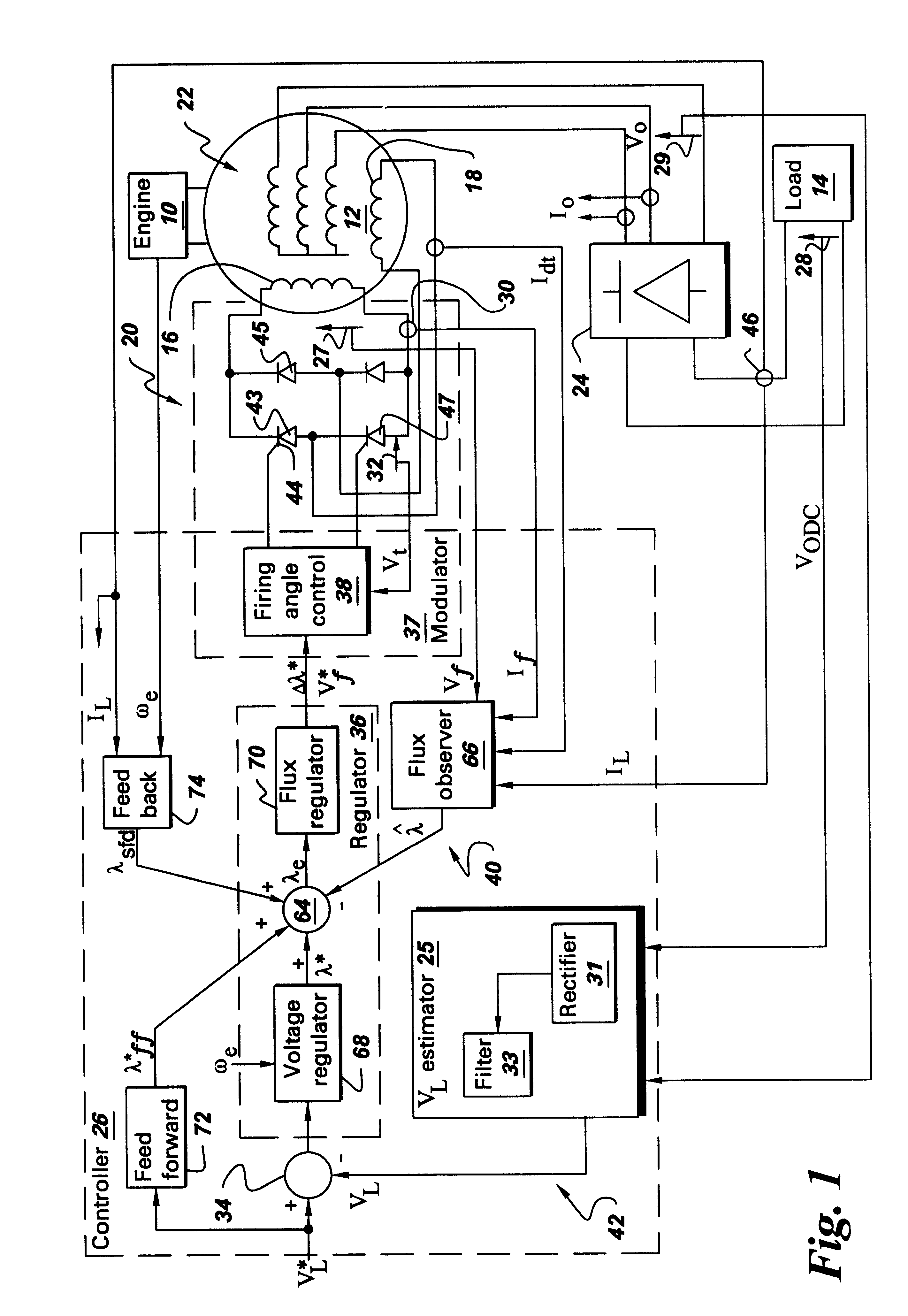
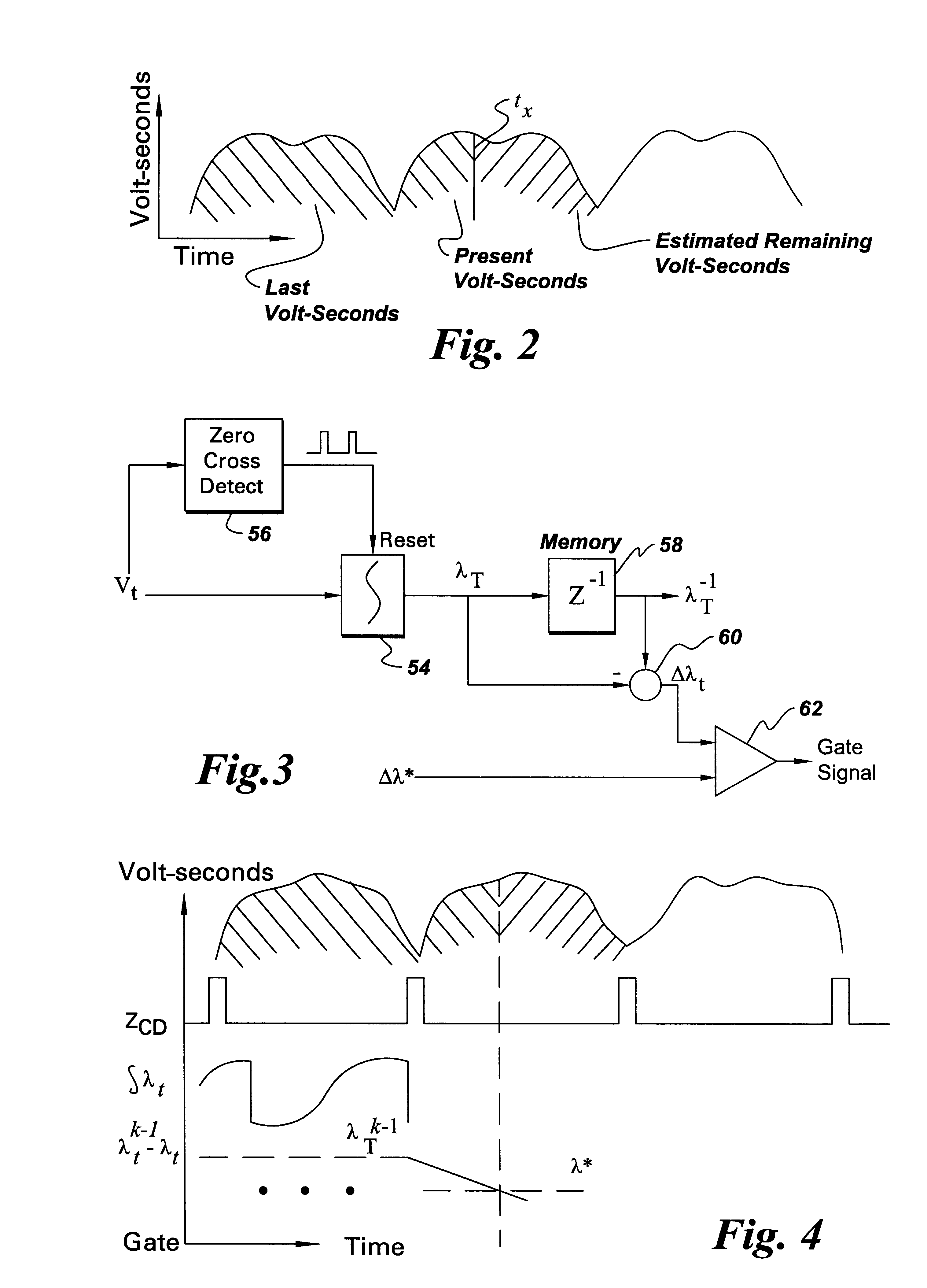
A wound field synchronous machine control system comprises: an auxiliary winding for obtaining auxiliary AC voltage from the wound field synchronous machine; a phase controlled rectifier for rectifying the auxiliary AC voltage and supplying rectified DC voltage to the wound field synchronous machine; and a controller. The controller is configured for using a voltage signal across the auxiliary winding to obtain volt-second values of the auxiliary winding and using the volt-second values for firing angle control of switches of the phase controlled rectifier. Alternatively or additionally, the controller is configured for obtaining airgap flux values of the wound field synchronous machine and using the airgap flux values for firing angle control of switches of the phase controlled rectifier.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Rotary electric machine for vehicle and control device thereof
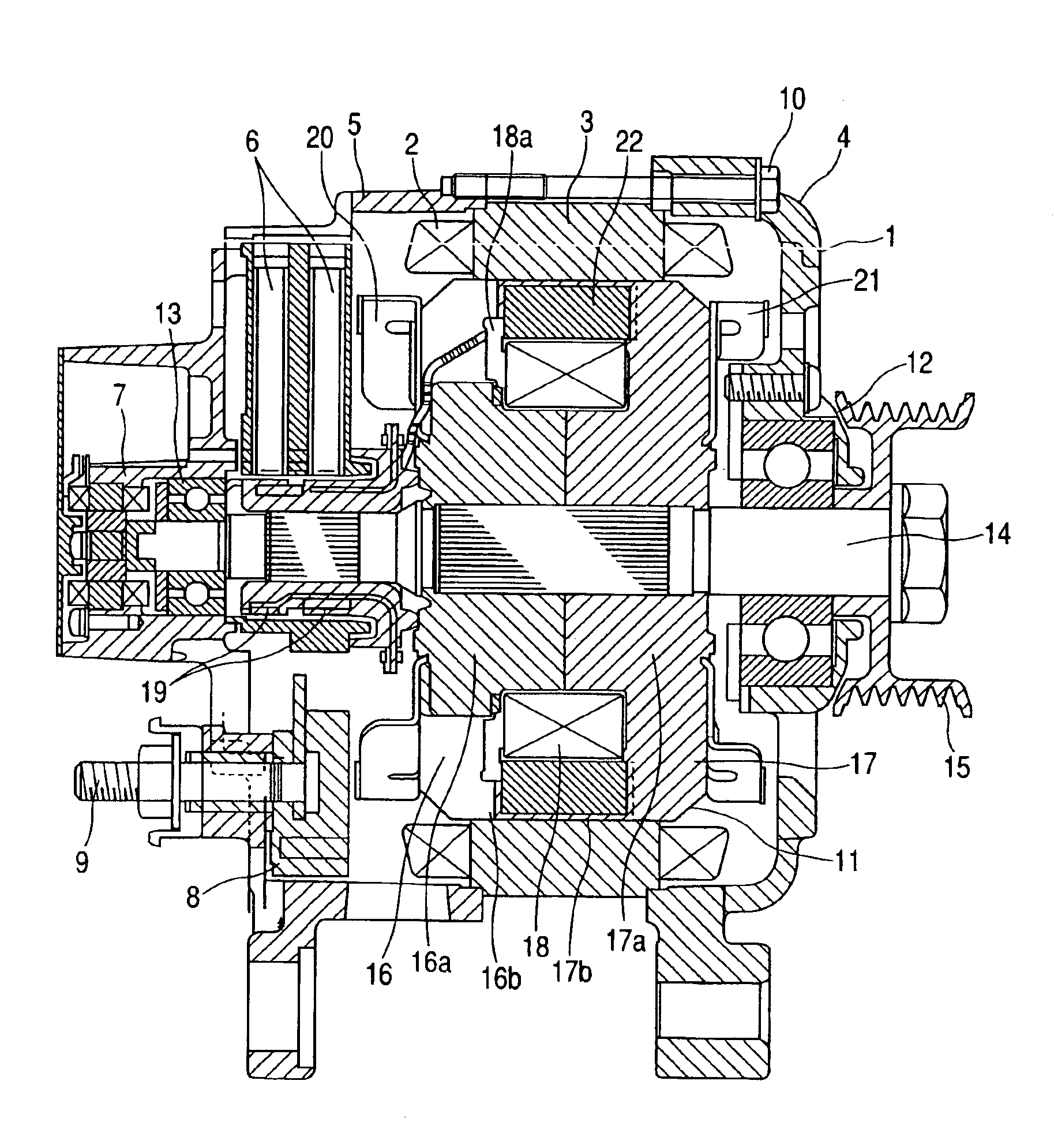
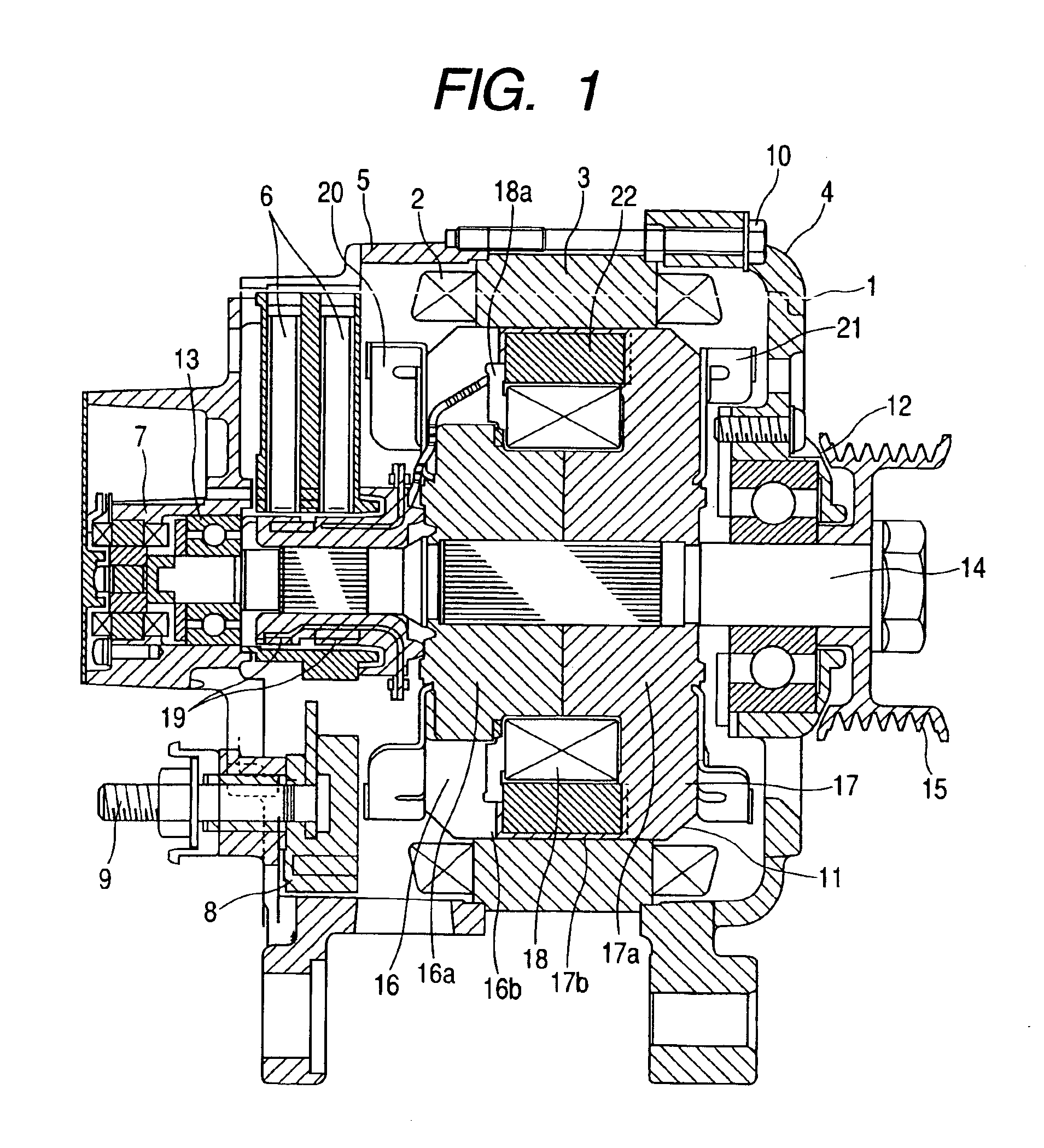
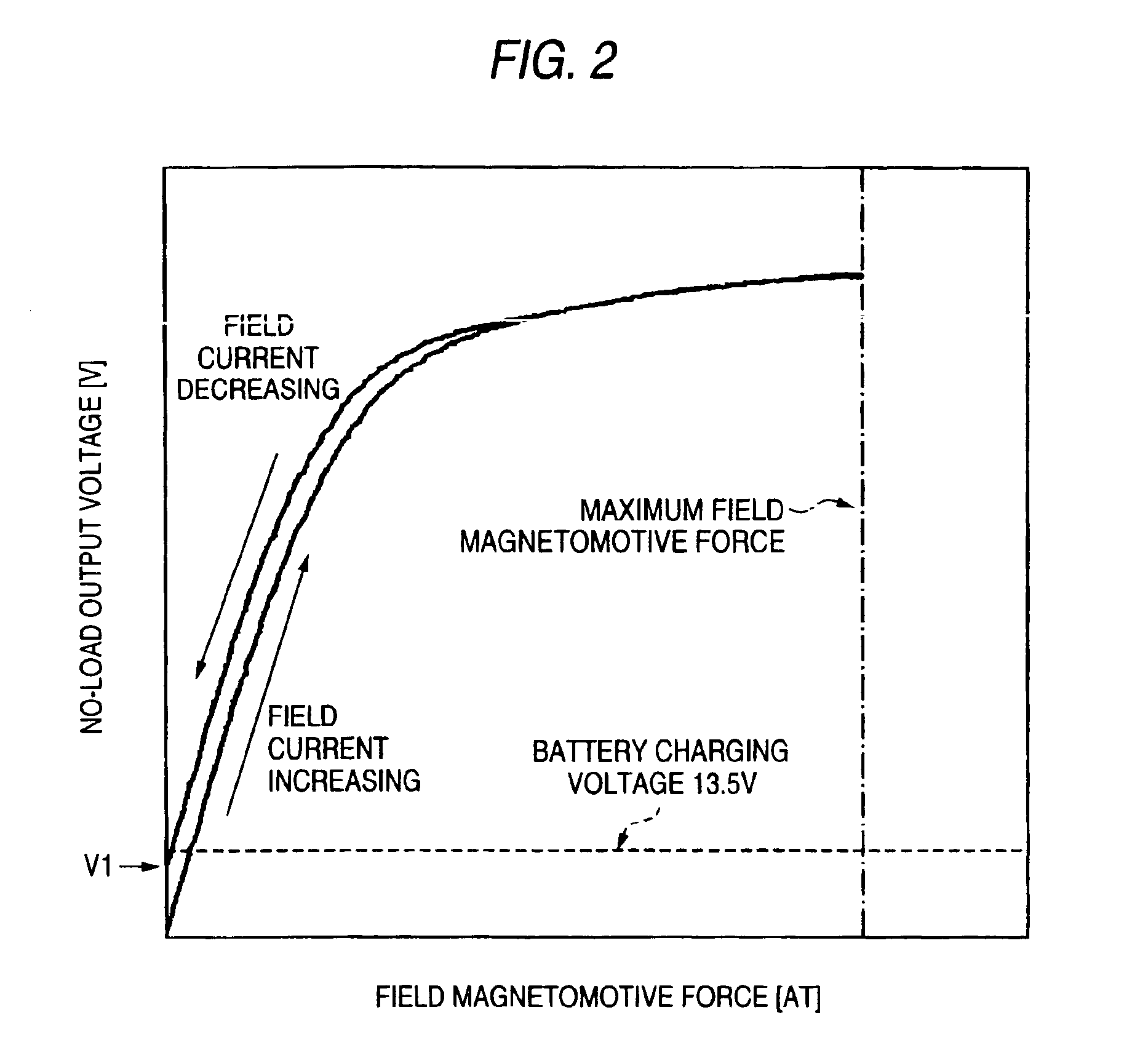
The rotary electric machine includes an armature core constituting a stator having an armature coil for charging a vehicle battery with its output voltage; rotor cores disposed inside the armature core with a predetermined gap therebetween and made up of magnetic pole parts formed as claw poles so that adjacent magnetic poles are different and cylindrical parts carrying a field coil; and permanent magnets provided in the magnetic circuit of the rotor cores for supplying magnetic flux along with the field coil to the armature core. The magnetizing force of the permanent magnets with respect to the armature core is set so that at a predetermined speed the output voltage of the armature coil immediately after a field current passed through the field coil is returned to zero from the maximum magnetizing force exerted by the field current does not exceed the charging voltage of the battery.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Field controllable rotating electric machine system with magnetic excitation part
InactiveUS20090045765A1Easy to controlField-weakening controlDC motor speed/torque controlWindingsElectric machineElectrical polarity
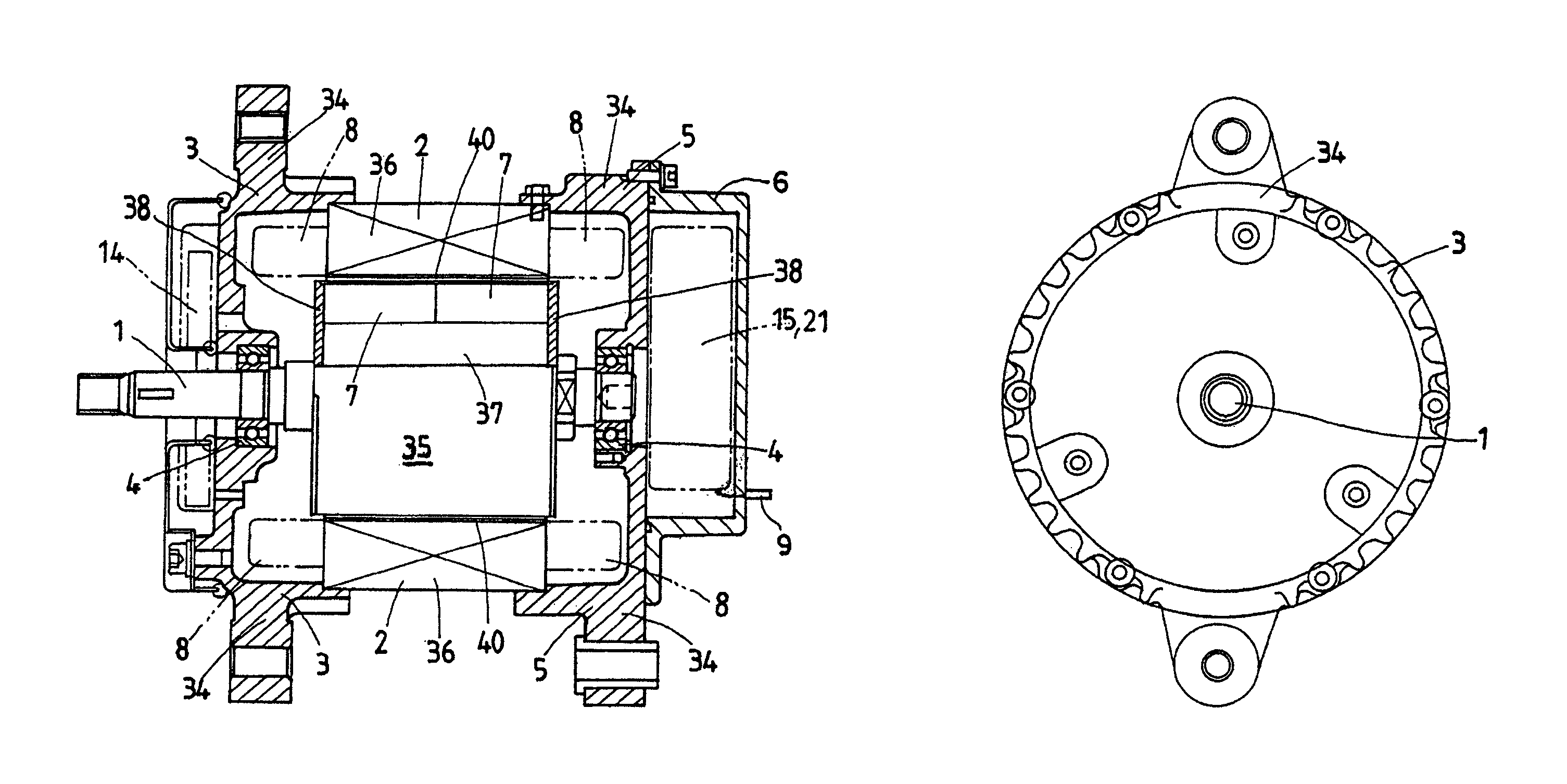
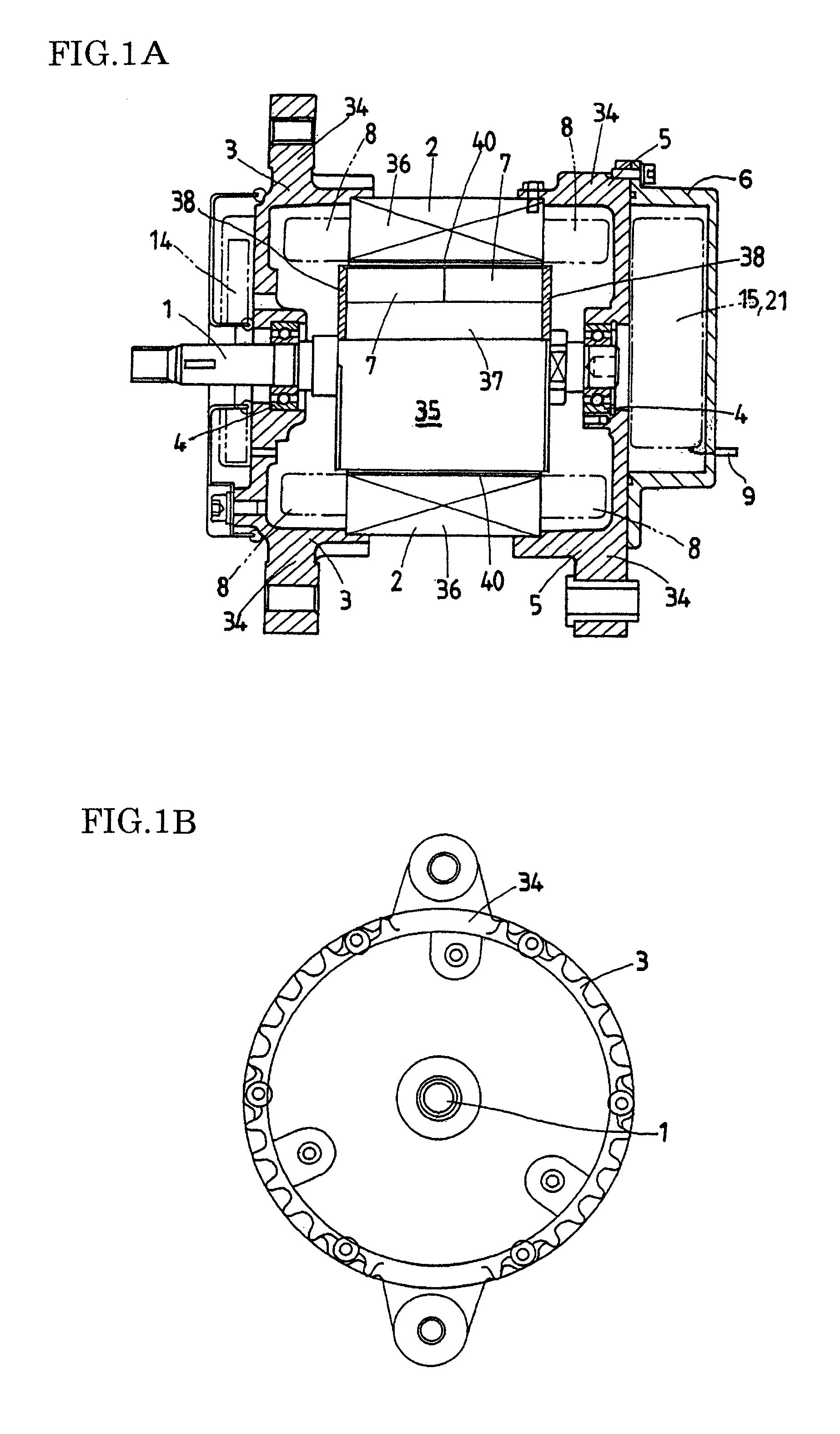
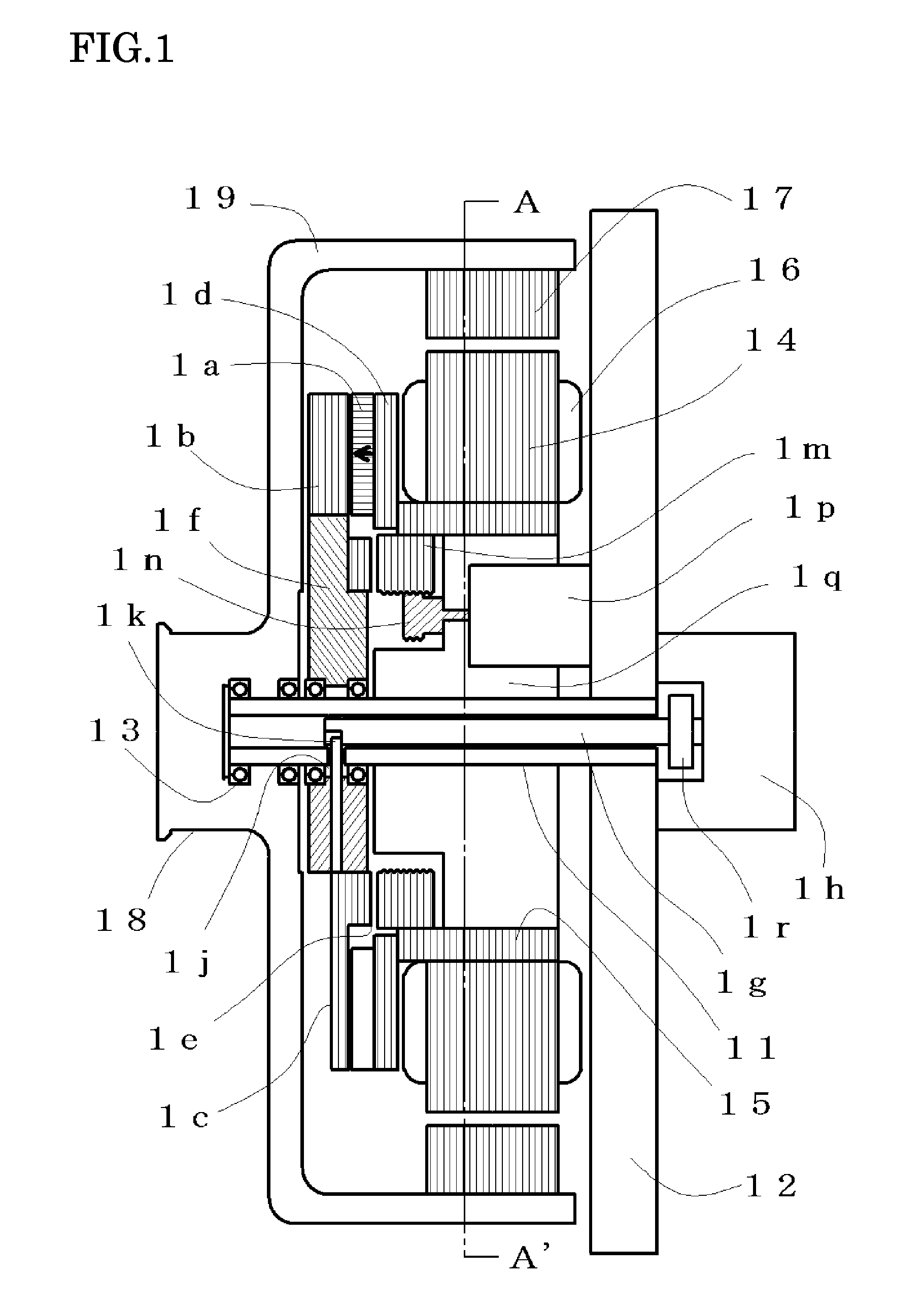
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine system, every magnetic salient pole group to be magnetized in a same polarity is collectively magnetized by a magnetic excitation part. In the magnetic excitation part, a main magnetic flux path in which a magnetic flux circulates through the armature and a bypass magnetic flux path are connected to the field magnet in parallel. Magnetic flux amount in each path is controlled by mechanical displacement. Thereby, the rotating electric machine system and the magnetic flux amount control method in which magnetic field control is easy are provided. Also, means and method are provided so that a power required for the displacement may be made small by adjusting magnetic resistance of the above magnetic flux path.
Owner:KURA LAB
Starter-generator operable with multiple variable frequencies and voltages
A starter-generator system is configured to be operable at multiple variable frequencies. The starter-generator includes a rotor and a stator. The rotor is configured to rotate and has a single main field winding wound thereon. The stator has at least a first stator winding set and second stator winding set independently wound thereon. Upon electrical excitation and rotation of the rotor the starter-generator supplies electrical power from each of the stator winding sets at different frequencies. Also, upon electrically exciting one or both of the stator winding sets with appropriate AC power, the rotor will rotate and generate a starting torque.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Wound field synchronous machine control system and method
InactiveUS20030094917A1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlMachine controlControl system
A wound field synchronous machine control system comprises: an auxiliary winding for obtaining auxiliary AC voltage from the wound field synchronous machine; a phase controlled rectifier for rectifying the auxiliary AC voltage and supplying rectified DC voltage to the wound field synchronous machine; and a controller. The controller is configured for using a voltage signal across the auxiliary winding to obtain volt-second values of the auxiliary winding and using the volt-second values for firing angle control of switches of the phase controlled rectifier. Alternatively or additionally, the controller is configured for obtaining airgap flux values of the wound field synchronous machine and using the airgap flux values for firing angle control of switches of the phase controlled rectifier.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
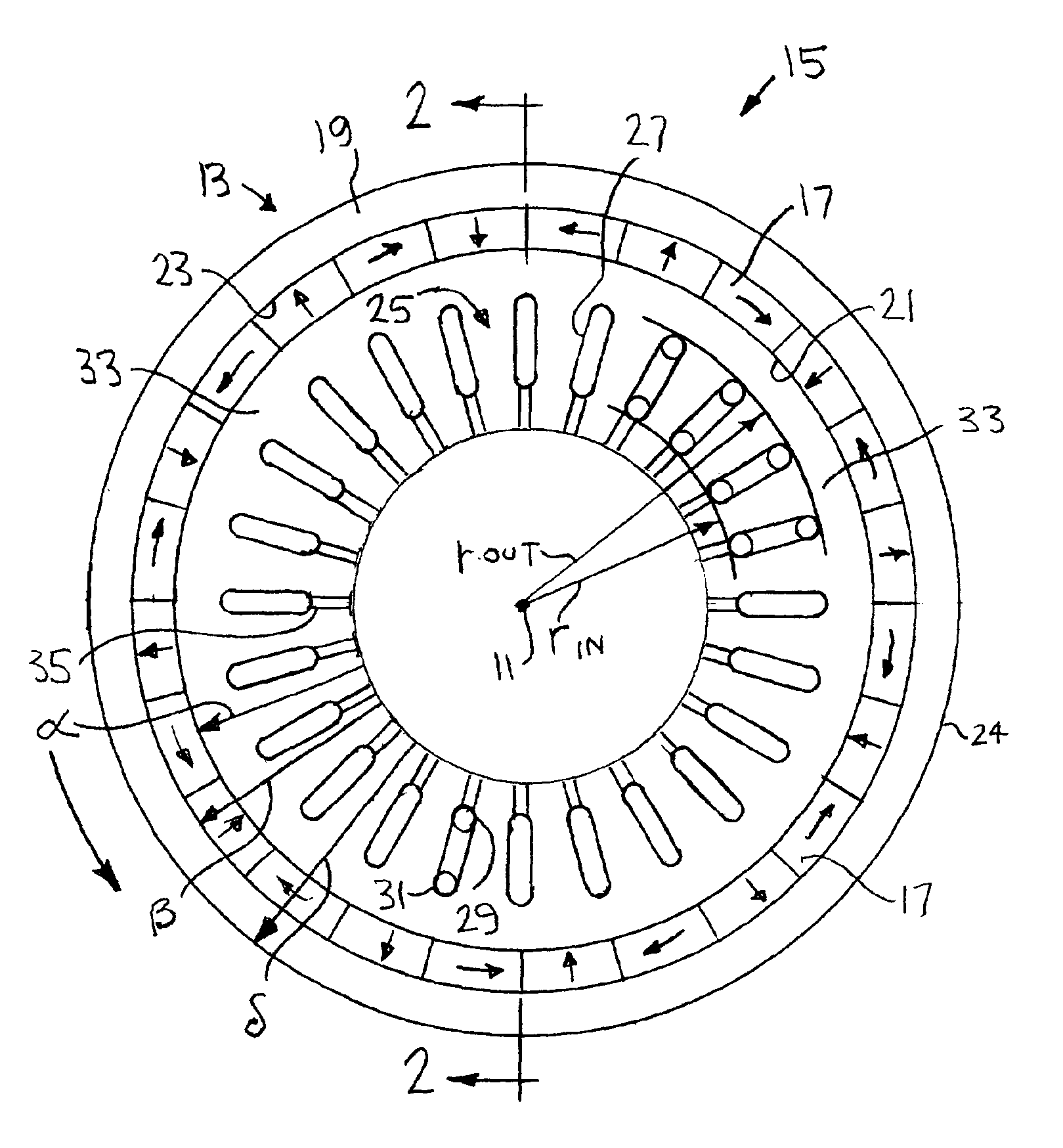
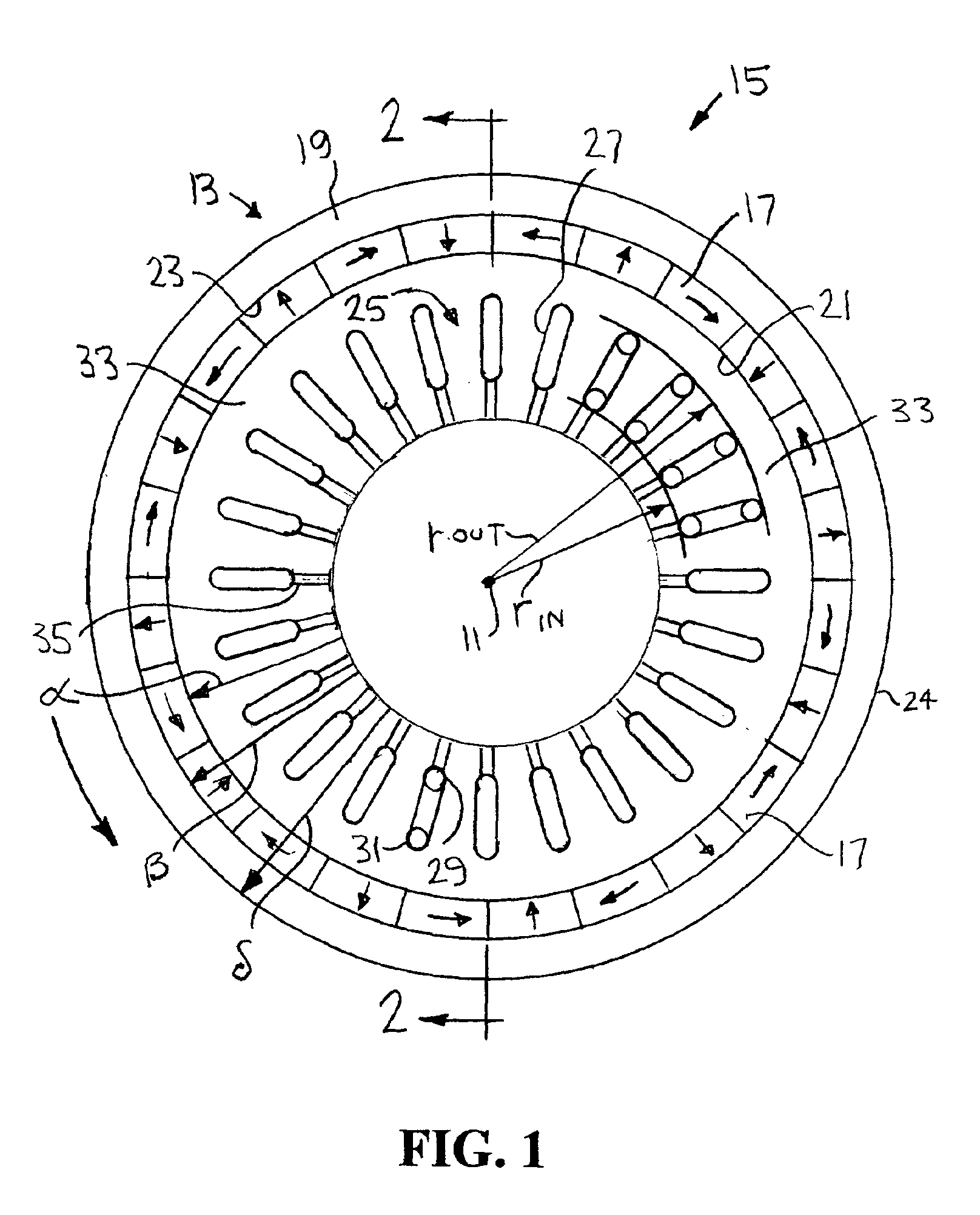
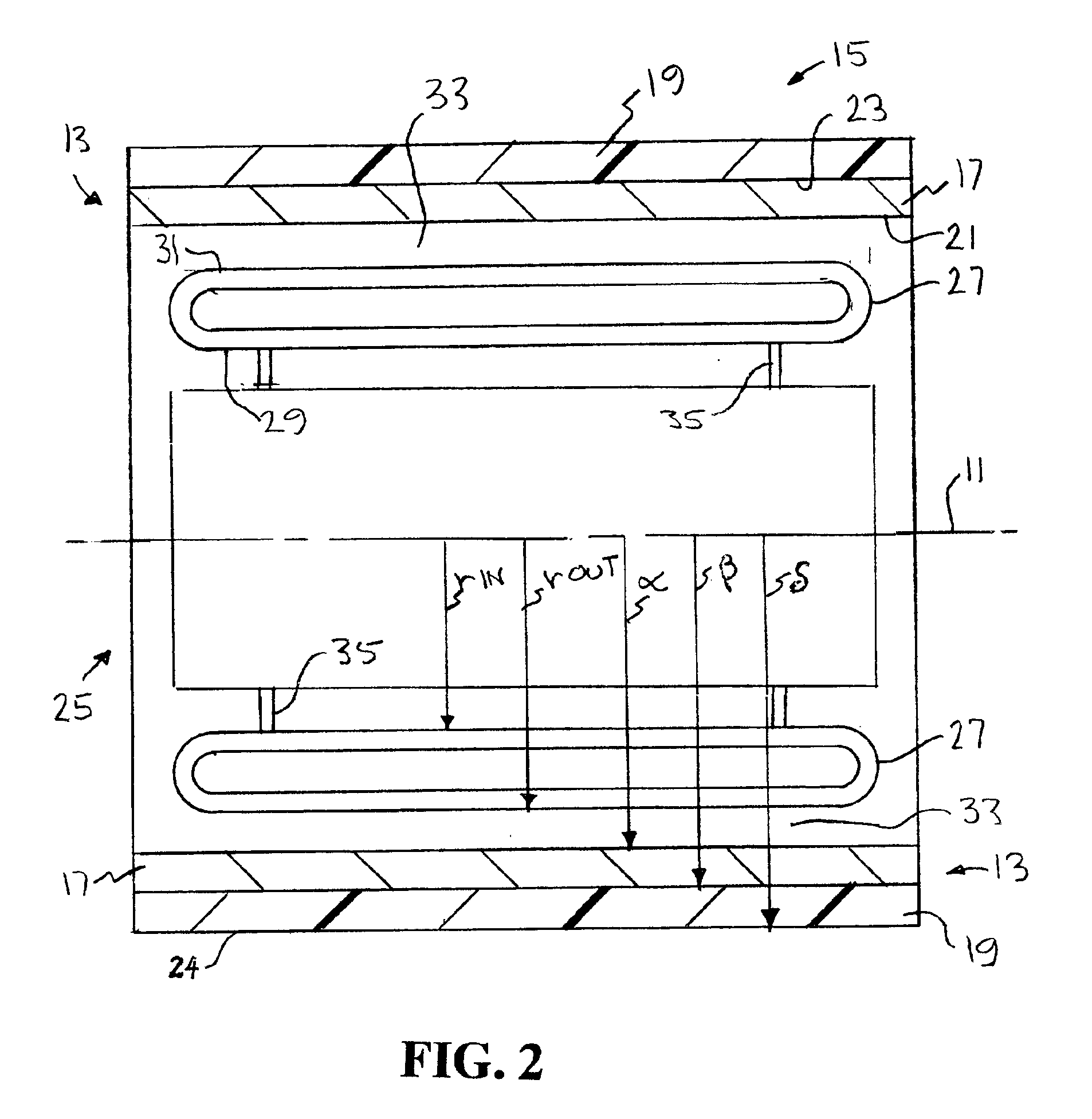
Variable reluctance generator
InactiveUS7151359B2Easy to operateAvoid the needAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersEngineeringConductor Coil
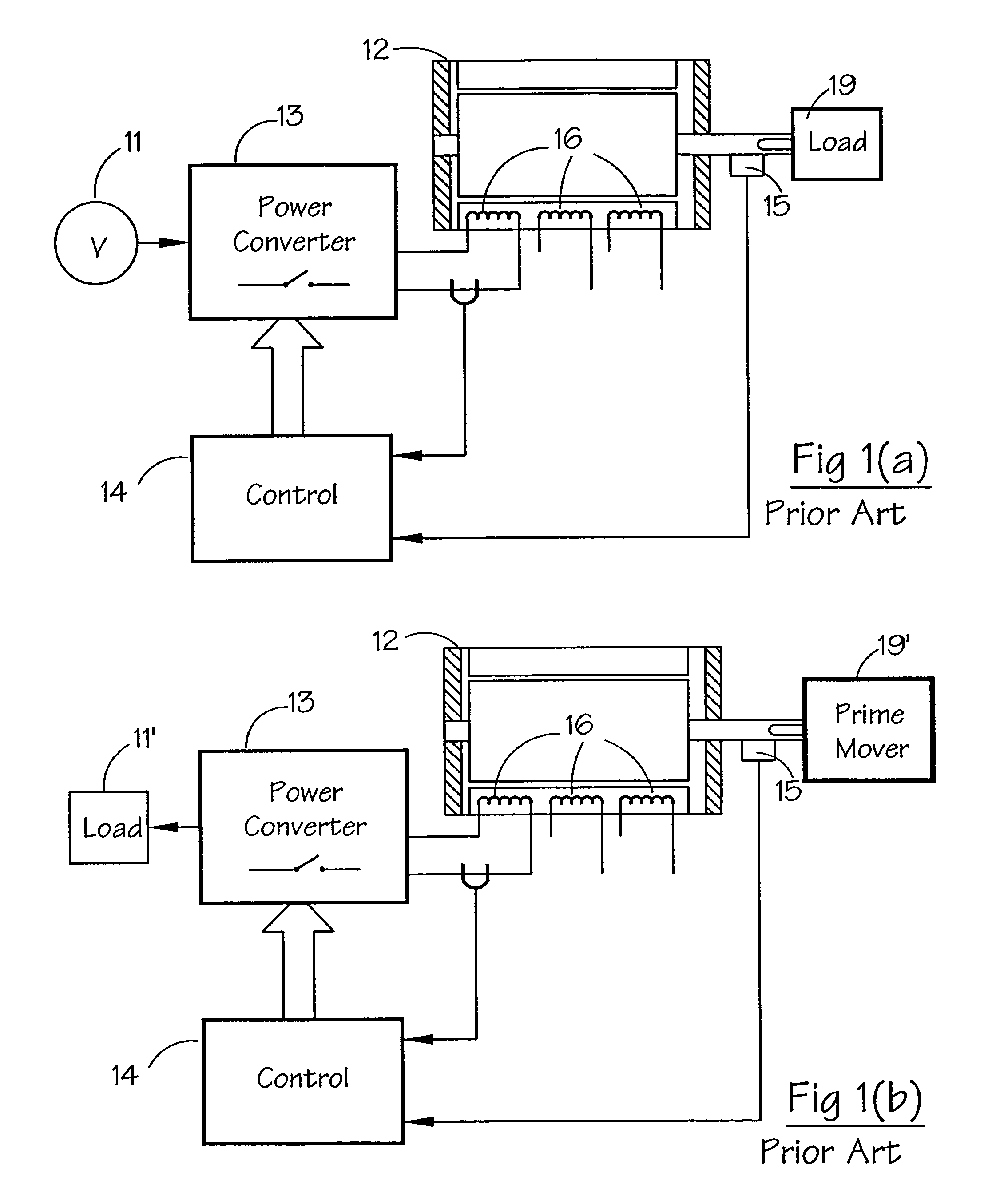
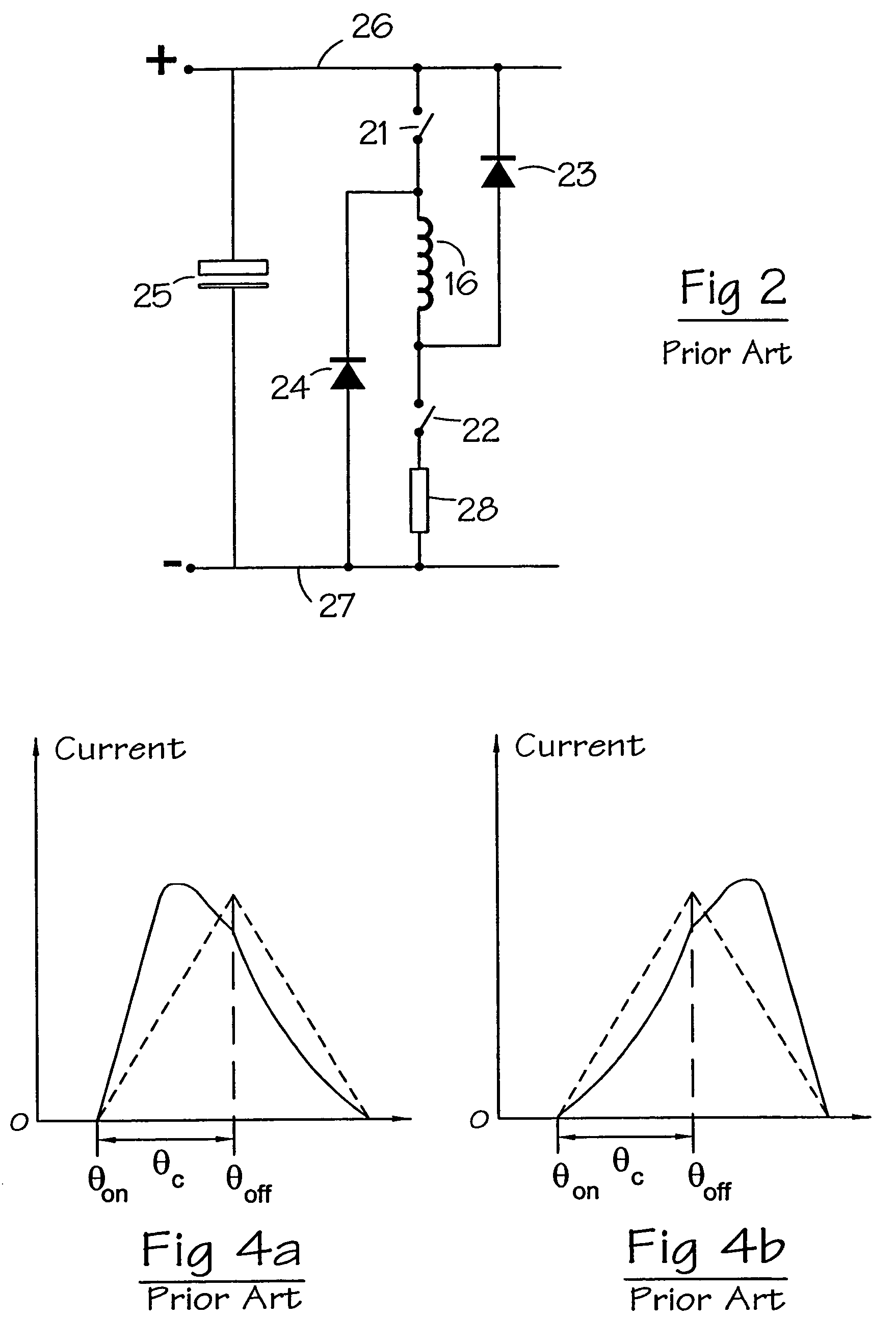
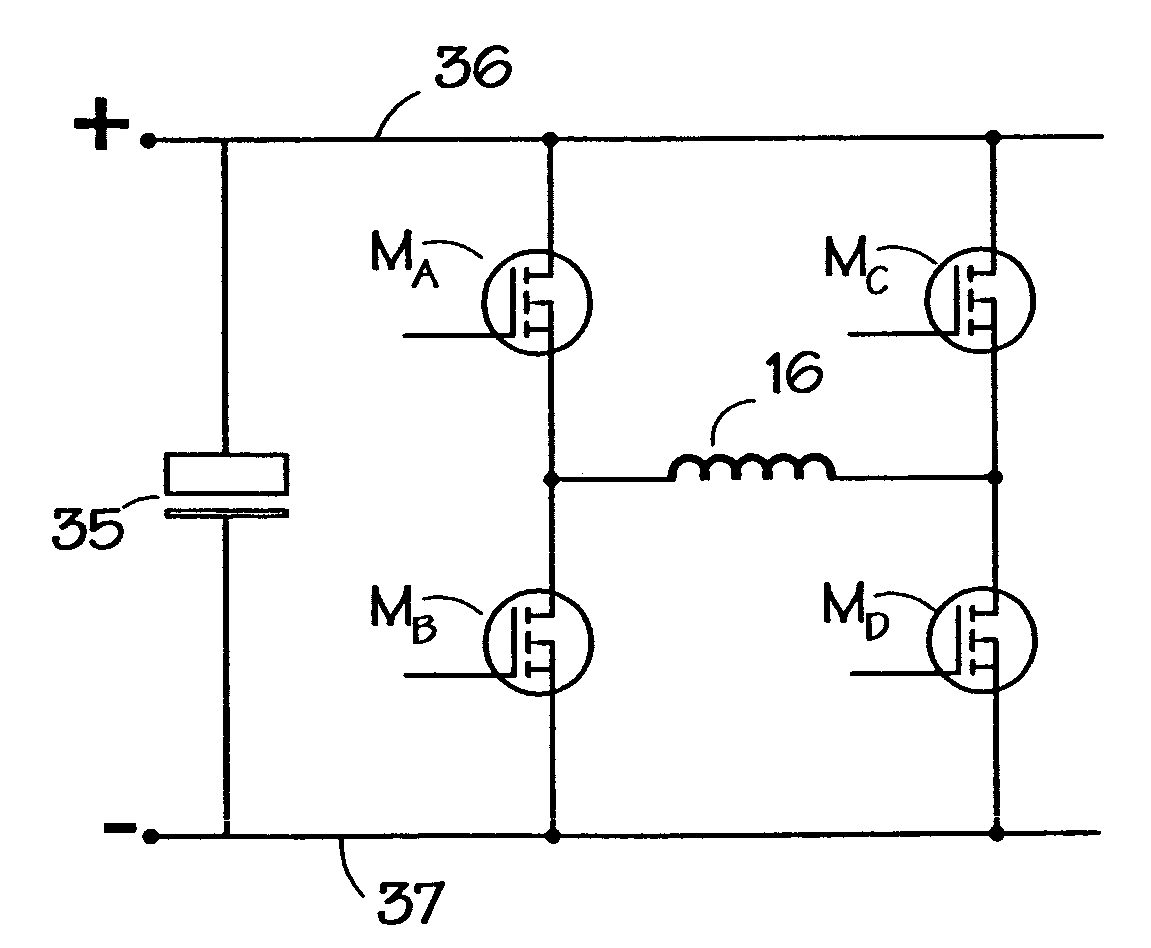
A variable reluctance generator has phase windings and a bias winding. By controlling the excitation produced by the bias winding, the speed of the machine or the DC link, a power converter using only diodes can supply power to a DC bus. A method of operating a variable reluctance machine as a generator, the machine having at least one phase winding, includes creating a bias flux linking the or at least one phase winding, and limiting the phase voltage to a magnitude below that otherwise induced in the phase winding by the bias flux.
Owner:NIDEC SR DRIVES
Starter-generator operable with multiple variable frequencies and voltages
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Field controllable rotating electric machine system with flux shunt control
InactiveUS7567006B2Field-weakening controlAvoid large displacementSynchronous generatorsElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic tension forceRelative displacement
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine, a magnetic field pole part opposing an armature is composed to be divided into a surface magnetic pole part and a magnetic excitation part so as to be capable of being relatively displaced. The magnetic excitation part supplies a magnetic flux to a magnetic salient pole. The magnetic flux from the field magnet is divided into a main magnetic flux pathway that circulates through the armature side and a bypass magnetic flux pathway that does not pass through the armature, and thereby, the magnetic flux of the main magnetic flux pathway is changed. The magnetic resistances of the main magnetic flux pathway and the bypass magnetic flux pathway are composed so that total magnetic flux amount from the field magnet is maintained constant, and then a magnetic force preventing the relative displacement is maintained small.
Owner:KURA LAB
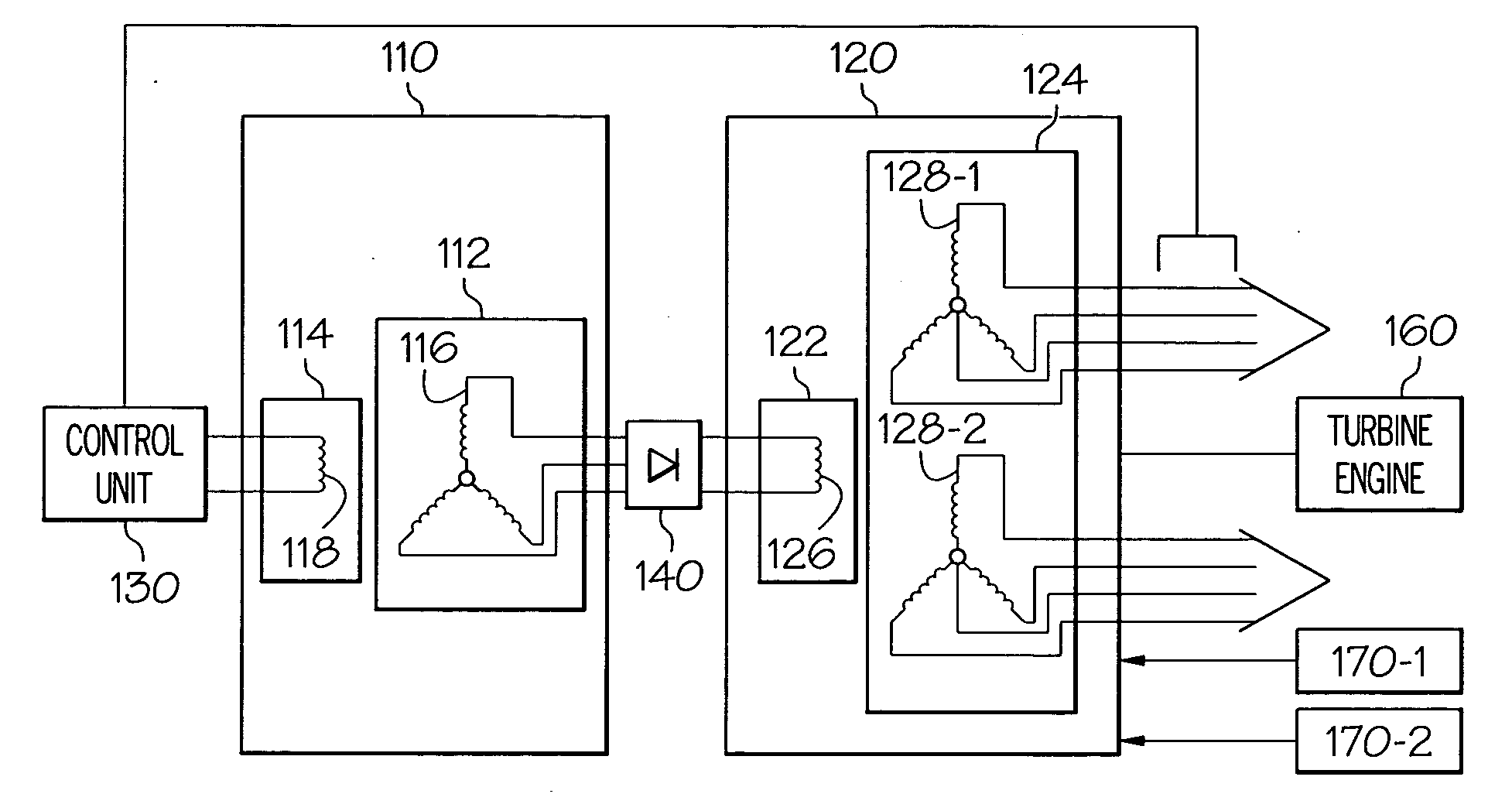
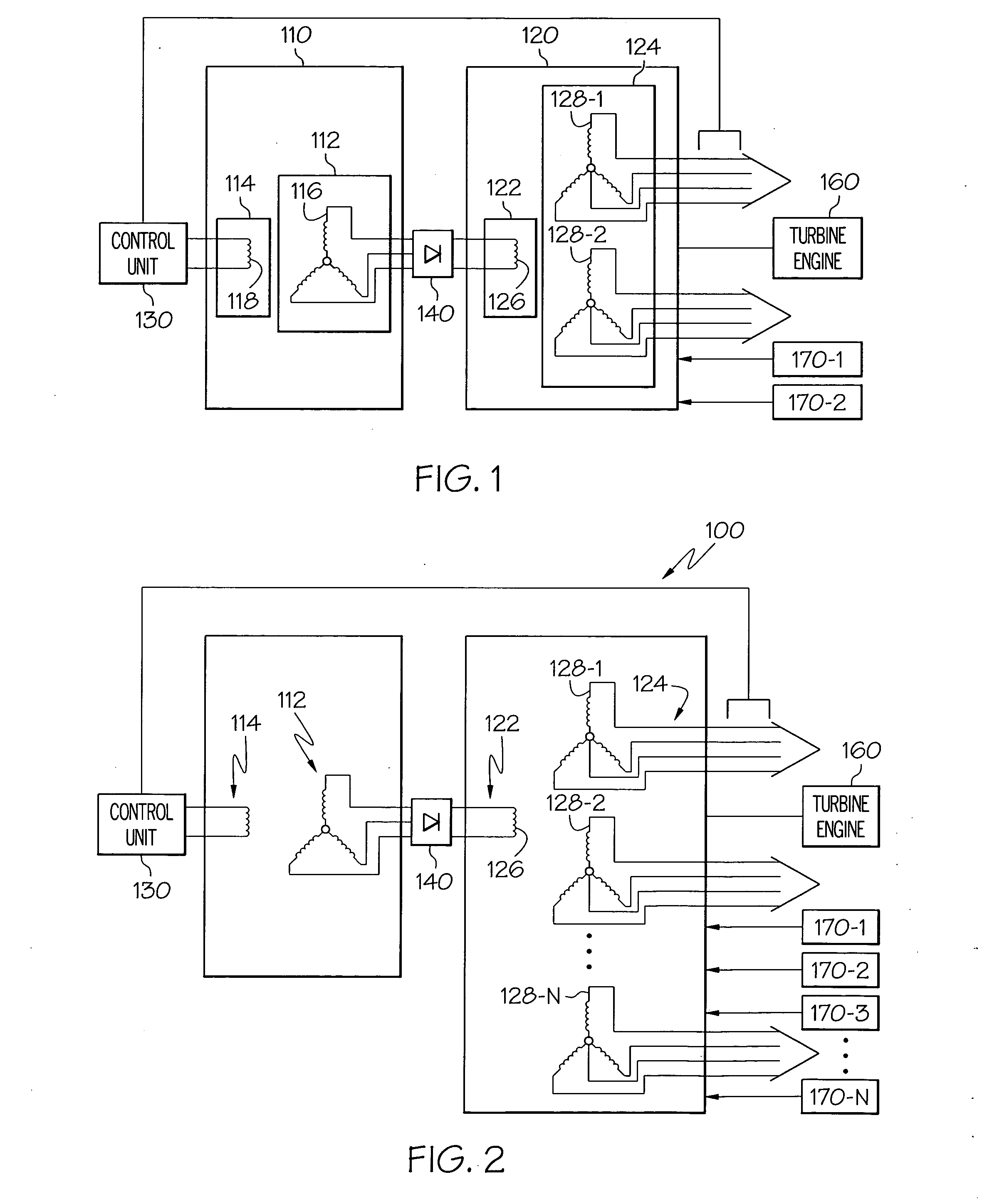
Gas turbine engine starter generator that selectively changes the number of rotor poles
InactiveUS6995478B2Improve wear lifeLow costSynchronous generatorsGas turbine plantsStarter generatorGas turbines
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, that may be operated in either a motor mode or an generator mode. The machine includes a main rotor that is selectively configurable as an M-pole rotor or an N-pole rotor. The machine can also include DC brushes that are selectively moveable into, and out of, electrical contact the main rotor, to thereby electrically couple and decouple a DC power source to and from, respectively, the rotor windings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
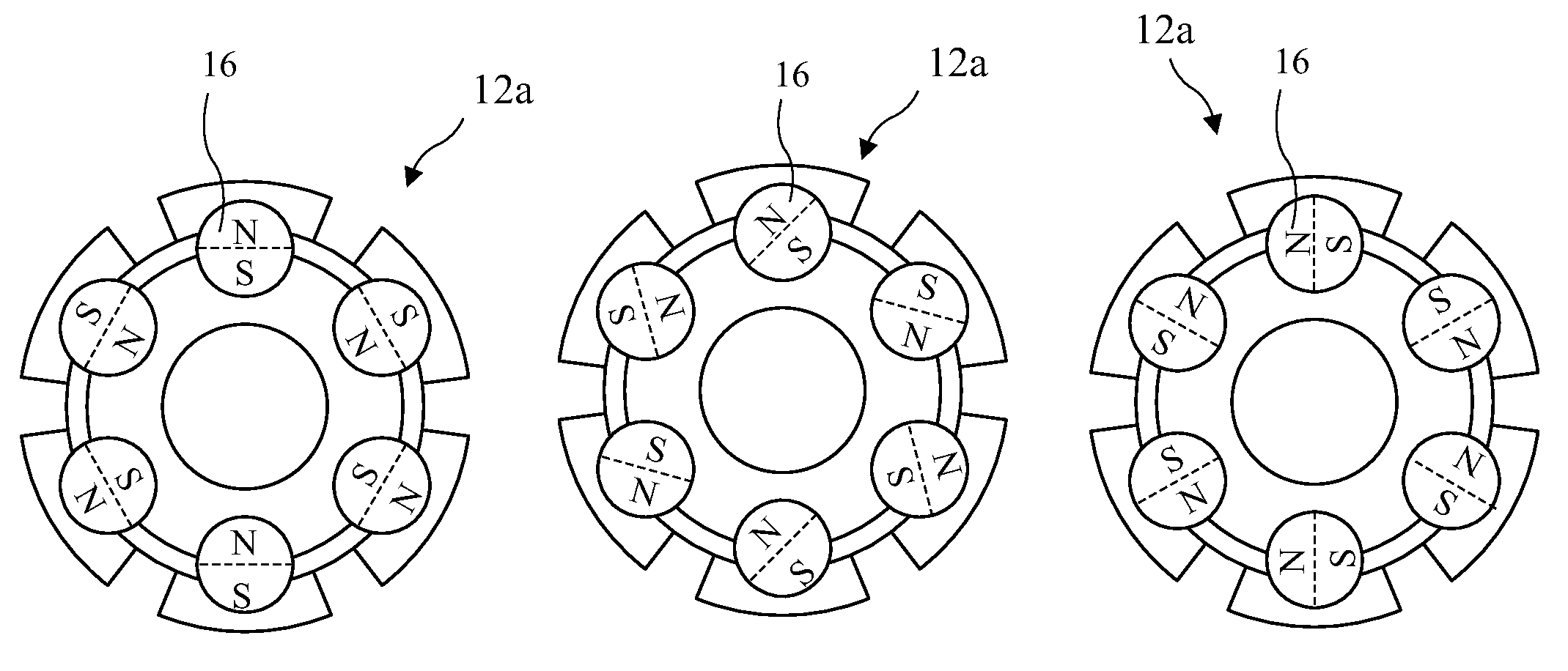
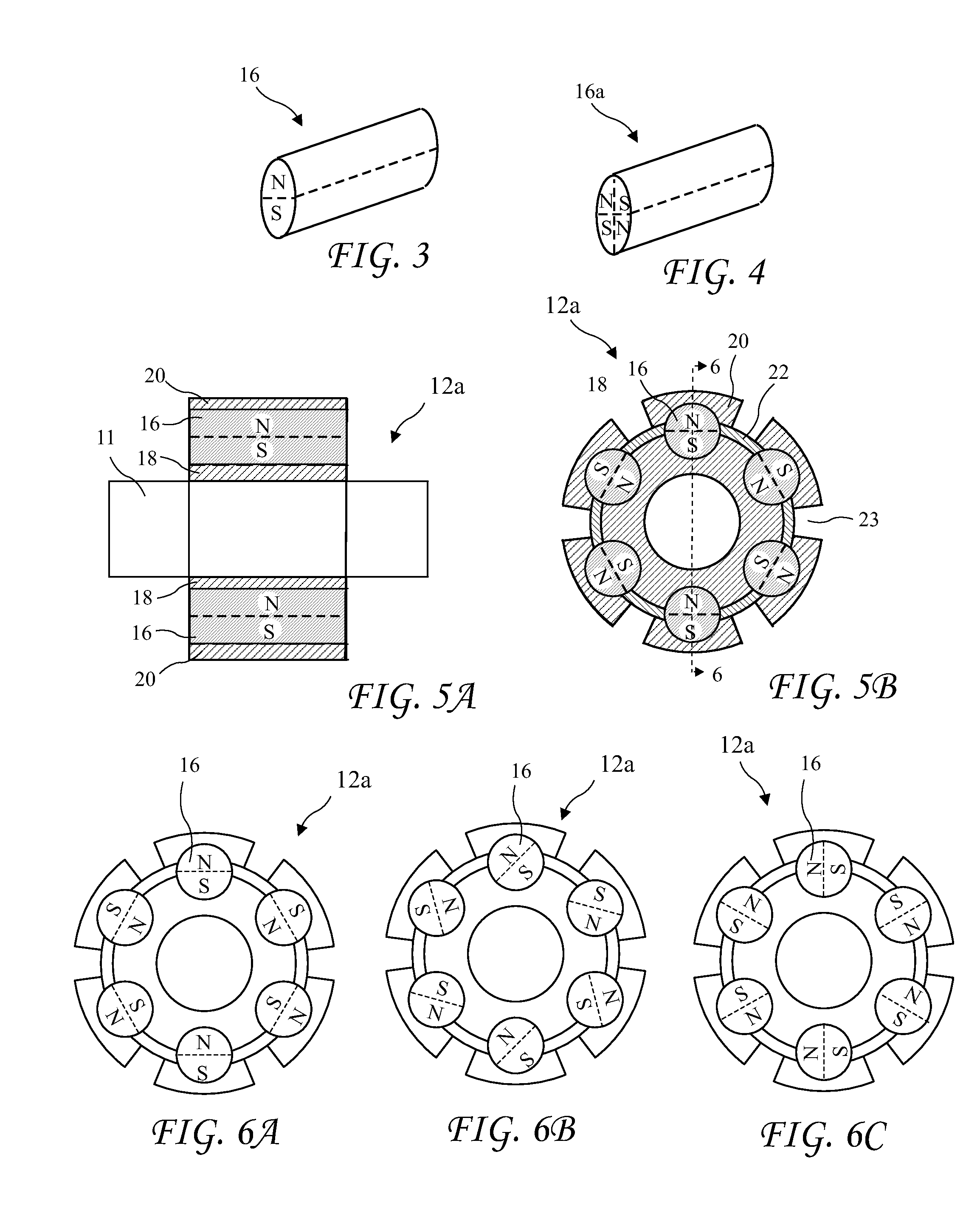
Windmill Generator with Mechanically Tuneable Permanent Magnetic Field
InactiveUS20120074913A1Improved starting torqueHigh RPM efficiencySynchronous generatorsWindingsPole pieceConductor Coil
Apparatus and method for tuning the magnetic field of windmill generators to obtain efficient operation over a broad RPM range. The windmill generator includes fixed windings (or stator) inside a rotating rotor carrying permanent magnets. The permanent magnets are generally cylindrical and have North and South poles formed longitudinally in the magnets. Magnetically conducting circuits are formed by the magnets residing in magnetic conducting pole pieces (for example, low carbon or soft steel, and / or laminated insulated layers, of non-magnetizable material). Rotating the permanent magnets, or rotating non-magnetically conducting shunting pieces, inside the pole pieces, either strengthens or weakens the resulting magnetic field to adjust the windmill generators for low RPM torque or for efficient high RPM efficiency. Varying the rotor magnetic field adjusts the voltage output of the windmill generators allowing the windmill generator to maintain a fixed voltage output.
Owner:MOTOR GENERATOR TECH INC
Voltage regulated permanent magnet generator
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Field controllable rotating electric machine system with flux shunt control
InactiveUS20090026864A1Field-weakening controlAvoid large displacementSynchronous generatorsElectromagnets without armaturesRelative displacementMagnetic tension force
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine, a magnetic field pole part opposing an armature is composed to be divided into a surface magnetic pole part and a magnetic excitation part so as to be capable of being relatively displaced. The magnetic excitation part supplies a magnetic flux to a magnetic salient pole. The magnetic flux from the field magnet is divided into a main magnetic flux pathway that circulates through the armature side and a bypass magnetic flux pathway that does not pass through the armature, and thereby, the magnetic flux of the main magnetic flux pathway is changed. The magnetic resistances of the main magnetic flux pathway and the bypass magnetic flux pathway are composed so that total magnetic flux amount from the field magnet is maintained constant, and then a magnetic force preventing the relative displacement is maintained small.
Owner:KURA LAB
Gas turbine engine starter generator that selectively changes the number of rotor poles
InactiveUS20050206352A1Reduce weightLow costSynchronous generatorsMotor/generator/converter stoppersStarter generatorElectricity
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, that may be operated in either a motor mode or an generator mode. The machine includes a main rotor that is selectively configurable as an M-pole rotor or an N-pole rotor. The machine can also include DC brushes that are selectively moveable into, and out of, electrical contact the main rotor, to thereby electrically couple and decouple a DC power source to and from, respectively, the rotor windings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
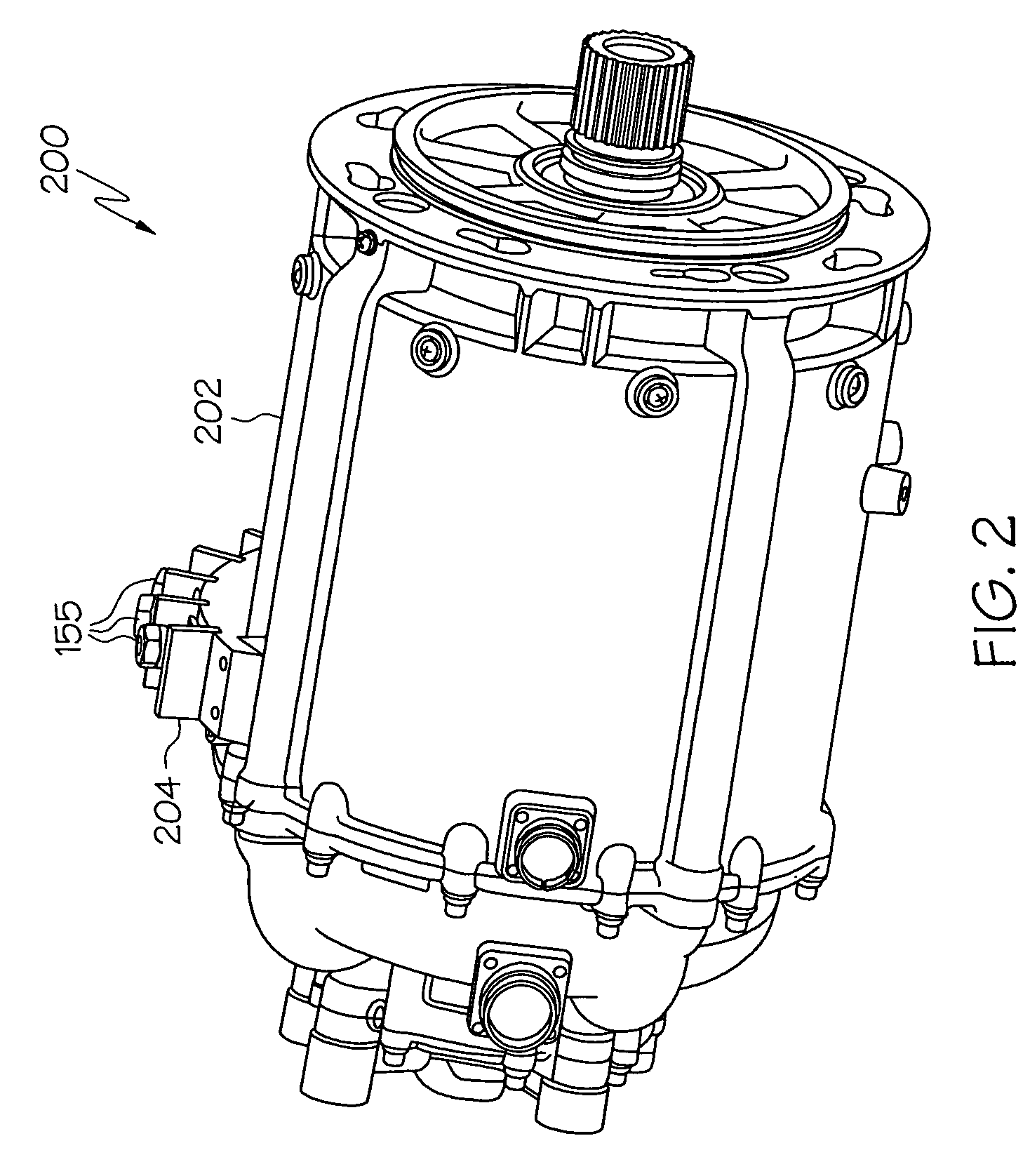
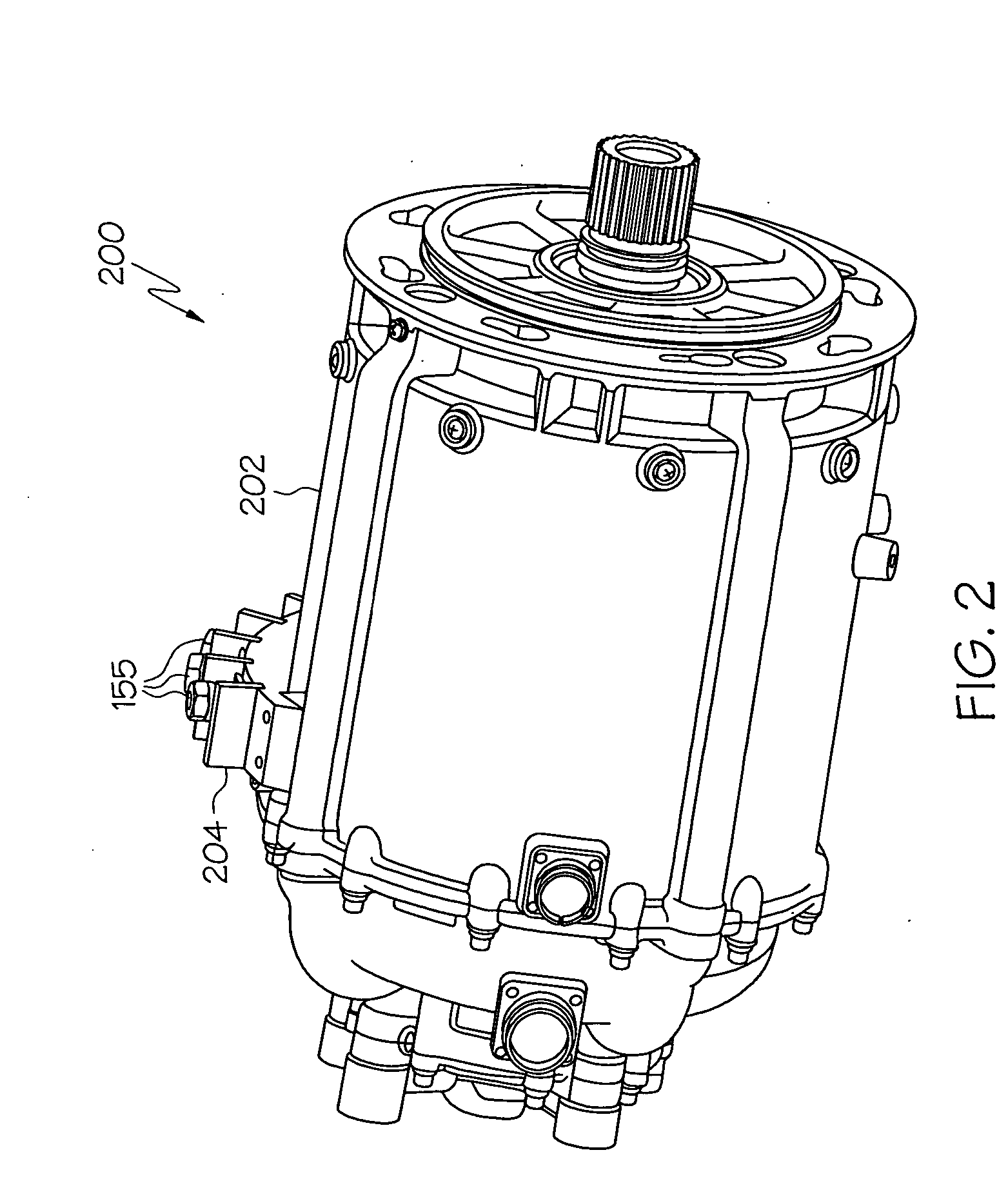
Fault tolerant architecture for permanent magnet starter generator subsystem
ActiveUS20050237034A1Highly reliable and fault tolerant systemOperational securityWindingsMagnetic circuitFault tolerant architectureStarter generator
A permanent magnet starter / generator subsystem configured in a fault tolerant architecture is described herein for small engine applications. The system allows for lighter system weight, improved system reliability, higher performance capability and reduced maintenance.
Owner:ASTRONICS ADVANCED ELECTRONICS SYST
Circuit for use with switched reluctance machines
A switched reluctance machine is energized by phase circuits with four active switches, for example MOSFETs, arranged in a bridge configuration. The switches are capable of conducting current in both a first direction and a second direction and are capable of operating as a diode. The direction of current flow through the phase winding is reversed when changing from motoring to generating and from generating to motoring. The ratings of the switches are set in accordance with the energy supply and energy return currents.
Owner:NIDEC SR DRIVES
Method for the active damping of the drive train in a wind energy plant
InactiveUS7501798B2High componentsHigh trainWind motor controlEngine fuctionsControl theoryWind power
A method for the active damping of a drive train in wind energy plant, with the following steps: the actual value of the generator rotational speed is acquired and amplified via an oscillatory delay element, the oscillatory delay element has a predetermined natural oscillation frequency (ωE), which is smaller than the smallest natural frequency of the drive train, and a difference between the actual value of the rotational speed and the amplified value for the rotational speed is connected to a controller as actuating variable, which determines a correction moment for a generator control.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
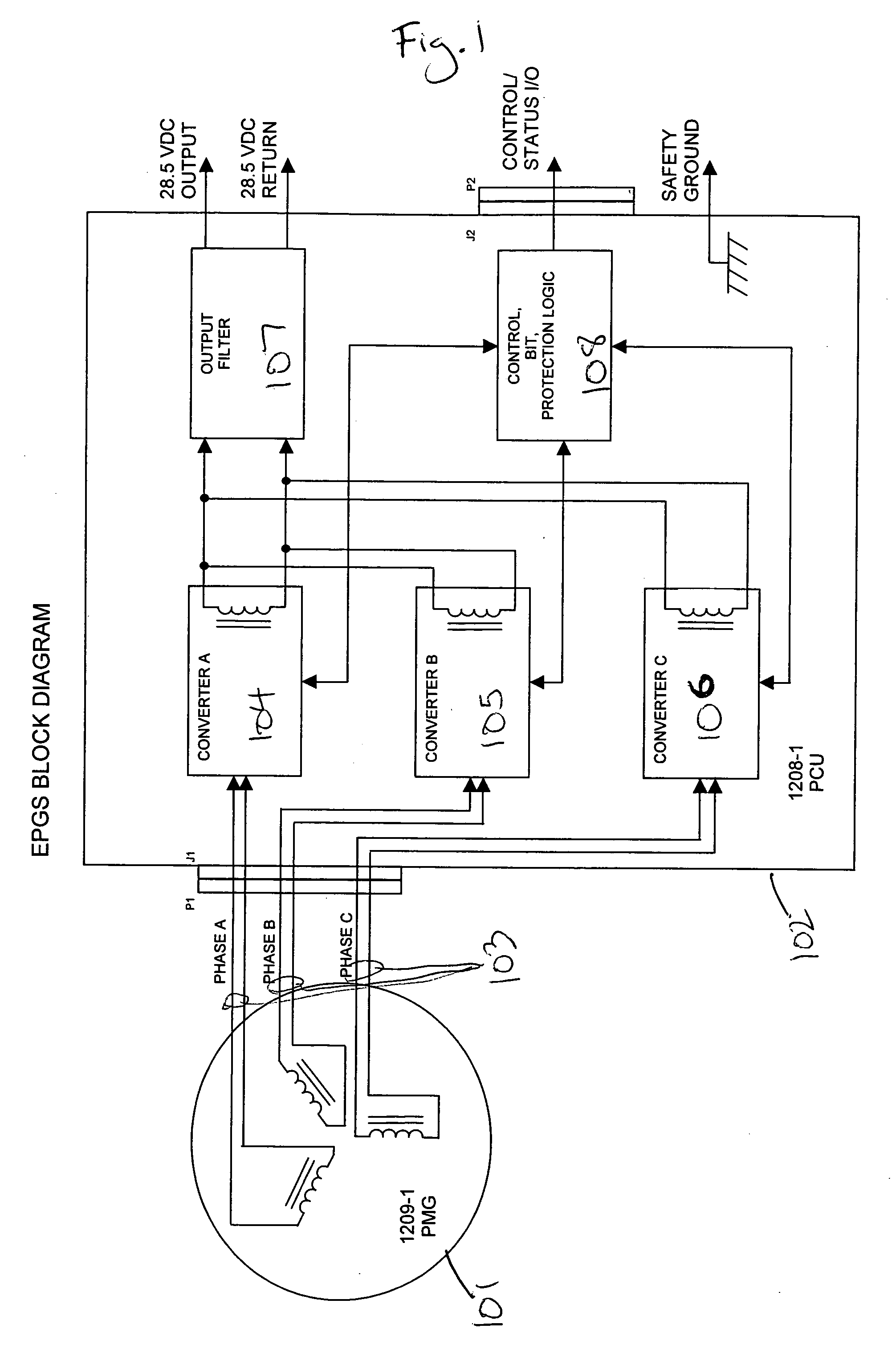
Variable speed electric machine and method for generating electric energy
ActiveUS20130207391A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectric machinePower grid
A variable speed electric machine and a method for generating electric energy is provided. The electric machine includes an outer stator with a first set of field windings. Further, the electric machine includes a modulator outer rotor that is concentric and is located proximate to the outer stator. The modulator outer rotor is operatively coupled to an input shaft. Furthermore the electric machine includes a permanent magnet inner rotor concentric to the modulator outer rotor. The electric machine also includes an inner stator with a second set of field windings. The inner stator is concentric to the inner rotor and is operatively coupled to an electric grid. The outer stator, the modulator outer rotor, inner stator and the inner rotor are magnetically coupled with each other so as to maintain a constant electric frequency at the inner stator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
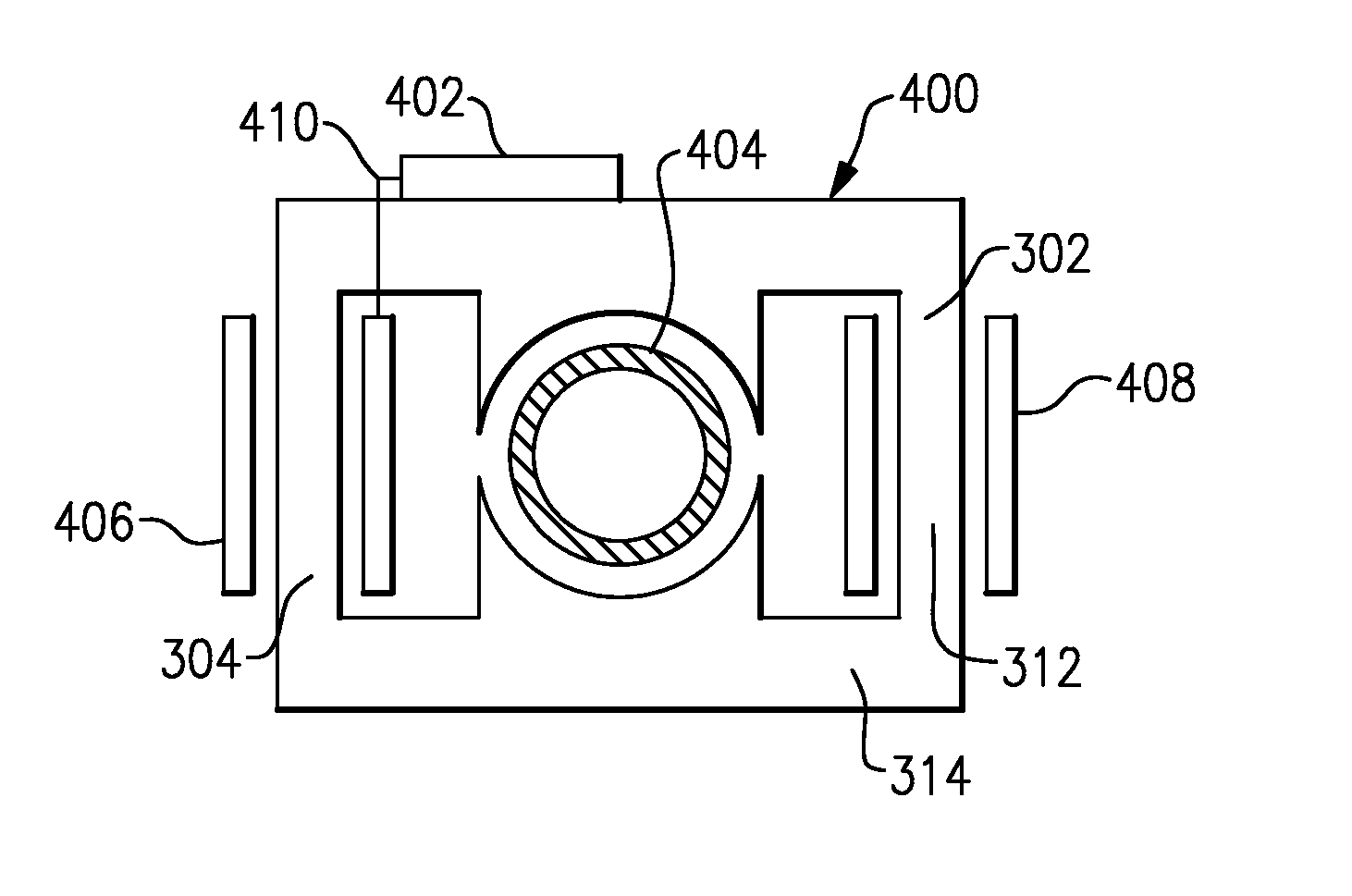
Method and apparatus for controlling rotary machines
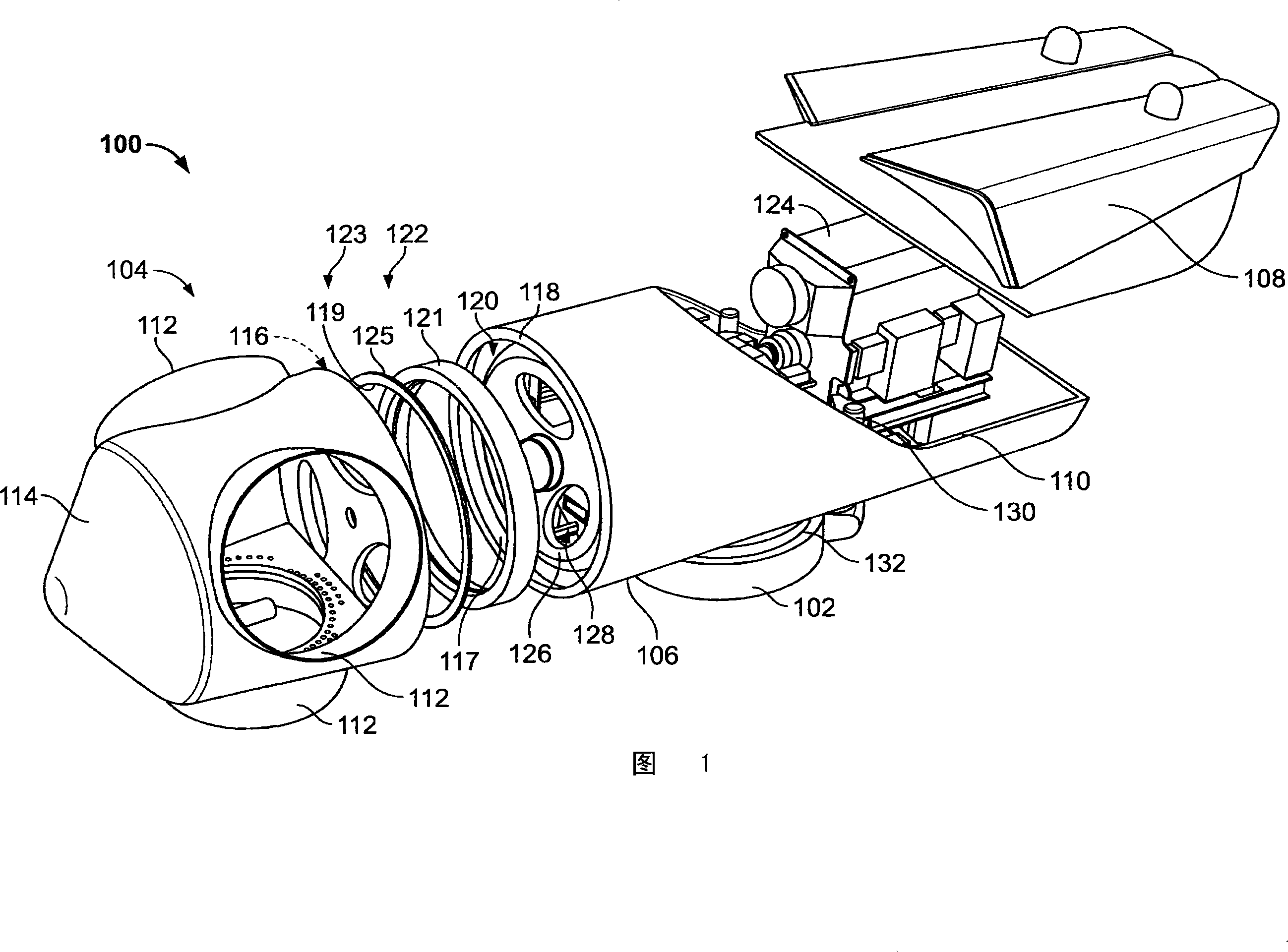
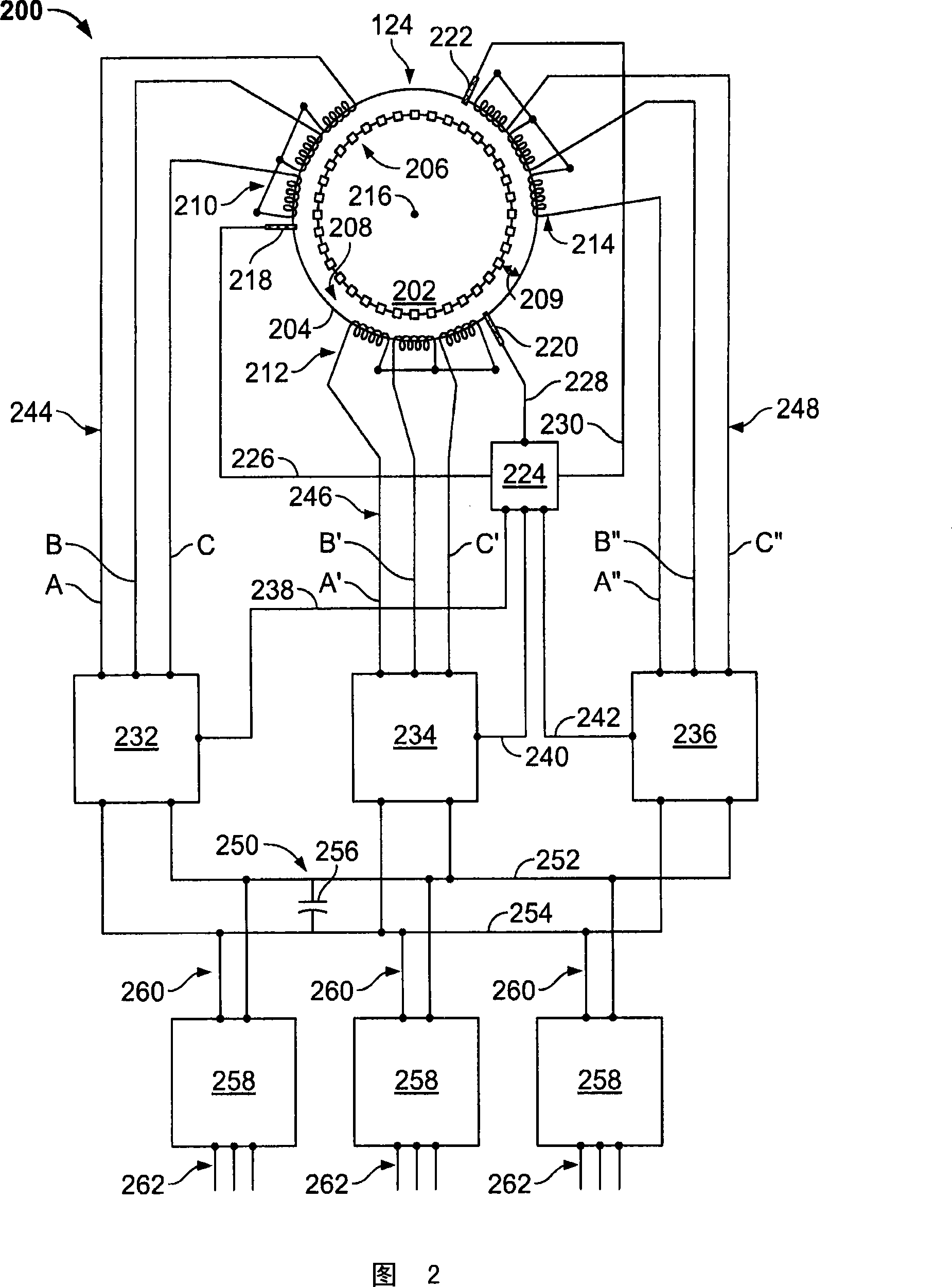
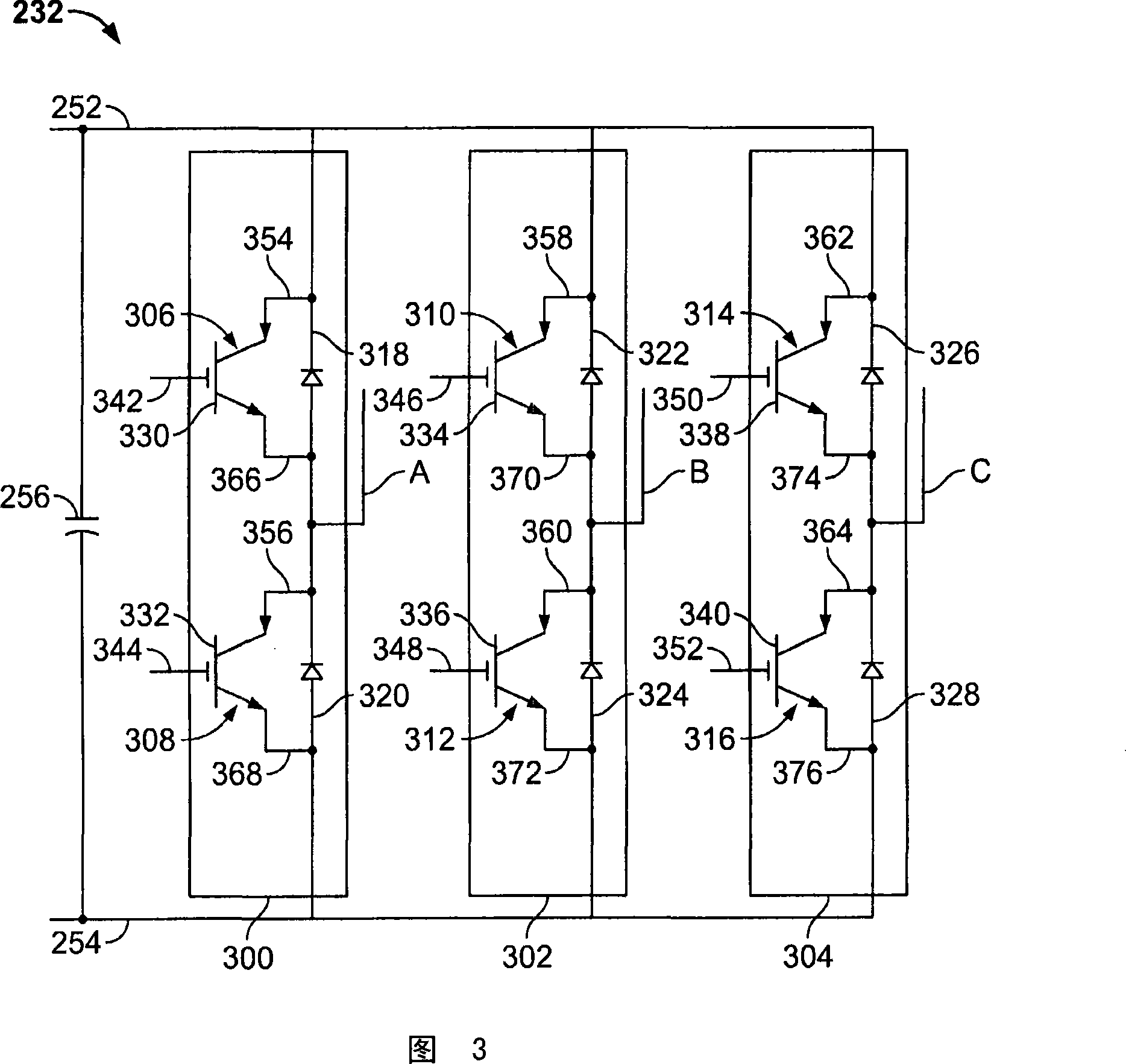
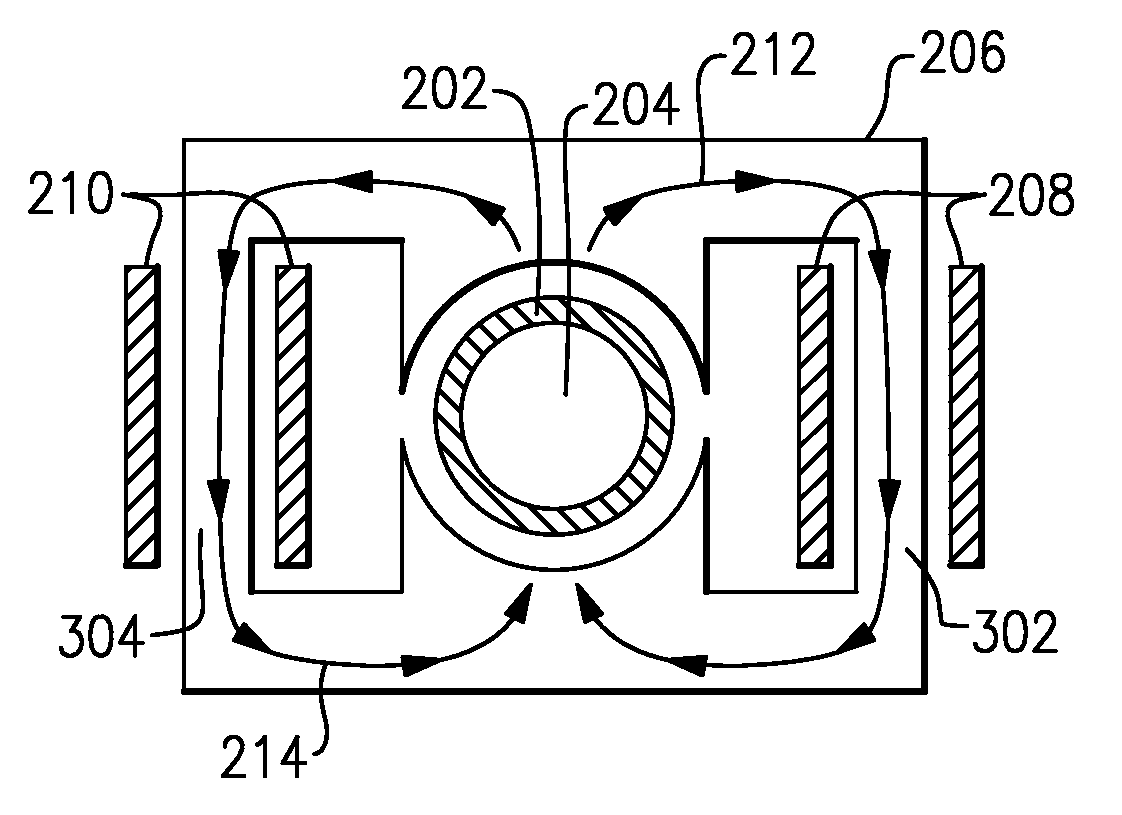
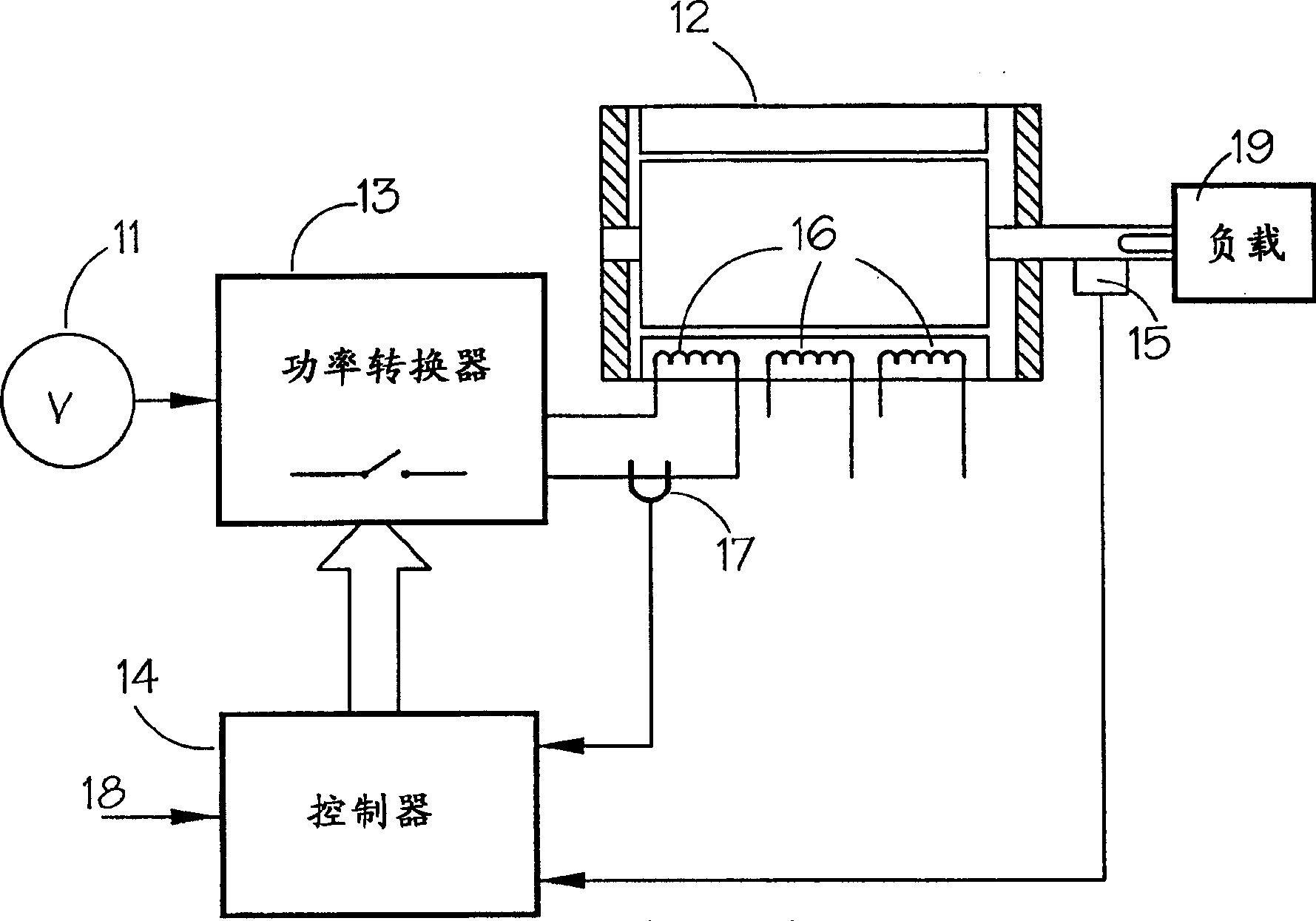
The invention provides a generator (100, 400, 500). The generator includes at least one rotating member (202, 418, 518); at least one stationary member (204) arranged to define a gap (208, 424, 524) between a portion of the rotating member and a portion of the stationary member ), wherein the gap is configured to facilitate the transfer of a controllable magnetic flux therethrough; and a gap control system (200) comprising at least one gap measurement assembly (218, 220, 222, 428, 528), at least one power a transducer (232, 234, 236) and at least one controller (224) electronically connected to the measurement assembly and the transducer and configured to adjust the size of the gap by adjusting the magnetic flux .
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Voltage regulated permanent magnet generator
ActiveUS20100181969A1Synchronous generatorsWindingsVoltage regulationPermanent magnet synchronous generator
A single phase AC generator uses a rotor contained within a stator. The stator has an armature winding and a control winding which is capable of having its magnetic permeability adjusted, thereby limiting the output voltage of the armature winding. The stator additionally has two core sections.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Circuit for on-off reluctance motor
A switched reluctance machine is energized by phase circuits with four active switches, for example MOSFETs, arranged in a bridge configuration. The switches are capable of conducting current in both a first direction and a second direction and are capable of operating as a diode. The direction of current flow through the phase winding is reversed when changing from motoring to generating and from generating to motoring. The ratings of the switches are set in accordance with the energy supply and energy return currents.
Owner:NIDEC SR DRIVES
Field controllable rotating electric machine system with magnetic excitation part
InactiveUS7999432B2Field-weakening controlEasy to controlWindingsDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineElectrical polarity
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine system, every magnetic salient pole group to be magnetized in a same polarity is collectively magnetized by a magnetic excitation part. In the magnetic excitation part, a main magnetic flux path in which a magnetic flux circulates through the armature and a bypass magnetic flux path are connected to the field magnet in parallel. Magnetic flux amount in each path is controlled by mechanical displacement. Thereby, the rotating electric machine system and the magnetic flux amount control method in which magnetic field control is easy are provided. Also, means and method are provided so that a power required for the displacement may be made small by adjusting magnetic resistance of the above magnetic flux path.
Owner:KURA LAB
Power generating system with flux regulated generator
A method for generating and controlling power by means of at least one controlled permanent magnet machine (PMM) with a permanent magnet (PM) rotor and a stator with a magnetic flux diverter circuit for controlling the output of the PMM, comprises the steps of: rotating the PM rotor at a velocity sufficient to develop a high frequency alternating current (HFAC) power output from the stator; transforming the HFAC output to produce a desired non-HFAC power output; sensing desired power output parameters; generating a control signal responsive to the sensed parameters; and applying the control signal to the magnetic flux diverter circuit to control the desired power output.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
System and method for AC power generation from a reluctance machine
InactiveUS20070102936A1Small sizeReduce weightAC motor controlVector control systemsSynchronous reluctance motorControl system
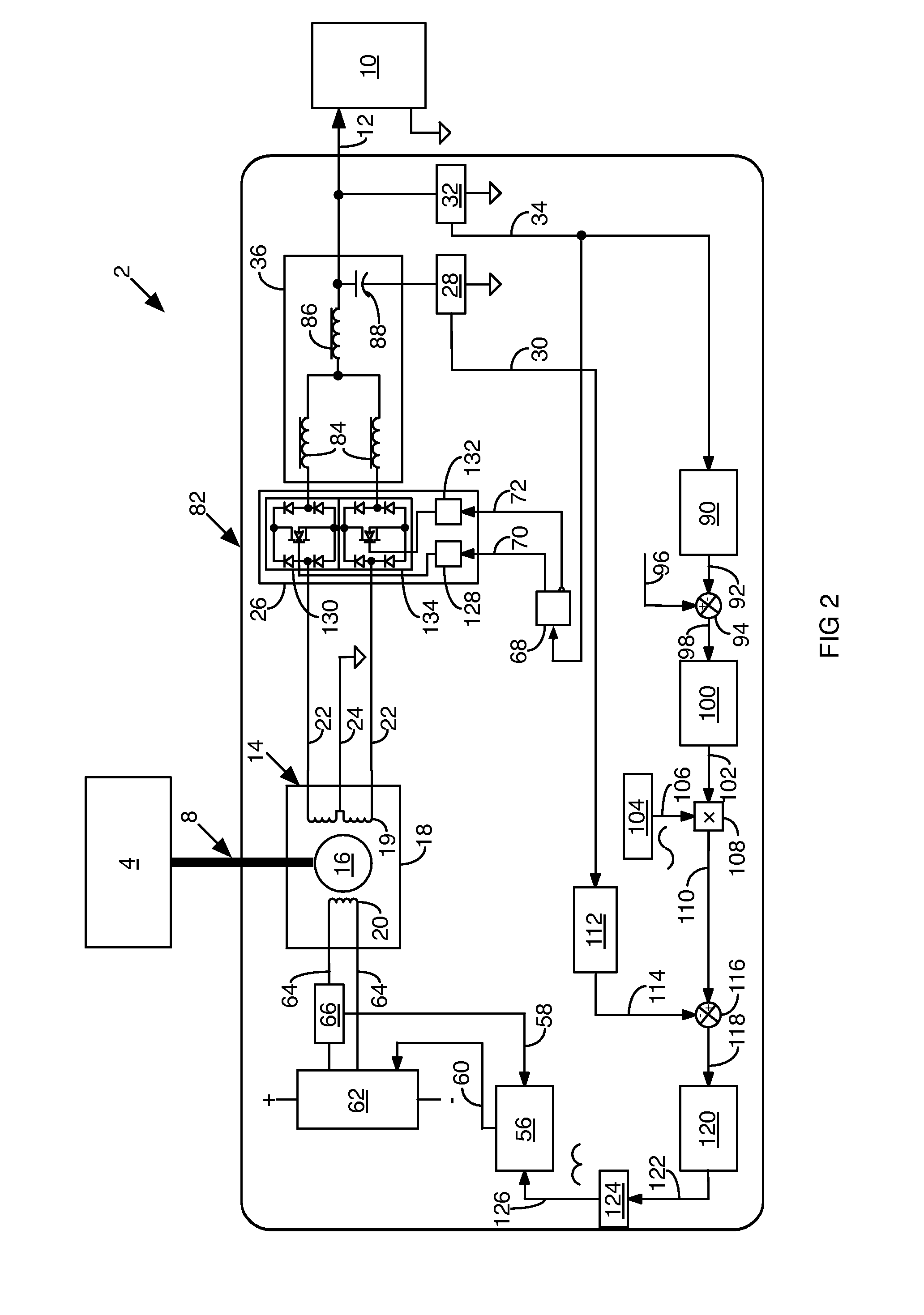
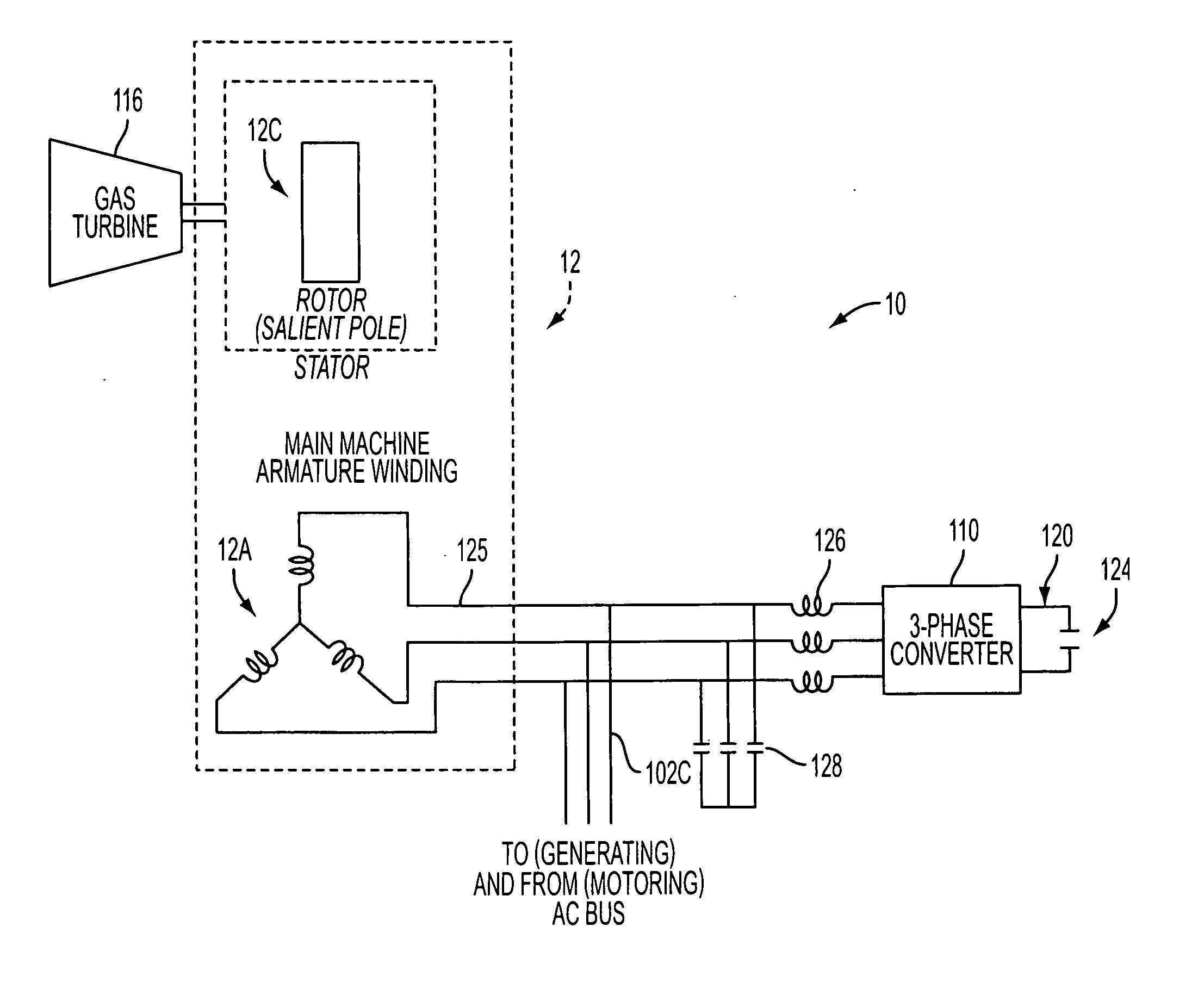
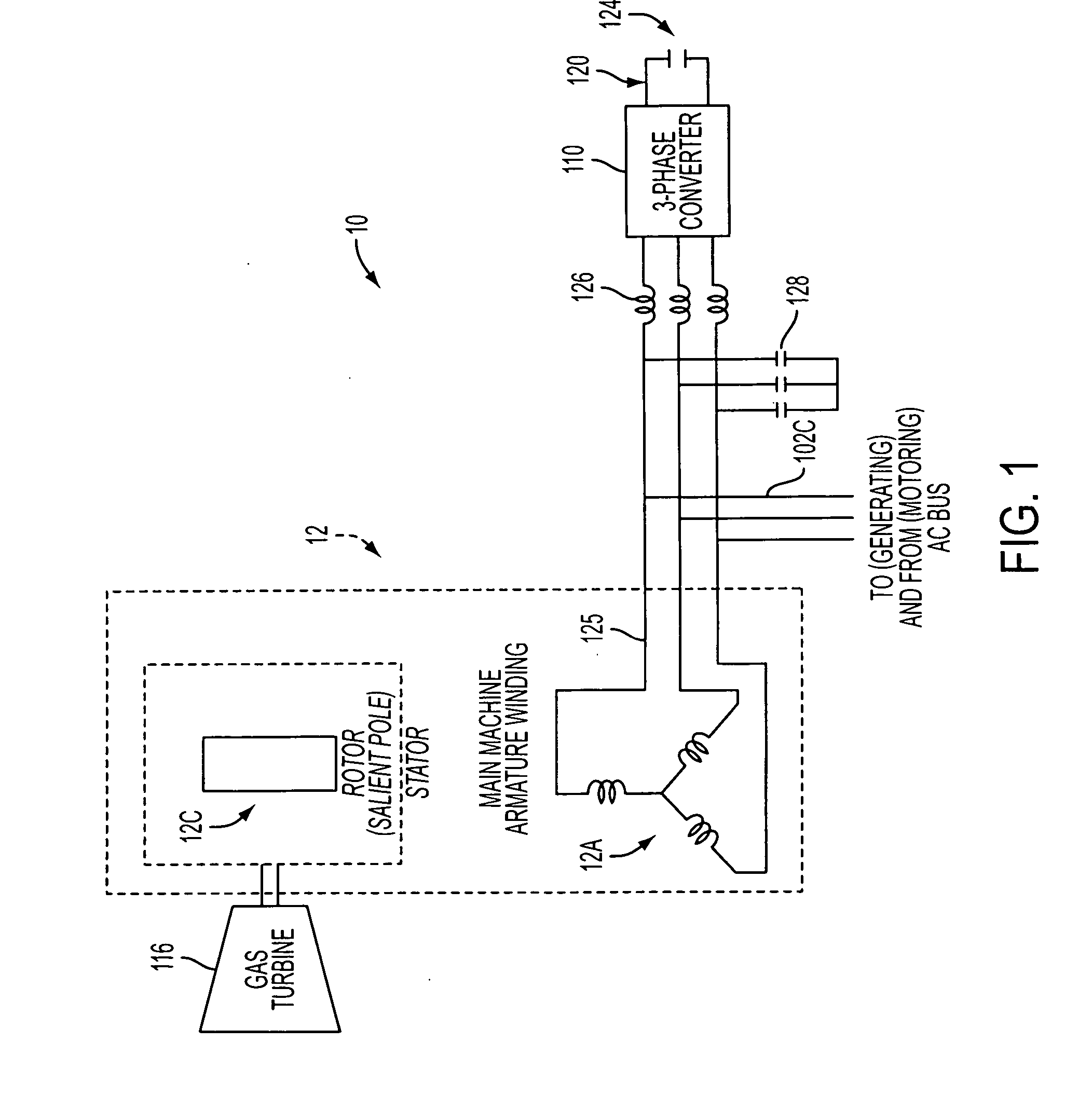
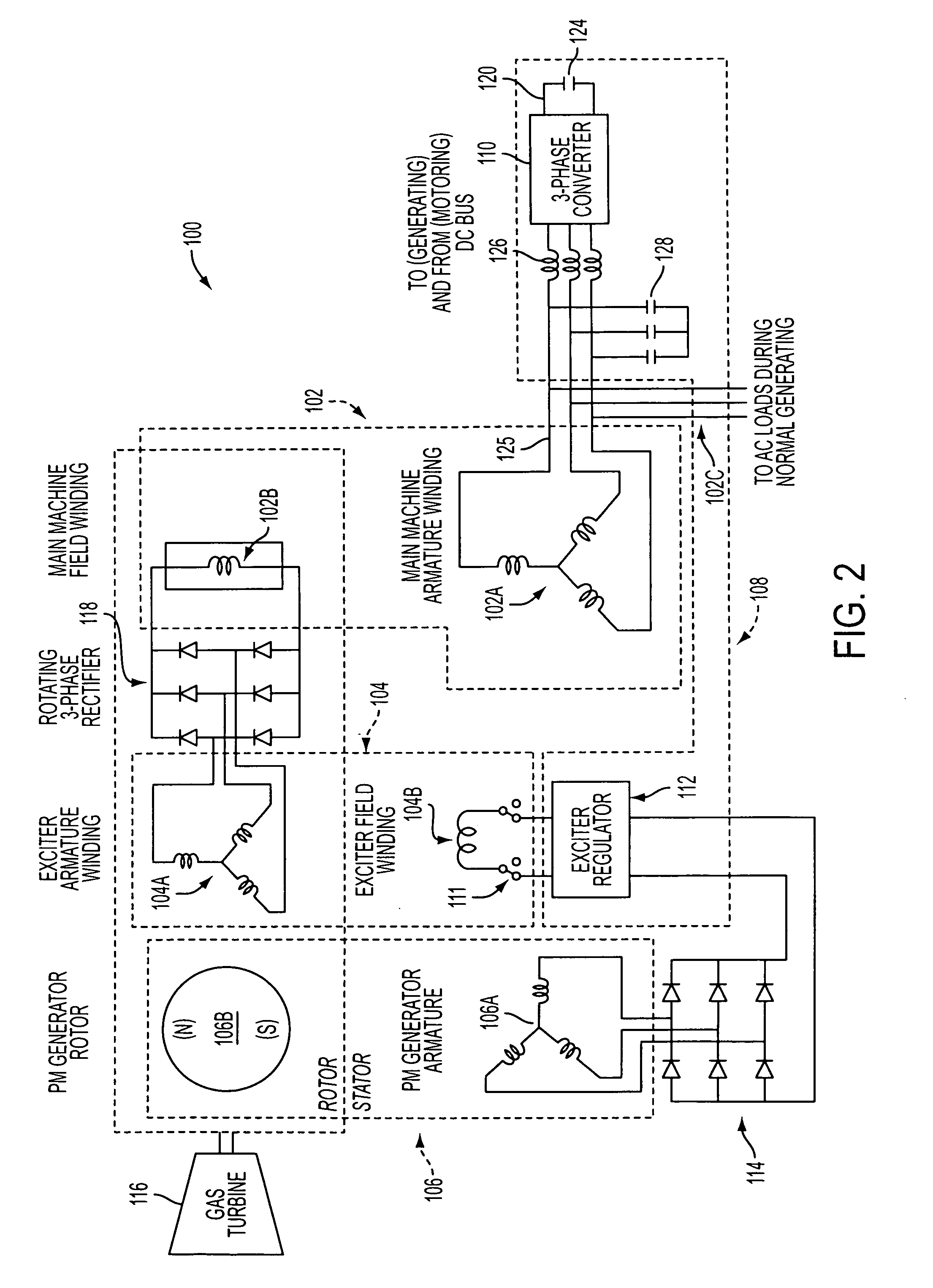
A system and method is provided for generating AC power using a synchronous reluctance machine (12) or a salient-pole synchronous machine (102) and a power converter (110). The present invention can be used to achieve power production for a synchronous reluctance machine (12), or can be used to achieve AC power from a traditional salient-pole synchronous machine / starter (102) without dependence upon a rotor current which is subject to failure. In the power generation system, the control system and method can include a power converter (110), controlled by a voltage command and at least one of a measured AC bus (125) current and voltage, and a DC link (120) voltage, for use with a synchronous reluctance machine (102) and a prime mover (116), such that movement of the rotor of the synchronous reluctance machine (102) can be used to produce at least partial AC power generation on the AC bus (125).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
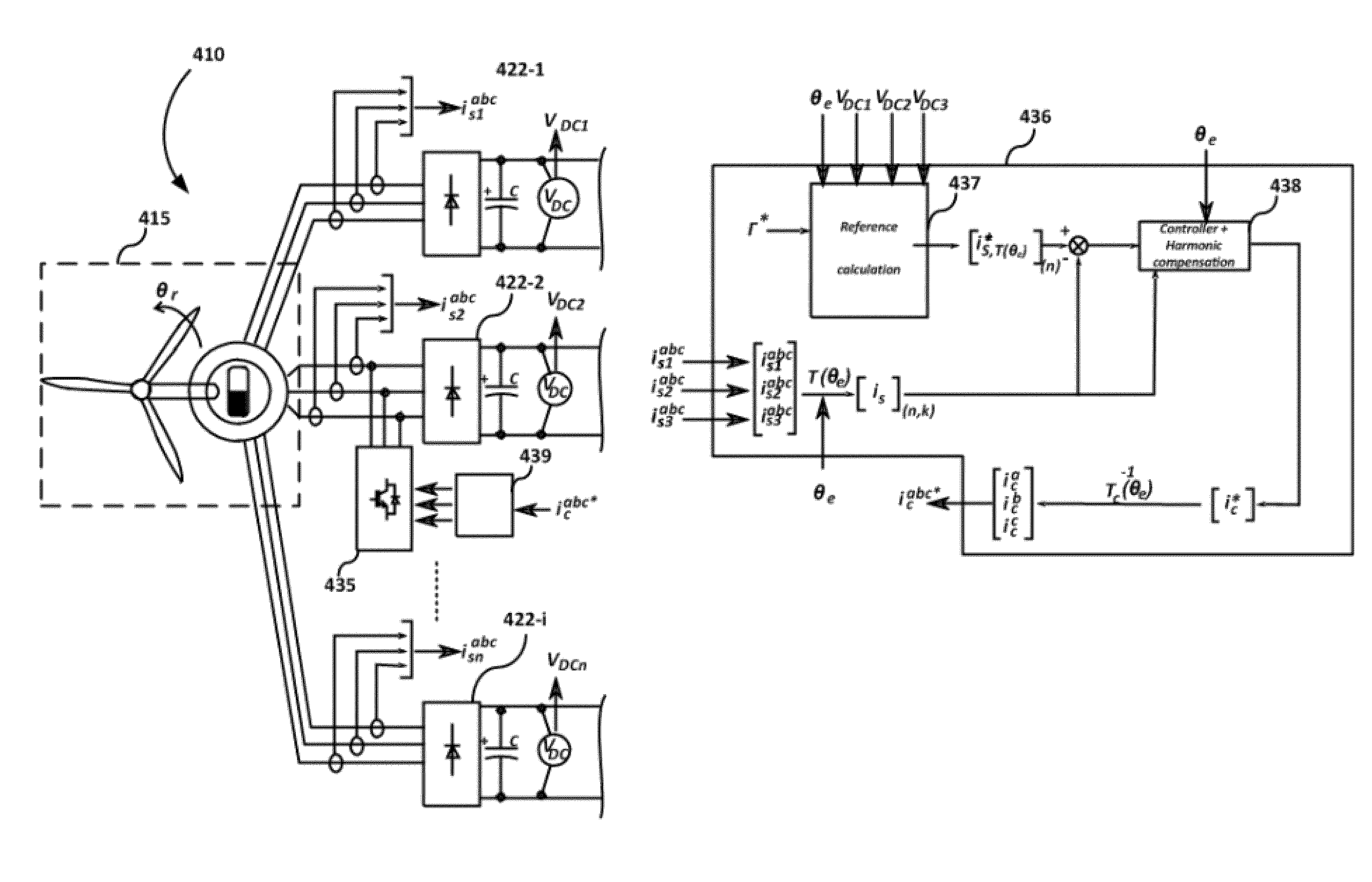
Harmonics mitigation in multiphase generator-conversion systems
ActiveUS20160322924A1Small sizeEmission reductionVector control systemsControl by magnetic circuit reluctanceHarmonic mitigationEngineering
Multiphase generator-conversion systems are disclosed. The system includes a multiphase generator having one rotor and m+1 number of electromagnetically coupled stators, each stator having a plurality of phase legs. The system includes a converter having m+1 conversion lines, each conversion line connected to the plurality of phase legs of one of the m+1 stators. Each conversion line has a rectification module. At most m of the m+1 rectification modules has an active filtering converter. At least one of the m+1 rectification modules has a passive rectifier. At least one of the active filtering converters is configured to directly control its current to vary the magnetic flux of the stator to which it is connected and indirectly affect the magnetic flux of the rest of the stators through the electromagnetic coupling. Also disclosed are wind turbines that include generation conversion systems and methods of mitigating harmonics in multi-phase generator-conversion systems.
Owner:GE RENEWABLE TECH WIND BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com