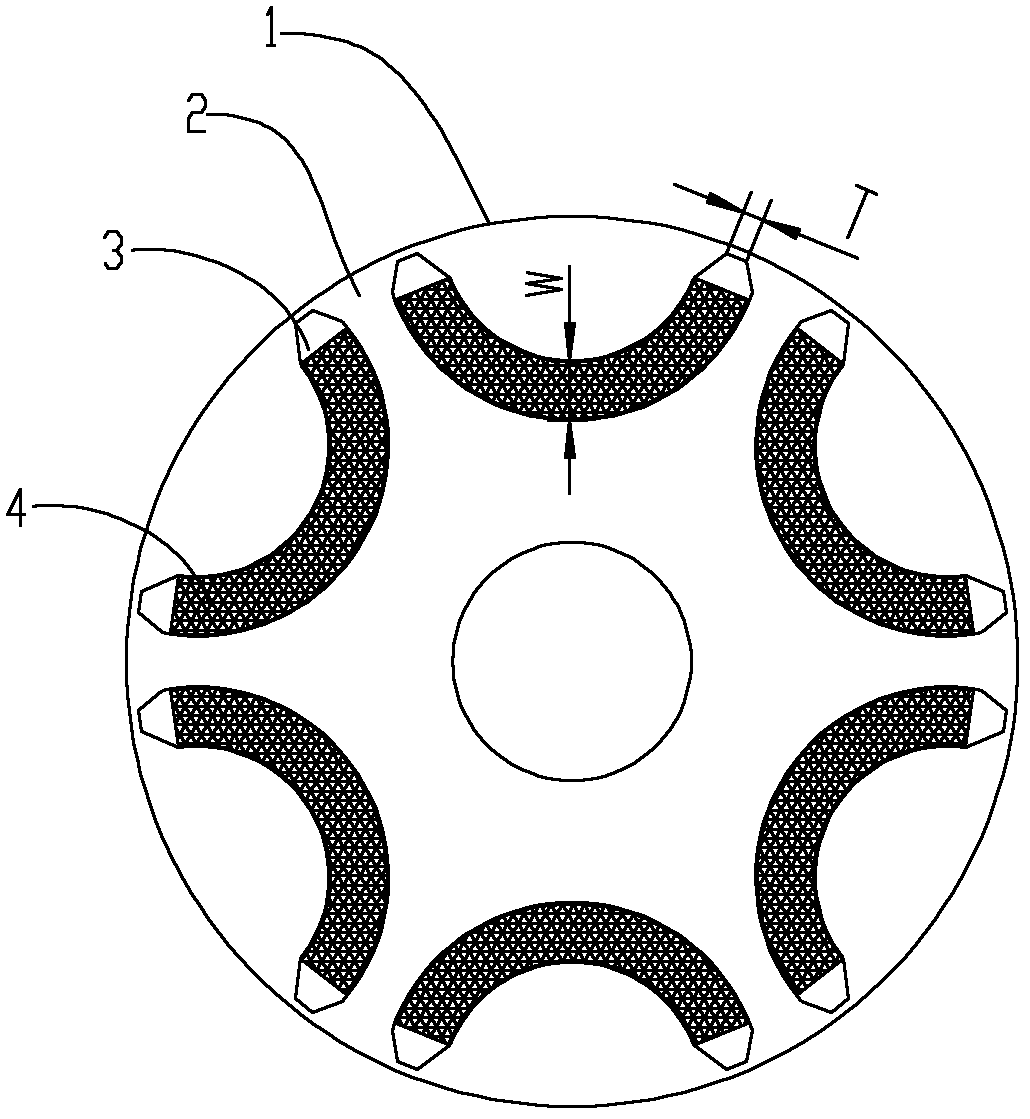
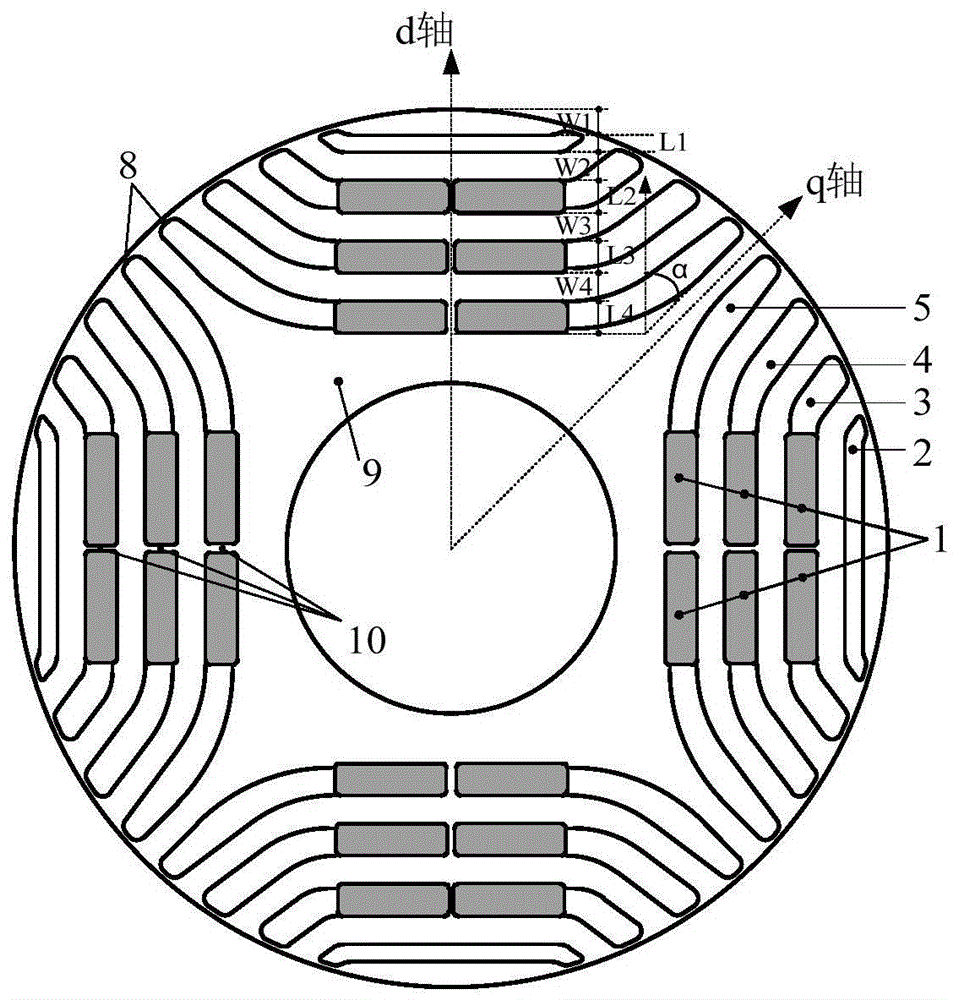
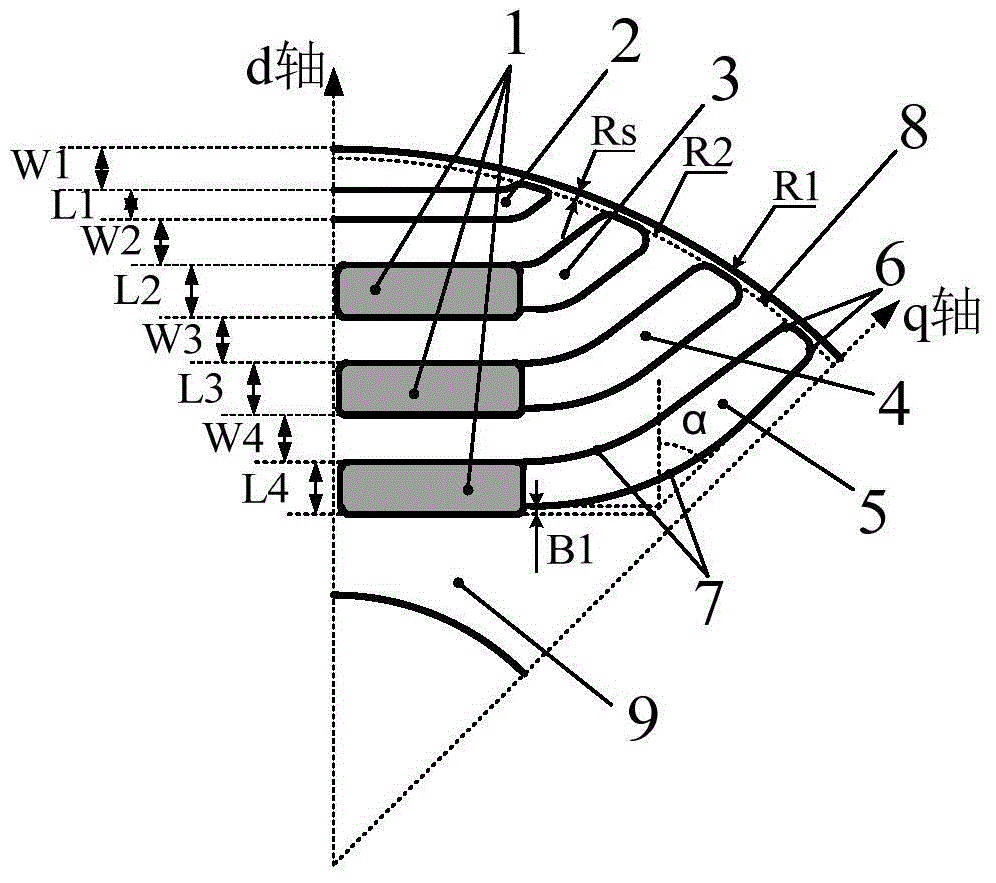
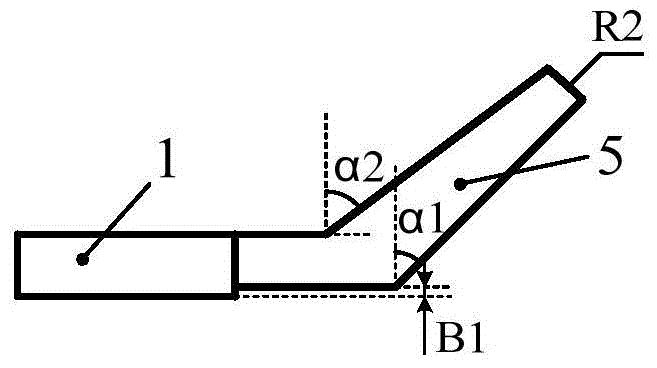
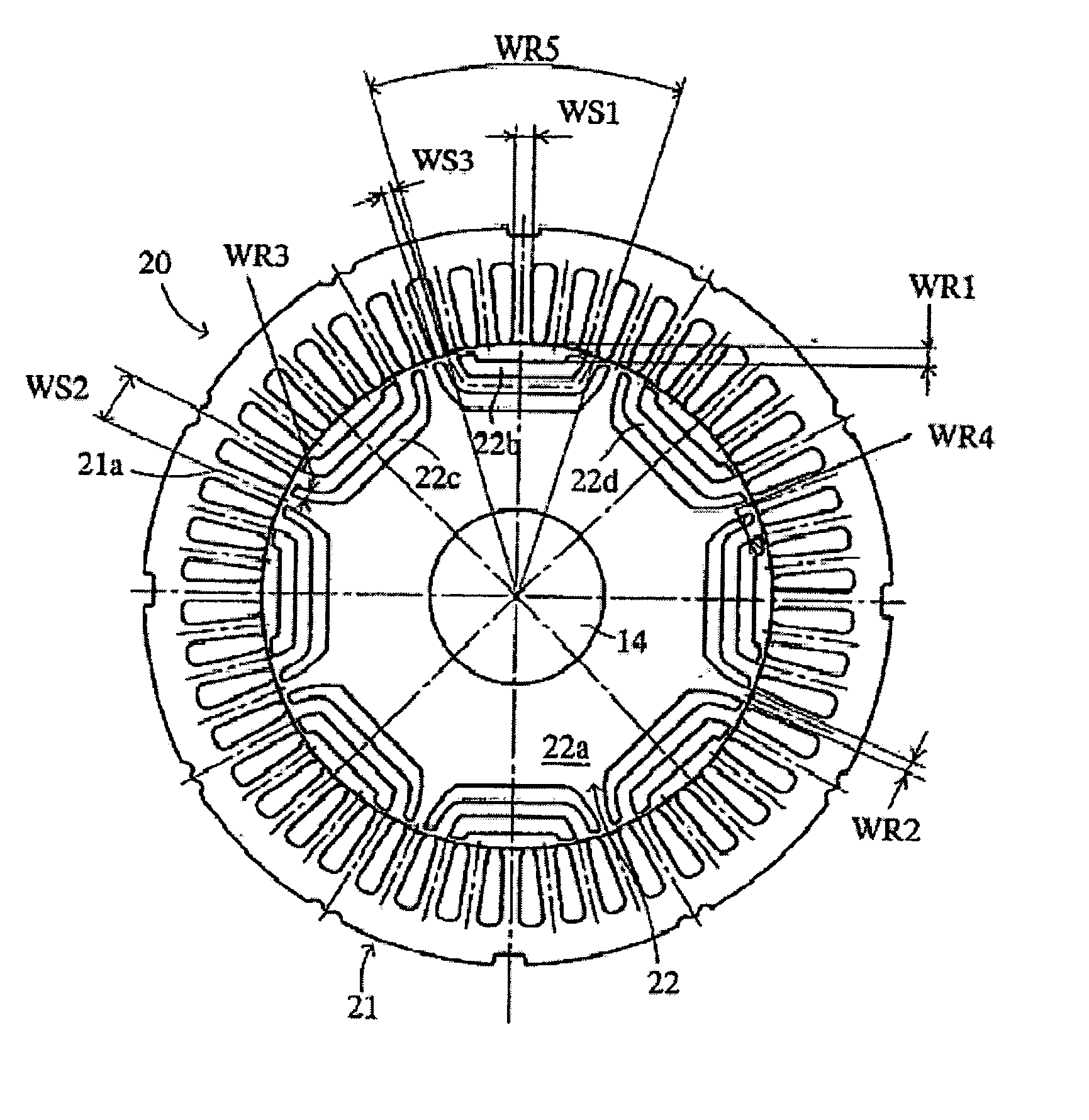
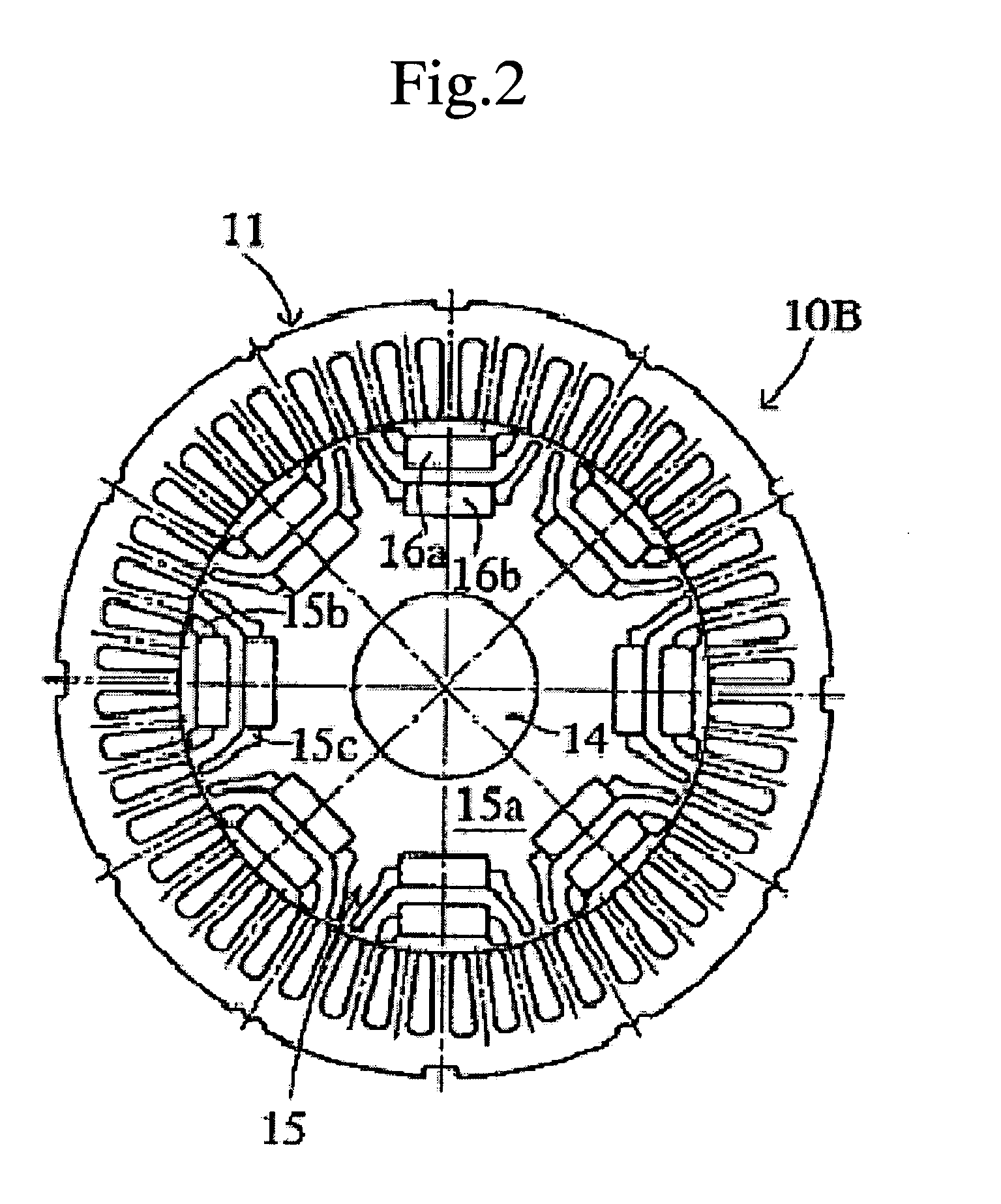
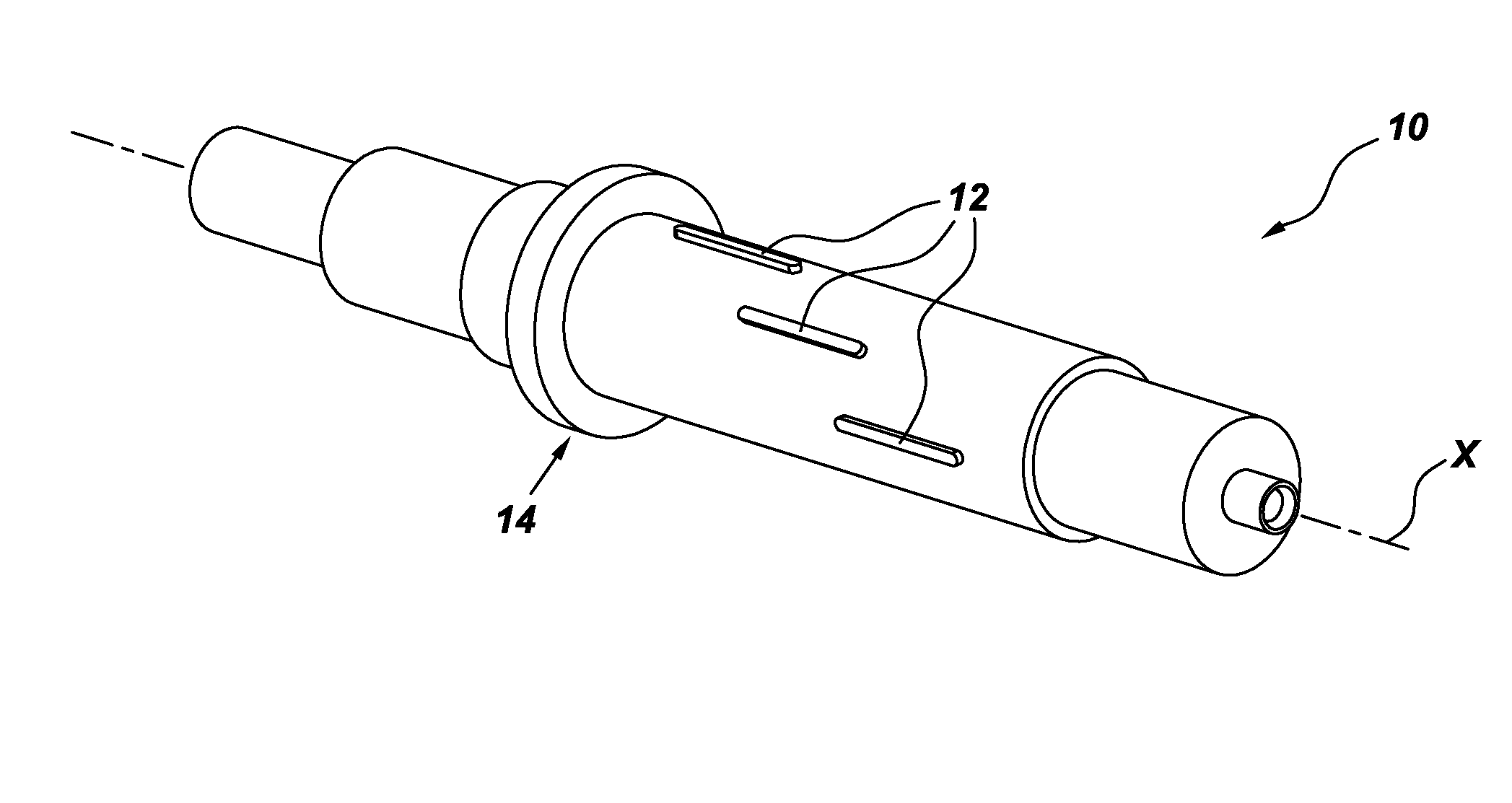
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
547 results about "Synchronous reluctance motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
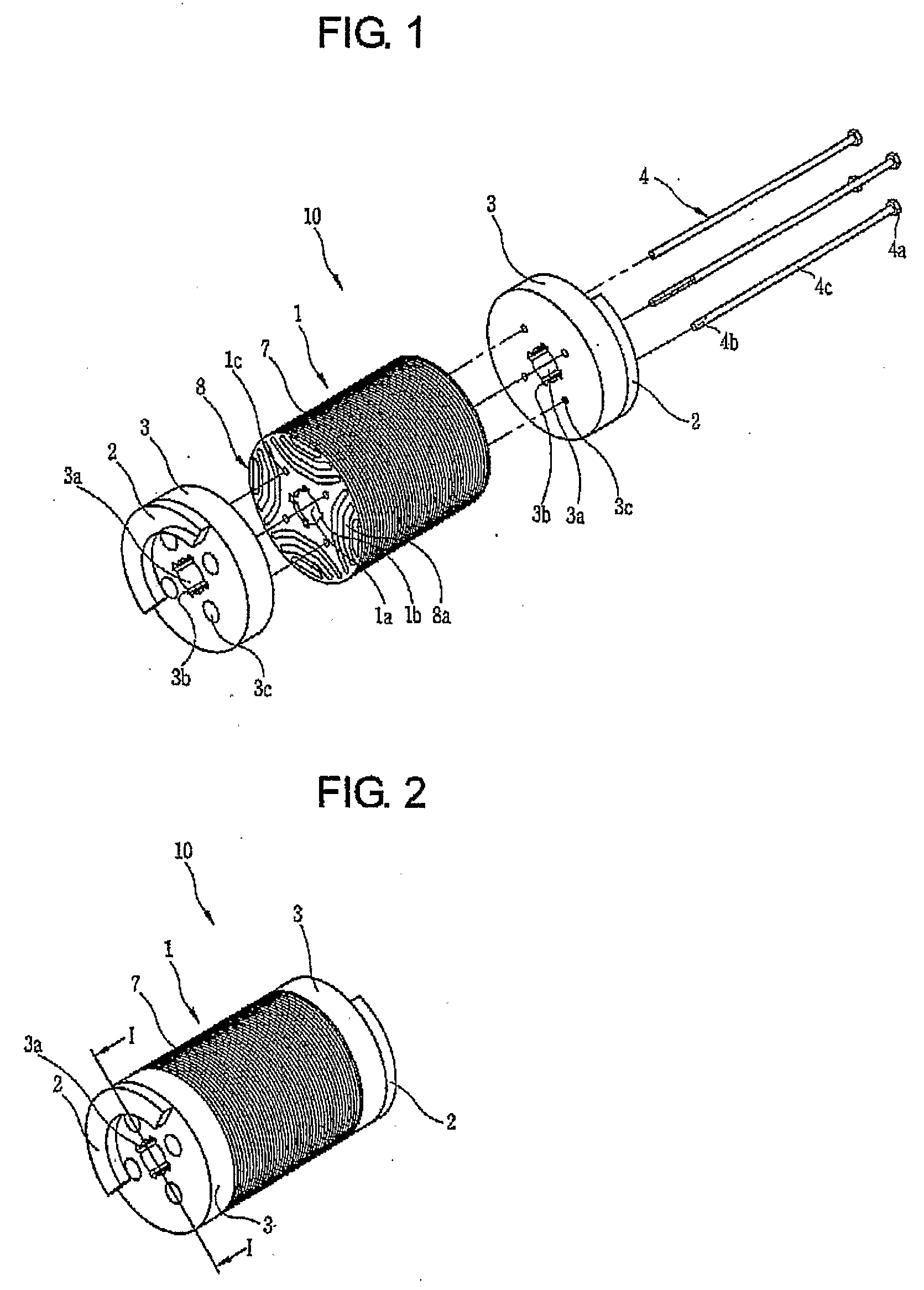
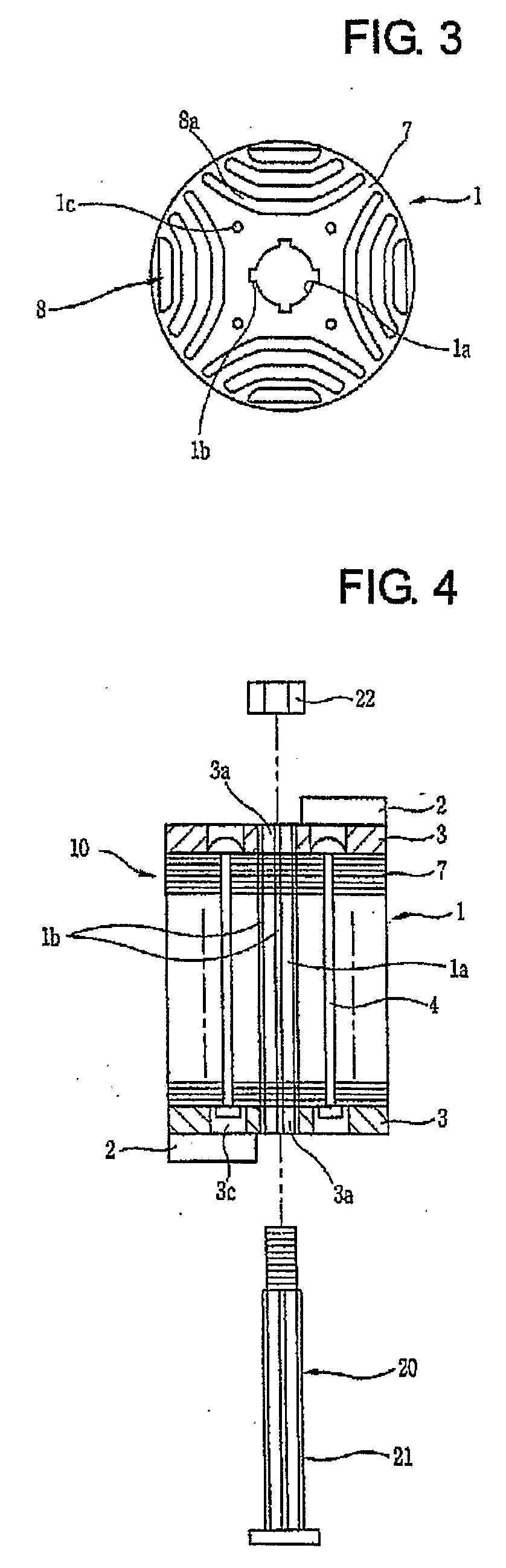
The synchronous reluctance motor has no synchronous starting torque and runs up from stand still by induction action. There is an auxiliary starting winding. This has increased the pull out torque, the power factor and the efficiency.
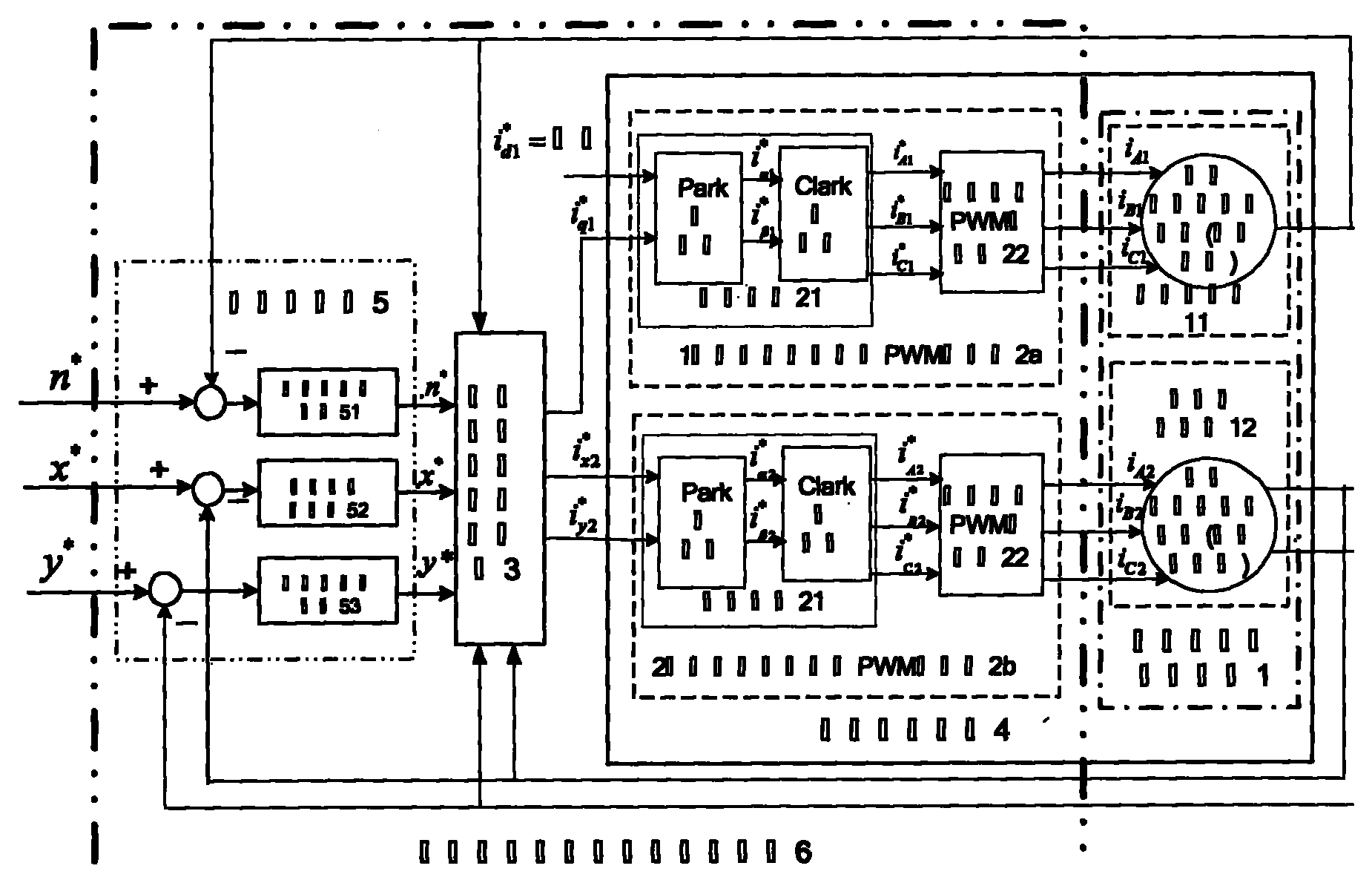
Fault tolerant control system for multi-phase permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motors
ActiveUS20160028343A1High torque outputElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsSynchronous reluctance motor
A fault tolerant control system for a multi-phase permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor utilizes vector control to provide safe operation under various phase loss fault conditions. Specifically, the vector control of the present invention utilizes a fault tolerant algorithm that receives a torque input and an electrical current feedback signal from the motor. Thus, in the presence of a fault condition, the vector control applies the optimal torque angle to the motor, while reducing the phase currents to an optimized value to lessen the saturation effect in the motor, so as to ensure that the motor delivers maximum torque output in the presence of such faults. As such, the control system allows the motor to operate safely with high reliability, which is highly desirable, such as in electric vehicles and the aerospace industry.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
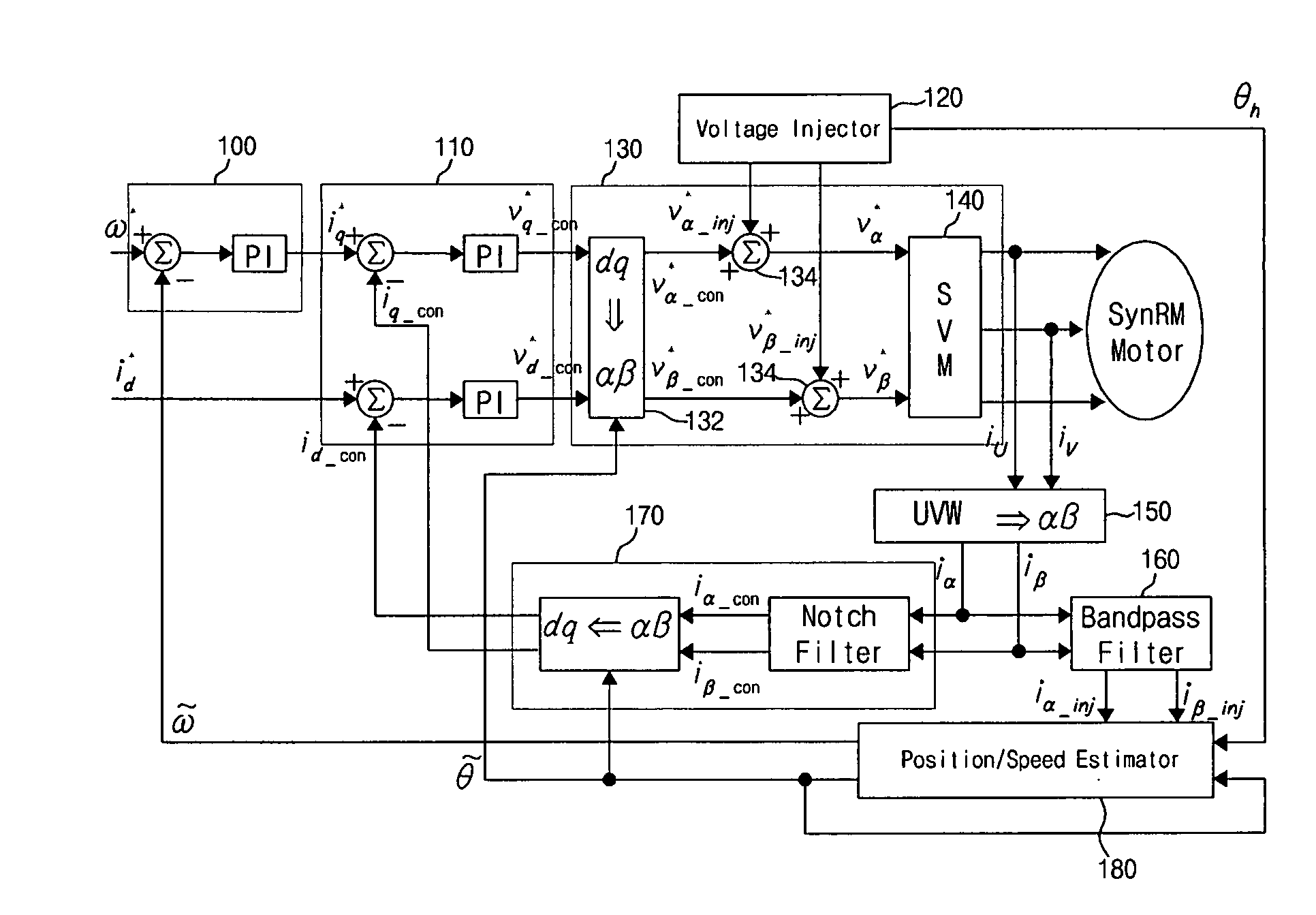
Method and device for controlling startup of motor
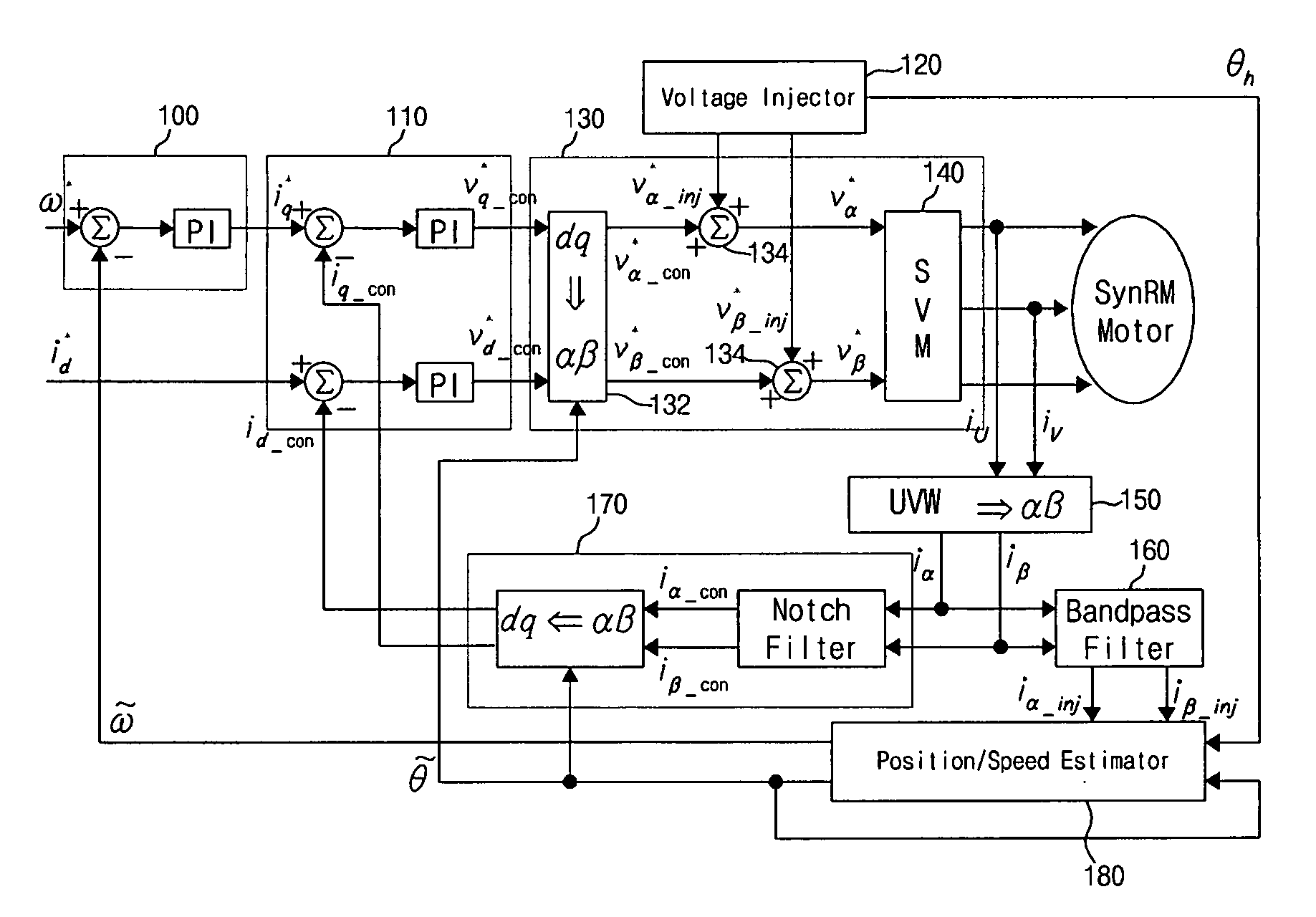
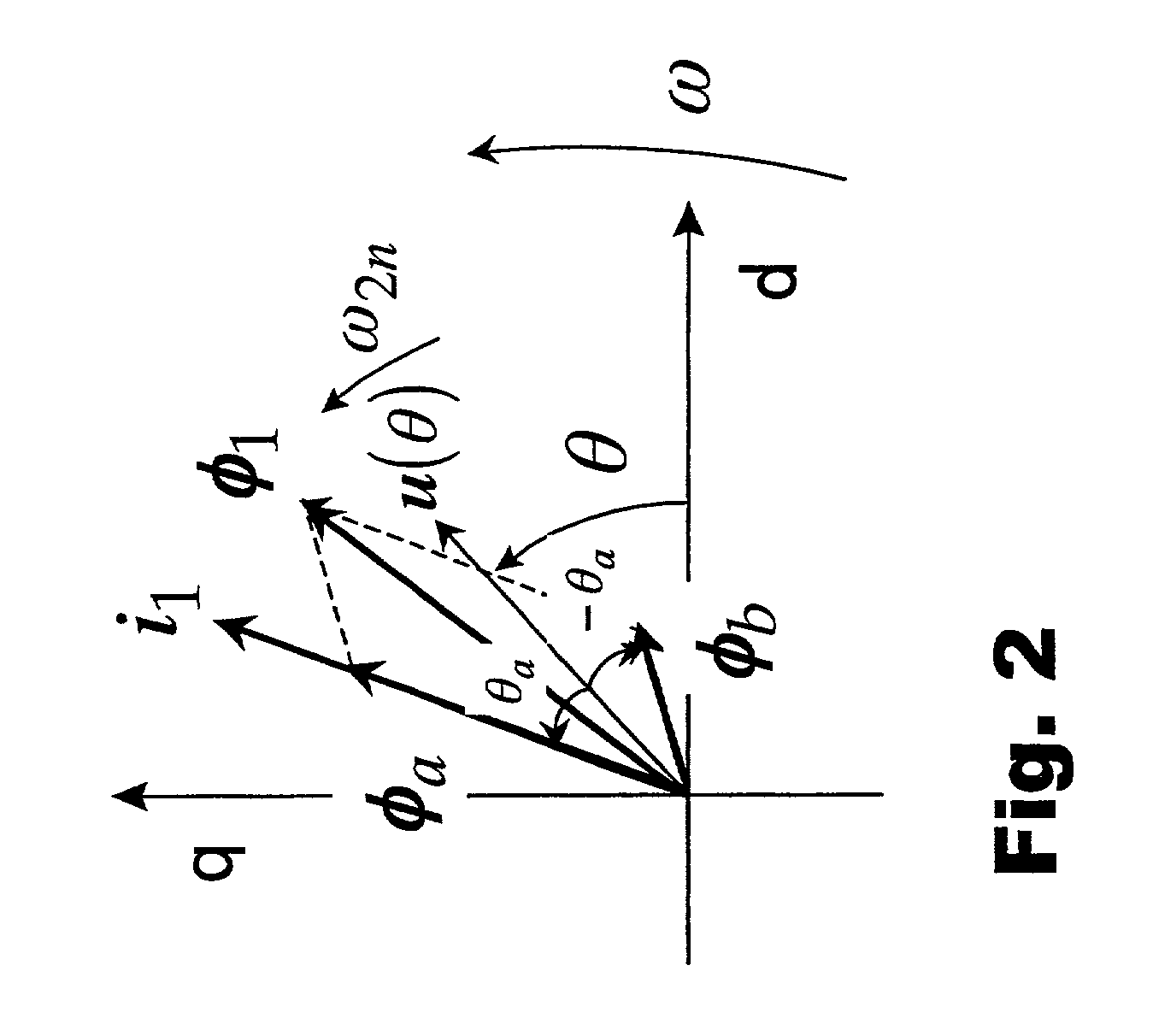
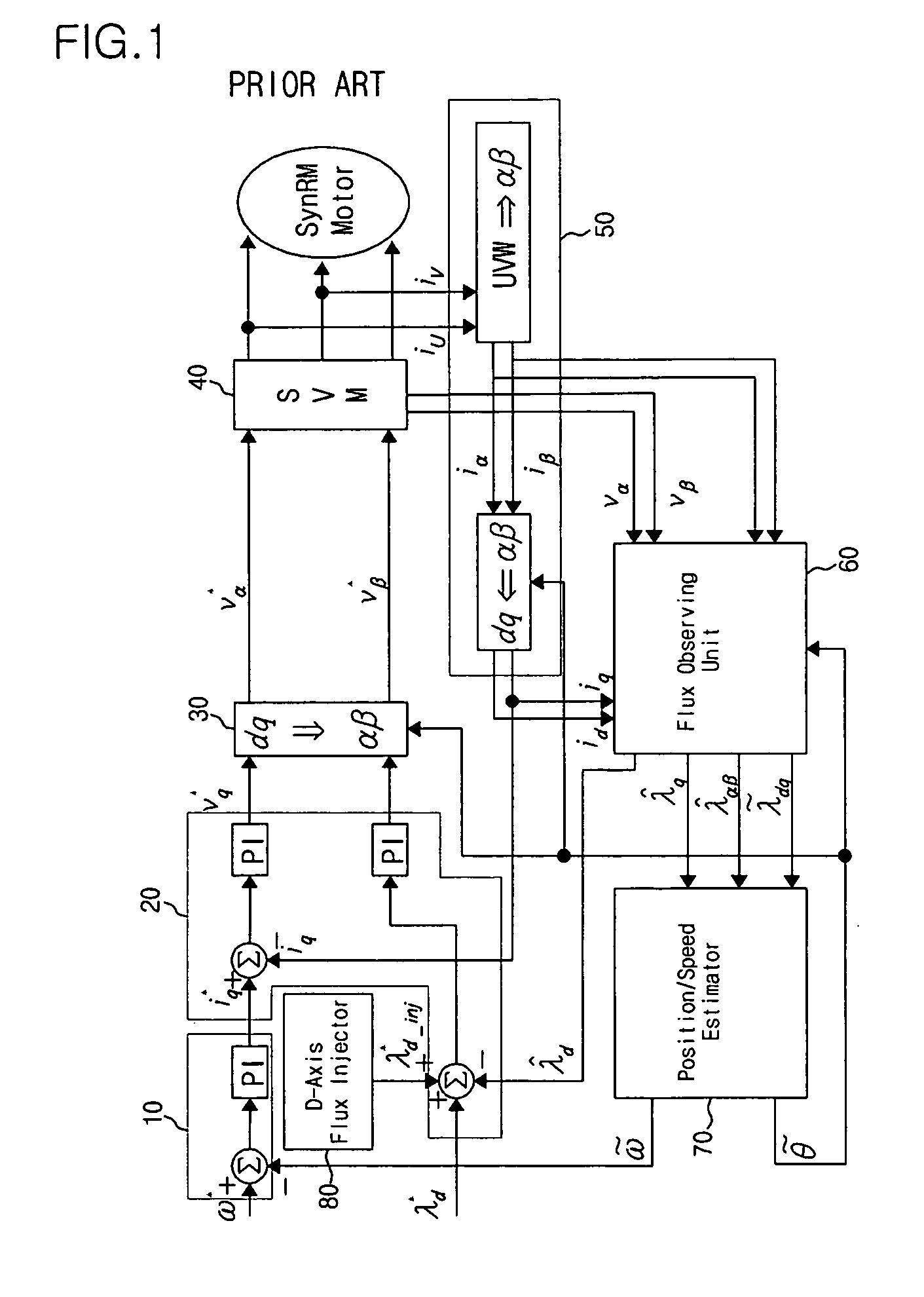
ActiveUS20060119305A1AC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlVoltage generatorSynchronous reluctance motor
Disclosed is a method and device for controlling the startup of a synchronous reluctance motor. The device includes: a voltage injector which generates injection voltages to estimate an initial position of the rotor; a motor drive voltage generator which converts stationary-coordinate-system voltages including the injection voltages to three-phase motor drive voltages and applies the three-phase motor drive voltages to the motor; a current extractor which extracts response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages from two-phase stationary-coordinate-system currents converted from three-phase currents detected upon rotation of the motor; and a position / speed estimator which extracts response current components related to a rotor position from the response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages to calculate a rotor position error (e), and estimates the speed and position {tilde over (ω)},{tilde over (θ)} of the rotor from the calculated rotor position error (e).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for estimating rotor position and for sensorless control of a switched reluctance motor
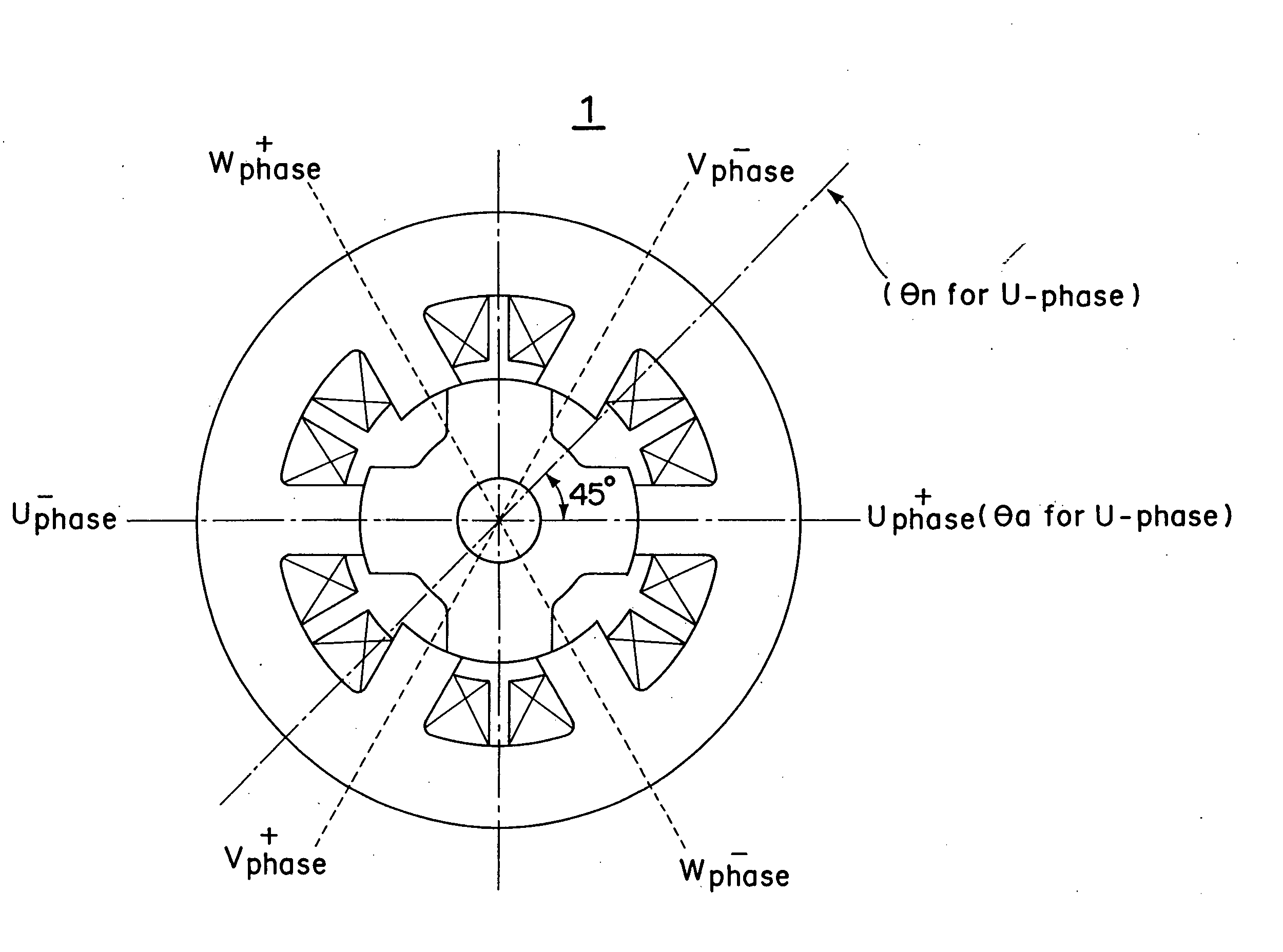
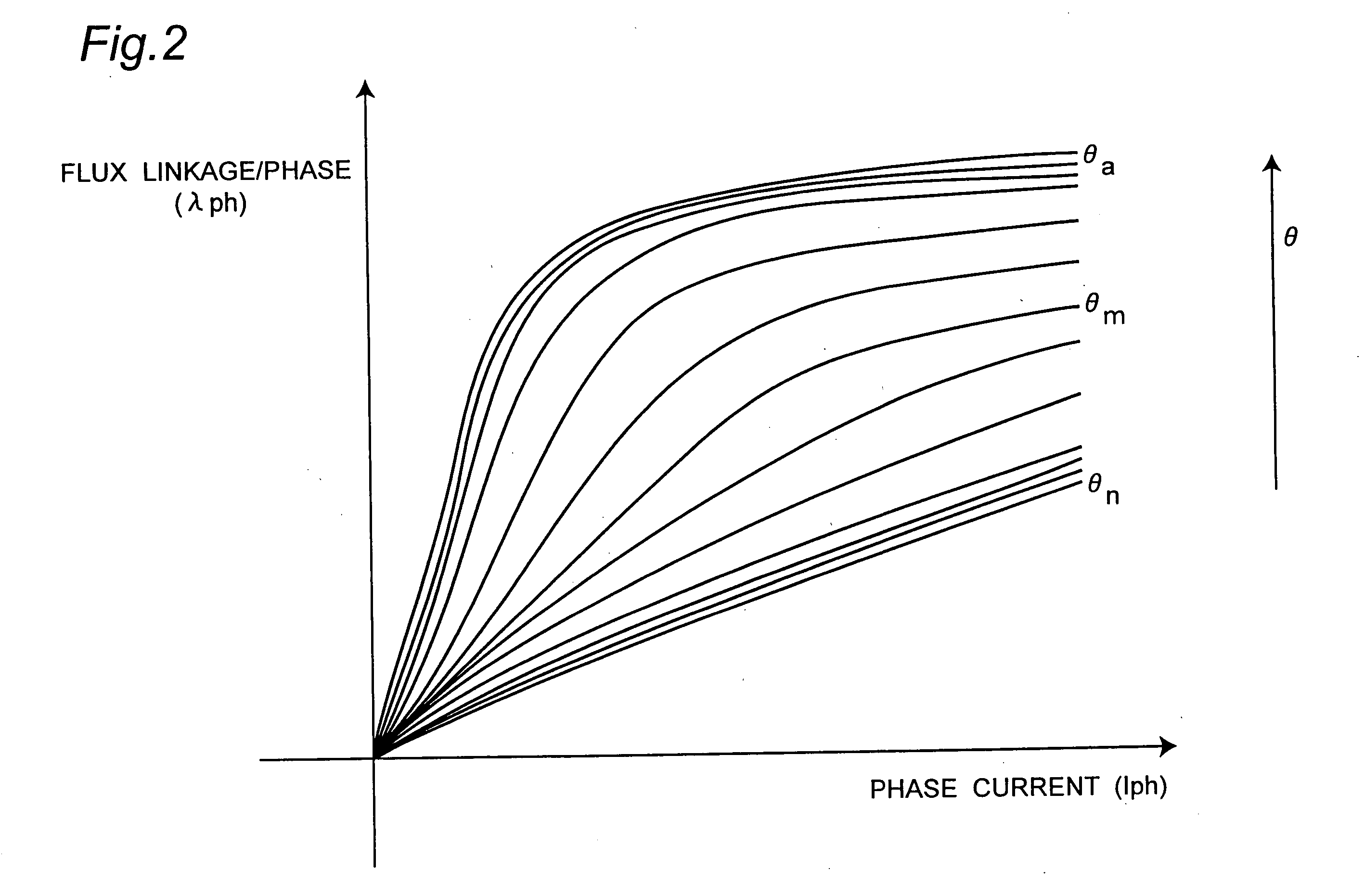
InactiveUS20060125427A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsSynchronous reluctance motor
A discrete rotor position estimation method for a synchronized reluctance motor is provided. A d.c.-link voltage Vdc and a phase current Iph are sensed. A flux-linkage λph of an active phase is calculated from the sensed d.c.-link voltage Vdc and the sensed phase current Iph. The calculated flux-linkage λph is compared with a reference flux-linkage λr. The reference flux-linkage λr corresponds to a reference angle θr which lies between angles corresponding to aligned rotor position and non-aligned rotor position in the synchronized reluctance motor. An estimated rotor position θcal is obtained only once when the calculated flux-linkage λph is greater than the reference flux-linkage λr.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
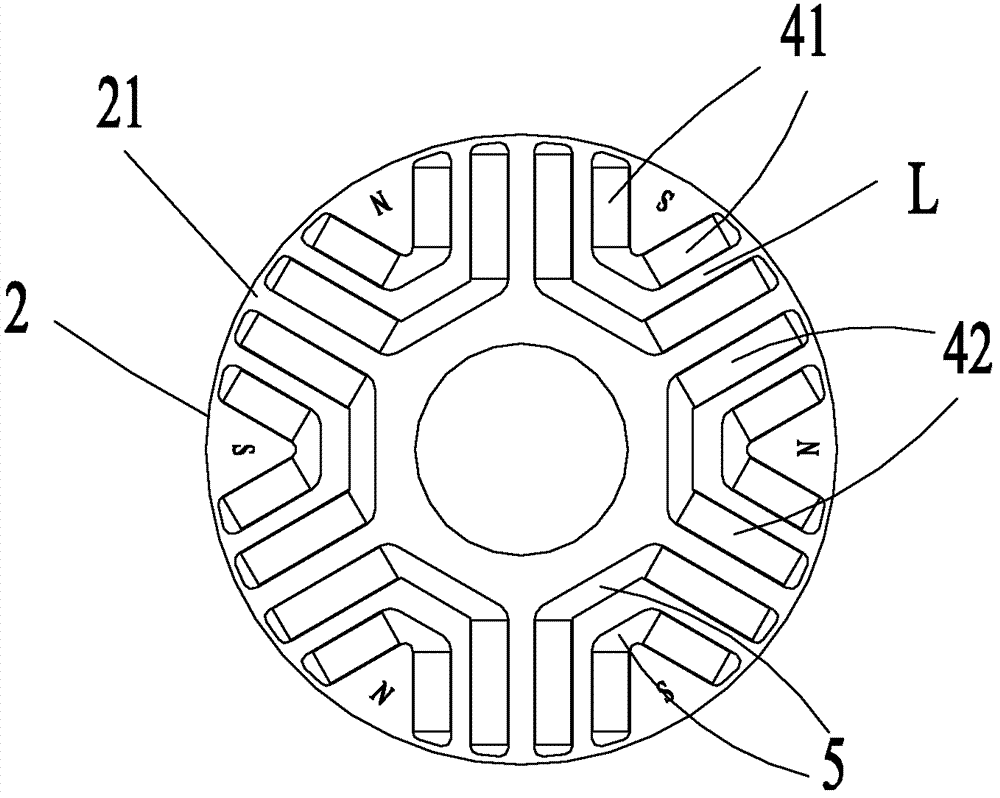
Flux barrier type synchronous reluctance motor and rotor thereof
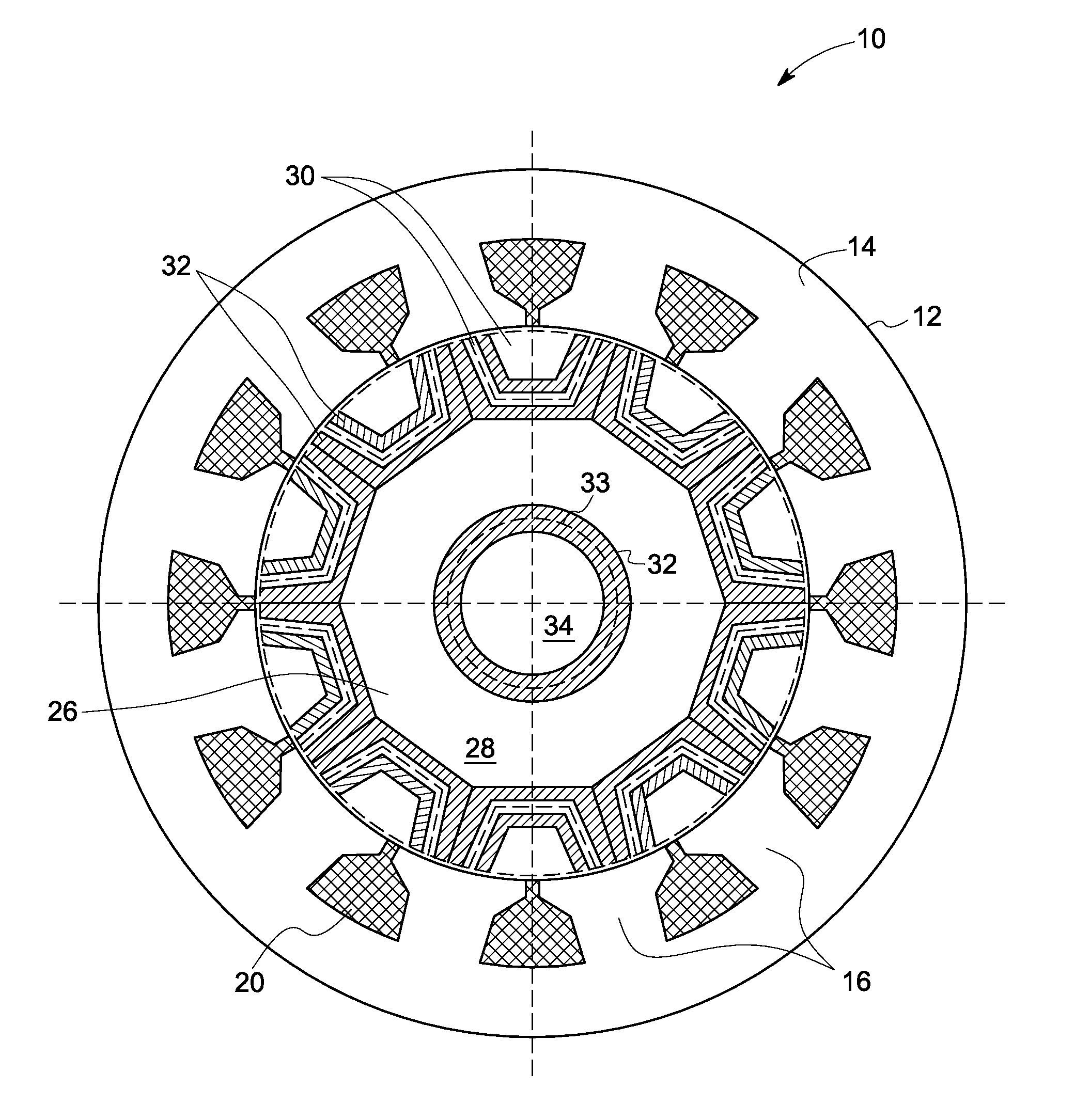
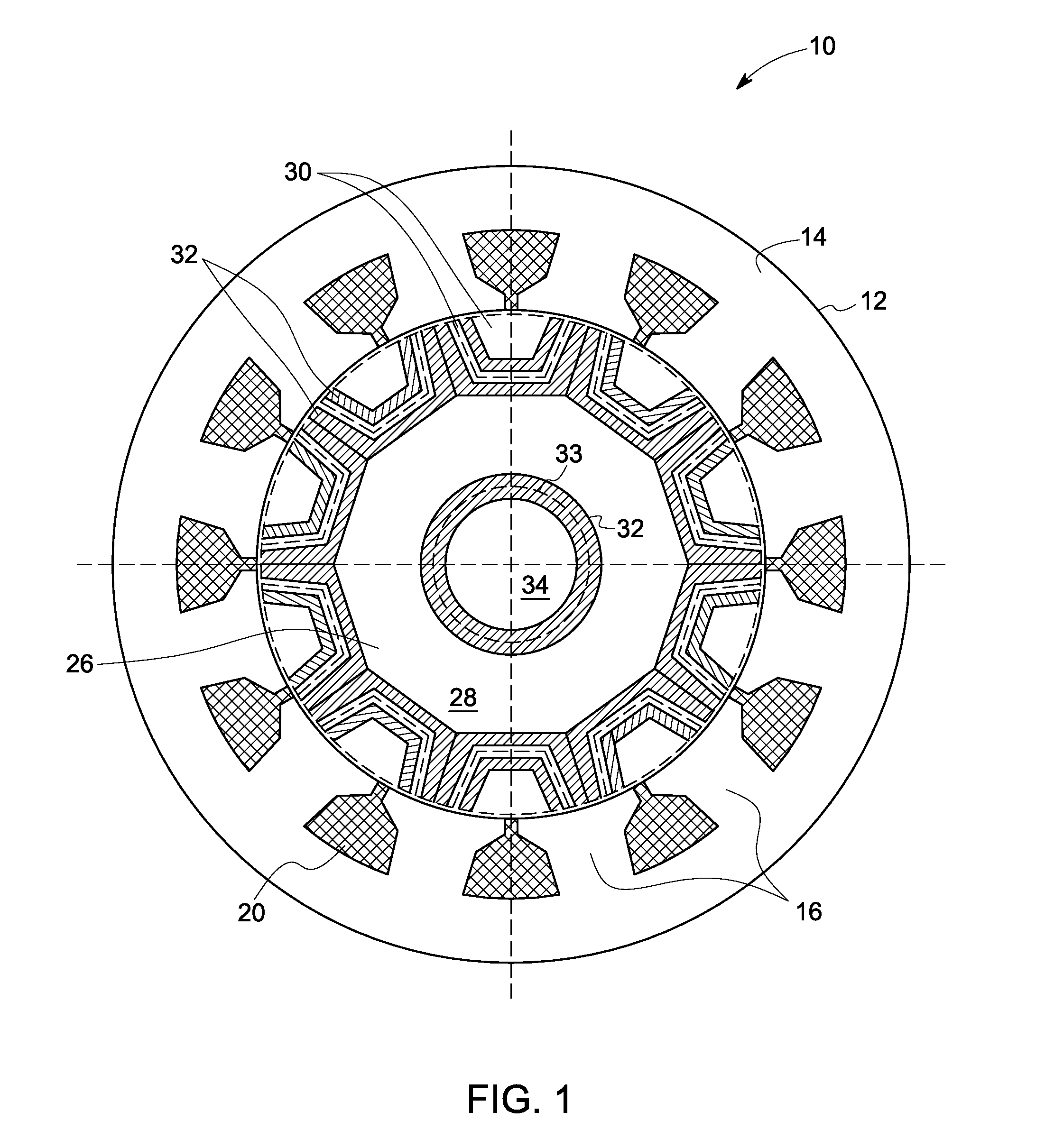
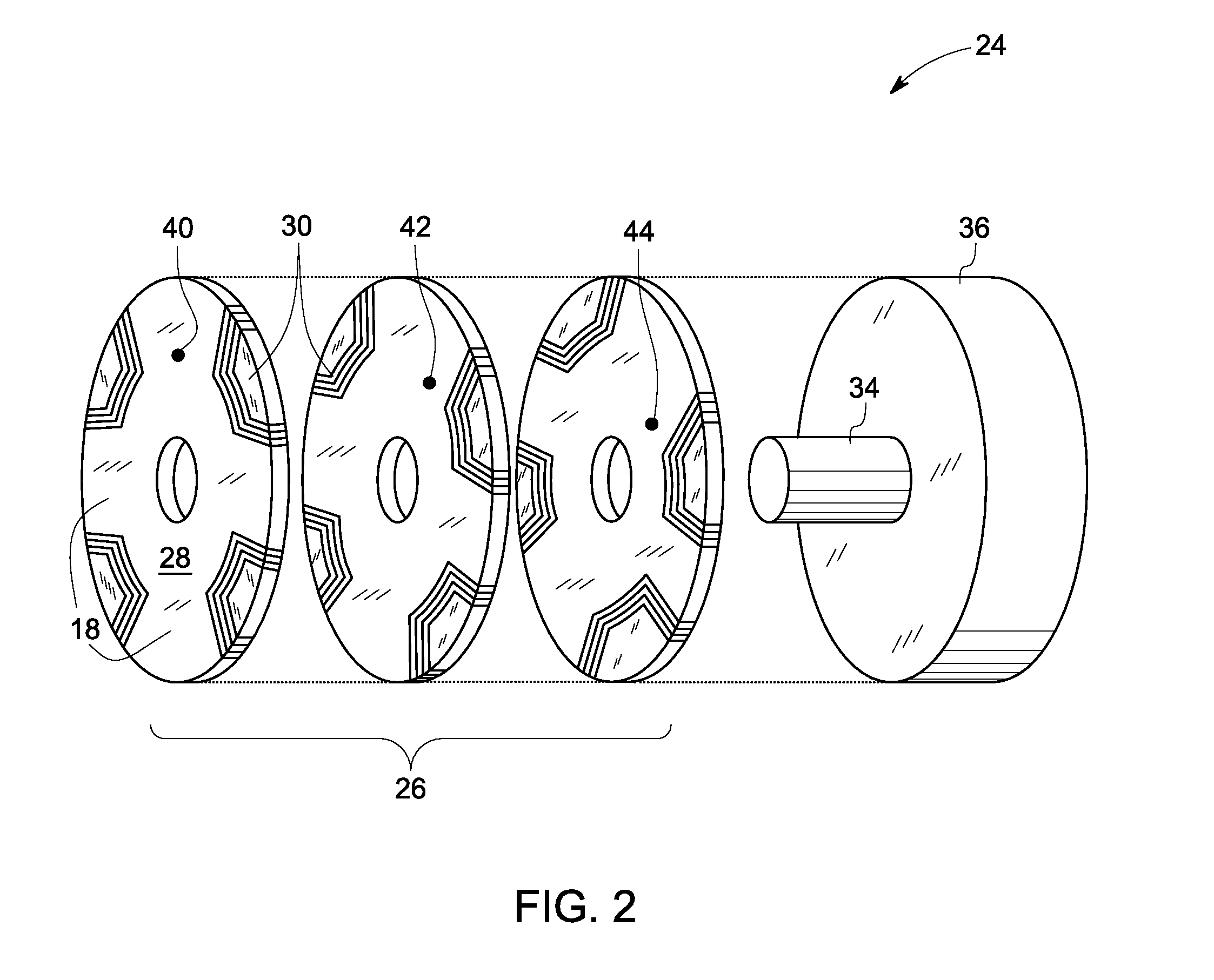
InactiveUS20060284512A1Shorten production timeReducing fabrication costSynchronous generatorsWindingsSynchronous reluctance motorManufacturing technology
A rotor of a flux barrier type synchronous reluctance motor comprises: a rotation shaft; a rotor core formed as a plurality of steel plates are laminated to one another, the steel plate having a shaft hole for inserting the rotation shaft, a plurality of flux barrier groups spaced from one another in a circumferential direction and having a plurality of flux barriers spaced from one another in a radial direction, and a coupling hole penetratingly-formed between the adjacent two flux barrier groups; and a coupling member inserted into the coupling hole and fixing the steel plate. Accordingly, a fabrication cost and an entire weight of the motor are decreased, and a fabrication process is facilitated with a shortened fabrication time. Also, a large coupling intensity is obtained and a magnetic saturation does not occur, thereby preventing a function degradation of the motor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
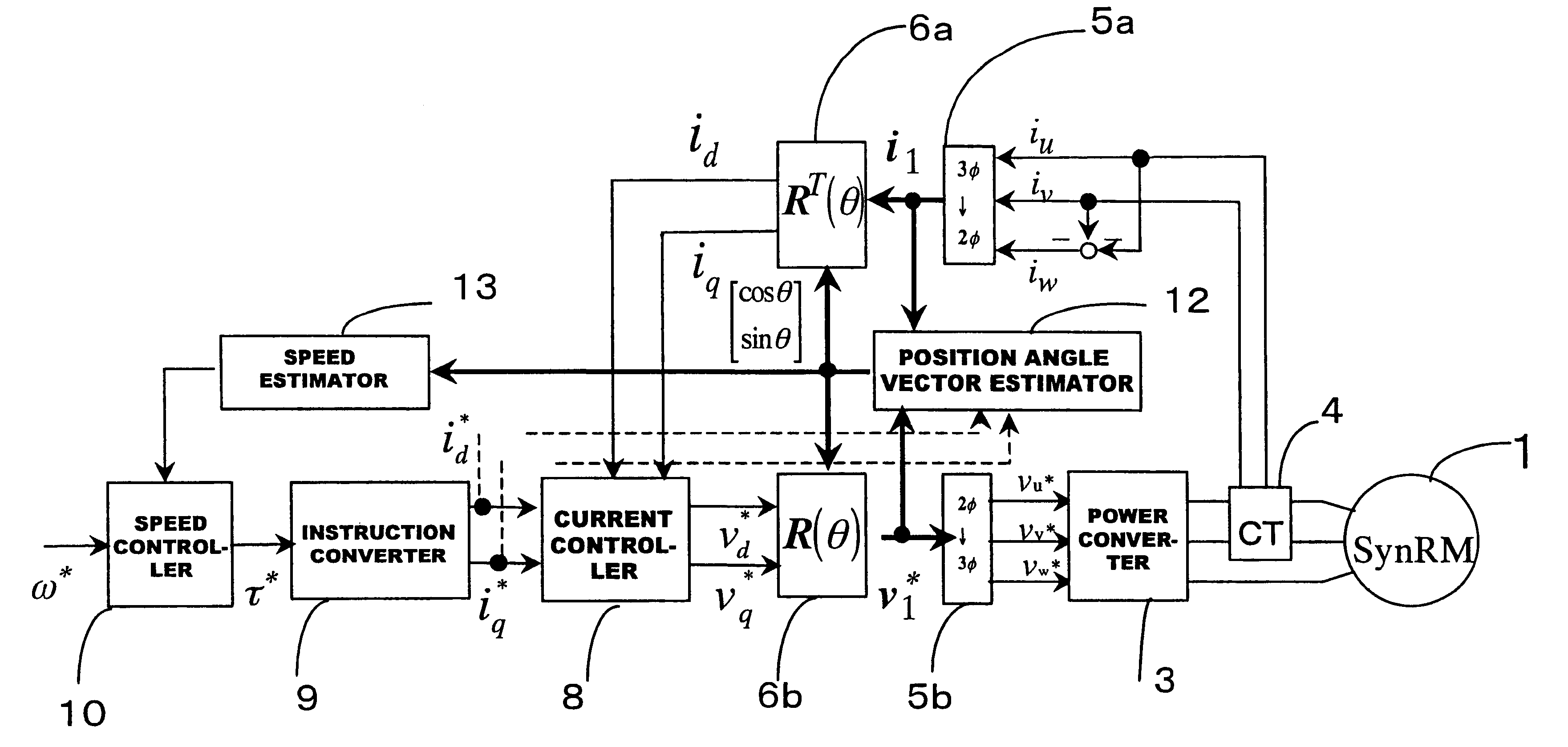
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
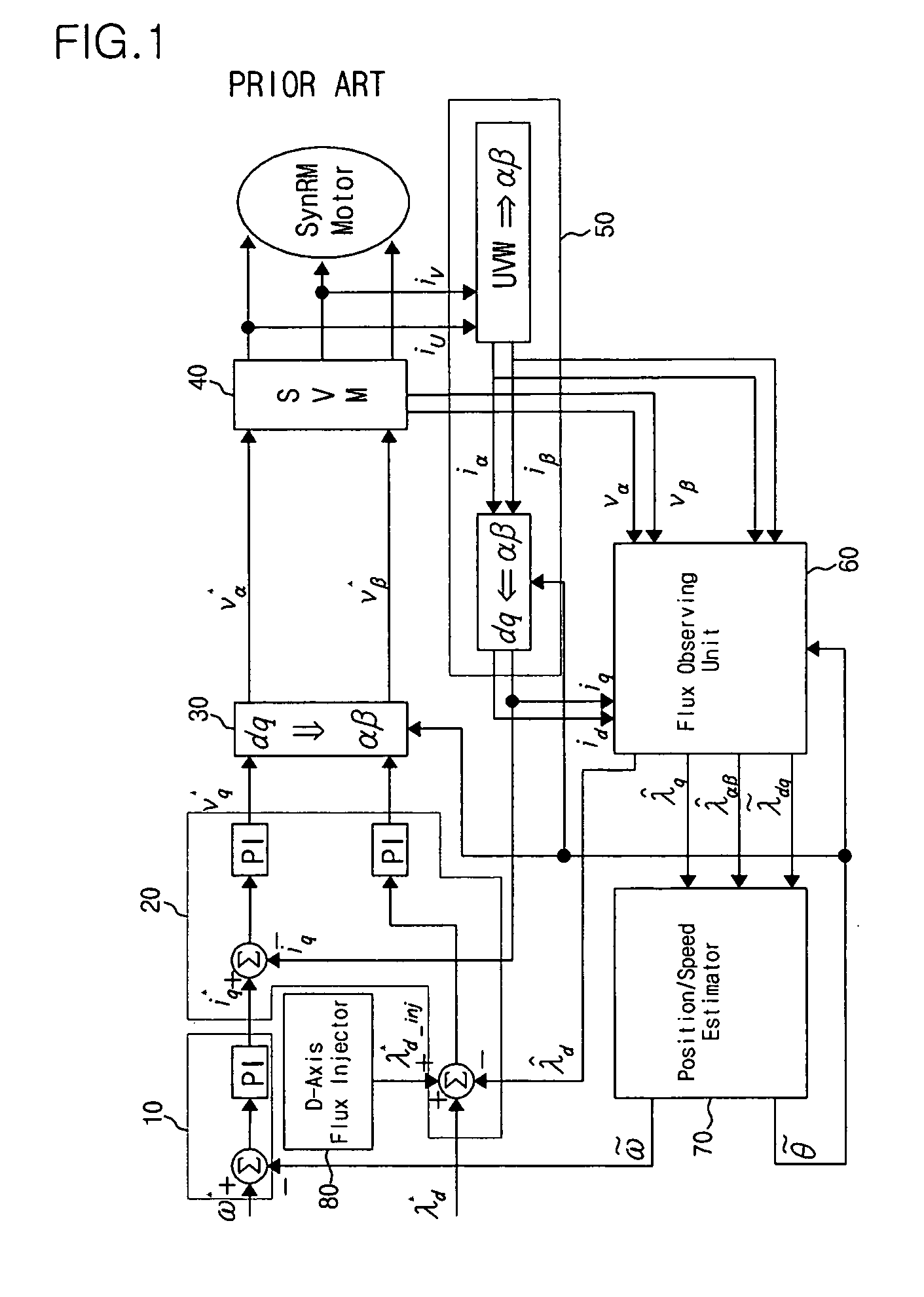
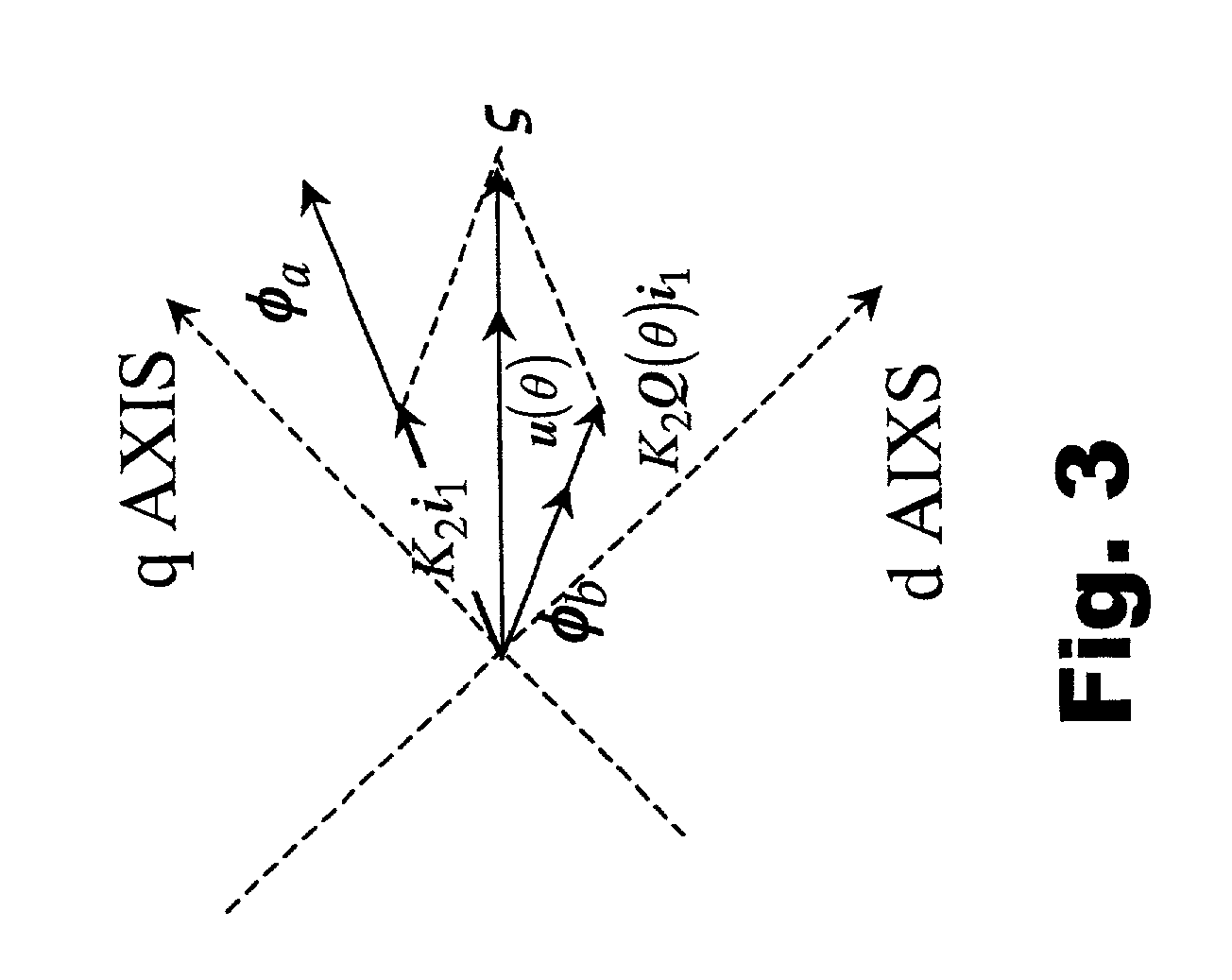
InactiveUS6339308B2Accurate and Efficient EstimationImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous reluctance motorControl vector
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators.A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Self-starting synchronous reluctance motor and rotor thereof
ActiveCN103208894ARaise the saliency ratioImprove efficiencySynchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsSynchronous reluctance motorInductance
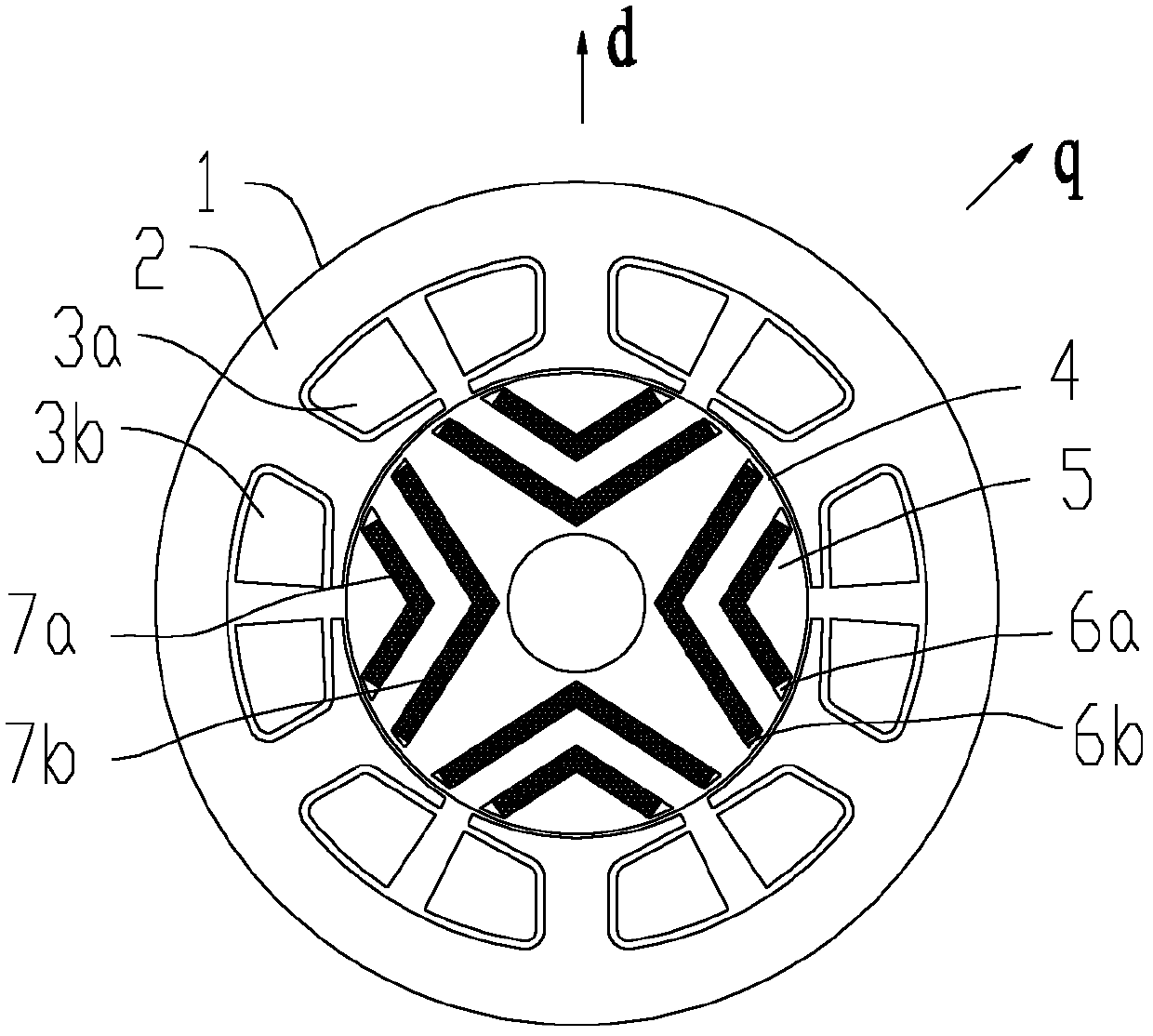
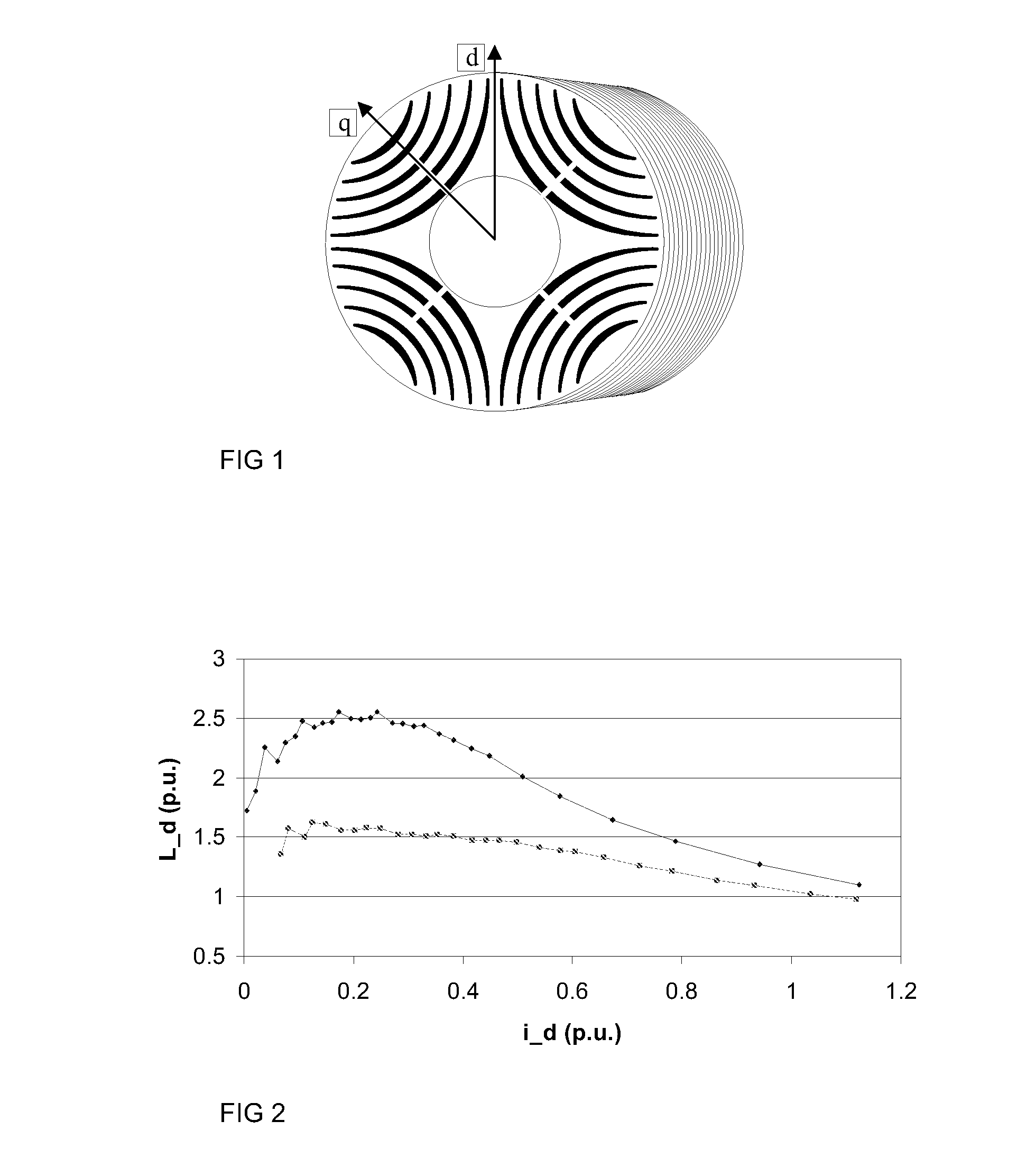
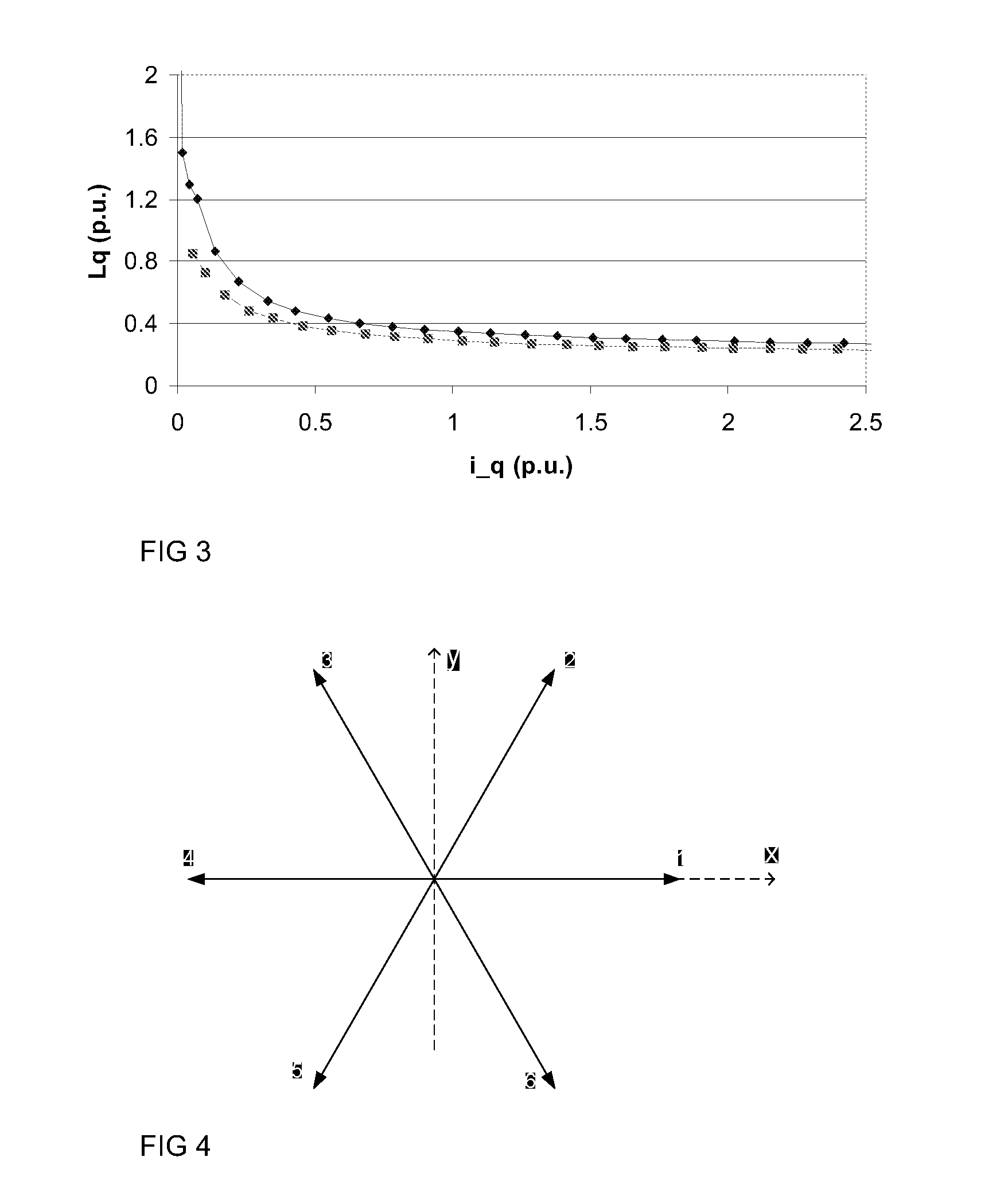
The invention provides a self-starting synchronous reluctance motor and a rotor thereof. The rotor of the self-starting synchronous reluctance motor comprises an iron core and squirrel-cage grooves, wherein magnetic flux separation grooves are arranged on the iron core, and the squirrel-cage slots are distributed along the periphery of the iron core. In the cross section of the rotor, the center line of the cross sections of the squirrel-cage slots deviates from the center circle of the iron core. The self-starting synchronous reluctance motor comprises a stator and the rotor of the self-starting synchronous reluctance motor. According to the self-starting synchronous reluctance motor and the rotor, the center line of the cross sections of the squirrel-cage grooves is led to deviate from the center circle of the iron core by adjusting the angle of the squirrel-cage grooves arranged on the rotor, magnetic permeability in the direction of the D axis is improved, magnetic permeability in the direction of the Q axis is reduced, inductance Ld in the direction of the D axis is increased and inductance Lq in the direction of the Q axis is reduced, namely salient pole ratio (Ld / Lq) of the motor is improved, and further motor efficiency is improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
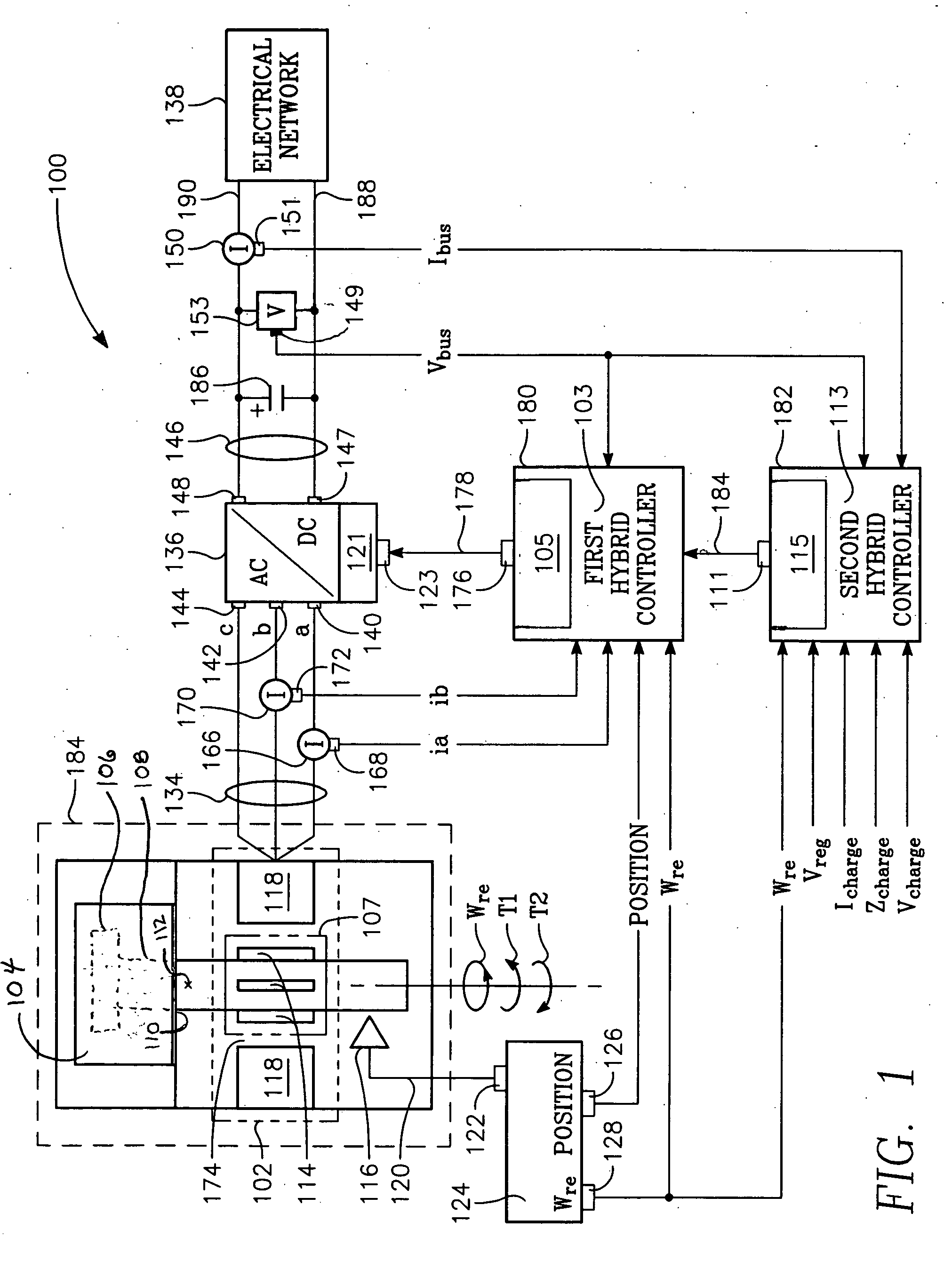
Feedforward controller for synchronous reluctance machines
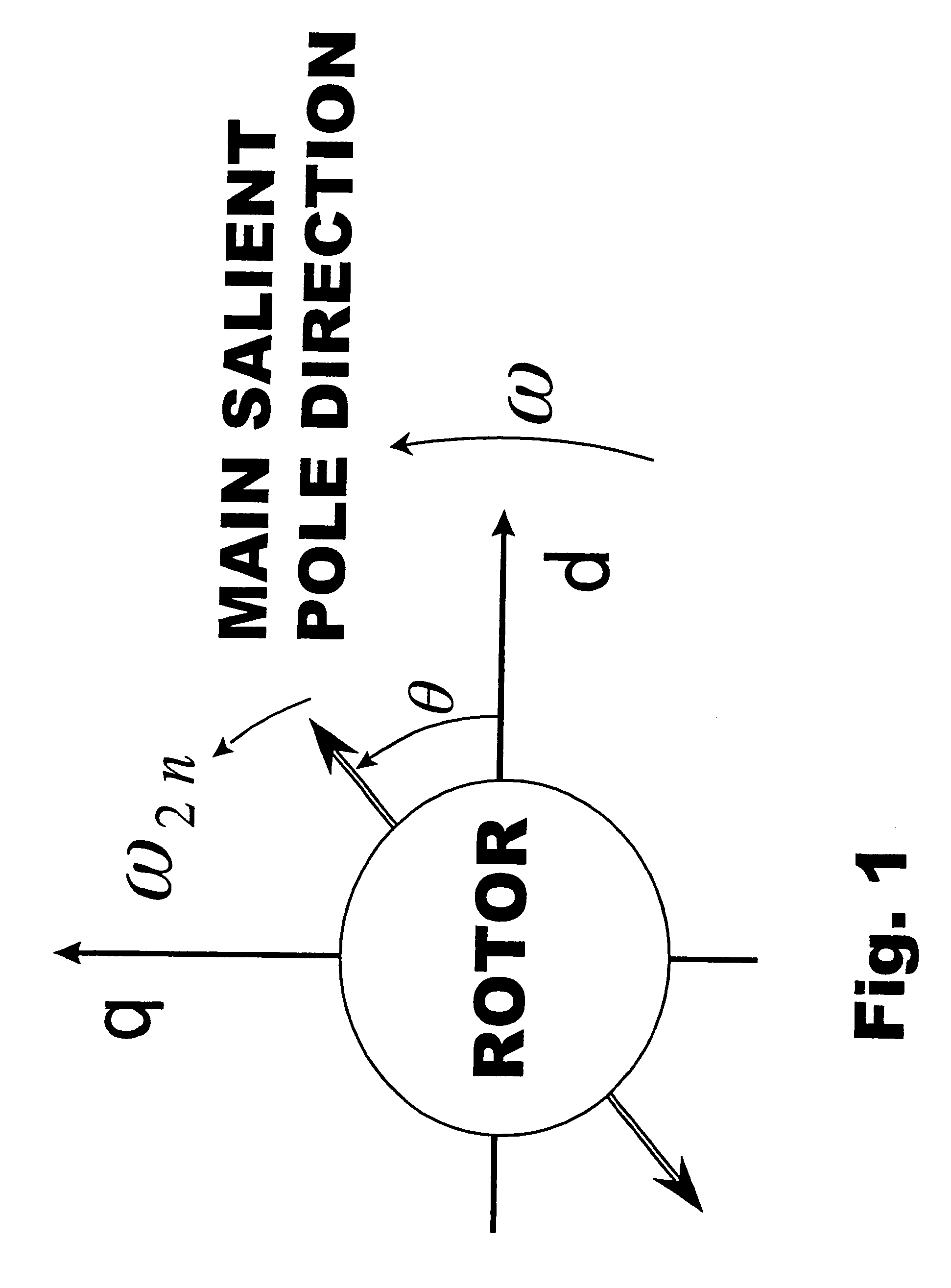
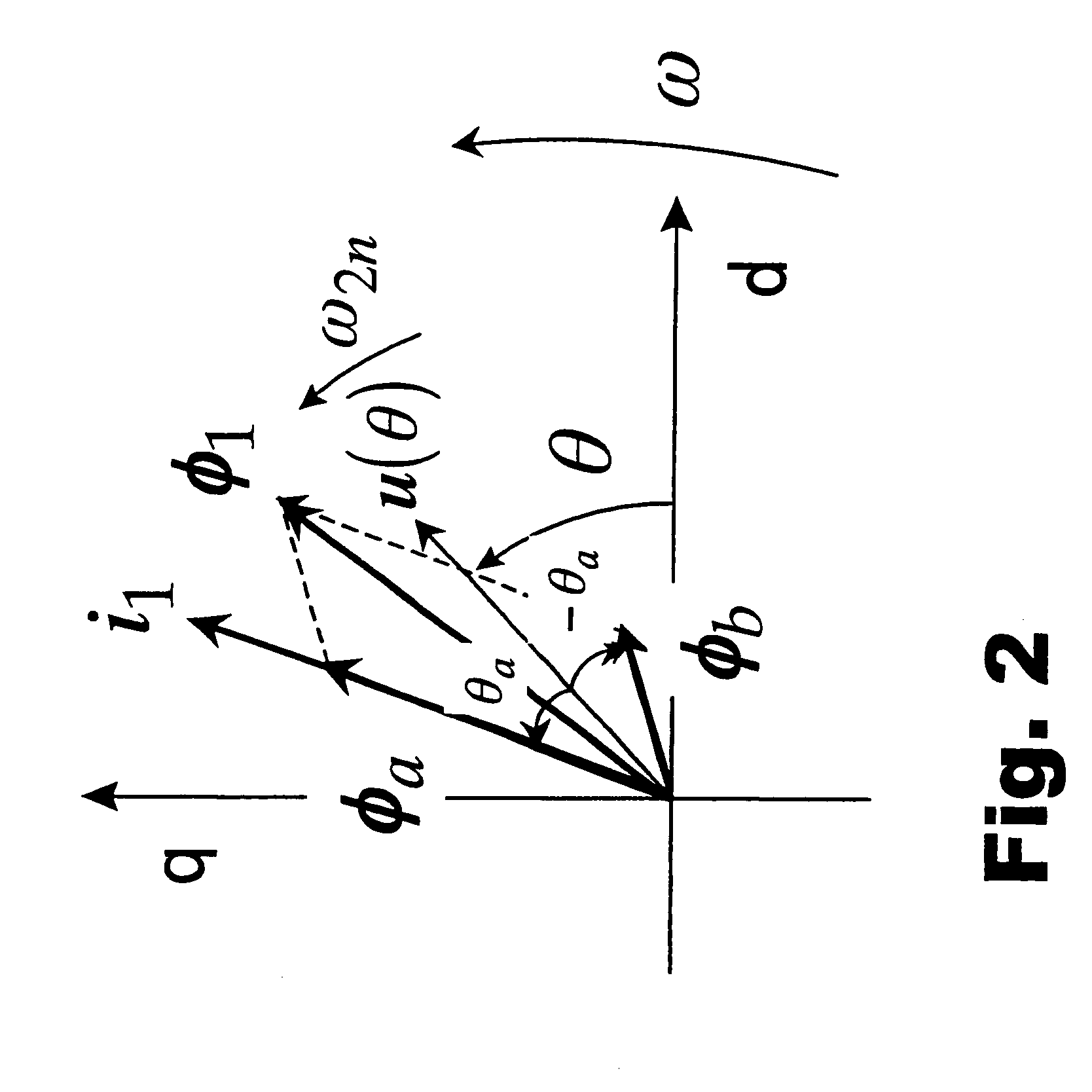
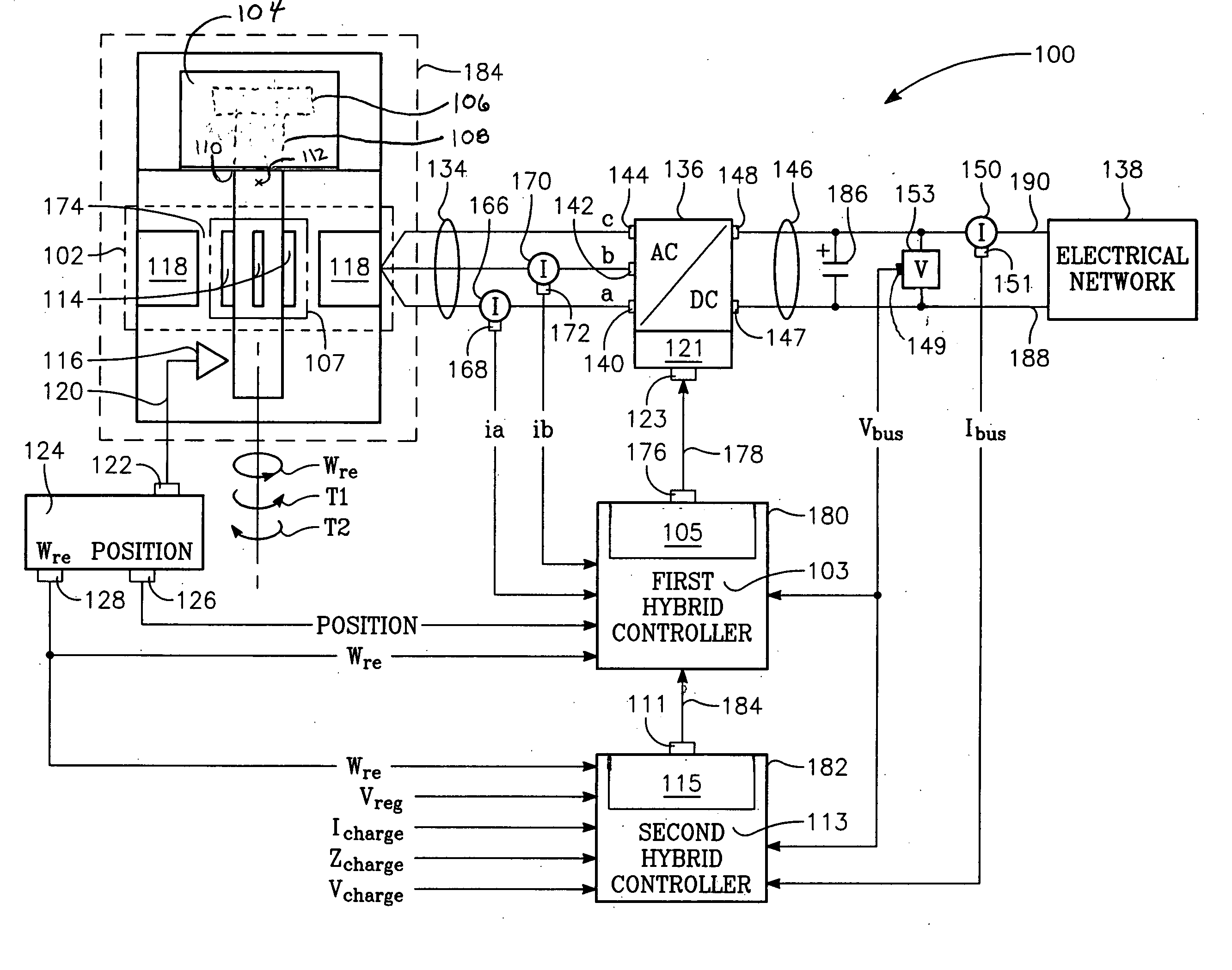
ActiveUS20050007061A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlSynchronous reluctance motorVoltage regulation
The present invention provides an electromechanical energy exchange system with a variable speed synchronous reluctance motor-generator having an all-metal rotor. A bi-directional AC-to-DC electric power converter interconnects the motor-generator with a DC bus. First and second hybrid controllers provide current regulation for the motor-generator and voltage regulation for the DC bus. Use of both feedback and feedforward control elements provides a controller particularly suited for operating high speed devices.
Owner:BEAVER AEROSPACE & DEFENSE
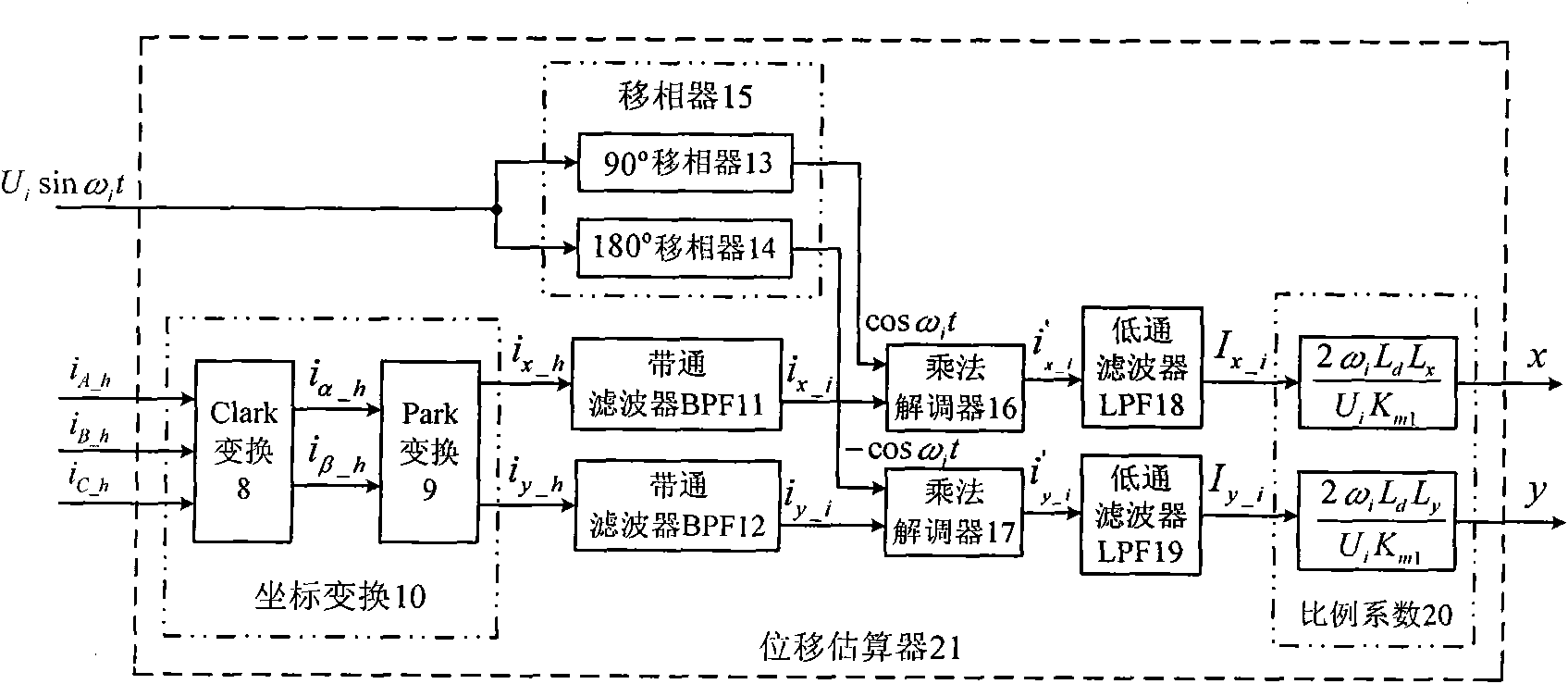
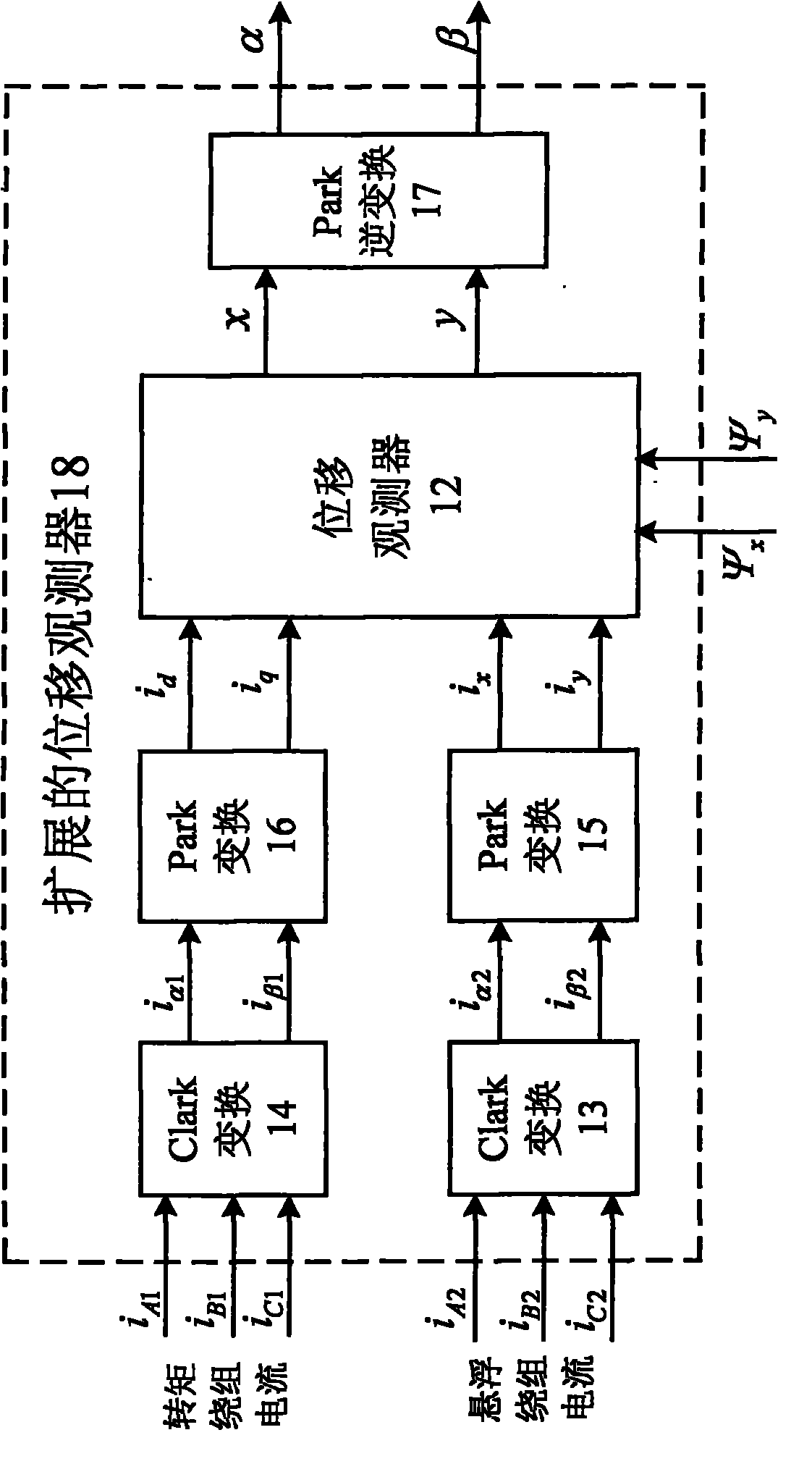
Displacement estimation method of bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor, method and device for controlling displacement-free sensor
InactiveCN101777862AEasy to detectAchieve estimatesElectronic commutatorsBandpass filteringSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention relates to a displacement estimation method of a bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor, comprising the following steps: constructing a band-pass filter BPF: sending coordinate- transformed suspension winding three-phase detection current into the band-pass filter BPF; extracting suspension winding high frequency induction current ix_i and iy_i through the BPF; then constructing a multiplication demodulator: taking the ix_i and iy_i as a first input signal of the multiplication demodulator; constructing a phase shifter, taking pulsation high-frequency voltage signal ud_i having gone through phase shift as a second input signal of the multiplication demodulator; obtaining I' and I signal after demodulation computation is carried out on the two input signals by the multiplication demodulator; then filtering high-frequency component of the I' and I' signal by a low-pass filter LPF, finally obtaining current components comprising rator radial displacement; afterwards multiplying corresponding scale factor to obtain estimated value of the radial displacement of a controller electric machine rator. With the method and the device for controlling the displacement-free sensor, the displacement sensor is not needed and a DSP is adopted to control an electrical machine with the assistance of a software.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
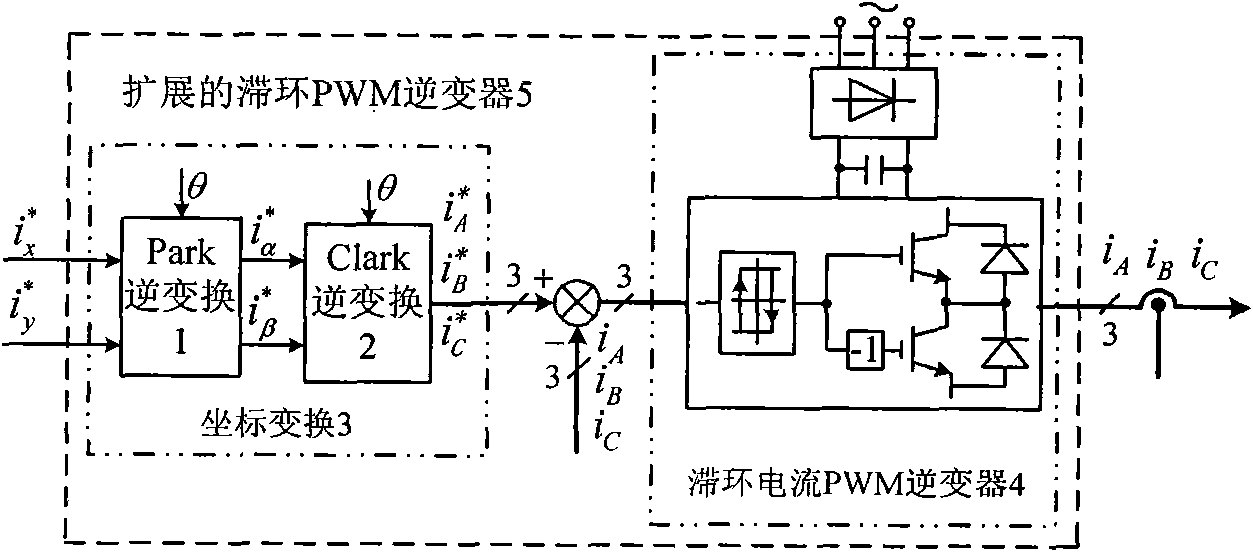
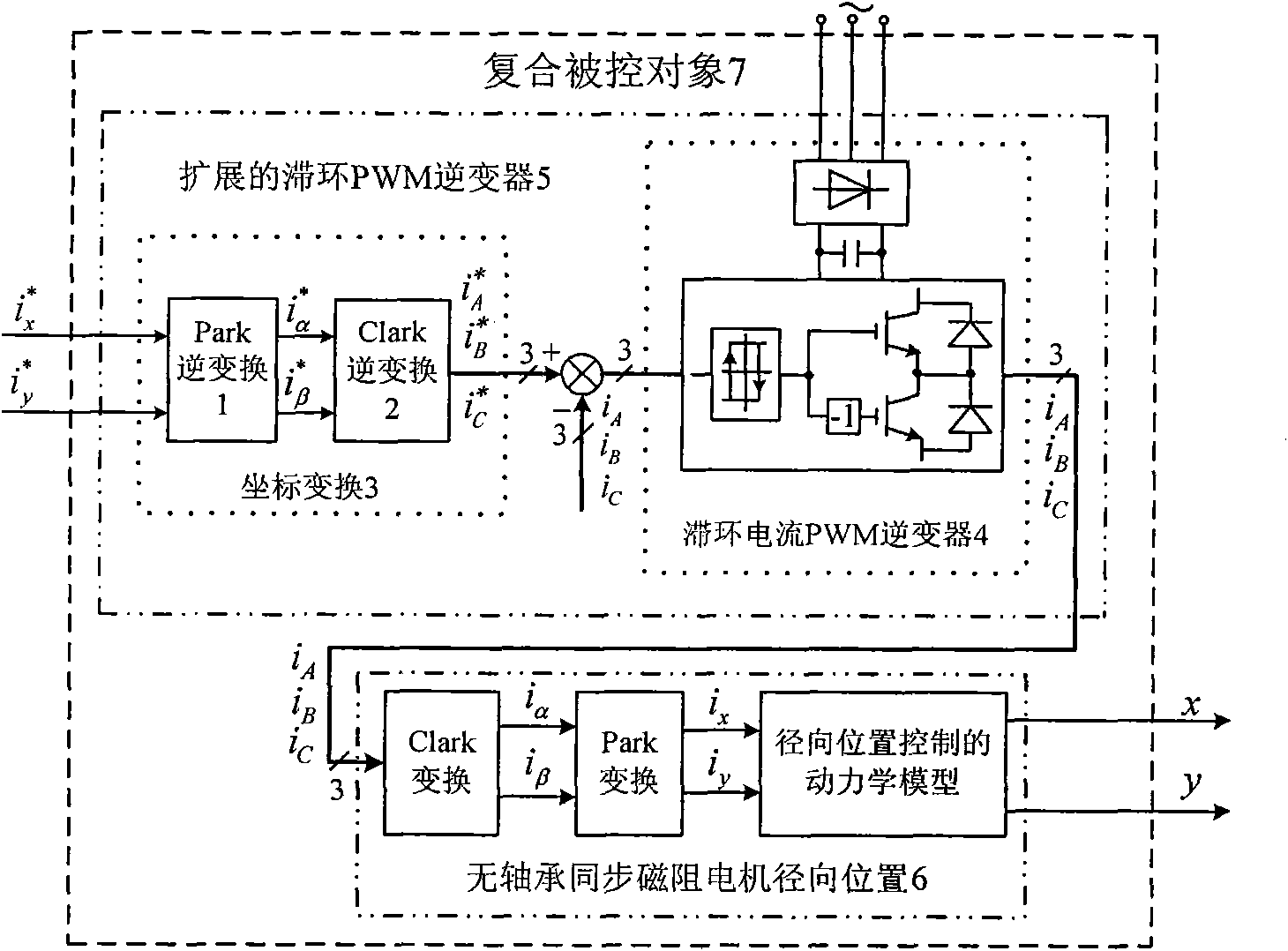
Support vector machine inverse system composite controller based on bearingless synchronous reluctance motor
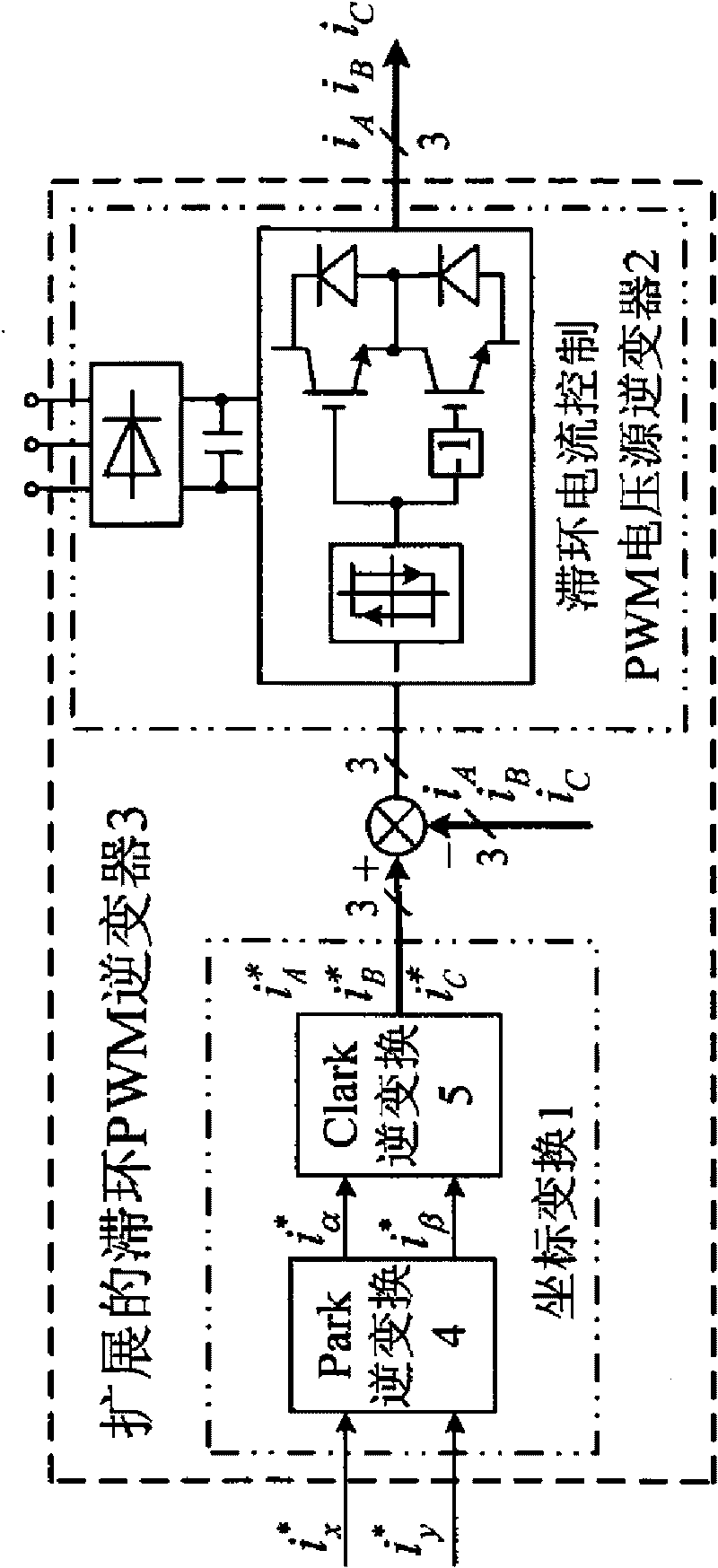
InactiveCN101814892AAchieve independent controlSimple structureAC motor controlVector control systemsHysteresisSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention relates to a support vector machine inverse system composite controller based on a bearingless synchronous reluctance motor. Two expandable current hysteresis loop PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) inverters and a bearingless synchronous reluctance motor to be controlled are used as a whole to form a composite object to be controlled; a support vector machine inverse system controller is constructed according to a mathematical model of the object to be controlled and is connected in series before the composite object to be controlled of the bearingless synchronous reluctance motor so as to realize the decoupling control between the electromagnetic torque and the radial levitation force of the motor as well as the radial levitation force in two vertical directions; on the basis, a rotating speed closed loop linear controller and two rotor position closed loop linear controllers are respectively designed for the rotating speed of the motor and the rotor positions to form a linear closed loop controller; an finally the linear closed loop controller, the support vector machine inverse system controller and two expandable current hysteresis loop PWM inverters commonly form the support vector machine inverse system composite controller for dynamically decoupling control on the bearingless synchronous reluctance motor. The control speed, the control precision and the dynamic and static performances of the system can pass parameters for adjusting the linear closed loop controller.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveCN107994698APrevent the risk of high temperature demagnetizationImprove securityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsSynchronous reluctance motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a 2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor, and relates to the field of the synchronous reluctance motor. At current, the reluctance motor can be only in operation by being equipped with a special controller, and needs a large number of rare earth permanent magnet material, so that the cost is high. The 2-magnetic-pole controller-free self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor comprises a machine base, a front end cover, a back end cover, a front bearing, a front bearing inner cover,a back bearing, a back bearing inner cover, a line stator, a rotor iron core, a rotary shaft, a bottom foot, a fan blade and a fan cover; the rotor iron core is formed by multiple iron core stampingsheets with two magnetic poles in an overlaying manner; rotary shaft holes are formed in the centers of the iron core stamping sheets; the two magnetic poles both comprise radially arranged reluctancegrooves of the same number; a fan-shaped permanent magnet is arranged in the middle of each reluctance groove; and an aluminum cast mouse cage is arranged on the periphery, on the outer sides of thereluctance grooves of the iron core stamping sheets, of the rotor iron core. By virtue of a combination of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and the synchronous reluctance motor in the technical scheme, and by combination of the aluminum cast mouse cage, use of a permanent magnet material is reduced, and high operation also can be realized without a controller, so that the motor cost is obviously lowered.
Owner:WOLONG ELECTRIC GRP CO LTD
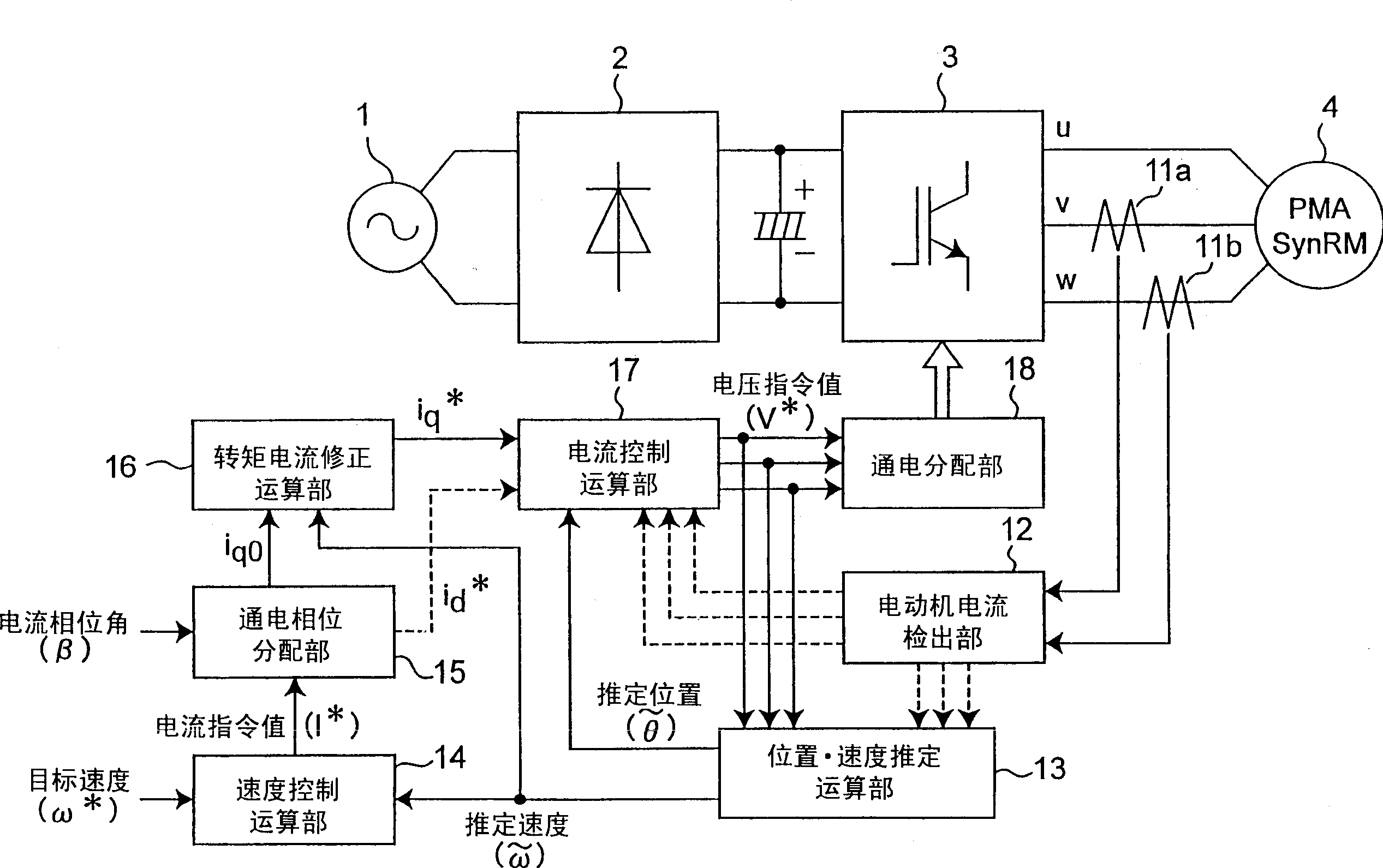
Synchronuos reluctance motor control device
InactiveCN1516918ASuppress changesReduce vibrationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlSynchronous reluctance motorLoad torque
A control apparatus of a synchronous reluctance motor includes a torque current correction unit (16) that generates a torque current command tracing a load torque so as to make the output torque of the motor coincide with the load torque. the control apparatus may further include a position and speed estimation unit (13) that estimates the position and speed based on three phase voltage equation to improve control performance in a voltage saturation state.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Vector control method for synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveUS20010024100A1Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl vectorSynchronous reluctance motor
In a driving control method for a synchronous reluctance motor, a novel vector control method is employed which does not need the salient pole position angle detector. More particularly, the present invention provides a vector control method which can accurately and efficiently estimate cosine and sine signals, being rotation signals for the vector rotators. A flux vector estimator 12a uses voltage and current information of a stator to estimate a stator flux vector by dividing it into an in-phase flux vector having the same direction as a current vector and a mirror-phase flux vector determined as a difference between the stator flux vector and the in-phase flux vector. A cosine and sine generator 12b uses the estimated in-phase and mirror-phase flux vectors to generate the cosine and sine values of an intermediate angle of the angles of such flux vectors and outputs a rotation signal of the vector rotators. Thus, vector control is established.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Synchronous induction motor and electric hermetic compressor using the same
ActiveUS7071650B2Single-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlElectrical conductorSynchronous reluctance motor
A synchronous induction motor has a stator having a main winding and an auxiliary winding; a rotor having a yoke, a permanent magnet embedded in the yoke and a secondary conductor provided in the vicinity of periphery of the yoke; and a starter. The starter has a starting capacitor connected in series with the auxiliary winding of the synchronous induction motor, and a switching unit to open / close a circuit from the starting capacitor to the auxiliary winding. The switching unit closes the circuit from the starting capacitor to the auxiliary winding when the synchronous induction motor is at rest, and opens the circuit after the synchronous induction motor is started. The synchronous induction motor is highly efficient and easy to re-start with low power consumption. The electric hermetic compressor equipped with the synchronous induction motor can perform with the similar effects.
Owner:PANASONIC APPLIANCES REFRIGERATION DEVICES SINGAPORE
Permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and mounting method thereof
ActiveCN102761221AImprove efficiencyImprove utilizationManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSynchronous reluctance motorMagnetic poles
The invention provides a permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor and a mounting method thereof. The permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor comprises a stator and a rotor, wherein the stator comprises a stator iron core and a concentrated winding, and the stator iron core comprises a plurality of convex magnetic poles; the convex magnetic poles comprise magnetic pole teeth and tooth boots, and the widths of the tooth boots are larger than the widths Lc of the magnetic pole teeth; the rotor comprises a rotor iron core and a plurality of permanent magnet groups, and a plurality of permanent magnet slot groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron cores; each permanent magnet slot group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnet slots, and each permanent magnet group comprises a permanent magnet arranged in a corresponding permanent magnet slot; the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet slot group have the same polarity, and the polarities of two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite; and a relation between a minimum interlayer distance g between two adjacent layers of permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group and the widths T of the tooth boots is disclosed in the specification. According to the permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor, the reluctance torque is maximally utilized, so that the efficiency of the motor reaches a higher level.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Method and arrangement for determining inductances of synchronous reluctance machine
ActiveUS20120123715A1Vector control systemsInductance measurementsSampling instantElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and an arrangement of determining inductances of a synchronous reluctance machine are provided. The method includes supplying a voltage pulse in the quadrature-axis or direct-axis direction of rotor, sampling currents generated by the supplied voltage pulse, and calculating values of flux at the sampling instants from the value of the supplied voltage pulse, the sampled current values and a value of the stator resistance. The method also includes calculating synchronous inductance of the machine by dividing the calculated flux values by the corresponding sampled currents, and / or calculating transient inductance of the machine as a derivative of the flux with respect to current, and storing the calculated values as a function of current.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
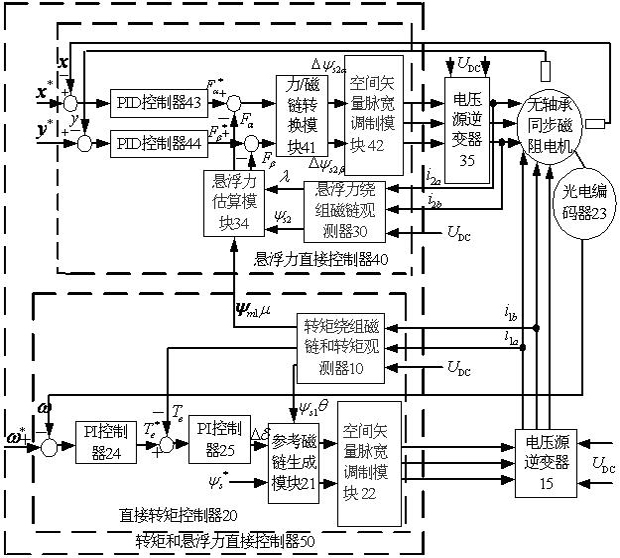
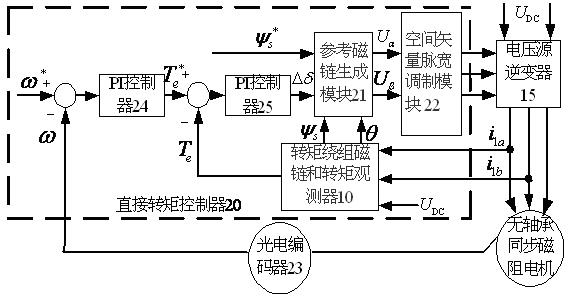
Bearingless synchronous reluctance motor torque and suspension force direct controller and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102082544AGuaranteed uptimeEasy to control independentlyElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSynchronous reluctance motorClassical mechanics
The method discloses a bearingless synchronous reluctance motor torque and suspension force direct controller and a construction method thereof. The bearingless synchronous reluctance motor torque and suspension force direct controller consists of a direct torque controller with a rotating speed and torque double closed loop and a suspension force direct controller with a rotor displacement and suspension force double closed loop, wherein the direct torque controller consists of two proportional plus integral (PI) controllers, a torque winding flux linkage and a torque observer, a reference flux linkage generating module and a space vector pulse width modulation module; and the suspension force direct controller consists of two proportional plus integral plus derivative (PID) controllers, a torque winding flux linkage and torque observer, a suspension force winding flux linkage observer, a suspension force estimation module, a force / flux linkage conversion module and a space vector pulse width modulation module. By the controller and the construction method, motor torque and radial suspension force are independently controlled, stable suspension and operation of a motor rotor are ensured and high motor operating performance is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor and motor thereof and installation method of motor
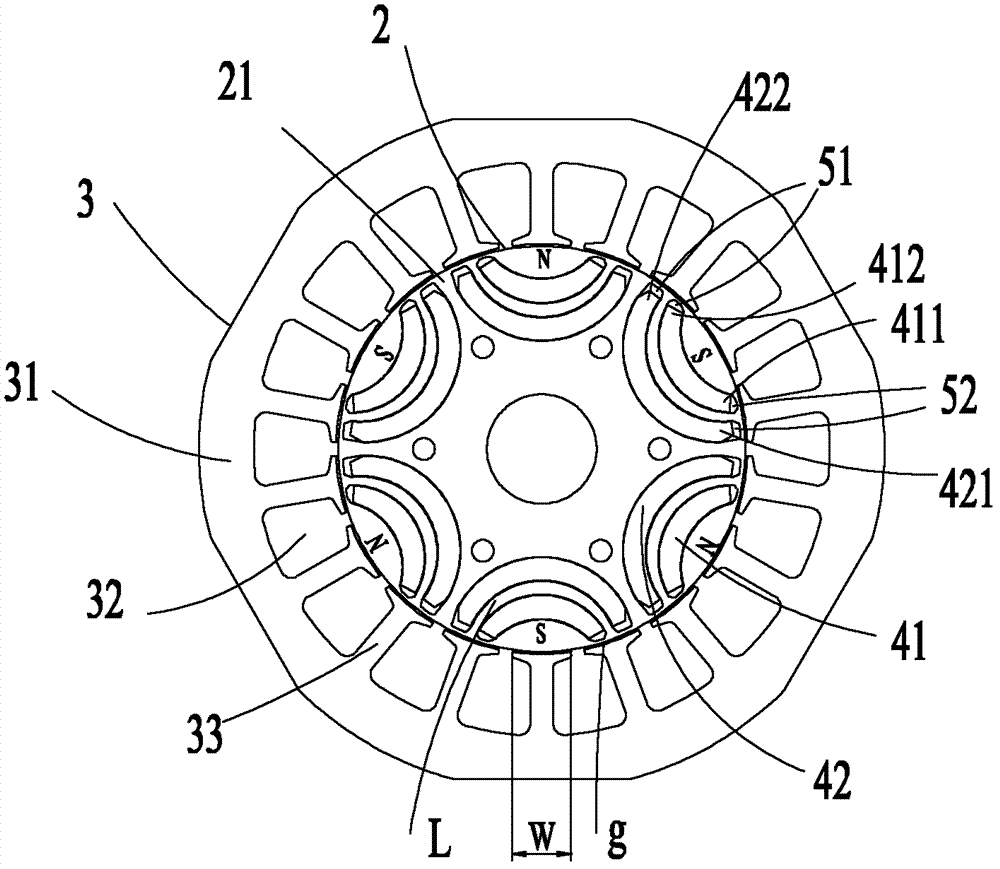
InactiveCN102790457AImprove operational reliabilityImprove resistance to demagnetizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorReluctance motor
The invention provides a permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor, a motor thereof and an installation method of the motor. The permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor comprises a rotor iron core and a plurality of permanent magnet groups, a plurality of permanent magnet groove groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron core with rotor axis serving as a circle centre in a peripheral direction, each permanent magnet groove group comprises a single layer or multilayer of permanent magnet grooves, the number of the permanent magnet groups is identical to that of the permanent magnet groove groups, each permanent magnet group comprises a single layer or multilayer of permanent magnets which are respectively embedded into the permanent magnet grooves of the corresponding permanent magnet groove groups, the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group have the same polarity, the polarities of the two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite, the end portion of at least one layer of permanent magnet groove in the plurality of permanent magnet groove groups is a sharpened end provided with a cutting face, and width T of the sharpened end cutting face of a permanent magnet groove with the sharpened end and middle width W meet the following relation. By means of the motor rotor, the motor thereof and the installation method of the motor, the whole demagnetization resistant capacity and operation reliability of the motor are improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor which can be used in high-speed situation
ActiveCN104901452ASafe high-speed operation capabilityMaximize output capacityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic barrierSynchronous reluctance motor
The present invention discloses a permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor which can be used in a high-speed situation. The permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor comprises a rotor core, magnetic barriers distributed on the rotor core and magnetic steels arranged in the magnetic barriers. Four layers of ship-shaped magnetic barriers are distributed under each pole of the rotor core, and each layer of magnetic barriers is formed by the connection closing of a straight line part which is in the middle and is perpendicular to a d axis direction and oblique straight line parts which are at two ends and are in an alpha angle direction with the d axis. According to the permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor rotor, the optimal design of the motor rotor is carried out, and thus a motor has the advantages of high efficiency, high torque density, high power factor, strong anti-demagnetization ability and convenient manufacture.
Owner:SHANGHAI GIE EM
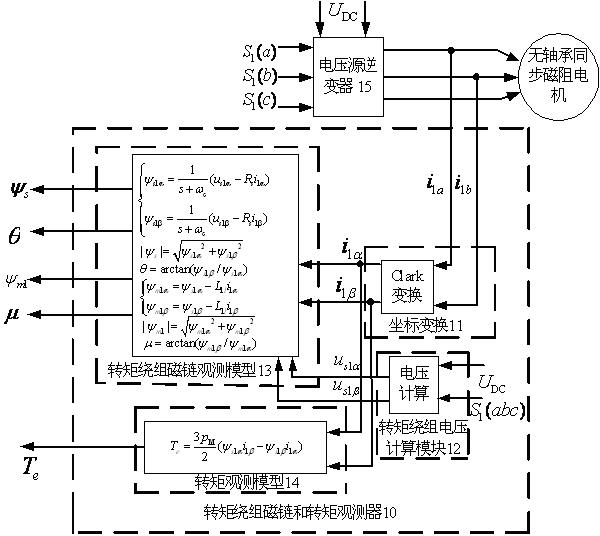
Bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor rotor displacement soft measurement and suspension system construction method
InactiveCN102158158ASimple structureLow costVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlElectricitySynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses a bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor rotor displacement soft measurement method, which comprises the following steps of: first establishing a back electromotive force model of a suspension winding of a motor, namely, performing coordinate transformation on three-phase detection current and voltage of the suspension winding, transmitting the transformed detection current and voltage into the back electromotive force model to generate back electromotive forces ealpha2 and ebeta2 of a stator; then constructing an expanded flux linkage observer of the suspension winding, namely, acquiring flux linkage observed values Psix and Psiy by taking the back electromotive forces as input signals of the expanded flux linkage observer; and finally constructing an expanded displacement observer, namely, performing the coordinate transformation on the three-phase detection current of a torque winding and the suspension winding by taking the flux linkage observed values Psix and Psiy as a first input signal of the expanded displacement observer, and finally acquiring the rotor displacement observed values alpha and beta under biphase stationary coordinates by taking the transformed detection current as second and third input signals of the expanded displacement observer. A bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor suspension system constructed by the method saves a displacement sensor, can realize a rotor displacement soft measurement technology and the high-speed and stable suspension running of a controlled motor, and has the advantages of simple structure, easily realized algorithm, quick dynamic response and the like.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
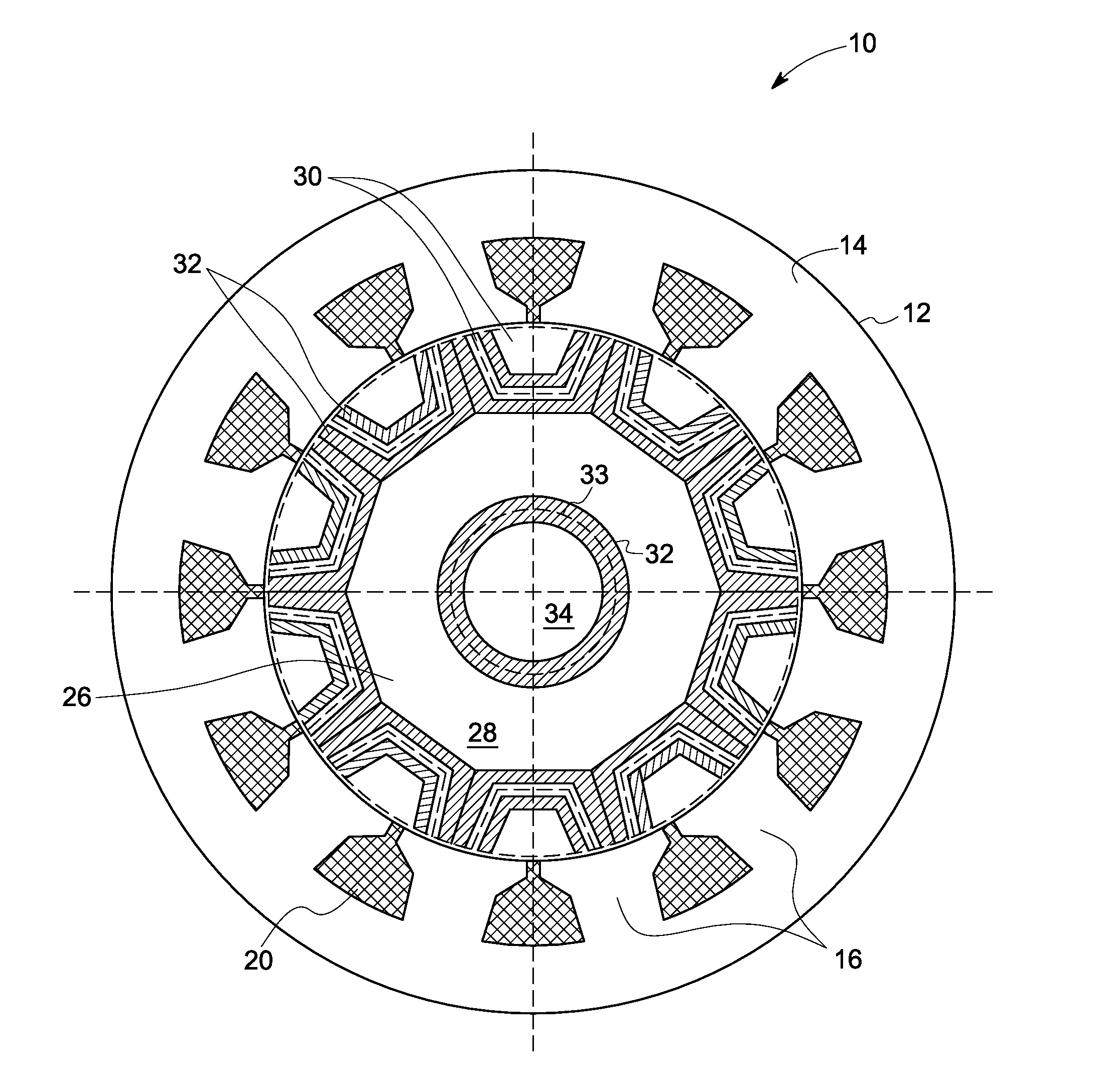
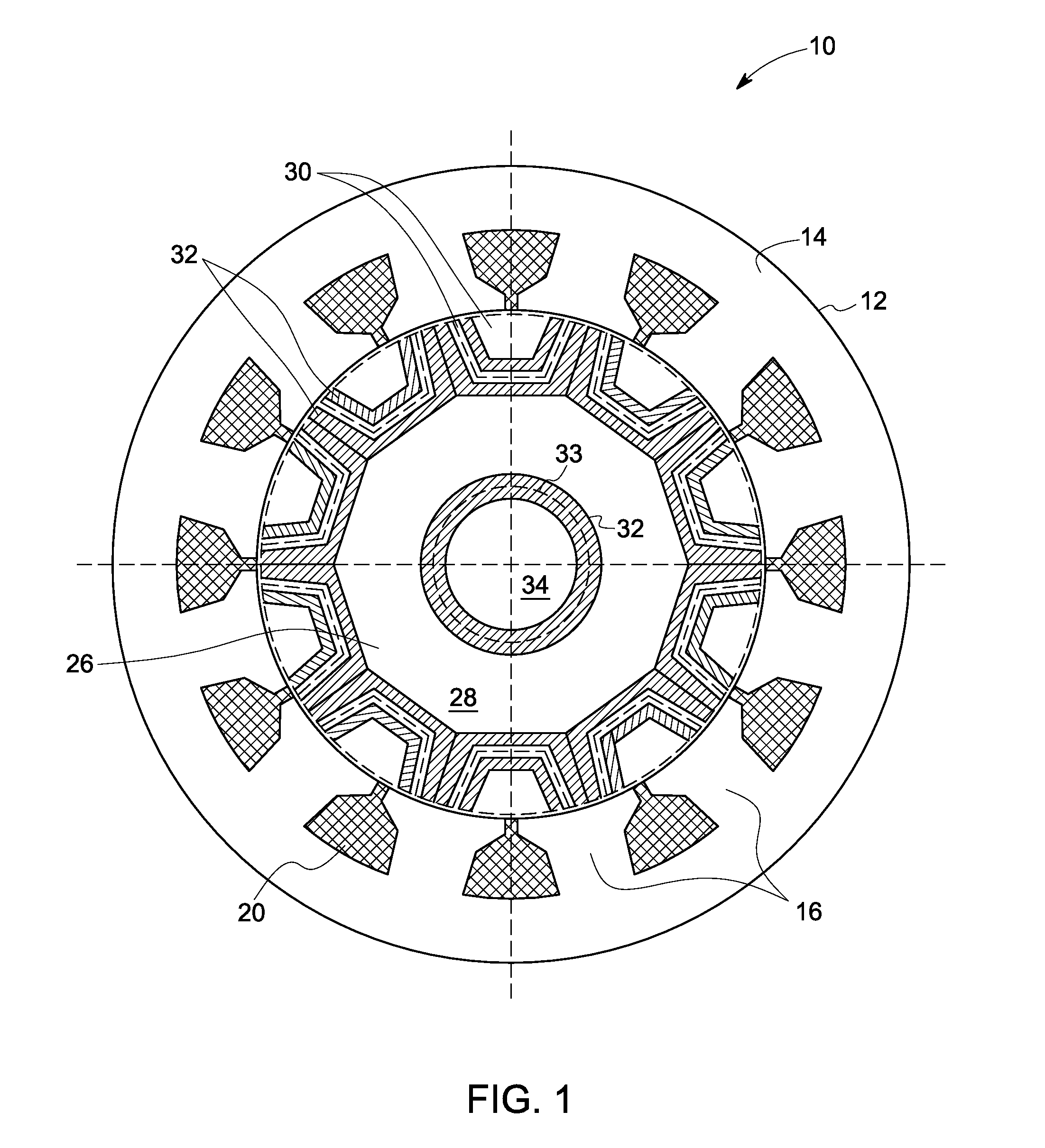
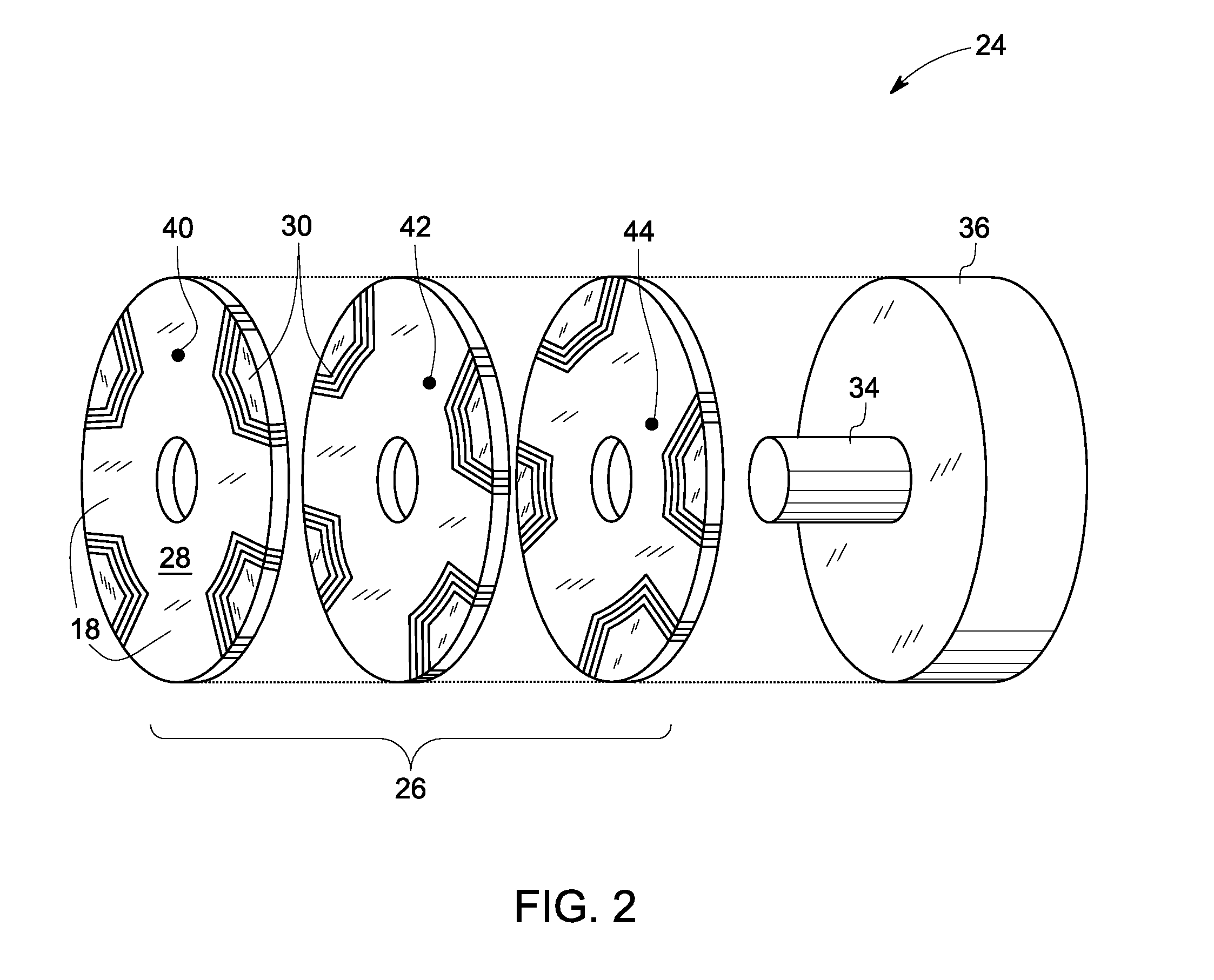
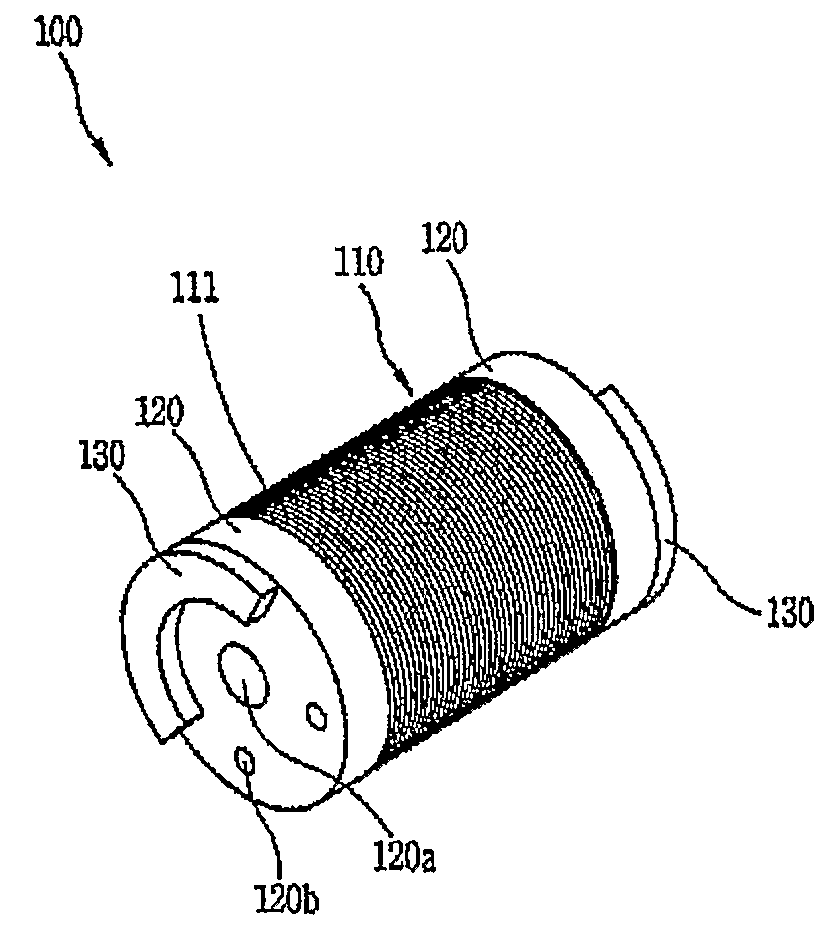
Synchronous reluctance machine with a novel rotor topology
InactiveUS7489062B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsCooling/ventillation arrangementSynchronous reluctance motorEngineering
A synchronous reluctance machine that has a stator and a rotor shaft operationally disposed within the confines of the stator. Laminations are axially stacked to form boat shaped segments. A plurality of selected boat shaped segments form a selected number of rotor poles about the rotor shaft and a plurality of support bars disposed intermittently between the boat shaped segments. Each segment of lamination is boat shaped with angular acuity facing towards the stator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for controlling startup of motor
ActiveUS7271562B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlVoltage generatorSynchronous reluctance motor
Disclosed is a method and device for controlling the startup of a synchronous reluctance motor. The device includes: a voltage injector which generates injection voltages to estimate an initial position of the rotor; a motor drive voltage generator which converts stationary-coordinate-system voltages including the injection voltages to three-phase motor drive voltages and applies the three-phase motor drive voltages to the motor; a current extractor which extracts response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages from two-phase stationary-coordinate-system currents converted from three-phase currents detected upon rotation of the motor; and a position / speed estimator which extracts response current components related to a rotor position from the response current components iα-inj, iβ-inj in respect to the injection voltages to calculate a rotor position error (e), and estimates the speed and position {tilde over (ω)},{tilde over (θ)} of the rotor from the calculated rotor position error (e).
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
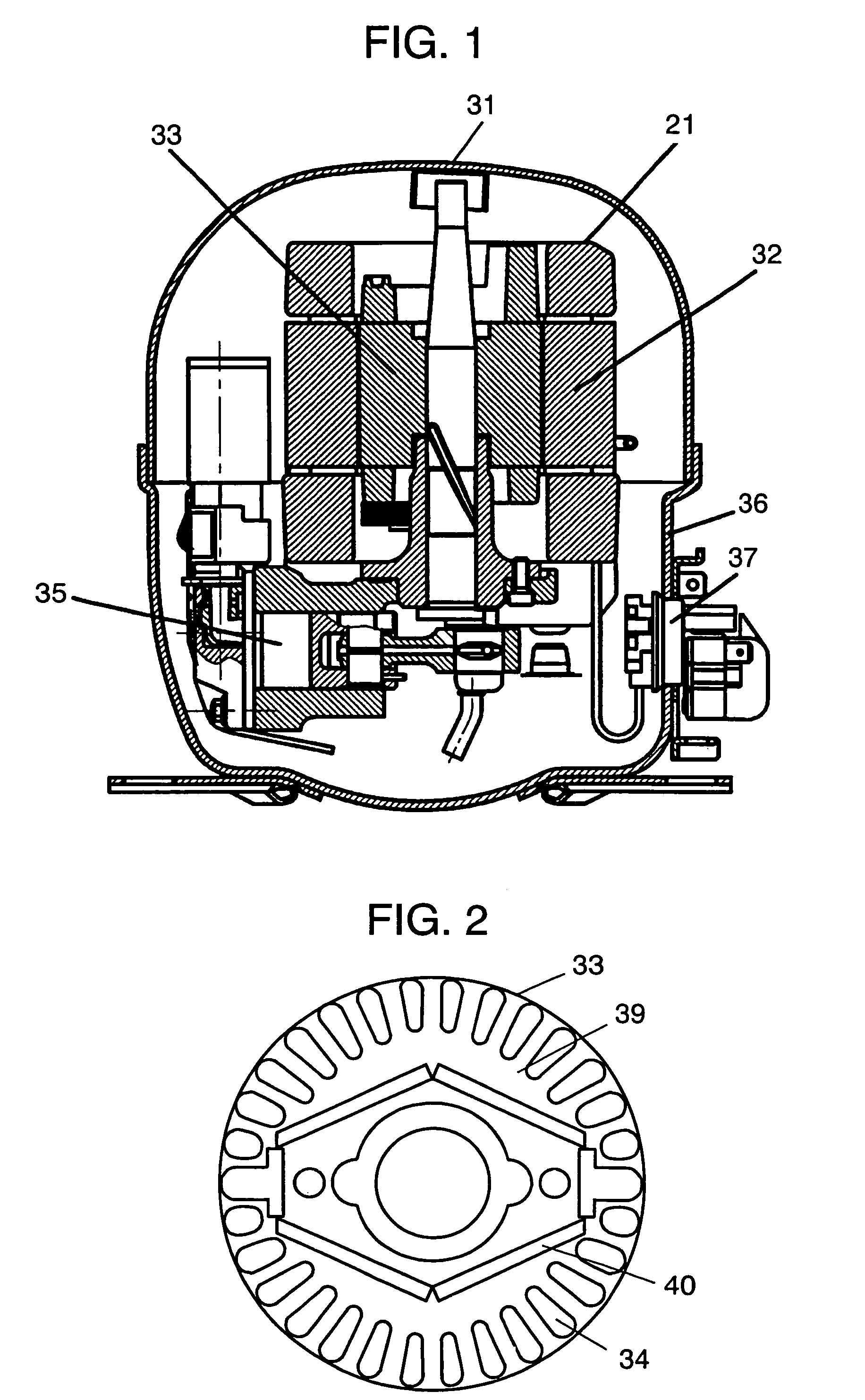
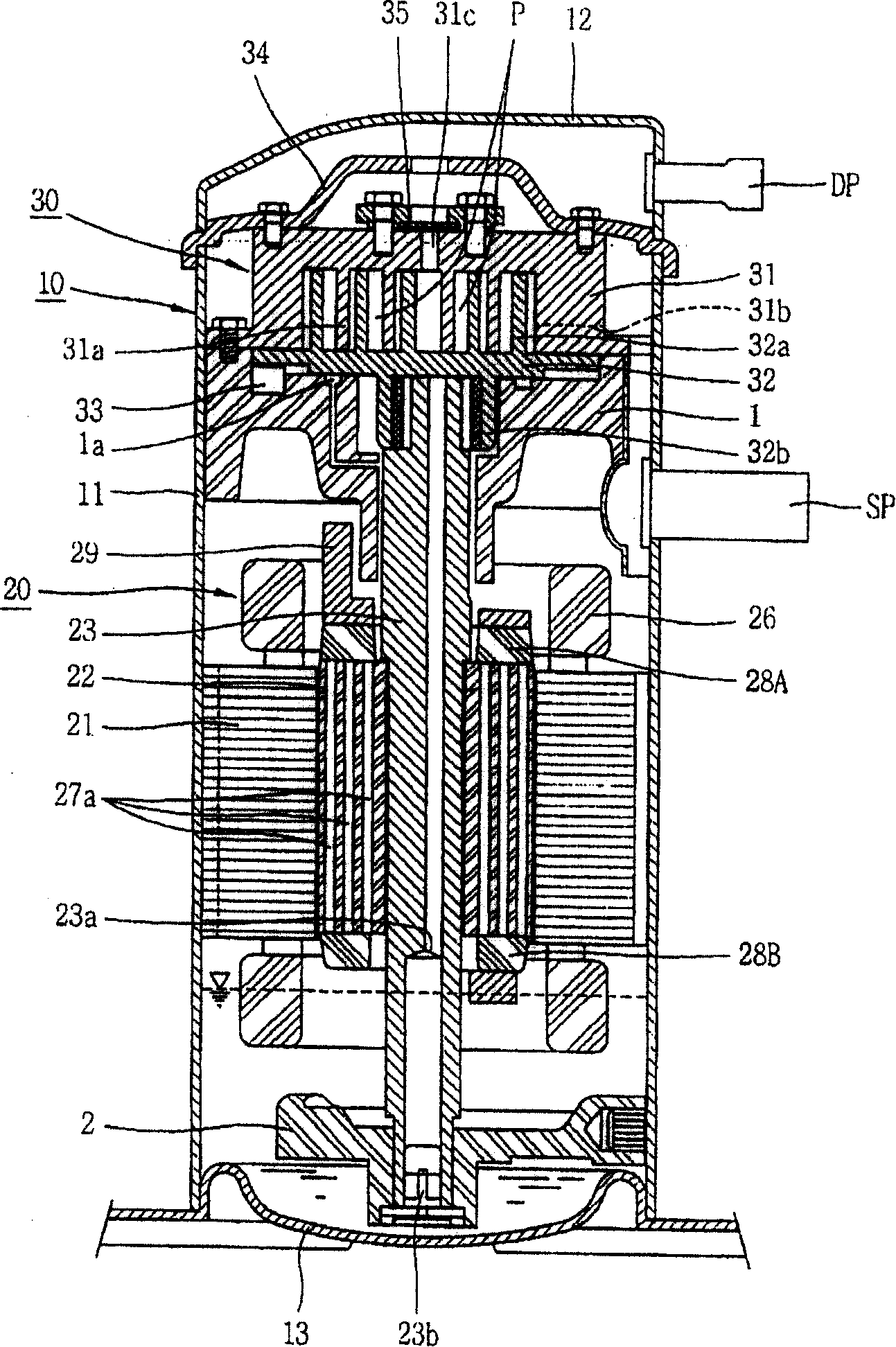
Compressor and air conditioner containing the same
InactiveCN101230856AMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous reluctance motorChlorofluorocarbon
The invention relates to a scroll compressor. When a freezing medium containing hydroflurocarbon (HFC) is used, fatty acid ester oil is used for smoothing. When a freezing medium containing hydrogen chlorofluorocarbon (HCFC) is used, fatty acid mineral oil is used for smoothing. A driving motor is a synchronous reluctance motor which is provided with a rotor comprising a plurality of flat laminated sheets. Each flat laminated sheet is provided with a plurality of magnetic flux barriers extending in directions of a circumference and a radius. An insulation film formed from a crystal plastic film is inserted between a winding and a motor stator, and the winding is formed from metal lines having an enamel coating. The characteristics cause the distortion of the driving motor to be reduced. In addition, the invention reduces wastage caused by the slippage of the driving motor, and reduces the heat wastage caused by the heat generation of the rotor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and device for inversely controlling fuzzy compensation of radial position of bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor
InactiveCN101741297AAchieve decouplingQuick responseAC motor controlVector control systemsHysteresisSynchronous reluctance motor
The invention discloses a method and a device for inversely controlling the fuzzy compensation of the radial position of a bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor, which is suitable for the suspension operation control of the bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor. The control method comprises: forming a composite controlled object by using an expanded hysteresis loop PWM inverter and the radial position of a controlled motor; reconstructing an inverse system of the composite controlled object; connecting the inverse system before the composite controlled object in series to compound a pseudo linear system consisting of two radial position subsystems; and designing a closed-loop fuzzy compensator for the pseudo linear system to perform decoupling control of the radial position of the controlled motor. The control device comprises the inverse system, the closed-loop fuzzy compensator and the expanded hysteresis loop PWM inverter. The method and the device are used for building a novel decoupling control device of the bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor to realize the high-performance suspension control of the motor and are widely used in alternating current power transmission and servo systems using the bearing-free synchronous reluctance motor as a power device, have a simple control system algorithm, have the advantage of high load disturbance resistance and have high dynamic and static adjustment performance.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF INFORMATION TECH
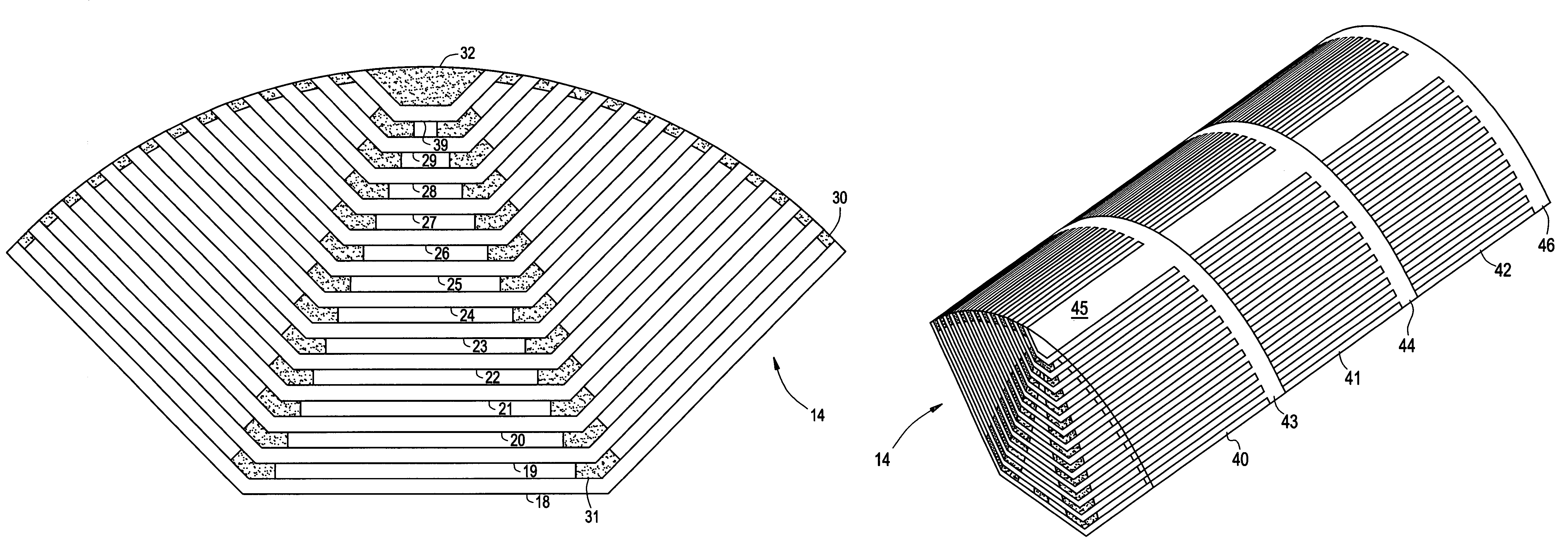
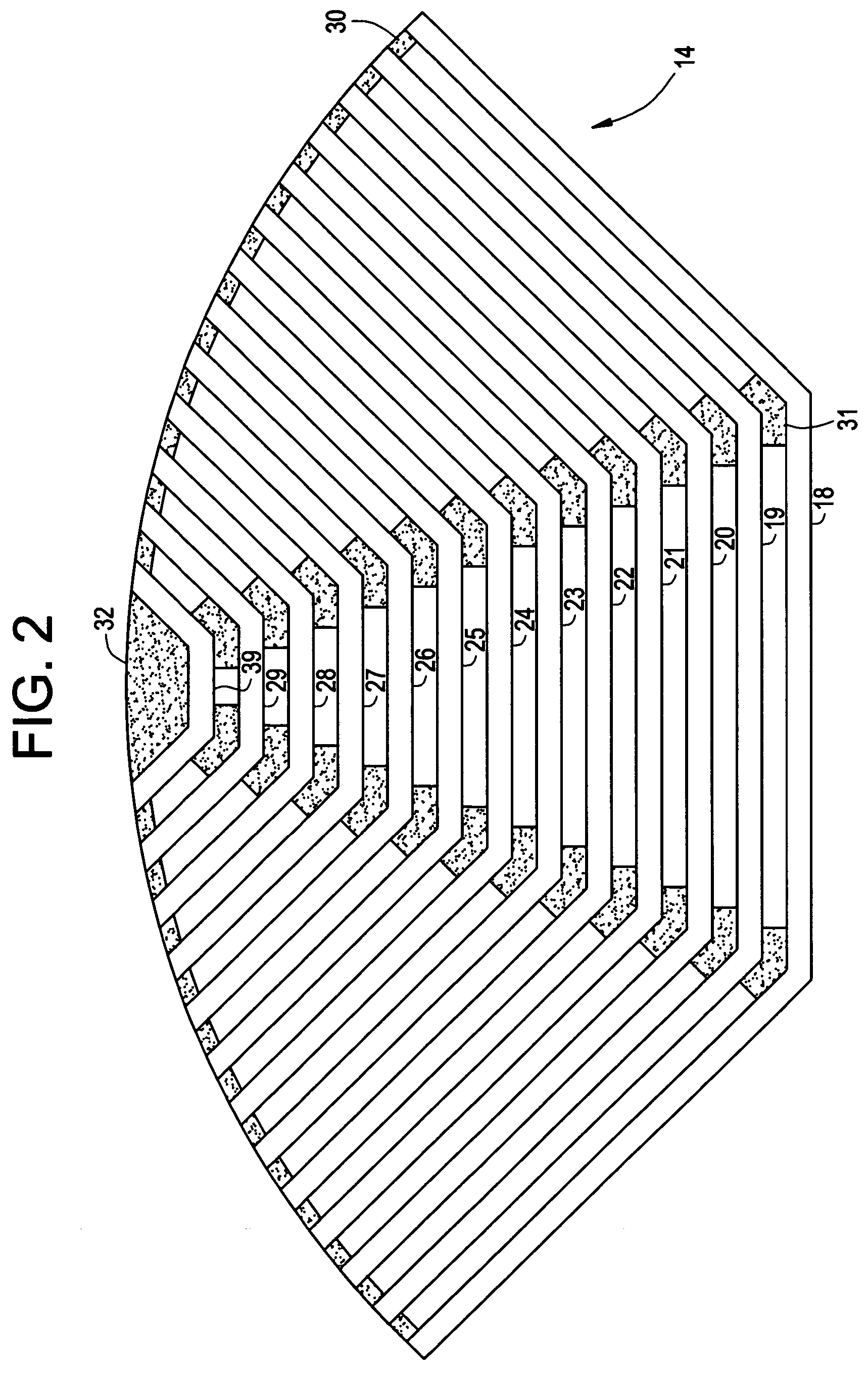
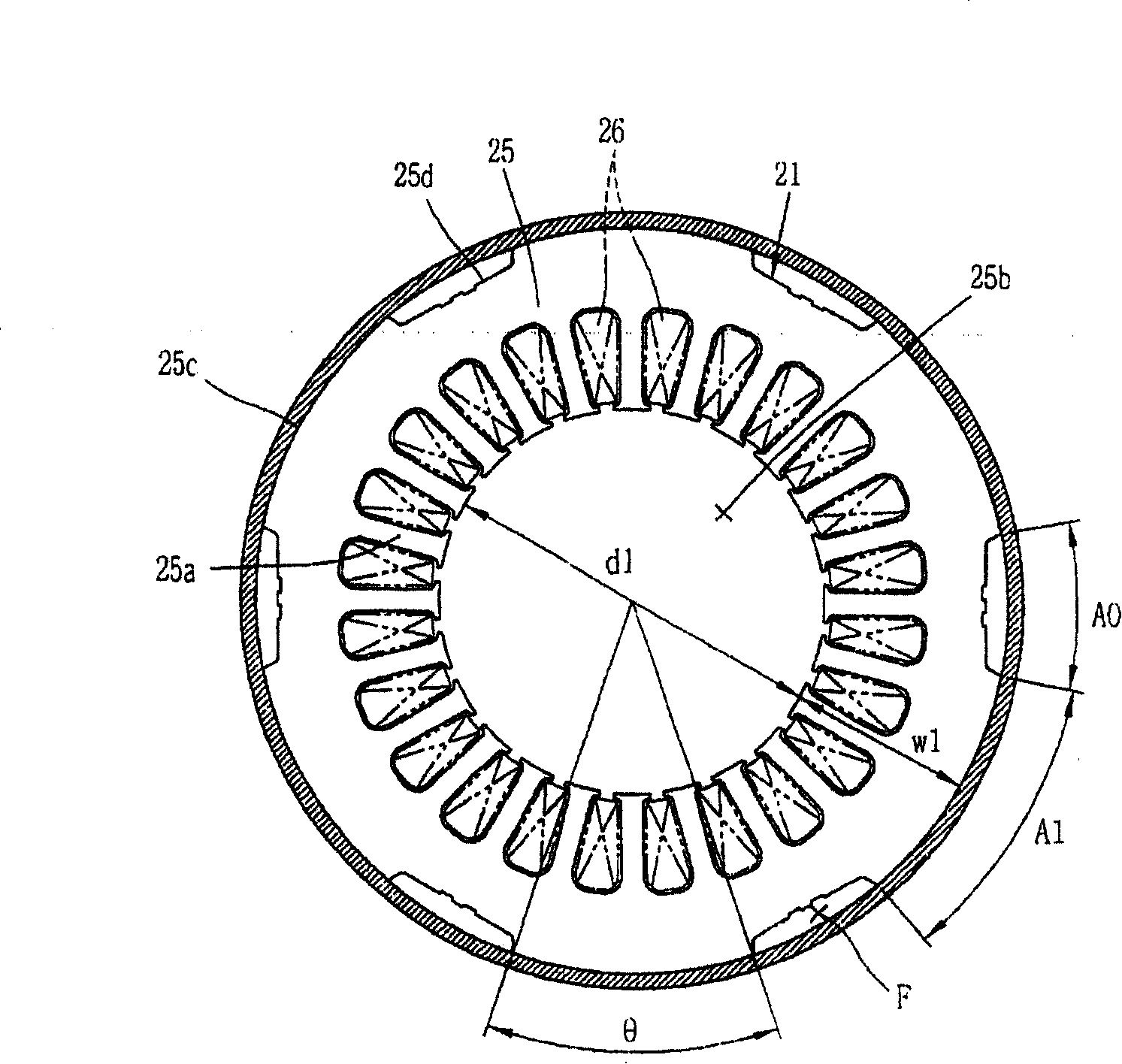
Synchronous reluctance motor
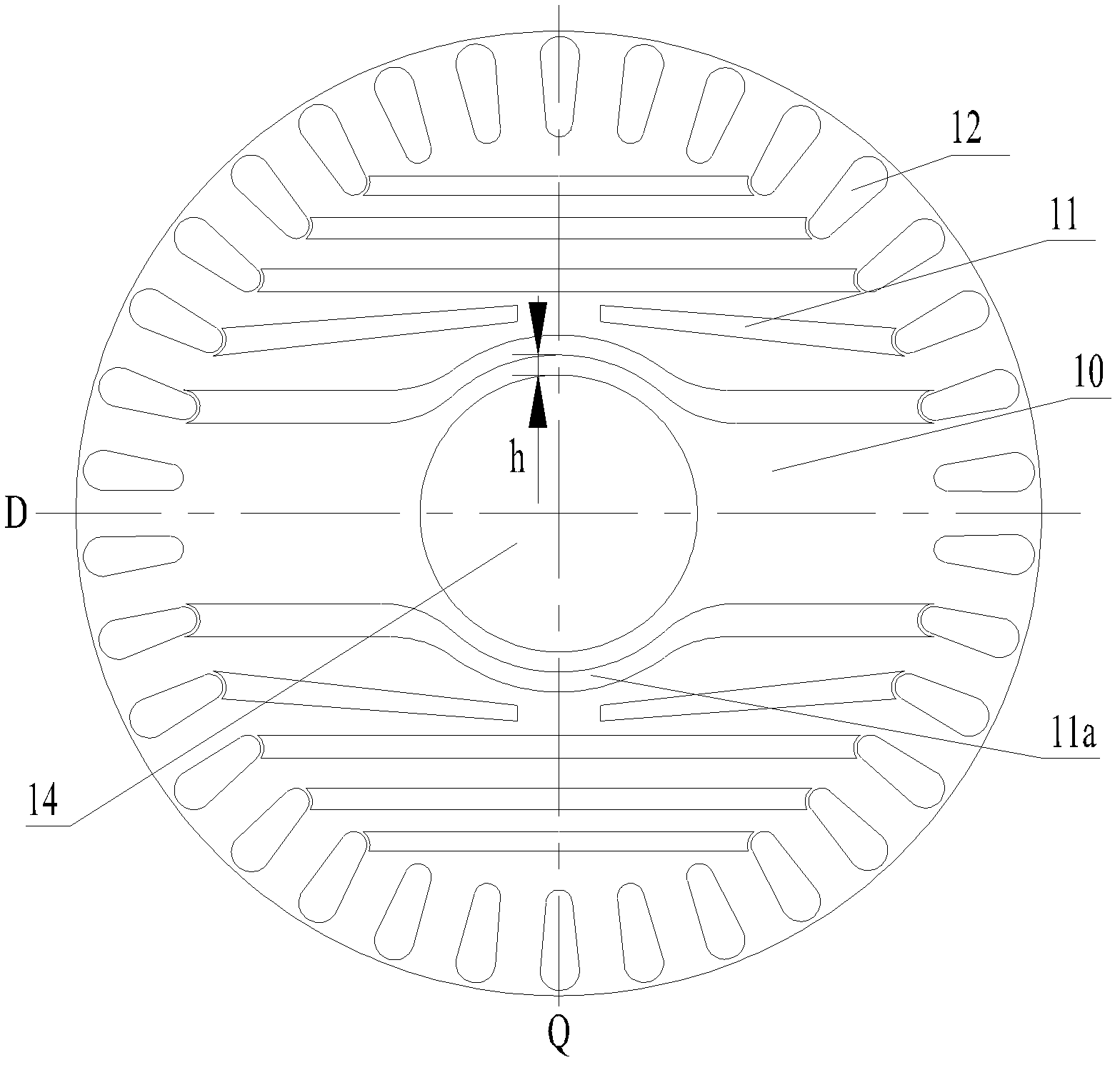
InactiveUS20050110355A1High torqueReducing torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsSynchronous reluctance motorMagnetic poles
In a synchronous reluctance motor having a rotor having a plurality of pairs of an outer side slot formed at an outer periphery side and an inner side slot formed at inner side of the rotor. The distance between the outer periphery of the rotor and the outer side slot is determined to be the width of the stator magnetic pole portion of the stator multiplied by 0.7 to 1.3. A first total magnetic flux amount of an outer side permanent magnet disposed in the outer side slot is determined to be larger than or equal to a second total magnetic flux amount of an inner side permanent magnet disposed in the inner side slot.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
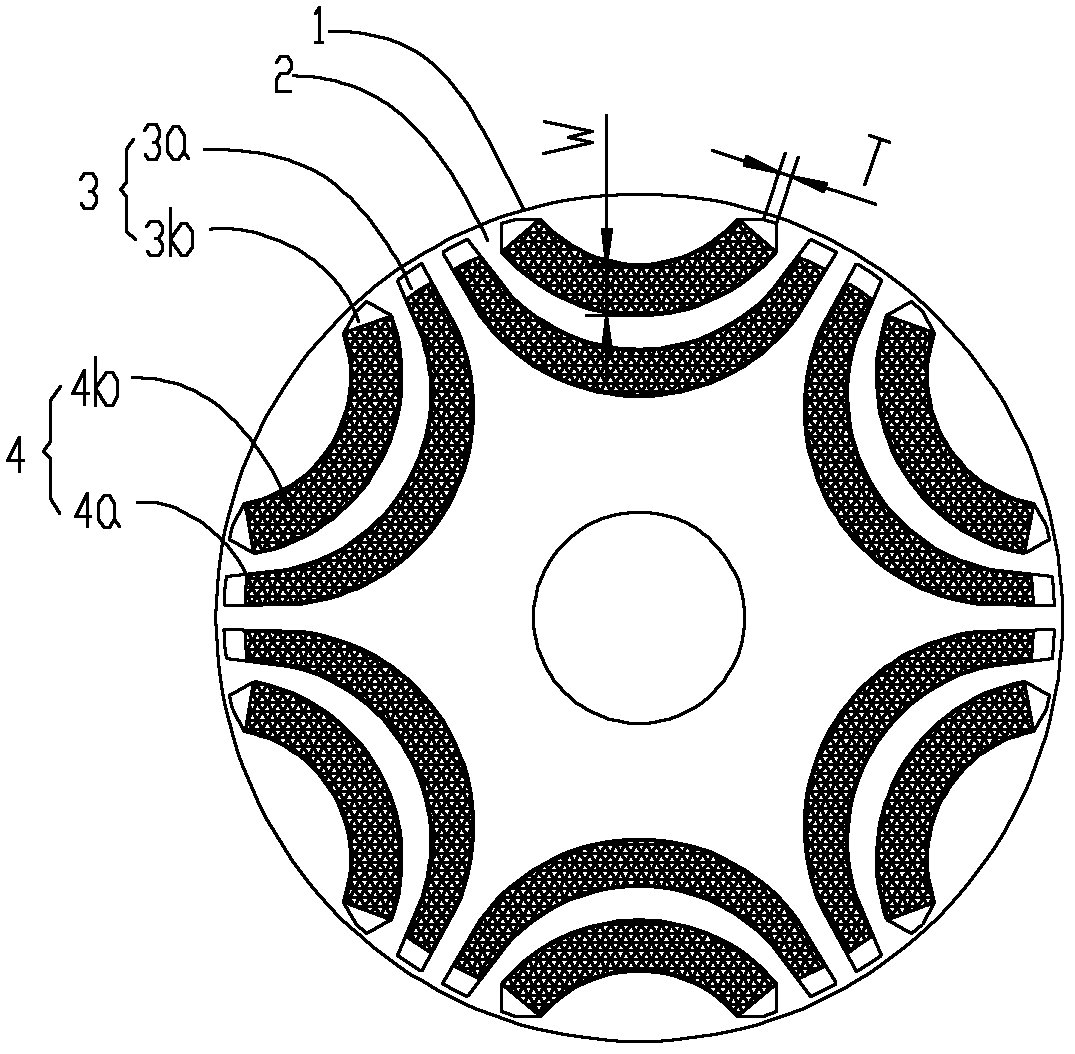
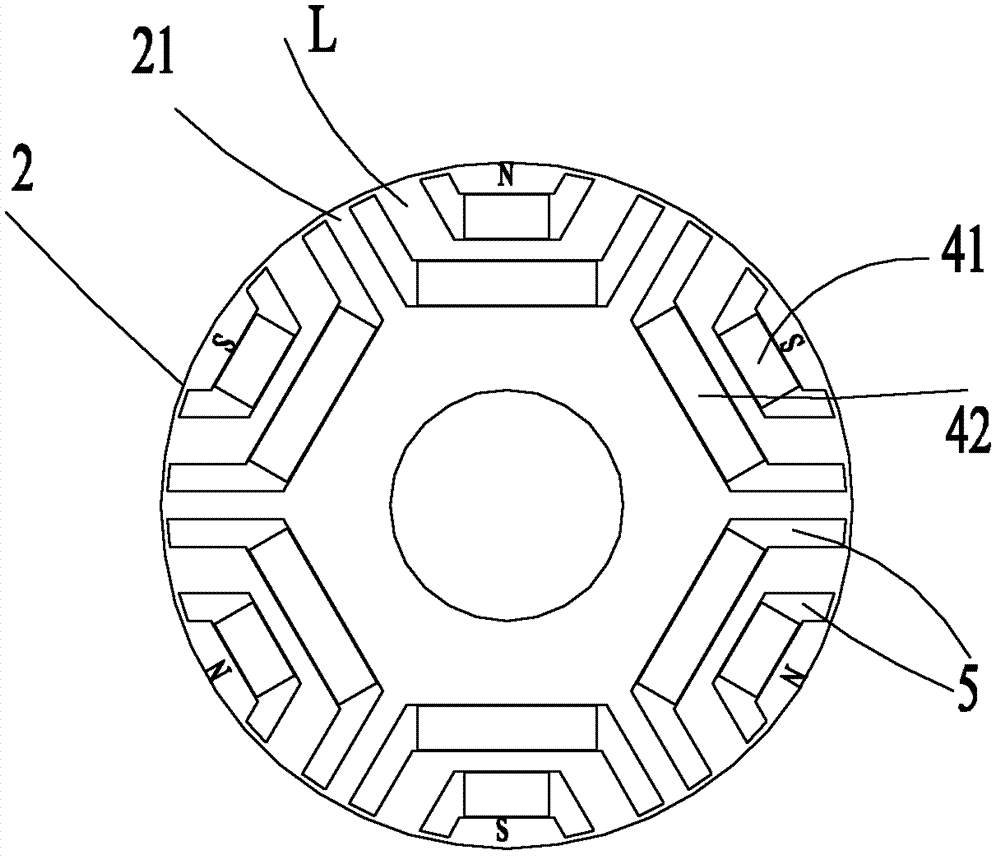
Permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, rotor of motor and mounting method of motor
ActiveCN102761222AImprove efficiencyImprove utilizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorMagnet
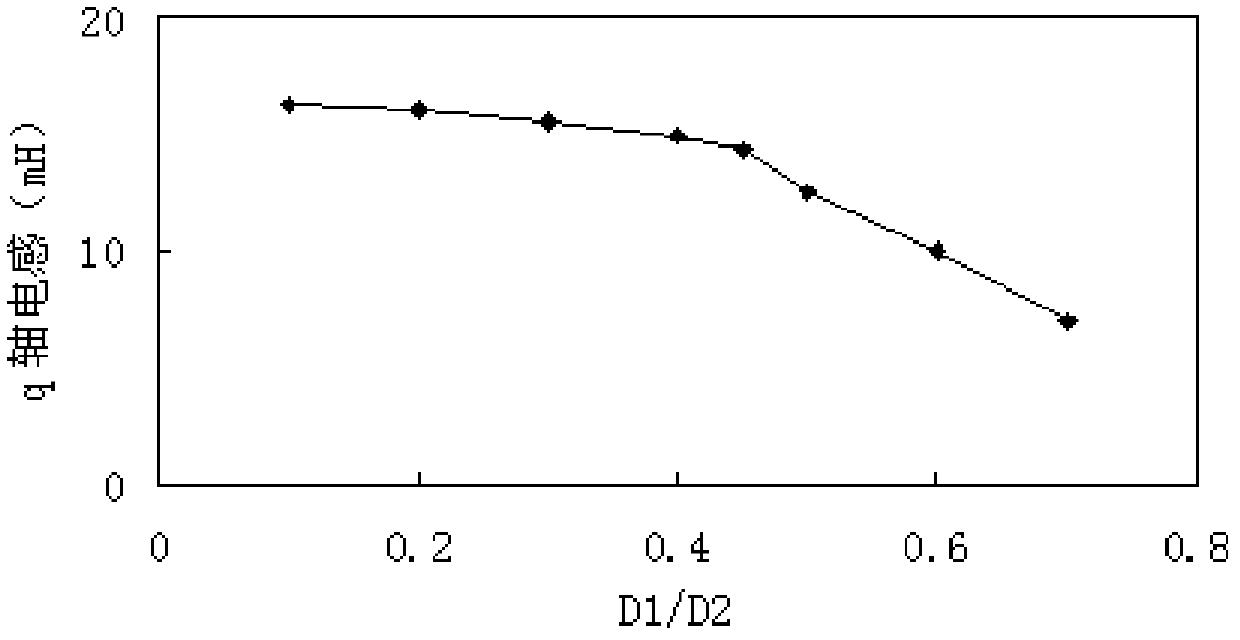
The invention provides a permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, a rotor of the motor and a mounting method of the motor. The rotor of the permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor provided by the invention comprises a rotor iron core and four permanent magnet groups; four permanent magnet groove groups are uniformly distributed on the rotor iron core along the circumferential direction by using the rotor centre of the rotor as the centre of a circle; each permanent magnet groove group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnet grooves; each permanent magnet group comprises at least two layers of permanent magnets which are cooperatively embedded in the permanent magnet grooves of the corresponding permanent magnet groove groups, respectively; and the permanent magnets in each permanent magnet group are of the same polarity, and the polarities of two adjacent permanent magnet groups are opposite, wherein the diameter D1 of an internal circle tangential tothe vertexes, facing the rotor centre, of the innermost-layer permanent magnets in the four permanent magnet groups and the diameter D2 of the rotor meet the following relationship: D1 / D2 is not lessthan 0.3 and not more than 0.45. According to the permanent-magnet-aided synchronous reluctance motor, the rotor of the motor and the mounting method of the motor, the placement depths of the permanent magnet layers of the motor rotor are designed so as to ensure that the reluctance torque of the motor is utilized to the maximum.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Interior permanent magnet machine having offset rotor sections
ActiveUS20150069863A1Efficient preparationMore technical efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorElectric machine
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
Permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor and manufacturing method thereof and motor
InactiveCN102790458AImprove efficiencyReduce processing difficultyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous reluctance motorElectric machine
The invention provides a permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor, a manufacturing method thereof and a motor with the motor rotor. The permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor rotor comprises a rotor iron core and permanent magnets, a plurality of groups of magnetic pole units are arranged in the rotor iron core, the permanent magnets are arranged in the magnetic pole units, each group of magnetic pole units comprises multilayer permanent magnet grooves which are distributed in a radial direction and used for accommodating the permanent magnets, magnetizers are arranged among the multilayer permanent magnet grooves, and materials of the magnetizers are different from those of the rotor iron core. The motor rotor, the manufacturing method thereof and the motor with the motor rotor have the advantages that a soft magnetic material and a press powder material are combined, the iron core can be configured according to different requirements, the machining difficulty is reduced, and the whole efficiency of the permanent magnet auxiliary synchronized reluctance motor is improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE REFRIGERATION TECH CENT OF ENERGY SAVING & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Synchronous reluctance machine
ActiveUS20080296994A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous reluctance motorConductor Coil
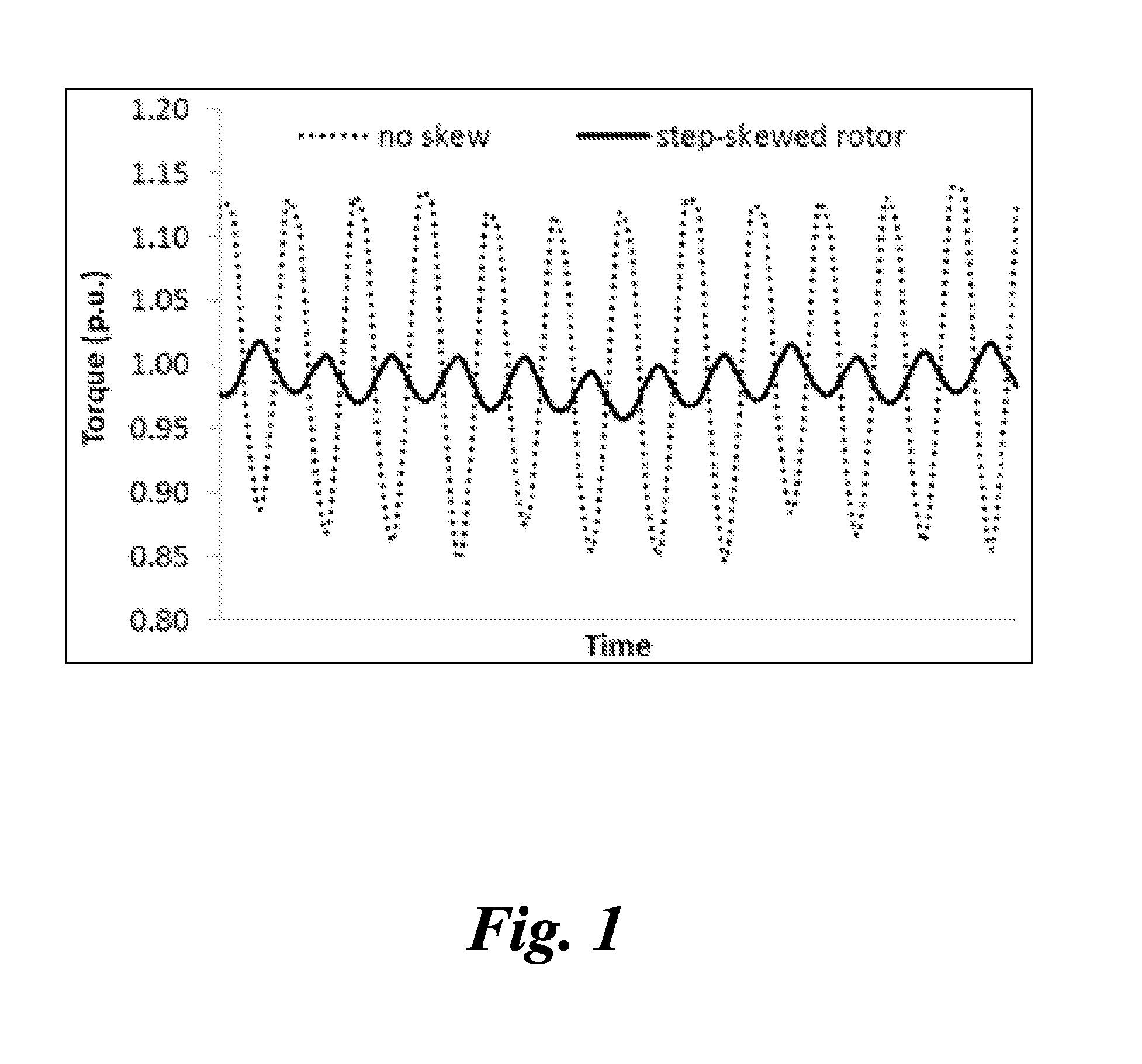
A synchronous reluctance machine is provided. The synchronous reluctance machine includes a stator having a stator core, the stator core including a number of fractional-slot concentrated windings wound around multiple stator teeth. The synchronous reluctance machine also includes a rotor having a rotor core and disposed with an air gap inside and concentric with the stator, wherein the rotor core includes a number of laminated sheets, wherein each of the laminated sheets is axially skewed with respect to neighboring ones of the laminated sheets, and wherein each of the laminated sheets includes multiple ferromagnetic regions and multiple non-ferromagnetic regions formed of a single material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Synchronous reluctance machine
ActiveUS7652404B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsSynchronous reluctance motorConductor Coil
A synchronous reluctance machine is provided. The synchronous reluctance machine includes a stator having a stator core, the stator core including a number of fractional-slot concentrated windings wound around multiple stator teeth. The synchronous reluctance machine also includes a rotor having a rotor core and disposed with an air gap inside and concentric with the stator, wherein the rotor core includes a number of laminated sheets, wherein each of the laminated sheets is axially skewed with respect to neighboring ones of the laminated sheets, and wherein each of the laminated sheets includes multiple ferromagnetic regions and multiple non-ferromagnetic regions formed of a single material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
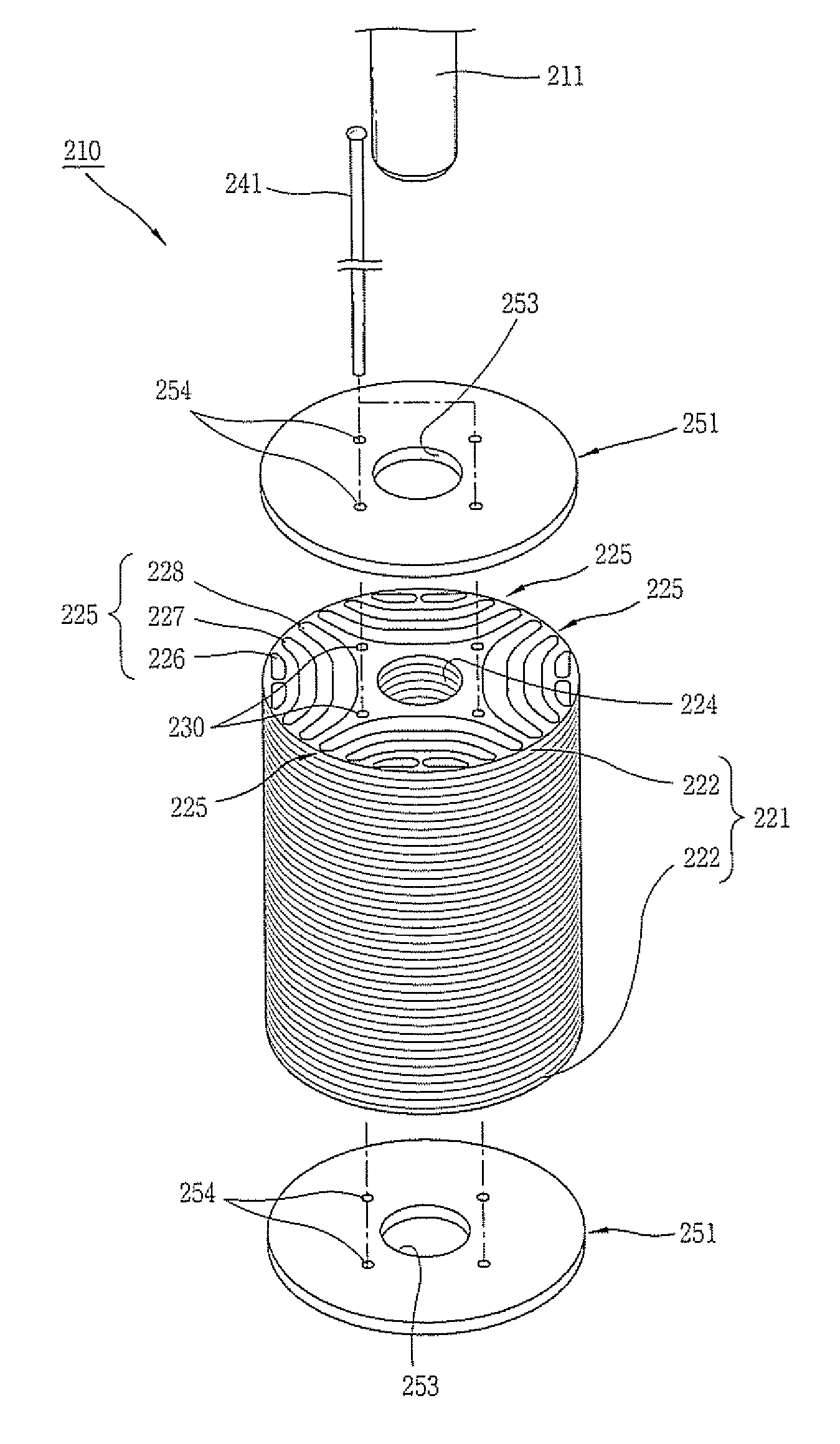
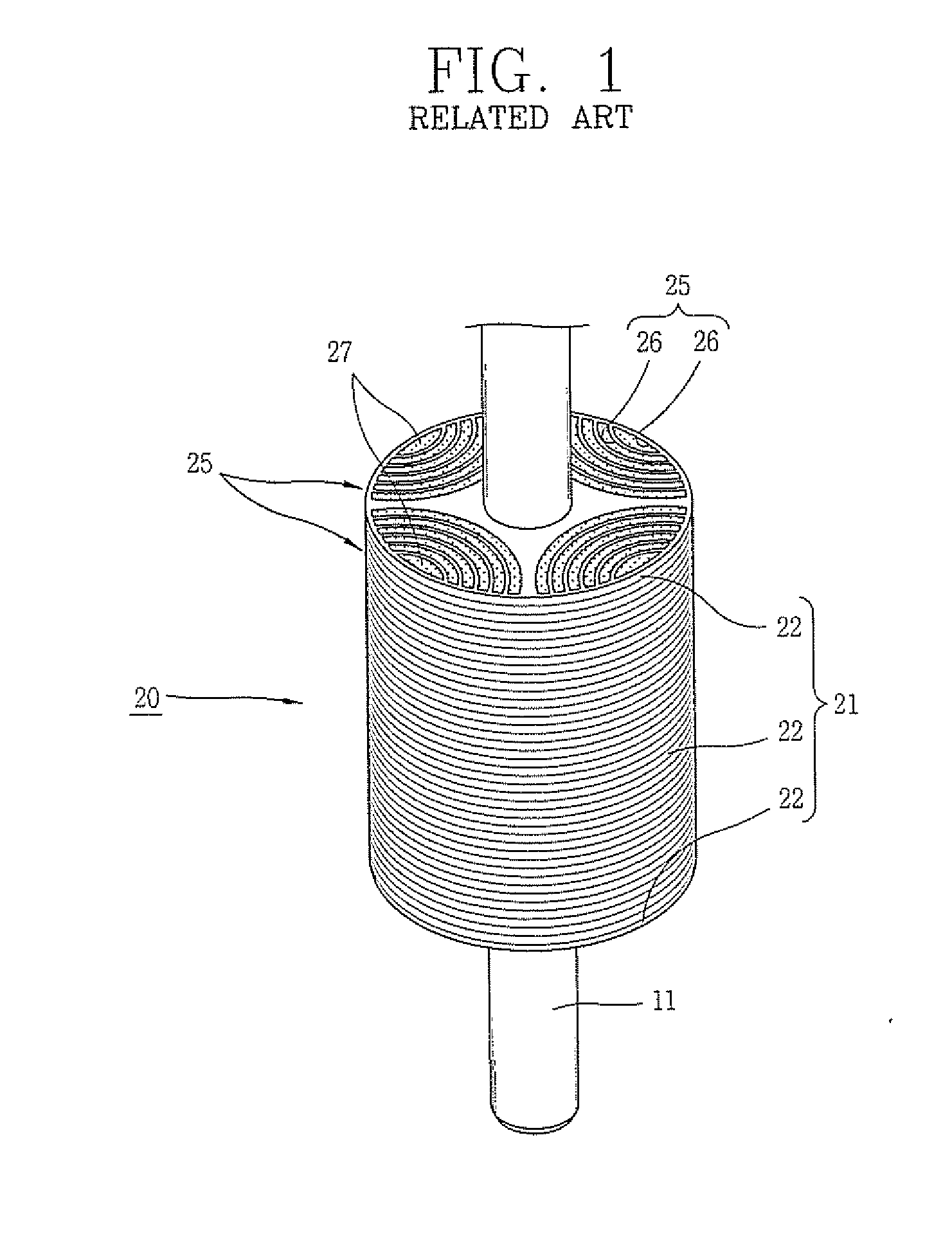
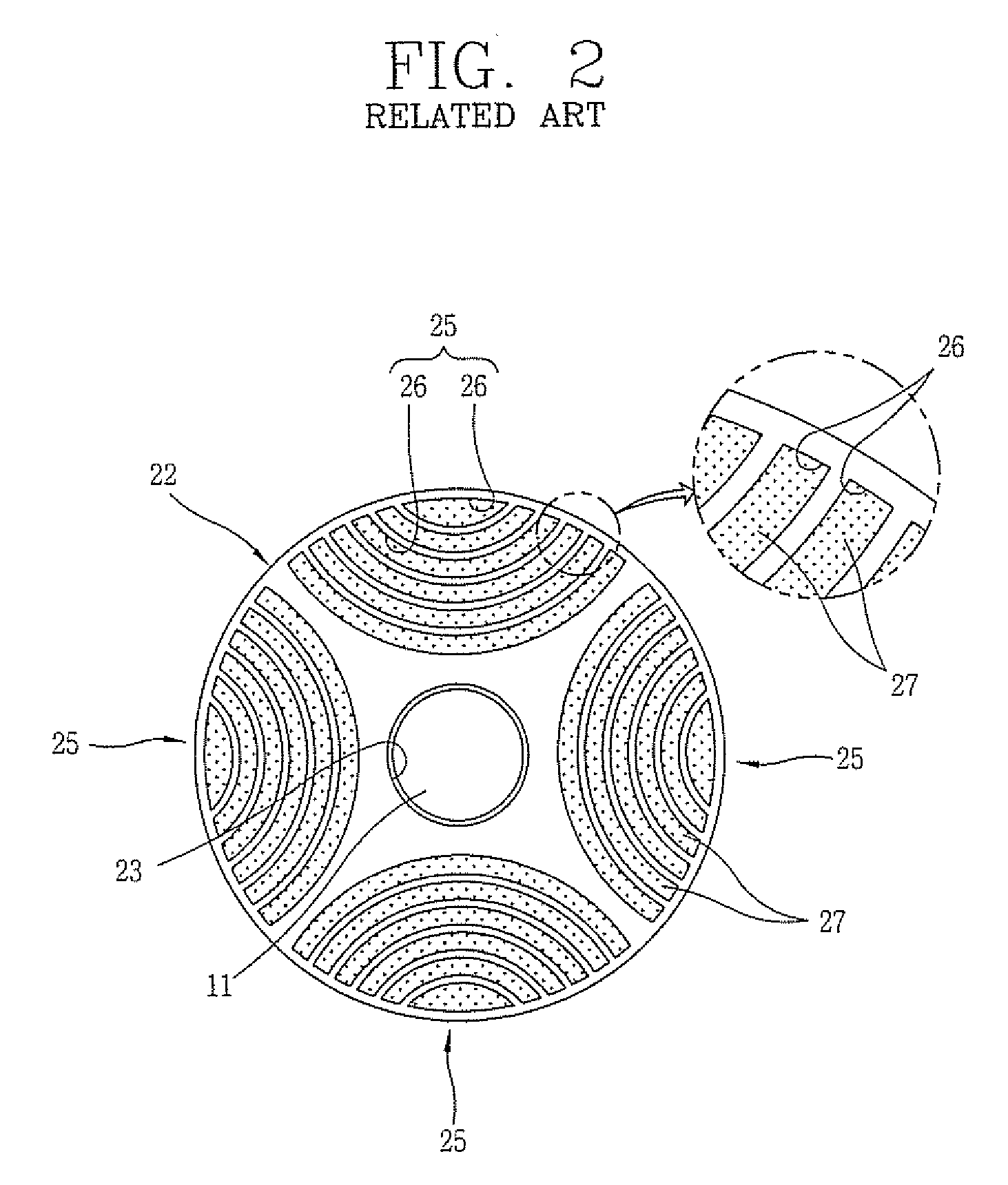
Rotor of Synchronous Reluctance Motor
InactiveUS20080211340A1Improving assembly characteristicEasy alignmentMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesSynchronous reluctance motorSilicon
A rotor of a synchronous reluctance motor, comprising: a laminated core formed by laminating a plurality of silicon steel sheets, and having a barrier formed at each of regions equally divided on the basis of the center of each silicon steel sheet and a guide pin hole formed between the barriers; end plates fixed to both side of the laminated core; a guide pin inserted into each of the guide pin holes; and a rivet installed by penetrating a hole of each barrier in order to couple the laminated core and the end plates with each other.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com