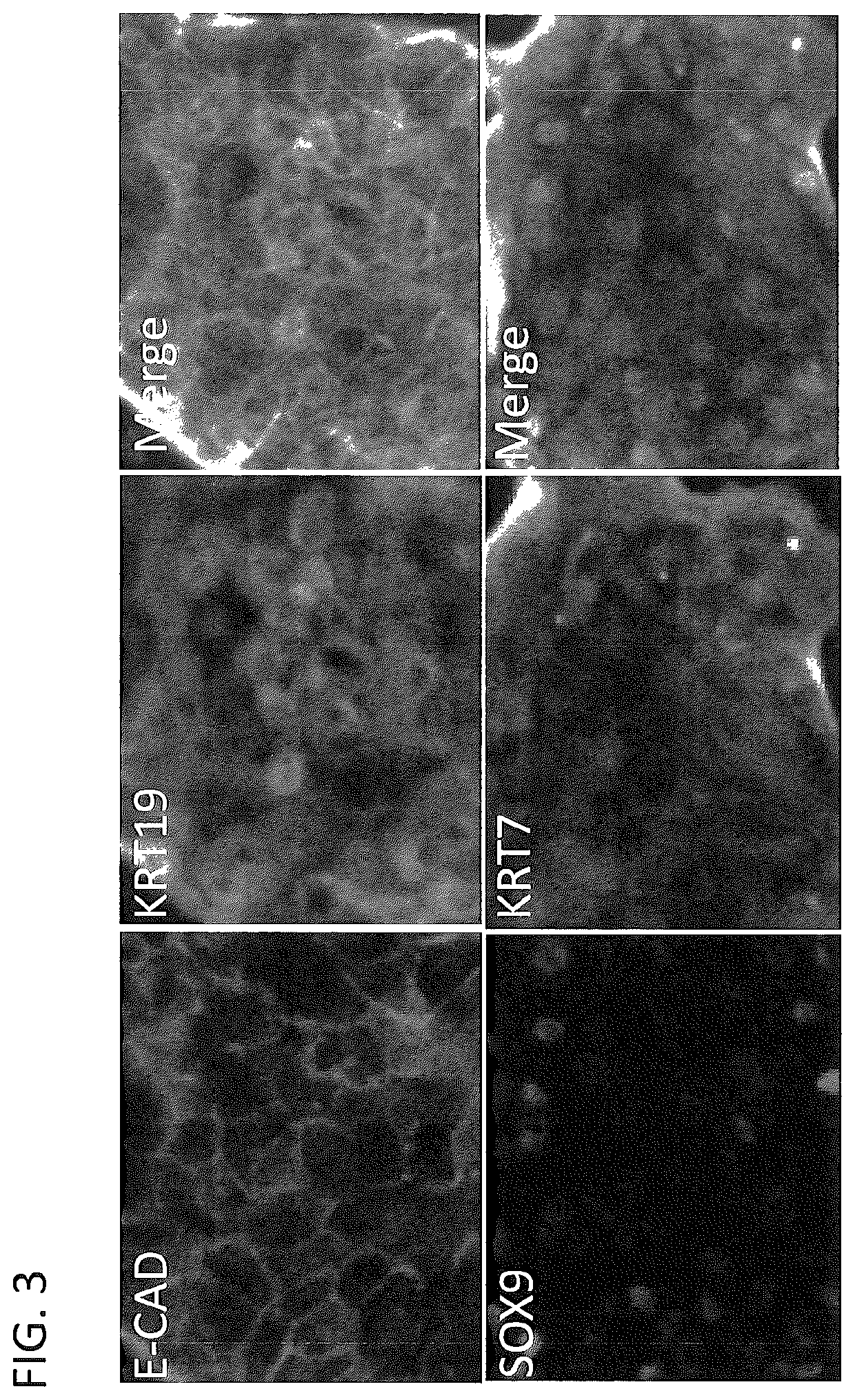
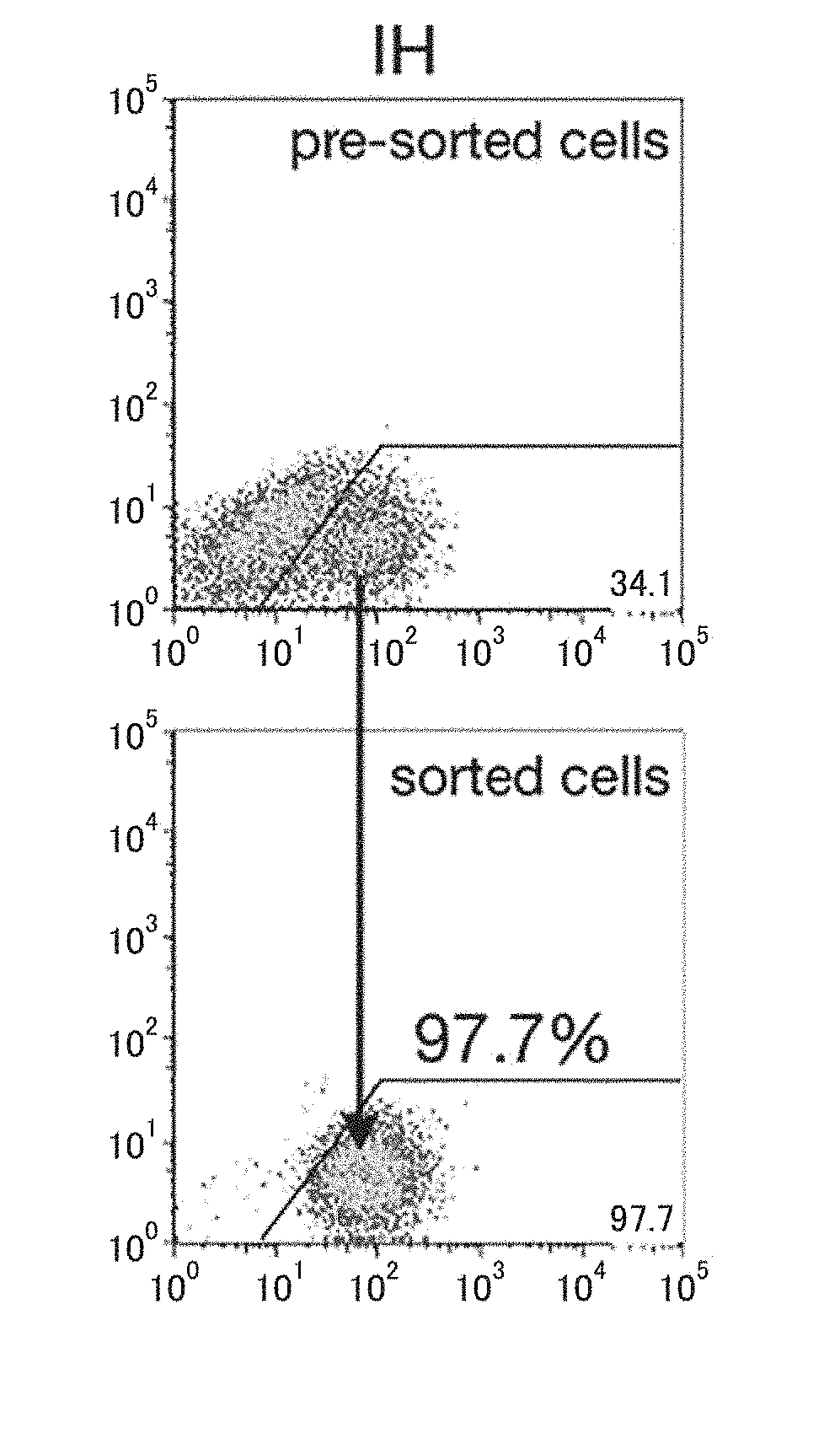
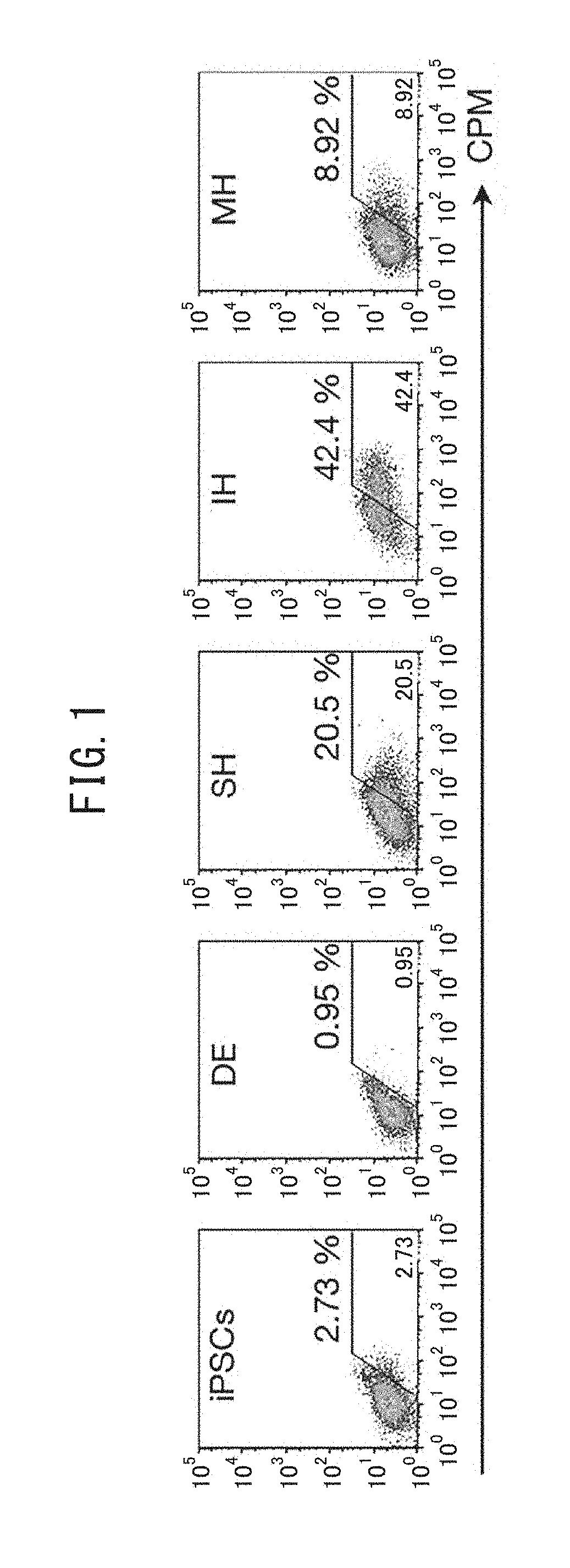
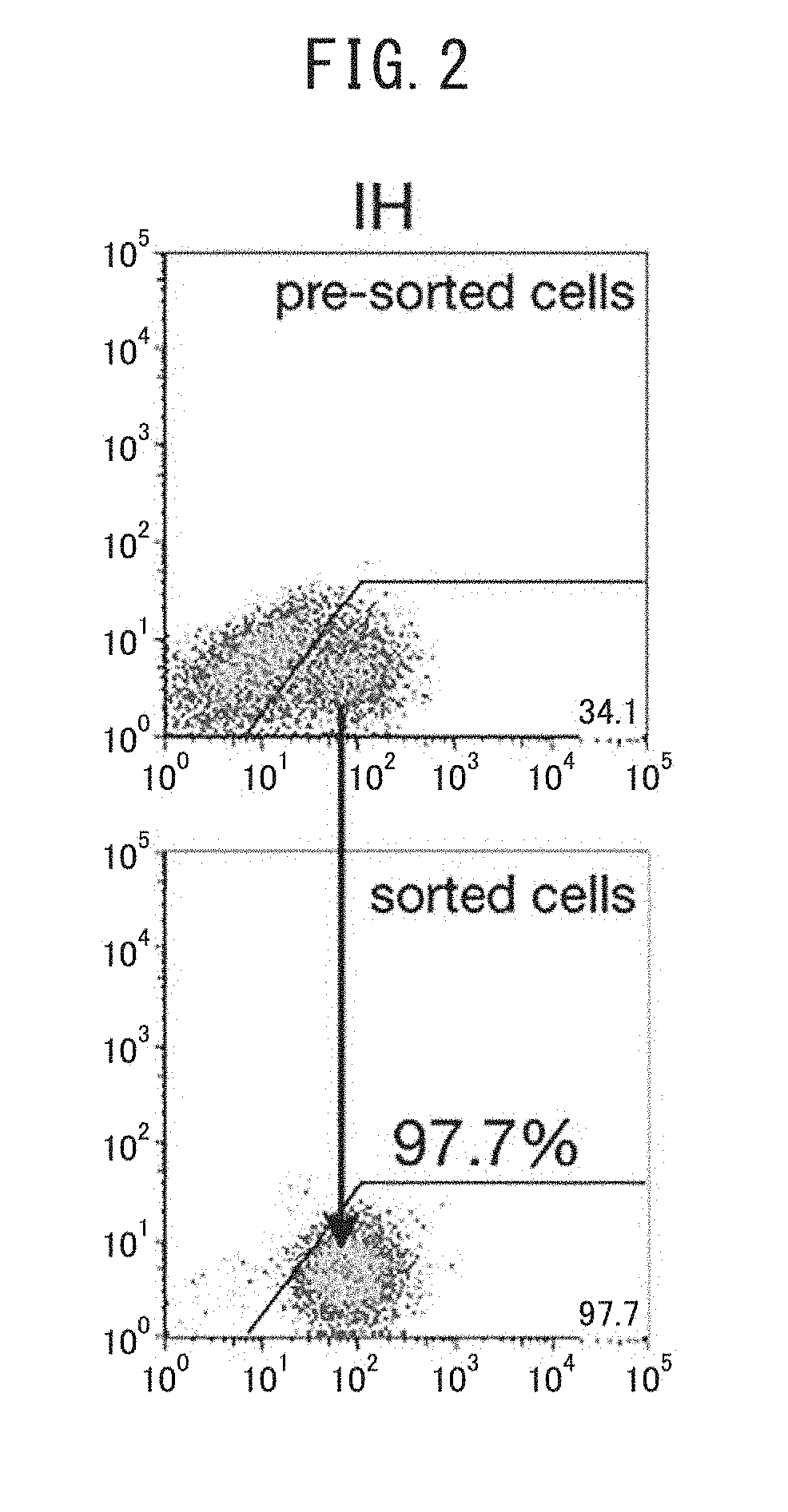
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Cholangiocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
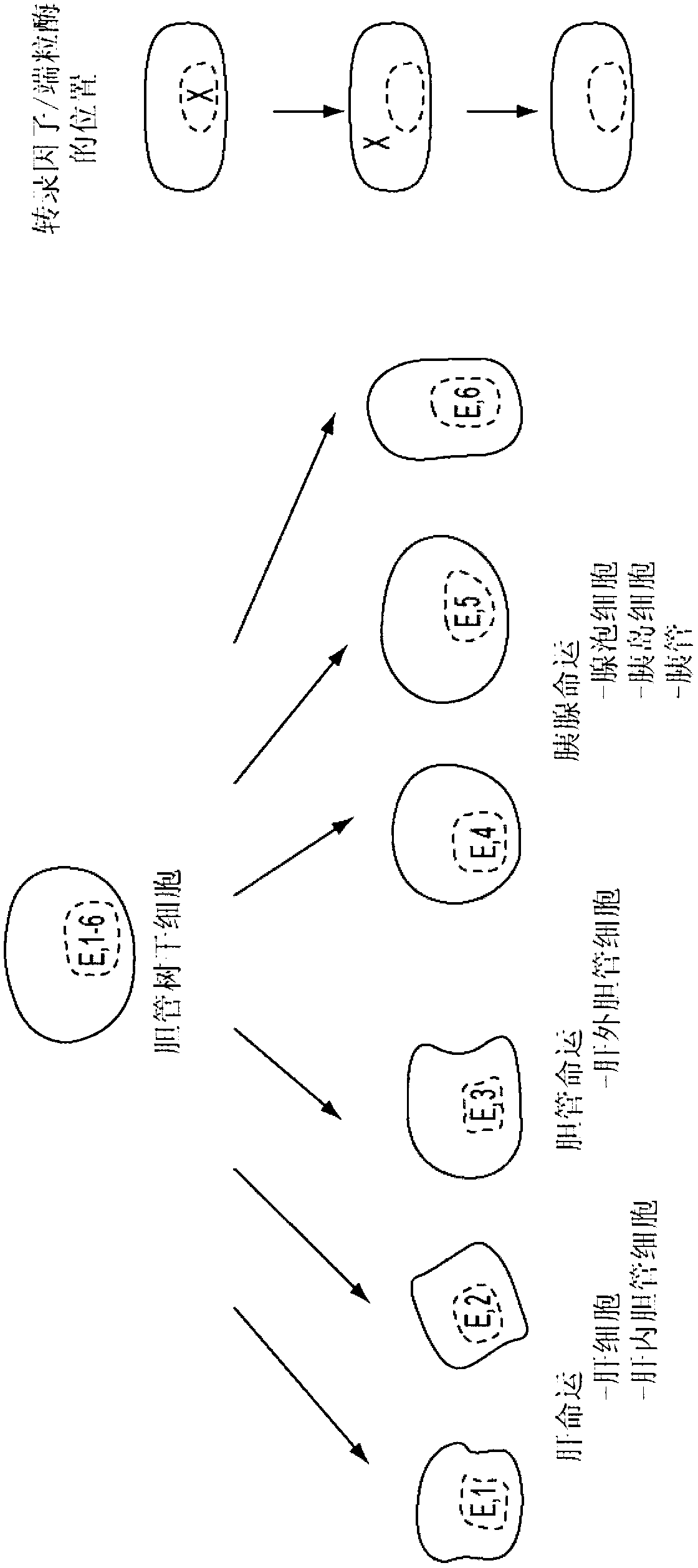
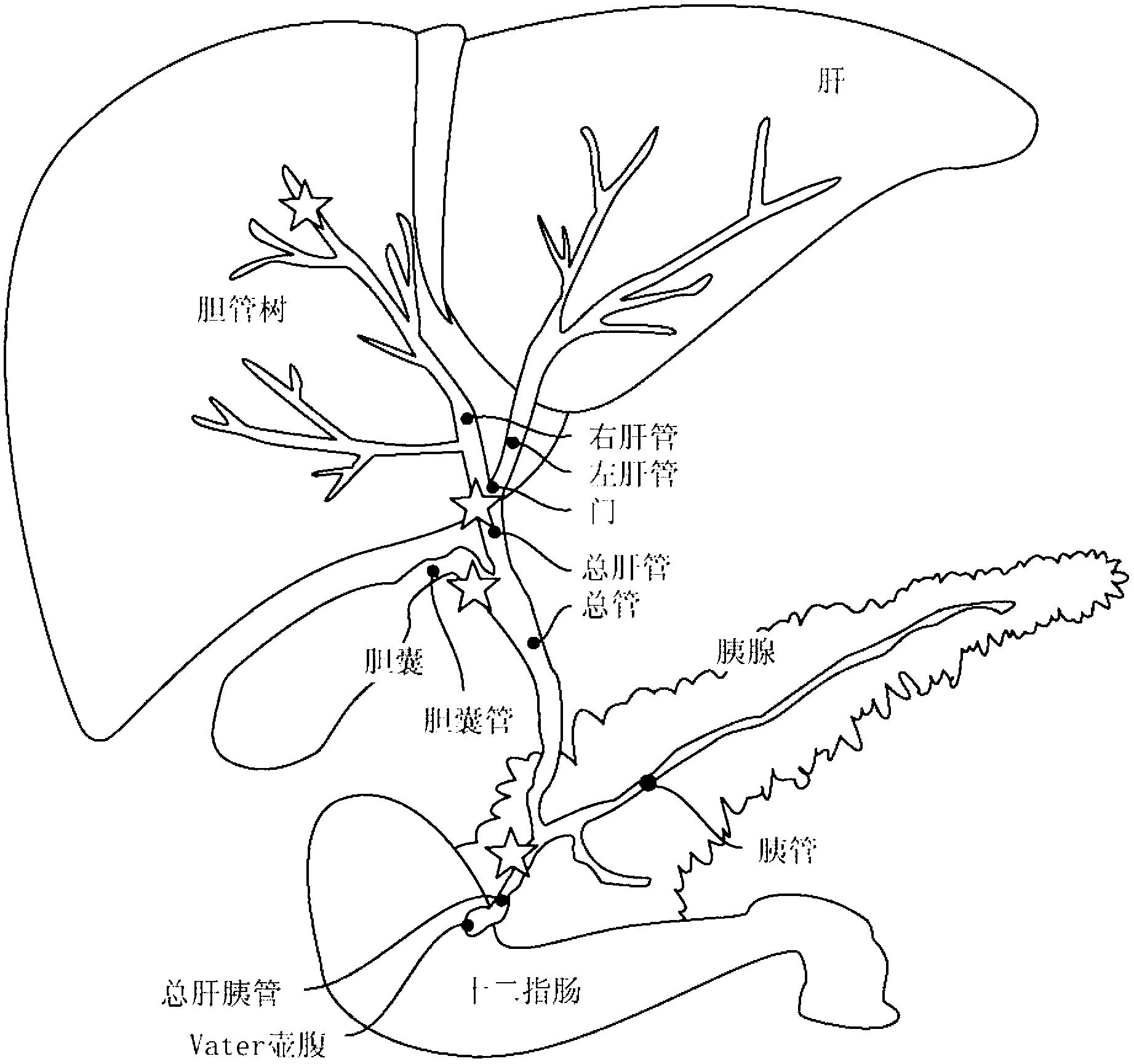
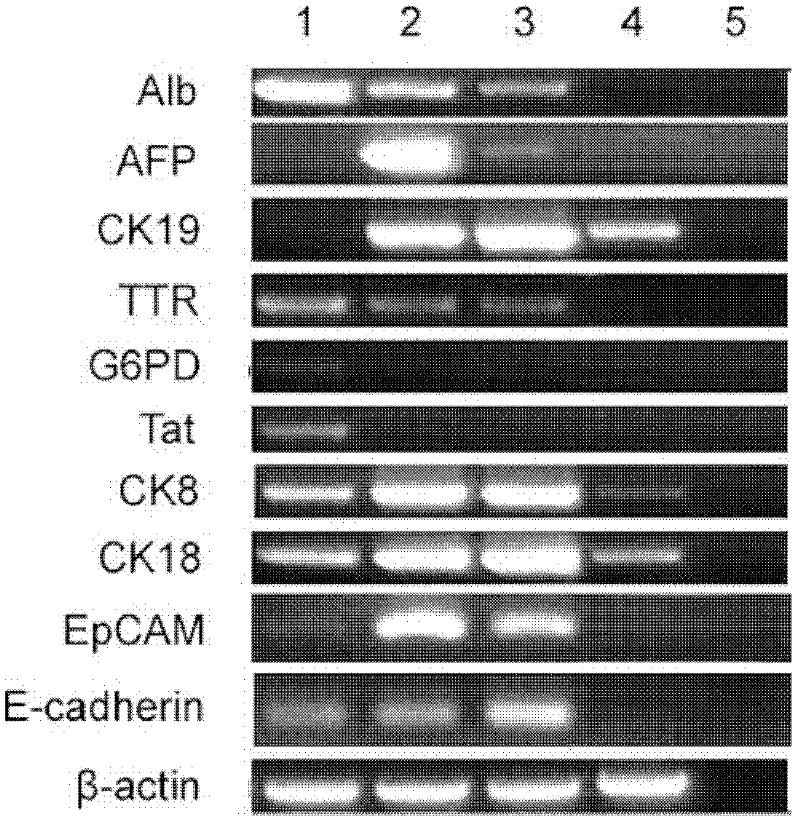
Cholangiocytes are the epithelial cells of the bile duct. They are cuboidal epithelium in the small interlobular bile ducts, but become columnar and mucus secreting in larger bile ducts approaching the porta hepatis and the extrahepatic ducts.
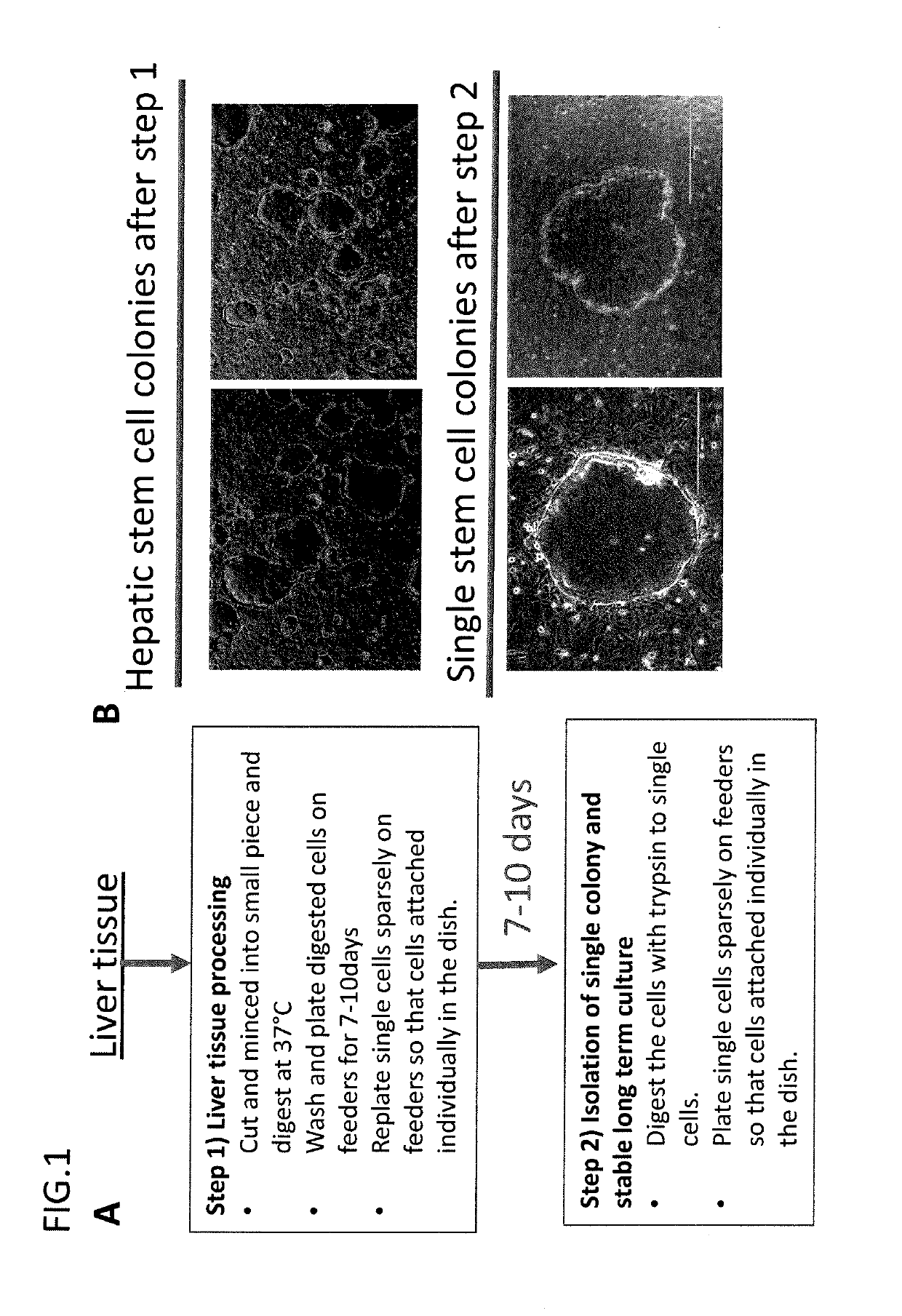
Processes for clonal growth of hepatic progenitor cells
A method of propagating mammalian endodermally derived progenitors such as hepatic progenitors, their progeny, or mixtures thereof is developed which includes culturing mammalian progenitors, their progeny, or mixtures thereof on a layer of embryonic mammalian feeder cells in a culture medium. The culture medium can be supplemented with one or more hormones and other growth agents. These hormones and other growth agents can include insulin, dexamethasone, transferrin, nicotinamide, serum albumin, beta-mercaptoethanol, free fatty acid, glutamine, CUSO4, and H2SeO3. The culture medium can also include antibiotics. Importantly, the culture medium does not include serum. The invention includes means of inducing the differentiation of the progenitors to their adult fates such as the differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells to hepatocytes or biliary cells by adding, or excluding epidermal growth factor, respectively. The method of producing mammalian progenitors is useful in that the progenitors can be used subsequently in one or more of the following processes: identification of growth and differentiation factors, toxicological studies, drug development, antimicrobial studies, or the preparation of an extracorporeal organ such as a bioartificial liver.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Methods and compositions for treating autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS8173129B2Increasing and maintaining numberTreating and stabilizing and preventing autoimmuneSenses disorderNervous disorderHeart cellsDisease
The invention features methods for increasing or maintaining the number of functional cells of a predetermined type, for example, insulin producing cells of the pancreas, blood cells, spleen cells, brain cells, heart cells, vascular tissue cells, cells of the bile duct, or skin cells, in a mammal (e.g., a human patient) that has injured or damaged cells of the predetermined type.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation and application of method
ActiveCN106754636AStable proliferationSolve problems that cannot be cultivated for a long timeVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsIn vitro transformationHepatica
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering technology, and in particular to a method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation and an application of the method. The invention provides a hepatocyte cholangiocyte-like transformation medium determined by chemical ingredients and / or a system which is composed of a hepatocyte mature medium and is applicable to long-term stable culture, amplification and differentiation of the primary hepatocytes; the invention also provides the method for in-vitro induction of cholangiocyte-like transformation of the primary hepatocytes and for long-term culture, amplification and differentiation; and with the application of the method, the cholangiocyte-like hepatocyte conversion of the primary hepatocytes can be induced in vitro, so that the obtained hepatocytes have characteristics of biliary epithelial cells and hepatic precursor cells, and the hepatocytes are applicable to long-term stable culture and amplification. The breedable cholangiocyte-like hepatocytes and hepatocytes, which are mature in differentiation, prepared by the invention are applicable to such aspects as toxicologic and pharmacological evaluation of compounds and drugs, researches and diagnosis & treatment of hepatitis viruses, treatment by hepatocyte transplantation, preparation of bioartificial liver and the like.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Methods and compositions for treating type 1 diabetes
ActiveUS7628988B2Increase secretionImprove bioavailabilitySenses disorderNervous disorderHeart cellsVascular tissue
The invention features methods for increasing or maintaining the number of functional cells of a predetermined type, for example, insulin producing cells of the pancreas, blood cells, spleen cells, brain cells, heart cells, vascular tissue cells, cells of the bile duct, or skin cells, in a mammal (e.g., a human patient) that has injured or damaged cells of the predetermined type.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods for generating hepatocytes and cholangiocytes from pluripotent stem cells
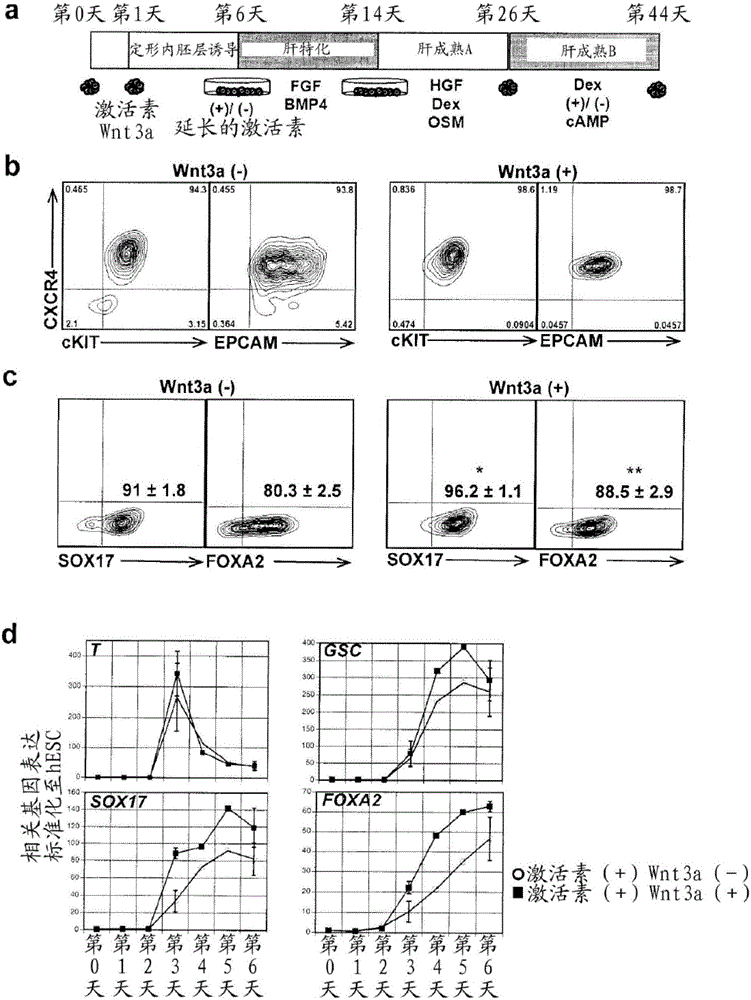
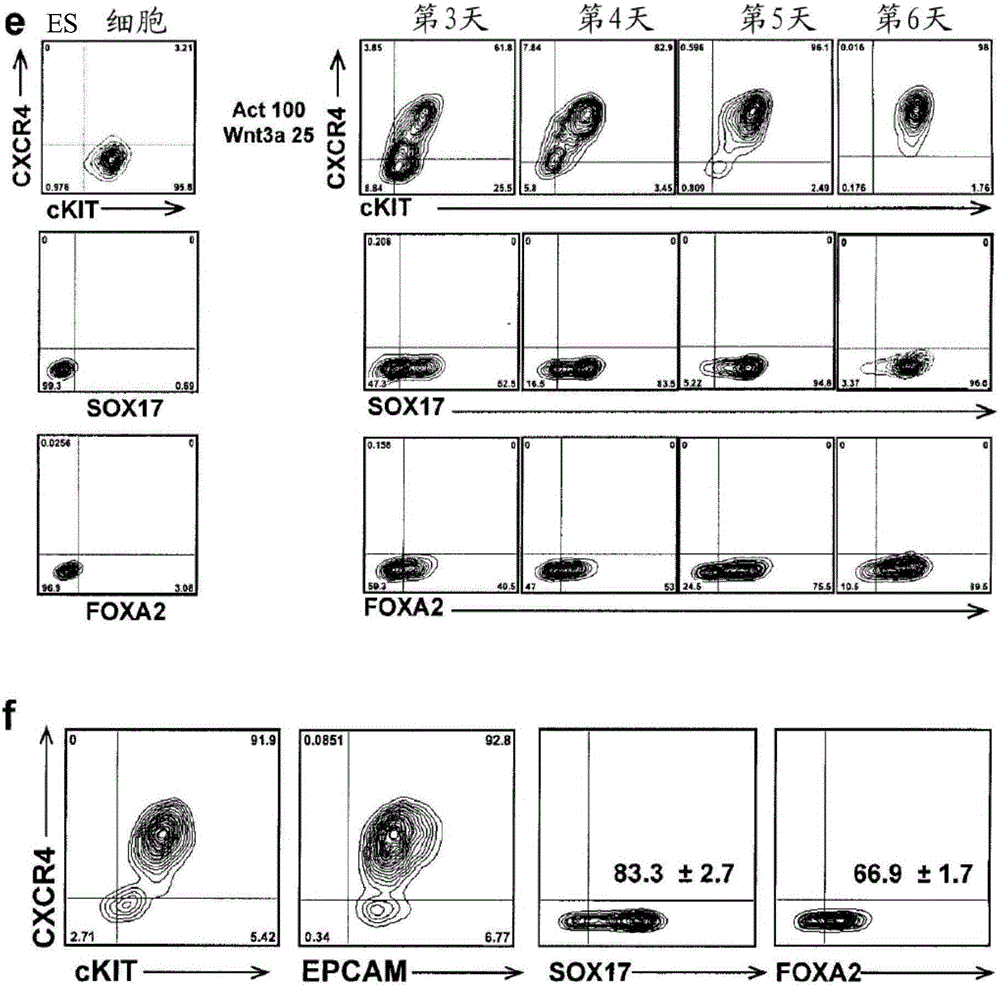
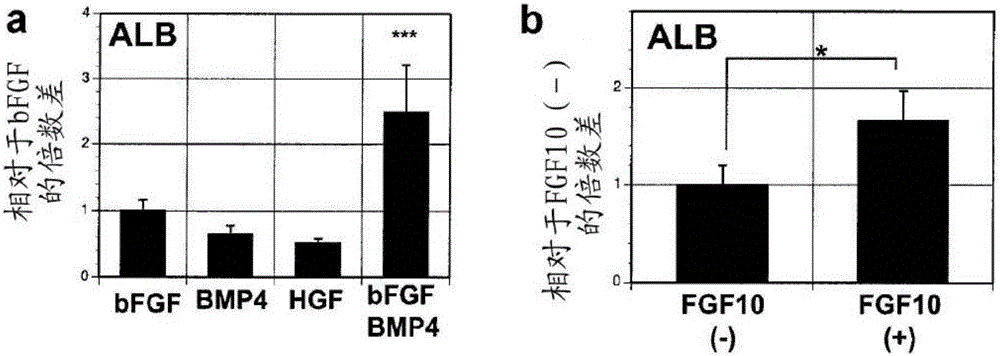
Methods for producing hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte lineage cells from pluripotent stem cells, the method comprising (a) specifying the extended nodal agonist treated induced endodermal cell population to obtain a cell population comprising hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte progenitors by contacting the extended nodal agonist treated induced endodermal cell population with specification media comprising a FGF agonist and a BMP4 agonist and / or active conjugates and / or fragments thereof; (b) inducing maturation, and optionally further lineage specification and / or expansion of the hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte progenitors of the cell population to obtain a population comprising hepatocyte lineage cells such as hepatoblasts, hepatocytes and / or cholangiocytes, the inducing maturation step comprising generating aggregates of the cell population. Optionally, the method also comprises activating the cAMP pathway within the aggregates and forming co-aggregates.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Processes for clonal growth of hepatic progenitor cells
A method of propagating mammalian endodermally derived progenitors such as hepatic progenitors, their progeny, or mixtures thereof is developed which includes culturing mammalian progenitors, their progeny, or mixtures thereof on a layer of embryonic mammalian feeder cells in a culture medium. The culture medium can be supplemented with one or more hormones and other growth agents. These hormones and other growth agents can include insulin, dexamethasone, transferrin, nicotinamide, serum albumin, β-mercaptoethanol, free fatty acid, glutamine, CuSO4, and H2SeO3. The culture medium can also include antibiotics. Importantly, the culture medium does not include serum.The invention includes means of inducing the differentiation of the progenitors to their adult fates such as the differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells to hepatocytes or biliary cells by adding, or excluding epidermal growth factor, respectively.The method of producing mammalian progenitors is useful in that the progenitors can be used subsequently in one or more of the following processes: identification of growth and differentiation factors, toxicological studies, drug development, antimicrobial studies, or the preparation of an extracorporeal organ such as a bioartificial liver.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
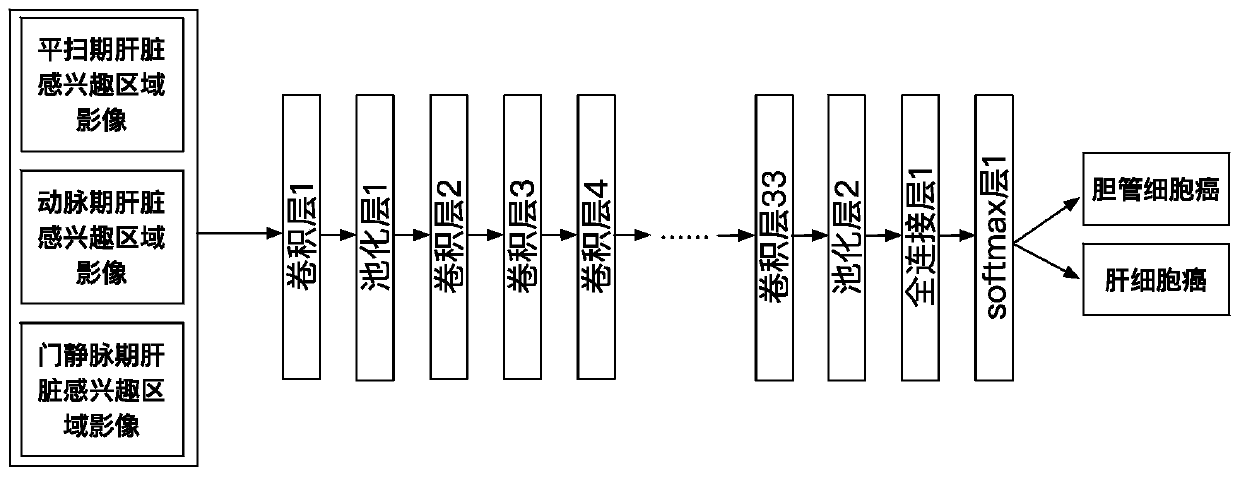
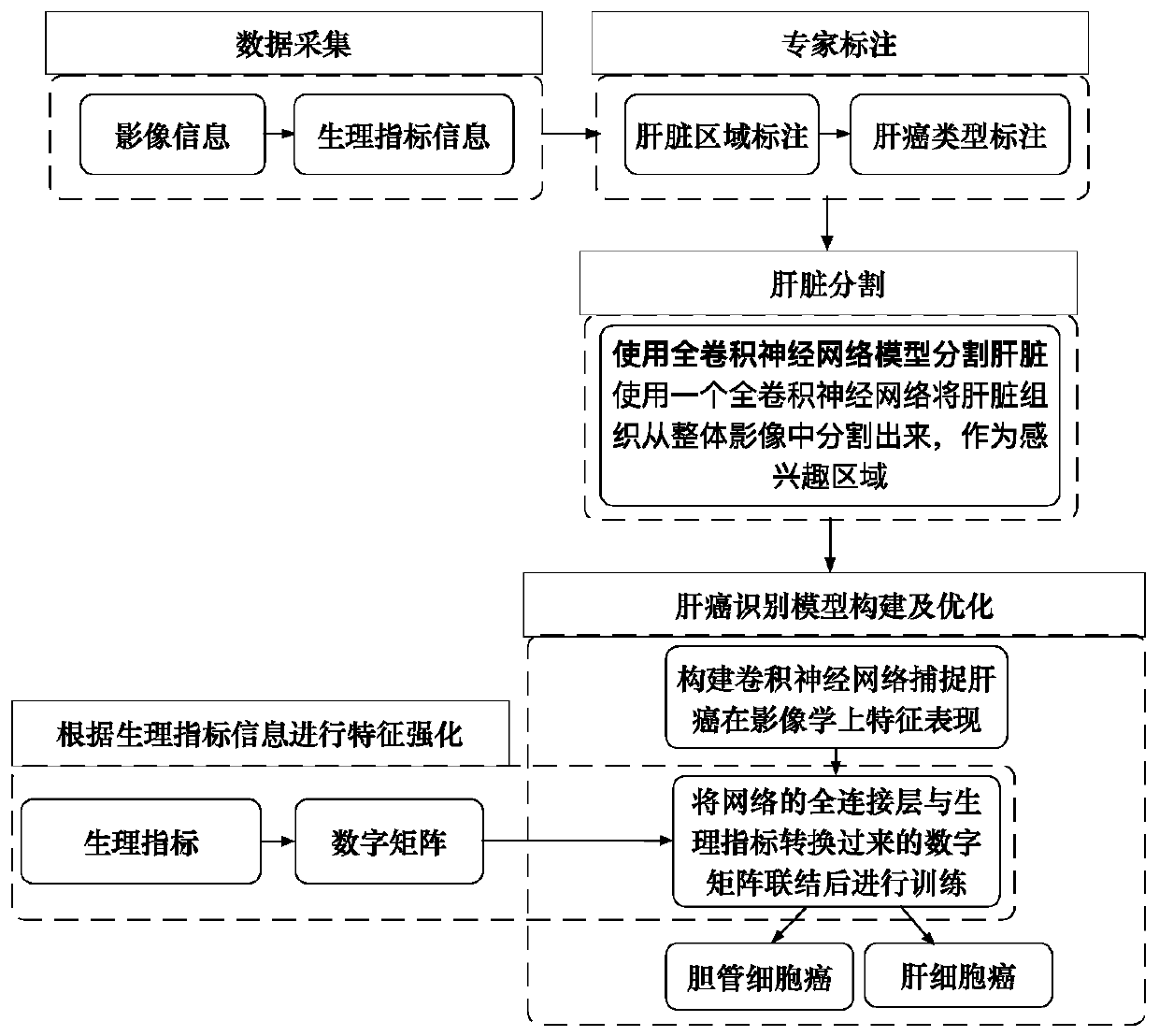
Automatic liver tumor classification method and device based on multi-stage CT image analysis
According to the liver tumor automatic classification method and device based on multi-stage CT image analysis, full-automatic bile duct cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma can be recognized,and a high-precision bile duct cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma recognition model is obtained. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scanning image, storing the contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scanning image as an arterial phase, a portal vein phase and a delay phase, and carrying out definite diagnosis on liver cancer categories to which all data belong to serve as a model training gold standard; (2) constructing a three-dimensional full convolutional neural network segmentation model, and segmenting the intrinsic characteristics ofthe liver tissue in each stage from the abdominal CT image through model training learning; (3) constructing a three-dimensional convolutional neural network classification model; and inputting the image data obtained by segmentation into a classification model for training, so as to enable the model to perform joint learning and training on the cancer features in multiple periods, thereby predicting the category to which the cancer belongs, comparing the prediction result with a gold standard, and supervising the training process of the model in a loss value feedback mode.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Liver normal temperature perfusion restoration system
InactiveCN105379707AAvoid compression deformationAvoid lossDead animal preservationPortal veinOxygen
The invention discloses a liver normal temperature perfusion restoration system. The system comprises a liver container. The liver container comprises a main body and an upper cover. The main body and the upper cover are fastened tightly. A silica gel flexible net is fixed to the main body of the liver container. The lower end of the main body of the liver container is provided with a blood return channel. The blood return channel is connected to a centrifugal pump by a blood storage tank. The front end of the blood storage tank is provided with a filter film. An outlet end of the centrifugal pump is connected to an oxygenator. The oxygenator is connected to an oxygen control device. A blood pipe of the oxygenator is divided into two paths by a heat exchanger, one path is used for hepatic artery perfusion by a roller pump and the other path is used for direct portal vein perfusion. Liver artery forms a pulsatile blood flow under the action of the roller pump so that physiological liver artery perfusion is simulated and bile duct cell protection is realized in perfusion. The system can keep hepatocyte aerobic metabolism at a normal temperature, realizes short-time restoration treatment on the liver and widens a liver source.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multipotent stem cells from the extrahepatic biliary tree and methods of isolating same
PendingUS20110135610A1Differentiate faster and moreBiocideHepatocytesPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
The present invention relates to a multipotent stem cell, multipotent cell populations, and an enriched multipotent cell population, each found in fetal, neonatal, pediatric, and adult biliary tree tissue and up to 72 hours post mortem (although preferentially, within 10 hours post mortem) and capable of maturing into multiple endodermal tissues that include liver, biliary and pancreatic tissues. The multipotent stem / progenitor cell and cell populations are found in peribiliary glands, and progenitors descending from them are present throughout the biliary tree including in the gallbladder. High numbers of the peribiliary glands are found in the branching locations of the biliary tree such as hilum, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, common duct, common hepato-pancreatic duct and gallbladder. Related multipotent cells, multipotent cell populations and their descendent progenitors are found throughout the biliary tree including in the gall bladder, which does not have peribiliary glands. Compositions comprising same, methods of identifying and isolating same, maintaining same in culture, expanding same in culture and differentiating or lineage restricting the same in vitro or in vivo to hepatic, biliary or pancreatic fates (e.g., as hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and / or pancreatic islet cells) are also provided. Methods of using the multipotent cells and / or multipotent cell populations are also provided.
Owner:SAPIENZA UNIV DE ROMA +1
Self-renewing pluripotent hepatic stem cells
The present invention provides clonal pluripotent hepatic stem cells using flow cytometry and in vitro single-cell-based assays. These cells possess multilineage differentiation potential and self-renewing capability. These cells may be clonally propagated in culture, to continuously produce hepatocytes and cholangiocytes as descendants while maintaining primitive stem cells. When expanded cells are transplanted into recipient animals, they morphologically and functionally differentiated into hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, with reconstitution of hepatocyte and bile duct structures. Furthermore, these cells differentiated into pancreatic ductal and acinar cells or intestinal epithelial cells when transplanted into pancreas or duodenal wall. Thus, the self-renewing multipotent stem cells persist in the developing mouse liver and can be induced to become cells of other organs of endodermal origin under appropriate microenvironment, providing new insight into therapies for diseases of the digestive system.
Owner:REPROCELL
Human hepatic progenitor cells and methods of use thereof
Liver progenitor cells immunoreactive for CD117, as well as for CD34 capable of proliferating in a culture; and differentiating in vivo into a hepatocyte, a cholangiocyte or a sinusoidal cell are provided. The cultures can be expanded over a large number of passages and integrate well after transplantation into adult liver.
Owner:NOVAHEP
Primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells
Hepatic progenitors comprise two populations of human hepatic stem cells, primitive and proximal hepatic stem cells, and two populations of committed progenitors, one for biliary cells and one for hepatocytes. Human primitive hepatic stem cells are a very small fraction of the liver cell population and give rise to proximal hepatic stem cells constituting a much larger fraction of the liver. Human proximal hepatic stem cells give rise to biliary and hepatocyte committed progenitors. Primitive and proximal stem cells are the primary stem cells for the human liver. Human primitive hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection from human livers or culturing human liver cells under conditions which select for a human primitive hepatic stem cell. Proximal hepatic stem cells may be isolated by immunoselection, or by culturing human liver cells under conditions which include a developmental factor. Proximal hepatic stem cells may also be isolated by culturing colonies comprising a primitive hepatic stem cell under conditions which include a developmental factor. Resulting compositions may be used for treating liver disorders and for producing bioartificial organs.
Owner:VESTA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
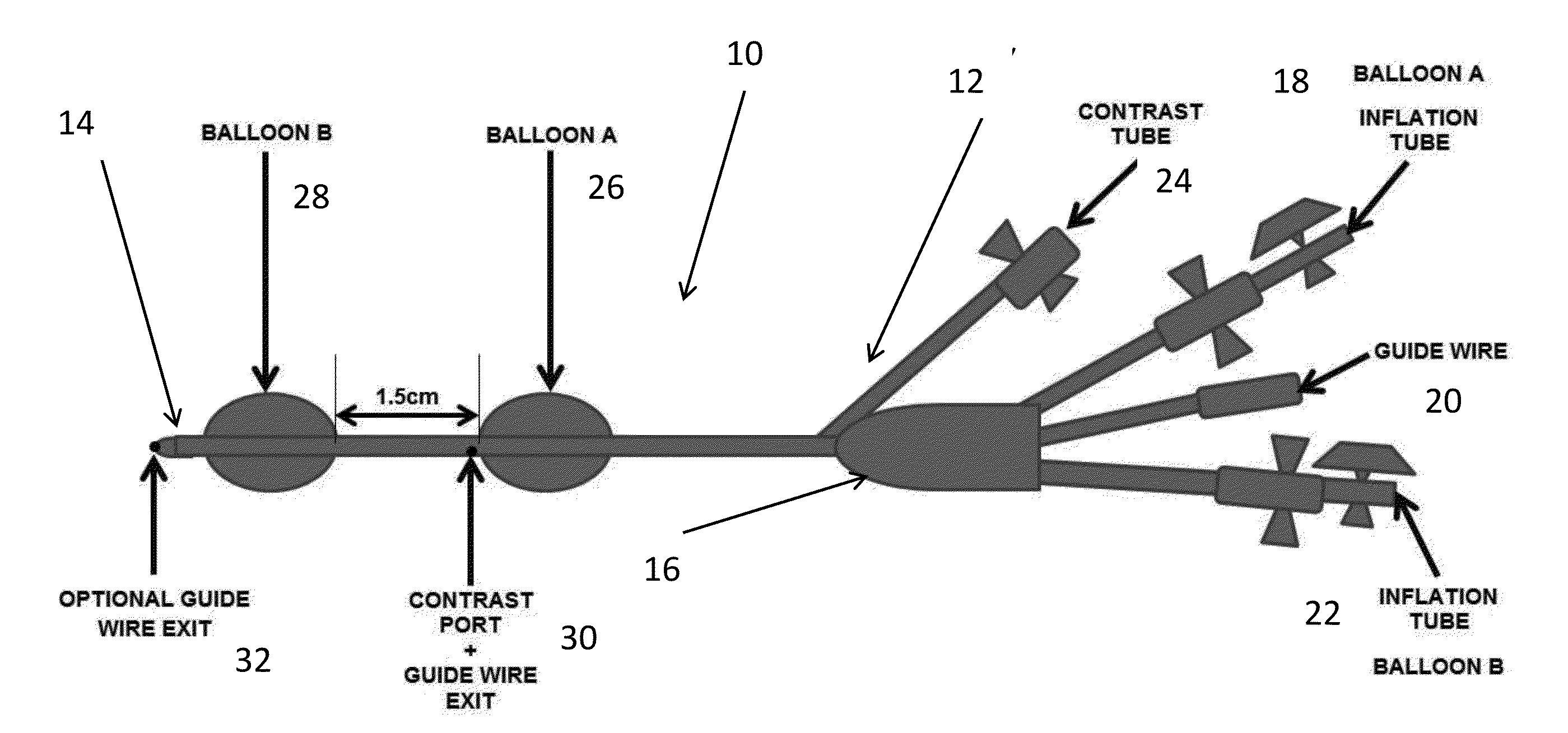
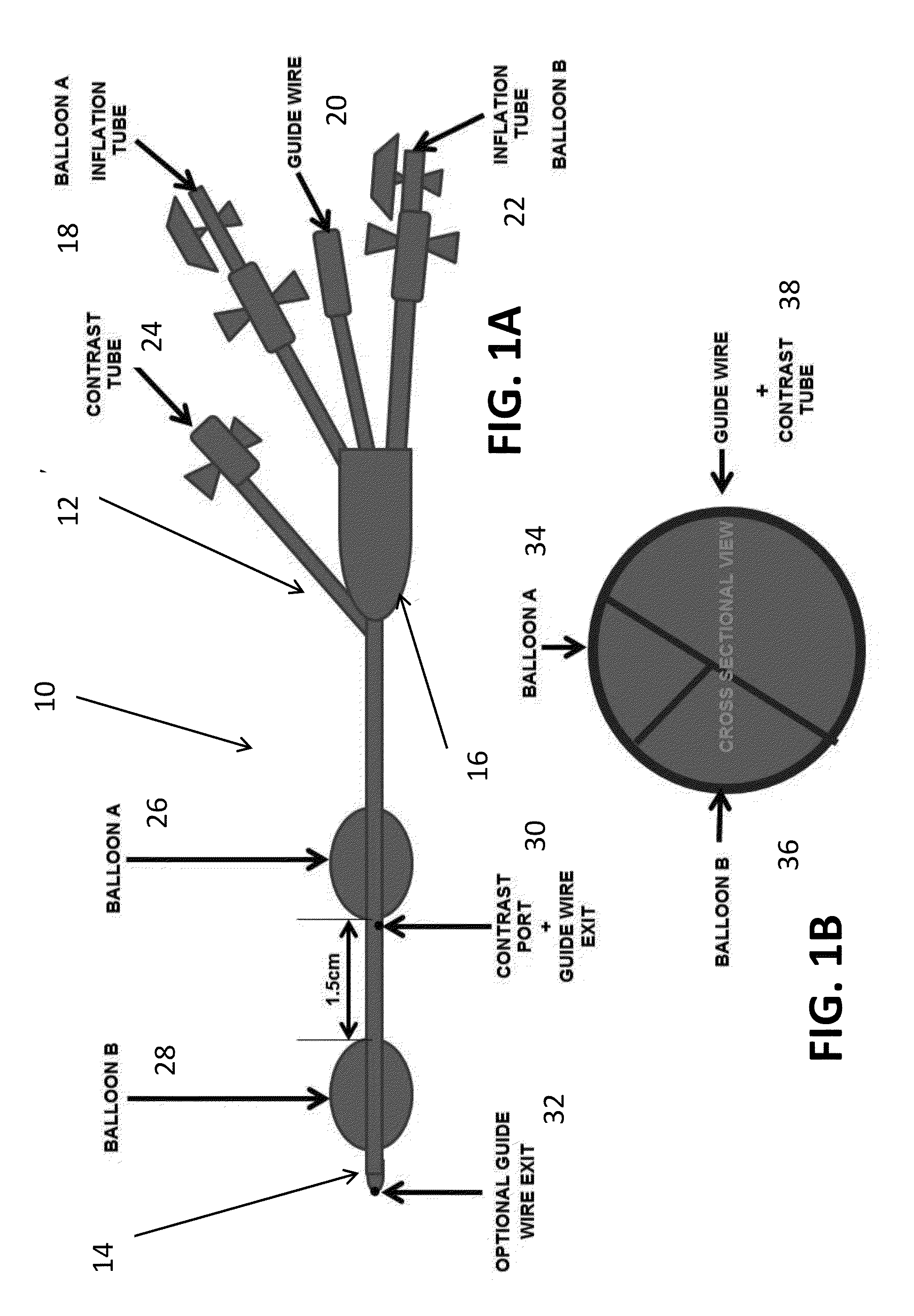
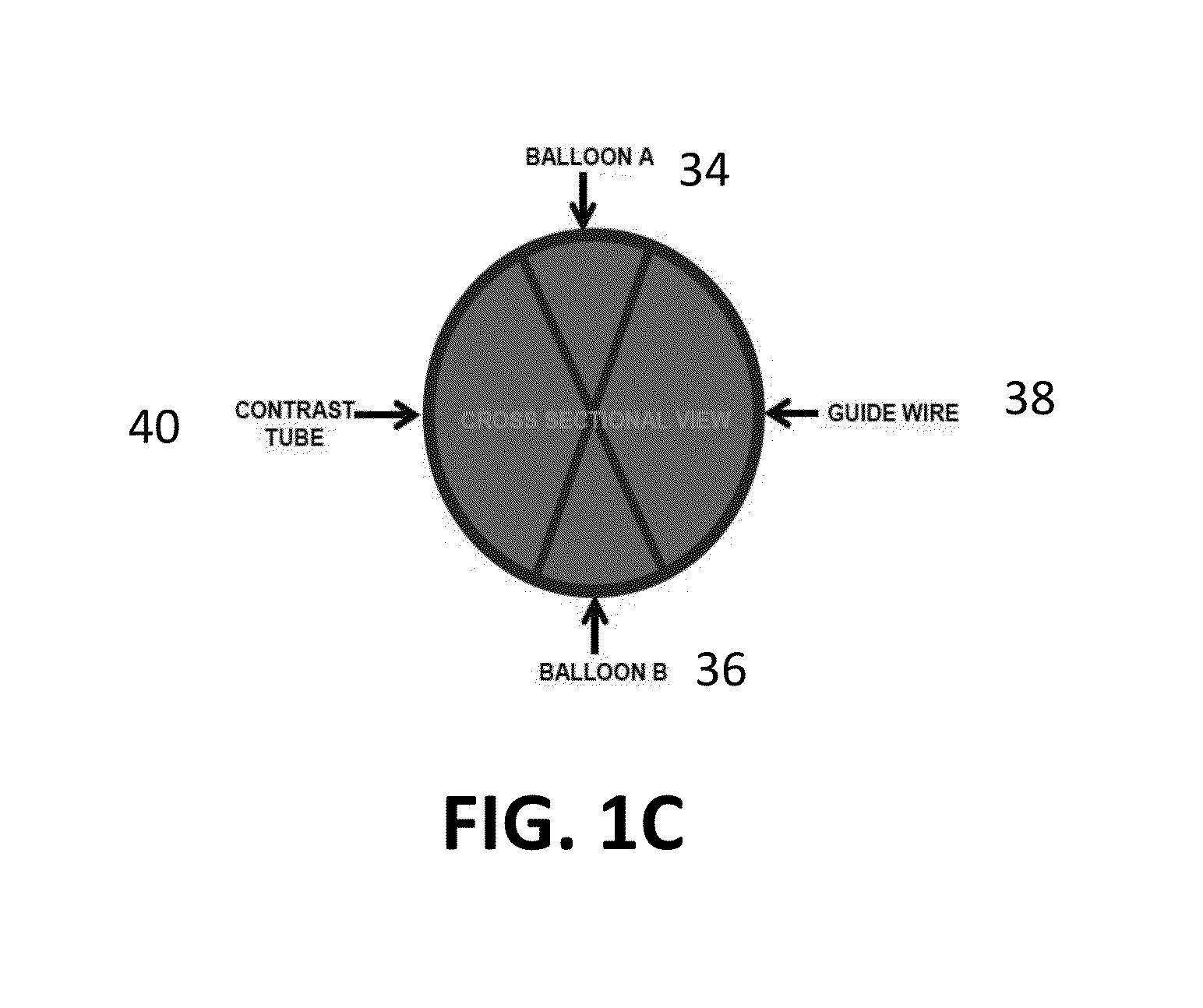
Dual Balloon Biliary Stone Extraction Device
InactiveUS20150150572A1Good choiceFacilitating its cannulationBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterGene deliveryBiliary epithelium
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for selective guide wire cannulation of a bile duct, removal of biliary calculi, and delivering hydrodynamic gene delivery are also provided. There is provided a method for straightening the terminal common bile duct to allow biliary calculi to be removed, assisting in creation of a gastoejunostomy, and selective guidewire cannulation. A method for isolating a segment of biliary epithelium for hydrodynamic gene delivery is also provided, in which a segment of the bile duct is isolated and plasmids (oncogenic or therapeutic) are injected under pressure to allow entry into cholangiocytes. There is also provided a method for isolating the cystic duct or left / right intrahepatic ducts to allow the insertion of a guide wire and subsequent therapy. A single catheter platform may be used to perform the above procedures.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
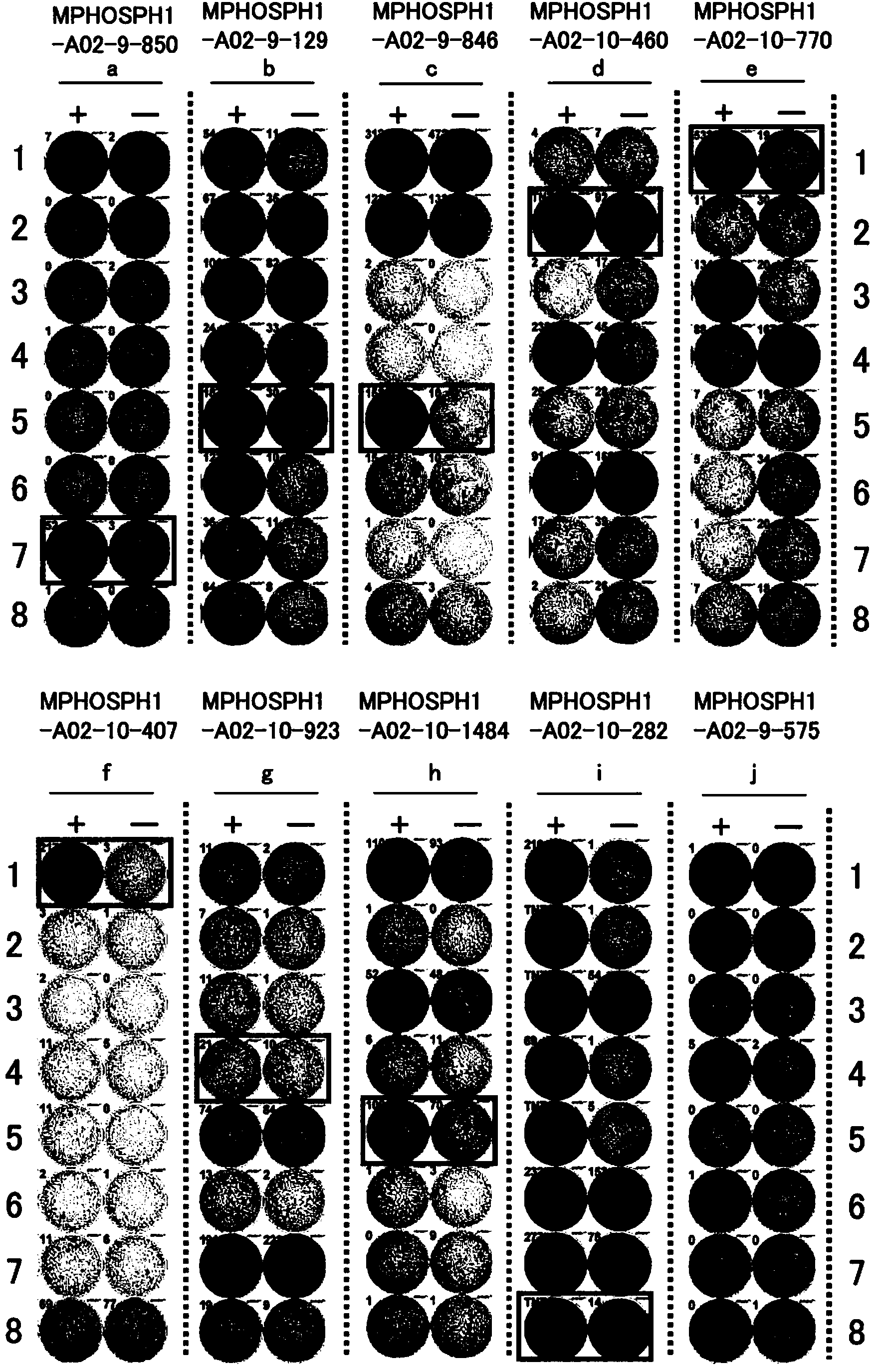
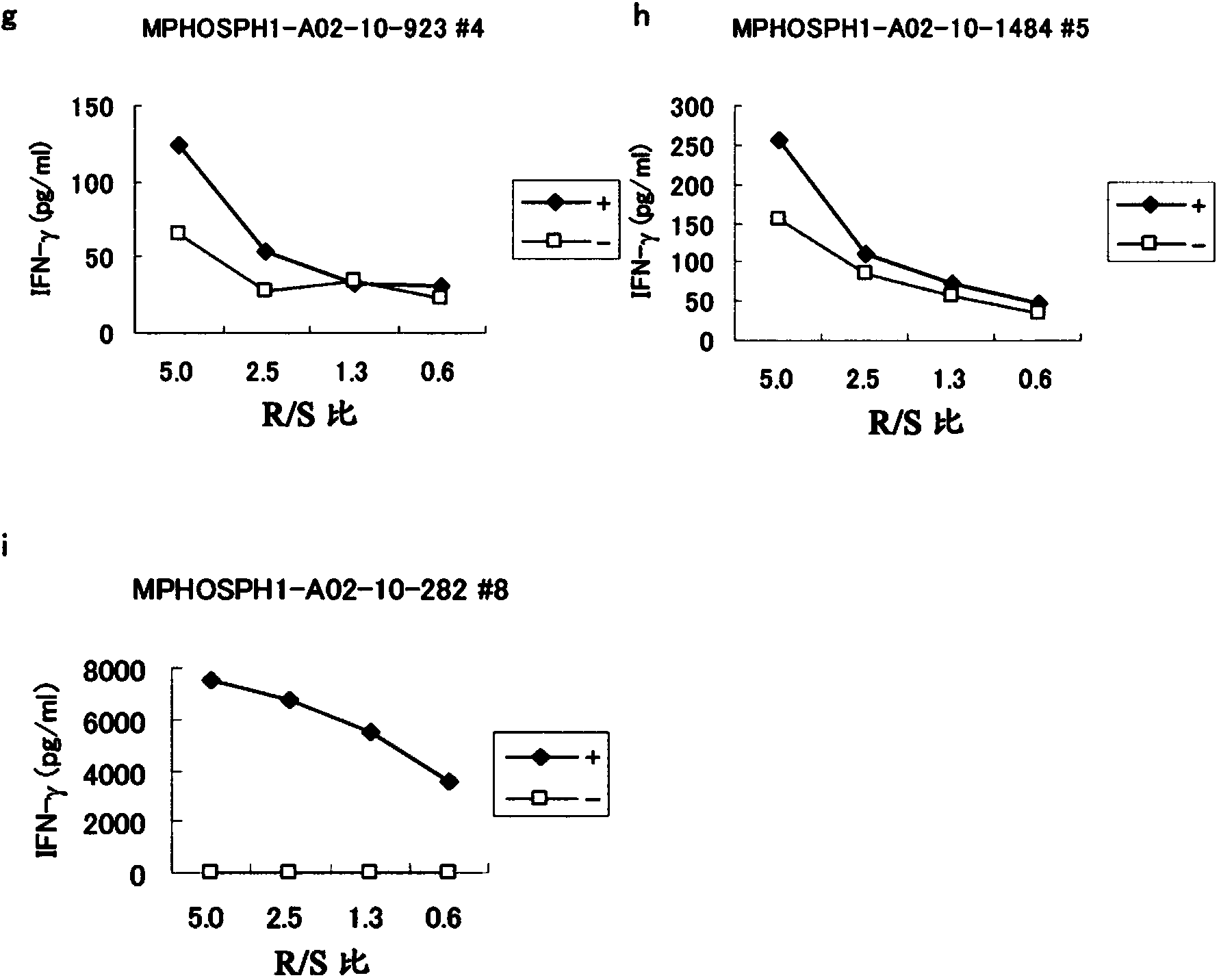
Mphosph1 peptides and vaccines including the same
As discussed in greater detail herein, isolated epitope peptides derived from MPHOSPH1 bind to an HLA antigen and induce cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and thus are suitable for use in the context of cancer immunotherapy, more particularly cancer vaccines. The inventive peptides encompass both the above-mentioned MPHOSPH1-derived amino acid sequences and modified versions thereof, in which one, two, or several amino acids are substituted, deleted, inserted or added, provided such modified versions retain the requisite CTL inducibility of the original sequences. Further provided are polynucleotides encoding any of the aforementioned peptides as well as pharmaceutical agents or compositions that include any of the aforementioned peptides or polynucleotides. The peptides, polynucleotides, and pharmaceutical agents or compositions of this invention find particular utility in either or both of the treatment and prevention of cancers and tumors, including, for example, bladder cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, cholangiocellular carcinoma, CML, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, NSCLC, lymphoma, osteosarcoma, prostate cancer, renal cancer and soft tissue tumor.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
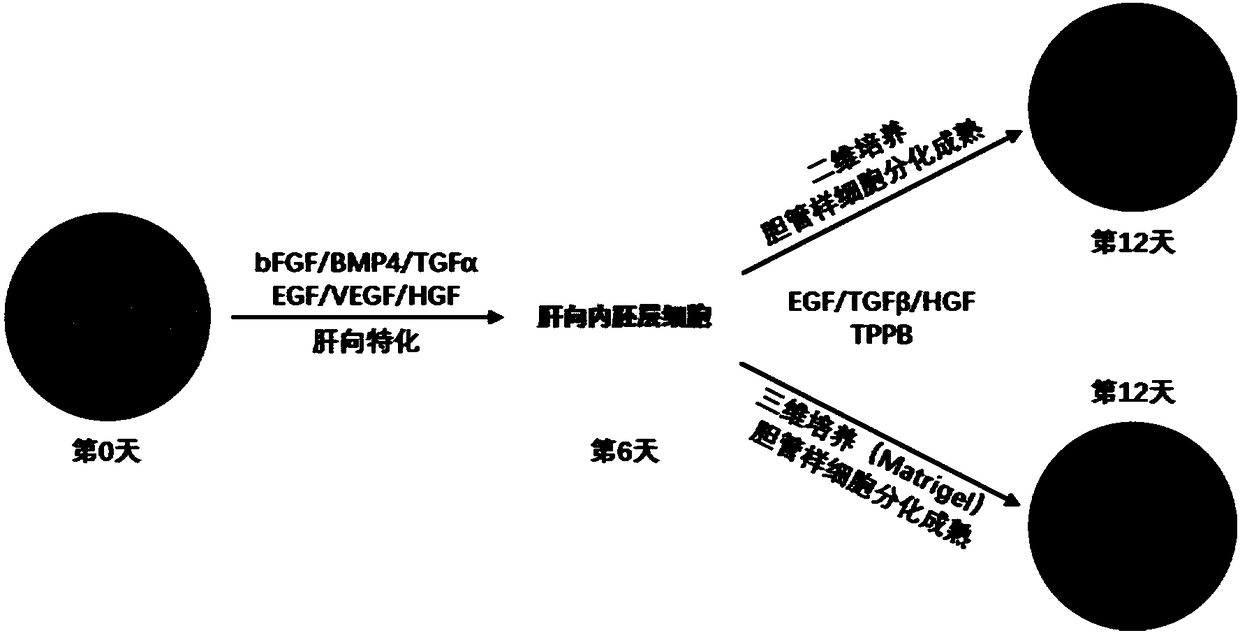
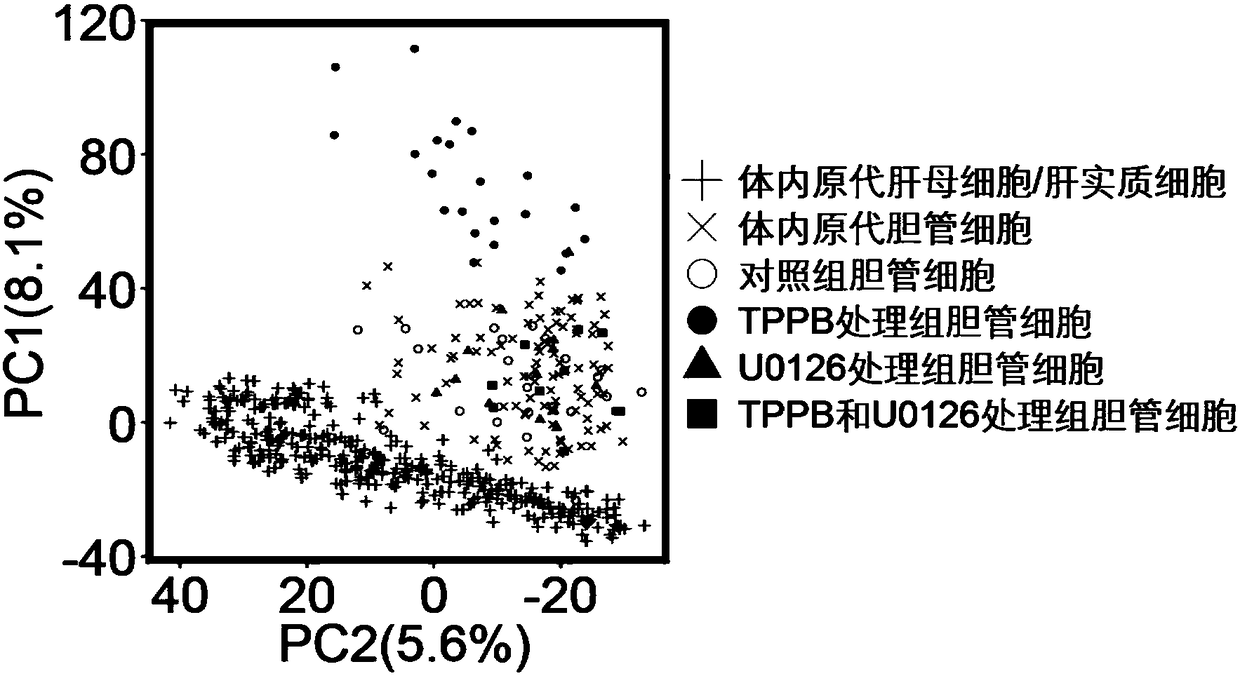
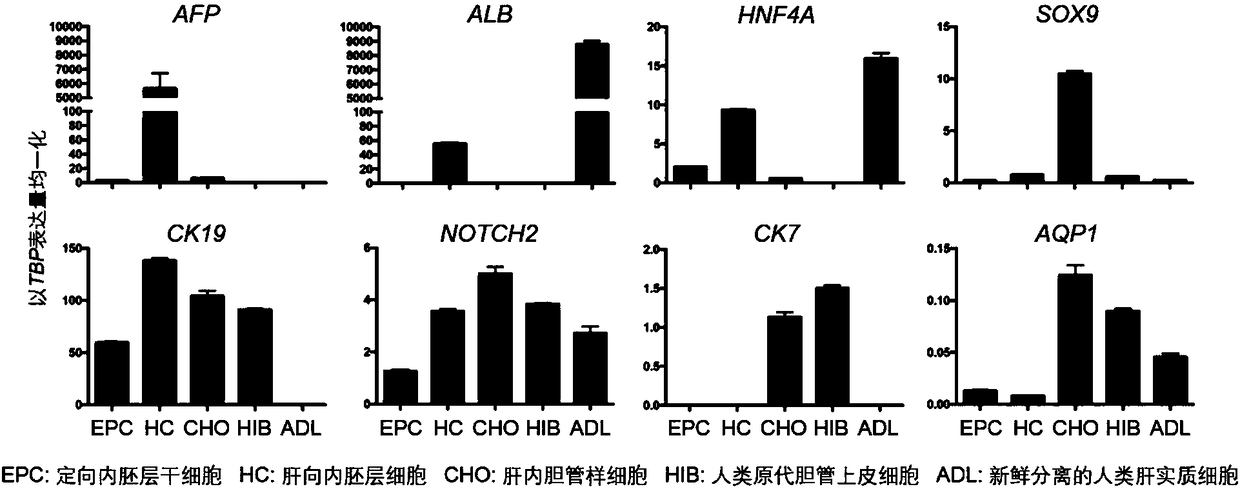
Method for promoting human cholangiocytes to differentiate and mature through MAPK/PKC signaling pathway activator
ActiveCN108865969AArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsGerm layerHuman bile
The invention provides a method for inducing directional endoderm stem cells to form intrahepatic bile duct-like cells. The method comprises the steps of directionally inducing directional endoderm stem cells to form liver directed endodermal cells, and differentiating the liver directed endodermal cells into human bile duct-like cells under directional action of a small molecular compound and theMAPK / PKC signaling pathway activator. The invention further provides human bile duct-like cells acquired through the method.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Multipotent stem cells from the extrahepatic billary tree and methods of isolating same
The present invention relates to a multipotent stem cell, multipotent cell populations, and an enriched multipotent cell population, each found in fetal, neonatal, pediatric, and adult biliary tree tissue and up to 72 hours post mortem (although preferentially, within 10 hours post mortem) and capable of maturing into multiple endodermal tissues that include liver, biliary and pancreatic tissues. The multipotent stem / progenitor cell and cell populations are found in peribiliary glands, and progenitors descending from them are present throughout the biliary tree including in the gallbladder. High numbers of the peribiliary glands are found in the branching locations of the biliary tree such as hilum, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, common duct, common hepato-pancreatic duct and gallbladder. Related multipotent cells, multipotent cell populations and their descendent progenitors are found throughout the biliary tree including in the gall bladder, which does not have peribiliary glands. Compositions comprising same, methods of identifying and isolating same, maintaining same in culture, expanding same in culture and differentiating or lineage restricting the same in vitro or in vivo to hepatic, biliary or pancreatic fates (e.g., as hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and / or pancreatic islet cells) are also provided. Methods of using the multipotent cells and / or multipotent cell populations are also provided.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Method for transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into hepatic stem cells
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical engineering. Liver transplantation is the only effective means that can be employed for treating liver diseases in late stage at present and is greatly limited in clinic use due to lack of liver sources. Hepatic stem cells have a self-updating capacity and a bidirectional differentiation capacity of differentiating into hepatocytes and cholangiocytes and therefore can provide an infinite number of donor cells for hepatocyte transplantation treatment in theory. The method for the transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into hepatic stem cells, which is provided by the invention, is to reprogram fibroblasts into hepatic stem cells which have the unique self-updating and bidirectional differentiation capacities of hepatic stem cells by using three transcription factors, namely c-Jun, Foxa2 and Hnf1beta. The inducible hepatic stem cells prepared by the method can be used as ideal cell sources for cell treatment of acute hepatic failure and liver diseases in medium and late stages, can be used as seed cells for medicine screening and tissue engineering livers and can provide an ideal research platform for researching cell biological characteristics of hepatic stem cells, liver development and the like.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
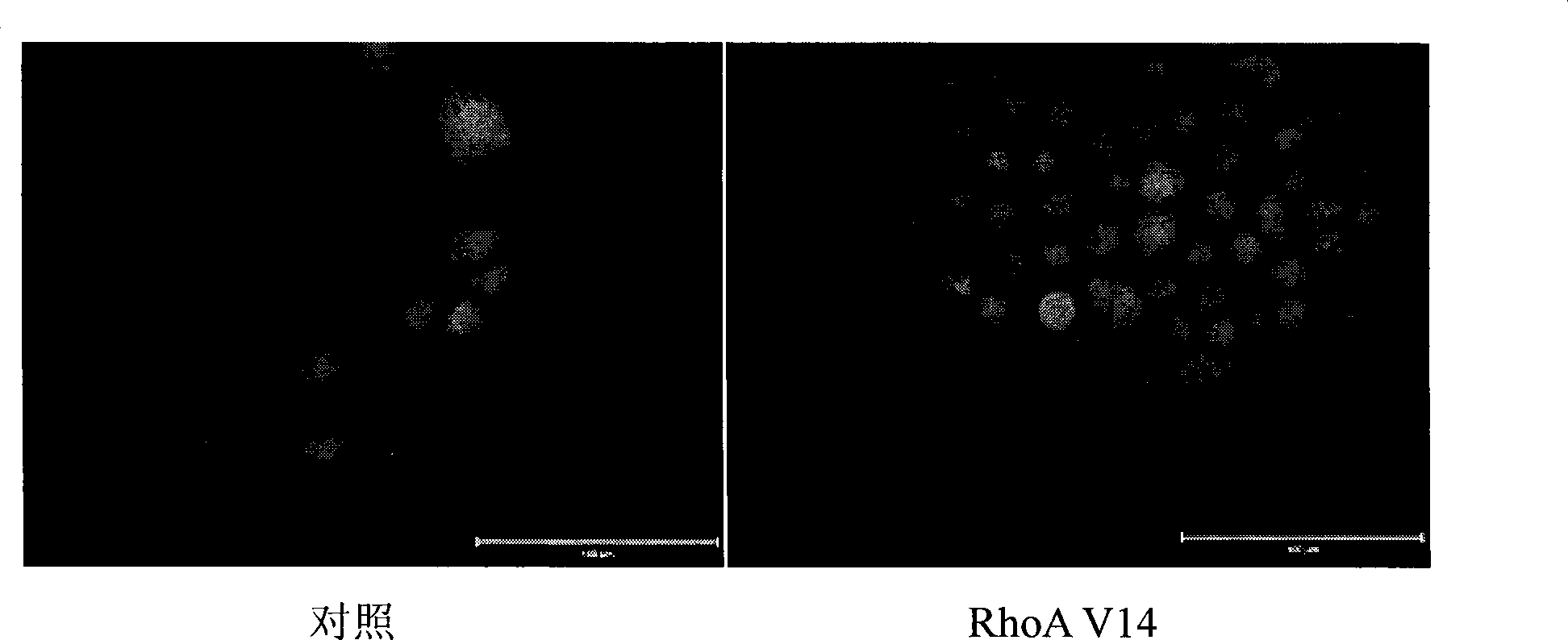
Method for inducing hepatic oval cells differentiation to bile duct cells and its special culture medium
The invention discloses a method for inducing hepatic oval cells to differentiate towards bile duct cells and a special culture medium used in the method. The culture medium is added with 1 to 6 percent of fetal calf serum, 1 to 3 percent of B27 and 0.05 to 0.15 percent of penicillin-streptomycin on the basis of an RPMI1640 culture medium. The method for inducing the differentiation comprises the following steps: 1) leading RhoA mutant genes into the oval cells WB-F344 to obtain WB-F344 cells of a high-expression RhoA gene activity mutant; and 2) inoculating the WB-F344 cells of the high-expression RhoA gene activity mutant into the special culture medium where the hepatic oval cells are induced in vitro to differentiate into the bile duct cells, and culturing the WB-F344 cells at a temperature of 37 DEG C with 5 percent of CO2 to obtain the bile duct cells. The method provides a new approach to obtain the bile duct cells and has wide application prospect.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
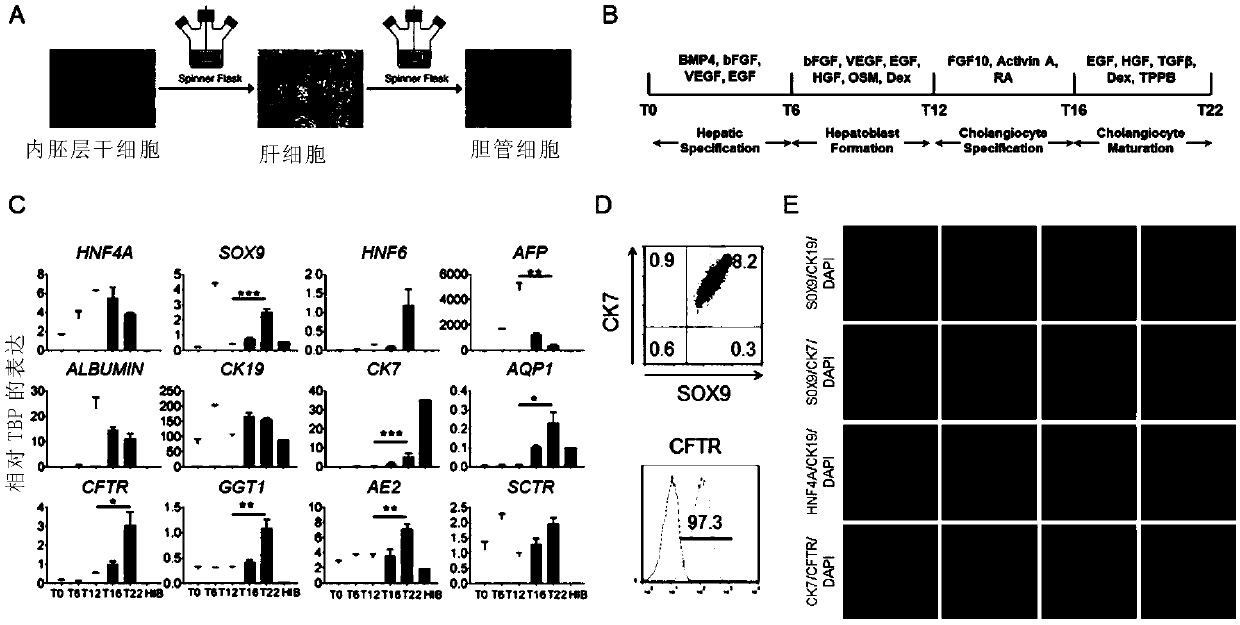
Derivation of hepatic stem cells and mature liver cell types and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190161734A1Enhance stem cell proliferationPrevent stem cell differentiationHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsDiseaseLiver Stem Cell
This application describes liver stem cells (LSC), and differentiated hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and 3D cellular structures derived therefrom. Methods for producing LSC and mature, differentiated hepatocytes and cholangiocytes in culture are provided. Also provided are cell culture systems and cell culture media for producing a homogenous population of liver stem cells that remain in an undifferentiated state over multiple passages in culture. The LSC and methods are useful for producing homogenous populations of hepatocytes and cholangiocytes for downstream applications. The LSC can be transplanted into subjects to treat liver diseases.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
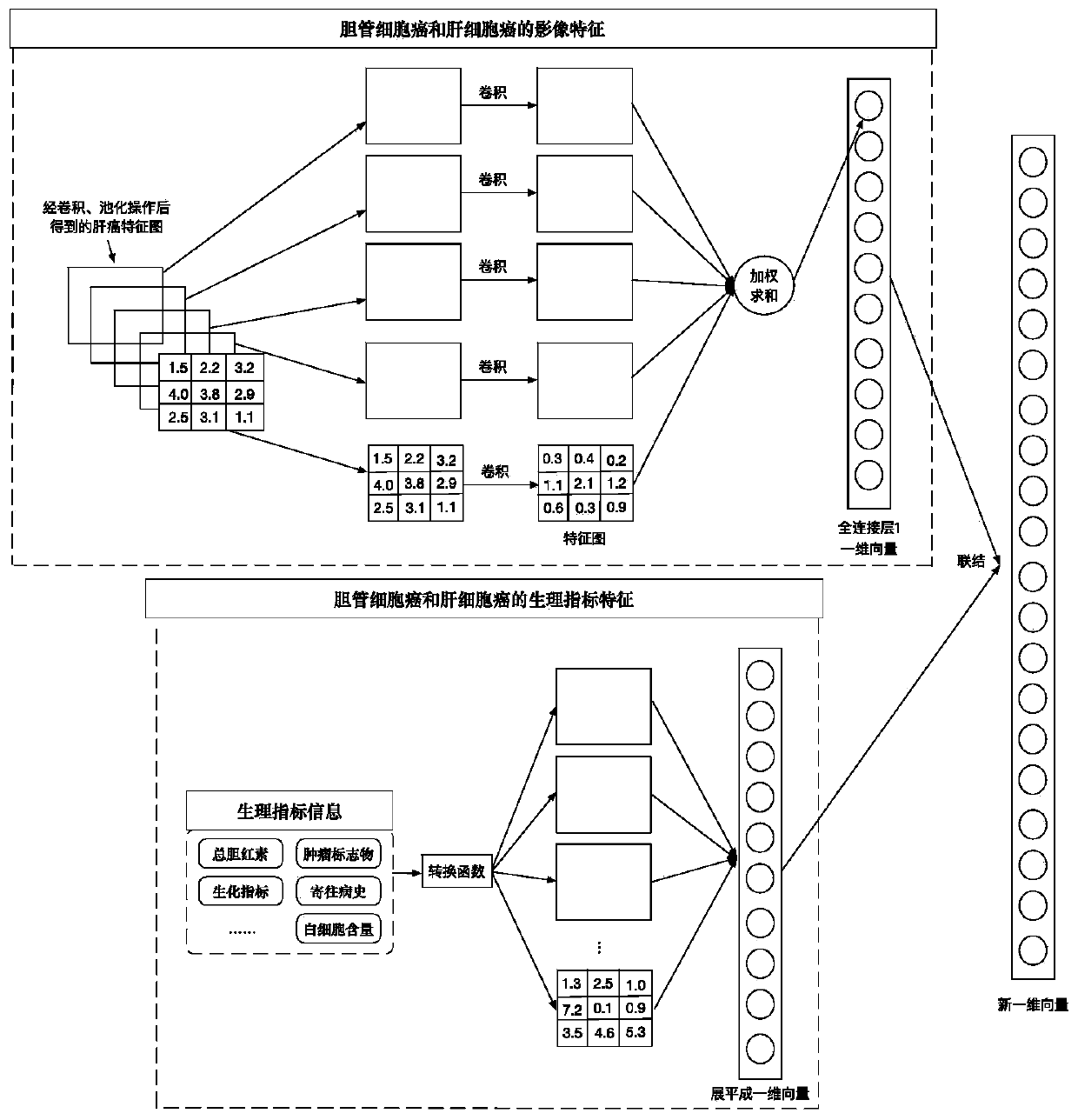
Automatic liver tumor classification method and device based on physiological indexes and image fusion
PendingCN110910371AImprove recognition accuracyRobustImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extraction algorithmImaging data
The invention discloses an automatic liver tumor classification method and device based on physiological indexes and image fusion so that good robustness is realized for different patients during identification. A complex feature extraction algorithm does not need to be artificially designed . Full-automatic feature learning and extraction are realized, combined learning and mining are carried out on feature expression differences of the bile duct cell carcinoma and the hepatocellular carcinoma on images and expression differences of the bile duct cell carcinoma and the hepatocellular carcinoma on physiological indexes, and identification accuracy of the model is improved. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an image and physiological index database of bile duct cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, and collecting an abdomen CT image of a patient and corresponding physiological indexes recorded by a doctor; marking all the acquired image data, drawing a livertissue area in the image data, judging whether the liver tissue area belongs to the cholangiocarcinoma or the hepatocarcinoma, and marking the liver tissue area as a gold standard for network training; constructing a three-dimensional full convolutional neural network segmentation model; and constructing a deep convolutional neural network classification model based on image and physiological index fusion.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
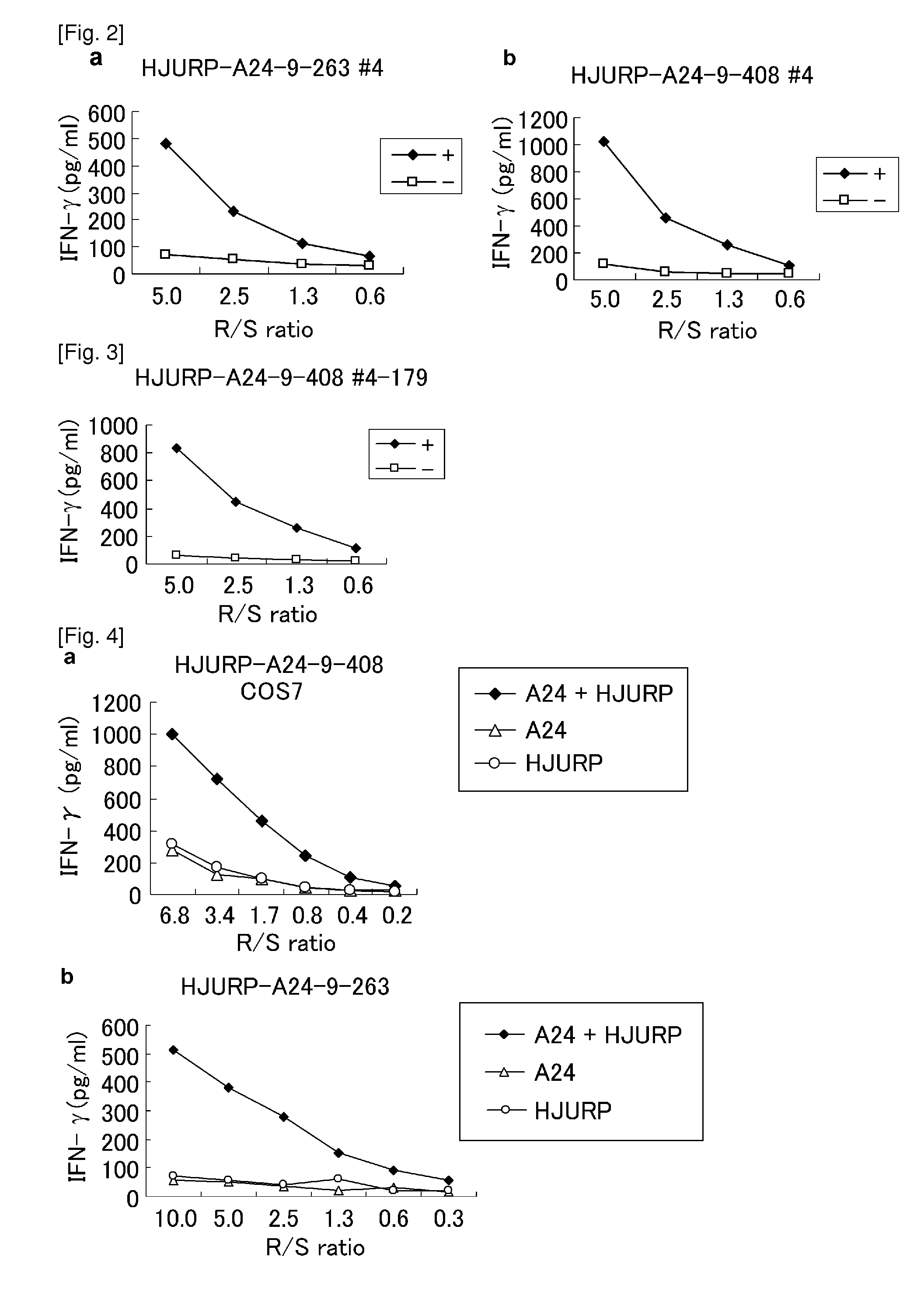
Hjurp peptides and vaccines including the same
ActiveUS20130064840A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsProstate cancerEsophagus Cancers
Isolated peptides derived from SEQ ID NO: 50 and fragments thereof that bind to an HLA antigen and induce cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and thus are suitable for use in the context of cancer immunotherapy, more particularly cancer vaccines are described herein. The inventive peptides encompasses both the above mentioned amino acid sequences and modified versions thereof, in which one, two, or several amino acids sequences substituted, deleted, added or inserted, provided such modified versions retain the requisite cytotoxic T cell inducibility of the original sequence. Further provided are nucleic acids encoding any of the aforementioned peptides as well as pharmaceutical agents, substances and / or compositions that include or incorporate any of the aforementioned peptides or nucleic acids. The peptides, nucleic acids, pharmaceutical agents, substances and compositions of this invention find particular utility in the treatment of cancers and tumors, including, for example, AML, bladder cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, cholangiocellular carcinoma, CML, colorectal cancer, esophagus cancer, Diffused-type gastric cancer, liver cancer, NSCLC, lymphoma, osteosarcoma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, renal carcinoma, SCLC, soft tissue tumor and testicular tumor.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
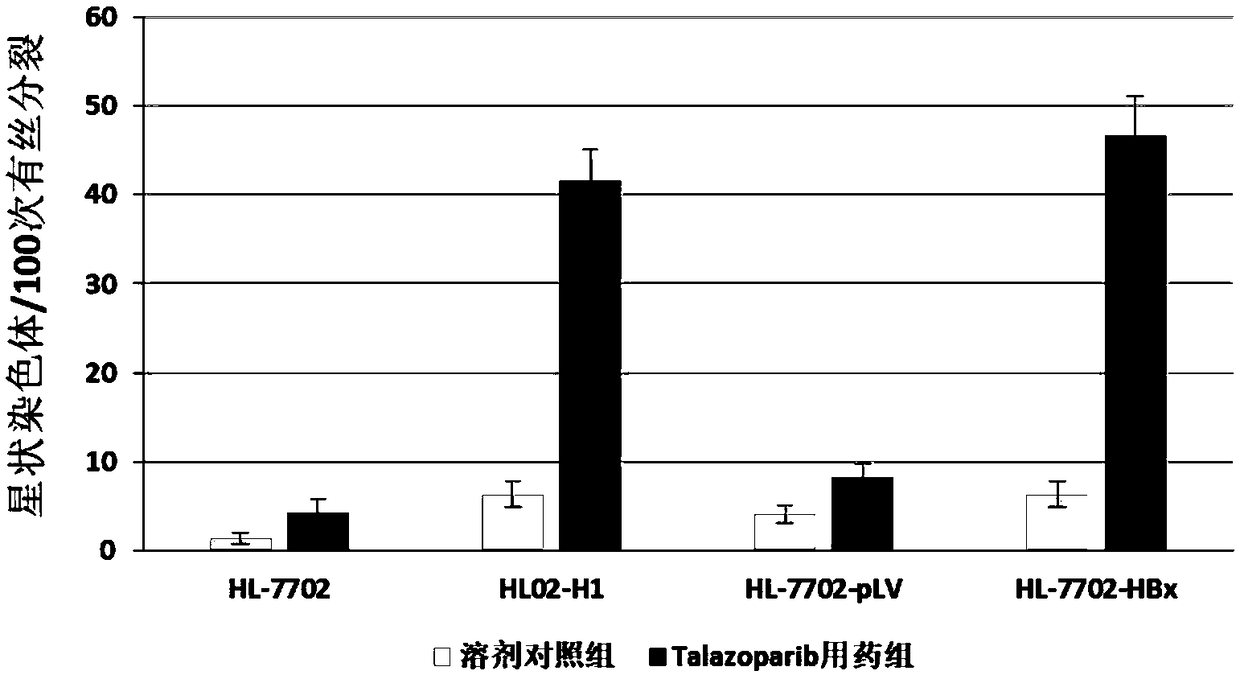
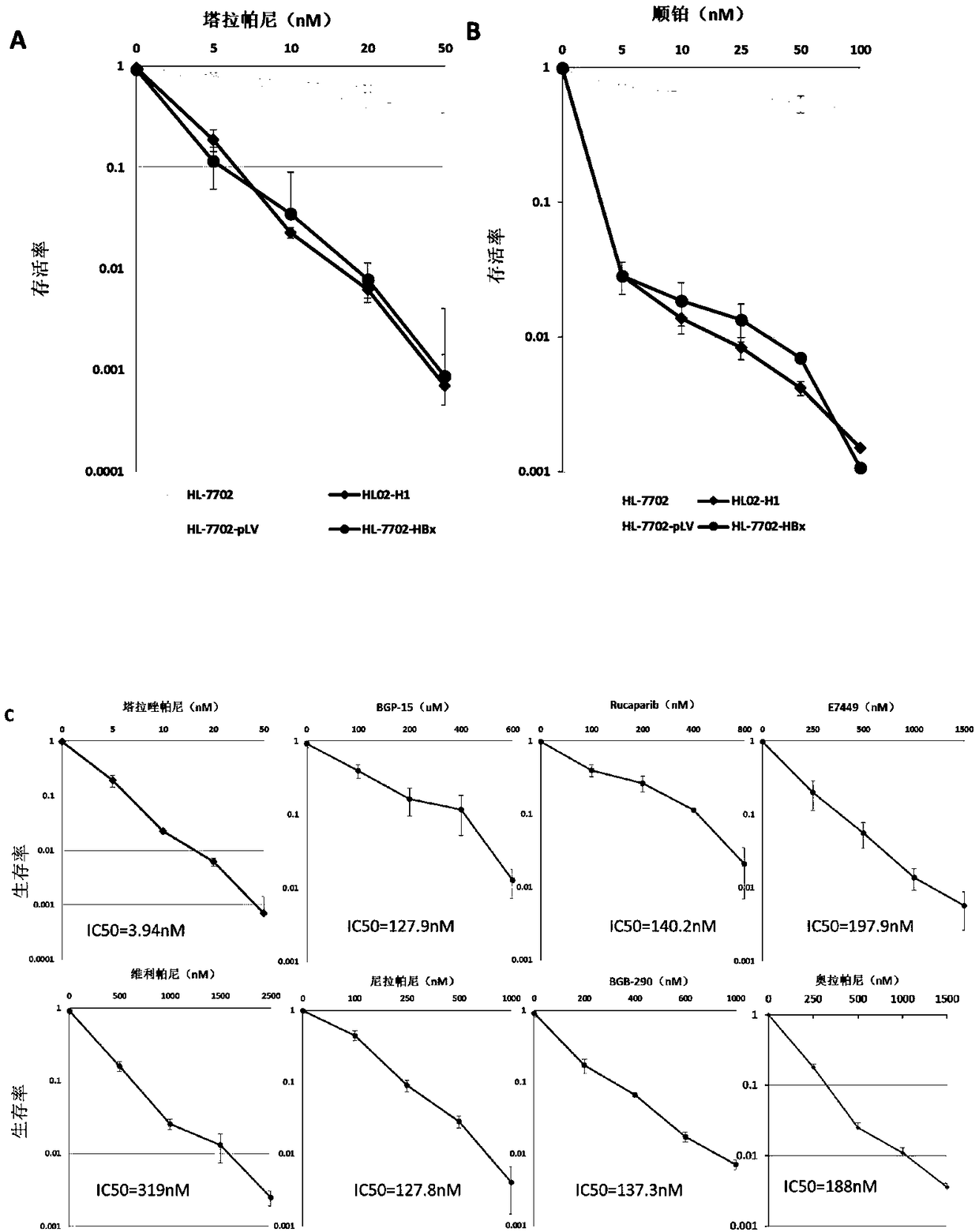
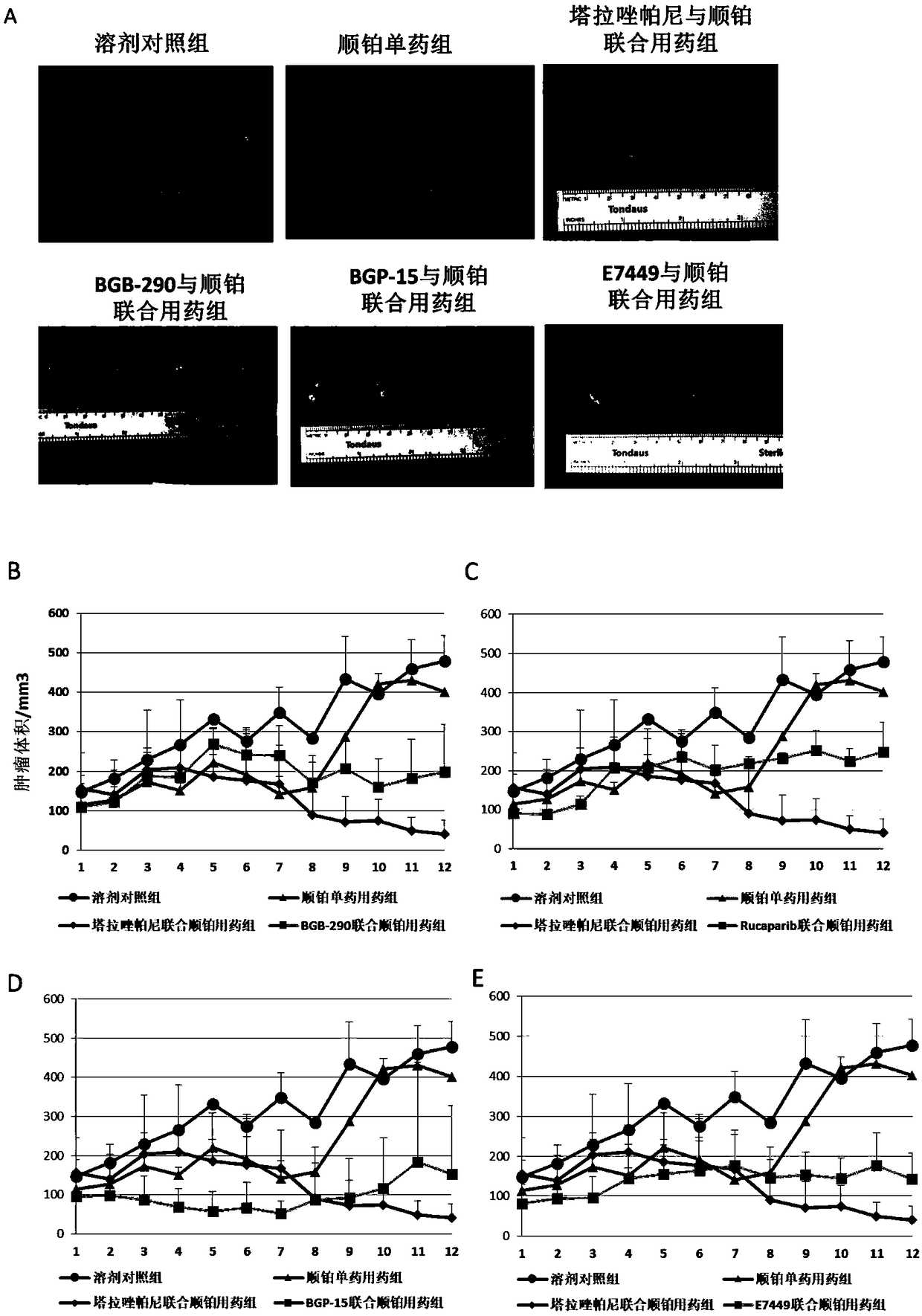
Use of Talazoparib in preparation of drugs for treating or preventing diseases related with hepatitis virus
ActiveCN109364079AGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemCancer cellChronic hepatitis
The invention discloses use of a PAPP inhibitor Talazoparib or salt and solvate thereof in the preparation of drugs for treating or preventing diseases related with hepatitis virus. The diseases are infected by hepatitis B virus, are related with the infection of the hepatitis B virus and include acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, hepatic fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, liver cancer or cholangiocellular carcinoma and the like; by utilizing a Talazoparib single drug or combining the Talazoparib single drug with other anticancer drugs, host cells of the hepatitis B virus can be effectively eliminated, and the growth of positive cancer cells of the hepatitis B virus can be effectively inhibited; and compared with other types of PARP inhibitors such as Olaparib, Talazoparib has obvious advantageson the dosage and the treatment effect that: Talazoparib can be used for relatively effectively controlling the infection of the hepatitis B virus, inhibiting the development of positive cancers of the hepatitis B virus and relatively effectively controlling the proliferation of the positive cancers, with relatively large volume (not smaller than 400mm<3>) of the hepatitis B virus in a relativelylater period in a relatively low dosage range (0.015mg / kg / d-0.275mg / kg / d and is a unique anti-cancer drug for healing the type of tumors at present.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN +1
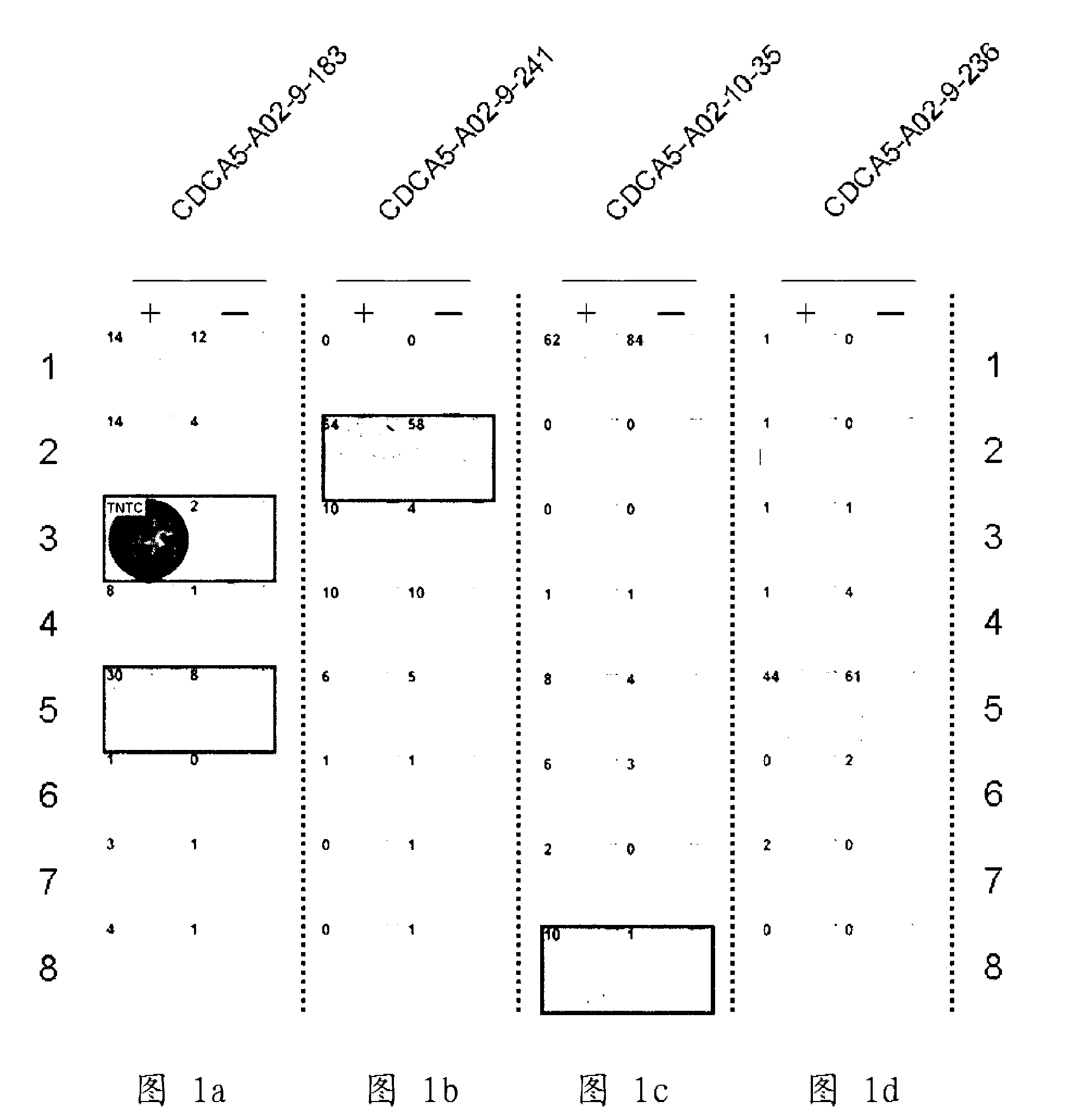
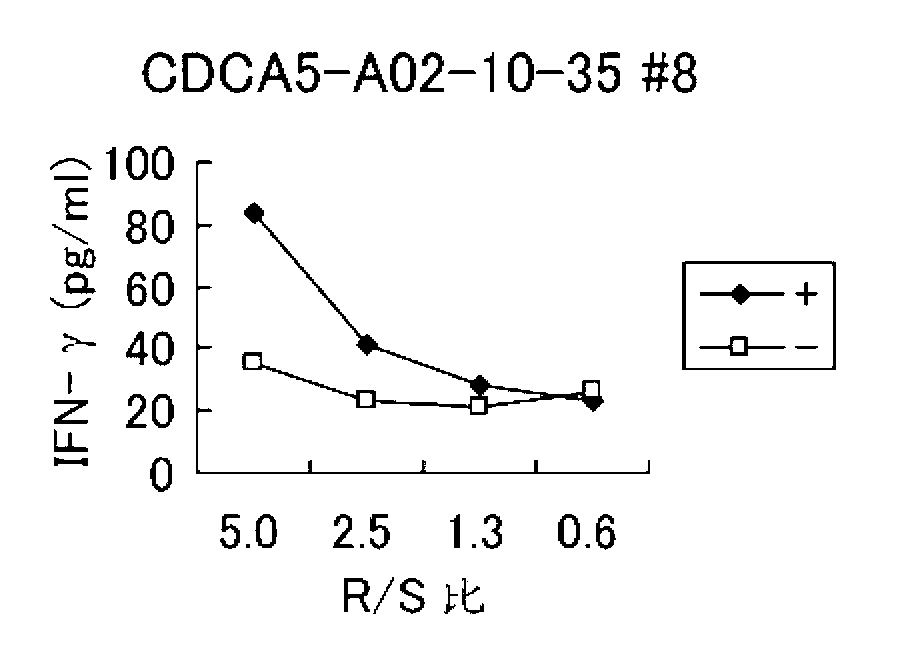
Cdca5 peptides and vaccines including the same
Isolated peptides derived from SEQ ID NO: 21 and fragments thereof that bind to an HLA antigen and induce cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and thus are suitable for use in the context of cancer immunotherapy, more particularly cancer vaccines, are described herein. The inventive peptides encompass both the above mentioned amino acid sequences and modified versions thereof, in which one, two, or several amino acids are substituted, deleted, inserted or added, provided such modified versions retain the requisite HLA binding and / or CTL inducibility of the original sequences. Further provided are nucleic acids encoding any of the aforementioned peptides as well as pharmaceutical agents, substances and / or compositions that include or incorporate any of the aforementioned peptides or nucleic acids. The peptides, nucleic acids, pharmaceutical agents, substances and compositions of this invention find particular utility in the treatment of cancers and tumors, including, for example, AML, bladder cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, cholangiocellular carcinoma, CML, colorectal cancer, esophagus cancer, gastric cancer, gastric diffuse-type cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, prostate cancer, SCLC and soft tissue tumor.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Method for preparing functional bile duct cells by using entoderm stem cells on scale and application of functional bile duct cells
The invention provides a method for preparing functional bile duct cells by using entoderm stem cells on scale and application of the functional bile duct cells, and specifically, the invention provides a method for inducing human entoderm stem cells to be differentiated into bile duct cells and / or bile duct cell populations. The method comprises the following step: culturing entoderm stem cells in a culture system, so as to obtain functional bile duct cells and / or bile duct cell populations. The functional bile duct cells and / or bile duct cell populations prepared by using the method have very high differentiation rates and purity, and in addition, the bile duct cells and / or bile duct cell populations prepared by using the method can be used as in-vitro models of medicine screening and medicine toxicity evaluation.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genome recombination fingerprint for characterizing hHRD homologous recombination deficiency and identification method thereof
The invention relates to a novel method for identifying homologous recombination deficiency and application thereof. More particularly, the present invention relates to a characteristic genome recombination fingerprint which is related to hHRD type homologous recombination repair deficiency and is resolved by using high throughput genome re-sequencing, bioinformatics analysis and statistical correlation analysis. The characteristic hHRD recombination fingerprint is caused by the functional deficiency of a specific homologous recombination repair mechanism (namely CRL4WDR70-H2B mono-ubiquitination pathway), and comprises the total frequency of genome recombination in a single sample, the composition of chromosome structure variation types and site-specific copy number variation. The recombinant fingerprint is used for identifying infectious diseases or tumors with the characteristic mutant fingerprint, and is used for guiding targeted drug treatment of PARP inhibitors. The invention relates to the method and application thereof for diseases including but not limited to breast cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial (like) cancer, ovarian clear cell cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, skin cancer and gastric cancer with such characteristics, as well as hepatitis B virus infection or related liver fibrosis cirrhosis, liver cancer and cholangiocarcinoma.
Owner:成都吉诺迈尔生物科技有限公司 +1
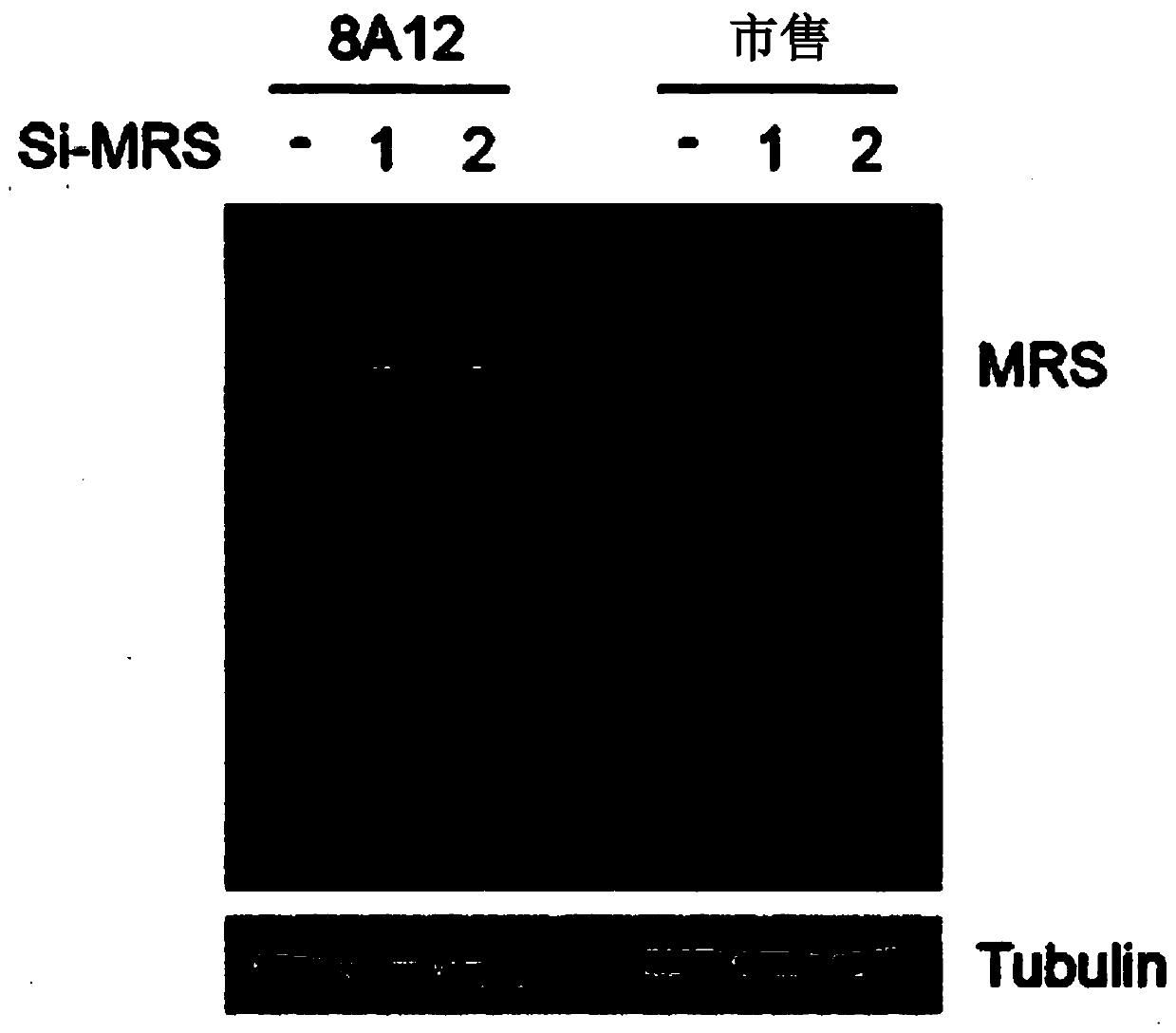
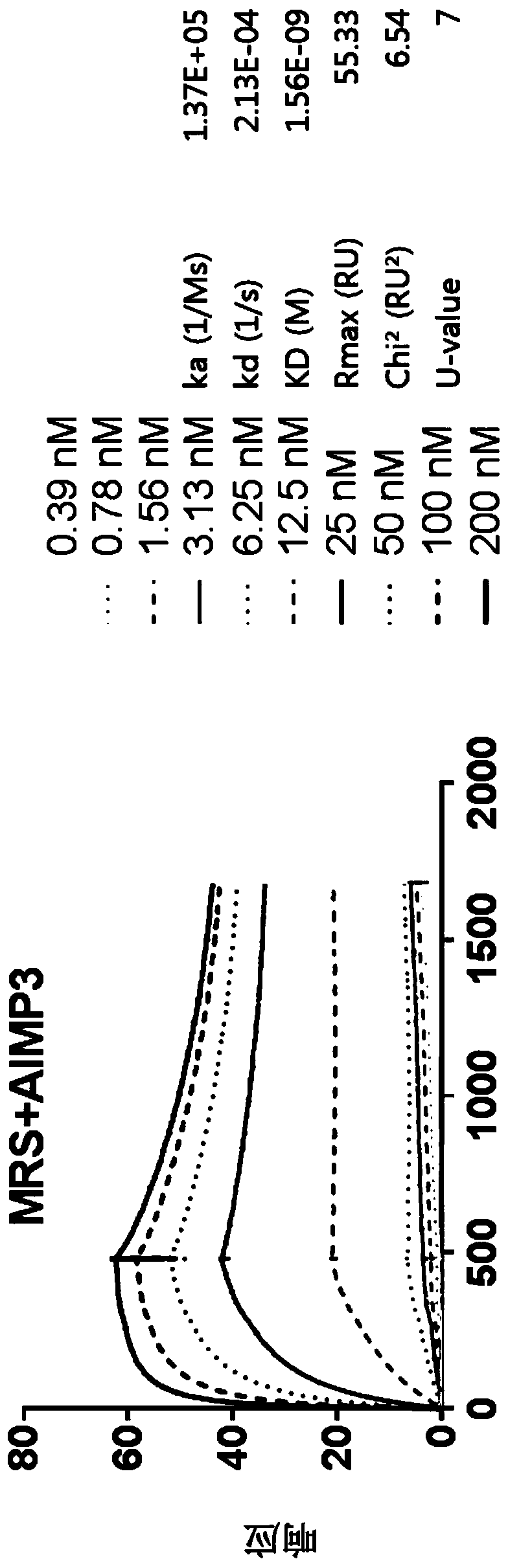
Method for diagnosis of bile duct cancer using methionyl-trna synthetase in bile duct cell
PendingCN110998327AClear sensitivityClear featuresPreparing sample for investigationLigasesCancer cellOncology
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosis of bile duct cancer, using methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MRS) in bile duct cells and, more particularly, to a composition for diagnosing bile ductcancer, comprising an agent with which an expression level of methionyl-tRNA synthetase protein is measured, a diagnostic kit, and a method for qualitative or quantitative analysis of MRS to provide information necessary for the diagnosis of bile duct cancer. According to the present invention, MRS retains a very high value as a diagnostic marker for bile duct cancer in terms of rapidity and accuracy because MRS allows determination to be made to see whether bile duct cancer is present or absent for bile duct cells, which have been classified as atypical cells by conventional pathological examination methods. Hence, the present invention provides a method for discriminating between cancer cells and normal cells in atypical cells and can make a definite diagnosis of cancer with almost 100 %in all of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy in contrast to many conventional cancer markers with which an actual result of diagnosis is substantially difficult to obtain at a cell level (that is, cytodiagnosis).
Owner:温口特
Methods of producing in vitro liver constructs and uses thereof
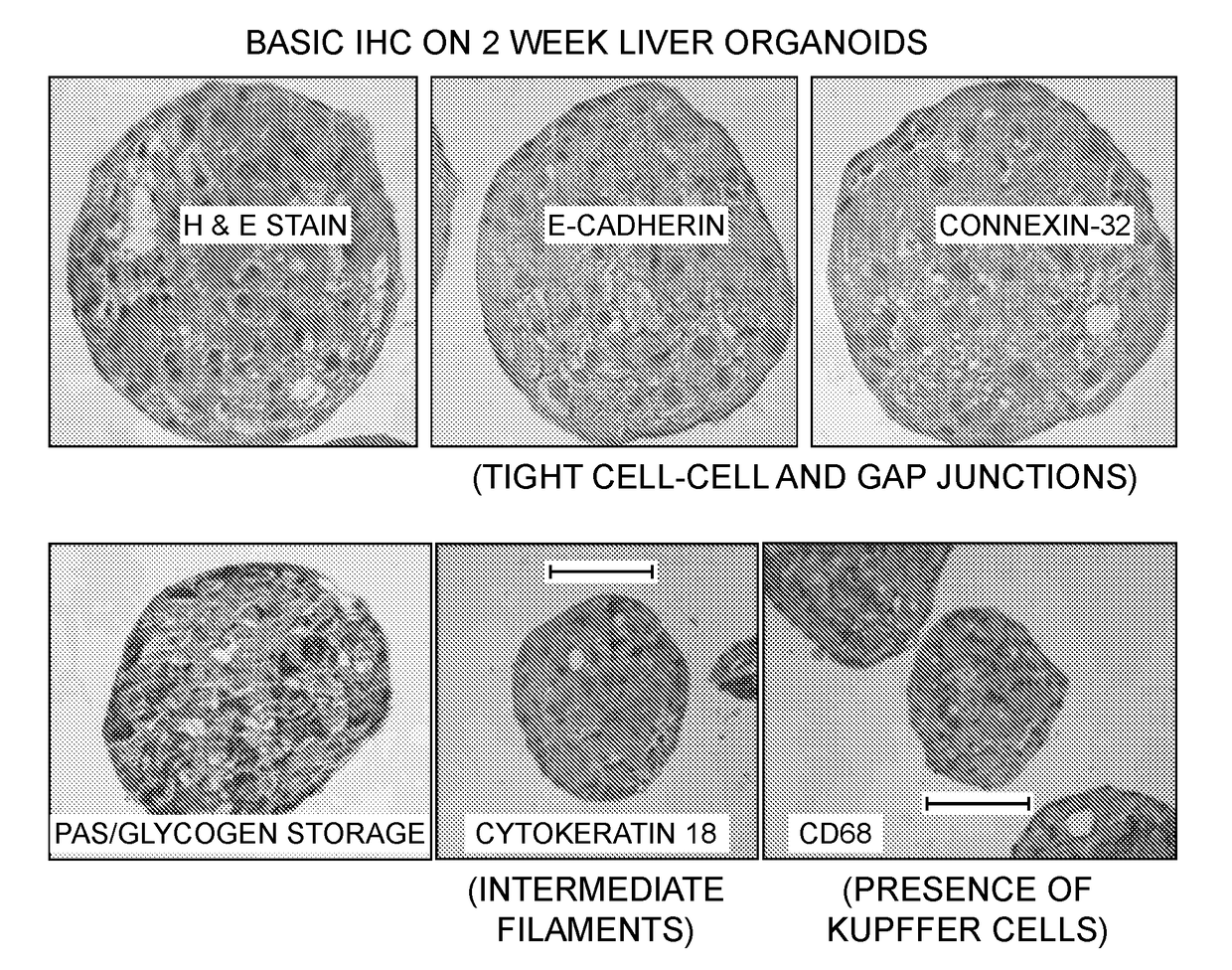
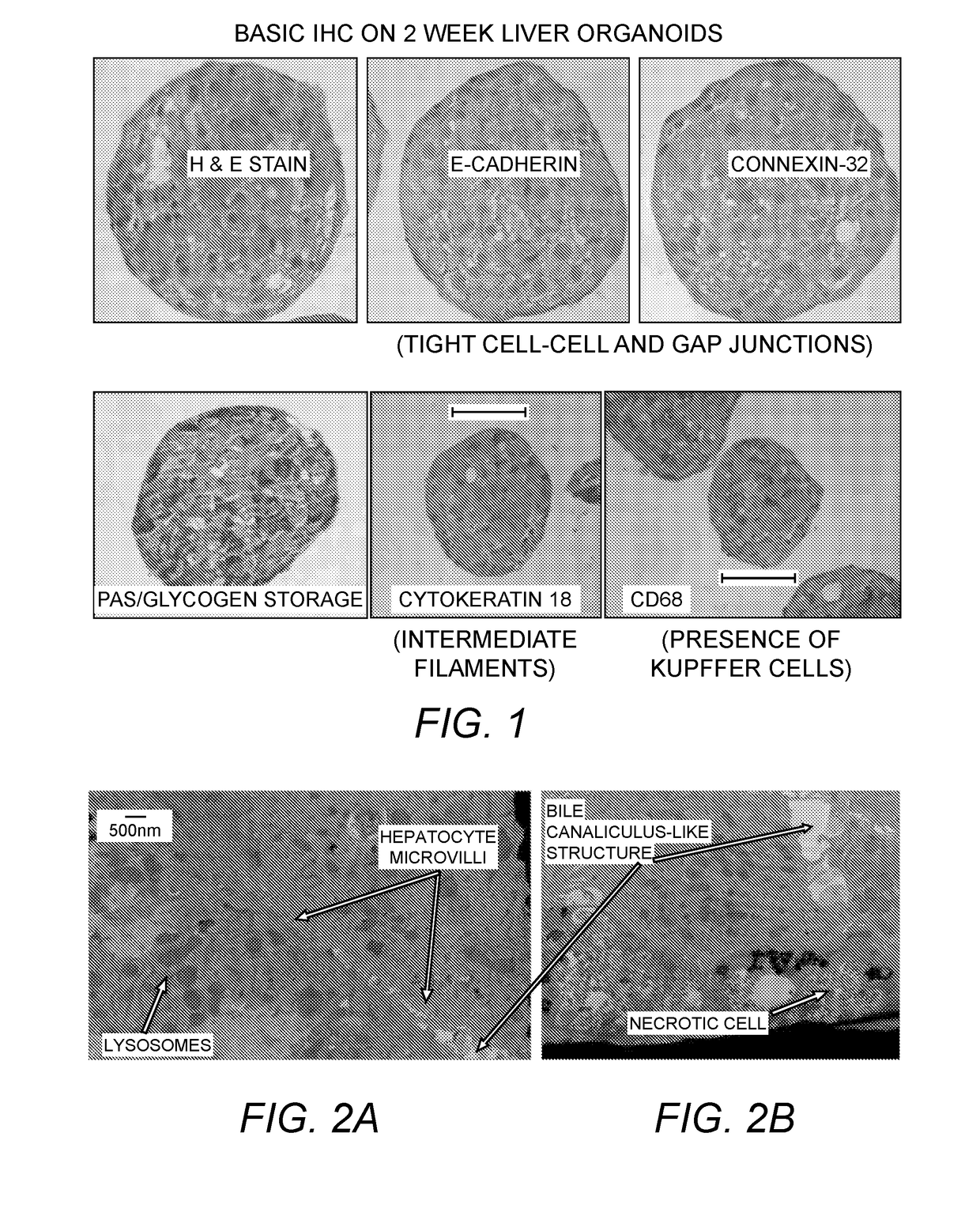
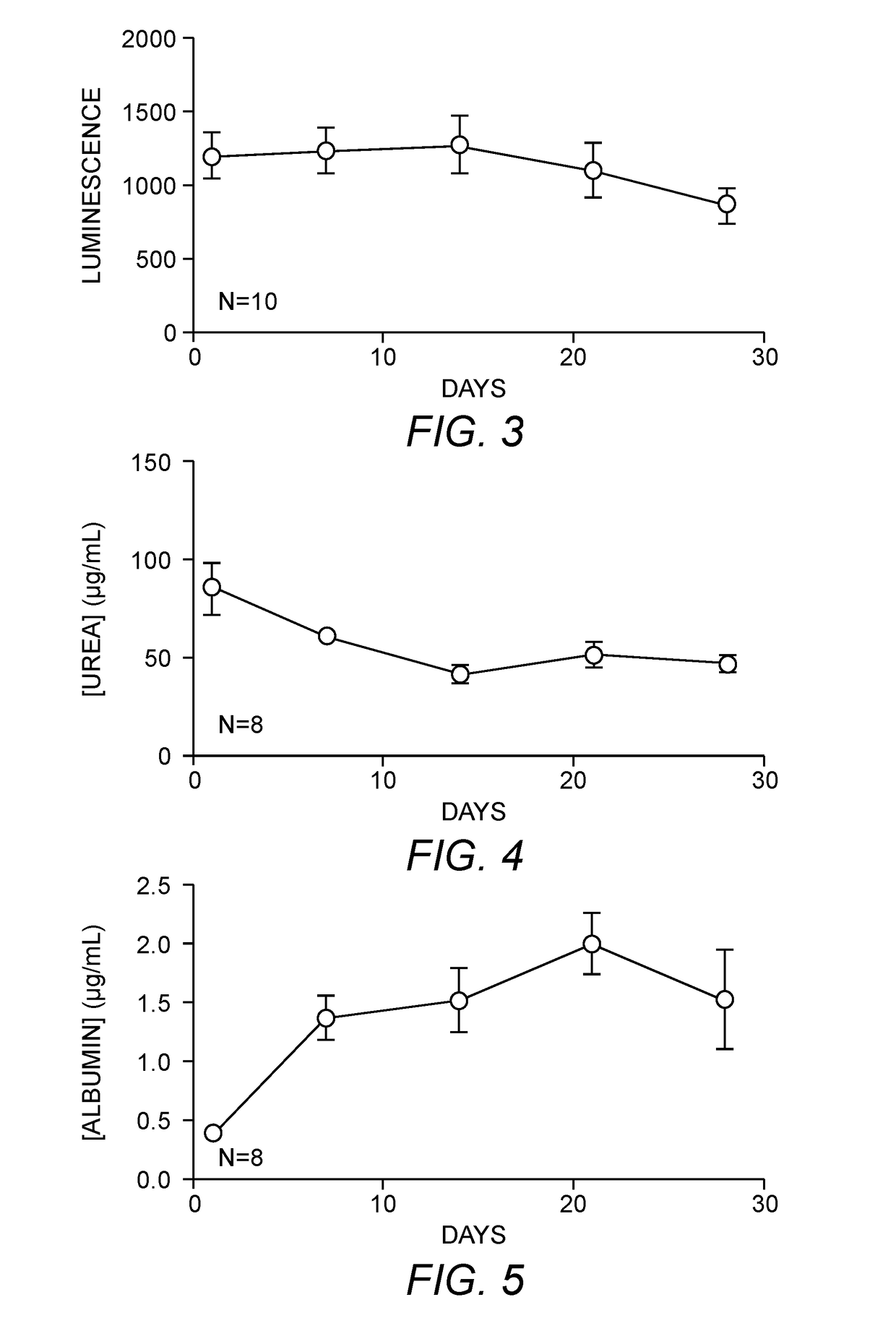
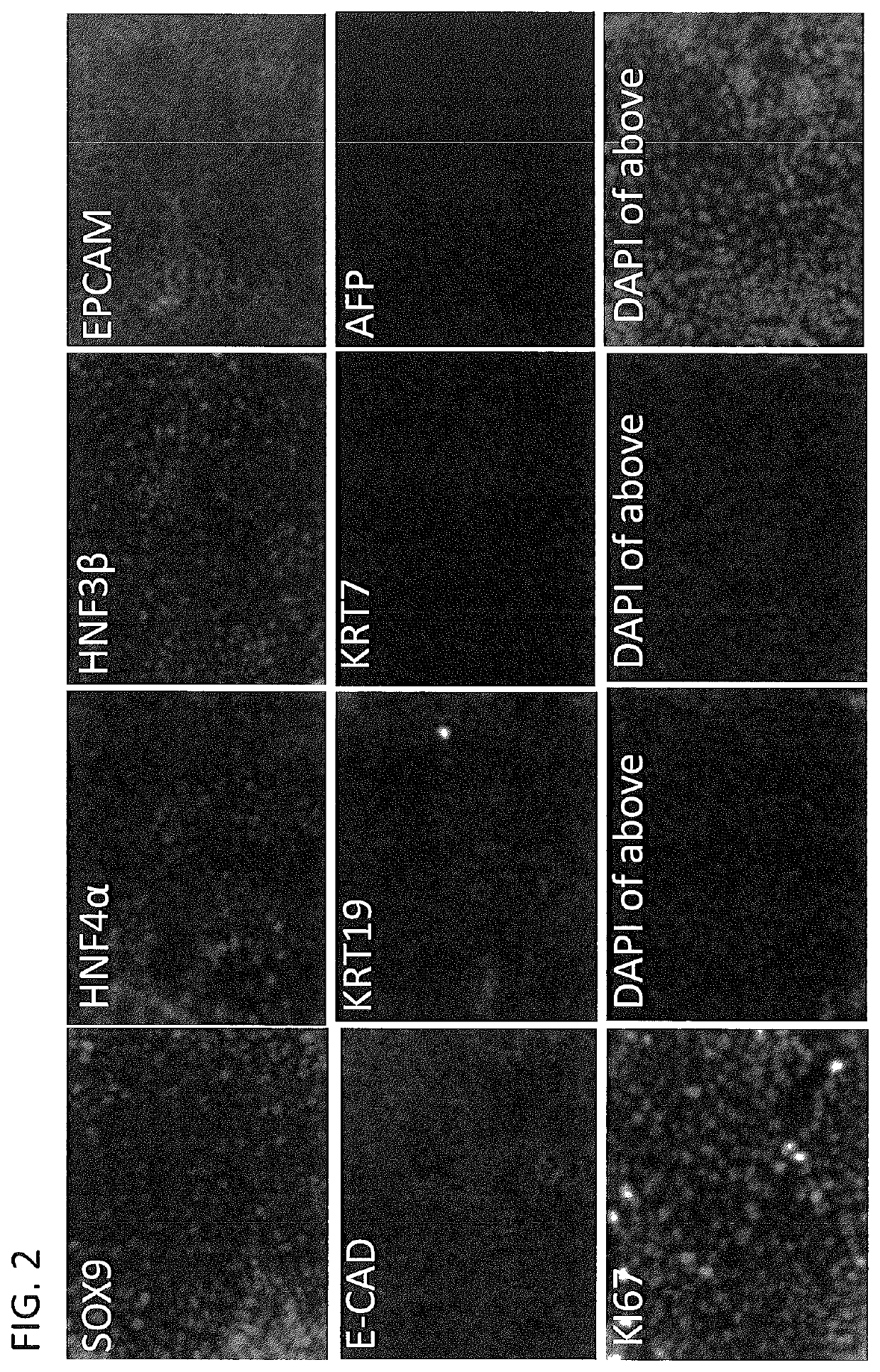
Provided herein are cell compositions useful for making artificial liver constructs. The cell composition my include, in combination, (a) hepatocyte cells, (b) Kuppfer cells, (c) hepatic stellate cells, (d) sinusoidal endothelial cells, and (e) cholangiocyte cells.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Derivation of hepatic stem cells and mature liver cell types and uses thereof
ActiveUS10683484B2Enhance stem cell proliferationPrevent stem cell differentiationHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsCell culture mediaCell type
This application describes liver stem cells (LSC), and differentiated hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, and 3D cellular structures derived therefrom. Methods for producing LSC and mature, differentiated hepatocytes and cholangiocytes in culture are provided. Also provided are cell culture systems and cell culture media for producing a homogenous population of liver stem cells that remain in an undifferentiated state over multiple passages in culture. The LSC and methods are useful for producing homogenous populations of hepatocytes and cholangiocytes for downstream applications. The LSC can be transplanted into subjects to treat liver diseases.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Hepatocytes and hepatic non-parenchymal cells, and methods for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20180147242A1High purityEfficient mannerHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsCell FractionProgenitor
The present invention pertains to hepatocytes, liver progenitor cells, cholangiocytes, liver sinusoidal endothelial progenitor cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic stellate progenitor cells, hepatic stellate cells, and liver cellular tissue models, as well as to methods for preparing these cells. The present invention also pertains to a cell fraction comprising liver progenitor cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial progenitor cells, or hepatic stellate progenitor cells. The present invention also pertains to a pharmaceutical composition or kit comprising the above-mentioned cells, a liver cellular tissue model, or a cell fraction. The present invention also pertains to: a method for screening liver disease treatment agents; a method for evaluating the hepatotoxicity of drugs, hepatocytes for infectious disease models, and a method for preparing the same; infectious disease model tissues and a method for preparing the same; as well as a method for screening infectious liver disease treatment agents.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Application of THBS1 cytokine in preparation of medicament for treating hepatic failure
InactiveCN110448679APromote regenerationImprove biochemical indicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemUpper gastrointestinalHepatorenal syndrome
The invention discloses application of a THBS1 cytokine in preparation of a medicament for treating hepatic failure. The temperature for transport and storage of the THBS1 cytokine-containing medicament is 2-8 DEG C, the humidity is 45-75%, and the THBS1 is a member of an ABCA superfamily and is mainly used for mediating transmembrane transport of lipids. In the application of the THBS1 cytokine in preparation of the medicament for treating hepatic failure, the biochemical indexes of patients can be significantly improved, the bilirubin level is lowered, the transaminase is reduced, the bloodcoagulation function is improved, the albumin level is raised, hepatocyte death is inhibited, regeneration of hepatocytes and bile duct cells is promoted, fatal complications such as major upper gastrointestinal duct bleeding, severe hepatic encephalopathy and hepatorenal syndromes are prevented, the survival time is significantly prolonged, and the survival rate is increased.
Owner:杭州笙源生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com