Method for promoting human cholangiocytes to differentiate and mature through MAPK/PKC signaling pathway activator
A signal pathway and activator technology, applied in the field of MAPK/PKC signal pathway activator to promote the differentiation and maturation of human cholangiocytes, can solve the problem of not fully reflecting the physiological and pathological characteristics of bile ducts in vivo, limiting the scope of application, reliability, and expression level low level problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
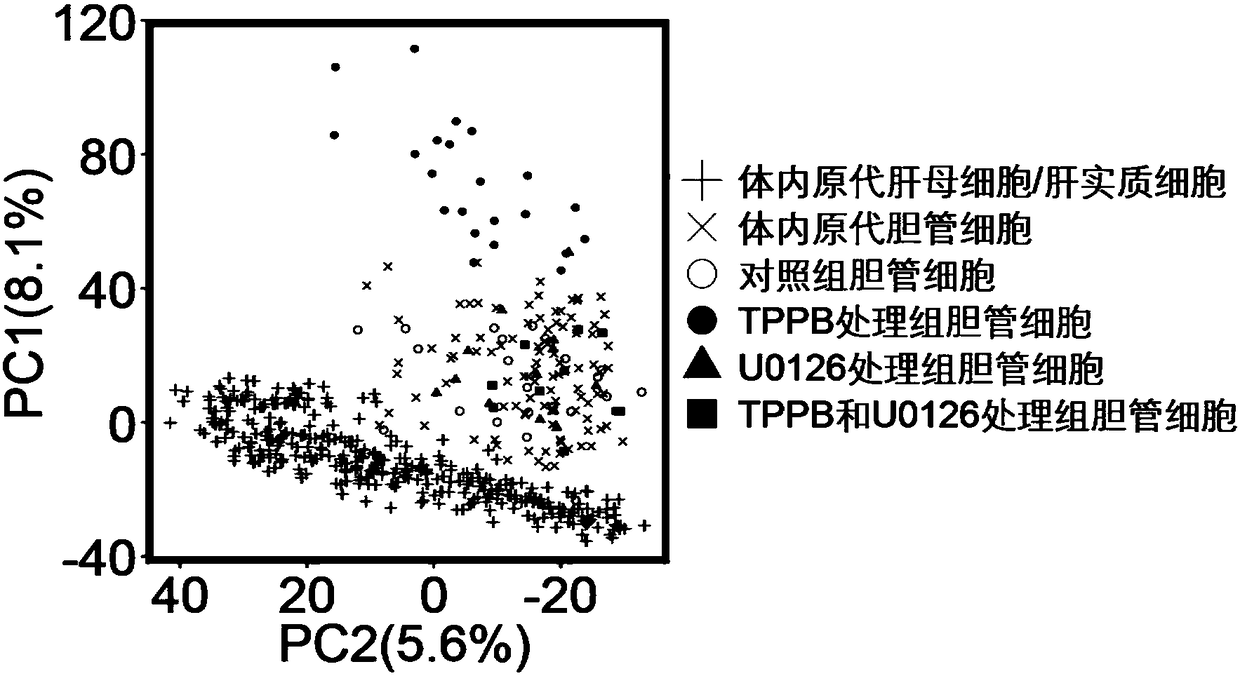
[0031] Example 1: The effect of TPPB on the differentiation and maturation of mouse intrahepatic cholangiocytes
[0032] 1) Differentiation and development of mouse intrahepatic cholangiocytes
[0033] C57BL / 6-strain female mice and C3H-strain male mice from 8 to 12 weeks old came from Victoria Lihua Company (Beijing), and offspring mice (B6C3F1) obtained from mating were used for subsequent experiments. B6C3F1 female mice of about six weeks are mated with B6C3F1 male mice of eight to twelve weeks, and the vaginal suppository is found in the next morning, which is recorded as embryonic development (E) 0.5 days. All mice were housed in a sterile environment at 23 ± 2°C for 12 hours with day and night cycles, and fed with autoclaved food and water. All mouse experiments were carried out in strict accordance with the management regulations of the Experimental Animal Center of Peking University.
[0034] Take liver buds or fetal livers at 10.5, 11.5, 12.5, 13.5, 14.5, 15.5, and ...
Embodiment 2
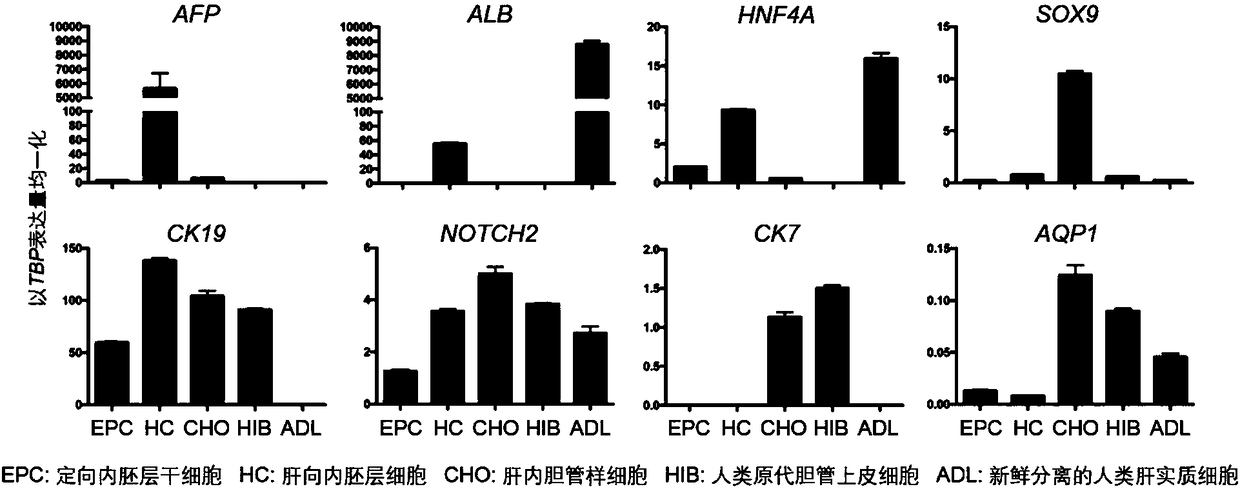
[0039] Example 2: Preparation and maintenance of human committed endoderm stem cells
[0040] Committed endoderm stem cells (EP cells) were prepared from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) using the method disclosed in WO 2012 / 178215 Al by Gadue et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) (purchased from Shanghai Zhongqiao Xinzhou Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) were treated with glutamine (2 mM), MTG (4.5×10 -4 M), activin A (100ng / ml) and CHIR99021 (2M) in the RPMI medium induced for 1 day, followed by glutamine (2mM), ascorbic acid (50g / ml), MTG (4.5 × 10 -4 M), bFGF (5ng / ml) and activin A (100ng / ml) in the RPMI medium for directional induction for 2 days, and finally in the RPMI medium containing glutamine (2mM), ascorbic acid (50g / ml), MTG (4.5×10 -4 M), bFGF (5 ng / ml) and activin A (100 ng / ml) were induced in SFD medium for 2 days. The CXCR4+ / CD117+ cells were sorted out by flow cytometry to obtain human committed endoderm stem cells.
[0041] The resulting...
Embodiment 3
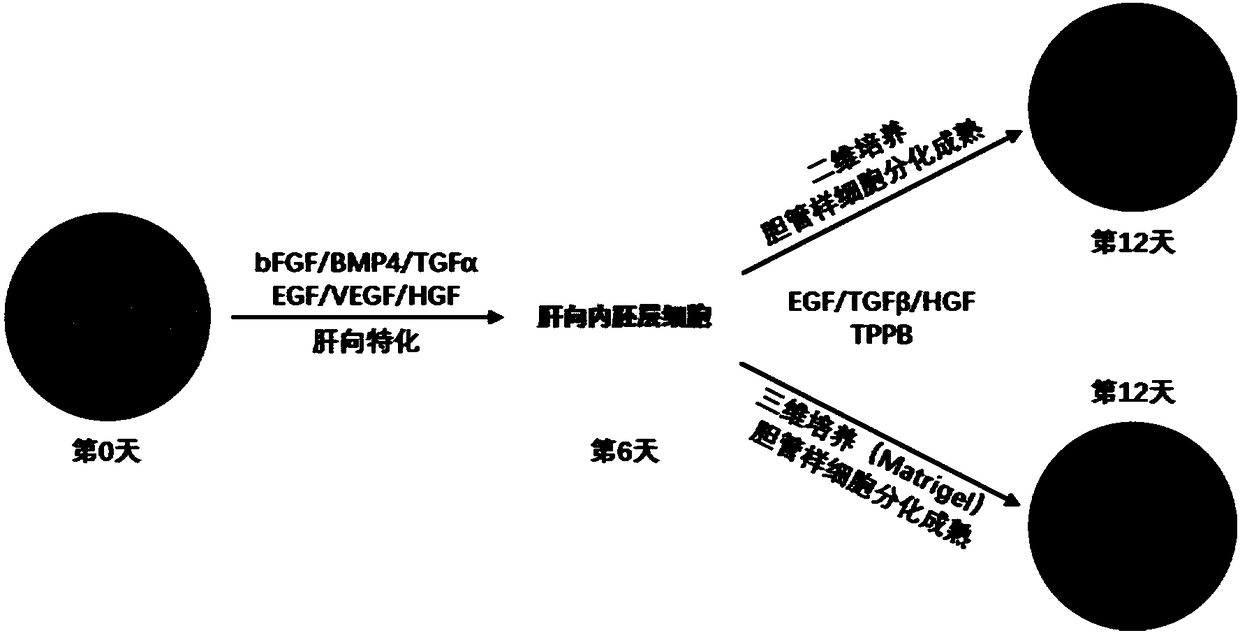
[0042] Example 3: Directed differentiation of endoderm stem cells from liver to endoderm
[0043] Committed endoderm stem cells were differentiated into the liver by suspension culture, and the cell density was 1 million / ml differentiation medium (containing BMP4 (50ng / ml), bFGF (10ng / ml), VEGF (10ng / ml), EGF (10ng / ml) ml), TGFα (10ng / ml), HGF (25ng / ml), Dex (40ng / ml), glutamine (2mM), ascorbic acid (50g / ml) and MTG (4.5×10 -4 M) SFD medium), add 100μl matrix collagen solution and pre-cooled cell suspension to each 3ml medium, mix well, place in a low-adsorption culture dish for directional differentiation, the differentiation time is 6 days, and replace every 2 days medium once.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com