Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Transport activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Macromolecular conjugates of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein inhibitors and uses therefor
ActiveUS20080171793A1Increased intestinal fluid secretionAvoid transportBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseSecretory diarrhea
Provided herein are bioactive agents comprising a compound that inhibits the ion transport activity of a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and that is linked to a macromolecule that interacts with a cell that expresses CFTR. The bioactive agents described herein are useful for treating diseases, disorders, and sequelae of diseases, disorders, and conditions that are associated with aberrantly increased CFTR activity, for example, secretory diarrhea.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fragments of p97 and uses thereof
ActiveUS9364567B2Reduce cardiotoxicityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiagnostic agentMelanotransferrin
Provided are fragments of human p97 (melanotransferrin) polypeptides having blood-brain barrier (BBB) transport activity, including variants and combinations thereof, conjugates comprising the p97 fragments, and related methods of use thereof, for instance, to facilitate delivery of therapeutic or diagnostic agents across the BBB.
Owner:BIOASIS TECH
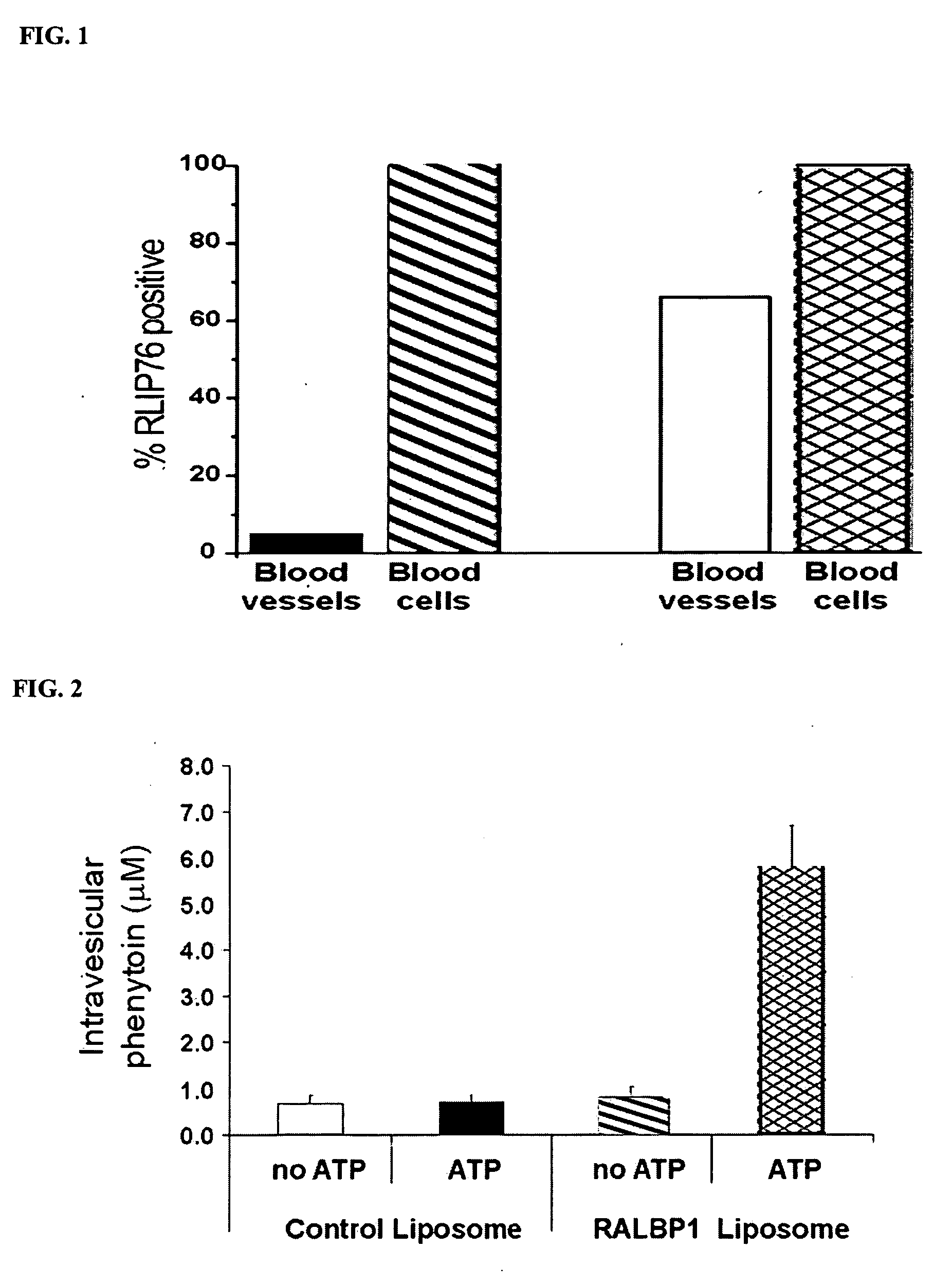
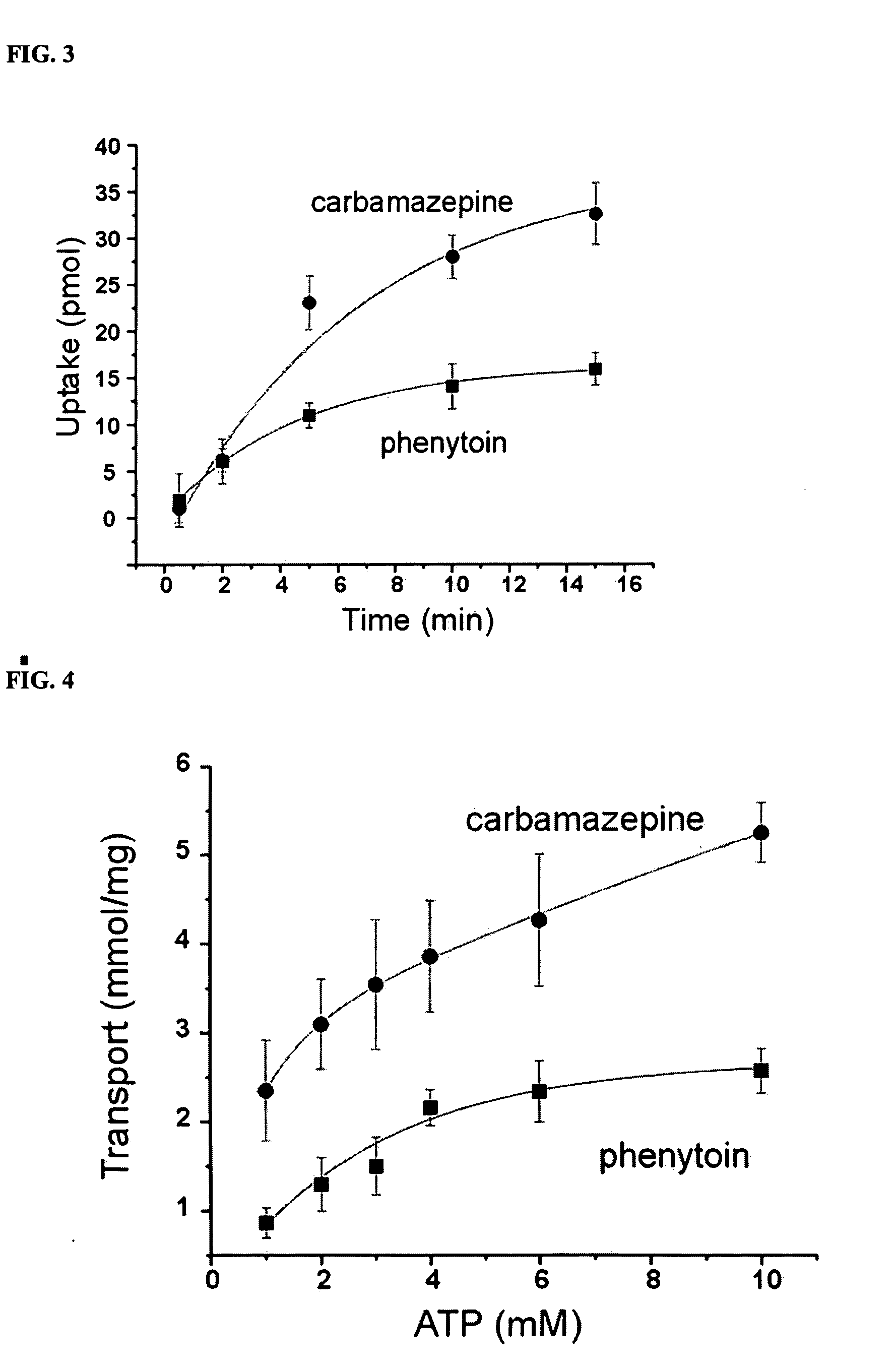
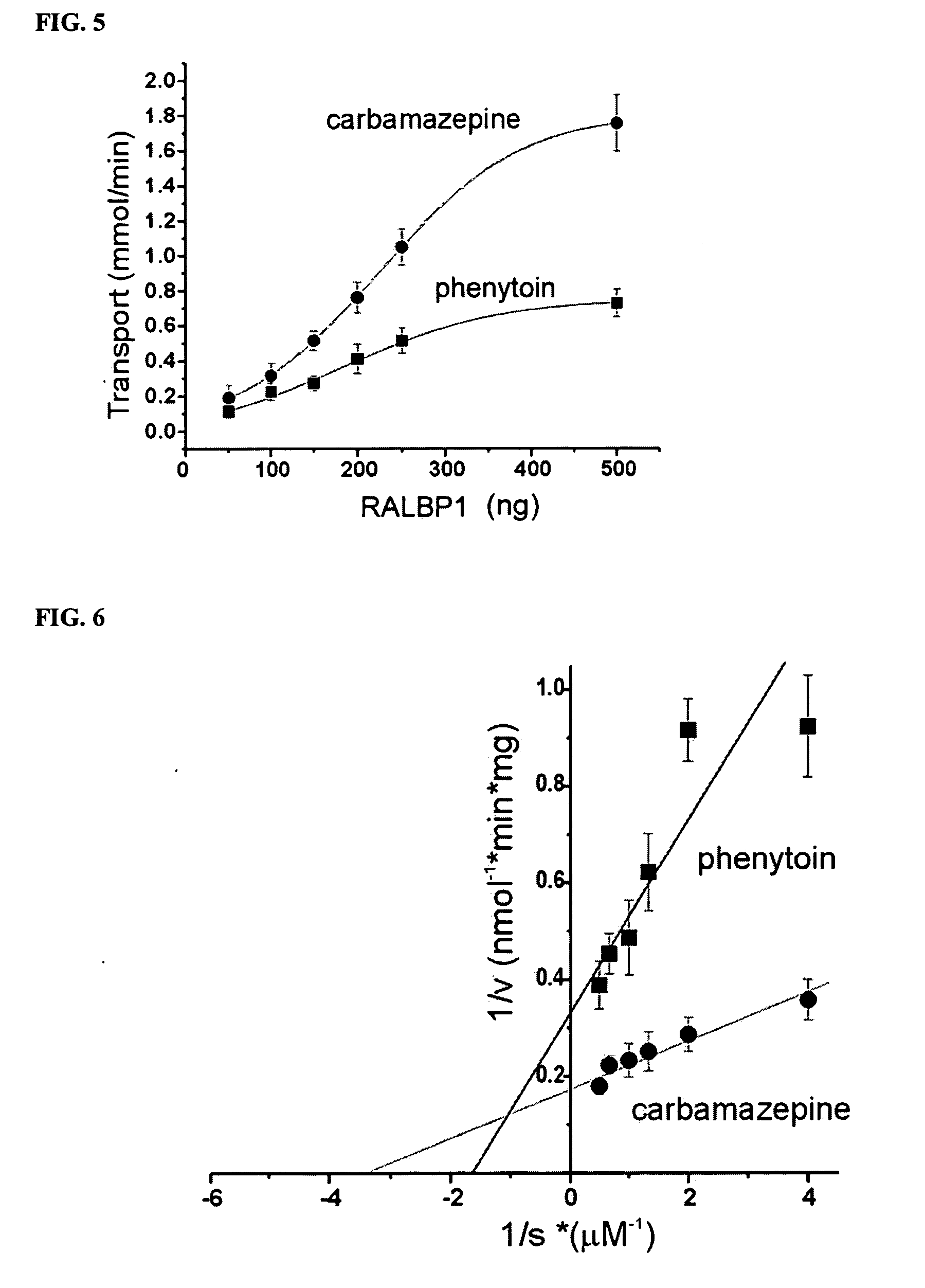
Therapies for cancer using RLIP76
InactiveUS20060182749A1Reduce the numberReduced potencyOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsRalA binding protein 1Cancer research
The present invention is a composition identified as a region of ralA binding protein 1, wherein the region neighbors a membrane-associated portion of the ralA binding protein 1, reduces transport activity and membrane association of the ralA binding protein 1 and kills cells undergoing uncontrolled cell growth in a subject that has cells undergoing uncontrolled cell growth. The region is used to generate medicines that kill malignant cells and tumorigenic cells. Medicines may be in the form of antibodies, si-RNA and small molecules that recognize the region.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and system for controlling transport sequencing in a process tool by a look-ahead mode
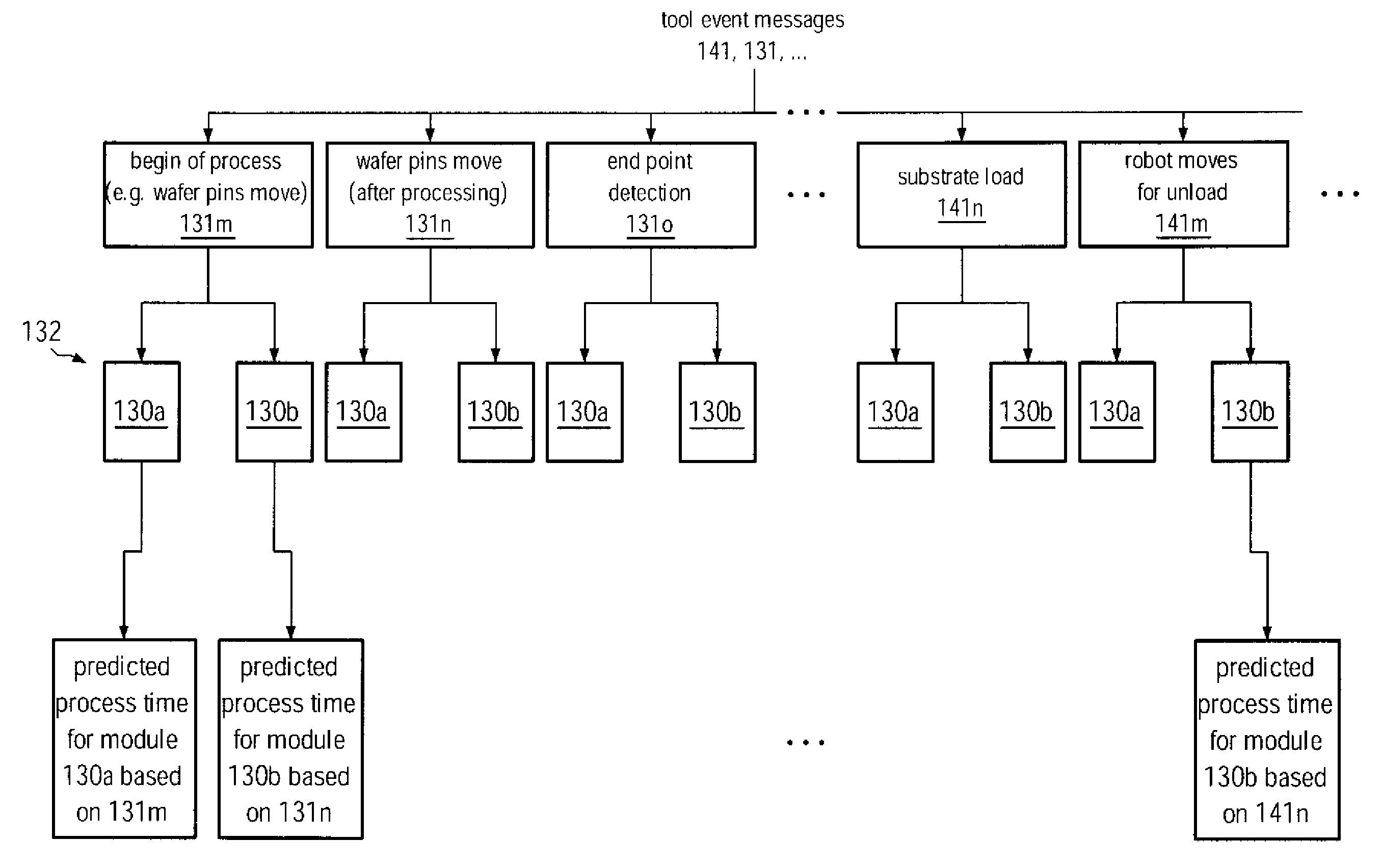
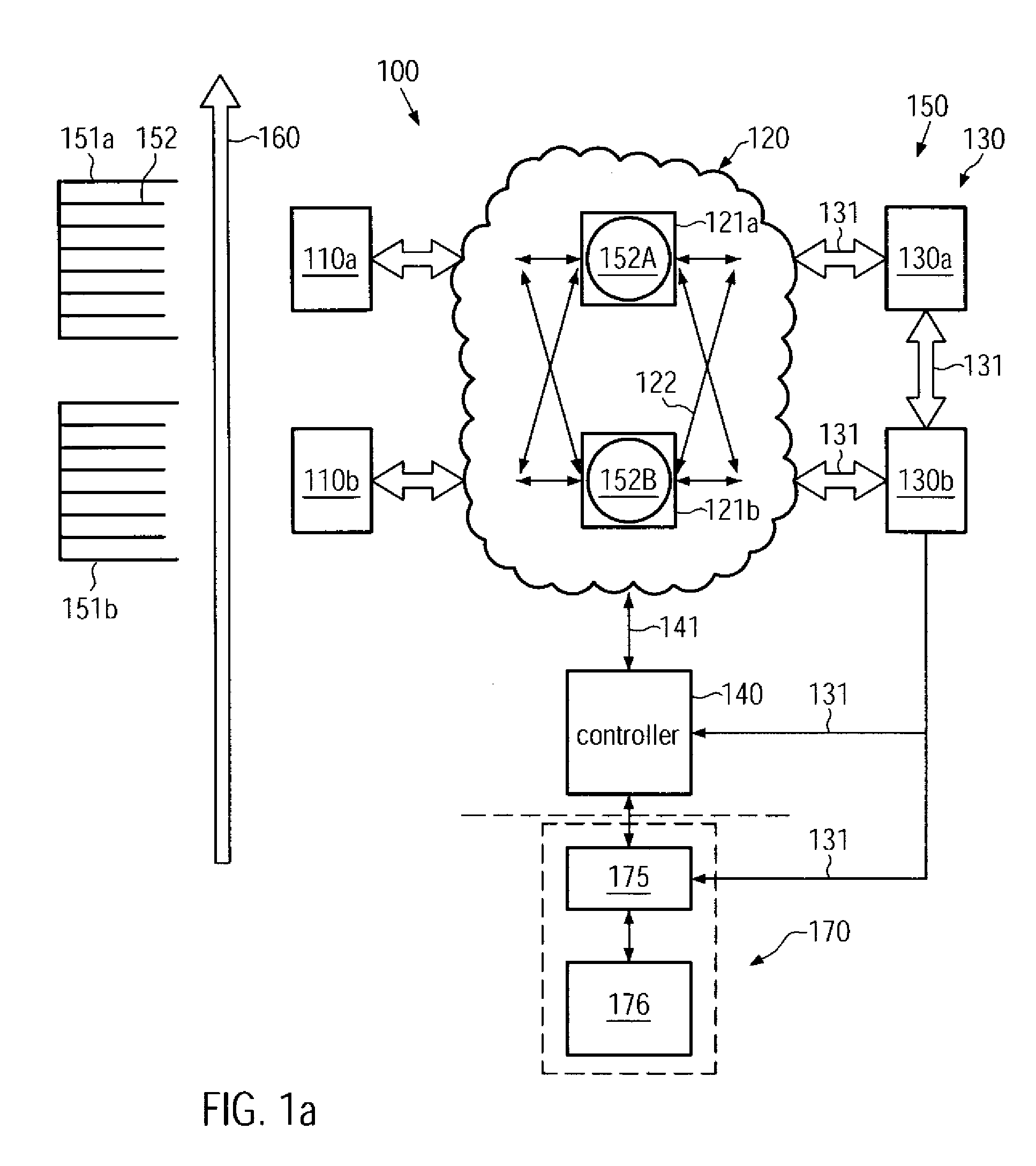
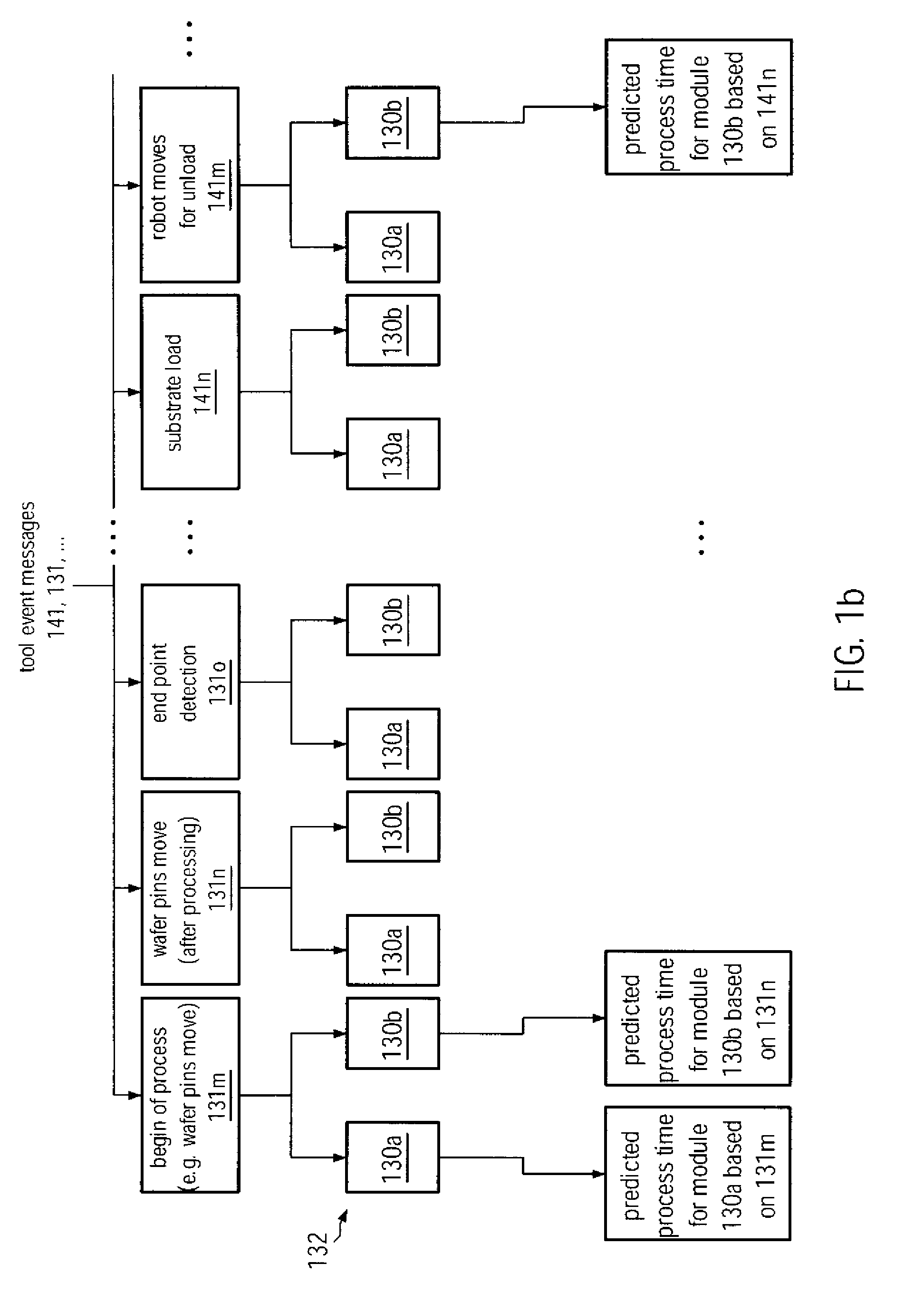
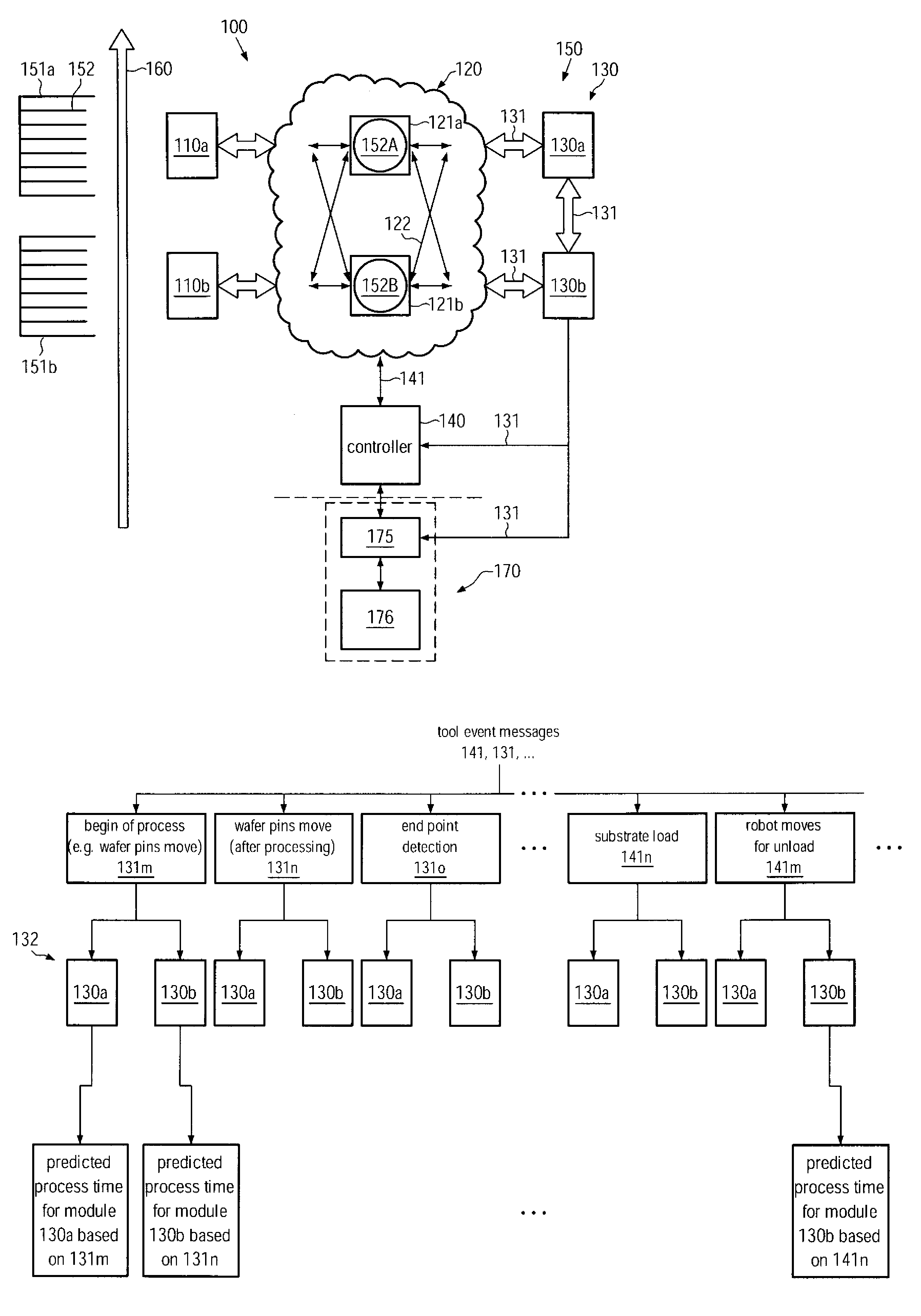
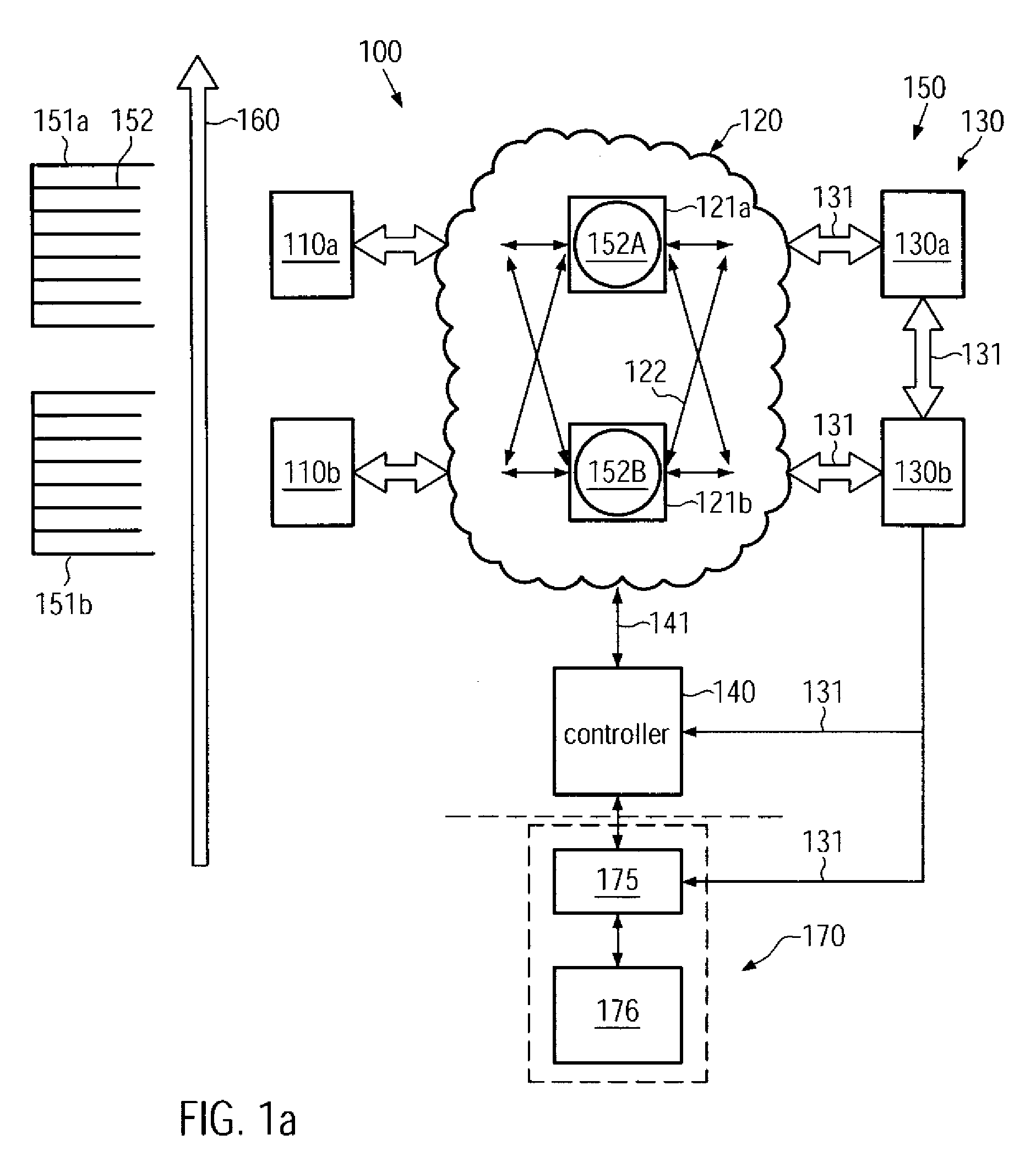
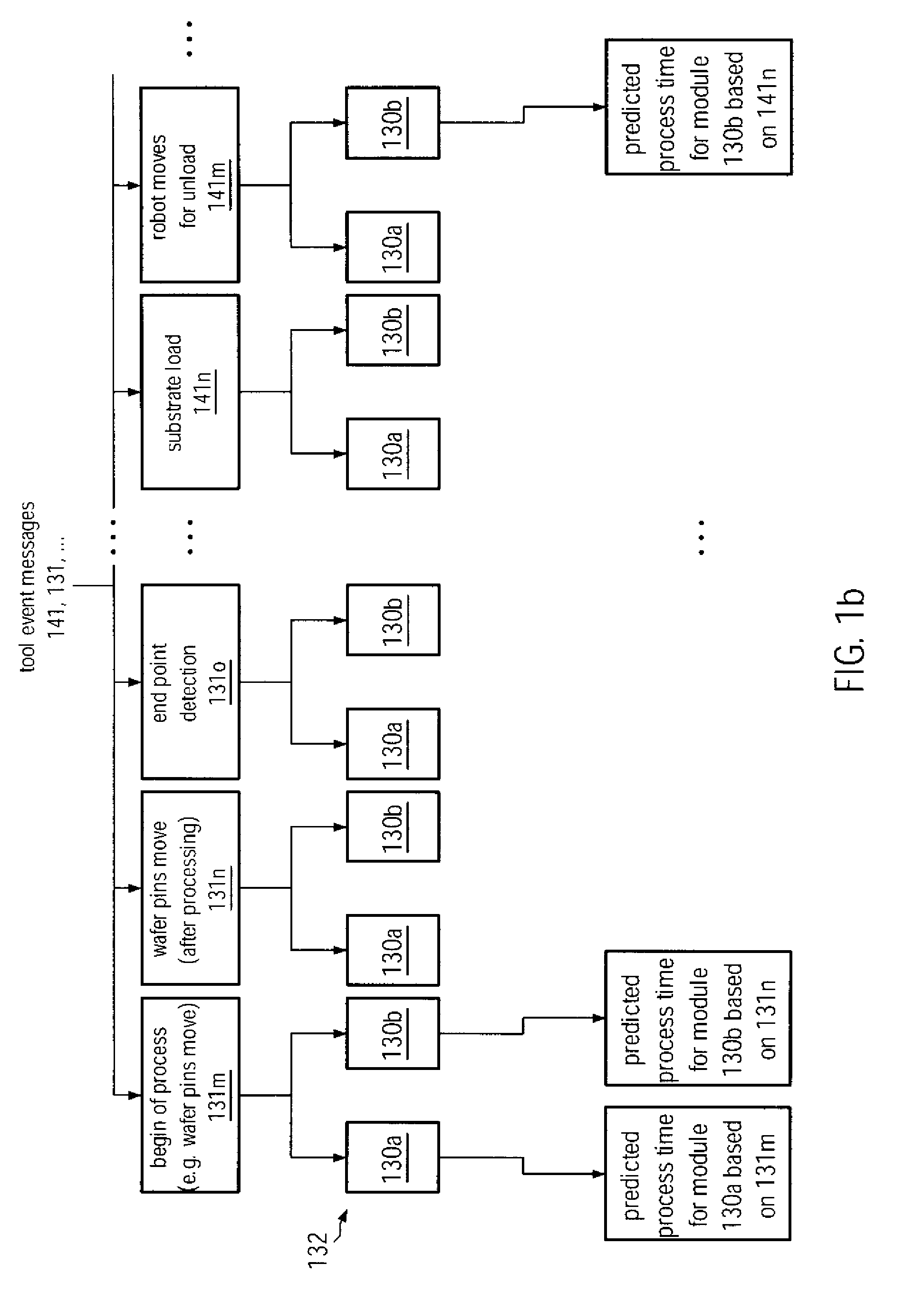
ActiveUS20090088895A1Improve performanceEnhanced look-ahead functionalityProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsProcess moduleHandling system
By providing a look-ahead functionality for a tool internal substrate handling system of process tools on the basis of a process history, the tool internal substrate sequencing may be significantly enhanced. The look-ahead functionality enables a prediction of process time of substrates currently being processed in a respective process module, thereby enabling the initiation of transport activity for substrate load operations in order to significantly reduce the overall idle time of process modules occurring during substrate exchange.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fragments of p97 and uses thereof
ActiveUS20160324937A1Reduce cardiotoxicityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiagnostic agentTransferrin
Provided are fragments of human p97 (melanotransferrin) polypeptides having blood-brain barrier (BBB) transport activity, including variants and combinations thereof, conjugates comprising said p97 fragments, and related methods of use thereof, for instance, to facilitate delivery of therapeutic or diagnostic agents across the BBB.
Owner:BIOASIS TECH
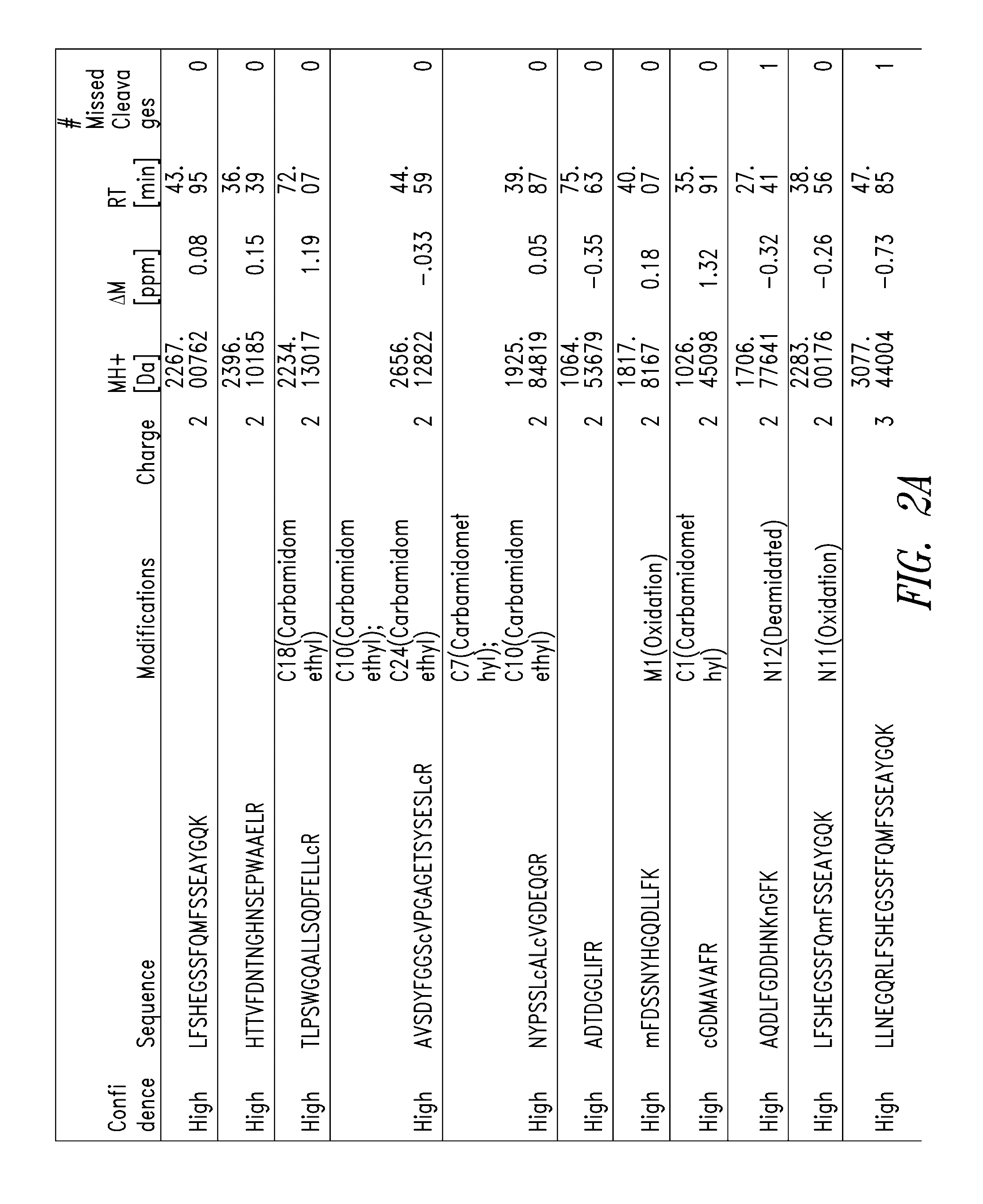
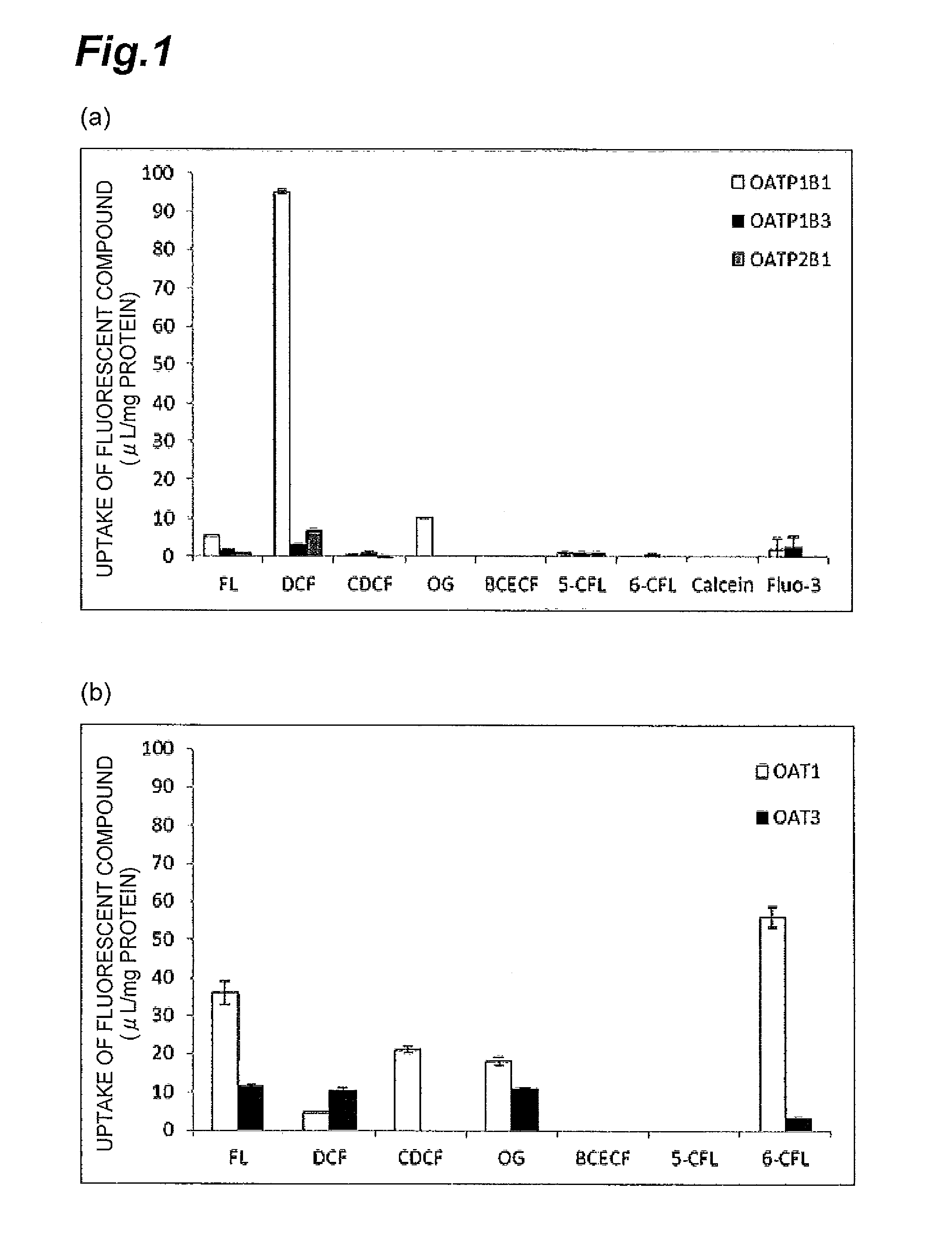
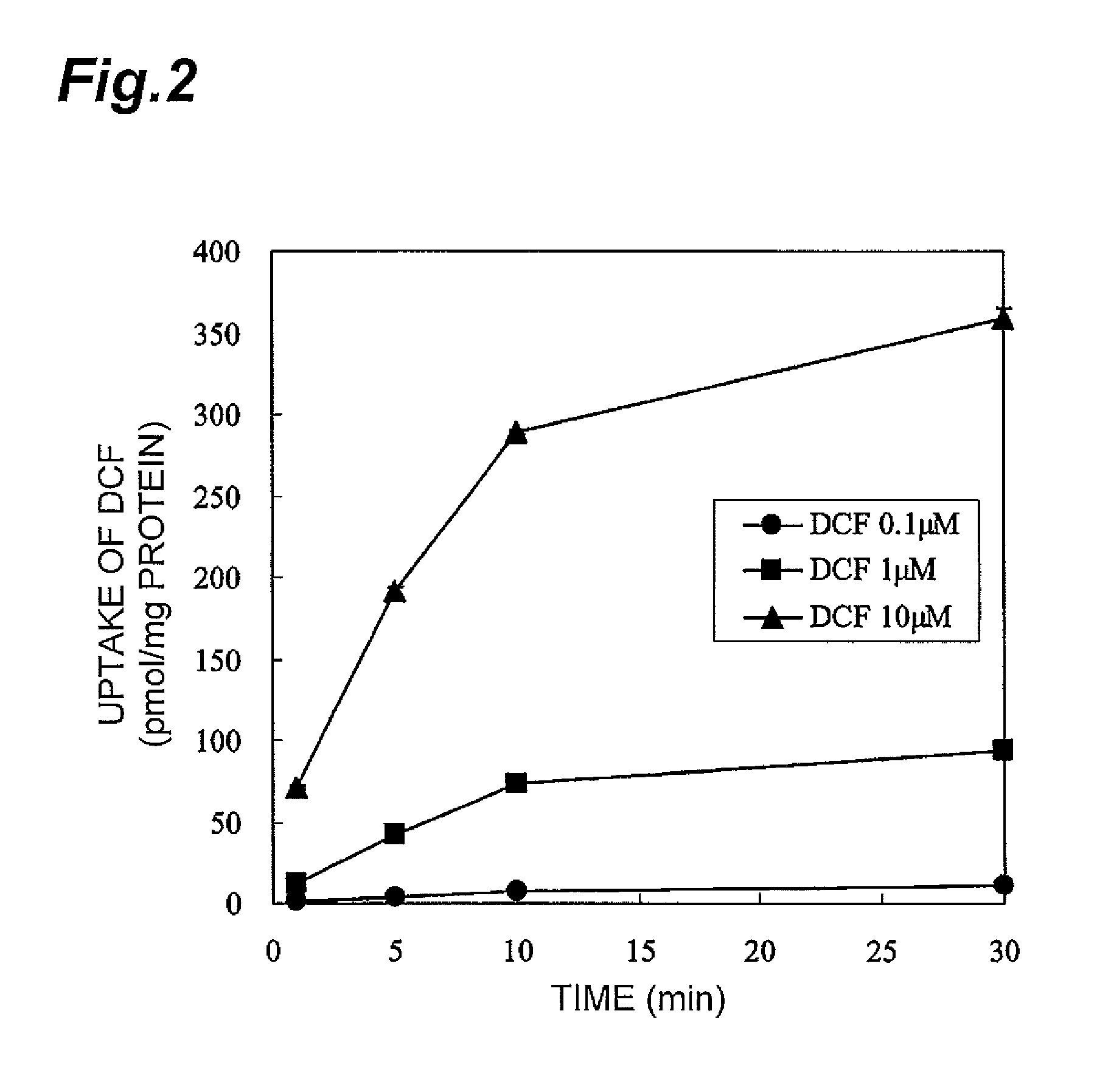
Method for screening for compound capable of enhancing or inhibiting OATP1B1 transport activity, and method for determining expression level of OATP1B1
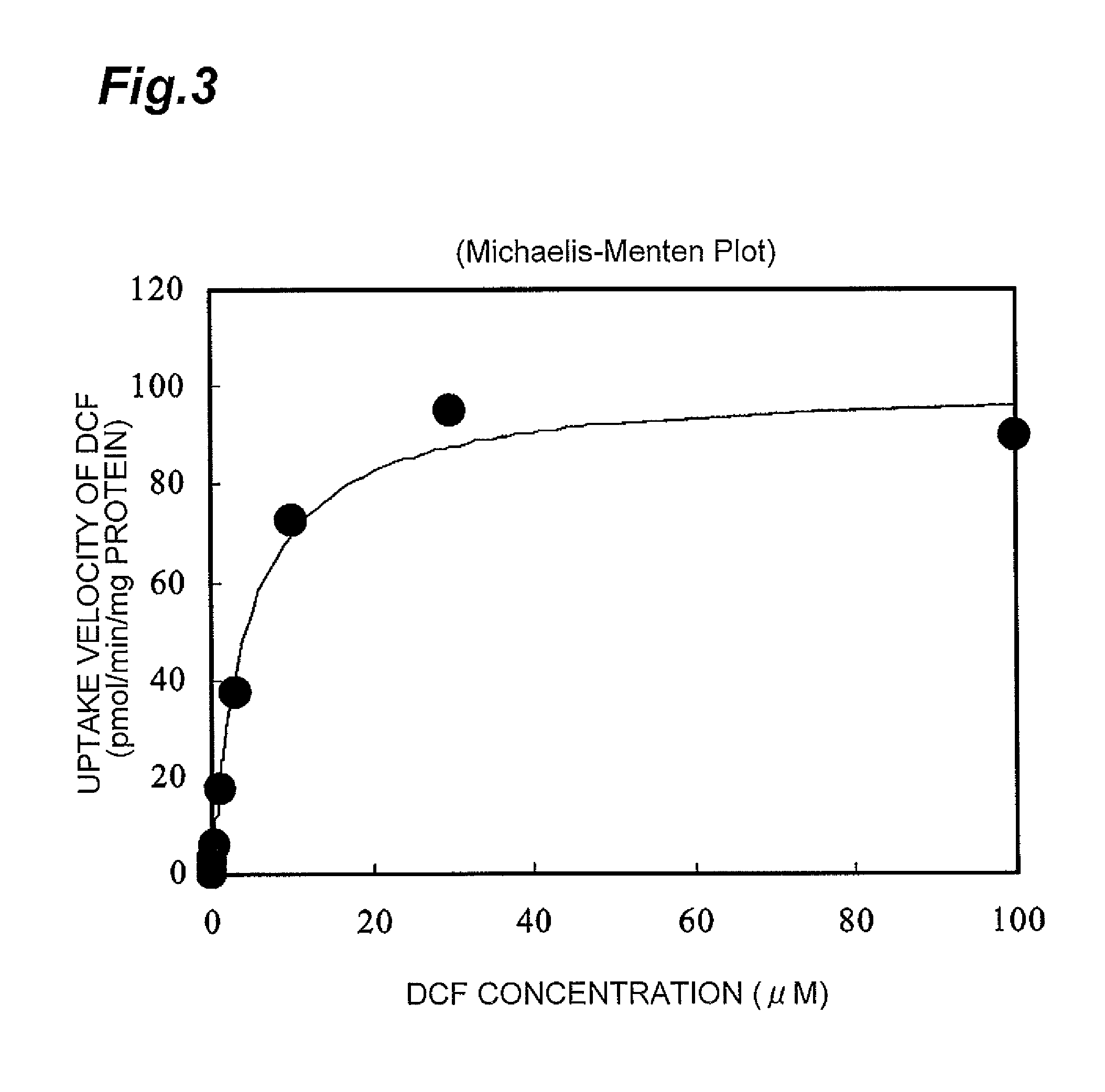
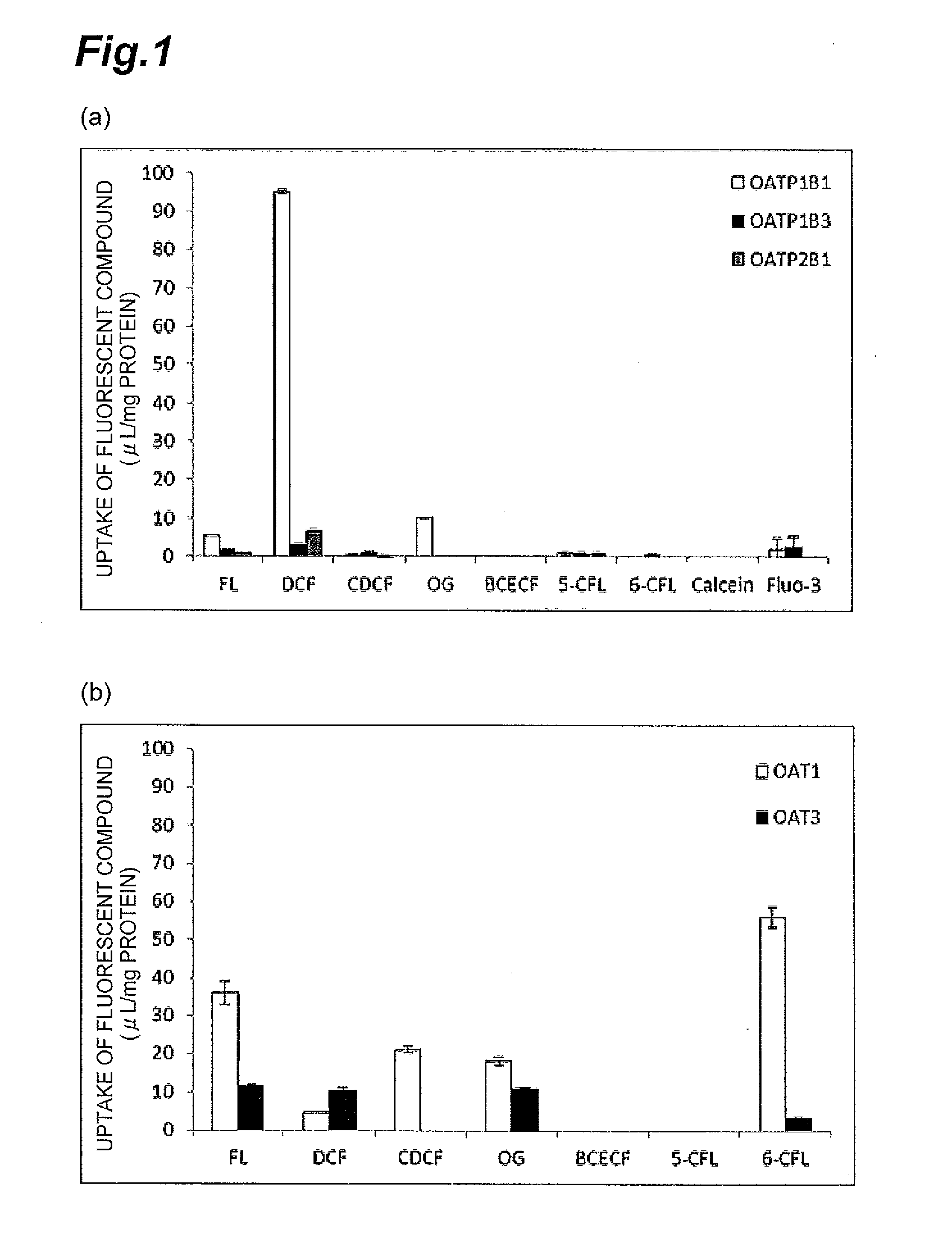
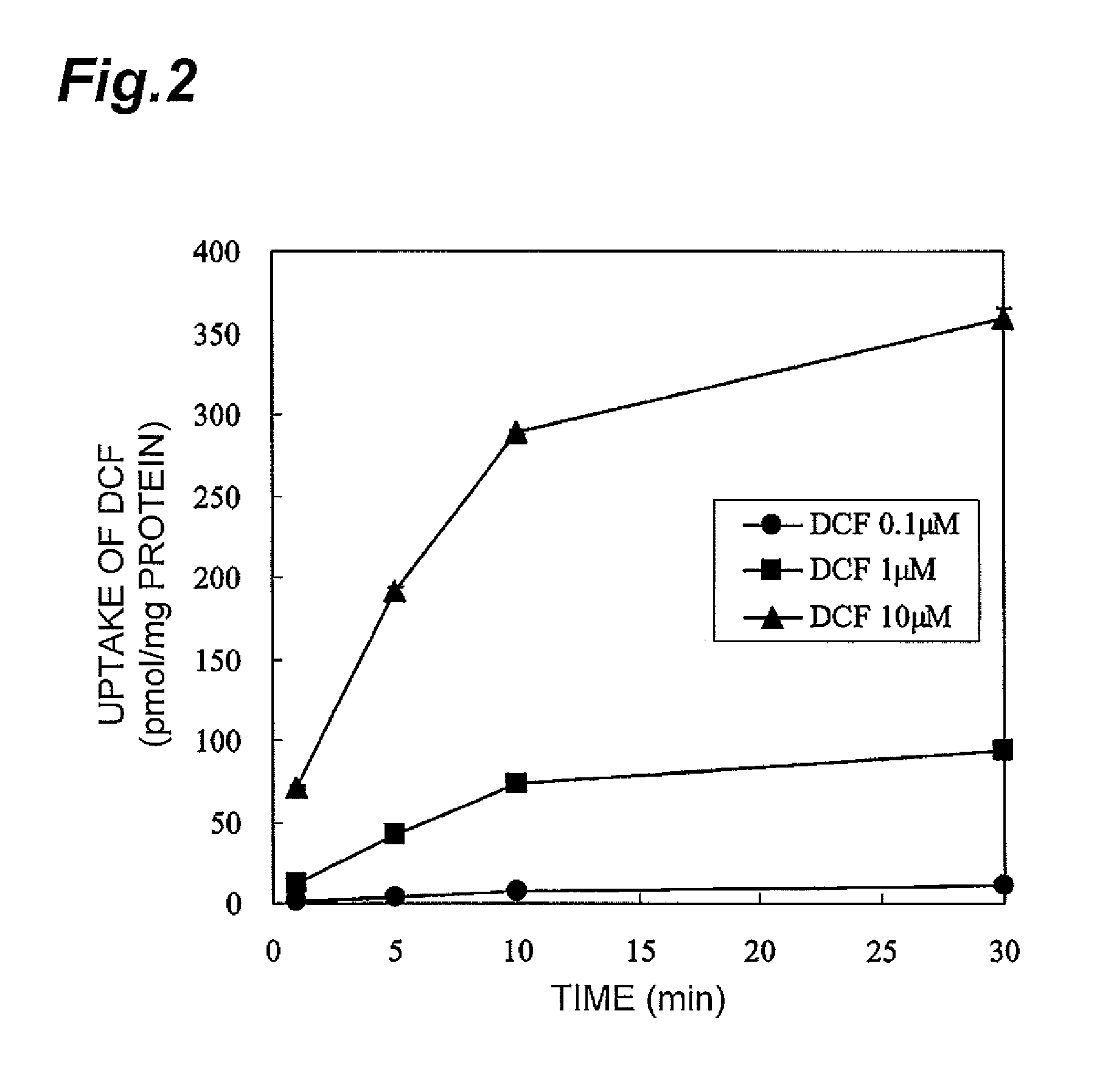
ActiveUS8945865B2Enhances and inhibits transport activityEasy to operateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMeasurement testDichlorofluorescein
The present invention provides a method of screening for a compound that enhances or inhibits the transport activity of OATP1B1, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention also provides a use of dichlorofluorescein in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1. The present invention further provides a method for measuring the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention further provides a use of a kit including dichlorofluorescein and positive cells expressing OATP1B1 in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
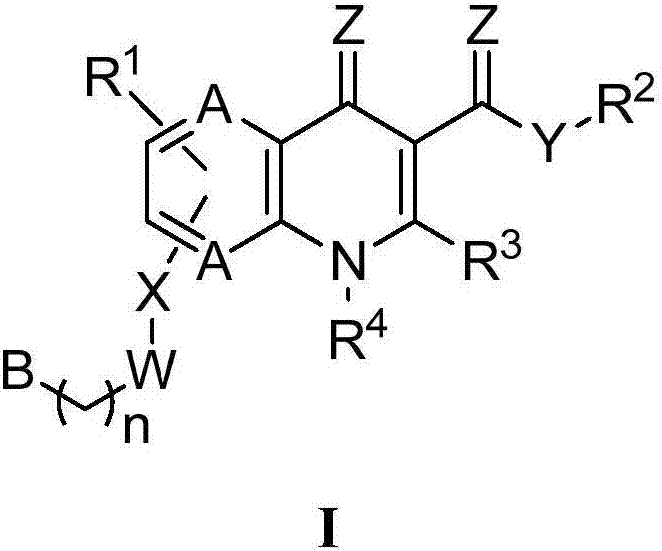
Monocarboxylate transport modulators and uses thereof
ActiveCN107406390AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAbnormal tissue growthOrgan transplant rejection
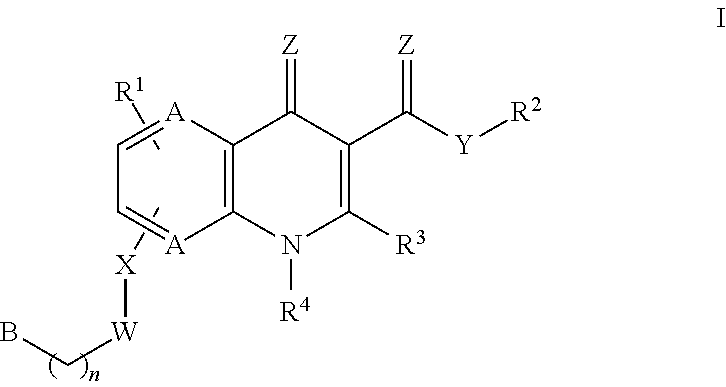
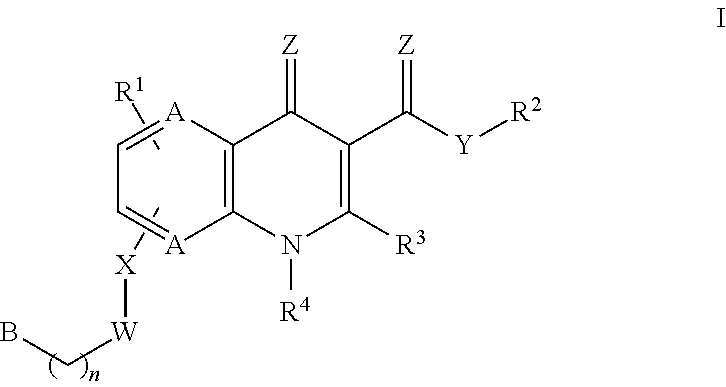
The invention generally relates to the field of monocarboxylate transport modulators, e.g., monocarboxylate transport inhibitors, and more particularly to new substituted-quinolone compounds, the synthesis and use of these compounds and their pharmaceutical compositions, e.g., in treating, modulating, forestalling and / or reducing physiological conditions associated with monocarboxylate transport activity such as in treating cancer and other neoplastic disorders, inflammatory diseases, disorders of abnormal tissue growth and fibrosis including cardiomyopathy, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, tissue and organ transplant rejection, and malaria.
Owner:NEGI THERAPEUTICS
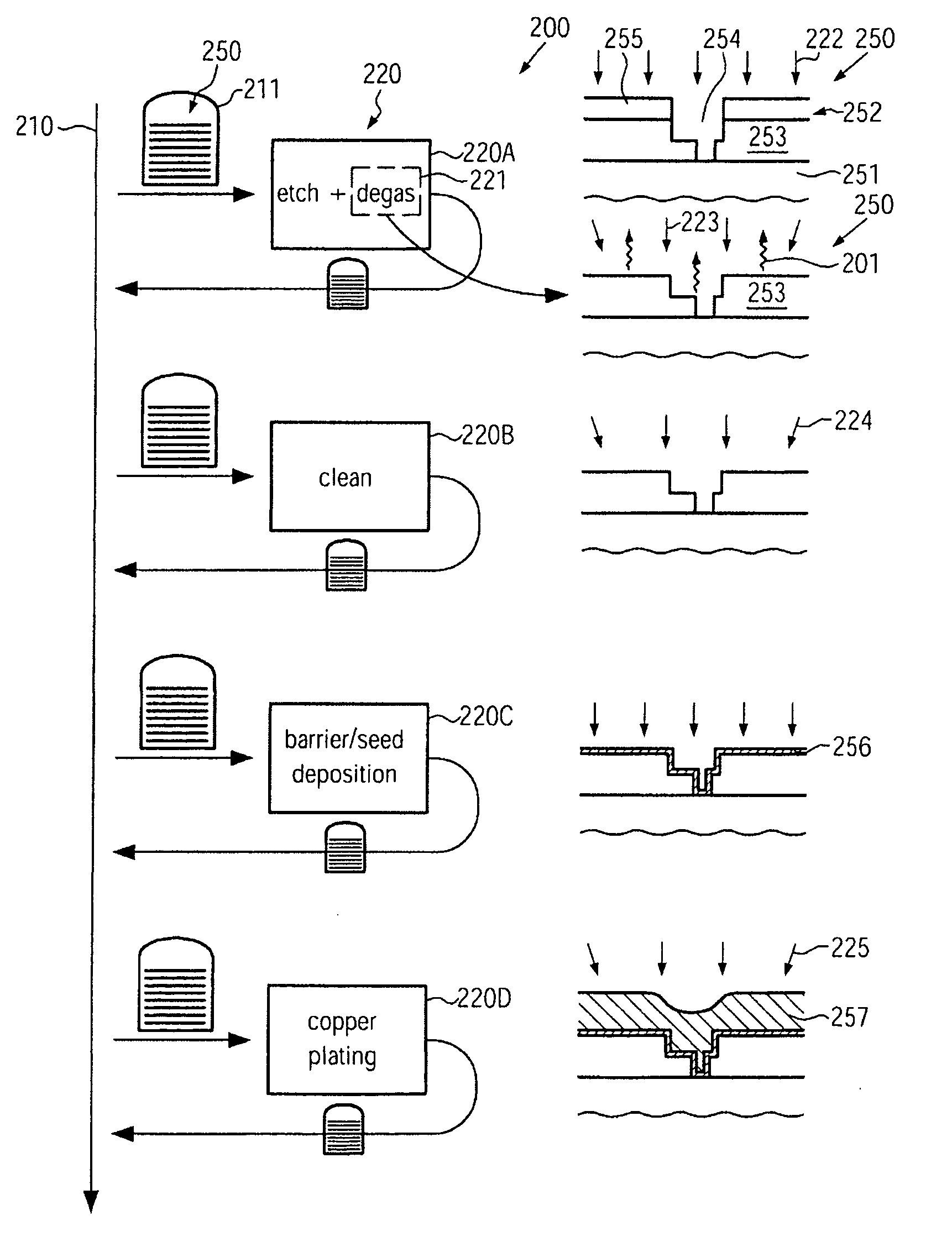
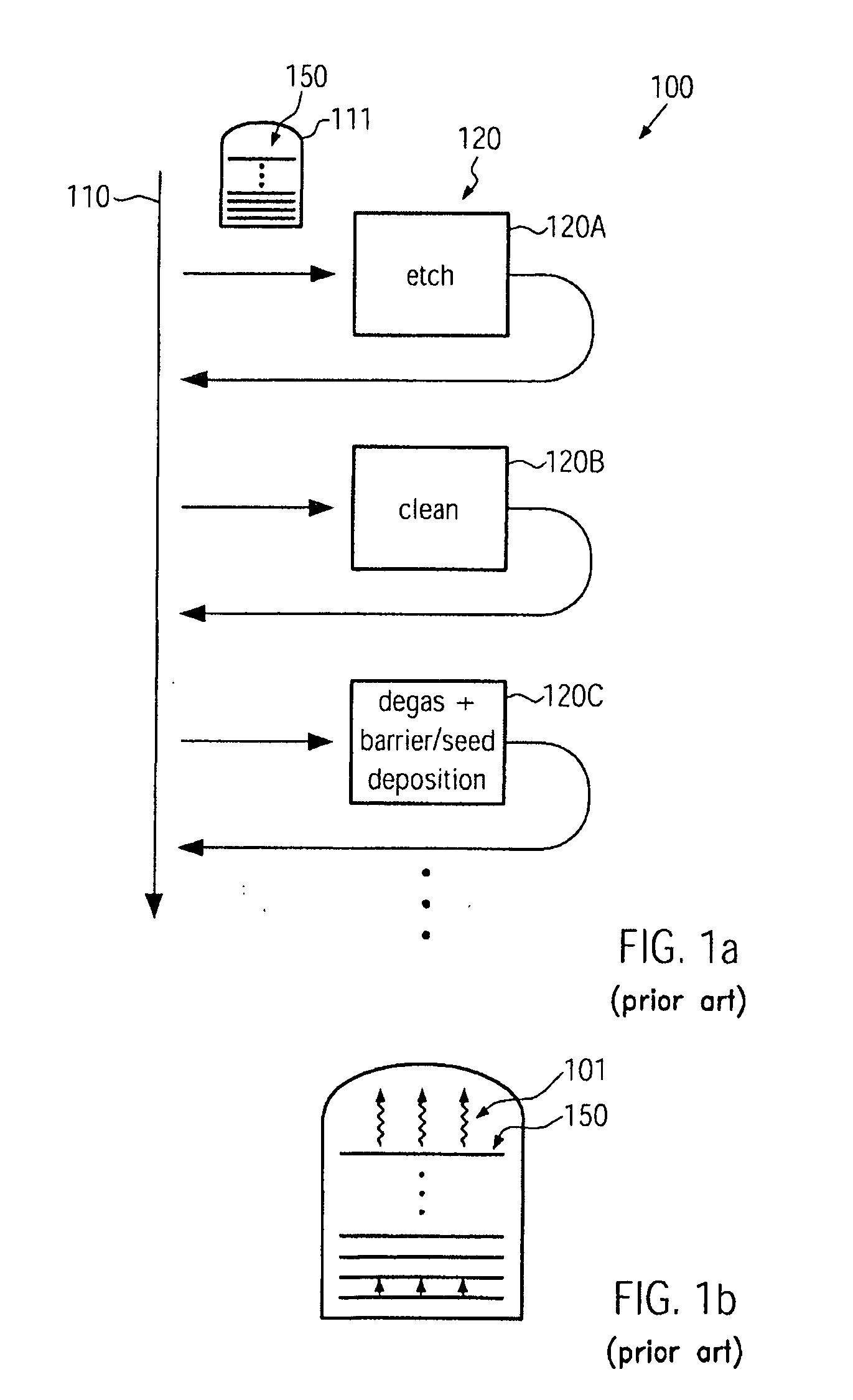
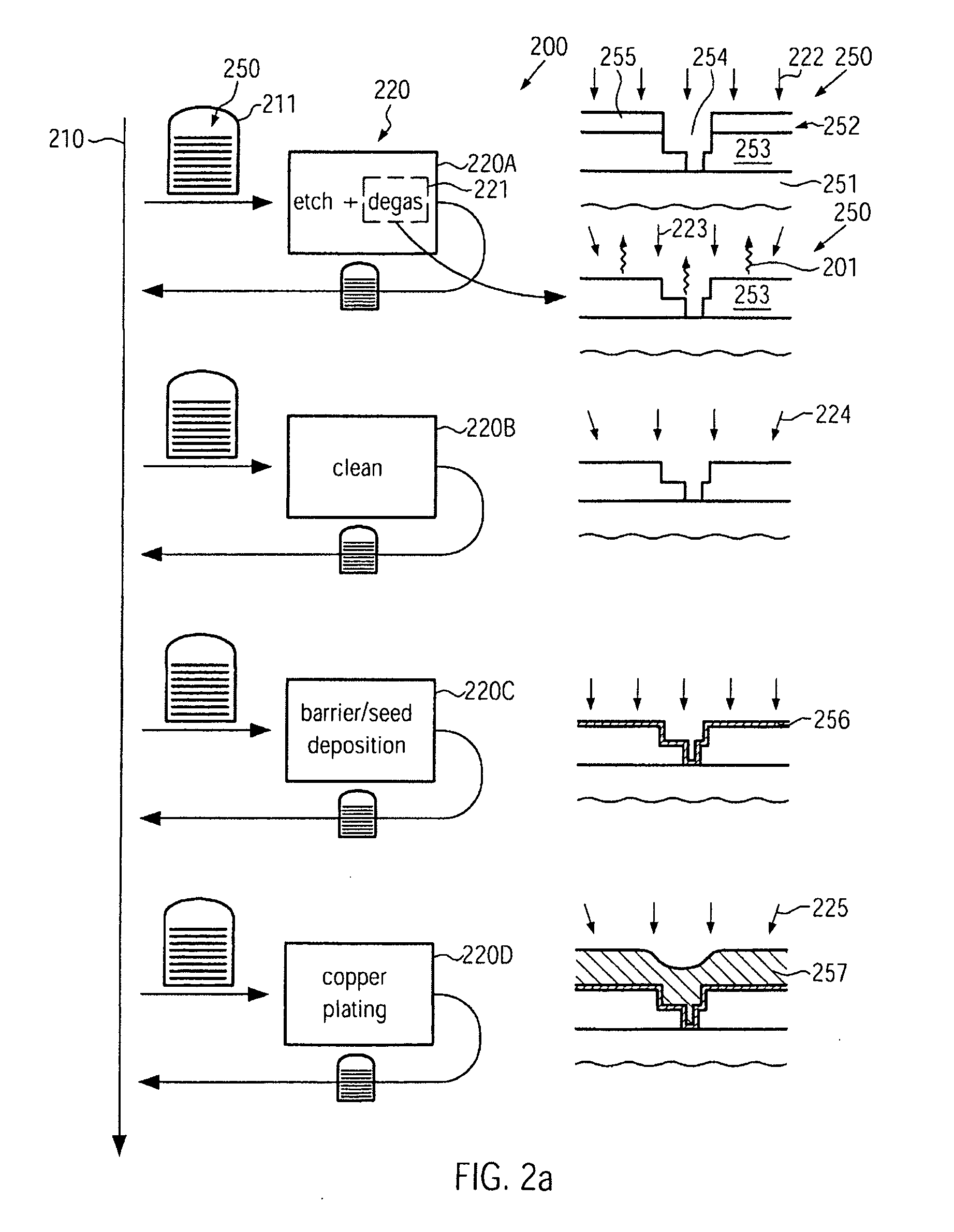
Method for reducing metal irregularities in advanced metallization systems of semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20090298279A1Reduce probabilityReduce irregularitiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
In a manufacturing sequence for forming metallization levels of semiconductor devices, out-gassing of volatile components after an etch process may be initiated immediately after the etch process, thereby reducing the probability of creating contaminants in other substrates and transport carriers during transport activities. Consequently, the defect rate of deposition-related irregularities in the metallization level may be reduced.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Trehalose transporter gene and method of introducing trehalose into cells
InactiveUS20090111176A1Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsConcentration gradientMembrane potential
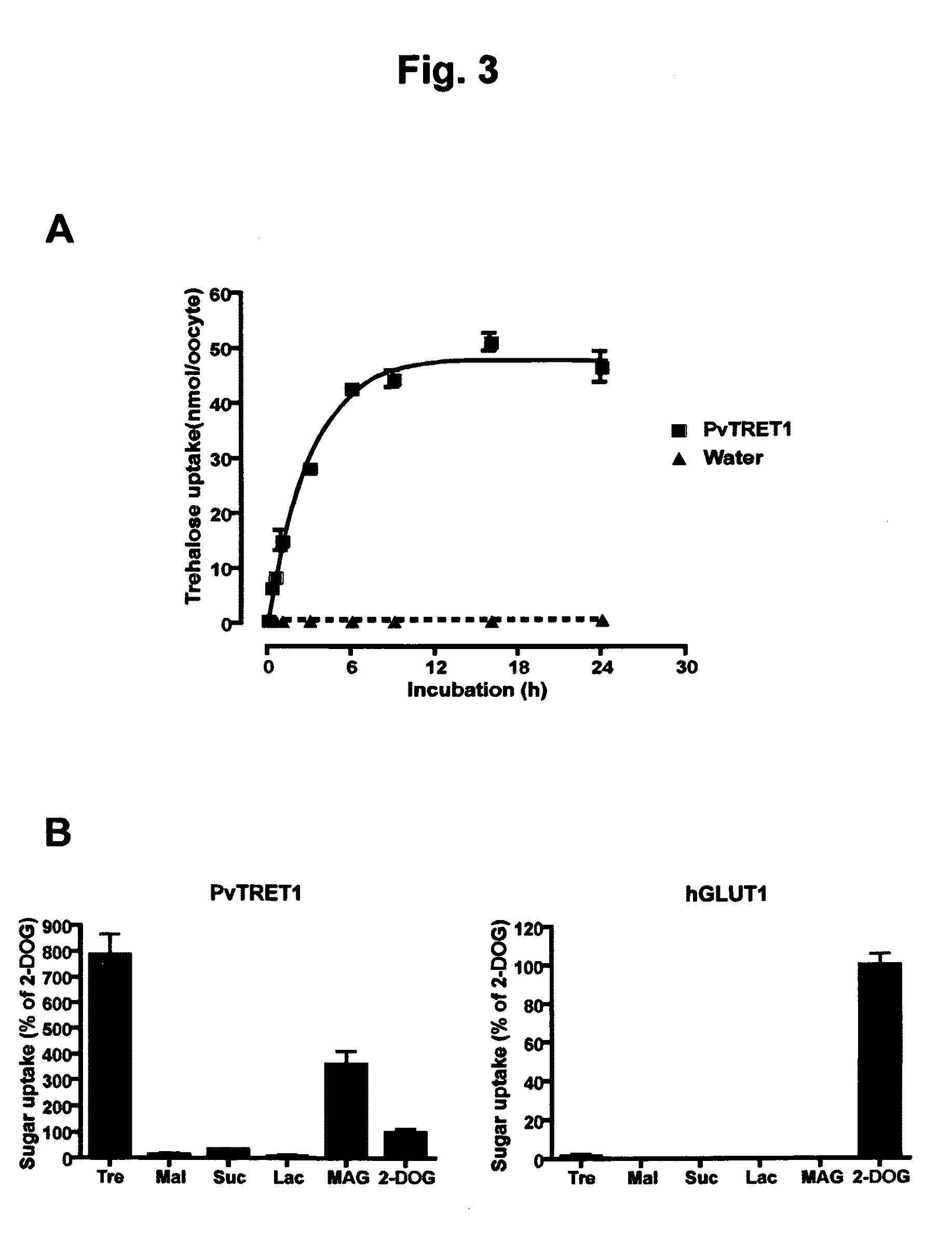
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
Plant strong salt-resistant gene AtNHXS1 and its coding protein and application
The invention provides a novel plant strong salt tolerant gene AtNHXS1 acquired through DNA reshuffling technology, and the ionic transport activity of Na+ / H+ antiporter protein coded by the gene is stronger than that of wild Na+ / H+ antiporter protein ATNHX1. A nucleotide sequence of the gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 also comprises genes of the nucleotide sequence of sequence 1 in a sequence table with the homology between 70 and 100 percent, or a nucleotide sequence of an amino acid sequence of sequence 2 in a coded sequence table. The new Na+ / H+ antiporter has a protein of the amino acid sequence of sequence 2 in the sequence table, protein of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 with the homology between 70 and 100 percent, or protein which replaces, deletes or adds one or a plurality of amino acids in the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 with the same homology. The invention also provides the construction of recombinant vector, the transgenic plant and other methods so as to apply the gene and the protein, thereby cultivating a novel variety of transgenic plant with strong capacity of salt tolerance or other improved biologic characters.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Novel plant strong-salt resistance gene NHXFS1, encoding protein and use thereof
InactiveCN101413004AImprove salt resistanceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPlant peptidesNucleotideWild type
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and provides a novel plant strong salt-tolerant gene NHXS1 obtained by a restructuring technology. A nucleotide sequence of the plant strong salt-tolerant gene NHXS1 is SEQ ID NO: 1, or a DNA sequence which has 70 to 100 percent homology with the SEQ ID NO: 1 nucleotide sequence or a DNA sequence for coding a protein sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2. Na + / H + antiporter NHXS1 colded by the gene has stronger ion transport activity than the wild-type Na + / H + antiporter AtNHX1. The invention also provides methods for construction of recombinant vectors and transgenic plants to apply the genes and proteins, and can culture a novel breed of transgenic plant with stronger salt-tolerant property or other improved biological characteristics.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
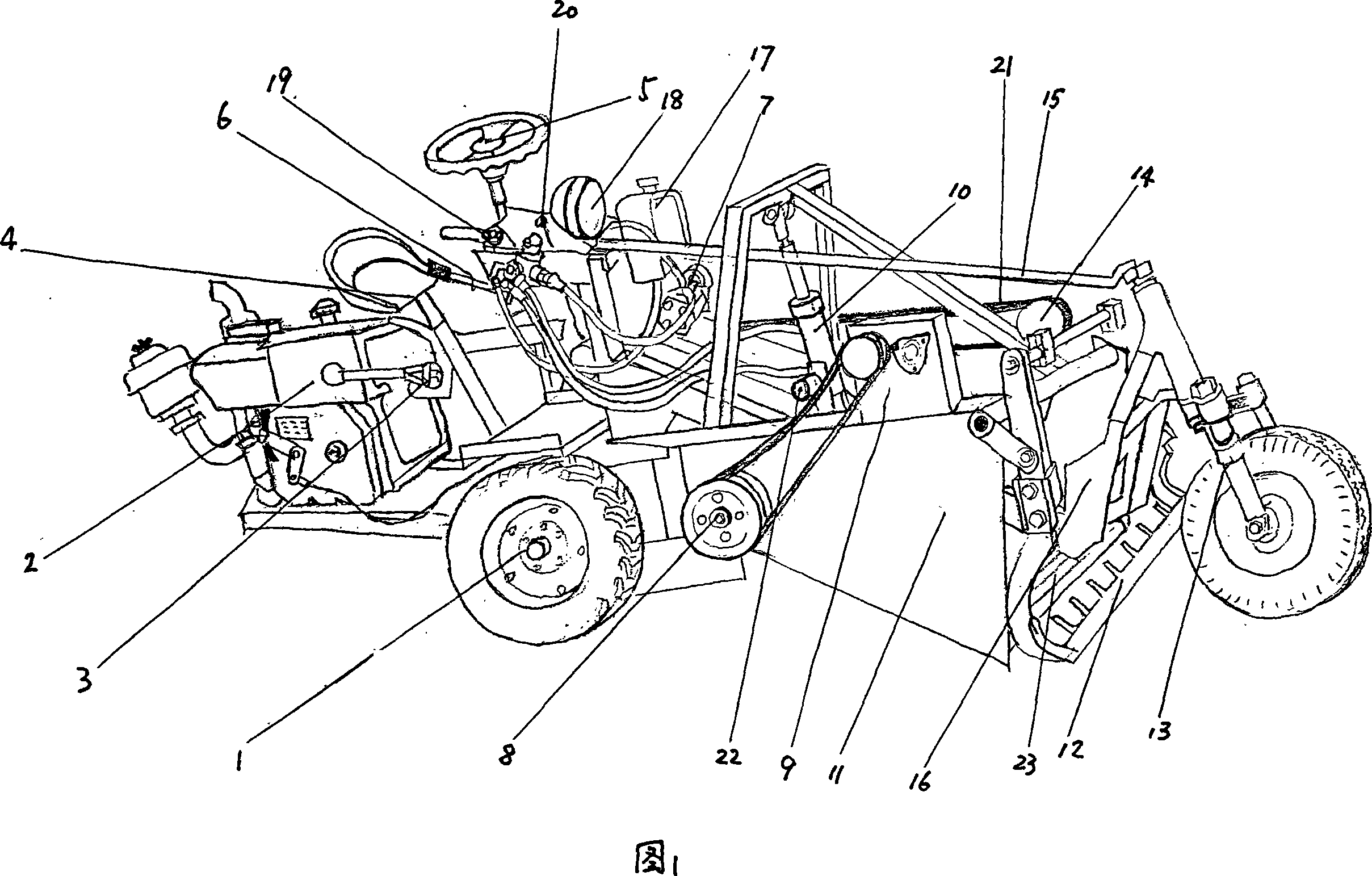
Self-propelled garlic digging harvester
InactiveCN101053297AReduce labor intensityImprove labor productivityDiggersHydraulic cylinderDrive shaft
The present invention discloses a self-walking type garlic harvester comprising engine, transmission system, chassis, traversing mechanism, active bit, the said transmission system has three branches, one branch drives garlic harvester to moving; one branch drives active bit to digging by transmitting triangle belt, eccentric bearing and transmission system; and one branch drives transportation chain and sieve plate to riddling and transporting activity by transmitting triangle belt, gear box assembly, sieve plate driven shaft and belt pulley; the chassis hinges with back end of big frame assembly, the chassis and the middle of big frame assembly are connected by hydraulic cylinder assembly, to adjust digging depth of active bit by hydraulic cylinder lifting. The present invention has the advantages of lightening labor intensity of manual harvesting garlic by mechanization means, and improving labor productivity. The present garlic harvester also is used for other fruit harvesting.
Owner:魏云高
Phenylsulfoxyoxazole compound inhibitors of urea transporters
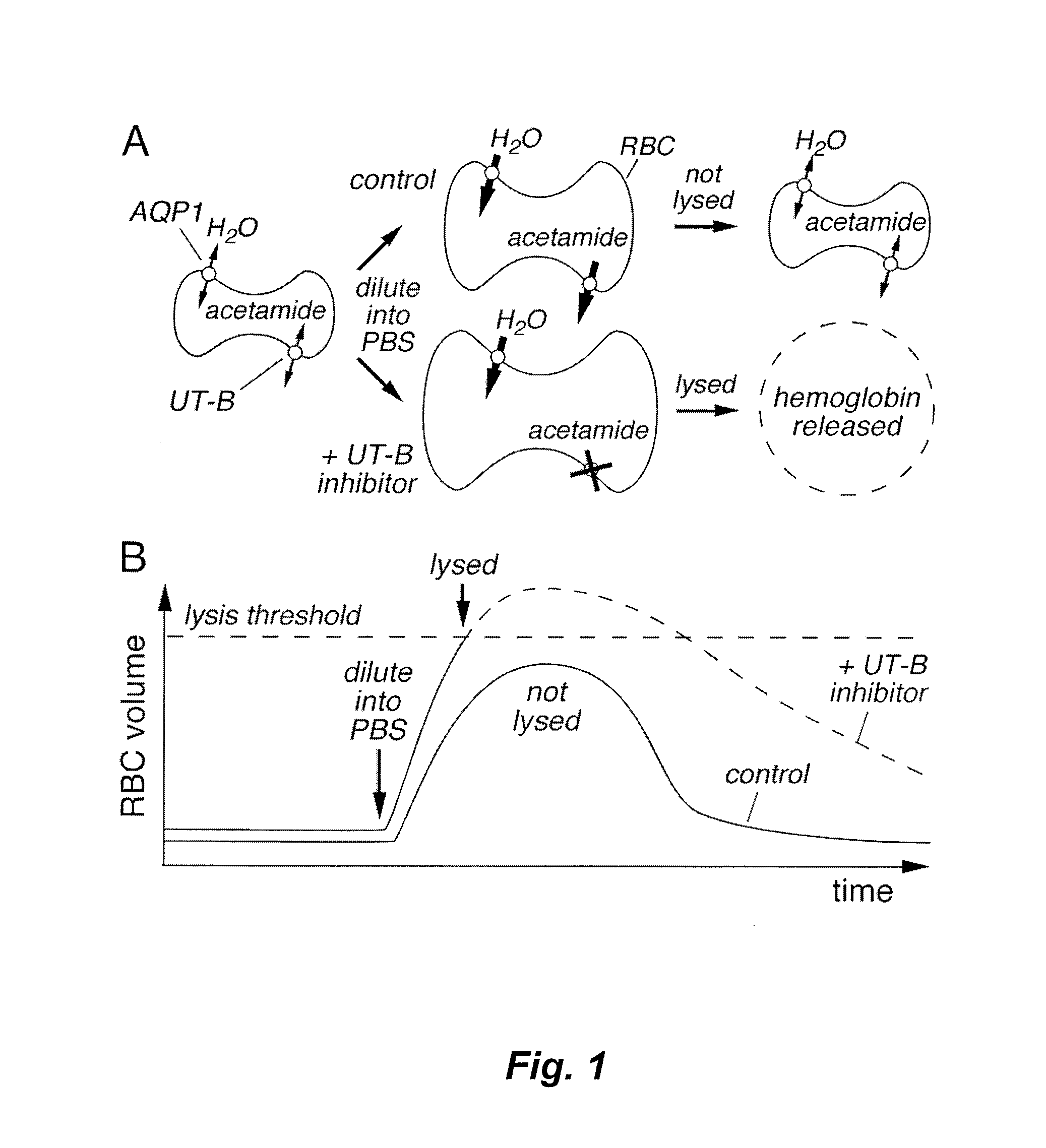
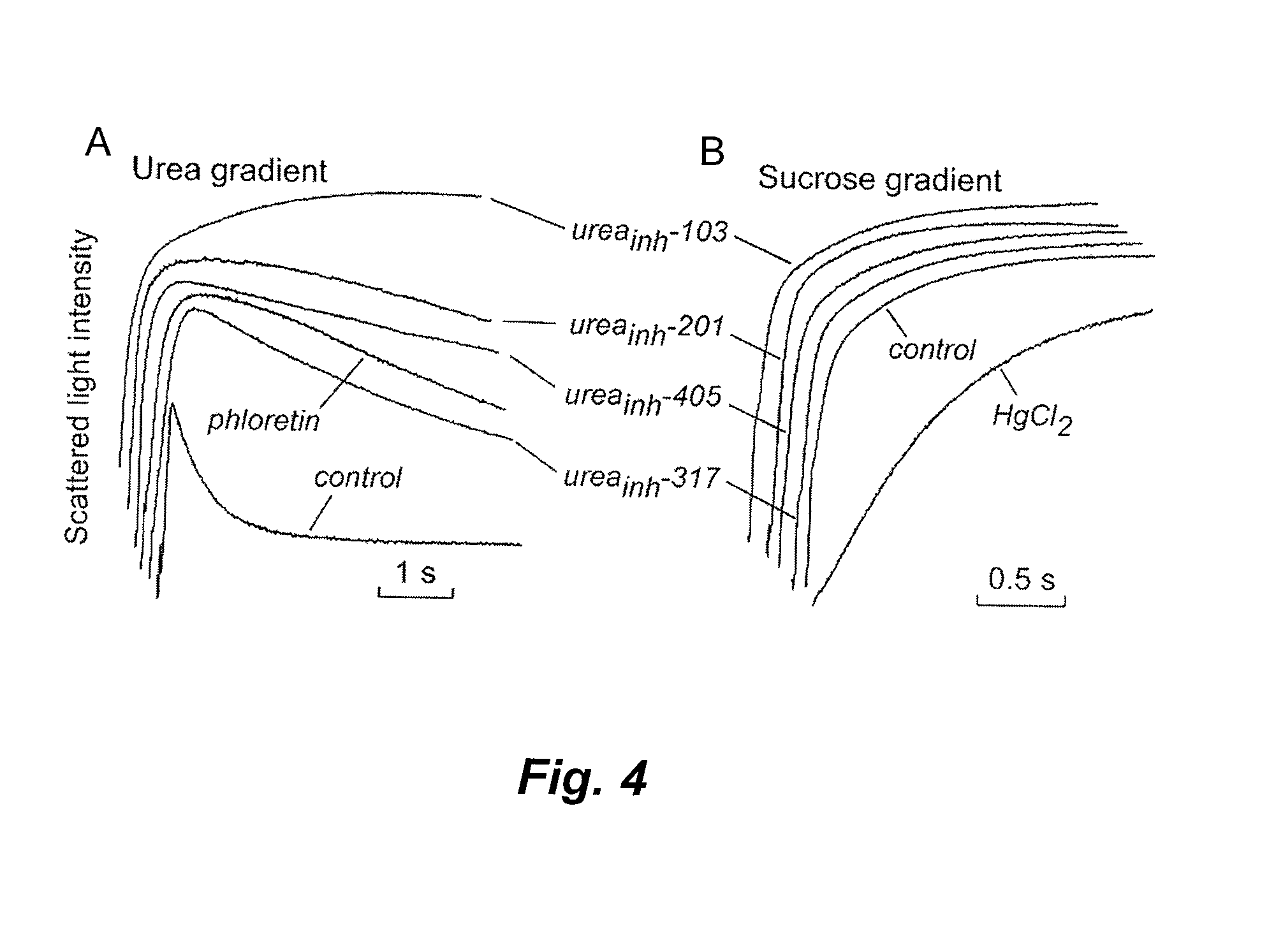
Provided herein are small molecule compounds that alter the transport activity of solute transporters, particularly urea transporters. The compounds described herein belong to the phenylsulfoxyoxazole, phenylsulfoxyimidazole, phenylsulfoxythiazole class of compounds. The compounds described herein are useful for increasing solute clearance in states of fluid overload and for treating cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic diseases, disorders, and conditions. Methods for identifying and using these agents that inhibit urea transporters are described herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Plasmid, phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and directed evolution method
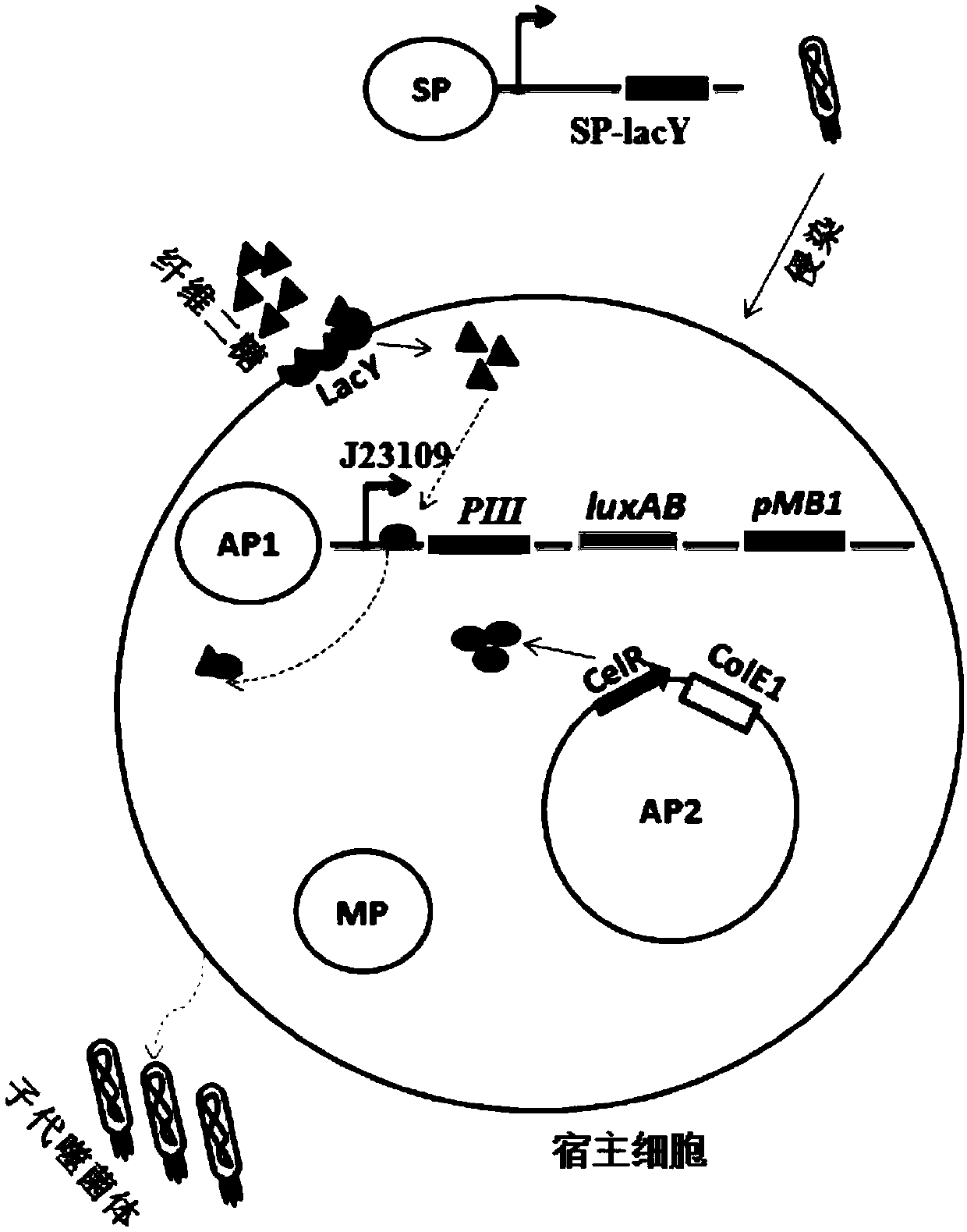
ActiveCN109943581ADisinhibition effectAchieve directed evolutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetBinding site
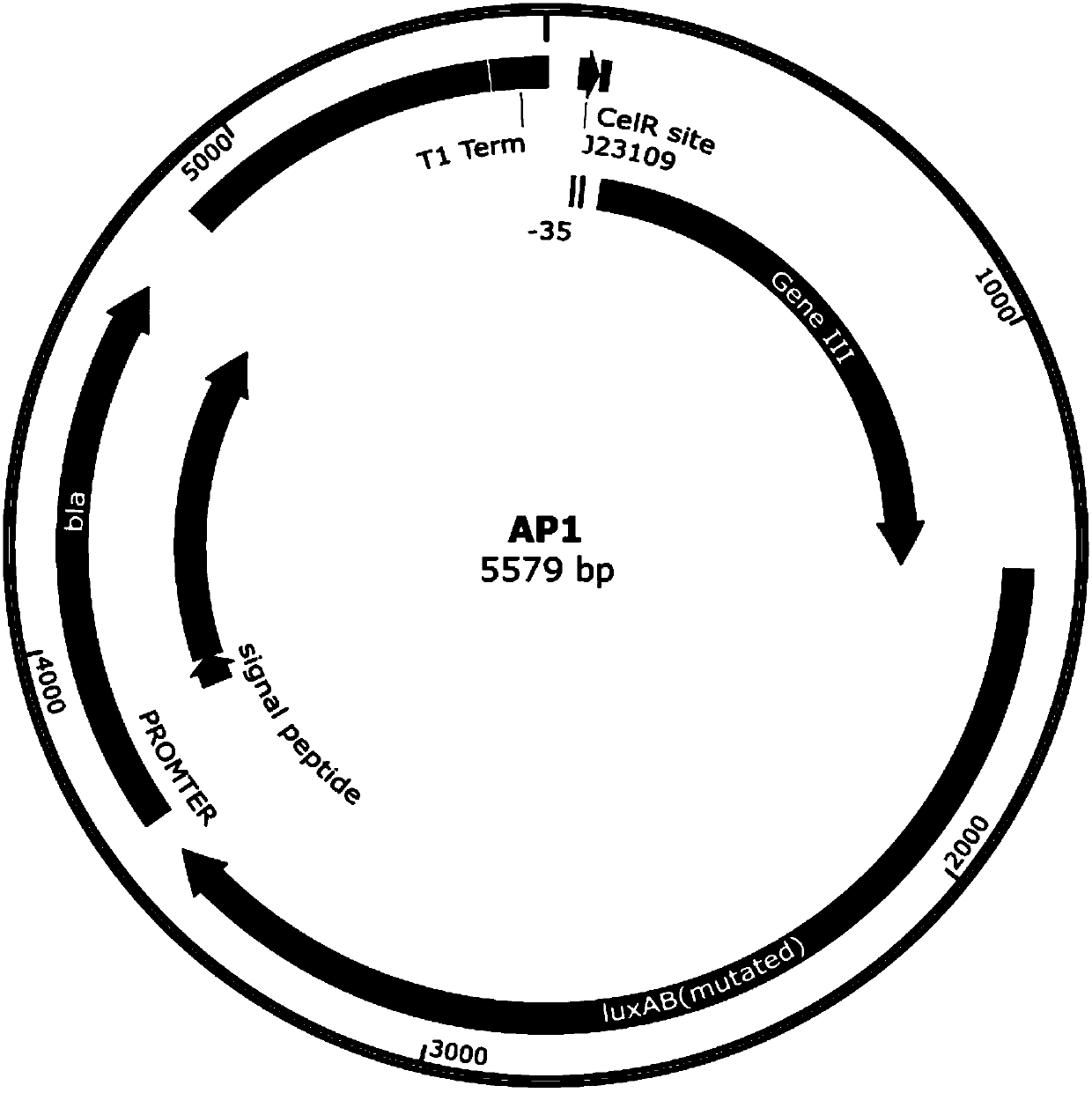
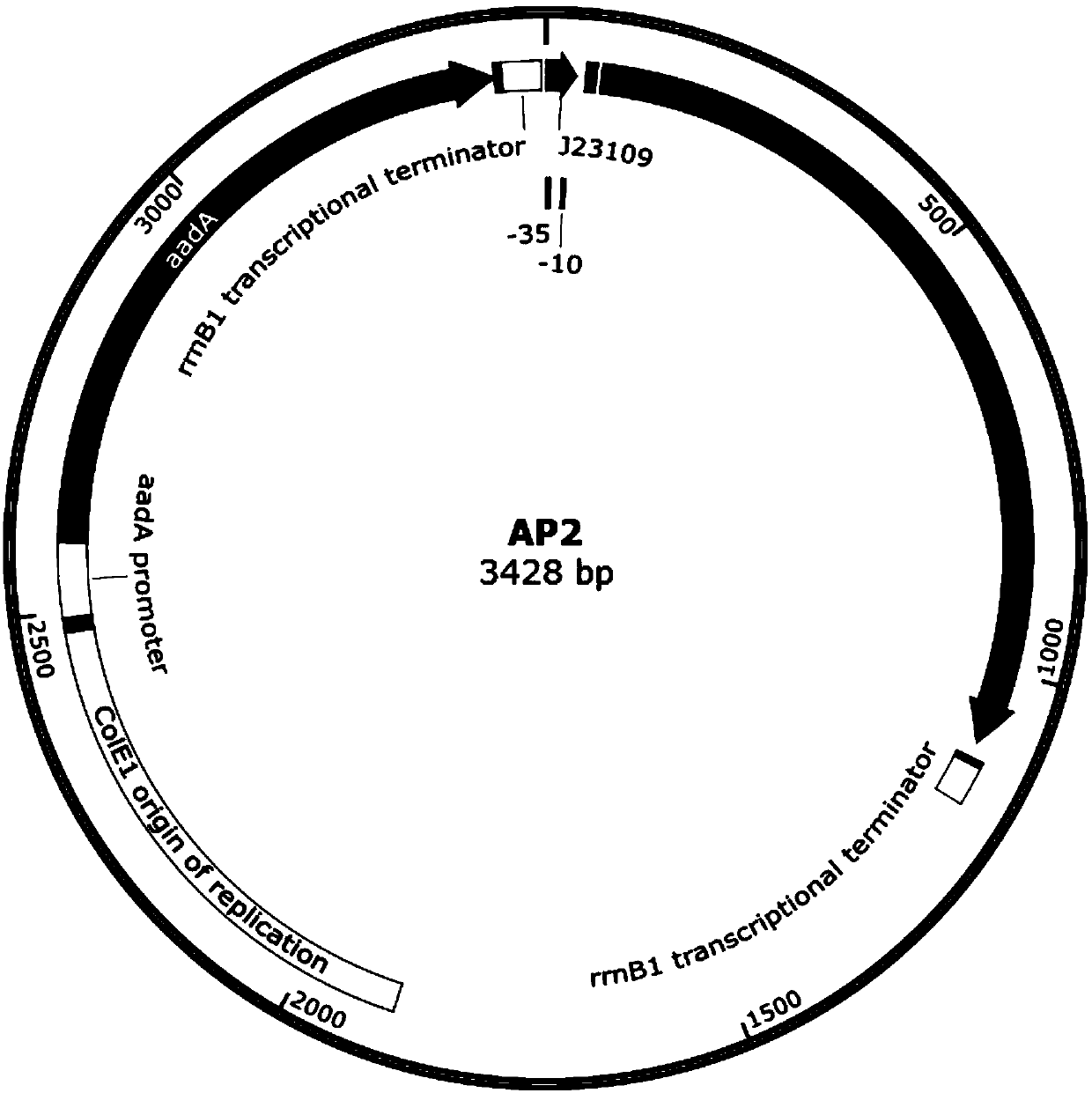
The invention relates to the field of directed evolution of membrane proteins, in particular to a plasmid, a phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and a directed evolution method. The plasmid comprises one or two of a plasmid AP1and a plasmid AP2; the plasmid AP1 carries a gIII gene, and a functional protein recognition site is arranged between a promoter of the plasmid and a ribosome binding site; the plasmid AP2 carries a functional protein gene. According to the plasmid, the phage-assisted continuous directed evolution system and the directed evolution method, the new assisting plasmids AP1 and AP2 are designed, the transport activity of the target protein to intracellular and extracellular substrate molecules and the gIII expression on the AP1 are coupled, the reproductive capability of SP and the activity of the target protein are coupled in the indirect mode, and the effect of continuous directed evolution of the target protein is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Reduced phosphotransferase system activity in bacteria
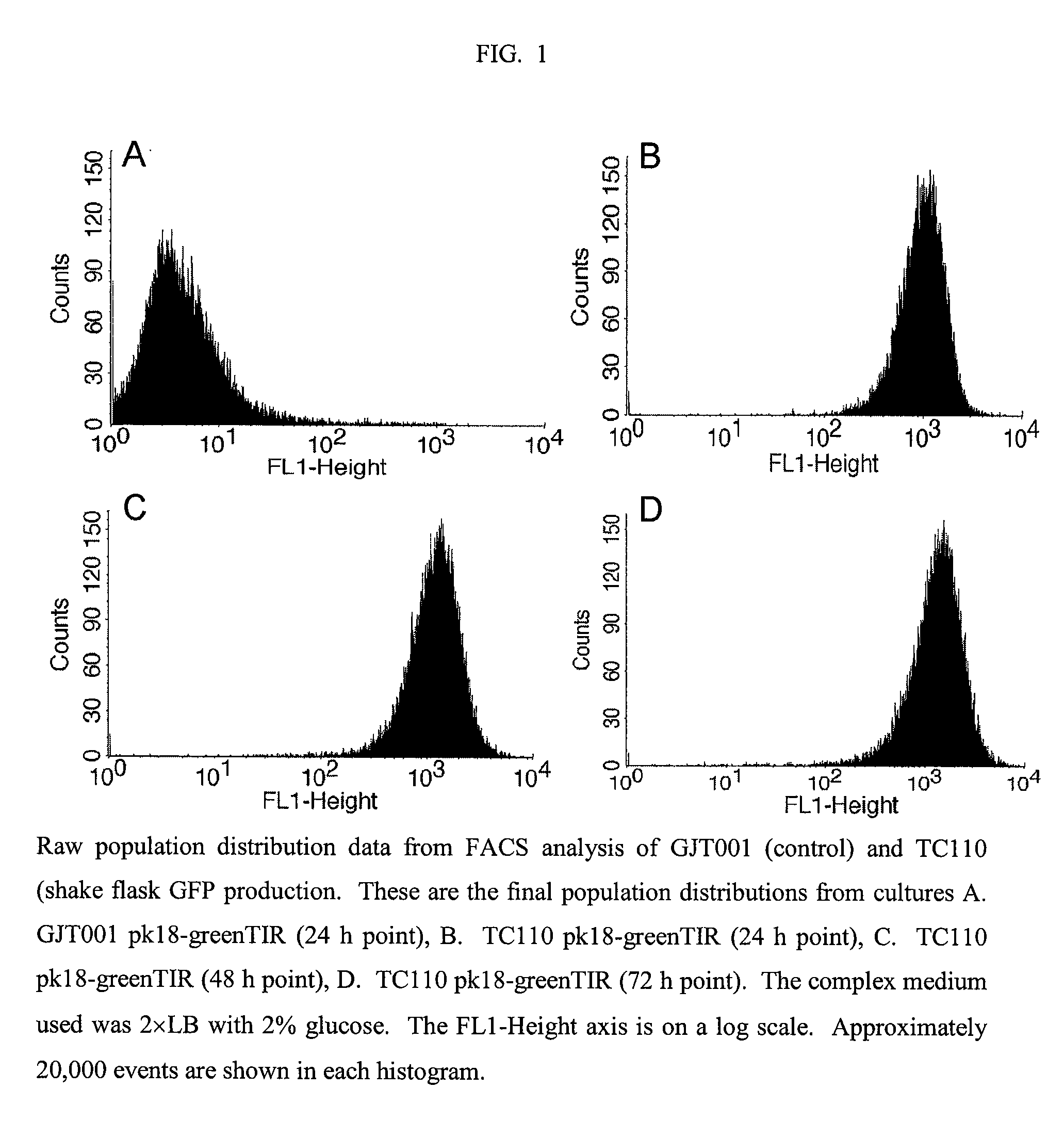
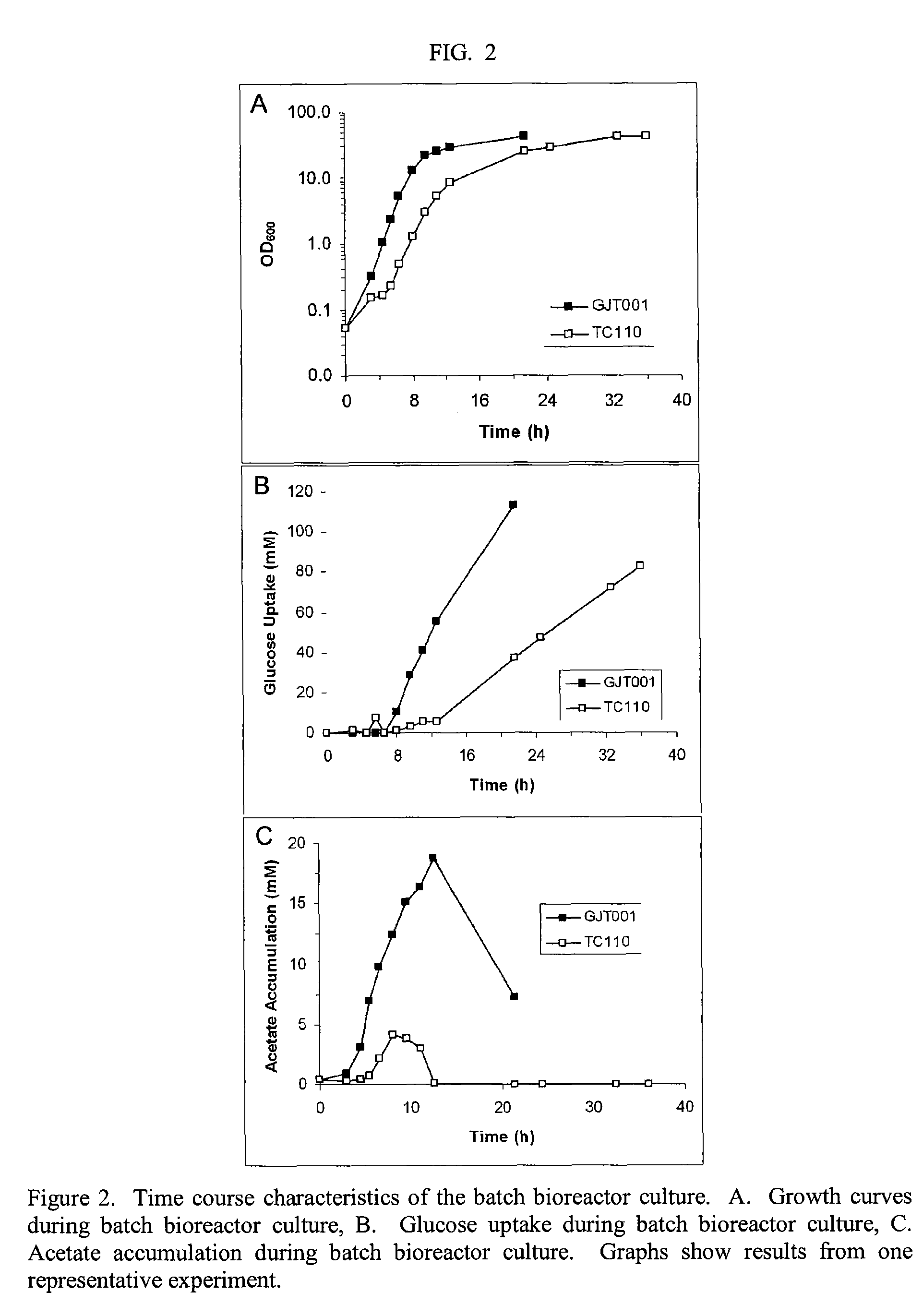
A method of producing biological products using bacteria with an inactivated ptsHI and wild type err and no added glucose transport activity and which consumes nearly all glucose in the media is described. The ΔptsHI bacteria produce large quantities of recombinant protein without producing significant amounts of acetate. The bacteria grow well on standard LB broth without additional supplementation.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Two- or multiple-piece insulating body system for producing medium high voltage cable fittings
InactiveCN101203992AImprove electrical strengthImprove insulation performanceCoupling device detailsCable fittingsCurve shapeSelf locking
A two- or three-part insulator system (1) is described for the production of medium and high voltage cable fittings with self-locking electrically insulating closures for e.g. securing cable connections, said system comprising at least a first insulator (2), which has a linear spherical-like locking element (3) set at the engagement surface (4) on its front face, which snap-fits with the second insulator (5) ) engages with a complementary receiver (6) at the engagement surface (4) on the front face of the ). Insulators (2, 5) form the electrical insulation of medium and high voltage cable fittings, each comprising an inner side (1.1) directed towards the cable connection and an outer side (1.2) directed towards the surrounding area, and at least one insulator (2 or 5) covers the active voltage transport connection elements, while the two insulators (2, 5) to be connected in cross-section form a closed linear spherical-like closing locking element (3) and a complementary receiving element (6) is set as the locking element The head area (7) of (3) and the opening area (7) of the receiving element (6) are in a pair of concavo-convex curved shapes, and each has a neck area (8) and a shoulder area (9) adjacent to the neck area, the The neck region may be bounded by the bending point of the inflection. Both insulators (2, 5) are provided on the inner side (1.1) and the outer side (1.2) with a conductive layer (10, 11) extending over at least one of the two insulators (2, 5) across the The engagement surfaces (4) on the front face, entering the head region or the opening region (7), respectively, at least up to the point of inflection of the inflection, are spaced from each other there. In the joined state of the two insulators (2, 5), the conductive layers (11.1, 11.2) and (10.1, 10.2) placed on the outer side (1.2) and inner side (1.1), respectively, at least on the joint surface ( 4) Contact each other.
Owner:CELLPACK
Phenylsulfoxyoxazole compound inhibitors of urea transporters
Provided herein are small molecule compounds that alter the transport activity of solute transporters, particularly urea transporters. The compounds described herein belong to the phenylsulfoxyoxazole, phenylsulfoxyimidazole, phenylsulfoxythiazole class of compounds. The compounds described herein are useful for increasing solute clearance in states of fluid overload and for treating cardiovascular, renal, and metabolic diseases, disorders, and conditions. Methods for identifying and using these agents that inhibit urea transporters are described herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modular genomes for synthetic biology and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS20080286871A1Maximize and minimize protein productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiBiotechnologyOrganism
The invention provides methods and compositions for assembling a modular replacement genome in a host microorganism. After such assembly, the host organism's genome is inactivated or ablated to permit full control of host cellular functions by the replacement genome. A modular replacement genome comprises an assembly of nucleic acid fragments, or segments, derived from one or more natural organisms or from synthetic polynucleotides or from a combination of both. Such an assembly, or set, of segments making up a replacement genome comprises a substantially complete set of genes and regulatory elements for carrying out minimal life functions under predefined culture conditions. The invention provides modular genomes having modules that are amenable to facile replacement, deletion, and / or additions. Such modules may be synthetic polynucleotides and may be designed for controlling gene content, excluding of genes that encode inhibitors or otherwise undesirable competing enzymes that divert a host cell from desired metabolic / synthetic processes; modifying codon usage to maximize or minimize protein production; modifying regulatory elements, including promoters, enhancers, repressors, activator, or the like, to modulate gene expression; balancing enzymatic and transport activities to optimize fluxes of substrates, intermediates, and products in metabolic pathways, and like objectives.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
Application of plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL)
InactiveCN101955947AImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringTransport systemOpen reading frame
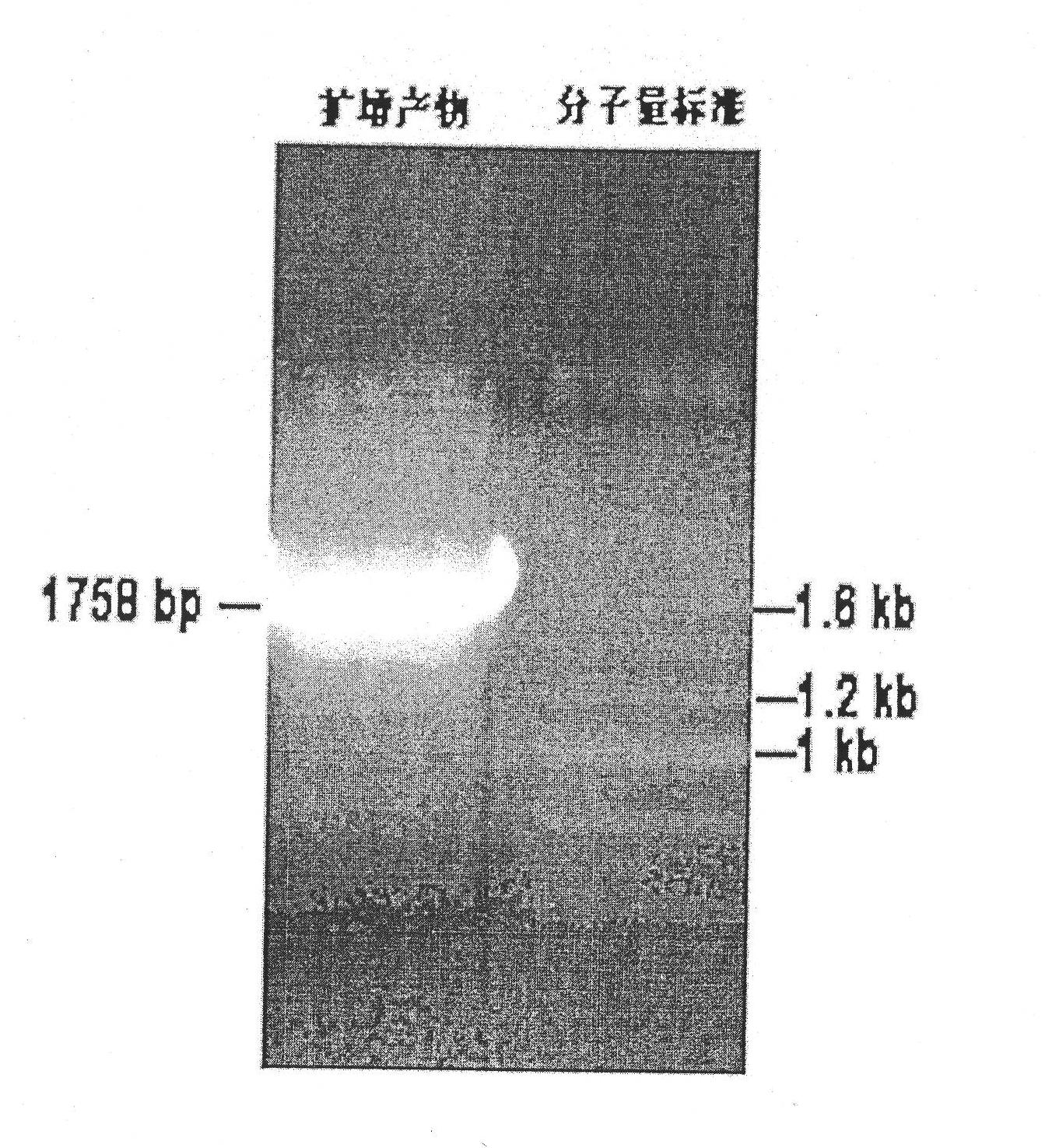
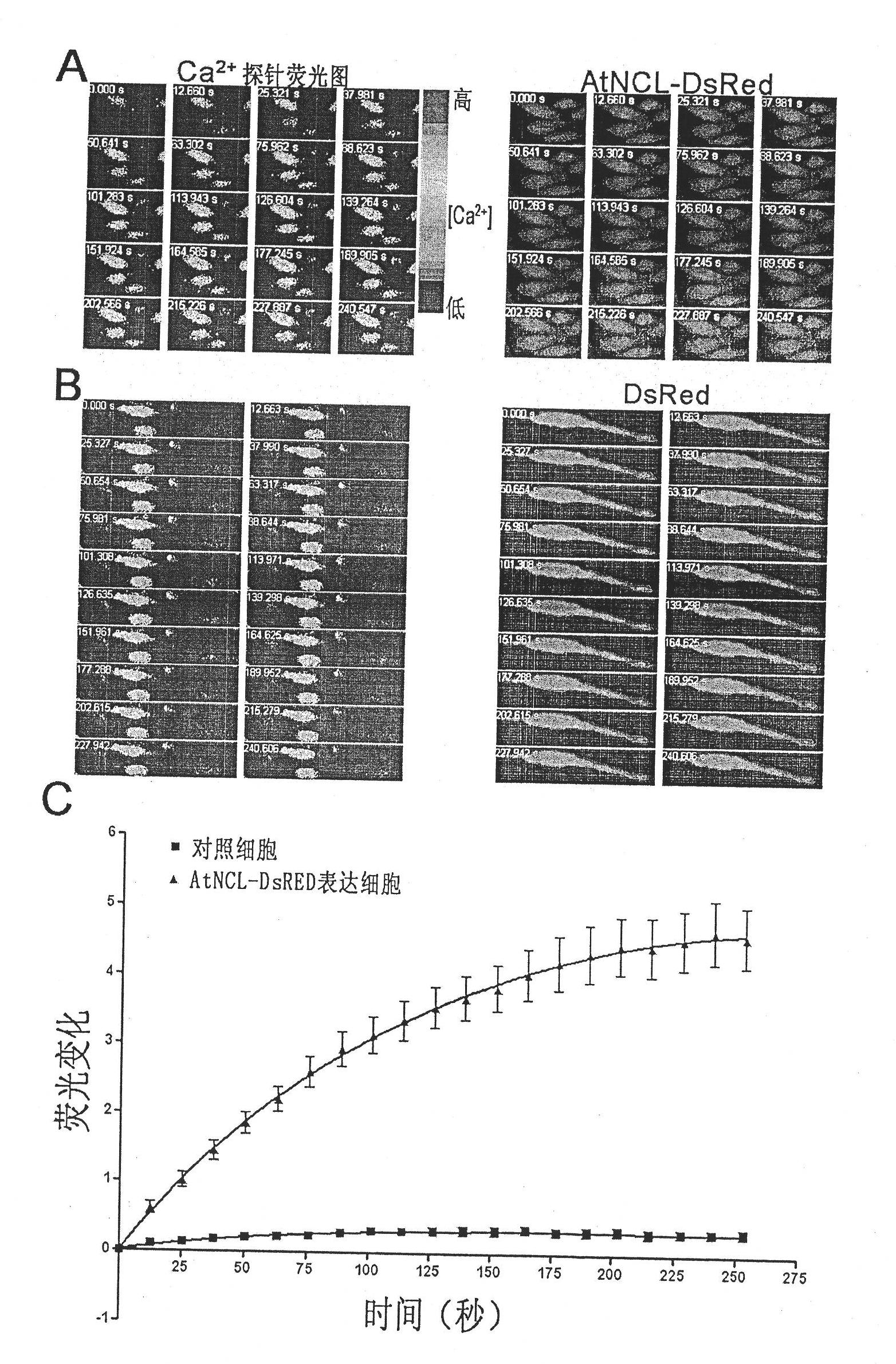
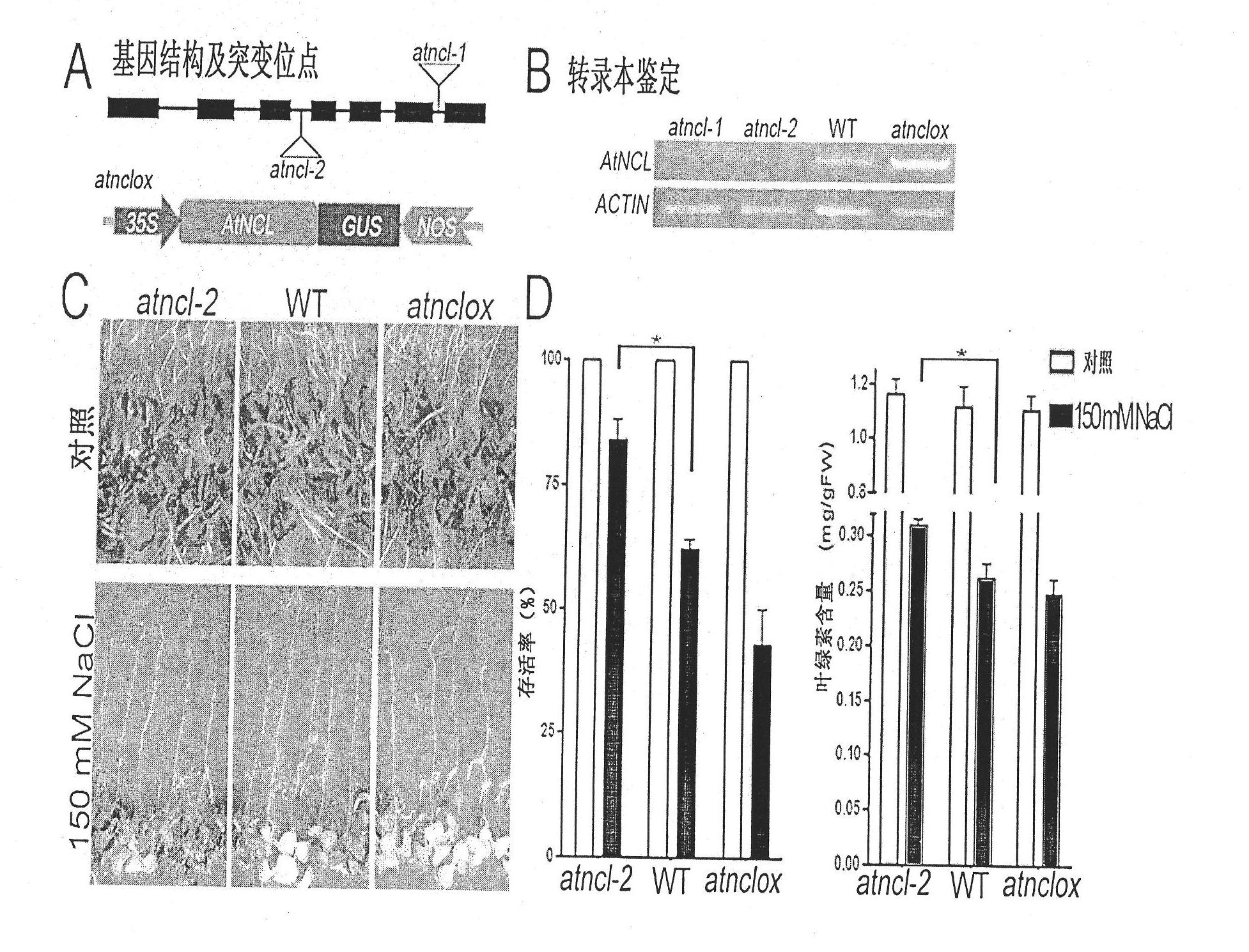
The invention discloses a plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL) and application of the sodium-calcium transport activity of the coding protein thereof in breeding salt-resistant variety of crop. The number of a model plant Arabidopsis thaliana sodium-calcium exchanger gene (AtNCL) in an Arabidopsis thaliana genome database (TAIR) is Atlg53210; the total length of the open reading frame of the gene is 1,758bp, and protein consisting of 585 amino acid residues is coded. Experiments prove that AtNCL participates in the elimination process of calcium signals of plant response to salt stress, and that a new ion transport system exists in the plant. By regulating the expression of the plant sodium-calcium exchanger gene through the crop transgenic technology according to the characteristics of AtNCL, a new crop variety with improved salt resistance can be obtained.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Method for testing microbial activity of artificial wet land sewage treatment system
ActiveCN101251473AKeep healthyAvoid incomplete extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansConstructed wetlandDry weight
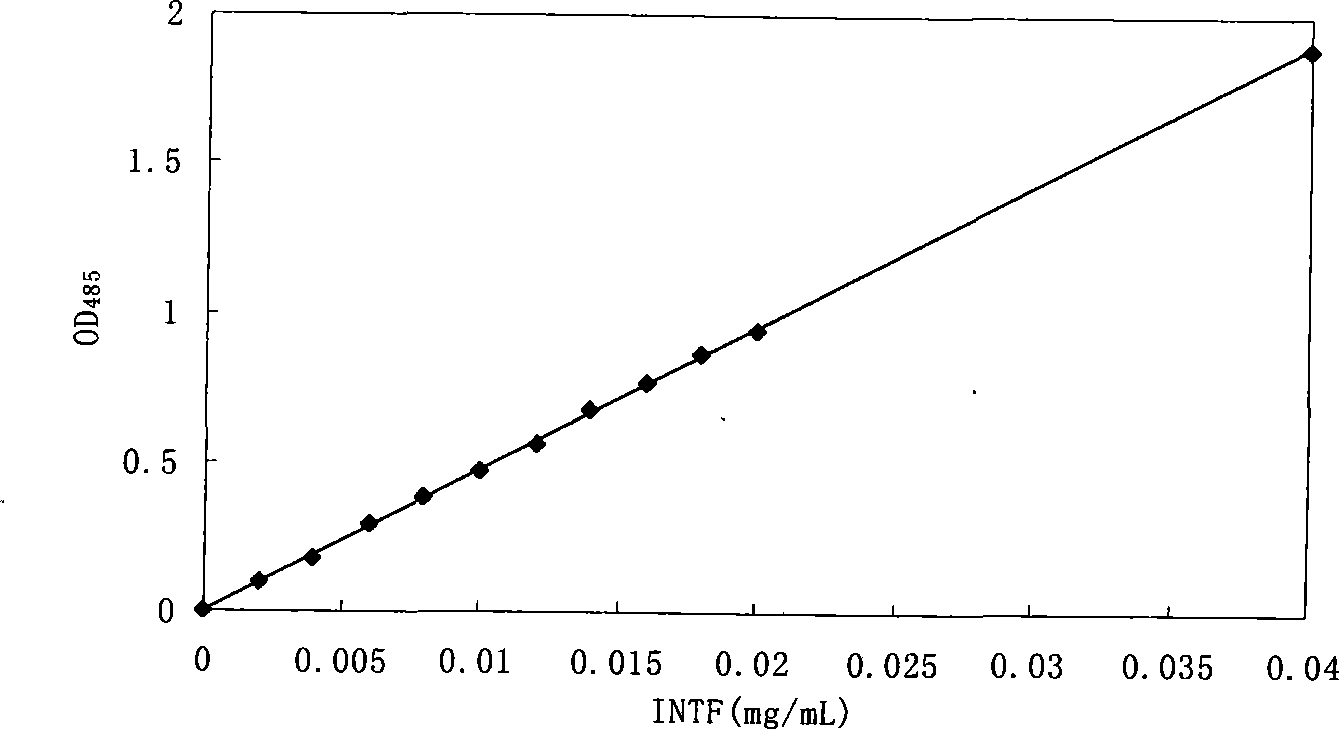
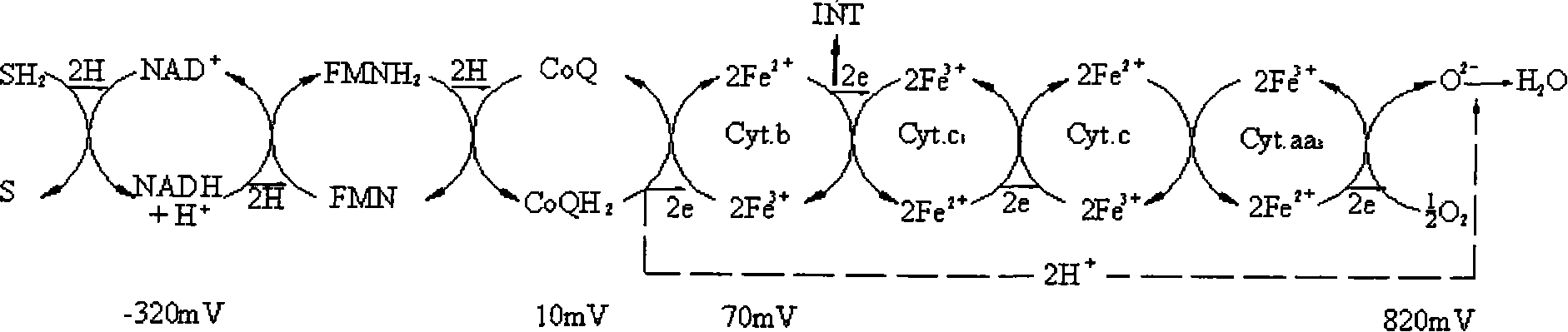
The present invention provides a microorganism activity detection method for constructed wetland sewage treatment system, comprising the following basic steps of constructed wetland microorganism sampling, cultivation, extraction, measurement and calculation. The present invention adopts iodine nitro group tetrazolium as an electron acceptor, cancels oxygen removal step on the basis of the strongelectron affinity of INT, adopts 2h as the cultivation time, and uses ethanol as extractant to extract INTF inside microorganism cells. The detection method has the advantages that: the INT is strongin electron affinity and the ability of competing with oxygen for electrons; the present invention can be used to detect the electron transport system activity of aerobic, anaerobic and denitrification nitrogen removal microorganisms in constructed wetland systems, finishes extraction process under the condition of normal temperature, and avoids incomplete extraction, extractant evaporation and other problems which are caused by high temperature; the microorganism dry weight direct determination method is combined with the detection process of microorganism electron transport activity, thereby avoiding errors caused by different matrixes and plant rhizosphere biomass as well as uneven sampling.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN INST GRP
Method and system for controlling transport sequencing in a process tool by a look-ahead mode
ActiveUS8126588B2Improve performanceFunction increaseProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsProcess moduleHandling system
By providing a look-ahead functionality for a tool internal substrate handling system of process tools on the basis of a process history, the tool internal substrate sequencing may be significantly enhanced. The look-ahead functionality enables a prediction of process time of substrates currently being processed in a respective process module, thereby enabling the initiation of transport activity for substrate load operations in order to significantly reduce the overall idle time of process modules occurring during substrate exchange.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for screening for compound capable of enhancing or inhibiting oatp1b1 transport activity, and method for determining expression level of oatp1b1
ActiveUS20140024070A1Enhances and inhibits transport activityDetected safely and inexpensivelyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionScreening methodDichlorofluorescein
The present invention provides a method of screening for a compound that enhances or inhibits the transport activity of OATP1B1, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention also provides a use of dichlorofluorescein in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1. The present invention further provides a method for measuring the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells, using dichlorofluorescein. The present invention further provides a use of a kit including dichlorofluorescein and positive cells expressing OATP1B1 in measurement of the expression level of OATP1B1 in test cells.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
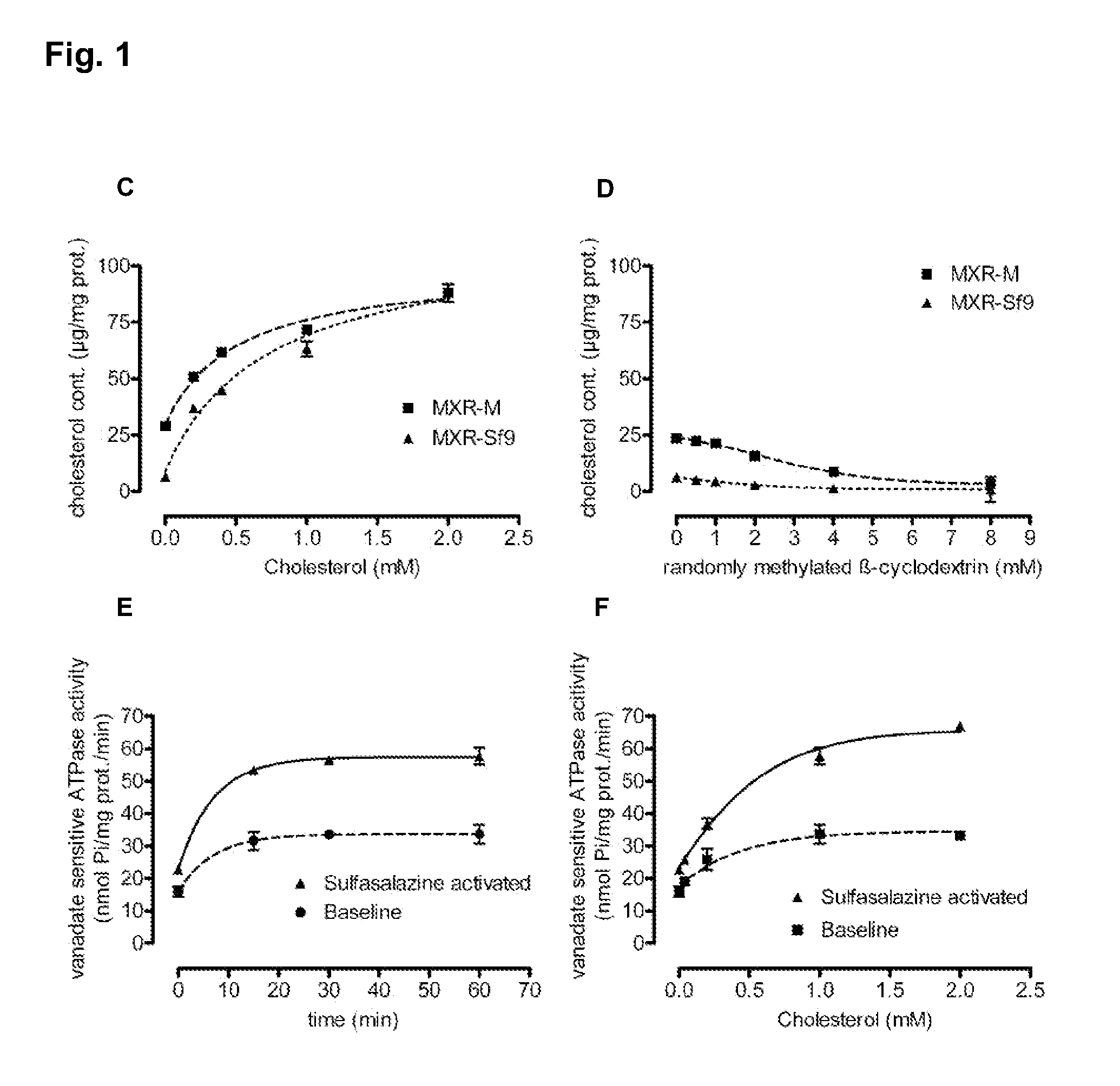
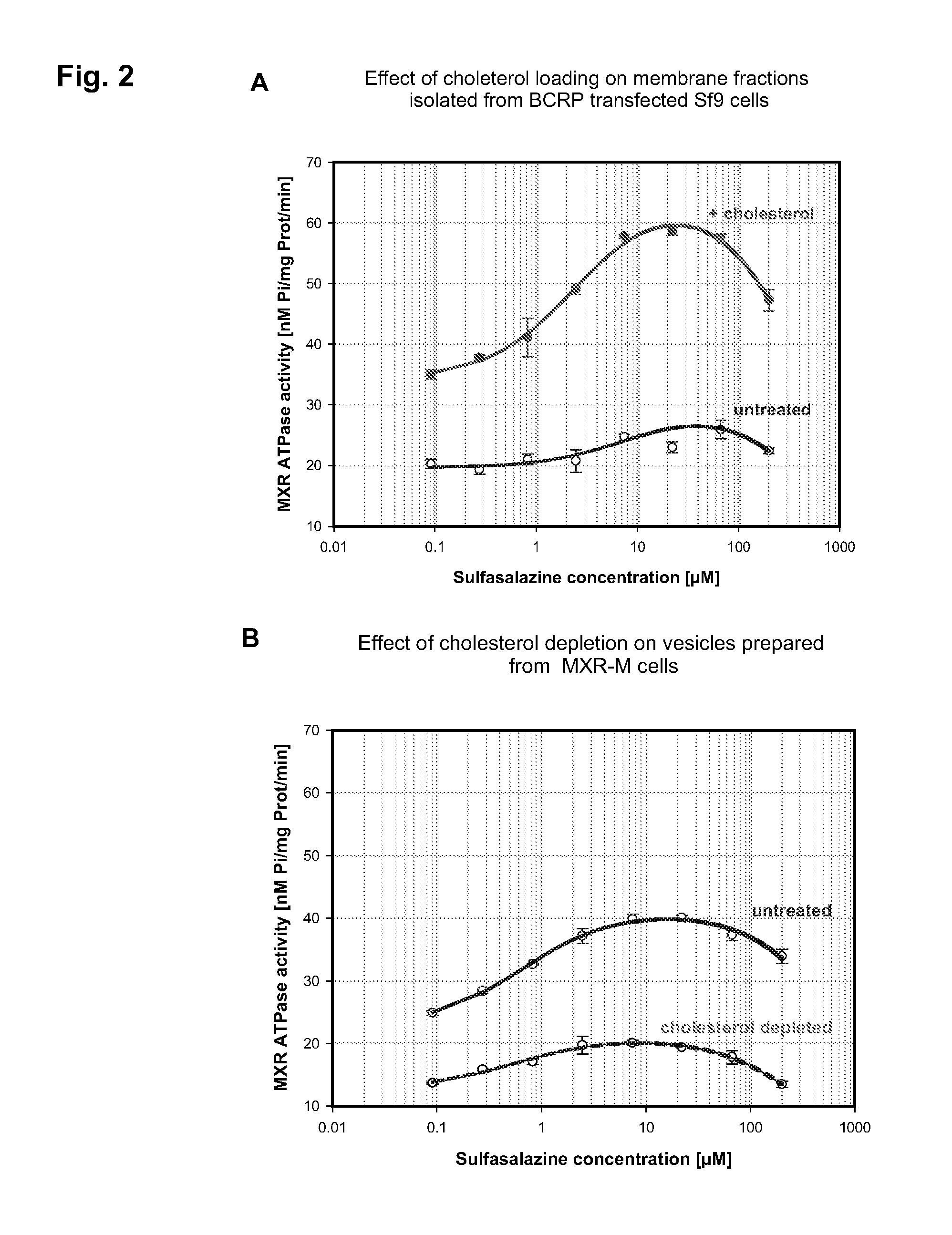
Cholesterol loaded insect cell membranes as test proteins
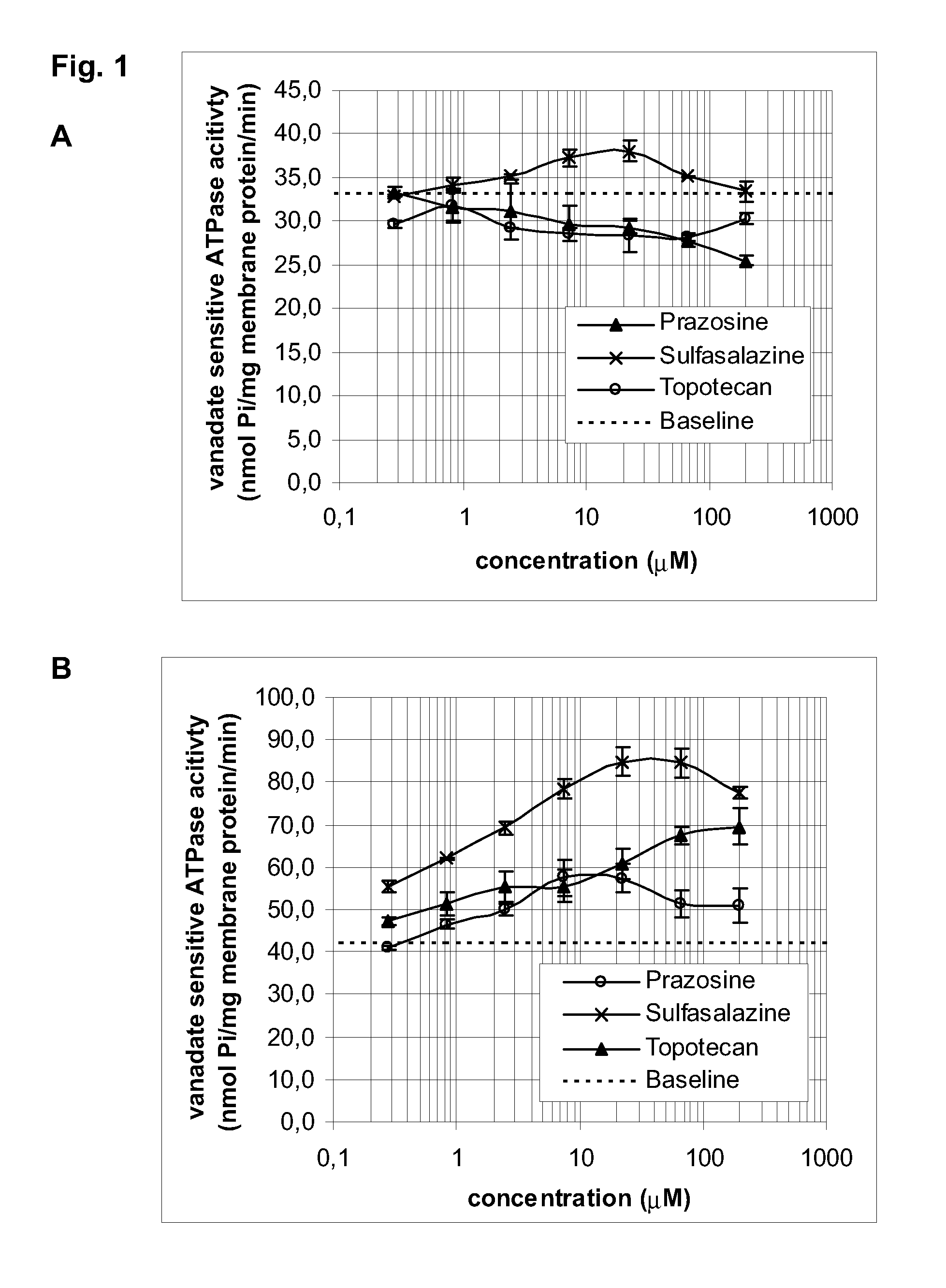
The invention provides for a novel cholesterol loaded insect cell membrane preparation having an increased cholesterol level as compared to physiological cholesterol levels of insect cell membranes or to control insect cell membrane preparations without cholesterol loading, wherein said cholesterol loaded membrane preparation comprises an ABC transporter protein having an increased substrate transport activity due to increased cholesterol level of the membrane. The invention also relates to reagent kits comprising the preparations of the invention. The invention also relates to methods for manufacturing said preparations and methods for measuring any type of activity of the ABC transporters present in the cholesterol loaded membranes as well as studying or testing compounds and interaction of compounds and ABC transporters, in this assay systems. The invention also provides for a test system useful for testing whether ABC transporter proteins can be activated by cholesterol in an insect cell membrane.
Owner:SOLVO BIOTECH
Modulators of slc22a7
InactiveUS20140090094A1Reduce intracellular levelCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesCell biologyTransport activity
The present invention is directed to the identification of modulators for SLC22A7 transporter and therapeutic uses thereof. Hence, in one embodiment the present invention relates to a method for identifying and / or obtaining a compound capable of modulating glutamate transport, comprising contacting a test compound with a system for measuring those transport activity, which system comprises an SLC22A7 polypeptide or a functional fragment thereof, and a substrate for measuring glutamate transport by the system; and detecting an altered level of the those transport activity of the SLC22A7 polypeptide or functional fragment in the presence of the test compound compared to the described transport activity in the absence of the test compound and / or presence of a control.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Modular genomes for synthetic biology and metabolic engineering
The invention provides methods and compositions for assembling a modular replacement genome in a host microorganism. After such assembly, the host organism's genome is inactivated or ablated to permit full control of host cellular functions by the replacement genome. A modular replacement genome comprises an assembly of nucleic acid fragments, or segments, derived from one or more natural organisms or from synthetic polynucleotides or from a combination of both. Such an assembly, or set, of segments making up a replacement genome comprises a substantially complete set of genes and regulatory elements for carrying out minimal life functions under predefined culture conditions. The invention provides modular genomes having modules that are amenable to facile replacement, deletion, and / or additions. Such modules may be synthetic polynucleotides and may be designed for controlling gene content, excluding of genes that encode inhibitors or otherwise undesirable competing enzymes that divert a host cell from desired metabolic / synthetic processes; modifying codon usage to maximize or minimize protein production; modifying regulatory elements, including promoters, enhancers, repressors, activator, or the like, to modulate gene expression; balancing enzymatic and transport activities to optimize fluxes of substrates, intermediates, and products in metabolic pathways, and like objectives.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
Therapies for seizure disorders using RLIP76
InactiveUS20060104982A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGenetic material ingredientsRalA binding protein 1Chemical compound
The present invention is a composition identified as a coding region of ralA binding protein 1, wherein the region neighbors a membrane-associated portion of the ralA binding protein 1 and directly effects transport activity and membrane association of the ralA binding protein 1. The composition is used to identify chemical compounds (e.g., antibodies, si-RNA and small molecules) that recognize ralA binding protein 1. The composition and methods of using the composition identify, via screening of chemical libraries, compounds that bind ralA binding protein 1 and medicines for the treatment of seizure disorders.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Peptide transporting to chromoplasts in petals and method of constructing plant having yellowish petals by using the same
InactiveUS8143478B2Impart yellowish flower colorEnhance yellowish flower colorPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPetalEnzyme protein
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Method of increasing cell permeability to trehalose by recombinantly producing a trehalose transporter
InactiveUS7892789B2Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesVertebrate cellsConcentration gradientFat bodies
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
Monocarboxylate transport modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180290978A1Efficient transportOrganic chemistryAntipyreticAbnormal tissue growthOrgan transplant rejection
The invention generally relates to the field of monocarboxylate transport modulators, e.g., monocarboxylate transport inhibitors, and more particularly to new substituted-quinolone compounds, the synthesis and use of these compounds and their pharmaceutical compositions, e.g., in treating, modulating, forestalling and / or reducing physiological conditions associated with monocarboxylate transport activity such as in treating cancer and other neoplastic disorders, inflammatory diseases, disorders of abnormal tissue growth and fibrosis including cardiomyopathy, obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, tissue and organ transplant rejection, and malaria.
Owner:NIROGY THERAPEUTICS INC
Application and expression vectors of paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1
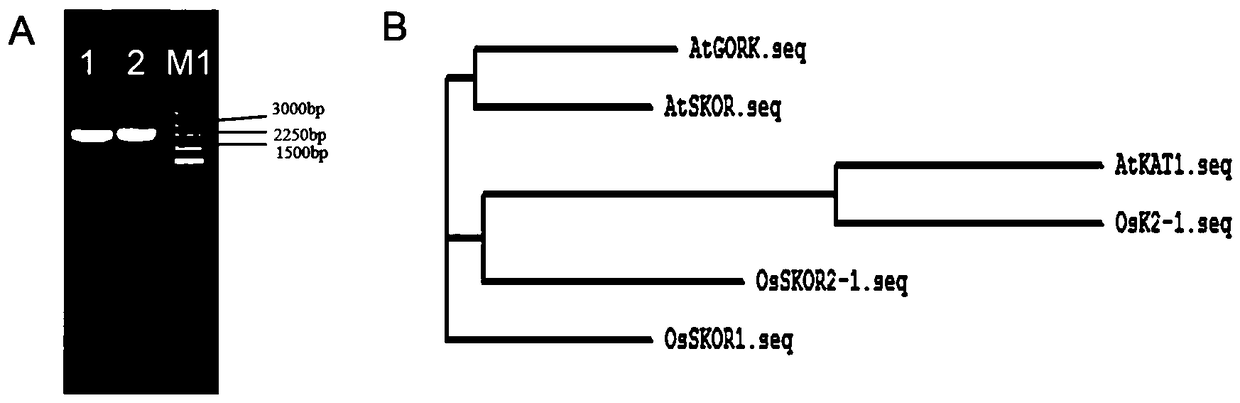
ActiveCN109082428AImprove effective utilizationStomatal opening increasedPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceINCREASED EFFECT
The invention relates to application and expression vectors of a paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1. The paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 is obtained through cloning. The gene is mainly expressed in paddy rice overground part mesophyll and stomatal guard cells, and the gene protein has transport activity for mediating potassium ion inward absorption. The invention discovers the application of the paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 in the increasing of crop photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance and transpiration rate and in the increasing of nitrogen utilization efficiency in crop high-nitrogen environments for the first time. The animal expression vector and the plane overexpression vector of the paddy rice stomata open type potassium ion channel gene OsK2-1 evidently increase the biomass and grain yield of paddy rice modified by the OsK2-1 gene and especially has a good yield increasing effect and promising application prospect under a high-nitrogen condition.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com