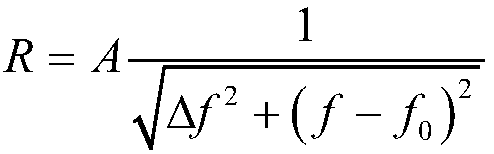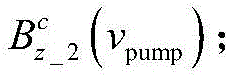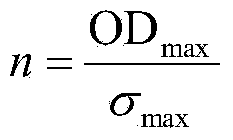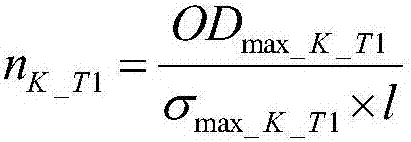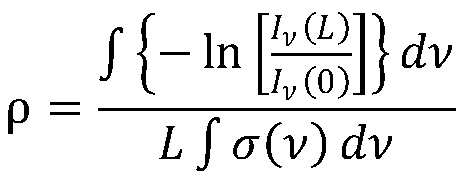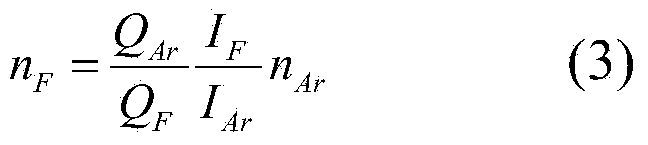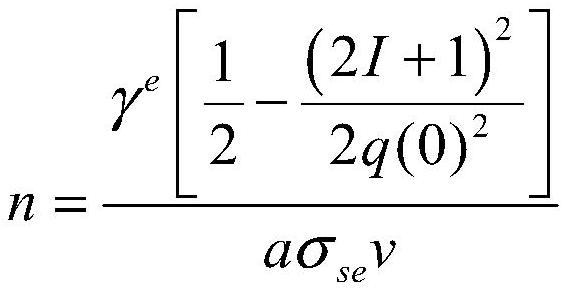Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Atomic density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
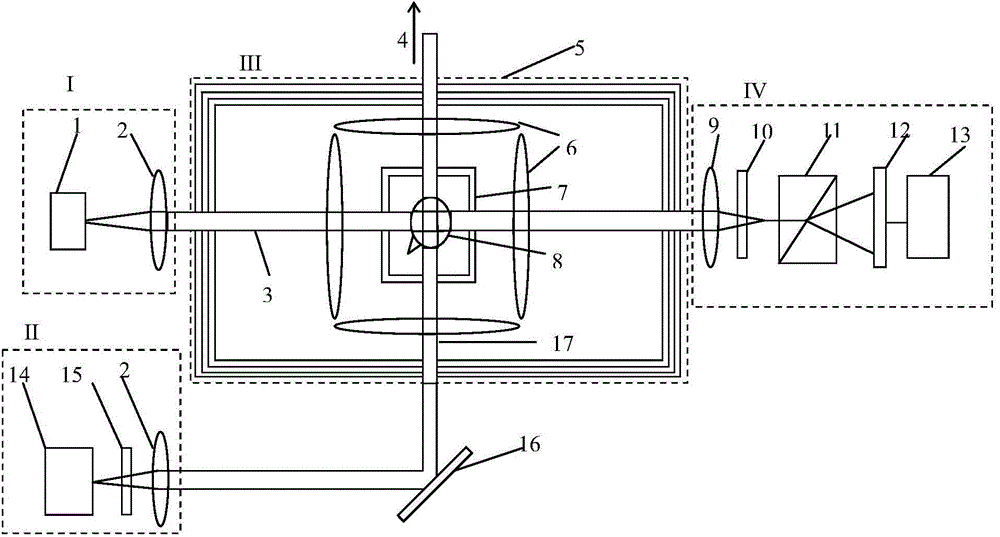
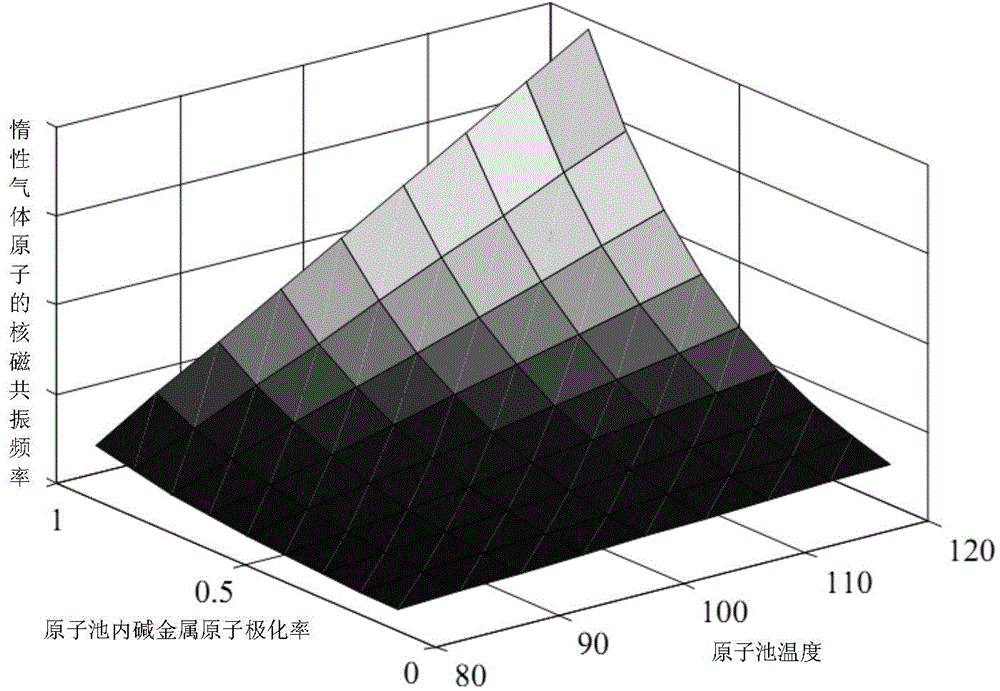
Method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time
ActiveCN104833690ADoes not affect the structureEasy to measureAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePolarizabilityProton NMR
The invention provides a method for measuring alkali metal atomic polarizability of a nuclear magnetic resonance gyro in real time and belongs to the field of atomic physics. The method includes: measuring alkali metal atomic densities of an atomic pool at different temperatures, measuring atomic nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of inert gas caused by polarization of alkali metal atoms, and thus acquiring polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool without changing the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the magnetic field environment; building a three-dimensional model of changes in nuclear magnetic resonance frequency of the inert gas in the atomic pool along with temperature and the alkali metal atomic polarizability, measuring the frequency shift of atomic NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) of the inert gas at any temperature point while the nuclear magnetic resonance frequency normally runs, and thus calculating the polarizability of the alkali metal atoms in the atomic pool in real time. The method has the advantages that the method is simple, no influence is caused to the optical path structure of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro and the method is of great significance to improving the performance of the nuclear magnetic resonance gyro.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
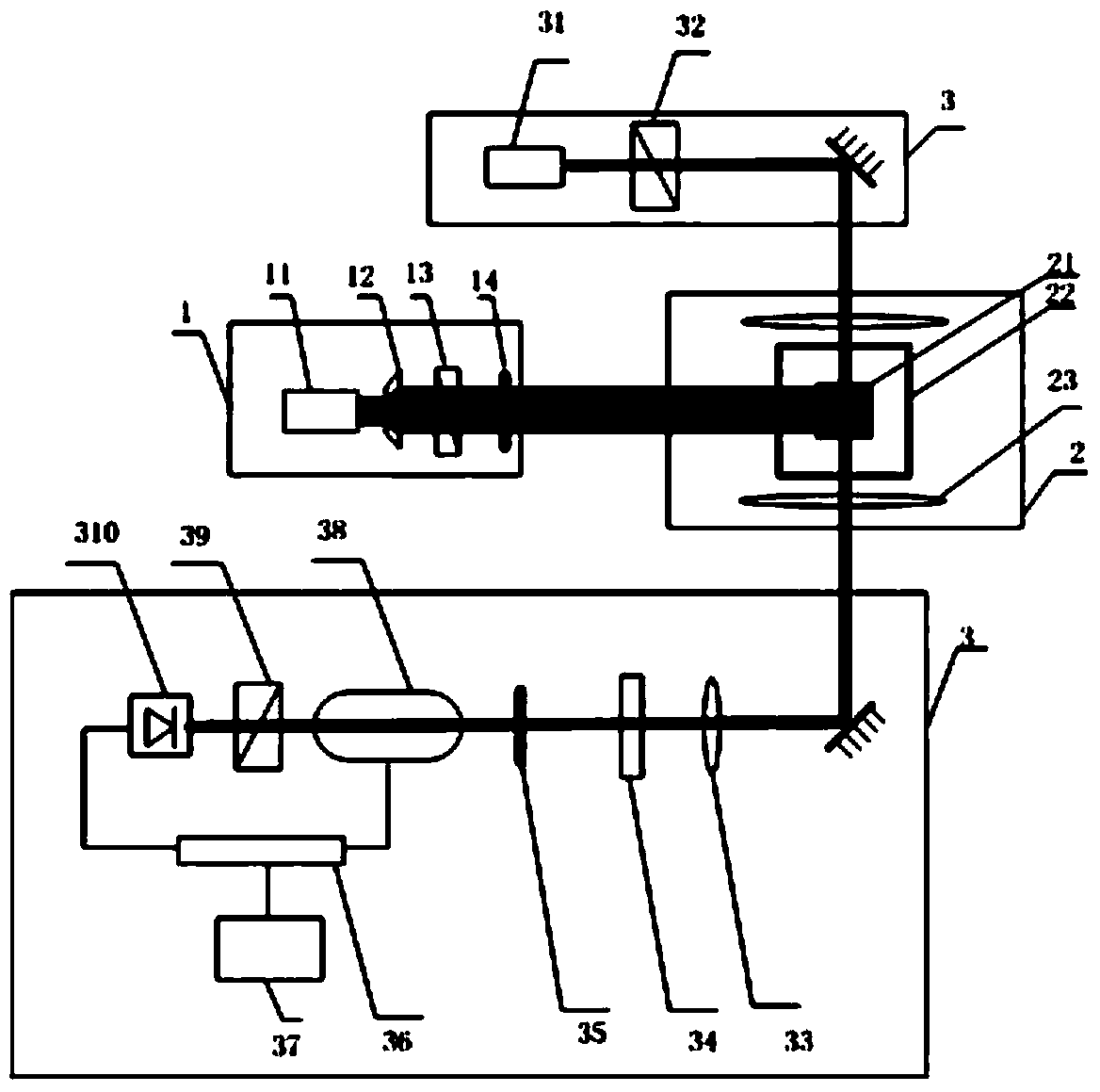
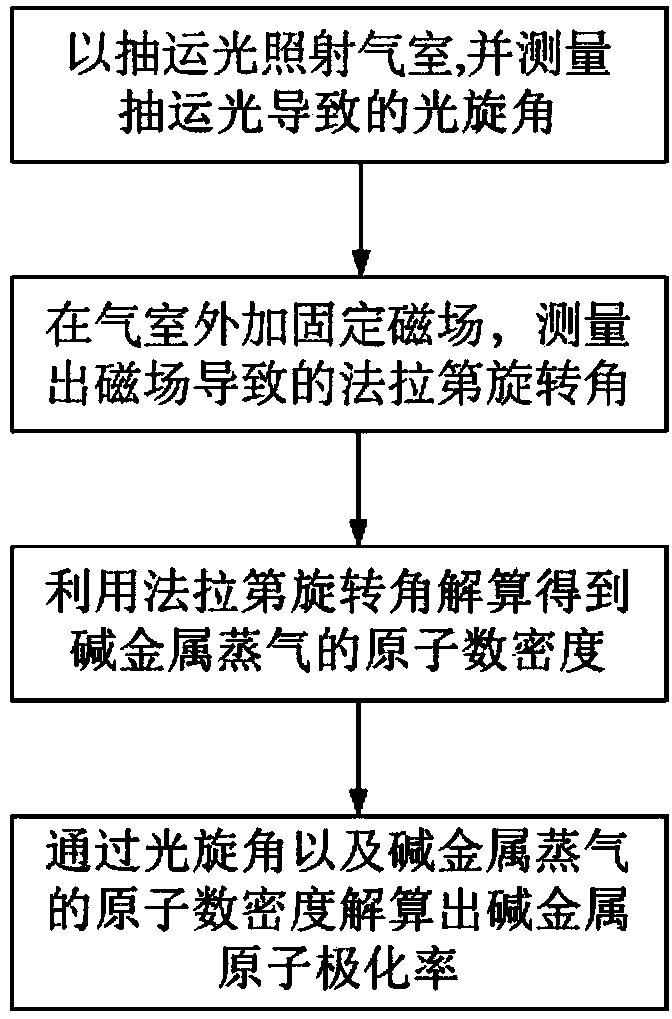
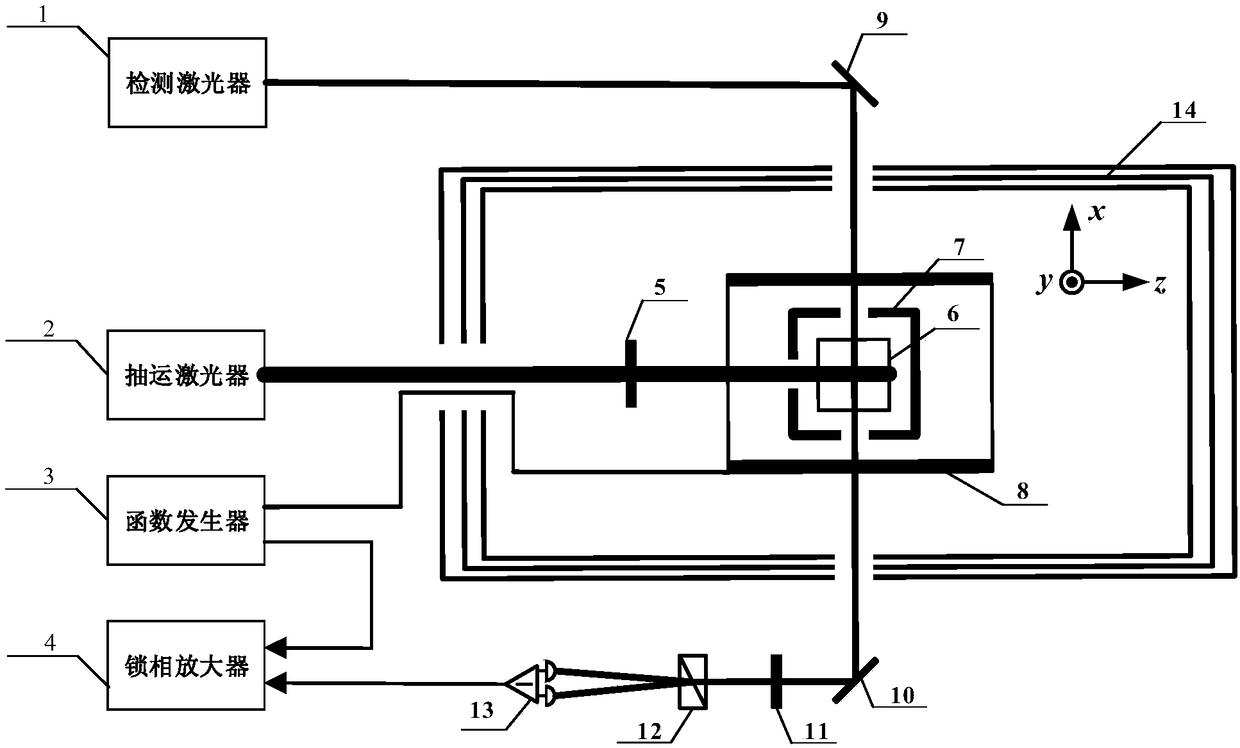
Integrated measurement device for atomic density and polarizability of alkali metal vapor
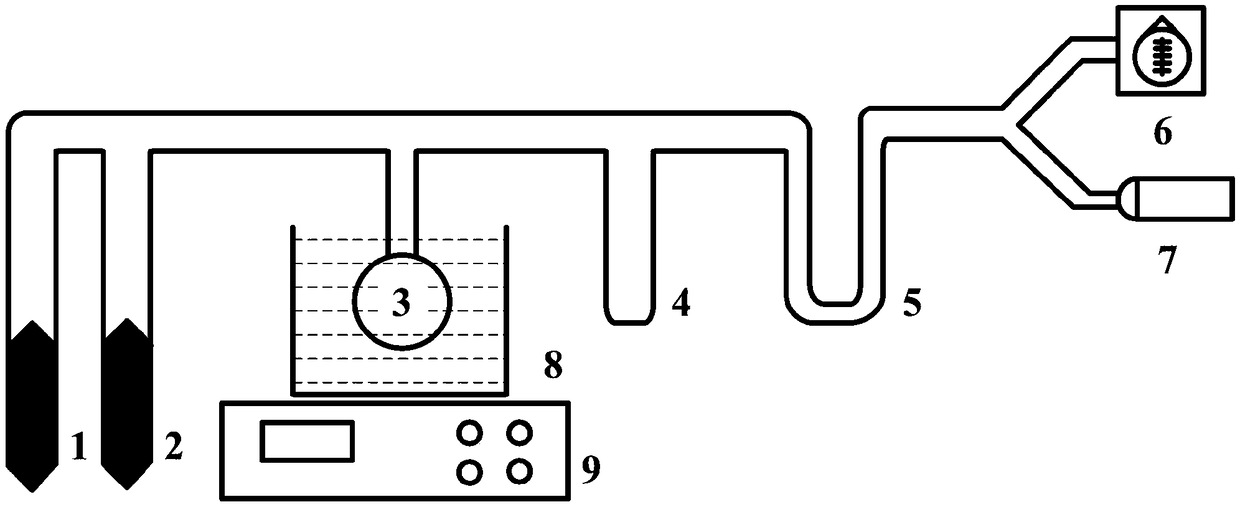
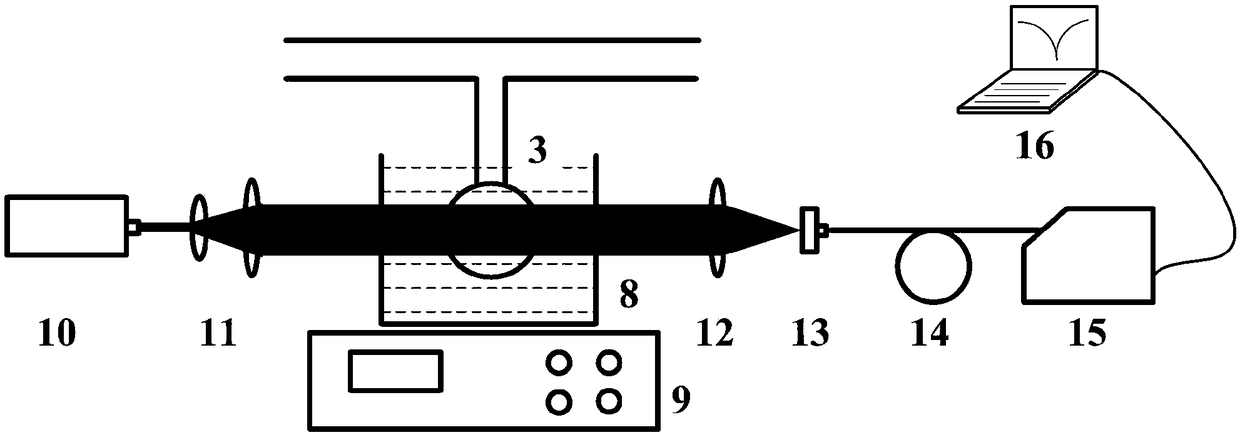
The invention discloses an integrated measurement device for atomic density and polarizability of alkali metal vapor. The device comprises a drive laser subsystem, a measuring and sensing unit subsystem and a detection unit subsystem, wherein the measuring and sensing unit subsystem has the function of providing a physical carrier and testing conditions for measurement of density and polarizability; the drive laser subsystem has the function of polarizing alkali metal atoms in an air chamber; and the detection unit subsystem has the functions of measuring a deflection angle of detection light under different testing conditions and calculating the deflection angle to obtain the atomic density and polarizability. According to the device, pumping light is generated to irradiate the air chamber by utilizing the drive laser subsystem, a fixed magnetic field is applied to generate a Faraday rotating angle in the measuring and sensing unit subsystem, the deflection angle of the detection light is measured by utilizing the detection unit subsystem, and finally the atomic density and polarizability are calculated through a data processor. The device has the characteristics of simple measurement system and high measurement accuracy and has important significance for improving the inertia of atoms and the magnetic field measurement sensitivity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
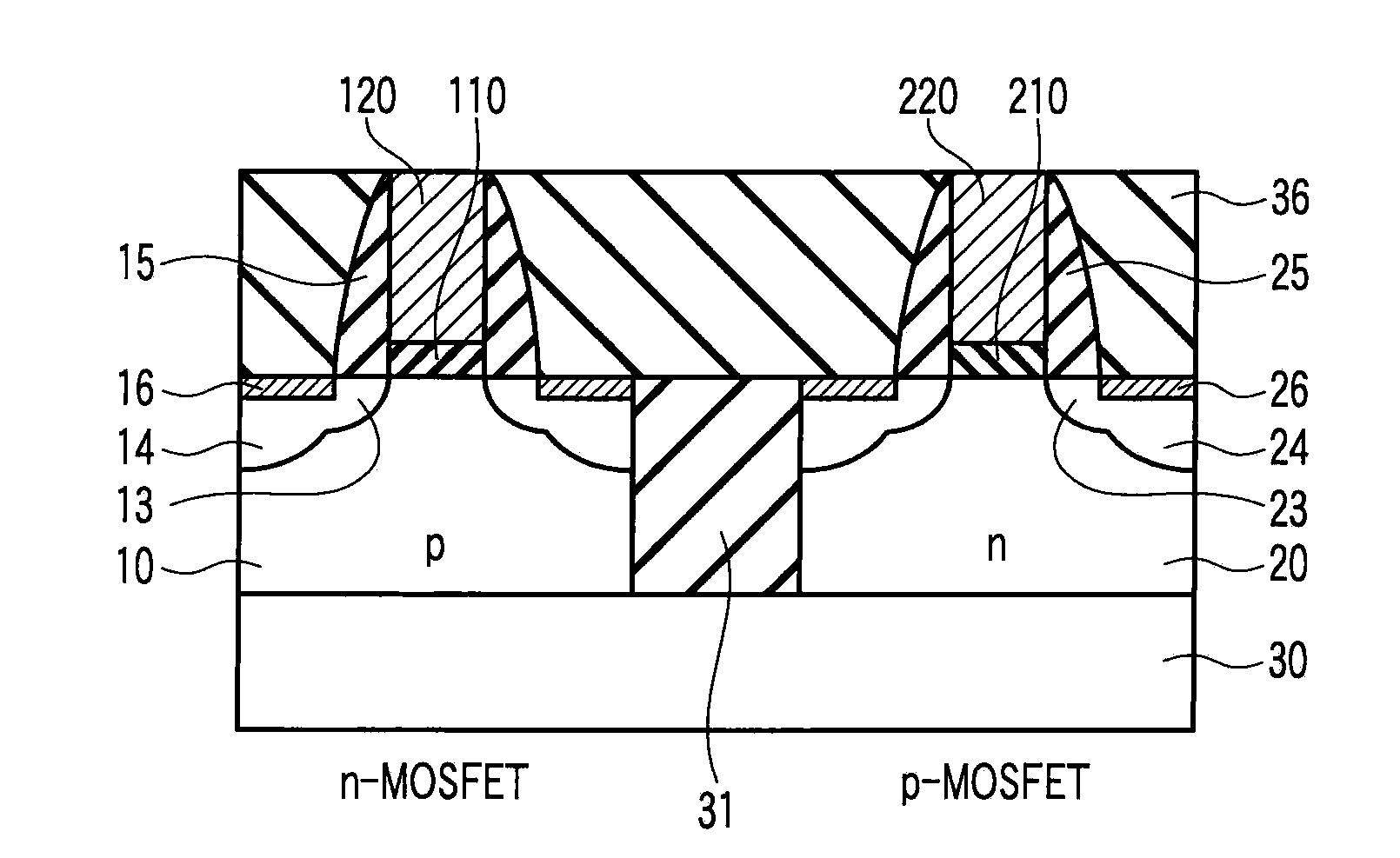
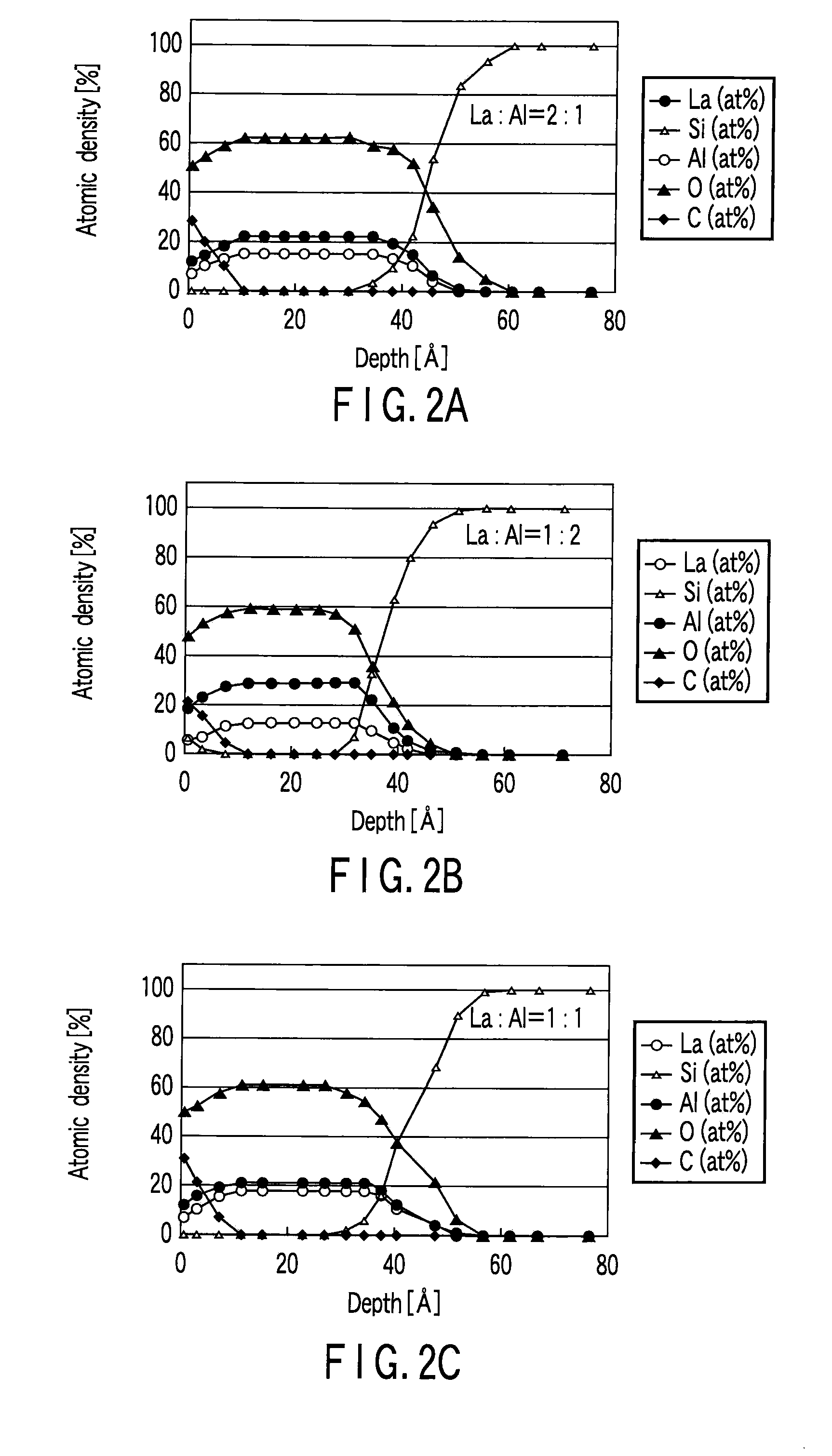
Complementary semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
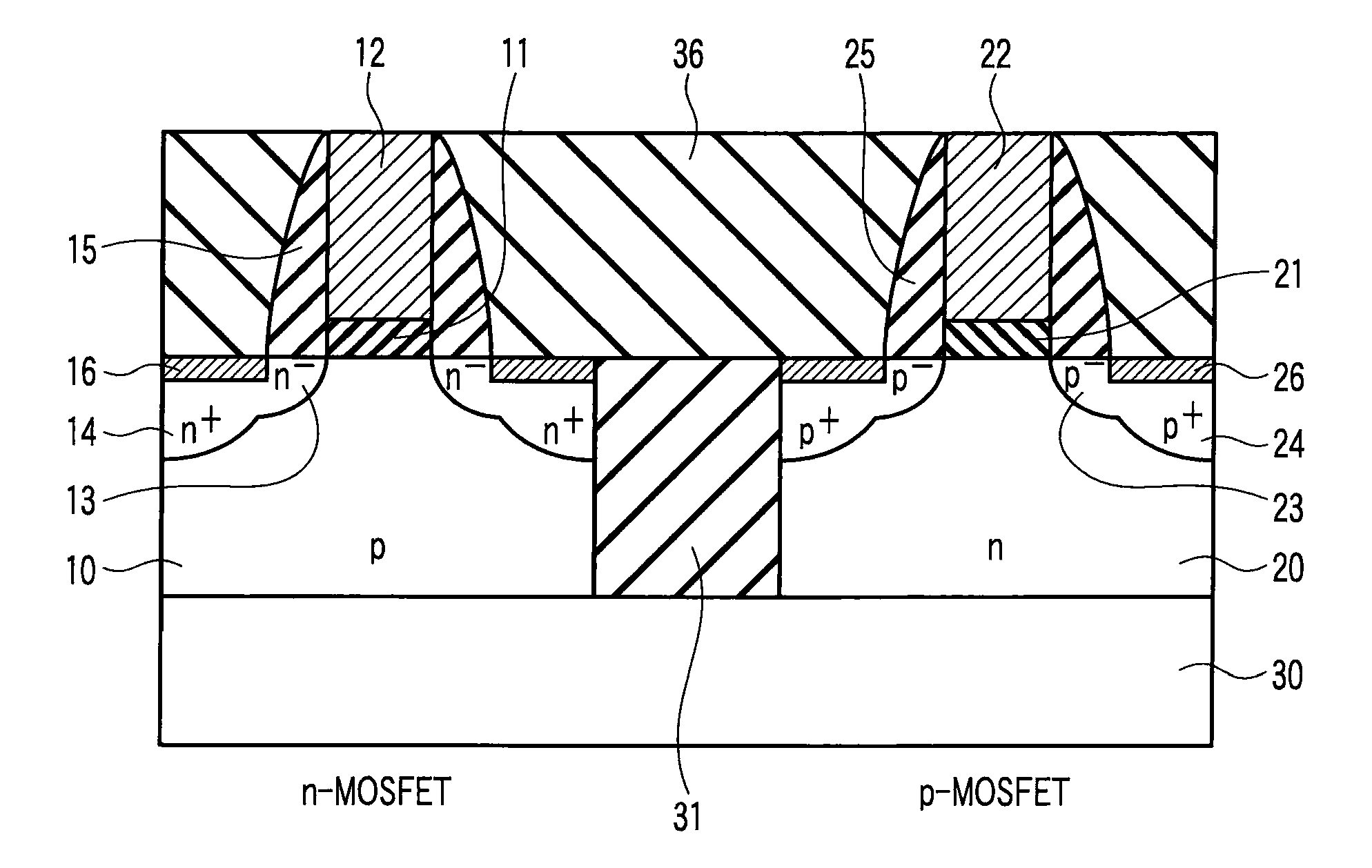
InactiveUS20090114995A1Increased tensile strainSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialAtomic density
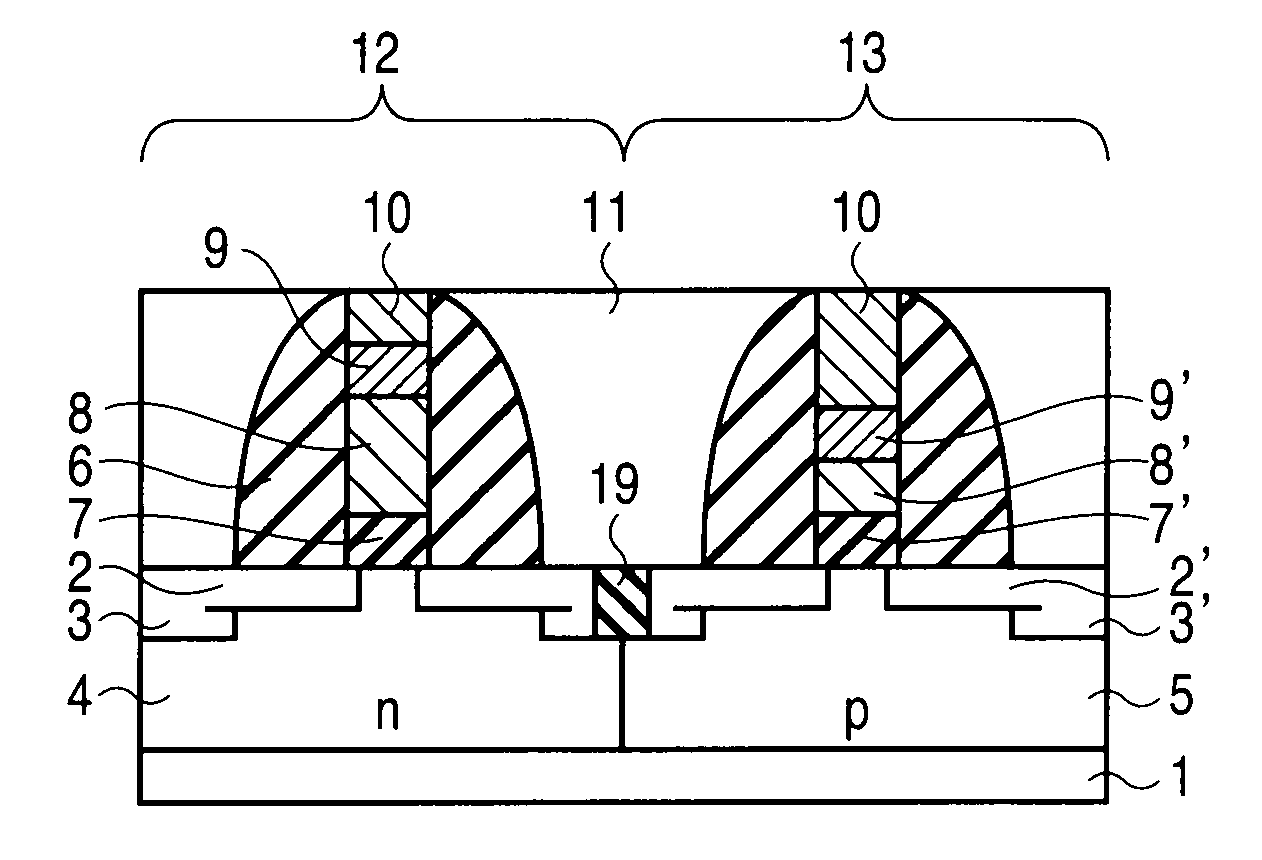
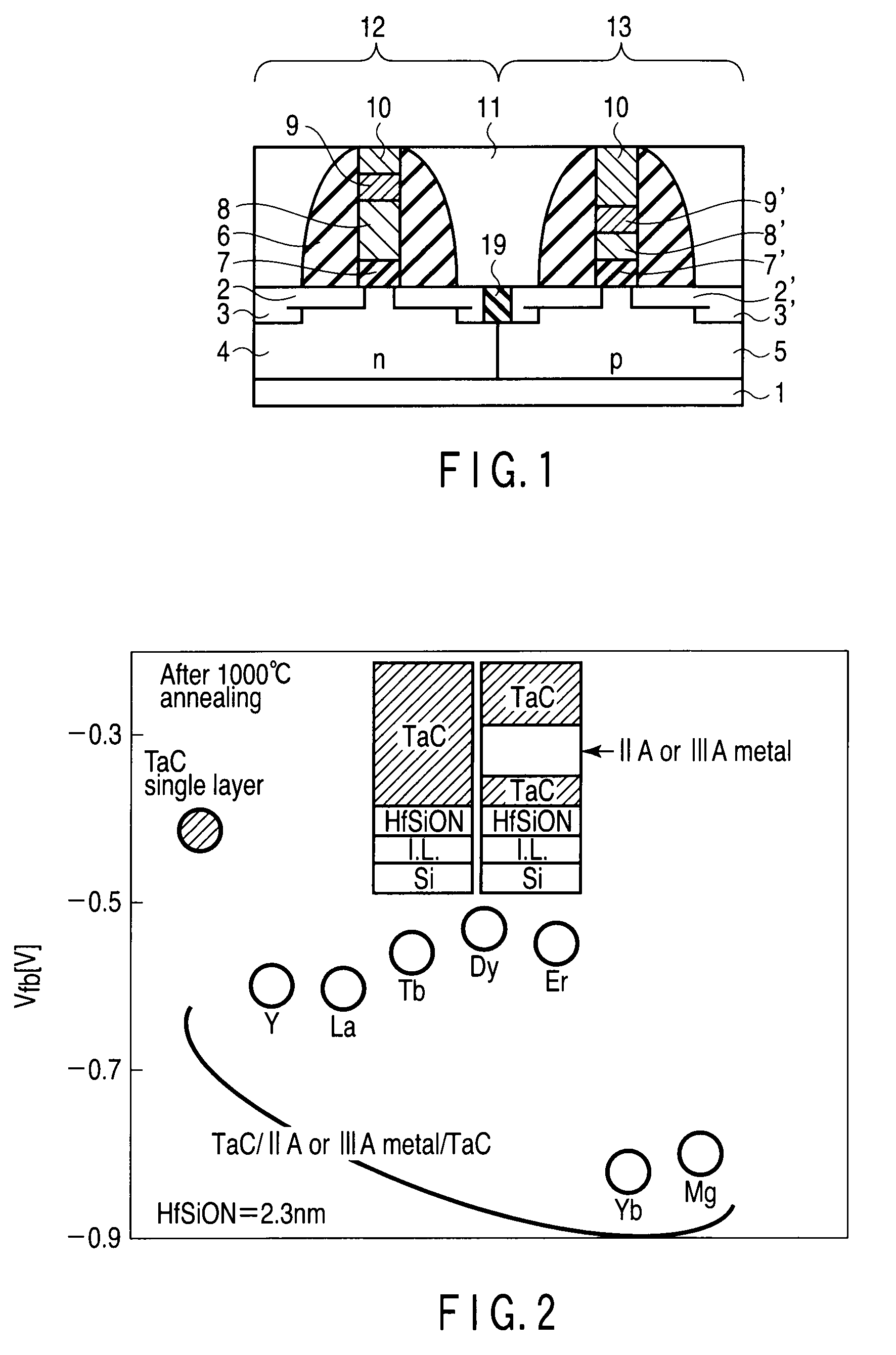
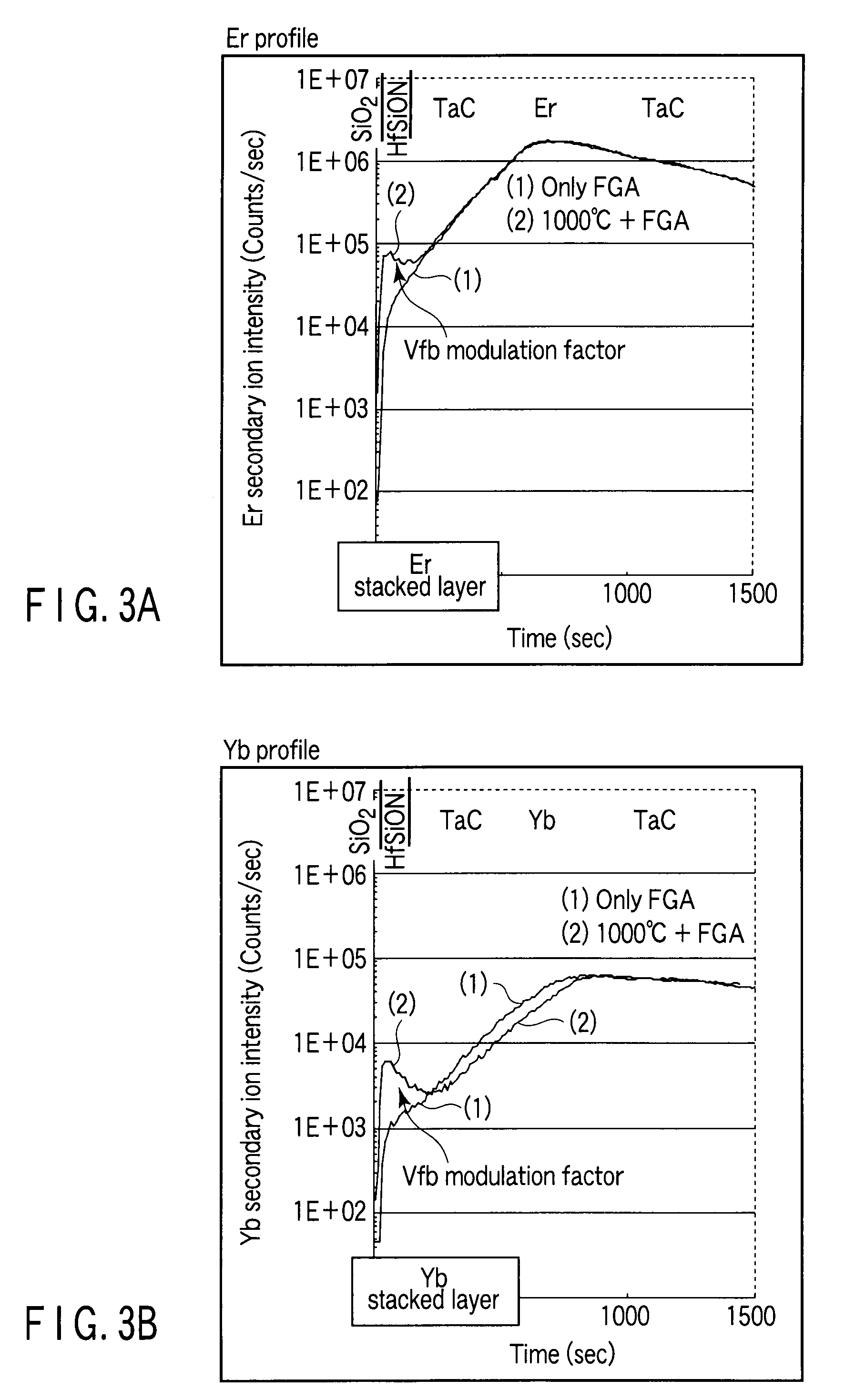
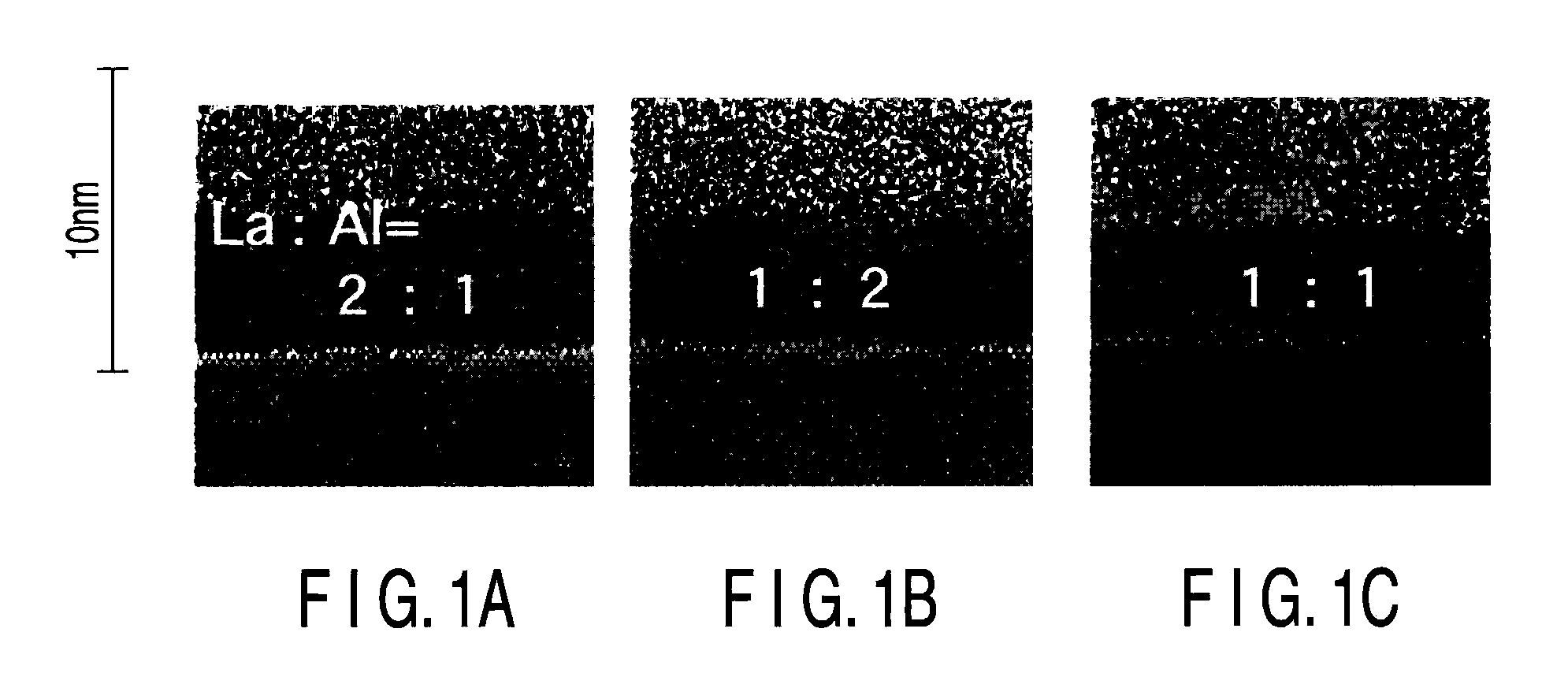
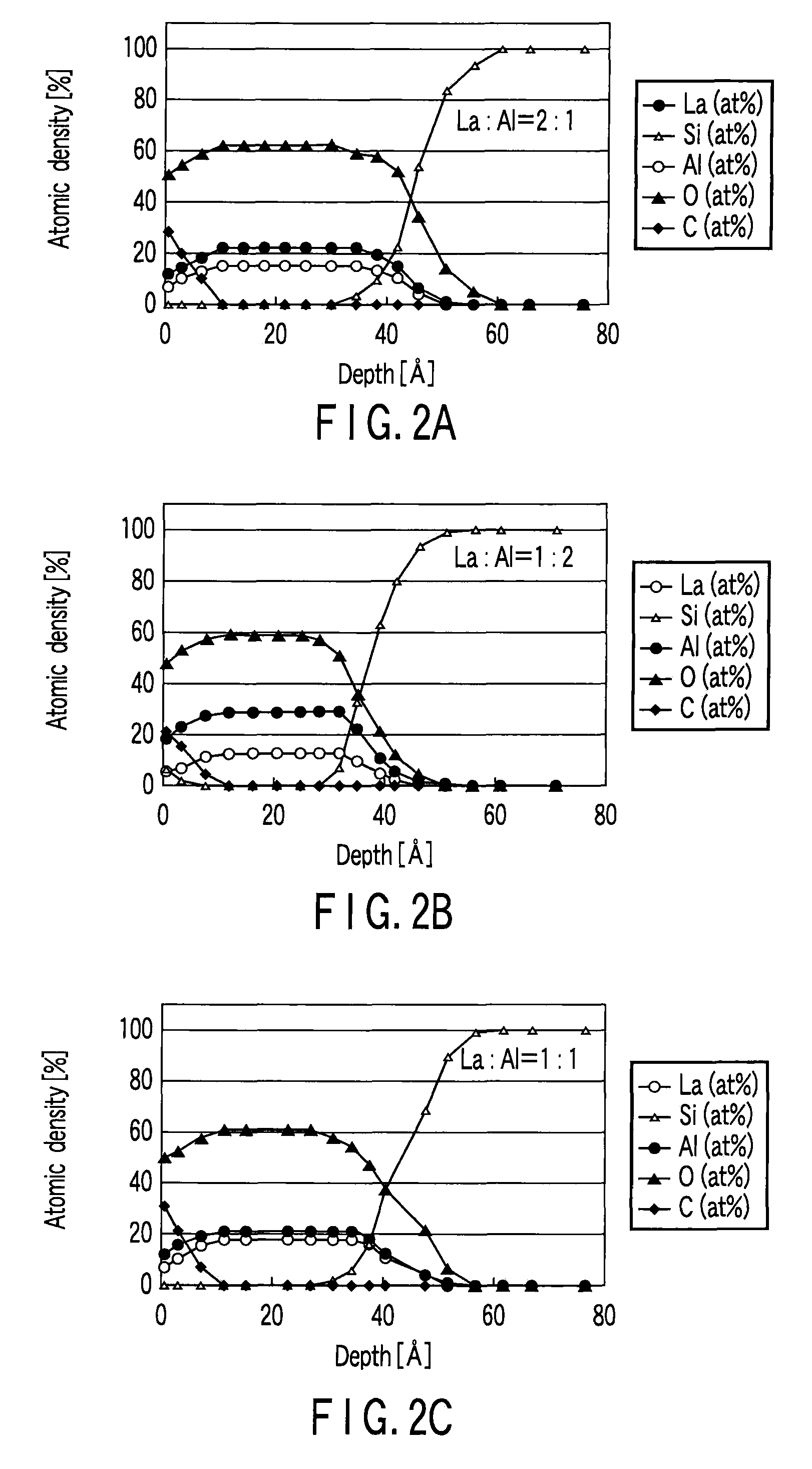
A complementary semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first semiconductor region formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate, a second semiconductor region formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate apart from the first semiconductor region, an n-MIS transistor having a first gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the first semiconductor region, and a first gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, and a p-MIS transistor having a second gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the second semiconductor region, and a second gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, an atomic density ratio Al / La in the second gate insulating film being larger than an atomic density ratio Al / La in the first gate insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
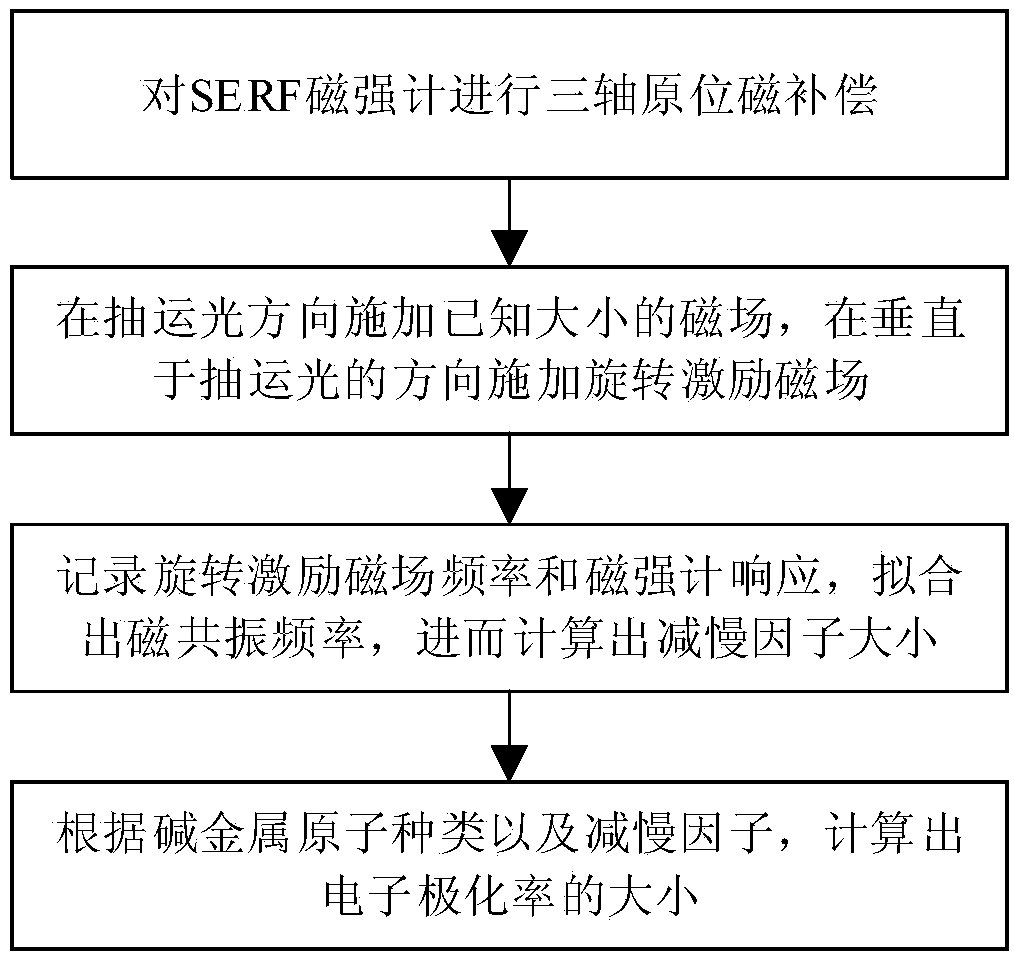
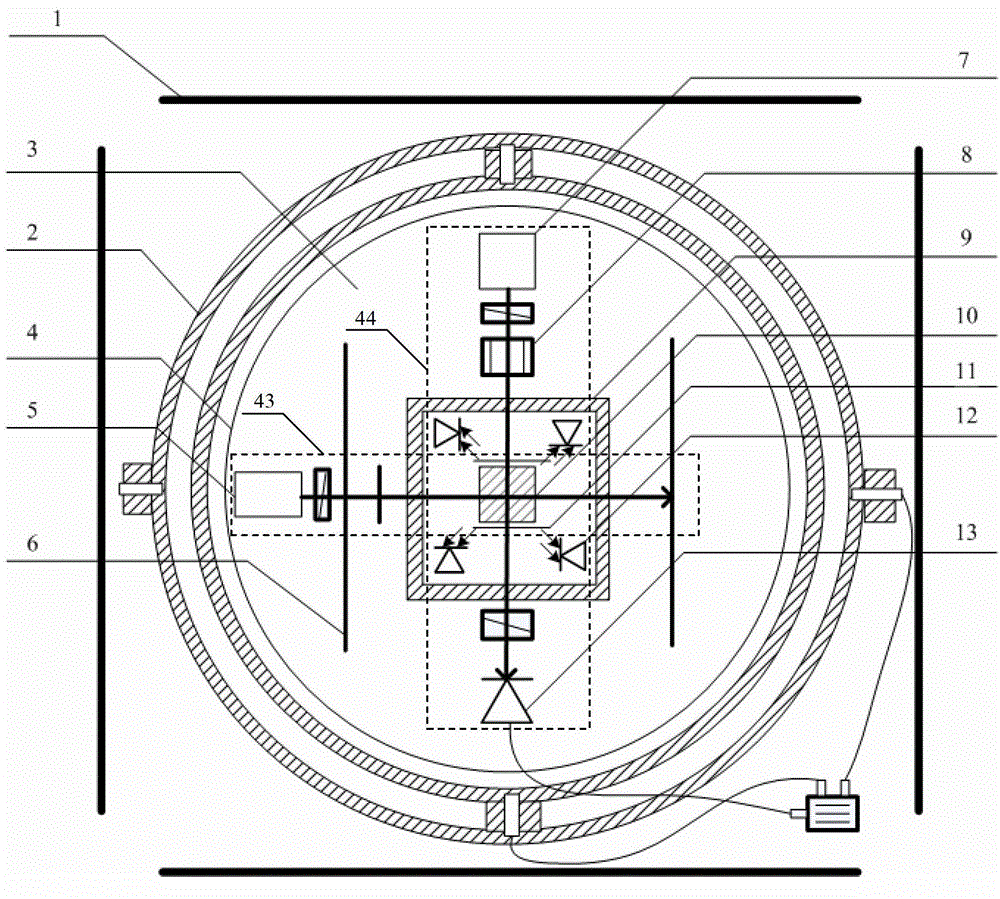
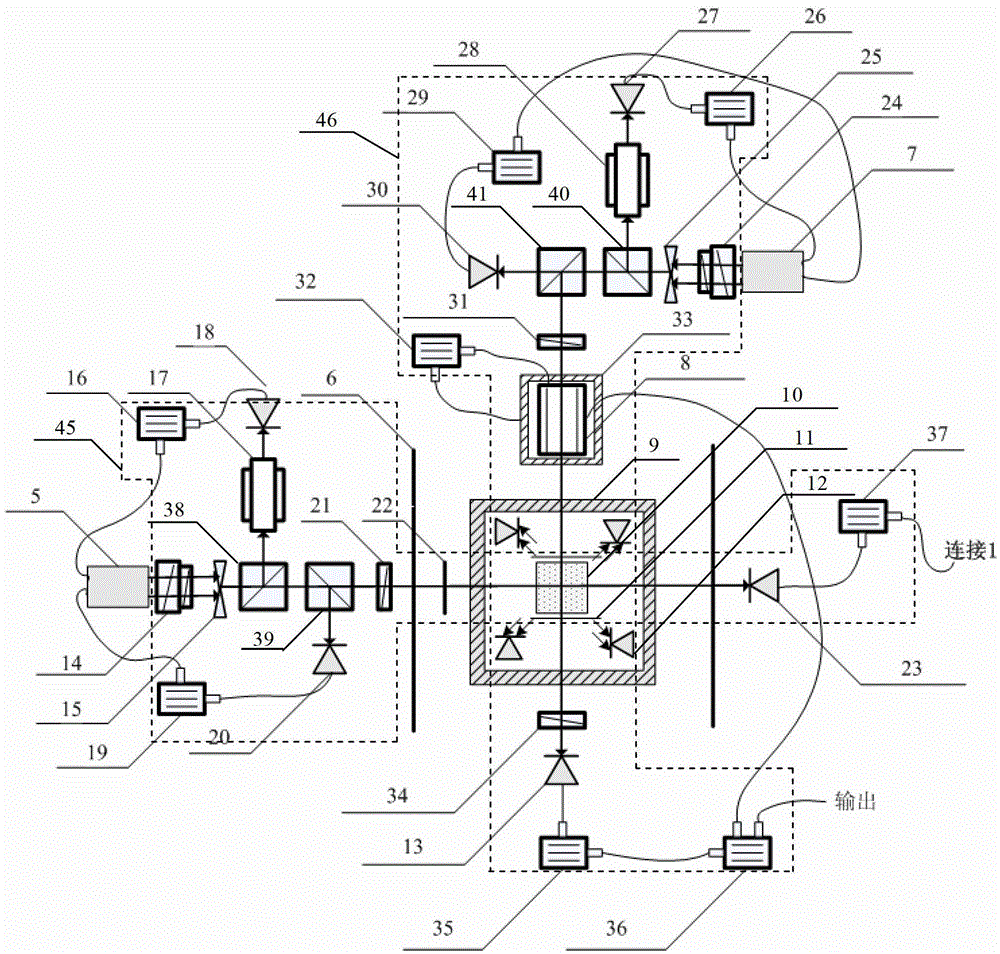
SERF atom magnetometer electron polarizability measurement method
InactiveCN108445428AHigh precisionMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurement devicePolarizability
The present invention relates to an SERF (Spin-Exchange Relaxation-Free) atom magnetometer electron polarizability measurement device and method. A traditional method measures a Faraday rotation anglegenerated by penetrating an atomic chamber by a linear polarization laser to calculate and obtain an electron polarizability, and the method is easy to be influenced by atomic density errors and rotation angle detection errors and is limited in measurement precision. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: measuring a resonant frequency of an SERF atom magnetometer in a magnetic field with a known size, and employing the resonant frequency, the size of the magnetic field and the gyromagnetic ratio of electrons to calculate electron slowing factors in an SERF state so asto calculate the electron polarizability according to a function relation of the slowing factors and the electron polarizability. The measurement precision is dependent on the precision of the appliedmagnetic field and the measurement precision of the resonant frequency, and is not limited to the atomic density and rotation angle detection errors, and therefore, the SERF atom magnetometer electron polarizability measurement device and method are higher in precision compared to the prior art.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Fullerene molecular gyroscope
ActiveCN102914298AIncrease the number ofLong spin relaxation timeTurn-sensitive devicesSpin effectMicrowave method
The invention relates to a fullerene molecular gyroscope which is characterized in that: atoms or molecules are embedded in the fullerene, so as to prevent spin collision exchange relaxation and spin collision damage. The micro-crystallizing standard solid molding is adopted, so that the fullerene molecules are arrayed according to a certain structure and the sensitive atomic density is increased. An optical and microwave method is adopted for controlling and detecting the atomic energy level, so that the detection for a dead axle and an inertia signal of the atoms or molecules in an inertia space is realized. The fullerene molecular gyroscope has the advantages of high sensitivity and excellent heat stability and has an important value for developing a new generation solid gyroscope based on an atomic spin effect and with high precision, high stability and small volume.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Real-time online atomic density measuring method suitable for atom magnetometer
The invention discloses a real-time online atomic density measuring method suitable for an atom magnetometer. The method comprises the specific steps that an alkali metal air chamber of the atom magnetometer is firstly heated; then the pumping light power is reduced, and a direct-current magnetic field is applied a coil, in the direction z, of the atom magnetometer; then sine wave field sweeping and data collecting of the atom magnetometer in the direction y are completed through a ZI lock-in amplifier; then the output signal of the ZI lock-in amplifier and the magnetic resonance line width of the atom magnetometer are subjected to fitting through a Lorenz curve; finally, the alkali metal atom density of the atom magnetometer is calculated. According to the method, the blank that in the prior art, no fast and effective real-time online atom density measuring method is filled in, and theoretical guidance and reference are provided for improving of the sensitivity of the atom magnetometer.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
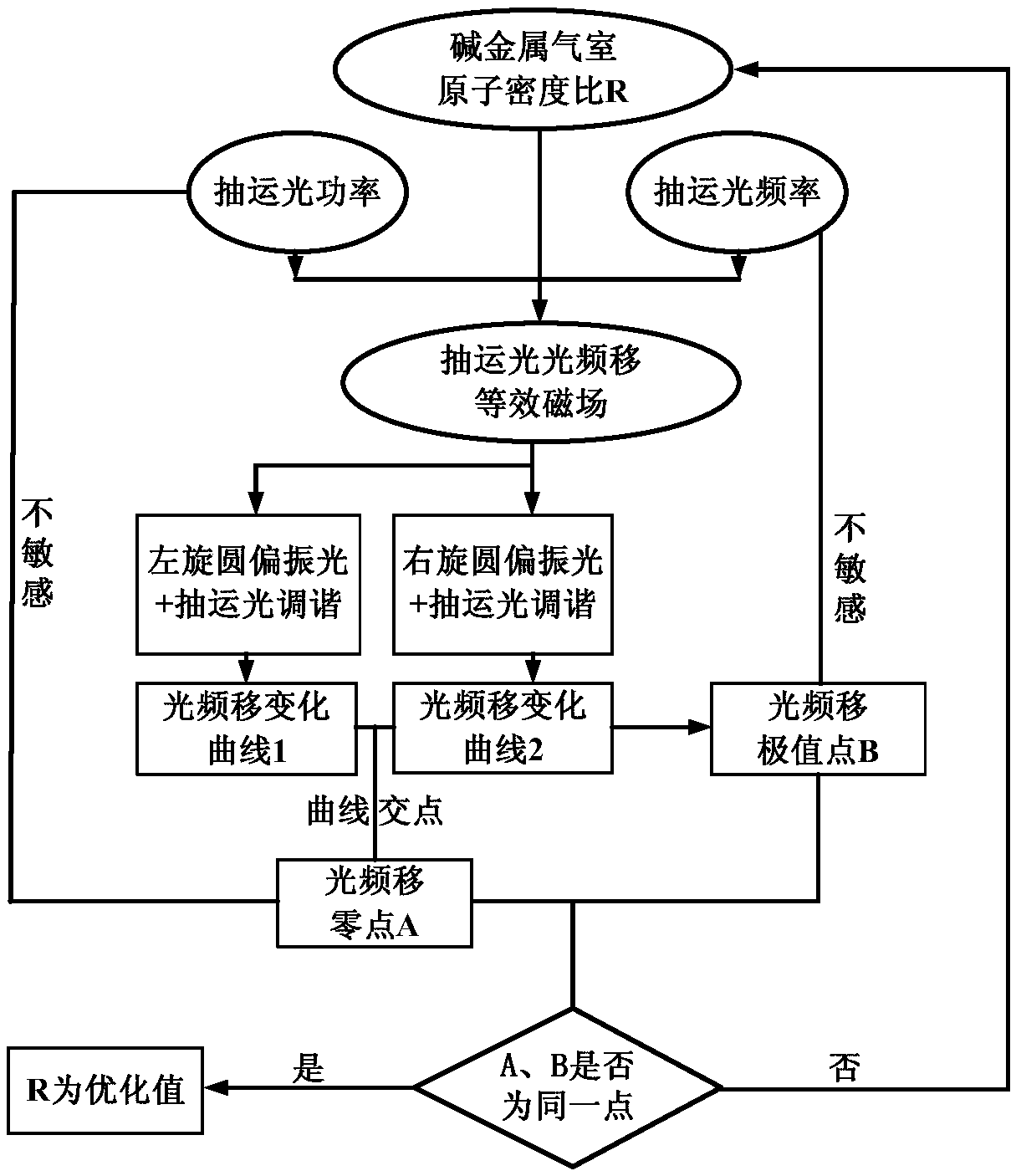
Optical frequency shift inhabitation method of SERF atom magnetometer
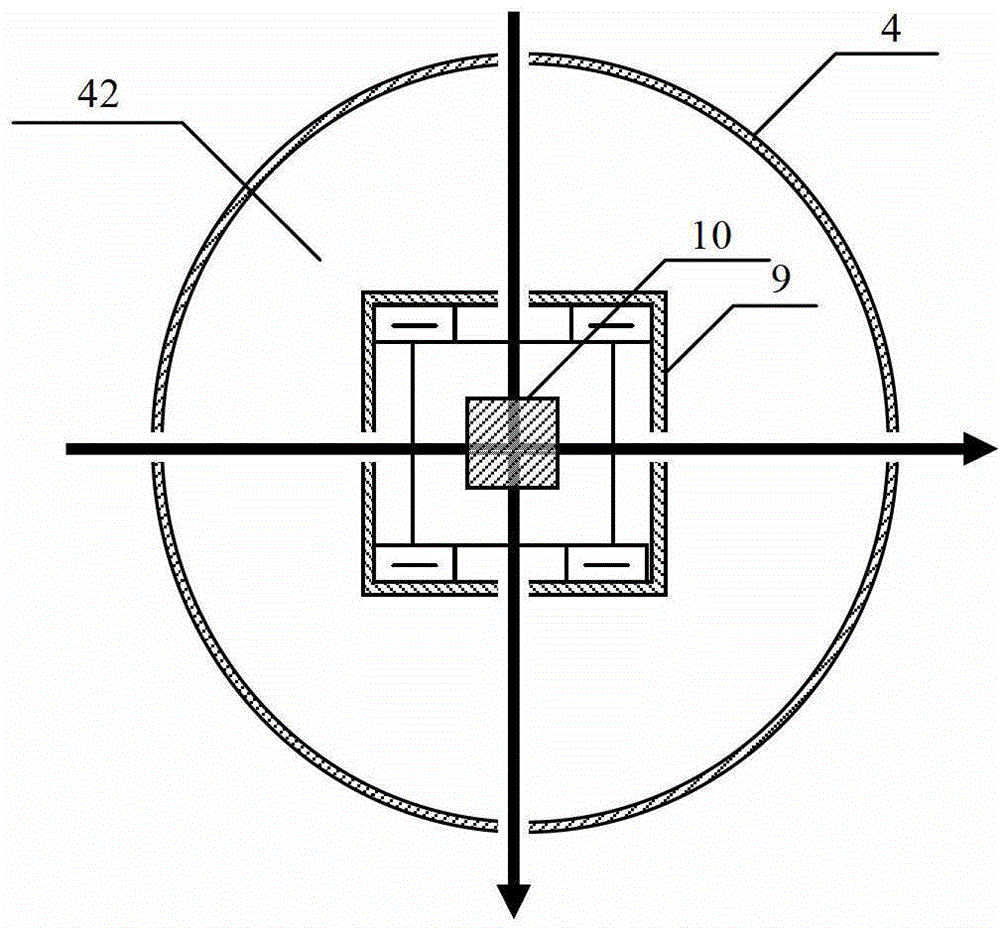
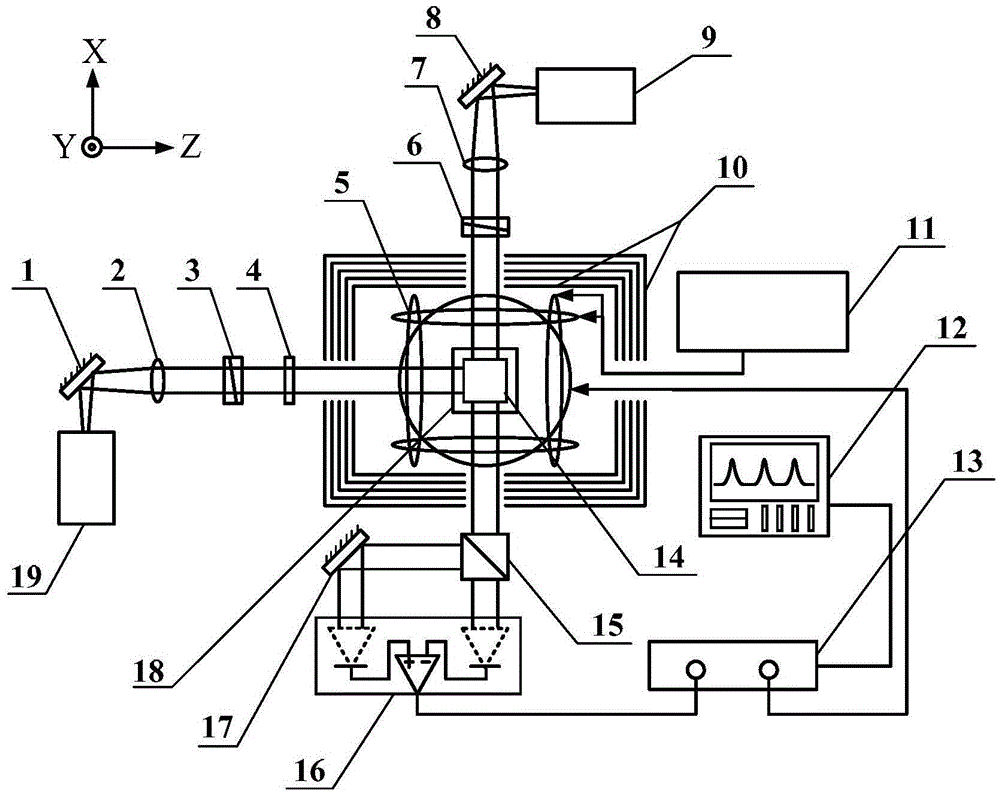
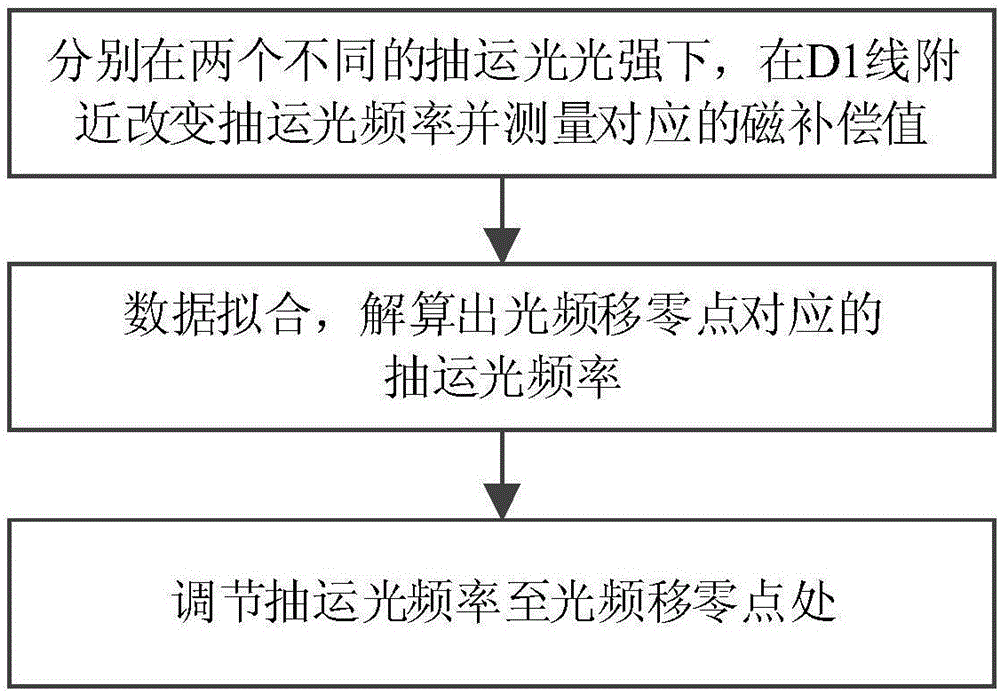
ActiveCN106226713AIncrease atomic densityHigh precisionMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFrequency shiftAtomic density
The invention relates to an optical frequency shift inhabitation method of an SERF atom magnetometer. In the normal optical frequency shift inhabitation method of an SERF atom magnetometer, the frequency of the pumping light is adjusted to be in the center of a spectral line of an atomic absorption spectrum. However, an alkali metal air chamber of the SERF atom magnetometer is characterized by high atomic density and big buffering gas pressure, so the center of the spectral line is hard to obtain. Therefore, the definition of the normal optical frequency shift inhabitation method is not high. According to the optical frequency shift inhabitation method provided by the invention, under two different pumping light strengths, by combining the three dimensional in-situ magnetic compensation technology, the size of the magnetic field sensed by atoms corresponding to the different pumping light frequencies is measured, and theoretic fitting and resolving on the measured data, so optical frequency shift null points can be precisely found, thereby achieving sufficient inhabitation of the optical frequency shift. The optical frequency shift inhabitation method provided by the invention is independent of measurement of the atomic absorption spectrum, and the optical frequency shift inhabitation level depends on the precision of the magnetic compensation, so compared with the normal method, the optical frequency shift inhabitation method provided by the invention is quite high in inhabitation precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Pressure-broadening-based alkali metal stream atomic density measuring method
ActiveCN103439218AOvercoming the problem of large density measurement errorAvoiding the Problem of Density Measurement ErrorsSpecific gravity measurementPositive pressurePhysical chemistry
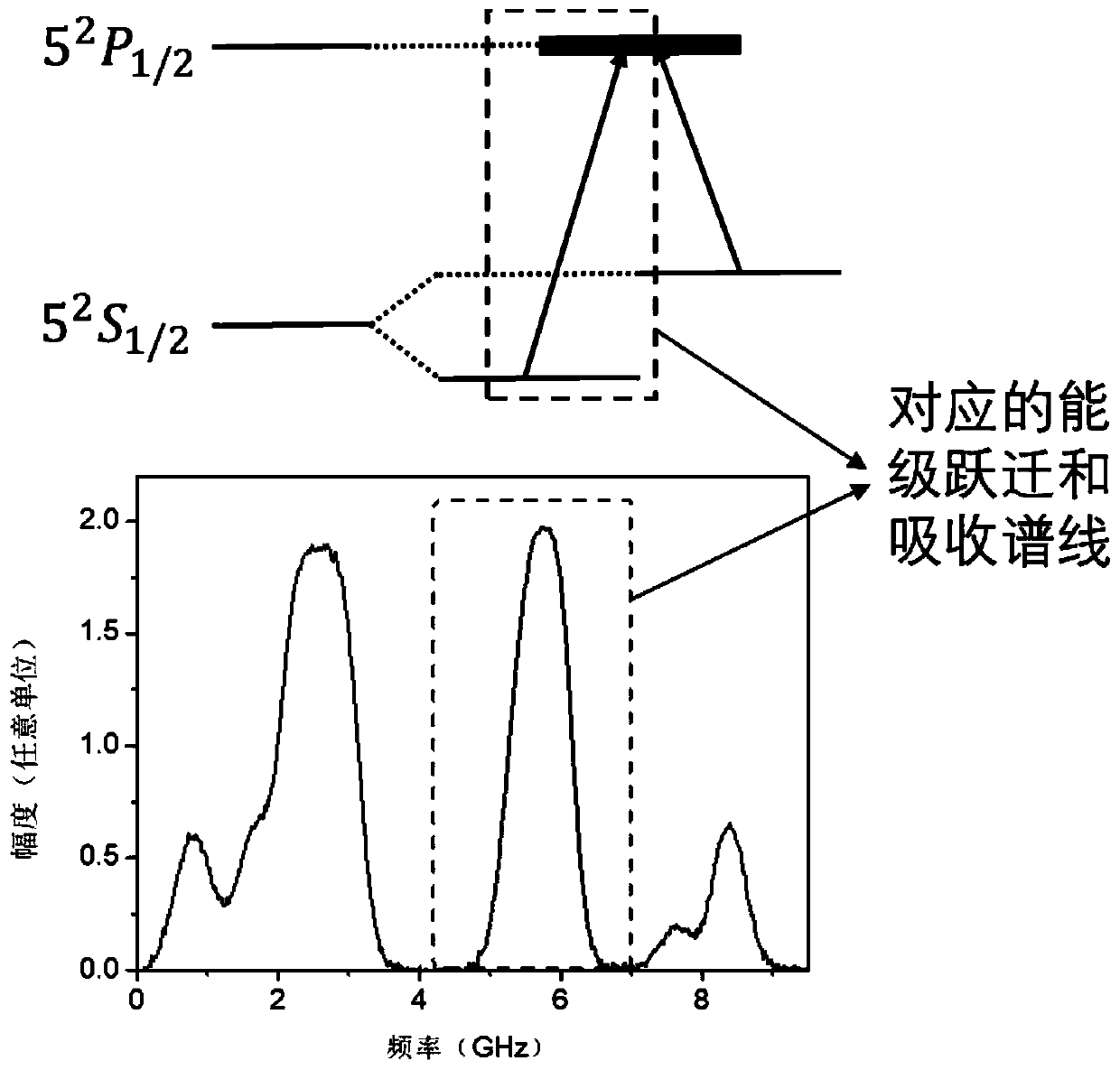
The invention discloses a pressure-broadening-based alkali metal stream atomic density measuring method, relating to an alkali metal atomicity density measuring method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, producing an alkali metal air chamber filled with positive pressure gas and uniformly heating; secondly, radiating the air chamber by utilizing stable-powder laser and carrying out frequency sweeping so as to measure an absorption curve of the alkali metal, and carrying out negative logarithm taking processing to obtain an optical depth curve; finally, carrying out lorentz nonlinear fitting on the obtained data, acquiring the overall width of a half peak value of a lorentz curve, thus obtaining pressure broadening parameters and further obtaining the air pressure of the filled gas; obtaining the atomicity density of alkali metal steam according to a peak value of the lorentz curve, thereby realizing the measurement of the atomic density and gas pressure intensity of the alkali metal air chamber.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Variable cross-section channel structure of low-power cusped magnetic field plasma thruster
InactiveCN105736272ALower heat transfer coefficientGuaranteed effective constraintsMachines/enginesUsing plasmaIonizationAtomic density
The invention relates to a variable cross-section channel structure of a low-power cusp magnetic field plasma thruster, which relates to the field of cusp magnetic field plasma thrusters. The present invention aims to solve the problem that under the low power working condition of the existing tangential magnetic field plasma thruster, the insufficient ionization leads to performance degradation when the current density is low, and the performance degradation is also caused by the intensified interaction between the plasma and the wall surface when the current density is high. The problem. The channel is constructed by a ceramic channel and a permanent magnet. The ceramic channel is a one-piece structure, which is divided into two sections: the upstream part of the channel and the downstream part of the channel. The channel structure gradually expands from the upstream part of the channel to the downstream part of the channel. The outer wall of the ceramic channel is used for To achieve clearance fit with the inner wall of the permanent magnet. This structure increases the atomic density and ionization rate in the upstream ionization area, and at the same time reduces the interaction with the channel wall during the accelerated ejection of ions generated by ionization, prolonging the life of the thruster. It is used in the low power working condition of the tangent magnetic field plasma thruster.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material, cutter and preparation method of material
InactiveCN104759240AHigh hardnessImprove thermal stabilityUltra-high pressure processesSuperhard materialAlloy
The invention discloses a diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material, a cutter and a preparation method of the material. The material is characterized in that diamond and cubic boron nitride are used as raw materials, the pre-treatment and the forming are performed on the raw materials to obtain a blank; the blank assembled with a sintering unit is arranged in a high temperature and high pressure device, wherein the intensity of pressure is 7-25GPa, the temperature is 1000-2700 DEG C, the sintering solution strengthening lasts for 10s-30min, the sizes of obtained crystal grains are uniform, and interfaces of the crystal grains are tight and closed; the compact-structure diamond-cubic boron nitride type universal superhard cutter material which is high in atomic density, is in a three-dimensional network shape and has strong covalent bonds can be formed by boron atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms at the crystal interfaces between the diamond and the cubic boron nitride. The universal superhard material is processed into a cylinder with the same height; two ends of the cylinder are polished and finished and then are processed to be in triangular cylinder shapes with the side lengths and the thicknesses of 2-3mm, the processed cylinder and a steel alloy base body are welded under the vacuum degree being 1*10<-3>Pa at the temperature being 800 DEG C, and then the laser processing is performed, so that the superhard alloy cutter in which the radius of the circular arc of the knife point is 0.4-0.8mm is obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
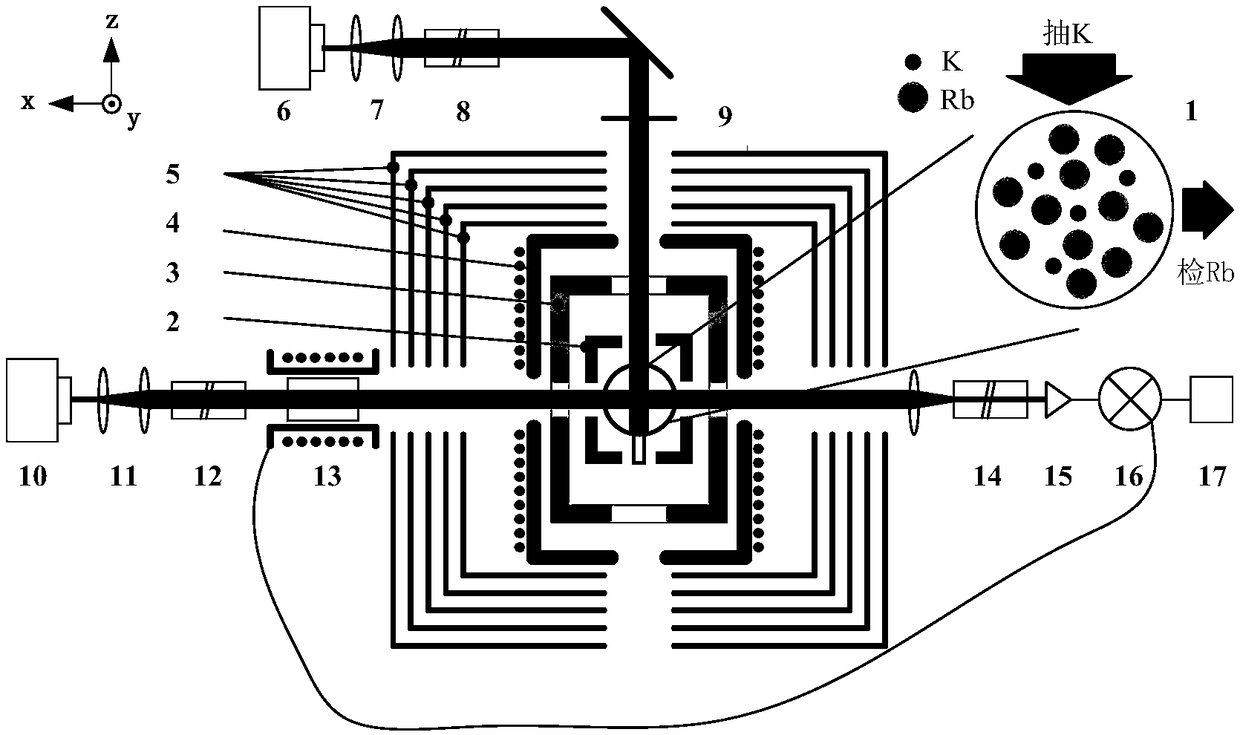
Hybrid optical pumping SERF atom magnetometer device and density ratio optimization method thereof
ActiveCN108490374AImprove uniformityImprove efficiencyMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesViewpointsDensity ratio
The invention discloses a hybrid optical pumping spin exchange relaxation-free (SERF) atom magnetometer device and a density ratio optimization method thereof. The density ratio optimization method optimizes the alkali metal atomic density ratio of the magnetometer from the viewpoint of optical frequency shift suppression and improvement of signal stability of the magnetometer, and finally realizes the optimum alkali metal atomic density ratio which is insensitive to the pumping optical power and the pumping optical frequency fluctuation. Compared with a traditional single alkali metal SERF atom magnetometer, the hybrid optical pumping SERF atom magnetometer has the advantage of uniform atomic polarizability. Compared with a traditional mixed optical pumping SERF atom magnetometer, the hybrid optical pumping SERF atom magnetometer comprehensively considers the interaction and influence of alkali metal atomic density ratio, optical frequency shift, pumping optical power and pumping light frequency, and is a multi-physical-quantity coupling optimization method. The density ratio optimization method of the hybrid optical pumping SERF atom magnetometer can effectively improve signal stability of the SERF atom magnetometer.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
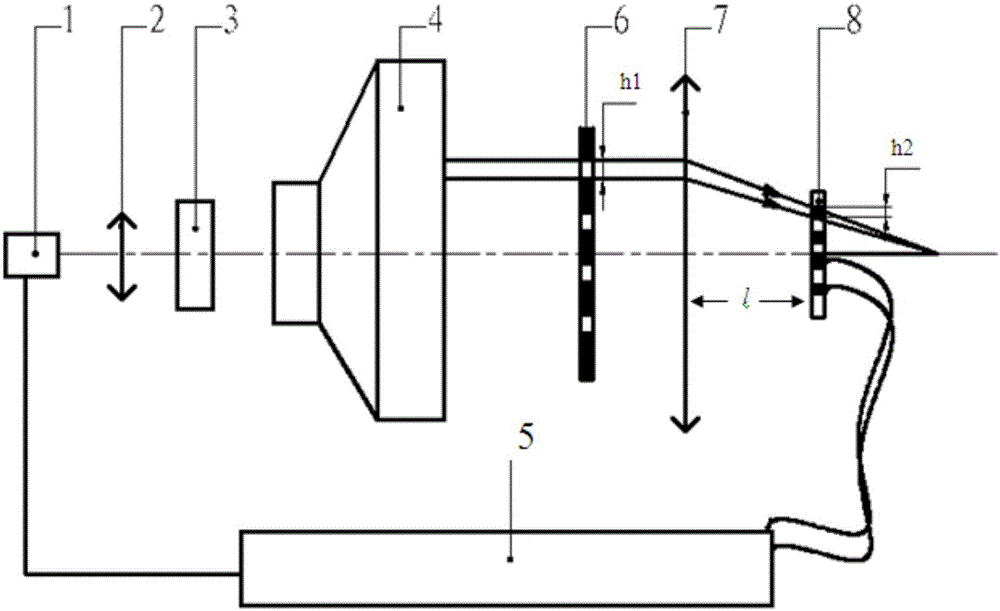
Detection device and method for metal steam atomic density of microstructure alkali metal gas chambers
ActiveCN105043930AGuaranteed similarityEnsure consistencySpecific gravity measurementSignal processing circuitsLight beam
The invention relates to a detection device and method for the metal steam atomic density of microstructure alkali metal gas chambers, and relates to the technical field of detection of microstructure alkali metal gas chambers. The detection device and method for the metal steam atomic density of the microstructure alkali metal gas chambers solve the problems that an existing alkali metal gas chamber detection device can only detect the gas chambers one by one, consequently, much time is consumed for light path modulation, the detection cost is high, and the consistency of detection of all gas chamber units cannot be ensured. The microstructure alkali metal gas chambers and a photoelectric tube array have similarities, light beams transmitted out of the gas chambers are focused by convex lenses and then are transmitted to corresponding photoelectric tubes respectively, a collecting signal processing circuit is used for comparing and analyzing detection signals and detection signals of a standard gas chamber, and finally detection of the metal steam atomic density of all the gas chamber units is achieved. The detection device and method for the metal steam atomic density of the microstructure alkali metal gas chambers are suitable for detection of chip atomic clocks, microstructure atomic magnetometers, minitype atomic spinning tops and other microstructure devices, and especially suitable for detection of imaging systems with the wafer-level microstructure alkali metal gas chambers as magnetic array imaging sensing units.
Owner:NO 49 INST CHINESE ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
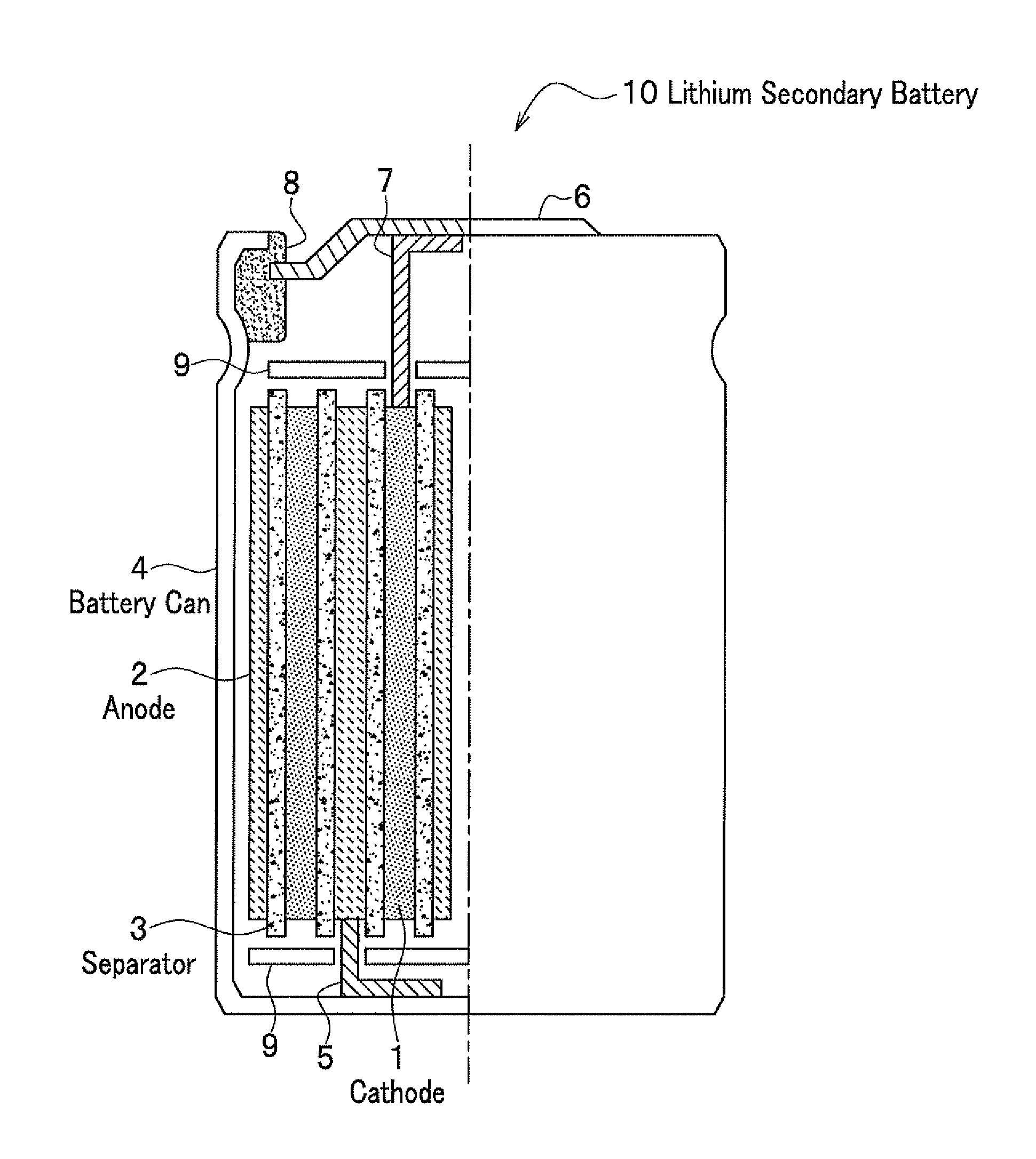
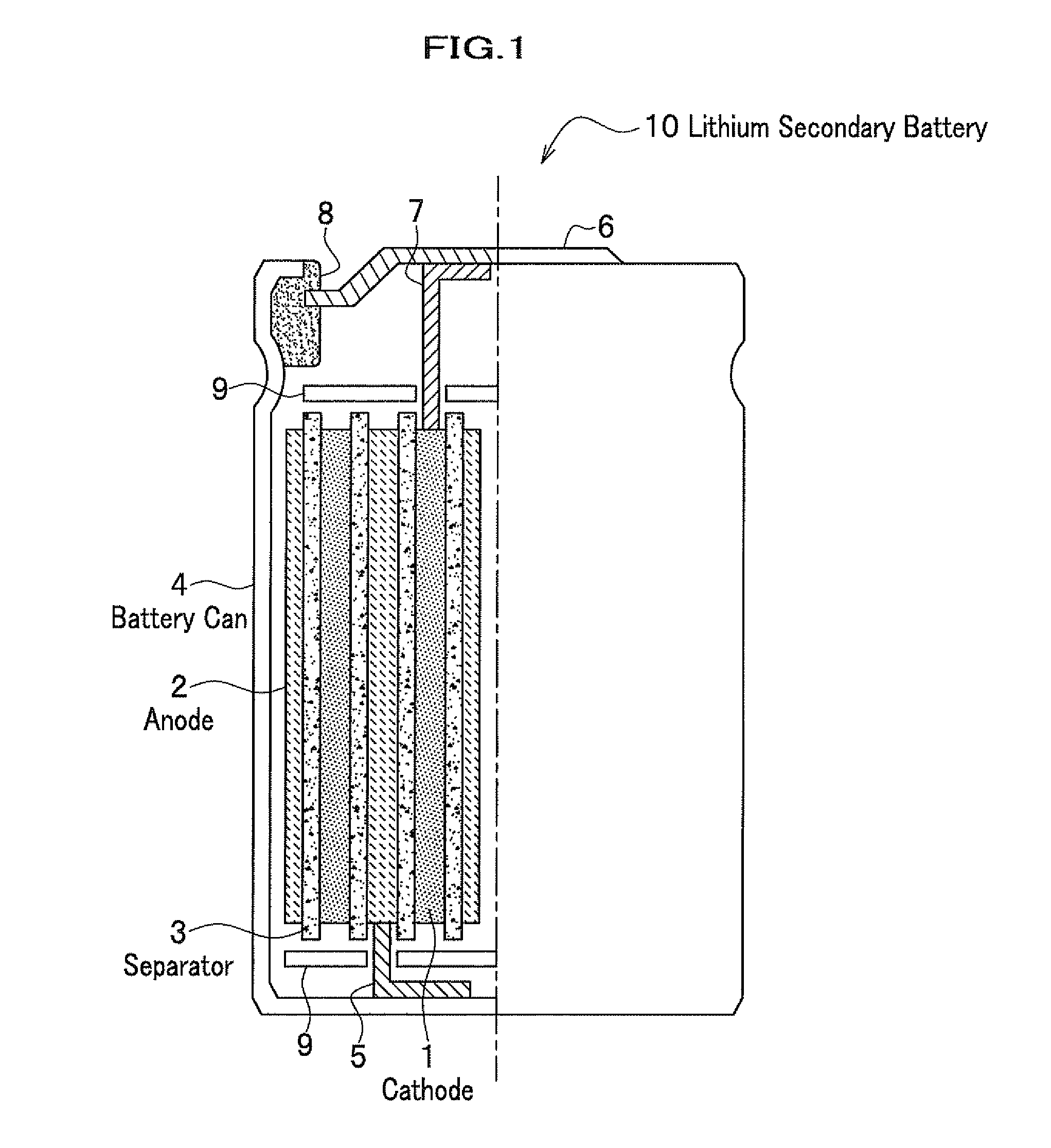
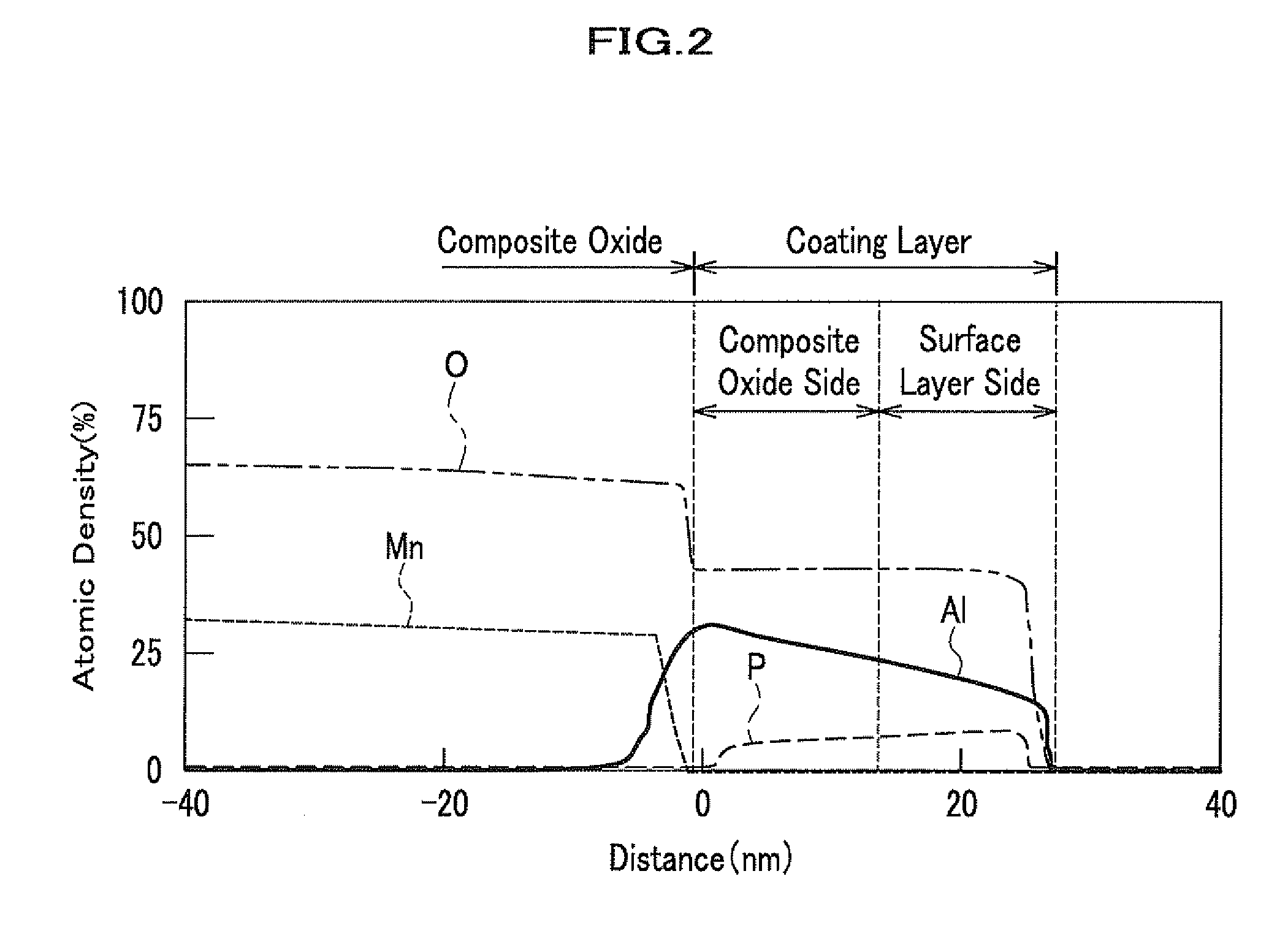
Cathode material for lithium secondary battery, lithium secondary battery, and secondary battery module using the battery
InactiveUS8951448B2Stably suppressing manganese dissolutionExcellent in high-temperature charge/discharge cycle profileMachining electrodesConductive materialElectrical batteryManganese
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090321844A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricAtomic density
A semiconductor device includes pMISFET and nMIS formed on the semiconductor substrate. The pMISFET includes, on the semiconductor substrate, first source / drain regions, a first gate dielectric formed therebetween, first lower and upper metal layers stacked on the first gate dielectric, a first upper metal layer containing at least one metallic element belonging to groups IIA and IIIA. The nMISFET includes, on the semiconductor substrate, second source / drain regions, second gate dielectric formed therebetween, a second lower and upper metal layers stacked on the second gate dielectric and the second upper metal layer substantially having the same composition as the first upper metal layer. The first lower metal layer is thicker than the second lower metal layer, and the atomic density of the metallic element contained in the first gate dielectric is lower than the atomic density of the metallic element contained in the second gate dielectric.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Process for production of molecular devices
InactiveUS20050215731A1Increase atomic densityHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryNanowireVolumetric Mass Density
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of effectively producing a nano-particle and a nano-wire, and others. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of producing a molecular device including: the use of a molecular structure having a higher atomic density in the periphery than in the interior and bonding residues in the periphery; and a step of crosslinking the bonding residues, and the method of producing a molecular device according to claim 1, characterized in that the molecular structure is constituted by a skeleton portion having a skeleton structure, and a terminal portion which is arranged in the outer shell of the skeleton portion, has a higher atomic density than that of the skeleton portion and has bonding residues; and that in the step of crosslinking the bonding residues, the bonding residues in the terminal portion of the molecular structure are crosslinked to form the molecular structure into a shell structure, and others.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Lamination-recombination passive film used for front surface of single-crystalline-silicon solar cell
InactiveCN102610661AFill hanging buildGood optical matchingLayered productsPhotovoltaic energy generationAmorphous siliconSilicon oxide
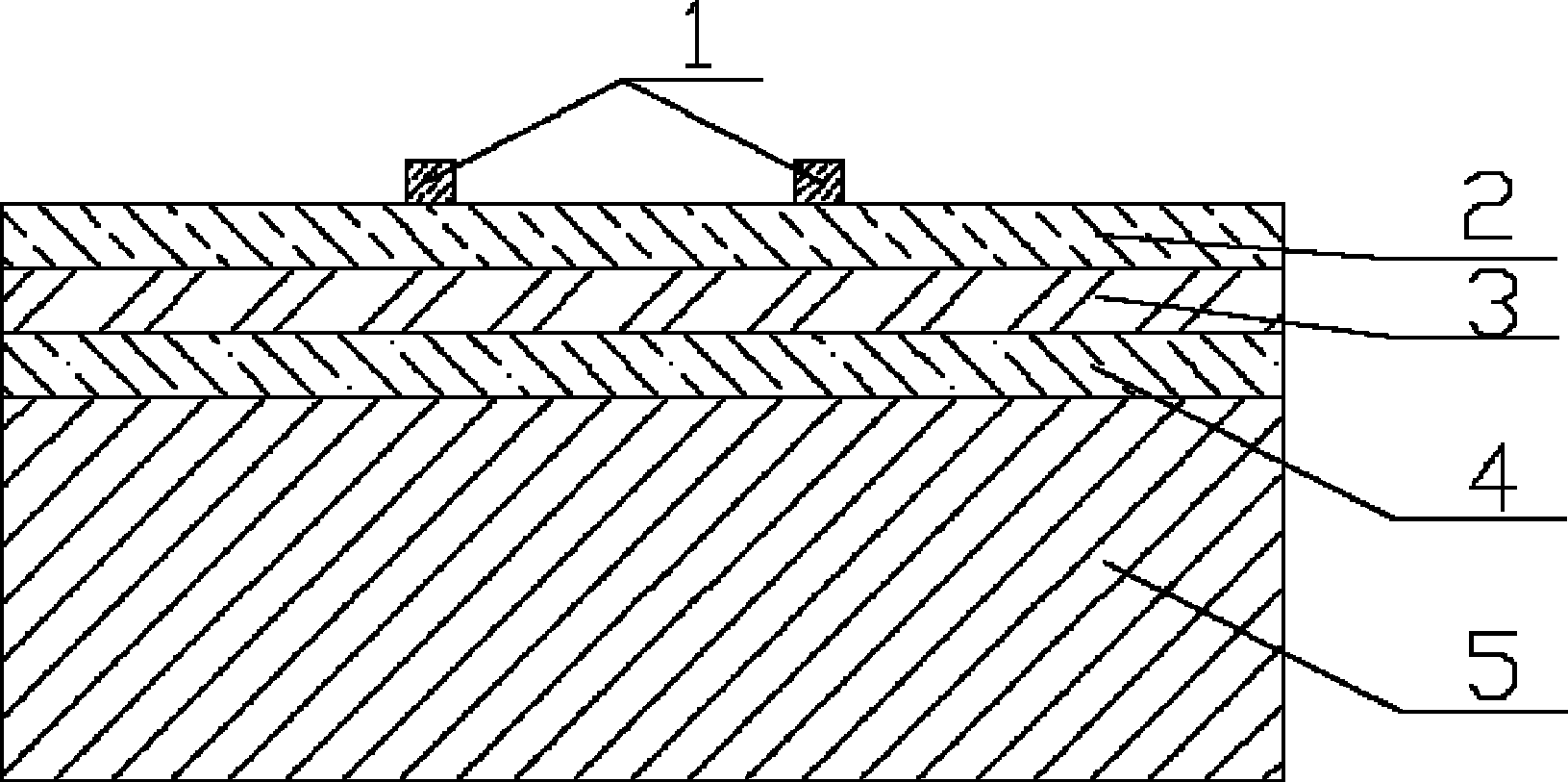
The invention discloses a lamination-recombination passivation layer used for the front surface of a monocrystalline silicon solar cell. A silicon oxide thin film (4), a hydrogenated amorphous silicon thin film (3) and a silicon nitride thin film (2) are arranged on the front surface of a solar cell monocrystalline silicon substrate (5) from the inside to the outside in sequence. According to the lamination-recombination passive film, the surface state density of the cell is in the same order of magnitudes with the atomic density of silicon, the overhanging units on the surface of the cell are filled effectively by the hydrogenated amorphous silicon thin film, the silicon nitride thin film plays the role of passivation and antireflection simultaneously, and the whole passivation layer has good optical matching property with EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) and glass for packaging.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC YIXING MAGI SOLAR POWER TECH
Cylindrical microwave cavity of diffuse reflection laser cooling atom
ActiveCN104090481AImprove performanceSimple structureApparatus using atomic clocksResonant cavityMicrowave cavity
The invention provides a cylindrical microwave cavity of a diffuse reflection laser cooling atom, wherein the cylindrical microwave cavity is applied to a miniaturized space cold atomic clock. The cylindrical microwave cavity is formed by connecting an upper cover and a lower base through screws. The cylindrical microwave cavity is utilized to achieve the effects of the cooling atom and a microwave resonant cavity, has the advantages that a central zone of the cooling atom of a cylindrical cavity is high in cold atomic density and the cylindrical resonant cavity is high in quality factor and easy to machine, can simplify the structure of the cold atomic clock greatly, reduces the weight of the atomic clock, and improves the signal to noise ratio of clock signals and system stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mixed pumped alkali metal gas chamber density ratio control method
InactiveCN108827888AFast and efficient productionDensity Ratio Fast and EffectiveColor/spectral properties measurementsPurification methodsDensity ratio
The invention discloses a mixed pumped alkali metal gas chamber density ratio control method. The method utilizes a distillation purification method to control the atomic weight of an alkali metal sothat the density ratio of the two alkali metal atoms is changed, and accurately control the density ratio by combination of a distillation temperature and a molecular pump pumping speed. Compared withthe traditional mixed pumped alkali metal gas chamber density ratio control method, the method provided by the invention utilizes an oil bath pot to control a distillation temperature so that the temperatures in the alkali metal gas chamber are more uniform and accurate. The method utilizes a white light source to perform spectral absorption measurement of an alkali metal gas chamber and calculates an alkali metal atomic density ratio. The method realizes on-line control and on-line measurement and greatly improves the precision of the mixed pumped alkali metal gas chamber density ratio and the preparation efficiency of the gas chamber.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Image-forming method
InactiveUS20110129776A1Increase speedImprove image qualityElectrographic processes using charge patternSurface layerAmorphous silicon
An image-forming method is provided which enable high-quality images to be formed over a long time period. In the image-forming method, an electrophotographic photosensitive member is used having a surface layer formed of a hydrogenated amorphous silicon carbide in which a ratio of the number of carbon atoms to the sum of the number of silicon atoms and the number of the carbon atoms in the surface layer is 0.61 or more and 0.75 or less, and the sum of the atomic density of the silicon atoms and the atomic density of the carbon atoms in the surface layer is 6.60×1022 atoms / cm3 or more, and the peak wavelength of pre-exposure light is shorter than the peak wavelength of image exposure light.
Owner:CANON KK
Single-beam mixed light pumping system and background light intensity suppression method thereof
ActiveCN112834967AImprove polarizability uniformityHigh sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLight beamParticle physics
The invention discloses a single-beam mixed light pumping system and a background light intensity suppression method thereof. The method can greatly improve the atomic density, enhance the signal intensity, and increase the atomic density through the fast spin exchange collision between different alkali metal atoms through a mixed light pumping technology, thereby improving the sensitivity of a magnetometer, reducing the bias of a detection signal at the same time, improving the sensitivity of the atom magnetometer, and having wide application scenes in the biomedical fields such as heart-brain magnetism.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Complementary MISFET semiconductor device having an atomic density ratio aluminum/lanthanum (Al/La) in the gate insulating layer of PMIS is larger than that of the NMIS
A complementary semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first semiconductor region formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate, a second semiconductor region formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate apart from the first semiconductor region, an n-MIS transistor having a first gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the first semiconductor region, and a first gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, and a p-MIS transistor having a second gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the second semiconductor region, and a second gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, an atomic density ratio Al / La in the second gate insulating film being larger than an atomic density ratio Al / La in the first gate insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Construction method of 3D micro/nano structure
ActiveCN111646428ASolve construction problemsPlay a role in promotingMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention discloses a construction method of a 3D micro / nano structure, which comprises the following steps: (1) fixing a material source on a substrate, and carrying out vacuumizing; (2) focusingthe focus of the electron beam at a place having a distance of 0-100nm away from the surface of the material source in the step (1) to form an interface local area containing the focus of the electron beam and surface layer atoms; and (3) controlling the focus of the electron beam to move point by point according to the designed 3D micro / nano structure to achieve the construction of the 3D micro / nano structure. According to the construction method of the present invention, focusing electron beam focus heat radiation is used for regulating material source surface layer atoms; the surface atomkinetic energy is increased; the constraint of surface energy is overcome, and the atons escape from the surface; and meanwhile, surface layer atoms of a material source are diffused to a low-densityarea due to the imbalance of the atomic density of an interface local area and the potential energy difference, so that the real-time construction of a three-dimensional structure under a micro / nano scale is achieved, the fusion development of a nano technology and 3D printing is promoted, and the application and popularization values are relatively good.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
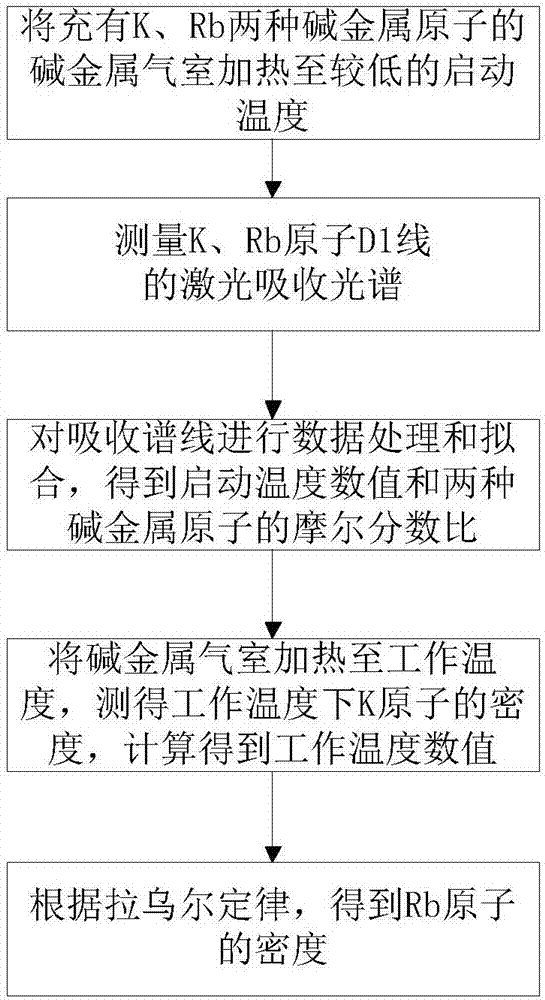
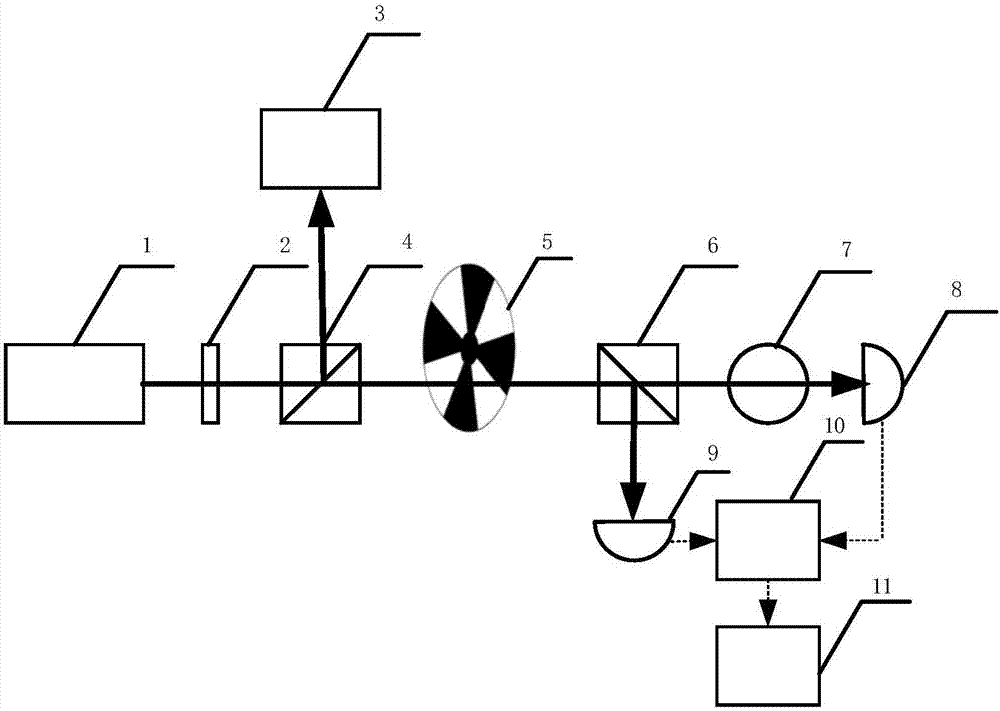
Hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method
ActiveCN107167437AHigh measurement accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsCurve fittingWorking temperature
The invention relates to a hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method. The method comprises the steps of heating an alkali metal gas chamber filled with K and Rb up to starting temperature, and measuring to obtain laser absorption spectrums of the K and the Rb to obtain densities of the K and the Rb at the starting temperature, and associating Raoult's law to obtain the starting temperature as well as ratios of saturated vapor pressures to molar fractions of the K and the Rb at the starting temperature; heating the gas chamber up to working temperature, wherein the density of the Rb is very high and the absorption is very strong near a resonance point in an SERF state, carrying out curve fitting to obtain a greater deviation of the density of the Rb, and accordingly obtaining the density of the K by means of a spectral absorbing method; combining the known molar fraction of the K, and calculating to obtain the working temperature; combining the molar fraction of the Rb to obtain the saturated vapor pressure of the Rb at the working temperature, and further obtaining the density of the Rb at the working temperature. The hybrid optical pumping-based accurate atomic density measurement method is suitable for the situation that during hybrid optical pumping, the saturation absorption spectrum is very high in atomic number density and is very strong in absorption at the both sides of a resonant peak, so that the density is difficult to obtain by means of a fitted curve.
Owner:杭州诺驰生命科学有限公司
Method for simulating influence of heating technology on premelting and melting of crystal boundaries by aid of crystal phase-field process
The invention relates to a method for simulating the influence of a heating technology on premelting and melting of crystal boundaries by the aid of a crystal phase-field process, and belongs to the field of technologies for simulating crystals. The method includes steps of (1), building a crystal phase-field model, in other words, building the crystal phase-field model on the basis of an idea of the traditional phase-field process, introducing a periodic function form into the model, and setting periodic partial-time average atomic densities as order parameters to obtain a free energy function expression of crystals; (2), determining a numerical process and calculation parameters. The method has the advantages that premelting and melting microstructure morphology at different heating rates is researched by the aid of a simulated calculation process and the crystal phase-field process, the widths of liquid-phase films at the crystal boundaries are quantitatively calculated by an excess mass process when the crystal boundaries are premelted and melted at the different heating rates, accordingly, the widths of the liquid-phase films at the crystal boundaries are quantified when the crystal boundaries are premelted and melted, structural relations among numerical values of the widths of the liquid-phase films and the atomic crystal boundary structures are illustrated, and an effect is perfect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Differential absorption method-based atomic density and population measuring device and method
ActiveCN110146410AEliminate measurement effectsImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecific gravity measurementMeasurement deviceInstability
The invention provides a differential absorption method-based atomic density and population measuring device and method. According to the differential absorption method-based atomic density and population measuring device and method of the invention, two pulse light sources are adopted, wherein one of the pulse light source serves as signal light, and the other pulse light source serves as opticalpumping light; after the two beams of light are combined, the combined light is transmitted along two light paths, wherein one of the two light paths is provided with an atomic pool and serves as a signal light path, and the other light path is not provided with any atomic pool and serves as a calibration light path of absorption spectral lines; after the two paths of light are converted into electric signals through a detector, the two paths of electric signals are subtracted from each other; and therefore, influence in the absorption spectral lines which is caused by the instability of thelight paths and the light sources can be removed, and measurement accuracy is improved. Atomic density at each energy level is determined through each fine absorption peak of the absorption spectral lines, and therefore, the blank of the population measurement of each atomic level can be filled. The method can be further used for measuring the initial states of atoms prepared by optical pumping.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
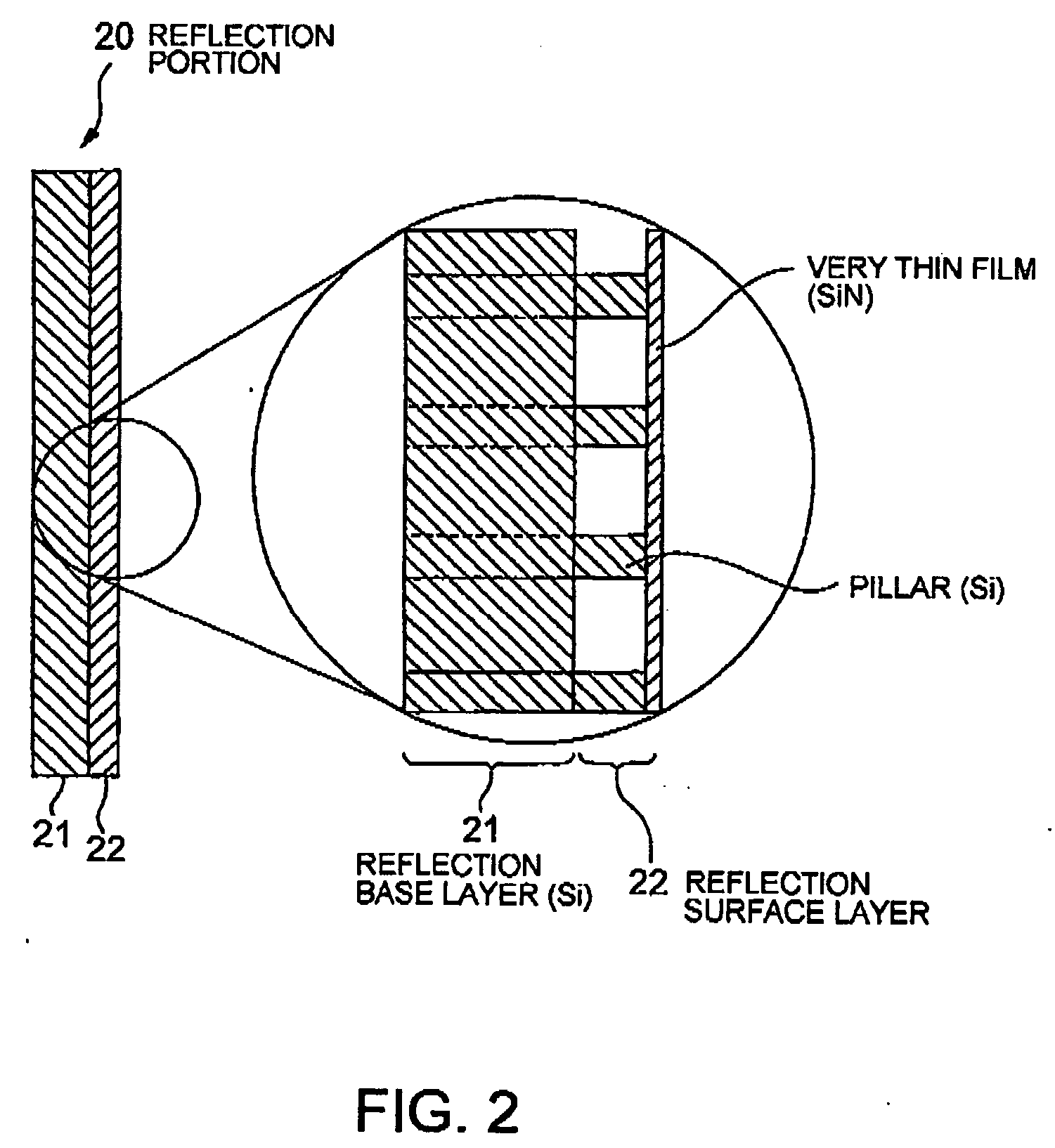
Atomic reflection optical element
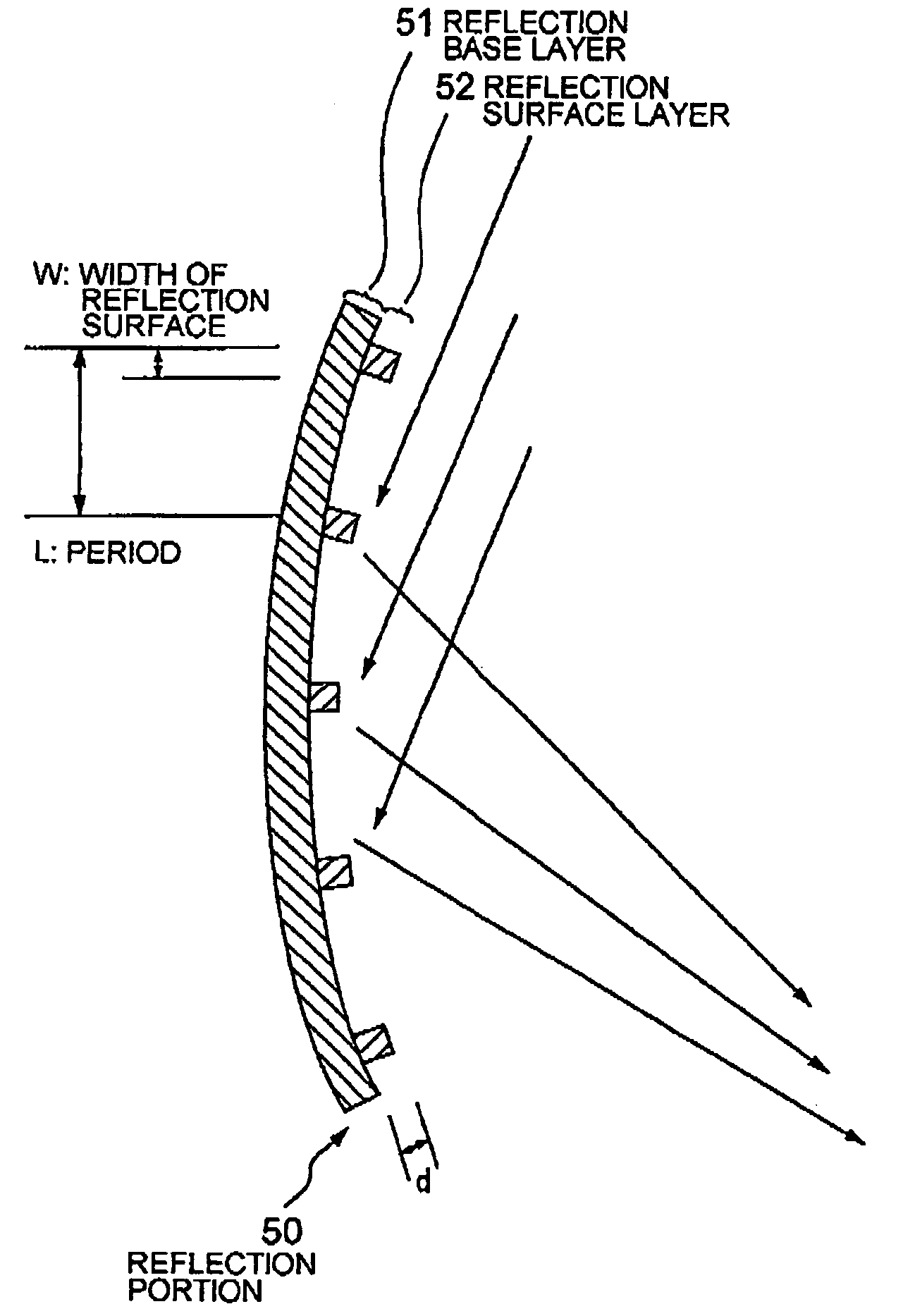
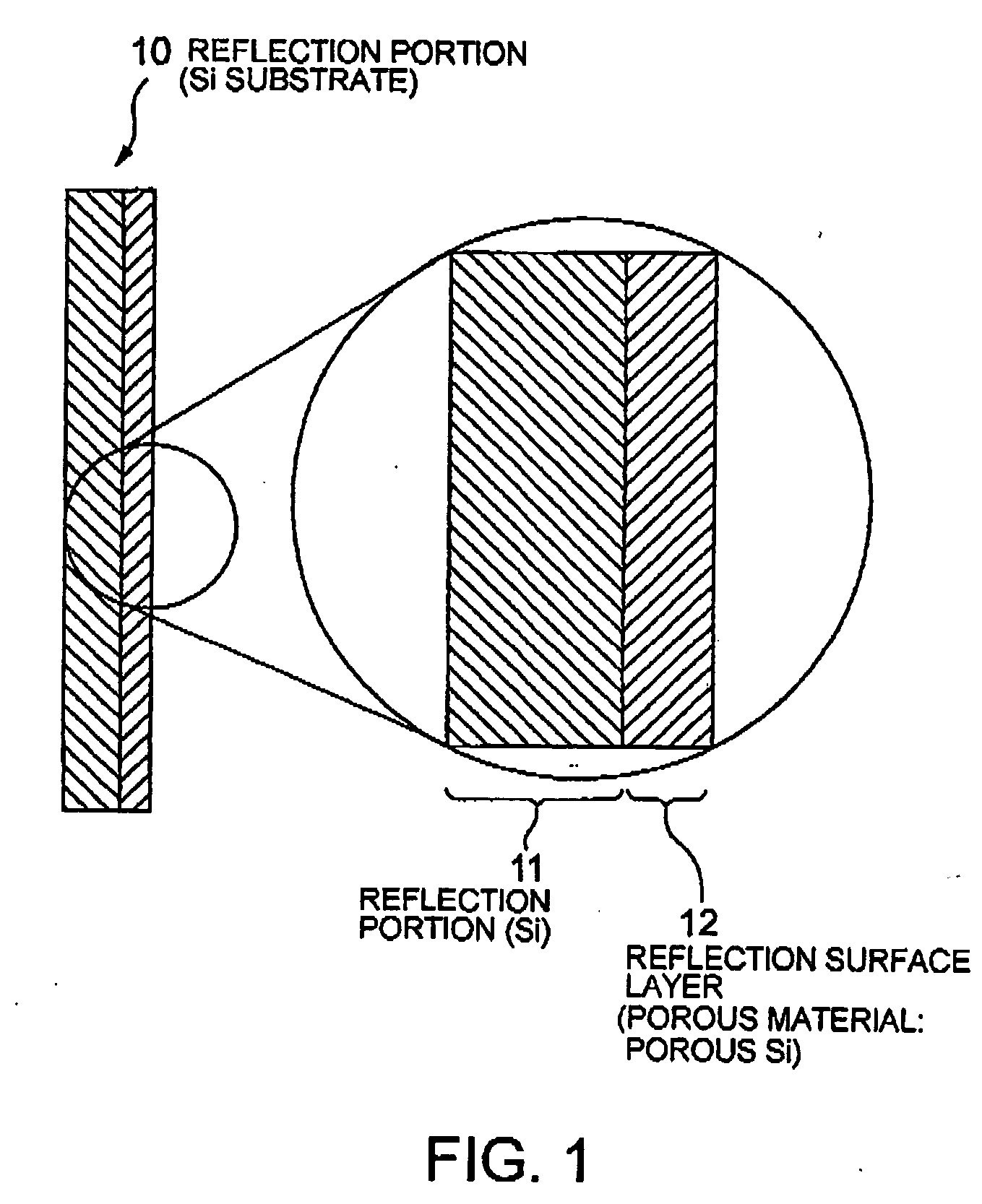
InactiveUS20040238733A1Reflectance can be increasedReduce areaLaser detailsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionAtomic densitySurface structure
An atomic reflection optical element for an atomic wave (de Broglie wave) so constituted as to increase the reflectance of an atomic wave by reducing the apparent atomic density of reflection plane; for example, a porous surface structure, a structure supporting a very thin film, or a structure in which the insular portion (reflection surface) of a reflection-diffraction grating is narrowed is used for this purpose. The above arrangement can provide an atomic reflection optical element having a high atomic wave coherent reflection power.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
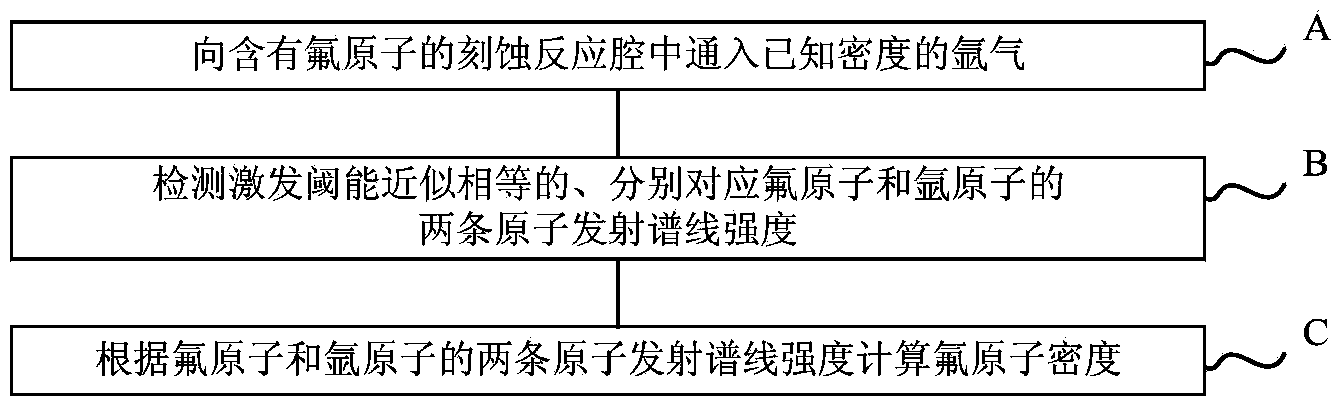
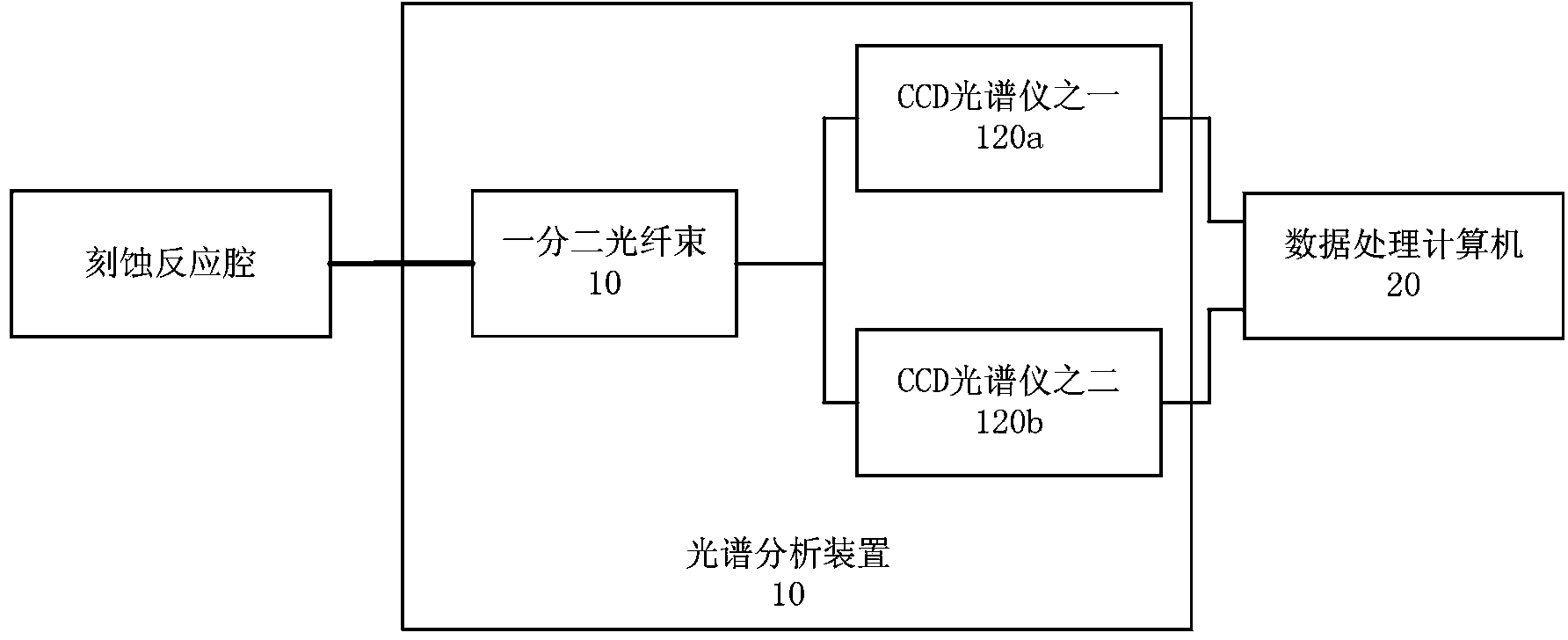
Spectrum detection method and system for fluorine atom density in plasma etching process
The invention discloses a spectrum detection method and system for the fluorine atom density in a plasma etching process. The spectrum detection method and system have the advantages of no electron temperature influence, high accuracy, capability of being widely applied to various etching process conditions and the like. The method comprises the following steps: introducing argon gas with the known density into an etching reaction cavity containing fluorine atoms; detecting the intensity of two atomic emission spectral lines which are approximately same in excitation threshold energy and correspond to fluorine atoms and argon atoms respectively; calculating the fluorine atom density n[F] according to the intensity of the two atomic emission spectral lines of the fluorine atoms and the argon atoms by a calculation formula described in the specification, wherein in the formula, Q[F] represents the speed coefficient of the electron impact excited ground-state fluorine atoms, Q[Ar] represents the speed coefficient of the electron impact excited ground-state argon atoms, Q[Ar] / Q[F] is known physical quantity, I[F] is the corresponding spectral line intensity of the fluorine atoms, I[Ar] is the corresponding spectral line intensity of the argon atoms, and n[Ar] is the ground-state argon atom density.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
One-dimensional high-defect NiO nanowires prepared by electrostatic spinning and catalytic application thereof
ActiveCN103991914AHigh catalytic efficiencyNanotechnologyNickel oxides/hydroxidesN dimethylformamideNanowire
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-defect nanowires NiO and photocatalytic application of the NiO nanowires. The method is mainly characterized in that nickel acetate, N,N-dimethylformamide and polyvinylpyrrolidone used as precursors are subjected to a simple electrostatic spinning process to synthesize lots of one-dimensional composite nanowires on an aluminum foil. After a non-equilibrium calcination process, abundant steps, knots and other surface defects are generated on the NiO nanowire surface due to the escape of gas phases, generation of pores and holes and the like, and the surface energy is lowered, so that the high-energy surface of the NiO can be preserved, thereby greatly enhancing the catalytic efficiency. The atomic density of the exposed high-energy surface is defined and quantitatively calculated to enhance the photocatalytic efficiency in a controllable way, thereby providing the direction for the subsequent catalysis research.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
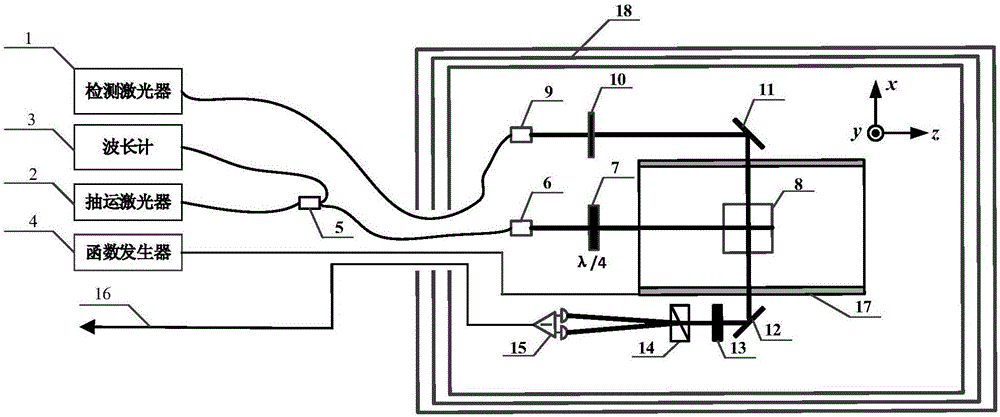
Single-beam SERF atom magnetometer and alkali metal atom density measurement method
PendingCN113740786ARealize in-situ measurementReduce constraintsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLine widthResonance line
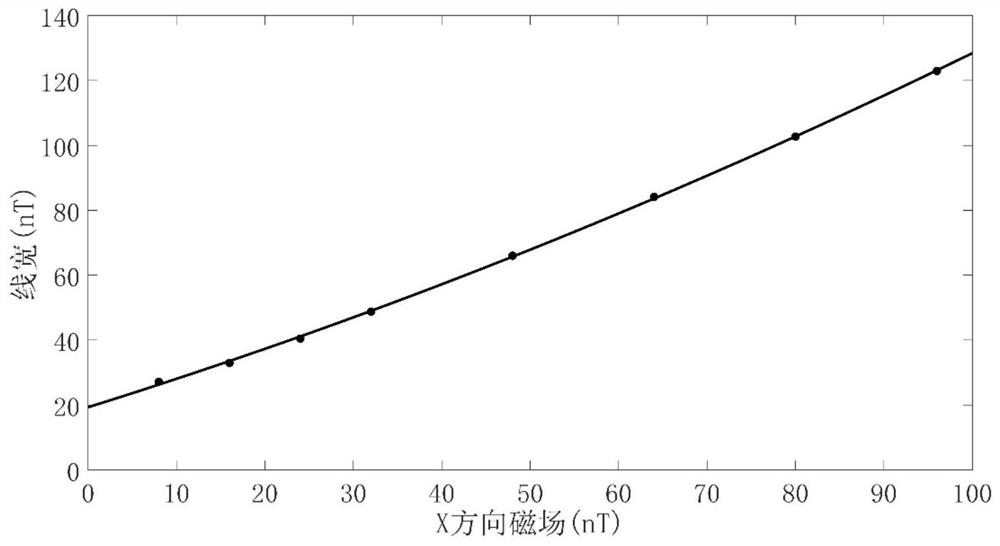
The invention discloses a single-beam SERF atom magnetometer and an alkali metal atom density measurement method, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, compensating the magnetic field intensity of the center position of the single-beam SERF atom magnetometer in three directions to zero, and heating an alkali metal gas chamber to enable alkali metal atoms to reach an SERF state; then applying a constant direct-current magnetic field along the direction of one sensitive axis, applying a bias magnetic field with modulation and a bias magnetic field which continuously changes and crosses a zero point along the direction of the other sensitive axis, and recording an output signal of the magnetometer to obtain a magnetic field resonance curve with a dispersion line type; further obtaining the magnetic field resonance line width under different direct-current magnetic fields along the X-axis direction; obtaining the relation between the magnetic field resonance line width and the direct-current magnetic field size through quadratic function fitting; and finally, calculating the alkali metal atomic density by using the quadratic term coefficient of the quadratic function, so that the in-situ measurement of the alkali metal atomic density is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method for simulating discharge process of discharge chamber of Kaufman ion thruster
ActiveCN111044822AImprove computing efficiencyCalculation speedElectrical testingPlasma diffusionParticle physics
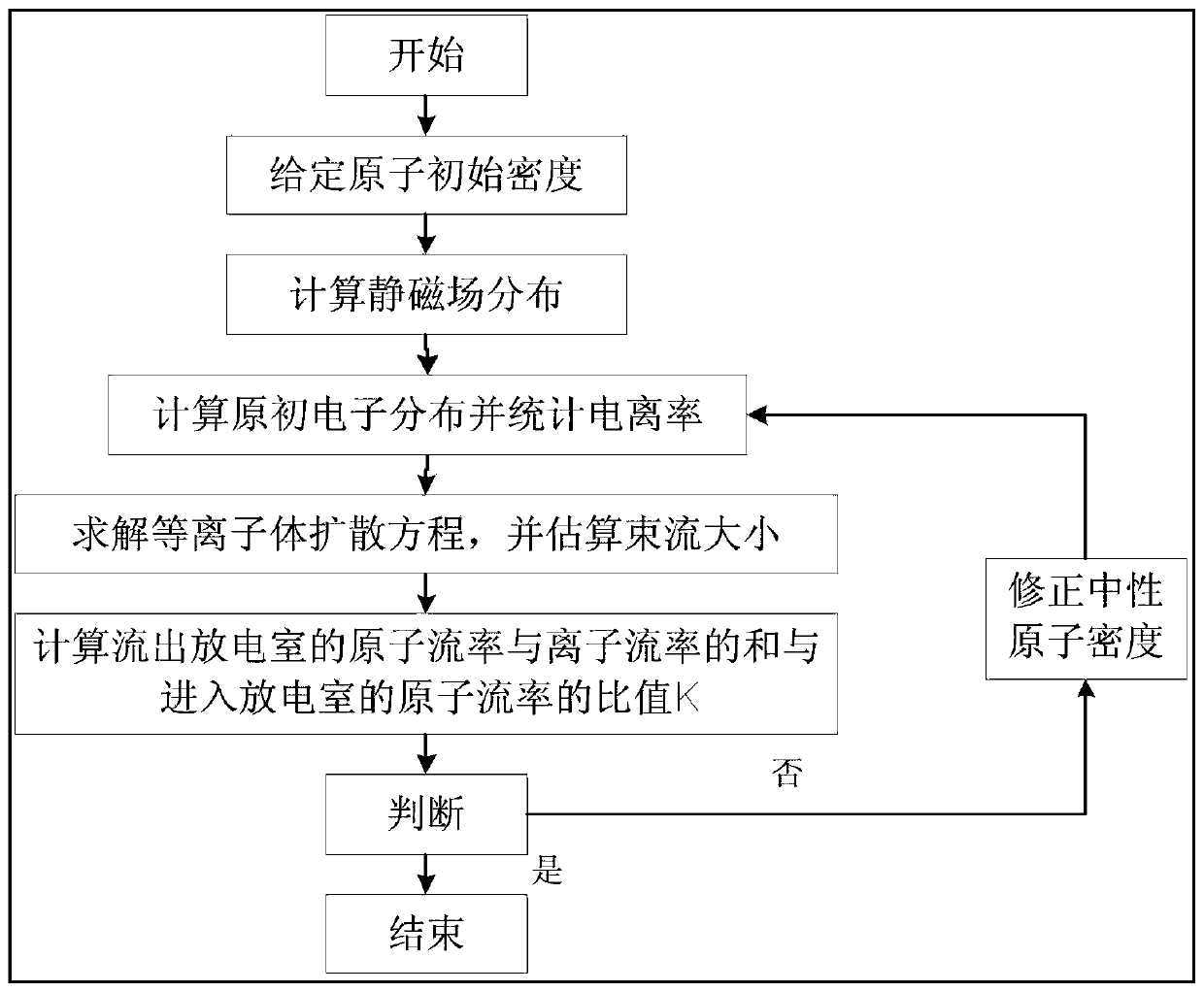
The invention relates to a method for simulating a discharge process of a discharge chamber of a Kaufmann ion thruster, mainly aims at the discharge chamber of the Kaufmann ion thruster and designs aset of efficient method for simulating the discharge process of the Kaufmann ion thruster from the characteristics of different particles in the discharge chamber. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: calculating initial density of atoms; calculating static magnetic field distribution; calculating primary electron distribution and counting an ionization rate; solving a plasma diffusion equation and estimating the size of a beam current; calculating a ratio k of the sum of an atomic flow rate and an ion flow rate flowing out of the discharge chamber to an atomic flow rate entering the discharge chamber; judging whether convergence occurs or not; if so, acquiring a convergence solution of the discharging process; and if not, correcting the neutral atom density, and then recalculating from the step 3. After simulation calculation by adopting the method, the discharge process of the Kaufman ion thruster can be effectively simulated, and the calculation precision is high compared with a test result.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com