Variable cross-section channel structure of low-power cusped magnetic field plasma thruster
A tangential magnetic field and plasma technology, applied in the field of variable cross-section channel structure, can solve the problems of intensified interaction between plasma and wall surface, performance degradation, insufficient ionization of flux density, etc., to reduce plume divergence angle and reduce ignition voltage , the effect of increasing the ionization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
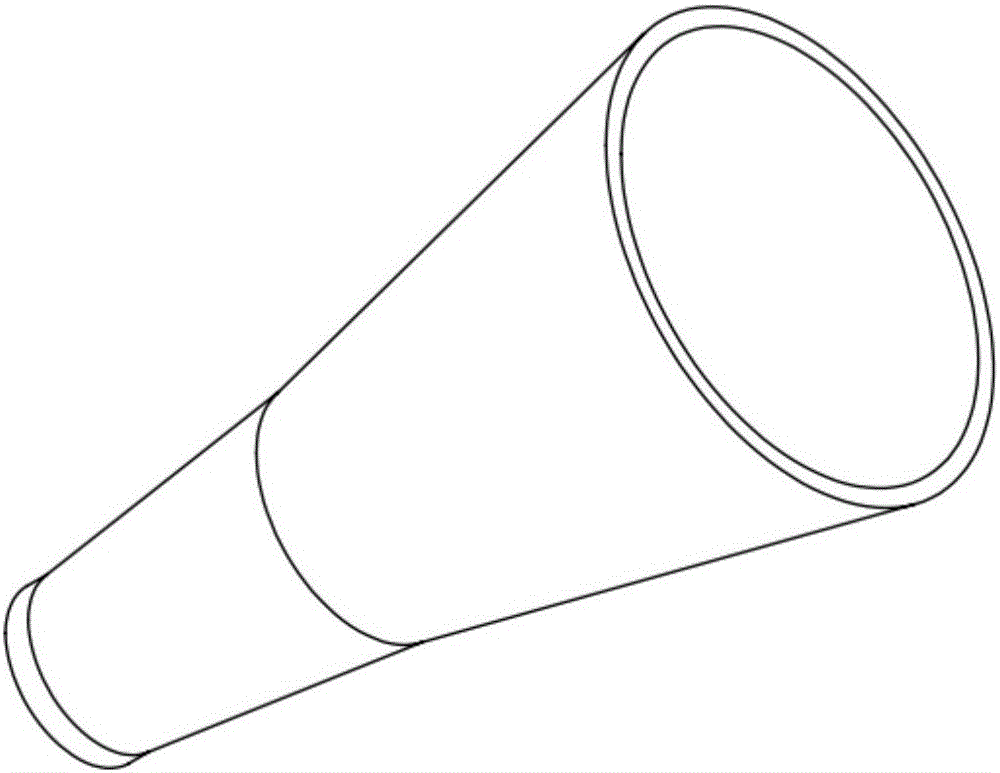
[0016] Specific implementation mode one: refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 Specifically explain this embodiment, a variable cross-section channel structure of a low-power tangent magnetic field plasma thruster described in this embodiment, the channel is constructed by a ceramic channel and a permanent magnet,
[0017] The ceramic channel is a one-piece structure, which is divided into two sections: the upstream part of the channel and the downstream part of the channel.
[0018] The one-piece structure is a channel structure gradually expanding from the upstream part of the channel to the downstream part of the channel. The outer wall of the ceramic channel is used to achieve clearance fit with the inner wall of the permanent magnet.
[0019] The expansion angle range of the upstream part of the channel is 0° to 20°, and the expansion angle range of the downstream part of the channel is 10° to 30°.
[0020] In this embodiment, if figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, both the cera...
specific Embodiment approach 2
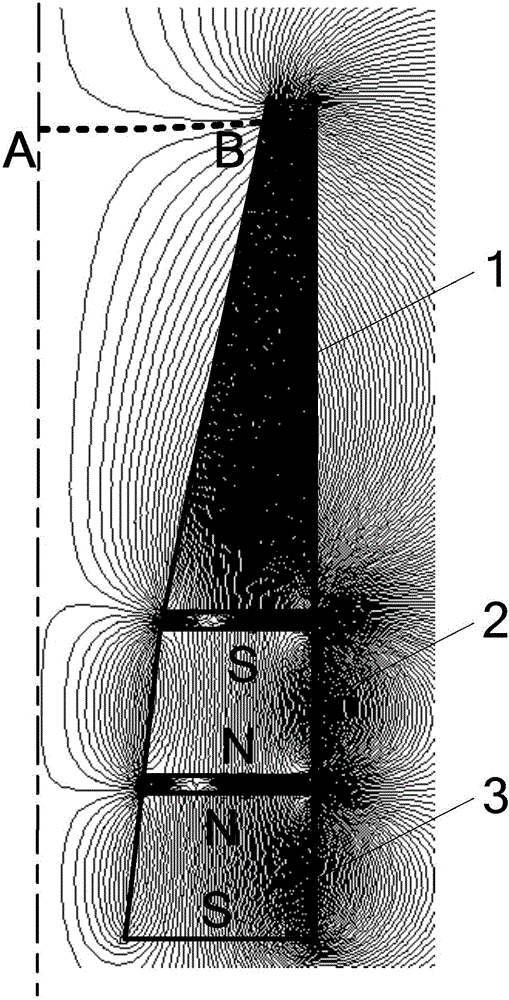
[0021] Specific implementation mode two: refer to Figure 4 Describe this embodiment in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the variable cross-section channel structure of a low-power tangent magnetic field plasma thruster described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the permanent magnet includes a first-stage permanent magnet. 1. The second-level permanent magnet 2 and the third-level permanent magnet 3, the first-level permanent magnet 1, the second-level permanent magnet 2 and the third-level permanent magnet 3 are arranged sequentially from the downstream to the upstream of the channel; the three permanent magnets are magnetized along the axial direction, And the magnetization directions of two adjacent permanent magnets are opposite;
[0022] The inner wall surface of the first-stage permanent magnet 1 and the outer wall surface of the downstream part of the channel realize clearance fit, and the length of the first-stage permanent magnet 1 is the same a...
specific Embodiment approach 3
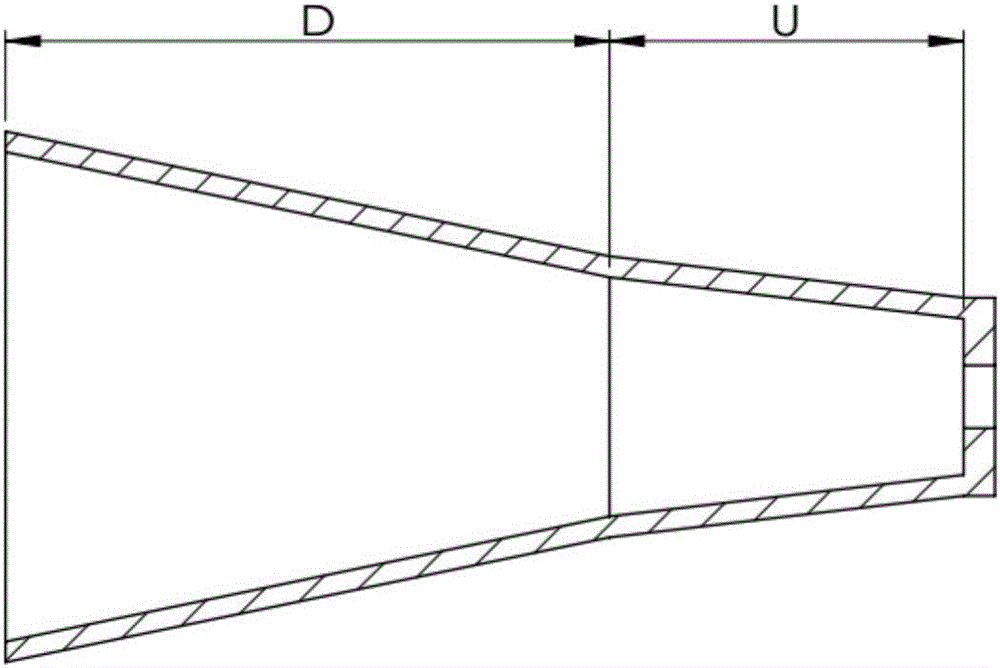
[0026] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further description of the variable cross-section channel structure of a low-power tangent magnetic field plasma thruster described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the material of the ceramic channel is boron nitride Ceramic, the wall thickness is 2mm, the minimum inner diameter of the upstream part of the channel is 15mm, the inner diameter of the outlet is 47mm, the expansion angle of the upstream part of the channel is 13°, and the expansion angle of the downstream part of the channel is 22°.
[0027] In this embodiment, the axial length of the upstream part U of the channel is the same as the total length of the second-stage permanent magnet 2 and the third-stage permanent magnet 3, and the axial length of the downstream part D of the channel is the same as the length of the first-stage permanent magnet 1, that is, the two expansion angles of the channel The interface corresponds to the second magnetic tip of the magnetic field...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Minimum inner diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com