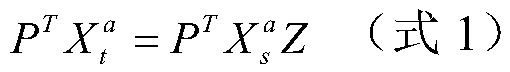Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55results about How to "Reduce Mismatch Problems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
C/C composite material superhigh temperature ceramic coating, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108530110AExtended service lifeReduce Mismatch ProblemsUltra-high-temperature ceramicsCeramic coating
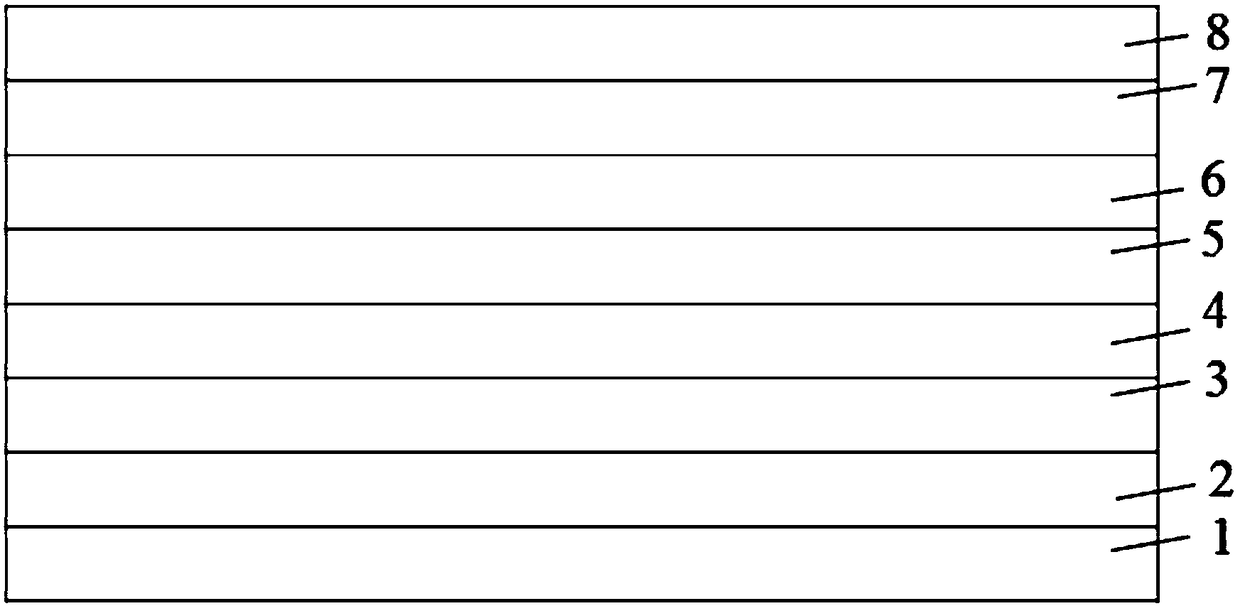
The invention discloses a C / C composite material superhigh temperature ceramic coating, and a preparation method thereof. The C / C composite material superhigh temperature ceramic coating is composed of an anti-oxidation SiC transition internal layer and a superhigh temperature ablation-resistant ceramic external layer; the superhigh temperature ablation-resistant ceramic external layer is composedof more than one ingredients selected from SiC, ZrC, HfC, TaC, TiC, ZrB2, HfB2, TaB2, and TiB2. The preparation method is suitable for industrialized production, is simple in equipment, is convenientin operation, is capable of controlling coating thickness, satisfying preparation requirements of large size C / C composite material superhigh temperature ceramic coating with complex shapes, and is asuperhigh temperature ceramic coating preparation method with excellent development potential.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Light-emitting diode with composite polar face electron blocking layer
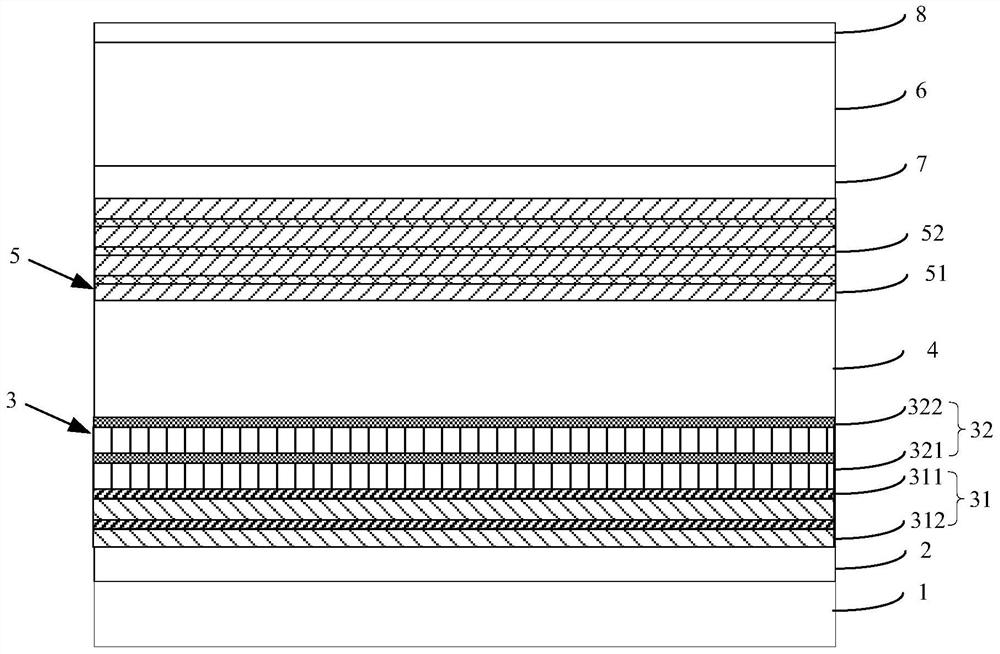
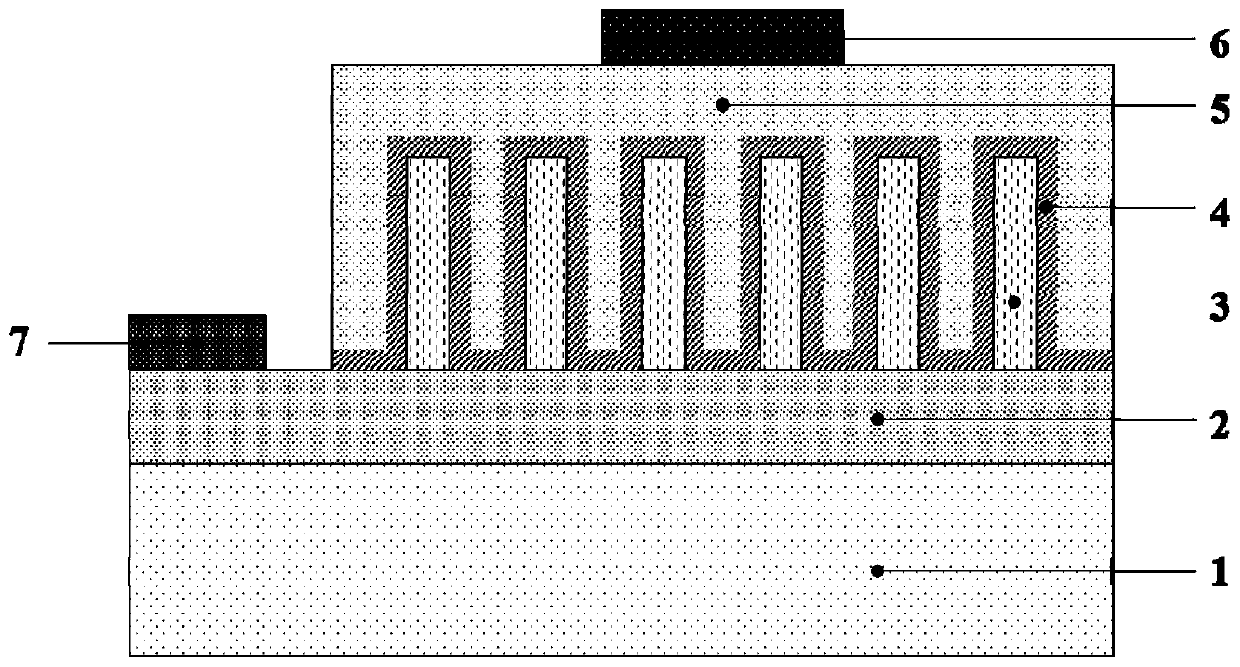
ActiveCN105870283AReduce leakage currentIncrease chanceSemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumElectron blocking layer
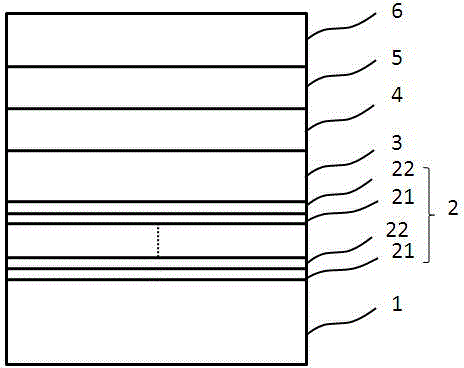
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode with a composite polar face electron blocking layer. The light-emitting diode comprises a substrate (101), a metal polar face n-type nitride layer (102), a metal polar face multiple quantum well layer (103), a metal polar face p-type nitride layer (104), a composite polar face p-type electron blocking layer (105) composed of a metal polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1051) and a nitrogen polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1052), a nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer (106), an n electrode (7) arranged on the metal polar face n-type nitride layer and a p electrode (8) arranged on the nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer, and the layers and the electrodes are arranged sequentially from bottom to top. A high electronic barrier is formed on a conduction band by the composite polar face electron blocking layer and blocks electrons from crossing a multiple quantum well active region to enter a p-type region, leakage currents can be reduced, and the probability of radiative recombination of the electrons and holes is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ceramic modification C/C composite material with ceramic coating layer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106977223AImprove erosion and ablation resistanceImprove linear expansion coefficientFiberMetallurgy
The invention relates to a ceramic modification C / C composite material with a ceramic coating layer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the ceramic modification C / C composite material comprises the following steps of performing density increase on a carbon fiber prefabricated body by a chemical vapor deposition process to obtain C / C porous bodies; performing more than once soaking-cracking process on the C / C porous body until the density of the ceramic modification C / C composite material reaches 1.8g / cm<3> or higher; obtaining the ceramic modification C / C composite material. According to the preparation method of the C / C composite material with the ceramic coating, a ceramic outer coating layer is mainly prepared on the surface of the ceramic modification C / C composite material. The method solves the problem of heat expansion coefficient unbalance of the base body and the coating, and has the advantages that the equipment and the process are simple; the operation is easy; the coating structure content is controllable; large-dimension and complicated-shape special-shaped workpieces can be prepared, and the like; great engineering application potential is realized.
Owner:湖南金钺新材料有限责任公司
GaN-based LED (Light-emitting Diode) epitaxy structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104393130AReduce Mismatch ProblemsQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchQuantum well
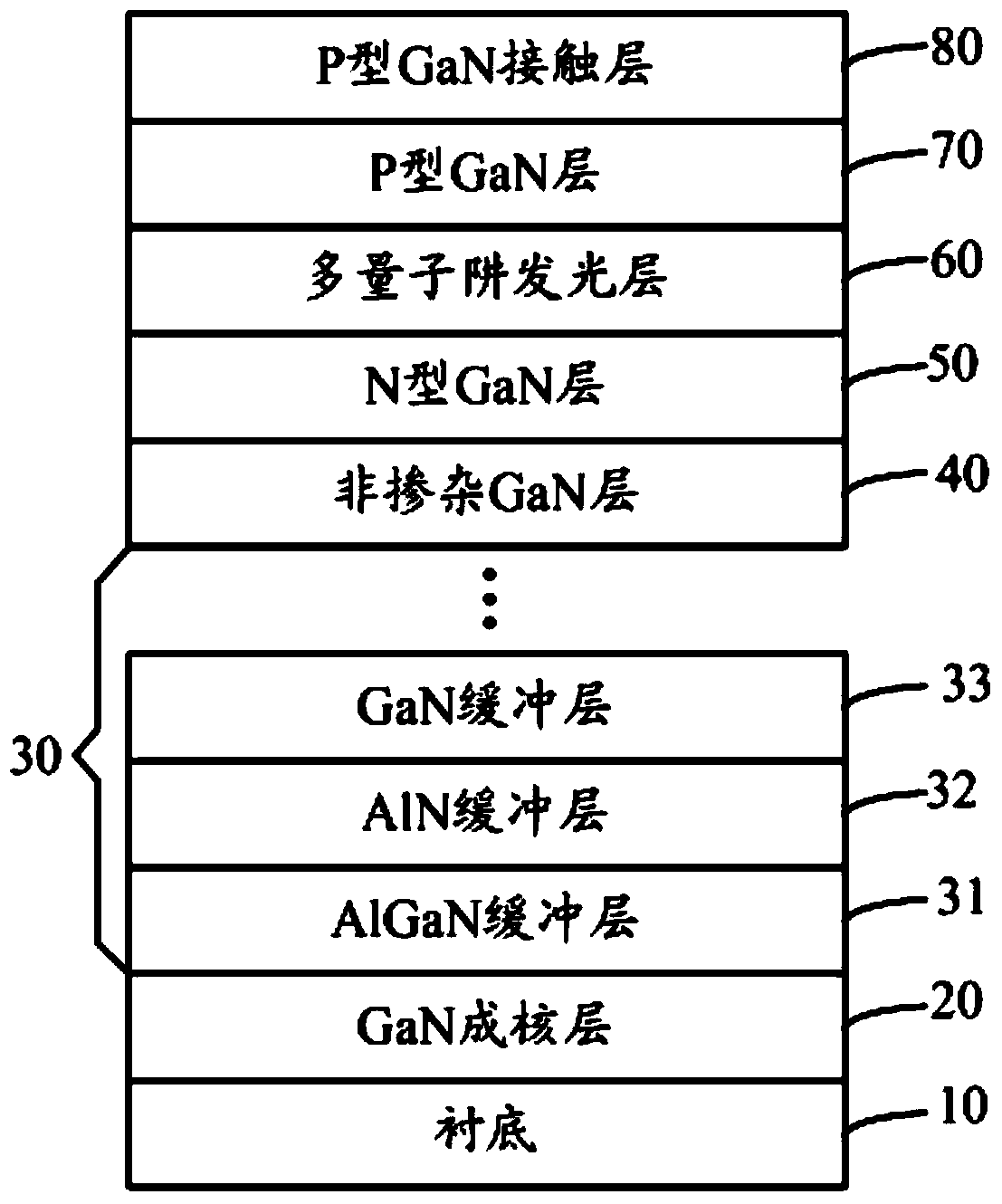
The invention discloses a GaN-based LED epitaxy structure and a preparation method thereof. The GaN-based LED epitaxy structure sequentially comprises a substrate, a GaN nucleating layer, a superlattice buffer layer, a non-doped GaN layer, an N type GaN layer, a multi-quantum-well luminescent layer, and a P type GaN layer, wherein the superlattice buffer layer adopts a superlattice structure which is prepared by alternately stacking a plurality of pairs of AlGaN buffer layers, AlN buffer layers and GaN buffer layers. The GaN-based LED epitaxy structure disclosed by the invention can relieve the lattice mismatch problem due to mismatch between the sapphire substrate and the GaN lattice, greatly reduces the warping of the epitaxial wafer during the whole high-temperature growth process, promotes the wavelength centrality and the yield of the epitaxial wafer, meanwhile effectively increases the GaN lattice quality, reduces the lattice dislocation density, and enables the optical-electrical characteristics of the device to be more stable.
Owner:FOCUS LIGHTINGS SCI & TECH
Light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN107452839AAvoid destructionReduce Mismatch ProblemsSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a fabrication method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductors. The fabrication method comprises the steps of providing a patterned sapphire substrate (PSS); forming an aluminum nitride buffer layer on a surface, on which patterns are arranged, of the PPS, wherein the aluminum nitride buffer layer comprises first parts and second parts, the first parts are arranged on the patterns, the second parts are arranged among the patterns; coating photoresist on the aluminum nitride buffer layer, wherein the thickness of the photoresist arranged on the first parts is smaller than the thickness of the photoresist arranged on the second parts; performing dry etching on the photoresist until the photoresist arranged at the tops of the first parts is removed; removing the tops of the first parts; laying a silicon dioxide material; removing the residual photoresist to form a silicon dioxide layered structure; and sequentially growing an N-type gallium nitride layer, a light emitting layer and a P-type gallium nitride layer. By the fabrication method, the epitaxial defect of a top end of the PPS caused by the aluminum nitride buffer layer can be prevented, and lattice mismatching also can be buffered by the aluminum nitride buffer layer.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Digital correction method for array analog to digital converter of high-performance CMOS image sensor
ActiveCN106027924AReduce Mismatch ProblemsGood dynamic performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCMOSImage sensor
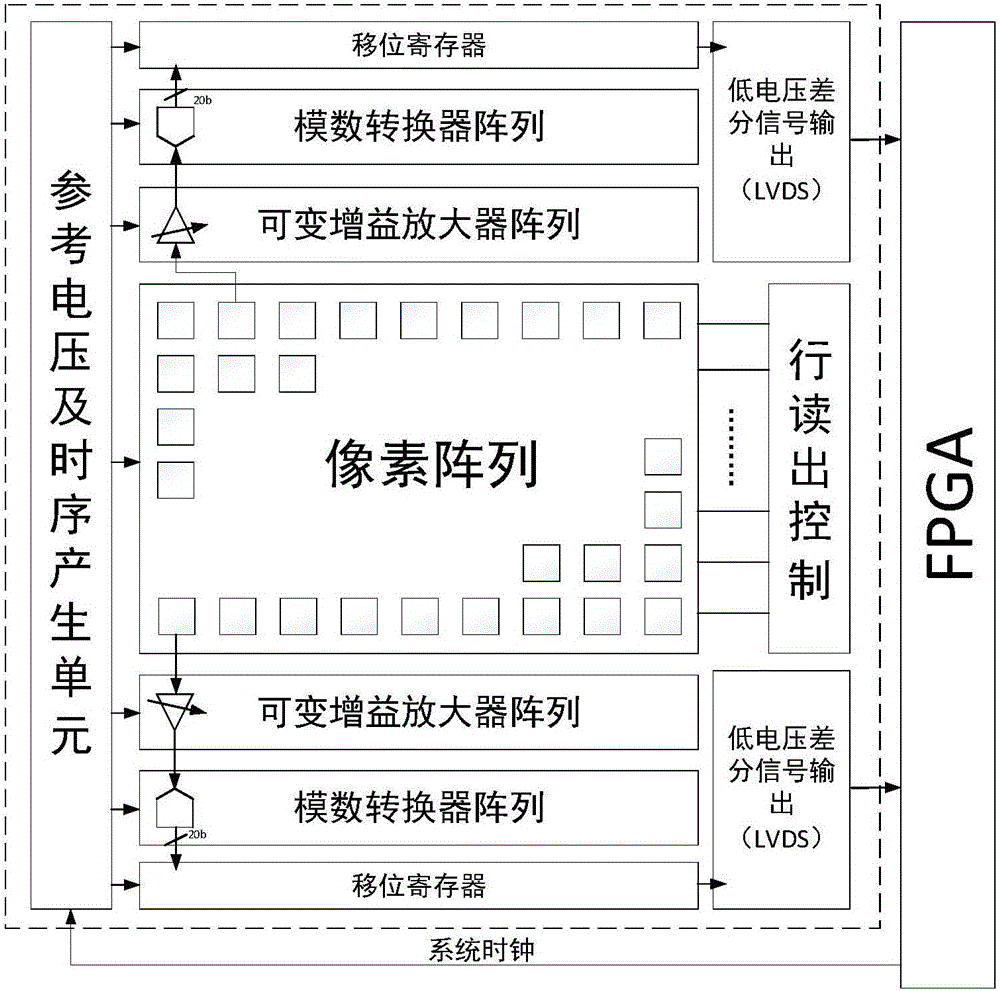
The invention belongs to the field of semiconductor image sensing, and specifically relates to a digital correction method for an array analog to digital converter of a high-performance CMOS image sensor. The invention provides an algorithm based on a multi-way collaborative digital correction technology. In particular, for the features that the number of the ADCs in the array ADC of the CIS is high, the area of a single ADC is very small and capacitance mismatch is high, according to the algorithm, an analog to digital converter array which is applied to the CIS and is realized by matching with the algorithm fully is designed. A low working voltage of 1.8V is employed in the integral design. The pixel voltage of the image sensor passes through a variable gain amplifier (VGA), then is directly sent to the analog to the digital converter (ADC) array for conversion, and then is sent to a digital correction engine for calculation. The array analog to digital converter applied to the CMOS image sensor is taken as an integral system. The mismatch problem due to the fact that the area of the single analog to digital converter of the array analog to digital converter is small is reduced to a great extent. According to the multi-way collaborative digital correction technology of the array analog to digital converter applied to the CMOS image sensor provided by the invention, the integral performance of the array analog to digital converter can be effectively improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Reaction diffusion connection method of ceramic composite material and metal
The invention relates to a reaction diffusion connection method of ceramic composite material and metal, which belongs to the technical field of connection of ceramic material and metal material, and is characterized in that corresponding mixed powder is added between the ceramic composite material and the metal, combustion reaction heat is generated under the activation of an electric field, and the ceramic composite material and the metal material are locally smelted respectively and generate diffusion reaction to form connection. The combustion synthesis of the metal powder forms an intermetallic compound with the performance between ceramic and metal, thus alleviating the problem of mismatching between the metal and the ceramic; and the action of the electric field causes elements between interfaces to diffuse mutually, thus being beneficial to improving the strength of the connecting interfaces. By combustion heat release, the method realizes the synthesis of an intermediate layer and the connection of metal and ceramic simultaneously, and has the characteristics of being low in energy consumption and high in connection strength.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Self-adaptive air filtering method based on iterative shrinkage weighted fusion
InactiveCN104459635AImprove estimation accuracyReduce Mismatch ProblemsWave based measurement systemsSmall sampleAir filter
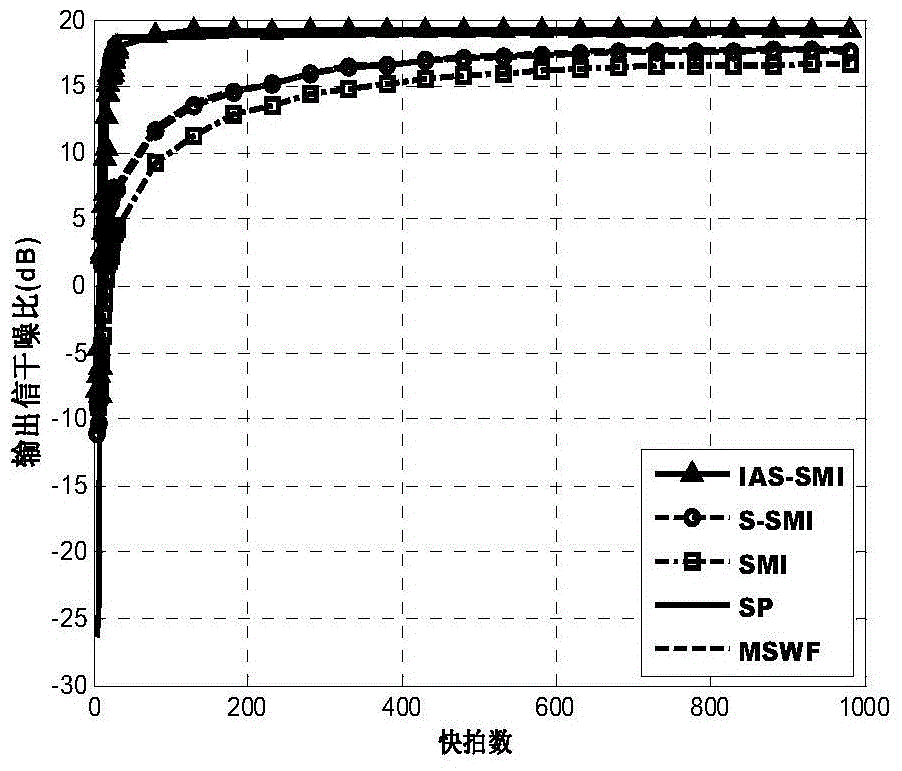
The invention discloses a self-adaptive air filtering method based on iterative shrinkage weighted fusion. The method comprises the steps that an array antenna receives data to build a signal model, and a sampling covariance matrix of the received data is obtained; a self-adaptive iteration way is adopted to update a priori covariance matrix on line; weighting coefficients of the sampling covariance matrix and the priori covariance matrix are calculated according to the minimum mean-squared error criterion, and an estimated covariance matrix is obtained through the shrinkage weighted fusion processing method; finally, the self-adaptive weight vector is calculated to carry out air filtering. The self-adaptive air filtering method can estimate the covariance matrixes with high precision on the condition of small samples, can effectively relieve the priori knowledge and current data model mismatch problem, avoids subspace dimensionality determination, has the advantages of being high in output signal to interference plus noise power ratio and convergence rate, and is effective for self-adaptive air filtering actual application.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
LED epitaxial wafer and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114725258AAvoid going too fastReduce warpage variationPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesPhysicsEngineering
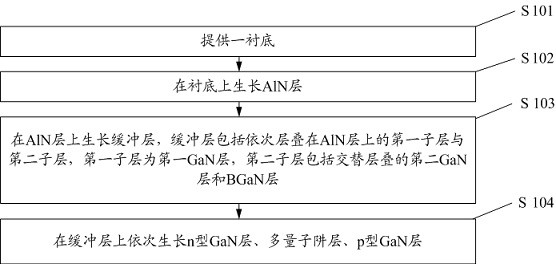
The invention provides an LED epitaxial wafer and a preparation method thereof, the LED epitaxial wafer comprises a substrate, and a low-temperature buffer layer, a three-dimensional growth layer, a two-dimensional growth layer and a GaN layer which are grown on the substrate in sequence, and the two-dimensional growth layer comprises a first sub-layer, a second sub-layer and a third sub-layer which are grown in sequence; wherein the first sub-layer is a periodic composite layer formed by repeatedly overlapping an AlGaN layer and a BGaN layer, the second sub-layer is a growth pause layer, and the third sub-layer is a periodic composite layer formed by repeatedly overlapping and growing a BN layer and an SiN layer. According to the LED epitaxial wafer, the two-dimensional growth layer is specially designed, and the composite two-dimensional growth layer is adopted, so that the LED epitaxial wafer which is higher in surface flatness, smaller in dislocation density, better in antistatic capacity, few in defect extending to a quantum well and improved in luminous intensity can be obtained.
Owner:JIANGXI ZHAO CHI SEMICON CO LTD
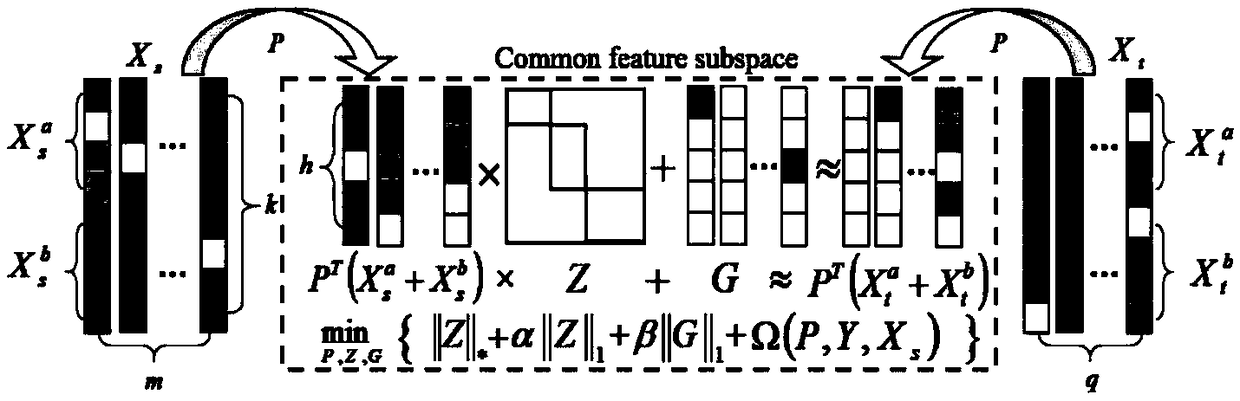
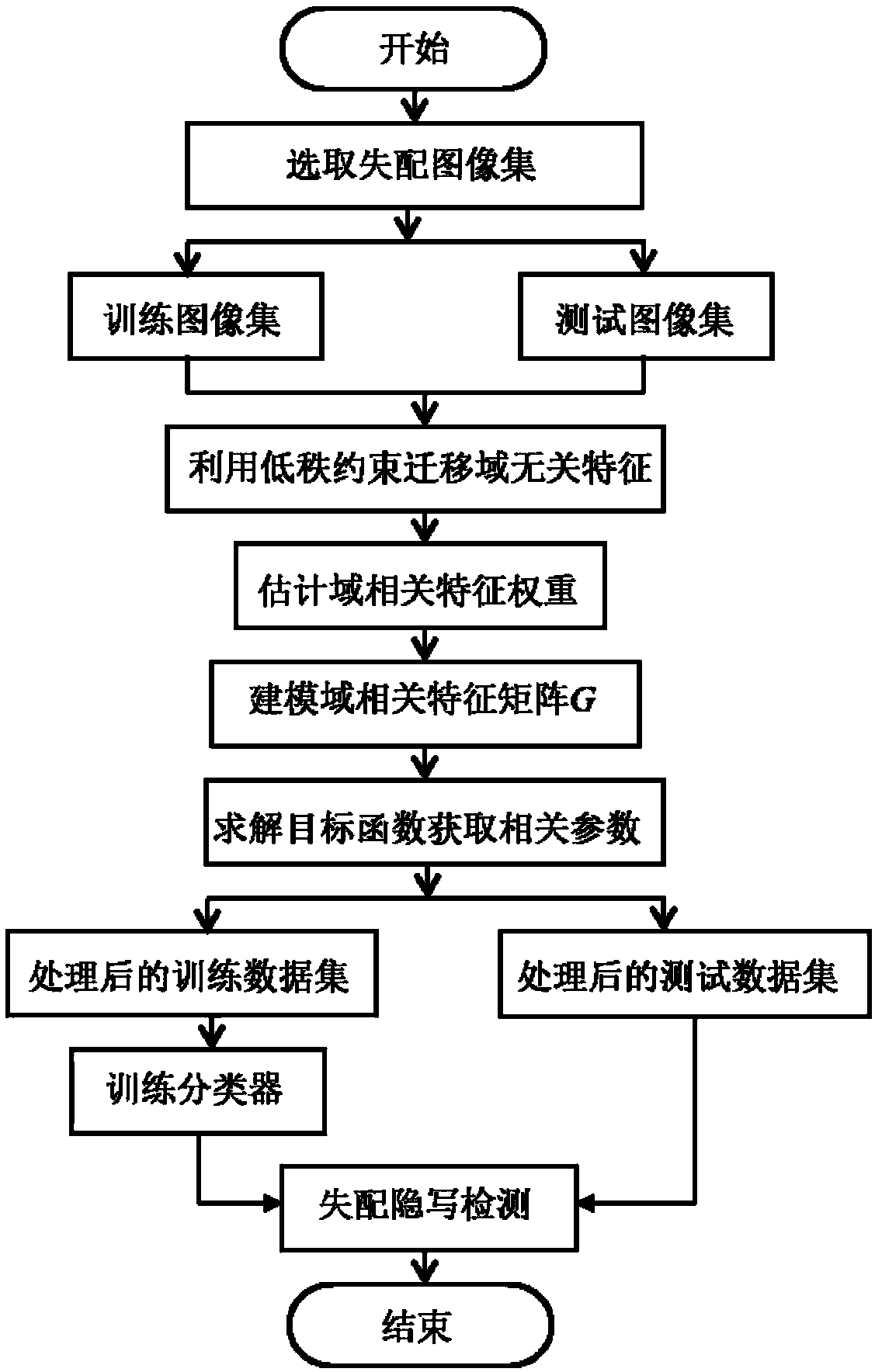
JPEG image mismatch steganography analysis method based on heterogeneous characteristic subspace migration
ActiveCN109348229ASmall discreteReduce the differenceDigital video signal modificationSteganalysisAugmented lagrange multiplier method
The invention relates to a JPEG image mismatch steganography analysis method based on heterogeneous characteristic subspace migration. The method provided by the invention takes characteristics of different fields as a combination of domain-independent and domain-related characteristic subspaces, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly providing a low-rank constrained domain-independent characteristic migration method, and realizing local information migration by utilizing local data characteristics between different fields; secondly, based on sparse representation of modeling domain-related characteristics, measuring influence produced by field change on the modeling domain-related characteristics; and finally, by virtue of the steps, constructing an objective function, andsolving by virtue of an imprecise augmented Lagrange multiplier method. Unique global information of the domain-related characteristics is considered while local information migration is realized in adomain-independent characteristic subspace, so that characteristic differentiation degree between a cover image and a stego image can be improved, detection effect of mismatch steganography analysiscan be beneficially improved, and great significance is produced to the mismatch steganography analysis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Nitride light-emitting diode structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104900773ALow priceMature technologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchQuantum well
The invention provides a nitride light-emitting diode structure and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a glass substrate; stacking a buffer layer structure on the glass substrate, wherein the buffer layer structure is composed of cycles of SiAlN layers and AlGaN layers, and the number of cycles is 1-5; and then, growing a non-doped gallium nitride layer, an N-type layer, a quantum well structure layer and a P-type layer sequentially. According to the invention, the substrate is made of glass which is cheap and technologically mature, and the SiAlN and AlGaN buffer layer is grown on the substrate. Therefore, the constant of lattice mismatch between the substrate and an epitaxial layer is improved, and the photoelectric performance of light-emitting diodes is improved.
Owner:ANHUI SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
ZnO-based nanorod/ quantum well composite ultraviolet light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106601884AAchieving pure UV electroluminescenceReduce Mismatch ProblemsSemiconductor devicesExciton binding energyQuantum well
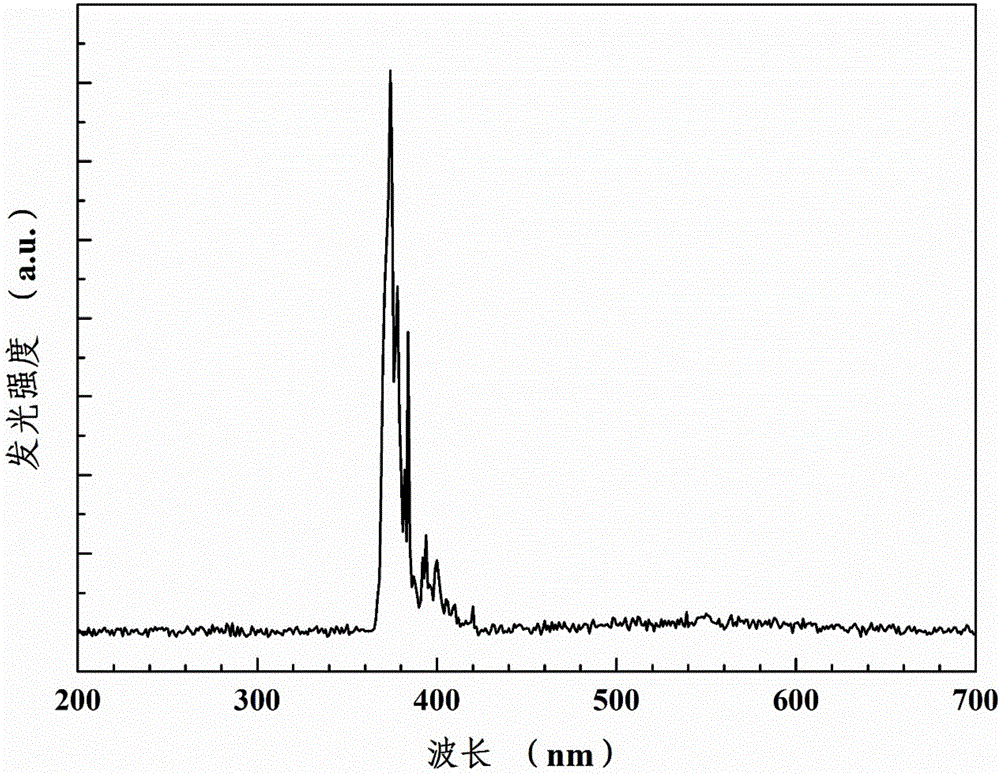
The invention discloses a ZnO-based nanorod / quantum well composite ultraviolet light-emitting diode and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode comprises a substrate. The substrate is provided with an n-type ZnO thin film layer, a ZnO nanorod array, a ZnO / Zn1-xMgxO quantum well active layer, a p-type NiO thin film layer and a first electrode from the bottom up in sequence. A second electrode and the ZnO nanorod array are arranged on the n-type ZnO thin film layer in parallel; and the ZnO / Zn1-xMgxO quantum well active layer covers the ZnO nanorod array, 0.1<=x<=0.3. The light-emitting diode electroluminescent peak wavelength is around 374 nm, and full width at half maximum of the photoluminescence peak is around 17 nm; the light-emitting diode structure can give full play to the advantages of direct broadband gap and high exciton binding energy of the ZnO material and the like, so that polarization effect is reduced effectively, material and interface quality can be improved, effective area of the active layer is increased, light extraction efficiency is improved and spectrum monochromaticity is improved; and besides, low-temperature preparation can be realized, cost is low and industrialization can be realized easily.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112366261AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce mismatchSemiconductor devicesMolecular physicsMaterials science
The invention discloses a light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of light emitting diode manufacturing. The AlGaN sub-layers and the first GaNsub-layers which are alternately stacked can release certain stress in the growth process, and dislocation defects accumulated in the first composite layer are few. The buffer layer further comprisesa second composite layer stacked on the first composite layer, and the structure of the second composite layer can be a second GaN sub-layer and a MgN sub-layer which are alternately stacked, and a second GaN sub-layer and a BN sub-layer which are alternately stacked. The Mg atoms and B atoms in the BN sub-layer are small in particle size, vacancies generated by defects and dislocations in crystals can be filled in the growth process, so that the formation of the dislocations and the defects is reduced, the crystal quality of the buffer layer is improved, and the luminous efficiency of the finally obtained light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer is also improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Epitaxial structure of Si-based gallium nitride device
PendingCN111063726AHigh electron mobilityImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchGallium nitride
An epitaxial structure of a Si-based gallium nitride device belongs to the technical field of microelectronics. The epitaxial structure comprises a substrate, a nucleating layer, a buffer layer, a high-resistance layer, a channel layer and a barrier layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, wherein the nucleating layer is formed by ALN / GaN cyclic growth, and the buffer layer is formed by InN / SiN / GaN in a cyclic growth mode and comprises an InN crystal nucleus layer, a reticular structure SiN thin layer and a GaN filling layer. According to the invention, the ALN / GaN nucleating layer is circularly grown to relieve lattice mismatch and thermal mismatch of the substrate and the epitaxial layer, and the InN / SiN / GaN buffer layer can greatly reduce the dislocation density of the material and improve the lattice quality, thereby improving the electron mobility, breakdown voltage, leakage current and other characteristics of the HEMT device.
Owner:西安电子科技大学芜湖研究院
Light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112397622AImprove crystal qualityReduce Mismatch ProblemsSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of light emitting diode manufacturing. A buffer layer comprises a first sub-layer and a second sub-layer, and the first sub-layer plays a role in transition. The second sub-layer stacked on the first sub-layer comprises second GaN layers and BGaN layers which are alternately stacked. On one hand, lattice mismatch is relieved, a good foundation is provided for growth of a subsequent epitaxial structure, and on the other hand, the BGaN layers can be inserted into or fill blank positions caused by dislocation due to the fact that the volume of B atoms is small, and defects existing in the buffer layer are reduced. Moreover, B atoms can play a certain role in positioning, so that dislocation is prevented from continuing moving into an n-type GaN layer and a multi-quantum well layer, and the crystal quality of the finally obtained light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer iseffectively improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Surface treatment method of graphite substrate and preparation method of TaC coating
The invention discloses a surface treatment method of a graphite substrate and a preparation method of a TaC coating, and the surface treatment method comprises the following steps: cleaning and drying the graphite substrate, putting the graphite substrate into a reaction chamber of plasma modification equipment, closing an air inlet valve, vacuumizing the reaction chamber, and then introducing oxygen or argon to fill the reaction chamber; adjusting the air inlet valve to stabilize the vacuum degree of the reaction chamber at 10-100Pa, starting to discharge a radio frequency power supply, andperforming oxygen plasma or argon plasma to bombard the surface of the graphite substrate so as to increase the roughness of the surface of the graphite substrate and improve the activity of the surface of the graphite substrate; and performing TaC coating deposition after treatment by the method. The formed TaC coating can be tightly combined with a graphite substrate and is not easy to fall off,and the thermal shock resistance is greatly improved; and the process is simple, efficient, low in energy consumption, low in production cost and short in production period.
Owner:湖南中科顶立技术创新研究院有限公司 +1
Method for preparing non-polar zinc oxide thin film on silicon-based substrate
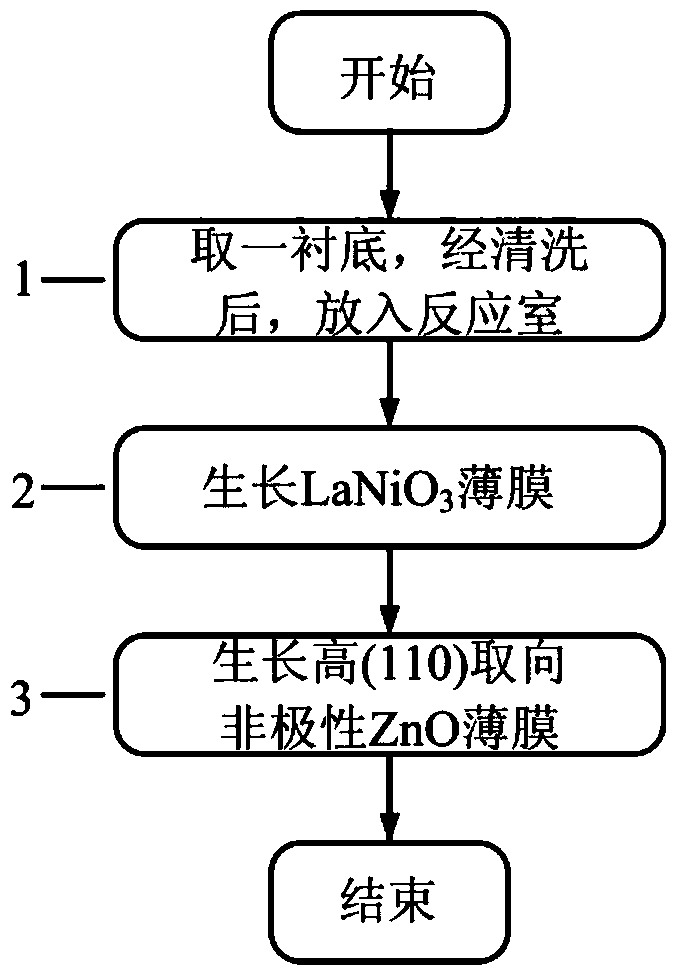
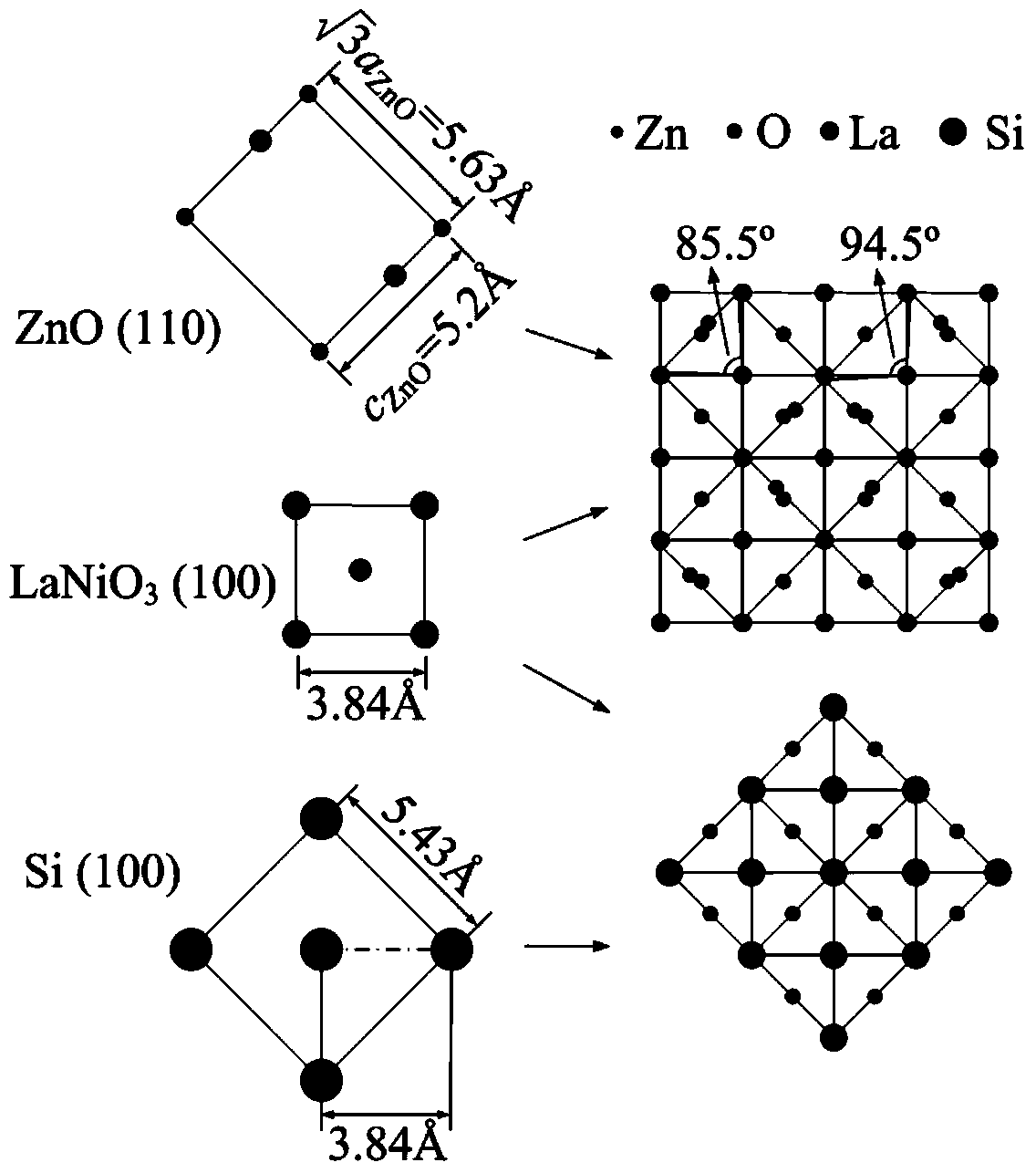
InactiveCN103643212AOrientation controlControl the degree of crystallizationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotoluminescenceLuminescence
The invention provides a method for preparing a high (110) oriented non-polar zinc oxide thin film on a Si-based substrate. The method comprises the steps of taking Si as a substrate, taking a ZnO target material as a zinc source and an oxygen source, taking Ar as working gas, taking O2 as reaction gas, adopting a magnetron sputtering method, controlling the vacuum degree below 8*10<-4>Pa, controlling the growth temperature at 100-400 DEG C and simultaneously introducing Ar and O2 in a certain proportion to prepare the thin film. The method comprises the steps of growing a (100) oriented LaNiO3 (LNO) buffer layer on the Si-based substrate and growing a high (110) oriented ZnO thin film on a (100) LNO / Si substrate. By adding the LNO buffer layer, the growth of the high (110) oriented non-polar ZnO thin film can be effectively realized, the band-edge emission in a photoluminescence spectrum is obviously enhanced, and a defect luminescence peak is obviously weakened.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Multi-layered composite tube with ceramic lining and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN100432010CImprove mechanical propertiesIncreased interlaminar shear strengthCeramic coatingSteel tube
The invention relates to a multilayer ceramic lining composite tube and its preparation method, is a composite steel tube taking intermetallic compound and titanium compound as ceramic lining, which belongs to the technique field of gradient composite material. The invention conqueres the disadvantage of bad mechanical combine construction and mechanics property of ceramic coating and metal coating, when ceramic lining composite tube is prepared with self-spread centrifugal burning method. The invention is characterized in that filling mixture of pulverous reaction raw material in the steel tube and fixing it on the rotary mechanism, When rotate speed is at 1500-2000rpm, igniting reaction raw material with ignition device and making them form high-heat self-spread reaction; the products synthesized form layered lining layer on the inwall of the steel tube according to different density; the construction of the lining layer synthesized is ordinally steel tube, intermetallic compound, titanium compound ceramic, alumina ceramic along radial. The bonding strength, mechanics property, abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance had enhanced remarkably in this invention.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
LED epitaxial growth method suitable for small-spacing display screen
ActiveCN111769180AReduce Mismatch ProblemsReduce tiltSemiconductor devicesPhysical chemistryElectron blocking layer
The application discloses an LED epitaxial growth method suitable for a small-spacing display screen. The method comprises the following steps: processing a substrate; growing a low-temperature bufferlayer GaN; growing an undoped GaN layer; growing a Si-doped N type GaN layer; growing a multi-quantum well layer; growing an AlGaN electronic barrier layer; growing a Mg-doped P type GaN layer; and then performing cooling. The growth of the multi-quantum well layer sequentially comprises the steps: growing an InGaN well layer; growing an H2 atmosphere InGaN: Si layer; growing an N2 atmosphere InGaN: Mg layer; growing an H2 and N2 mixed atmosphere InGaN: Mg / Si layer; growing an InGaN protective layer; and growing a GaN barrier layer. The method provided by the invention solves the problem thatthe blue shift amount of the light emitting wavelength of the LED is large in the existing LED epitaxial growth, and the light emitting efficiency of the LED is improved, the working voltage is reduced and the anti-static capability is enhanced.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
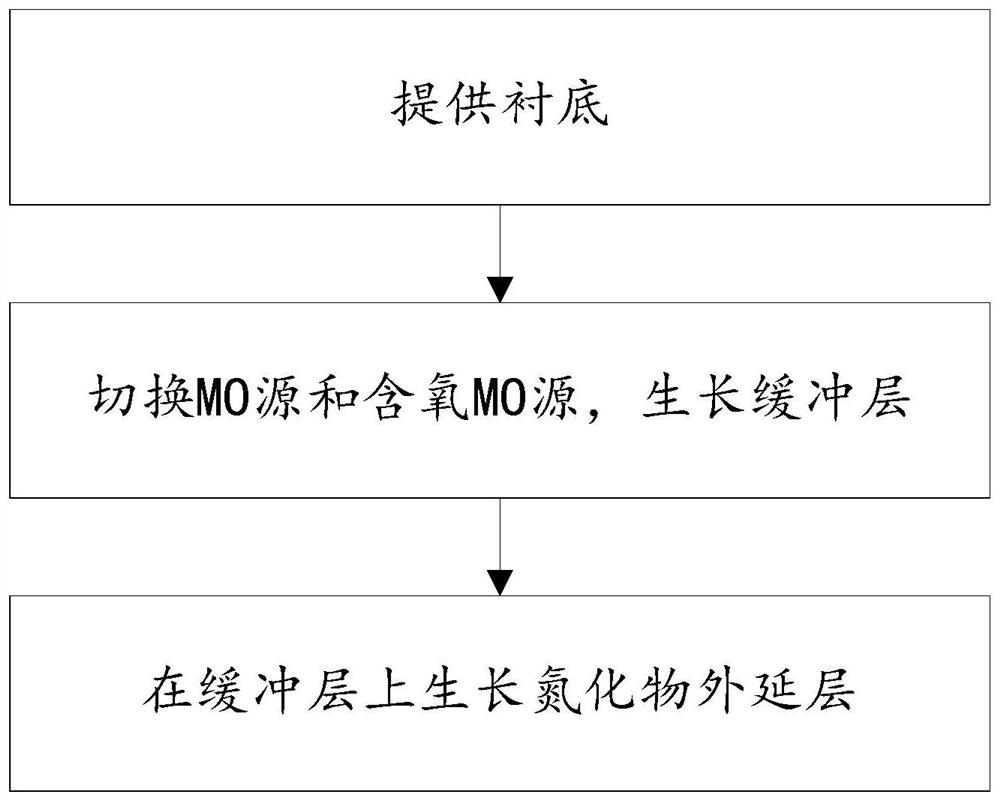
Nitride epitaxial layer preparation method and semiconductor epitaxial wafer thereof
ActiveCN114574959AQuality improvementImprove distribution uniformityPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureLattice mismatchPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a nitride epitaxial layer preparation method and a semiconductor epitaxial wafer thereof. The method comprises the following steps: providing a substrate; a buffer layer is grown on the substrate, the buffer layer comprises a nitride buffer layer and an oxygen-containing buffer layer, and the nitride buffer layer and the oxygen-containing buffer layer are grown by alternately switching an MO source and an oxygen-containing MO source in a periodic cycle mode to serve as precursor materials; and growing a nitride epitaxial layer on the buffer layer. The oxygen-containing buffer layer is grown through the oxygen-containing MO source process, on one hand, the in-situ growth oxygen-containing buffer layer has good lattice mismatch relaxation, relieves lattice adaptation and releases the stress of the substrate and the epitaxial layer, and a high-quality gallium nitride epitaxial layer with low dislocation density can be obtained; the distribution uniformity and nucleation density of oxygen-containing buffer crystal grains are improved, and a high-quality nitride epitaxial layer is obtained; on the other hand, the technological process is simple, pollution risks in the substrate and epitaxial layer transfer process are reduced, repeatability is good, and large-scale production is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF ADVANCED SEMICON CO LTD
Method for growing gallium nitride film on silicon substrate
InactiveCN110752146AReduce Mismatch ProblemsImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyLattice mismatchGallium nitride
The invention discloses a method for growing a gallium nitride film on a silicon substrate. According to the method for growing the gallium nitride film on the silicon substrate, a nitride composite buffer layer is epitaxially grown on the Si substrate, and the nitride composite buffer layer can relieve lattice mismatch and prevent a reflow etching reaction. A group of superlattices are grown on aGaN transition layer, and the superlattices can release part of tensile stress and can filter part of threading dislocation. By adopting the method, the crystal quality of a GaN epitaxial film material can be significantly improved, surface cracks are eliminated, and the GaN epitaxial film material which can be used for device development and application is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING HUAJINCHUANGWEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion
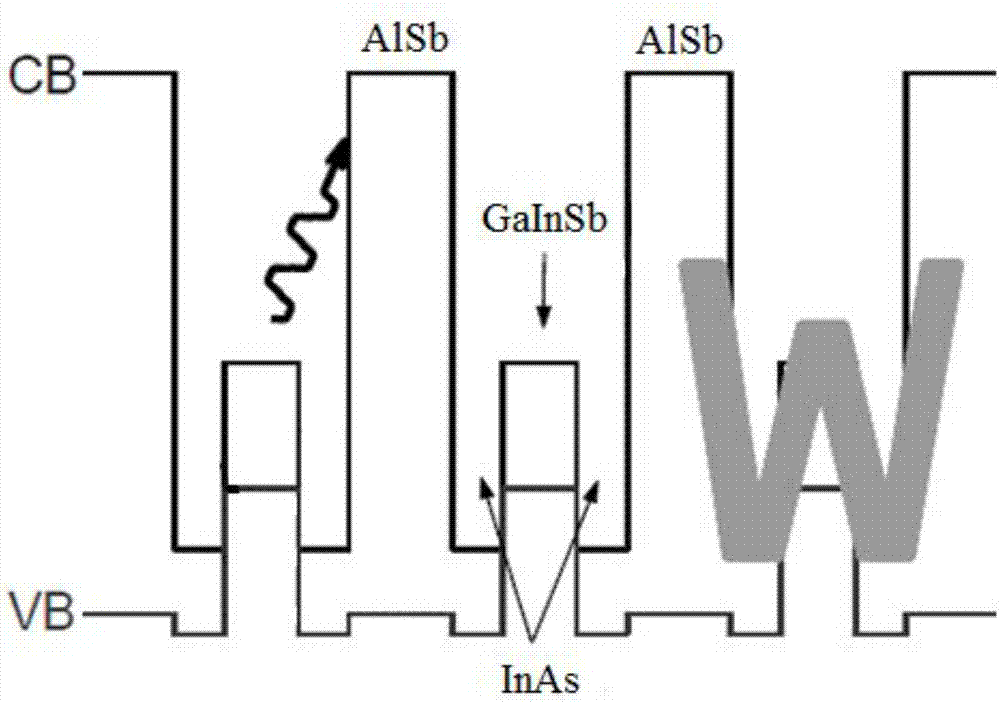
ActiveCN104638517AReduce stressReduce Mismatch ProblemsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellRoom temperature
The invention relates to a W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor lasers. The existing InAs / GaInSb W type antimony-based semiconductor laser is difficult to realize luminescence at room temperature, and is less in output power of luminescence at low temperature (73K). The W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion sequentially comprises a GaSb substrate, a GaSb buffer layer, a P type GaSb contact layer, a P type quantum well, an intrinsic quantum well, an N type quantum well and an N type InAs contact layer from bottom to top, wherein the P type quantum well, the intrinsic quantum well and the N type quantum well respectively have a multi-period structure; the structure of each single-period quantum well in each multi-period structure is a sandwich structure that a GaInSb hole quantum well is clamped by double InAs electronic quantum wells; the outer layer is a pair of AlSb alloy limiting layers. The W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion is characterized in that the GaInSb hole quantum well is formed by 3 to 9 layers of Ga1-xInxSb layers, wherein x is equal to 0.05-0.35; the value of x of the Ga1-xInxSb layer in the middle is maximal; the Ga1-xInxSb layers on two sides are distributed in 1 to 4 levels from the middle to two sides; the values of x of two Ga1-xInxSb layers at the same level are the same, and the values of x of the Ga1-xInxSb layers from the middle to two sides are gradually reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
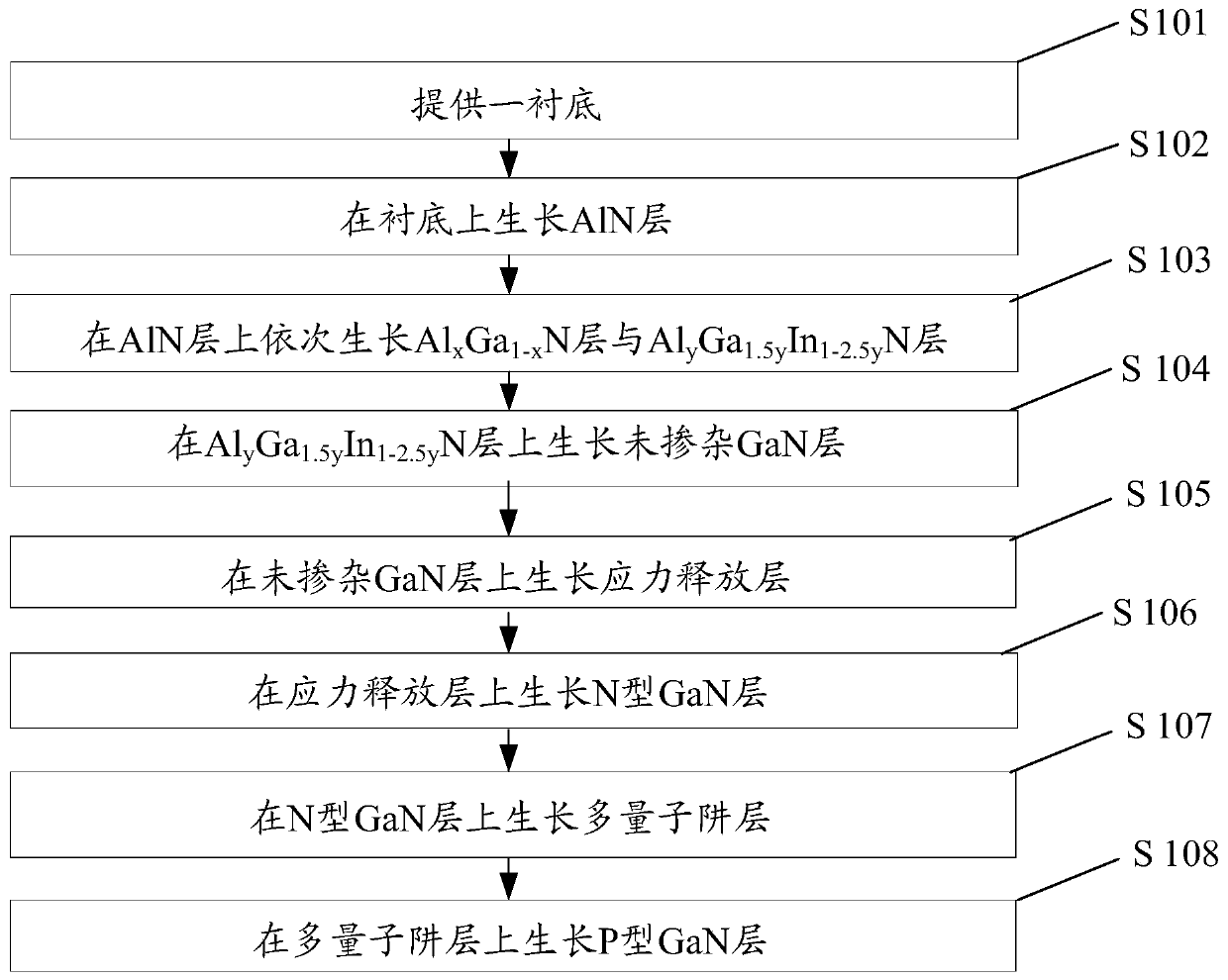
Epitaxial wafer of light-emitting diode and preparation method of epitaxial wafer
ActiveCN109904286AReduce defectsImplementation flawSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses an epitaxial wafer of a light-emitting diode and a preparation method of the epitaxial wafer and belongs to the field of semiconductor optoelectronics. According to the method,an Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer and an Al<y>Ga<1.5y>In<1-2.5y>N layer are sequentially arranged between an AlN layer and an undoped GaN layer, Al components in the Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer and the Al<y>Ga<1.5y>In<1-2.5y>N layer can be within the ranges of 0.4<=x<=1 and 0.2<=y<=0.4, and when the Al components in the Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer and the Al<y>Ga<1.5y>In<1-2.5y>N layer are within the ranges, lattice mismatch between the AlN layer and the undoped GaN layer can be relieved. Moreover, the Al component in the Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer and the Al component in the Al<y>Ga<1.5y>In<1-2.5y>N layer are both graduallyreduced along the growing directions of the two layers, the Al components in the two layers are equal at the interface of the two layers, therefore, connection of the AlN layer and the undoped GaN layer can be well realized, defects generated due to lattice mismatch between the AlN layer and the undoped GaN layer are reduced, the crystal quality of the epitaxial wafer of the finally obtained light-emitting diode is improved, and the luminous efficiency of the finally obtained light-emitting diode is improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
ZnO-based nanorod/quantum well composite ultraviolet light-emitting diode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106601884BAchieving pure UV electroluminescenceReduce Mismatch ProblemsSemiconductor devicesElectricityExciton binding energy
The invention discloses a ZnO-based nanorod / quantum well composite ultraviolet light-emitting diode and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode comprises a substrate. The substrate is provided with an n-type ZnO thin film layer, a ZnO nanorod array, a ZnO / Zn1-xMgxO quantum well active layer, a p-type NiO thin film layer and a first electrode from the bottom up in sequence. A second electrode and the ZnO nanorod array are arranged on the n-type ZnO thin film layer in parallel; and the ZnO / Zn1-xMgxO quantum well active layer covers the ZnO nanorod array, 0.1<=x<=0.3. The light-emitting diode electroluminescent peak wavelength is around 374 nm, and full width at half maximum of the photoluminescence peak is around 17 nm; the light-emitting diode structure can give full play to the advantages of direct broadband gap and high exciton binding energy of the ZnO material and the like, so that polarization effect is reduced effectively, material and interface quality can be improved, effective area of the active layer is increased, light extraction efficiency is improved and spectrum monochromaticity is improved; and besides, low-temperature preparation can be realized, cost is low and industrialization can be realized easily.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112366261BImprove luminous efficiencyReduce mismatchSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeMaterials science
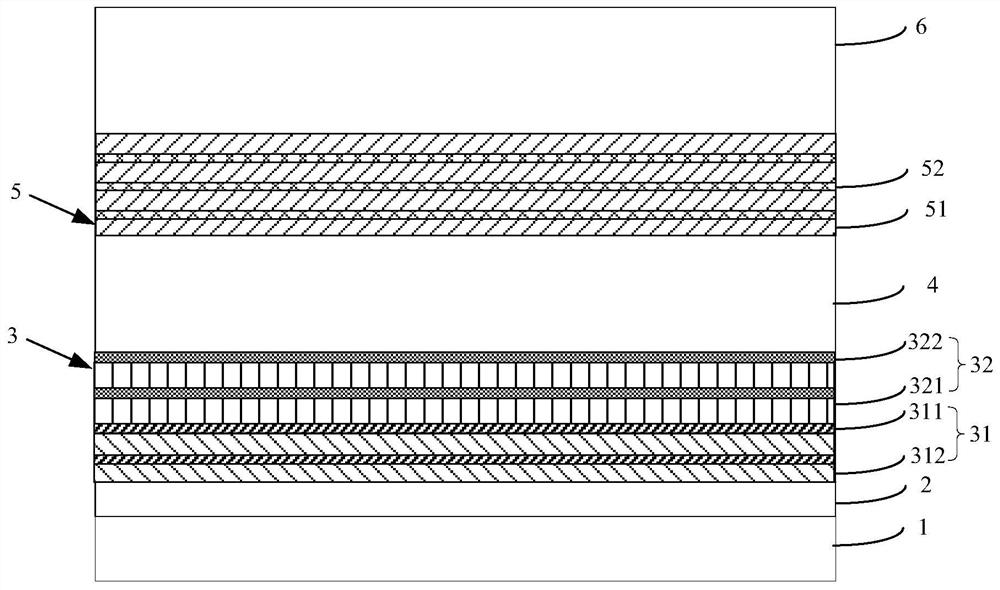
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of light-emitting diode production. The alternately stacked AlGaN sub-layers and the first GaN sub-layer can release certain stress during the growth process, and less dislocation defects will be accumulated in the first composite layer. The buffer layer also includes a second composite layer stacked on the first composite layer, and the structure of the second composite layer can be alternately stacked second GaN sublayers and MgN sublayers, alternately stacked second GaN sublayers and BN sublayers . Mg atoms and B atoms in the BN sublayer have small particle sizes, which can fill the vacancies generated by defects and dislocations in the crystal during growth, thereby reducing the formation of dislocations and defects, improving the crystal quality of the buffer layer, and finally obtaining The luminous efficiency of the light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer is also improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
W-type antimony-based semiconductor laser with ga In ratio gradient
ActiveCN104638517BReduce stressReduce Mismatch ProblemsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellRoom temperature
The invention relates to a W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion, which belongs to the technical field of semiconductor lasers. The existing InAs / GaInSb W type antimony-based semiconductor laser is difficult to realize luminescence at room temperature, and is less in output power of luminescence at low temperature (73K). The W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion sequentially comprises a GaSb substrate, a GaSb buffer layer, a P type GaSb contact layer, a P type quantum well, an intrinsic quantum well, an N type quantum well and an N type InAs contact layer from bottom to top, wherein the P type quantum well, the intrinsic quantum well and the N type quantum well respectively have a multi-period structure; the structure of each single-period quantum well in each multi-period structure is a sandwich structure that a GaInSb hole quantum well is clamped by double InAs electronic quantum wells; the outer layer is a pair of AlSb alloy limiting layers. The W type antimony-based semiconductor laser with gradually varied Ga In proportion is characterized in that the GaInSb hole quantum well is formed by 3 to 9 layers of Ga1-xInxSb layers, wherein x is equal to 0.05-0.35; the value of x of the Ga1-xInxSb layer in the middle is maximal; the Ga1-xInxSb layers on two sides are distributed in 1 to 4 levels from the middle to two sides; the values of x of two Ga1-xInxSb layers at the same level are the same, and the values of x of the Ga1-xInxSb layers from the middle to two sides are gradually reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and growth method thereof
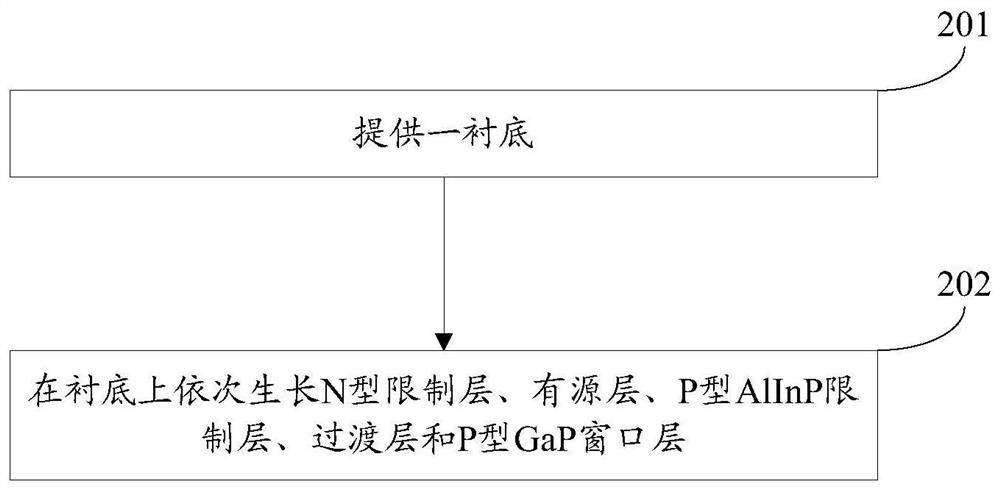
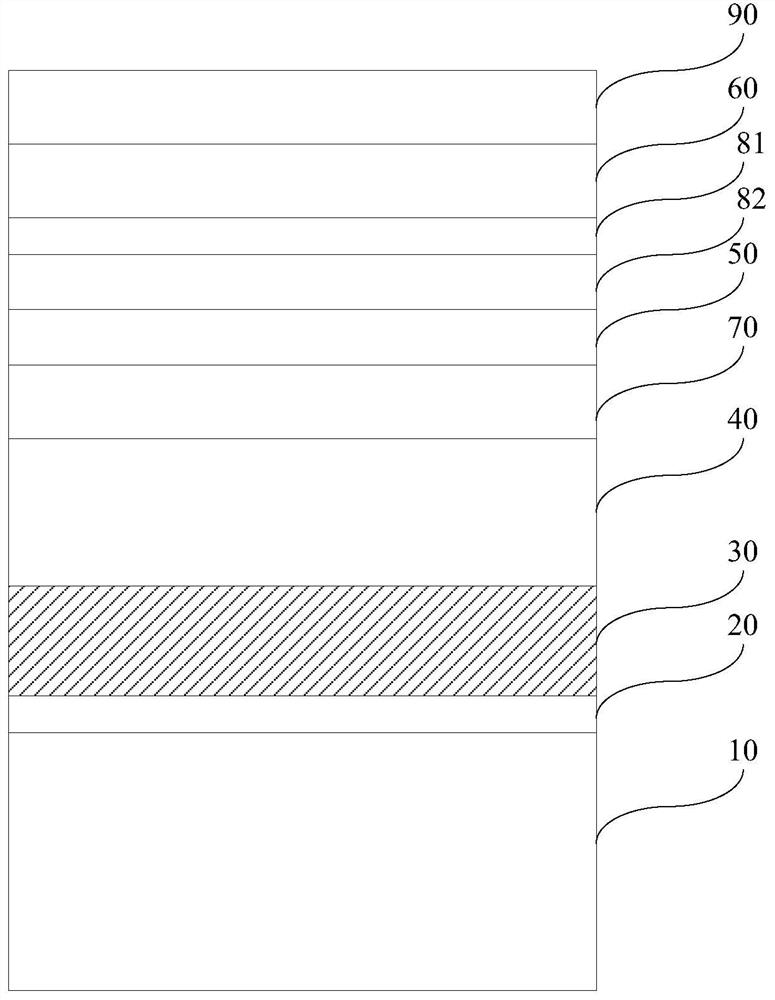
ActiveCN110379898BAffect light transmittanceAffect light transmittance reductionSemiconductor devicesCrystallographyActive layer
The invention discloses a light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a growth method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductors. The epitaxial wafer comprises a substrate, an N-type limiting layer, an active layer, a P-type AlInP limiting layer, a transition layer and a P-type GaP window layer, which are stacked in sequence. The transition layer comprises (N+1) first sub-layers and N second sub-layers, which are alternately stacked; each first sub-layer is an AlGaInP layer; the content of the Al component in the (N+1) first sub-layers is gradually decreased in the direction from the P-type AlInP limiting layer to the P-type GaP window layer, and the content of the Ga component in the (N+1) first sub-layers is gradually increased in the direction from the P-type AlInP limiting layer to the P-type GaP window layer; each second sub-layer is a GaP layer, and the total thickness of the N second sub-layers is 1 / 200-1 / 20 of the total thickness of the (N+1) first sub-layers. The light-emitting efficiency of an LED can be improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK SUZHOU
Semiconductor HEMT device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN113097163AReduces the possibility of crackingNot easy to fall offSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCarbon filmEngineering
The invention provides a semiconductor HEMT device and a manufacturing method thereof. The semiconductor HEMT device comprises: a substrate; a heat conduction layer which is located on the surface of one side of the substrate, and comprises a plurality of supporting structures arranged at intervals and a heat conduction structure, wherein the supporting structures are located on the surface of one side of the substrate; the heat conduction structure is located on the surface, on the same side as the supporting structures, of the substrate, and gaps among the multiple supporting structures are filled with the heat conduction structure; and an insulating layer which covers the surface of the side, back to the substrate, of the heat conduction structure, and further covers the surfaces of the sides, back to the substrate, of the multiple supporting structures, wherein the heat conduction structure is a carbon film. According to the semiconductor HEMT device, through the arrangement of the heat conduction layer, stress concentration caused by thermal mismatch of the device can be reduced, and the possibility of cracking of the device is reduced.
Owner:深圳市红与蓝企业管理中心(有限合伙)
A gallium nitride-based light-emitting diode and its preparation method
ActiveCN105870278BPromote perfectionImprove and adjust warpageSemiconductor devicesLattice mismatchGallium nitride
The invention discloses a gallium nitride based light emitting diode and a preparation method therefor, and belongs to the technical field of the semiconductor. The gallium nitride based light emitting diode comprises a sapphire substrate, and a buffer layer, a non-doped GaN (gallium nitride) layer, a stress improvement layer, an N type GaN layer, an active layer, a P type electron barrier layer and a P type GaN layer which are laminated on the sapphire substrate in sequence, wherein the stress improvement layer is formed by elements of Al, Ga and N under the atmosphere of N2 and H2 at a volume ratio of 2:1 to 1:1; and the surface of the stress improvement layer is uneven. According to the gallium nitride based light emitting diode, the stress improvement layer which is formed by the elements of Al, Ga and N under the atmosphere of N2 and H2 at a volume ratio of 2:1 to 1:1 is laminated between the non-doped GaN layer and the N type GaN layer, so that the lattice mismatch between the sapphire and the GaN is relieved, and the crystal quality of the light emitting diode is improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK SUZHOU
A gallium nitride-based light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and its preparation method
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com