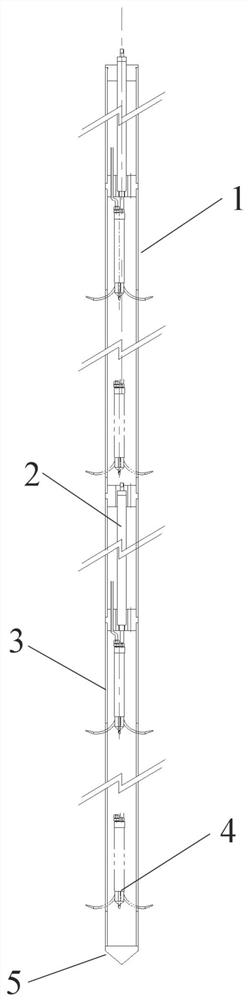
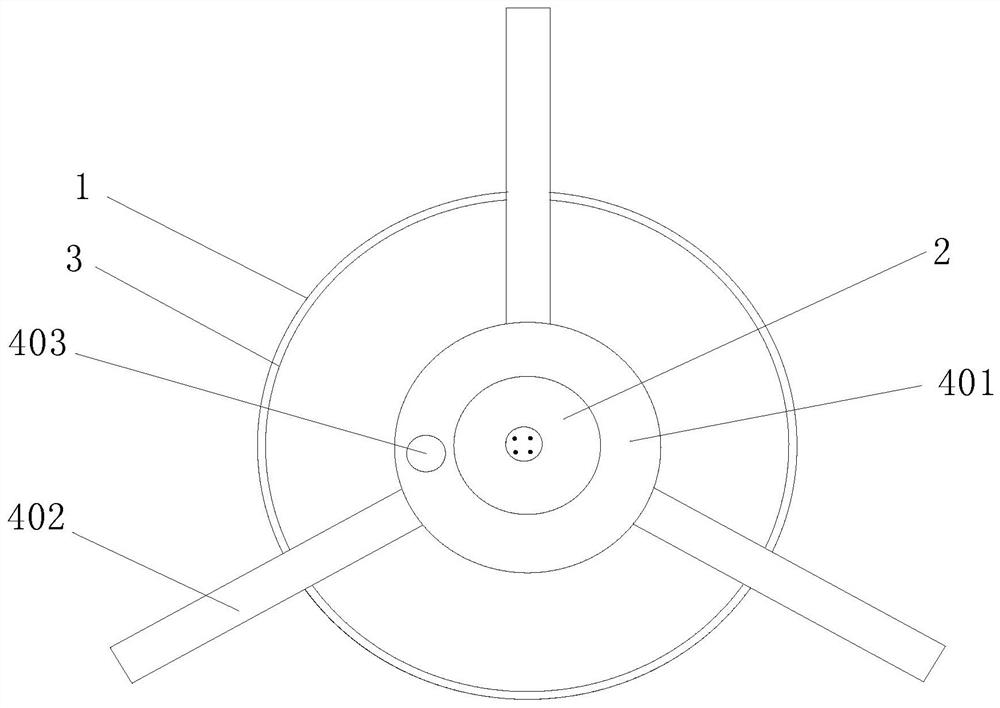
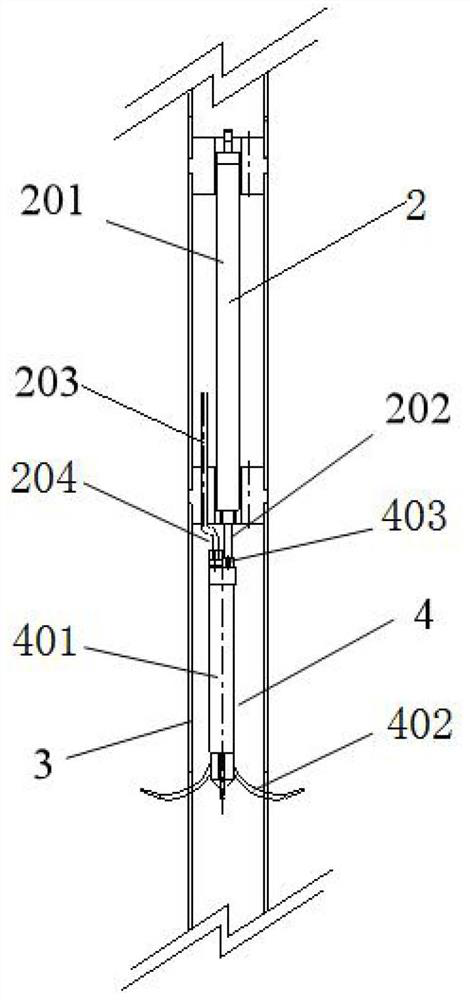
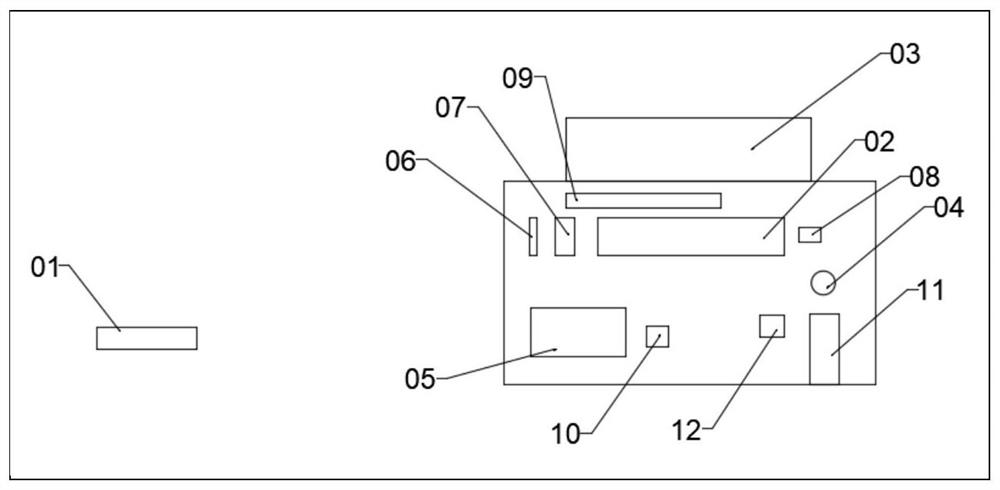
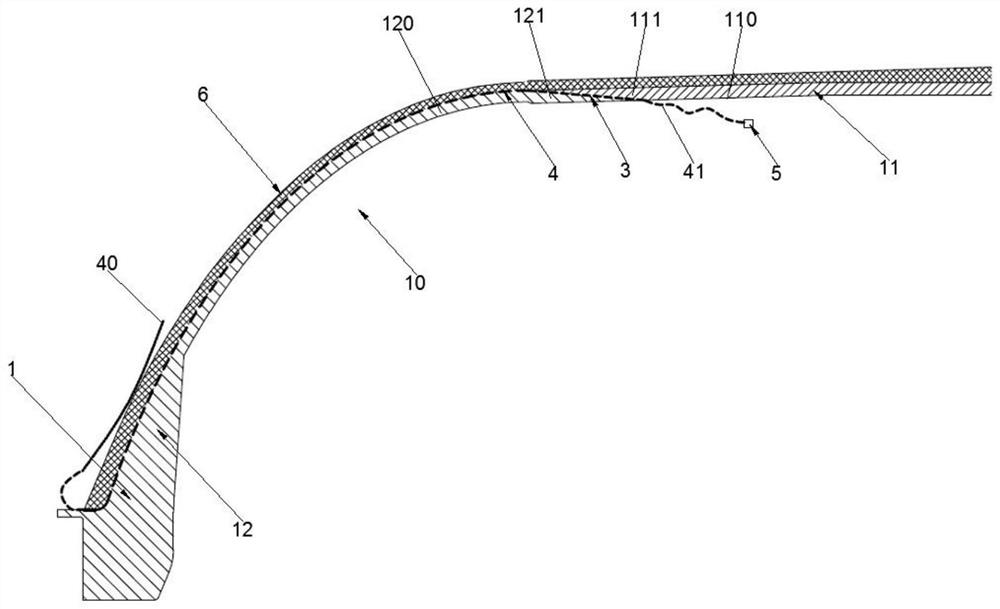
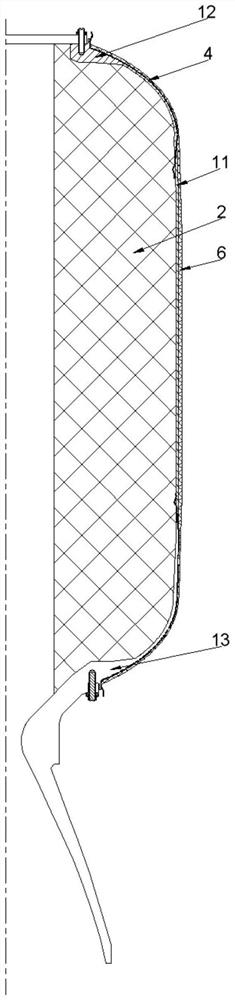
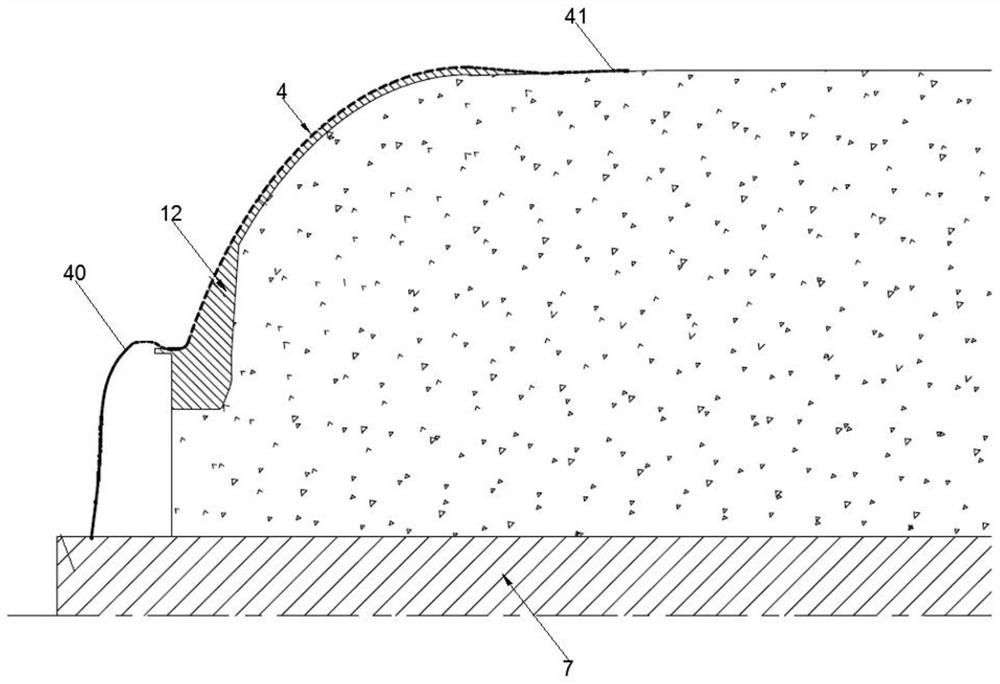
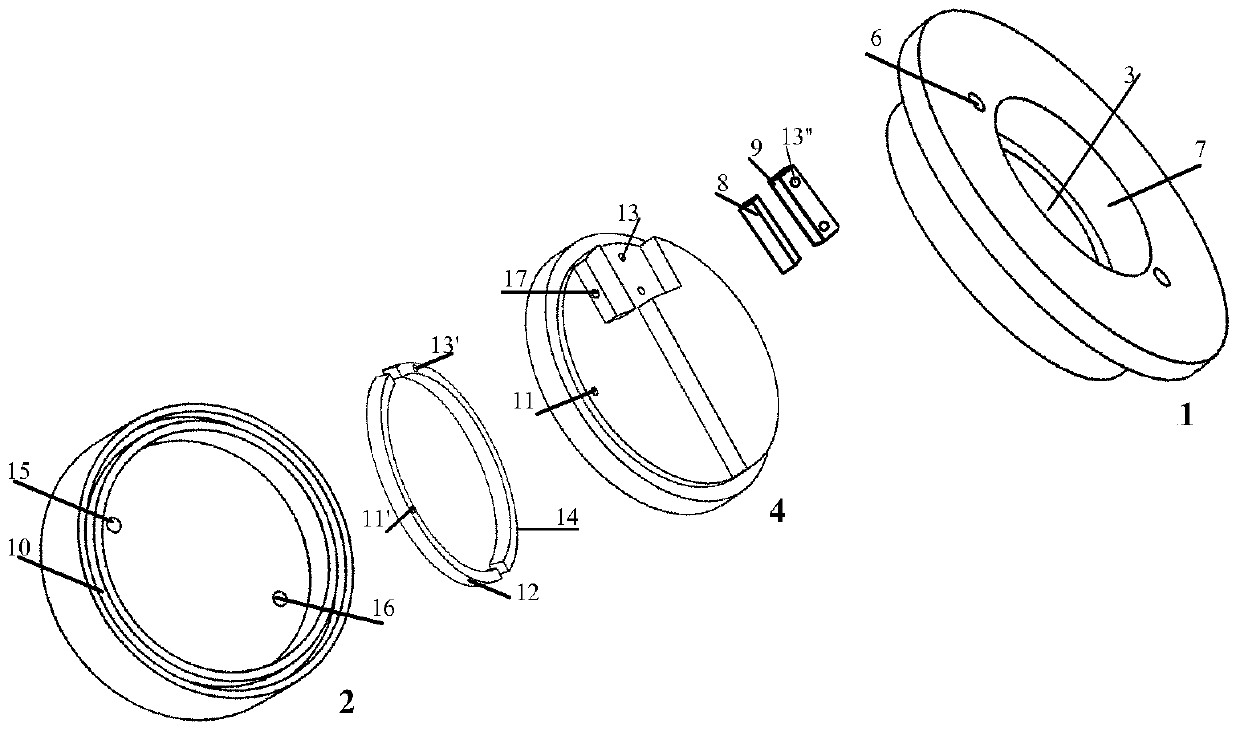
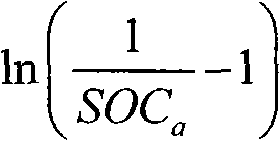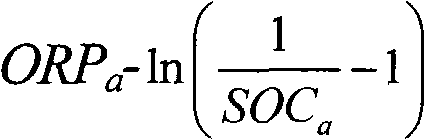Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Realize in-situ monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
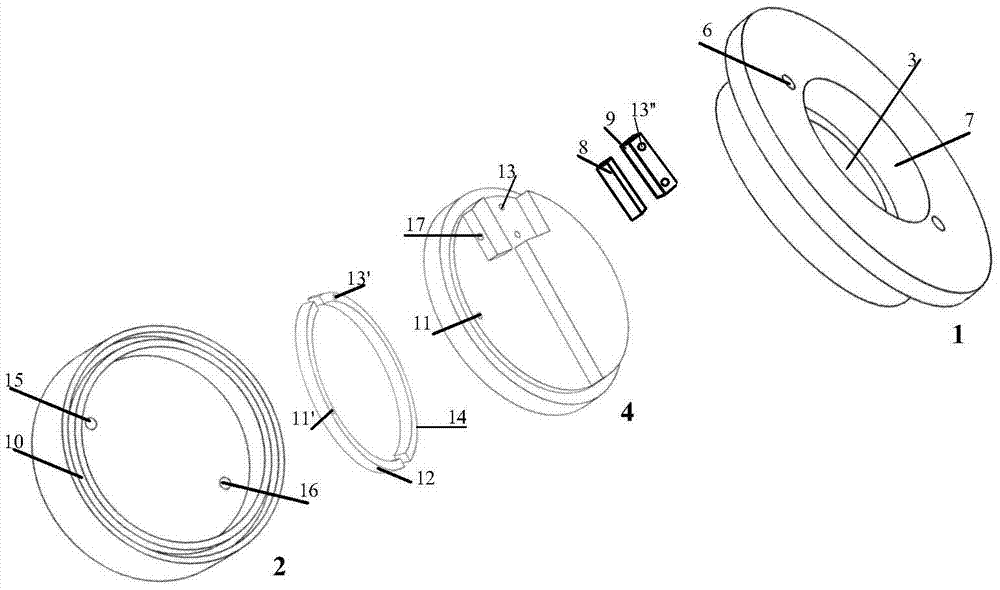
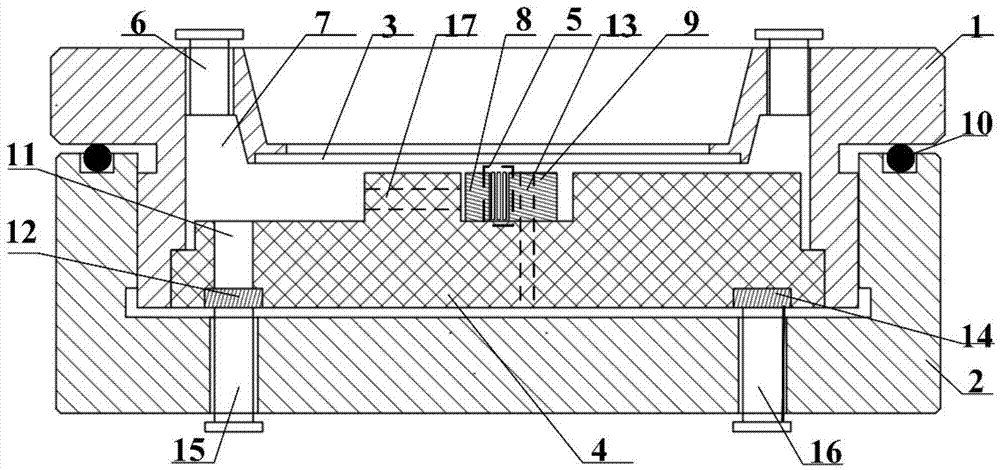
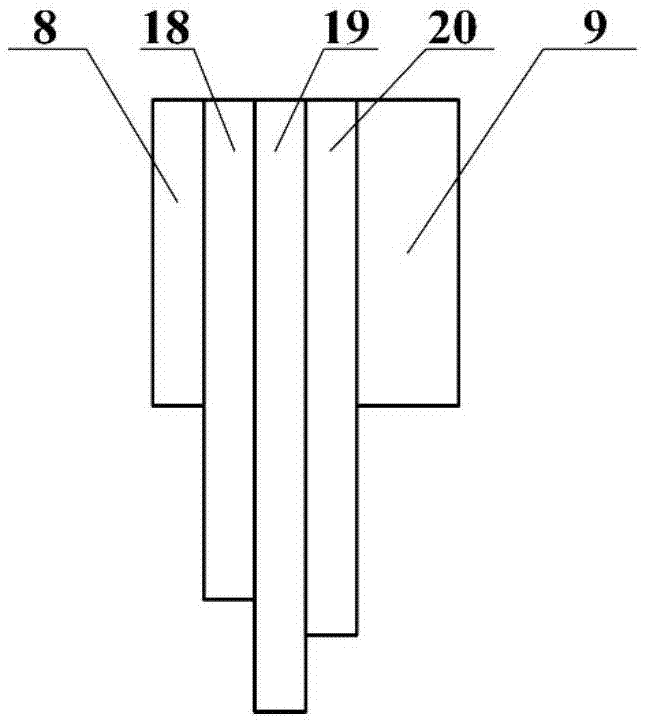
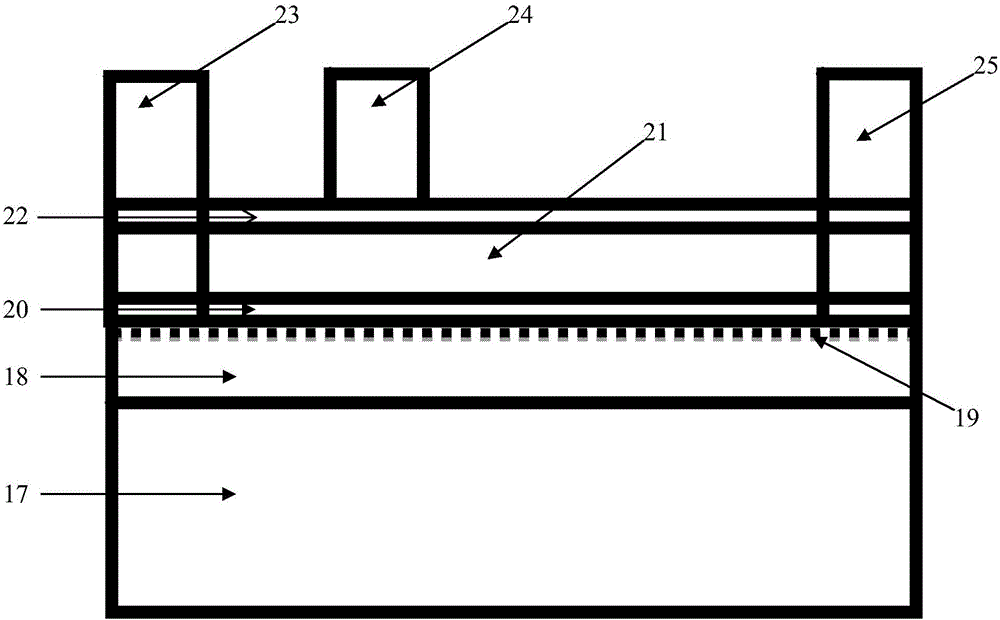
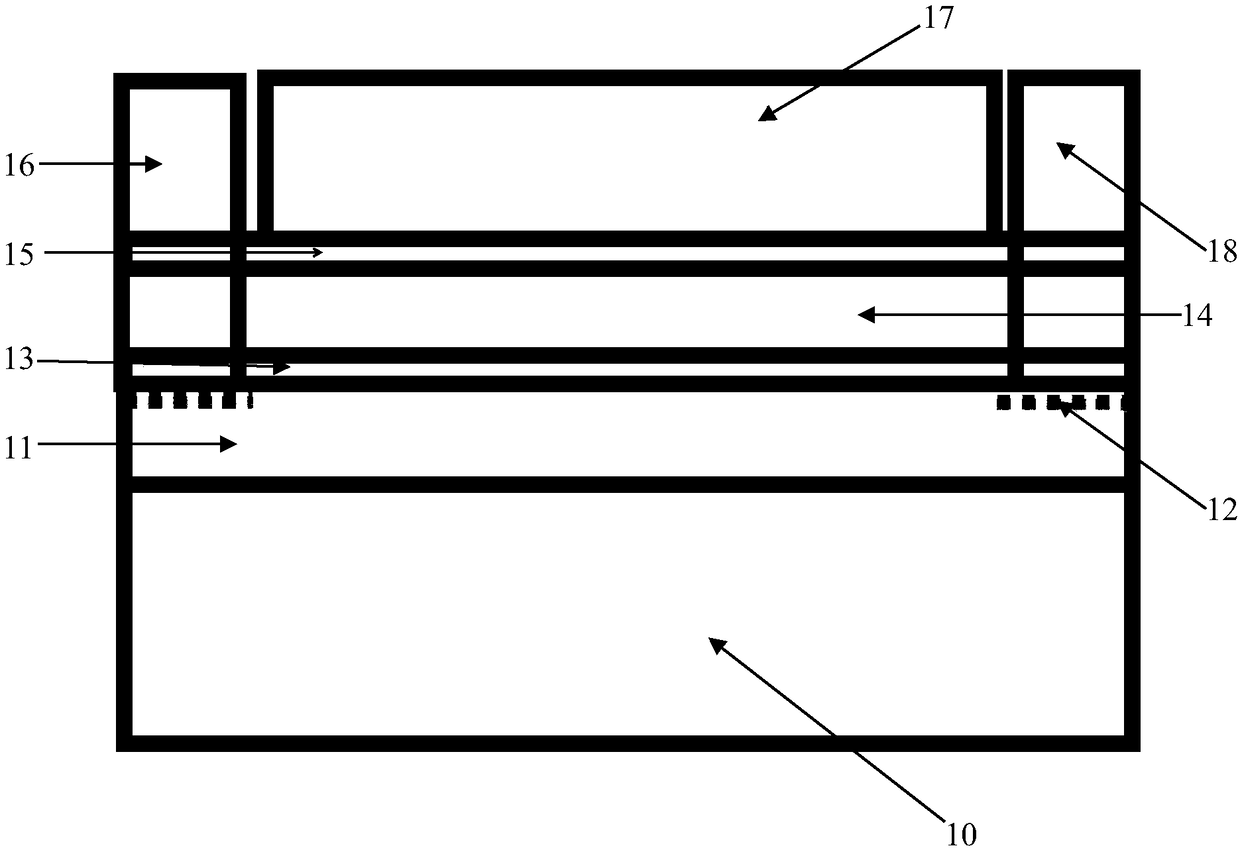
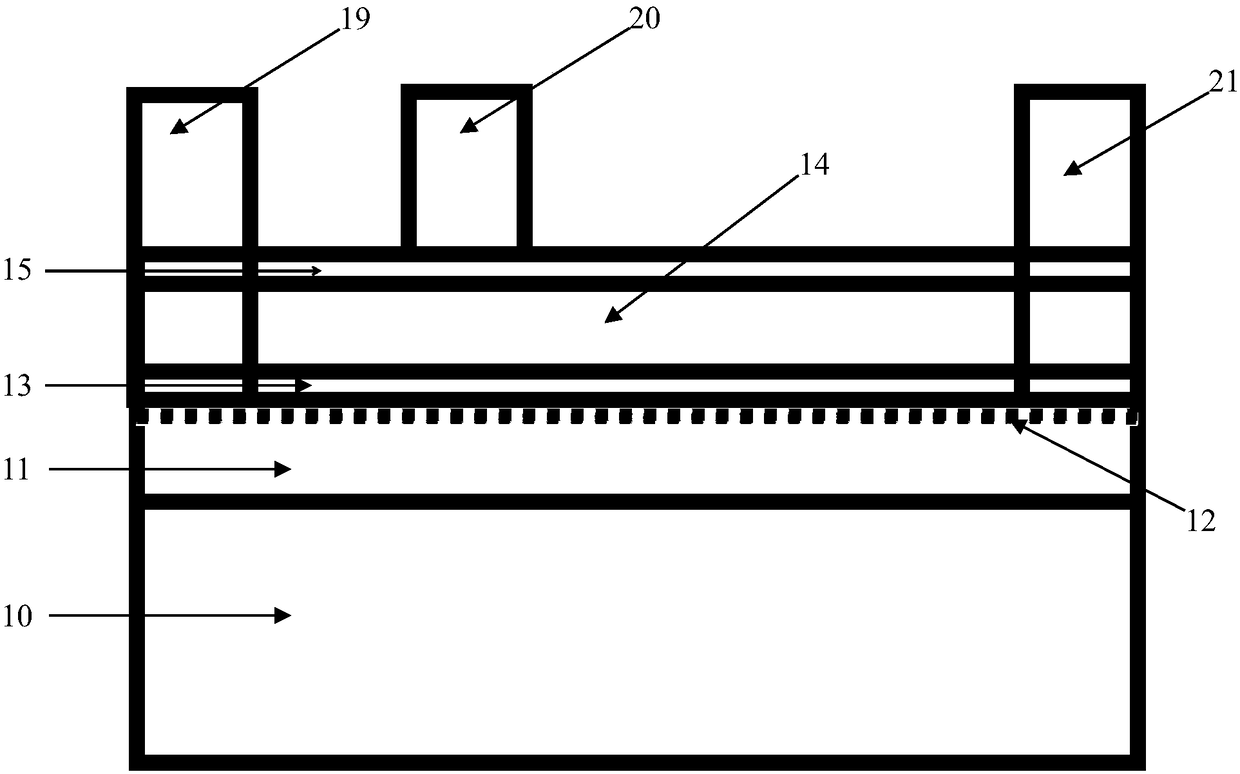
In-situ monitoring method of state of charge of anode electrolyte of vanadium battery
InactiveCN101968532ARealize in-situ monitoringRegenerative fuel cellsSecondary cellsVanadium redox batteryState of charge
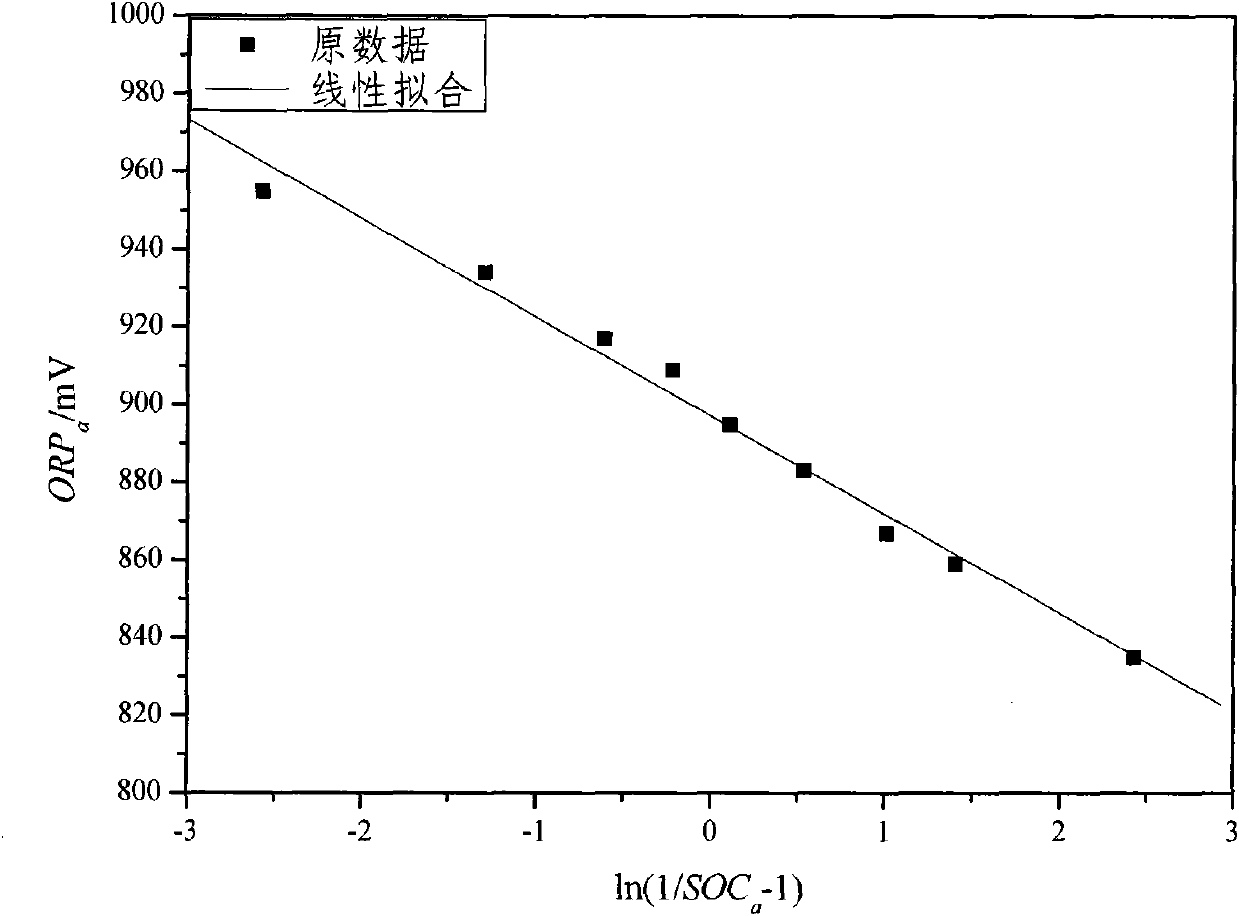
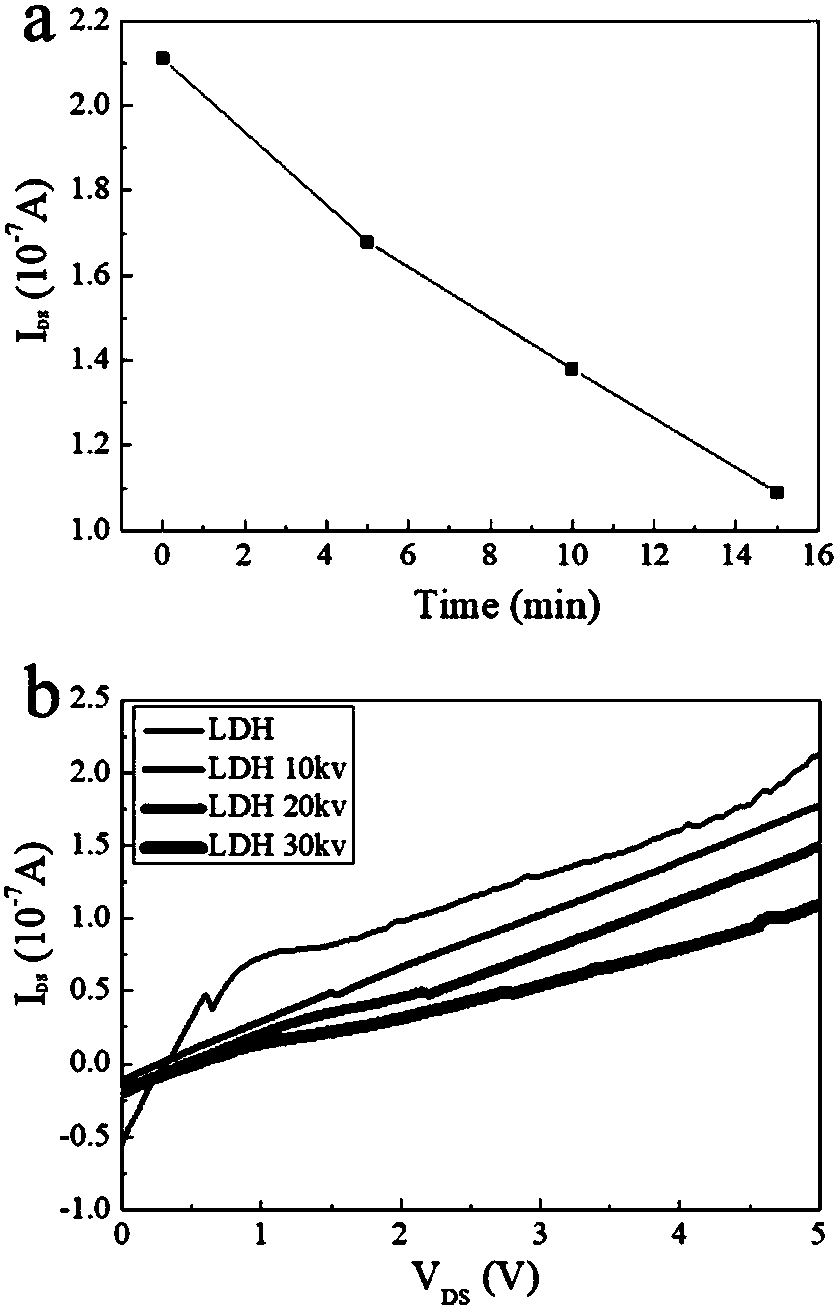
The invention relates to the monitoring technology of the state of charge (SOC) of electrolyte of a vanadium redox flow battery, in particular to an in-situ monitoring method of the SOC of the anode electrolyte of the battery. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the oxidation reduction potential value ORPa of the anode electrolyte of the vanadium redox flow battery; establishing a relation equation according to the principle that the ORPa value is in linear relation with SOCa (the SOC of the anode electrolyte) in an open interval (0,100%), and then performing temperature correction and temperature substitution on the equation to obtain an ORPa-SOCa relation equation which has universality on the temperature of the anode electrolyte; and comparing the SOCa value calculated by the equation with the SOCa value measured by a potentiometric titration method to obtain the error of less than plus or minus 1.50%, thus finally realizing in-situ monitoring of the SOC of the anode electrolyte.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
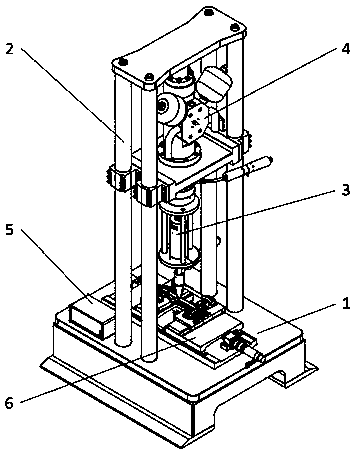
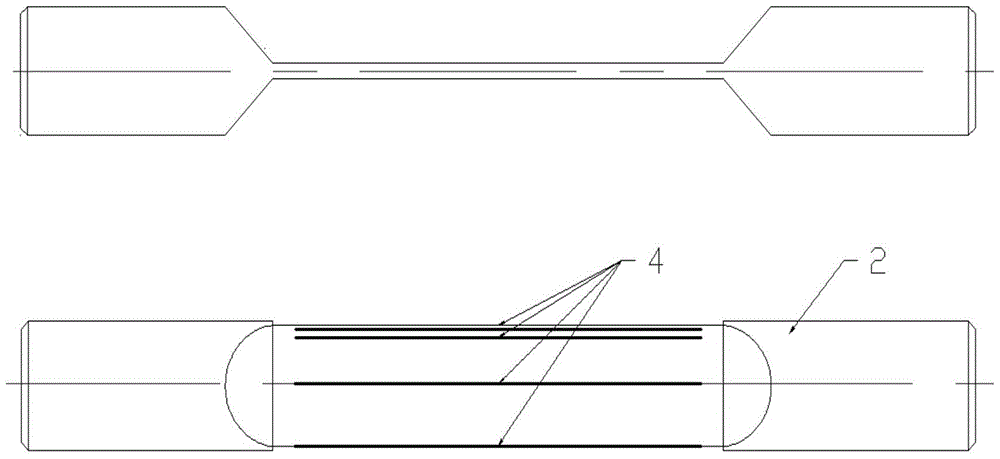
Device and method for testing fatigue mechanical property of material under tensile-bending composite load
PendingCN109883833ARealize in-situ monitoringNovel structureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesScientific instrumentEngineering
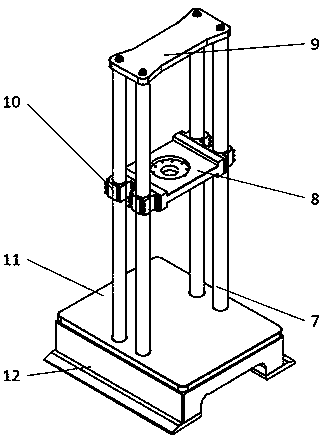
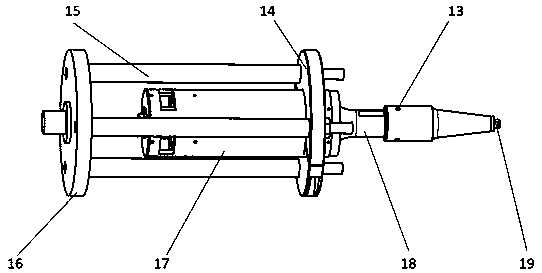
The invention relates to a device and a method for testing the fatigue mechanical property of a material under a tensile-bending composite load, and belongs to the field of precision scientific instruments and material testing. The device comprises a vibration isolation base, a supporting frame, an ultrasonic loading module, a hydraulic loading module, a tensile loading module and an ultrasonic flaw detection module; the supporting frame is connected with the vibration isolation base; the hydraulic loading module is connected with the supporting frame through a connecting flange; the ultrasonic loading module is connected with the hydraulic loading module through a thread; and the tensile loading module and the ultrasonic flaw detection module are arranged on the vibration isolation base.The device has the advantages as follows: high-frequency and high-load cross-range loading can be realized; ultrahigh-frequency bending fatigue loading and tensile-bending static dynamic composite load loading can be realized; and the tensile loading module can ensure accurate centering of tested material samples. The tested material samples made of different materials and having different sizes can be subjected to high-frequency fatigue testing under the static dynamic composite load; and a reliable means is provided for service performance analysis of key materials in aerospace and numerousfields.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
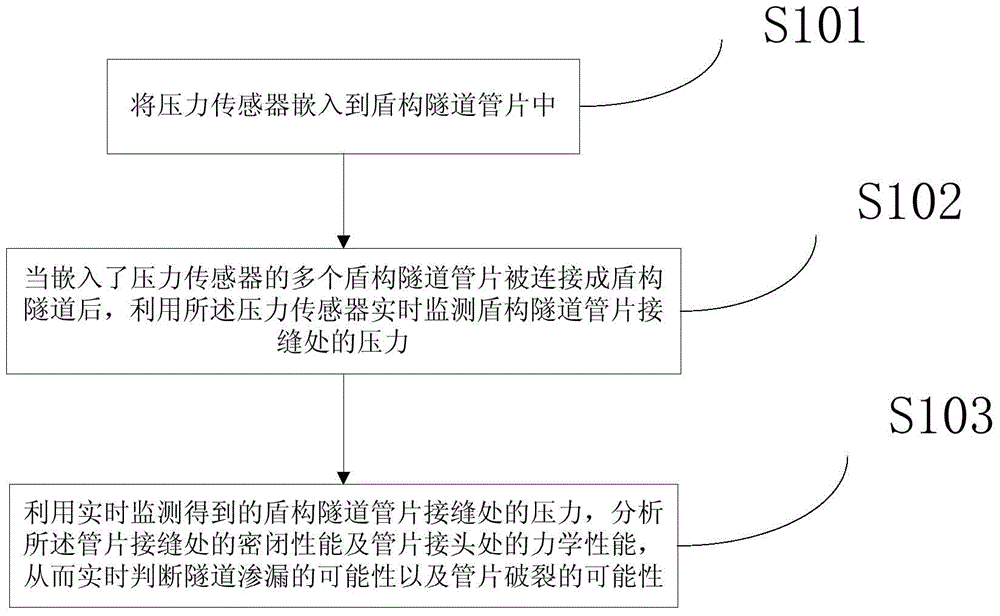
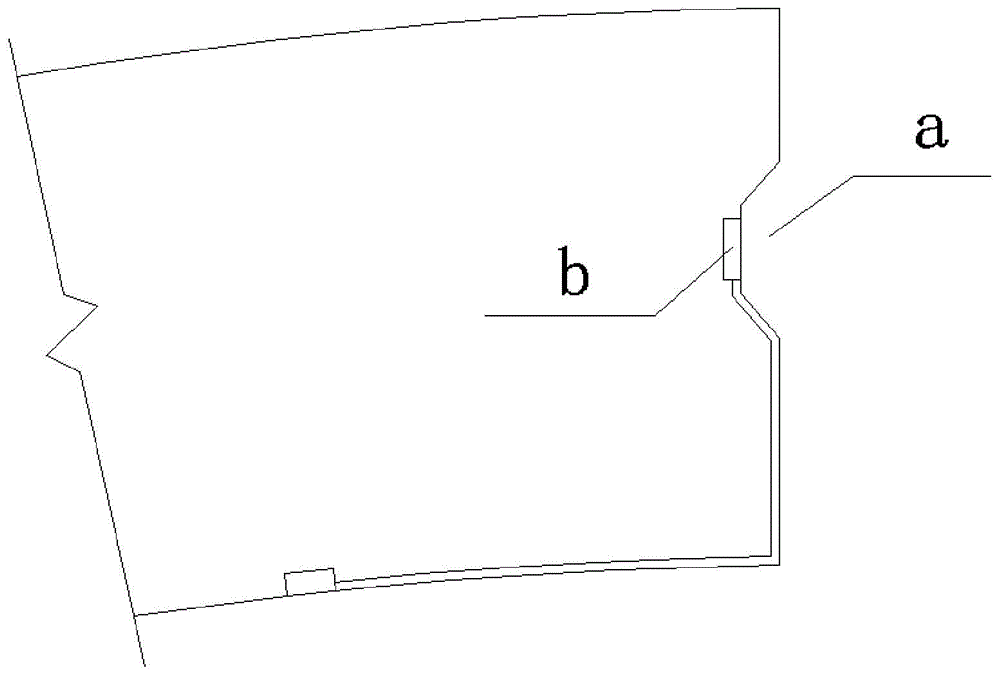
Shield tunnel segment joint stress in-situ measurement method
InactiveCN105987778ARealize in-situ monitoringNot corrosiveForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFiberGrating
The invention relates to a shield tunnel segment inner force monitoring method, in particular, a joint shield tunnel segment joint stress in-situ measurement method, and belongs to the crossing field of tunnel engineering field monitoring and construction technology. According to the method of the invention, a fiber grating pressure sensor is inserted into the interior of each segment, so that the sensors and the segments are connected together to form an integrated body to jointly bear a force; when the joint pressure of the segments is measured, a sheet rubber made of the same material with a rubber sealing strip of the corresponding shield segment is pasted on the outer surface of the corresponding fiber grating pressure sensor inserted into the segment, so that the correctness of load transfer can be ensured; the contact pressure of the rubber sealing strip at the joint of the shield segments is measured in real time, so that the stress condition of the joint of the shield segments in a tunnel construction and operation period can be determined, and the mechanical behavior and waterproof sealing performance of the shield segments can be analyzed, and therefore, the work condition of a shield liner joint can be evaluated. The joint shield tunnel segment joint stress in-situ measurement method of the invention has the advantages of high practicability and high effectiveness. With the method adopted, the stress state of the joint between the segments can be monitored in real time in situ, and the problem of difficulty in monitoring the inner force of the joint of the shield segments in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SOUTH INVESTMENT GRP CO LTD +1
Wireless remote monitoring system and wireless remote monitoring method for reactive compensation device
InactiveCN103001233ARealize remote monitoringReal-time detection of running status dataReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationSystems intergating technologiesPower qualityGeneral Packet Radio Service
The invention discloses a wireless remote monitoring system and a wireless remote monitoring method for a reactive compensation device. The system comprises a CAN (controller area network) bus communication circuit and a wireless transceiving module which form a monitoring node of the wireless remote monitoring system. The CAN bus communication circuit comprises a microcontroller and a CAN bus transceiver. The microcontroller acquires data on reactive compensation device nodes and transmits the acquired data to the CAN bus transceiver through an eCAN controller, the wireless transceiving module transmits the data to a sever through GPRS (general packet radio service) and Internet, a database is built at the server for storing and managing data of different nodes, and the sever transmits a actuating signal to the reactive compensation device along the same path through power grid power quality information acquired by the server. The wireless remote monitoring system and the wireless remote monitoring method guarantees data acquisition, data processing, data calculation and data safety, satisfies local monitoring of the reactive compensation device, and realizes remote monitoring.
Owner:ZHUZHOU NAT ENG RES CENT OF CONVERTERS
Vertical electrochemical battery device for in-situ photodynamic measurement
ActiveCN105445347AMeet the light transmittance requirements of optical on-site measurementSatisfy light transmission requirementsElectrical testingUsing optical meansLithiumElectrochemistry
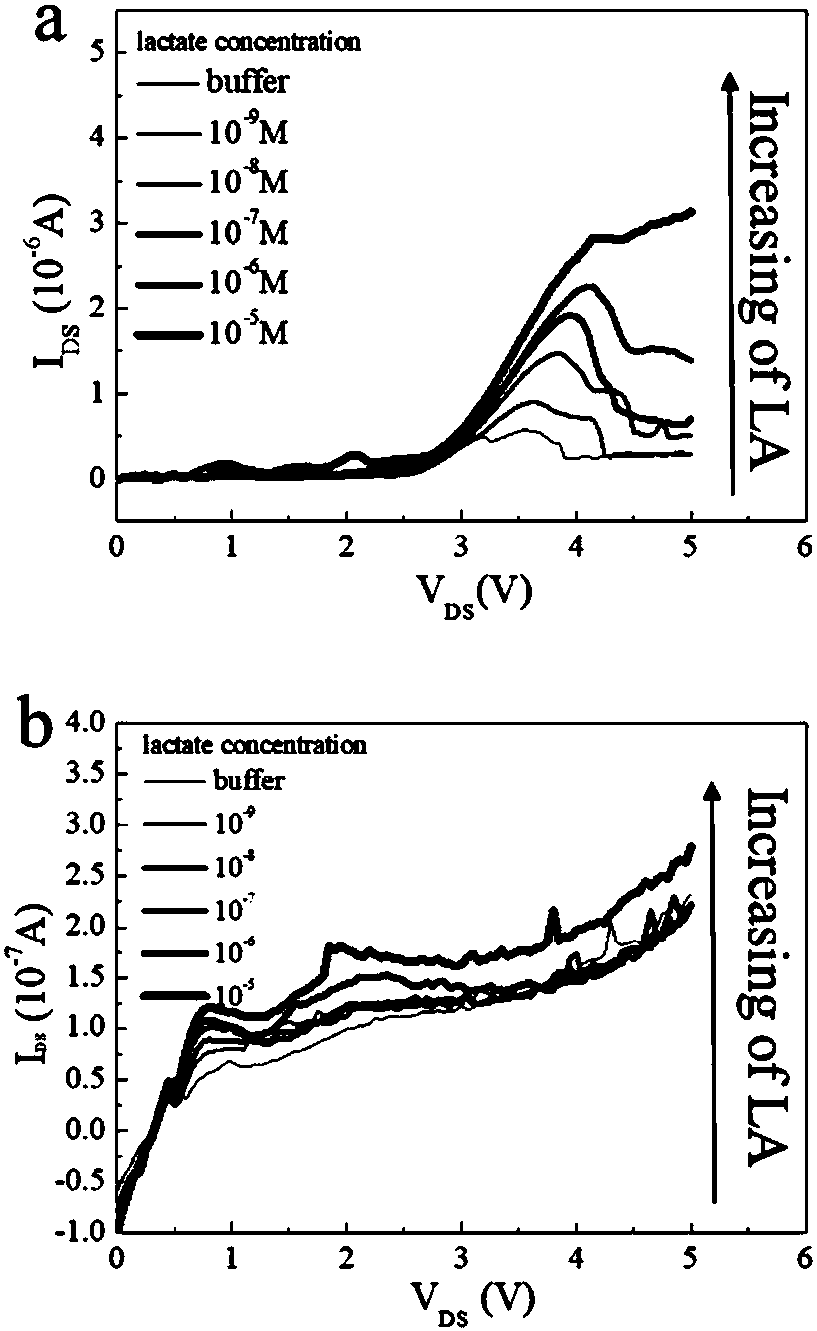
The invention relates to a vertical electrochemical battery device for in-situ photodynamic measurement. The device comprises a battery upper cover, a battery lower cover, a quartz optical window, a fixing electrode inner bushing, an electrode part and a conductive connection part. The device is characterized in that the electrode part is composed of a research electrode, a membrane and a counter electrode. The cross sections of the electrodes are parallel to the quartz window. A counter electrode sheet is fixed to an open groove of the fixing electrode inner bushing. The electrode part is arranged between the counter electrode sheet and a research electrode sheet. The counter electrode is arranged on one side of the counter electrode sheet, and the research electrode is arranged on one side of the research electrode sheet. By means of the placement mode of the electrode sheets, the cross sections of the electrode sheets can be observed, in-situ monitoring of the diffusion process of lithium ions and interface conditions of current collectors and substrates is achieved, and the movable electrode sheets can meet substrate and constraint conditions required by different tests.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Femtosecond laser processing parameter confocal Raman microspectroscopy in-situ monitoring method and device
InactiveCN109270047AImprove processing qualityRealize integrationRaman scatteringMicro nanoManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser processing parameter confocal Raman microspectroscopy in-situ monitoring method and device, and belongs to the technical field of laser precision detectionand femtosecond laser processing and manufacturing. A laser confocal axial monitoring module with a high axial resolution is organically integrated with a femtosecond laser processing system, a confocal system curve maximal point is utilized for conducting nanoscale monitoring and sample axial processing size measurement on the sample axial position, real-time focus fixing of the sample axial position and high-precision measurement of the size of a processed micro-nano structure are achieved, and the drifting problem and the high-precision online detection problem in the measurement process are solved; a confocal Raman microspectroscopy detection module is utilized for monitoring and analyzing information such as molecular structures of sample materials subjected to femtosecond laser processing, the information is integrated through a computer, microstructure femtosecond laser high-precision processing and micro-domain form performance in-situ monitoring analysis are integrated, and the controllability of microstructure femtosecond laser high-precision processing and the processing quality of the samples are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
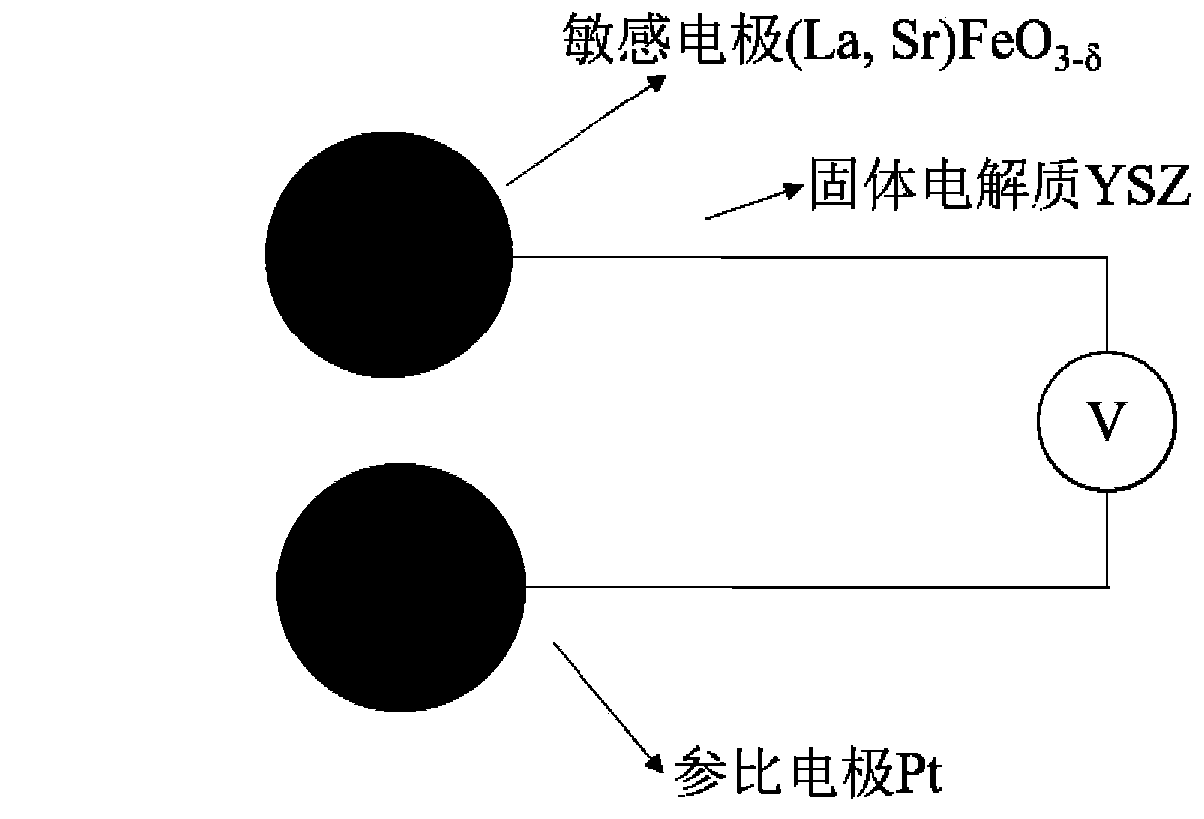
Mixed potential type hydrogen gas sensor using strontium doped lanthanum ferrite as sensitive electrode and preparation method thereof
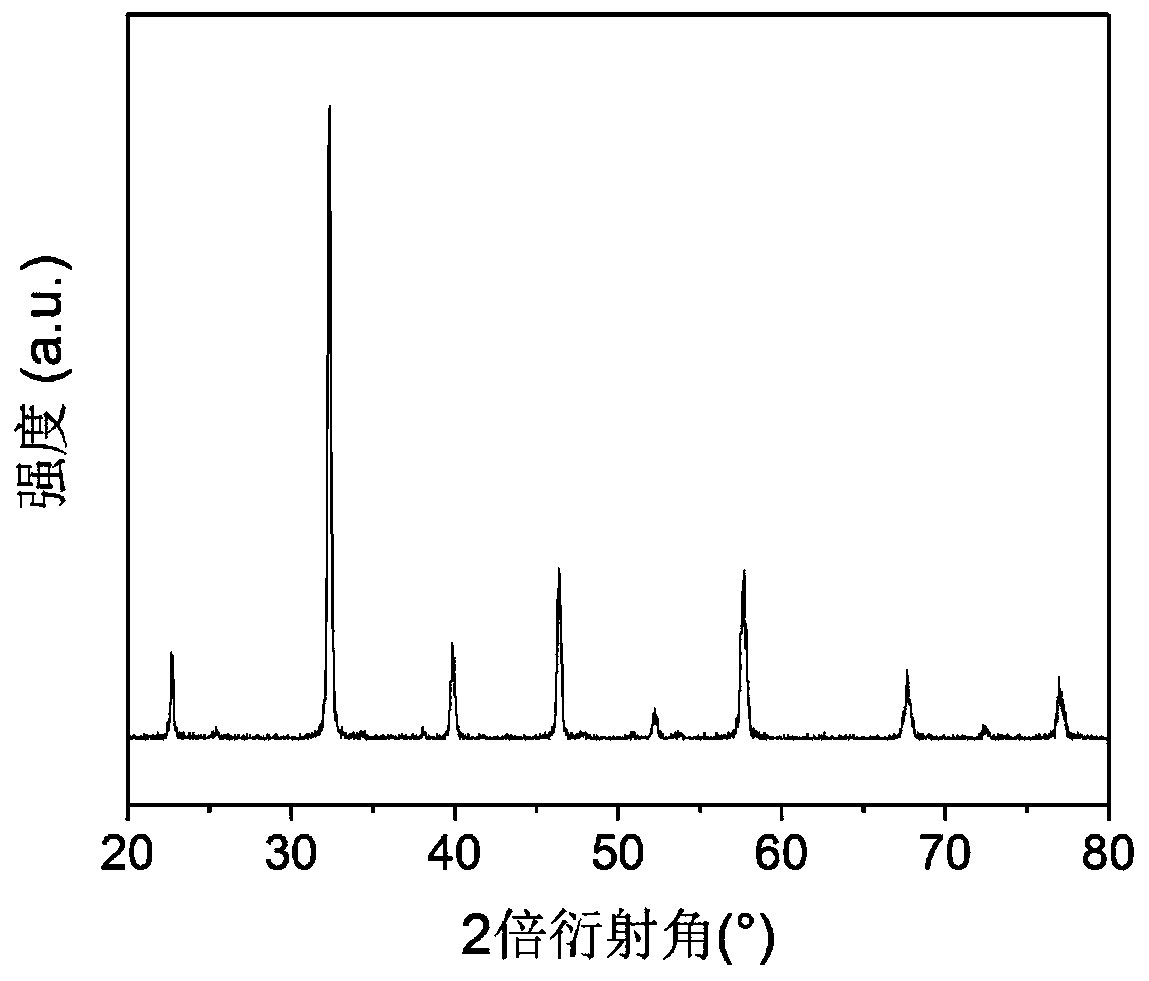
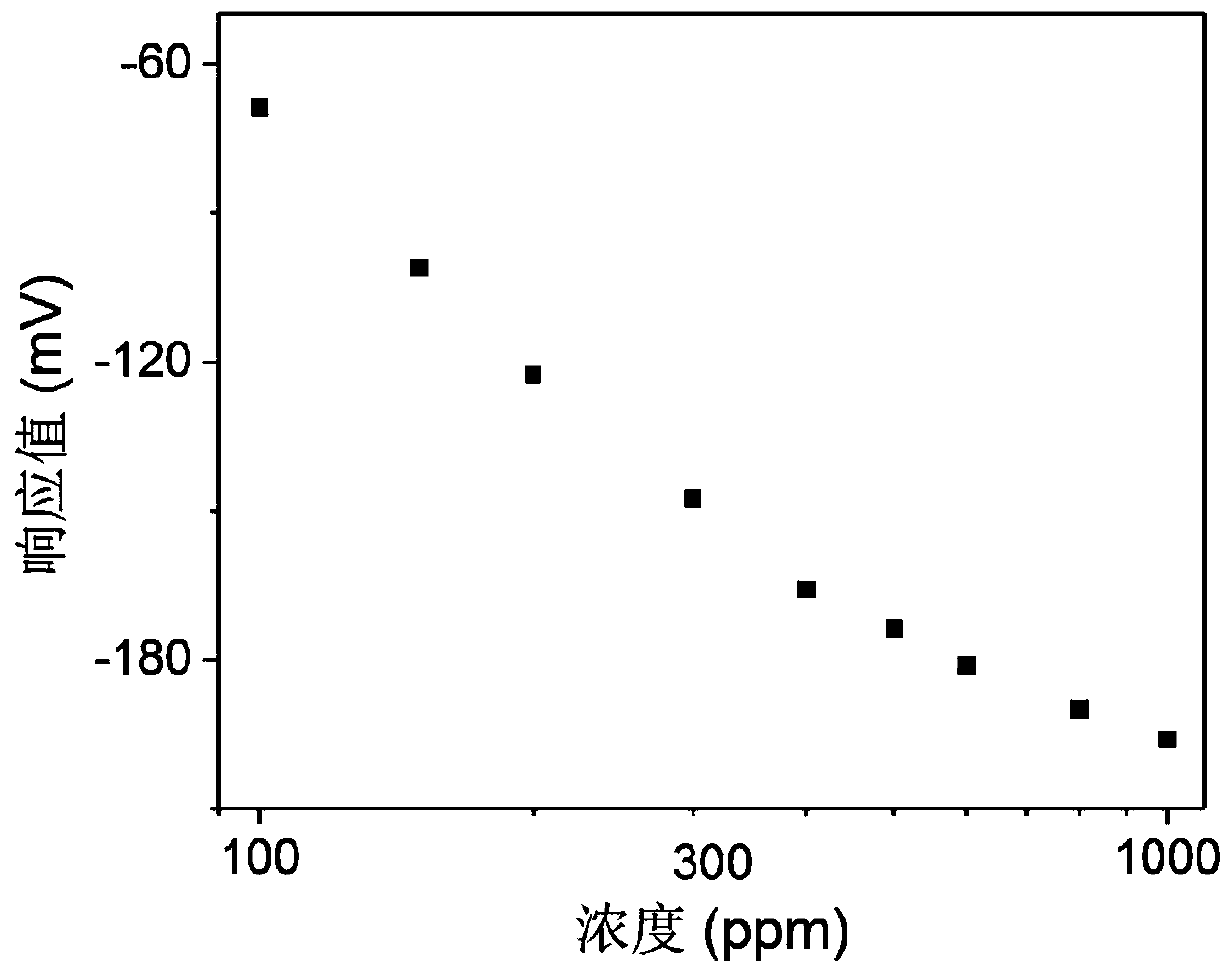
InactiveCN110031523AExcellent gas sensitivity response characteristicsHigh responseMaterial electrochemical variablesLanthanumElectricity
The invention discloses a mixed potential type hydrogen gas sensor using strontium doped lanthanum ferrite as a sensitive electrode and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof a gas sensor. The mixed potential type hydrogen gas sensor can be used for in situ detection of hydrogen gas at a high temperature, and consists of a perovskite oxide (La,Sr)FeO<3-Delta> sensitiveelectrode, a solid electrolyte (YSZ, GDC and the like) and a reference electrode (metallic Pt, Au and the like); and the sensitive electrode and the reference electrode can be positioned at the sameside or different sides of the solid electrolyte. The perovskite oxide (La,Sr)FeO<3-Delta> with excellent electrocatalytic activity on the hydrogen gas is used as a sensitive electrode material; and the built sensor has a high response value, excellent selectivity and high response-recovery speed on the hydrogen gas.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nitrogen oxide detector and small automatic nitrogen oxide monitoring device using detector
InactiveCN103674914AAutomate the processRealize automatic monitoringFluorescence/phosphorescenceSite monitoringNitrogen oxides
The invention discloses a nitrogen oxide detector and a small automatic nitrogen oxide monitoring device using the detector. The nitrogen oxide detector comprises a reactor with a conical cavity reaction chamber, wherein a heater is arranged at one end of the reactor; a heat insulation plate and a refrigerator are arranged at the other end of the reactor in sequence; an optical filter is arranged on the heat insulation plate; due to the adoption of the high-finish conical cavity reaction chamber, fluorescent light generated by the reaction of NO and O3 is absorbed by a diode after being reflected and refracted by the inner wall surface of the reaction chamber repeatedly; the content of a nitrogen oxide in a sample gas is determined by a detected weak fluorescent light signal. The detector has high stability; the size of the overall detector is small; accurate nitrogen oxide monitoring data can be provided; the small automatic nitrogen oxide monitoring device manufactured by utilizing the nitrogen oxide detector can be directly arranged outdoors for sampling and measuring, can be hung on a wall or a telegraph pole randomly, and online, real-time, accurate, automatic and on-site monitoring of NO, NO2 and NOx in air can be realized; compared with the conventional monitoring equipment, the small automatic nitrogen oxide monitoring device has the advantages that the cost for installation, operation and maintenance can be saved.
Owner:HEBEI SAILHERO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION HIGH TECH
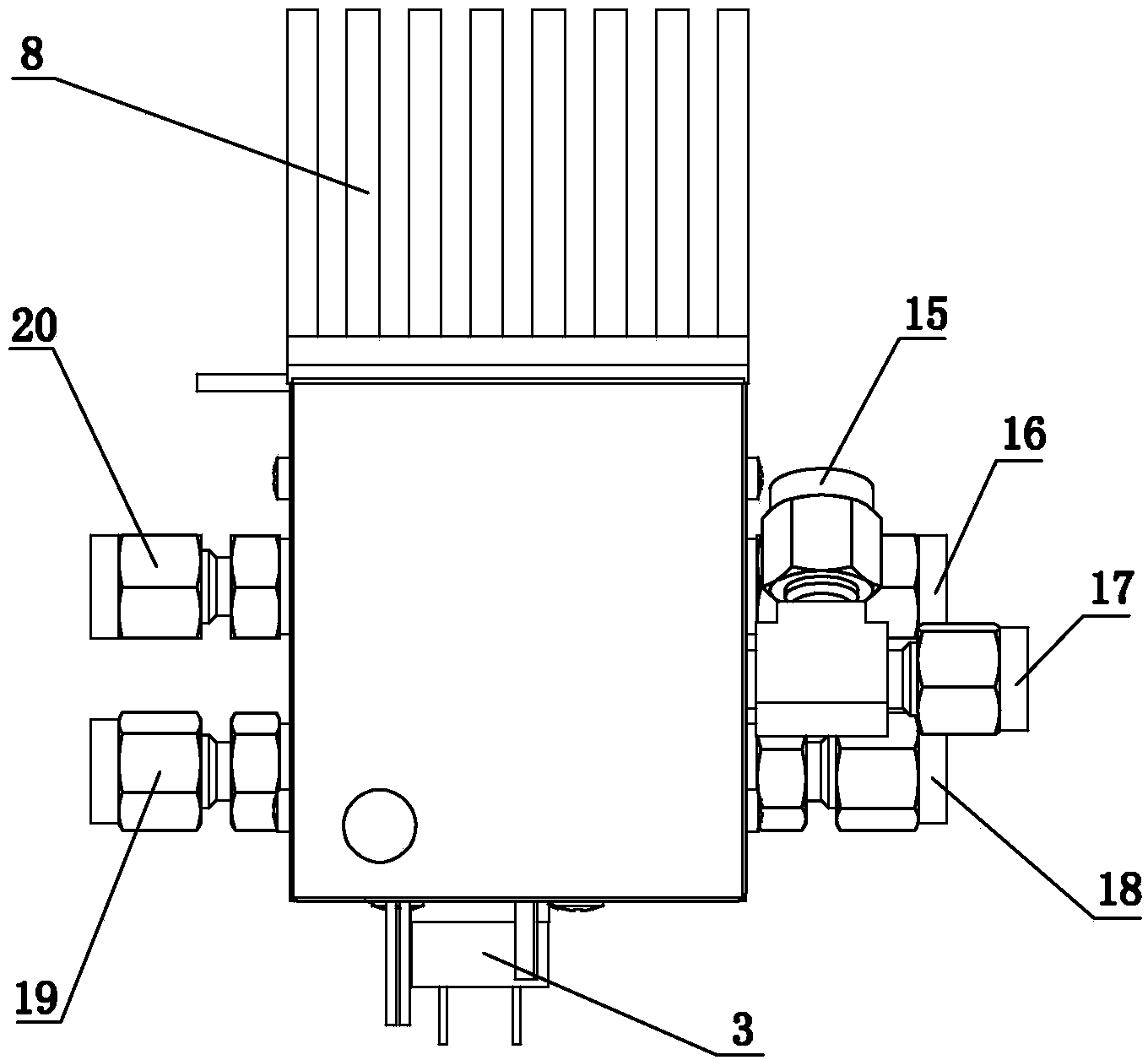
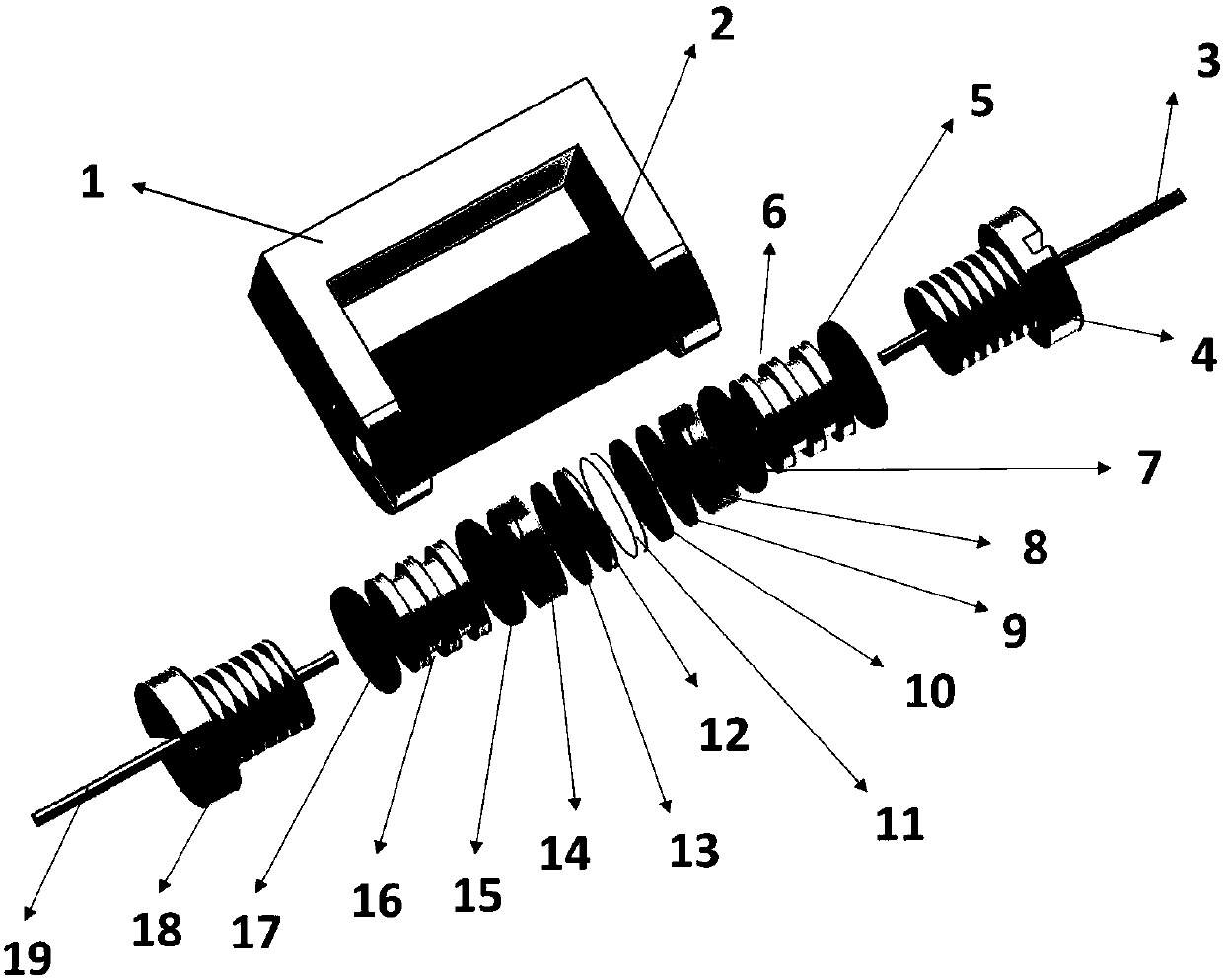
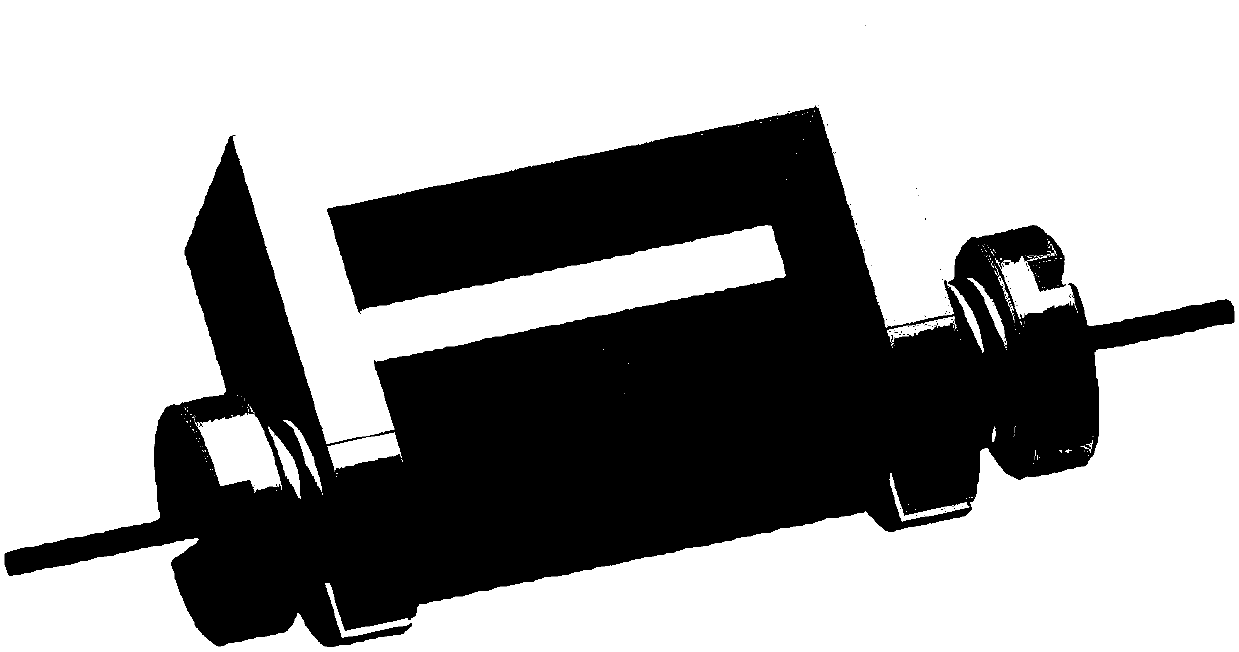
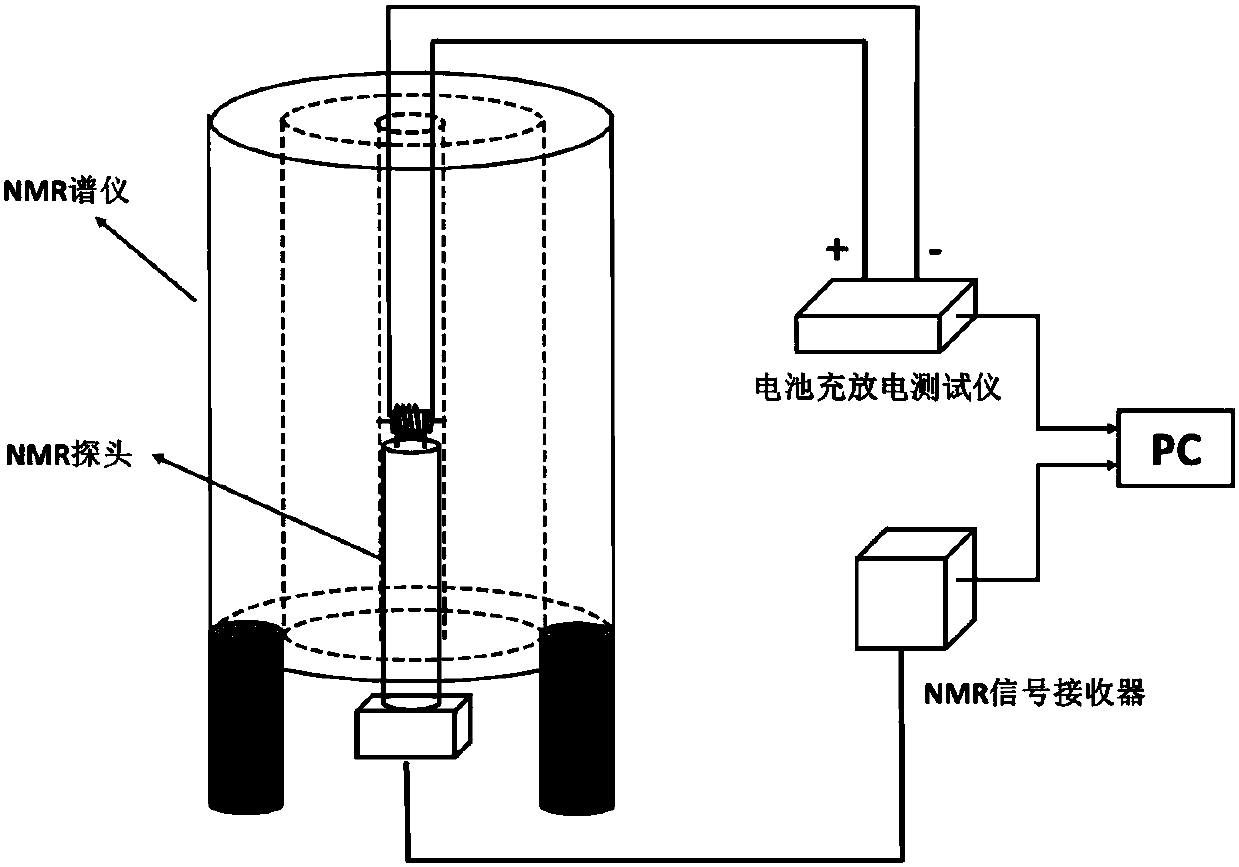
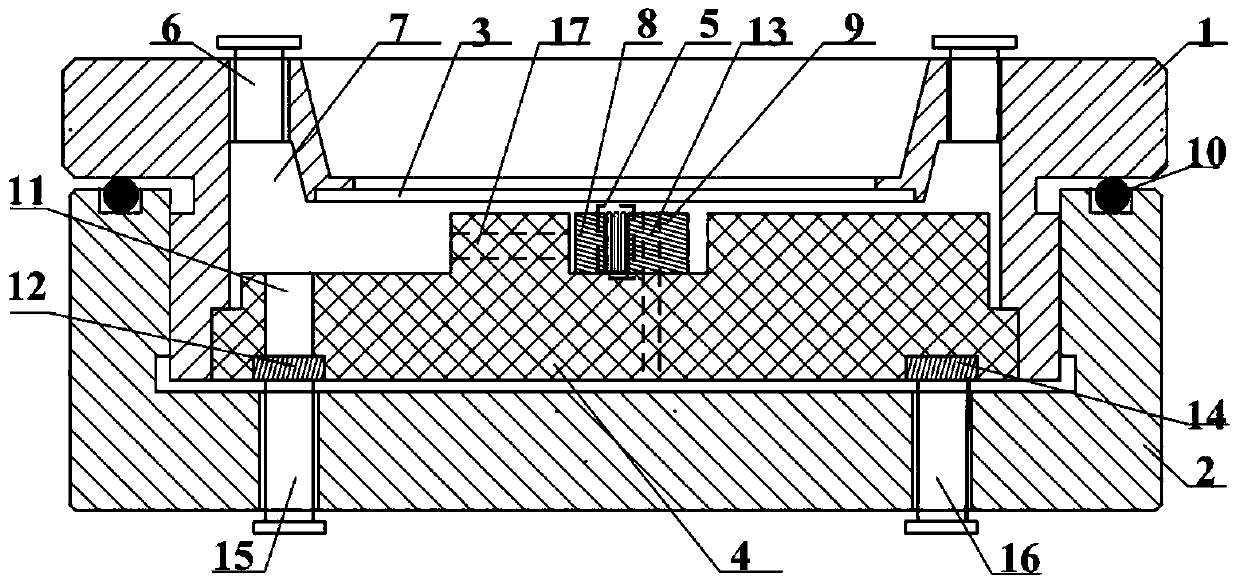
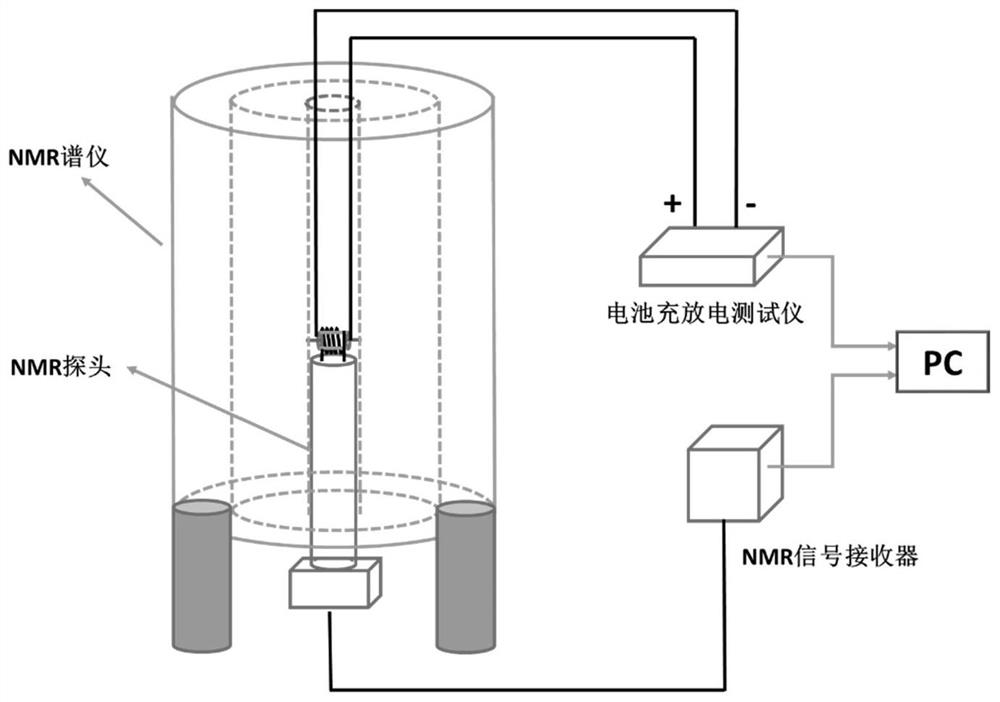
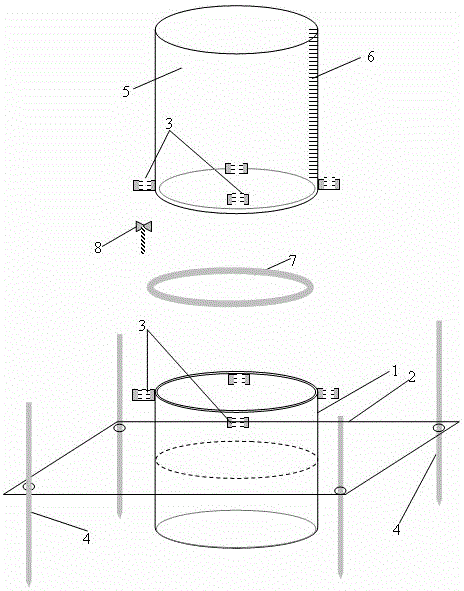
Nuclear magnetic resonance in-situ battery test accessories and test method thereof
ActiveCN109752657AGuaranteed uptimeRealize in-situ monitoringFinal product manufactureElectrical testingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceBattery charge
The invention relates to nuclear magnetic resonance in-situ battery test accessories, which comprise a battery fixing frame, a cylindrical shell, a tension nut, a first fixing cover with a central through hole, a first sealing ring, a second sealing ring, a first insulation sealing gasket, a first current collector, a positive electrode plate, a diaphragm, a negative electrode plate, a second current collector, a second insulation sealing gasket, a third sealing ring, a fourth sealing ring and a second fixing cover containing a central through hole. The device is simple and the sealing performance is good, and meanwhile, the loading and unloading operations are simple and convenient, and in-situ on-line detection of a battery in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer can be efficientlyrealized. The invention further discloses a test method for in-situ detection of battery charging and discharging processes by using the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Femtosecond laser machining and monitoring method and device based on confocal Raman-LIBS-mass spectroscopy detection
InactiveCN109187725AImprove processing qualityStrong process controllabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRaman scatteringMicro structureManufacturing technology
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser machining and monitoring method and device based on confocal Raman-LIBS-mass spectroscopy detection, and belongs to the fields of a laser precision detection technology and a femtosecond laser machining and manufacturing technology. A laser confocal axial monitoring module and a femtosecond laser machining system are organically fused, and the axial position of a sample is subjected to high-precision in-situ monitoring and sample axial machining size measurement by utilizing a curve peak point of a differential confocal system, so that the sample drift problem and the high-precision online detection problem in the measurement process are solved; and a Raman spectroscopy detection module, an LIBS spectroscopy detection module and a mass spectrograph are used for carrying out monitoring analysis on information such as molecular structures, elements, ions and the like of a sample material after femtosecond laser machining, and the information is fused through a computer, so that the high-precision femtosecond laser machining of a micro-structure and the in-situ monitoring analysis of the morphology performance of a micro-region are integrated, and the controllability of the femtosecond laser machining precision of the micro-structure, the machining quality of the sample and the like are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
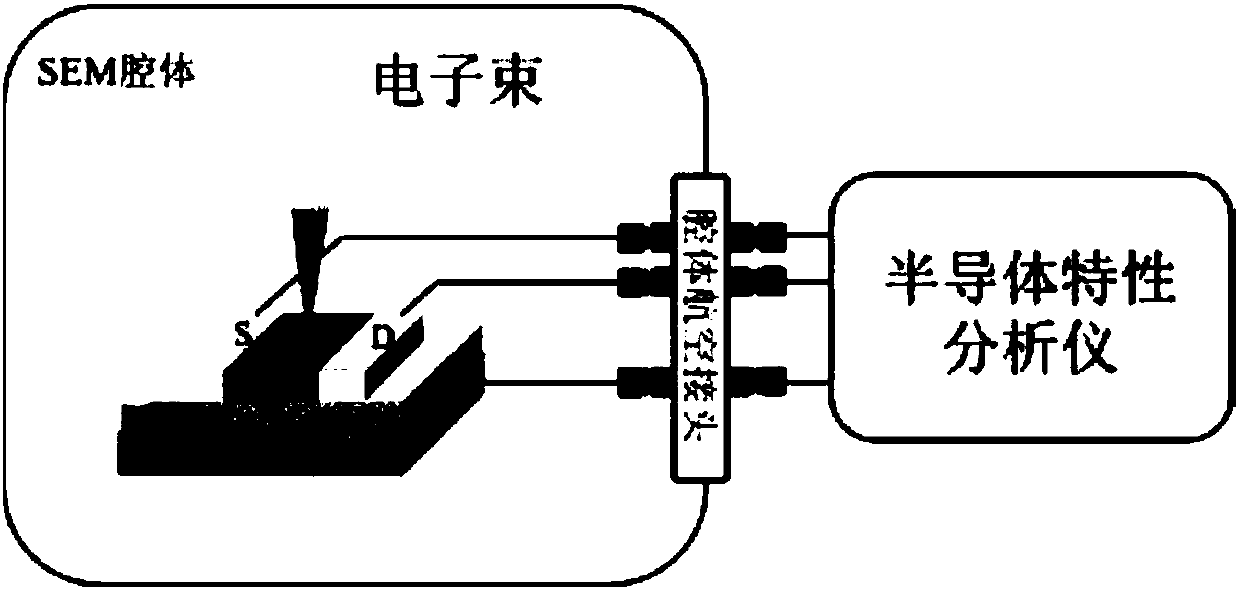
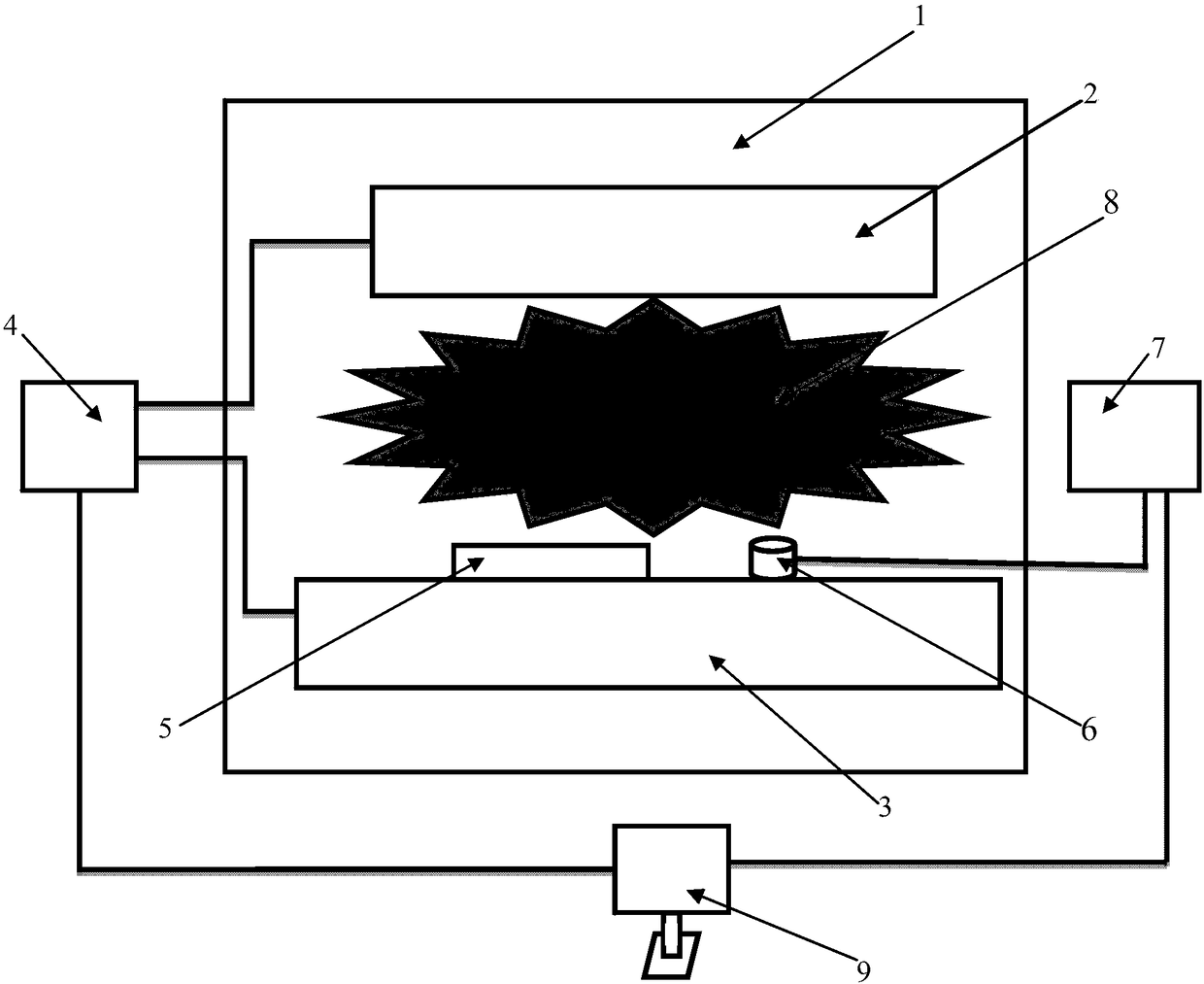
Method for control and in-situ detection of enzymatic activity under irradiation of electronic beams
InactiveCN108018329ABig advantageImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial resistanceScanning electron microscopeElectron microscope
The invention discloses a method for control and in-situ detection of enzymatic activity under irradiation of electronic beams. The method includes the following steps of 1, preparing a titanium dioxide thin-film field-effect tube; 2, carrying out enzyme immobilization; 3, putting a device into an SEM sample table, and adopting silicon as a gate electrode, wherein any two adjacent electrodes in agold electrode array are adopted as a source electrode and a leakage electrode, and the electrodes are connected with aerial connectors on a cavity through leads; 4, putting the device of the electrodes into a scanning electron microscope, and using the electronic beams for radiation; 4, conducting a conductance testing. On the basis of the titanium dioxide thin-film field-effect tube, enzymes arefixed to the field-effect tube, the electronic beams of the scanning electron microscope are adopted as the irradiation source, the electrodes of the field-effect tube are drawn to a semiconductor property analysis instrument outside an SEM cavity through the leads and a cavity connection port for conducting in-situ conductance measurement, and the enzyme activity is monitored through changes ofconductance. The generation of the electronic beams does not depend on any radioactive element, and in-situ monitoring of the enzyme activity under the irradiation of the electronic beams is achieved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and system for realizing P-type nitride enhanced HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor) through in-situ etching monitoring
ActiveCN105810607ARealize in-situ monitoringEasy to transformSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRepeatabilityNitride
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing a P-type nitride enhanced HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor) through in-situ etching monitoring. In one typical embodiment, through directly exposing an etching surface of an etching sample in a plasma and placing a test wafer plated with electrodes in an etching position equivalent to a sample in etching equipment, the etching rate on the sample is equal to that on the test wafer, so that an etching condition of a P-type semiconductor on the sample can be monitored through the change of the current between two electrodes on the test wafer, and then the obtained current signal is input into a computer and the computer controls the etching condition to realize a controllable and precise etching technology with feedback. According to the method and the system, the defects caused by realizing different etching depths through the single etching condition, the single etching rate and the etching time simply in the existing etching technology are effectively solved, and preparation of the P-type cap layer enhanced HEMT device can be realized at high precision and high repeatability.
Owner:SUZHOU NENGWU ELECTRONICS TECH
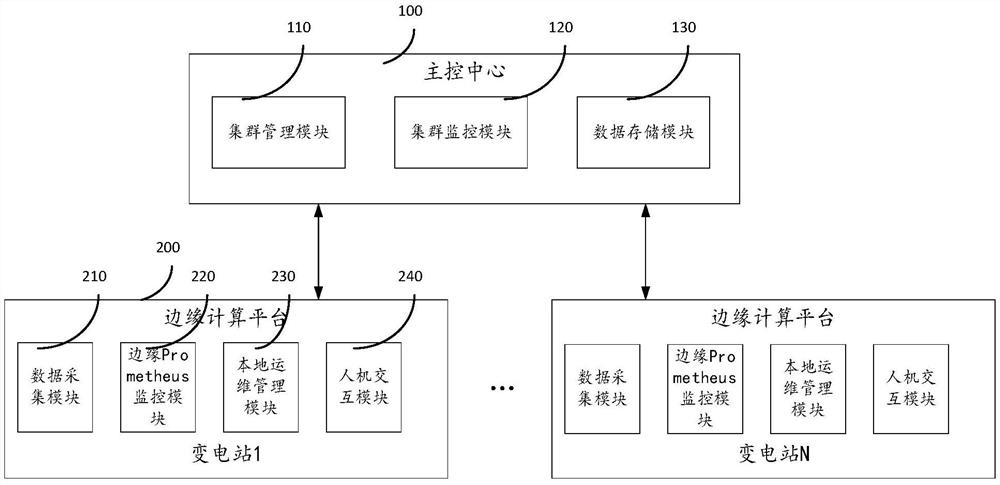
Distributed edge micro-cloud monitoring system based on container technology
PendingCN112769230ARealize in-situ monitoringGuaranteed operabilityCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemResource schedulingData acquisition module
The invention discloses a distributed edge micro-cloud monitoring system based on a container technology. The system comprises a main control center and an edge computing platform; the main control center comprises a cluster management module, a cluster monitoring module and a data storage module; the edge computing platform is arranged in a local server of each transformer substation and communicates with the main control center, the edge computing platform comprises a data acquisition module, an edge Prometheus monitoring module and a local operation and maintenance management module, and when a network is smooth, the edge computing platform normally acquires operation data of the transformer substation and uploads the operation data to the main control center, and at the same time receives and responds to a management and operation and maintenance control command sent by the main control center; when the network is not smooth, the edge computing platform can also ensure basic operation and maintenance capabilities such as monitoring acquisition, local resource scheduling, local resource allocation and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN COMTOP INFORMATION TECH
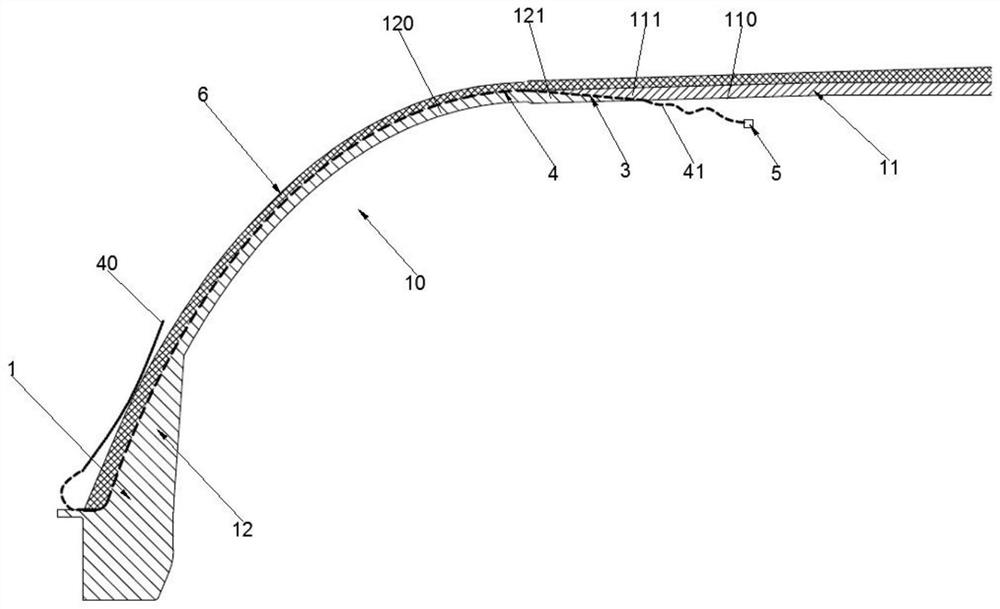
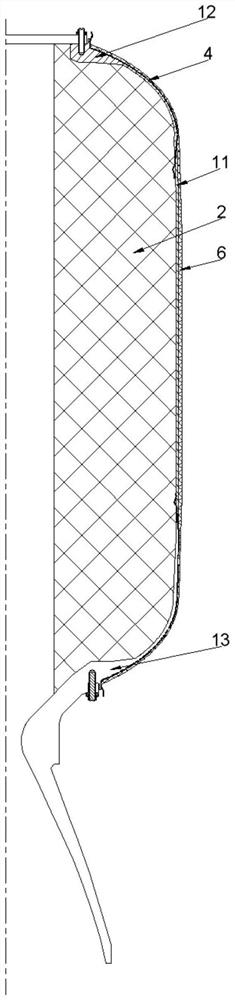
Solid rocket engine shell, solid rocket engine and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111779593AEnhanced State Prediction CapabilitiesReduce inspectionOptical fibre/cable installationDomestic articlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a solid rocket engine shell, a solid rocket engine and a manufacturing method thereof. The solid rocket engine shell comprises a winding layer, a heat insulation structure, aplurality of optical fibers and a plurality of sensors; the heat insulation structure is internally provided with a propellant storing space used for containing a propellant grain and is provided witha light path channel extending in the circumferential direction of the heat insulation structure; and the winding layer is wound around the outside of the heat insulation structure. The multiple optical fibers are arranged in the outer circumferential direction of the heat insulation structure at intervals, the optical fibers and the heat insulation structure are bonded together, the optical fibers comprises leading-out ends and built-in ends, the leading-out ends extend out of the heat insulation structure, the built-in ends extend into and are embedded into the light path channel in the busdirection of the heat insulation structure and extend into the propellant storing space, and the built-in ends of the optical fibers are connected with the sensors; and the sensors are used for monitoring the propellant grain (a propellant storing interface or propellant grain interior). The solid rocket engine comprises the solid rocket engine shell and the propellant grain filled in the propellant storing space.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
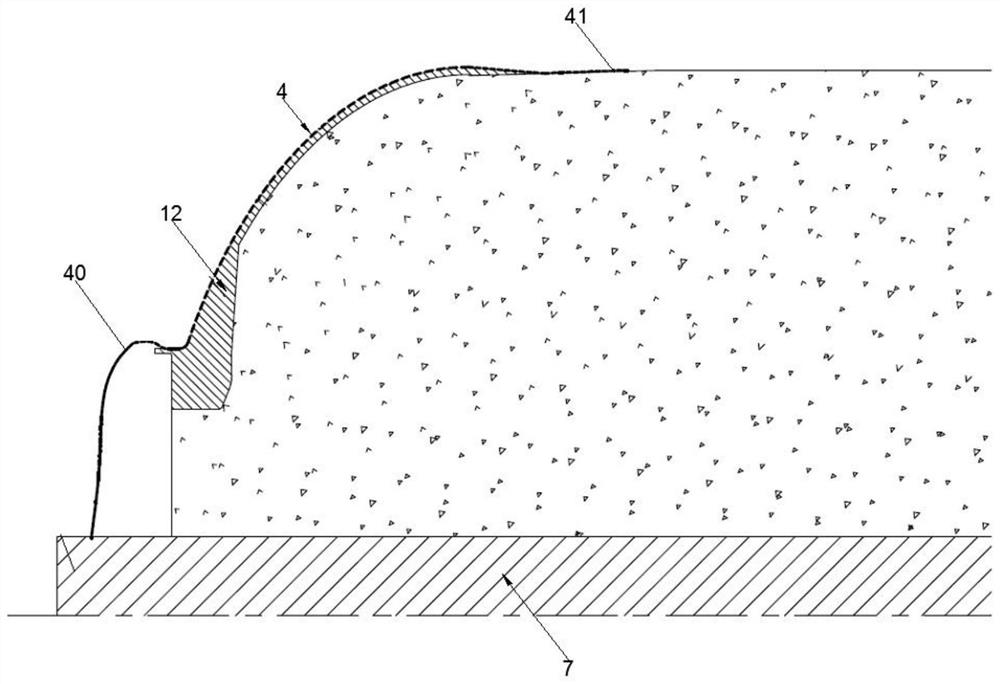
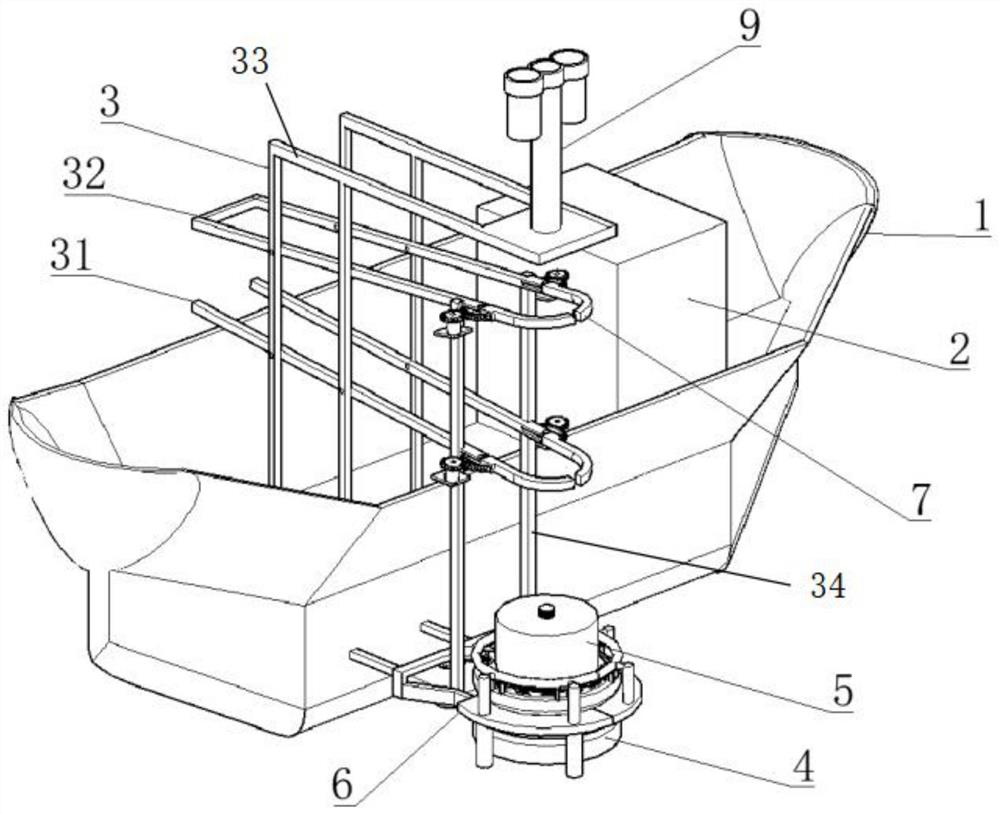
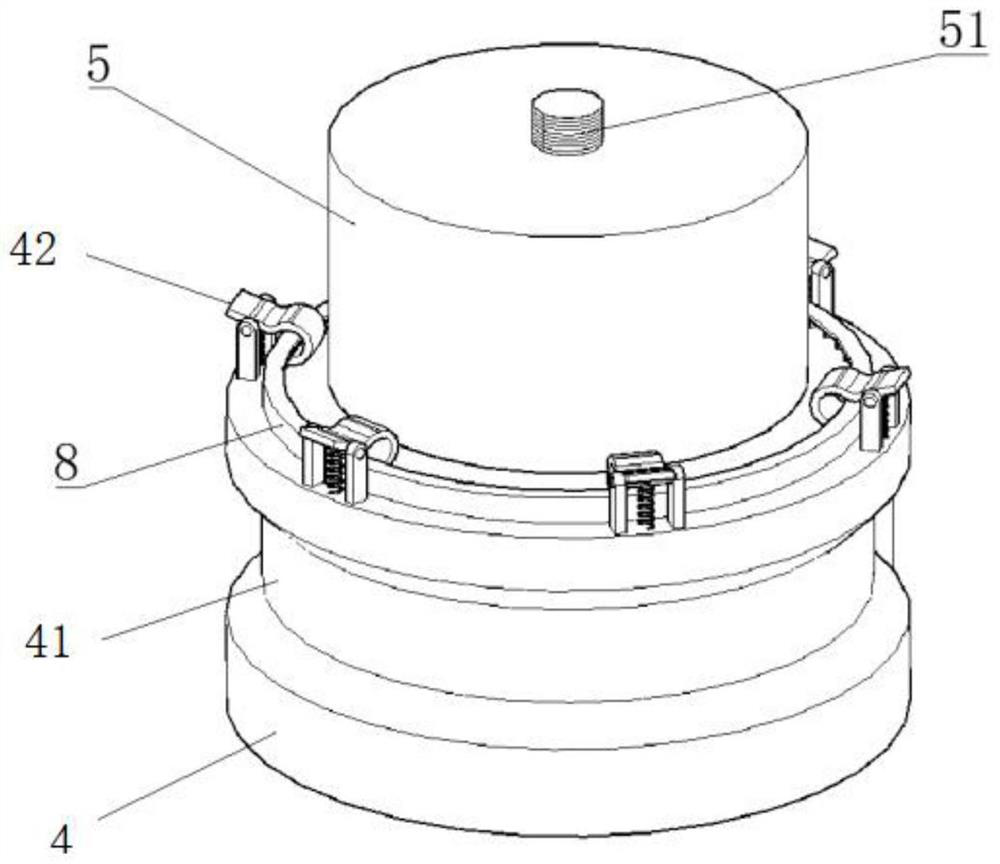
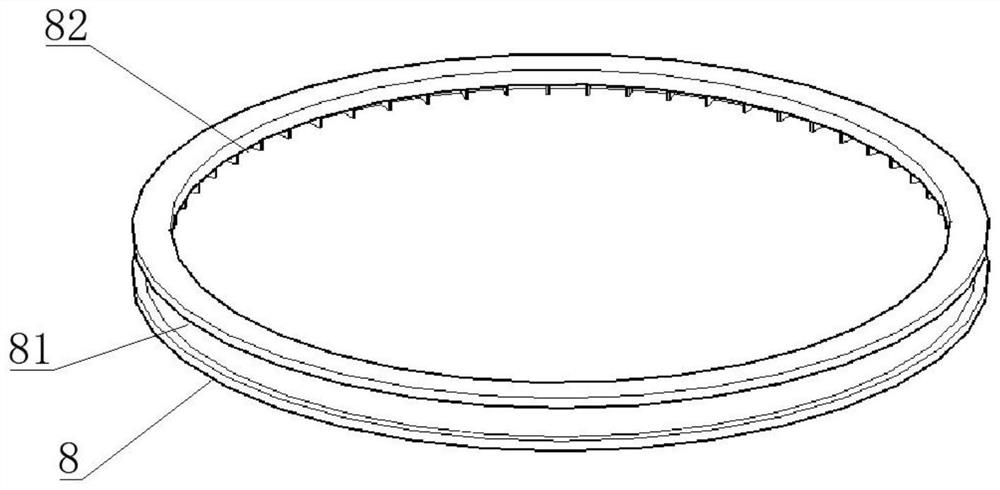
Unmanned ship water quality monitoring monitor shipborne support and unmanned ship
PendingCN114475913ARealize in-situ monitoringUnmanned surface vesselsVessel partsStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a shipborne support for a water quality monitoring monitor of an unmanned ship. The shipborne support comprises a placing frame, a collecting frame and a supporting frame, and the supporting frame is vertically fixed to a ship body of the unmanned ship; the collecting frame is located above the containing frame. The placing frame comprises two placing rods fixed to the supporting frame, and the heights of the placing rods are gradually decreased from the middle of the ship body to the outer side of the ship body. The collecting frame comprises two collecting rods fixed to the supporting frame, and the heights of the collecting rods are gradually increased from the middle of the ship body to the outer side of the ship body. The ends, located on the outer side of the ship body, of the two containing rods and the two collecting rods are each rotationally connected with a limiting ring, the right ends of the limiting rings are in an arc shape, the two limiting rings on the two containing rods are symmetrically distributed, and the two limiting rings on the two collecting rods are symmetrically distributed. The collecting frame is used for placing the collected mounting plate and the monitor, and the placing frame is used for placing the mounting plate and the monitor to be mounted. The invention further relates to an unmanned ship provided with the shipborne support.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Method and system for realizing p-type nitride enhanced hemt through in-situ etch monitoring
ActiveCN105810607BRealize in-situ monitoringEasy to transformSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower flowRepeatability
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing a P-type nitride enhanced HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor) through in-situ etching monitoring. In one typical embodiment, through directly exposing an etching surface of an etching sample in a plasma and placing a test wafer plated with electrodes in an etching position equivalent to a sample in etching equipment, the etching rate on the sample is equal to that on the test wafer, so that an etching condition of a P-type semiconductor on the sample can be monitored through the change of the current between two electrodes on the test wafer, and then the obtained current signal is input into a computer and the computer controls the etching condition to realize a controllable and precise etching technology with feedback. According to the method and the system, the defects caused by realizing different etching depths through the single etching condition, the single etching rate and the etching time simply in the existing etching technology are effectively solved, and preparation of the P-type cap layer enhanced HEMT device can be realized at high precision and high repeatability.
Owner:SUZHOU NENGWU ELECTRONICS TECH
An in-situ monitoring method for steel bar corrosion and stress state in concrete
ActiveCN104215569BSolving Corrosion Monitoring ProblemsAvoid destructionWeather/light/corrosion resistanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationContinuous measurementStress concentration
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Foundation layered settlement monitoring device and assembling method thereof
ActiveCN112982357AEnsure consistencyStable jobHeight/levelling measurementIn situ soil foundationArchitectural engineeringStructural engineering
The invention relates to a foundation layered settlement monitoring device and an assembly method thereof. The monitoring device comprises a settlement pipe which is vertically buried in a drill hole of a foundation, and is provided with a plurality of settlement monitoring units along the extension direction of the settlement pipe; each settlement monitoring unit comprises a displacement sensor arranged in the settlement pipe and an anchor head monitoring device connected with the displacement sensor; the anchor head monitoring device comprises an anchor head base, a telescopic anchor head arranged in the anchor head base and an anchor head driving source for driving the telescopic anchor head; a strip-shaped hole allowing the telescopic anchor head to penetrate through is formed in the side wall of the settlement pipe; the anchor head driving source drives the telescopic anchor head to penetrate through the strip-shaped hole to be inserted into the foundation; and the telescopic anchor head can move up and down in the strip-shaped hole along with the foundation. According to the assembling method, the laying and using method of the foundation layered settlement monitoring device is provided, the workload of drilling and burying is reduced, in-situ monitoring of different positions is achieved, and the monitoring efficiency and the monitoring precision are improved.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
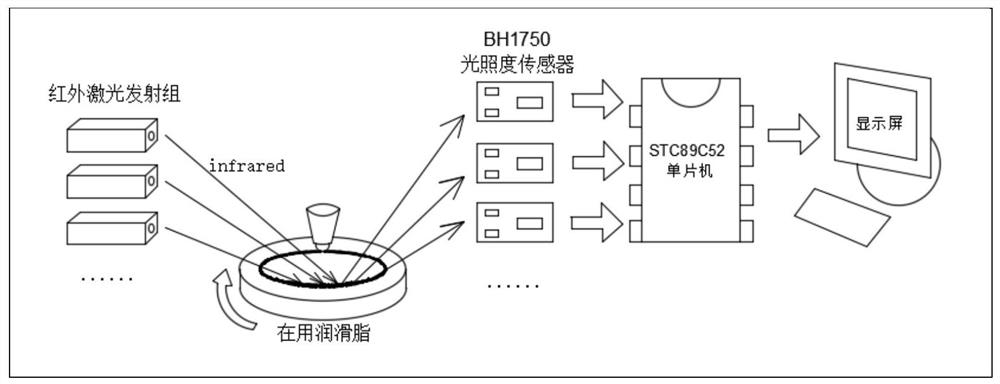
System and method for online monitoring of lubricating grease decay degree by infrared point laser transmitter
ActiveCN108931502BTargetedIncrease profitScattering properties measurementsLaser transmitterMicrocontroller
A system and method for online monitoring the degree of decay of lubricating grease by utilizing infrared dot laser emitters are disclosed. A plurality of the infrared dot laser emitters emit infraredlight with different wavebands onto the lubricating grease; reflected light signals are received by luminous intensity sensors, and processed by a sing chip microcomputer to obtain infrared luminousintensity changes of wavebands corresponding to characteristic functional groups such as methyl, carbonyl and hydroxyl; a lubricating grease service lifetime parameter K model quantized by characteristic quantities is built by utilizing an experiment database; and the degree of decay of lubricating grease is represented by the parameter K in real time and quantificationally to make a real-time judgment on the service lifetime, thus achieving on-line monitoring of the service lifetime of the lubricating grease.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Femtosecond laser machining and monitoring method based on back light splitting pupil differential confocal Raman-LIBS-mass spectroscopy detection
InactiveCN109187726AImprove processing qualityStrong process controllabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRaman scatteringMicro structureSpectrograph
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser machining and monitoring method based on back light splitting pupil differential confocal Raman-LIBS-mass spectroscopy detection, and belongs to the fieldsof a laser precision detection technology and a femtosecond laser machining and monitoring technology. The method can be used for femtosecond laser machining and online monitoring, and online detection of physical property comprehensive parameters. A back light splitting pupil laser differential confocal axial monitoring module and a femtosecond laser machining system are organically fused, and the axial position of a sample is subjected to high-precision in-situ monitoring and sample axial machining size measurement by utilizing a back light splitting pupil differential confocal system; anda Raman spectroscopy detection module, an LIBS spectroscopy detection module and a mass spectrograph are used for carrying out monitoring analysis on information such as molecular structures, elements, ions and the like of a sample material after femtosecond laser machining, and the information is fused through a computer, so that the high-precision femtosecond laser machining of a micro-structureand the in-situ monitoring analysis of the morphology performance of a micro-region are integrated, and the controllability of the femtosecond laser machining precision of the micro-structure, the machining quality of the sample and the like are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Solid rocket motor casing, solid rocket motor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111779593BEnhanced State Prediction CapabilitiesReduce inspectionOptical fibre/cable installationDomestic articlesFiberMechanical engineering
The application relates to a solid rocket motor housing, a solid rocket motor and a manufacturing method thereof. The solid rocket motor housing includes a winding layer, a thermal insulation structure, a plurality of optical fibers and a plurality of sensors. The charge space of the thermal insulation structure is provided with an optical path channel extending along the circumference of the thermal insulation structure; the winding layer is wound outside the thermal insulation structure. A plurality of optical fibers are arranged at intervals along the outer circumference of the thermal insulation structure, and the optical fiber is bonded to the thermal insulation structure. The optical fiber includes a lead-out end and an embedded end. It is in the optical channel and extends into the charge space; the embedded end of the optical fiber is connected with a sensor, and the sensor is used to monitor the propellant grain (the charge interface or the inside of the grain). The solid rocket motor comprises a solid rocket motor case and a propellant grain filled in the charge space.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Vertical electrochemical cell setup for in situ photomechanical measurements
ActiveCN105445347BMeet the light transmittance requirements of optical on-site measurementSatisfy light transmission requirementsElectrical testingUsing optical meansLithiumElectrochemical cell
The invention relates to a vertical electrochemical battery device for in-situ photodynamic measurement. The device comprises a battery upper cover, a battery lower cover, a quartz optical window, a fixing electrode inner bushing, an electrode part and a conductive connection part. The device is characterized in that the electrode part is composed of a research electrode, a membrane and a counter electrode. The cross sections of the electrodes are parallel to the quartz window. A counter electrode sheet is fixed to an open groove of the fixing electrode inner bushing. The electrode part is arranged between the counter electrode sheet and a research electrode sheet. The counter electrode is arranged on one side of the counter electrode sheet, and the research electrode is arranged on one side of the research electrode sheet. By means of the placement mode of the electrode sheets, the cross sections of the electrode sheets can be observed, in-situ monitoring of the diffusion process of lithium ions and interface conditions of current collectors and substrates is achieved, and the movable electrode sheets can meet substrate and constraint conditions required by different tests.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Aquatic vegetable fat-cellulose acetate composite semi-permeable membrane bionic passive sampling device
InactiveCN104198221BGood for mass manufacturingShort equilibration timeWithdrawing sample devicesCellulose acetateSemipermeable membrane
The invention relates to an aquatic plant grease-cellulose acetate composite semipermeable membrane. Inexpensive and protogenetic aquatic plant grease is used as a main raw material, and highly hydrophilic cellulose acetate is used as an outer membrane material to prepare the aquatic plant grease-containing semipermeable membrane which has the advantages of uniform grease dispersion, large specific area and integrated structure. The balance time required for collection of hydrophobic organic pollutants in a water body can be shortened greatly, and costs of raw materials can be reduced significantly. The invention also provides a preparation tool and a preparation method for preparation of the aquatic plant grease-cellulose acetate composite semipermeable membrane. In addition, the invention provides a supporting external device suitable for in-situ sampling of organic pollutants in lakes, rivers and other water bodies. The simulation of aquatic plants can be realized for in-situ, accurate, convenient and low-cost monitoring of organic pollutants in water bodies.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Aquatic plant grease-cellulose acetate composite semipermeable membrane type bionic passive sampling device
InactiveCN102895887BGood for mass manufacturingShort equilibration timeWithdrawing sample devicesReverse osmosisCellulose acetateSemipermeable membrane
The invention relates to an aquatic plant grease-cellulose acetate composite semipermeable membrane. Inexpensive and protogenetic aquatic plant grease is used as a main raw material, and highly hydrophilic cellulose acetate is used as an outer membrane material to prepare the aquatic plant grease-containing semipermeable membrane which has the advantages of uniform grease dispersion, large specific area and integrated structure. The balance time required for collection of hydrophobic organic pollutants in a water body can be shortened greatly, and costs of raw materials can be reduced significantly. The invention also provides a preparation tool and a preparation method for preparation of the aquatic plant grease-cellulose acetate composite semipermeable membrane. In addition, the invention provides a supporting external device suitable for in-situ sampling of organic pollutants in lakes, rivers and other water bodies. The simulation of aquatic plants can be realized for in-situ, accurate, convenient and low-cost monitoring of organic pollutants in water bodies.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Two-wire loop power supply digital display intelligent temperature controller and transmitter integrated instrument
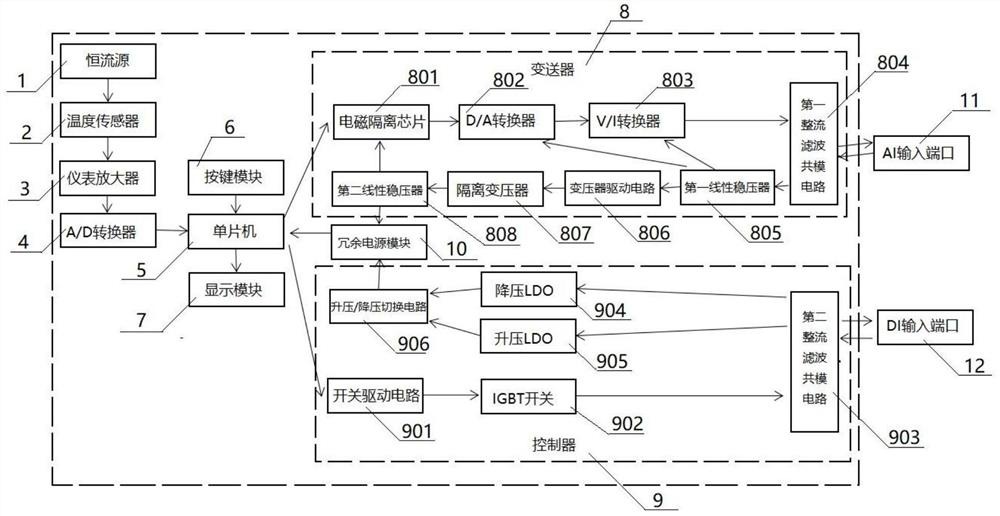
ActiveCN110764546BRealize two-wire systemSolve irreplaceable bottlenecksTemperature control using electric meansThermometer applicationsEquipment temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a two-wire loop power supply digital display intelligent temperature controller and a transmitter integrated instrument, which is used to connect with PLC controllers or DCS systems or electromagnetic valves, contactors and other equipment to realize temperature monitoring and remote transmission. , control, alarm and equipment protection, the present invention makes the temperature instrument step into micro-power consumption (micro-ampere level) from low power consumption (milliampere level), which will cause the fundamental improvement of the reliability and stability of the temperature instrumentation, and realize the On-site temperature monitoring and 4‑20mA remote transmission, control and alarm, remote transmission of the on-site equipment temperature signal to the DCS system or PLC controller, to complete the monitoring, control, alarm and alarm of equipment in various industries such as industry and transportation protection; the present invention combines temperature transmitter, temperature control switch, and digital display functions into one, realizes the micro power consumption 1-5mA signal mode and electrical isolation mode of the transmitter, and realizes the two-wire system of the temperature controller, without A separate power supply is required (three-wire thermostats are common on the market), but power is supplied through the signal loop to unconditionally replace the mechanical thermostat, which solves the bottleneck that the mechanical thermostat cannot replace for a long time. The protection failure (misoperation and refusal) caused by mechanical controller jamming and drift solves the safety hazard that the mechanical thermostat cannot monitor and cause the protection system to be uncontrollable, thereby improving the reliability of the protection system.
Owner:北京麦普兹微电科技有限公司
Method and device for performing tunnel advance borehole penetration-scribing test by using probe
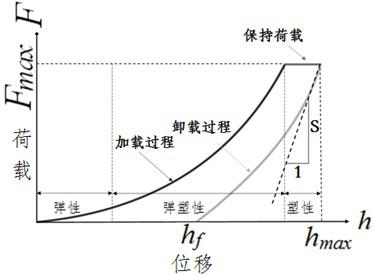
ActiveCN114354373AEase of field applicationReflect natureMining devicesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for performing tunnel advance borehole penetration-scribing test by using a probe. The probe comprises an axial loading device and a radial loading device. The method comprises the following steps: placing probes at different set depths of a drill hole; the radial loading device is pressurized to radially apply pressure to the hole wall for a penetration test; pressurizing the axial loading device to push the radial loading device in a radial pressure applying state to move along the axial direction of the drill hole to carry out a scribing test; and releasing the pressure of the radial loading device and the axial loading device, rotating the probe by a set angle by taking the center of the drill hole as an axis, and repeating the penetration test and the scribing test. In the rock in-situ testing process, penetration and scribing tests of the advance drill hole in different depths and in different directions can be completed, in-situ monitoring of stress fields and displacement fields in the axial direction and the radial direction of the advance drill hole is achieved, the whole process is convenient and rapid to operate and easy to apply in an engineering field, and the economical efficiency, the reliability and the operability of the field test are achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
A Metal Resistance Heating Device Coupled with Laser Processing
A metal resistance heating device coupled with laser processing, including a bracket, on which a mobile platform that moves horizontally and vertically is installed, and a heating device is placed on the mobile platform; the heating device includes an outer wall of a furnace body, and one end of the outer wall of the furnace body is connected to a furnace tail wall , the other end of the outer wall of the furnace body is connected to the furnace body top cover, and the outer side of the furnace body top cover is connected to the furnace head pushing device; the inner side of the furnace tail wall is connected to the furnace tail conductive block, and the furnace tail conductive block is connected to one end of the workpiece. One end is connected through the furnace head conductive block, furnace head electrode, series connection column and fixed conductive block. The fixed conductive block is equipped with a furnace head electrode top cover, and the fixed conductive block and furnace head electrode top cover are installed on the furnace body top cover; the workpiece is A lens window is provided on the outer wall of the upper furnace body, and a heat insulating layer is provided on the inner side of the outer wall of the furnace body; the fixed conductive block is connected with a furnace top pushing electrode; the invention uses a laser to process the workpiece while heat treatment, and the workpiece is Heat treatment offers new degrees of freedom.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
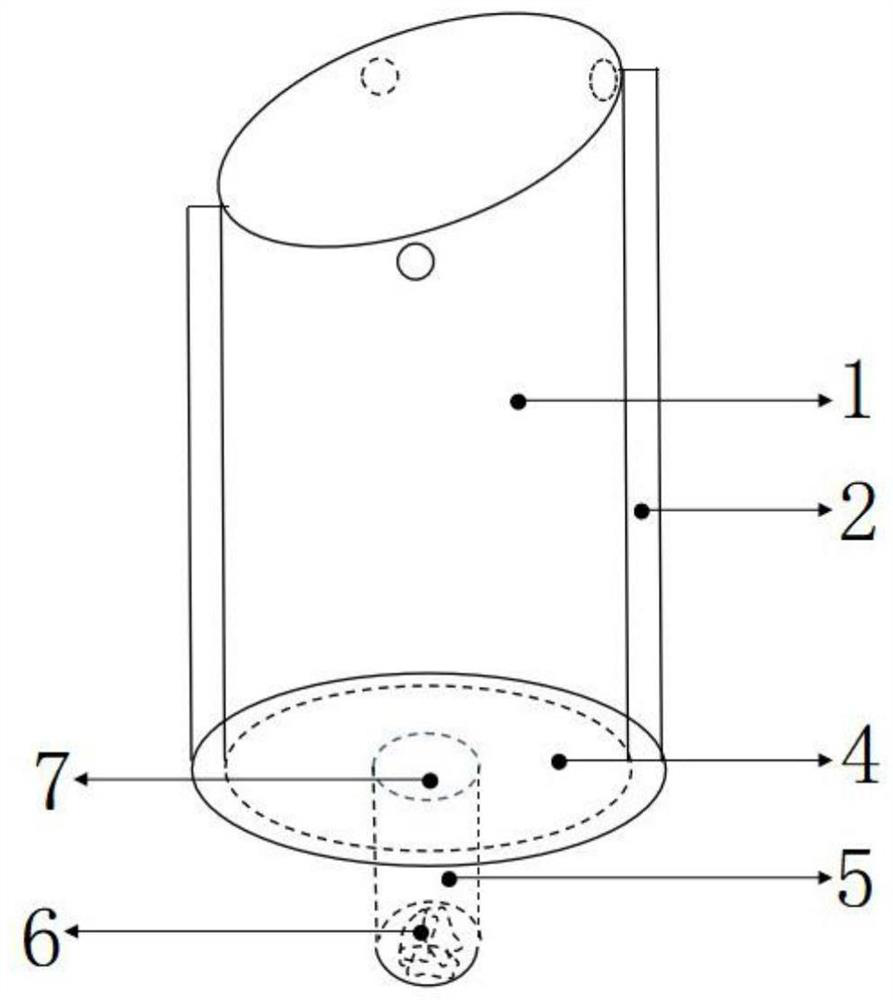
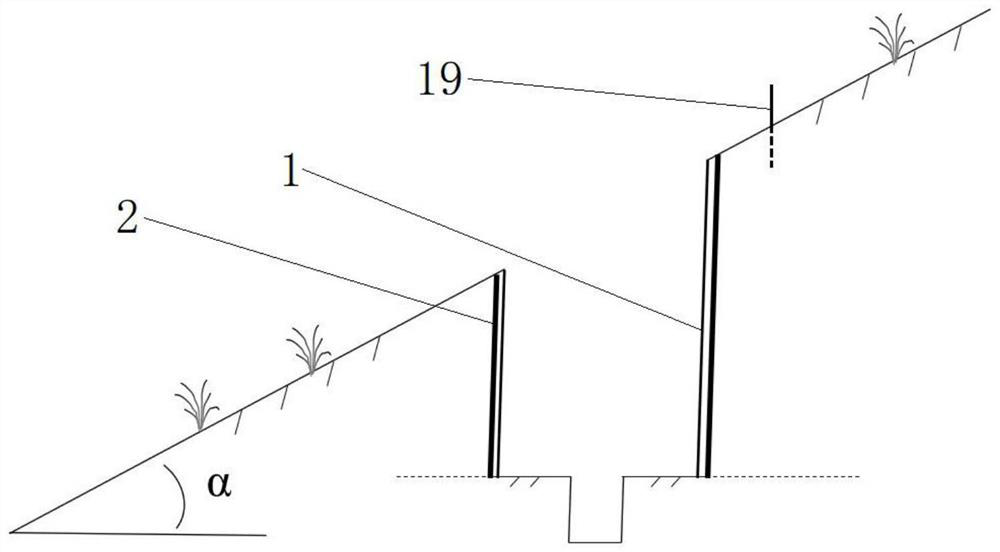
Slope grassland lysimeter
PendingCN113433023AAvoid interactionAvoid the influence of weighing valueWeighing by absorbing componentWater storageSoil science
The invention discloses a slope grassland lysimeter, and relates to the technical field of soil data measuring devices. The slope grassland lysimeter comprises a lysimeter soil barrel which comprises an inner barrel used for containing soil and an outer barrel used for sleeving the outer side of the inner barrel in a clearance manner; the first end of the inner barrel is open, the second end of the inner barrel is closed, the end face of the first end of the inner barrel is obliquely arranged so that the end face of the first end of the inner barrel can be flush with a slope when the inner barrel is vertically buried underground, and the second end of the inner barrel is provided with an infiltration mechanism used for storing water; openings are formed in the two ends of the outer barrel, and the first end face of the outer barrel is obliquely arranged to be flush with the first end face of the inner barrel; the slope grassland lysimeter further comprises a weighing mechanism which comprises a hoisting mechanism used for hoisting the inner barrel, and a weighing device which is arranged on the hoisting mechanism and used for weighing the inner barrel. Through the arrangement, the slope grassland lysimeter provided by the invention is suitable for slope grassland, has the characteristics of portability and simplicity in operation, and is convenient to carry, maintain and mount; soil disturbance is small, and in-situ monitoring of slope grassland evapotranspiration can be achieved; the cost is low, and popularization in the field is facilitated.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
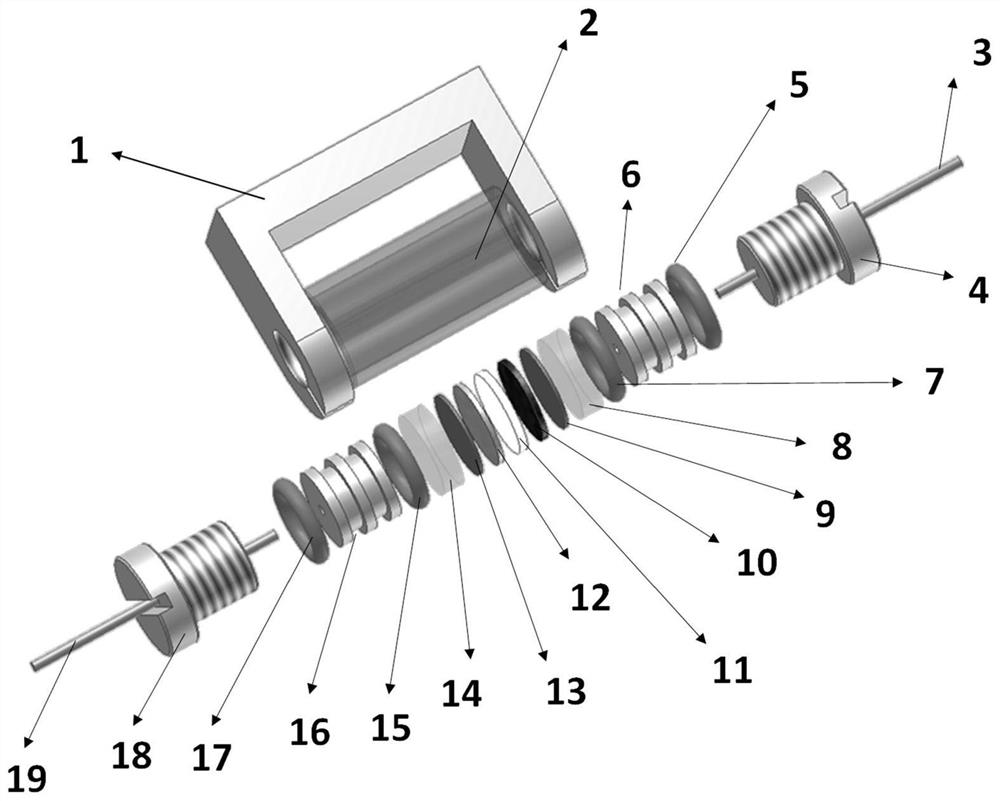
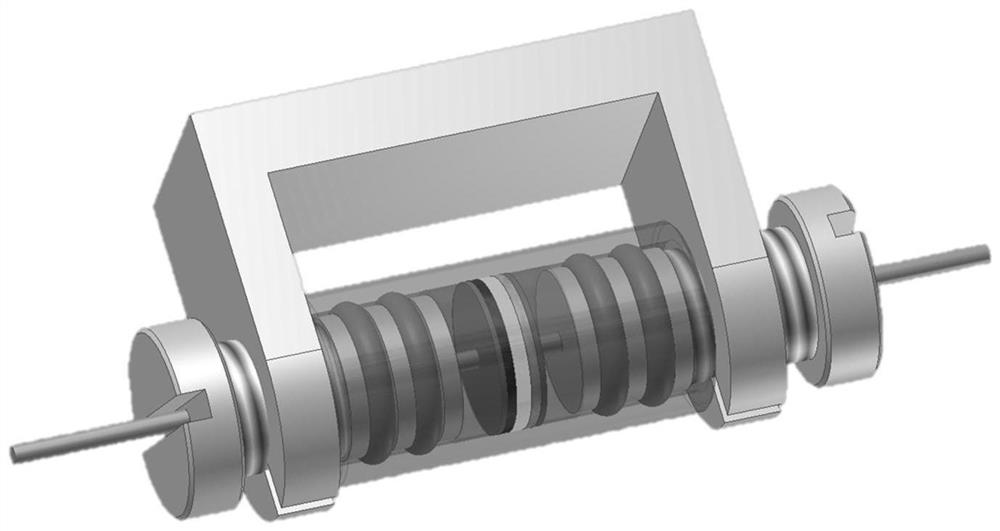
NMR in-situ battery test accessories and test methods
ActiveCN109752657BGuaranteed uptimeRealize in-situ monitoringFinal product manufactureElectrical testingBattery chargeNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This patent relates to a battery accessory for nuclear magnetic resonance in-situ testing, including a battery fixing frame, a cylindrical shell, a pressurized nut, a first fixing cover with a central through hole, a first sealing ring, a second sealing ring, a first insulating seal Pad, first current collector, positive electrode sheet, separator, negative electrode sheet, second current collector, second insulating gasket, third sealing ring, fourth sealing ring and second fixed cover with central through hole. The invention has the advantages of simple device, good sealing performance, convenient loading and unloading operation, and can efficiently realize in-situ on-line detection of the battery in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. The patent also discloses a test method for in-situ detection of battery charging and discharging process using a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ monitoring device for self-purification capacity of pollutants in shallow water area
ActiveCN102914627BRealize in-situ monitoringAchieve standardizationGeneral water supply conservationTesting waterRubber ringRetention time
The invention discloses an in-situ monitoring device for the self-purification capacity of pollutants in a shallow water area. The in-situ monitoring device comprises a lower fixed sleeve and an upper detachable sleeve, wherein both the upper sleeve and the lower sleeve are transparent cylinders with top and bottom openings respectively; a vertical ruler is arranged on the inner wall of the upper detachable sleeve; the lower fixed sleeve is sleeved with a plastic board capable of vertically sliding outside; four stainless steel rods respectively penetrate through four corners of the plastic board; grooves are respectively formed in circumferential surfaces where the two sleeves are abutted; corresponding lugs with threaded holes are respectively and uniformly distributed at abutted end parts; and when the upper sleeve and the lower sleeve are coaxially connected, transparent rubber rings are embedded into the grooves in the circumferential surfaces of the two sleeves and the two sleeves are sealed into a whole through lug screwing screws. The in-situ monitoring device is simple in structure and can be used for analyzing the change of the load of pollutants in the enclosed water body along the retention time by continuous or discontinuous sampling, so as to conveniently quantify the self-purification capacities of the pollutants in different time intervals in an in-situ manner; and the trend of the pollutants can be quantitatively analyzed by adopting means such as isotopic tracing and the like, so that the in-situ quantification and standardization of the self-purification capacity evaluation are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com