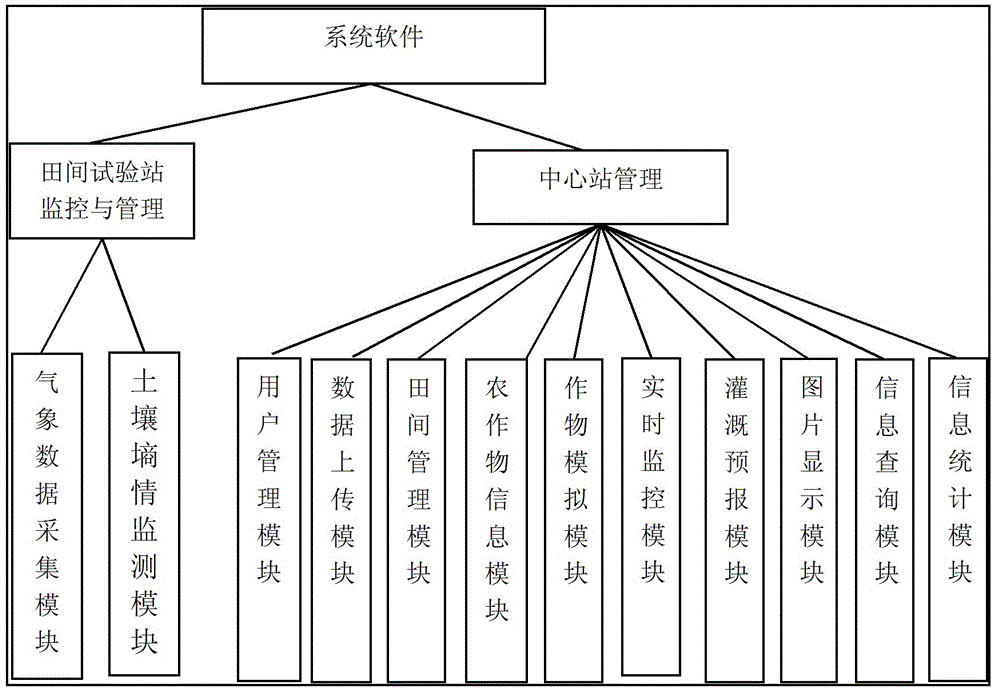
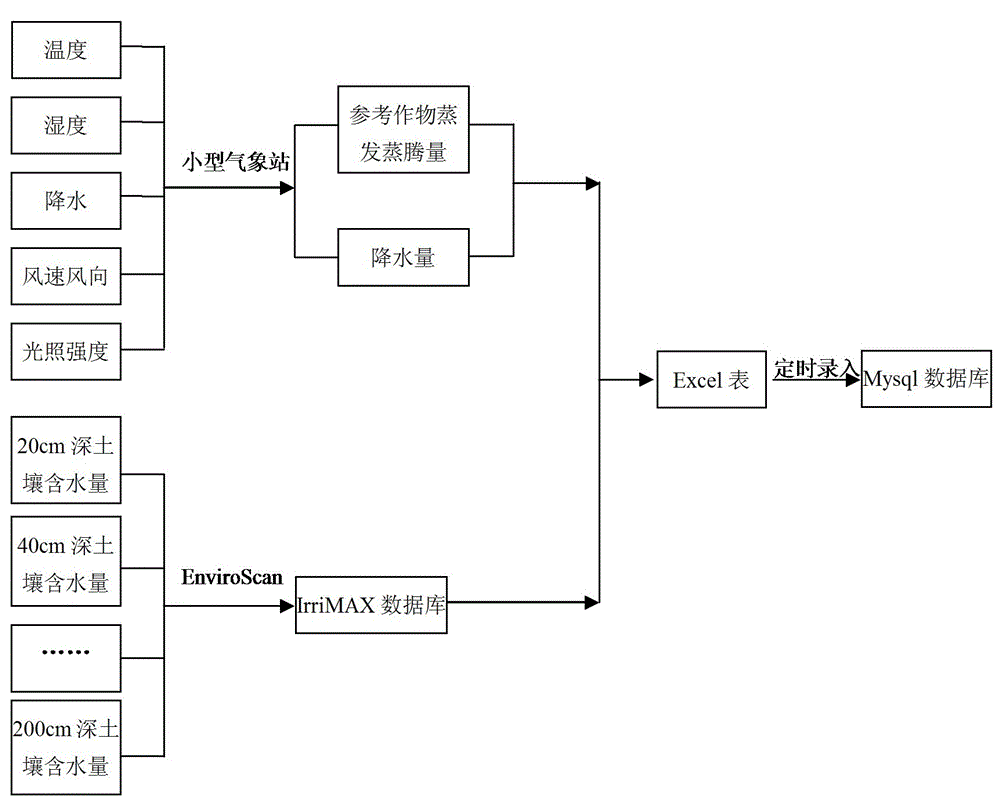
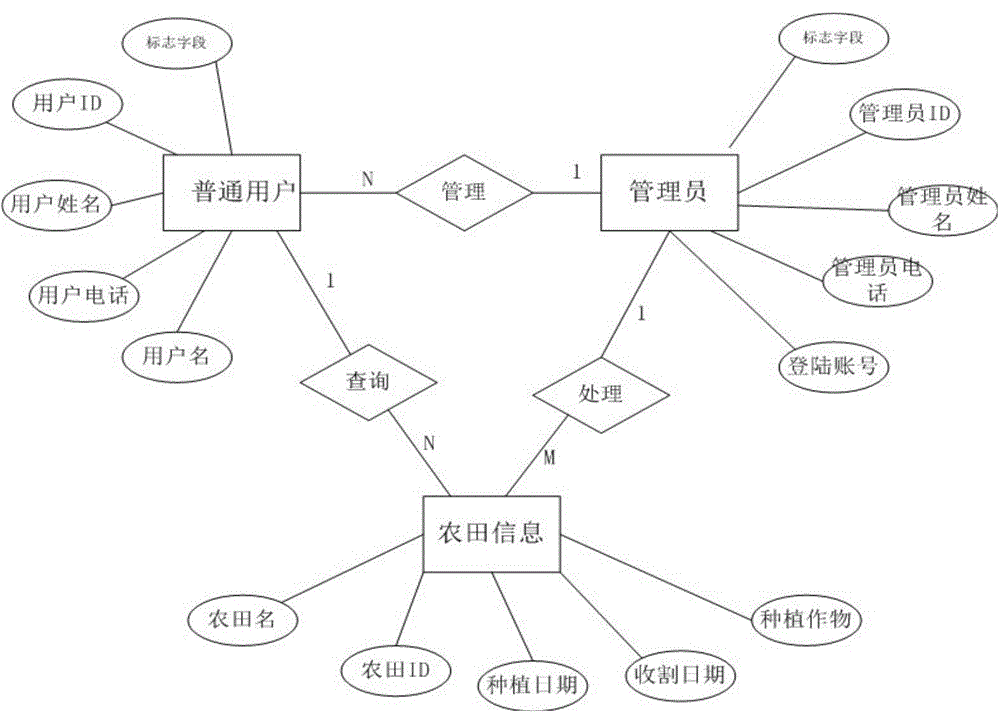
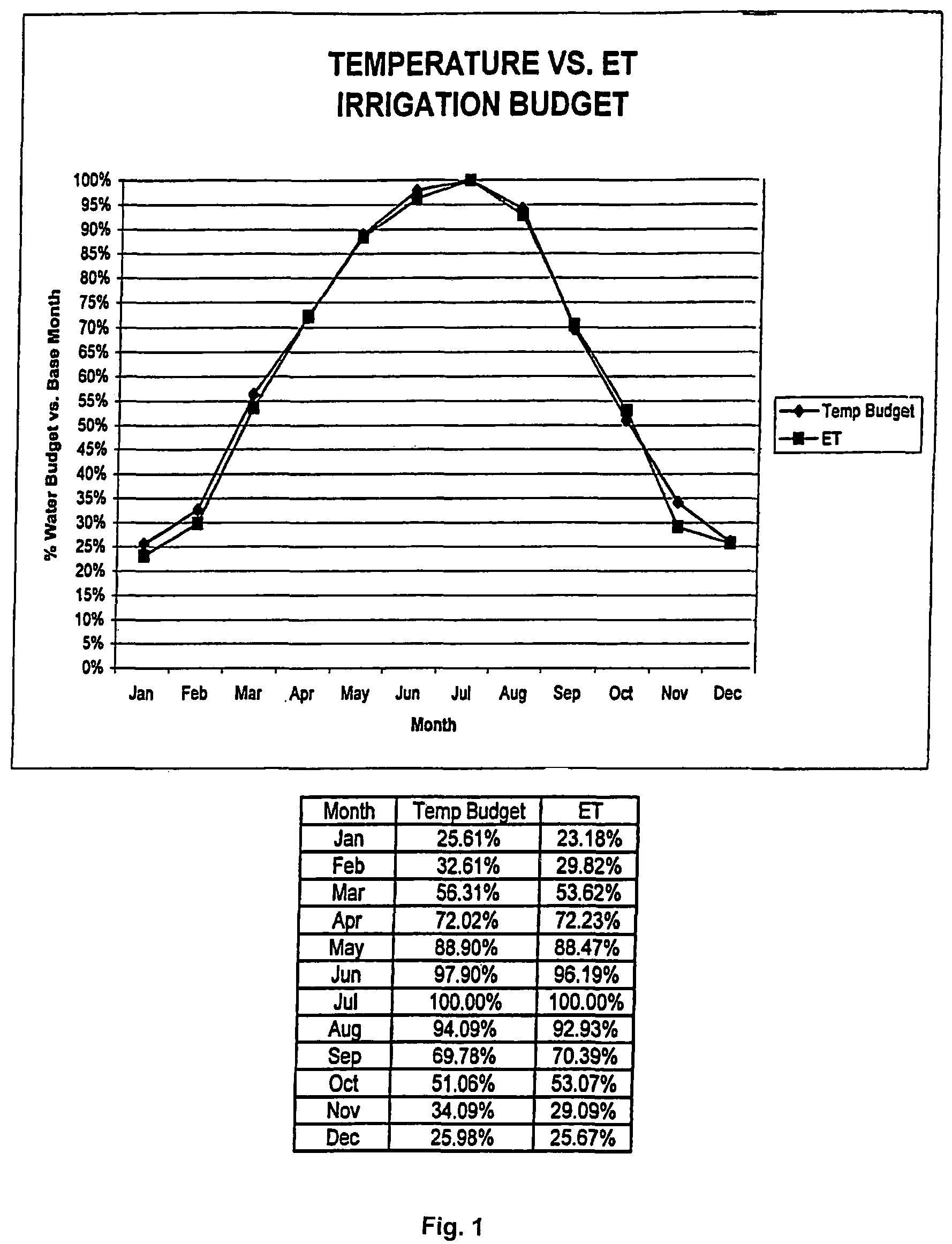
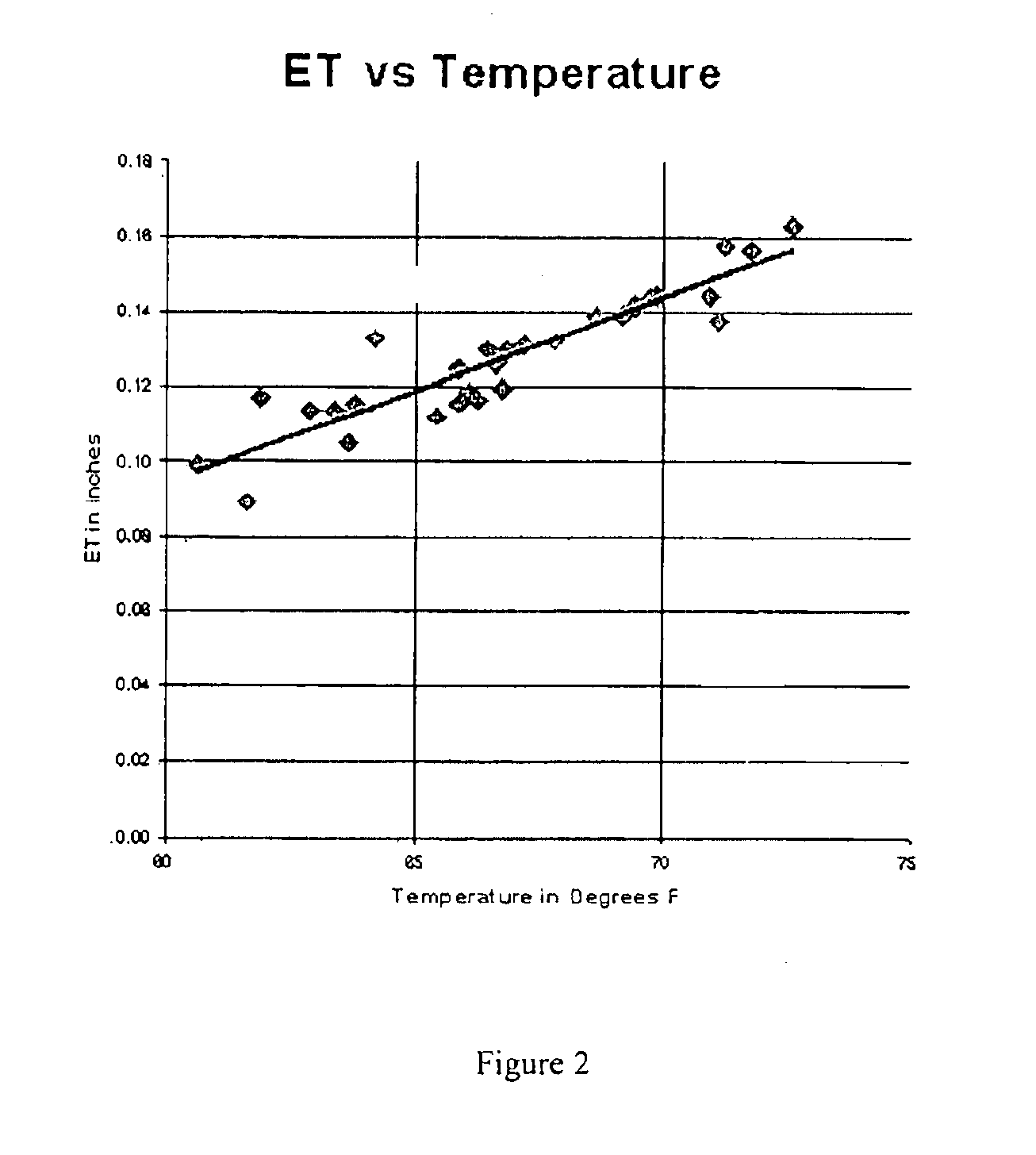
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
350 results about "Evapotranspiration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land and ocean surface to the atmosphere. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil, canopy interception, and waterbodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant and the subsequent loss of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle. An element (such as a tree) that contributes to evapotranspiration can be called an evapotranspirator.
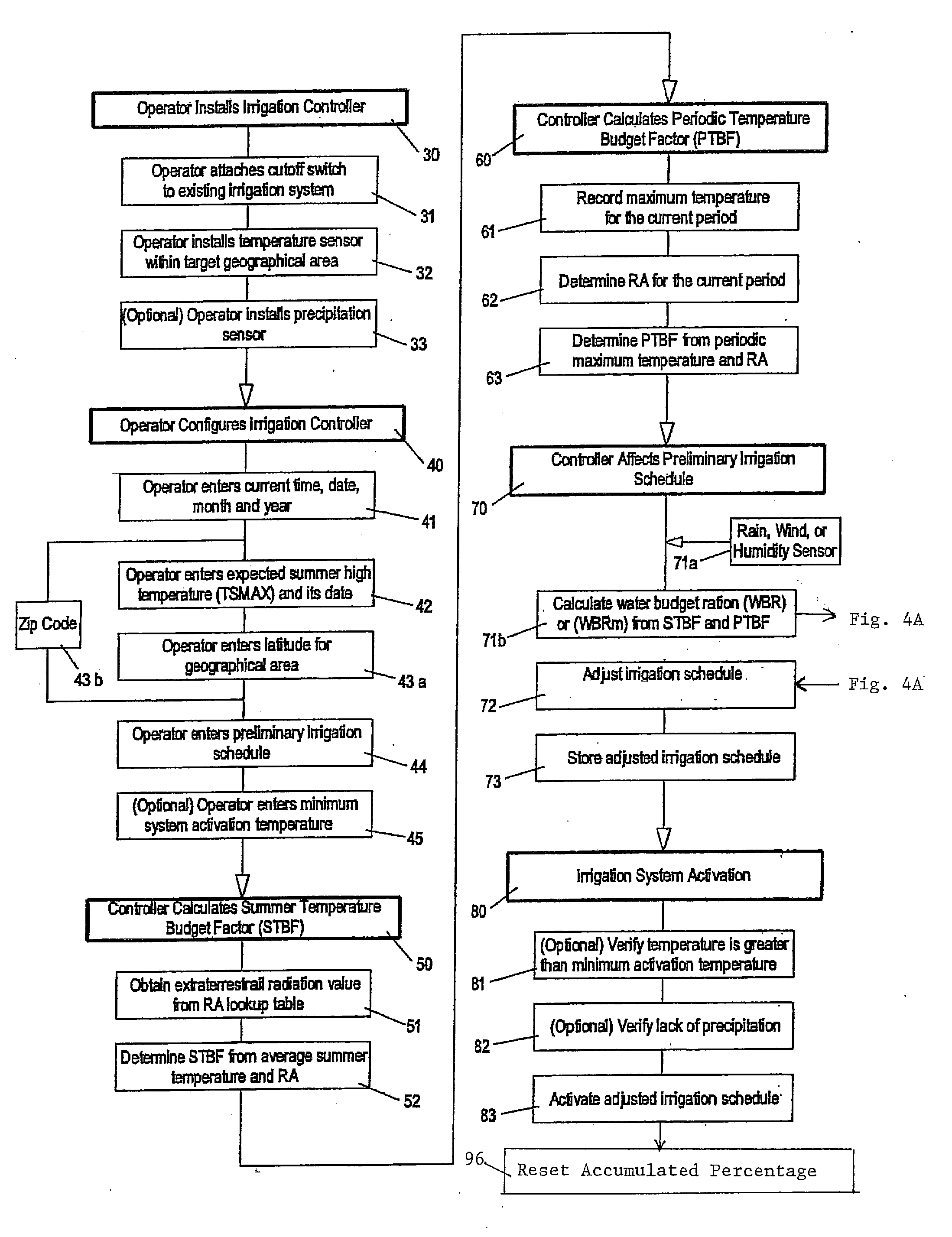
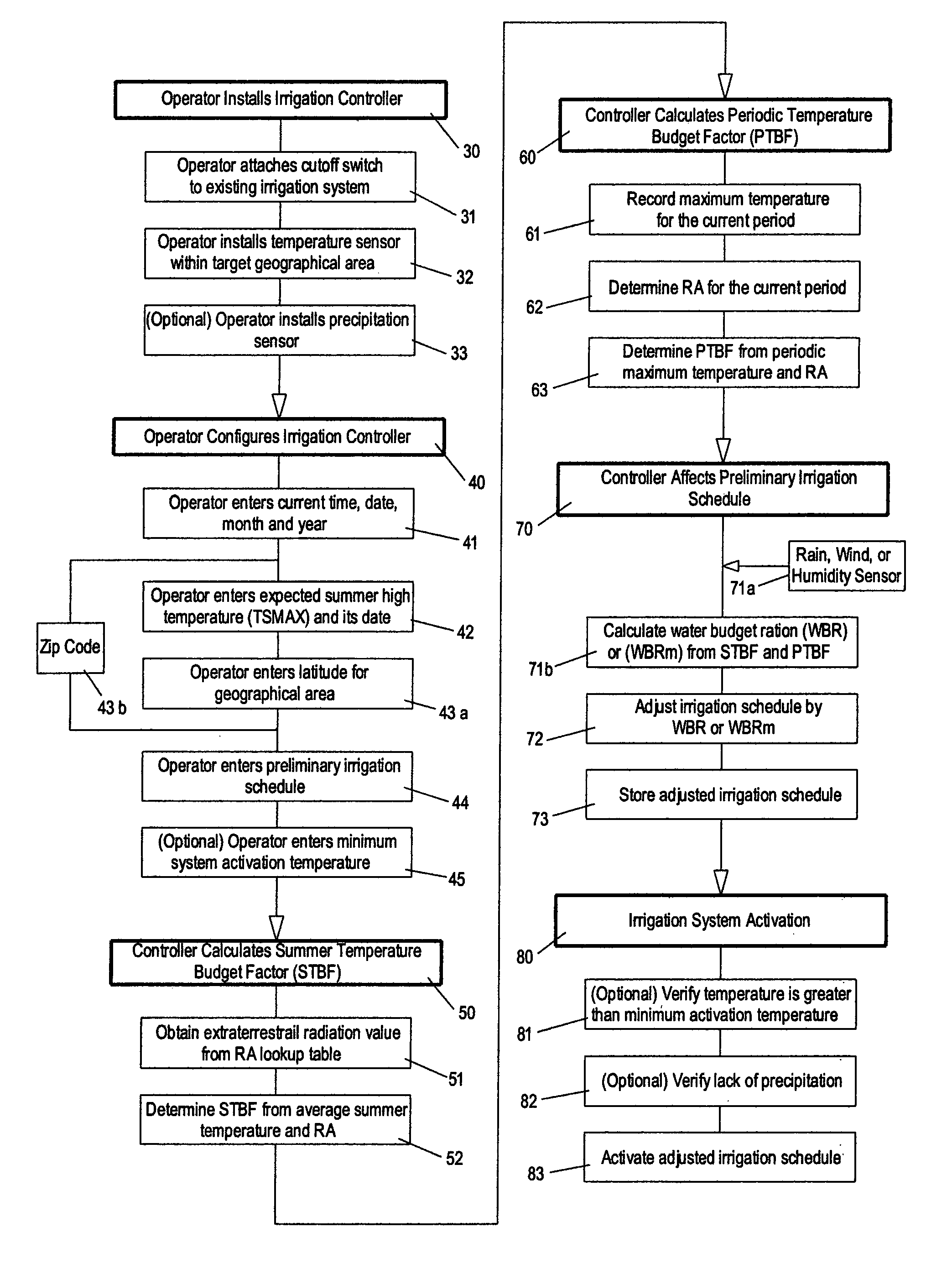
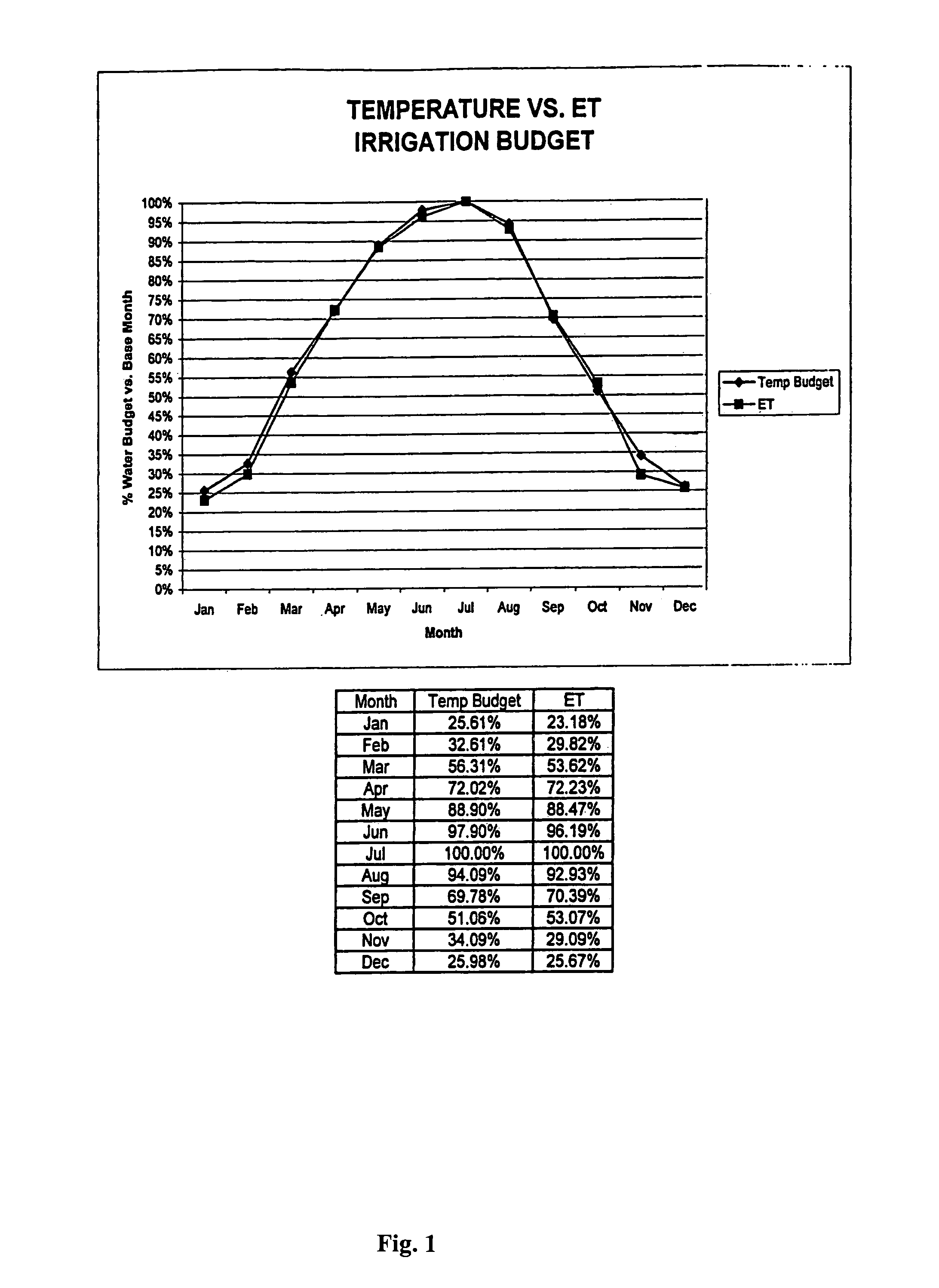
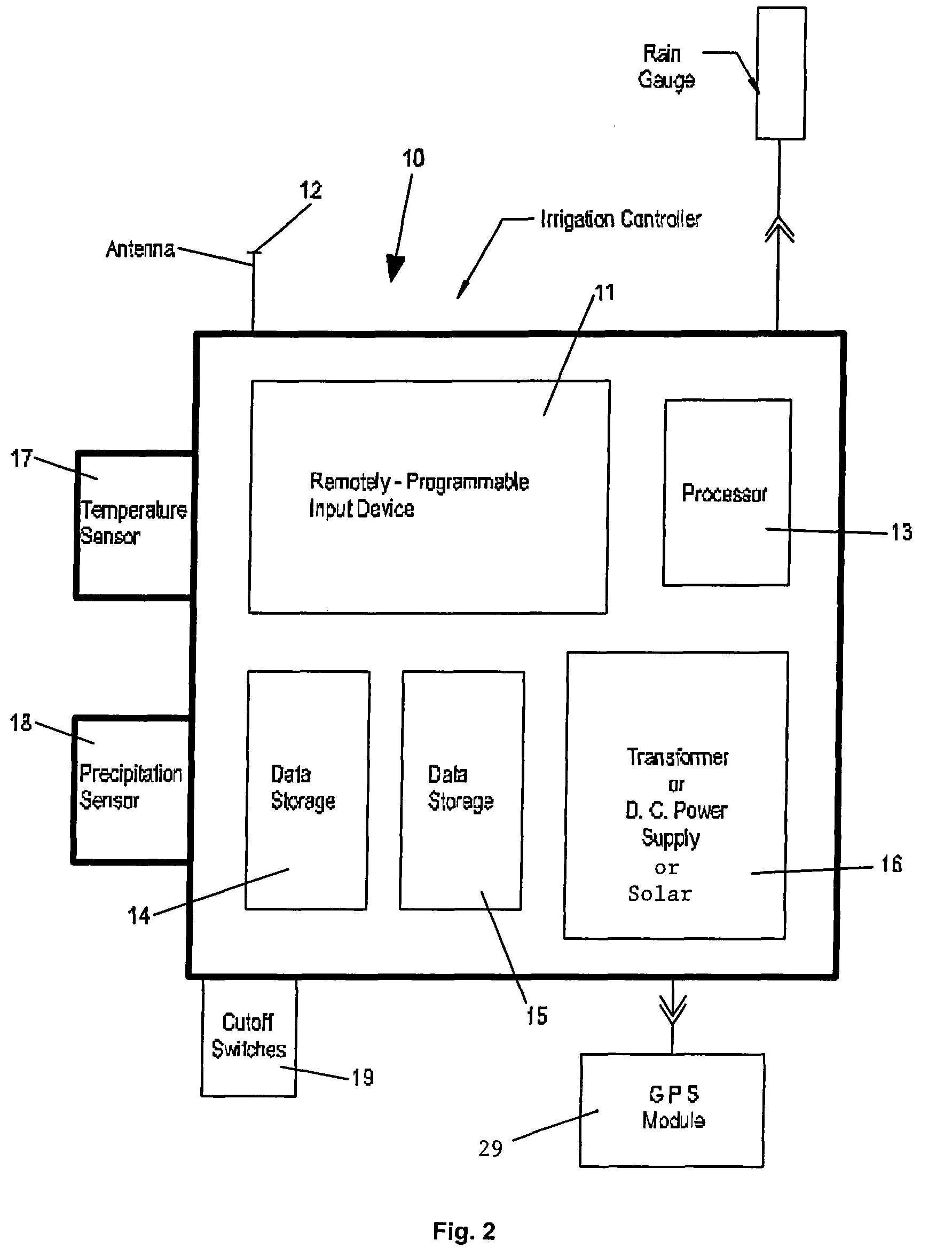
Irrigation water conservation with automated water budgeting and time of use technology
ActiveUS20110093123A1Improved wireless receptionMinimized overall profileSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationCurrent sensorTime of use
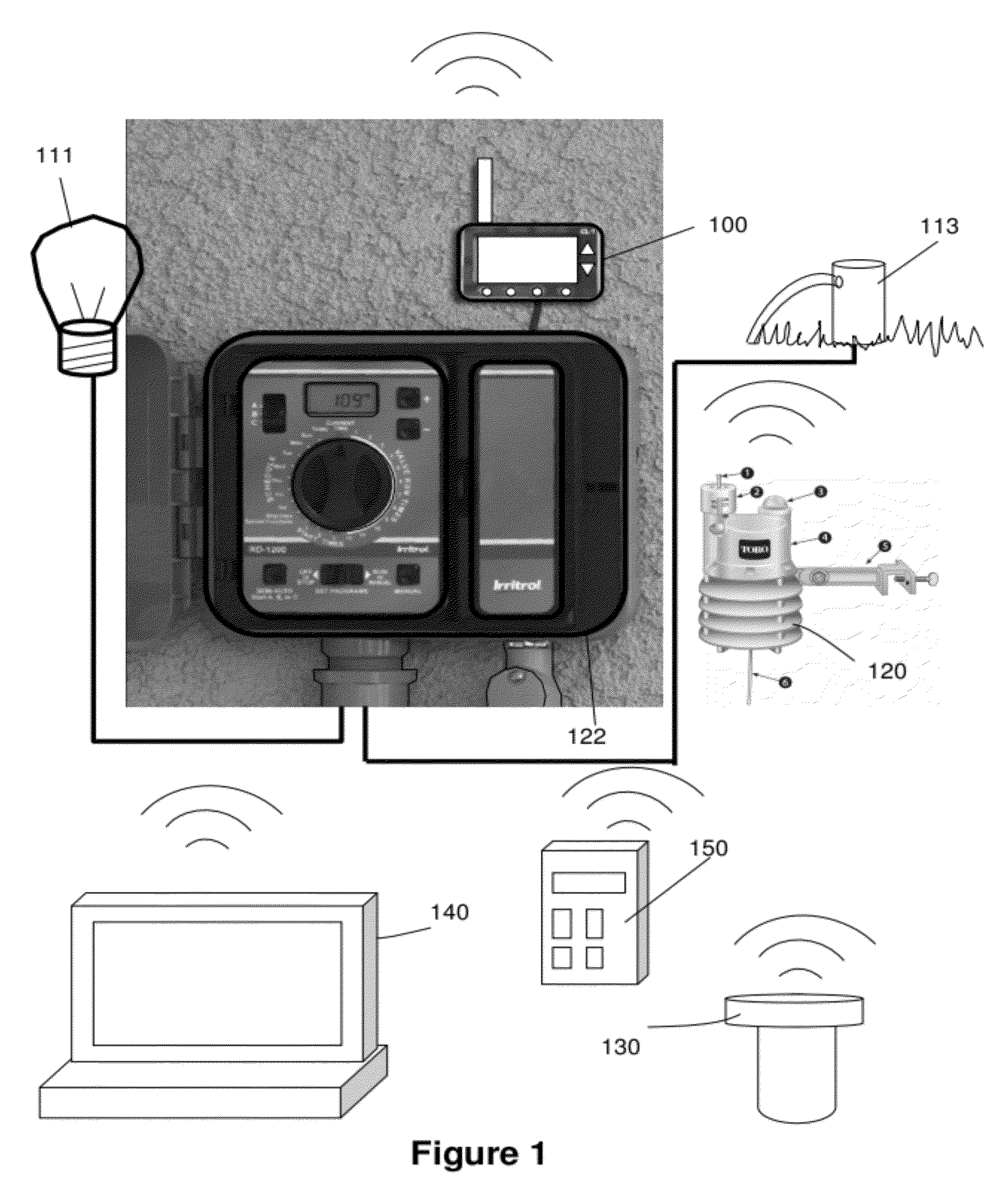
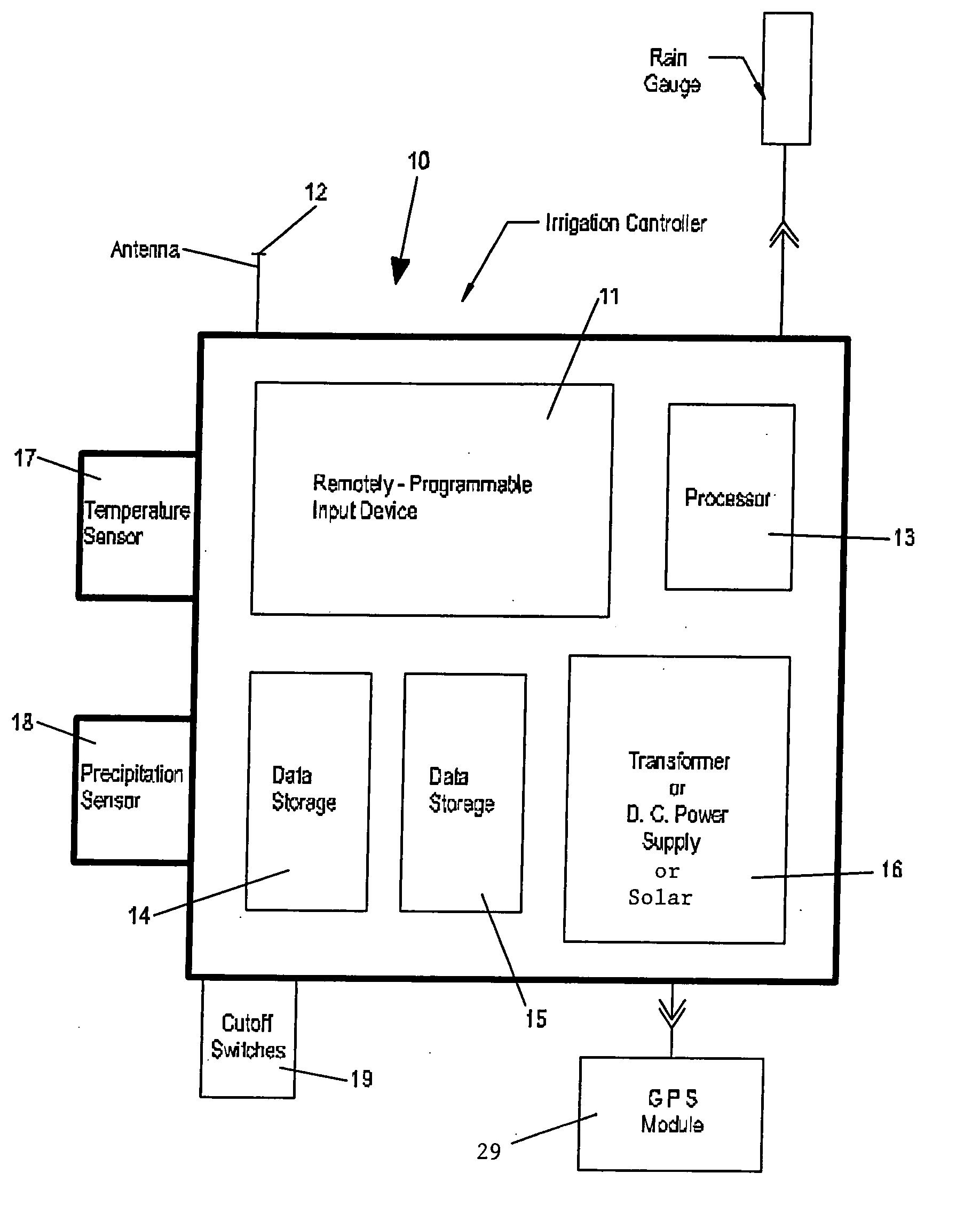
The present invention provides a multitude of embodiments for landscape water conservation with automated water budgeting or seasonal adjustment. Water budget automation may be implemented within an irrigation controller, by means of an add-on or a plug-in to the controller, or broadcast from a central location. The environmental data used for automated water budgeting may be historical including ambient temperature, wind, solar radiation, relative humidity, soil moisture, soil temperature, or evapotranspiration, or combinations thereof, or with a combination of current sensor data. The automated water budgeting may be accomplished with a percentage accumulation method which adjusts watering intervals and schedules, or on a daily percentage basis. In addition, government based restricted watering schedules may be combined within all the above embodiments to provide additional flexibility for water conservation.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
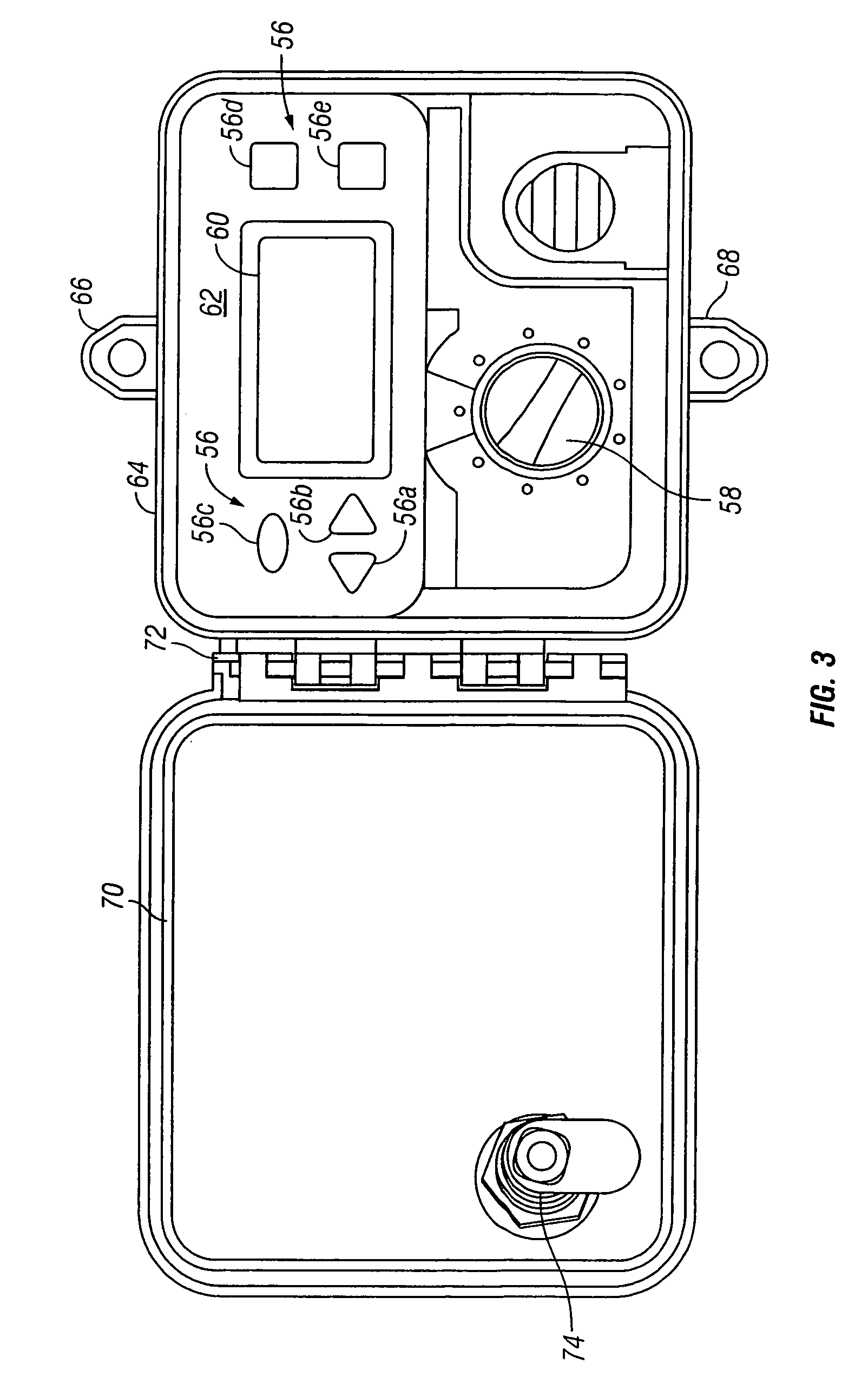
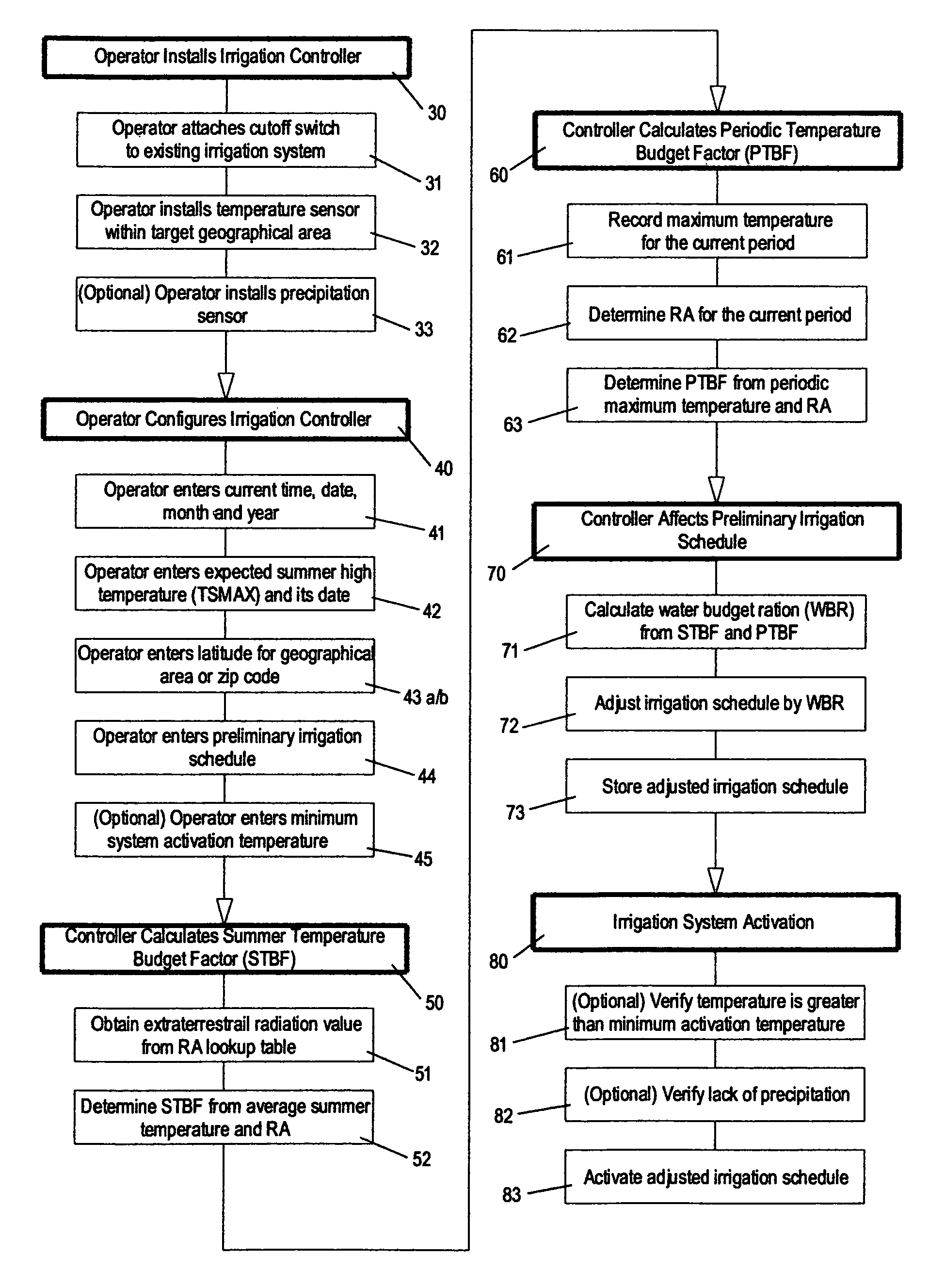
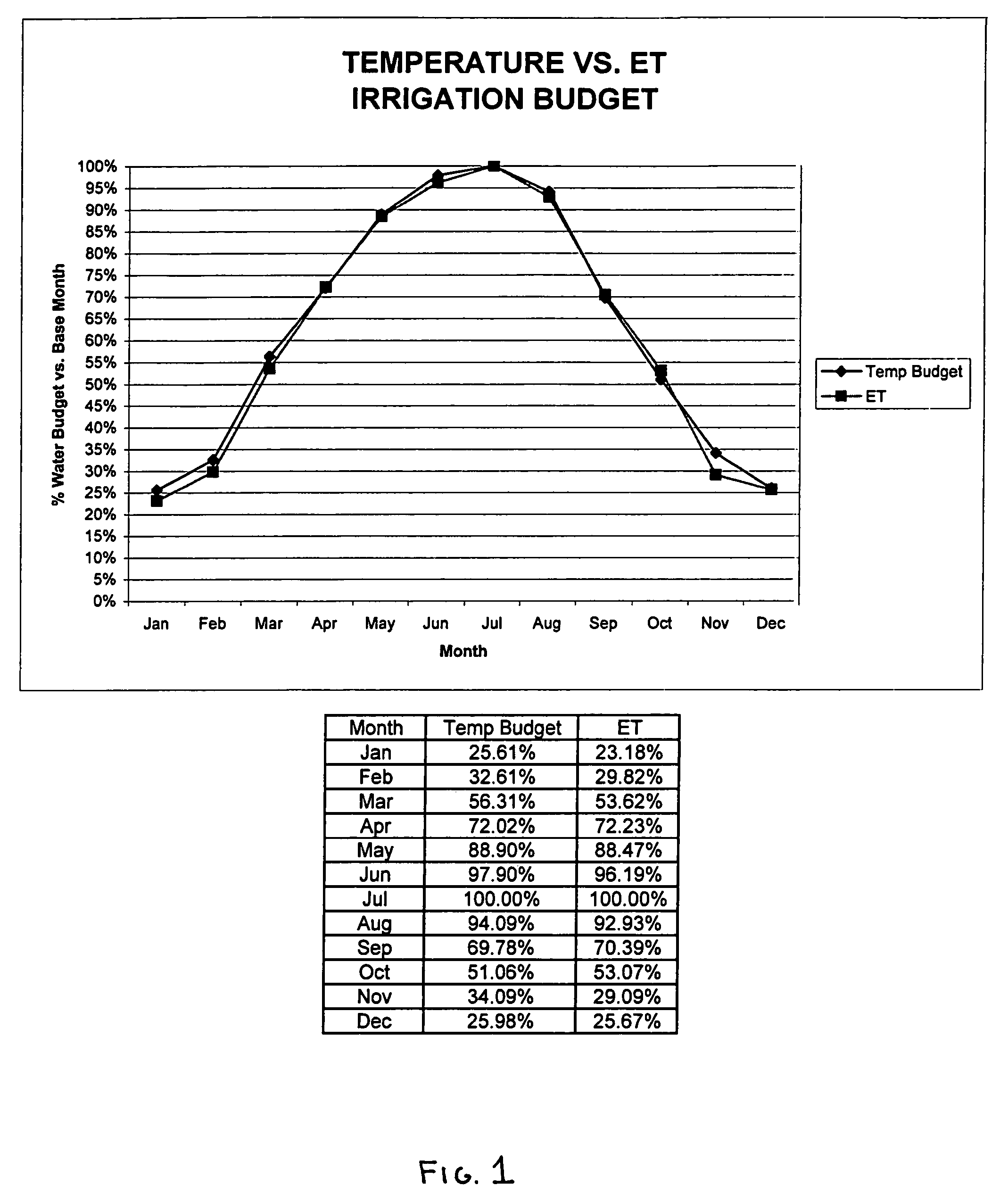
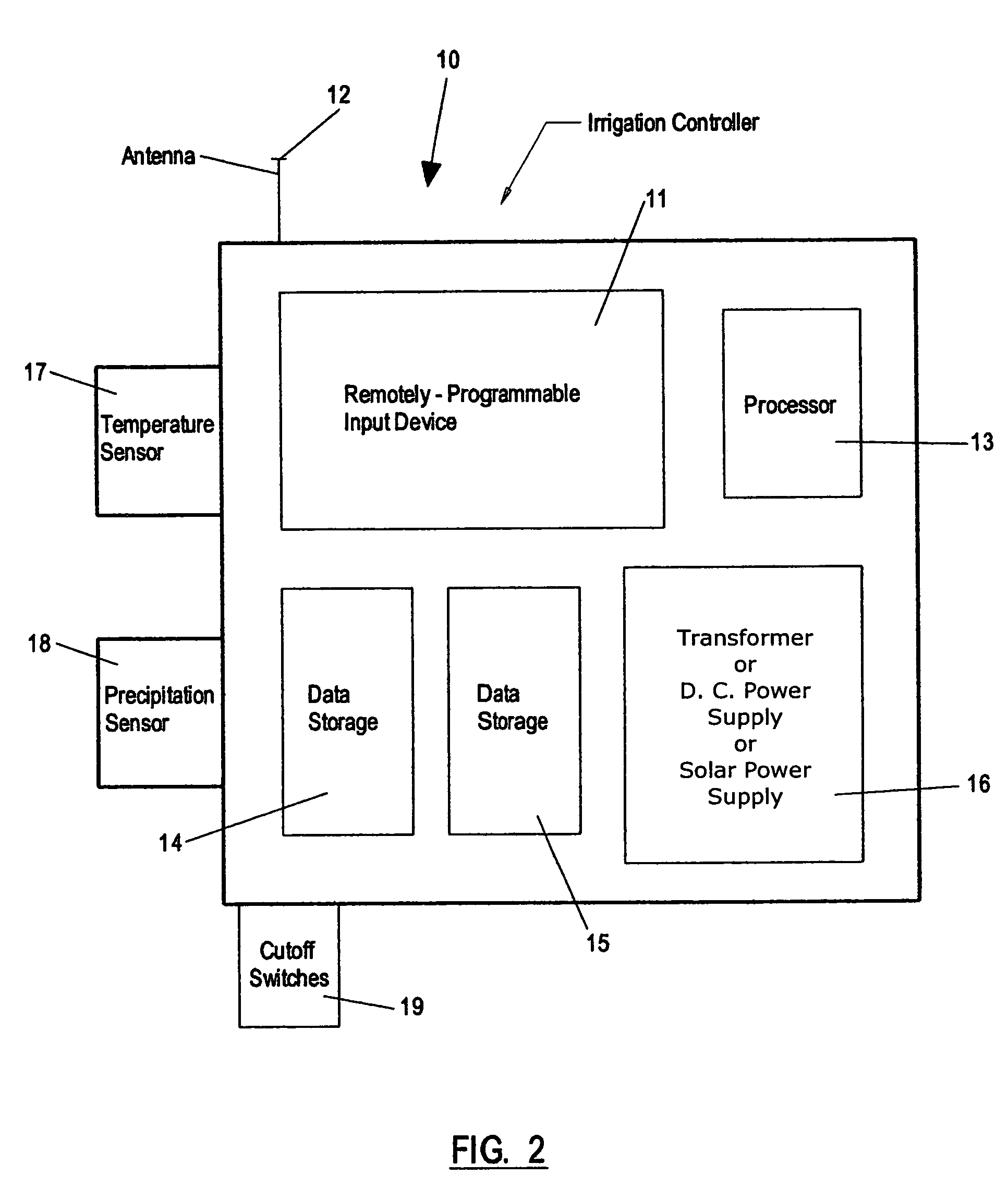
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS7266428B2Easy and less-expensive to installEasy and less-expensive to and and maintainSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationAgricultural engineeringControl theory
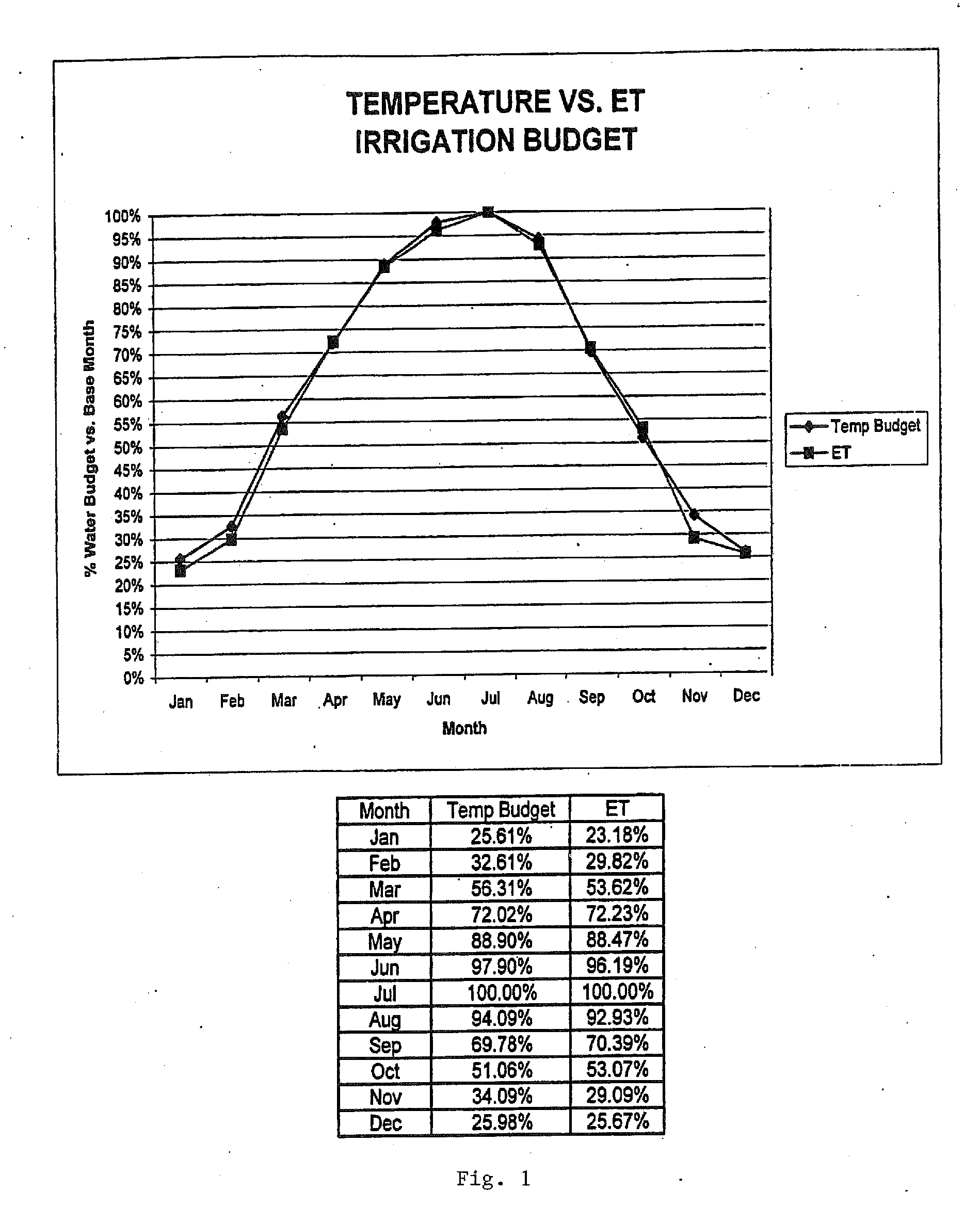
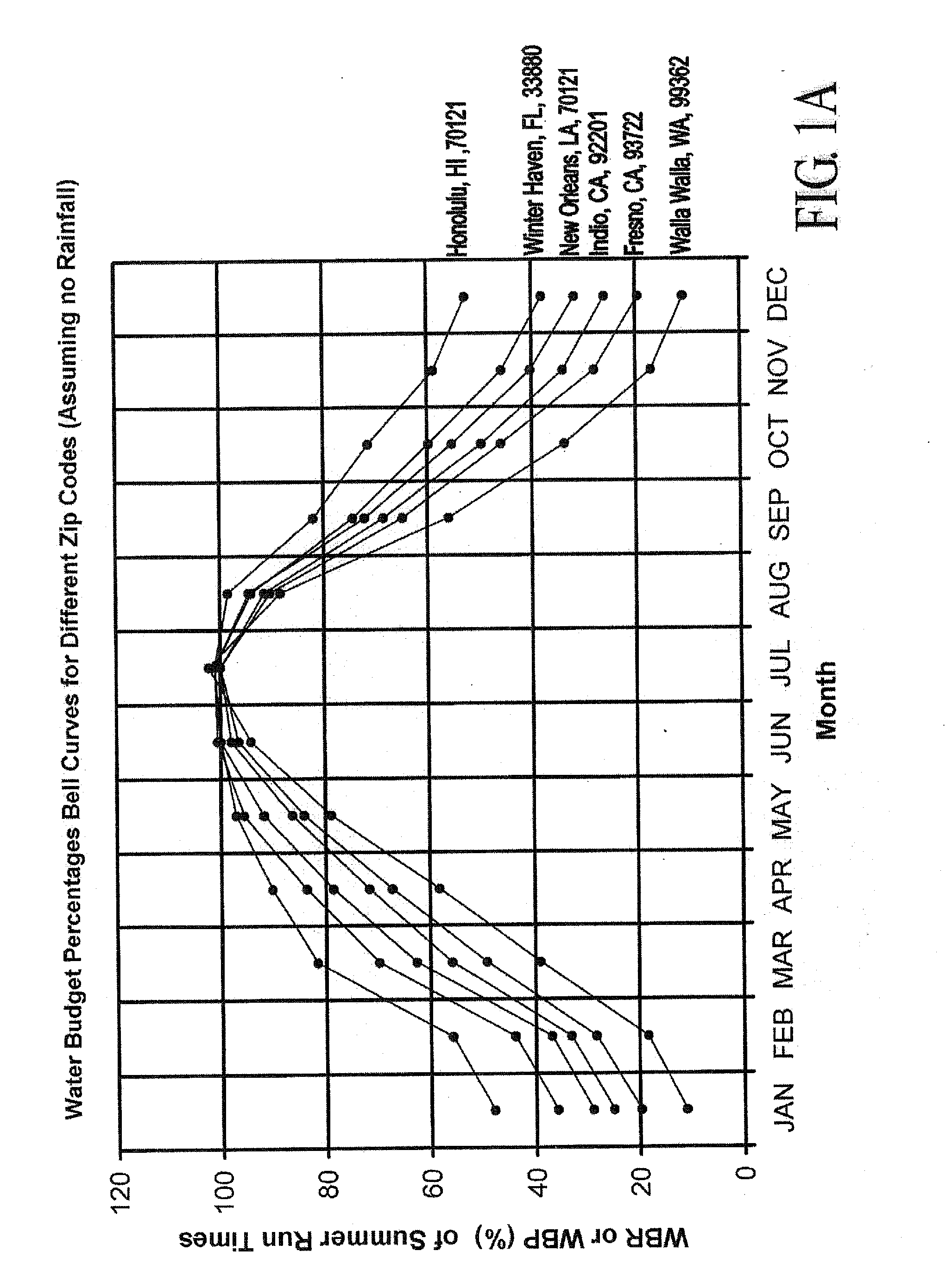
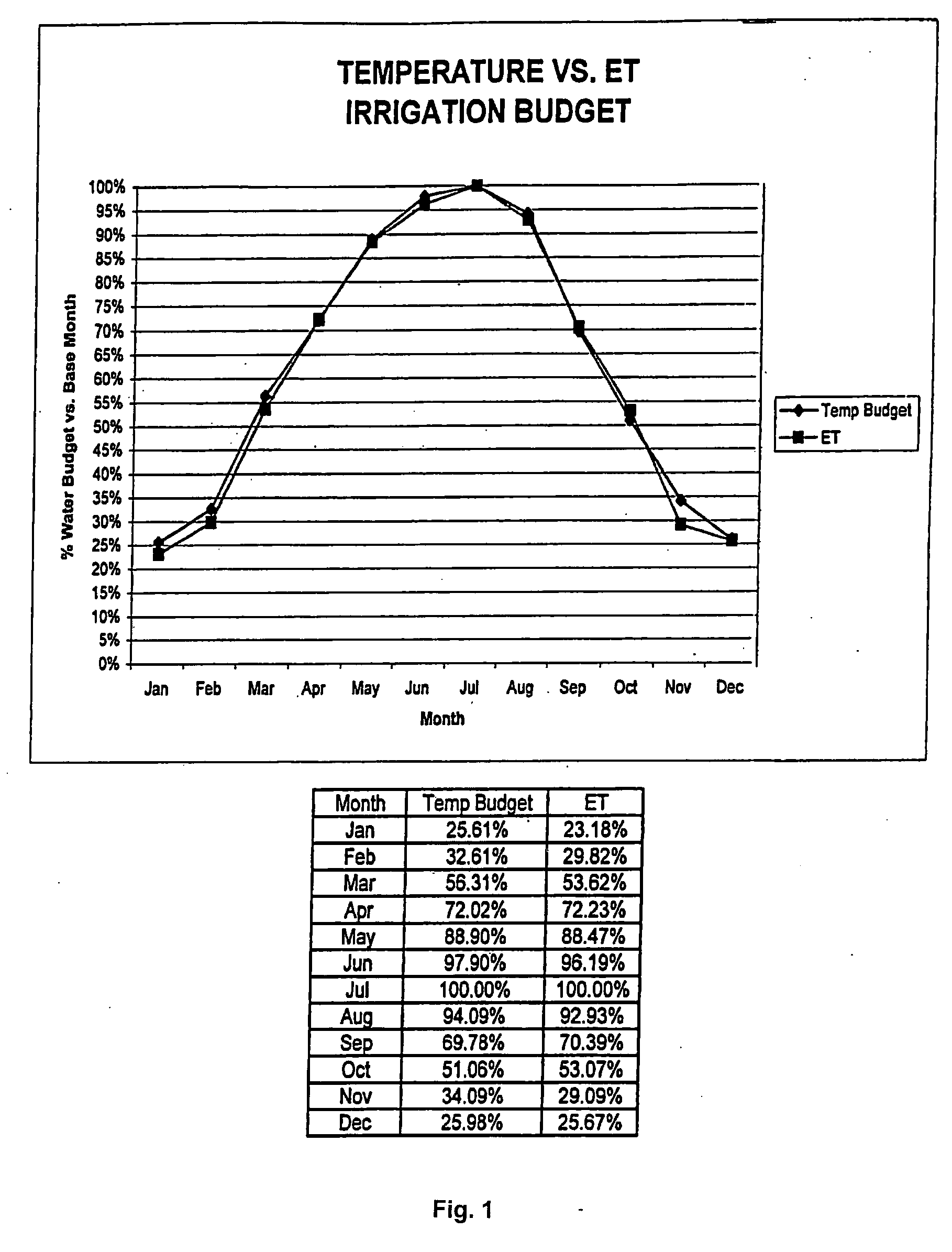
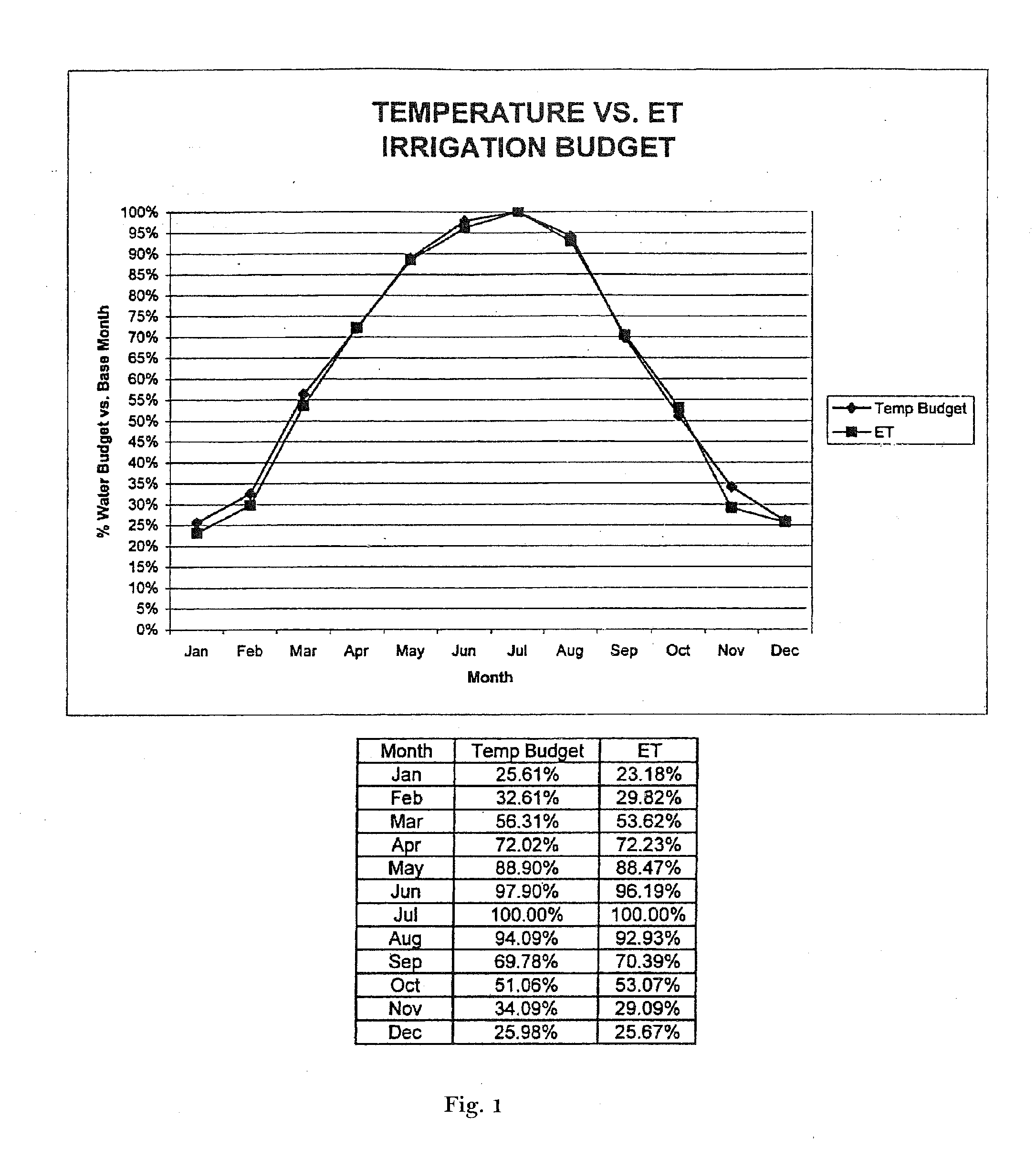
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with AC, DC, or ambient light powered irrigation controllers without the use of complex ET (evapotranspiration) data or ET related service fees. Programming may consist of the operator entering a preliminary irrigation schedule, and entering the local zip code. The controller then periodically calculates a water budget by comparing current (non ET) local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, and then modifies the preliminary schedule using the water budget. A number of embodiments are possible: stand-alone controllers with a temperature sensor attached directly to the microprocessor within that controller, or as a centrally placed CBM (Central Broadcast Module) which calculates a water budget percentage which is transmitted to one or more field controllers by wired or wireless means. Alternately, a TBM (Temperature Budget Module) that is separate from the controller is connected between the controller outputs and the valves, or mounted at the valves themselves. The TBM periodically calculates the ,water budget, monitors the controller outputs and adjusts the irrigation schedule based upon the water budget ratio. Because of its flexible capabilities with AC, DC, solar, or ambient light powered controllers, as a centrally broadcast water budget ratio in a wired or wireless configuration, or as an add-on to existing controllers or valves, its programming simplicity and close approximation to ET without its complications and cost, the present invention has the potential to save more water and minimize runoff than currently available ET methods.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
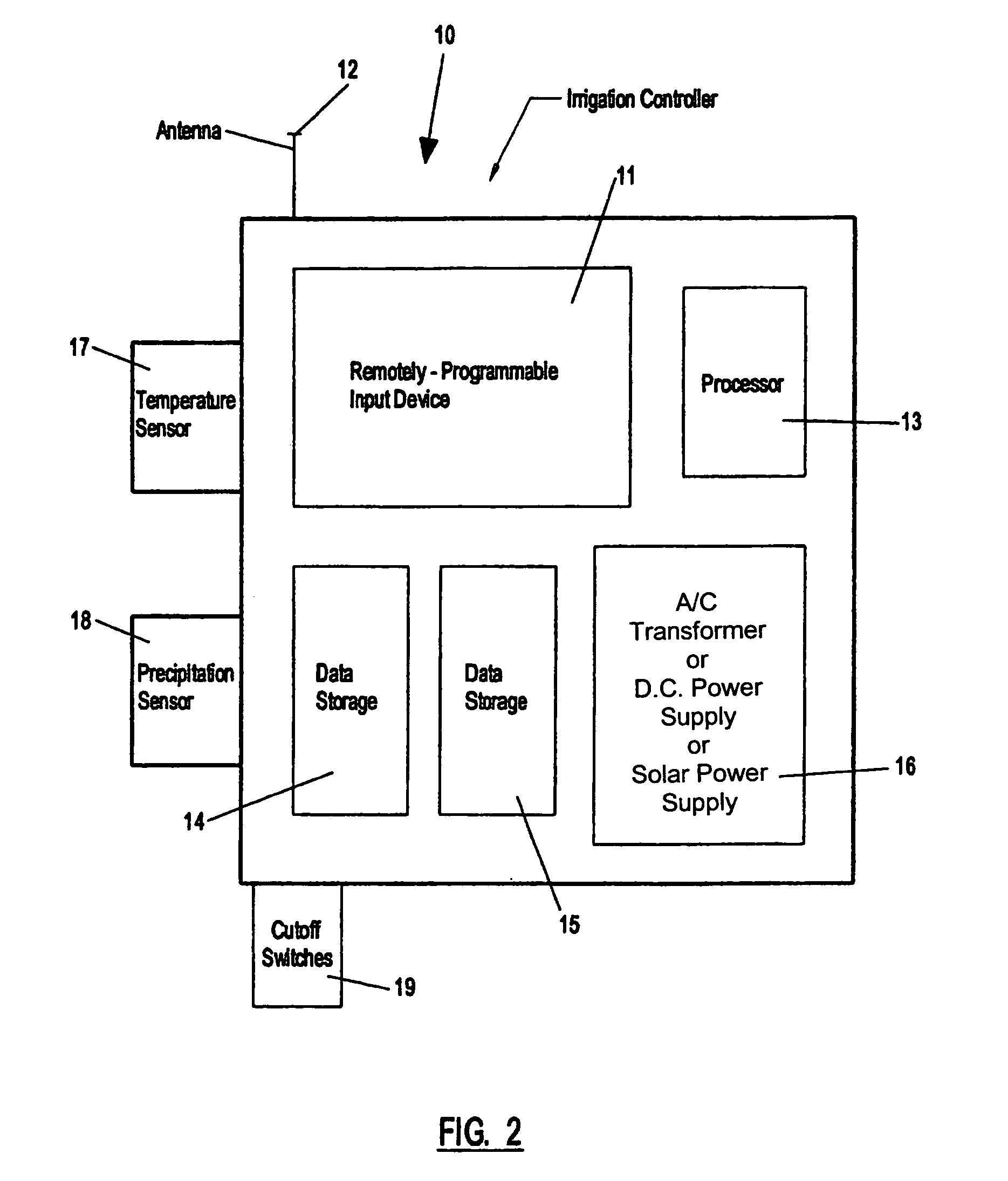
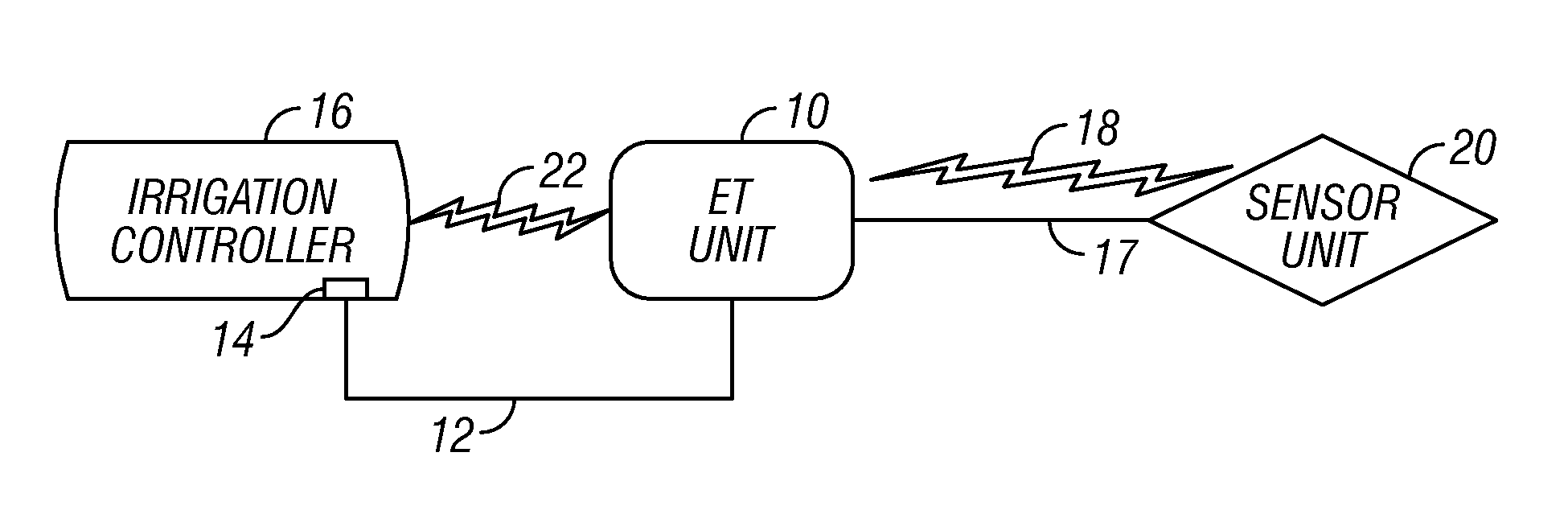
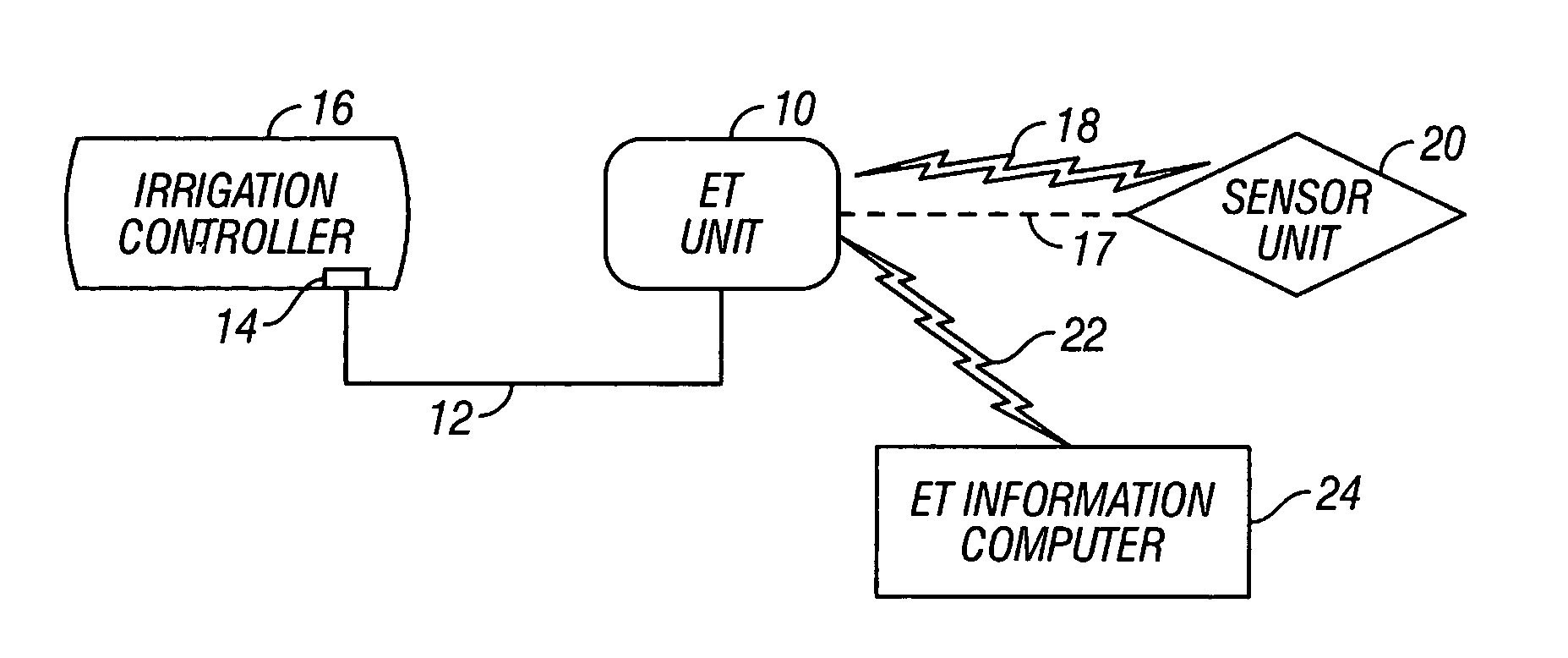
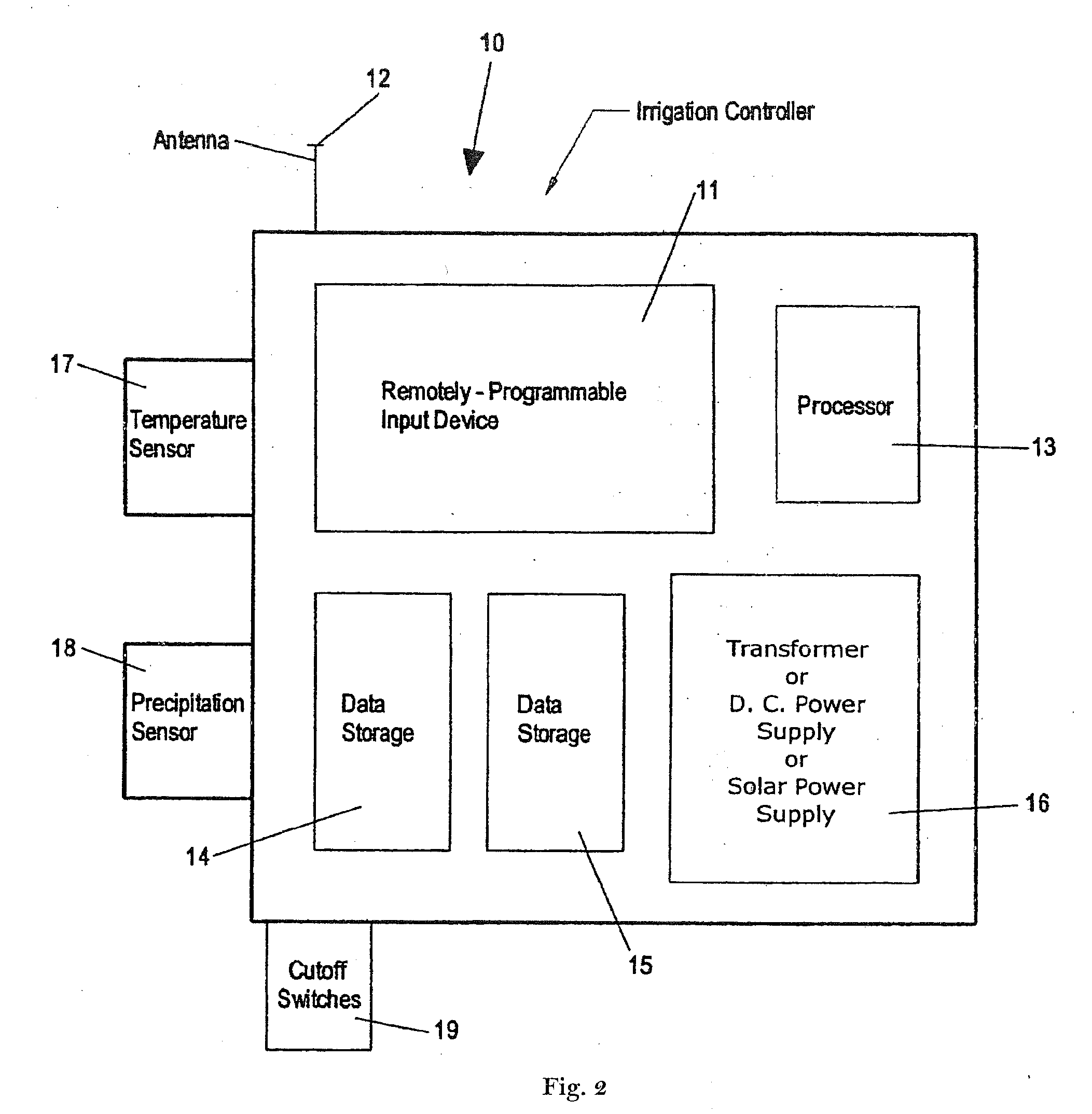
Evapotranspiration unit for re-programming an irrigation controller
ActiveUS7412303B1Increase and decrease frequencyIncrease or decrease lengthSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesTelecommunications linkCommunication link
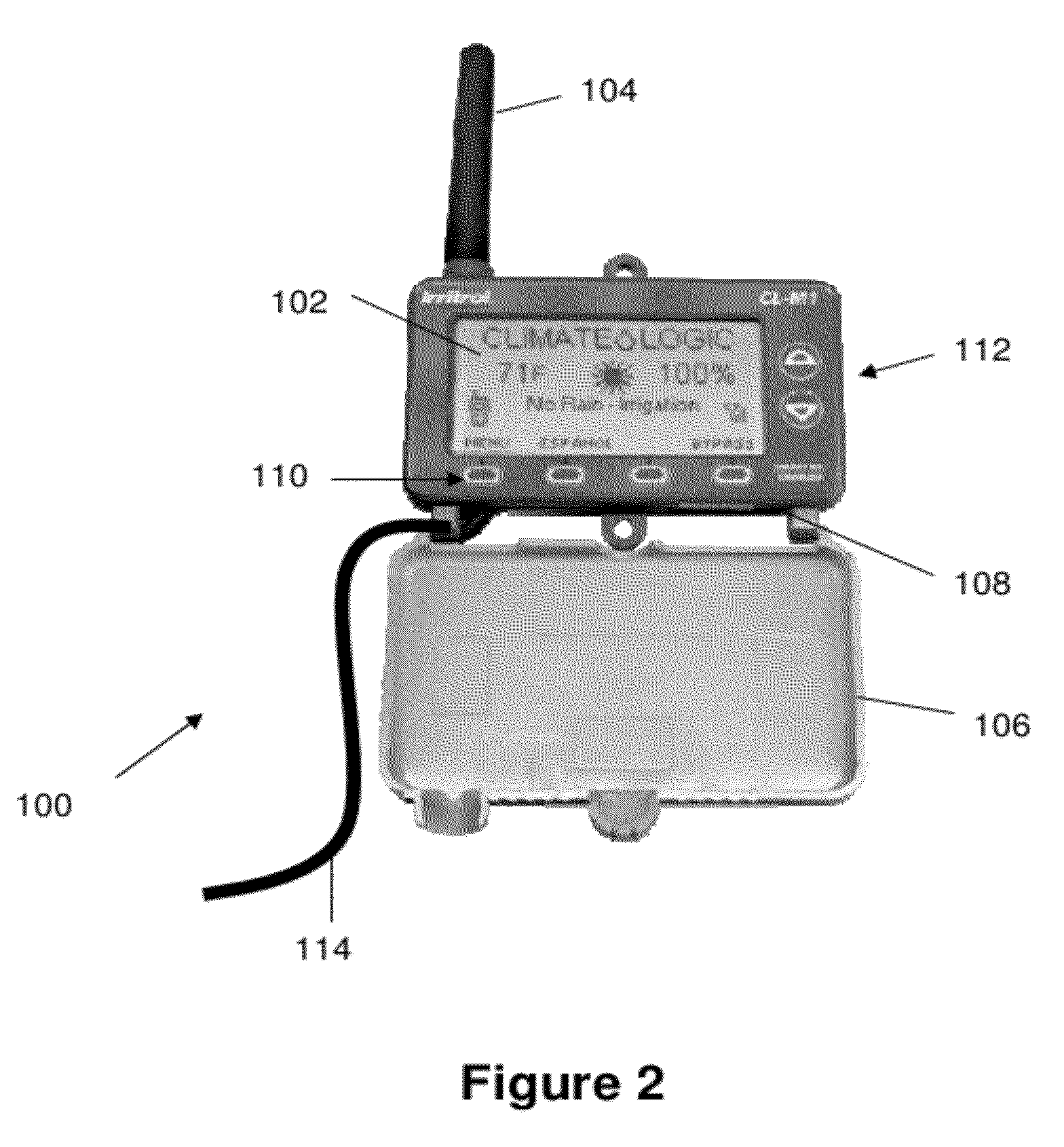
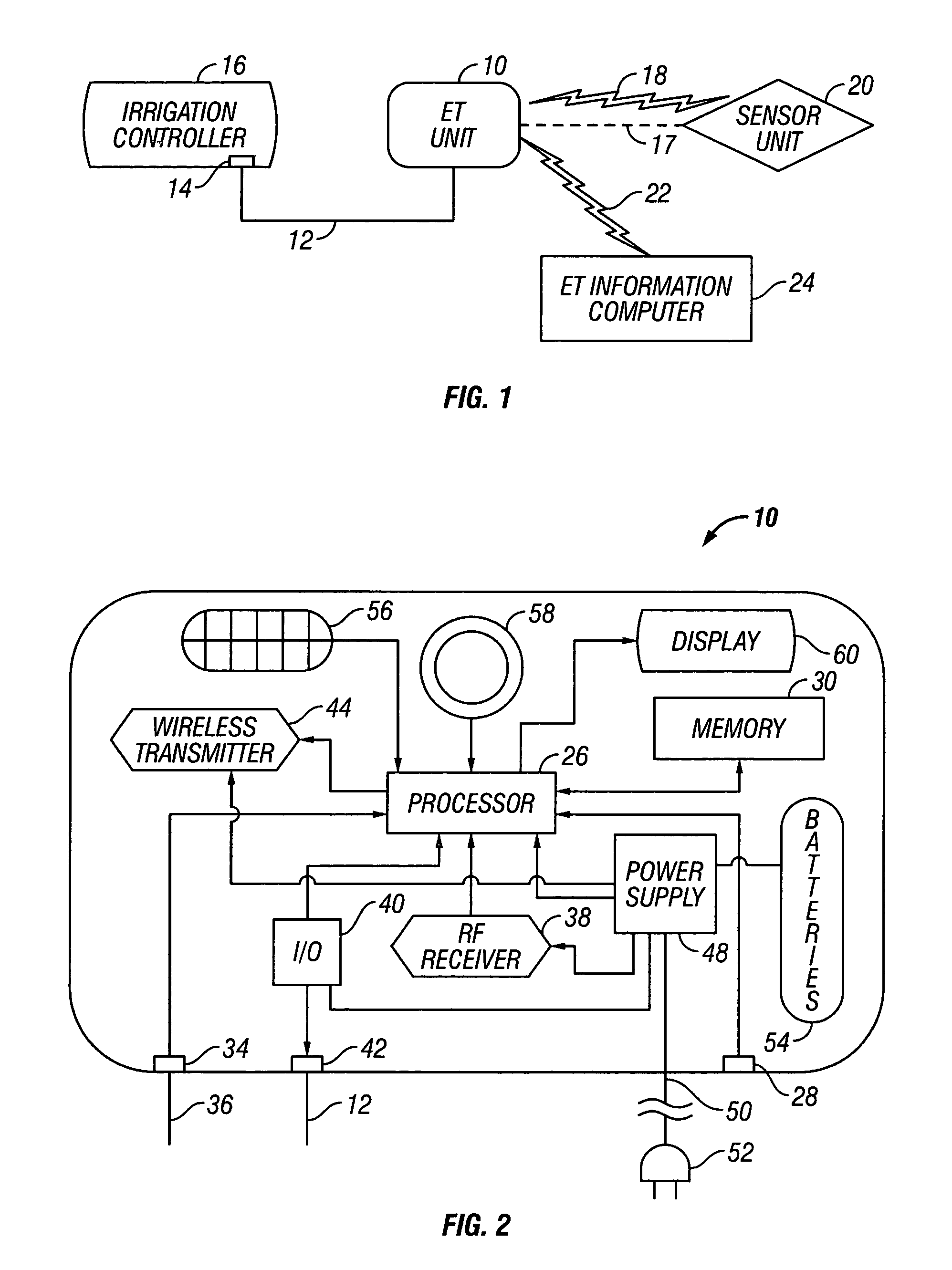
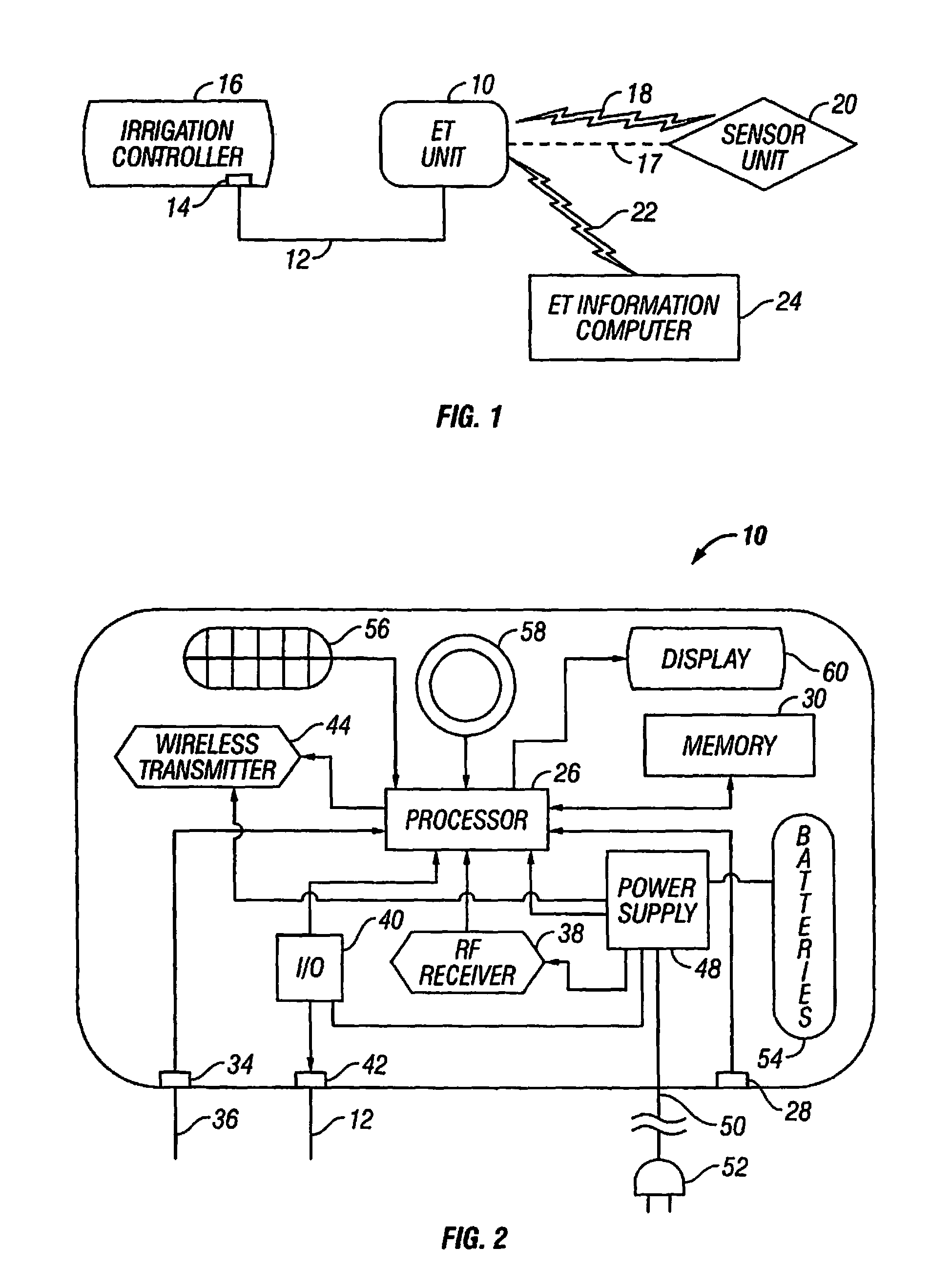
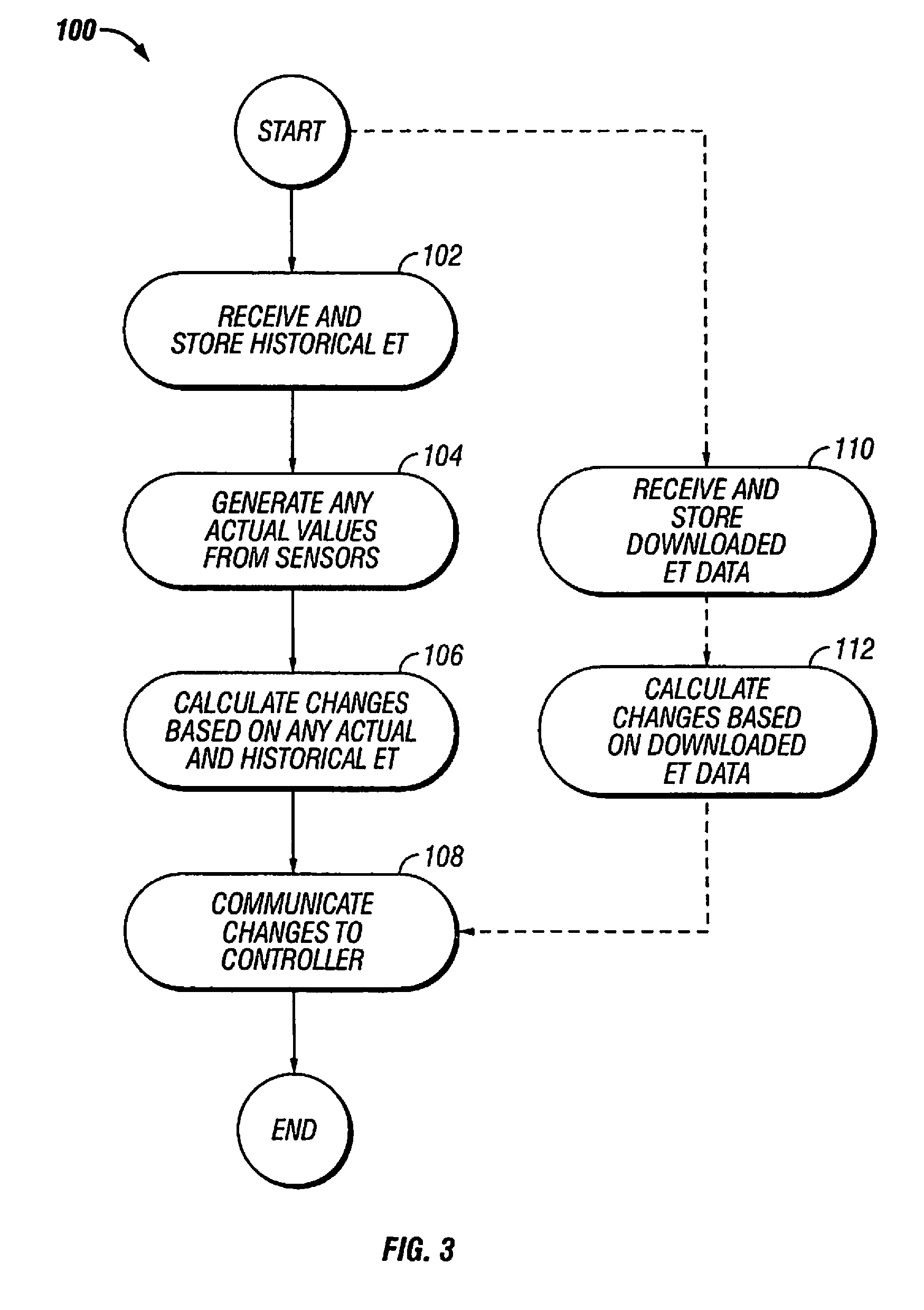
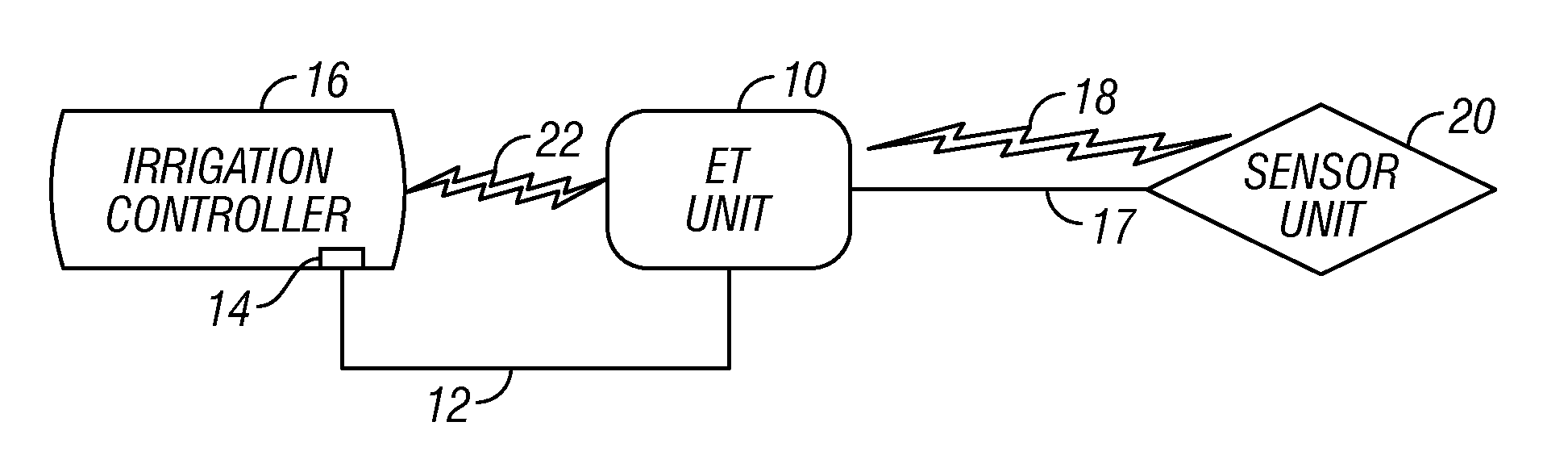
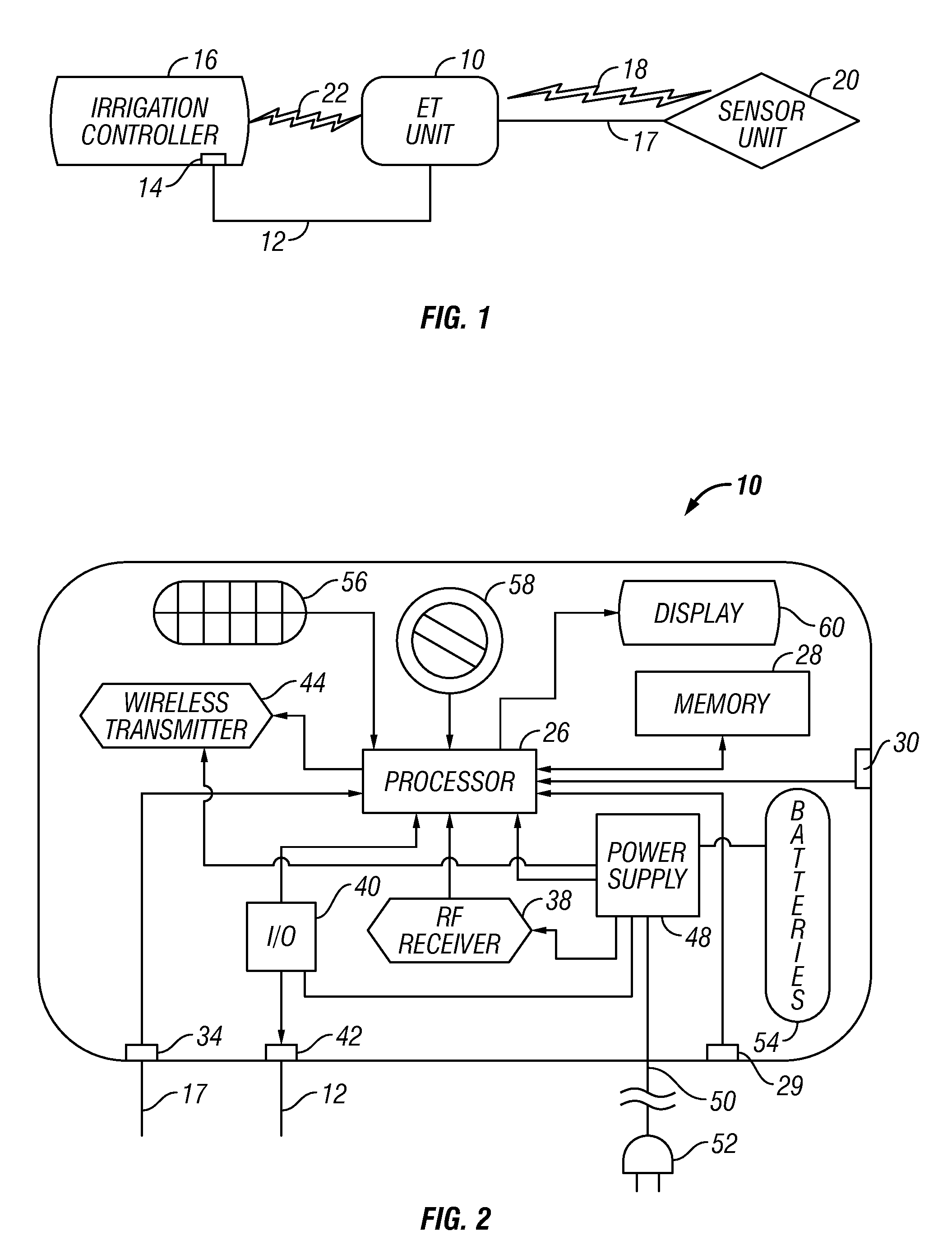
An evapotranspiration (ET) unit includes a first communication link, a processor and a second communication link. The first communication link receives actual ET data from a plurality of environmental sensors. The processor calculates changes to a set of watering schedules of a predetermined watering program of a separate irrigation controller based on the actual ET data. The changes can increase or decrease the frequency and / or length of ON times for selected stations. The second communication link transmits the changes to the irrigation controller.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS7058478B2Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationEngineeringEvapotranspiration
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with irrigation controllers based upon the ambient temperature and extraterrestrial radiation of a particular geographical area. It receives a preliminary irrigation schedule from the operator and computes a water budget ratio by comparing current local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, then modifying the preliminary irrigation schedule based upon that ratio. The present invention utilizes fewer variables, is less complex, and is much easier to install and maintain than the current evapotranspiration-based controllers.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Evapotranspiration unit for re-programming an irrigation controller
ActiveUS7877168B1Increase and decrease frequencyIncrease or decrease lengthSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationTelecommunications linkCommunication link
An evapotranspiration (ET) unit includes a first communication link, a processor and a second communication link. The first communication link receives actual ET data from a plurality of environmental sensors. The processor calculates changes to a set of watering schedules of a predetermined watering program based on the actual ET data. The changes can increase or decrease the frequency and / or length of ON times for selected stations. The second communication link transmits the changes to a separate irrigation controller.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Irrigation Controller With Weather Station
An irrigation control module is described that adjusts a watering schedule for a connected irrigation controller based on weather data provided by a local weather station. The irrigation control module can add additional weather-based irrigation schedule adjustments to an irrigation controller that may otherwise lack the hardware (e.g., wireless transmitter, sufficient memory) and software (e.g., evapotranspiration algorithms) to store and interpret weather data from a weather station.
Owner:TORO CO THE
Irrigation water conservation with temperature budgeting and time of use technology
ActiveUS20070293990A1Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesEngineeringCentral unit
The present invention provides numerous methods, systems and apparatus that use a novel form of water budgeting technology for water conservation without the use of complex ET (Evapotranspiration) data or methods. Embodiments include incorporating the technology directly into irrigation controllers, into modules added on to existing controllers, or into central units that broadcast a water budget that can alter the schedules of one, many, or selected groups of remotely located controllers or modules. The various methods of the present invention offer the choice of adjusting the station run times, accumulating the water budgets, altering the watering intervals, and / or combining the present water budgeting technology with local watering communities' restricted watering schedules. The result offers residential, commercial, and municipal users a wide range of practical choices for effective water conservation in landscape irrigation with temperature based water budgeting.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Field intelligent irrigation on-line control management method
InactiveCN104521699ADisplay real-time monitoring resultsClimate change adaptationWatering devicesCropEvapotranspiration
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Irrigation water conservation with temperature budgeting and time of use technology
ActiveUS7844368B2Minimizes runoffSimple calculationSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesEnvironmental resource managementAgricultural engineering
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
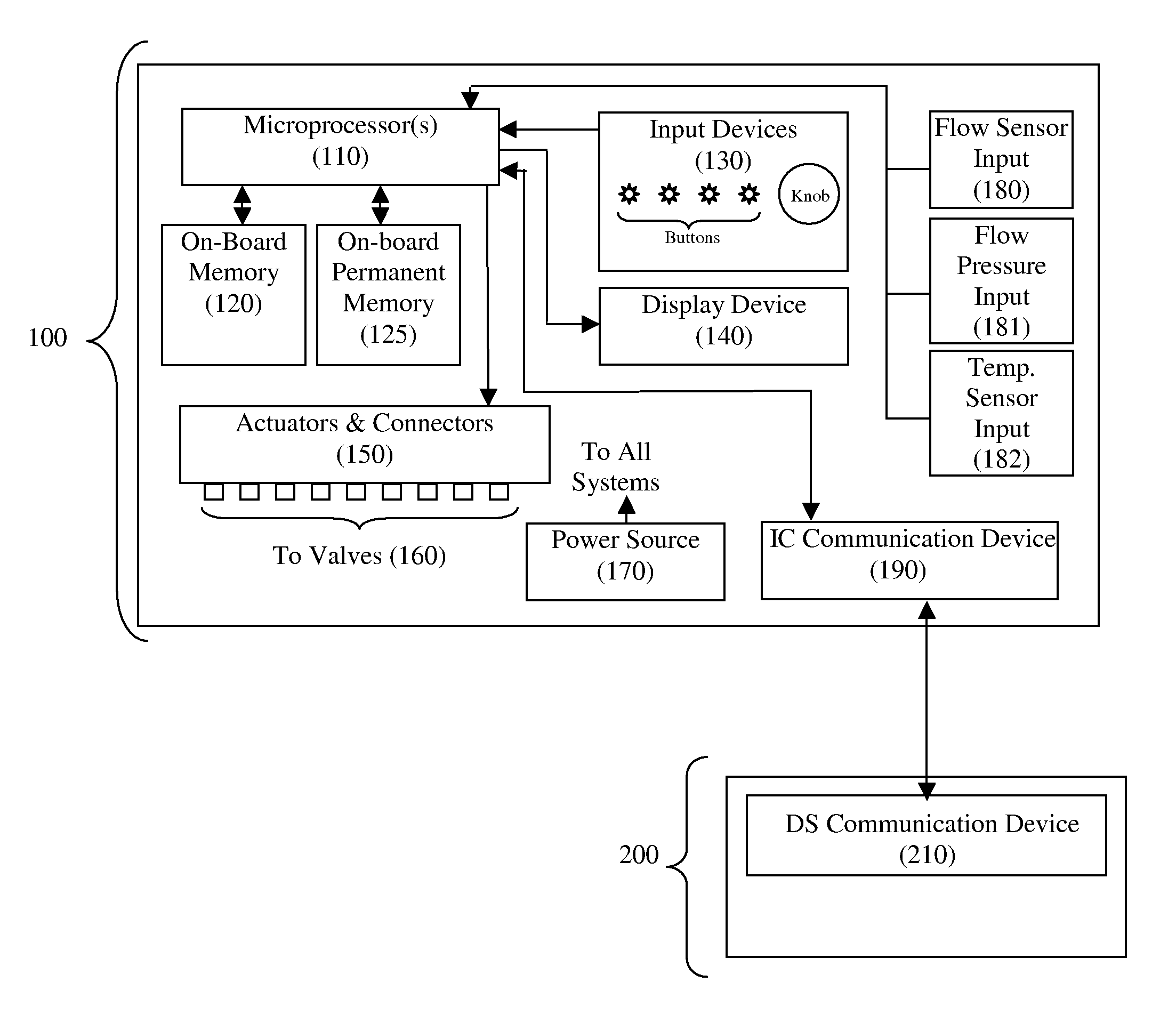
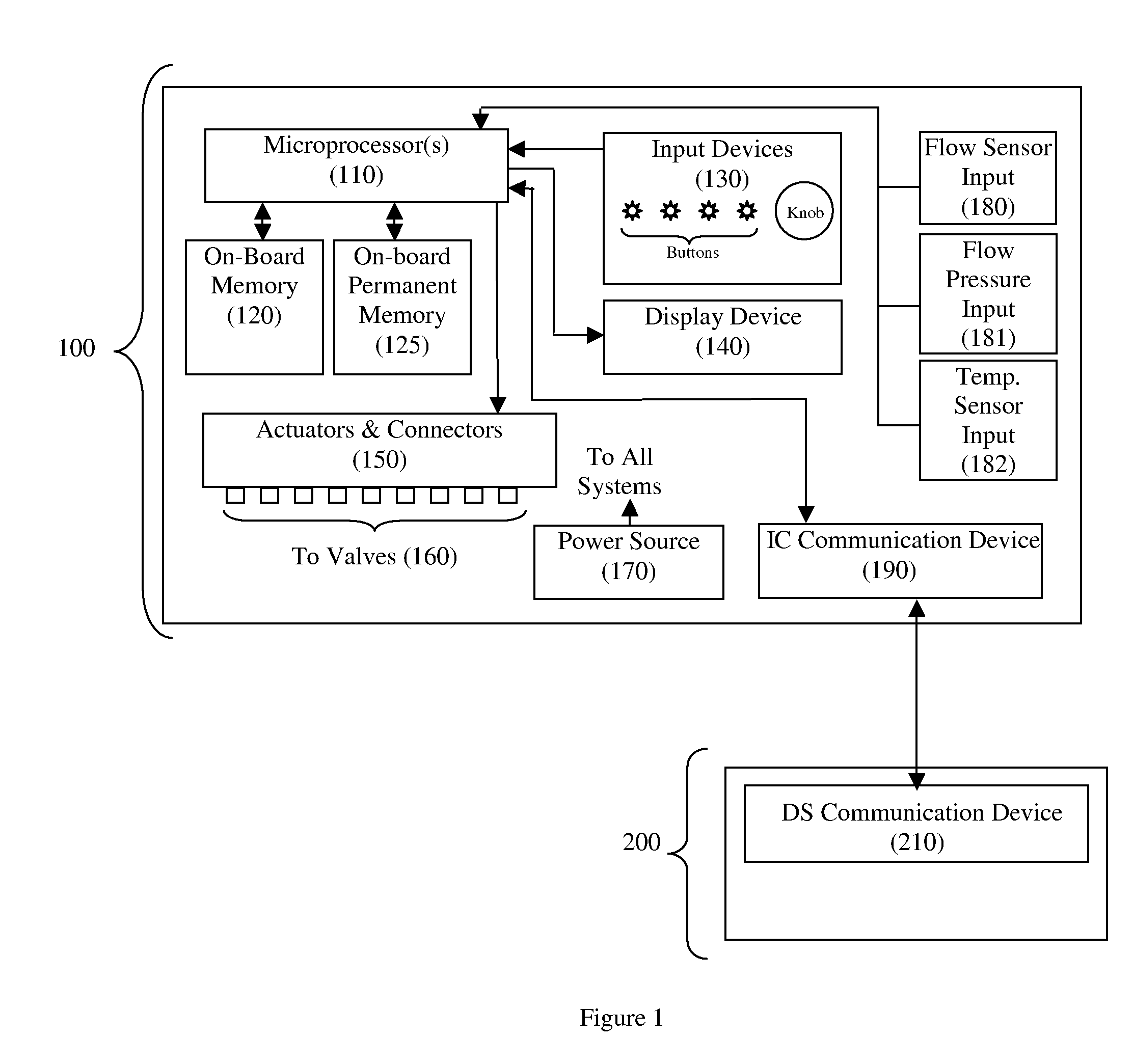
Irrigation Controller Communication System
An irrigation controller is programmed to automatically initiate communication with a data server to perform at least one of the following functions: (a) exchange irrigation data; (b) receive control data; and (c) receive synchronization data. The irrigation data can be station runtime history, evapotranspiration (ETo) data, rainfall, weather related information, irrigation faults and any other irrigation data. The control data can involve station runtime settings, cycle and soak settings, irrigation scheduling and any other irrigation control data. The synchronization data preferably includes a date and a time, originating from the data server, but can include other data that would be used to synchronize the communication between the irrigation controller and the data server. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention a microprocessor disposed in the irrigation controller is programmed to use the date and time to schedule a future contact with the data server.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVE +2
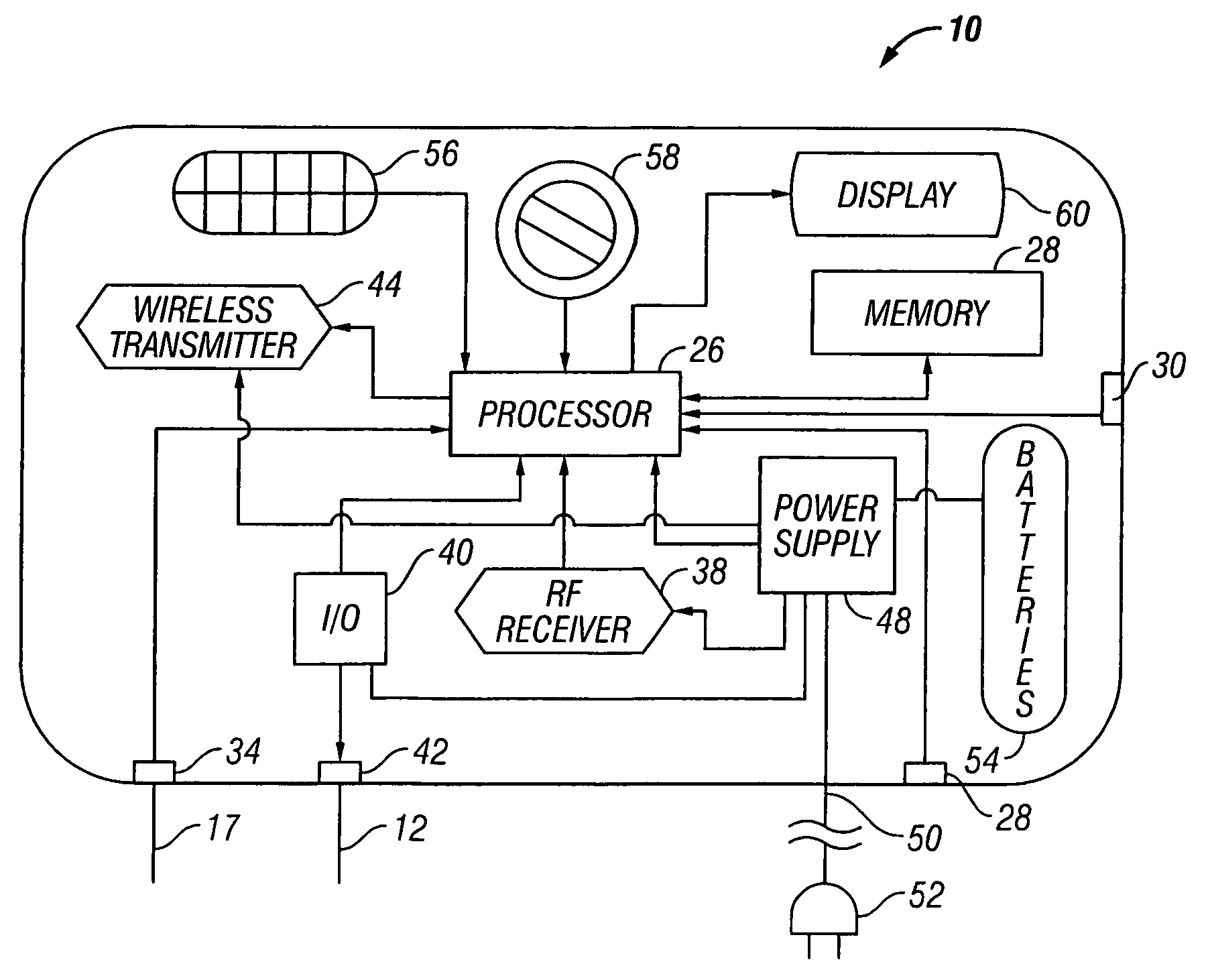
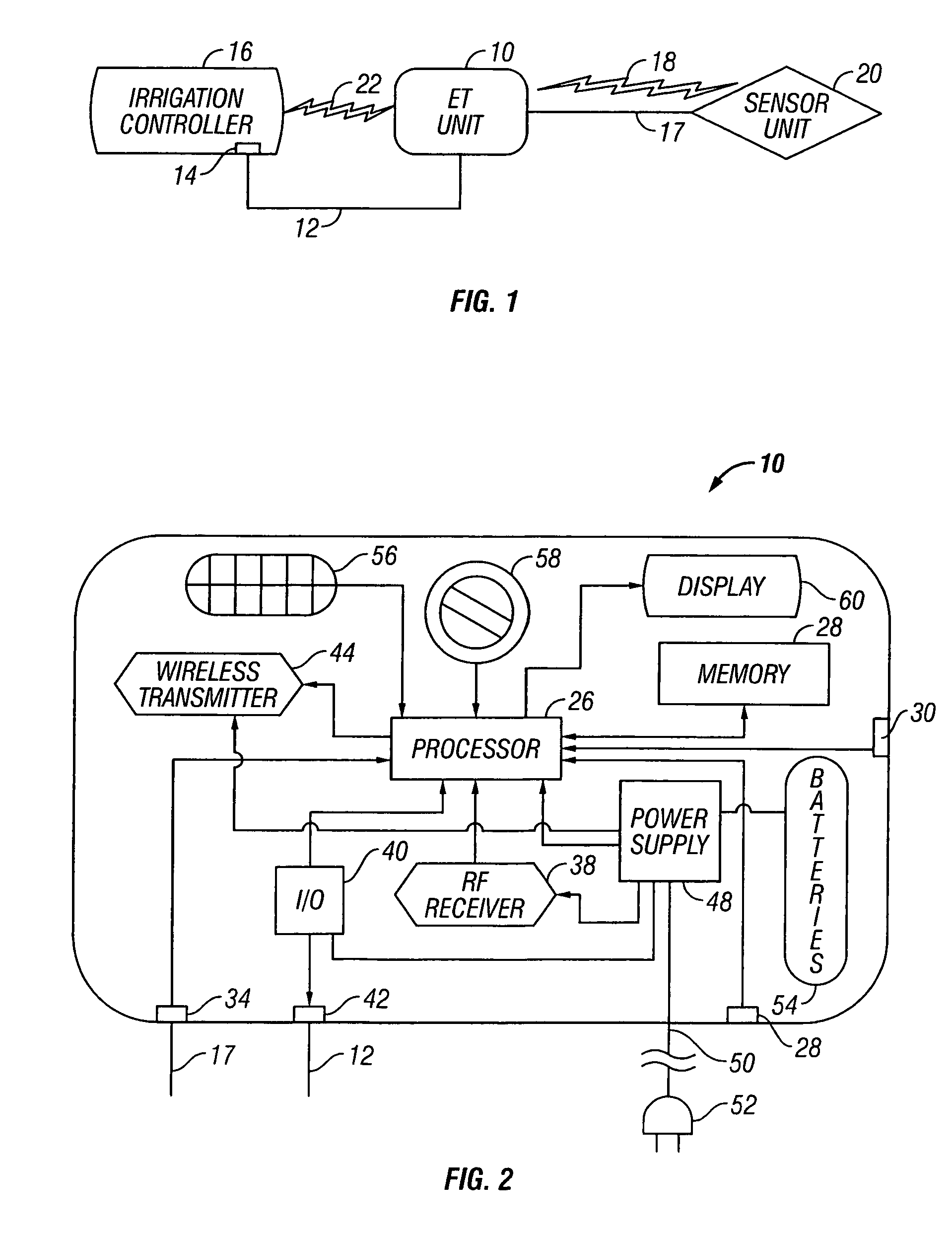
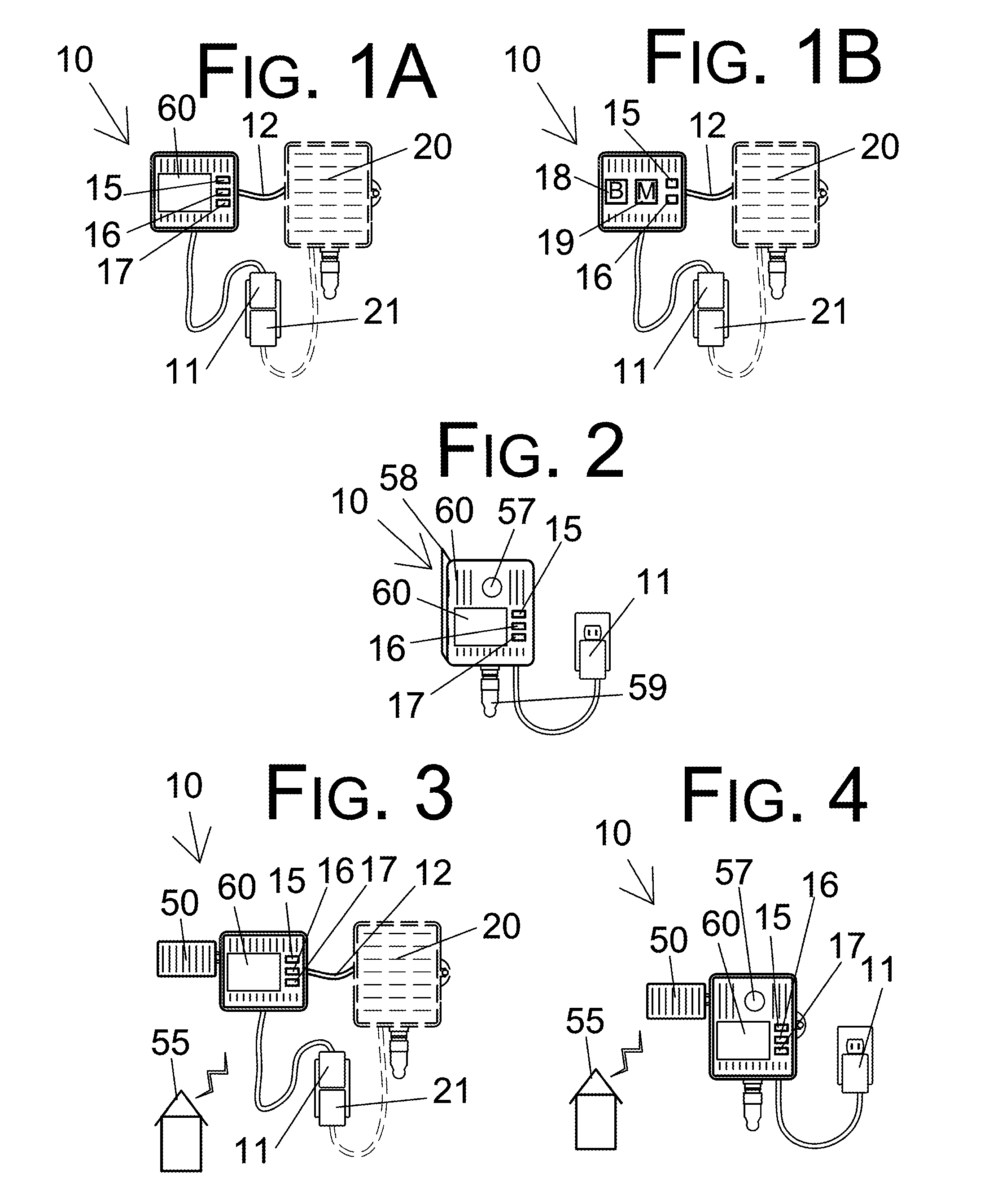
Evapotranspiration unit connectable to an irrigation controller
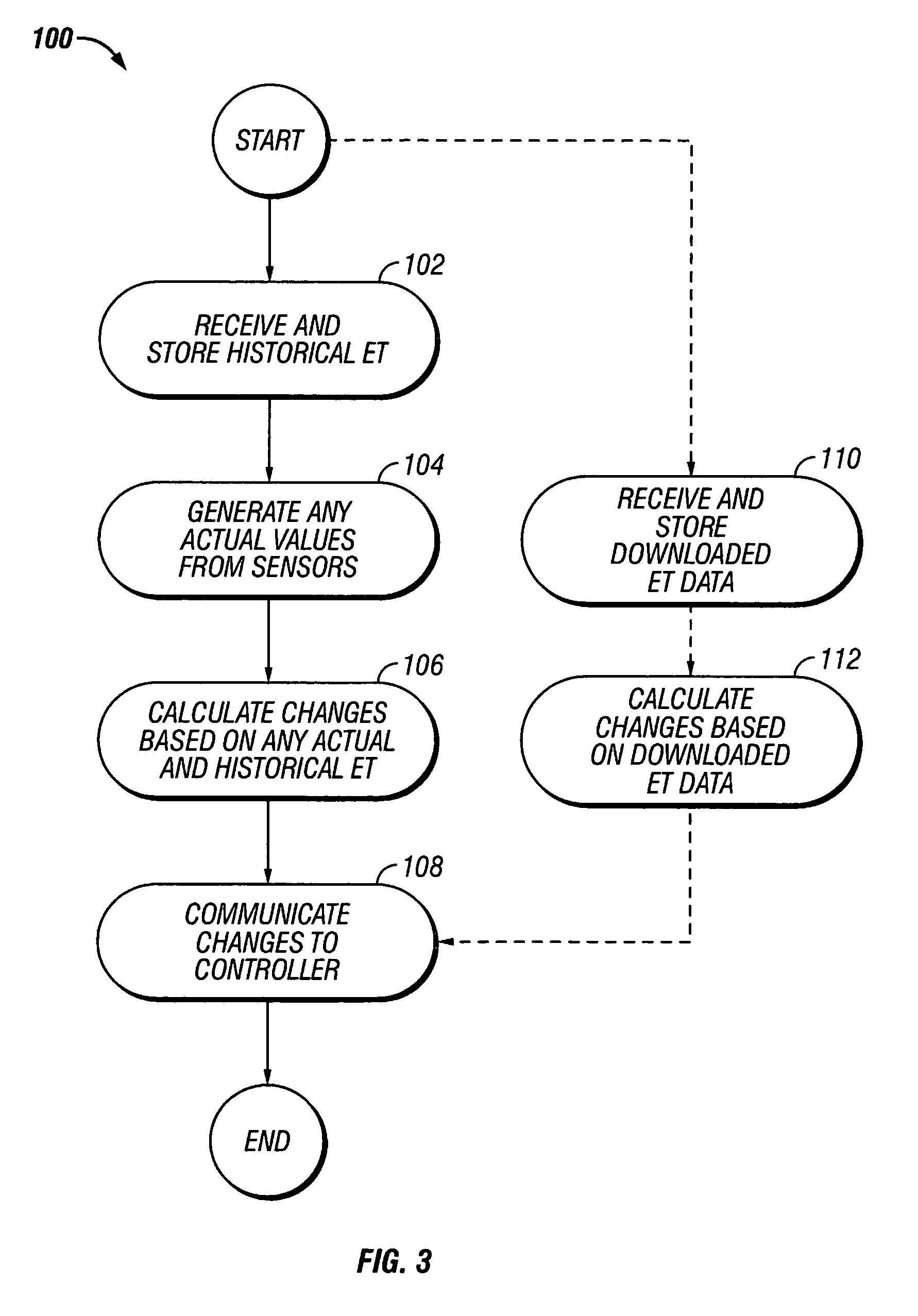
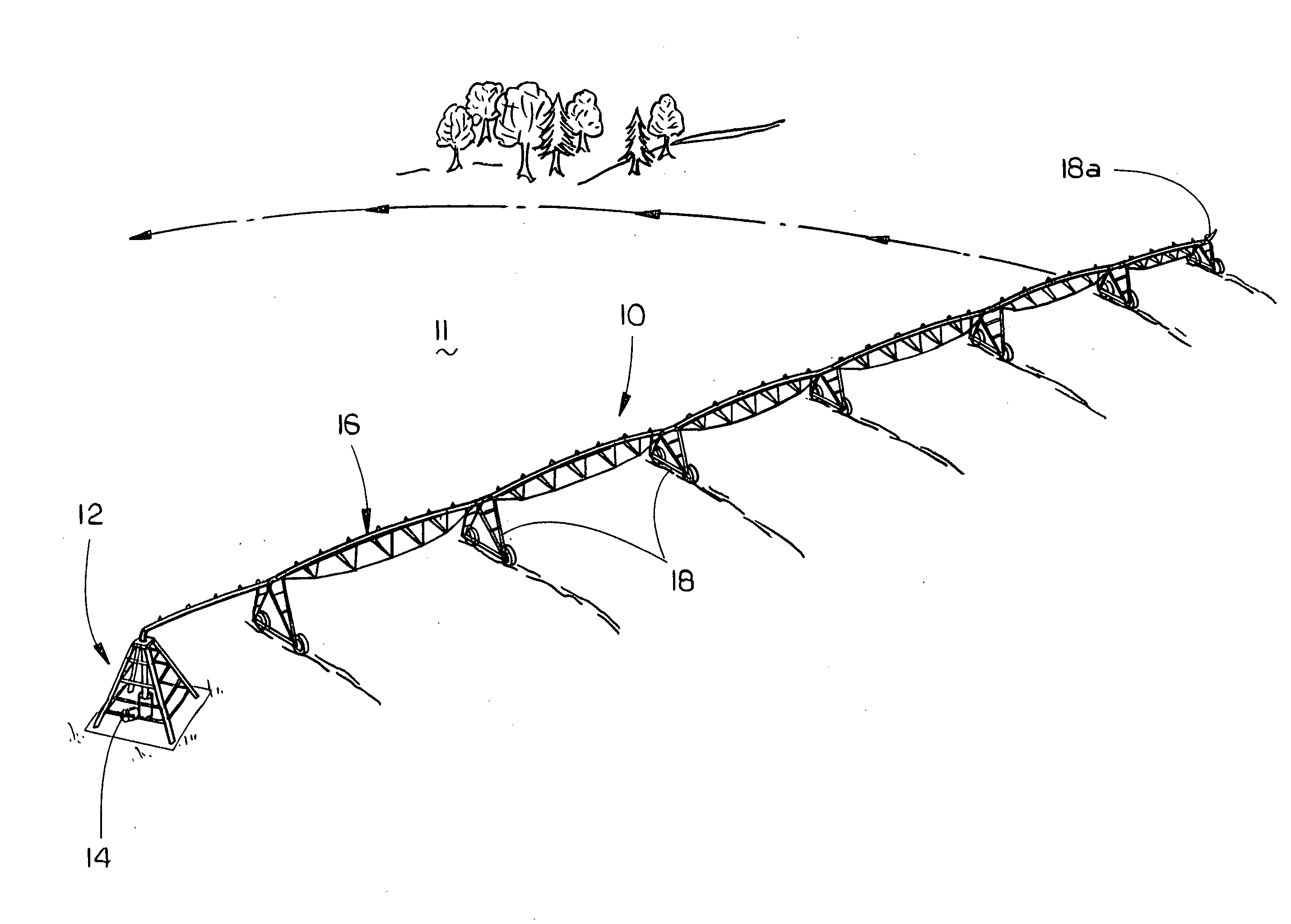
An evapotranspiration (ET) unit includes a processor and a memory for storing a historical set of components of ET data. The processor can communicate with one or more environmental sensors each capable of generating a signal representing an actual value to be substituted for a corresponding one of the components of the historical set. Preprogrammed algorithms enable the processor to calculate changes to a set of watering schedules of a predetermined watering program of an irrigation controller based on any substituted actual value and the remaining historical set of components. The ET unit 10 communicates the changes to the irrigation controller. Optionally the ET unit 10 can receive and store a downloaded actual set of components of ET data and preprogrammed default algorithms calculate the changes to the watering schedules solely based on the downloaded actual set of components of ET data, thus alleviating any need for utilization of the historical set of components of ET data and any actual values generated by the environmental sensors.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Irrigation controller using regression model
InactiveUS6892113B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-acting watering devicesAtmospheric pressureMoisture
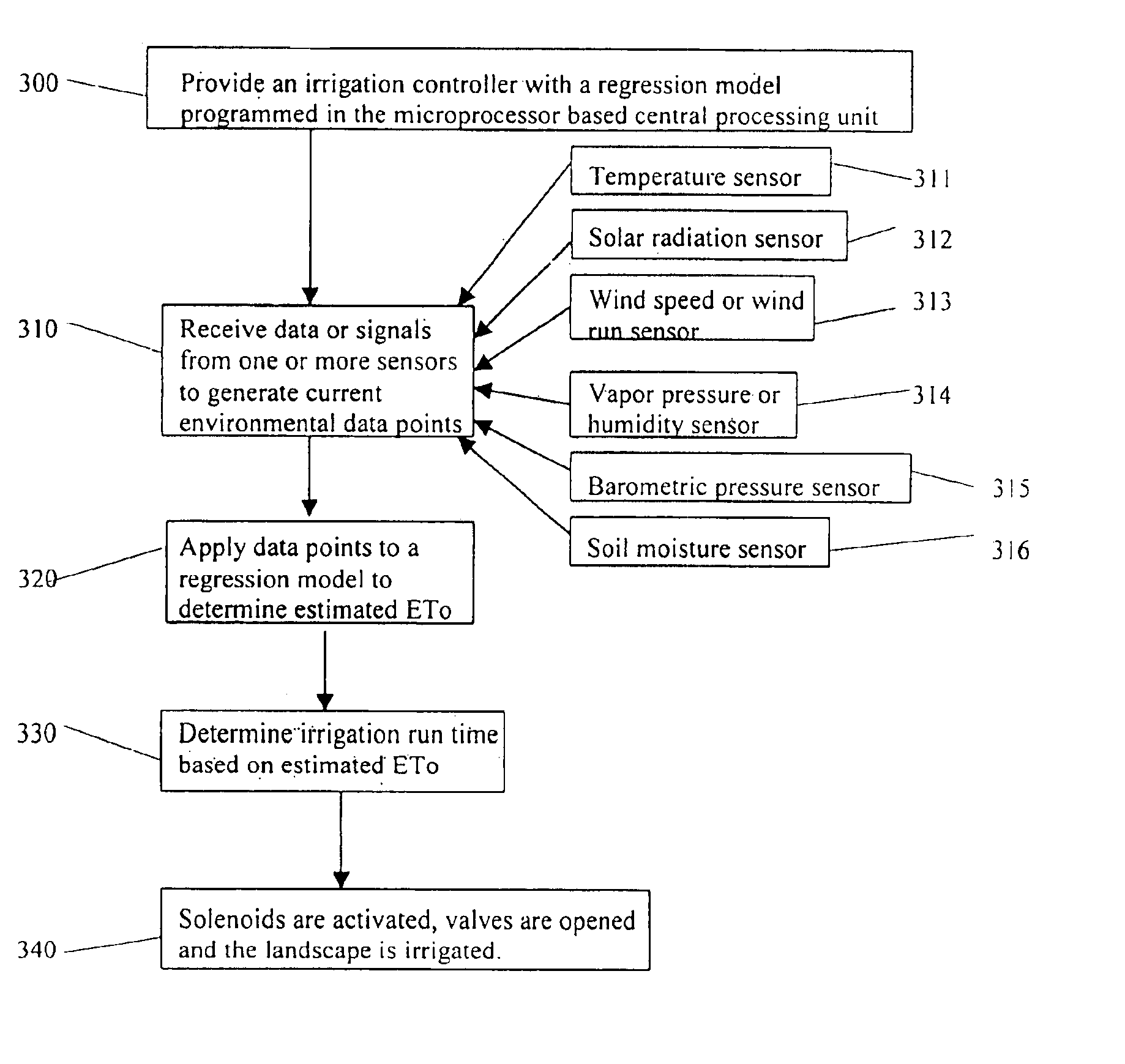
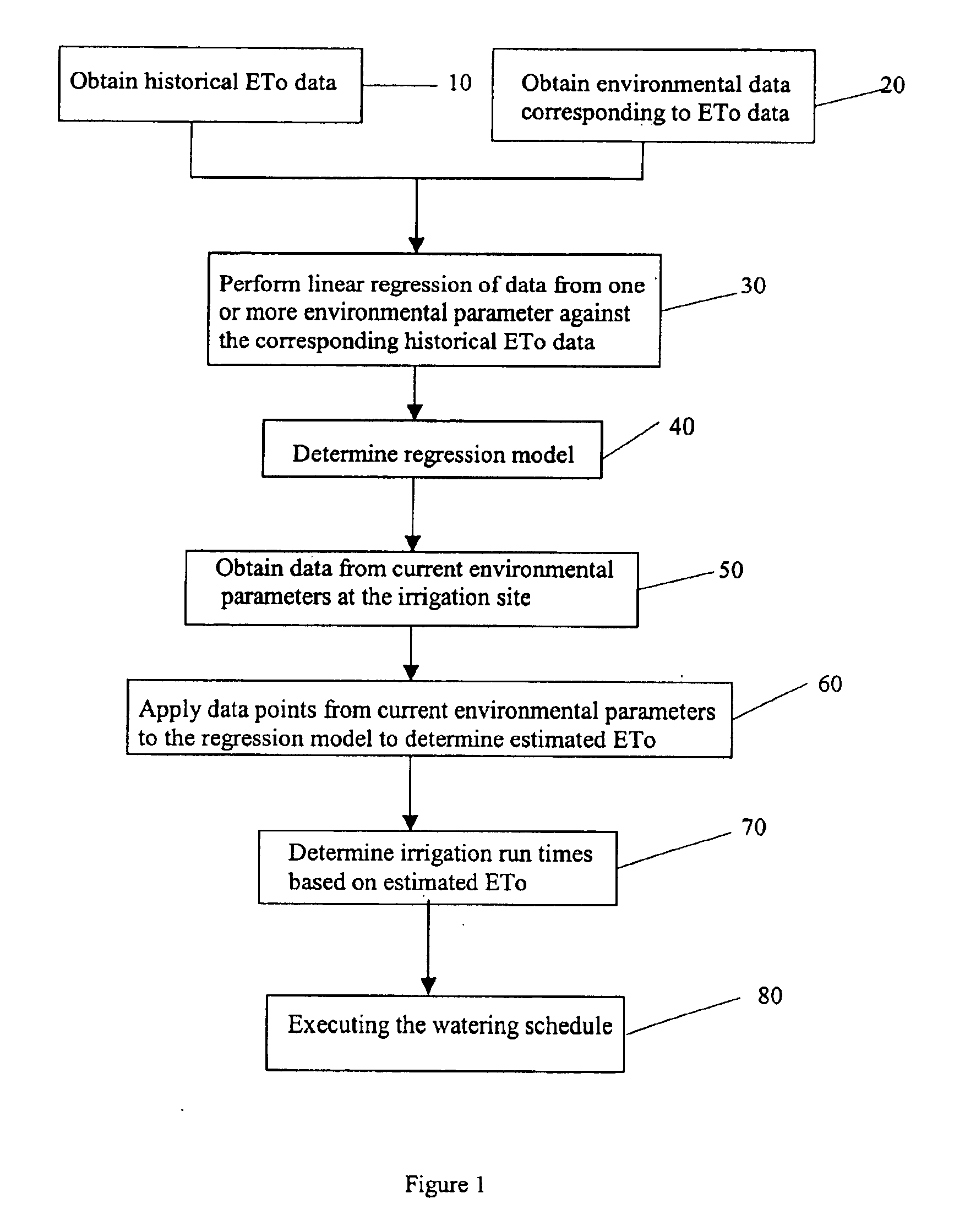
The present invention provides systems and methods in which an irrigation controller uses a regression model to estimate an evapotranspiration rate (estimated ETo), and uses the estimated ETo to affect an irrigation schedule executed by the controller. The regression model is preferably based upon a comparison of historical ETo values against corresponding historical environmental values, with the data advantageously spanning a time period of at least one month, and more preferably at least two months. Data for multiple environmental factors may also be used. The environmental factor(s) utilized may advantageously comprise one or more of temperature, solar radiation, wind speed, humidity, barometric pressure, and soil moisture. Values relating the environmental factor(s) may enter the controller from a local sensor, a distal signal source, or both.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST +2
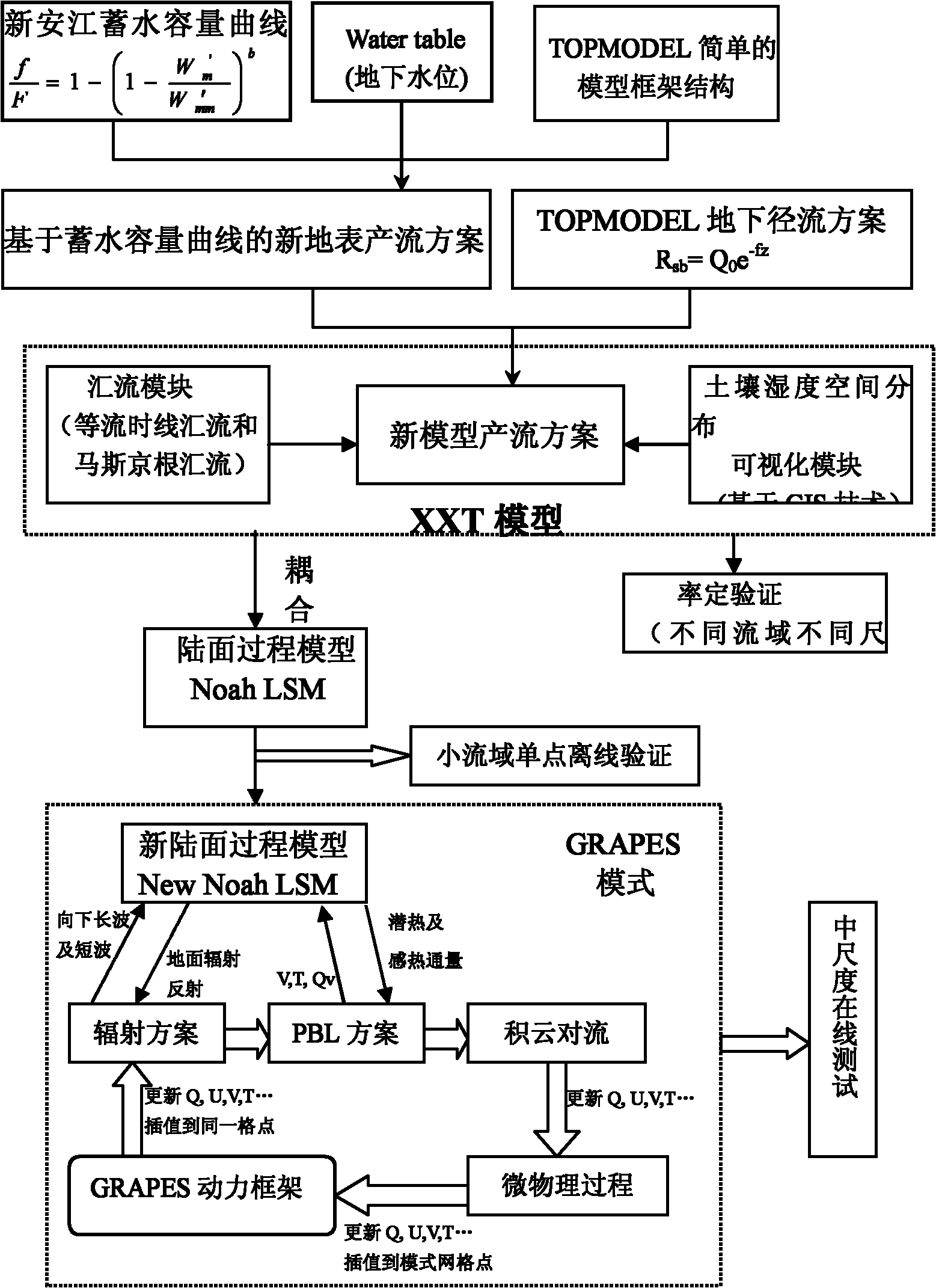
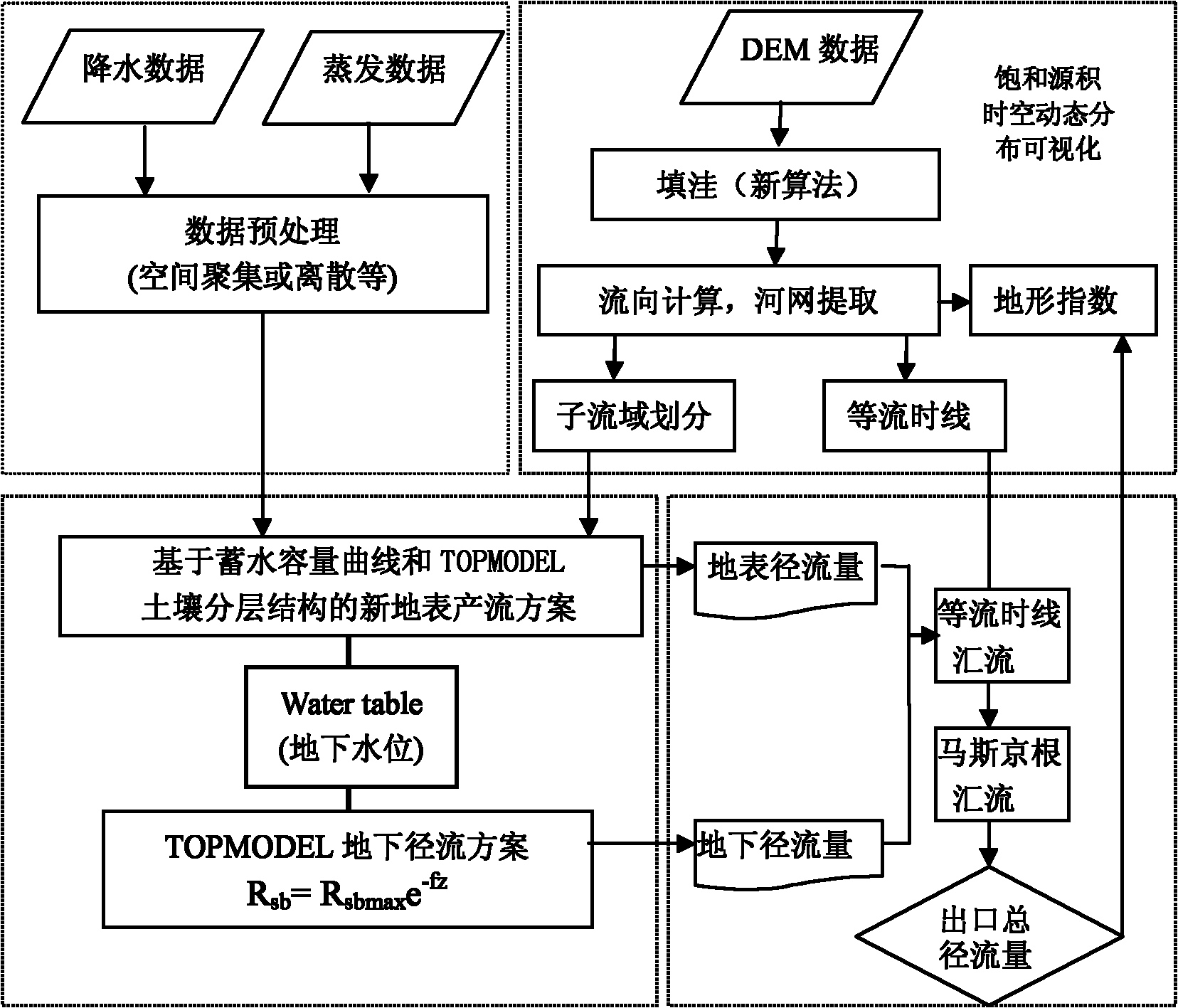
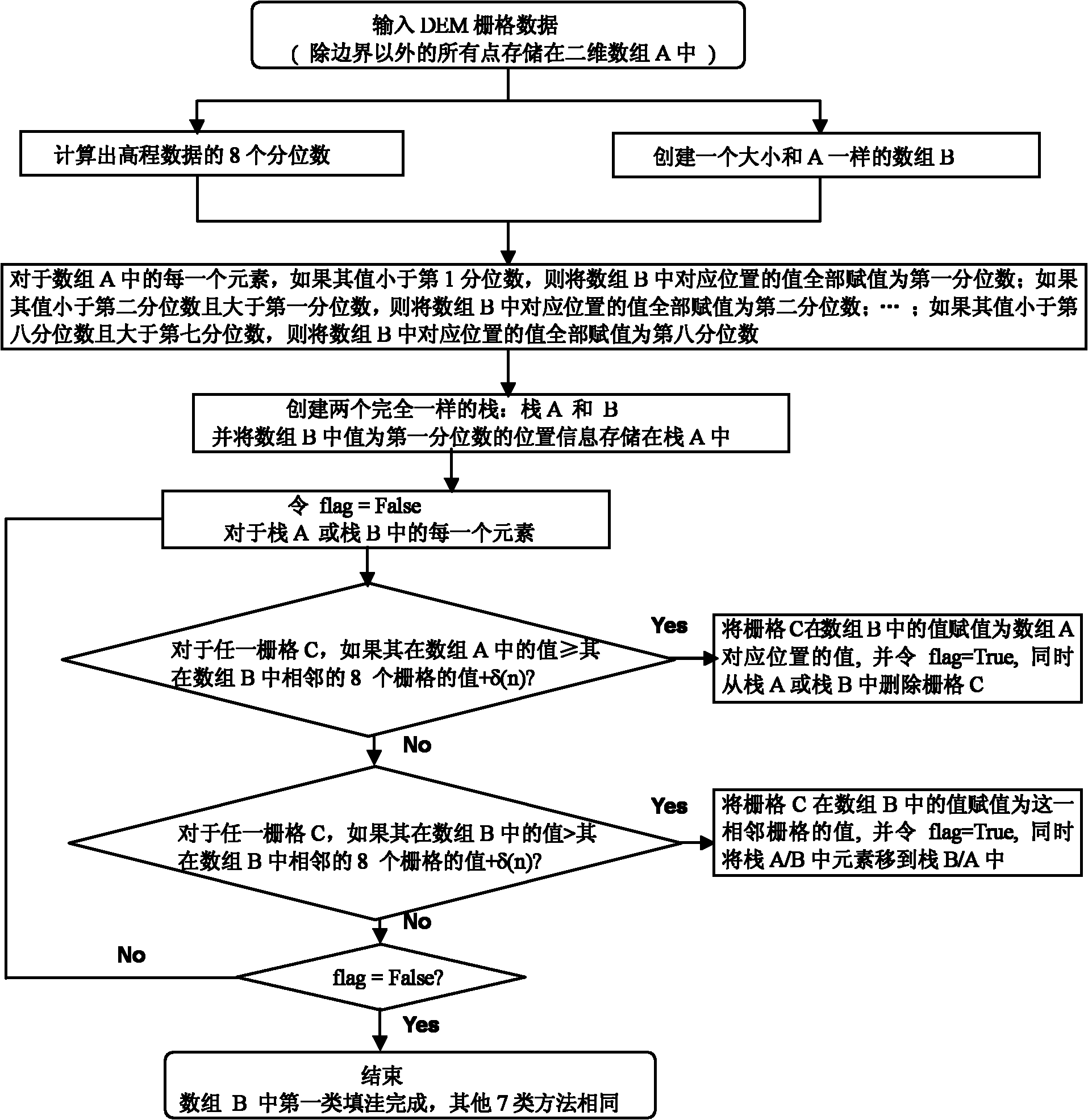
Watershed hydrological model design method based on storage capacity curve and TOPMODEL
InactiveCN102034003ASimple structureImprove efficiencyClimate change adaptationSpecial data processing applicationsAridHydrometry
The invention provides a watershed hydrological model design method based on a storage capacity curve and a TOPMODEL, which comprises the following steps: calculating surface runoff yield; calculating subsurface runoff yield; calculating evapotranspiration; applying a water balance equation; establishing a convergence mechanism; generating isochrones; dynamically and visually expressing soil moisture; and coupling with a Noah land surface model (Noah LSM). The method has a high simulation deterministic coefficient, is advantageous over a semi-distributed model TOPMODEL, a Xinanjiang model and distributed hydrological models such as an engineering and science summer institute (ESSI) model, a hydrologic engineering center hydrologic modeling system (HEC-HMS) model and a soil and water assessment tool (SWAT) model in the simulation of a daily runoff process and the simulation of a flood process, and overcomes the drawback that the conventional watershed hydrological model is usually inapplicable to hydrological process accurate simulation under large-scale, arid and semiarid conditions. The model of the invention can be successfully coupled with Noah LSM and improves the rainfall, soil moisture and runoff broadcasting capacity of a service weather research forecast mode, namely global / regional assimiliation prediction system (GRAPES)-mesoscale(MESO).
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS20060122736A1Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationPower controllerEngineering
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with AC, DC, or ambient light powered irrigation controllers without the use of complex ET (evapotranspiration) data or ET related service fees. Programming may consist of the operator entering a preliminary irrigation schedule, and entering the local zip code. The controller then periodically calculates a water budget by comparing current (non ET) local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, and then modifies the preliminary schedule using the water budget. A number of embodiments are possible: in stand-alone controllers with a temperature sensor attached directly to the microprocessor within that controller, or as a centrally placed CBM (Central Broadcast Module) which calculates a water budget percentage which is transmitted to one or more field controllers by wired or wireless means. Alternately, a TBM (Temperature Budget Module) that is separate from the controller is connected between the controller outputs and the valves, or mounted at the valves themselves. The TBM calculates the water budget, monitors the controller outputs and shortens the duration times as calculated by the water budget ratio. Because of its flexible capabilities with stand alone AC, DC, solar, or ambient light powered controllers, as a centrally broadcast WBR in a wired or wireless configuration, or as an add-on to existing controllers or valves, its programming simplicity and close approximation to ET without its complications and cost, the present invention significantly reduces that cost, has the potential to save more water and minimize runoff than currently available ET methods.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Irrigation system utilizing actual and historical components of ET data
An evapotranspiration (ET) unit includes a processor and a memory for storing a historical set of components of ET data. The processor can communicate with one or more environmental sensors each capable of generating a signal representing an actual value to be substituted for a corresponding one of the components of the historical set. Preprogrammed algorithms enable the processor to calculate changes to a set of watering schedules of a predetermined watering program of an irrigation controller based on any substituted actual value and the remaining historical set of components. The ET unit 10 communicates the changes to the irrigation controller. Optionally the ET unit 10 can receive and store a downloaded actual set of components of ET data and preprogrammed default algorithms calculate the changes to the watering schedules solely based on the downloaded actual set of components of ET data, thus alleviating any need for utilization of the historical set of components of ET data and any actual values generated by the environmental sensors.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Environmental and biotic-based speed management and control of mechanized irrigation systems
InactiveUS20100032495A1Save waterReducing wasteful overwateringSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationEvapotranspirationMoisture
A system that based on changes in agricultural crop or plant characteristics or dynamics, e.g., heat stress, water deficit stress, stem growth, leaf thickness, plant turgidity, plant color, nutrient composition, etc., or changes in environmental conditions, e.g., temperature, wind, pressure, relative humidity, dew point, precipitation, soil moisture, solar radiation, etc. or a combination of both, e.g., evapotranspiration, either automatically increases or decreases the speed or rate of movement or rotation of a mechanized irrigation system, e.g., center pivot, corner, linear, or lateral move irrigation system or similar, or reports a recommended increased or decreased speed or rate of movement or rotation of a mechanized irrigation system either directly or indirectly to the end user. The system responds directly or indirectly to data outputted from monitoring systems that gather and compile environmental (non-biotic), biotic or similar information from agricultural fields and crops.
Owner:ABTS KEVIN
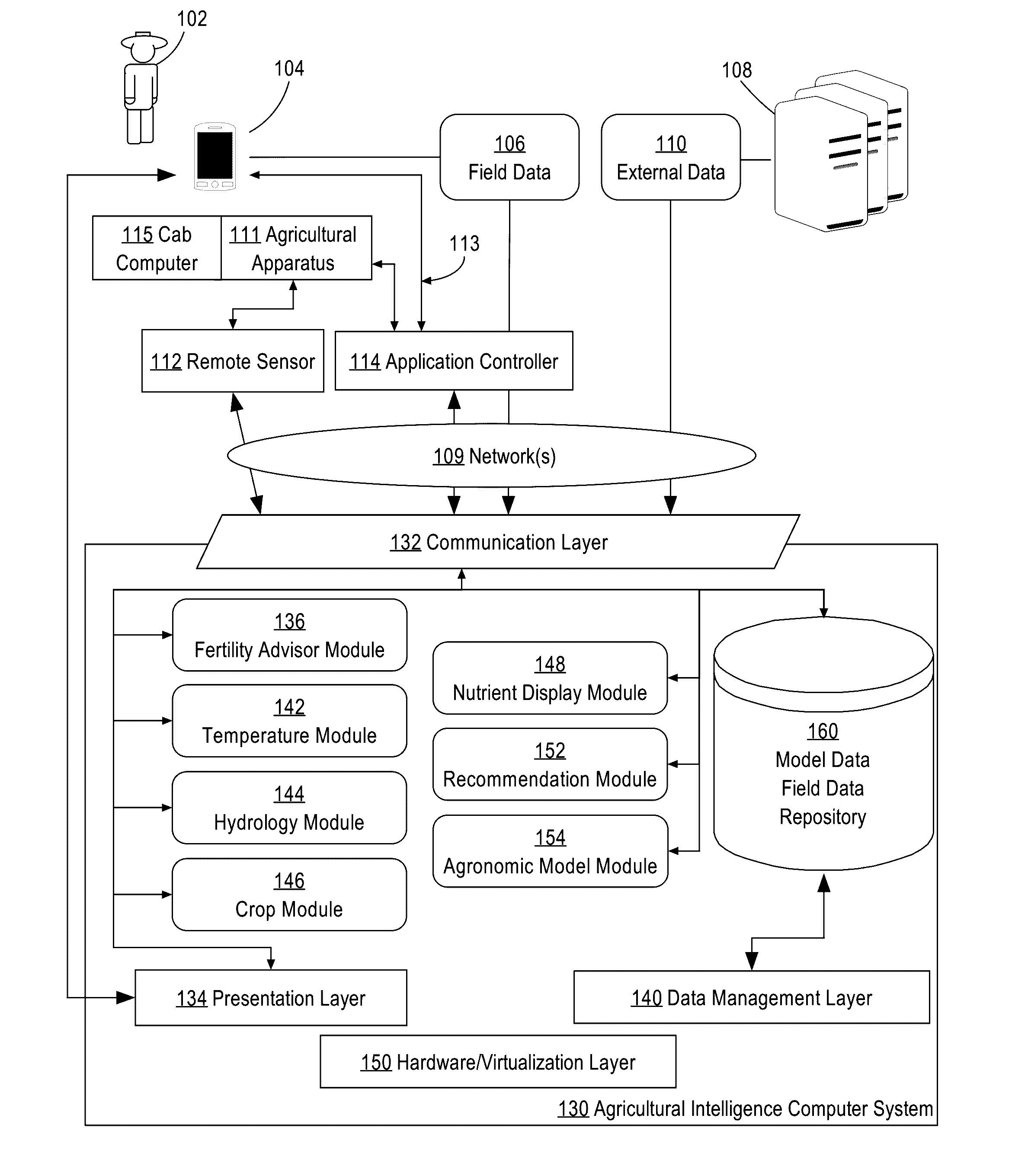
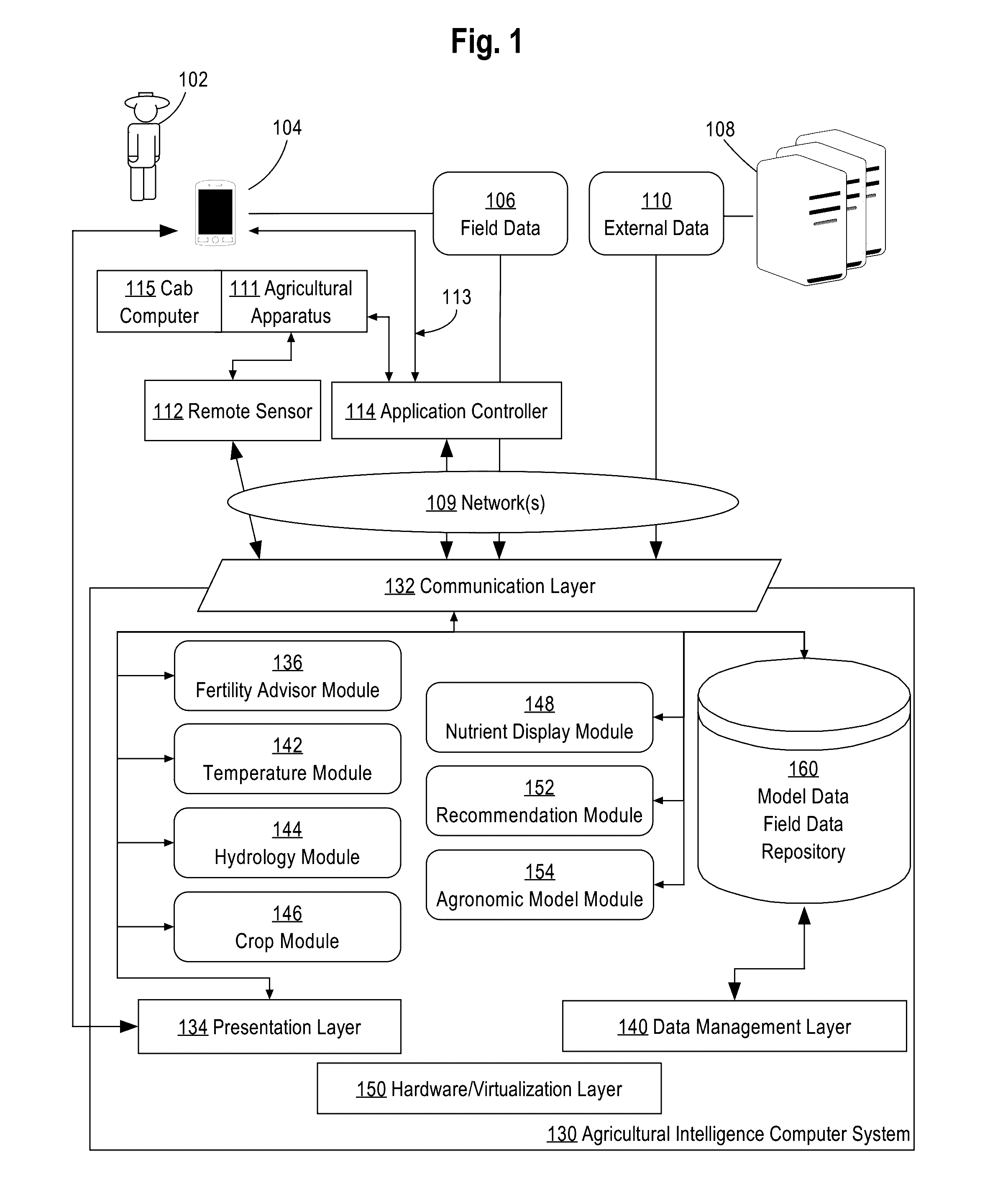
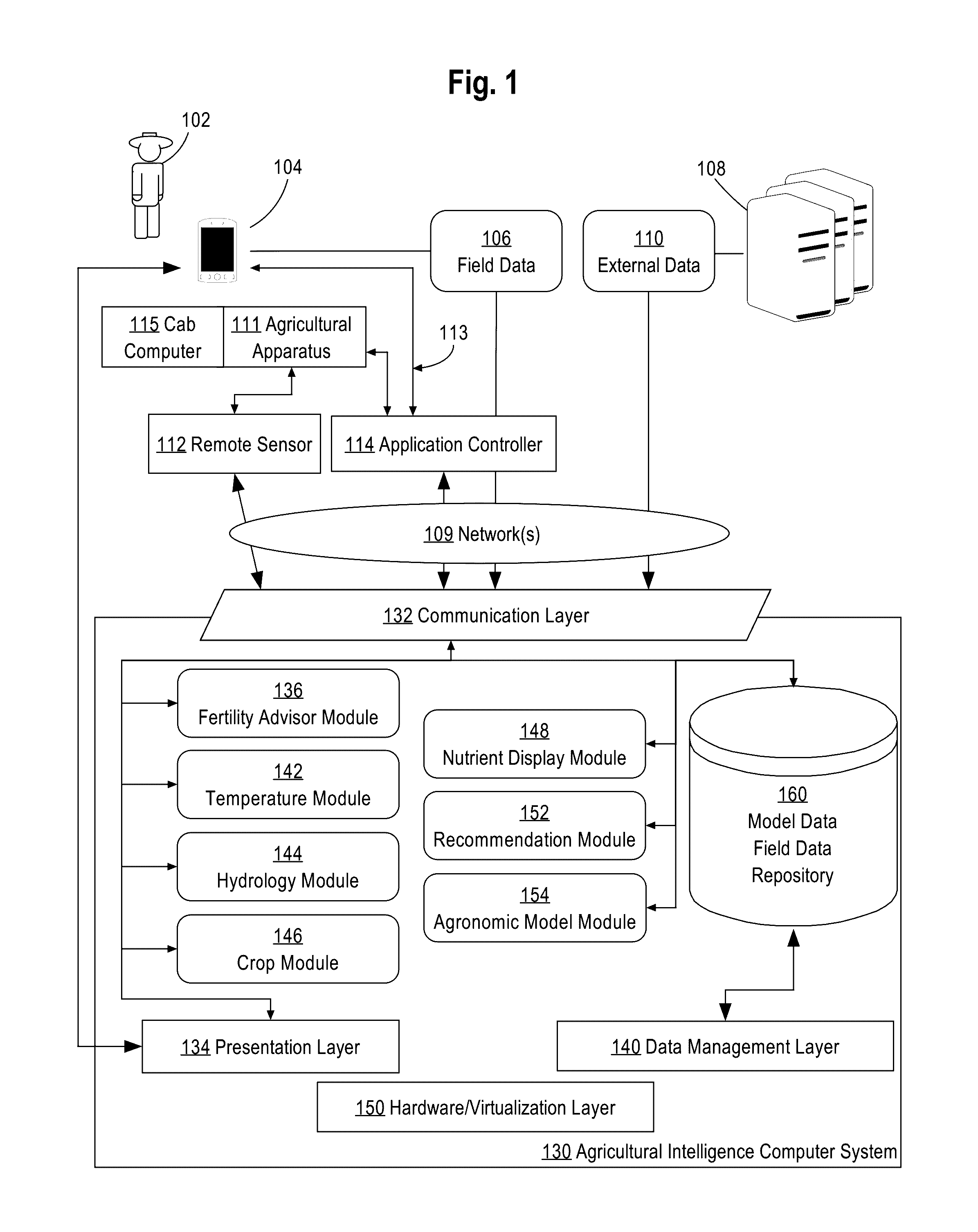
Generating Digital Models Of Nutrients Available To A Crop Over The Course Of The Crop's Development Based On Weather And Soil Data
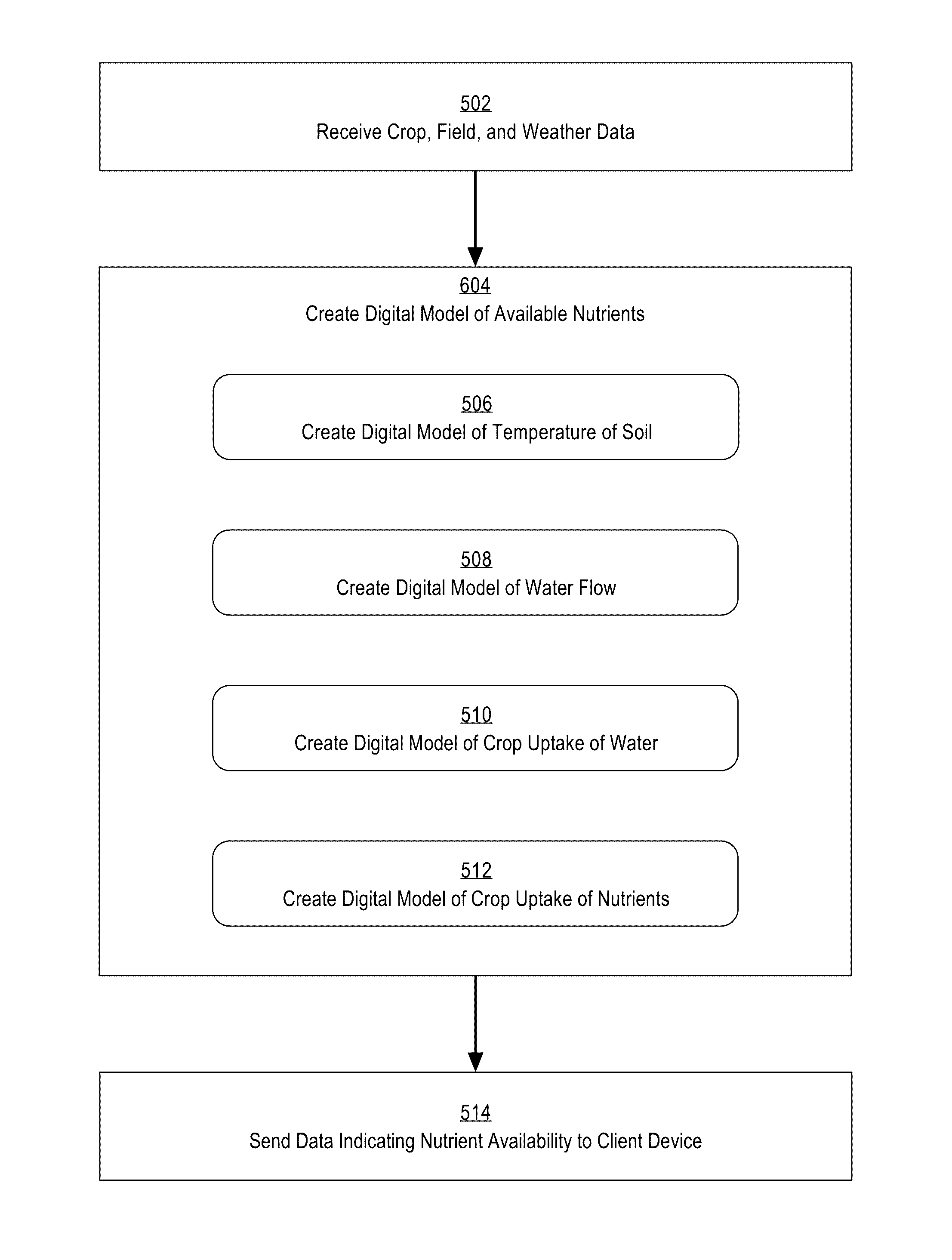
A system for generating digital models of nitrogen availability based on field data, weather forecast data, and models of water flow, temperature, and crop uptake of nitrogen and water is provided. In an embodiment, field data and forecast data are received by an agricultural intelligence computing system. Based on the received data, the agricultural intelligence computing system models changes in temperature of different soil layers, moisture content of different soil layers, and loss of nitrogen and water to the soil through crop uptake, leaching, denitrification, volatilization, and evapotranspiration. The agricultural intelligence computing system creates a digital model of nitrogen availability based on the temperature, moisture content, and loss models. The agricultural intelligence computing system may then send nitrogen availability data to a field manager computing device and / or use the nitrogen availability data to create notifications, recommendations, agronomic models, and / or control parameters for an application controller.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
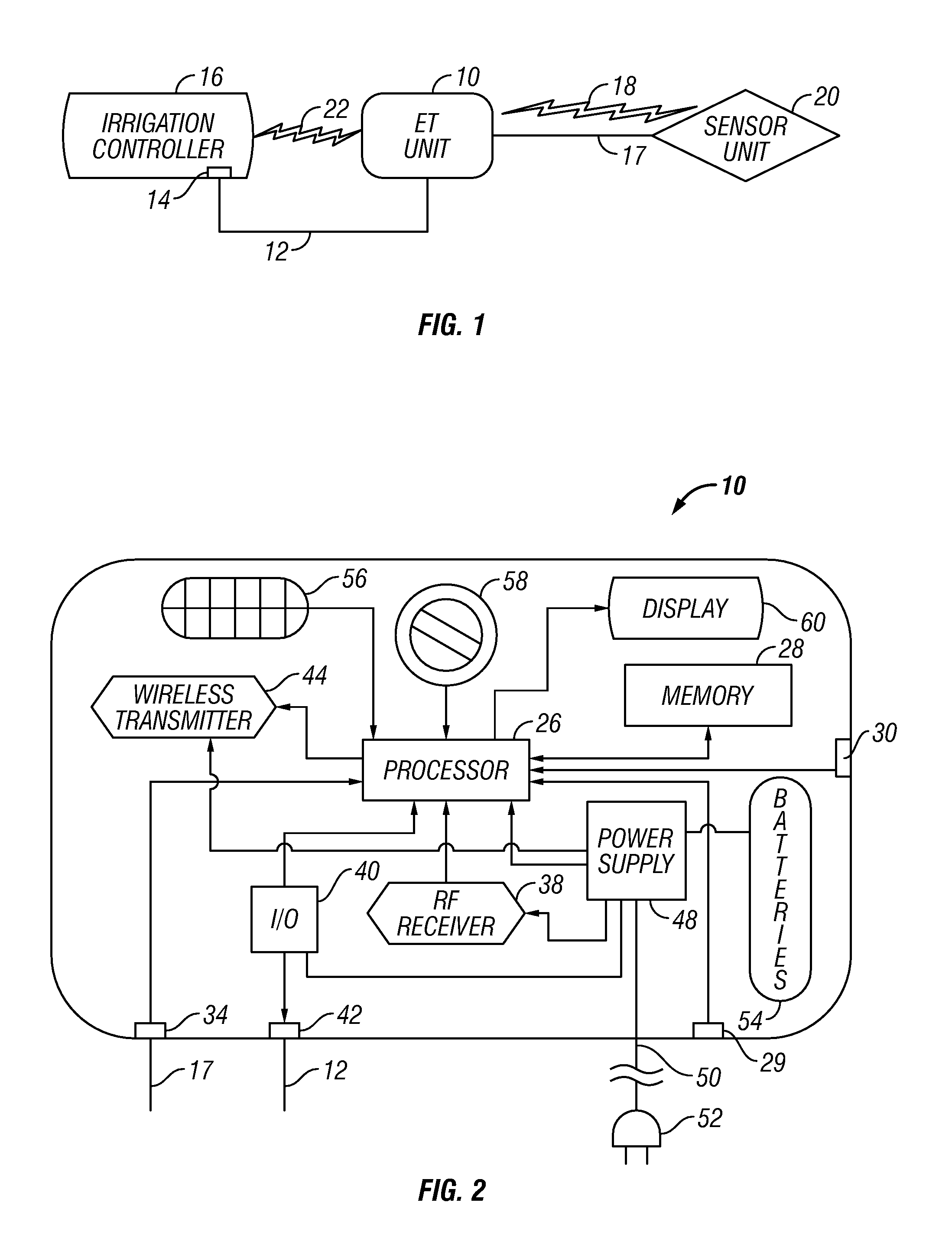
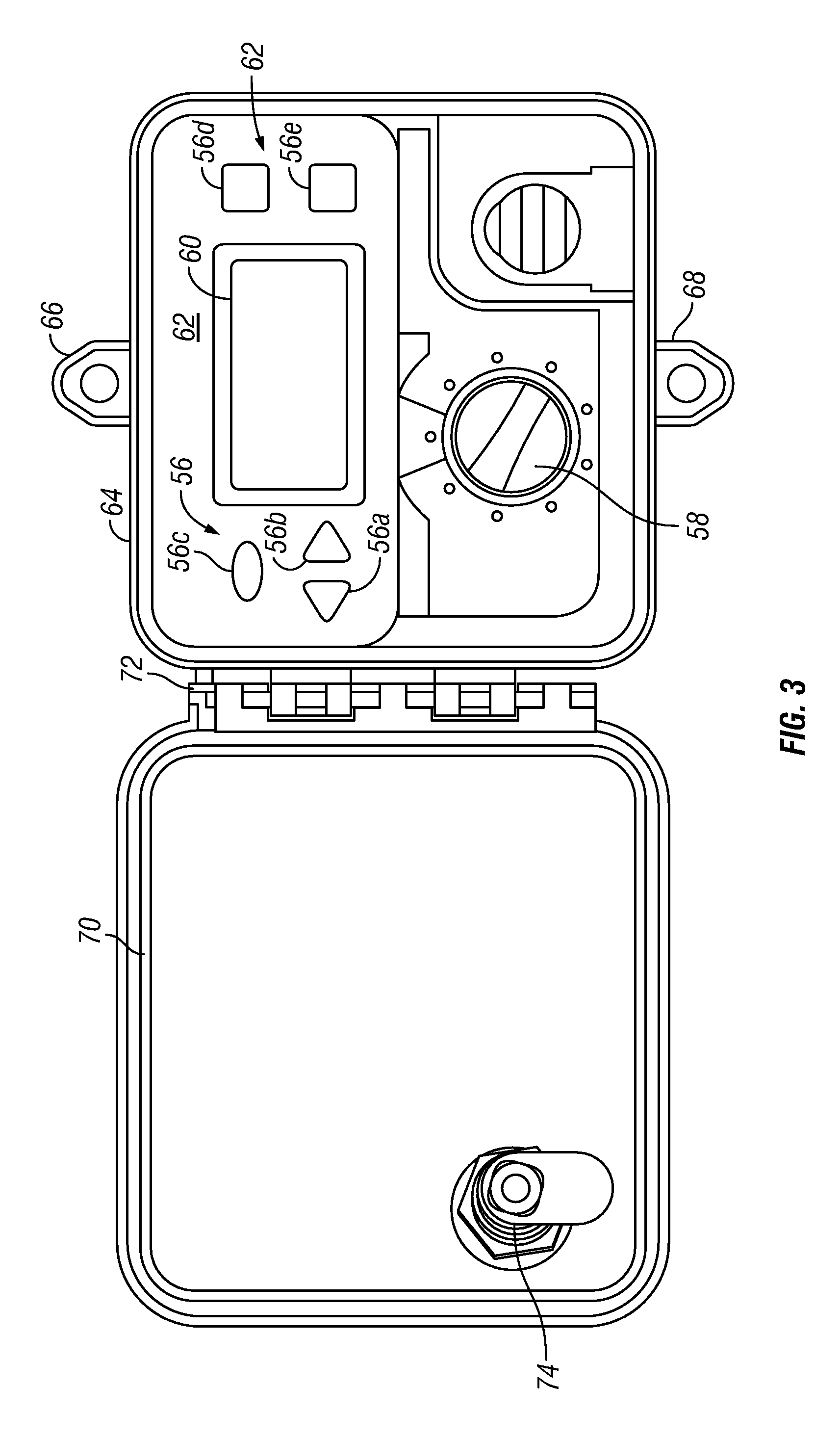
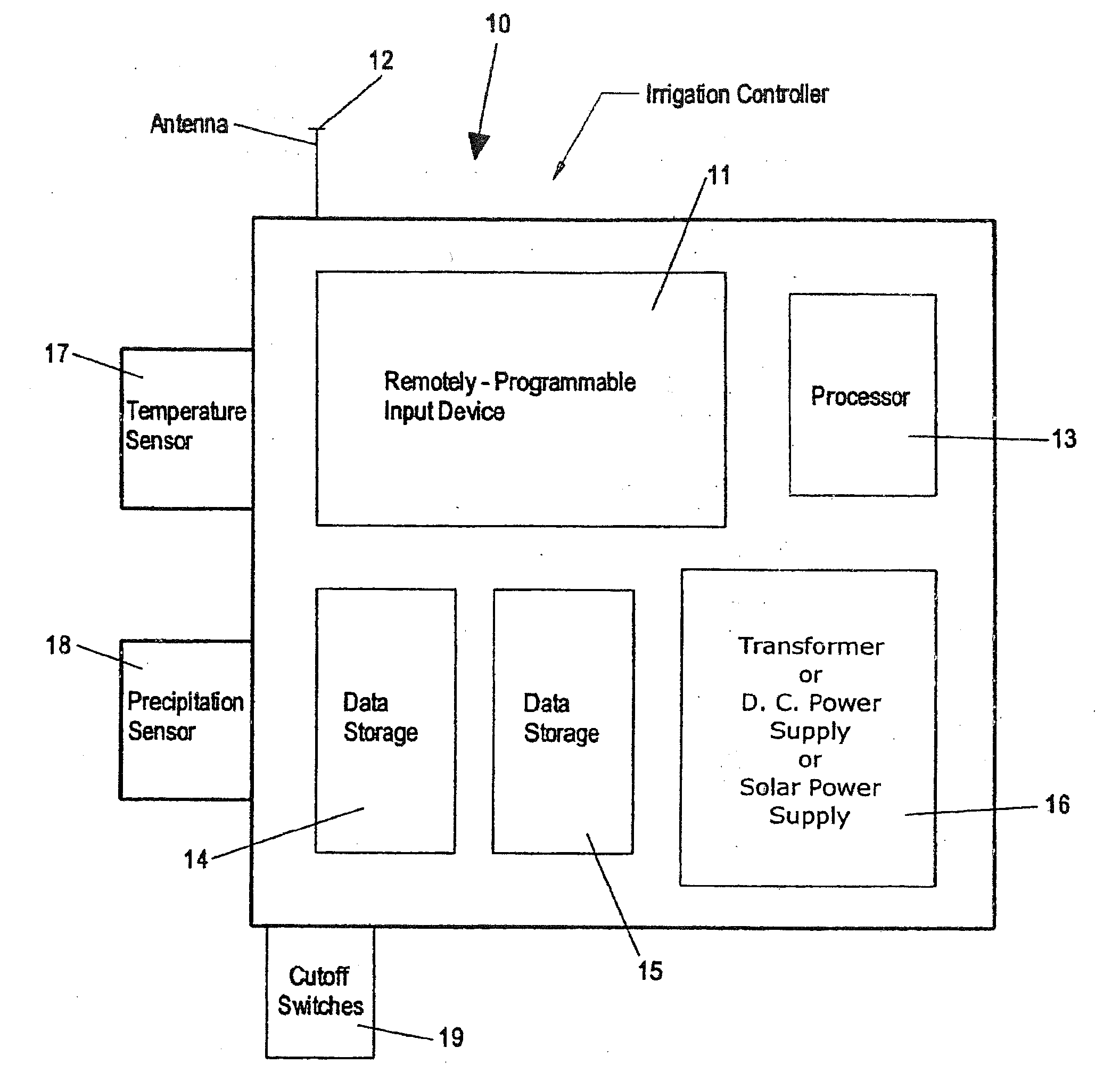
Irrigation controller with integral evapotranspiration unit
ActiveUS8548632B1Self-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationTelecommunications linkCommunication link
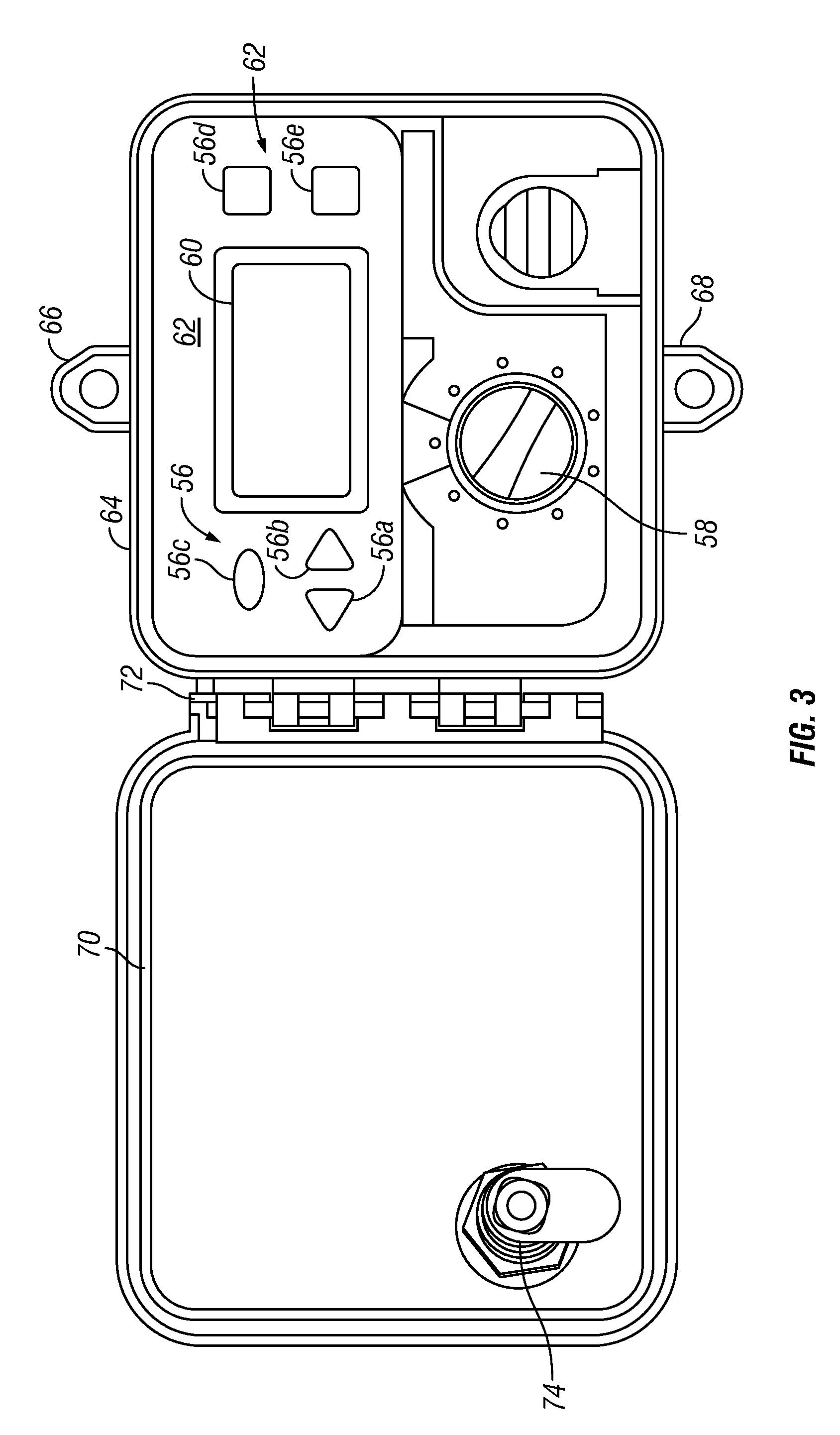
An irrigation controller includes a first processor and a memory for storing programming executable by the first processor. The irrigation controller further includes circuitry that enables a communication link that allows direct communication between the first processor and a sensor unit containing a second processor and a plurality of environmental sensors each capable of generating an actual component of ET data. At least one manually actuable control is operably connected to the first processor for inputting further ET-related information selected from the group consisting of plant type, soil condition, growth stage and sprinkler precipitation rate. The irrigation controller further includes programming that enables the first processor to calculate optimum watering schedules based upon the actual ET data and the ET-related information including increases and decreases in the frequency and / or length of ON times for at least one station.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Generating digital models of nutrients available to a crop over the course of the crop's development based on weather and soil data
A system for generating digital models of nitrogen availability based on field data, weather forecast data, and models of water flow, temperature, and crop uptake of nitrogen and water is provided. In an embodiment, field data and forecast data are received by an agricultural intelligence computing system. Based on the received data, the agricultural intelligence computing system models changes in temperature of different soil layers, moisture content of different soil layers, and loss of nitrogen and water to the soil through crop uptake, leaching, denitrification, volatilization, and evapotranspiration. The agricultural intelligence computing system creates a digital model of nitrogen availability based on the temperature, moisture content, and loss models. The agricultural intelligence computing system may then send nitrogen availability data to a field manager computing device and / or use the nitrogen availability data to create notifications, recommendations, agronomic models, and / or control parameters for an application controller.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
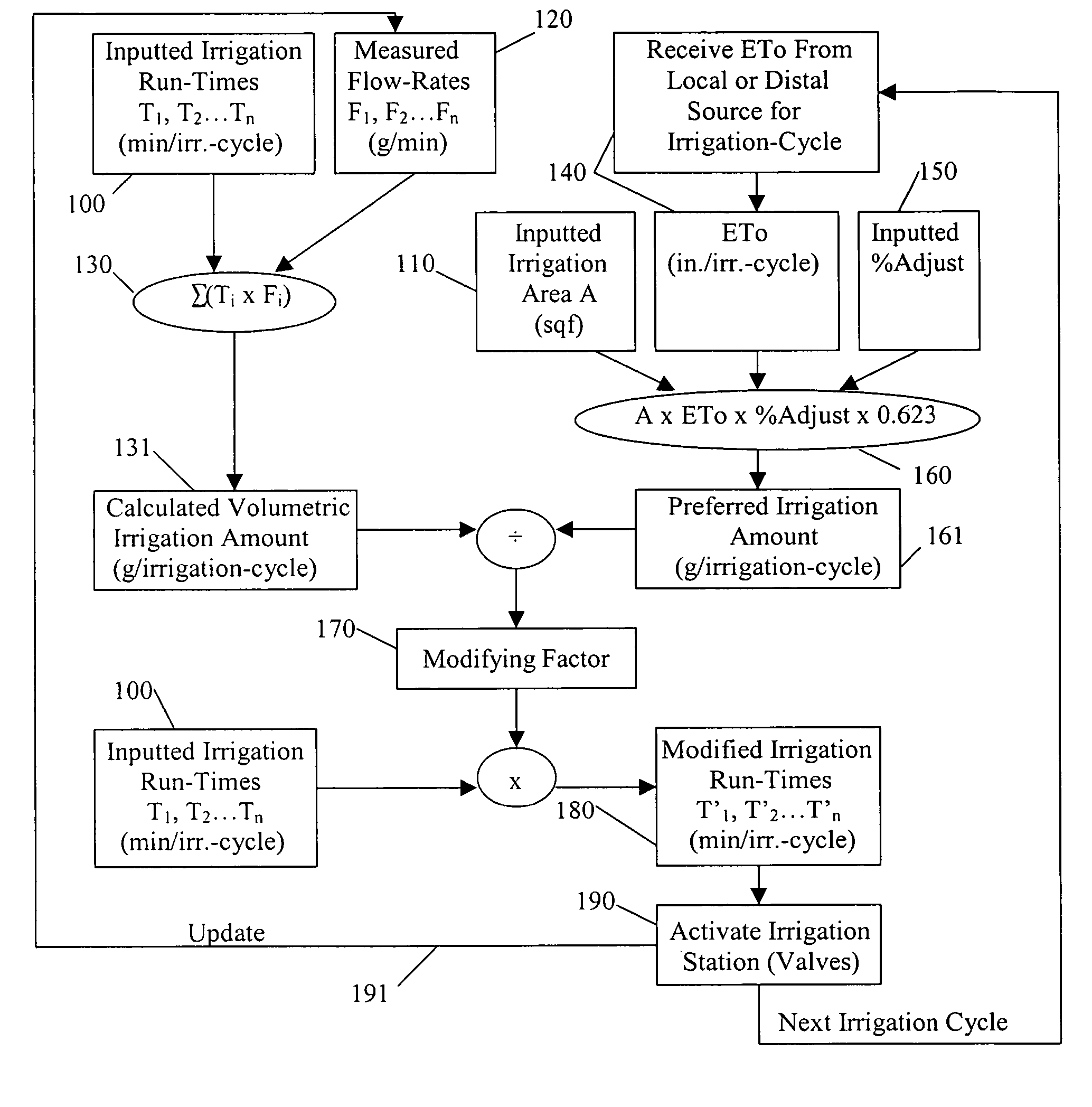
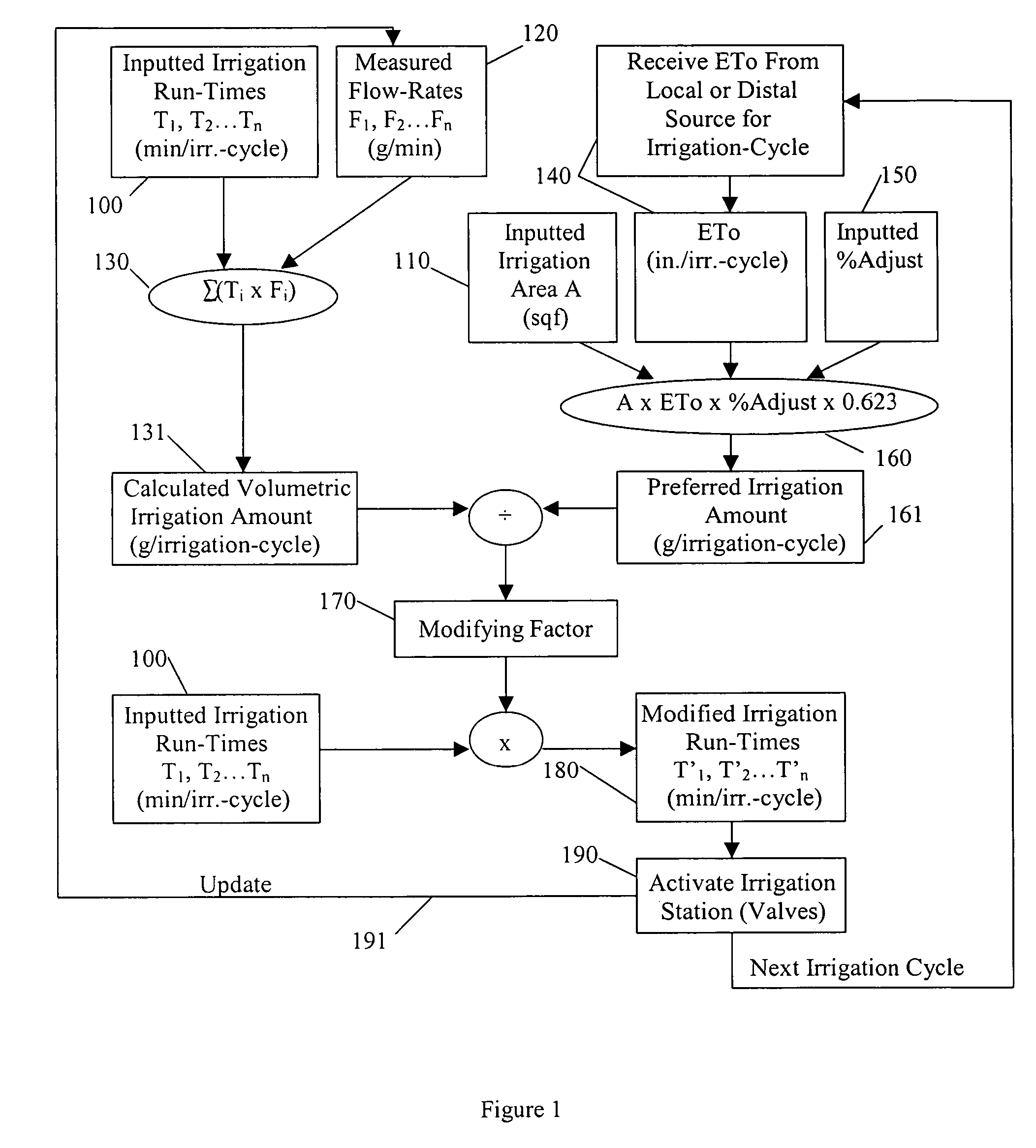
Water savings system
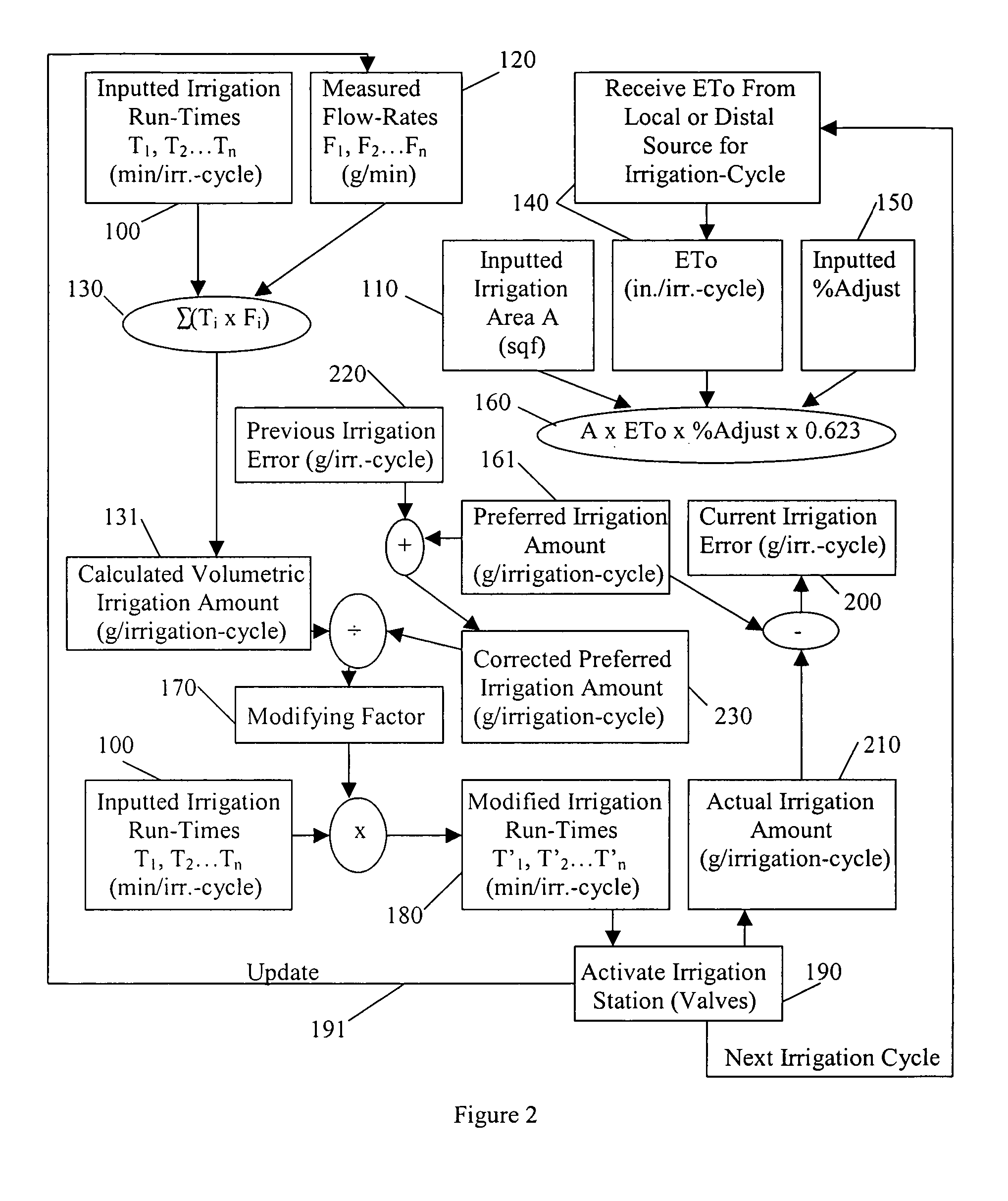
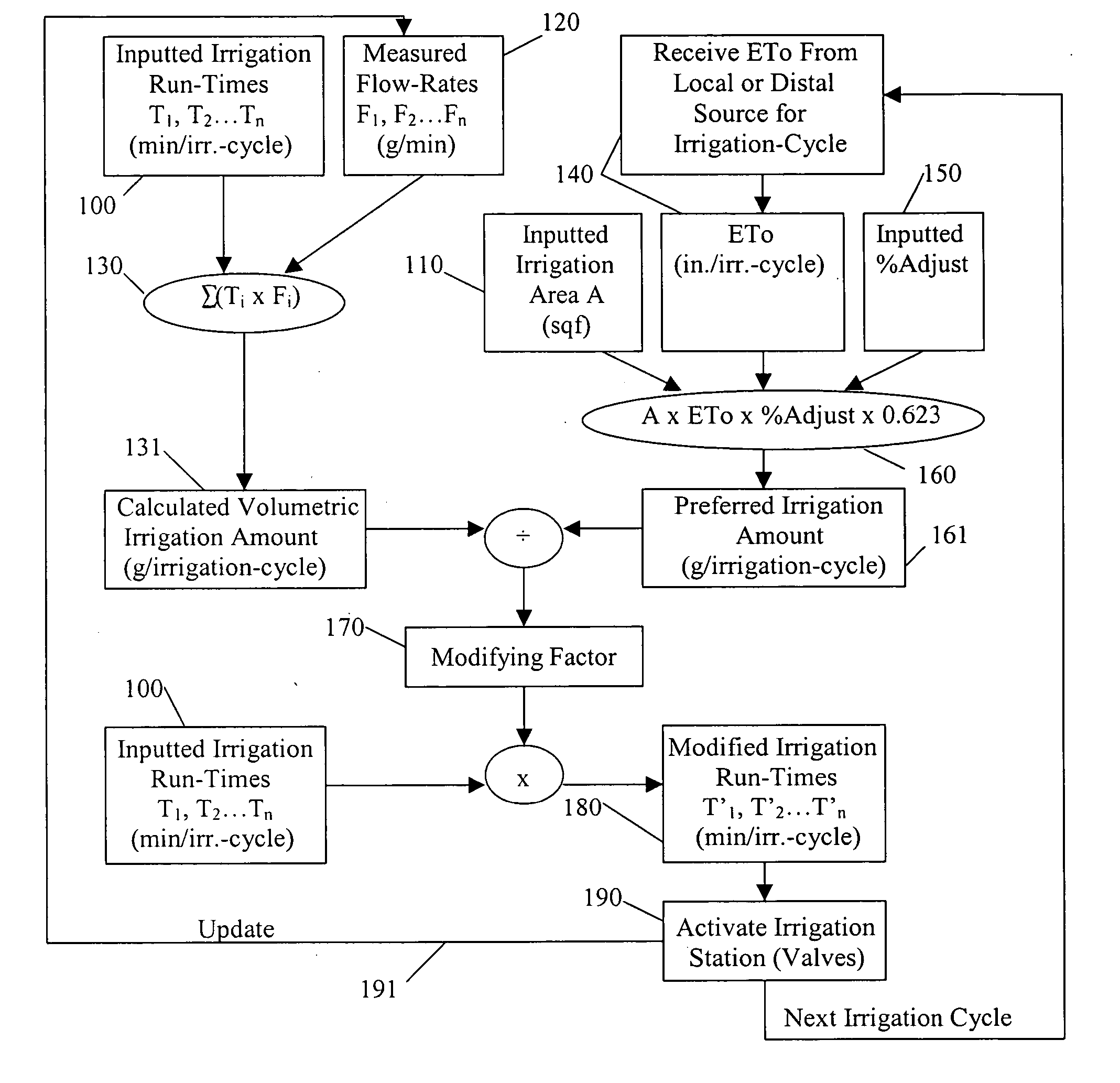
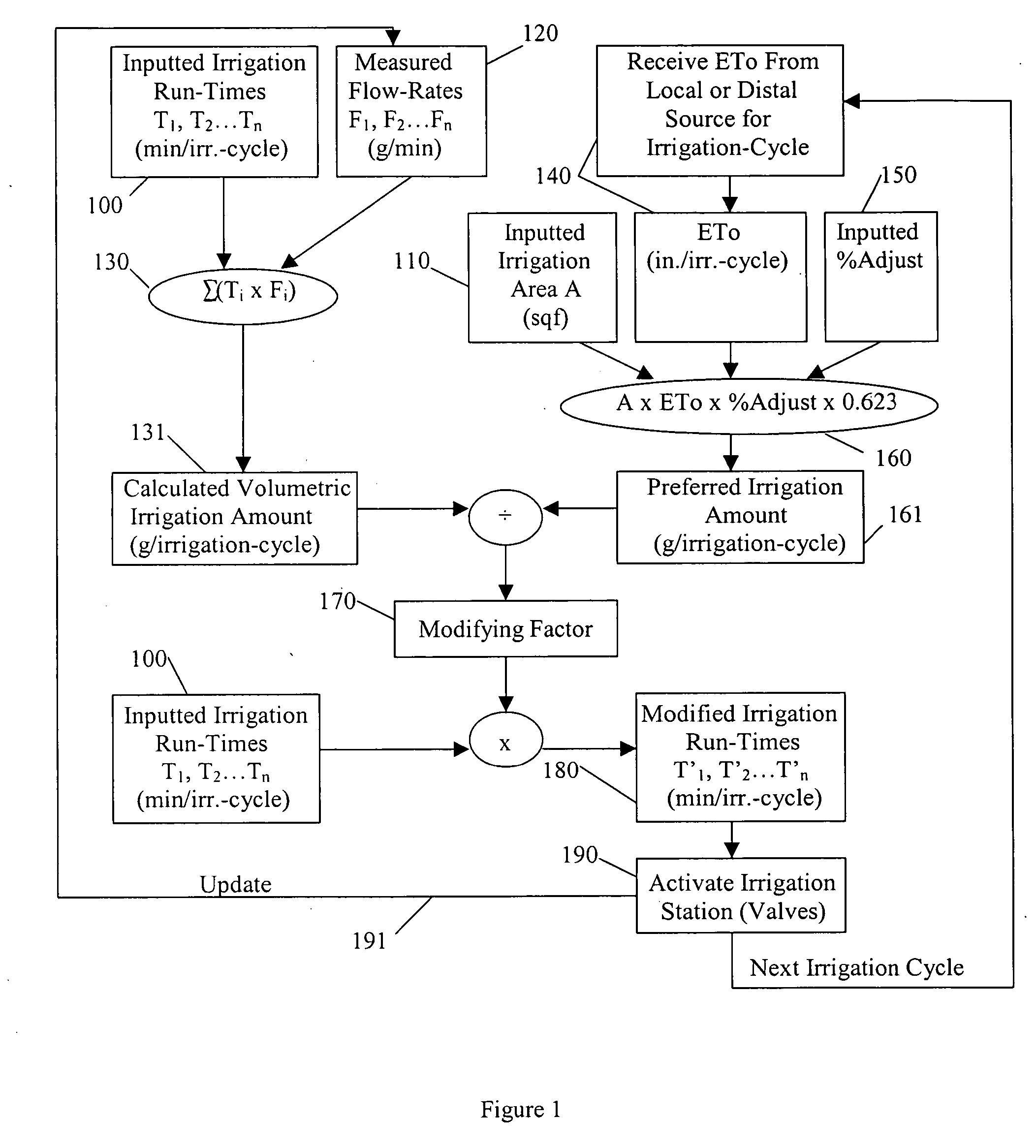
An irrigation controller has run-times that are modified as a function of a calculated volumetric irrigation amount and a preferred irrigation amount. The preferred irrigation amount is at least partly based on an evapotranspiration (ETo) value and the area of the irrigated site. The calculated volumetric irrigation amount is based on flow meter data and inputted irrigation run-times. Preferably the flow meter is a water meter that measures water distributed to the irrigation system and to other water using devices at the irrigated site, and the flow data is based on signature data. In addition to flow data, water pressure may be measured that corresponds with the flow data. It is anticipated that the function will involve the dividing of the preferred irrigation amount by the calculated volumetric irrigation amount to arrive at a modifying factor.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
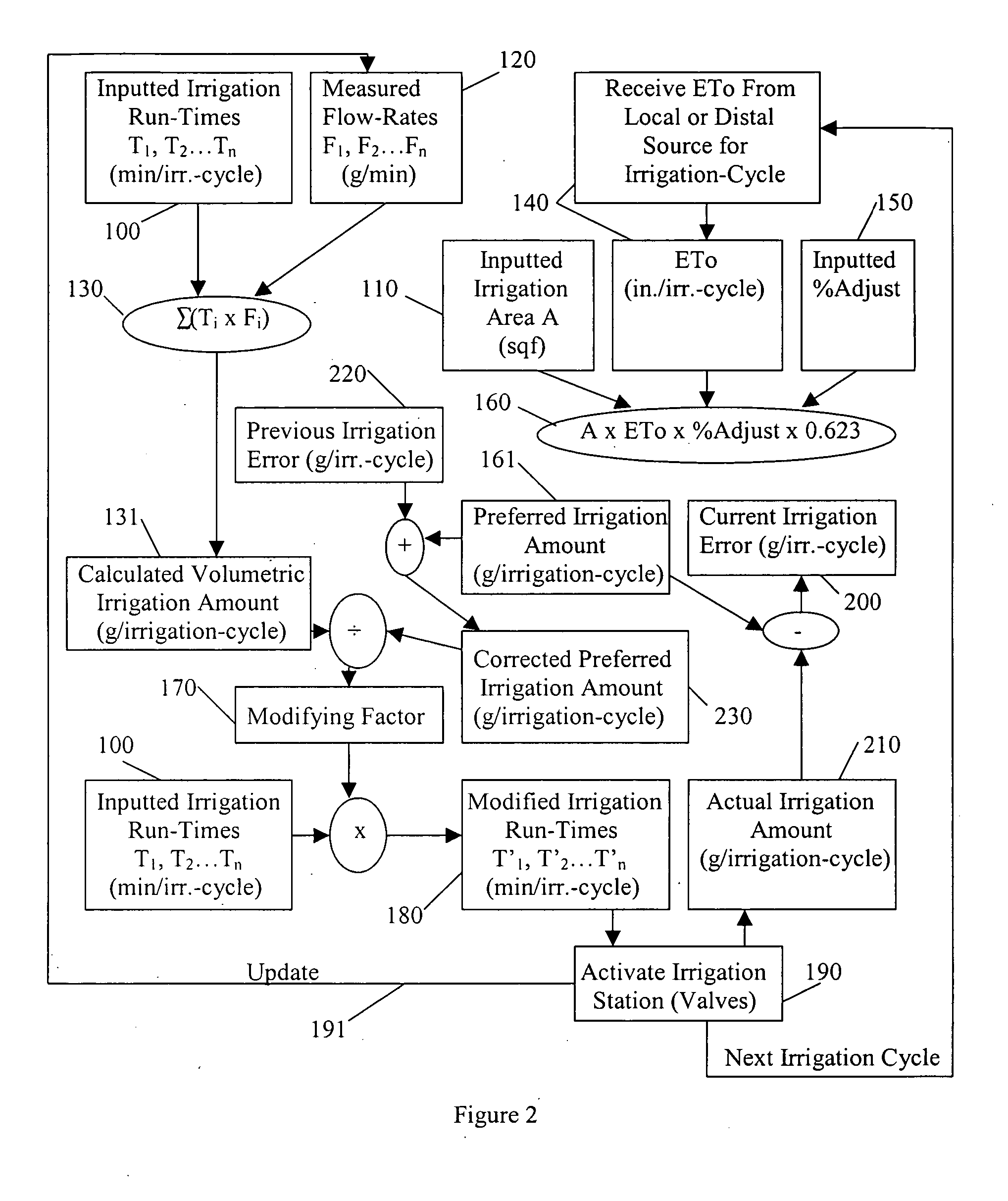
Water savings system
An irrigation controller has run-times that are modified as a function of a calculated volumetric irrigation amount and a preferred irrigation amount. The preferred irrigation amount is at least partly based on an evapotranspiration (ETo) value and the area of the irrigated site. The calculated volumetric irrigation amount is based on flow meter data and inputted irrigation run-times. Preferably the flow meter is a water meter that measures water distributed to the irrigation system and to other water using devices at the irrigated site, and the flow data is based on signature data. In addition to flow data, water pressure may be measured that corresponds with the flow data. It is anticipated that the function will involve the dividing of the preferred irrigation amount by the calculated volumetric irrigation amount to arrive at a modifying factor.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
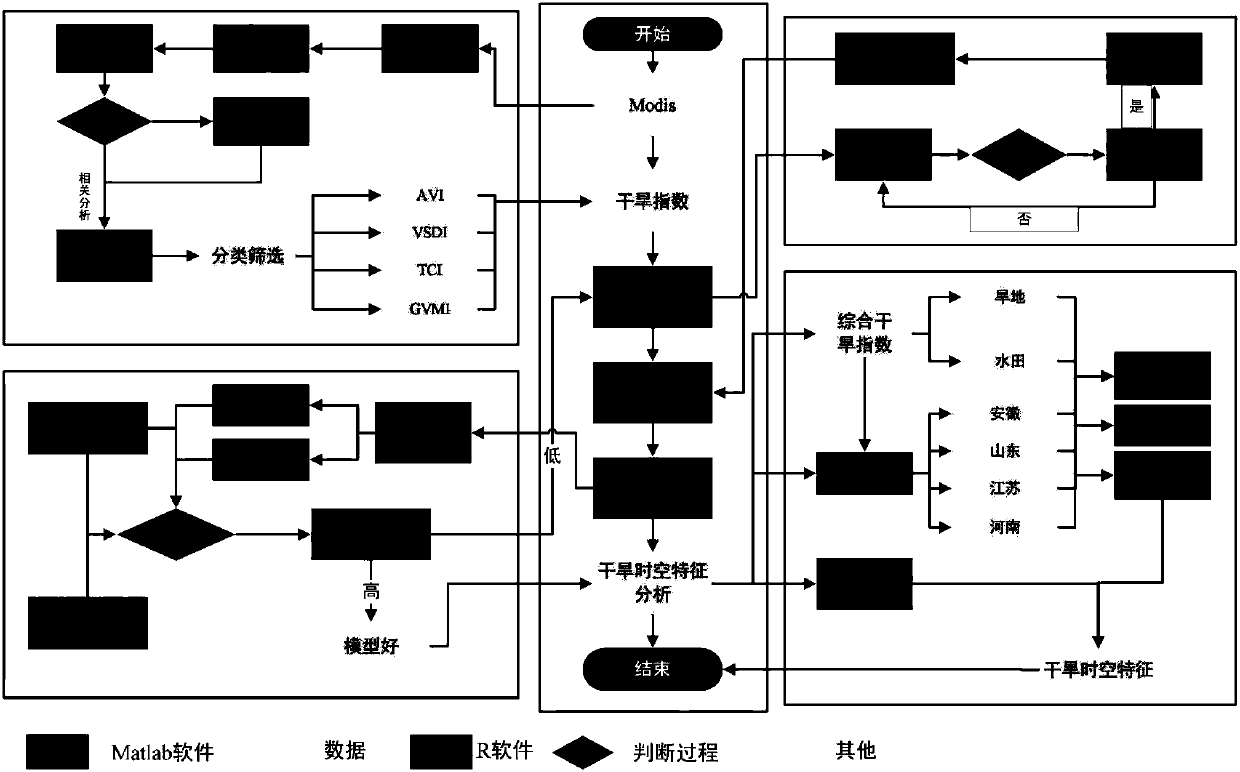
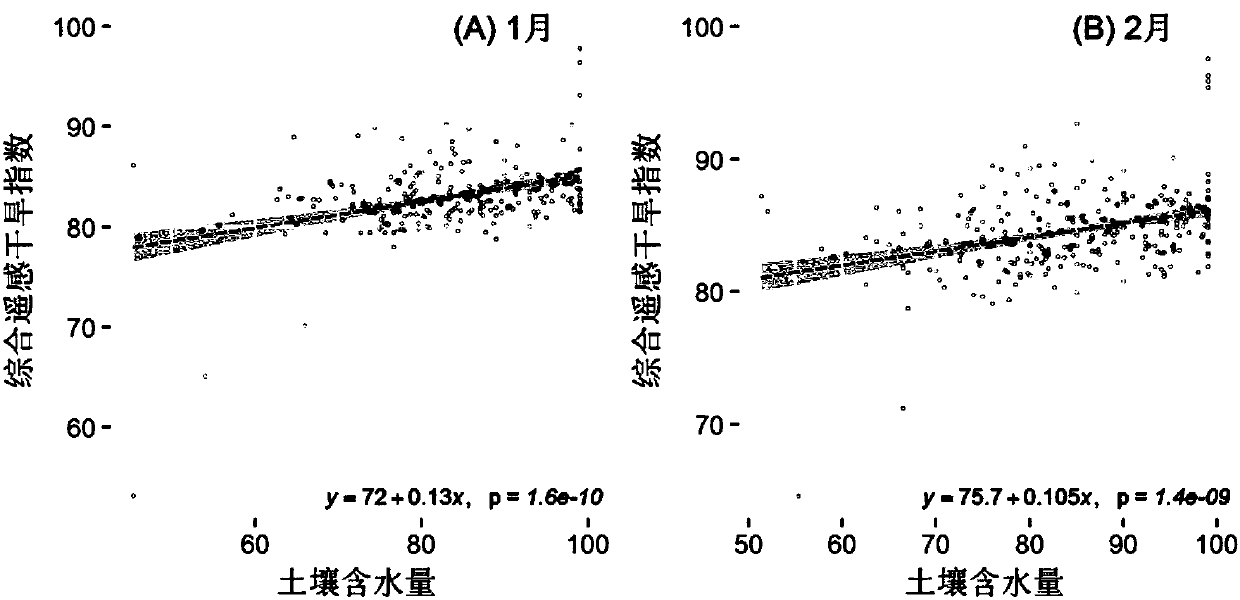
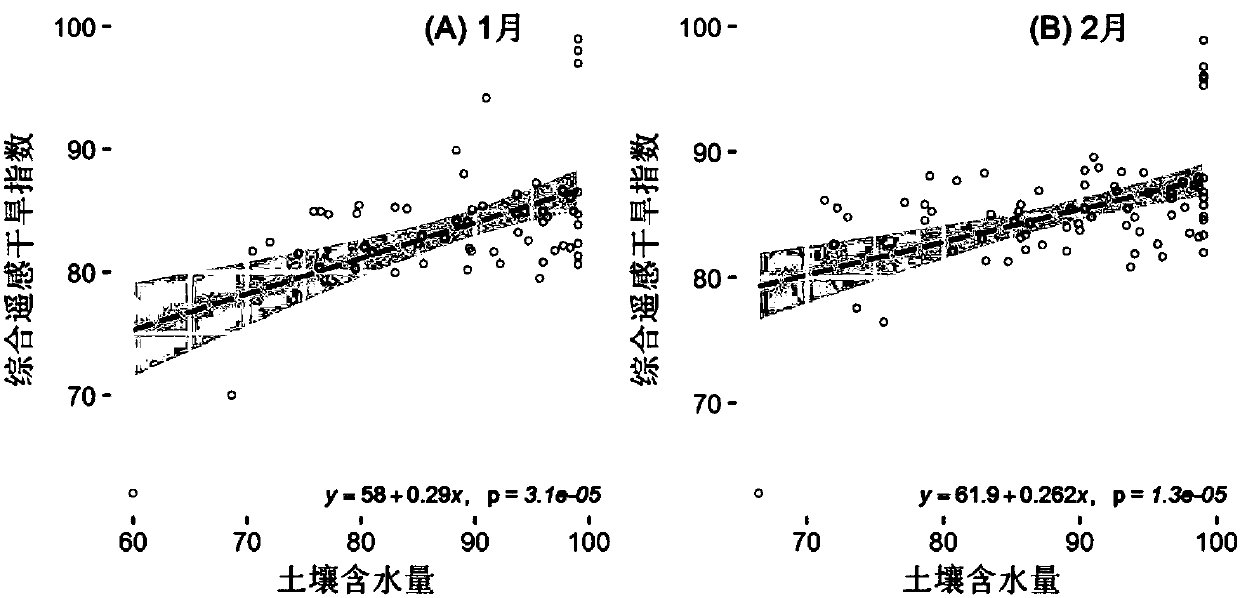
Agricultural drought monitoring method for multi-source remote sensing data
The invention provides an agricultural drought monitoring method for multi-source remote sensing data. According to the method, the following most frequently used four categories of agricultural drought remote sensing monitoring indexes (including 16 indexes) are selected: crop canopy temperature change ( 4 indexes), crop form and vegetation greenness change (5 indexes), soil water change (3 indexes) and crop canopy water contents (4 indexes); a constructed comprehensive remote-sensing drought model is checked and corrected by standard potential evapotranspiration indexes SPEI of a monitoringsite of a research region and 20 cm soil moisture status data, and drought of a data acquiring region can be monitored and evaluated in a large range. By the method, agricultural drought can be continuously, dynamically, quantitatively and visually monitored, analyzed and researched on fine space scale, and decision support and information service are provided for prevention and reduction of natural disasters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
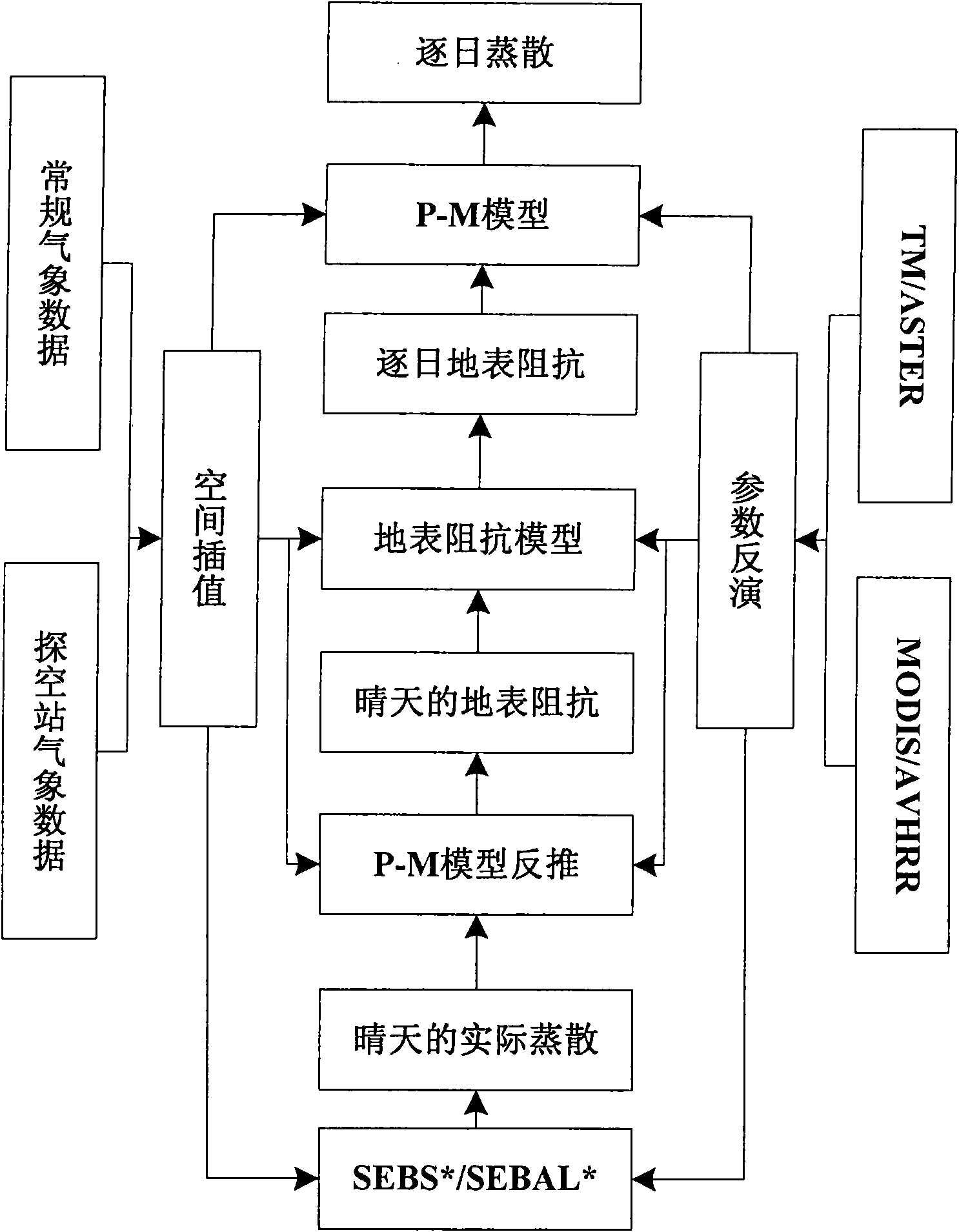
Method for monitoring regional evapotranspiration on the basis of remote sensing
InactiveCN101551459AHigh precisionImprove accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEffective surfaceDown scaling
The invention provides a method for monitoring the regional evapotranspiration on the basis of remote sensing, comprising the following steps of: (1) obtaining the multi-temporal and multi-resolution satellite remote-sensing image data at a specific region; (2) carrying out remote sensing inversion to the key parameters on the ground surface; (3) calculating the impedance of each pixel during the exchanging process of the geogas energy by a remote-sensing geogas exchanging model, calculating the sensible heat flux used for heating the air above each pixel, calculating the latent heat energy by an energy remainder formula and inquiring into effective surface impedance; (4) establishing a surface impedance model in a daily dimension so as to obtain a daily ground surface impedance; and (5) working out the daily evapotranspiration by applying a P-M model repeatedly and carrying out time accumulation and dimension down-scaling, thus finally determining the regional ground surface evapotranspiration. According to the validation of the practical measurement at multi-regions, the method for monitoring the regional evapotranspiration is proved to be effective.
Owner:BEIJING WISEWATCH INFORMATION TECH
Irrigation Controller Integrating Mandated No-Watering Days, Voluntary No-Watering Days, and an Empirically-Derived Evapotranspiration Local Characteristic Curve
InactiveUS20100256827A1Conserve waterEasy to operateWatering devicesFlow control using electric meansWater savingGeographic regions
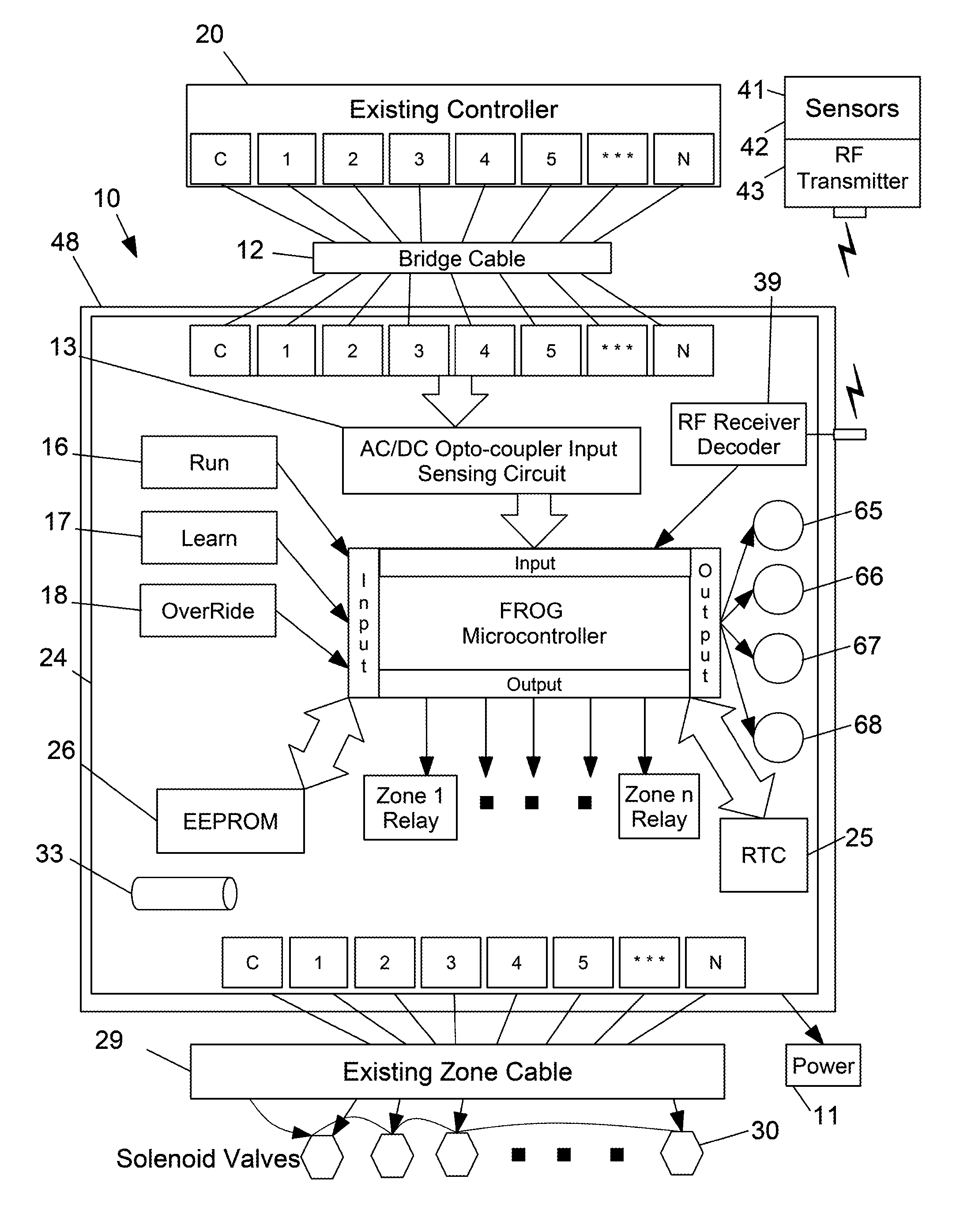
A convenient, easy-to-use, water-saving, and labor-saving FROG smart irrigation controller is provided, which determines the appropriate water budget for the specific geographic region based on the preloaded ETo Local Characteristic Curve and preloaded mandated and voluntary watering restrictions for the specific geographic location, with consideration given to the reduction in watering days, the increase in soil watering depth, and the day of year. Once set, the FROG provides incremental adjustments over the course of the year; the homeowner no longer needs to re-set the watering program seasonally to comply with local mandated and voluntary watering restrictions. Compliance is automatic and obligatory, meeting the water saving goals of the local water authority.
Owner:BRAGG BRUCE ALLEN +2
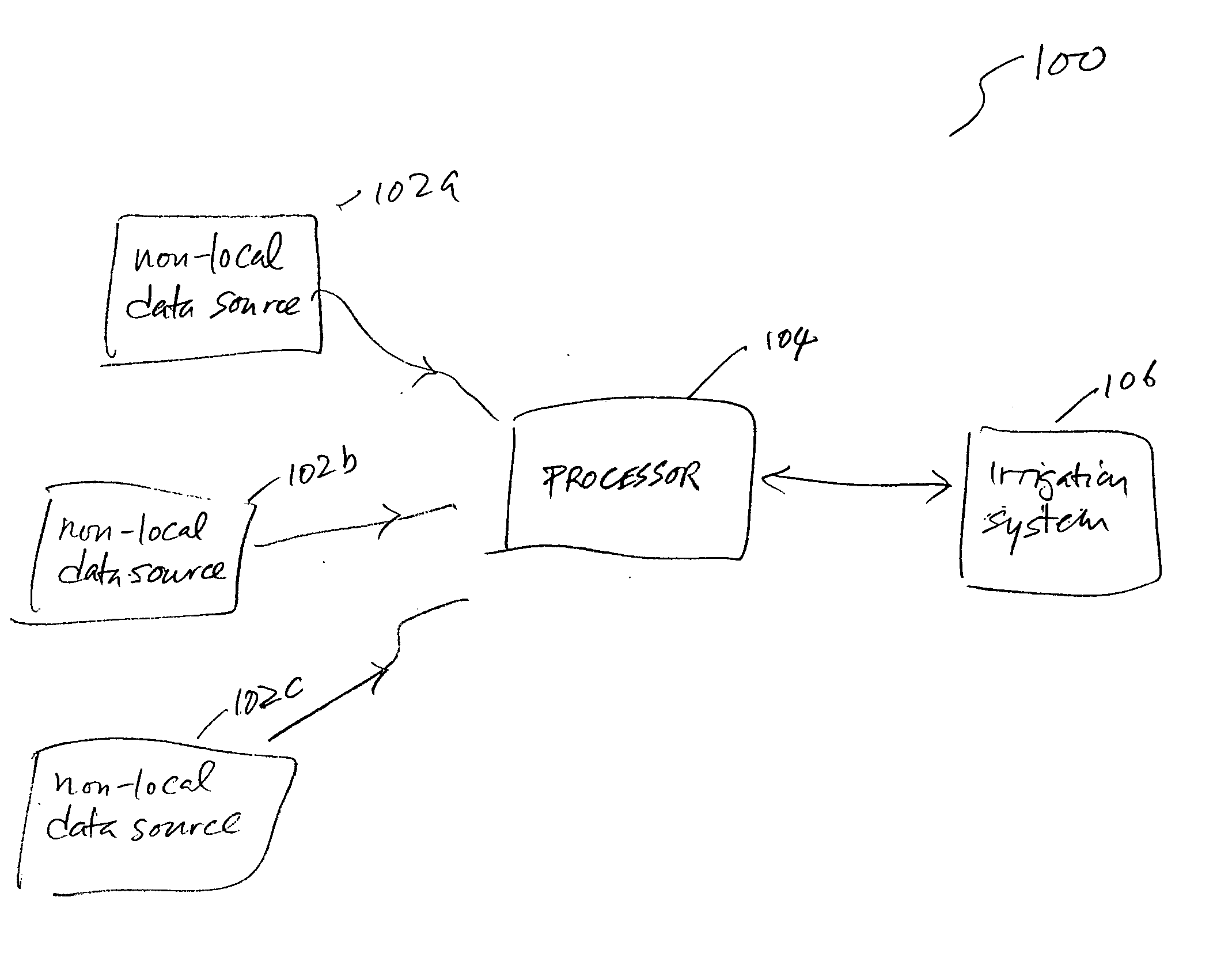
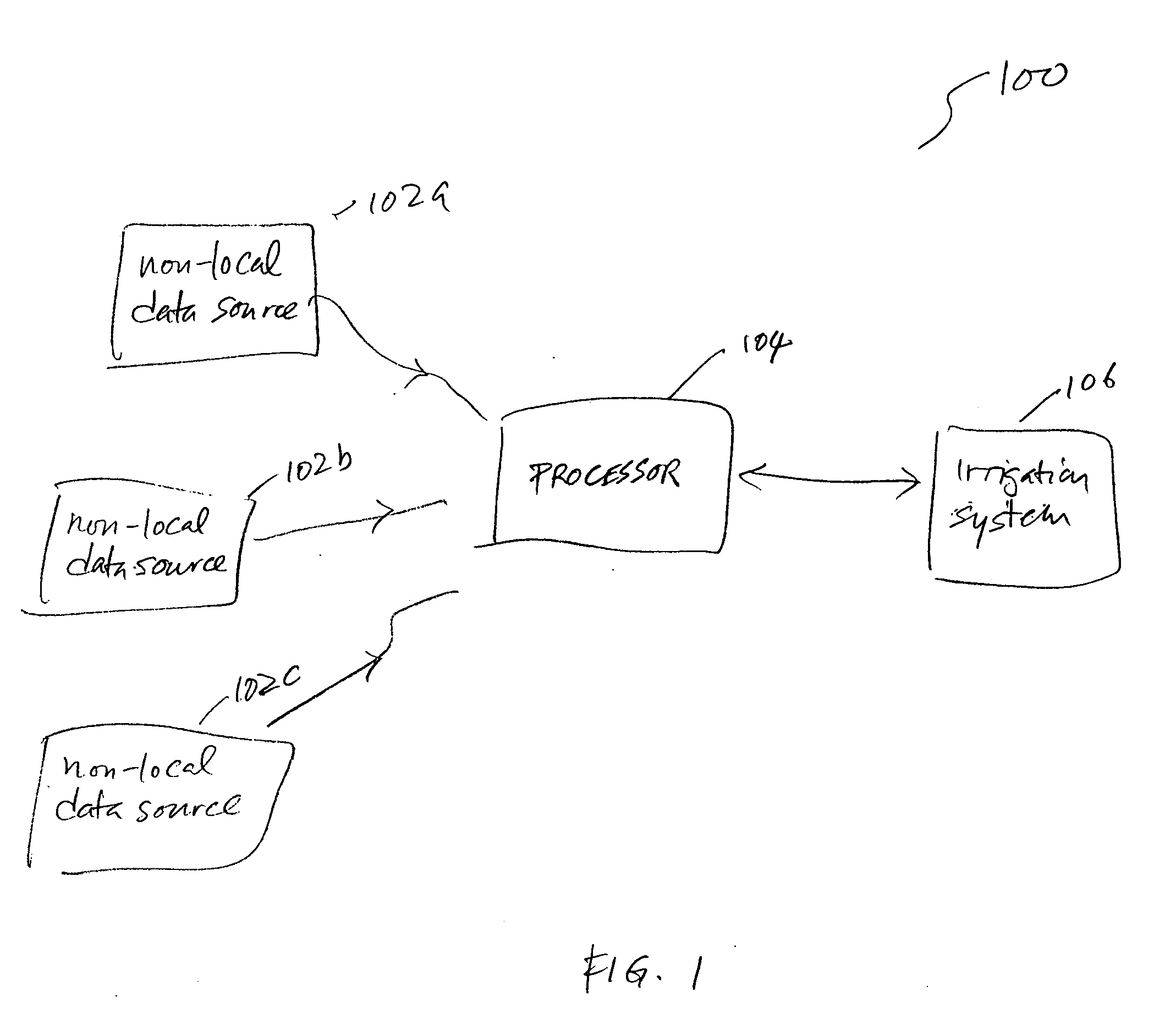
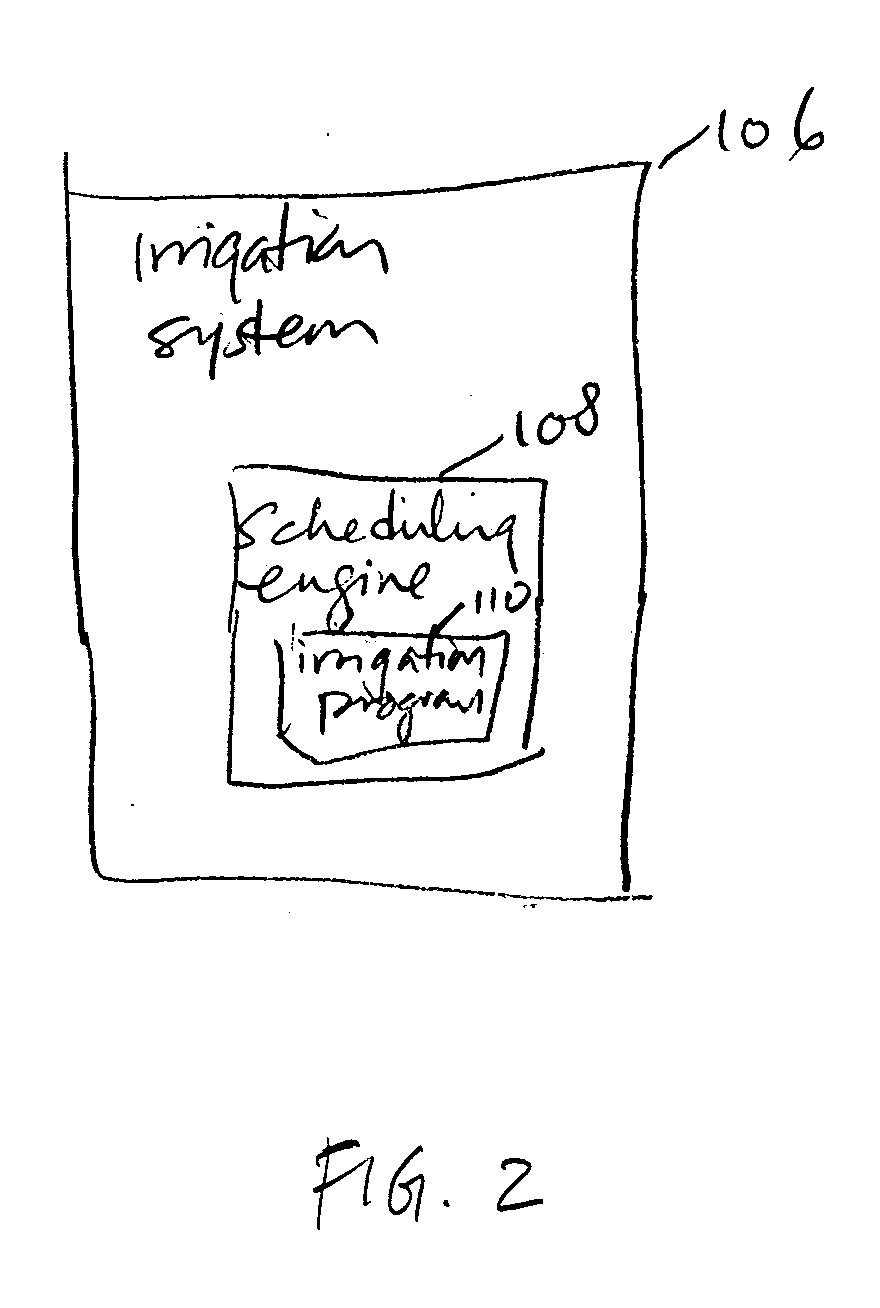
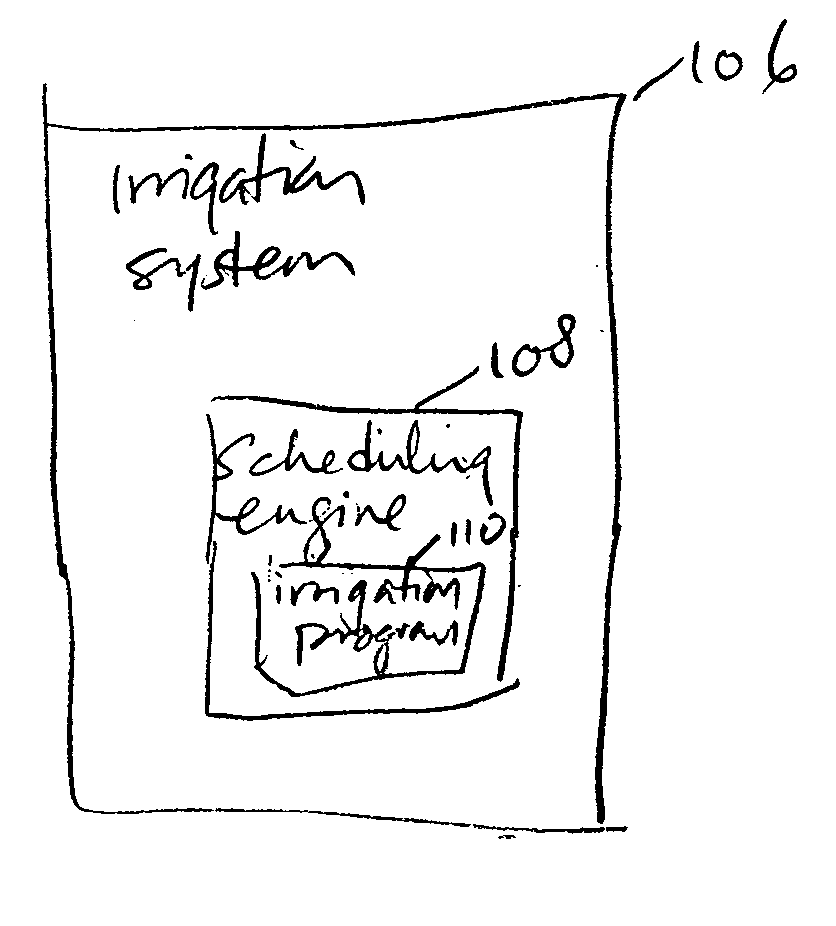
Method and system for controlling irrigation using computed evapotranspiration values
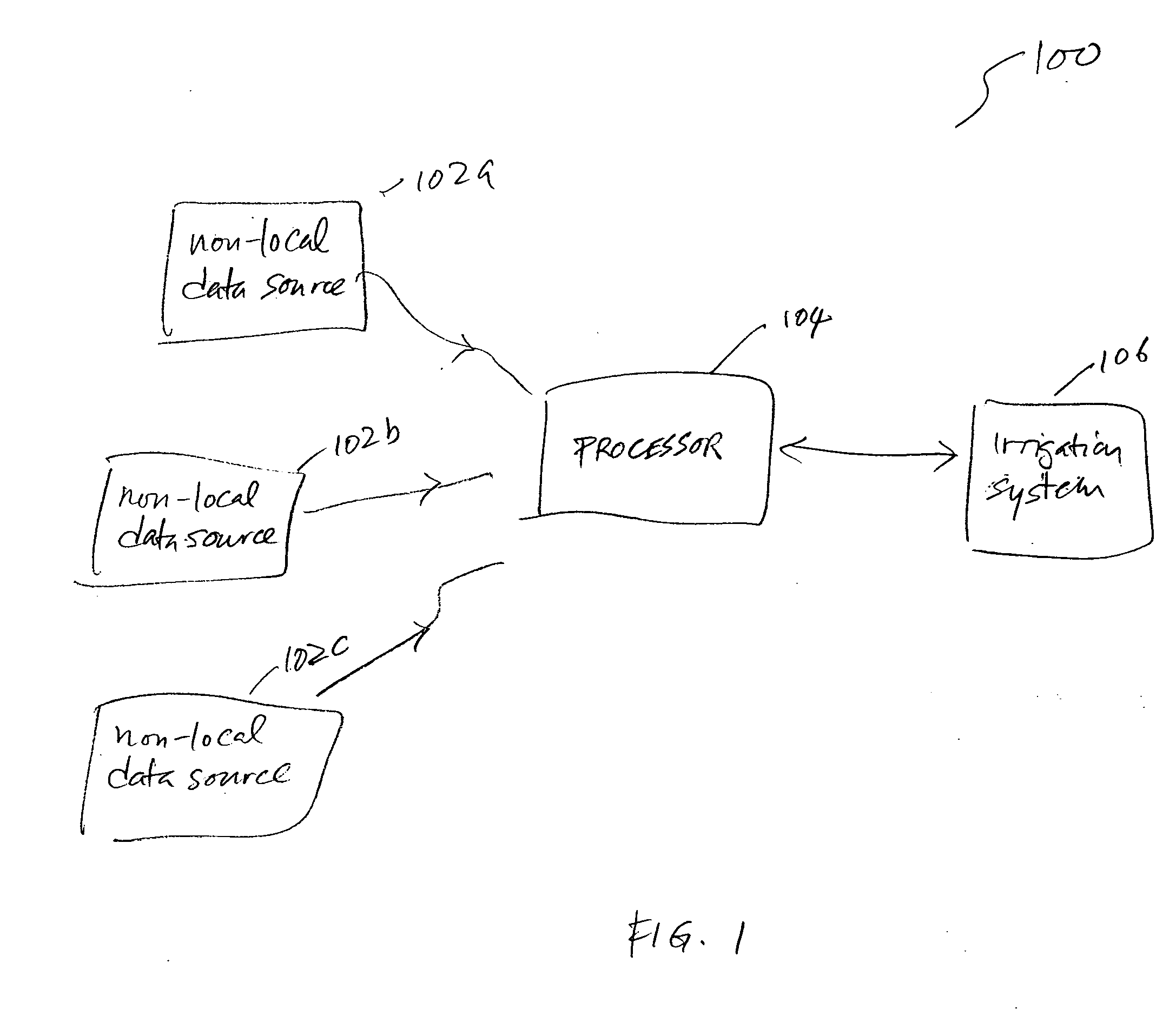
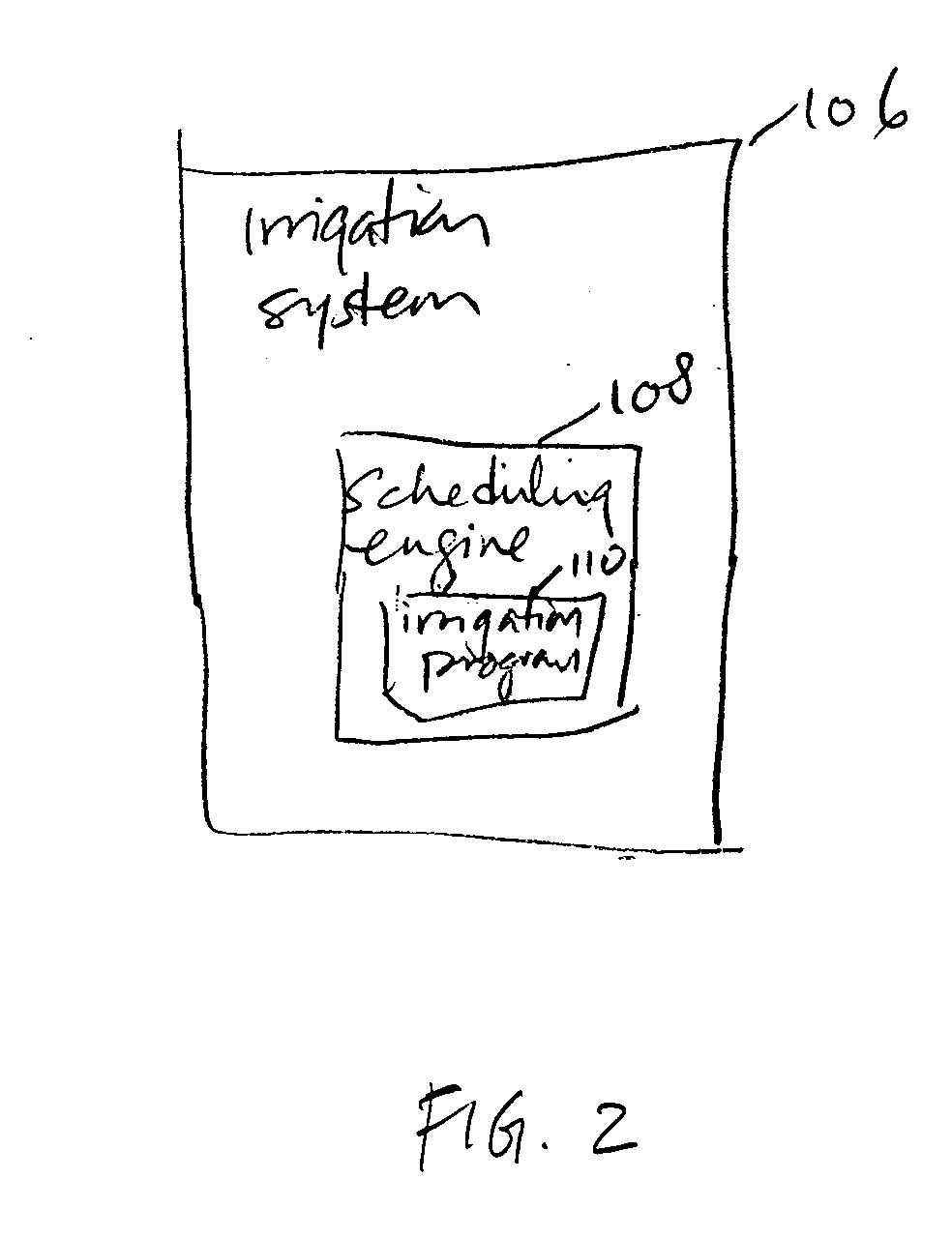
A system for providing irrigation control is provided. The system includes a number of non-local data sources for providing data, a processor and an irrigation system. The processor is configured to receive data from one or more of the non-local data sources and calculate an evapotranspiration (ET) value for an irrigation area that is non-local with respect to the non-local data sources. The irrigation system is located in the irrigation area and configured to receive the ET value from the processor and provide appropriate irrigation control for the irrigation area using the ET value.
Owner:HYDROPOINT DATA SYST
Method and system for providing offset to computed evapotranspiration values
ActiveUS20050119797A1Easy to adjustSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesEngineeringEvapotranspiration
A system for providing irrigation control is provided. The system includes a processor configured to calculate an offset to an evapotranspiration (ET) value and an irrigation system configured to receive the offset from the processor and provide appropriate irrigation adjustment based on the offset. The offset is calculated based on the ET value and the ET value has been previously provided to the irrigation system.
Owner:HYDROPOINT DATA SYST
Irrigation water management system
ActiveUS20110137827A1Efficient irrigationEfficiently determinedVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsWater useEvapotranspiration
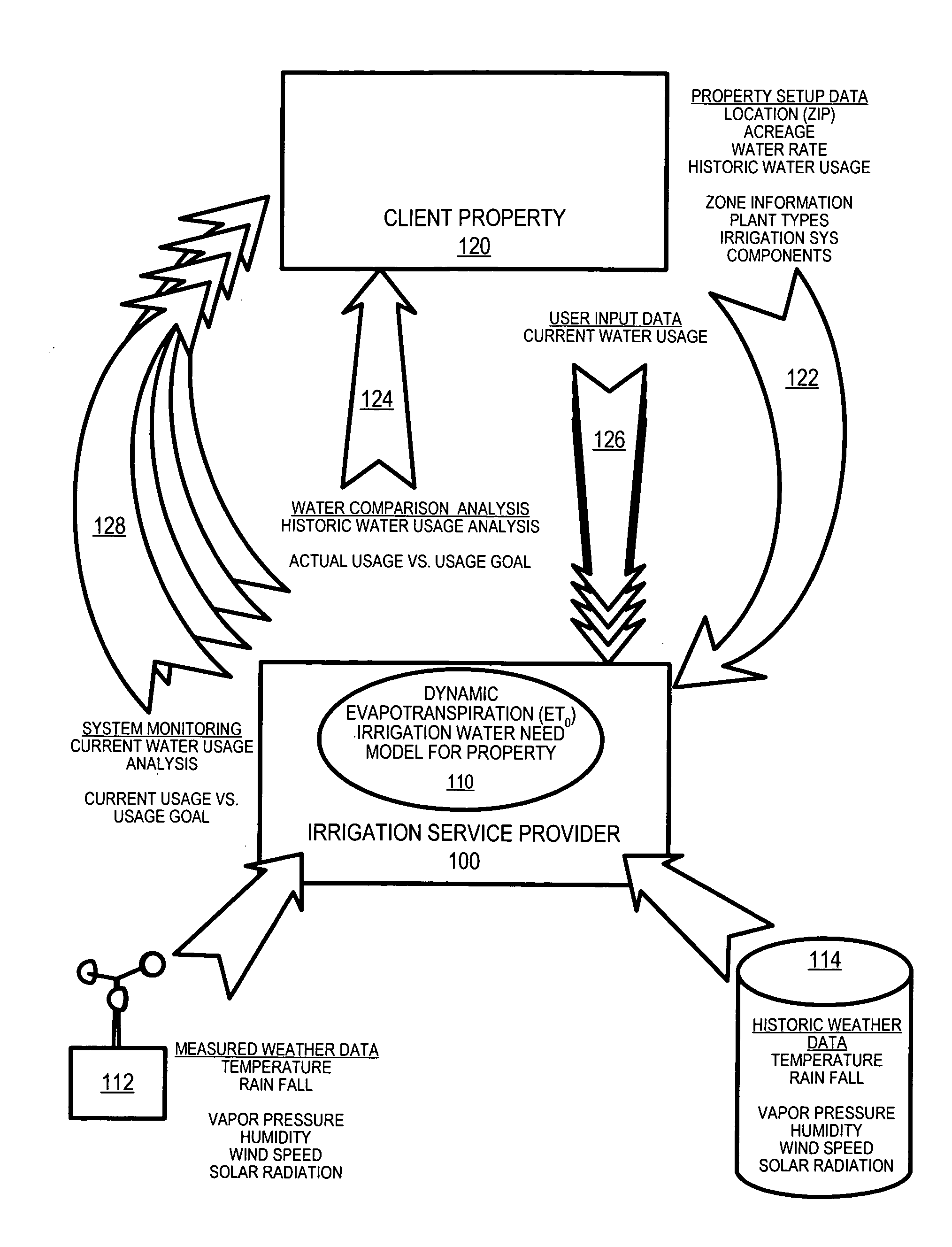
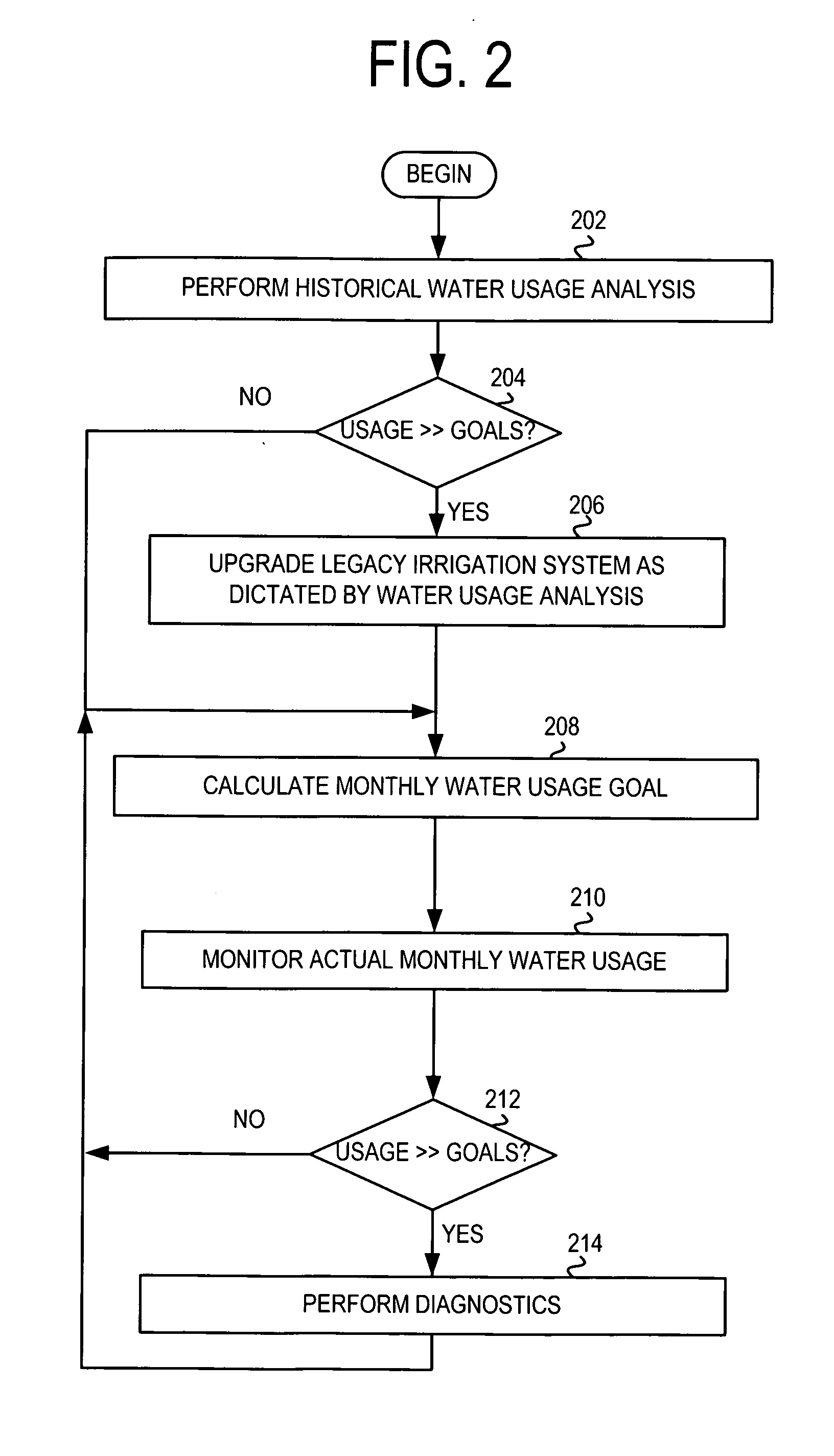
The efficiency of an irrigation system on a property is determined as a difference between the actual water usage at a property and the irrigation water need of the plant on the property. Data for the property are received including at least the location and irrigation area of the property. A reference evapotranspiration value for the property is determined using the solar radiation data derived from the location of the property. The irrigation water need of the property is then calculated from the reference evapotranspiration value and area. The irrigation water need is compared to the actual water use at the property to determined the efficiency of the irrigation system operating thereon.
Owner:TELSCO INDS
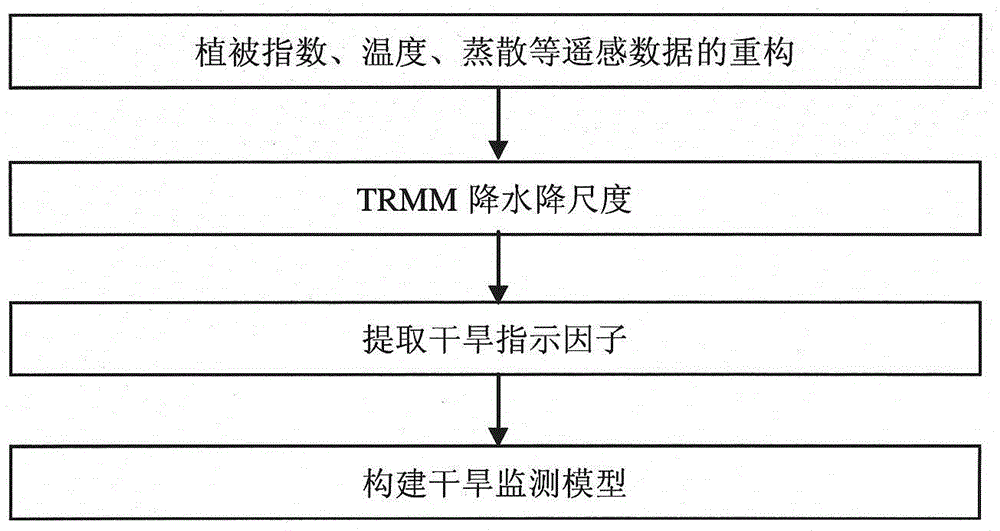
Data mining-based drought monitoring method
The invention discloses a data mining-based drought monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, data reconstruction is carried out on an MODIS vegetation index product, a land surface temperature product and an evapotranspiration product; 2, according to the vegetation index obtained in the first step and DEM data, downscaling is carried out on a TRMM rainfall product; 3, a vegetation anomaly index, a temperature anomaly index, an evapotranspiration anomaly index and a rainfall anomaly index are extracted again; and 4, a classification and regression tree model is used for building a statistical regression rule and a linear fitting model to obtain a drought monitoring model. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention comprehensively considers multi-source remote sensing spatial information, such as the rainfall, the evapotranspiration, the vegetation growth state, the land using type, the altitude and other factors, in the case of drought monitoring, spatial data mining is adopted, the drought monitoring model is built, and the drought monitoring precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
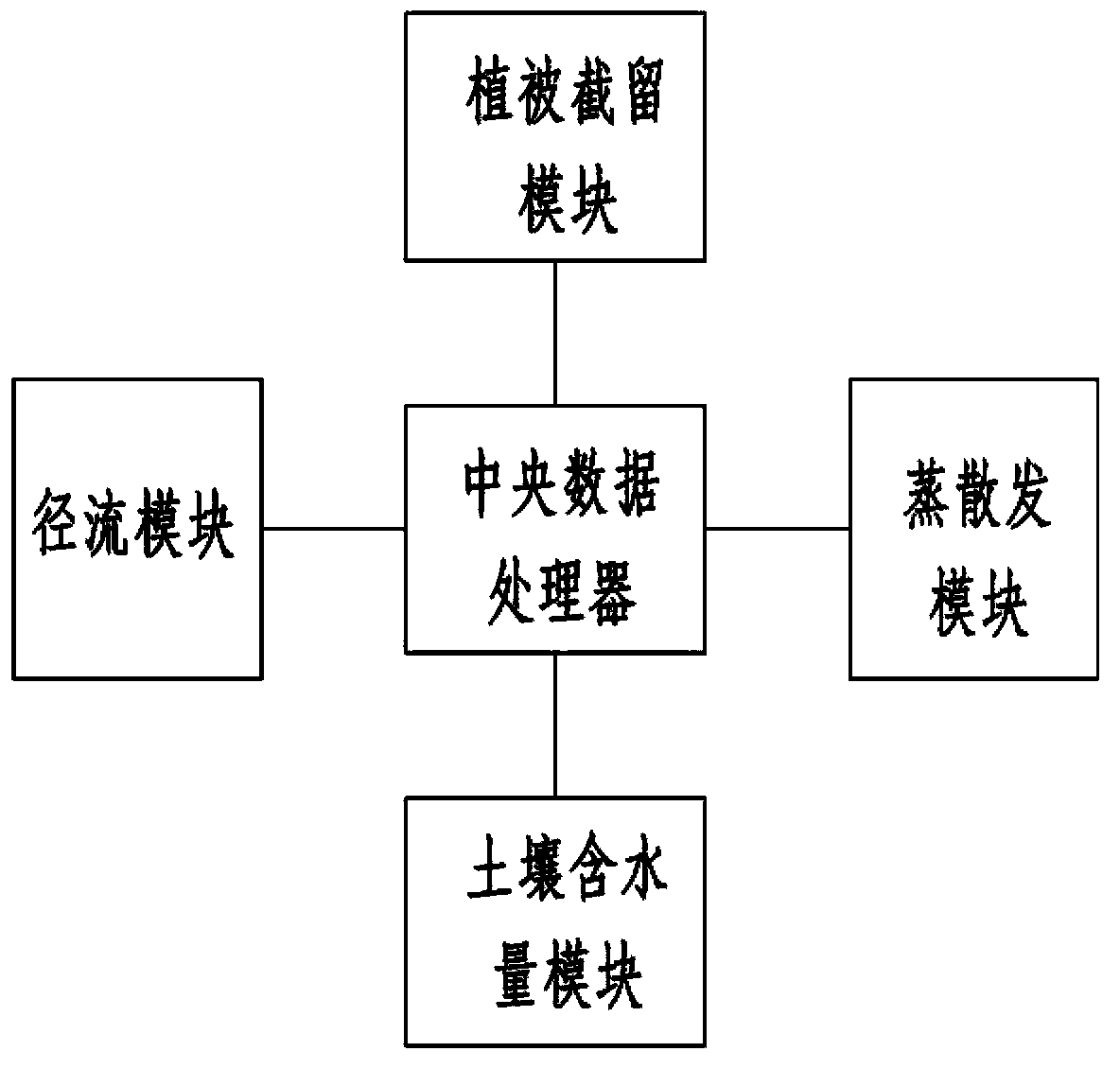
Model for farmland net irrigation water and irrigation water capacity estimation method
ActiveCN103413035AKeep abreast of water consumptionRealize real-time monitoringSpecial data processing applicationsVegetationProcess module
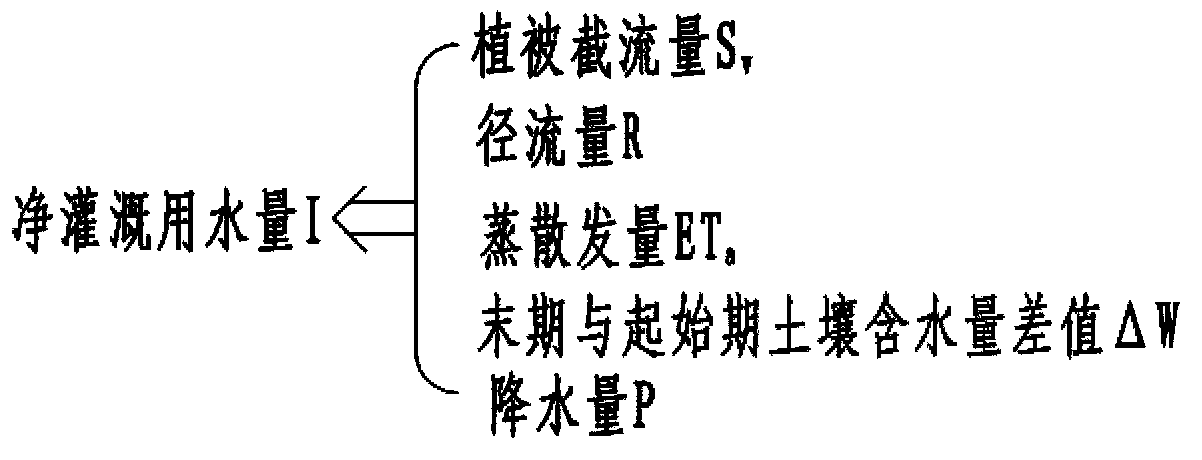
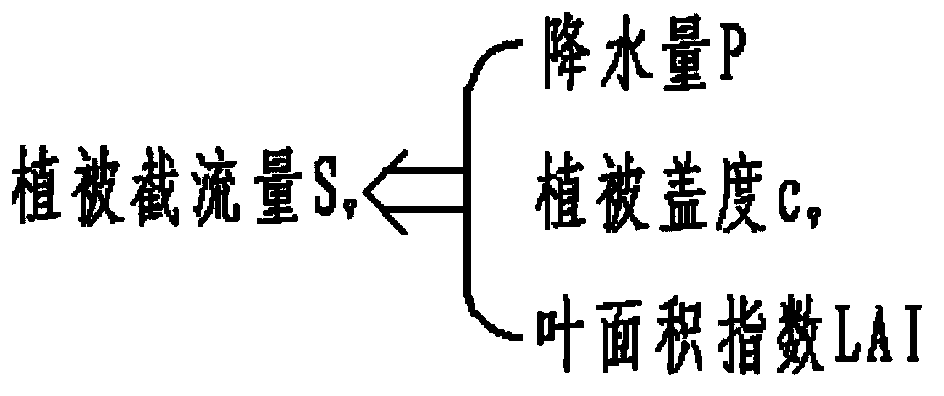
The invention relates to the field of ecological hydrology, in particular to a model for farmland net irrigation water. The model comprises a central data processor, a vegetation retention module, a runoff module, an evapotranspiration module and a soil water content module, wherein the central data processor realizes data transmission with the vegetation retention module, the runoff module, the evapotranspiration module and the soil water content module respectively. According to the model, large-scale nonuniformity of the earth surface is fully taken into consideration, spaces are dispersed into pixels; a part of parameters required by each sub-module in the model for the farmland net irrigation module is inversed on a pixel scale; an eco-hydrological process module is coupled; the whole process simulation of rainfall vegetation retention, soil water content, runoffs and evapotranspiration is performed; the farmland soil water content is monitored in real time; and whether a farmland is required to be irrigated or the required irrigation water capacity can be known in time, and situations that farmlands cannot be irrigated in time or the irrigation capacity is too large result in agricultural production loss and water resource waste are avoided.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS20120072037A1Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationEngineeringEvapotranspiration
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with irrigation controllers based upon the ambient temperature and extraterrestrial radiation of a particular geographical area. It receives a preliminary irrigation schedule from the operator and computes a water budget ratio by comparing current local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, then modifying the preliminary irrigation schedule based upon that ratio. The present invention utilizes fewer variables, is less complex, and is much easier to install and maintain than the current evapotranspiration-based controllers.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com