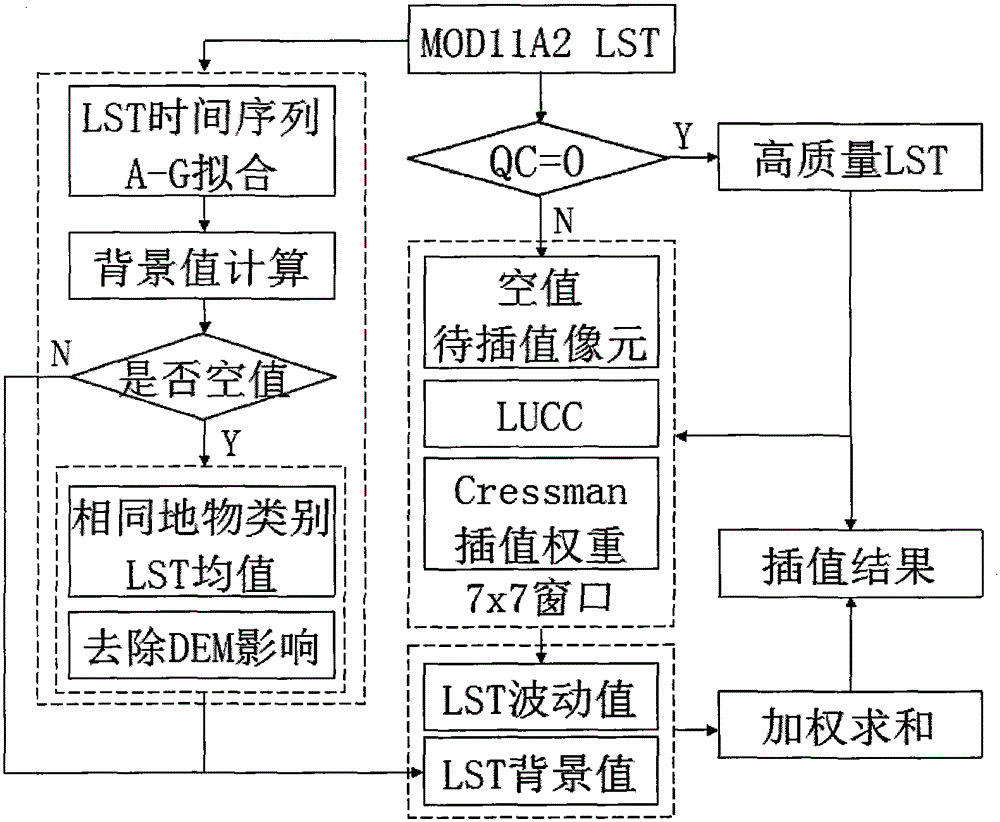
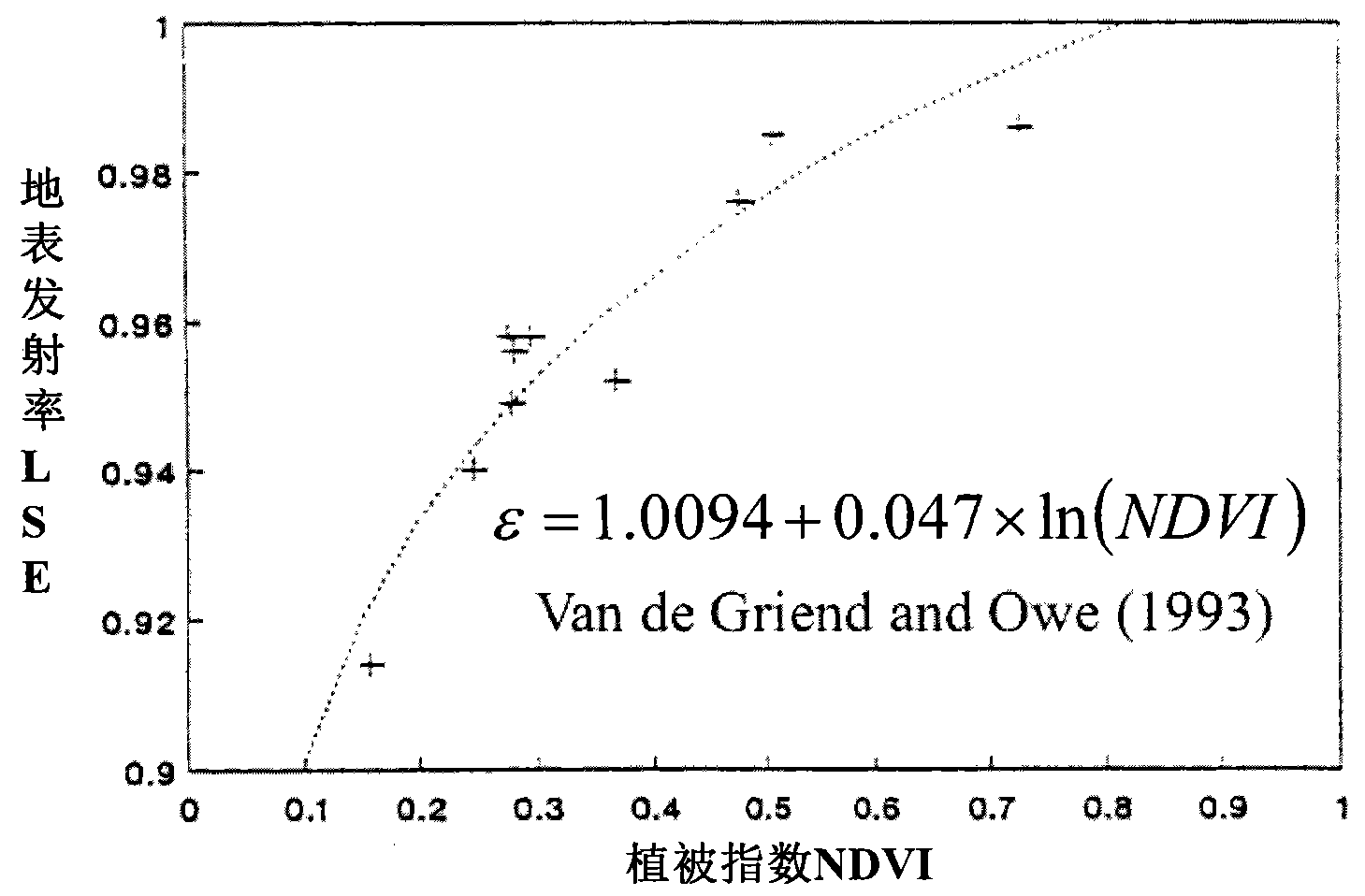
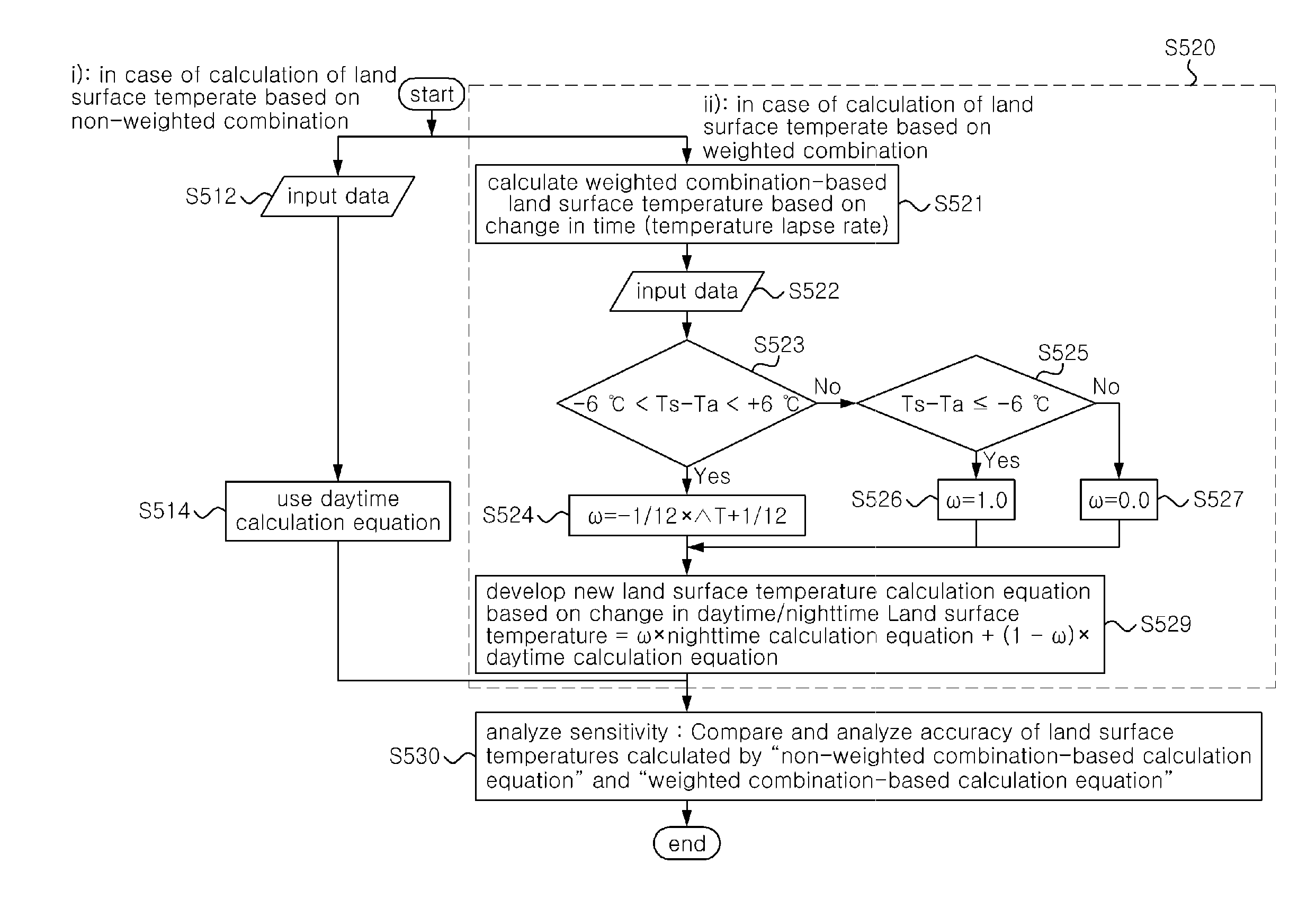
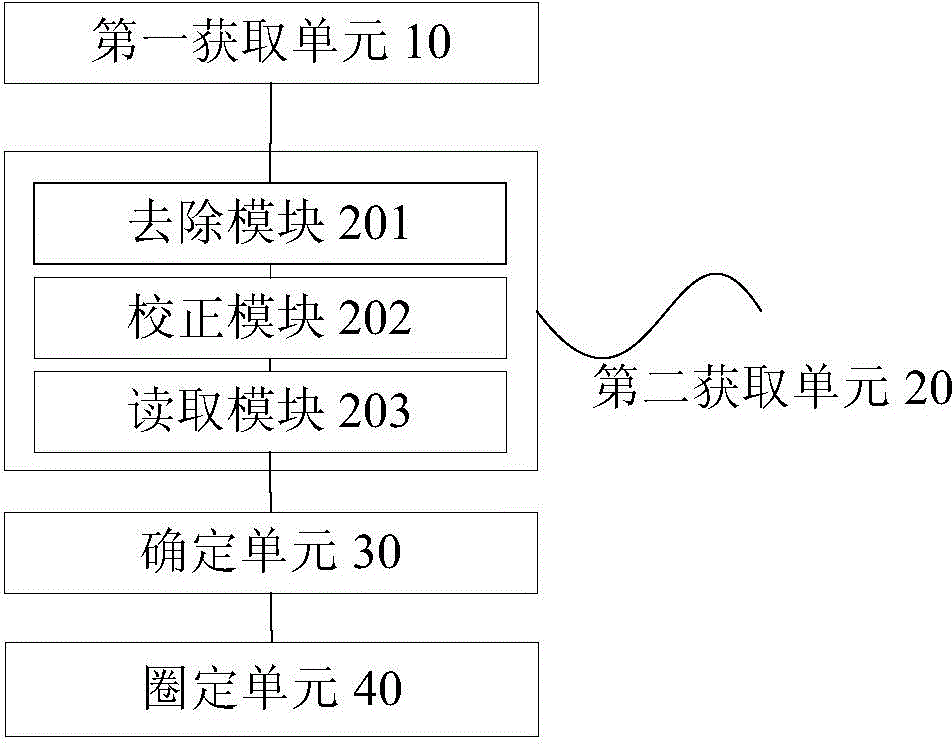
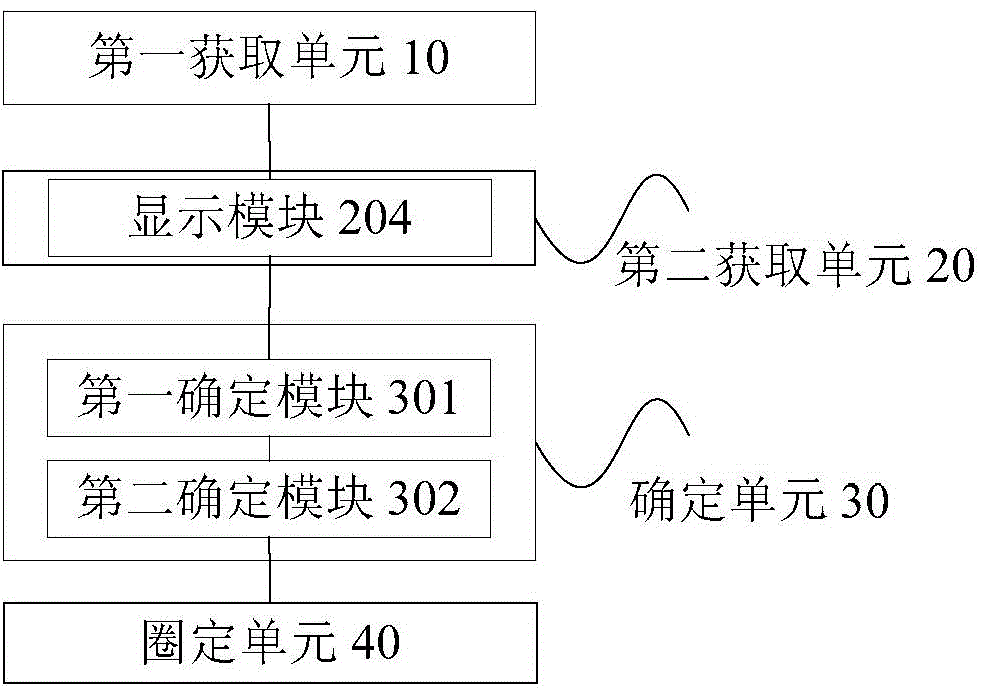
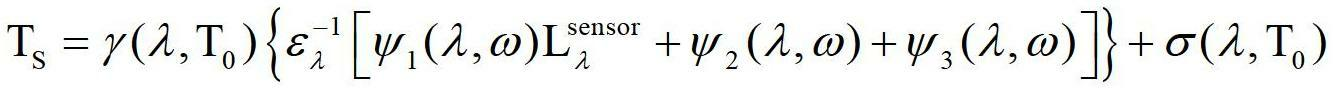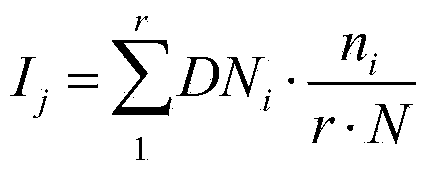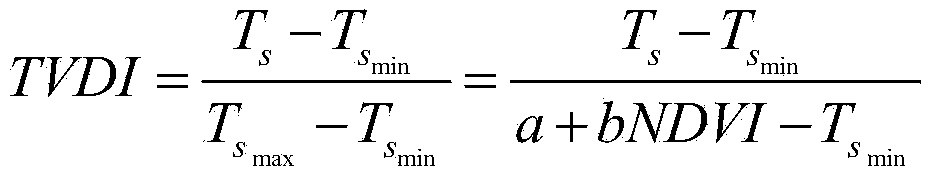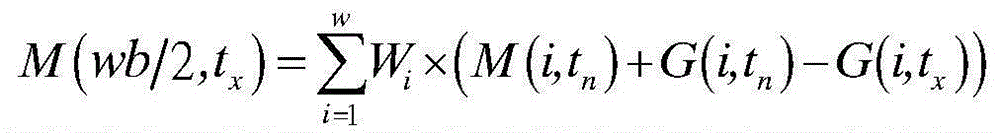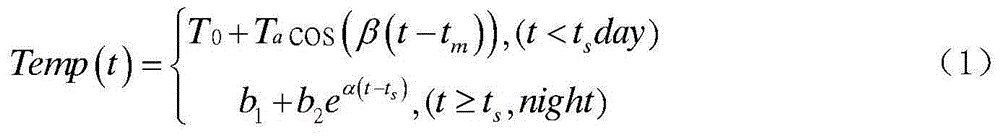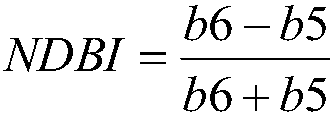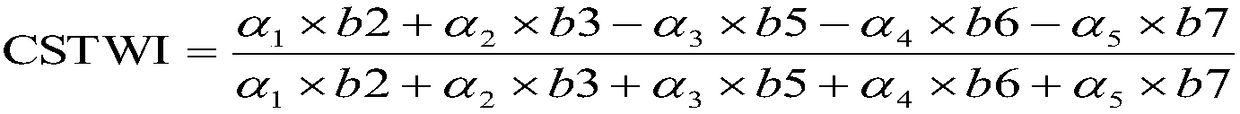Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Land surface temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agricultural drought grade monitoring method based on temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI)
The invention discloses an agricultural drought grade monitoring method based on a temperature vegetation drought index (TVDI). The method comprises the following steps of: 1, data preparation; 2, land surface temperature (LST) data reconstruction; 3, construction of crop plantation area normalized difference vegetation index-land surface temperature (NDVI-LST) feature space; 4, TVDI calculation; and 5, drought grade monitoring based on the TVDI. The invention brings forward an LST data reconstruction method based on multi-year background values and area fluctuation values, a cultivated land area multi-year NDVI-LST feature space is constructed for crops, the TVDI is calculated, a crop drought grade monitoring model based on a supervision classification idea is designed for drought grade remote sensing monitoring, the model can quite accurately reflect drought threat degrees of the crops under difference conditions in real time, and the method has great significance in monitoring, early warning and prevention of agricultural disasters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Method for inversing land surface temperature from MODIS data
InactiveCN101629850AGuaranteed synchronous fetchOvercome the disadvantages that are difficult to achieveRadiation pyrometryElectromagnetic wave reradiationWater vaporDisaster monitoring
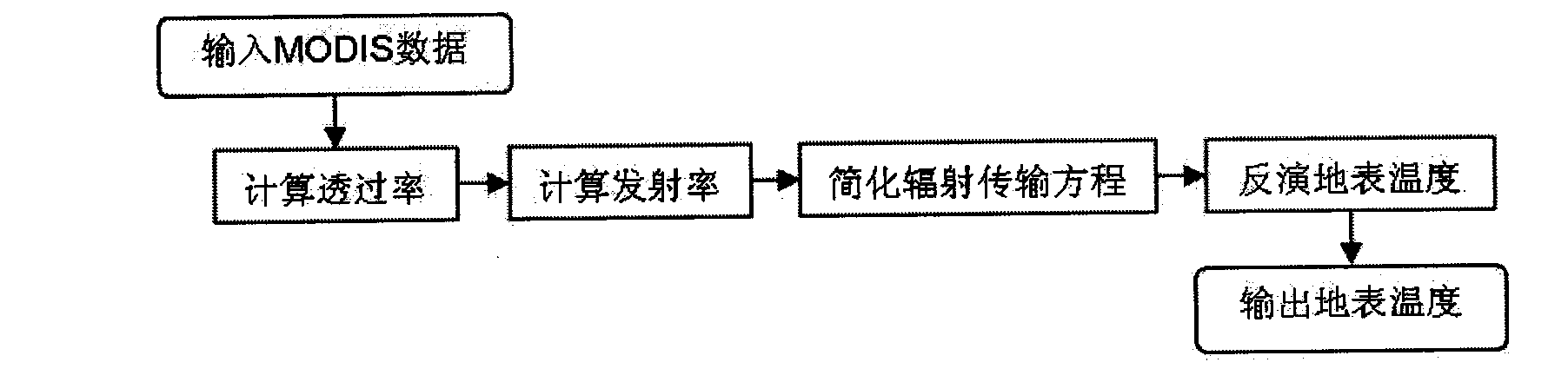
The invention relates to a method for inversing land surface temperature from MODIS data, which can be applied in meteorology, environmental monitoring, land management, agricultural condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and other remote sensing application departments. The method comprises four steps: the first step is to calculate the transmittance of 31st and 32nd wave bands of MODIS through water vapor content of atmosphere. The second step is to calculate the emissivity of the 31st and the 32nd wave bands of the MODIS sensor through vegetation index NDVI. The third step is to simplify a radiation transmission equation. The fourth step is to carry out inversion calculation on the MODIS data and obtain the land surface target object temperature and the emissivity distribution situation, so that the method can be used in meteorological forecasting, environmental monitoring, agricultural condition monitoring, disaster monitoring and other departments.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data
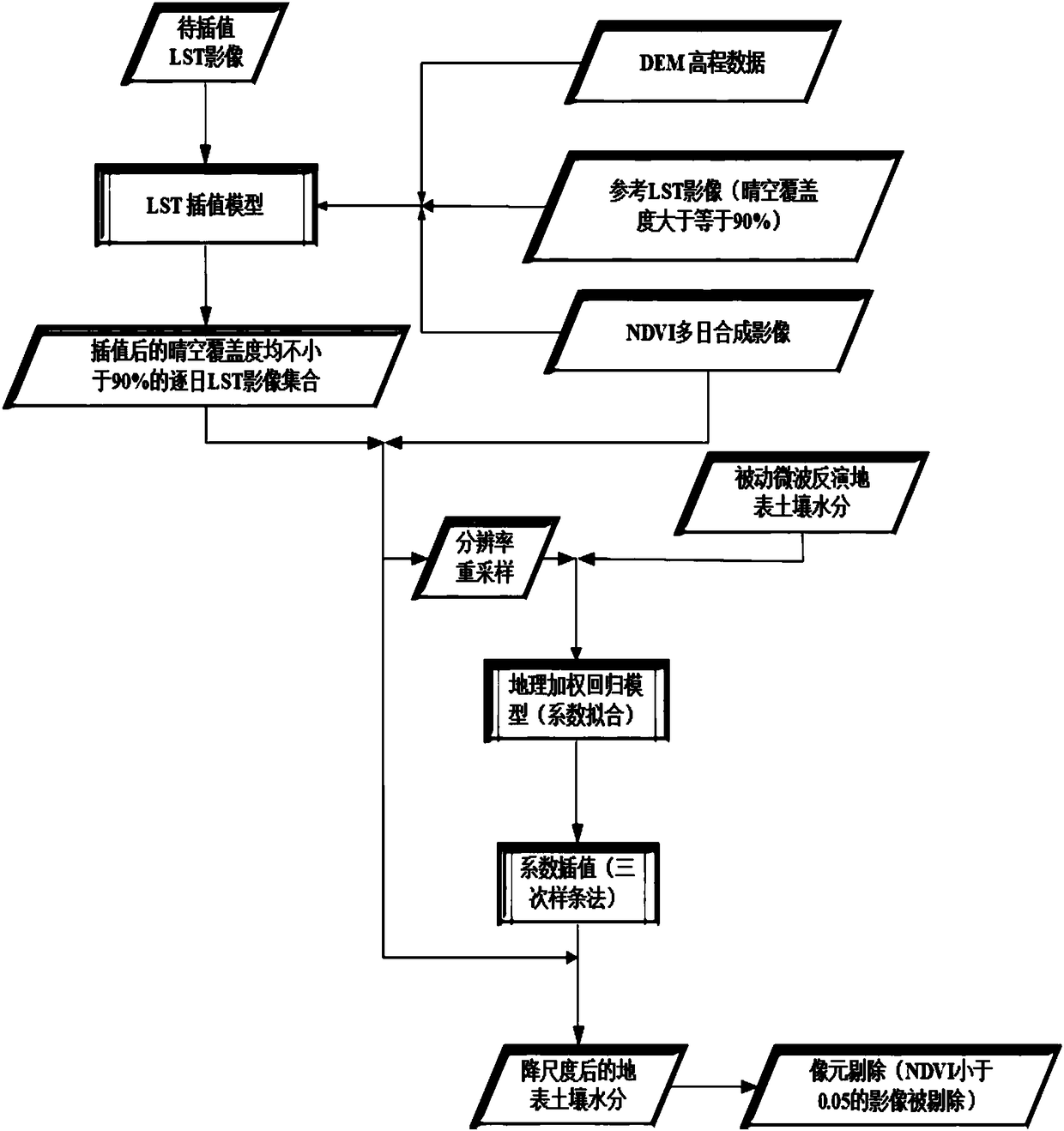
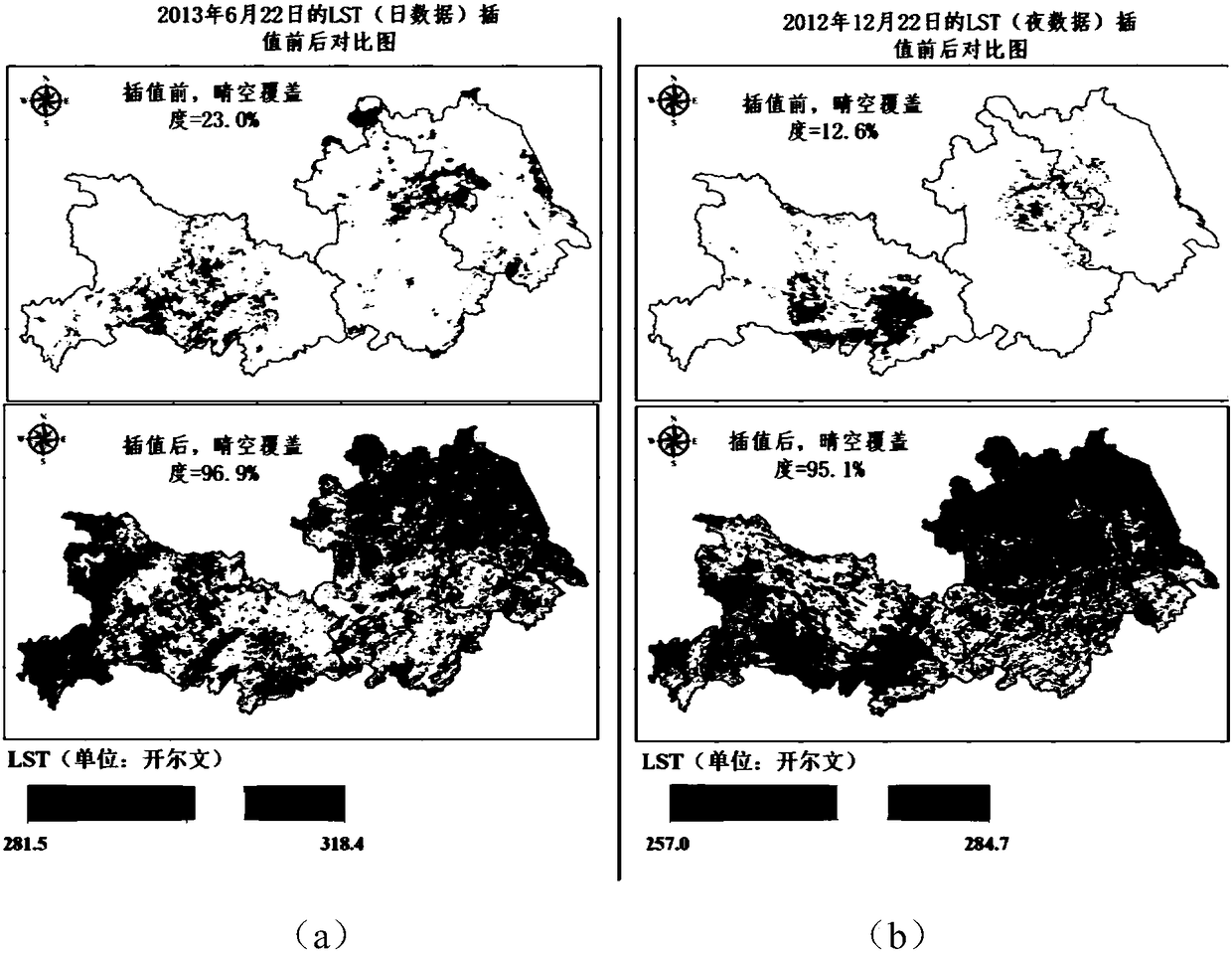
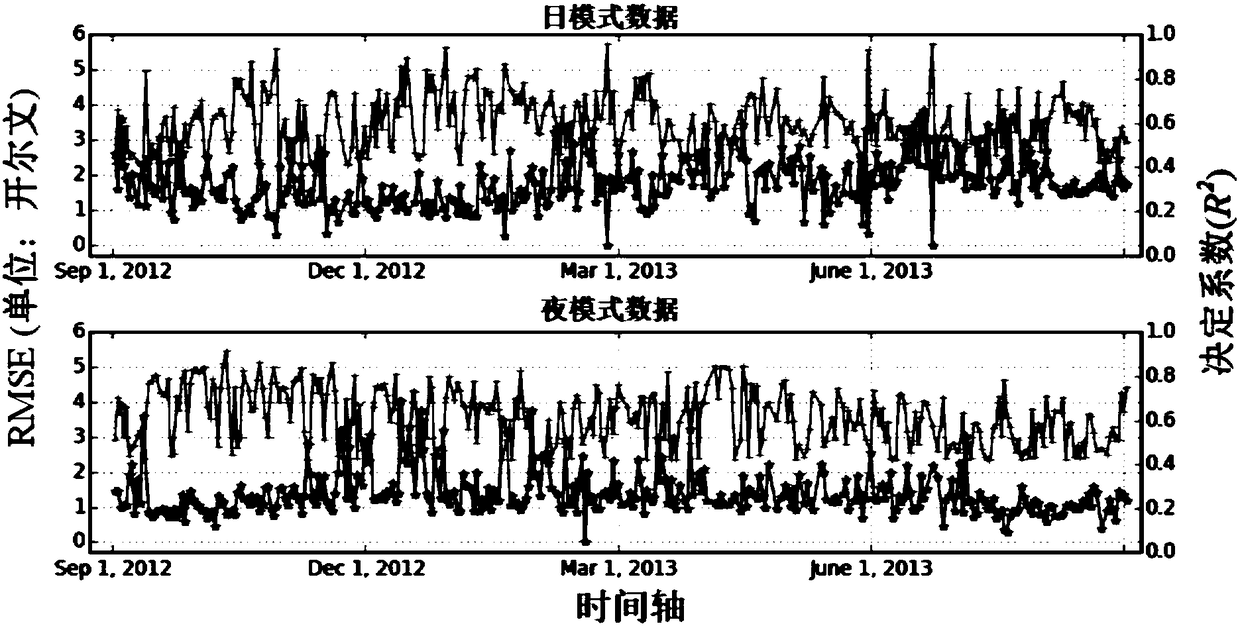
The invention discloses a land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data and is particularly applicable to cloudy and rainy areas. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and arranging a passive microwave soil moisture data set, an LST (land surface temperature) and NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) data set and DEM(digital elevation model) data; performing spatial interpolation on LST images with serious pixel deletion affected by cloud and rain by adopting an NDVI and DEM data set as auxiliary data to obtain aday-by-day LST data set almost totally covering a research area; constructing a mathematic relation model for microwave soil moisture with optical remote sensing LST and NDVI by a geographical weighted regression model, and obtaining a land surface soil moisture data set with high spatial resolution with the mathematic relation model. Through the adoption of the method, reliability of a descalingresult and universality of descaling in the wide-range research area are improved effectively, and precision and efficiency of wide-range space mapping and monitoring for soil moisture content in thecloudy and rainy areas are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Data mining-based drought monitoring method
The invention discloses a data mining-based drought monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, data reconstruction is carried out on an MODIS vegetation index product, a land surface temperature product and an evapotranspiration product; 2, according to the vegetation index obtained in the first step and DEM data, downscaling is carried out on a TRMM rainfall product; 3, a vegetation anomaly index, a temperature anomaly index, an evapotranspiration anomaly index and a rainfall anomaly index are extracted again; and 4, a classification and regression tree model is used for building a statistical regression rule and a linear fitting model to obtain a drought monitoring model. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention comprehensively considers multi-source remote sensing spatial information, such as the rainfall, the evapotranspiration, the vegetation growth state, the land using type, the altitude and other factors, in the case of drought monitoring, spatial data mining is adopted, the drought monitoring model is built, and the drought monitoring precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
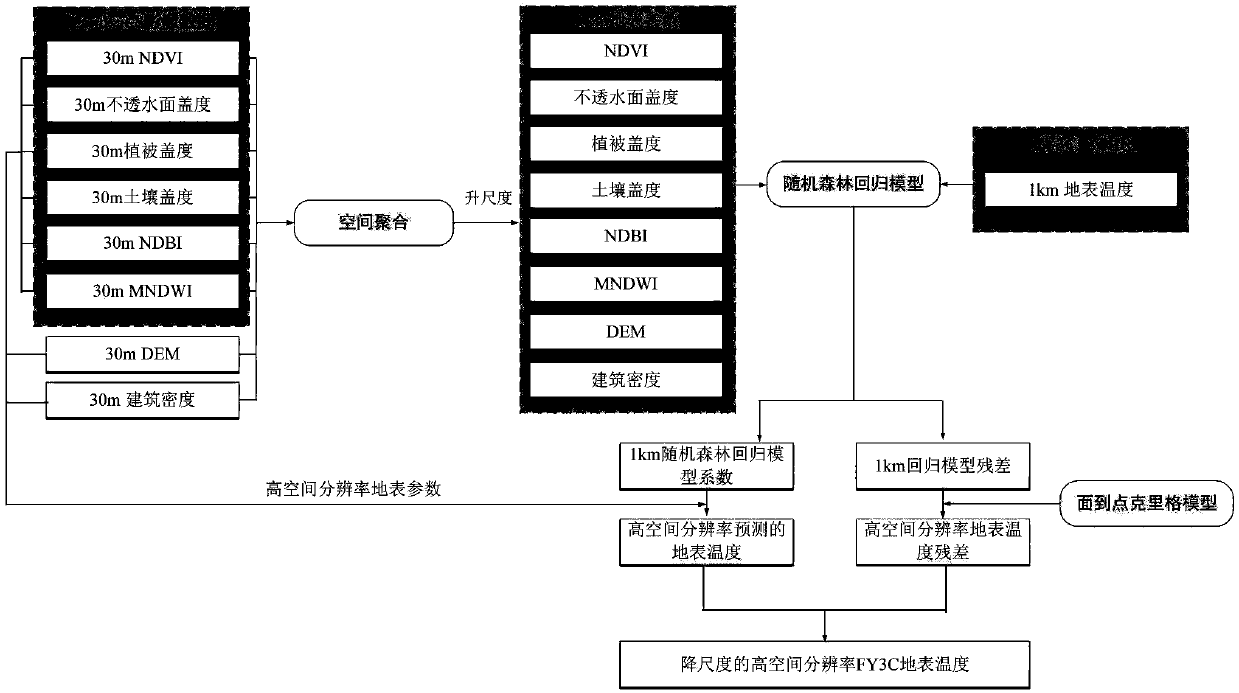
A method for reducing that scale of surface temperature space
InactiveCN109635309AWide coverageMake up for the lack of spatial resolutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBuilding densityImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for reducing that scale of surface temperature space. At first, that method quantitatively analyzes the surface temperature and the surface parameters including the impervious surface coverage, vegetation coverage, soil coverage, NDVI, NDBI, MNDWI, DEM, and the correlation between building density and its spatial distribution difference, Then the regression model of low spatial resolution land surface temperature products and related land surface parameters is established by using machine learning stochastic forest algorithm, land surface temperature with highspatial resolution can be predicted by combining the land surface parameters with high spatial resolution, Then the area-to-point Kriging interpolation method of geostatistics is used to reduce the residuals of the random forest regression model to improve the spatial resolution of the residuals, Finally, the high spatial resolution stochastic forest regression model and the surface-to-point Kriging interpolation residuals are added to generate high resolution and high precision surface temperature products to make up for the lack of spatial resolution of the existing surface temperature products.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOGRAPHY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587AImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
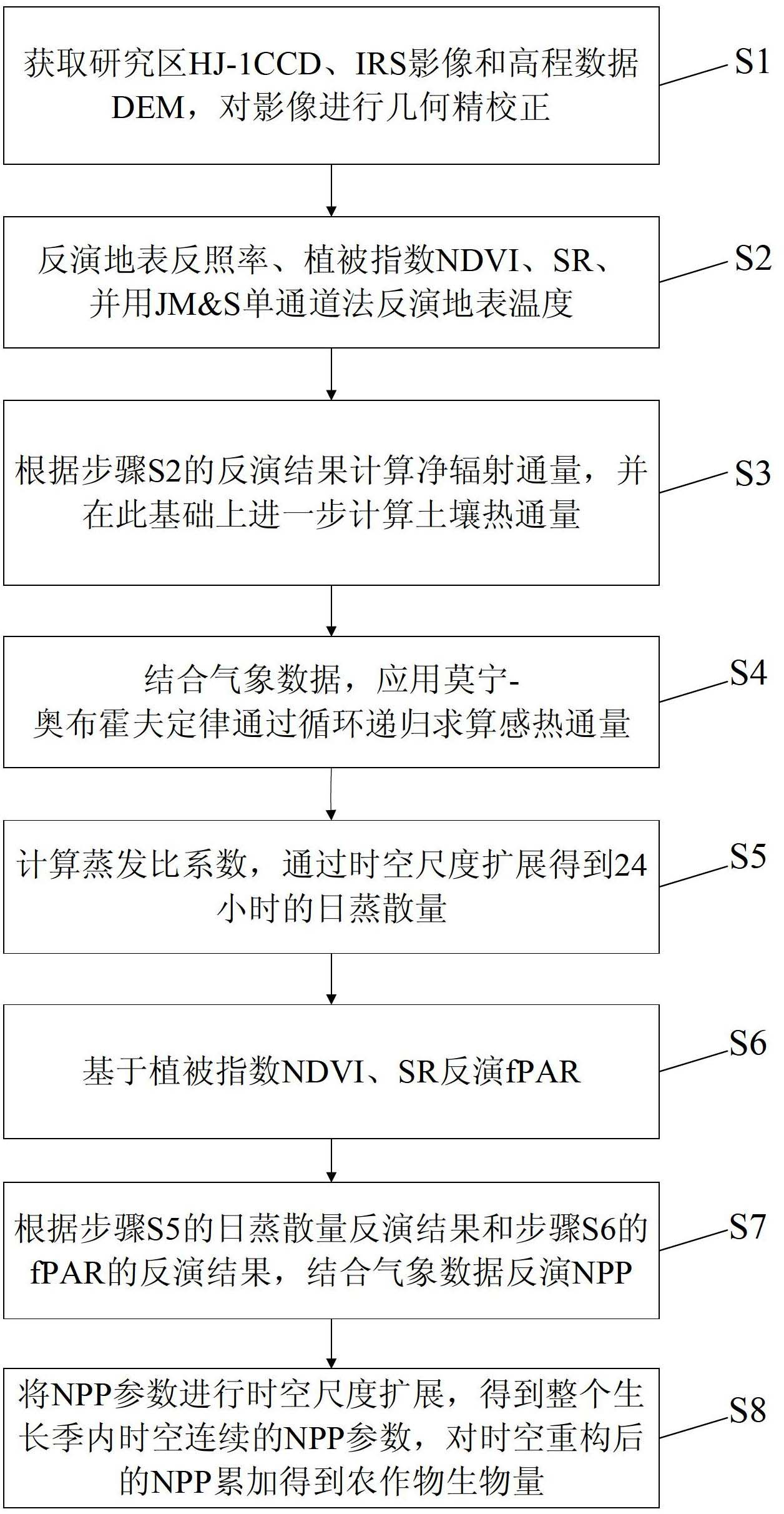
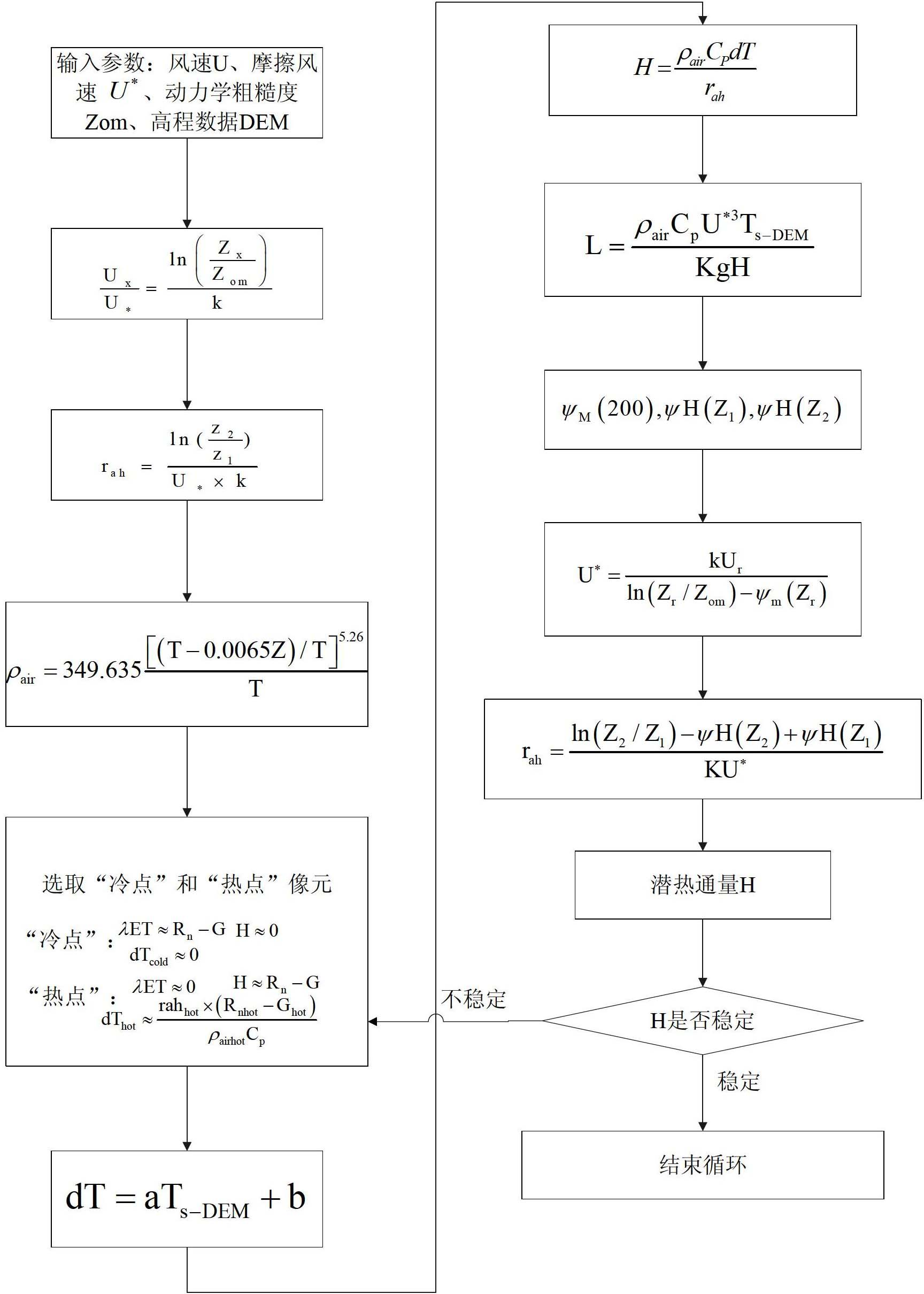
The invention discloses a crop biomass inversion method based on a SEBAL-HJ model. The crop biomass inversion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring HJ-1 CCD, IRS images and elevation data DEM in a research plot, and carrying out geometric fine revision to the images; S2, inversing a land surface albedo, NDVI, SR, land surface emissivity and inversing land surface temperature; S3, calculating net radiation flux according to inversion results in the S2, and further calculating soil heat flux on the basis; S4, calculating sensible heat flux through cyclic reduction; S5, calculating the coefficient of evaporation ratio and obtaining evapotranspiration per day through space-time dimension expansion; S6, inversing fPAR on the basis of vegetative cover indexes NDVI and SR; S7, inversing NPP according to the inversion results of evapotranspiration per day in the step S5 and the inversion results of fPAR in the step S6; and S8, obtaining crop biomass through the accumulation of NPP after space-time reconstruction. According to the invention, the high-precision inversion of crop biomass is achieved, and the amount of calculation is relatively smaller.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Urban impervious layer rate information extraction method based on multi-source remote sensing data
ActiveCN103824077AReduce adverse effectsImprove bindingCharacter and pattern recognitionWater layerArea type
The invention discloses an urban impervious layer information extraction method based on multi-source remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps: calculating normalized light brightness and performing area type segmentation on the urban surface based on a threshold segmentation method according to a night light brightness image; constructing enhanced normalized impervious layer indexes by utilizing the light brightness, the land surface temperature and normalized soil regulation vegetation indexes; and performing extraction operation on the impervious layer by constructing a linear quantitative relation between the enhanced normalized impervious layer indexes MNDISI in each type segmentation area and the impervious layer rate. The advantages of the multi-source remote sensing data are well combined, an adverse effect of spectral confusion on an estimation result of the impervious layer rate is effectively inhibited, and a novel way is provided for urban land utilization and environmental change monitoring.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Quick drought index monitoring method based on land surface temperature and vegetation index feature space
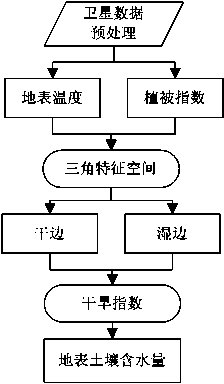
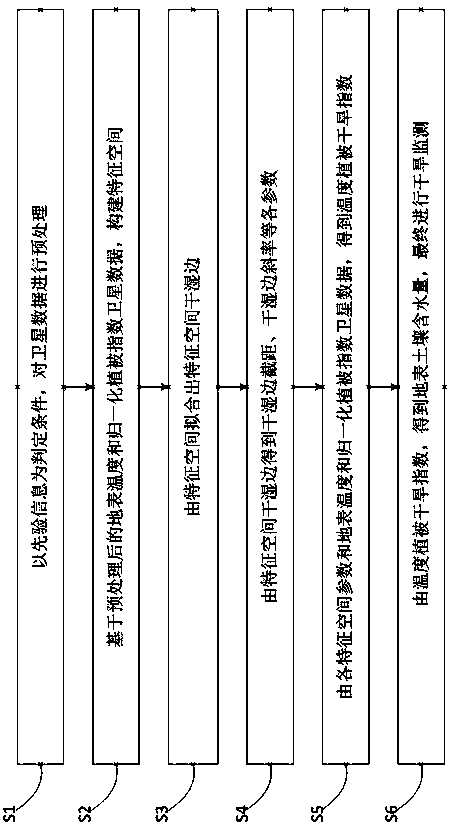
The invention discloses a quick drought index monitoring method based on a land surface temperature and vegetation index feature space. The method specifically comprises the following steps: remotely sensing land surface temperature and vegetation index of a monitored area by utilizing a satellite; taking prior information as a determination condition, and preprocessing the data of the satellite; constructing a feature space based on the preprocessed land surface temperature and normalized vegetation index satellite data; fitting out wet sides and dry sides of the feature space by the feature space; obtaining the intercept of the wet sides and the dry sides, the slopes of the wet sides and the dry sides and the like by the wet sides and the dry sides of the feature space; obtaining a temperature vegetation drought index according to each feature space parameter, the land surface temperature and the normalized vegetation index satellite data; obtaining the water content of land surface soil according to the temperature vegetation drought index, and finally performing drought monitoring. According to the method, the problems that the dry sides and the wet sides in the conventional feature space method are instable, variable difference is magnified excessively, and even an error phenomenon that the numerical values of the obtained parameters exceed the due physical meaning range of the parameters appears are solved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
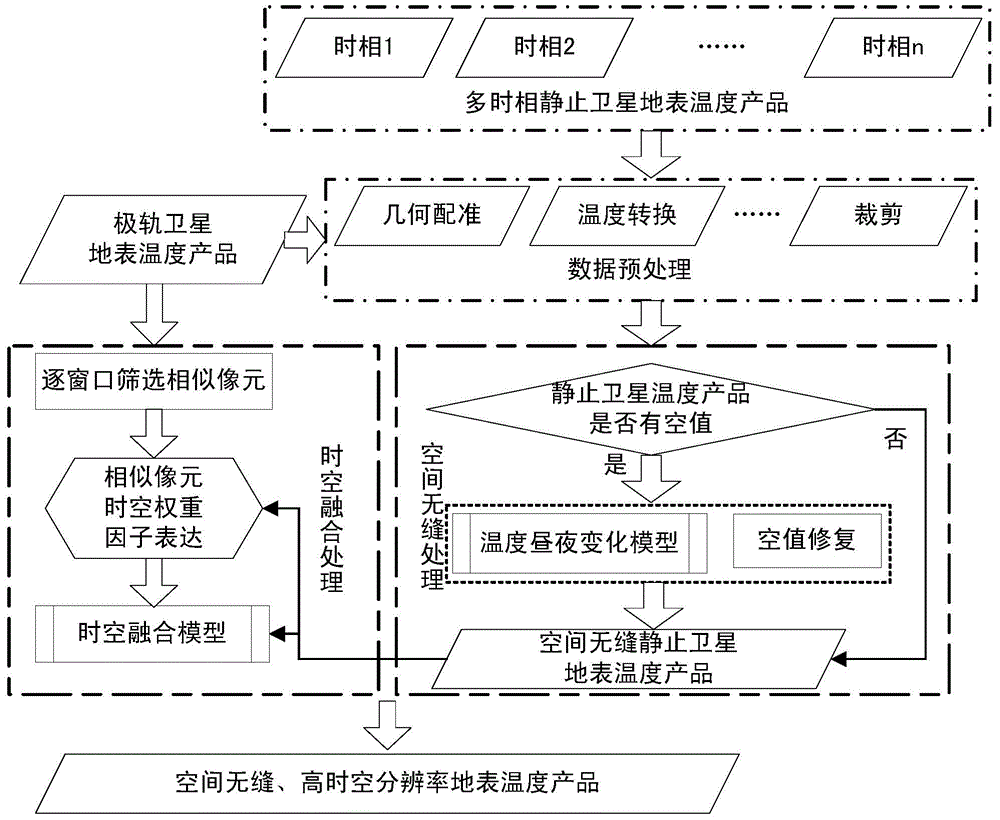
Space-time integrated fusion method of remote sensing land surface temperature data
InactiveCN105184076AHigh utility valuePrecise time resolutionSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataModel parameters
The present invention relates to the quantitative remote sensing data processing technology, and discloses space-time integrated fusion method of remote sensing land surface temperature data. The method comprises first pre-processing the remote sensing land surface temperature data, then solving land surface temperature diurnal change model parameters by using multidate temperature data and corresponding time, thus to realize space seamlessness, screening similar picture elements window by window on polar orbit satellite land surface temperature image data, and in combination with weight factors such as time difference, scale difference, similarity difference and Euclidean distance composed by an multidate motionless satellite and the above model, commonly establishing a space-time integrated fusion model and solving a high temporal-spatial resolution land surface temperature dataset for generating space seamlessness. According to the method provided by the present invention, space-time complementary information of land surface temperature data of the polar orbit satellite and the multidate motionless satellite and diurnal change rules of motionless satellite land surface temperature are fully utilized, and no auxiliary data is required, such that the method is easy to realize, high in practical value and applicable to remote sensing land surface temperature data operational running with seamless space and time.
Owner:广西壮族自治区基础地理信息中心
Multi-rule algorithm-based remote sensing data downscaling method
The invention discloses a multi-rule algorithm-based remote sensing data downscaling method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly aggregately calculating 9 data, such as a vegetation index, a digital elevation model, a daytime land surface temperature, a night land surface temperature, a terrain humidity index, a gradient, a land surface roughness, a land surface reflectance and a valley bottom flat index, of environment variable factors in 1km into 25km to serve as independent variables; carrying out modelling by taking TMPA 3B43 v7 rainfall data corresponding to a 25km resolution as dependent variables; and applying the established model onto 1km environment variable factors of corresponding geographic areas, so as to finally obtain high-precision rainfall prediction data in 1km. According to the multi-rule algorithm-based remote sensing data downscaling method, the rainfall prediction value of the 1km space resolution is finally obtained. The method is relatively high in prediction precision, simple, convenient and feasible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
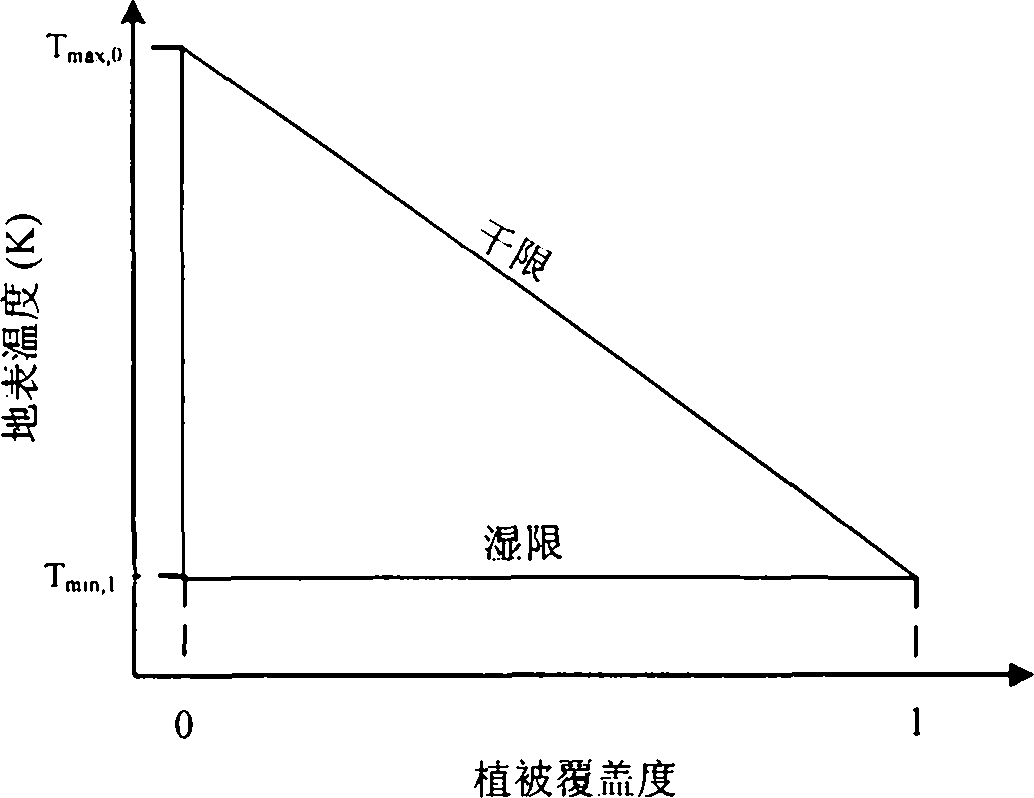
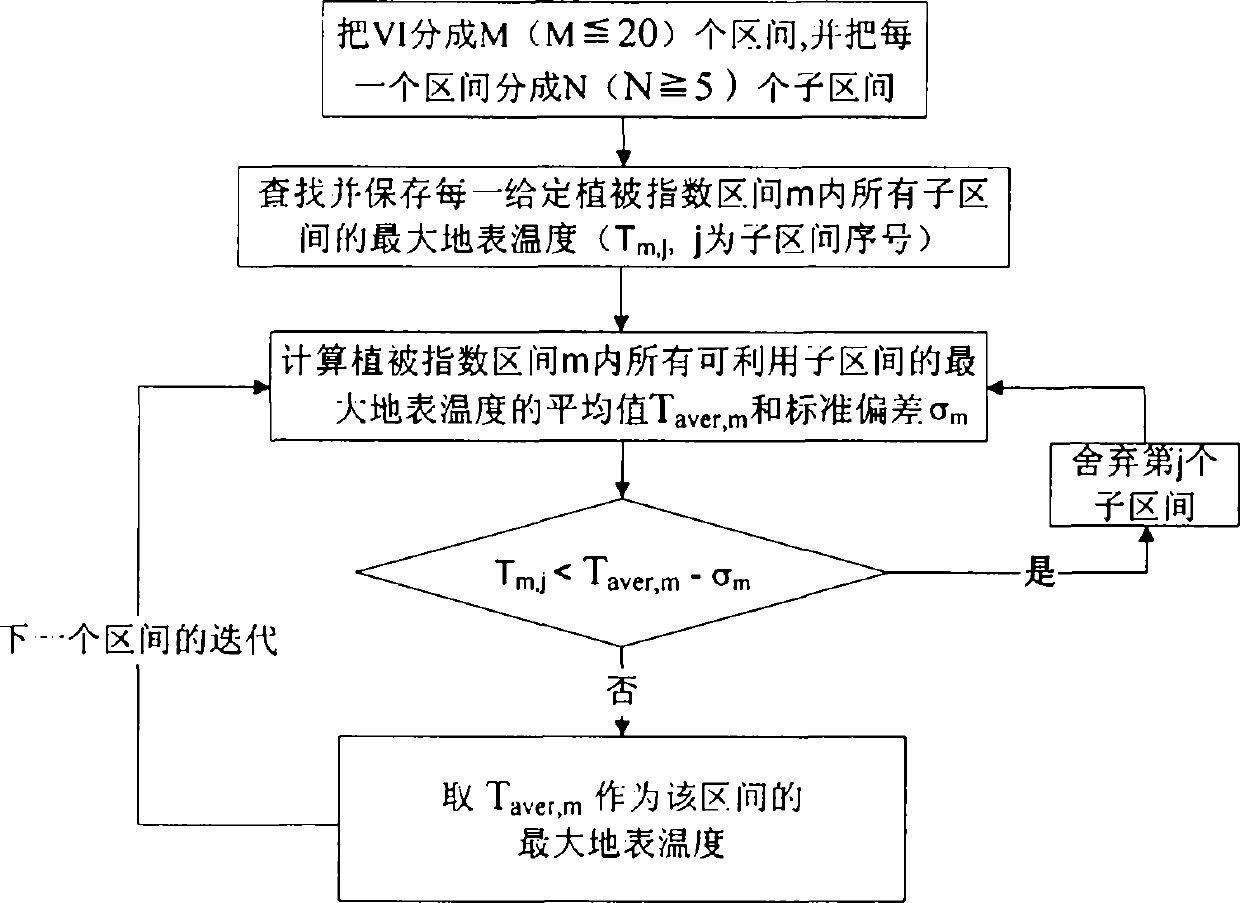
Land surface temperature-vegetation index feature space dry and wet limit selecting method and device
InactiveCN103793596AReduce uncertaintyAddress subjectivityEarth material testingSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainVegetation Index
The invention provides a land surface temperature-vegetation index feature space dry and wet limit selecting method and device. The method includes the steps of firstly, determining the size of a research area, and performing pretreatments such as projection conversion, resampling and cutting on satellite remote sensing image data; secondly, removing image metadata influenced by cloud and terrain; thirdly, using the rest image metadata to build a land surface temperature-vegetation index two-dimensional scatter diagram feature space; fourthly, sampling the highest land surface temperature corresponding to different vegetation index conditions obtained in the third step; fifthly, linear fitting the highest land surface temperature and vegetation indexes to obtain the dry limit of the feature space through threshold setting and an iteration algorithm; presuming that the wet limit temperature is a constant and equals to the dry limit temperature at the total vegetation cover to obtain the wet limit temperature. By the arrangement, the problems that the current land surface temperature-vegetation index feature space dry and wet limit selecting is high in subjective randomness and uncertainty, and the like are solved.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method for extracting mountain river information
InactiveCN108537795AReduce negative impactGood removal effectImage enhancementImage analysisRiver networkData information
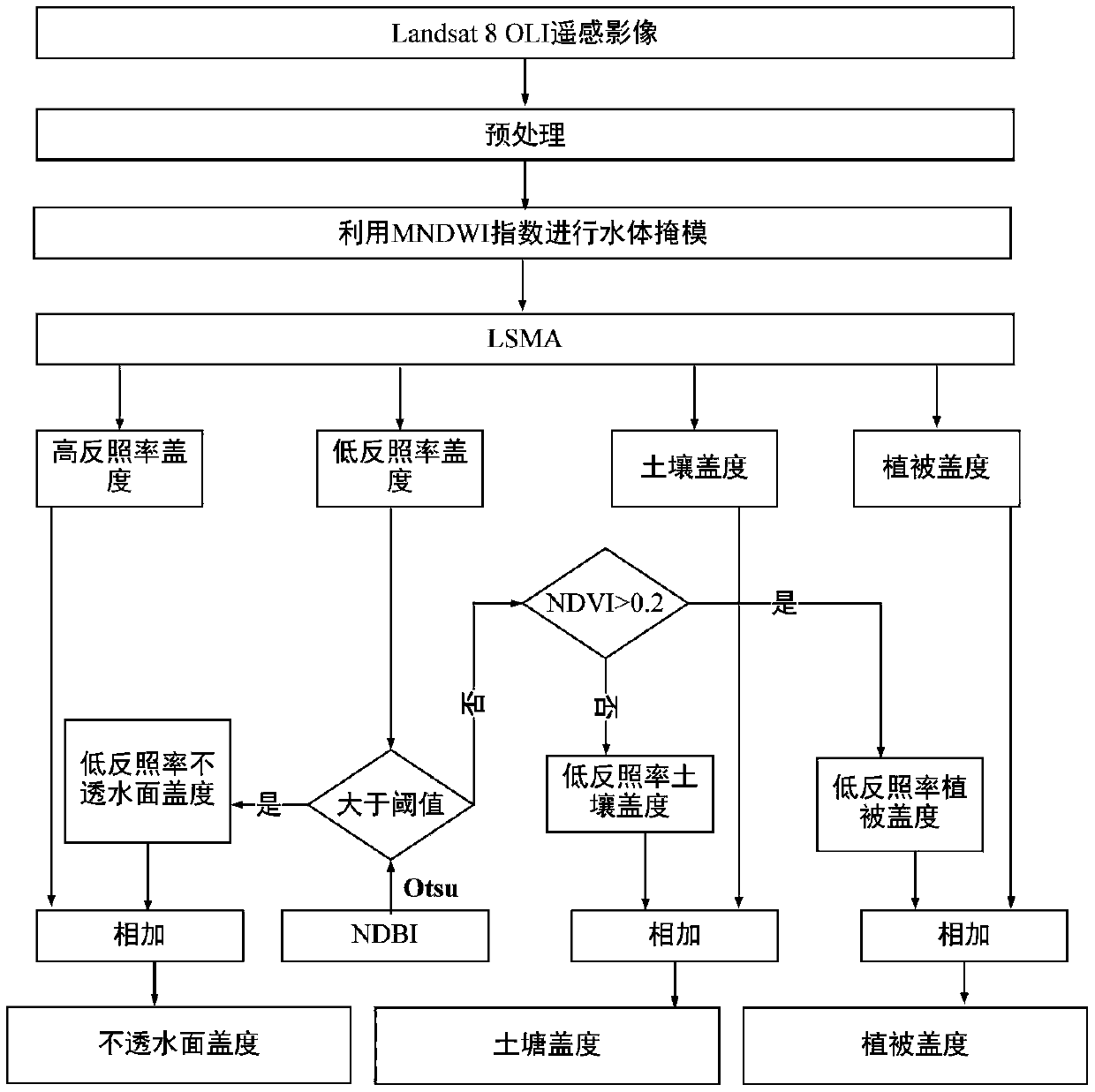
The invention discloses a method for extracting mountain river information. The method comprises the following steps: performing radiation calibration, atmospheric correction, mosaicing and cutting processing on remote sensing image data information of a land satellite Landsat 8 OLI; calculating a composite spectral threshold water index; extracting a mountain shadow of a study area according to DEM data of the study area; extracting a river network of the study area according to the DEM data of the study area, and establishing a river buffer area; calculating the land surface temperature of the study area; calculating surface albedo of the study area; calculating the NDBI (normalized difference build-up index) of the study area; resampling the land surface temperature, surface albedo andNDBI layer of the study area for standard treatment to eliminate incorrectly extracted building information; performing small hole elimination and gap filling on the extracted small rivers in the study area are filled by closed operation and filtering operation in mathematical morphology filtering. The technical problem that accuracy of information extraction for mountain rivers in the prior art needs to be improved is solved.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Drought index construction method based on passive microwave remote sensing
InactiveCN106897551AOvercomes vulnerability to weather conditionsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsInfrared remote sensingVegetation Index
The invention discloses a drought index construction method based on passive microwave remote sensing. The method comprises the specific steps that an inter-diurnal mask and an inter-monthly mask are constructed, and influences of mixed pixels of edges of a glacier, a snow cover and a water body on AMSR-E data during temperature retrieval are eliminated; a land surface temperature retrieval model is constructed through 10.8GHHz and 89.0GHz vertical polarization channel Tb of AMSR-E and used for performing retrieval on land surface temperature, wherein Tb is brightness temperature data of passive microwave remote sensing; a microwave normalized difference vegetation index model is constructed based on a microwave polarization difference index (MPDI); a dry edge equation and a wet edge equation of an MTVDI model are constructed based on the established land surface temperature retrieval model and vegetation index model; and the MTVDI model is established to simulate and monitor drought throughout the country month by month. The method has the advantages that the defect that visible light / near-infrared remote sensing is liable to influences of meteorological conditions is effectively overcome, and a great improvement is made to a TVDI model.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Land surface temperature (LST) inversion method based on HJ-1B IRS satellite data
The invention provides a land surface temperature (LST) inversion technology based on domestic HJ-1B satellite IRS sensor data. The LST inversion method based on the HJ-1B IRS satellite data mainly comprises the following steps that the land surface emissivity (LSE) is inverted through a vegetation index product of a MODIS, the LST is inverted through a mono-window algorithm, LST data in different time phases are converted into a benchmark time phase through a sensing image time-space fusion technology, and inlaying and cutting of area data are carried out. The LST inversion method based on the HJ-1B IRS satellite data adopts the sensing image time-space fusion technology, improves the LST inversion accuracy of the HJ-1B IRS data through a foreign MODIS sensor high-accuracy LST product, and meanwhile achieves the purpose of producing large-area same-time-phase HJ-1B IRS LST products.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
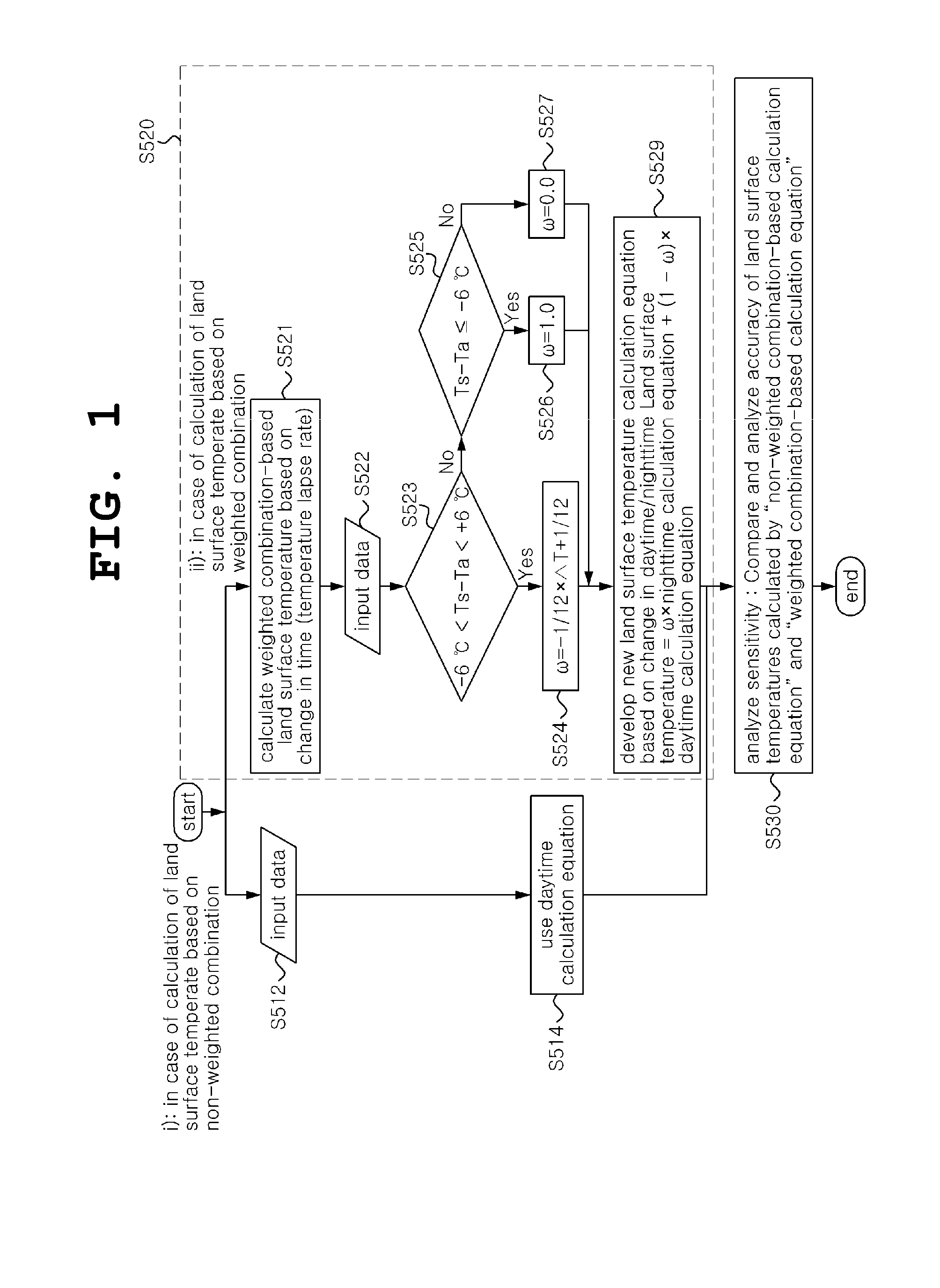
Method for estimating land surface termperature lapse rate using infrared image
ActiveUS20160097679A1Minimize atmospheric effectRadiation pyrometrySpecial data processing applicationsTransmittanceTemperature difference
A method of estimating land surface temperature lapse rate using an infrared image is disclosed. In the method of estimating land surface temperature lapse rate using an infrared image, a target area for the estimation of land surface temperature lapse rate is selected. The atmospheric transmittance of the target area is calculated. Reference temperature is estimated at a reference location set in the target area as desired. A temperature difference is calculated from the atmospheric transmittance and the estimated reference temperature, and then a temperature difference image is generated. Land surface temperature lapse rate is estimated from the temperature difference image and a Digital Elevation Map (DEM) in an identical area using an elevation-based temperature difference distribution.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
An urban entity boundary identification method integrating surface temperature and building index
ActiveCN109598273AAccurately getEasy to operateClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionIndustrial areaData source
The invention discloses a data fusion-based city built-up area entity boundary identification method. According to the method, the urban built-up area entity boundary can be more accurately positionedby combining the surface temperature and the building index of remote sensing inversion, the defect that urban edge industrial areas and urban and rural joint parts are difficult to identify is overcome, and the urban built-up area entity boundary is more scientifically identified. In addition, the data source only needs Landsat data, the operation is simple, the accuracy is high, and the boundary of the city built-up area can be quickly and accurately obtained. A large number of experiment results show that the boundary recognition accuracy rate reaches 94% or above, and the method is suitable for the fields of territory space planning, geographic national condition monitoring, urban spreading treatment analysis and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Karst rocky desertification information extraction method
InactiveCN107341492AAccurate extractionEfficient extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlbedoKarst rocky desertification
The invention provides a karst rocky desertification information extraction method which comprises the following steps: (1) data preparation: a lithological map, a land utilization graph and a rocky desertification spatial distribution map of the corresponding period; (2) screening of a region: screening a region where rocky desertification possibly occurs from a research region; (3) calculation of a factor spatial distribution map: calculating vegetation coverage, surface reflectance and land surface temperature; (4) calculation of a contribution rate of a factor; (5) fitting of a KRDIM (Karst Rocky Desertification Index Modle); and (6) rocky desertification grading. According to the karst rocky desertification information extraction method, a geographical detector model is used for calculating contribute rates of all factors to rocky desertification characterization, so that a quantitative evaluation index model capable of monitoring interpretations is built; and therefore, precise and efficient extraction of karst rocky desertification information can be realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Coal field fire area determining method and device
InactiveCN103605987AImprove monitoring accuracyEasy to determineOptical detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionBurn unitsLand surface temperature
The invention discloses a coal field fire area determining method and device. The coal field fire area determining method includes the steps of obtaining thermal infrared image data of a target area, obtaining land surface temperature information of the target area according to the thermal infrared image data of the target area, determining the position of the burning center of coal fire of the target area according to the land surface temperature information of the target area, and determining the burning area of a current coal field fire area in the target area according to the position of the burning center of the coal fire of the target area. By means of the coal field fire area determining method and device, the effect of improving monitoring accuracy of the coal field fire area is achieved.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +1
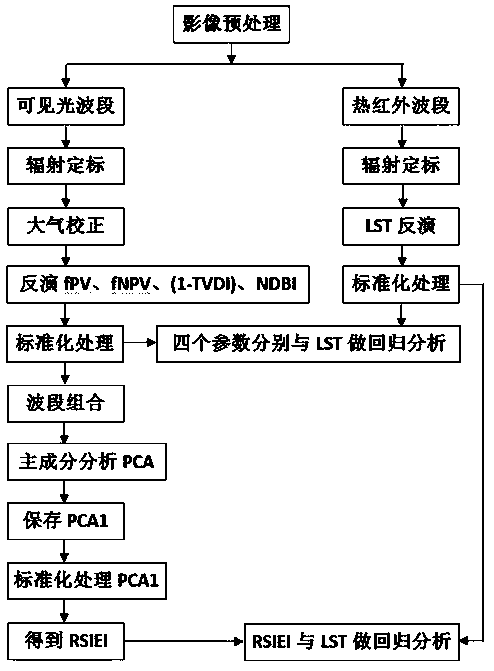
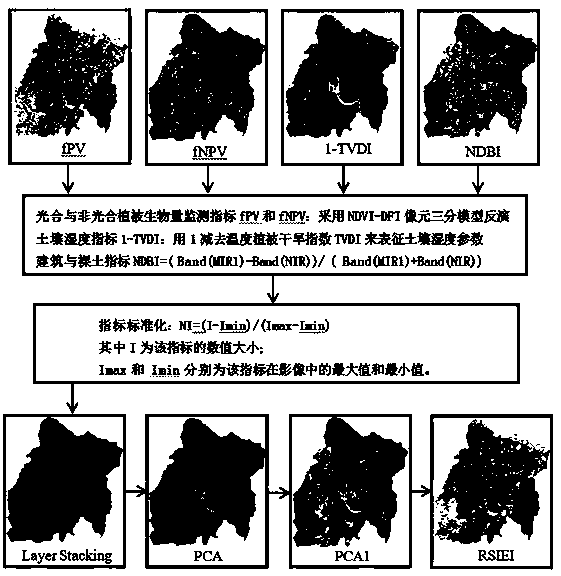
Construction method and application of remote sensing comprehensive ecological model RSIEI for evaluating ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of mining development dense area
ActiveCN110472357AThe method of determining the index weight is objective and reasonableComplex mathematical operationsBuilding densitySoil science
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a remote sensing comprehensive ecological model RSIEI for evaluating a ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of amining development dense area. The construction method comprises the following steps: inverting the surface temperature of a research area by using a radiation conduction equation method; representingthe earth surface vegetation biomass by using the photosynthetic vegetation coverage parameter and the non-photosynthetic vegetation coverage parameter; characterizing the soil moisture content by using the soil humidity index parameters; representing the bare soil and building density by using bare soil and building index parameters; and integrating the four basic ecological parameters based ona principal component analysis method to construct RSIEI. The application comprises the step of quantitatively analyzing the contribution of four ecological parameters to the ground surface thermal environment differentiation effect of the mining industry development dense region by means of a statistical method. The method is suitable for evaluating the thermal environment differentiation effectof mining development dense cities, and evaluating the surface thermal environment differentiation effect of small-scale mining development dense villages and towns with administrative boundaries as boundaries is also feasible.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system
InactiveCN106305371ARealize local irrigationRealize analysisMeasurement devicesTransmission systemsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceCloud base
The invention discloses a cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system. The cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system comprises a farmland production environment monitoring subsystem, a data analysis expert subsystem, a farmland ecological information publishing subsystem and an irrigation control subsystem, wherein the data analysis expert subsystem and the farmland ecological information publishing subsystem are arranged on a public cloud; the irrigation control subsystem and the farmland production environment monitoring subsystem are arranged on a private cloud. By adopting the system, the land surface temperature, soil moisture, video information and PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) index of a multi-user agricultural production place can be monitored comprehensively; farmland information is transmitted through Zigbee and GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), so that data analysis and processing can be performed, analysis and publishing of agricultural condition information are realized, an irrigation instruction can be issued according to a crop demand, and local irrigation of a farmland is realized through an automatic irrigation subsystem according to the irrigation instruction.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Estimation method and device of land surface temperature under cloudy condition
The invention provides an estimation method and device of land surface temperature under a cloudy condition. The method includes the following steps that: an optical land surface temperature data sample and a microwave brightness temperature data sample worldwide under a clear sky condition under are obtained; a mathematical regression relationship between the optical land surface temperature data sample and the microwave brightness temperature data sample is established; a microwave image and an optical image in a target area under a cloudy condition are obtained; microwave brightness temperature data corresponding to the microwave image are introduced into the mathematical regression relationship for calculation, so that microwave land surface temperature corresponding to microwave pixels can be obtained; and as for each microwave pixel, calculation is carried out by adopting different calculation methods according to the cloud layer coverage degree of the corresponding microwave pixel, so that a spatially-continuous optical land surface temperature product can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Land surface temperature inversion method based on spatio-temporal information of paired HJ-1B images
InactiveCN104236716APrecise inversionFacilitate Quantitative ApplicationsRadiation pyrometryTemporal informationAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a land surface temperature inversion method based on spatio-temporal information of paired HJ-1B images. The method is a new strategy for solving the problem that in application of an existing mono-window algorithm or a single-channel algorithm, parameters are difficult to obtain. The method comprises the implementation steps that, S1, the HJ-1B images of two paired time phases in a research area are obtained and preprocessed; S2, the preprocessed images are processed symmetrically in a boundary extension; S3, similar pixels are recognized, the number of the pixels is obtained, and the corresponding inversion method is determined; S4, according to the judgment result of S3, a radiation transfer equation set is built, and the land surface radiation value is worked out; S5, S3 and S4 are circularly carried out, the land surface radiation values of the whole research area in the two time phases are obtained, and abnormal value recognition and processing are carried out; S6, the land surface temperature is obtained through inversion according to the processed land surface radiation values. According to the land surface temperature inversion method based on spatio-temporal information of the paired HJ-1B images, the land surface temperature can be accurately obtained through inversion under the situation that relative parameters cannot be accurately obtained, and quantitative application of HJ-1B thermal infrared data can be effectively promoted.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-spatial-and-temporal-resolution land surface temperature fusion method based on multi-source satellite data
ActiveCN107610050AHigh precisionImage enhancementRadiation pyrometrySpacetimeLand surface temperature
The invention discloses a high-spatial-and-temporal-resolution land surface temperature fusion method based on multi-source satellite data, which is characterized by including the following steps: A,inputting multiple pieces of satellite image data, and preprocessing the satellite image data; B, selecting the preprocessed satellite image data for land surface temperature (LST) inversion; and C, carrying out fusion calculation on the result of LST inversion to get LST data with high spatial and temporal resolution. According to the invention, fusion calculation can be carried out on the imagedata of multiple satellite sensors to get more accurate land surface temperature with high spatial and temporal resolution.
Owner:北京航天绘景科技有限公司
Method for obtaining net carbon budget of regional scale forest ecological system
InactiveCN102592049AAchieving scalingOvercome the inability to reflect the carbon budget of large-scale forest ecosystemsSpecial data processing applicationsVegetation IndexModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer
The invention discloses a method for obtaining net carbon budget of a regional scale forest ecological system, belonging to the technical field of the combination of related vorticity technology and remote sensing image processing. The invention provides the method for obtaining the net carbon budget of the regional scale forest ecological system, which aims at solving the problems that the related vorticity technology only represents the carbon budget condition of an ecological system at the periphery of an observing tower, but can not reflect the carbon budget condition of the forest ecological system in a large scale. The method comprises the steps of selecting different forest flux observing stations; obtaining and preprocessing the data of MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer); obtaining and processing data NEE of the flux observing stations; according to the types of the forest ecological systems, utilizing SPSS (Statistical Product and Service Solution) software to respectively record net carbon exchanging NEE data of representative stations and corresponding parameter relevance of EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index), LSWI (Land Surface Water Index), LST (Land Surface Temperature) and LST'; generating a quantitative inverse model of the net carbon exchanging NEE of all types of forests; and testing and verifying the simulated results of the model so as to check the effectiveness. The method is used for obtaining the carbon budget condition of the forest ecological system in the large scale.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Method for evaluating daytime average evapotranspiration according to multi-temporal remote sensing data and meteorological data
ActiveCN105913149AReal-time key parametersReliable and accurate key parametersForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsSatellite dataEarth observation
The invention discloses a method for evaluating daytime average evapotranspiration according to multi-temporal remote sensing data and meteorological data. The method comprises the following steps of calculating a remote sensing ellipse parameter through a land surface temperature (LST) and a net surface shortwave radiation (NSSR), calculating evapotranspiration model coefficients n0-n5 by means of ALEX model analog data; and estimating a daytime average evapotranspiration ETd by means of the remote sensing ellipse parameter and the evapotranspiration model coefficients n0-n5. According to the method of the invention, a multi-temporal earth observation advantage of a stationary meteorological satellite is sufficiently utilized. Through multi-temporal satellite data and meteorological data, the daytime average evapotranspiration is directly obtained. The method settles a problem that the daytime average evapotranspiration can be obtained through inversing instantaneous evapotranspiration and performing time scale expansion in prior art, and furthermore realizes direct estimation for the daytime average evapotranspiration based on FY-2 stationary meteorological satellite data.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Mountain land surface temperature remote sensing inversion method
ActiveCN112487346AReduce mistakesMake up for the errorRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesTerrainEarth surface
The invention discloses a mountain land surface temperature remote sensing inversion method, which comprises the following steps of 1, downloading an on-board radiance product of a TIRS sensor carriedon a Landsat 8 satellite and a surface reflectance product of an OLI sensor, and carrying out data preprocessing; 2, calculating the surface emissivity; 3, calculating topographic parameters; 4, calculating atmospheric parameters; wherein the atmospheric parameters comprise atmospheric transmissivity, atmospheric uplink radiation and atmospheric downlink radiation; 5, carrying out mountain land surface temperature inversion. Aiming at complex terrains of mountain lands, terrain parameters such as gradient, slope direction and sky visual factors are introduced into a thermal radiation transmission equation, and a mountainous region surface temperature inversion method is established, so that errors caused by inversion of the mountainous region surface temperature by utilizing a conventional thermal radiation transmission equation are effectively reduced, and the mountain land surface temperature inversion precision is improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
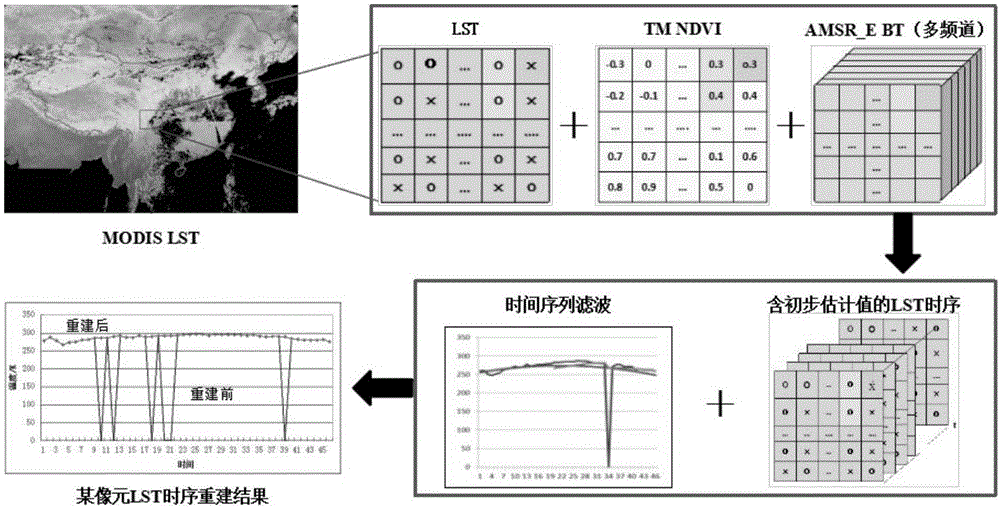
Under-the-cloud pixel LST estimation method based on microwave remote sensing and space-time information
InactiveCN106169058AReduced usabilityAvoid mockingImage enhancementImage analysisEstimation methodsSurface type
The invention discloses an under-the-cloud pixel LST estimation method based on microwave remote sensing and space-time information. The under-the-cloud pixel LST estimation method is characterized in that by considering land surface temperature space distribution consistency and periodicity of a time sequence, a statistical model and time sequence filtering are effectively combined together. A multi-channel statistical model based on passive microwave remote sensing is used for initial estimation of an under-the-cloud pixel LST value, and during an initial estimation process, an NDVI is used as classification basis for land surface coverage classification, and in addition, a conventional land surface type remote sensing product is abandoned to improve classification precision. An estimation value based on the statistical model is used as a background value to be filled in an LST time sequence, and by considering the influences of the former period and the latter period on a period without LST, a moving weighted filter is used to modify the estimation value to acquire an under-the-cloud pixel LST reconstruction result.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
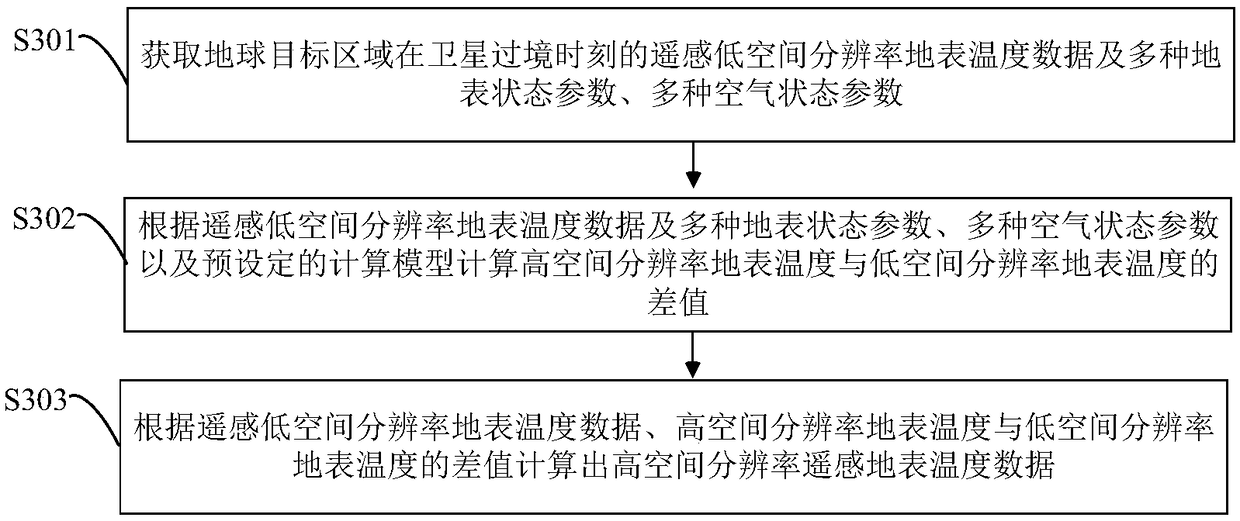
Method and device for calculating high spatial resolution remote sensing surface temperature data
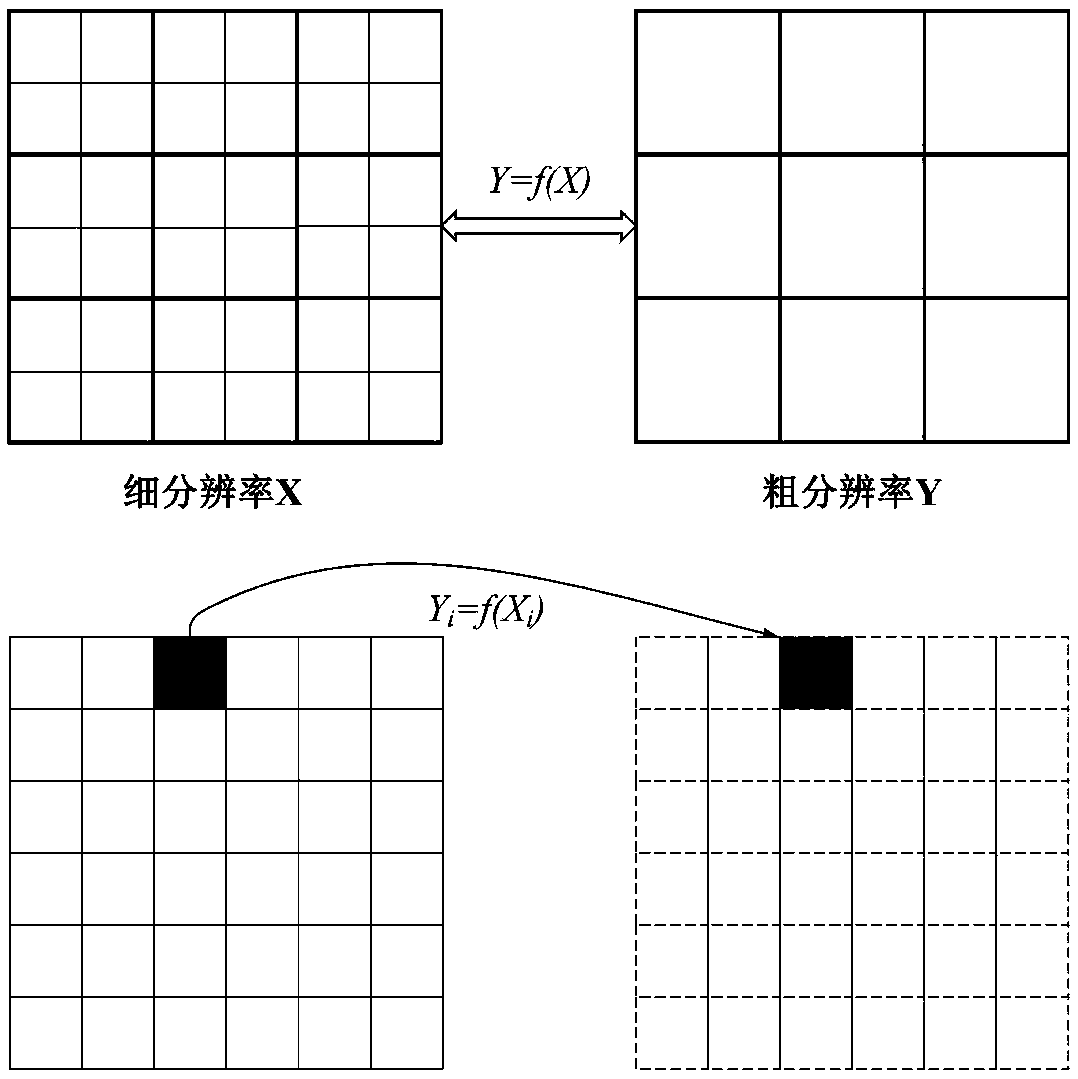
ActiveCN109271605AHigh precisionAchieving spatial downscalingThermometers using physical/chemical changesComplex mathematical operationsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
The invention provides a method and device for calculating high spatial resolution remote sensing surface temperature data, which relates to the field of remote sensing estimation of surface temperature. Firstly, the low spatial resolution land surface temperature data, many kinds of land surface state parameters and many kinds of air state parameters of the earth target area at the time of satellite transit are obtained. Then calculating the difference between the high spatial resolution surface temperature and the low spatial resolution surface temperature according to the remote sensing lowspatial resolution surface temperature data and the plurality of surface state parameters, the plurality of air state parameters and the preset calculation model; At last, based on that remote sensing low spatial resolution land surface temperature data, The difference between high spatial resolution land surface temperature and low spatial resolution land surface temperature is used to calculatethe high spatial resolution land surface temperature, and the precision of the high spatial resolution land surface temperature is high, so the spatial downscaling of the low spatial resolution surface temperature data is realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
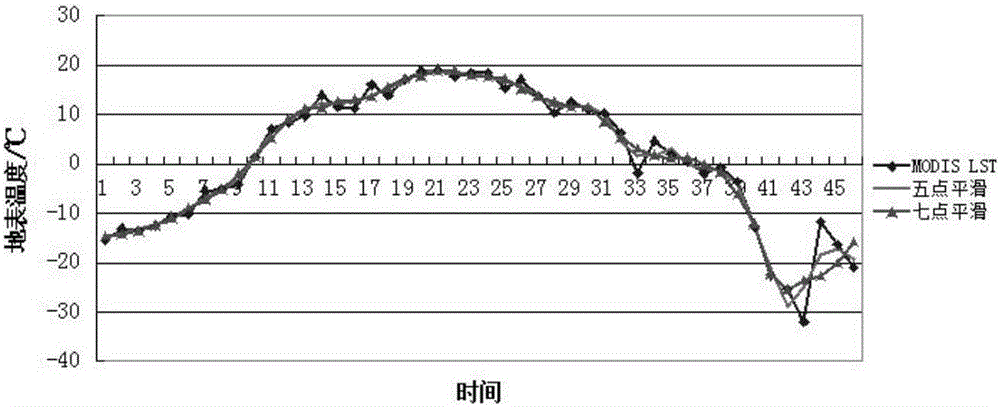
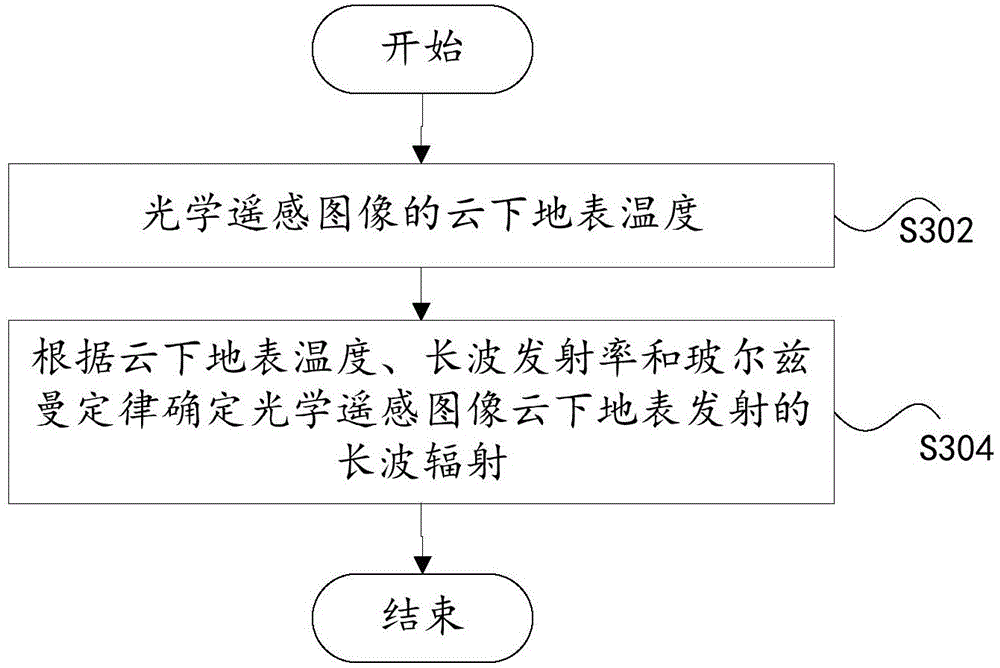
Estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud and emission long wave radiation
The present invention discloses estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud and emission long wave radiation. The estimation methods of optical remote sensing image land surface temperature under cloud comprises a step of determining the specific scope of all cloud layer cast shadows on an optical remote sensing image to be processed and obtaining the land surface temperature of a pure shadow area through image retrieval, a step of selecting a clear sky image with the interval of a preset time with the image to be processed as an intermediary image for a cloud layer coverage non-shadow area, determining one reference area on the optical remote sensing image to be processed, and obtaining the land surface temperature of the cloud layer coverage non-shadow area according to the temperature of the reference area, a step of determining a search area in the optical remote sensing image to be processed for the cloud layer coverage non-shadow area, and a step of obtaining the land surface temperature of a cloud layer coverage shadow area according to the land surface of the pure shadow area in the search area so as to realize the estimation of the land surface temperature in the condition of a cloud layer. Through the estimation methods, the estimation of the land surface temperature in the condition of the cloud layer can be realized.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
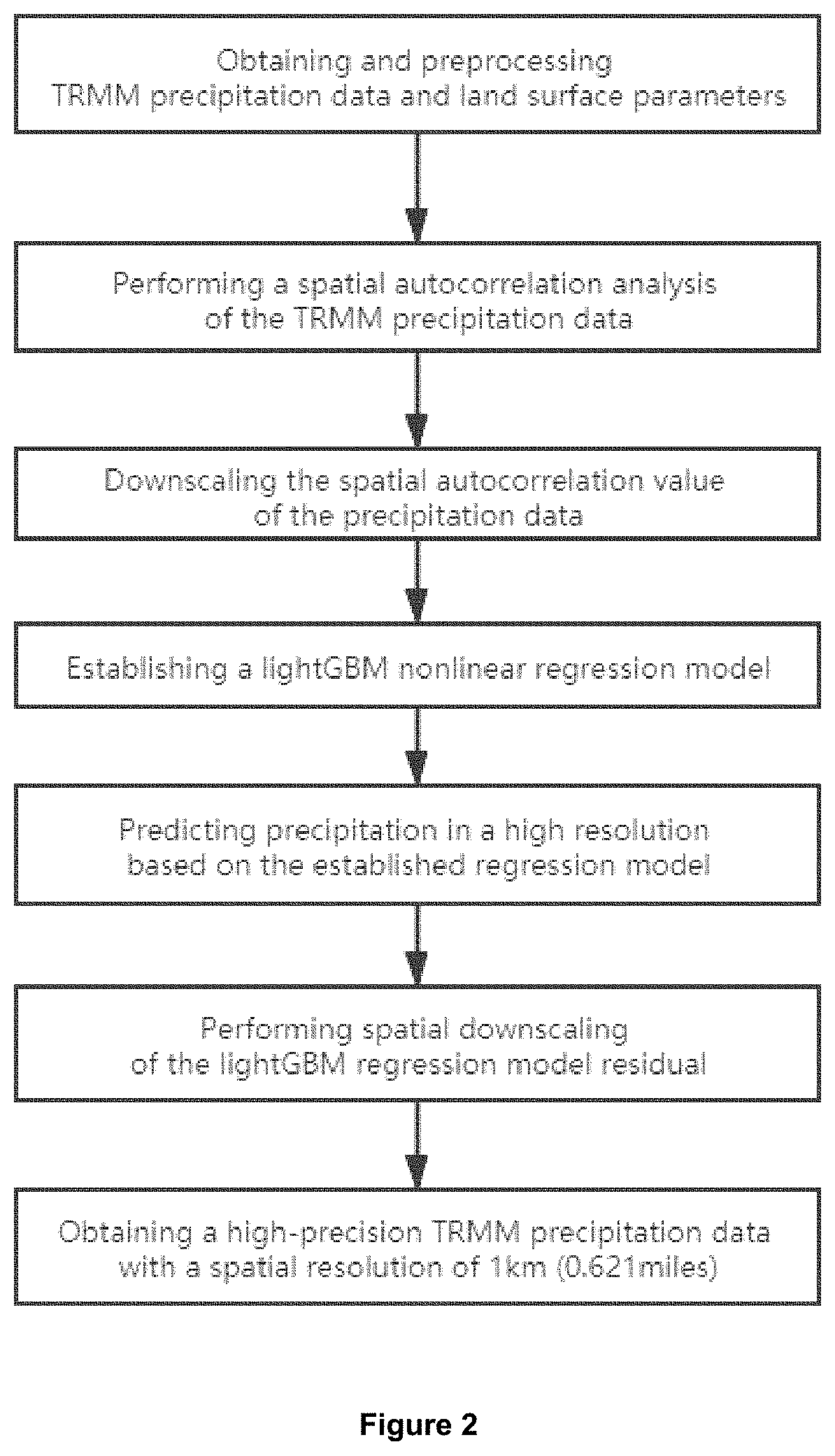
Spatial autocorrelation machine learning-based downscaling method and system of satellite precipitation data
ActiveUS20220043182A1Improve spatial resolutionAccurate areaRainfall/precipitation gaugesWeather condition predictionSatellite precipitationImage resolution
A spatial autocorrelation machine learning-based downscaling method of satellite precipitation data includes obtaining the TRMM precipitation data and the land surface parameters; preprocessing the land surface parameters to obtain DEM, day land surface temperature, night surface land temperature, day-and-night land surface temperature difference and NDVI with spatial resolutions of 1 km (0.621 miles) and 25 km (15.534 miles); performing a spatial autocorrelation analysis of the TRMM precipitation data to obtain an estimated spatial autocorrelation value of the precipitation data with a spatial resolution of 25 km (15.534 miles); downscaling the spatial resolution of the spatial autocorrelation value of the precipitation data from 25 km (15.534 miles) to 1 km (0.621 miles); establishing a nonlinear regression model; obtaining a precipitation downscaling data with a spatial resolution of 1 km (0.621 miles) based on the nonlinear regression model. A system and a terminal are also provided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOGRAPHY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com