Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
217 results about "Soil wetness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
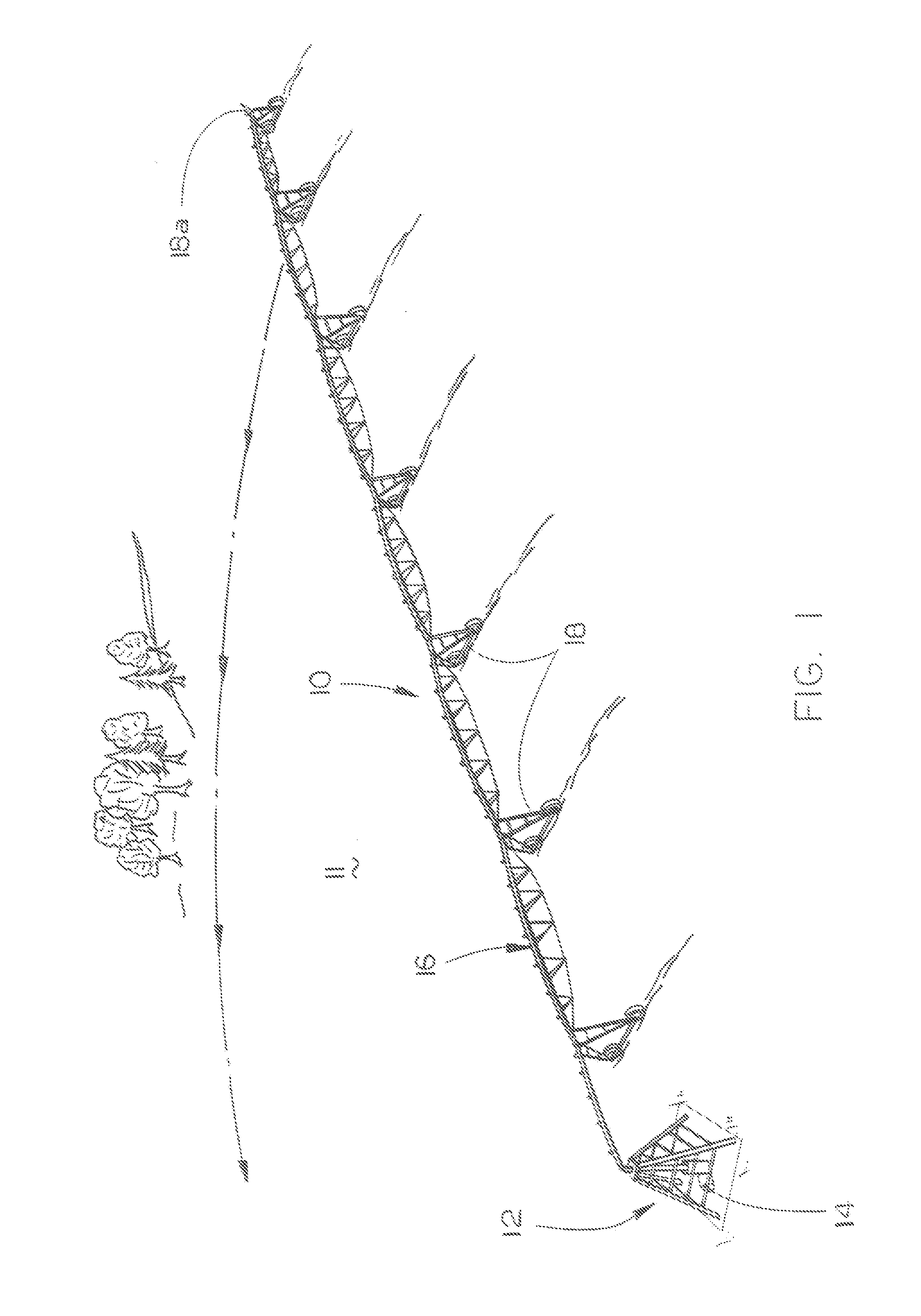
Relati~ Wetness of Soil (Water Potential) Water is held in soil as films by attraction between water molecules and soil particles. The wetness of soil depends on the thickness of the water films, which depend in turn on the amount of water and the number of soil particles on which it is spread.
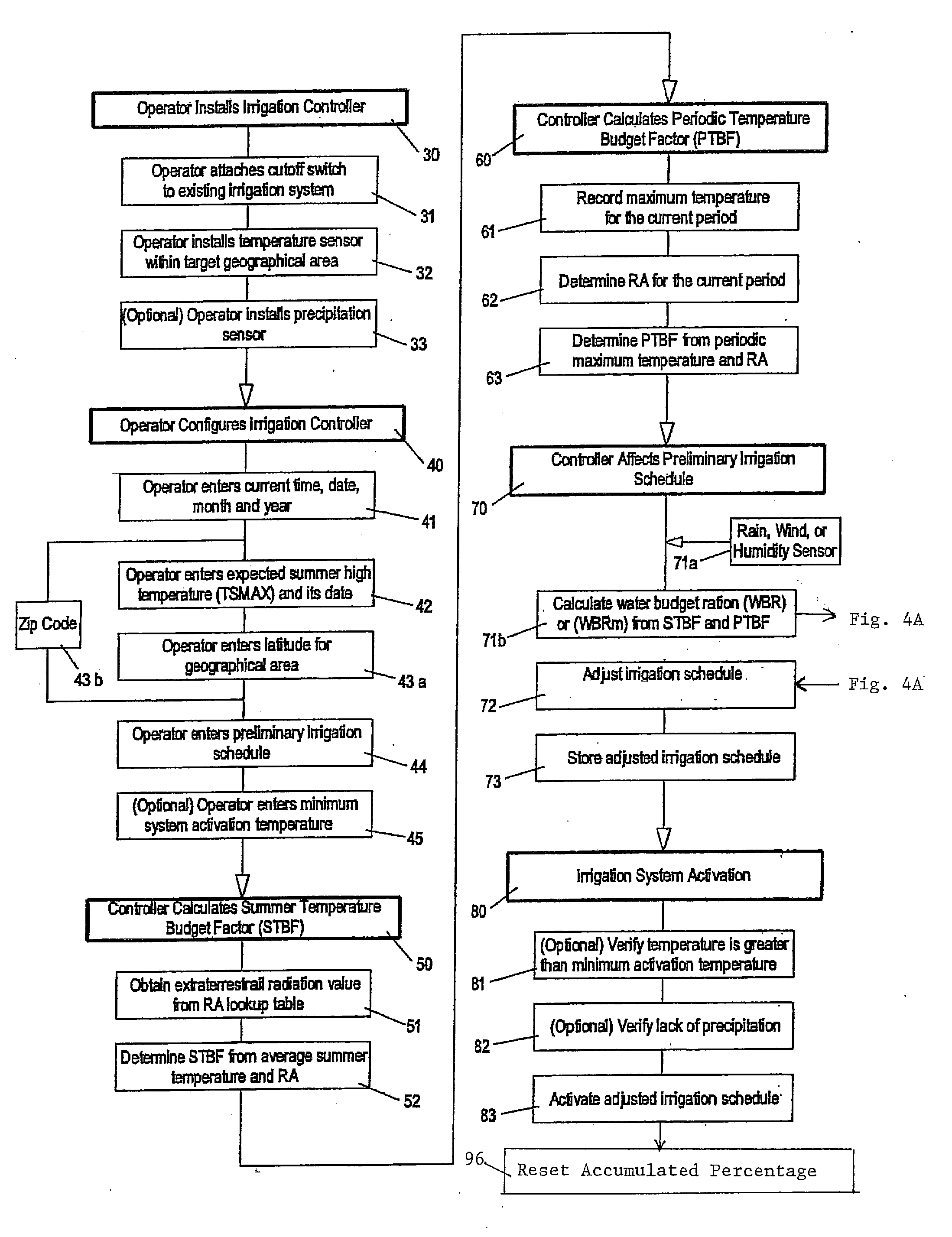
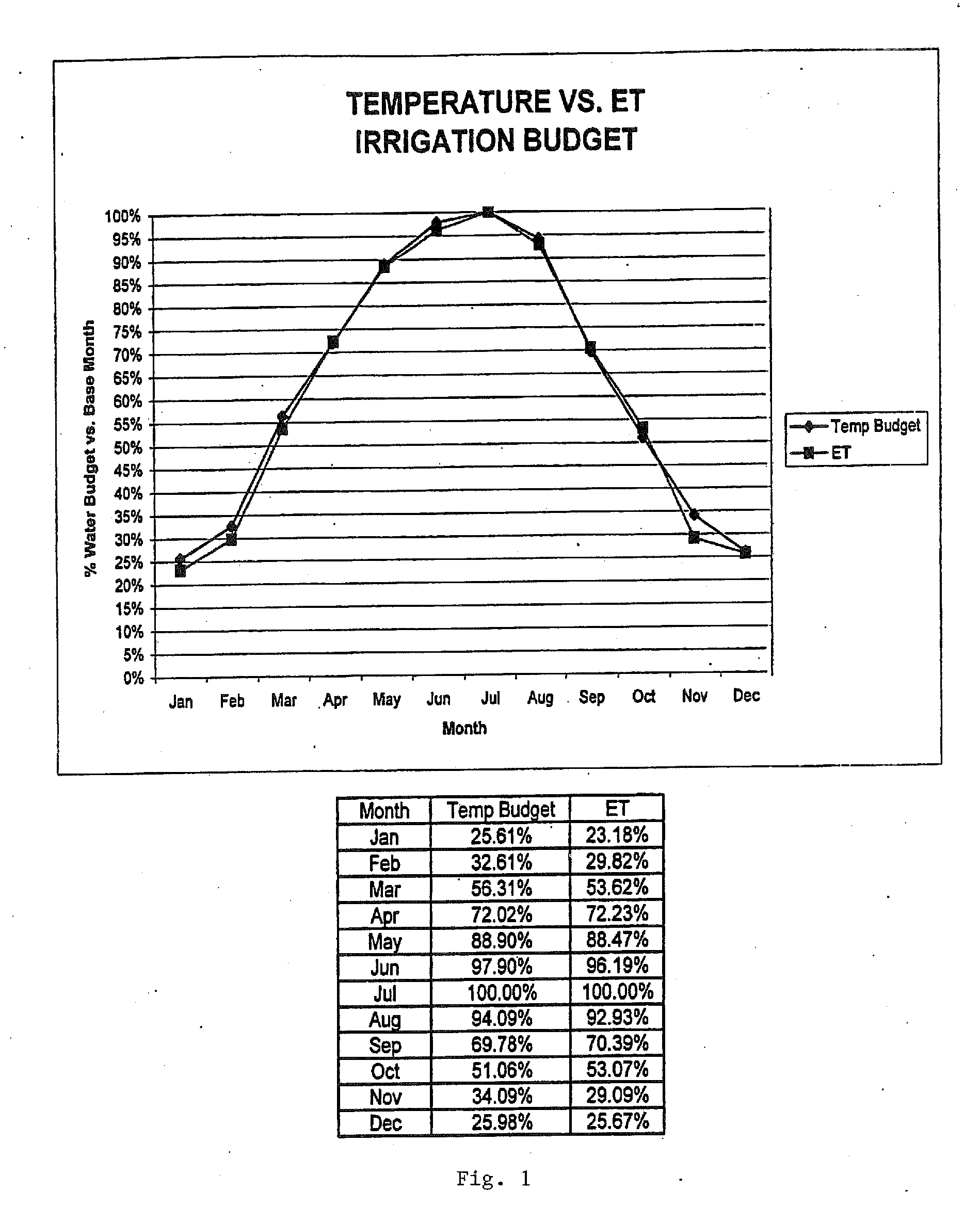
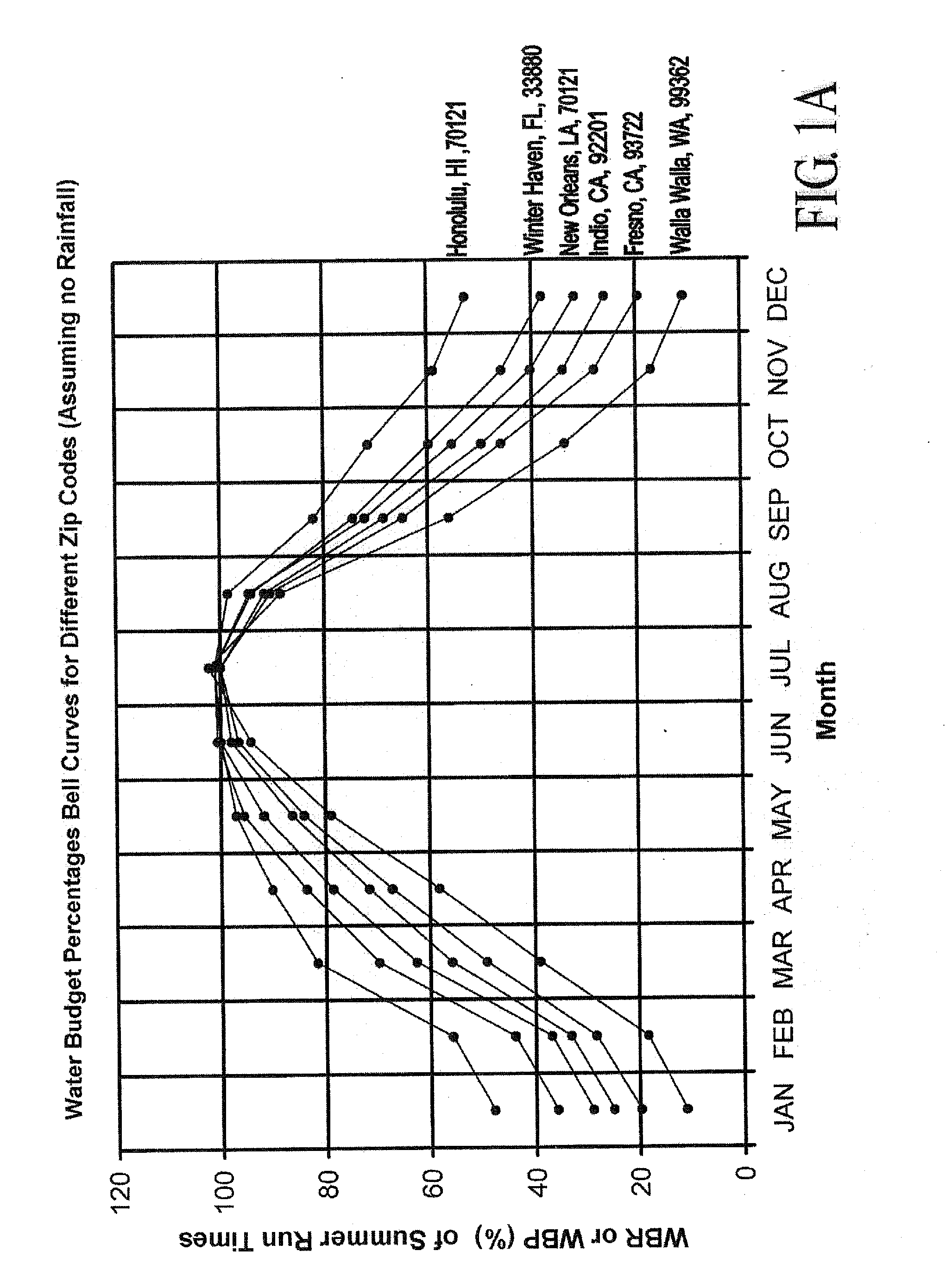
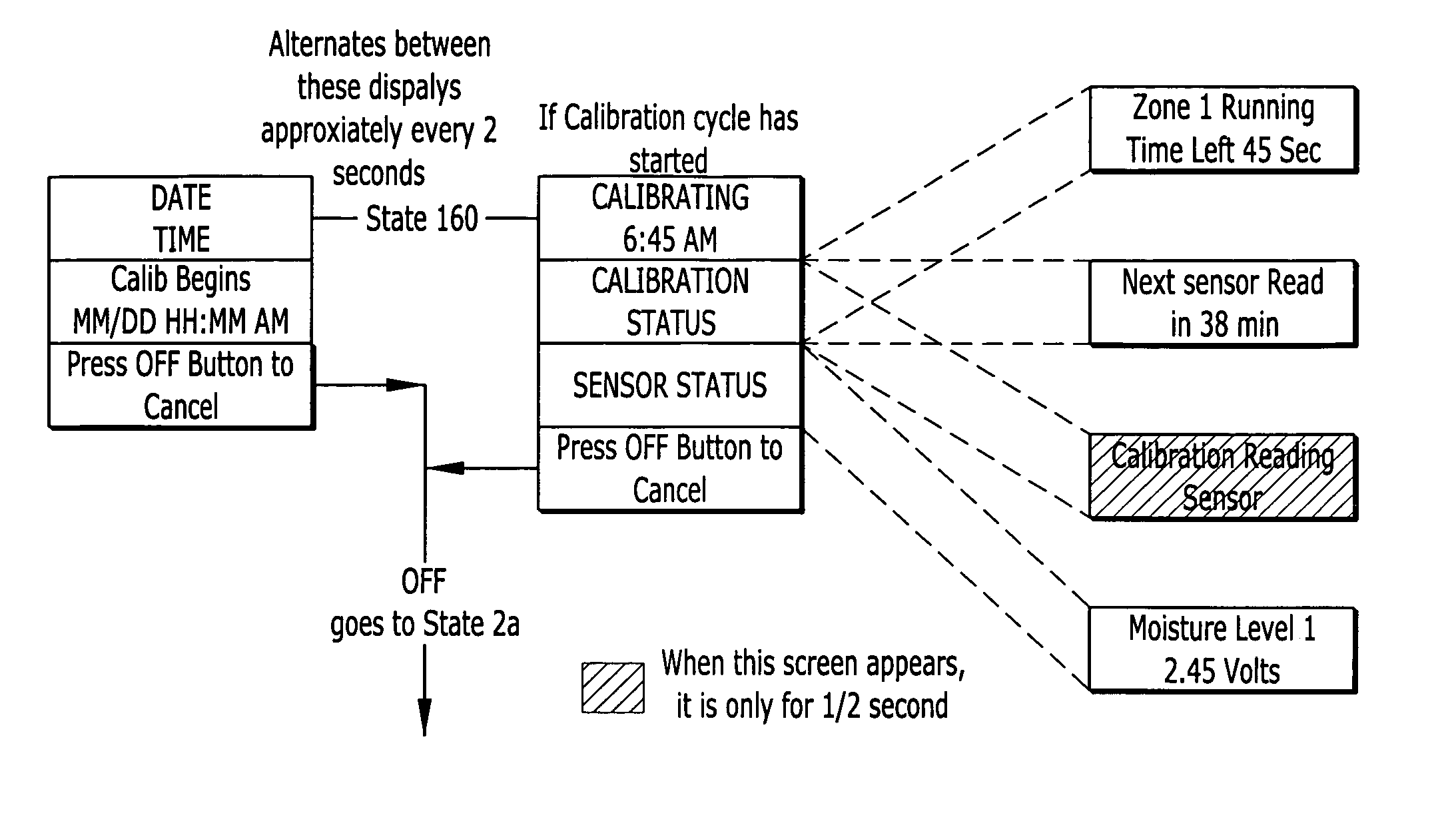
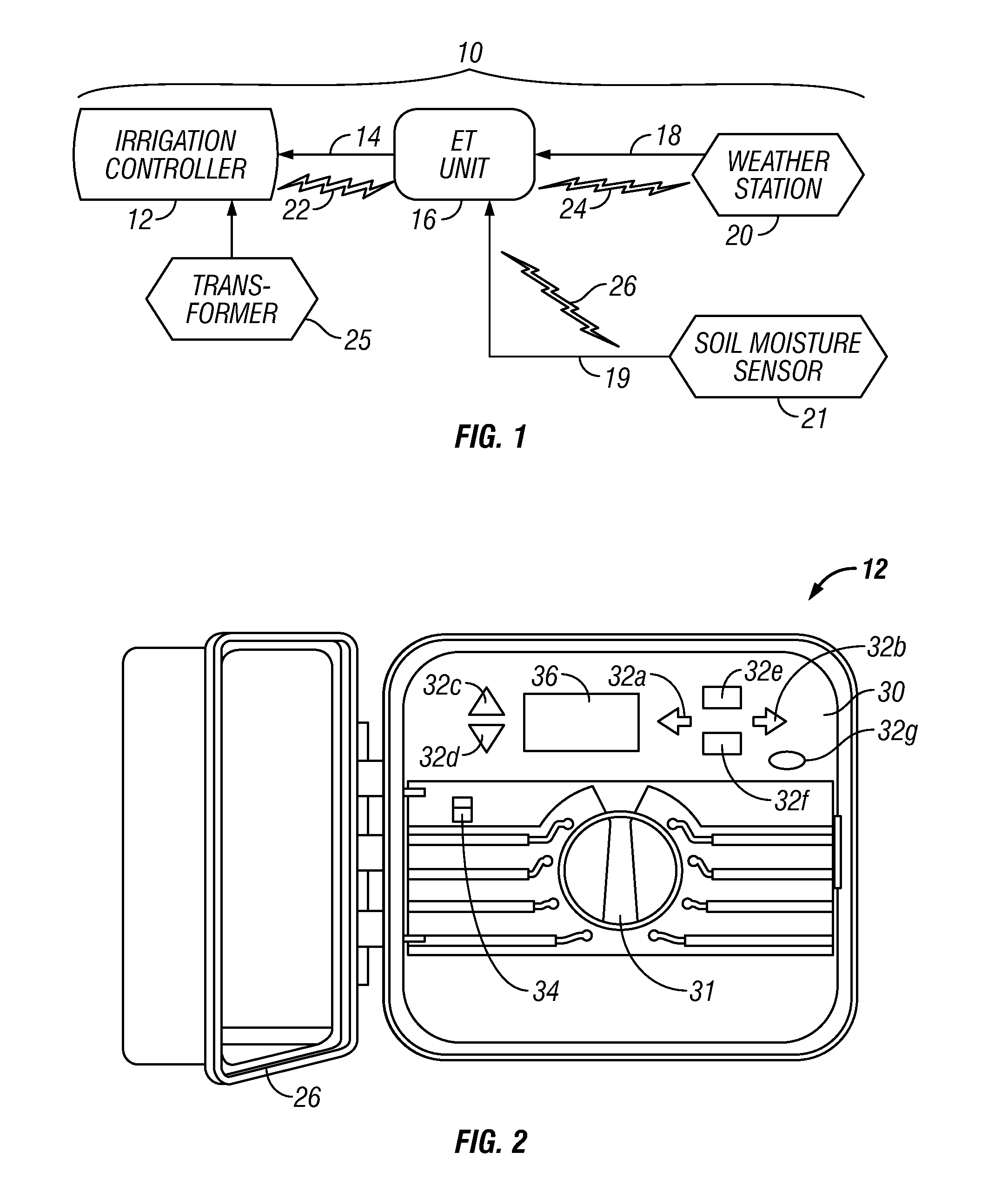
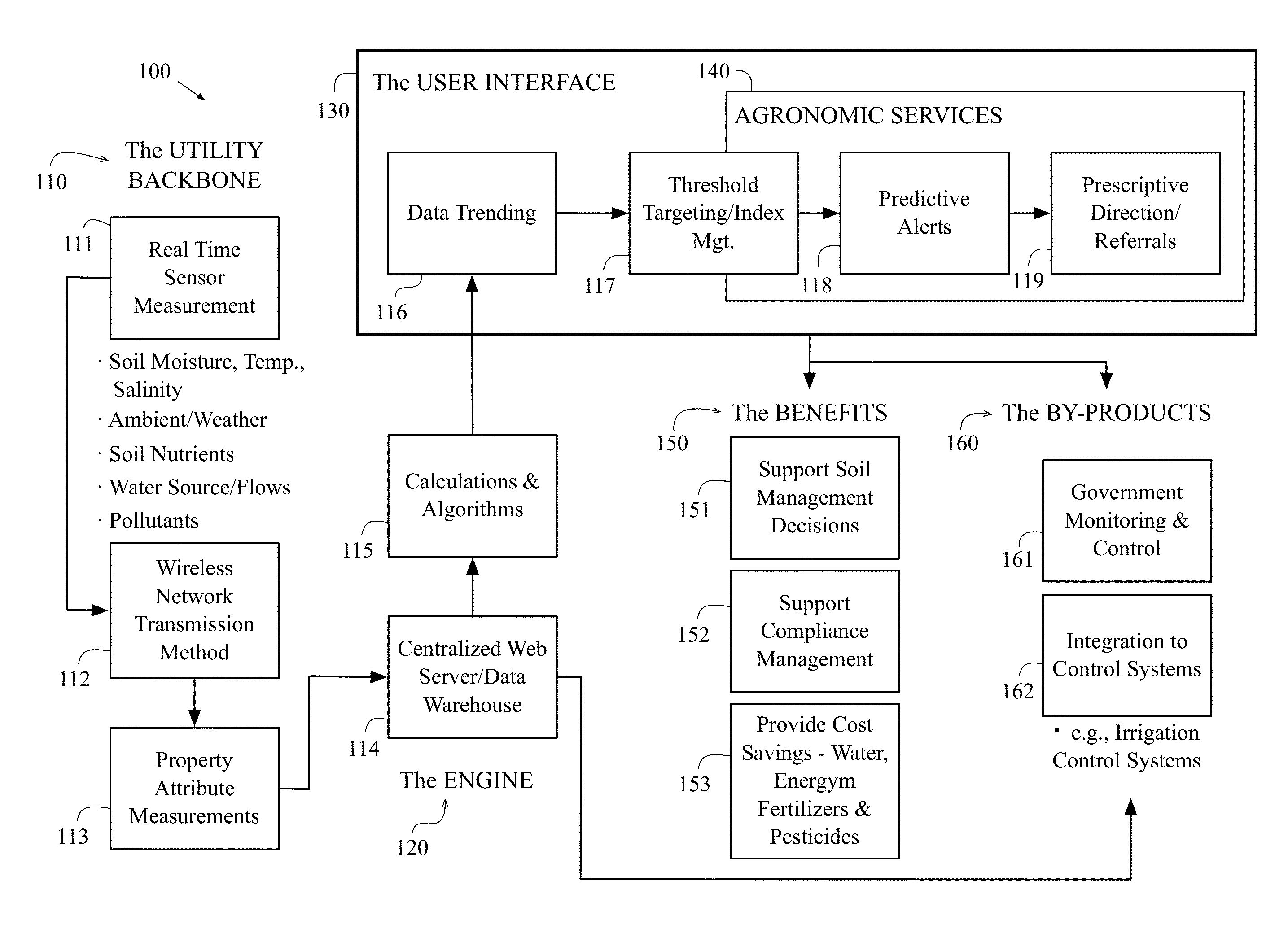
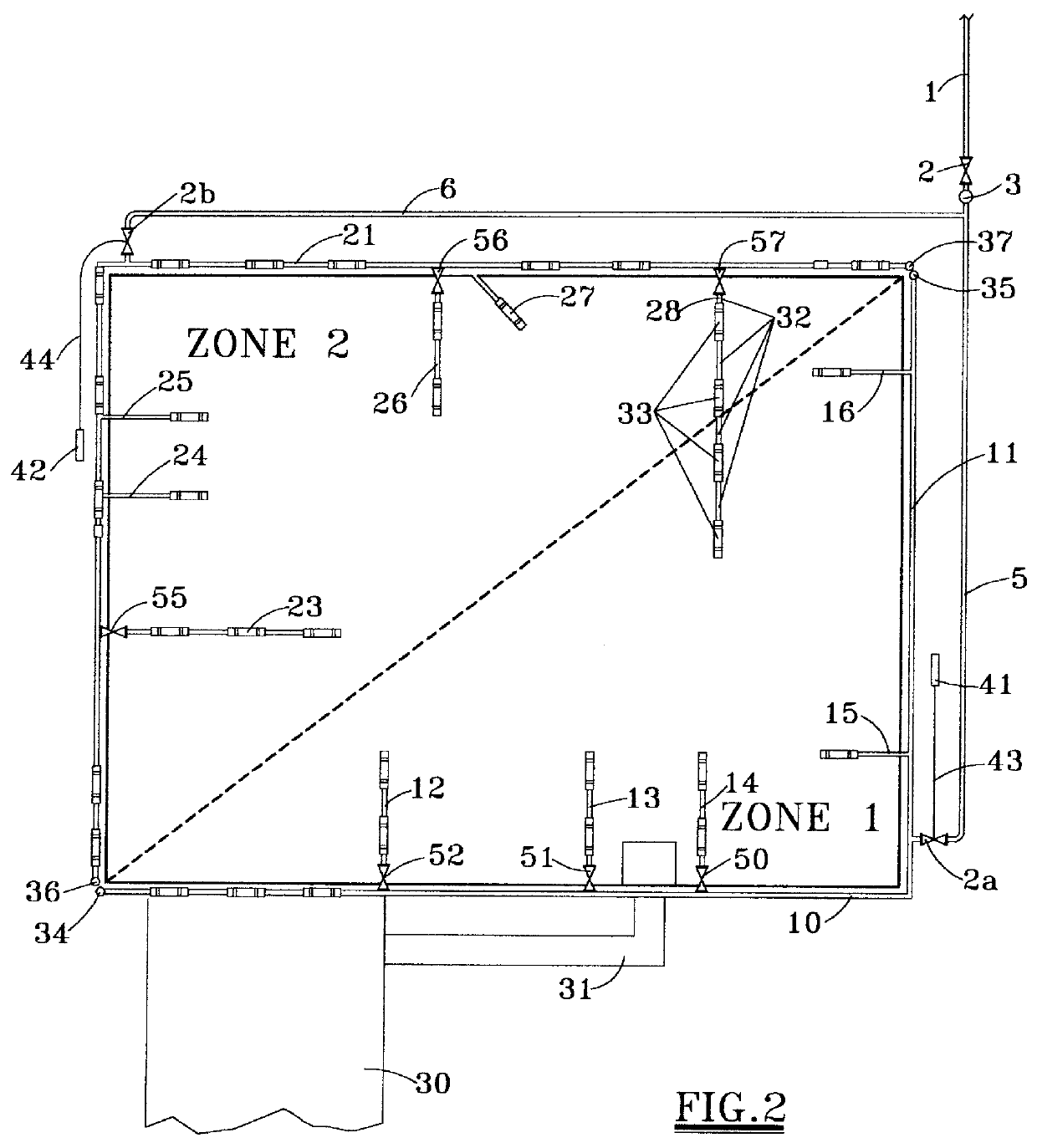
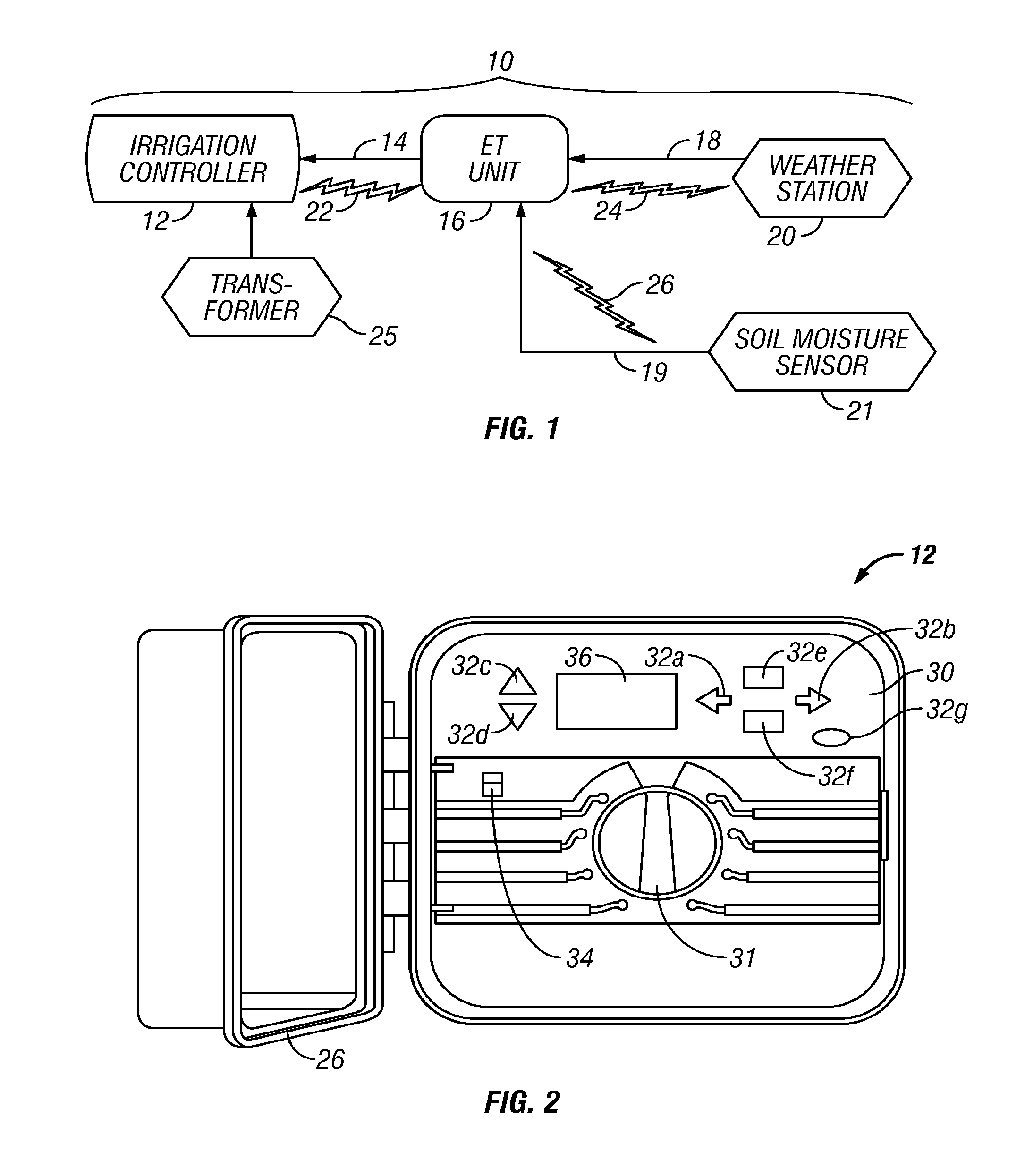
Irrigation water conservation with automated water budgeting and time of use technology
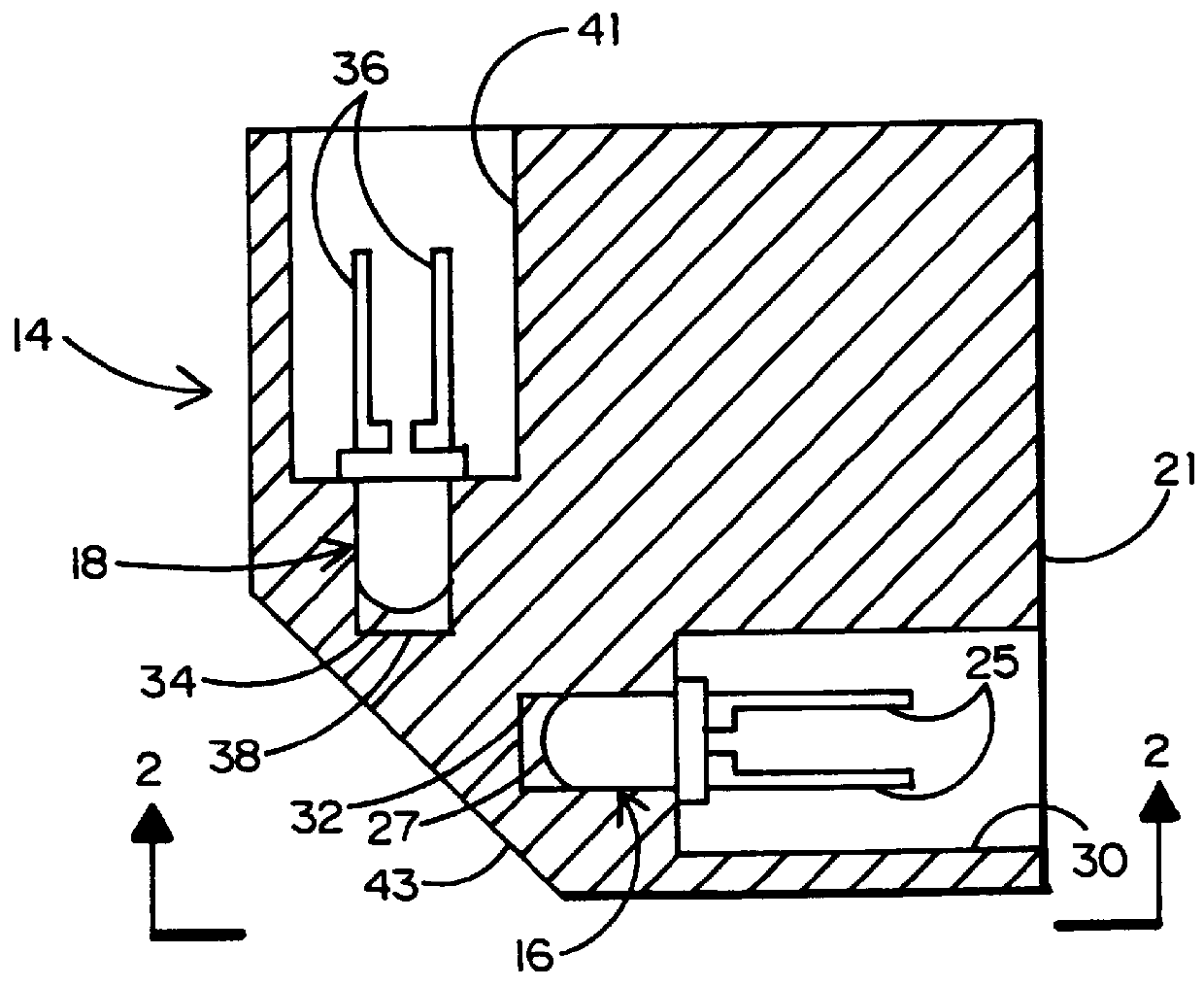
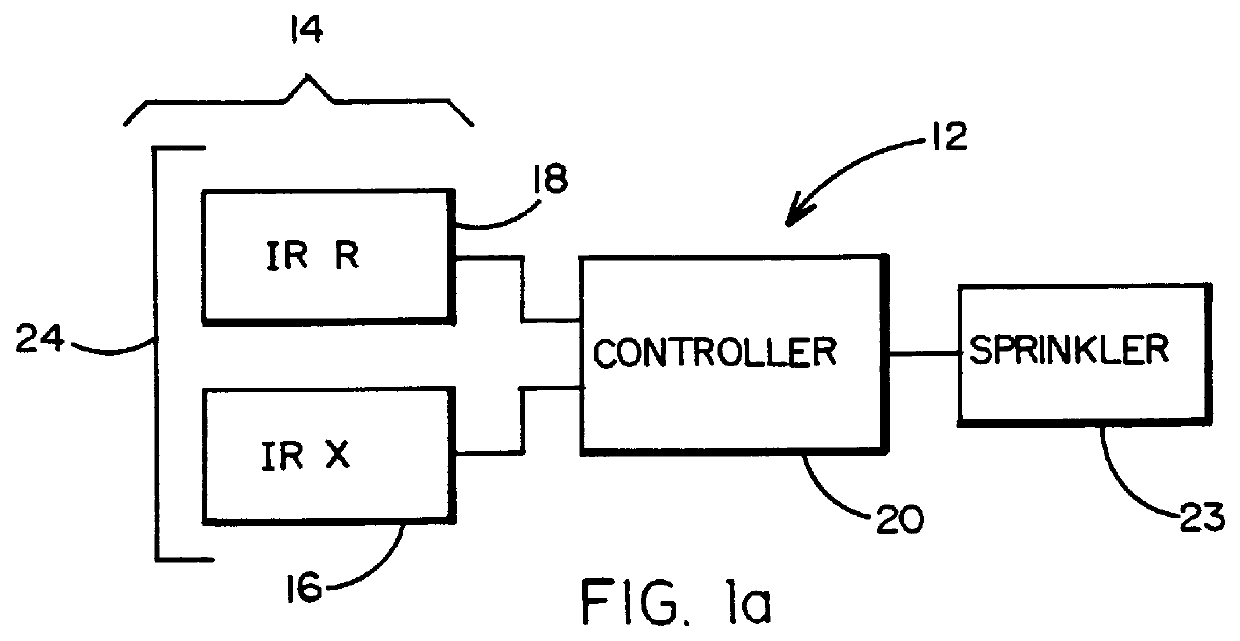
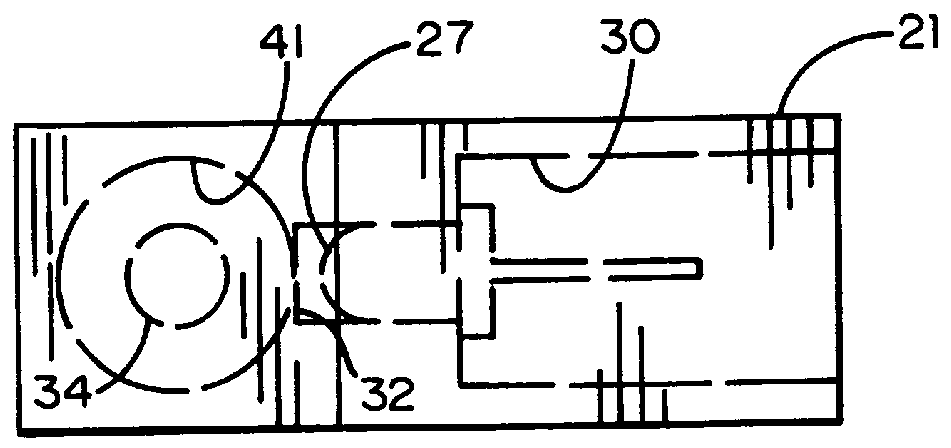
ActiveUS20110093123A1Improved wireless receptionMinimized overall profileSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationCurrent sensorTime of use
The present invention provides a multitude of embodiments for landscape water conservation with automated water budgeting or seasonal adjustment. Water budget automation may be implemented within an irrigation controller, by means of an add-on or a plug-in to the controller, or broadcast from a central location. The environmental data used for automated water budgeting may be historical including ambient temperature, wind, solar radiation, relative humidity, soil moisture, soil temperature, or evapotranspiration, or combinations thereof, or with a combination of current sensor data. The automated water budgeting may be accomplished with a percentage accumulation method which adjusts watering intervals and schedules, or on a daily percentage basis. In addition, government based restricted watering schedules may be combined within all the above embodiments to provide additional flexibility for water conservation.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Method and apparatus for optimizing soil moisture
ActiveUS7133749B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-acting watering devicesRunning timeSoil moisture content
A self-adjusting irrigation controller takes a pre-irrigation soil moisture reading prior to irrigation, chooses an amount of water to be dispensed corresponding to that reading from a table, and dispenses that amount of water. A predetermined length of time after the end of irrigation, the controller takes a post-irrigation soil moisture reading and compares the value of that reading to a predetermined target value. If the post-irrigation value differs substantially from the target value, the water amount corresponding to the pre-irrigation value in the table is adjusted to reduce that difference on the next scheduled irrigation cycle having that same pre-irrigation soil moisture reading. The target value is determined by watering the soil to field capacity, then computing the target value as a function of the reading of the sensor at field capacity. The controller thus converges toward an ideal runtime and follows changes in the environment. In the preferred embodiment, the soil moisture is indicated by sensor voltages, and the amount of water dispensed is governed by the runtime of the irrigation system.
Owner:TORO CO THE
Irrigation system with multiple soil moisture based seasonal watering adjustment
ActiveUS8793024B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWatering devicesSignal onSoil moisture sensor
An irrigation controller has a control panel including a display and a plurality of user inputs. A processor is operatively connected to the control panel and to a memory. A plurality of switches are operatively connected to the processor for turning a power signal ON and OFF to a plurality of valves that deliver water to a plurality of sprinklers in different zones. Programming is stored in the memory for implementing a seasonal adjustment feature that is independently operable with a plurality of individual watering programs to selectively energize the valves. The programming calculates a soil moisture requirement value for each program using a signal from at least one soil moisture sensor that is associated with a zone that is assigned to that watering program, and automatically modifies the watering program assigned to that zone through the seasonal adjust feature based on the soil moisture requirement value.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
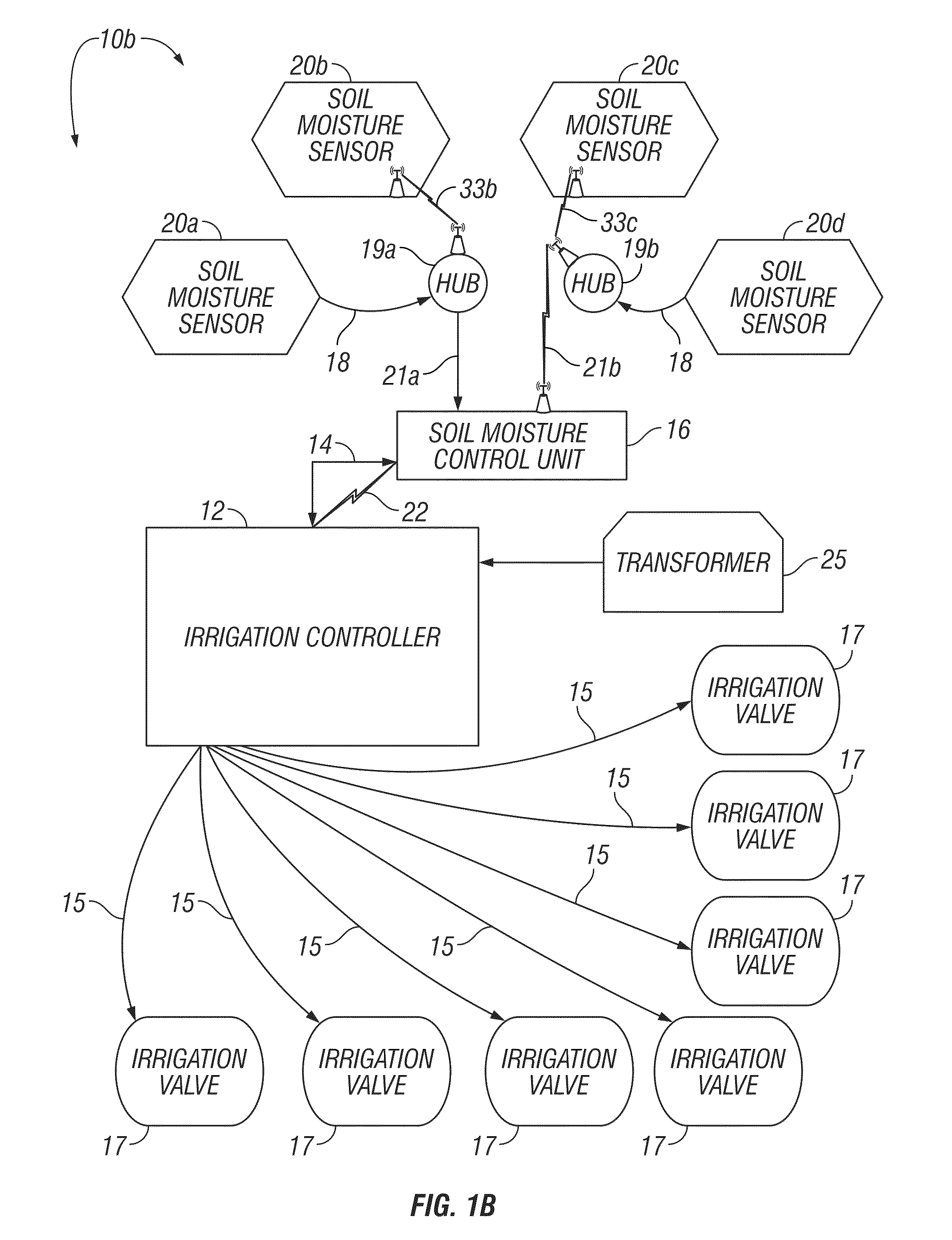
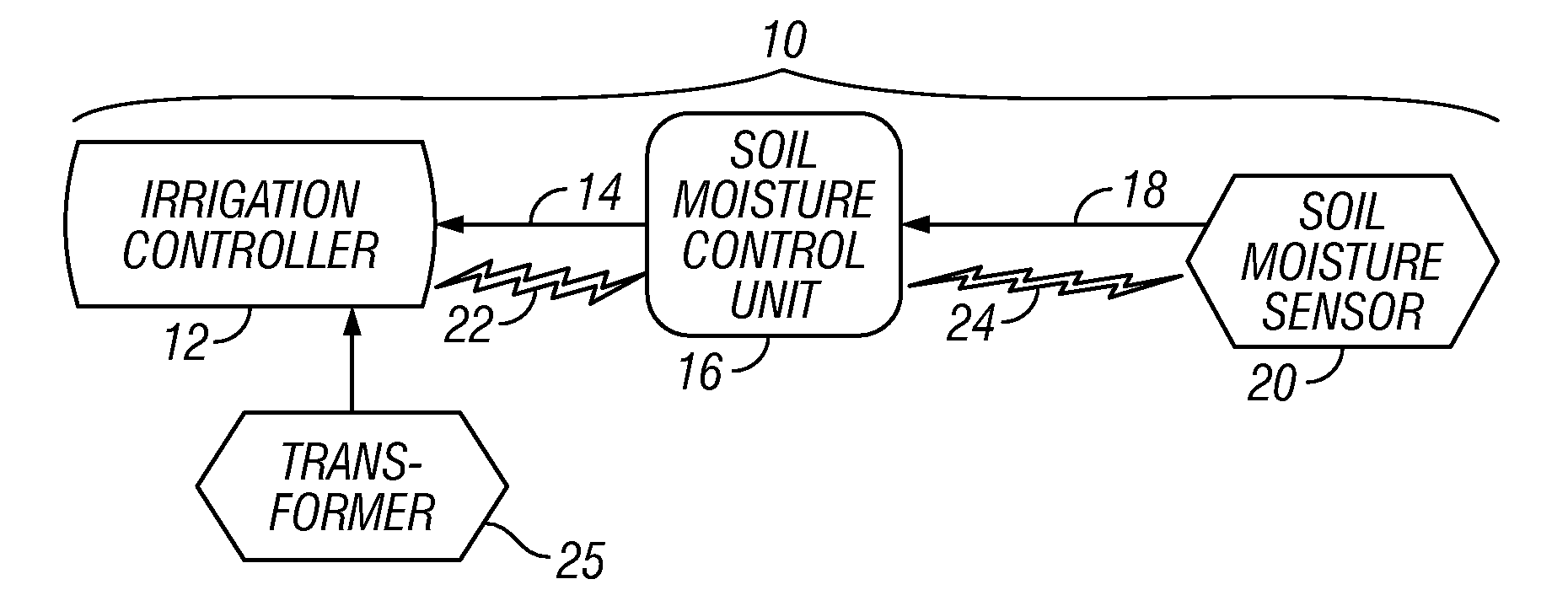
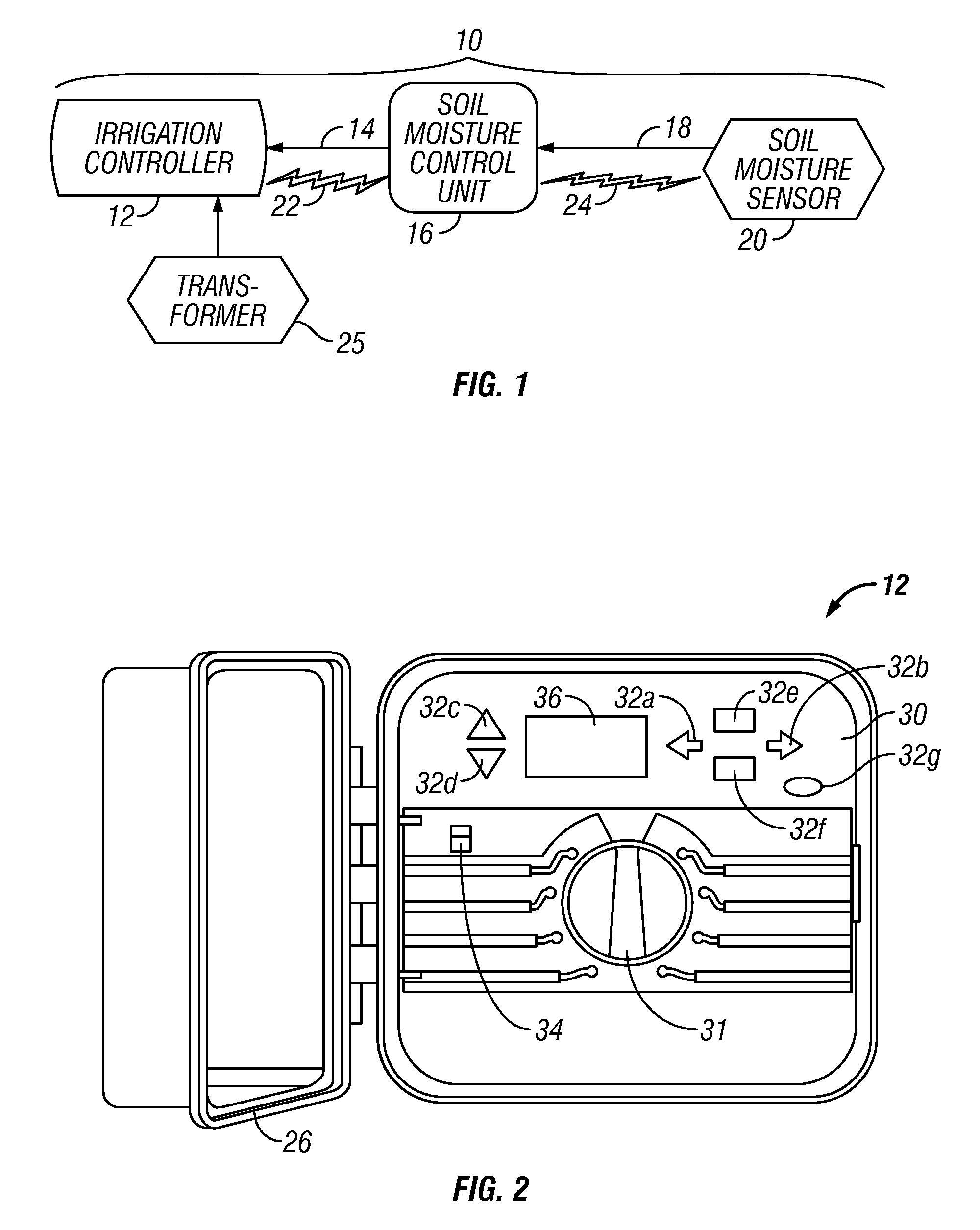
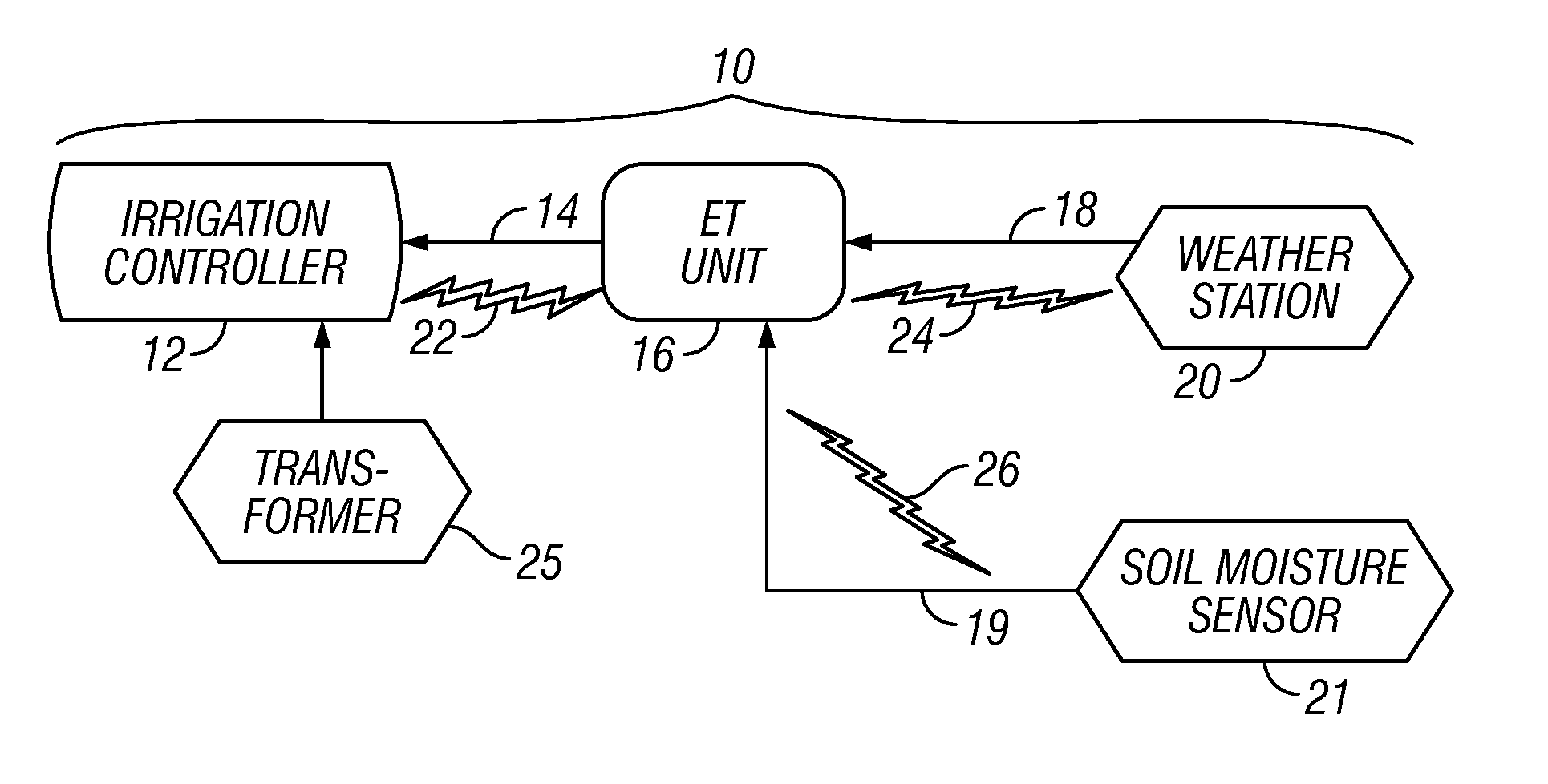
Irrigation System With Soil Moisture Based Seasonal Watering Adjustment
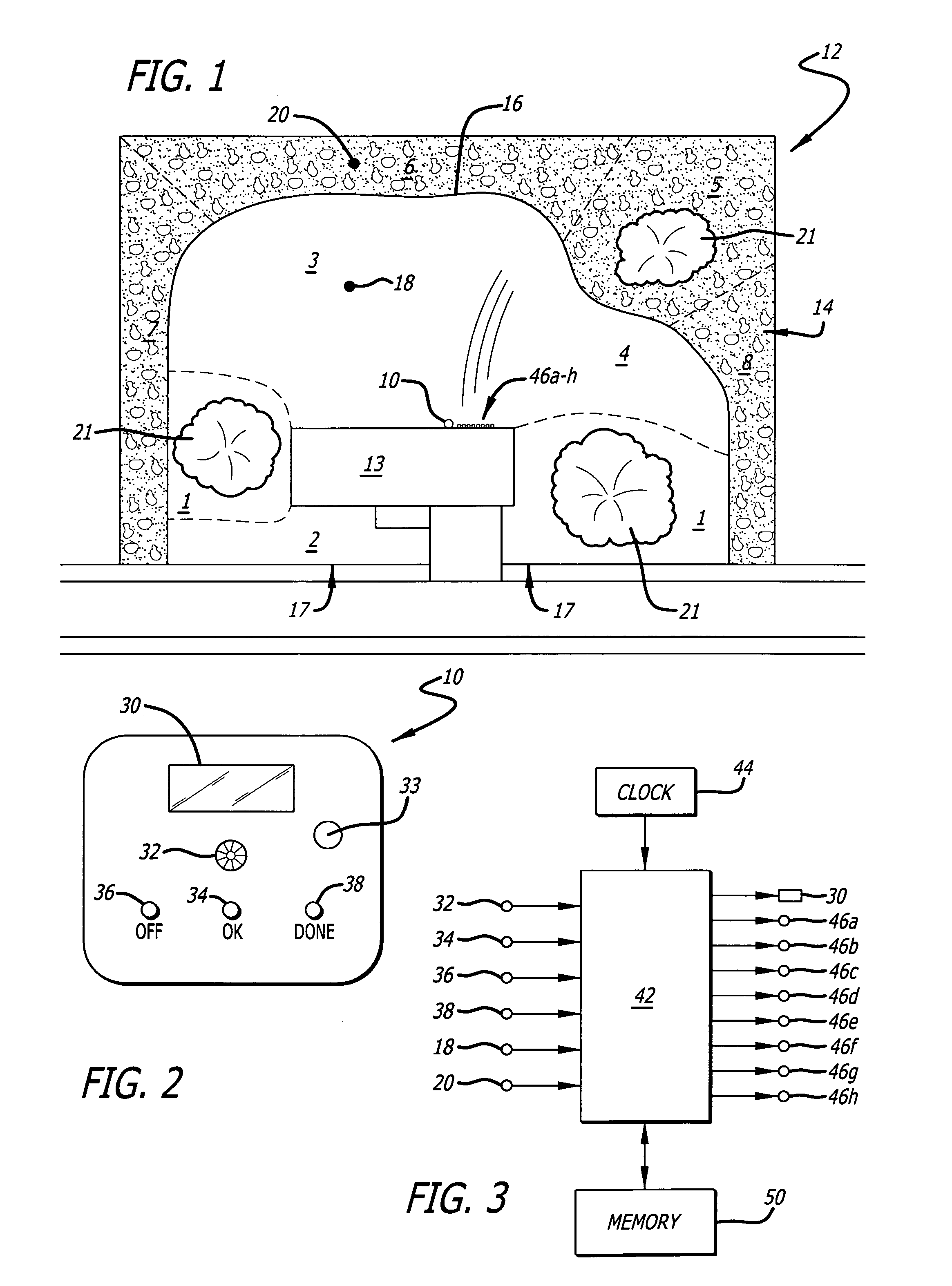
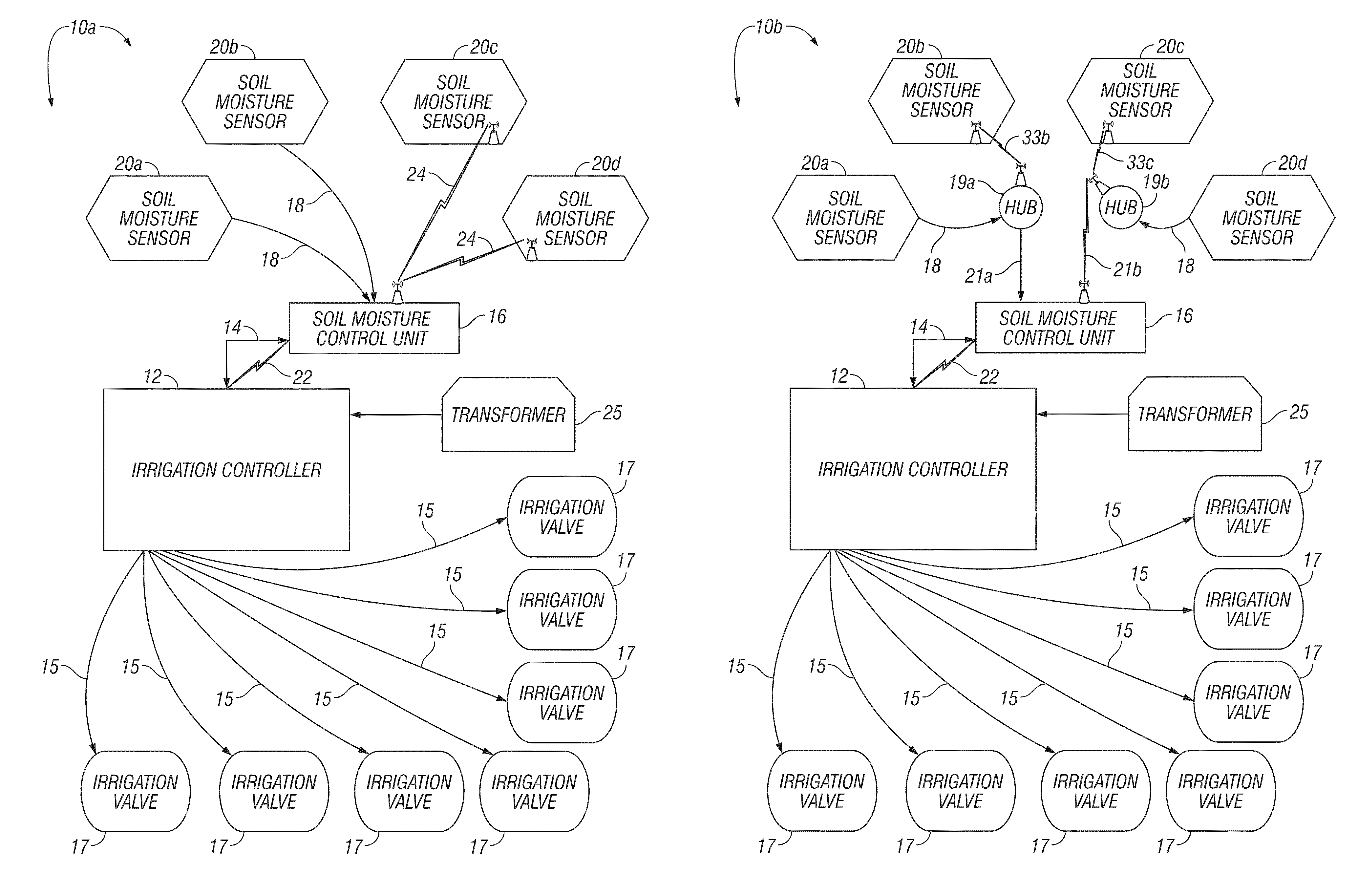
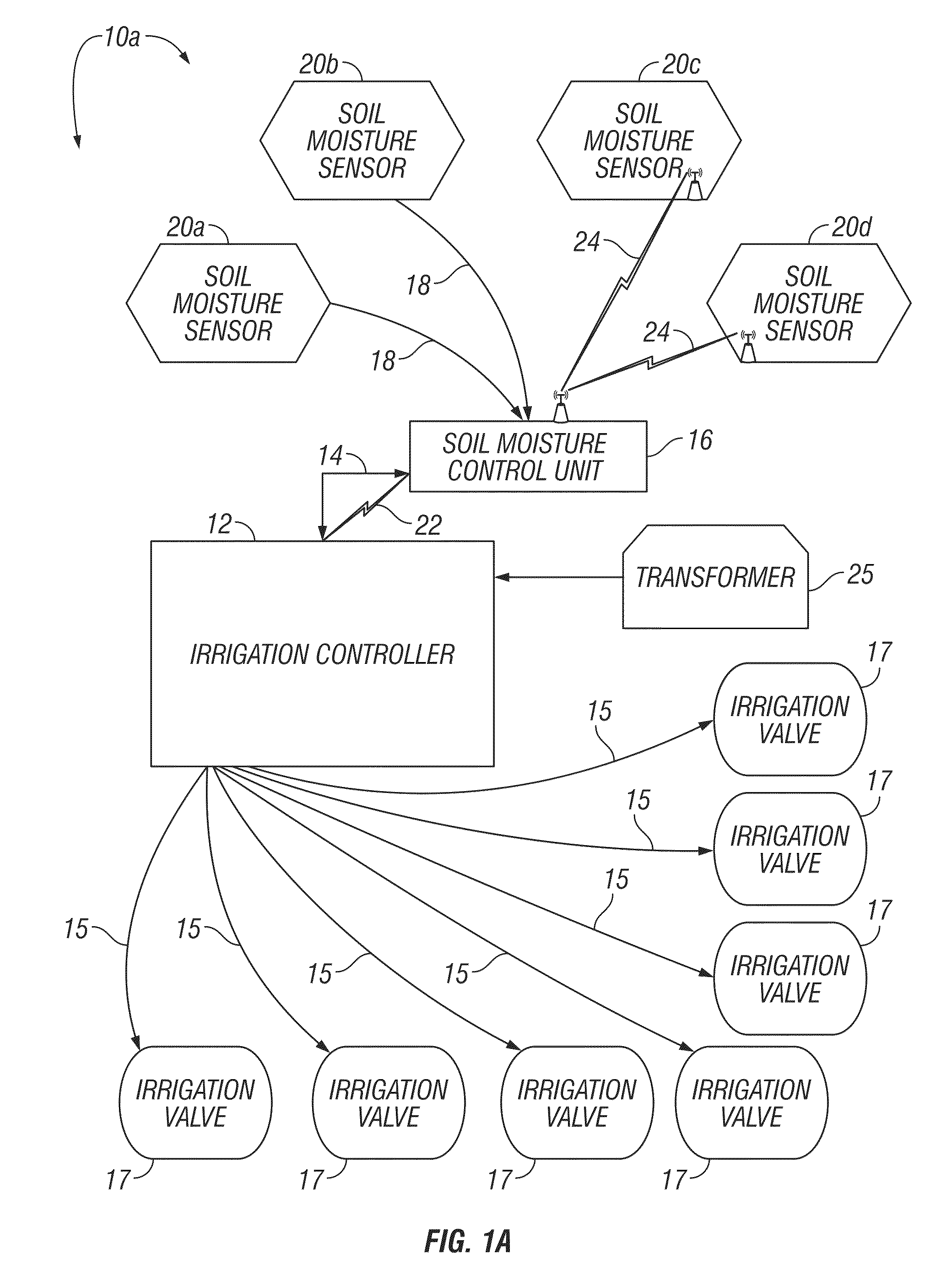
A soil moisture based irrigation system includes a stand alone irrigation controller with a seasonal adjust feature and a stand alone weather station including at least one soil moisture sensor. The soil moisture based irrigation system further includes a stand alone soil moisture control unit operatively connected to the irrigation controller and the soil moisture sensor. The soil moisture control unit includes programming configured to calculate an estimated soil moisture requirement value using a signal from the soil moisture sensor and to automatically modify a watering schedule of the irrigation controller through the seasonal adjust feature based on the estimated soil moisture requirement value to thereby conserve water while maintaining plant health.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Automatic soil moisture sensing and watering system
An automatic moisture sensing and watering system detects a moisture level within the soil. The automatic moisture sensing and watering system may be implemented in combination with a conventional automatic watering system to accurately control a moisture content of a plot of soil. Since a plant draws water directly from the soil, the automatic moisture sensing and watering system is adapted for controlling the moisture content of the soil itself, by measuring the moisture content within the soil. The watering period of an automatic watering system may be changed, based upon a detected moisture content within a plot of soil. Alternatively, an amount of water to be applied at a next watering period may be changed, based upon a detected moisture content within the plot of soil.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE IRRIGATION +1
Irrigation system with ET based seasonal watering adjustment and soil moisture sensor shutoff
An irrigation system includes at least one environmental sensor, such as a solar radiation sensor, that is installed on an irrigation site, and a soil moisture sensor that is also installed on the irrigation site. Programming allows an estimated ET value to be calculated based at least in part on the output signal of the environmental sensor. A pre-programmed watering schedule is automatically modified based on the estimated ET value to thereby conserve water while maintaining the health of plants on the irrigation site. The system automatically inhibits irrigation when an output signal of the soil moisture sensor indicates an amount of moisture in the soil is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
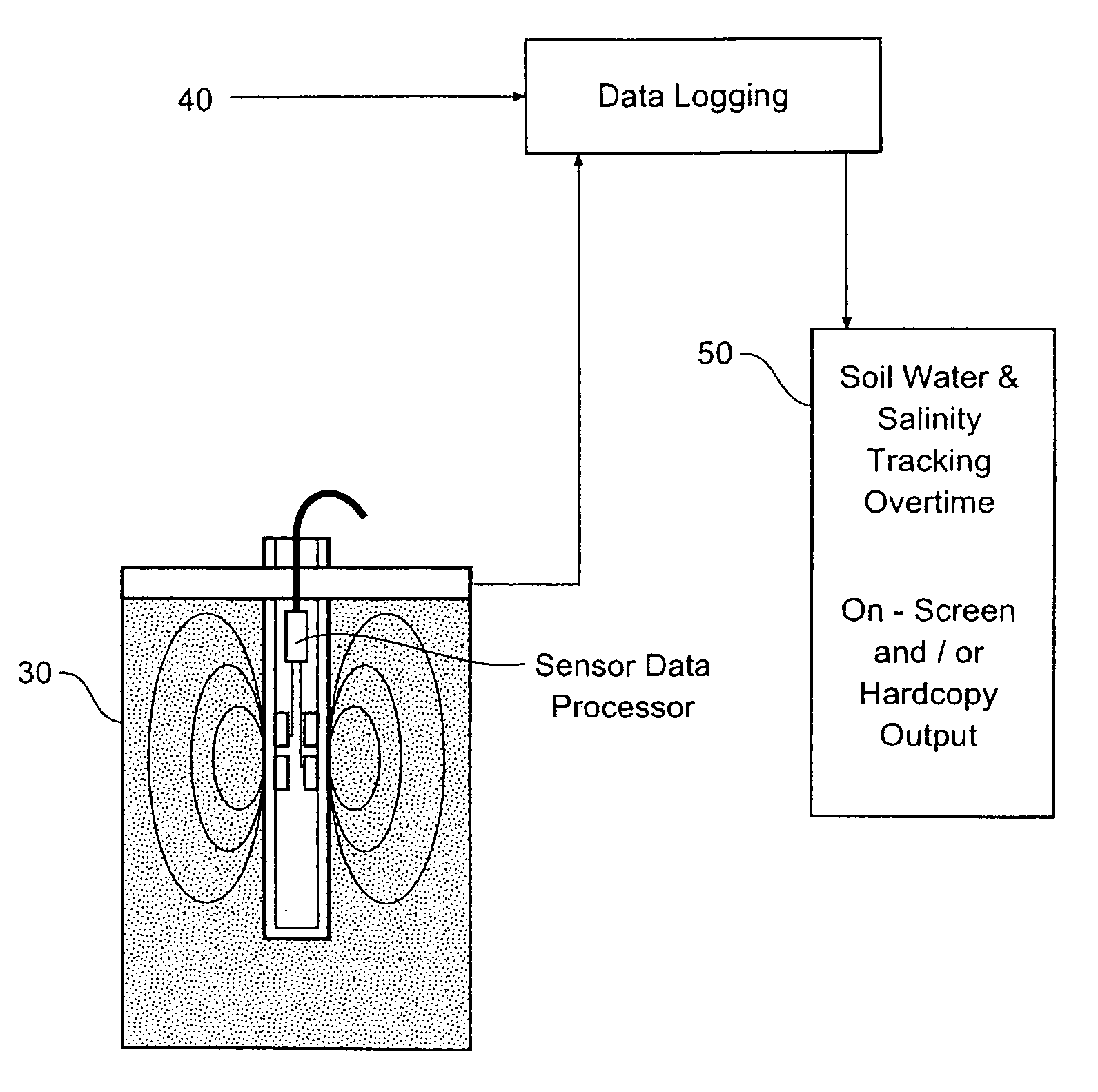
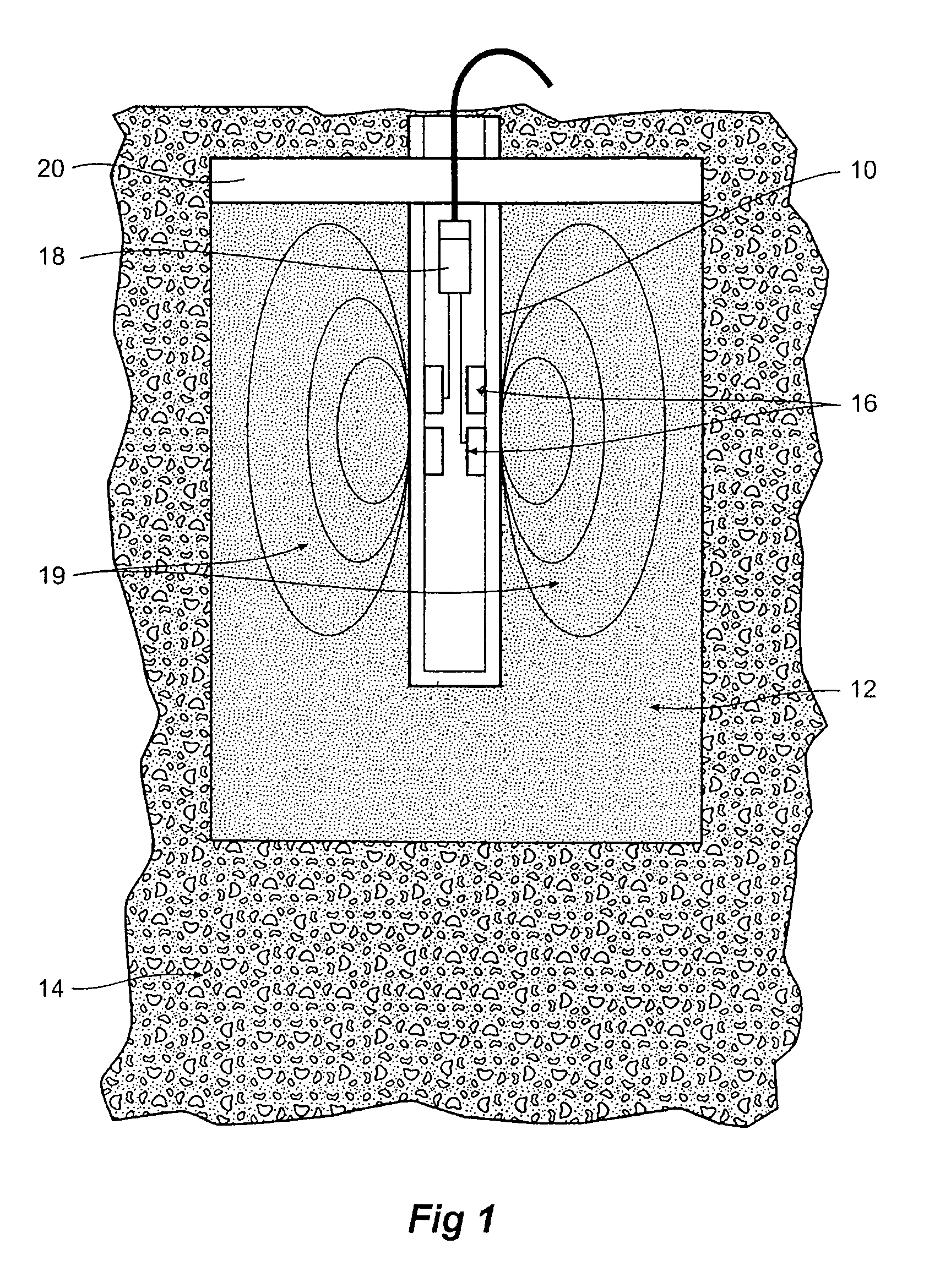
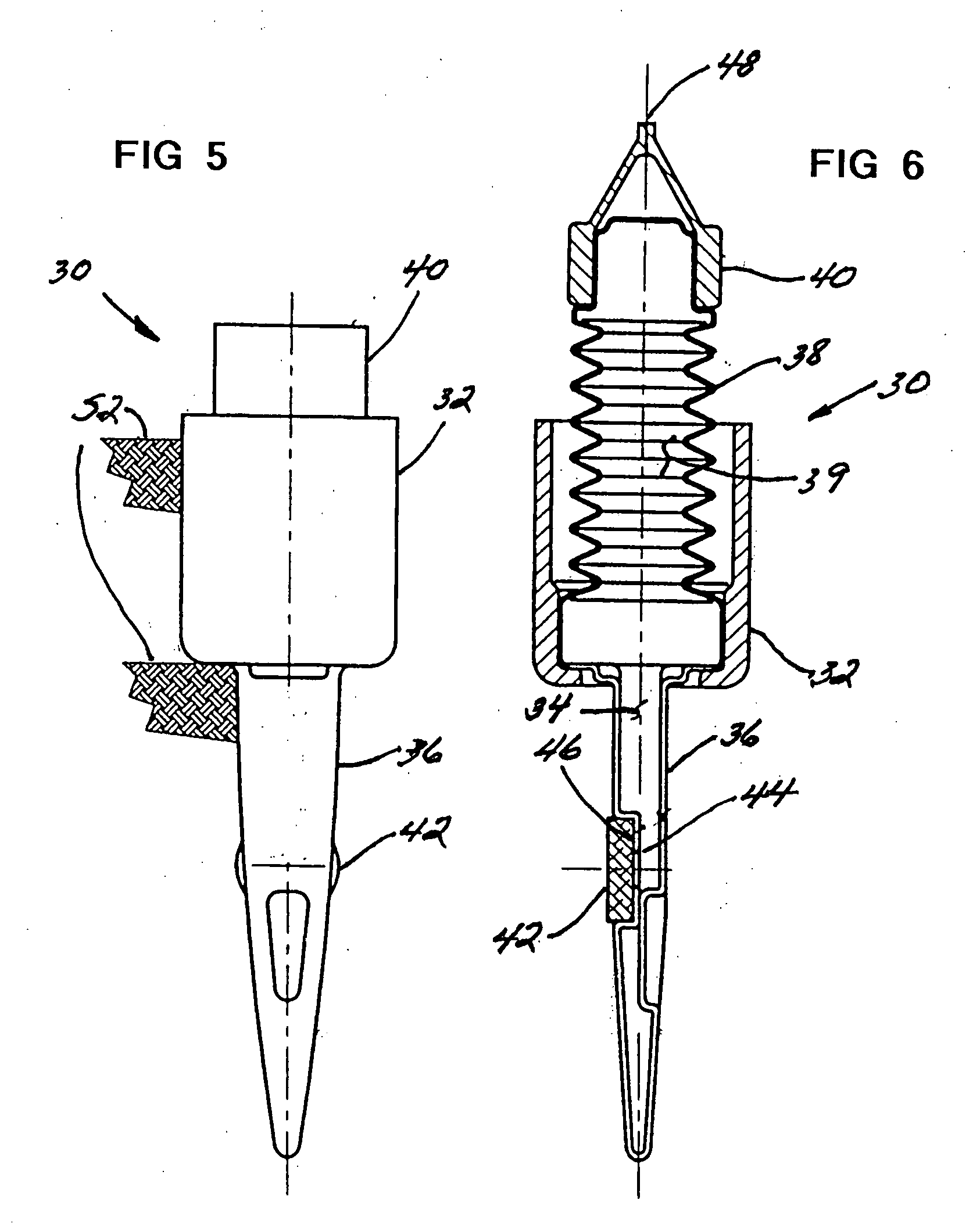
Soil matric potential and salinity measurement apparatus and method of use
A soil parameter measurement arrangement includes a capacitive based soil moisture and salinity sensor, a predetermined moisture migration medium located in a volume adjacent said sensor so that the medium substantially occupies the field of influence of said sensor. The medium is in moisture communication with the soil to be measured, and said sensor is adapted to measure and produce data representative of the volumetric water content of said medium. A sensor data processing means determines both the soil moisture and salinity of said medium. By using the measured volumetric soil moisture content and the moisture release curve of the medium, it is possible to derive the matric potential of the soil. The measured salinity of the medium corresponds to the salinity of the soil that is in moisture communication with the medium.
Owner:SENTEK
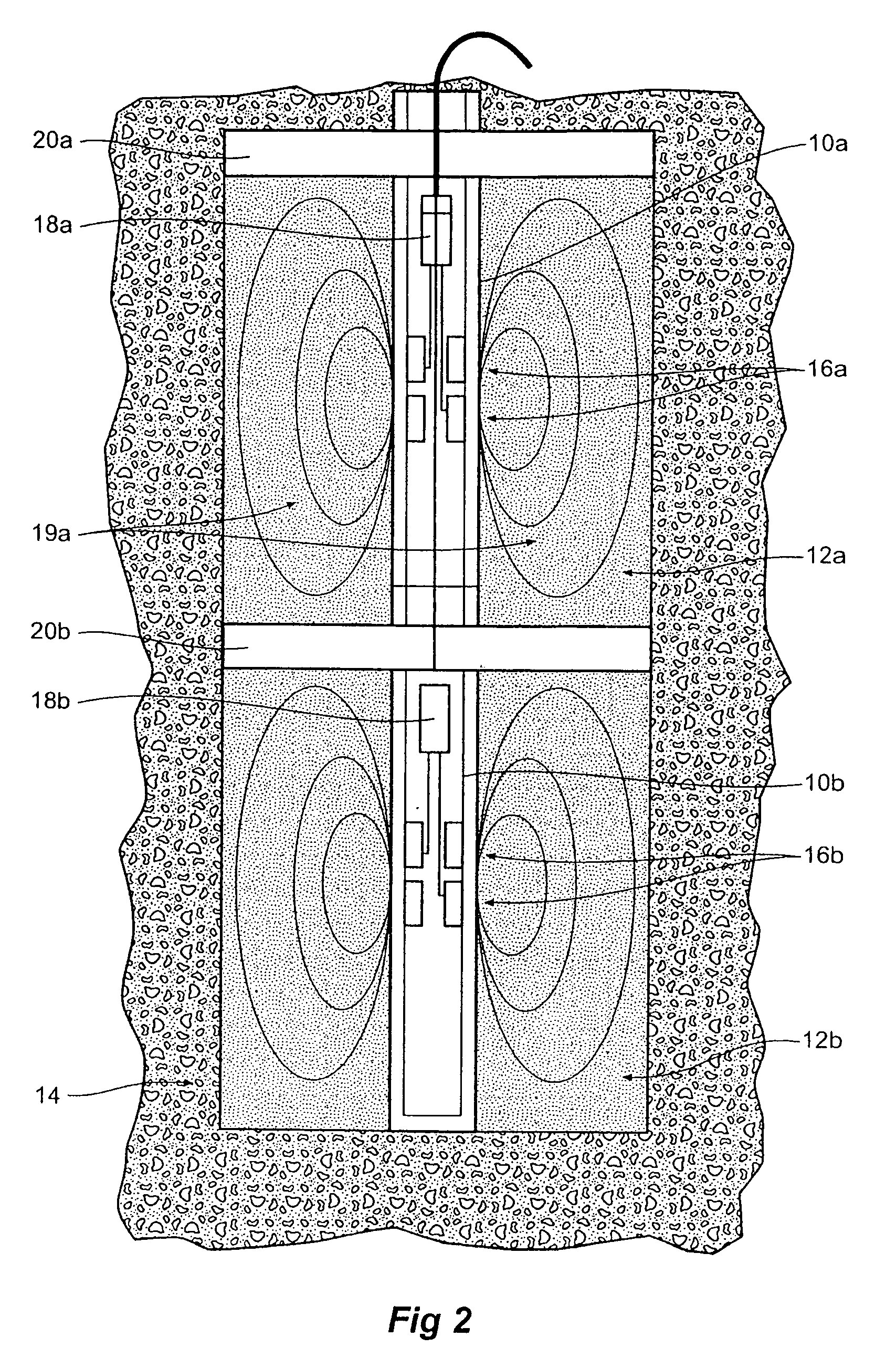
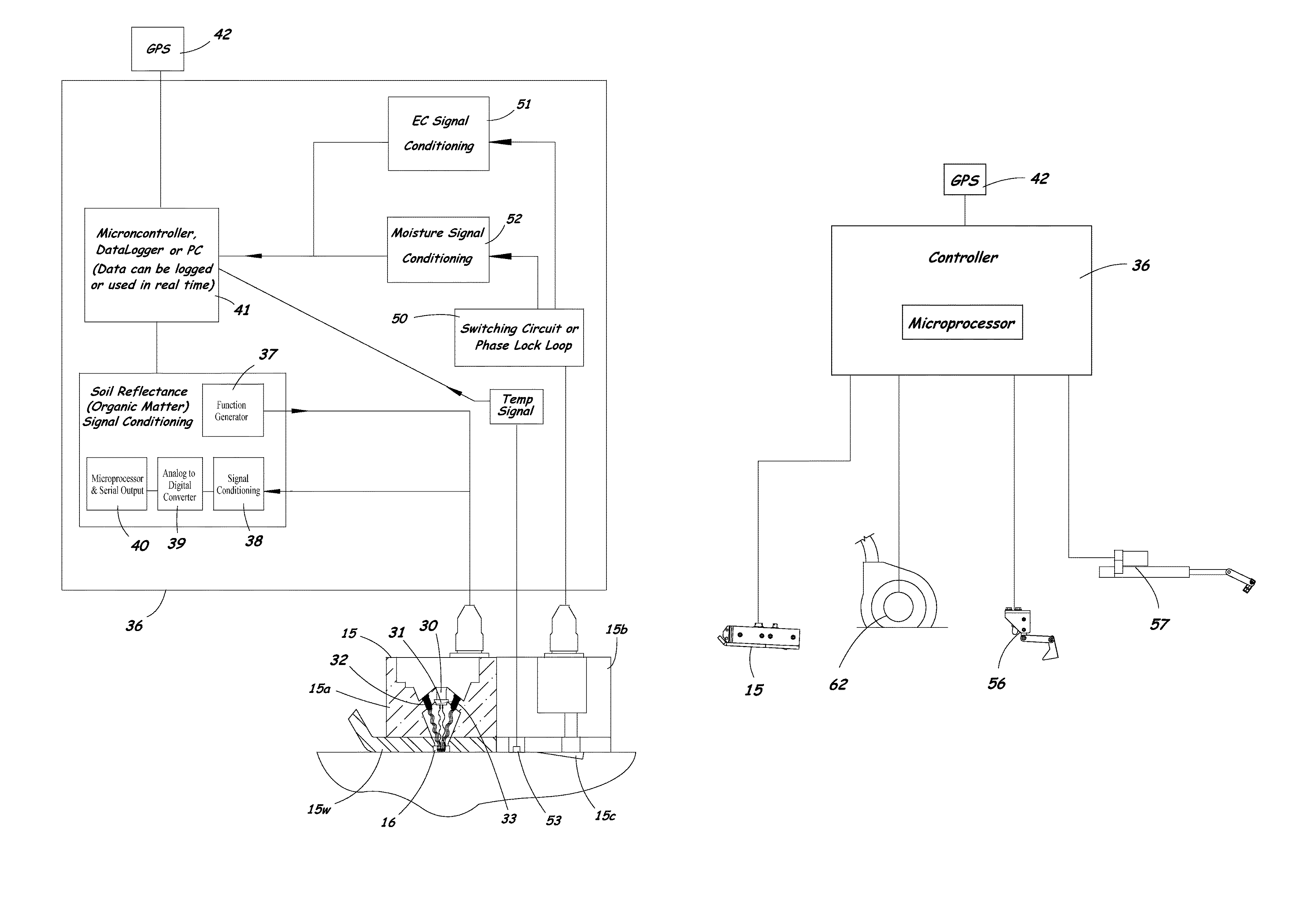
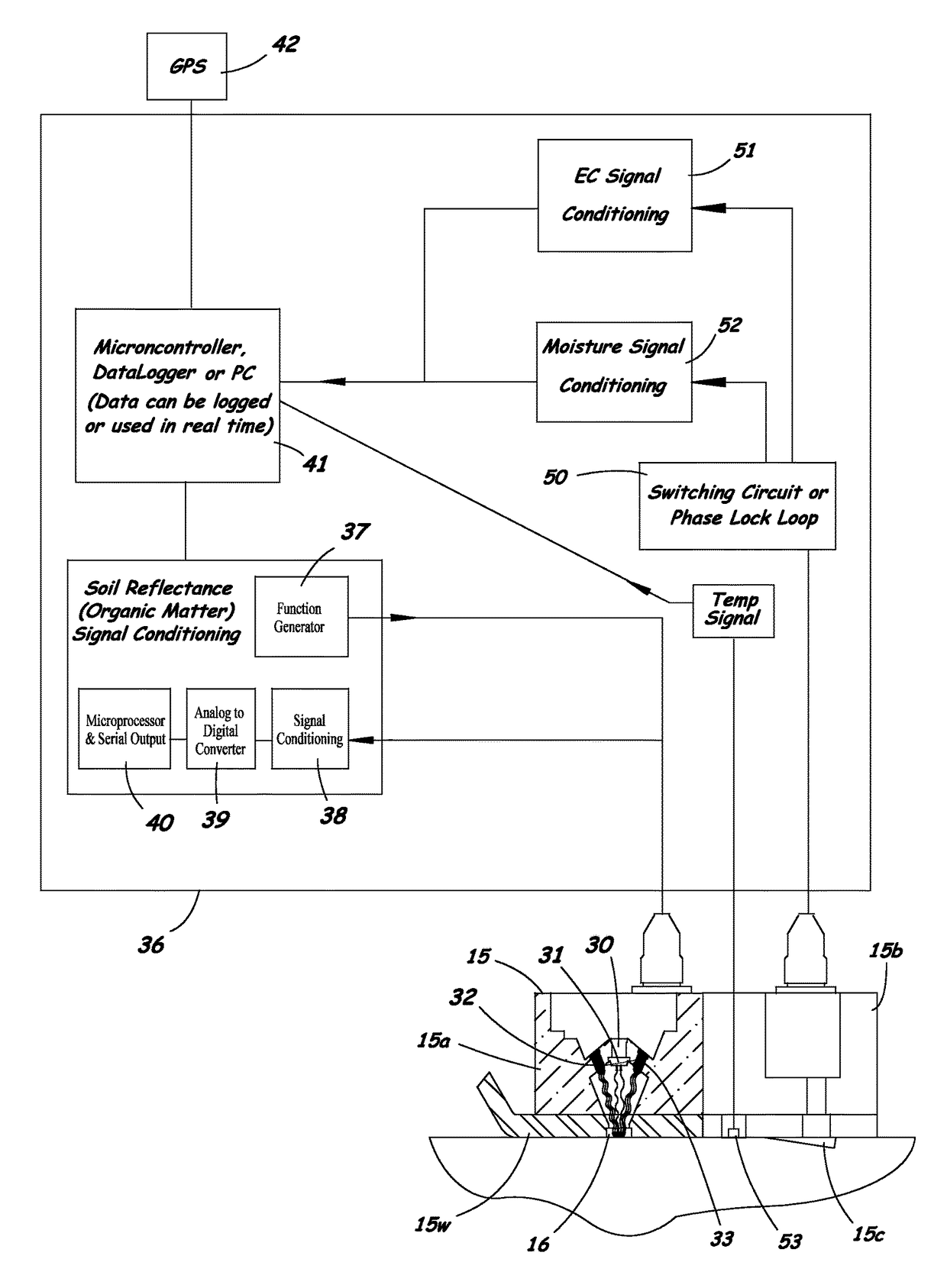
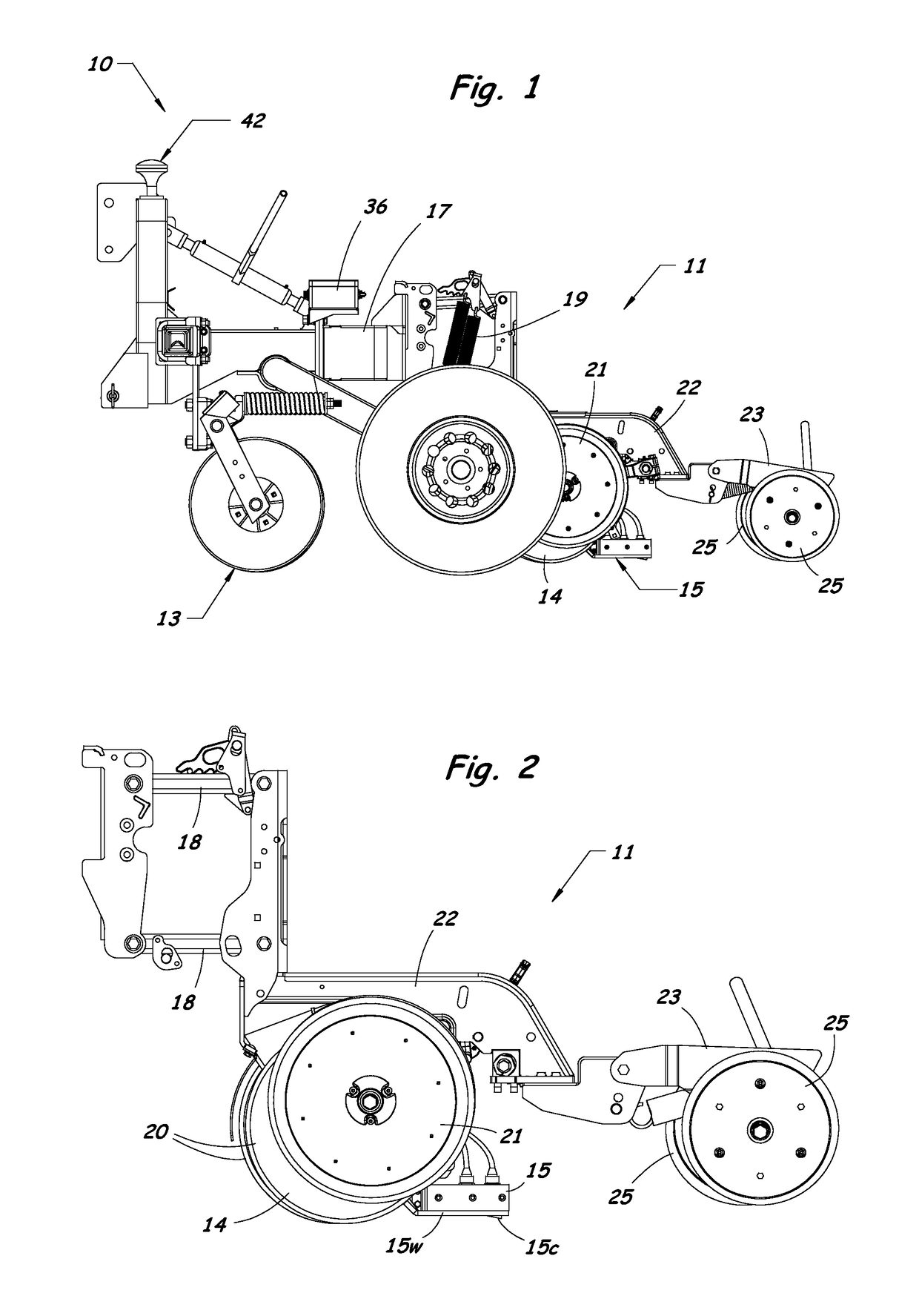
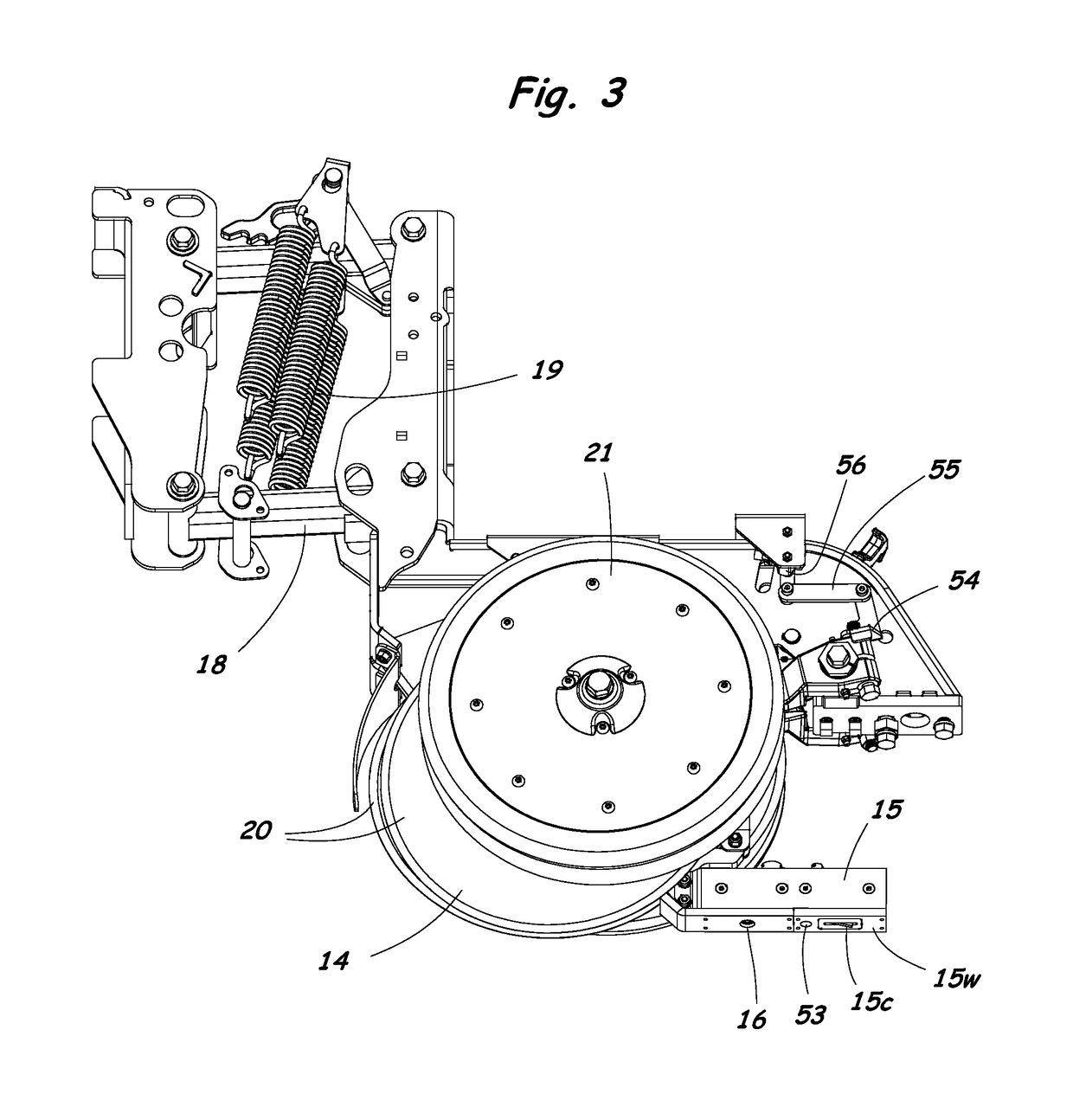
Agricultural planter with automatic depth and seeding rate control
An agricultural planter having sensors for measuring multiple soil properties adjusts planting depth and seeding rate in real time based on the measured soil properties. An optical module is carried by the planter for collecting soil reflectance data. A pair of soil contact blades protrude from or are embedded in the optical module for collecting soil EC data and soil moisture data. A switching circuit or phase lock loop allows the same soil contact blades to feed signals to both a soil EC signal conditioning circuit and a soil moisture signal conditioning circuit. The soil moisture data can be used to calibrate the soil EC data and the soil reflectance data to compensate for effects of changing soil moisture conditions across a field. The sensor module can be positioned behind a seed tube and used as a seed firmer, or incorporated into a seed tube guard.
Owner:VERIS TECH
Automatic efficient irrigation threshold setting
ActiveUS8862277B1Optimize plant growth plantOptimize plant plant healthResistance/reactance/impedenceWatering devicesTemporal changeSoil moisture sensor
A method and system for monitoring the dynamic response of soil moisture and setting a threshold in relation to the field capacity of a soil area is disclosed herein. By measuring the dynamic response of soil moisture under wet soil conditions, one can determine a practical field capacity for the soil, in-situ, based solely on the soil moisture sensor output. Essentially, by looking at how the soil moisture level varies with time one can determine the field capacity.
Owner:GREEN BADGE
Foundation soil moisture stabilization system
InactiveUS6082932APrevent overwateringAvoiding pressure injuriesSoil drainageProtective foundationEngineeringSoil moisture content
A system for stabilizing moisture content of soil around and beneath the foundation of a building. The system includes a source of pressurized water; one or more conduits buried in the soil around the building foundation, at least a portion of soil conduit being pervious to water, allowing water therein to enter said soil; and a remotely operated valve connecting the source of water to the conduits to permit or prevent flow of water, respectively, from the source of water to the conduits. A controller is operatively connected to the remotely operated valve for transmitting signals to the valve for opening and closing thereof in a predetermined time cycle. At least one soil moisture sensitive device is operatively connected to the controller and / or the valve for interrupting signals transmitted to the valve, to prevent opening of the valve when the moisture content of the soil exceeds a predetermined amount.
Owner:ANDERSON GARY L
Automatic efficient irrigation threshold setting
A method and system for monitoring the dynamic response of soil moisture and setting a threshold in relation to the field capacity of a soil area is disclosed herein. By measuring the dynamic response of soil moisture under wet soil conditions, one can determine a practical field capacity for the soil, in-situ, based solely on the soil moisture sensor output. Essentially, by looking at how the soil moisture level varies with time one can determine the field capacity.
Owner:GREEN BADGE
Construction process of roadbed structure with sand-based water-permeable bricks
InactiveCN103352407AStrong penetrating powerIncrease humidityIn situ pavingsClimate change adaptationBrickRoad surface
The invention relates to a construction process of a roadbed structure, in particular to a construction process of a roadbed structure with sand-based water-permeable bricks. The construction process is applicable to road surfaces of squares, business streets, gardens and the like and occasions such as outdoor tennis courts, basketball courts and ground track fields. The construction process comprises the following process steps: A, performing construction preparation; B, surveying and setting out; C, performing base layer construction; D, performing bearing layer construction; E, performing leveling layer construction; F, paving the sand-based water-permeable bricks; G, performing crack pouring; H, maintaining; I, cleaning on site. According to the construction, the sand-based water-permeable bricks serve as paving materials, so that the defects brought by the materials can be overcome well. Excellent water permeability and air permeability are achieved, so that rainwater can be permeated into the ground quickly, the ground surface water is supplemented, the humidity of soil is improved, and the survival conditions of ground surface plants and microorganisms are improved; water and heat can be absorbed, and the temperature and the humidity of local space of the ground surface can be adjusted, so that a great effect of relieving urban heat island effect is achieved.
Owner:宏盛建业投资集团有限公司
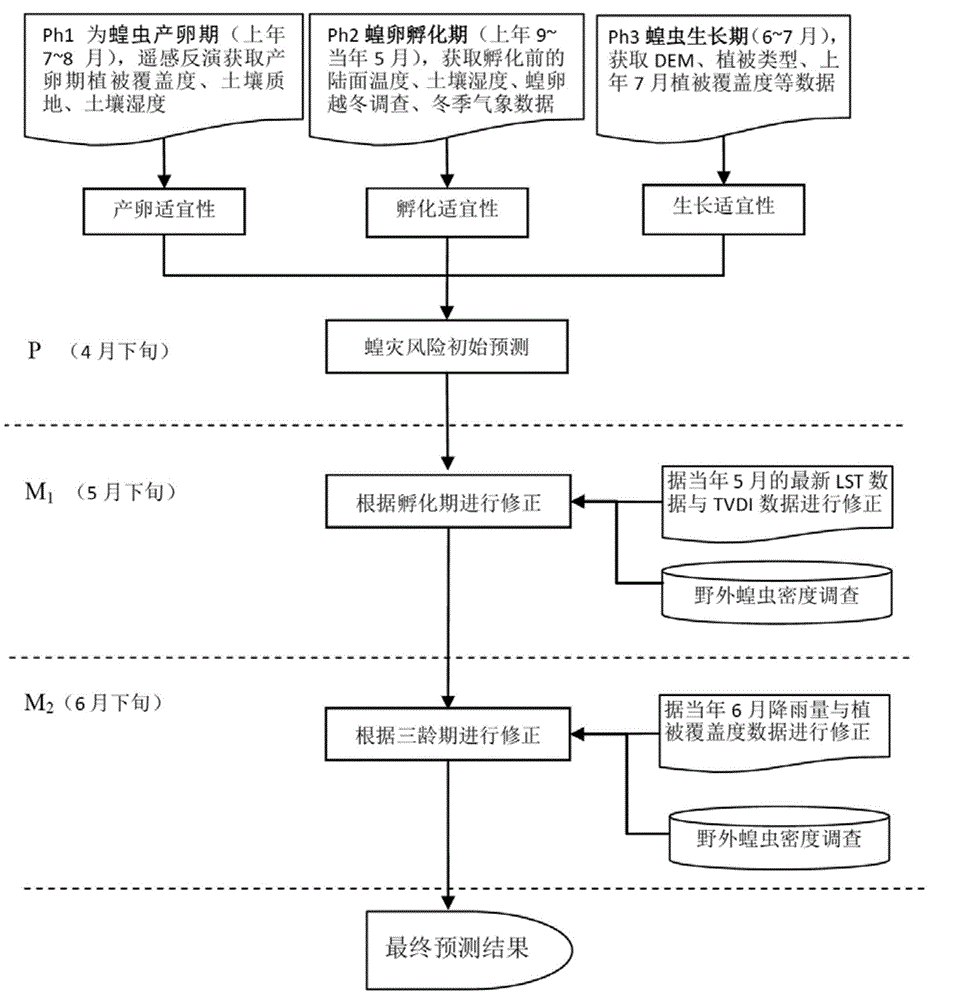
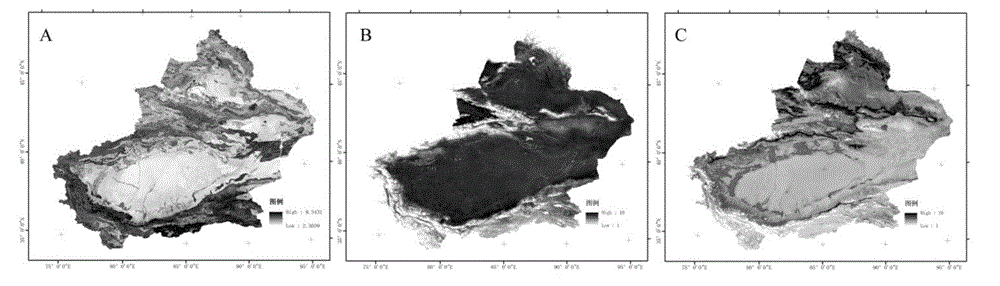
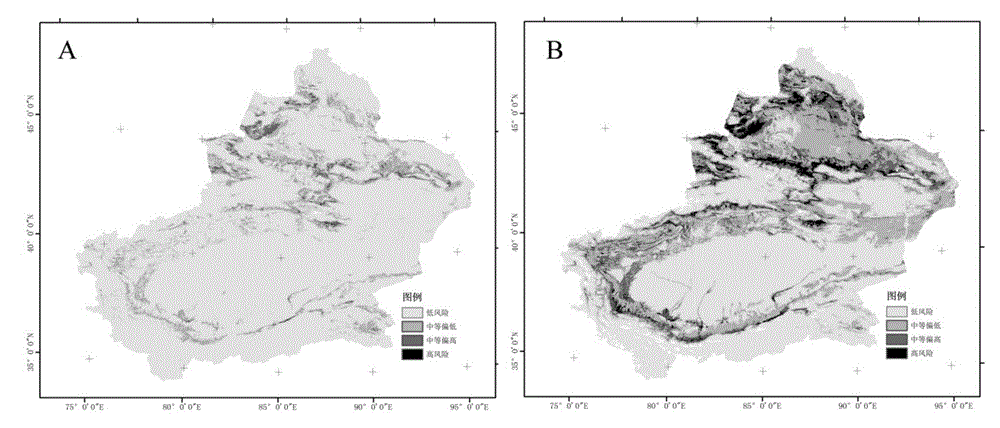
Remote sensing technology-based grassland locust plague progressive prediction method
ActiveCN103955606AHigh accuracy of resultsHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsVegetationSensing data
The invention discloses a remote sensing technology-based grassland locust plague progressive prediction method. According to the method, the distribution of key habitat elements which influencing the development of a grassland locust population is obtained by the means of quantitative remote sensing inversion, meteorological station observation and the like, wherein the key habitat elements subjected to remote sensing inversion comprises land surface temperature, vegetation coverage and soil moisture; the spawning suitability, the incubation suitability and the growth suitability of locusts are analyzed quantitatively by establishing an evaluation model, and a locust plague risk early prediction model is established; a locust plague risk level prediction result is corrected by utilizing the remote sensing observation of an incubation period and a third period and the locust density data measured in the field according to the incubation and development time axes of the locusts, and the situations of a grassland locust plague are predicted progressively. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the progressive update of sensitive habitat elements is obtained by performing quantitative inversion on remote sensing data with higher time resolution, so that the prediction precision of a locust plague monitoring and prediction model is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and system for measuring multiple soil properties
A method and system for measuring multiple soil properties on-the-go is provided on an implement for traversing a field. An optical module is carried by the implement for collecting soil reflectance data. A pair of soil contact blades protrude from or are embedded in the optical module for collecting soil EC data and soil moisture data. A switching circuit or phase lock loop allows the same soil contact blades to feed signals to both a soil EC signal conditioning circuit and a soil moisture signal conditioning circuit. The soil moisture data can be used to calibrate the soil EC data and the soil reflectance data to compensate for effects of changing soil moisture conditions across a field. The system can also be used on a planter to control planting depth and / or seeding rate in real time based on multiple soil properties collected during planting.
Owner:VERIS TECH
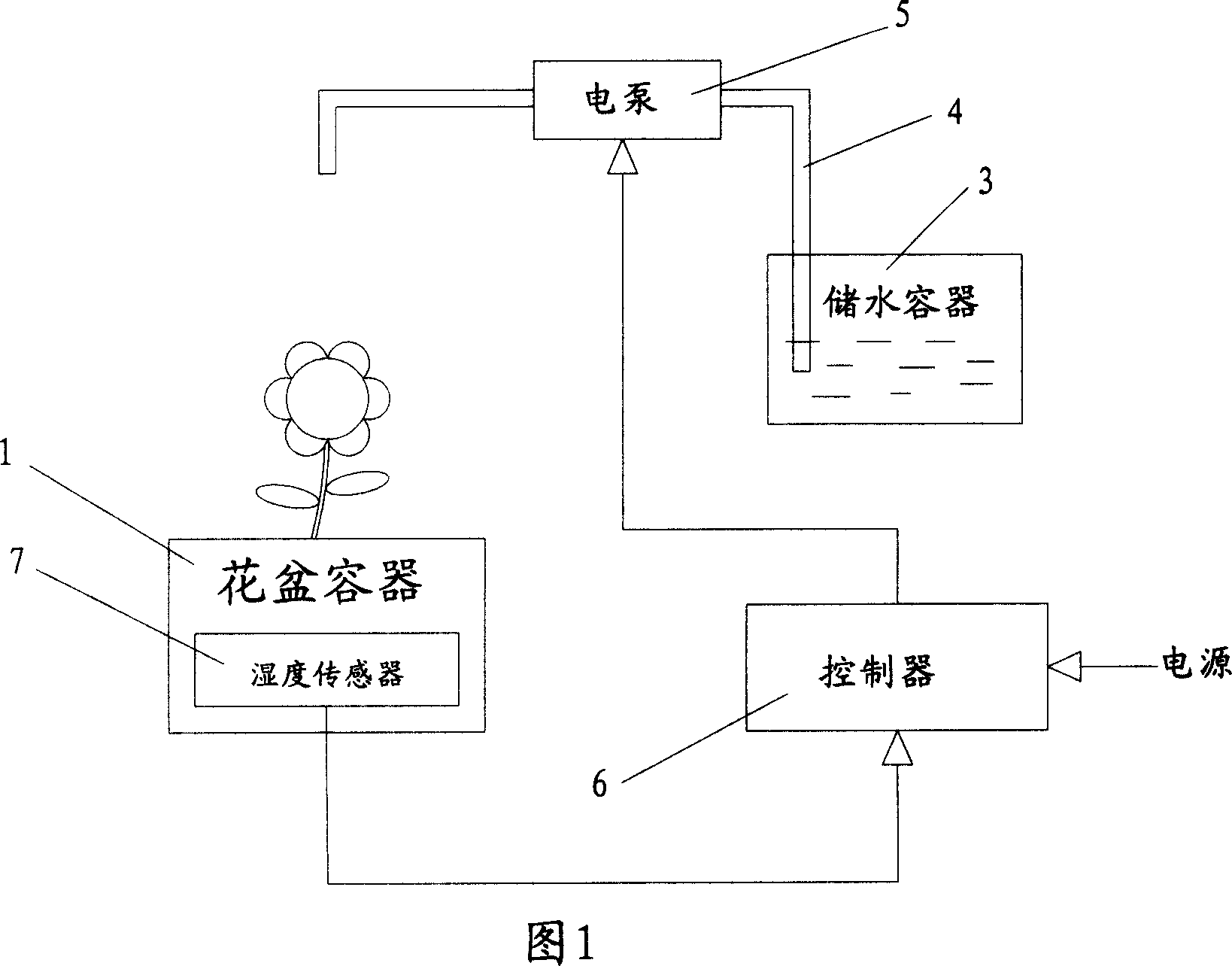
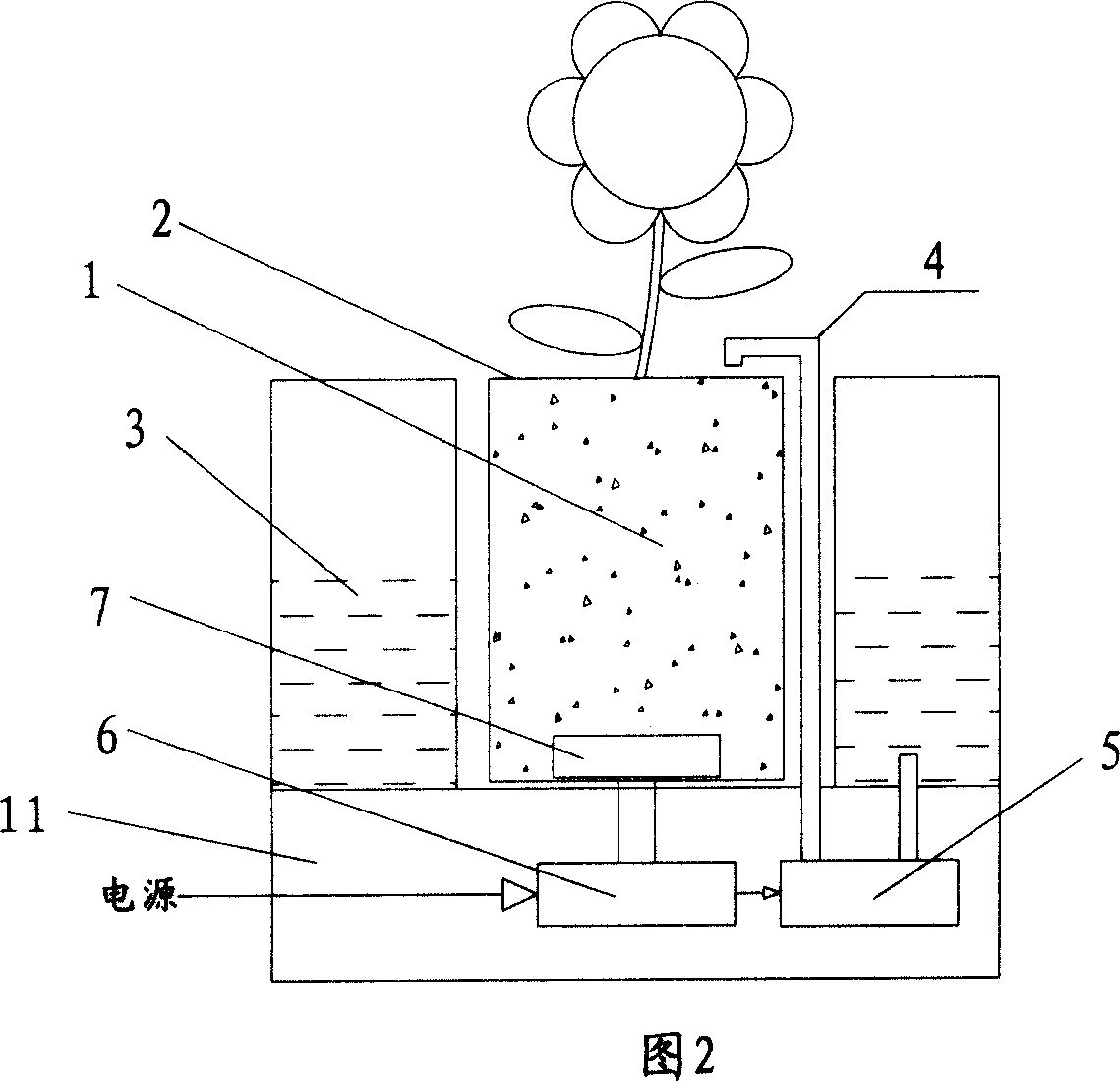
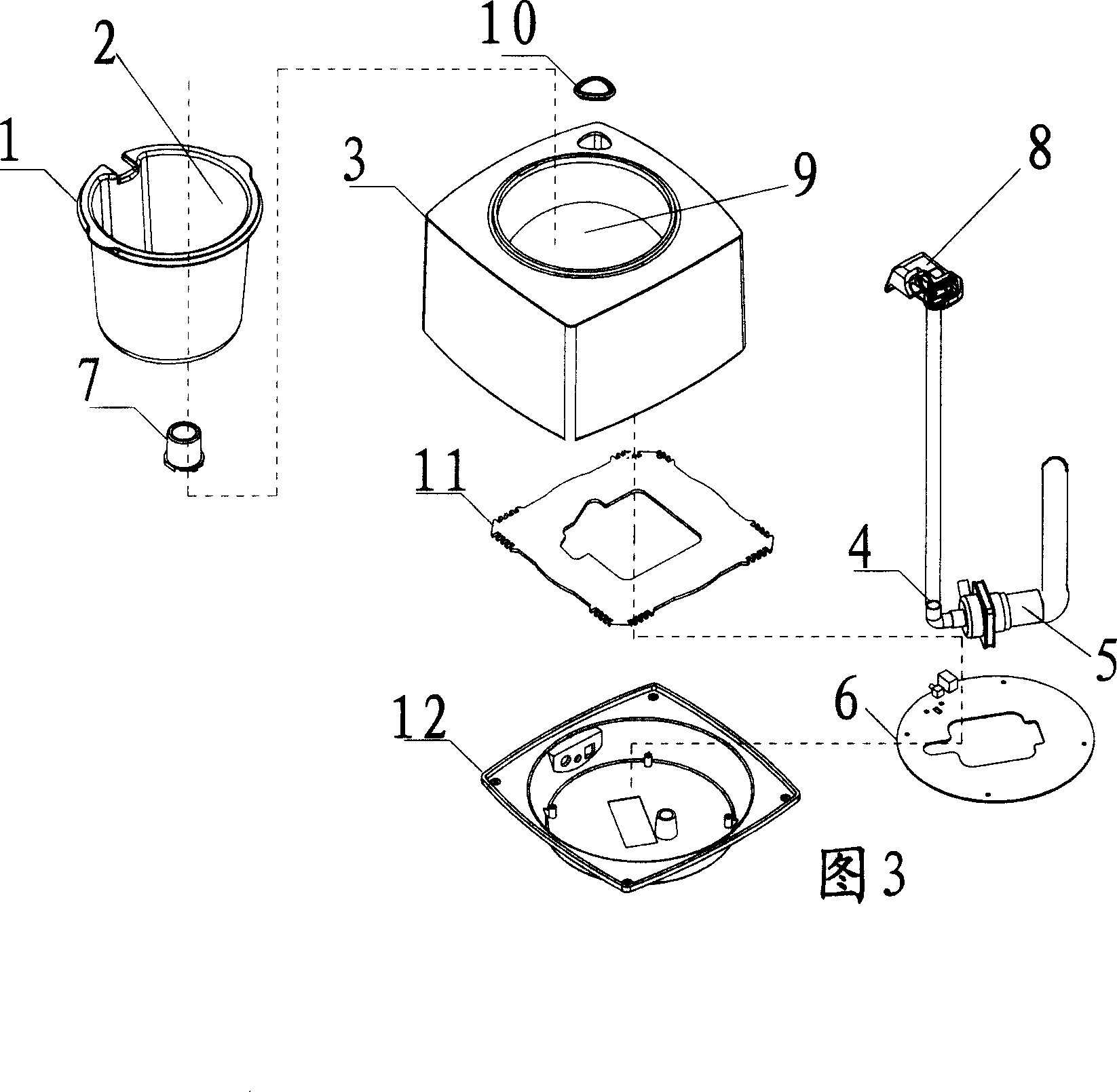
Flower pot with automatic watering function
InactiveCN101057546AEasy to producePrecise and reliable controlWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsWater sourceEngineering
The invention discloses a self-watering flowerpot, which comprises the following parts: flowerpot container with hole on the upper end to place soil, water reserving container besides the flowerpot container to reserve water, water delivery pipe with pump with one end extended into the water reserving container, controller to connect and control the pump on the water delivery pipe, wherein the soil moisture in the flowerpot container is less than the minimum value, the controller controls the pump to transmit water from the container to flowerpot; a moisture sensor is assembled in the soil of flowerpot container to sense the moisture of soil and transmit the detected signal to the controller, which controls whether to water the flowerpot. The invention improves intelligent degree without influenced by plant and environment, which is beneficial to grow with strong ornamental and decorative effect.
Owner:黄翔宇
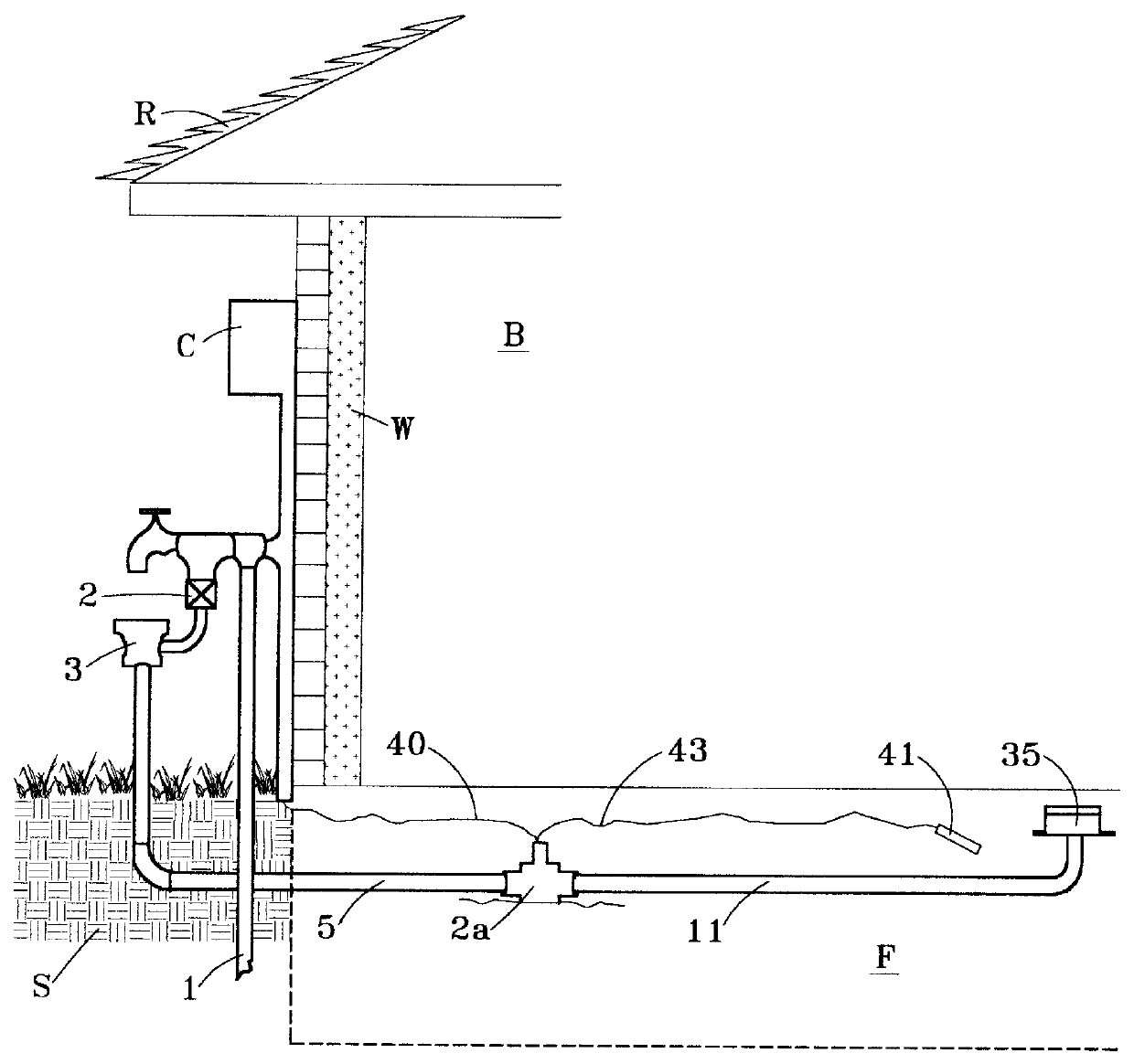
Apparatus for monitoring and regulating soil moisture
InactiveUS20070267515A1Precision wateringImproved and simplified and low-cost constructionSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesPlant rootsEngineering
A water moisture sensing and watering apparatus including a housing having a water chamber that is at least partially evacuatable. A porous sensor is communicably connected to the chamber. When the moisture in the soil is sufficiently high, the pores of the sensor filled sufficiently to become plugged so that a vacuum or low-pressure region and water are maintained within the chamber. When the moisture of the soil drops below a predetermined level, the moisture in the pores is pulled out by the soil and plant roots sufficiently for air to be transmitted through the pores of the sensor into the chamber, increasing pressure in the chamber and providing an indication that water is needed in the soil and, in certain embodiments, automatic watering the soil and plant roots.
Owner:SARGENT RONALD J
Untethered Irrigation Device and Method
InactiveUS20150359185A1Autonomous decision making processWatering devicesWater storage tankEngineering
A device for irrigating soil has a chassis having wheels or tracks for motion, the chassis having one or more water sprinklers with streams directed at the soil, a water storage tank, and a sloped catchment surface having one or more sloped planes or curved surfaces for receiving water from a refill station into the water storage tank, wherein, under the control of an electronic circuit, the irrigation device can refill the water tank by positioning any part of the catchment surface under a water stream from the refill station. A method has the steps of measuring soil moisture at remote locations, refilling the mobile robot using a gravity feed water stream, defining a route for distribution of water, traversing the irrigation routes, refilling water according to soil moisture measurements, storing photovoltaic energy in a battery, and rotating, to a compass heading such that the photovoltaic array is optimally oriented.
Owner:GUY JONATHAN
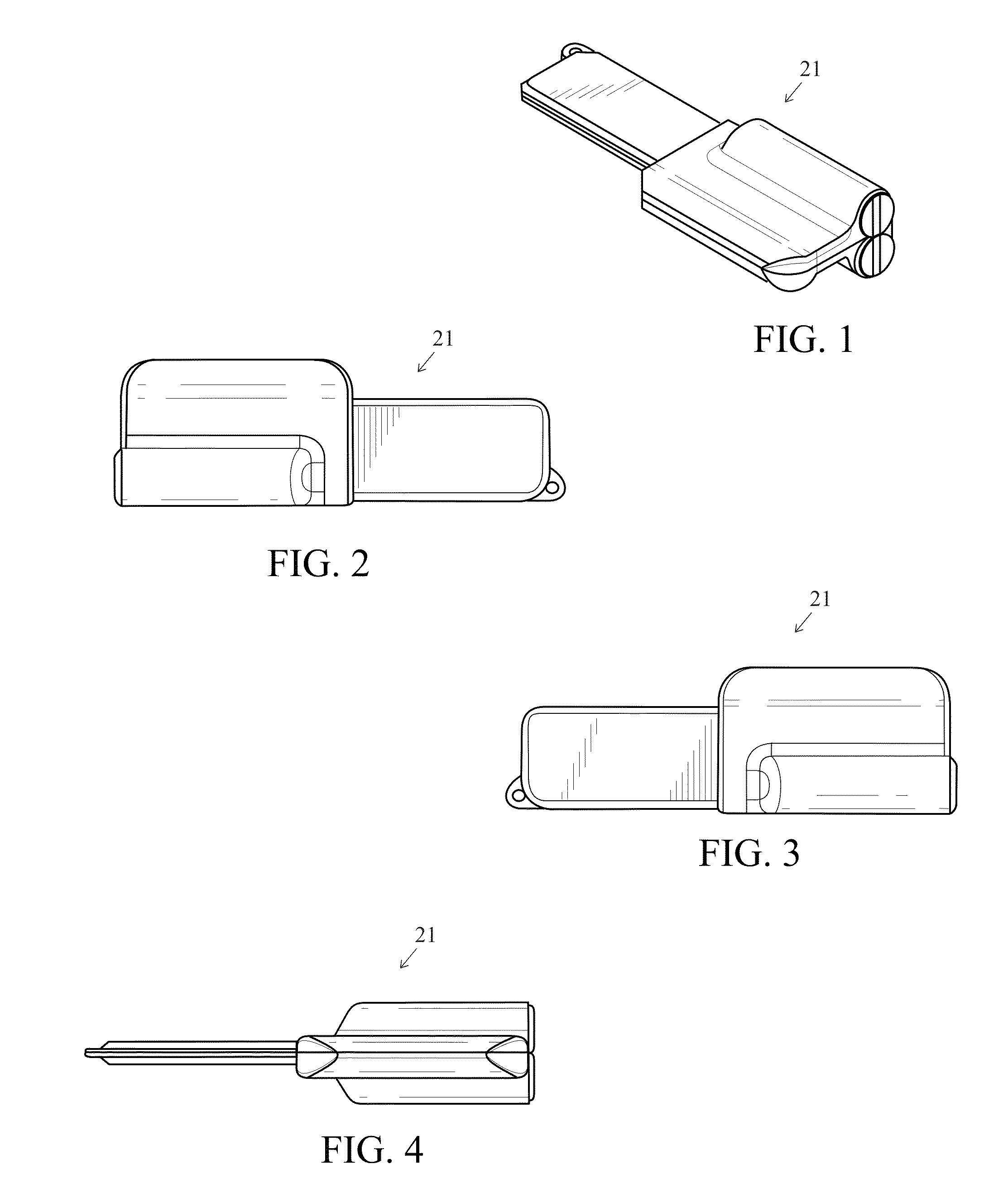
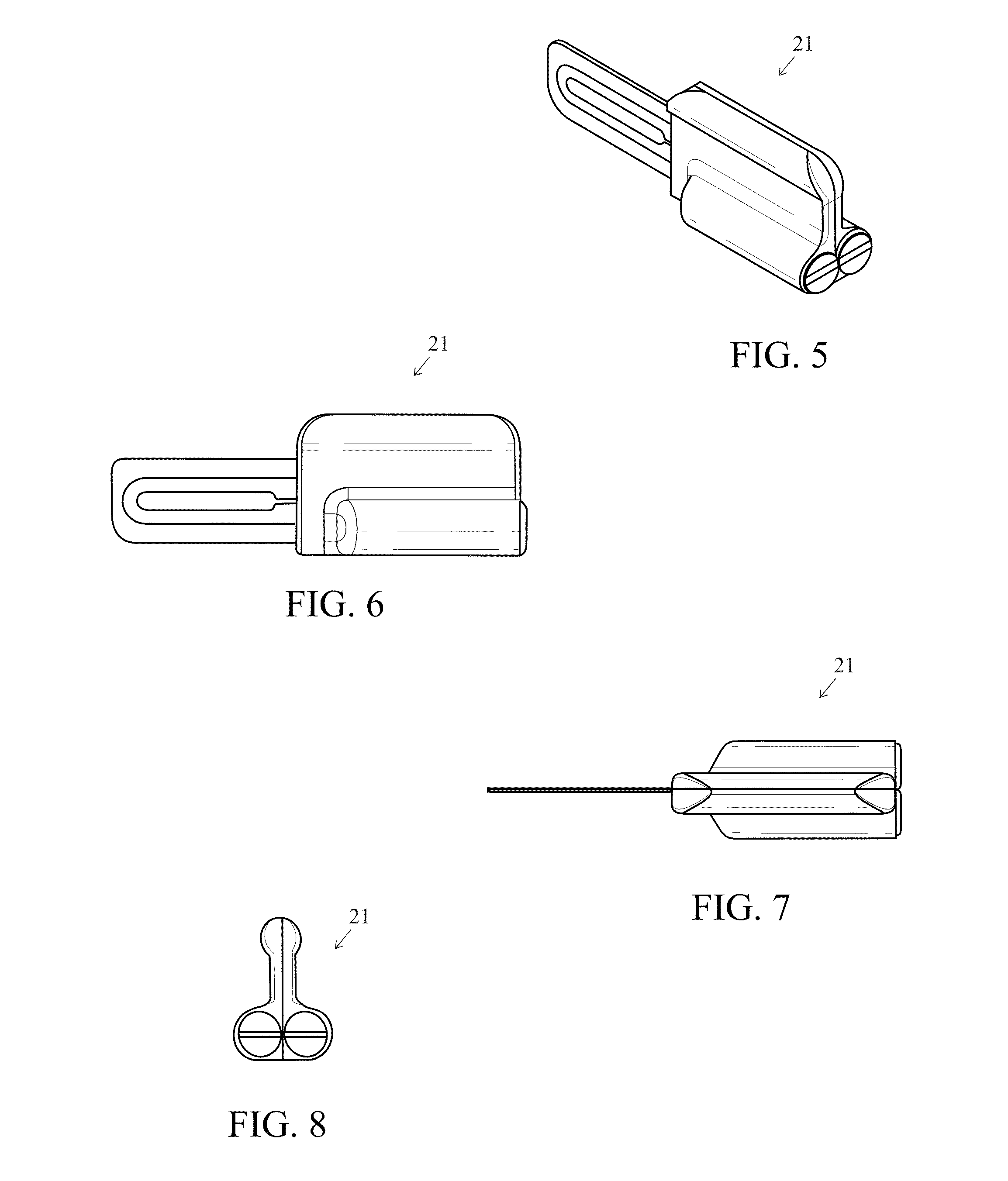
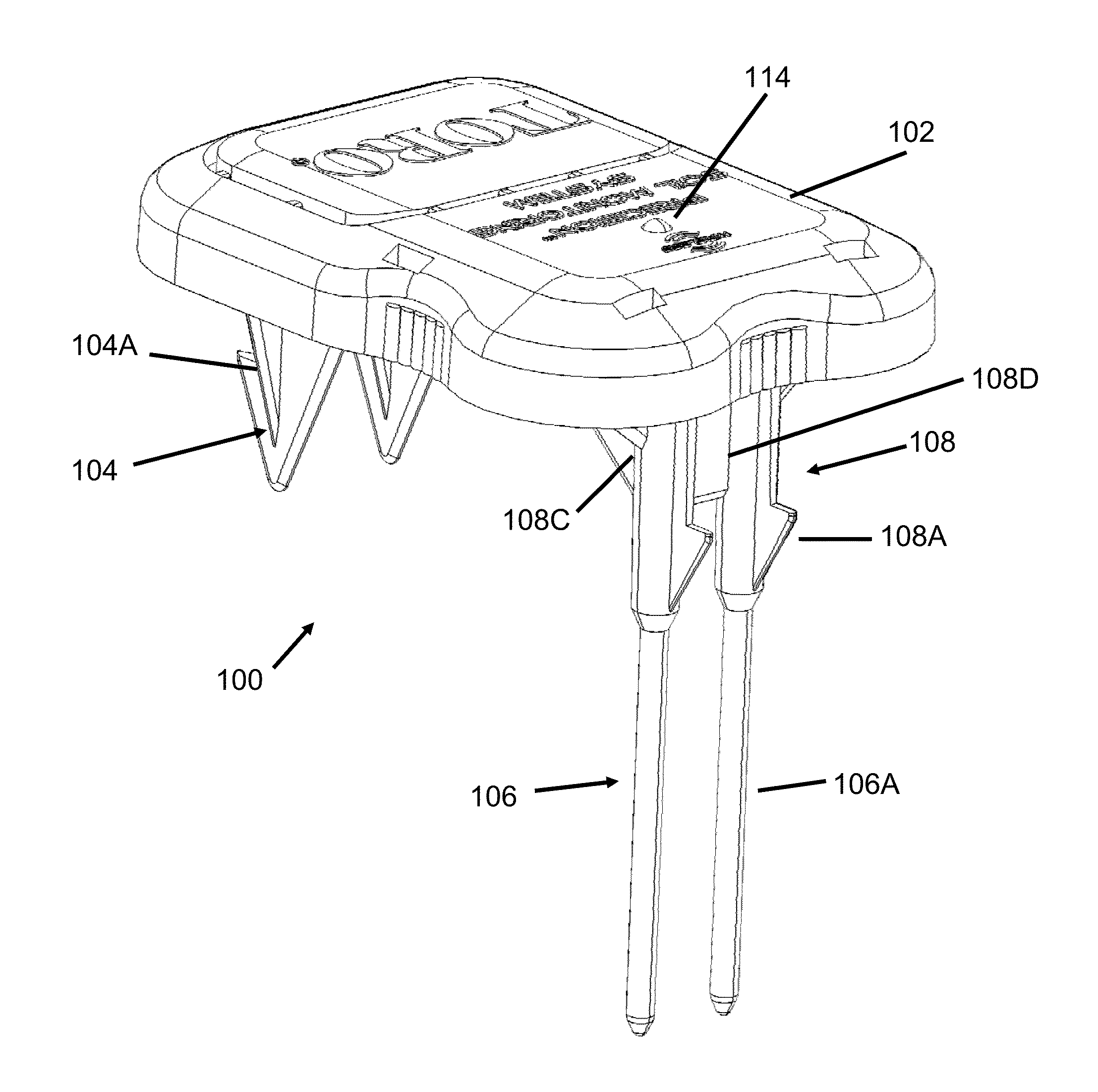
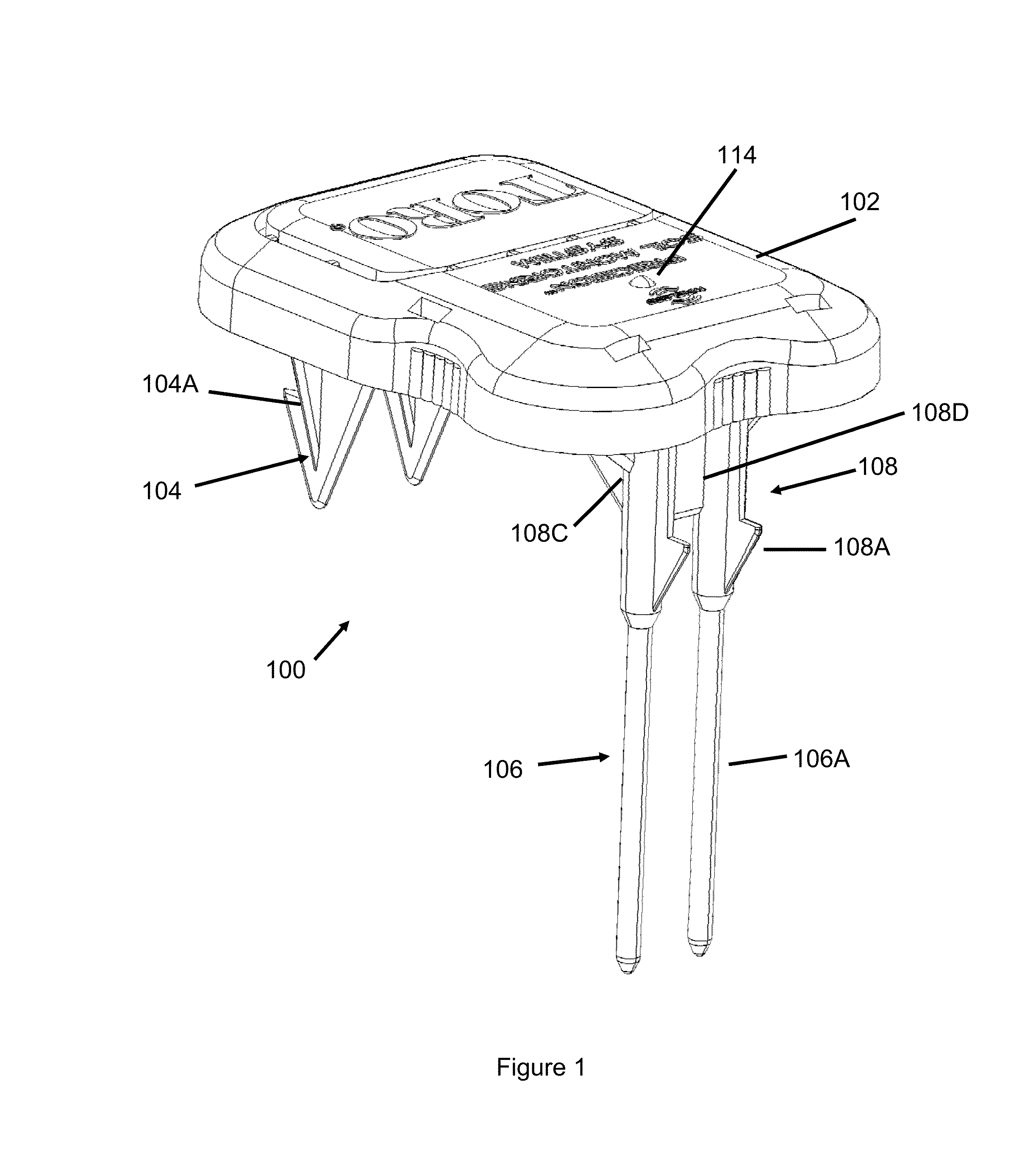
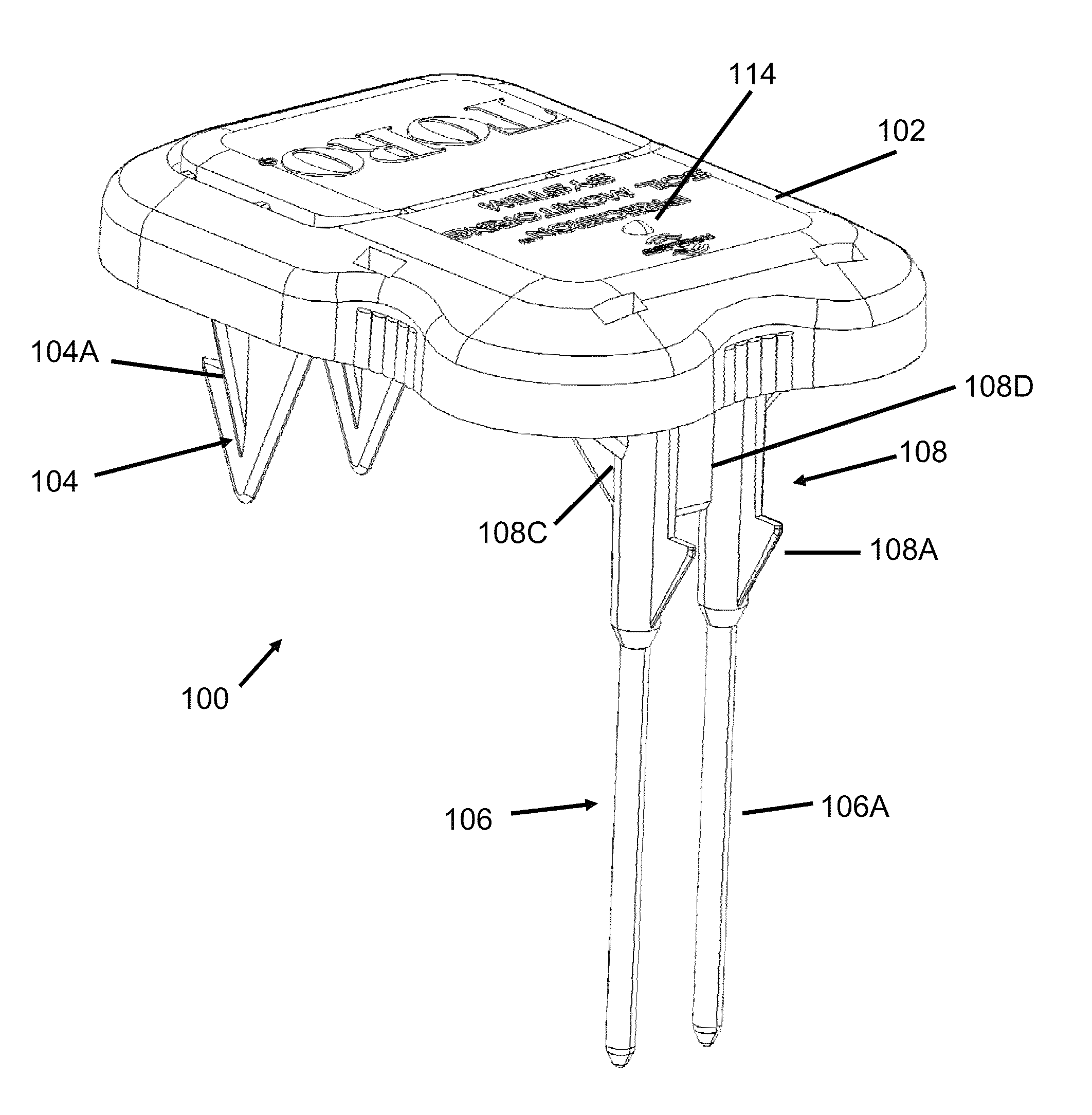
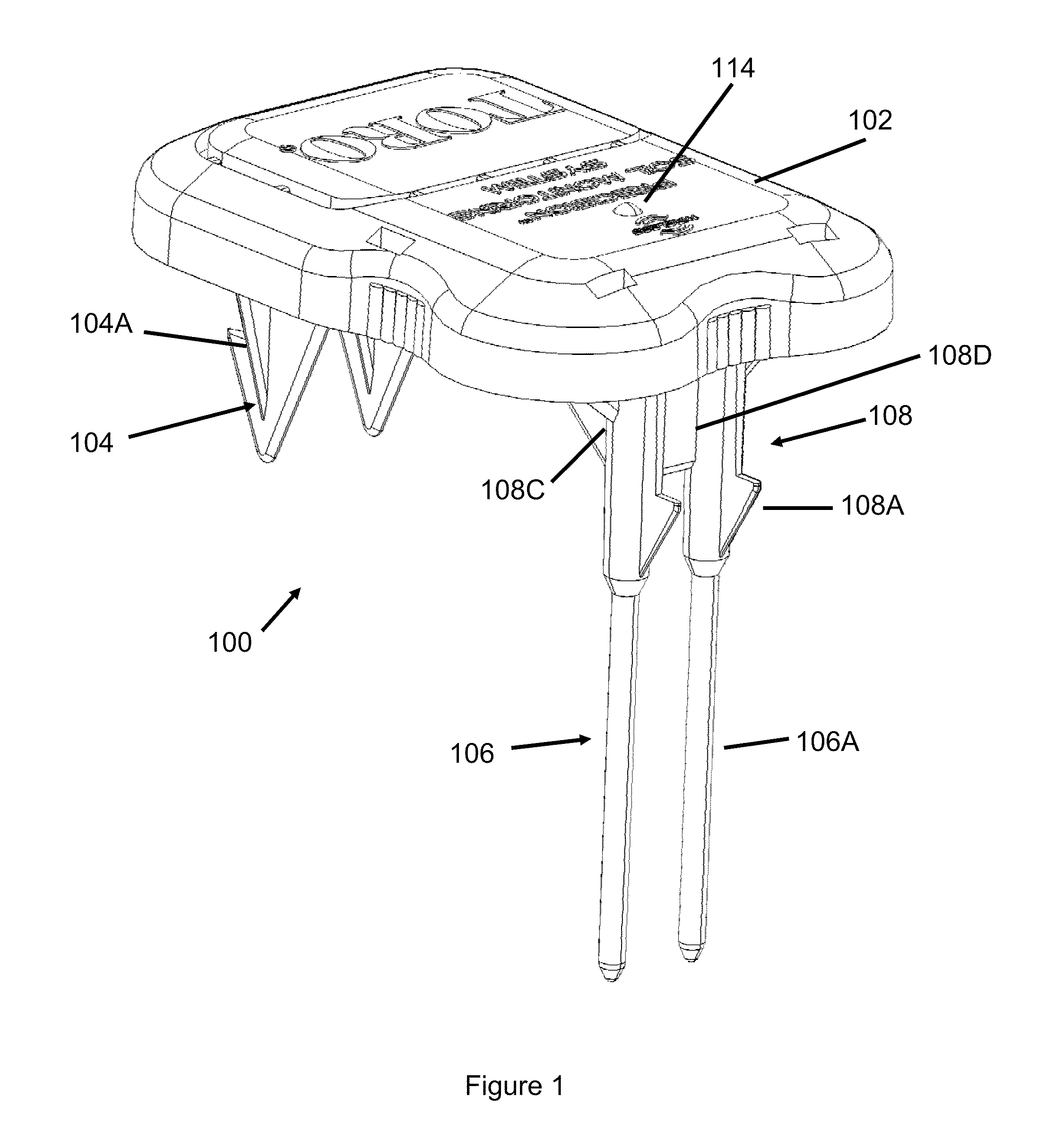
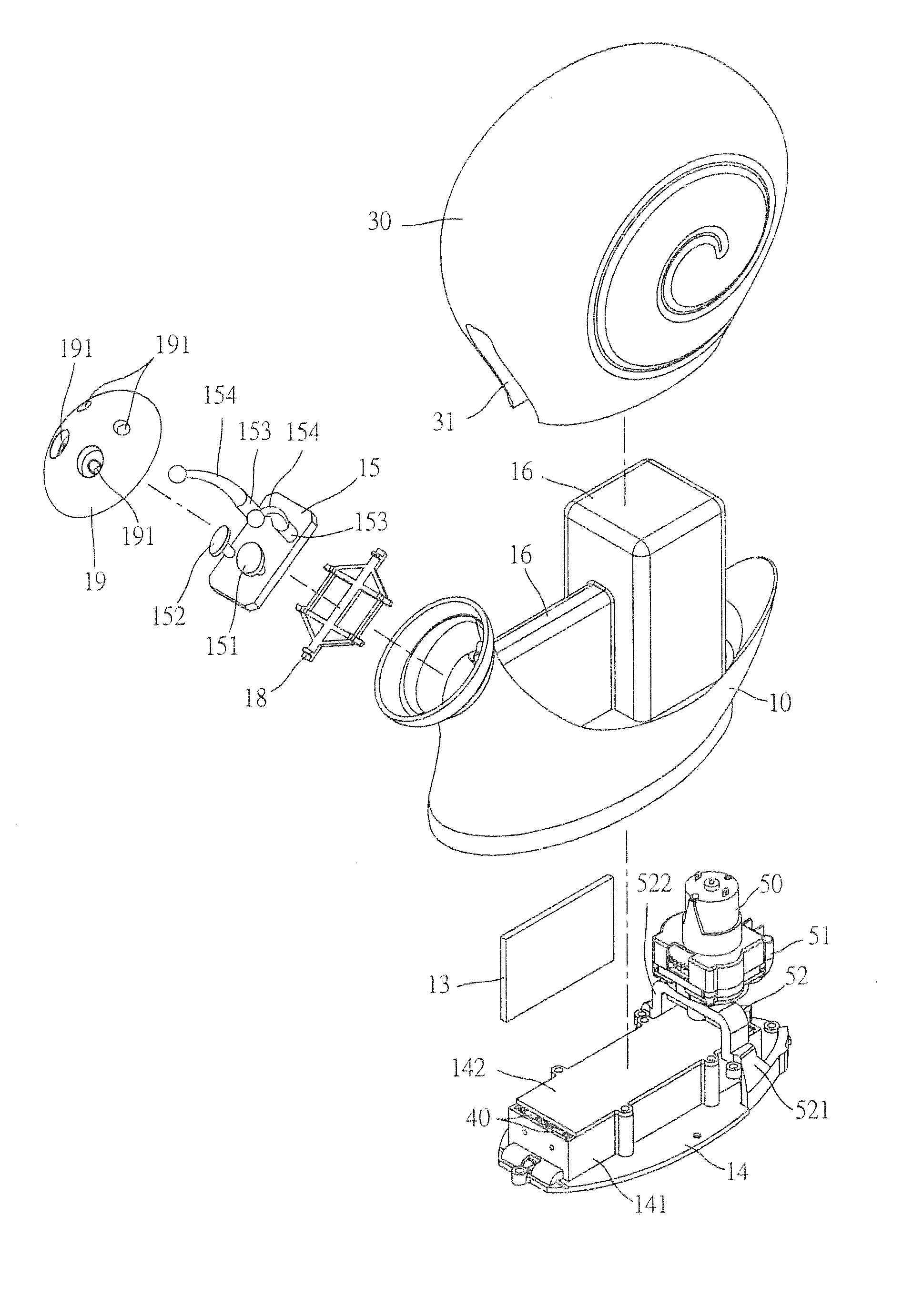
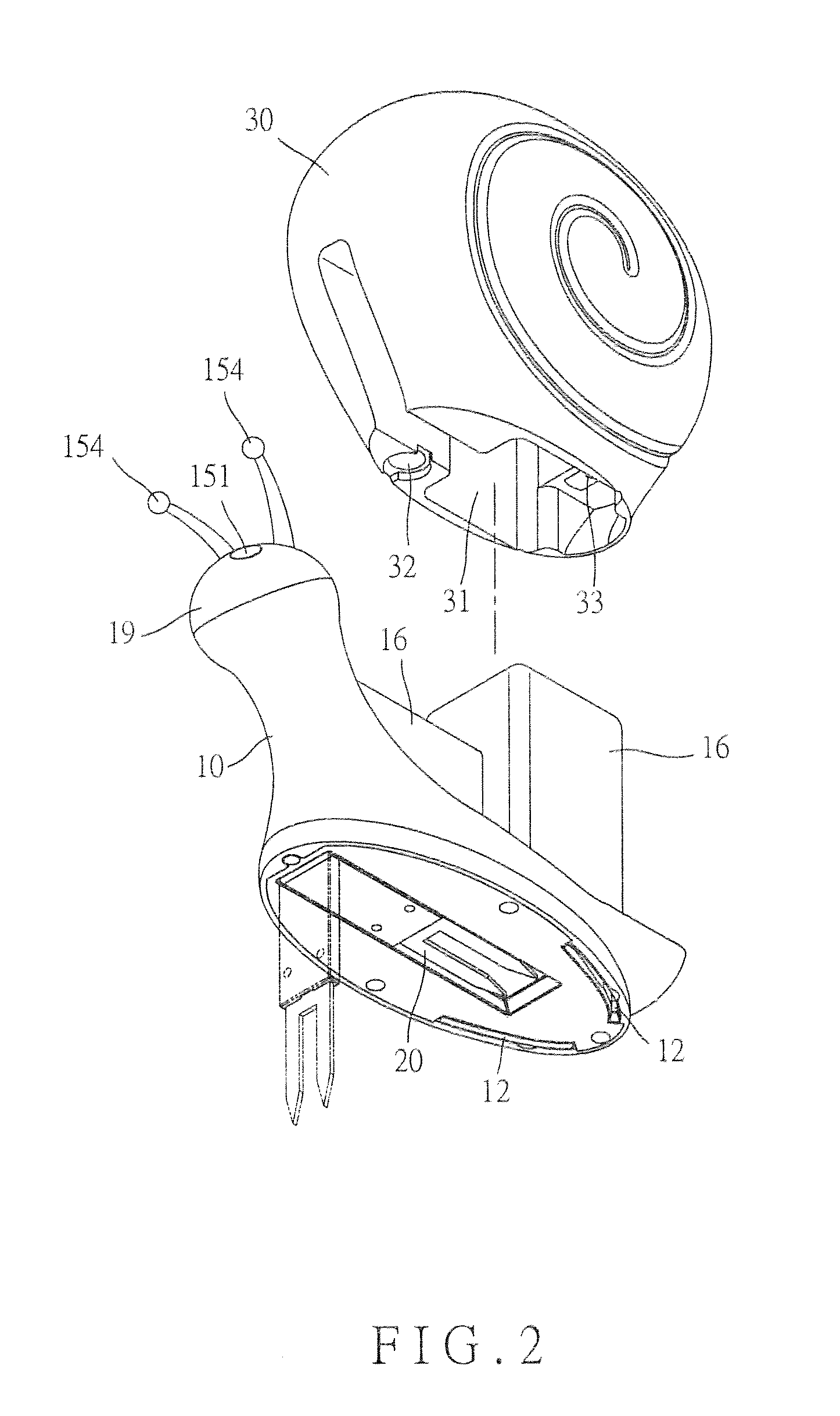
Soil Moisture Sensor
ActiveUS20130255783A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWatering devicesSoil moisture sensorEngineering
In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a soil moisture sensor for interrupting an irrigation schedule of an irrigation controller. The moisture sensor comprises a relatively flat body with two lower electrodes and two lower anchoring barbs. A receiver receives moisture readings from the sensor and compares moisture data to a predetermined moisture interrupt value or limit, over which irrigation is interrupted.
Owner:TORO CO THE
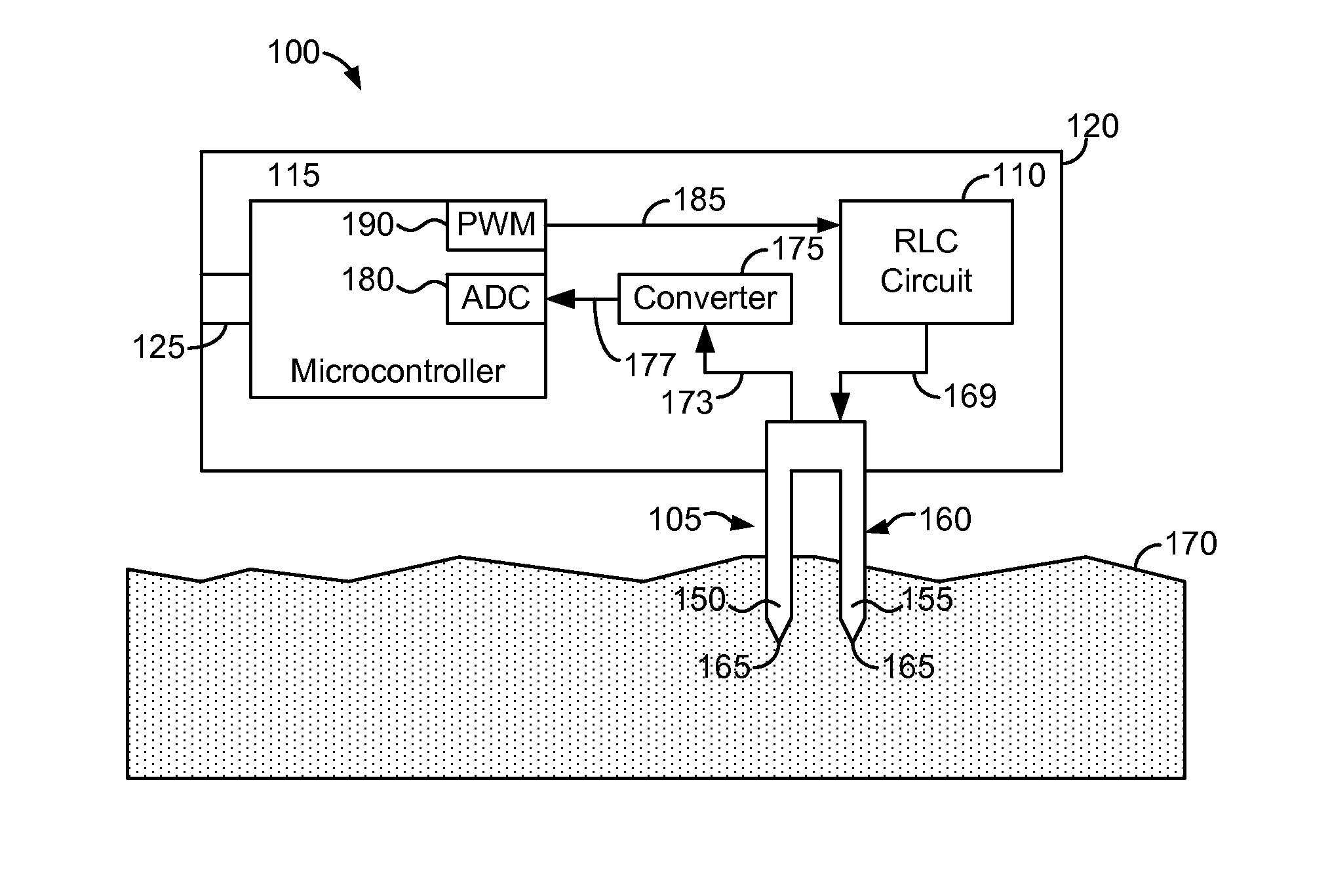
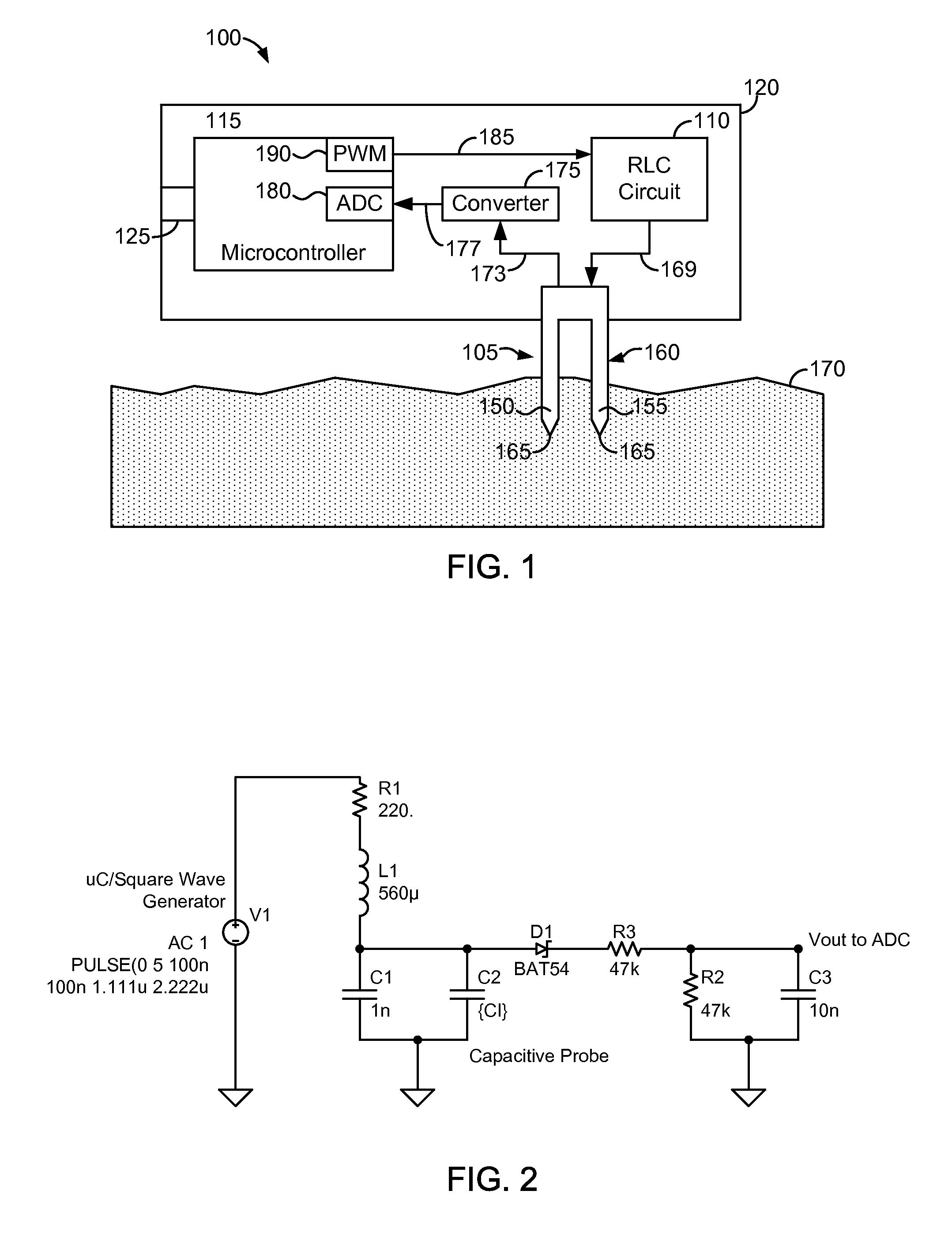
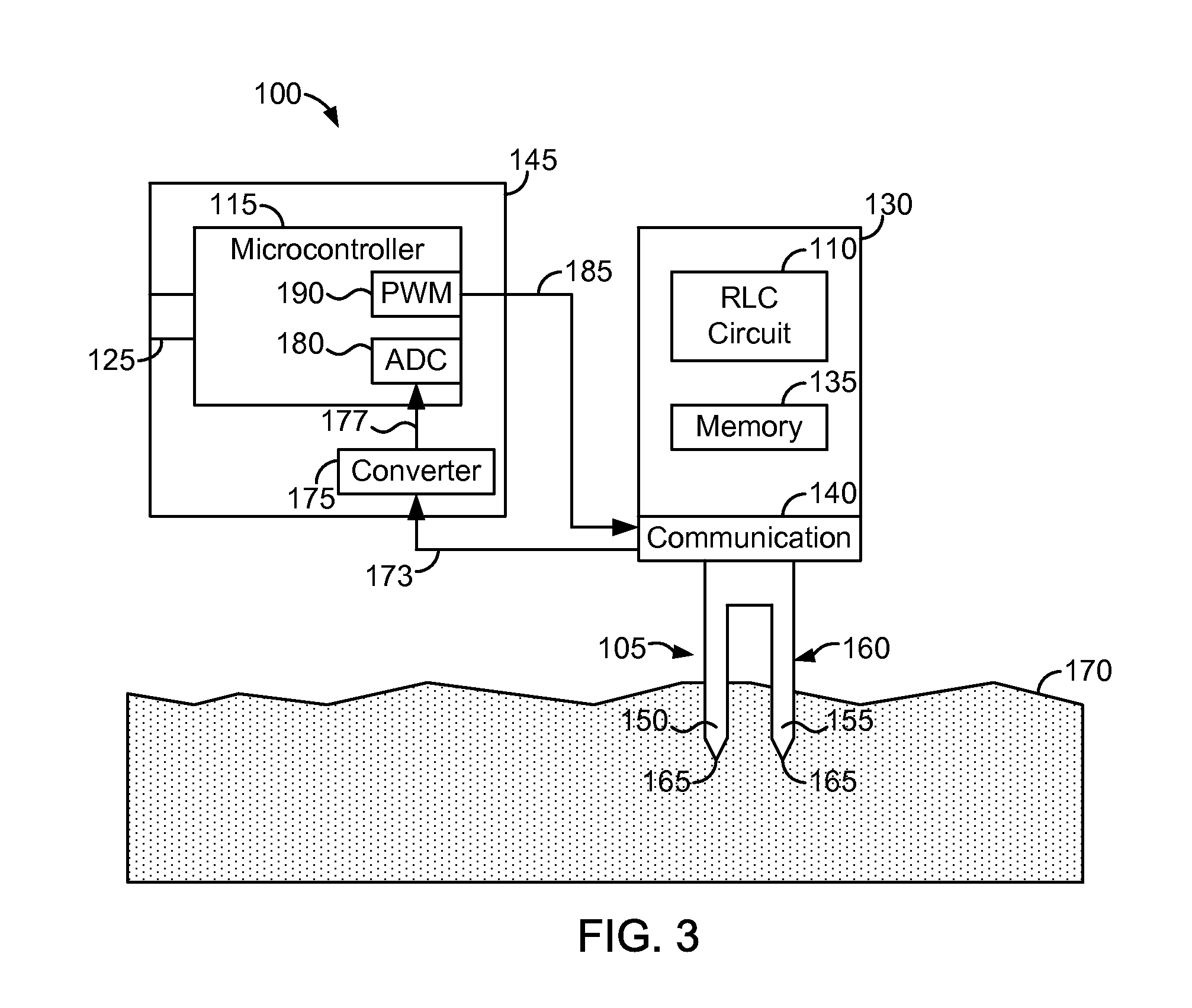
Soil moisture sensor
A soil moisture sensor includes a capacitive probe configured to be inserted into soil, a series RLC circuit electrically coupled to the capacitive probe, a microcontroller configured to determine the capacitance value of the soil and determine the moisture content of the soil from the capacitance value of the soil.
Owner:OY FISKARS AB
Soil moisture sensor
Owner:TORO CO THE
Rice dry-farming direct-seeding planting method
InactiveCN101785414ASimplify field operationsReduce production laborClimate change adaptationOrganic fertilisersNutrientDecomposition
The invention provides a rice dry-farming direct-seeding planting method, which is characterized by comprising the following: a, a step of preparing land, which is to level and harrow land before sowing, replenish pre-sowing water and keep soil moisture between 75 and 85 percent; b, a step of sowing, which is to uniformly sow rice seeds on the land finished in a step a, wherein the amount of seeds per each Mu of land is 2.5 to 5.4 kg; c, a step of earthing up, which is to earth up at a height of 1.5 to 3 centimeters after sowing is finished; d, a step of compacting, which is to compact after earthing up; and e, a step of spraying film, which is to add 0.03 to 0.06 kilogram of 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxy acetic acid serving as herbicide to 60 to 80 liters of water, mix and stir the materials and uniformly spraying the obtained product on the compacted land so as to finish the dry farming and direct seeding of rice. The rice dry-farming direct-seeding planting method can leave out two work links of cultivating seedlings and transplanting. After multifunctional degradable liquid mulching film is sprayed on ground, effective accumulated temperature can be increased; rice water shortage is alleviated; the physical and chemical properties of soil are improved; microbial activity is improved; the decomposition and release of soil organic substances are accelerated; the transfer of effective nutrient to plants is accelerated; and the photosynthetic efficiency and nutrient conveying rate of rice are improved. The method has the advantages of ensuring exuberant tillering tendency, low positions of tillering knobs and numerous big ears, saving water by 50 to 70 percent and increasing yield by about 10 percent.
Owner:于飞
Comprehensively intelligent irrigation method and system for artificial vegetation ground
InactiveCN104285762AGuaranteed healthy growthSave human effortClimate change adaptationWatering devicesSoil typeVegetation
The invention relates to a comprehensively intelligent irrigation method and system for the artificial vegetation ground. The comprehensively intelligent irrigation method and system are used for solving the problems that water is wasted, and irrigation quality cannot be guaranteed in the prior art. The comprehensively intelligent irrigation system comprises a plurality of paralleled irrigation terminals of an automatic irrigation network installed on the artificial vegetation ground, one or more soil moisture content probes are buried in irrigation area soil covered by each irrigation terminals of the automatic irrigation network, and an automatic switching mechanism is independently arranged on each irrigation terminal. The soil moisture content probes are connected and control the automatic switching mechanisms which the soil moisture content probes belong to and are connected and control the irrigation terminals through a central intelligent control system. The central intelligent control system determines the lower limit of the soil moisture content in the corresponding irrigation area according to types of vegetation or the types of vegetation and types of soil in each irrigation area. The central intelligent control system switches on the irrigation terminals in the corresponding irrigation area to carry out irrigation when the soil moisture content probes detect that the soil moisture content in the corresponding irrigation is lower than the lower limit of the moisture content. The comprehensively intelligent irrigation method and system have the advantages that automatic irrigation and fertilizer application as required can be achieved according to actual needs of the soil and the vegetation in the irrigation areas, water is saved obviously, labor is saved, irrigation quality is guaranteed, and healthy growth of the vegetation in the irrigation areas can be guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING KANGZHIWEI SCI & TECH
Protecting element for resisting drought, preventing disease, detoxicating and improving the growth of the plant
InactiveCN101116448AIncrease profitSolve the difficult problem of viral diseasesBiocidePlant growth regulatorsTrace element compositionDisease
The invention discloses an anti-drought, anti-disease and detoxication plant growth and protection chemical, which consists of moisturizing agent, virus tolerance agent, growth accelerating agent, nitrogen synergist, nutrient activating agent, humic acids, nitric acid rare earths and medium microelement; the moisturizing agent which undergoes the copolymerization reaction, decompression and drying processes is evenly mixed with other constituents according to a certain percentage, then the mixing agent undergoes measuring and packaging processes to become the anti-drought, anti-disease and detoxication plant growth and protection chemical. The invention combines all special activities of all constituents, achieves best comprehensive and balance functions, gives full play to the corresponding united and synergistic effects of all constituents, improves plant physiological functions, boosts plant growth and development, prevents and cures plant diseases, removes toxins from plant body, keeps soil moisture, activates soil nutrients, increases utilization rate of fertilizers, prolongs fertilizer efficiency period and lowers pollution on the environment. The invention is capable of being used with other fertilizers, which resolves the problem of the comprehensive and balance fertilization, creating or improving the living conditions needed for plant growth and protection, lowering costs caused by such harms as drought and diseases etc. and greatly increasing the crop yield.
Owner:丁肇珊
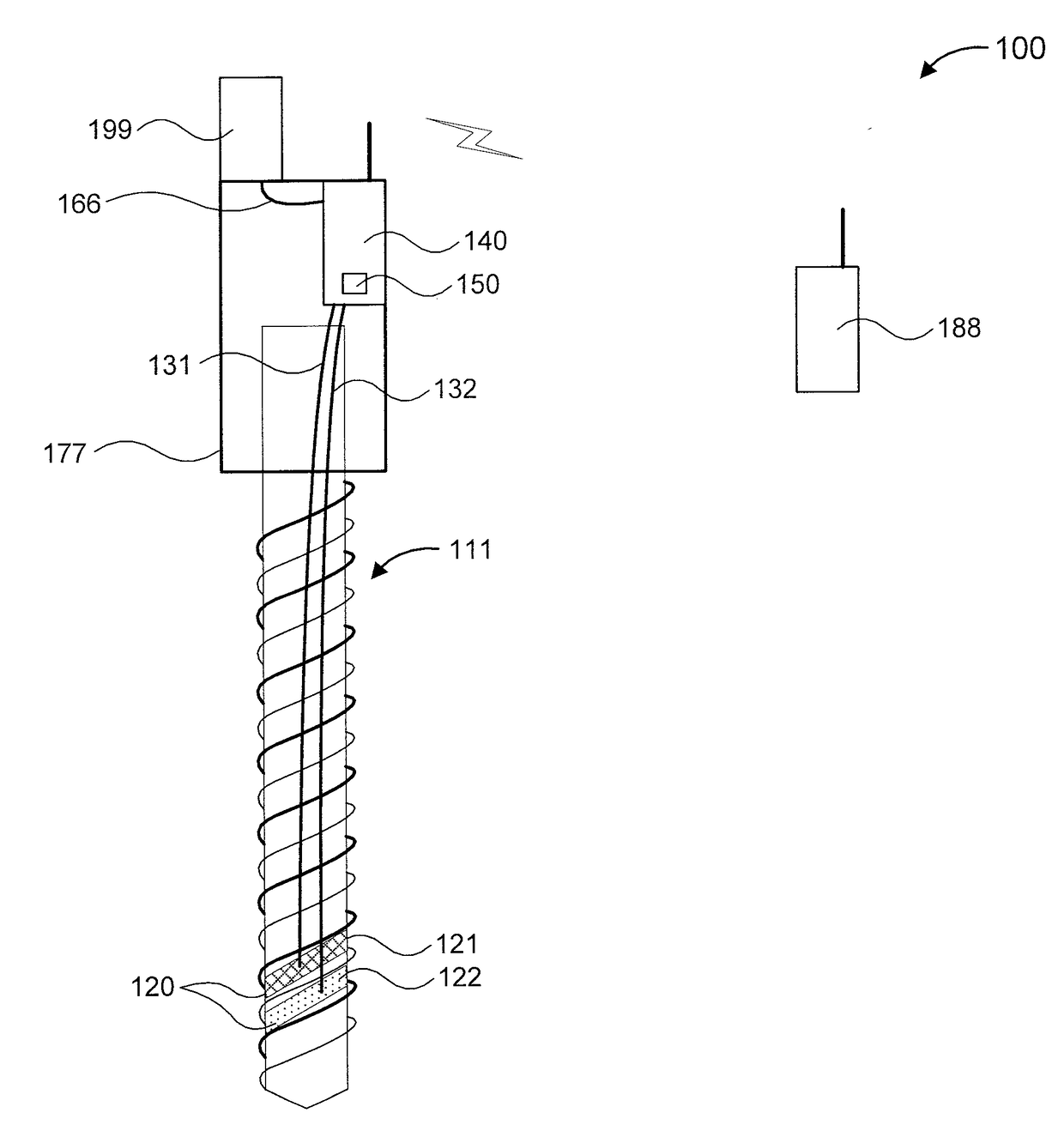
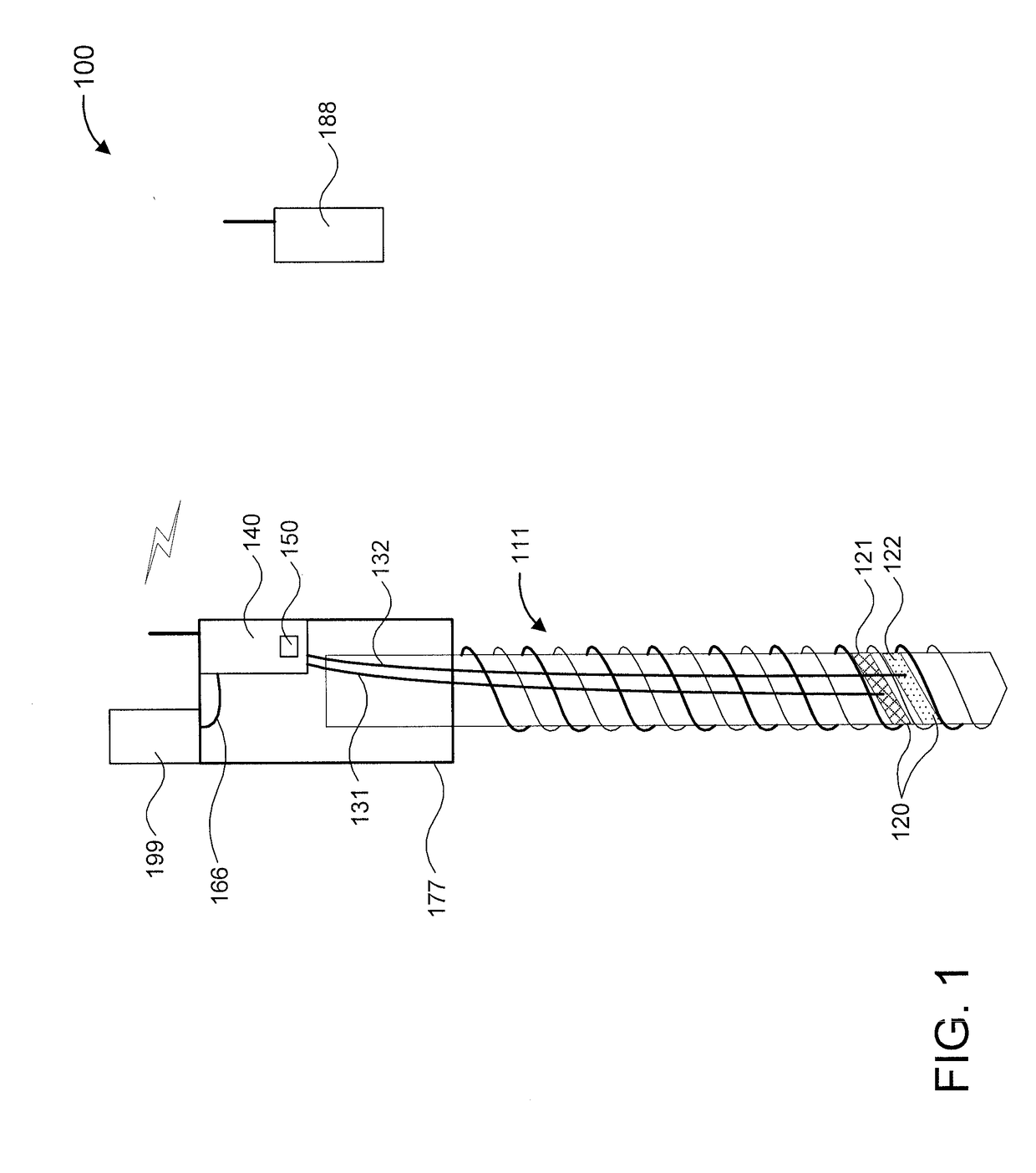
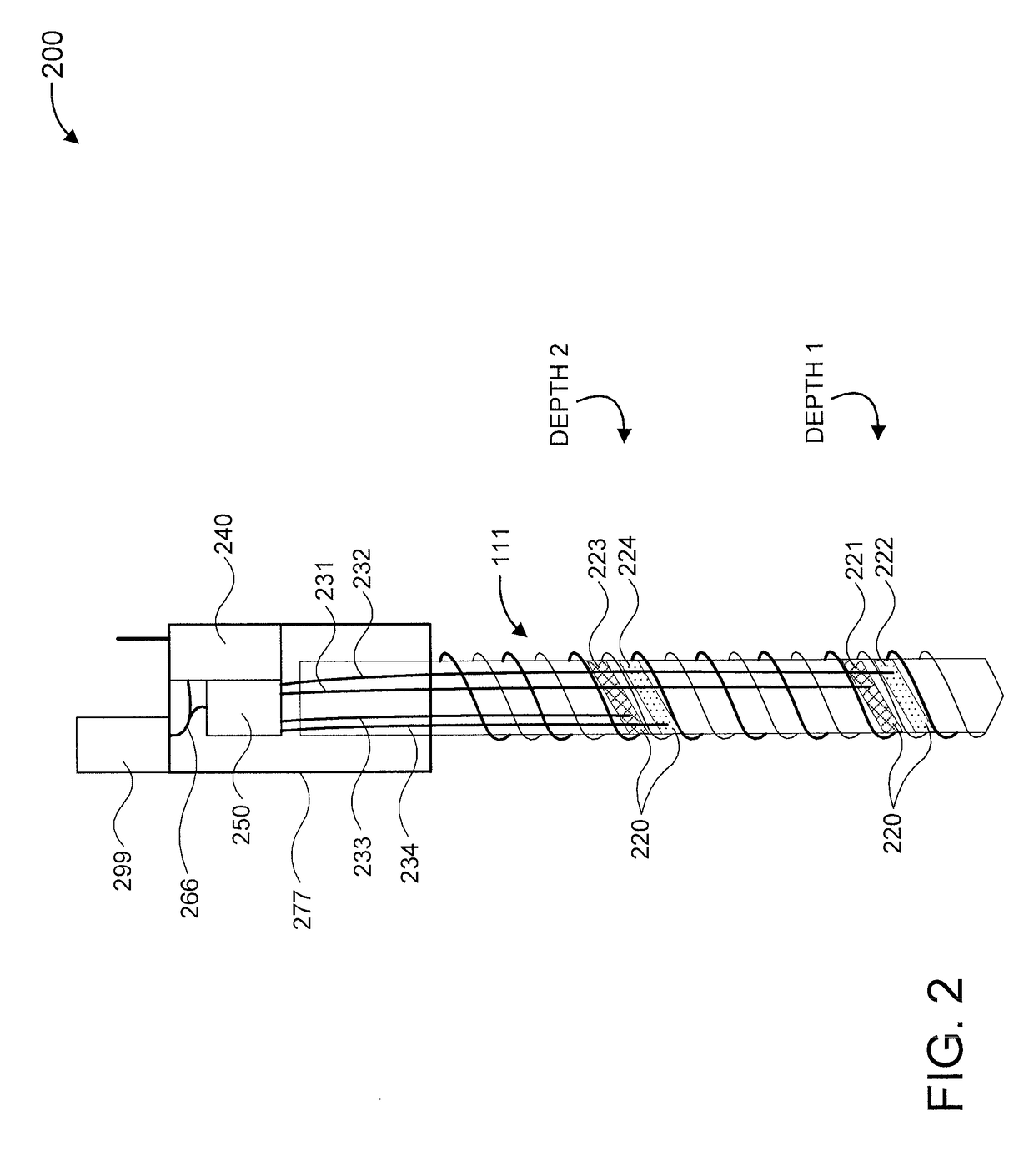
Soil moisture probing at variable depth
A soil moisture sensor and a soil moisture sensing system are provided. The soil moisture sensor includes a double groove helical structure having grooves and formed from an insulator. The soil moisture sensor further includes at least a first electrode and a second electrode formed from one or more metals deposited at at least two different locations on the grooves. The soil moisture sensor also includes a processor for processing a soil moisture measurement signal based on a conductivity between the electrodes. The soil moisture sensor additionally includes a wireless transmitter for transmitting the soil moisture measurement signal to a remote location.
Owner:IBM CORP
Irrigation system with et based seasonal watering adjustment and soil moisture sensor shutoff
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
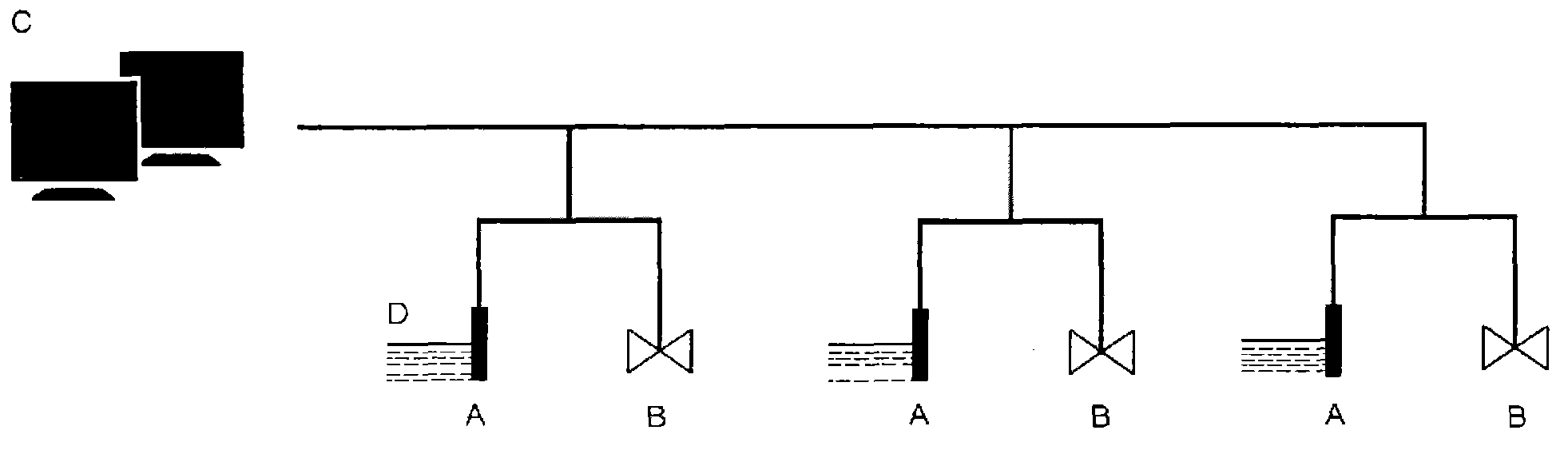
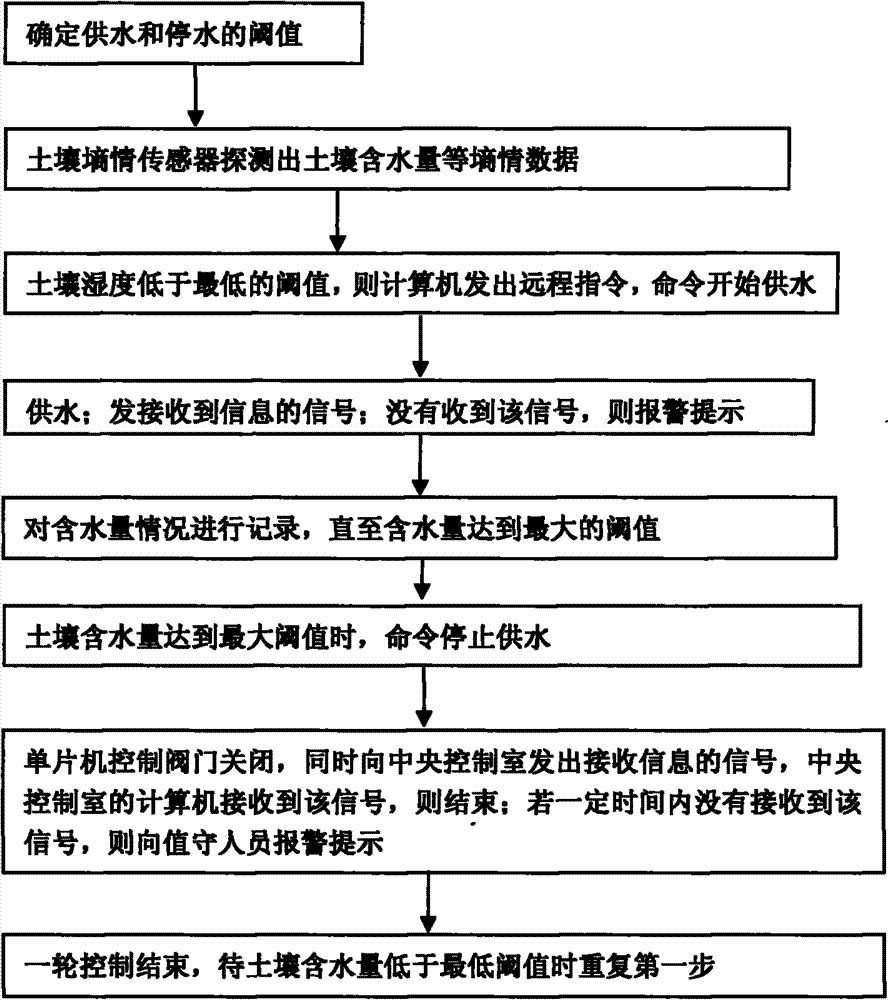
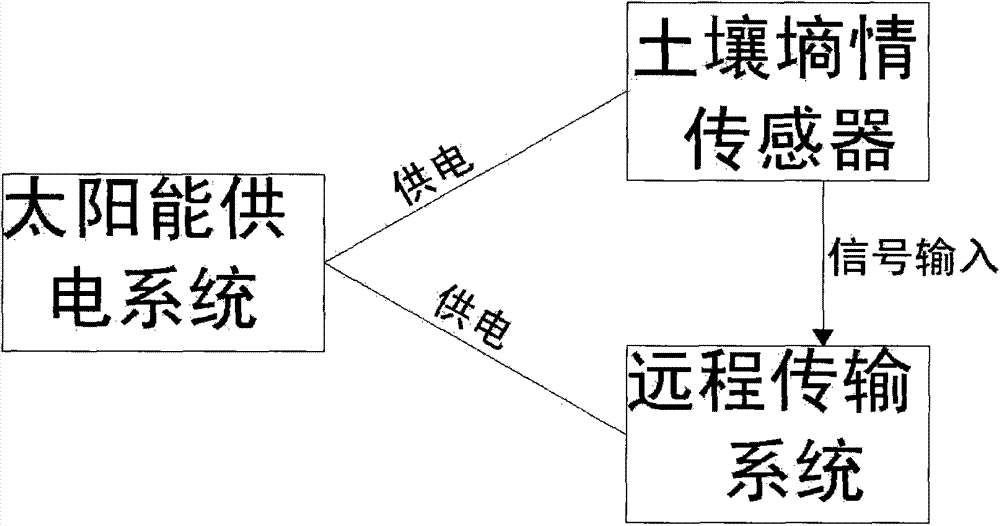
Passive water-saving irrigation method and facilities thereof
InactiveCN103583318AAccurate and reasonable useReduce workloadWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsMicrocontrollerEngineering
The invention discloses a passive water-saving irrigation method and facilities thereof. The method includes the steps that the step 1, threshold values for water supply and stop of the water supply are determined; the step 2, soil moisture contents like soil moistures are detected; the step 3, water is supplied when the soil moisture content is lower than the lowest threshold value; the step 4, signals receiving information are sent and received, and if the signals are not received, alarming and prompting are carried out; the step 5, the water content is recorded until the water content reaches the largest threshold value; the step 6, an instruction for stopping water supply is sent; the step 7, a single-chip microcomputer controls a valve to be closed, if a computer in a central control room receives the signals, the water supply is stopped; and if the signals are not received, the alarming and the prompting are carried out; the step 8, first-round control is stopped, and the step 1 is repeated when the soil moisture content is lower than the lowest threshold value. The passive water-saving irrigation facilities comprise a soil moisture content sensor part, the central control room part and an electric valve switching part. According to the passive water-saving irrigation method and the passive water-saving irrigation facilities, labor intensity is reduced, labor cost is saved, working environments are improved, accurate irrigation is achieved, water resources are utilized reasonably and efficiently, and waste and secondary pollution will not happen.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Iron tailing soil formation method
InactiveCN109168391AAvoid Waterlogging ProblemsLower the water tableFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentEngineering
The invention relates to an iron tailing soil formation method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) a tailing is leveled: a tailing site is leveled; (2) a ditch is arranged for drainage; (3) additive adding and tillage are carried out: a water retaining agent and an amendment are added below the surface of the iron tailing, and tillage is carried out; (4) a microbialagent is applied: the microbial agent is sprayed; (5) a plant is planted or cultivated; and (6) irrigation and maintenance are carried out: soil moisture is kept, a straw mat is laid for herbaceous plants, and effects of high temperature are alleviated. The construction method is simple, the price is reasonable, the greening effects are quick, the method is in line with local conditions, the application range is wide, the construction is easy, resources are saved, the greening effects are good, the tree survival rate can reach 90 to 95%, the survival rate of the herbaceous plants can reach 95to 98%, and the method can be applied to tailing soil formation greening projects in different areas, and has strong popularization and application.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
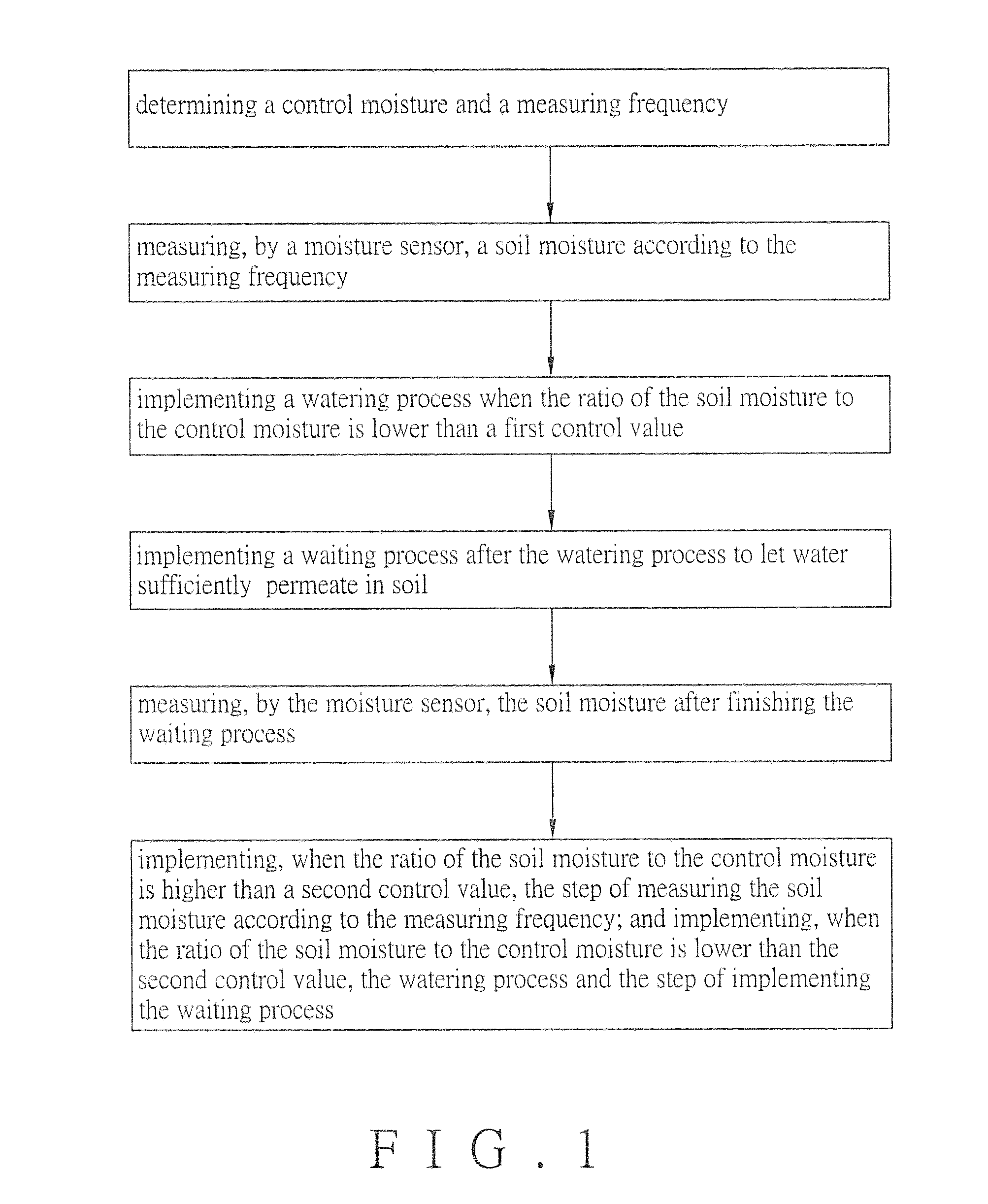
Watering control method by monitoring soil moisture
InactiveUS20150201570A1Impede acquisitionAvoid witheringWatering devicesPipeline systemsMoisture sensorSoil moisture content
The invention provides a method of controlling watering by monitoring soil moisture, including the steps of: determining a control moisture and a measuring frequency; measuring a soil moisture according to the measuring frequency by a moisture sensor; implementing a watering process when the ratio of the soil moisture to the control moisture is lower than a first control value; implementing a waiting process after the watering process; measuring the soil moisture using the moisture sensor after finishing the waiting process; and implementing the step of measuring the soil moisture according to the measuring frequency by the moisture sensor when the ratio of the soil moisture to the control moisture is higher than a second control value, and implementing the watering process and the step of the waiting process when the ratio of the soil moisture to the control moisture is lower than the second control value.
Owner:LIN MOU LI +2
Method of determining surface level, and a soil moisture sensor
ActiveUS8915131B2Accurate measurementSurveyClimate change adaptationSoil scienceSoil moisture sensor
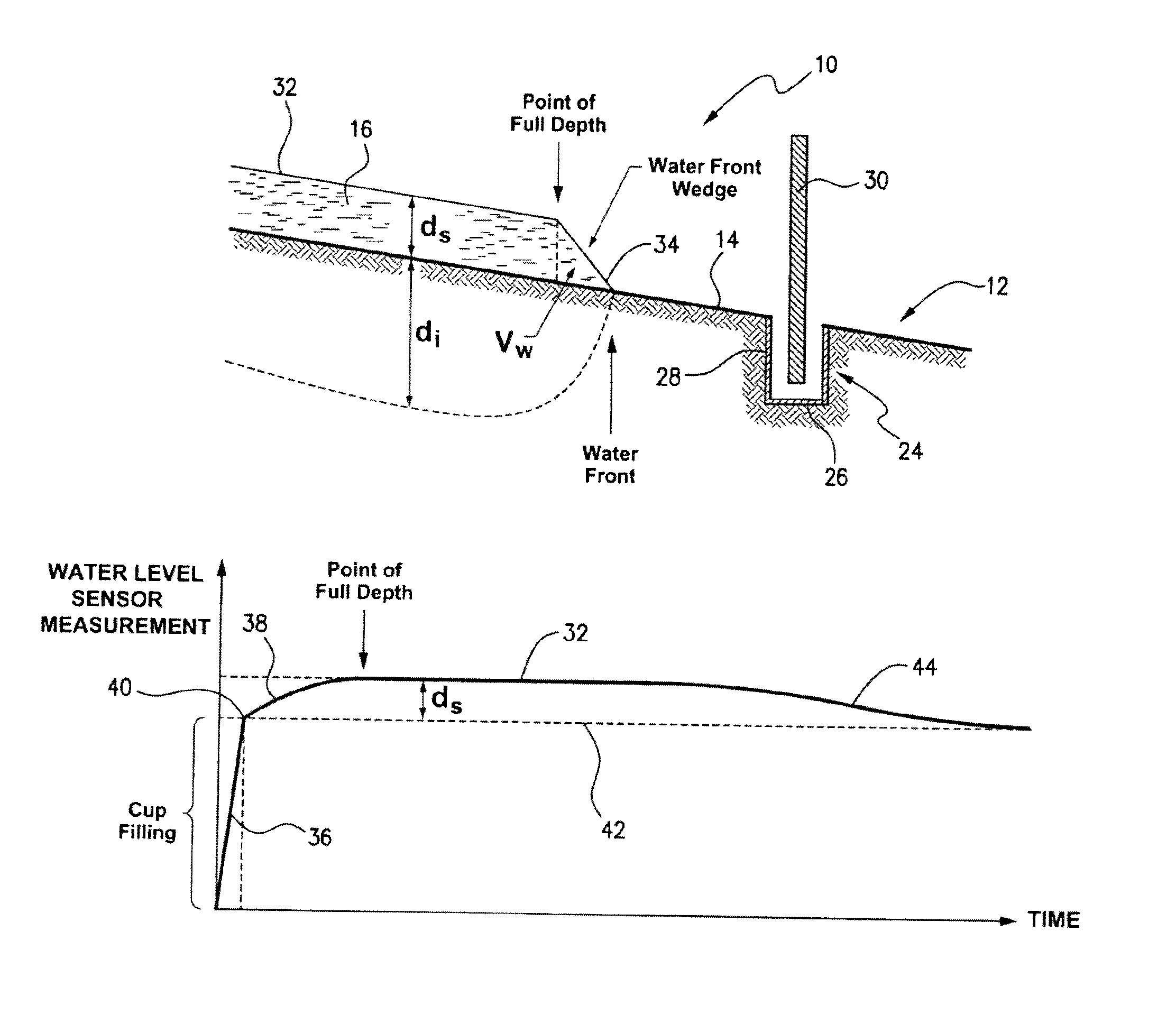
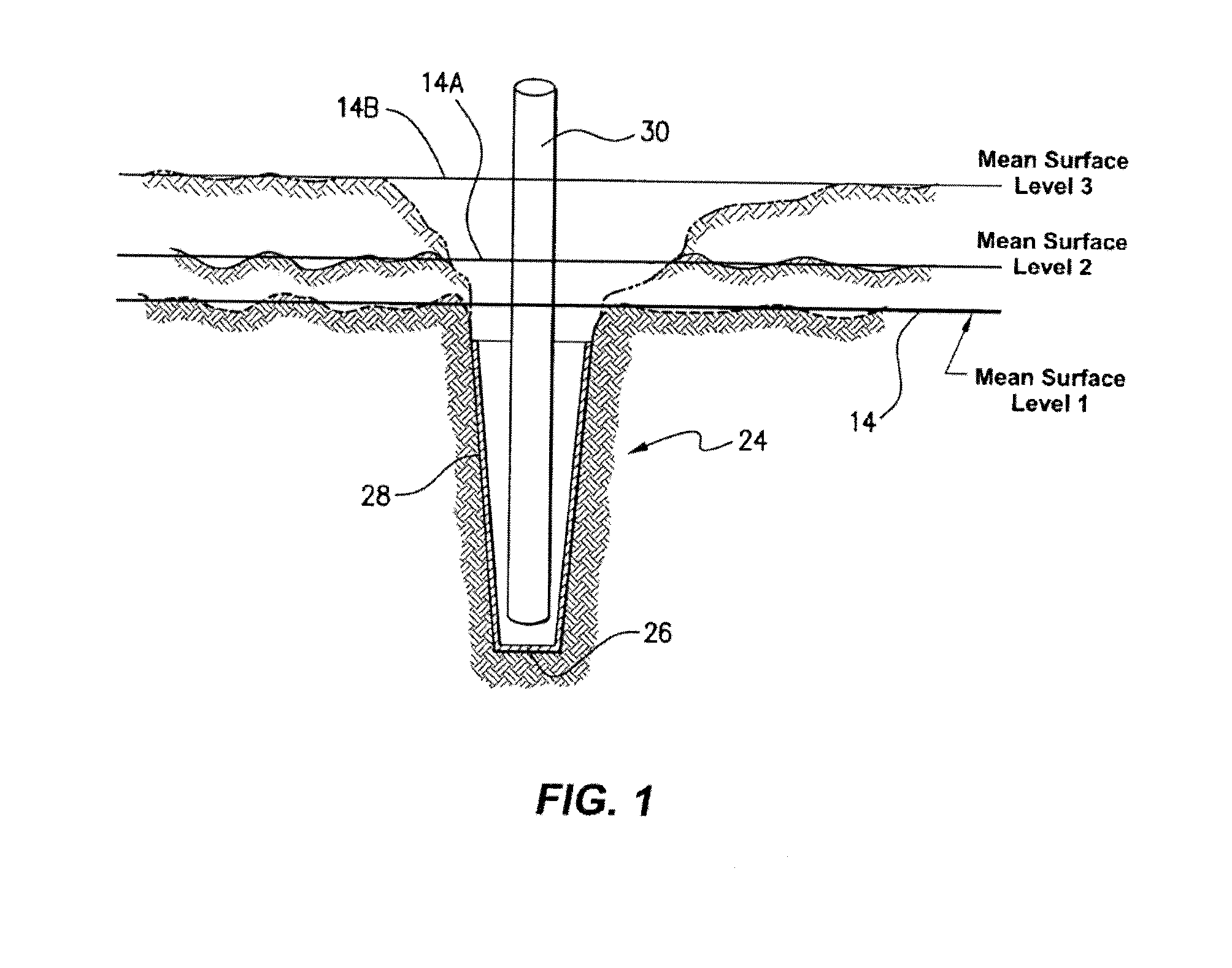
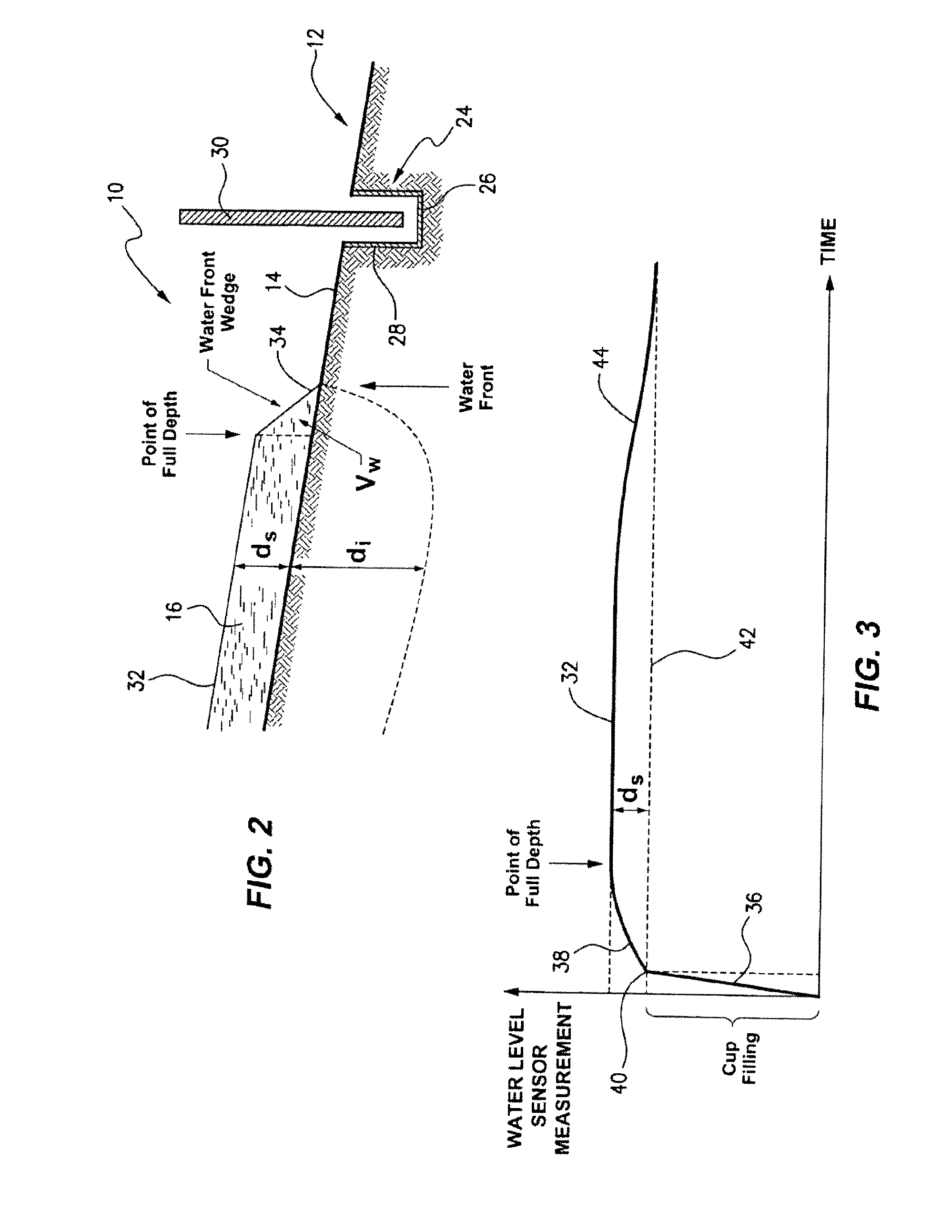
A method of determining the surface level of an area subject to flood, furrow or surface irrigation. The method includes the steps of providing at least one measuring cup positioned below the surface level but within the area and providing a water level sensor within or integrated with the at least one measuring cup. The levels provided by the water level sensor are used to calculate the surface level by determining the inflection point between the rapid increase of the monitored levels when the front of irrigation water passes the water level sensor. A further aspect of the disclosure is the provision of a soil moisture sensor, said sensor comprising an auger adapted to be inserted into the ground with minimum soil disturbance, said auger having means for measuring soil moisture.
Owner:RUBICON RES PTY LTD
Environmental and biotic-based speed management and control of mechanized irrigation systems
InactiveUS20120267447A1Increase and decreases speed and rate of movement and rotationIncreased and decreased and rateSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationMoistureEvapotranspiration
A system that based on changes in agricultural crop or plant characteristics or dynamics, e.g. heat stress, water deficit stress, stem growth, leaf thickness, plant color, nutrient composition, etc., or changes in environmental conditions, e.g., temperature, wind, pressure, relative humidity, dew point, precipitation, soil moisture, solar radiation, etc. or a combination of both, e.g., evapotranspiration, either automatically increases or decreases the speed or rate of movement or rotation of a mechanized irrigation system, e.g. center pivot, corner, linear, or lateral move irrigation system or similar, or reports a recommended increased or decreased speed or rate of movement or rotation of a mechanized irrigation system either directly or indirectly to the end user. The system responds directly or indirectly to data outputted from monitoring systems that gather and compile environmental (non-biotic), biotic or similar information from agricultural fields and crops.
Owner:CROPMETRICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com