Passive water-saving irrigation method and facilities thereof
A computer and specific technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, watering devices, gardening, etc., can solve the problems of high labor consumption, low degree of automation, low control accuracy, etc., and achieve low probability of error, high degree of automation, Use precise and reasonable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment:
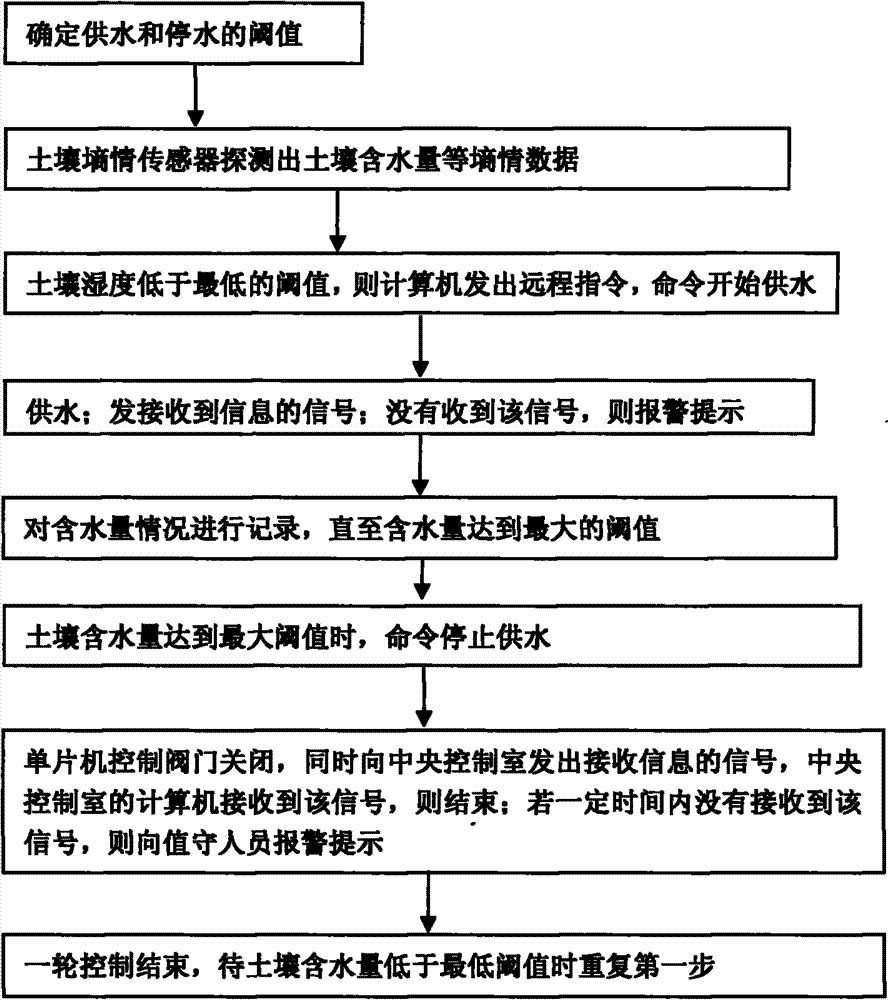
[0023] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the passive water-saving irrigation method. The specific process is as follows:
[0024] (1) First determine the optimal field water volume of field crops, that is, the soil moisture that is most suitable for the growth of the crops in different growth stages, and then input these data into the computer to determine the thresholds of water supply and water stoppage in different periods;
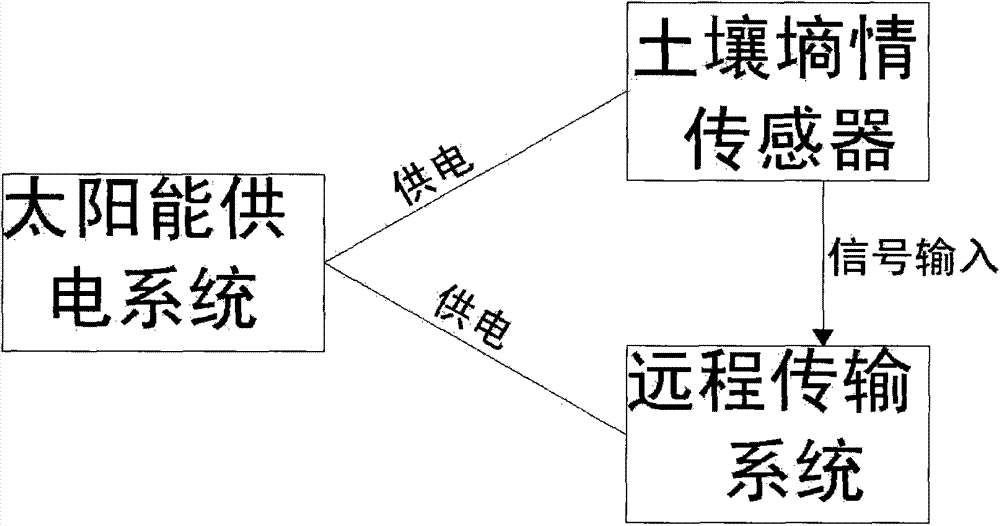
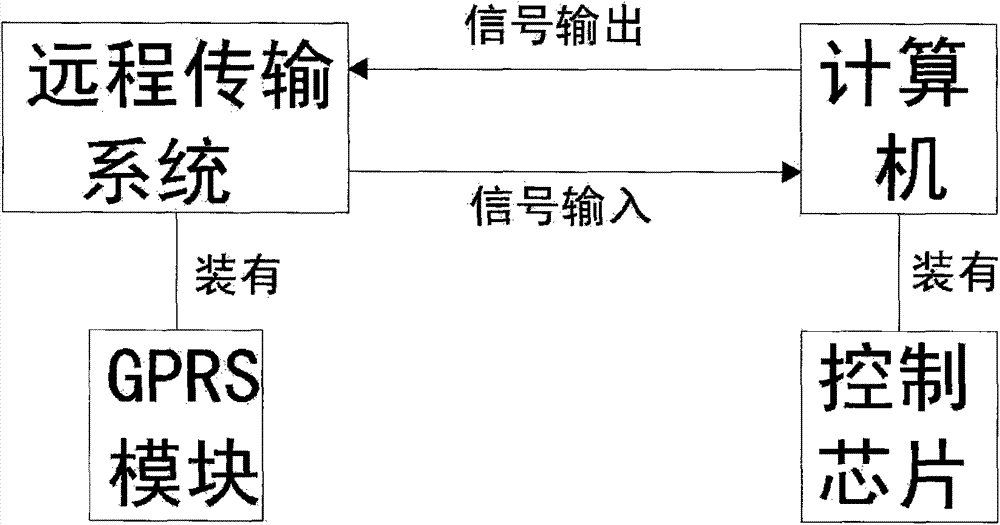
[0025] (2) After the equipment is debugged, the soil moisture sensor will detect the soil moisture content in the field, and the detected data will be transmitted to the central control room through the remote transmission system, and the remote transmission system in the central control room will receive the data and transmit it to the computer middle;
[0026] (3) The computer receives the data, if the soil humidity is grea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com