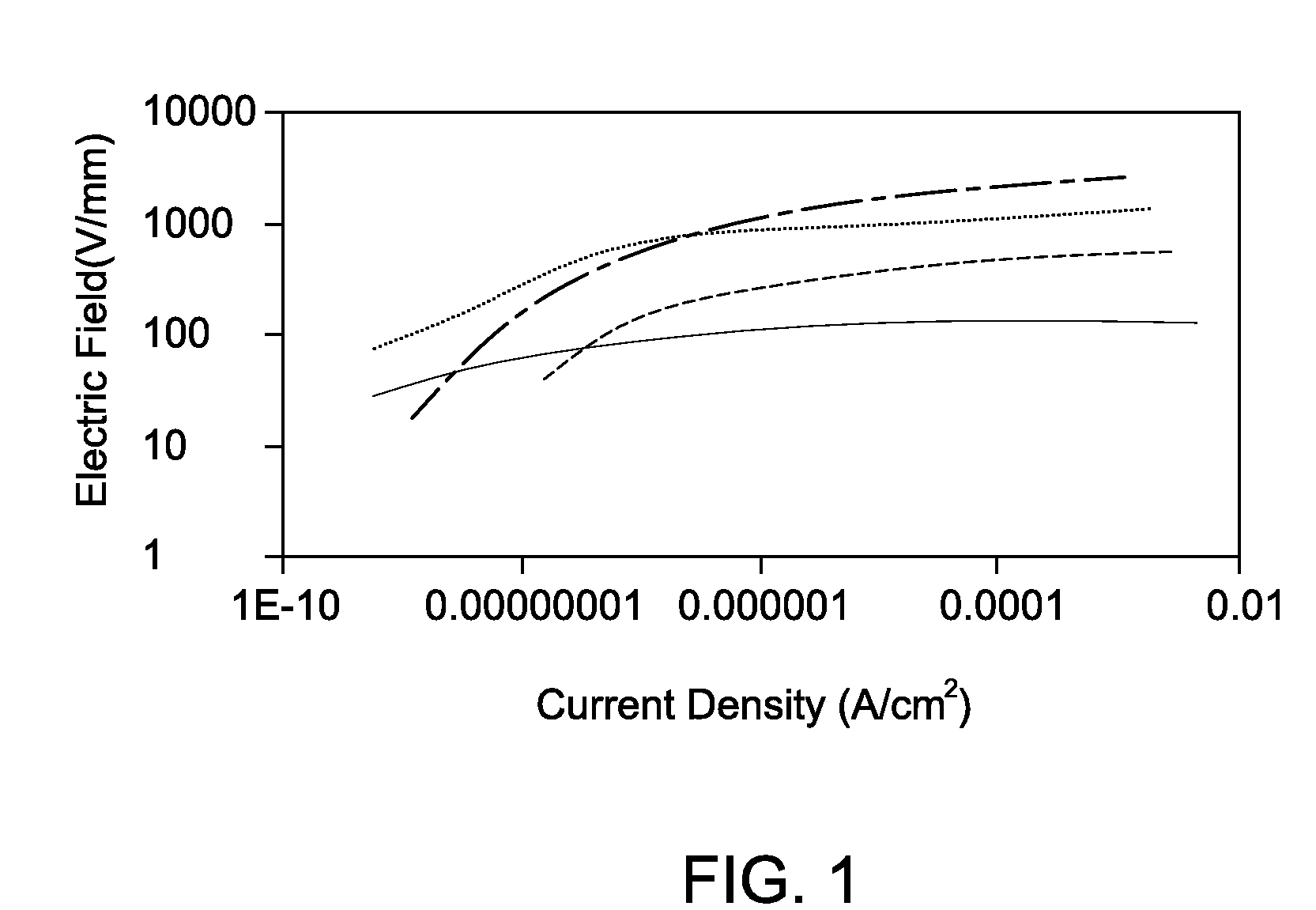
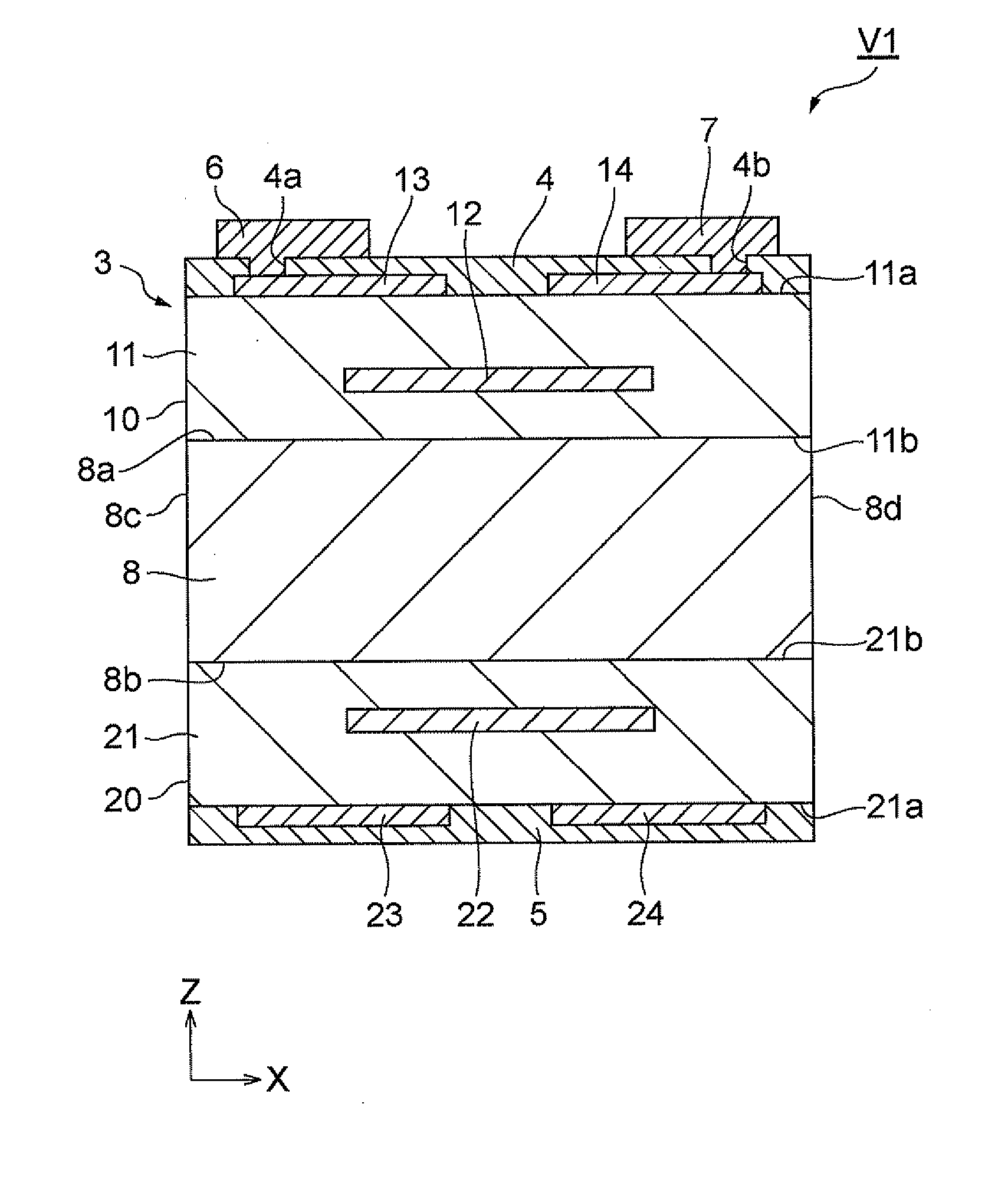
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
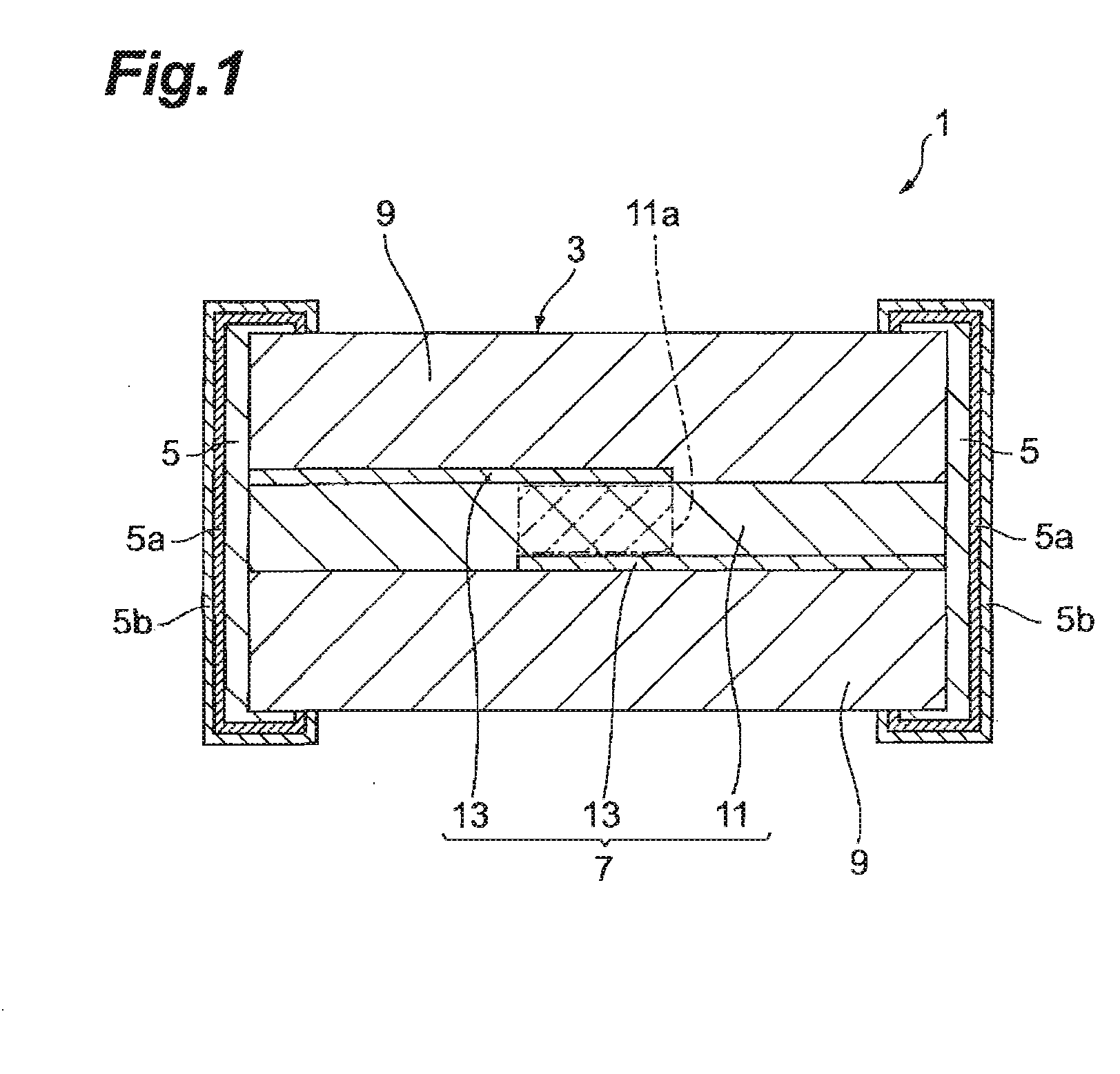
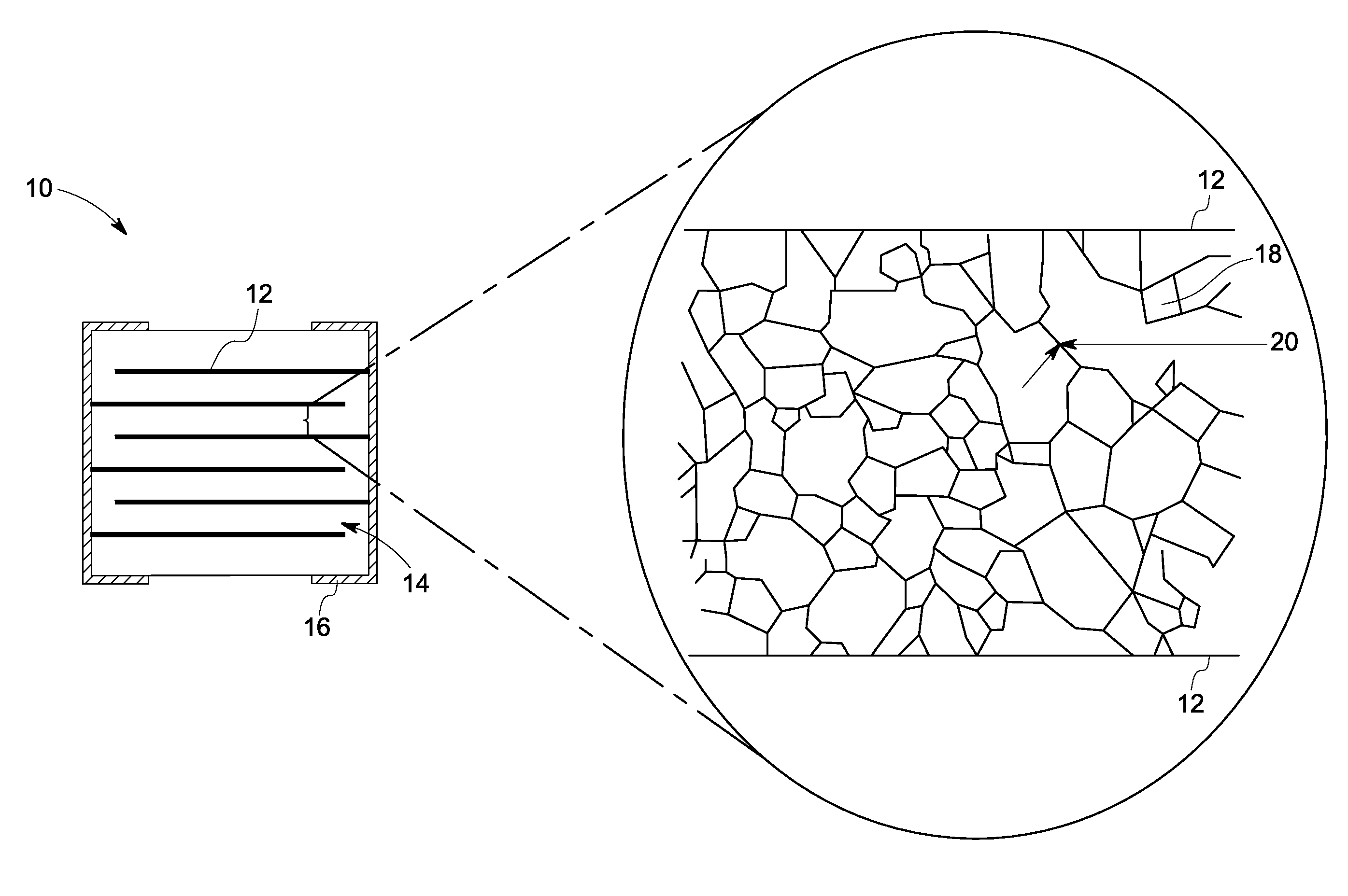
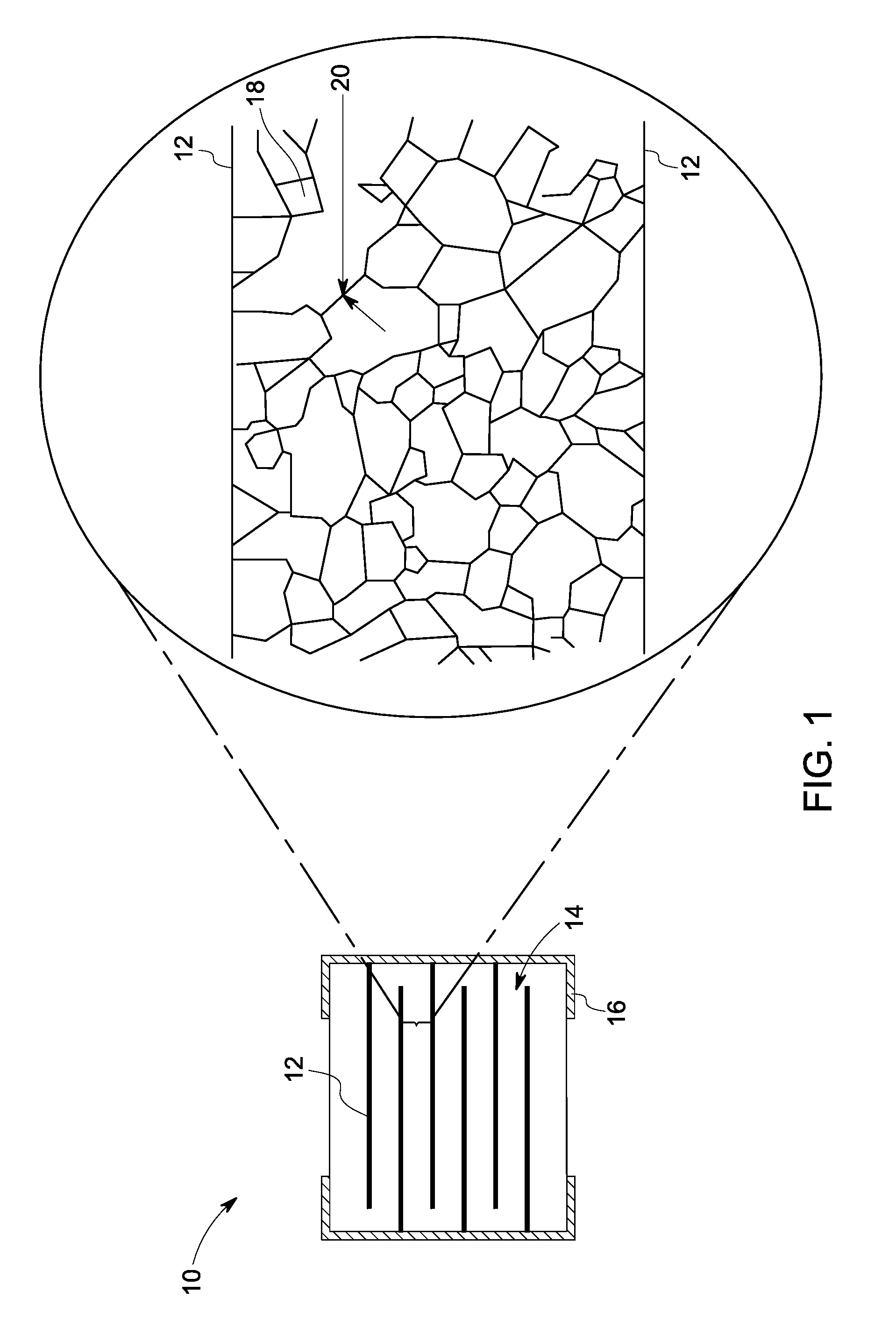
126results about "Thick film varistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
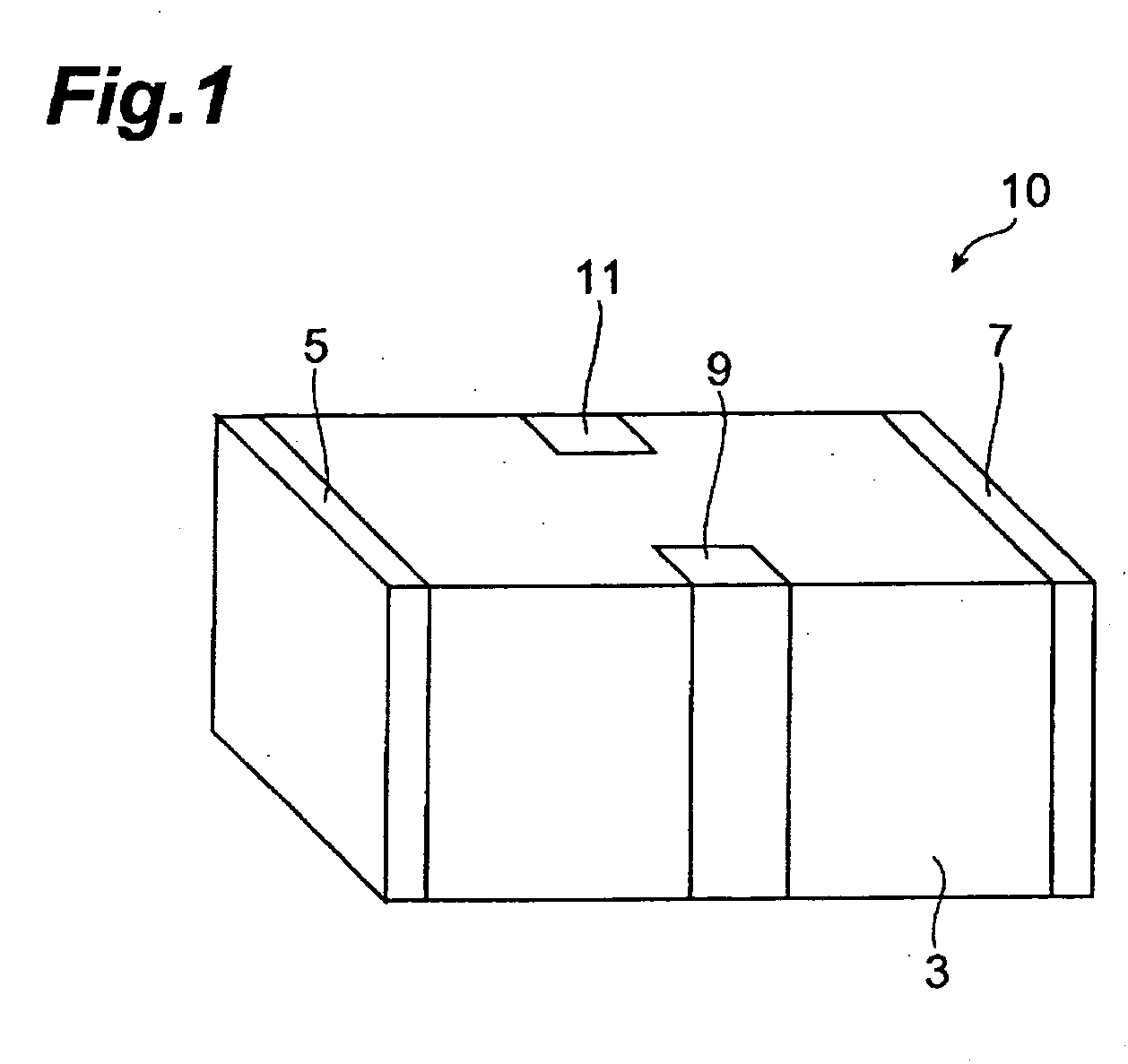
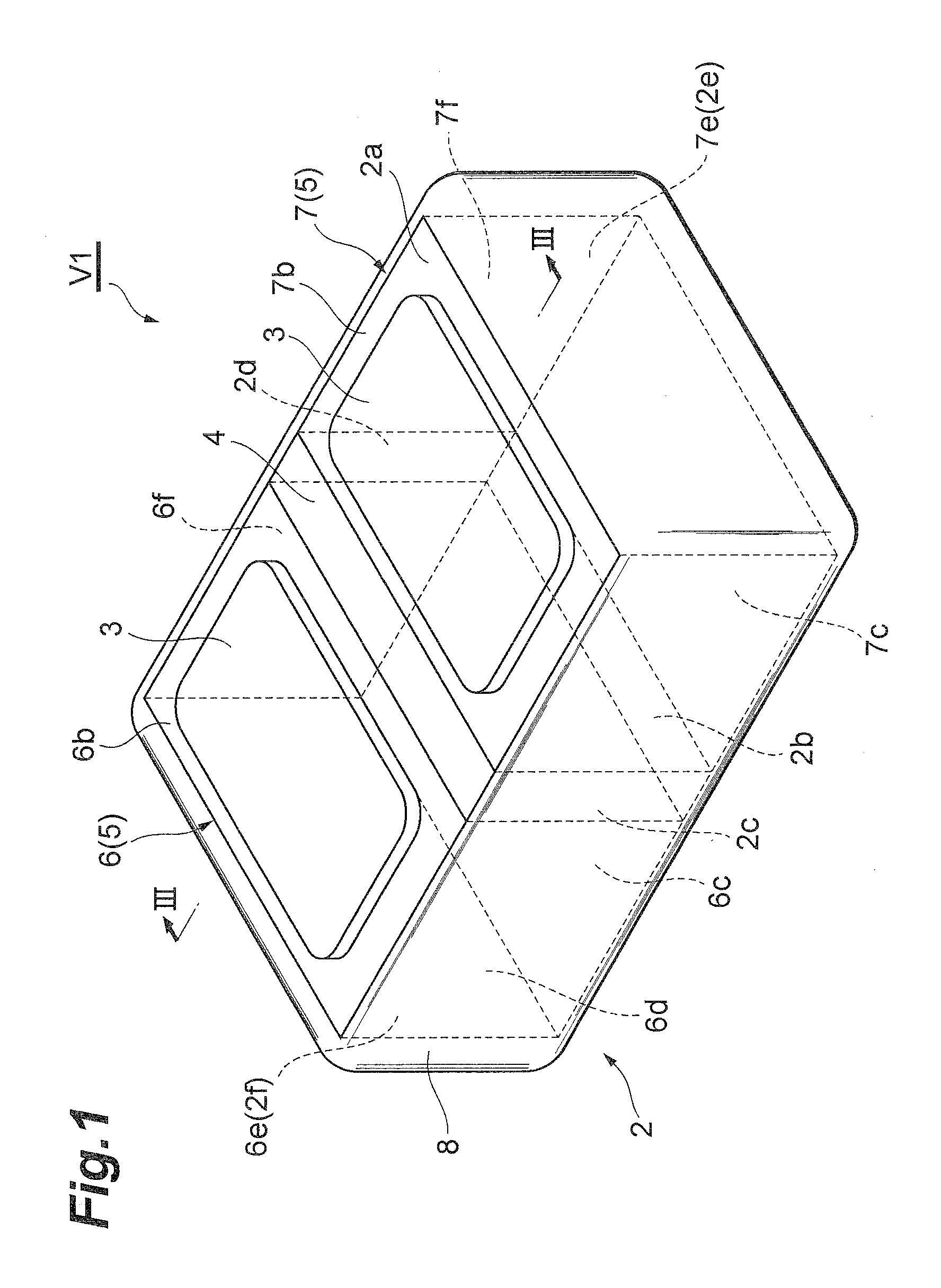
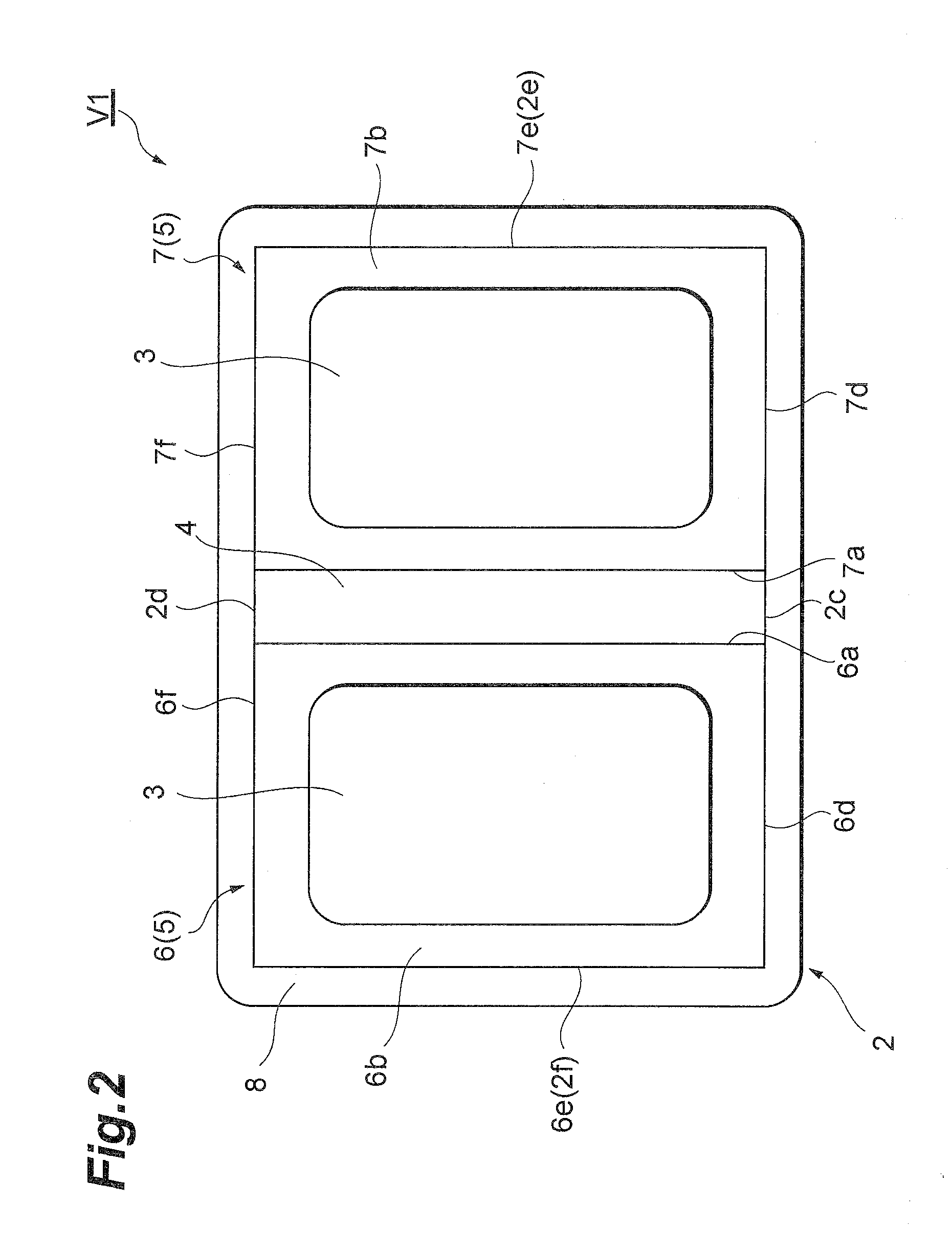
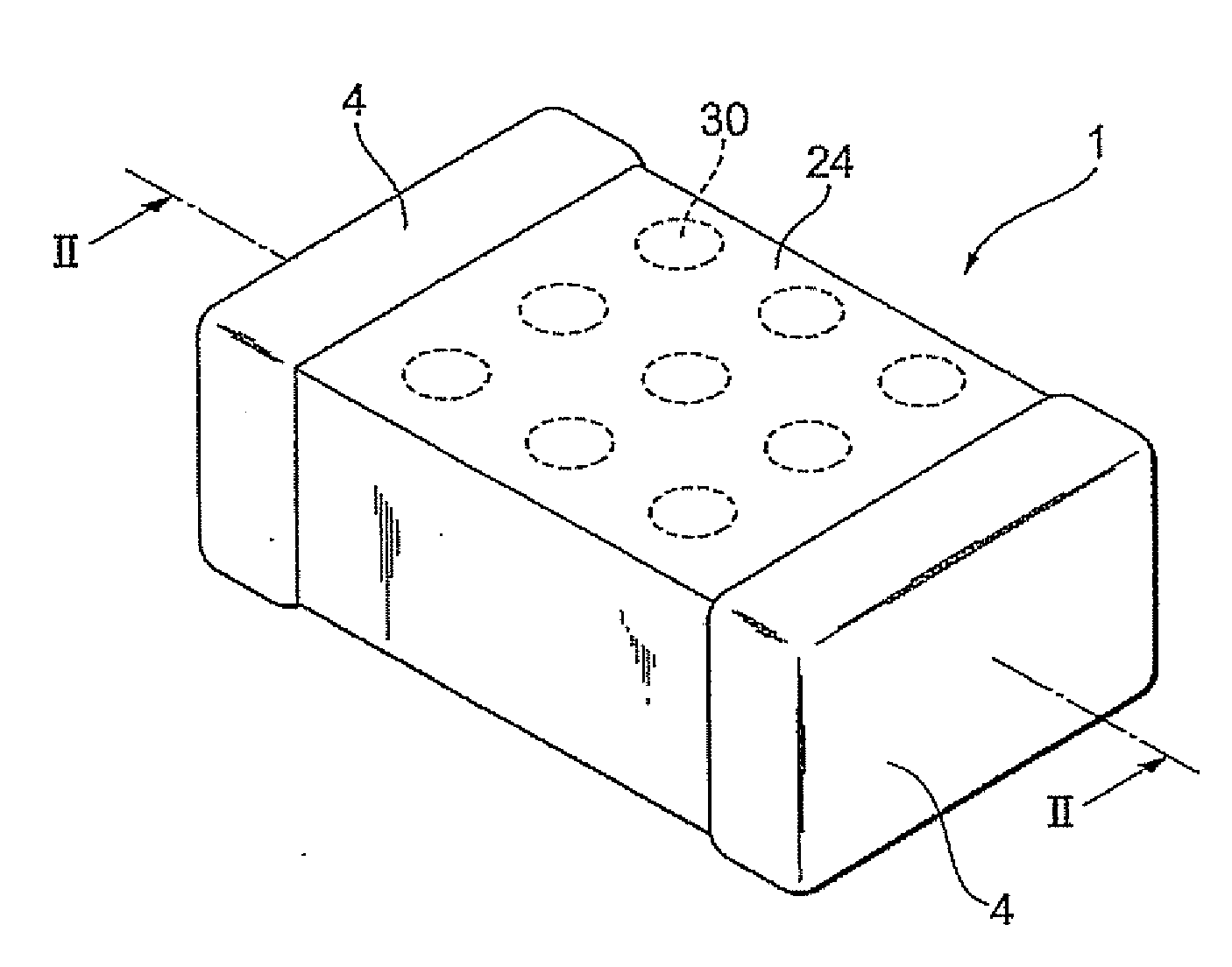
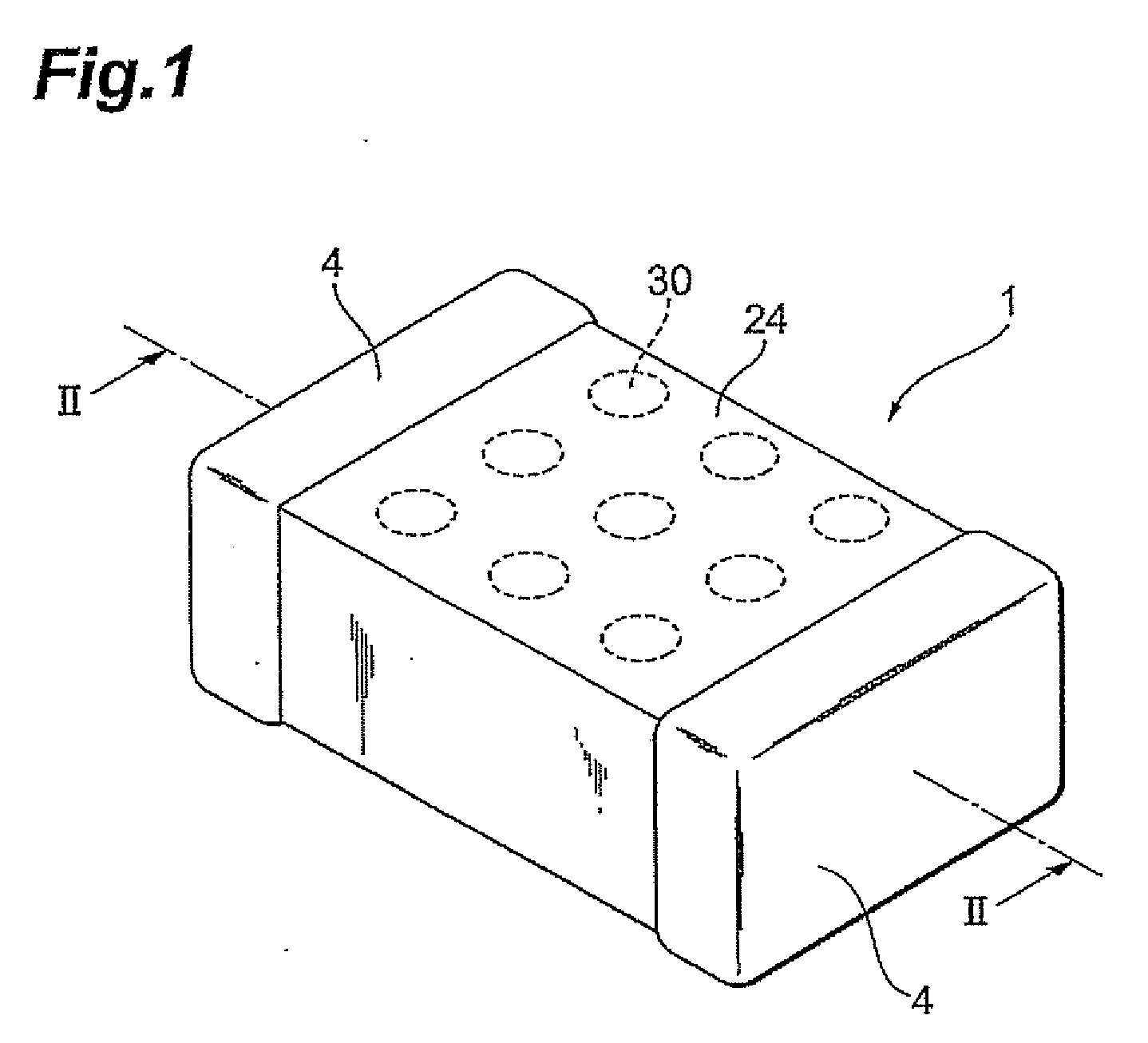
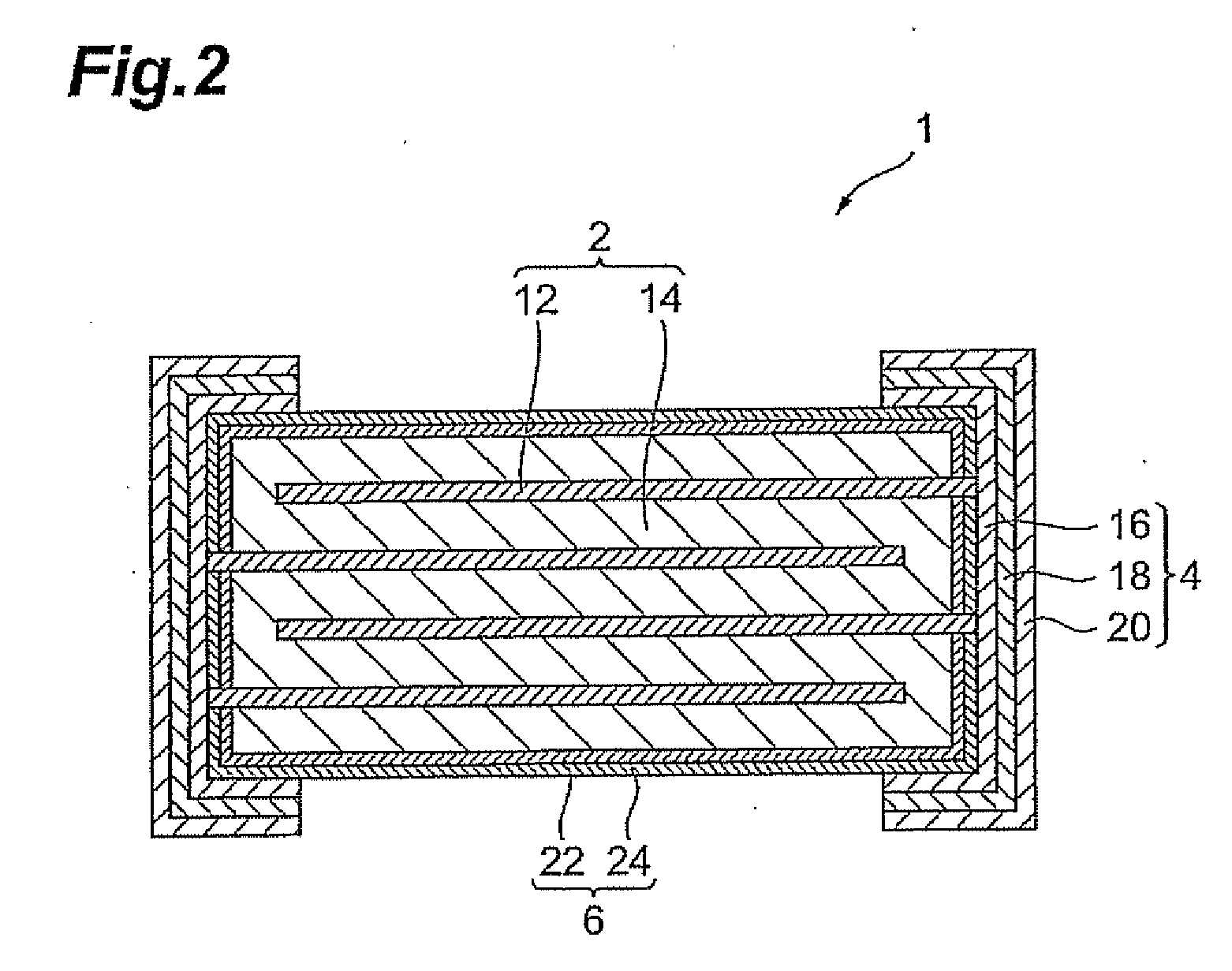
Very low profile multilayer components
InactiveUS20080165468A1Reduce inductanceReduce resistanceFixed capacitor electrodesPrinted electric component incorporationScreen printingEngineering
Methodologies are disclosed for producing multilayer electronic devices using a single screen printing mask. Plural layer devices are constructed by placing a common mask in alternating positions among alternating layers of support material such that, upon stacking of the plural layers, complimentary electrode structure is produced in alternating layers. Support material may be varied to produce different devices, including capacitors, resistors, and varistors. Multilayer electronic devices include multiple layers providing adjacent printed complimentary electrode layers having an upper surface, a lower surface, a front edge, and a back edge, and with lateral end portions of combined first and second layers trimmed so as to expose selected conductive patterns. Termination material is applied to at least such trimmed lateral end portions. A low inductance controlled equivalent series resistance (ESR) multilayer capacitor, includes at least two different pairs of electrodes, some of which have interdigitated respective side tabs. Termination material may be associated with such electrodes. In some instances, some electrodes may have dummy or anchor tabs associated with them but not electrically connected with them, to facilitate the formation of termination material at designated locations.
Owner:AVX CORP
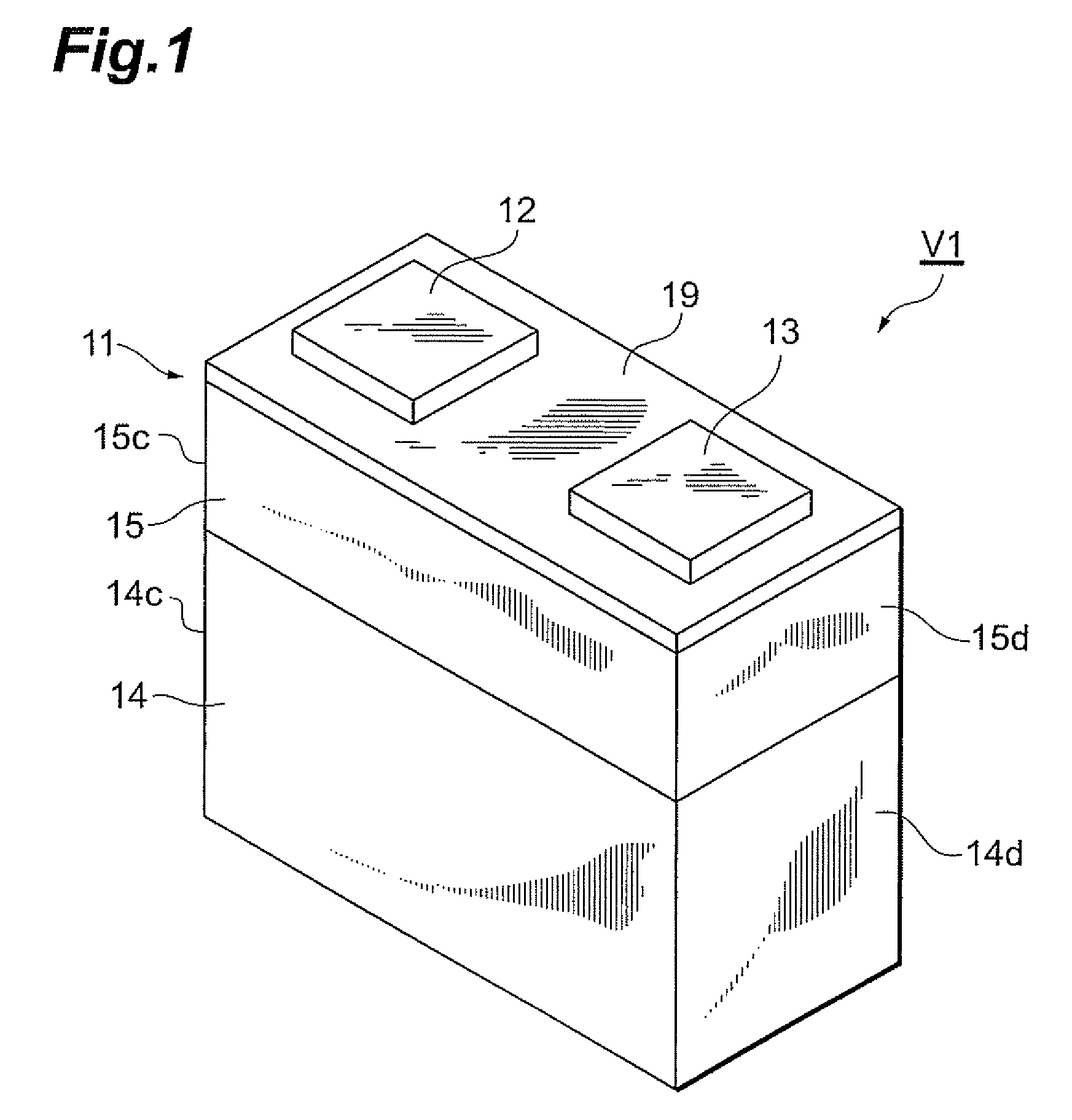
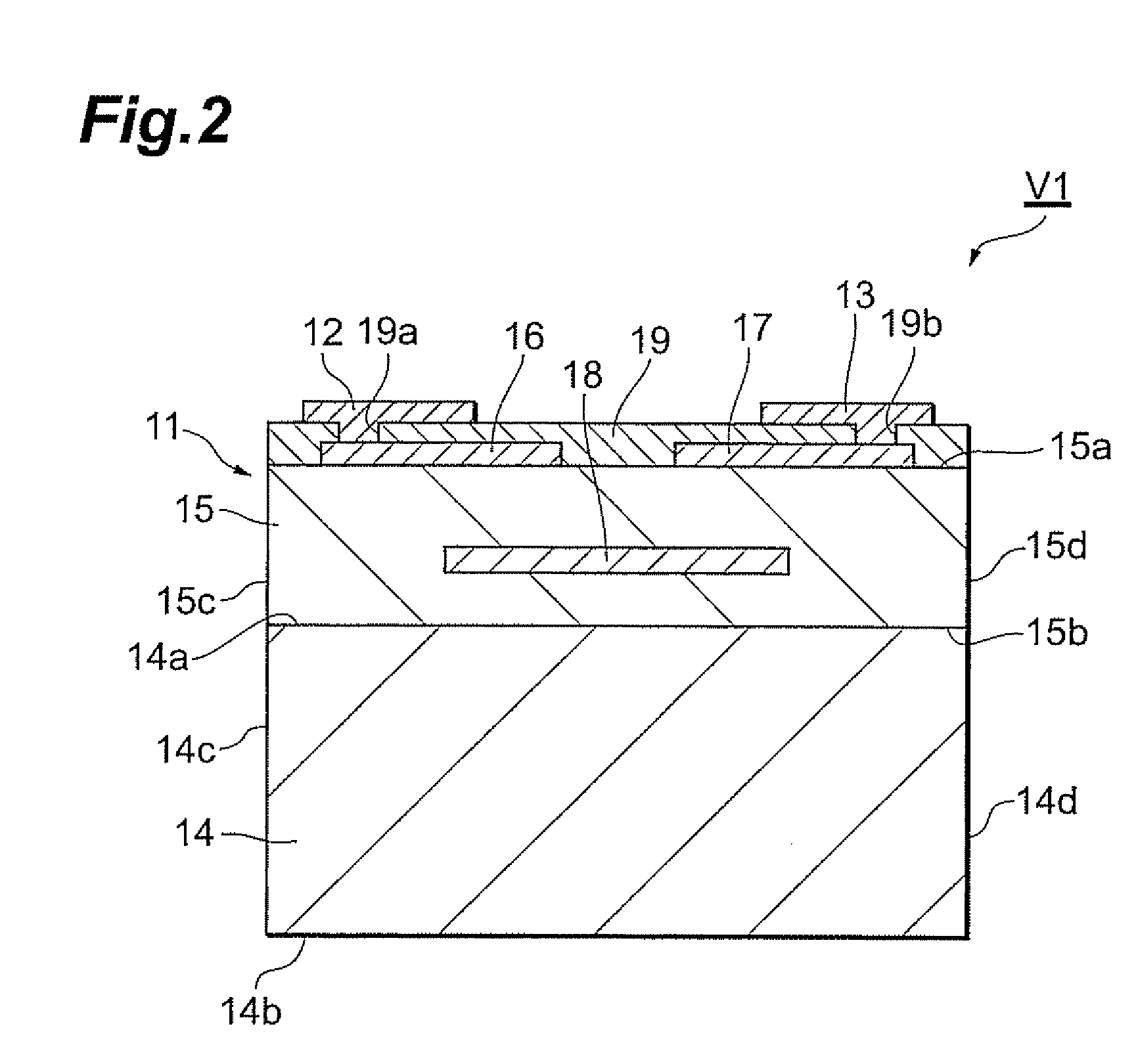
Light emitting device
ActiveUS7505239B2Effective coolingCurrent responsive resistorsSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
A light emitting device has a semiconductor light emitting element and a multilayer chip varistor. The multilayer chip varistor has a multilayer body with a varistor portion therein, and a plurality of external electrodes disposed on an outer surface of the multilayer body. The varistor portion has a varistor layer containing ZnO as a principal component and exhibiting nonlinear voltage-current characteristics, and a plurality of internal electrodes arranged to interpose the varistor layer between them. Each of the external electrodes is connected to a corresponding internal electrode out of the plurality of internal electrodes. The semiconductor light emitting element is disposed on the multilayer chip varistor. The semiconductor light emitting element is connected to corresponding external electrodes out of the plurality of external electrodes so as to be connected in parallel to the varistor portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Varistor and light emitting device
InactiveUS20080238604A1High bonding strengthAvoid crackingResistor terminals/electrodesCurrent responsive resistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceThermal radiation
In a varistor, a heat radiating portion contains the same components as ZnO that is the main component of a varistor element body, as metal oxides, thereby, the structural components of the varistor element body and the heat radiating portion are caused to be common. During firing, Ag contained in the heat radiating portion diffuses into the grain boundaries of ZnO, near the interface between surfaces of the heat radiating portion and the varistor element body. Consequently, in the varistor, cracks hardly occur between the varistor portion and the heat radiating portion during firing (or during binder removal), thereby, ensuring sufficient bonding strength between the varistor portion and the heat radiating portion. Therefore, heat conducted to the varistor portion is radiated efficiently conducting through electrically conducted paths formed in the heat radiating portion from the surface facing the varistor element body to other three surfaces of the heat radiating portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
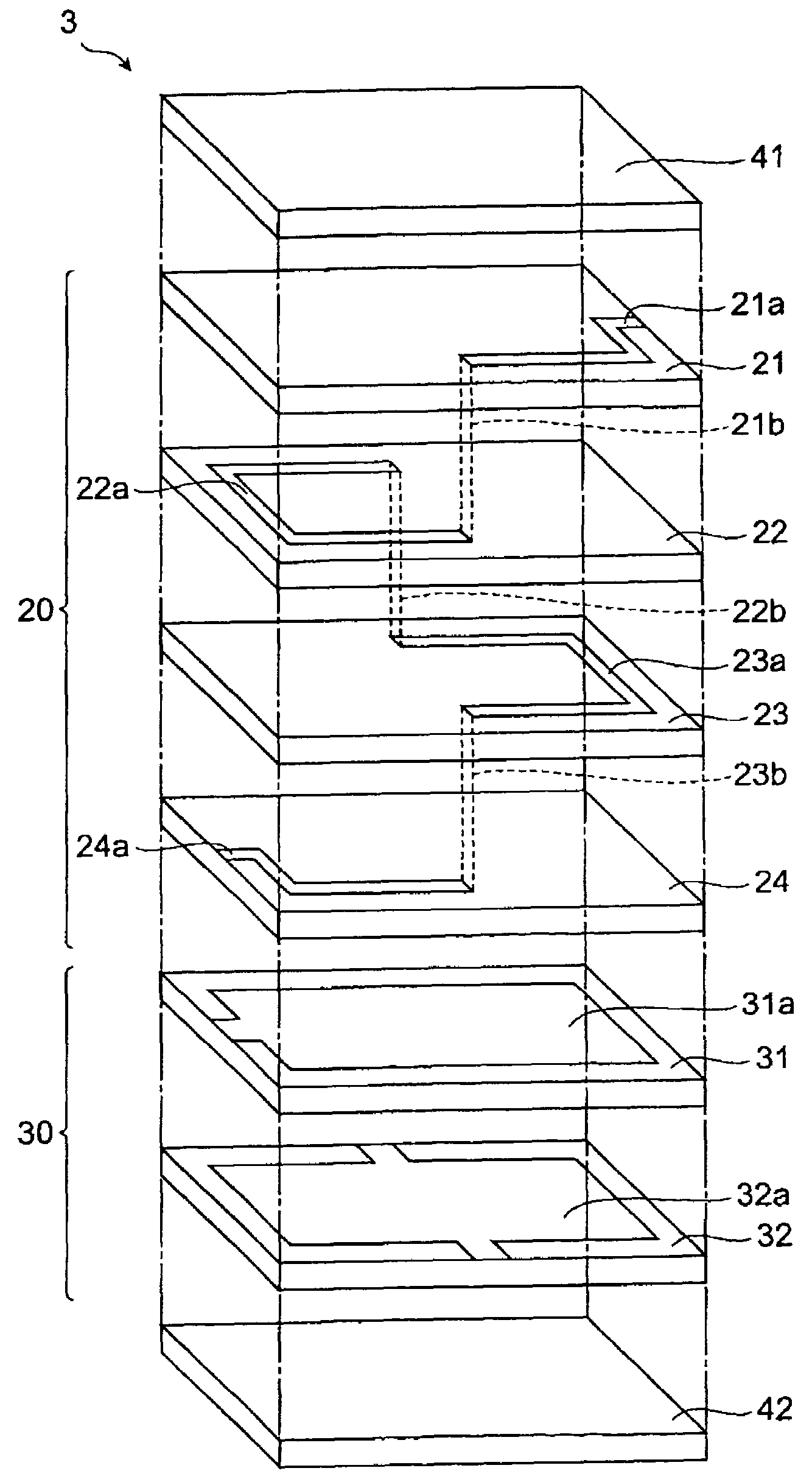
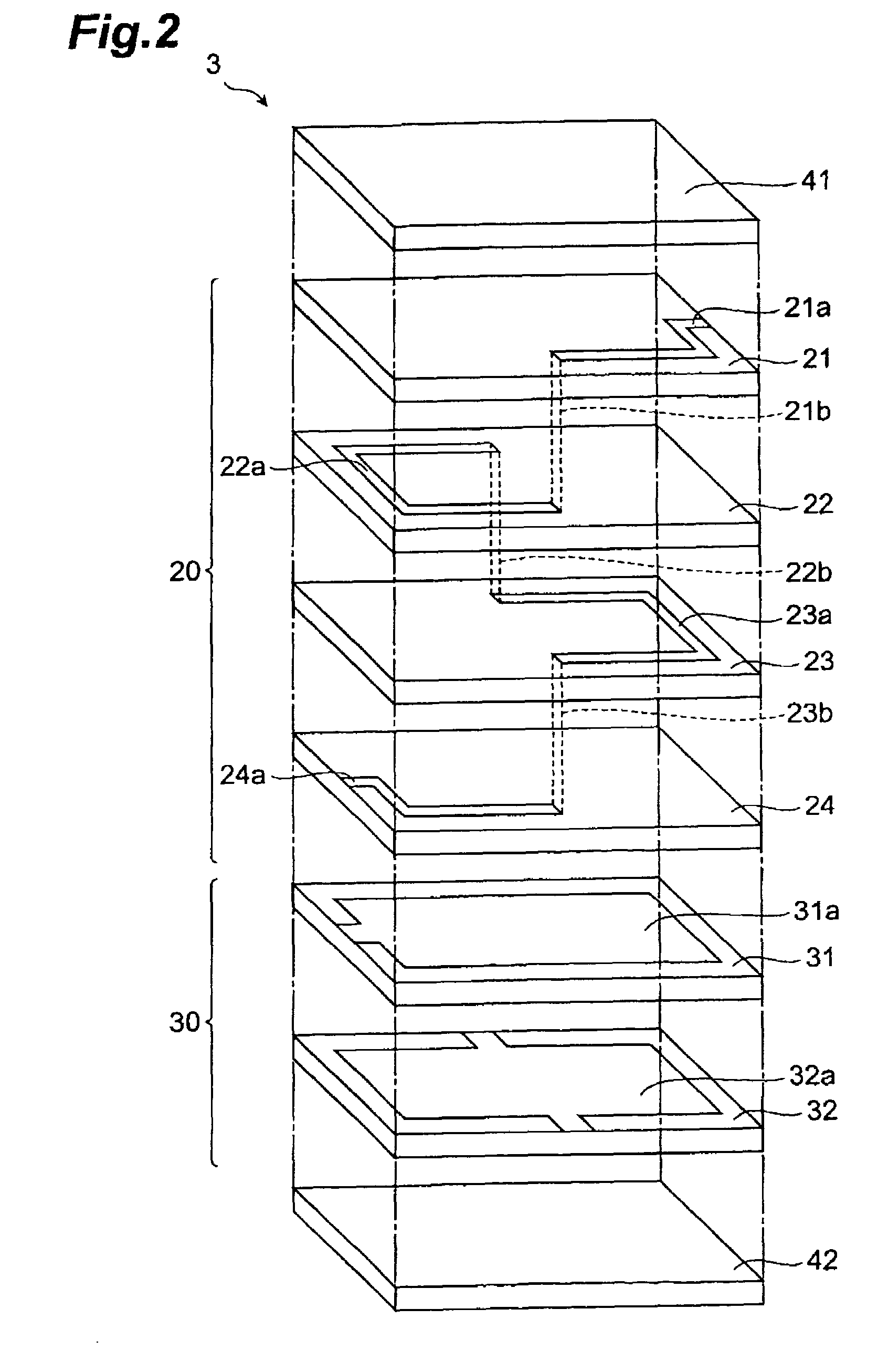
Multilayer filter
ActiveUS7652554B2Reduce flakingExcellent inductor characteristicMultiple-port networksSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorInductor
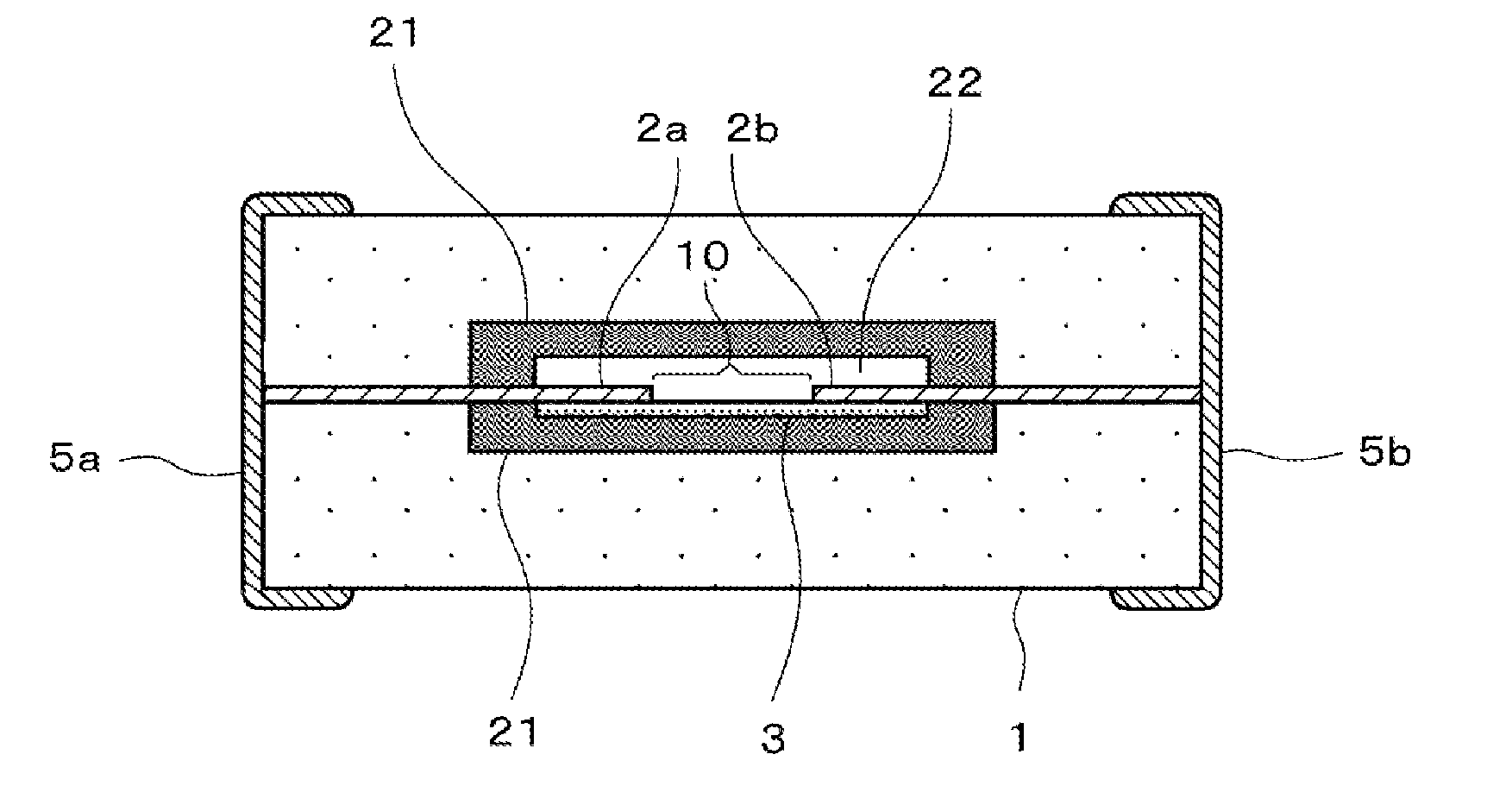
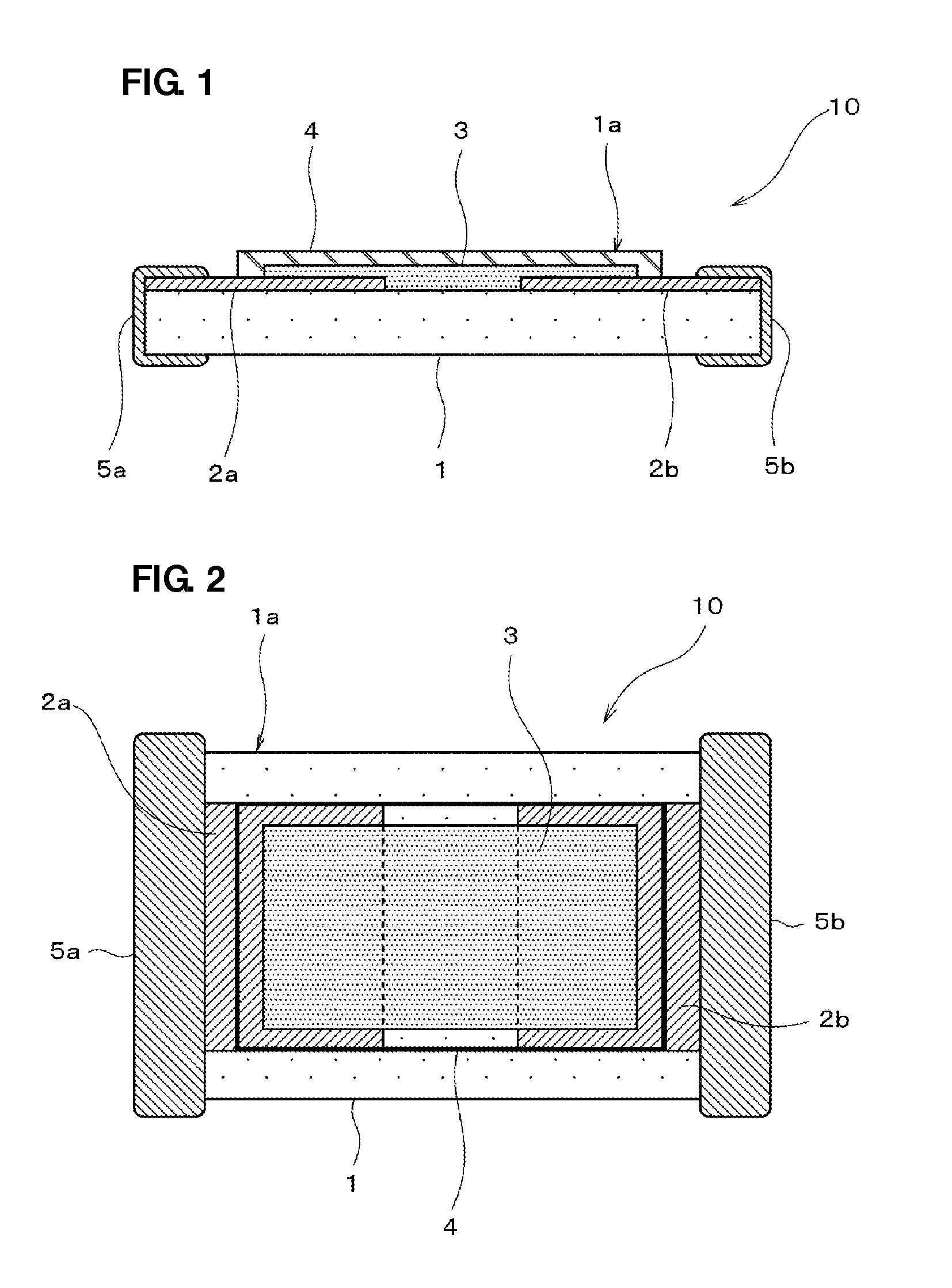
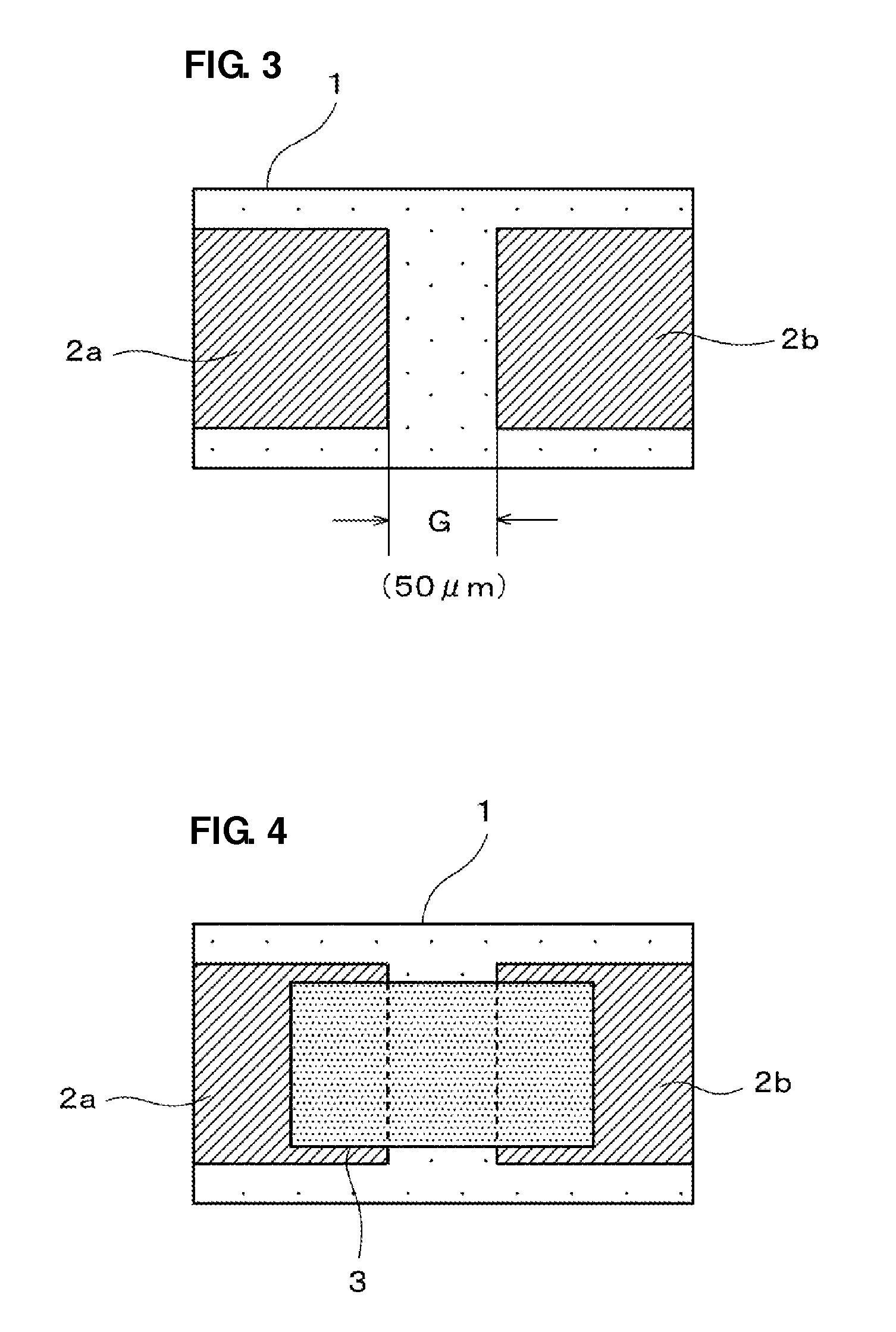
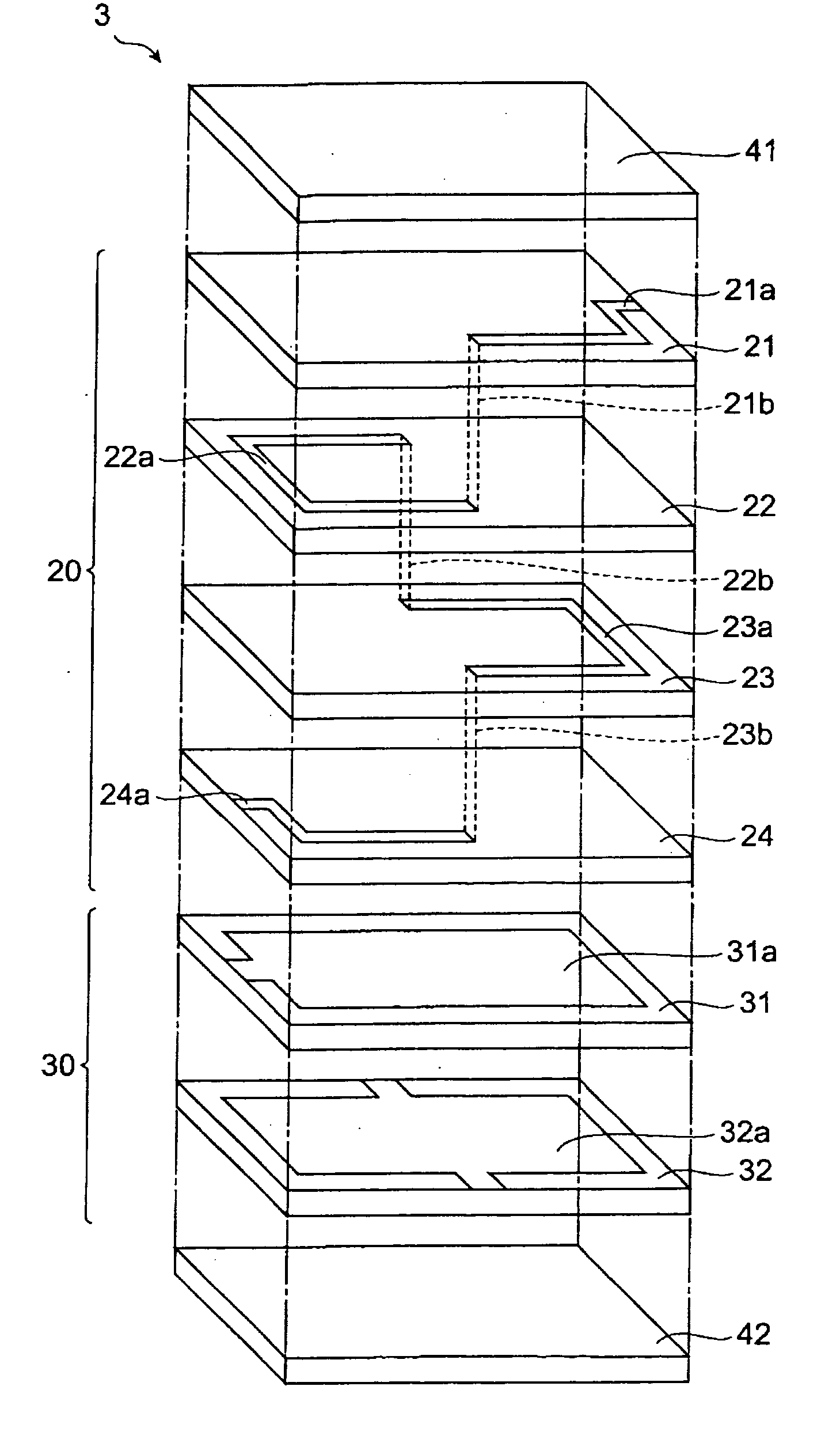
An object of the present invention is to provide a multilayer filter constructed so as to be less likely to suffer peeling between a varistor part and an inductor part. A multilayer filter 10 as a preferred embodiment has a structure in which a varistor part 20 and an inductor part are stacked. The varistor part 30 consists of a stack of varistor layers 31, 32 with internal electrodes 31a, 32a, and the varistor layers contain ZnO as a principal component, and contain at least one element selected from the group consisting of Pr and Bi, Co, and Al as additives. The inductor part 20 consists of a stack of inductor layers 21-24 with conductor patterns 21a-24a, and the inductor layers contain ZnO as a principal component and substantially contain neither Co nor Al.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Ceramic electronic component
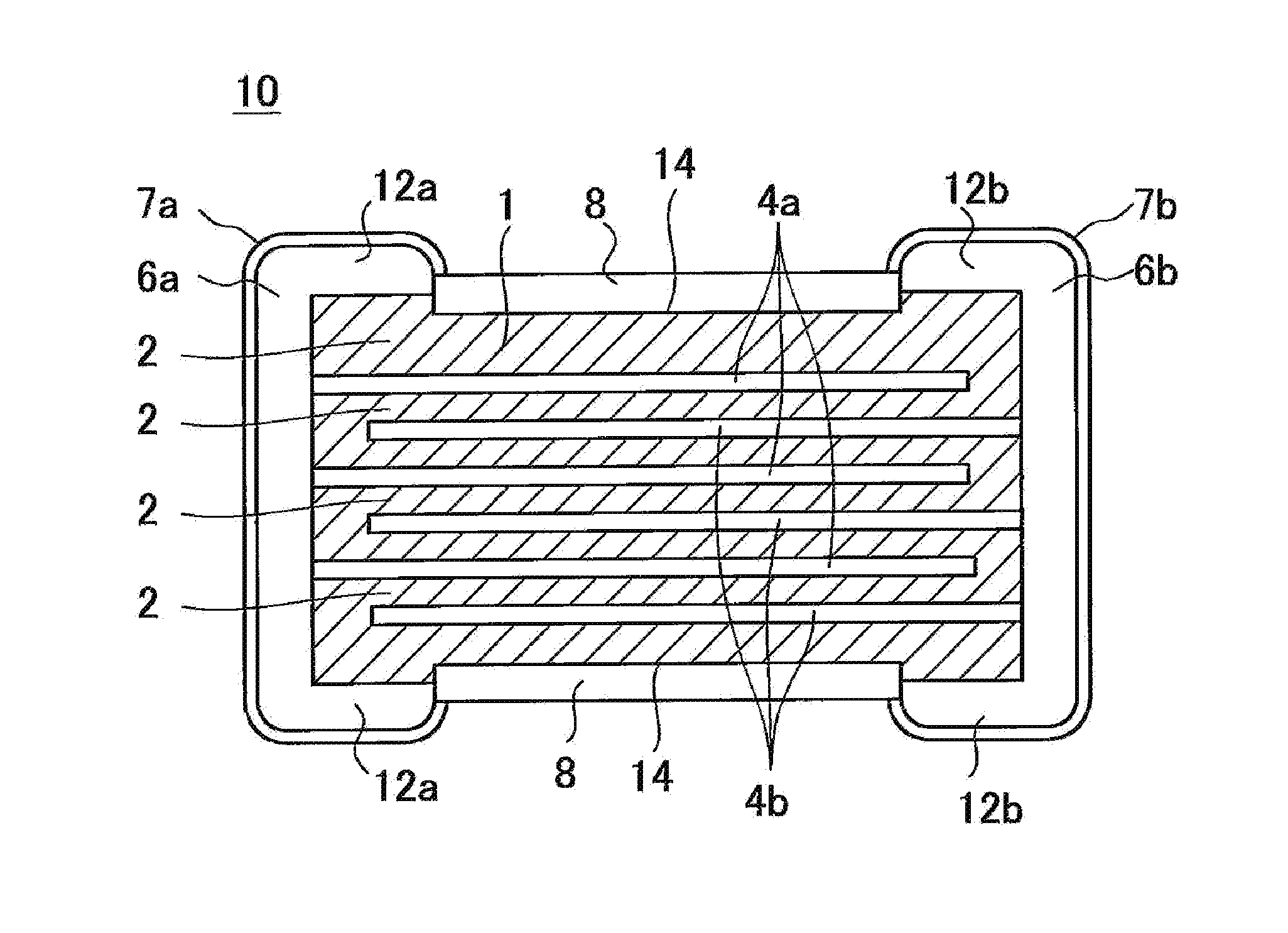
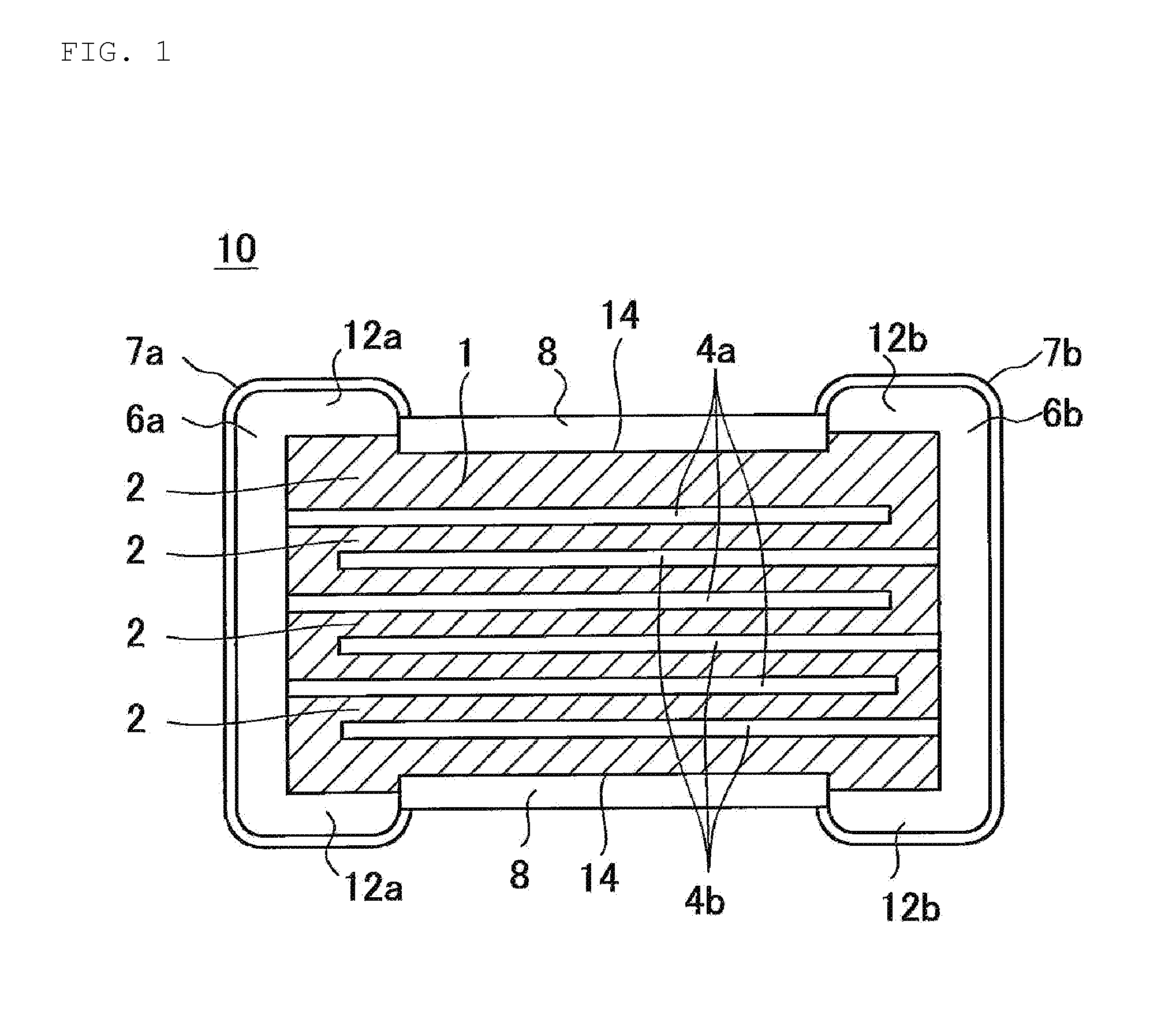
ActiveUS20160027561A1Good chemical resistanceReduce thicknessResistor terminals/electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricMetallurgyElectronic component
A ceramic electronic component that includes a ceramic element, and a coating film and external electrodes on a surface of the ceramic element. The coating film includes cationic elements from a constituent element of the ceramic element, which are ionized and deposited from the ceramic element, and a resin. The surface of the coating film is recessed relative to a surface of wrapping parts of the external electrodes on the surface of the ceramic element.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
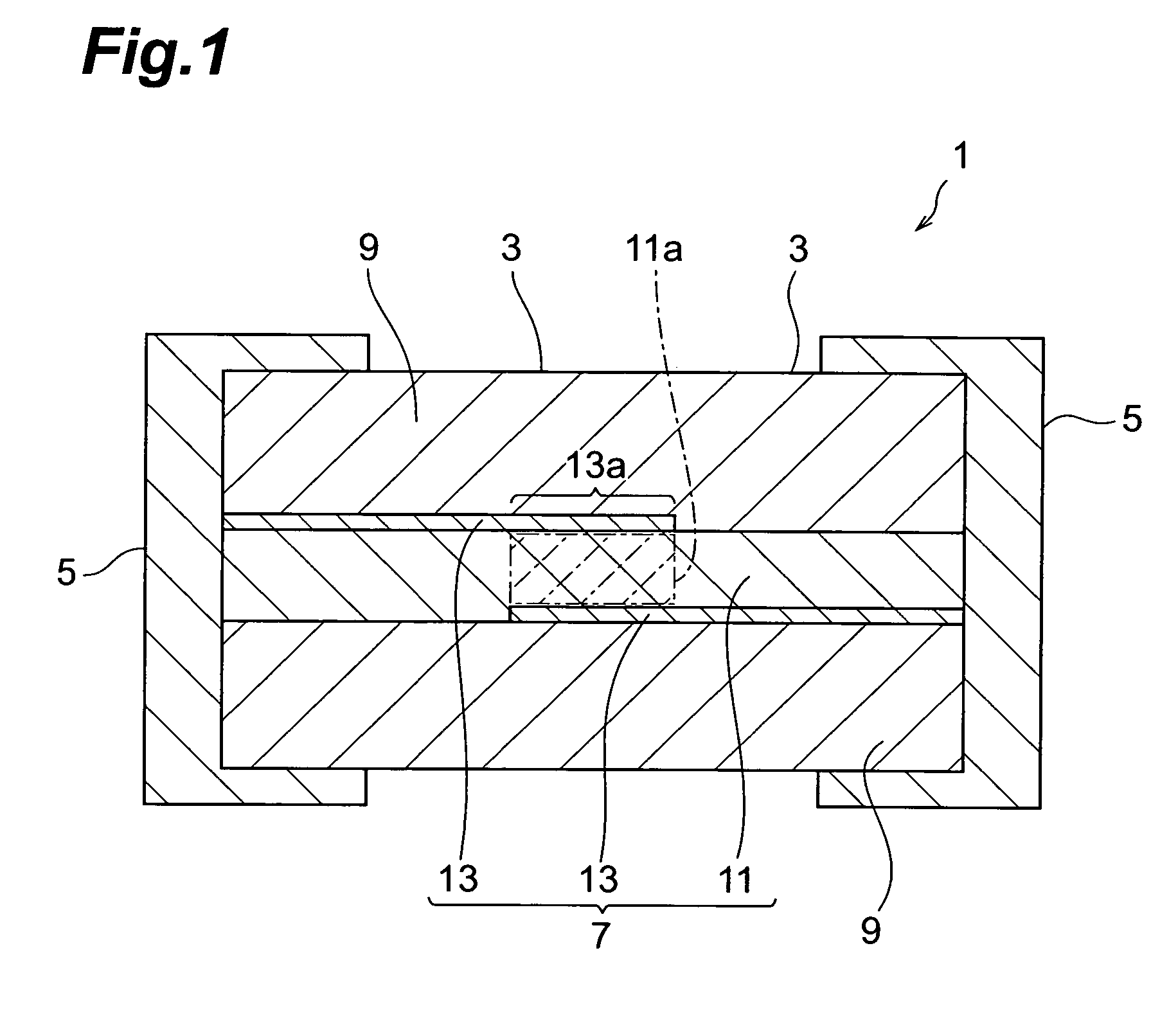
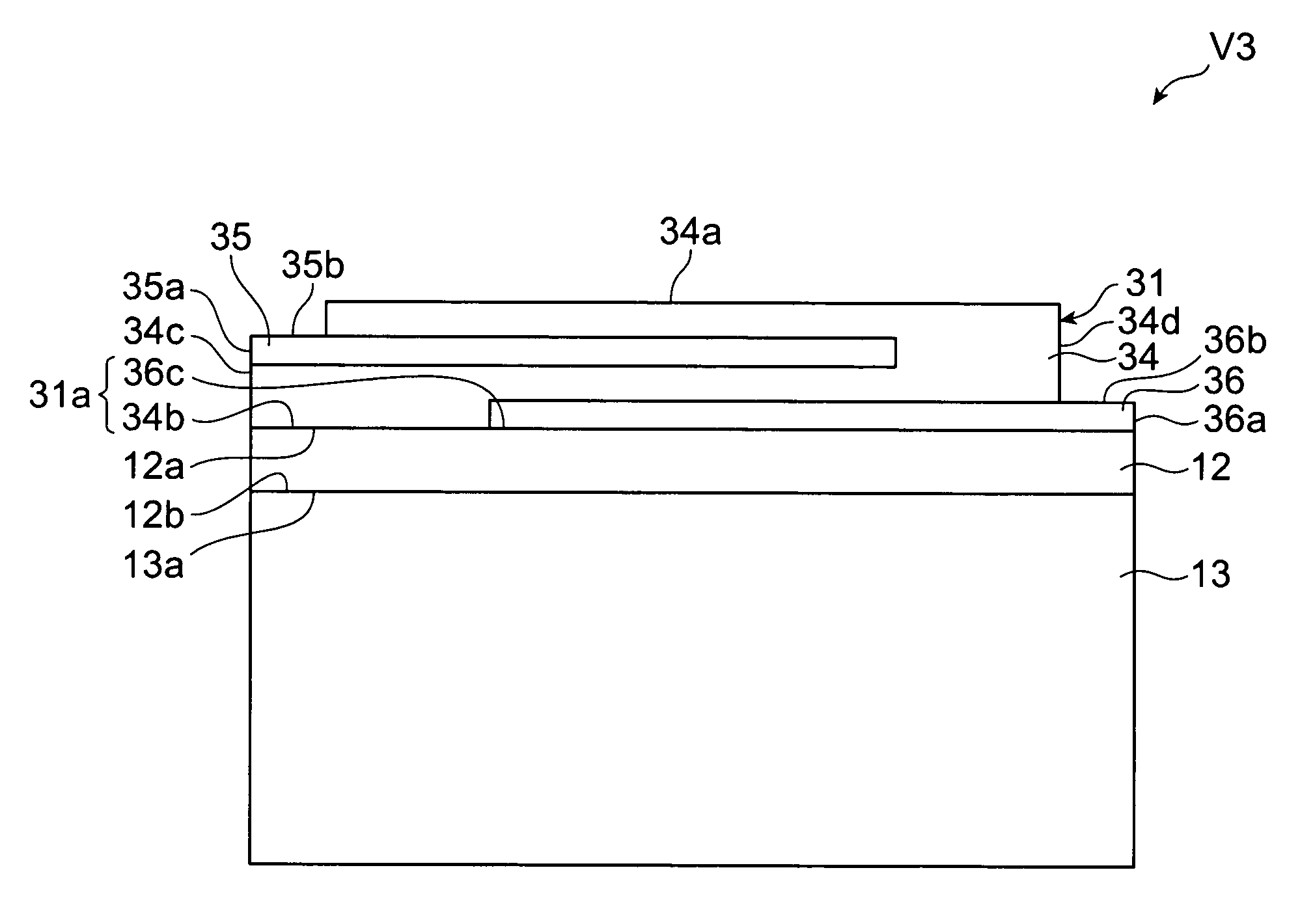
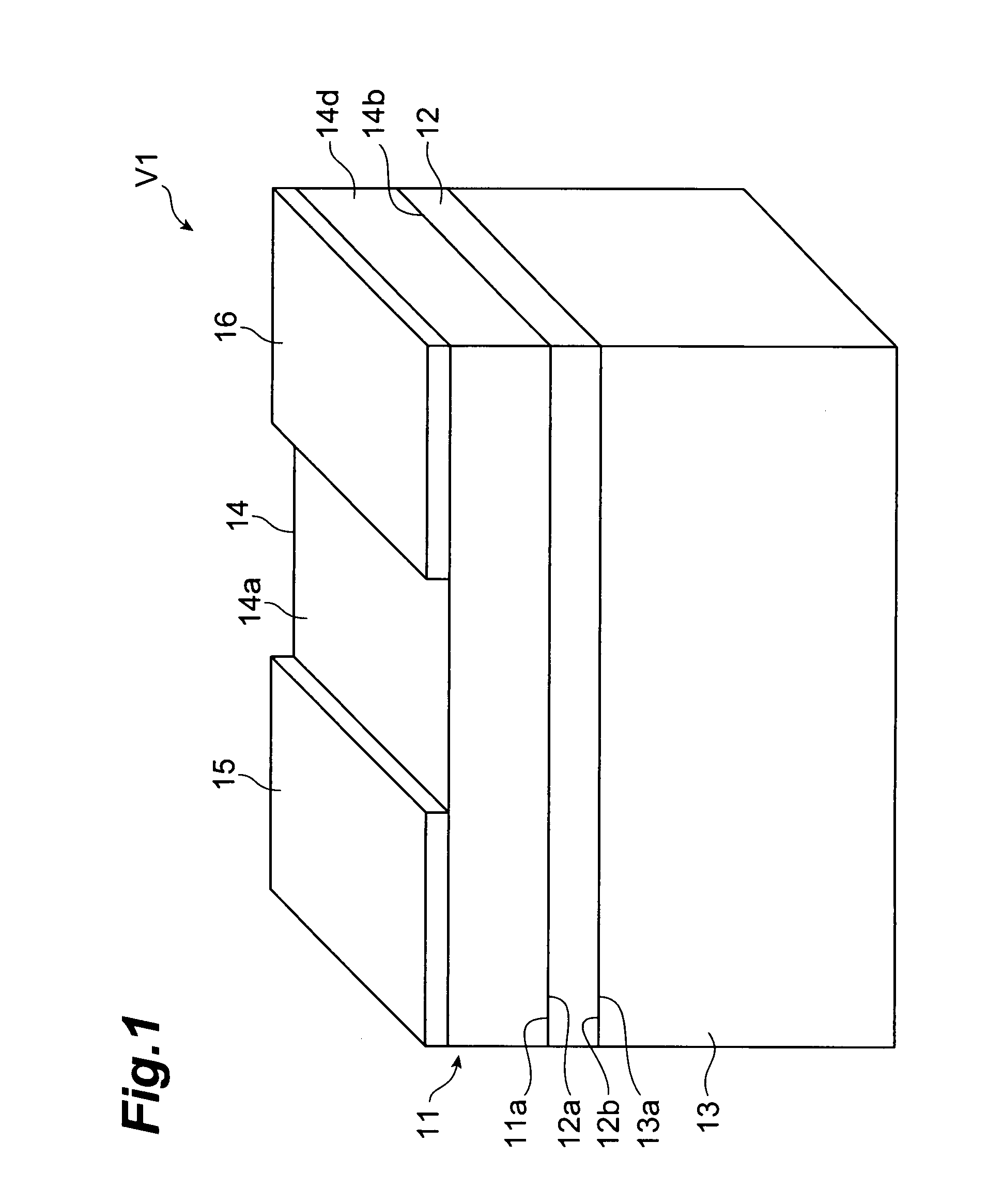
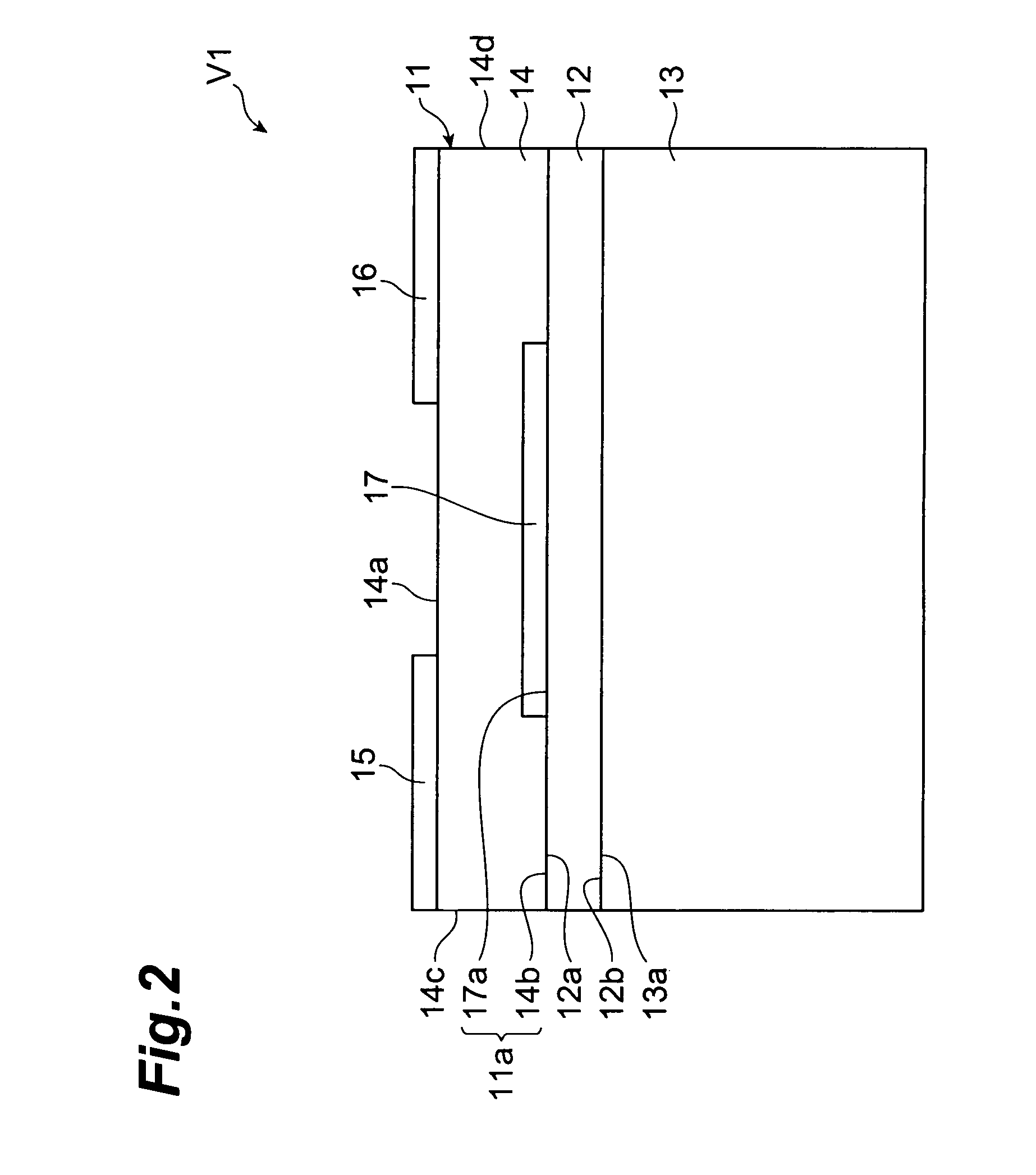
Multilayer chip varistor
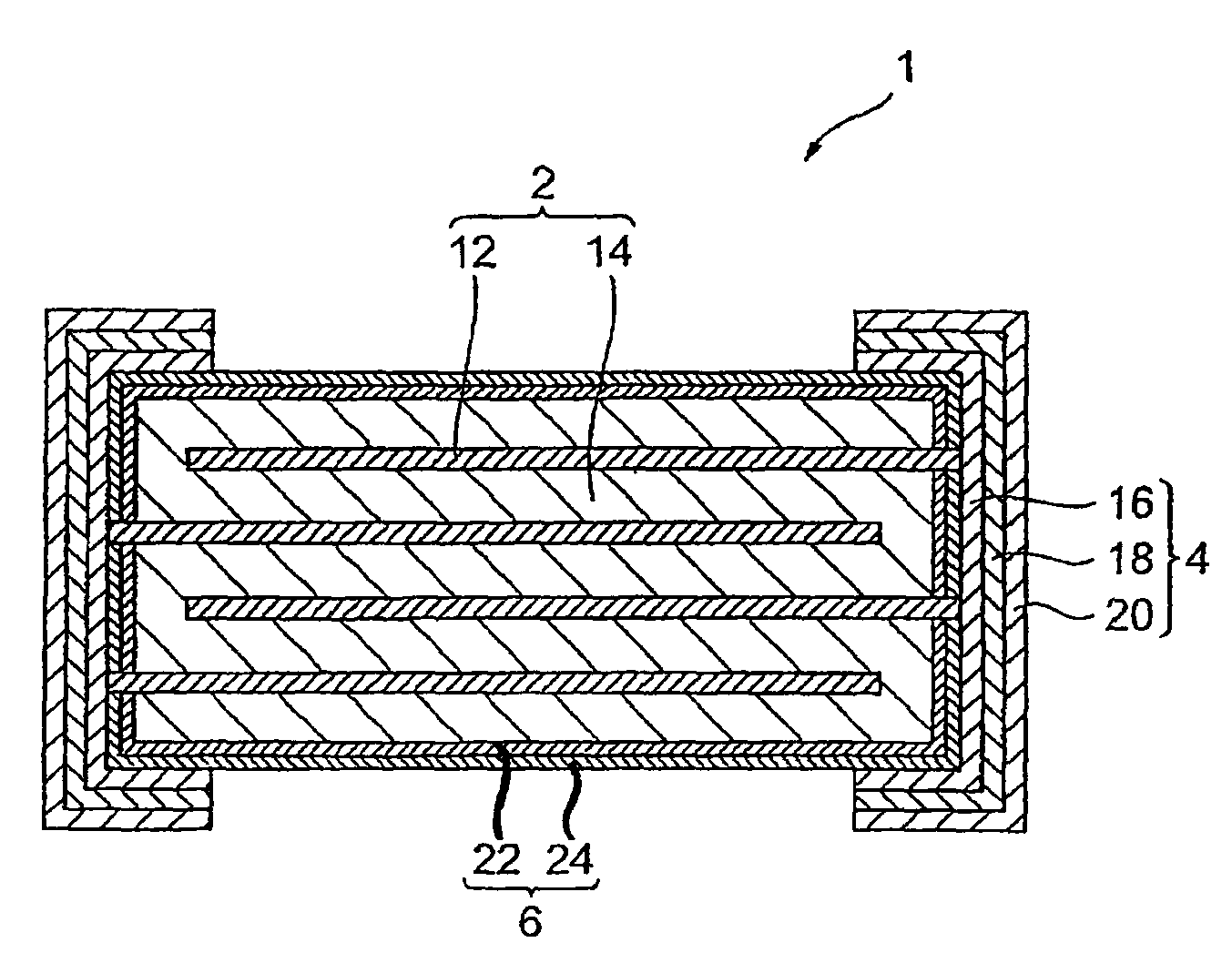
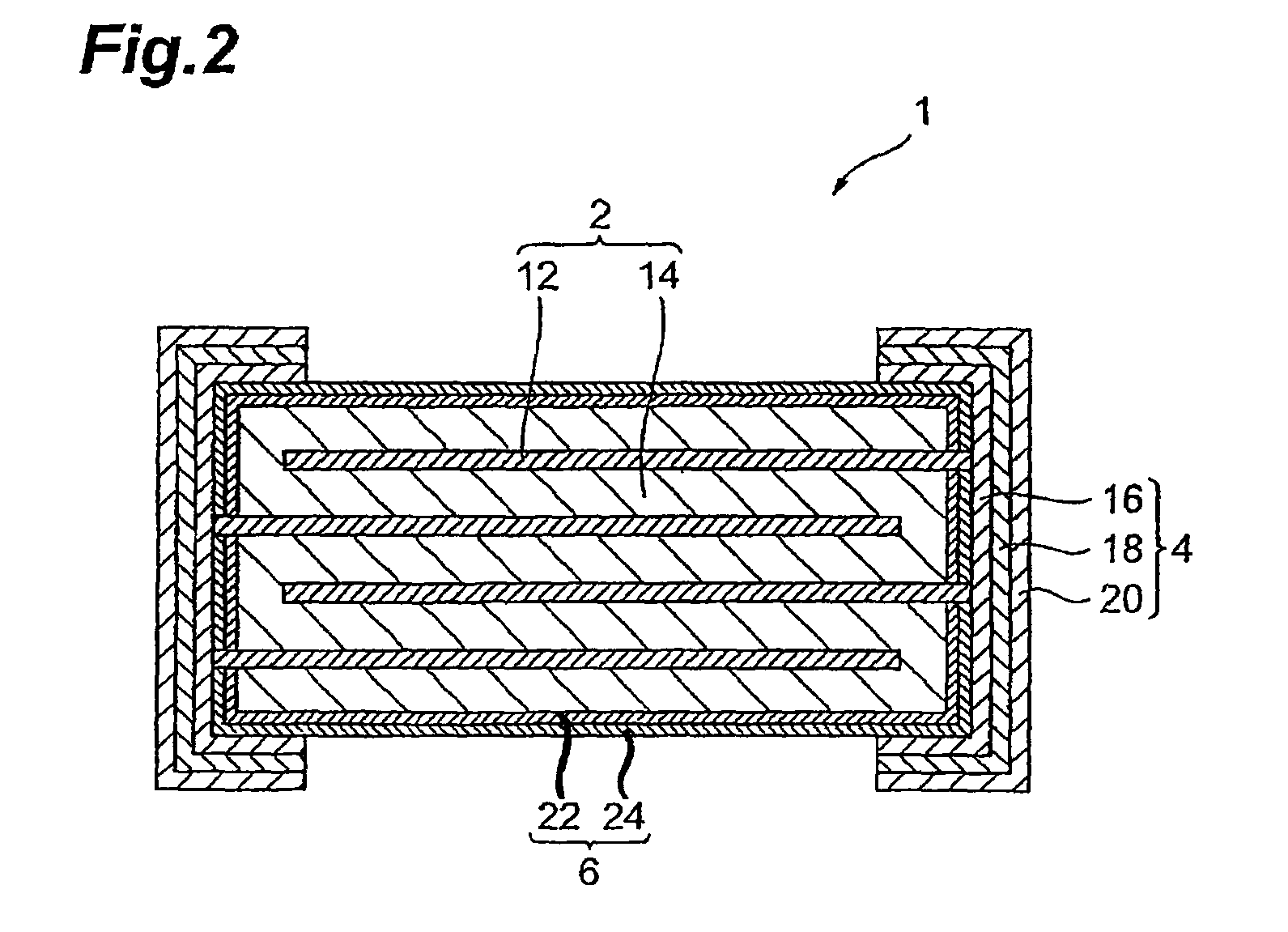
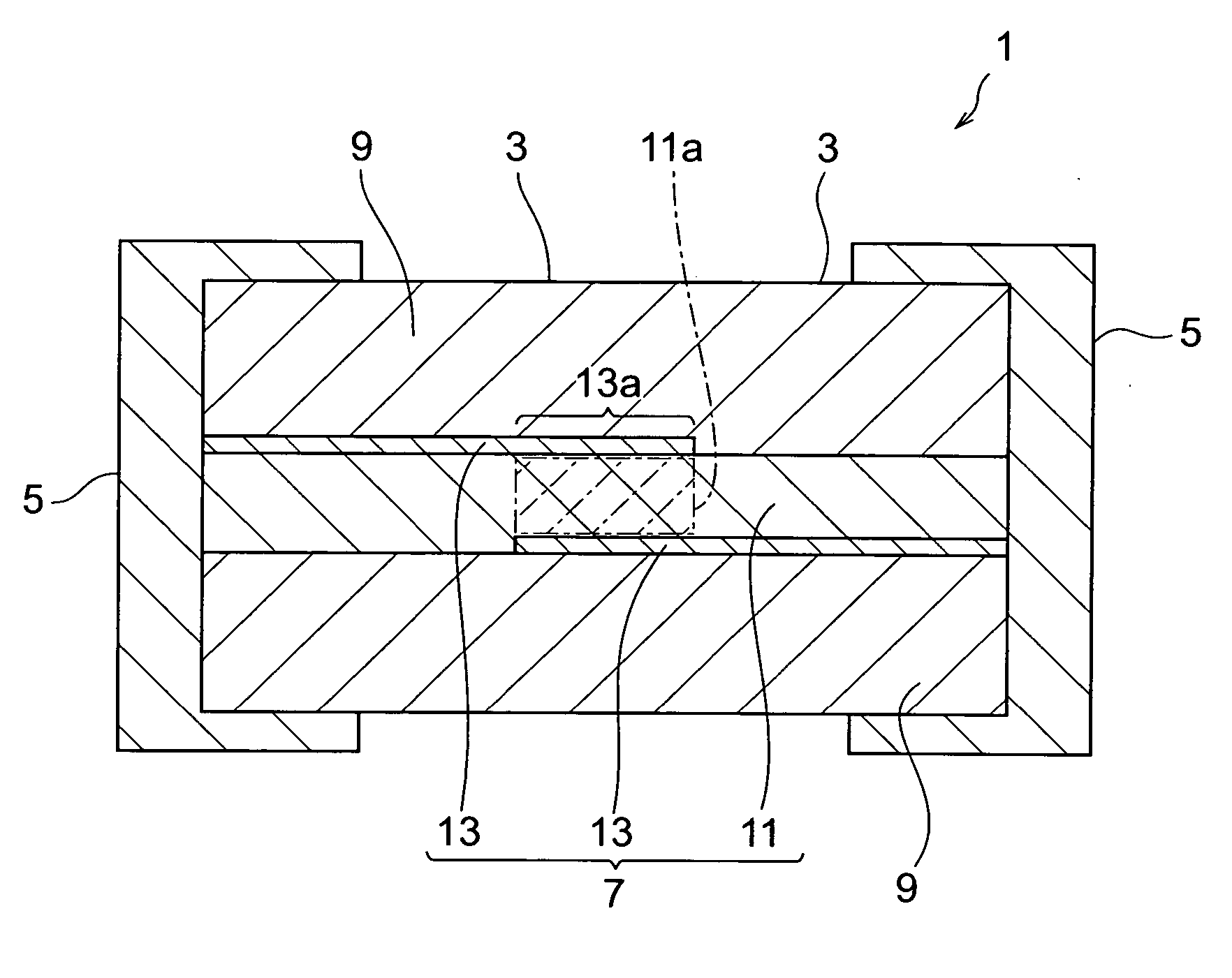
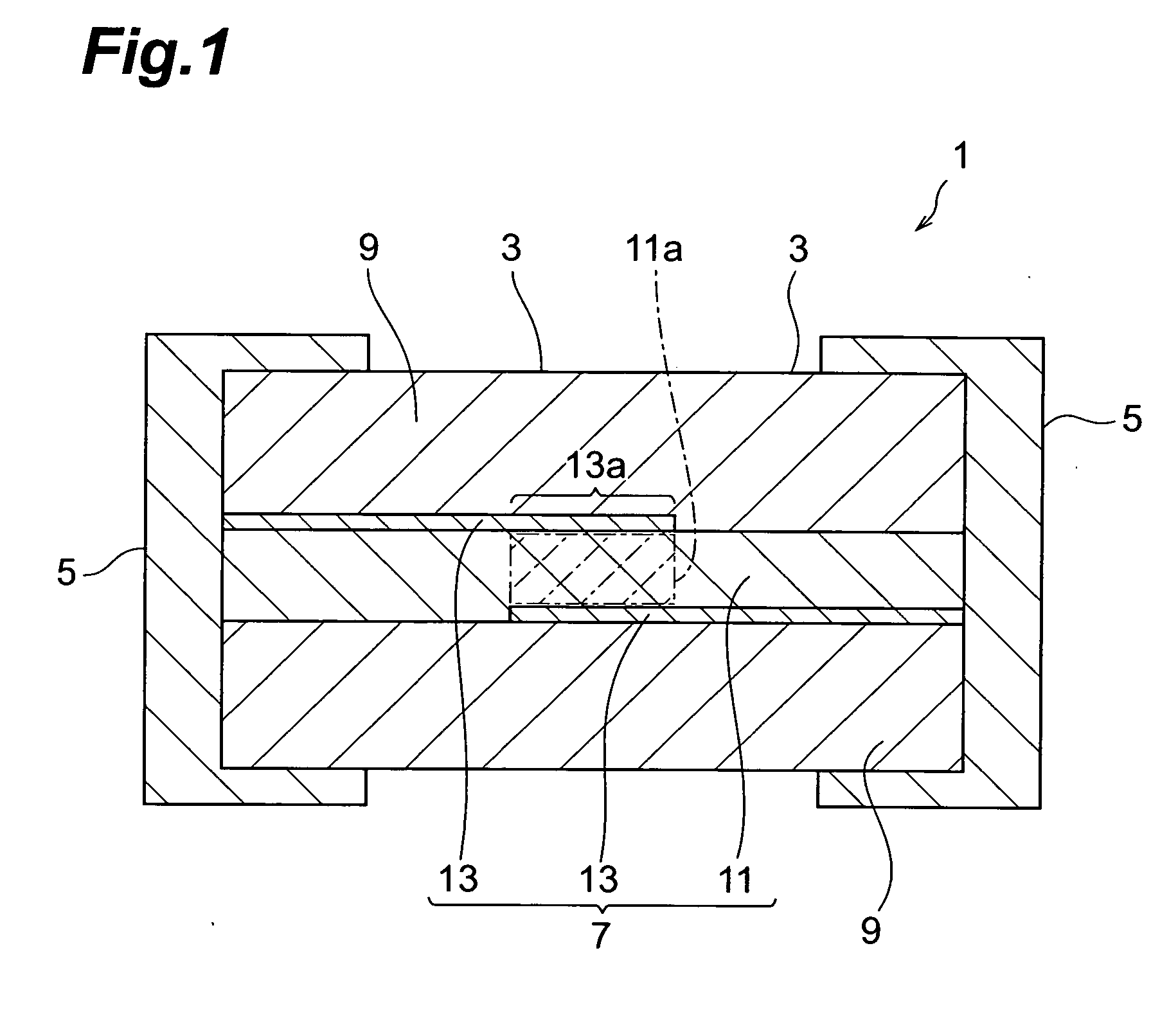
ActiveUS7167352B2Reduce capacitanceImprove the immunityFixed capacitor dielectricCurrent responsive resistorsDielectricVaristor
A multilayer chip varistor comprises a multilayer body and a pair of external electrodes formed on the multilayer body. The multilayer body has a varistor section and a pair of outer layer sections disposed so as to interpose said varistor section. The varistor section comprises a varistor layer developing a voltage nonlinear characteristic and a pair of internal electrodes disposed so as to interpose the varistor layer. The pair of external electrodes are connected to respective electrodes of the pair of internal electrodes. The relative dielectric constant of the outer layer sections is set lower than the relative dielectric constant of the region where the pair of internal electrodes in the varistor layer overlap each other.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
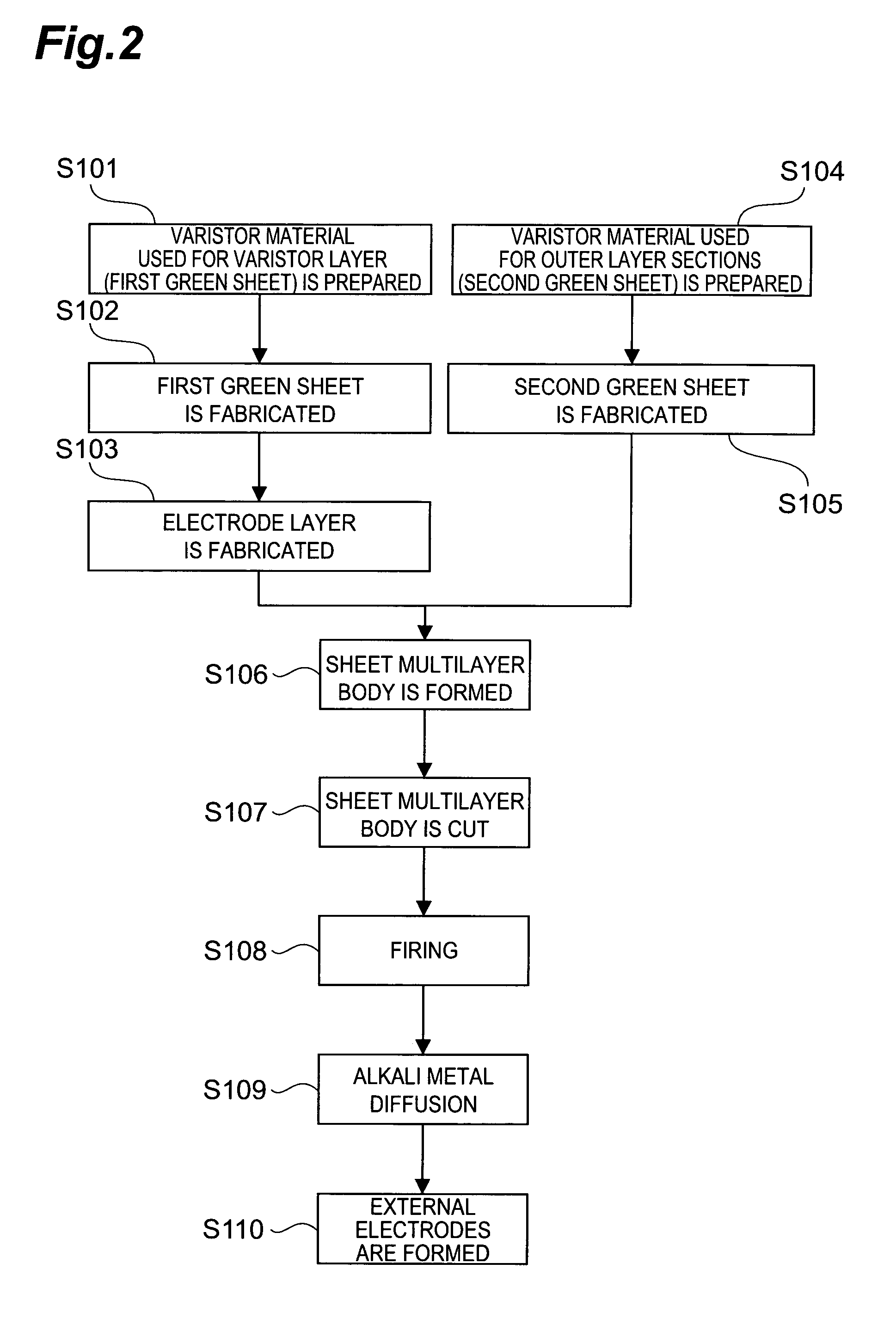
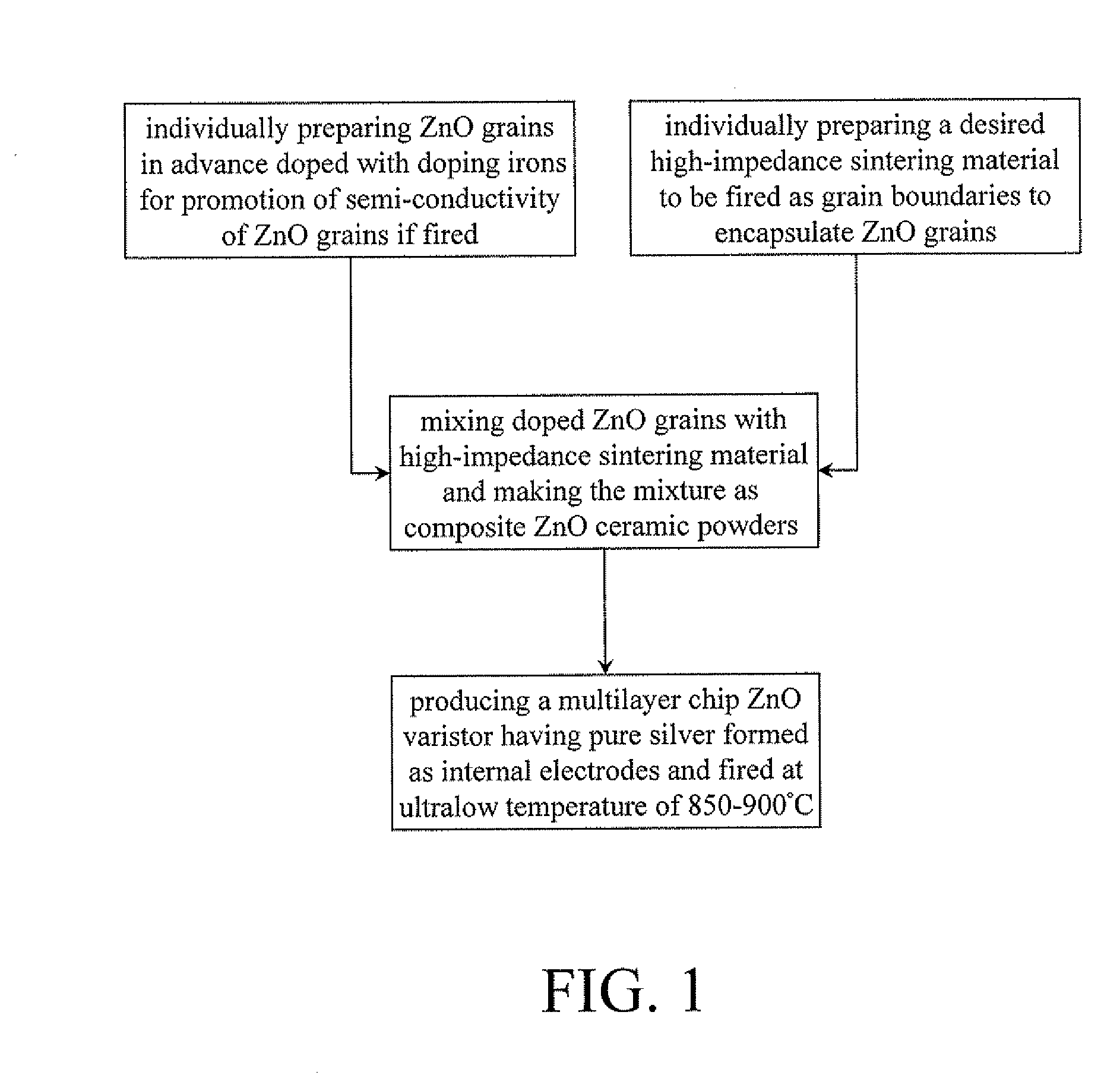
Process for producing multilayer chip zinc oxide varistor containing pure silver internal electrodes and firing at ultralow temperature
InactiveUS20120135563A1Low costGood chemical stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVaristor coresZincCost savings
A low-temperature firing process is available for cost saving to produce a multilayer chip ZnO varistor containing pure silver (Ag) formed as internal electrodes and calcined at ultralow firing temperature of 850-900° C., which process comprises:a) individually preparing ZnO grains in advance doped with doping ions for promotion of semi-conductivity of ZnO grains if calcined;b) individually preparing a desired high-impedance sintering material to be fired as grain boundaries to encapsulate ZnO grains;c) mixing the doped ZnO grains of Step a) with the high-impedance sintering material of Step b) in a predetermined ratio to form a mixture and proceeding with an initial sintering to have the mixture sintered and ground as composite ZnO ceramic powders, andd) processing the sintered mixture of Step c) to make multilayer chip ZnO varistors containing pure silver (Ag) internal electrodes but sintered at ultralow firing temperature of 850-900° C.
Owner:SFI ELECTRONICS TECH
Metal oxide varistor with built-in alloy-type thermal fuse
ActiveUS8780521B2Simple and compact structureRapid responseEmergency protective arrangement detailsThermally actuated switchesEngineeringAlloy
An electronic protection component incorporates both a varistor and an alloy-type thermal fuse. In one embodiment, a melting promoting agent or flux contacts and surrounds both the varistor and the fuse in common in a shared cavity of a case. In another embodiment, the fuse and the flux are disposed in an inner case, which is disposed in contact with the varistor in an outer case. Thus, the varistor and the thermal fuse are incorporated so that the speed of heat transfer is fast, the response time is fast, and the installation for use is convenient.
Owner:XIAMEN SET ELECTRONICS
Ceramic element
ActiveUS7813104B2Avoid surface lossPrevent adhesionFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsProtection layerElectrode
A ceramic element, including: a ceramic body having an internal electrode layer and a ceramic layer; an external electrode having a base electrode which is provided on the outside of the ceramic body so as to be electrically connected with the internal electrode layer, and a plating layer covering the outer surface of the base electrode; and a protective layer for covering at least a portion of the outer surface of the ceramic layer other than the portion covered by the external electrode, wherein the protective layer includes a first layer that is an insulating layer containing an insulating oxide, and a second layer that is an insulating layer containing the same insulating oxide as the first layer and an element that is the same as at least one of elements forming the ceramic layer, and the first layer and second layer are formed in that order from the inside.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
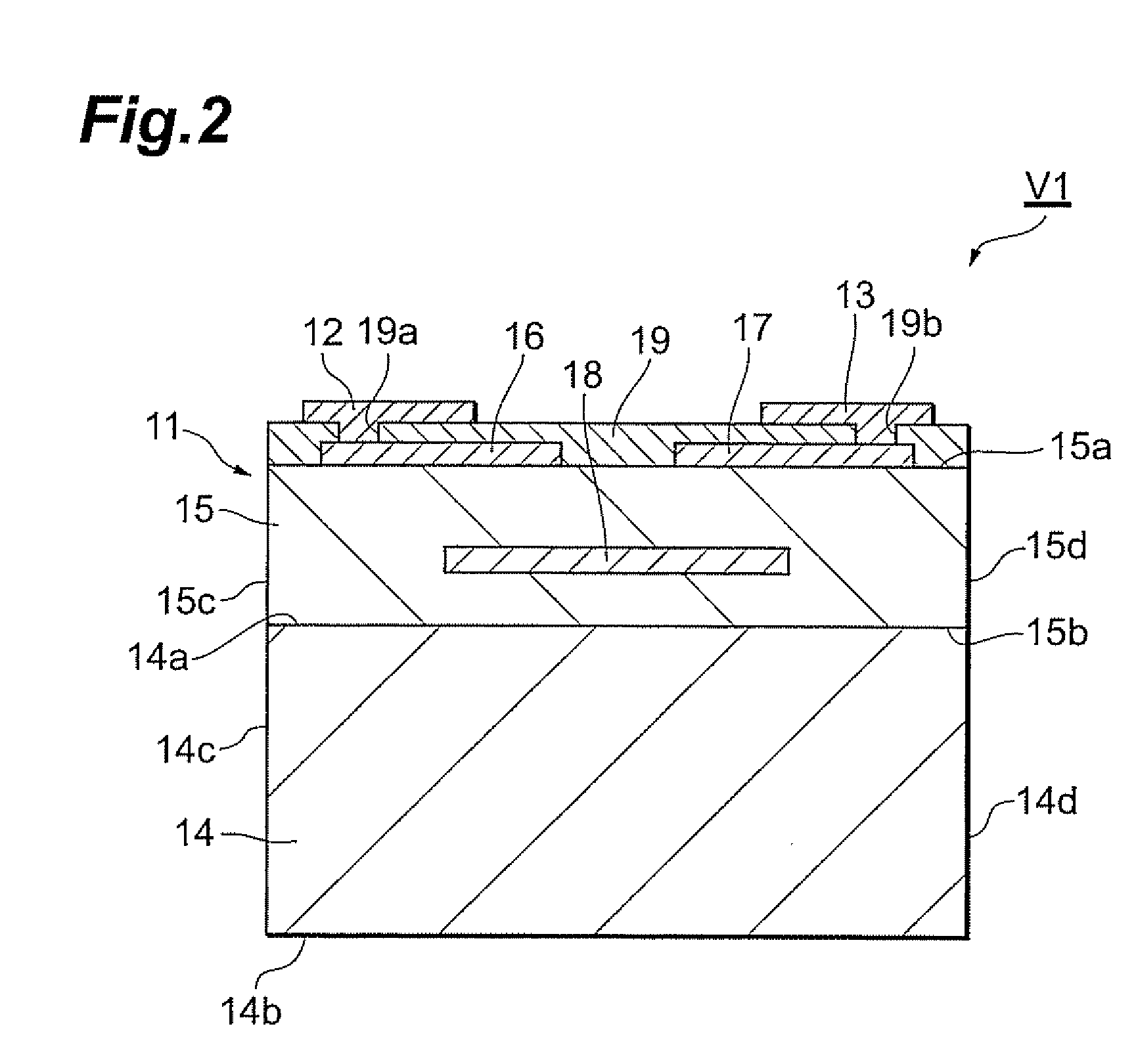
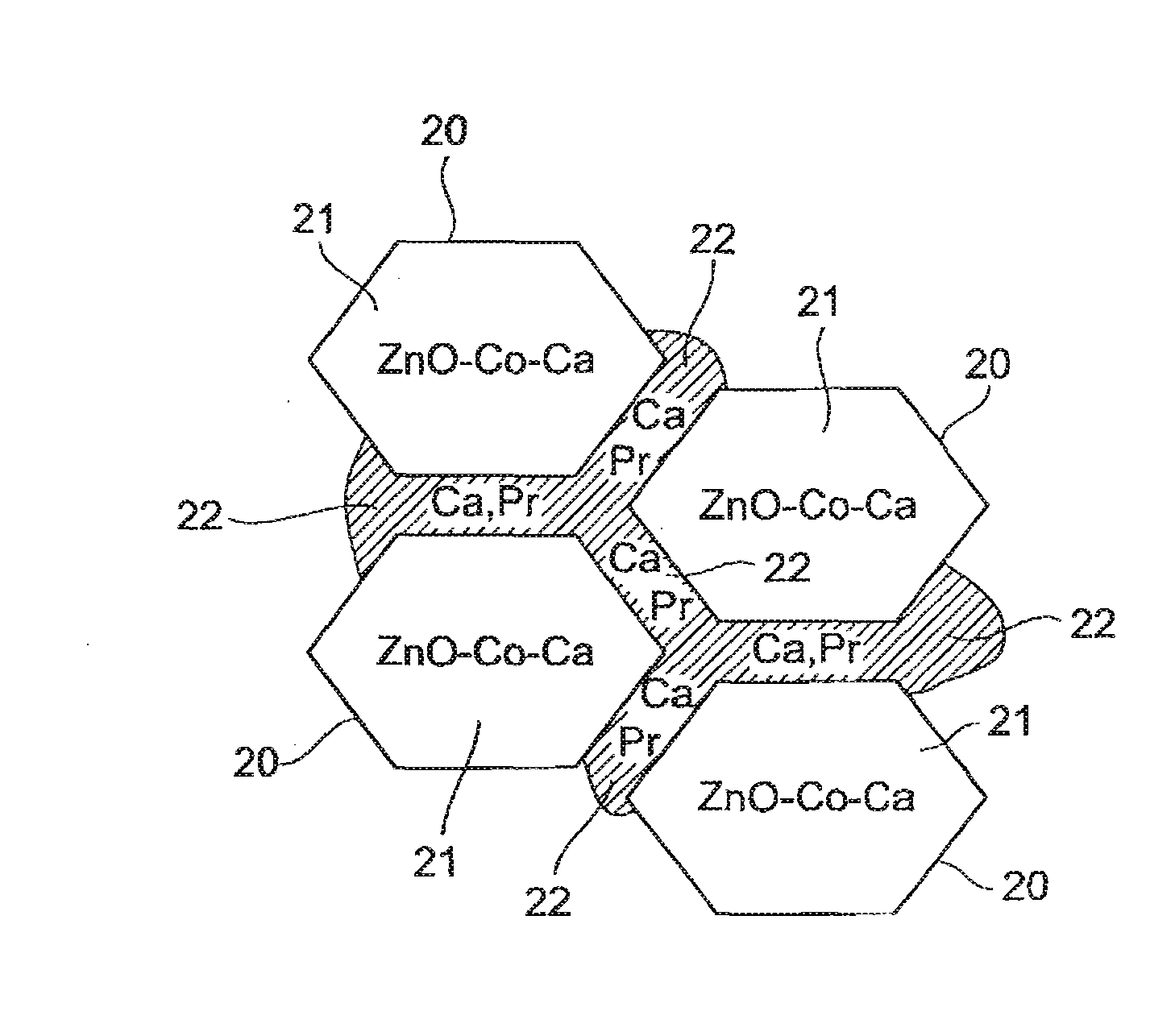
Varistor element
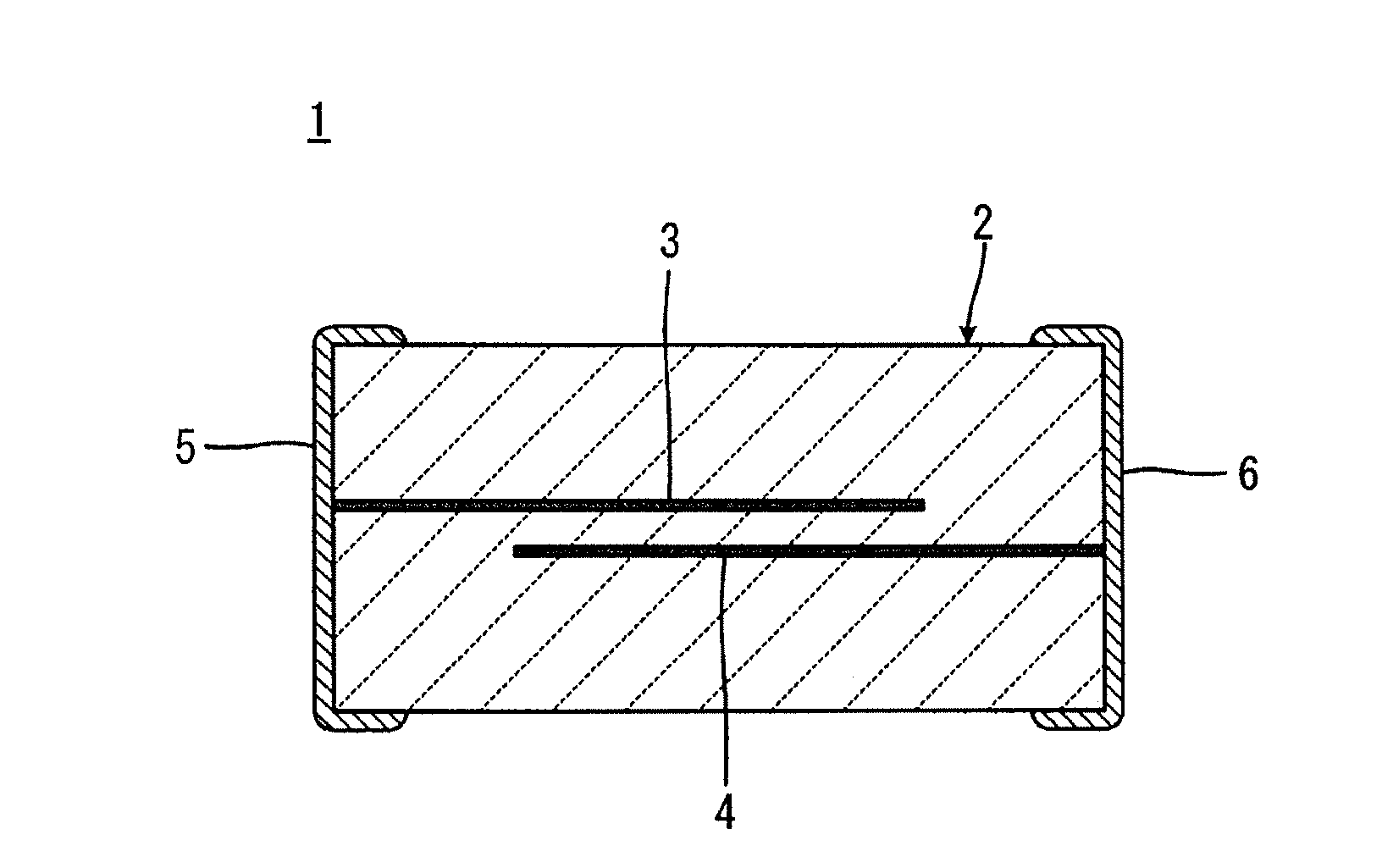
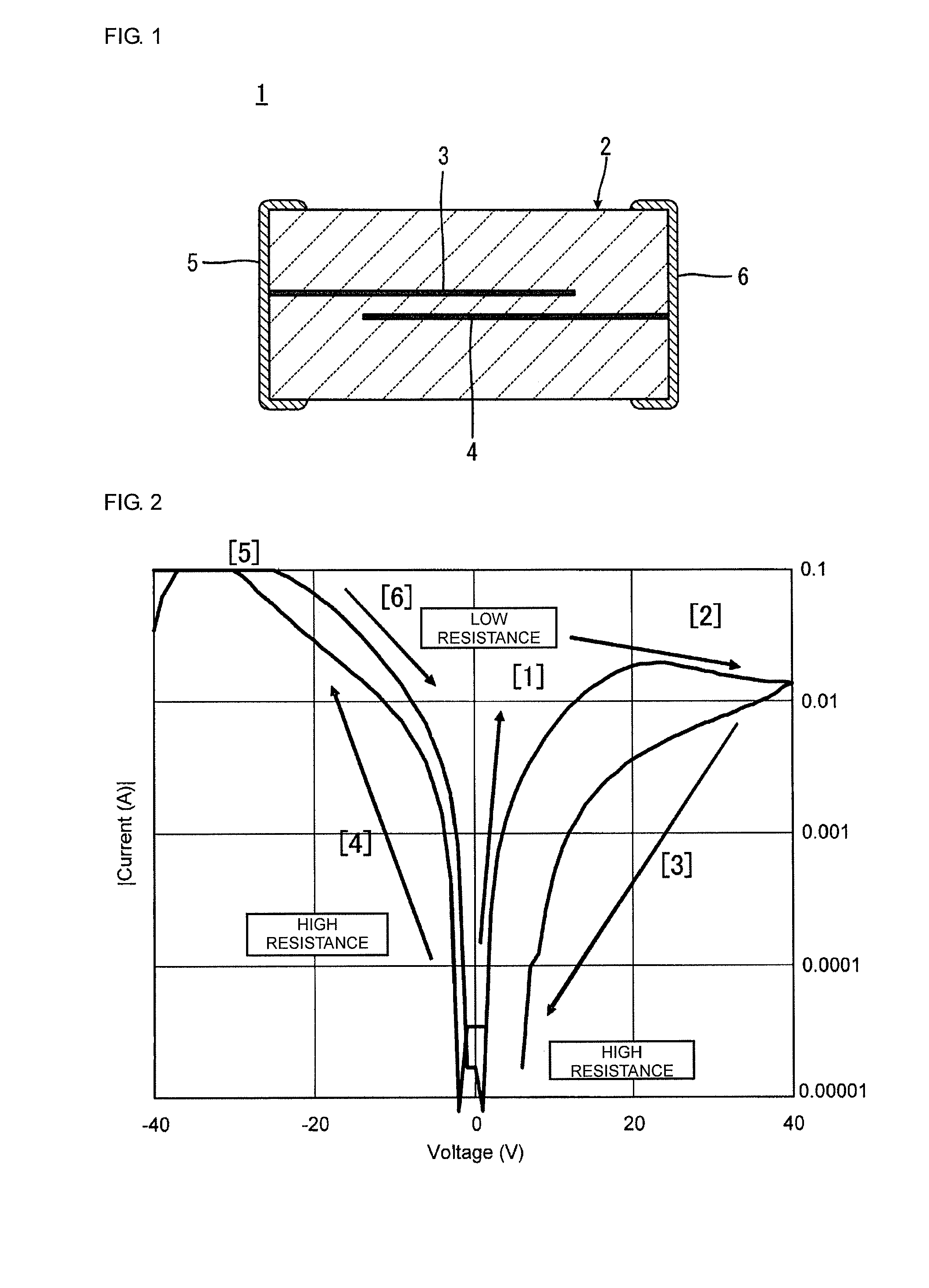
ActiveUS20080210911A1Reduce leakage currentStable temperature characteristicsCurrent responsive resistorsCeramicsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
In a varistor element, Ca exists in the grain interior of grains consisting primarily of ZnO in a varistor element body and Ca also exists in a grain boundary. In this crystal structure Ca replaces oxygen defects in the grain interior of grains consisting primarily of ZnO, in the varistor element body to make the ceramic structure denser Such crystal structure also decreases a ratio of an element tending to degrade the stability of the temperature characteristic of the varistor element, e.g., Si as a firing aid, in the grain boundary between grains. As a result, the varistor element has a stable temperature characteristic, which can decrease change in capacitance and tanδ (thermal conversion factor of resistance) against change in temperature.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Electronic device and method
An article is provided that includes a plurality of layers. Each layer includes a sinterable mass having a sinter temperature that is less than about 1000 degrees Celsius, and an inner electrode proximate to the sinterable mass. The inner electrode includes a material having a melting point that is within a determined temperature range of about 10 degrees Celsius to about 200 degrees Celsius relative to the sintering temperature. A method to make the article is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
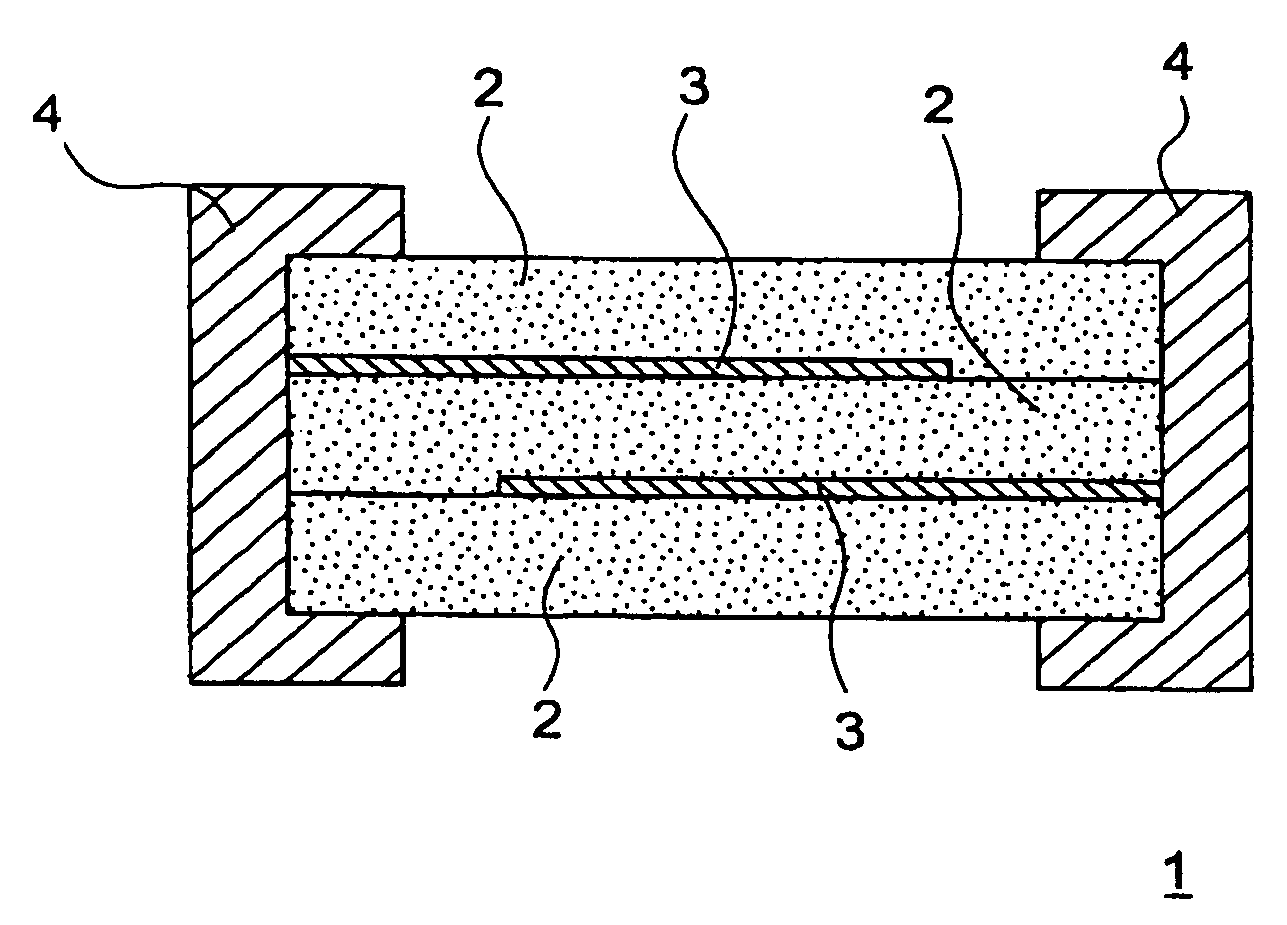
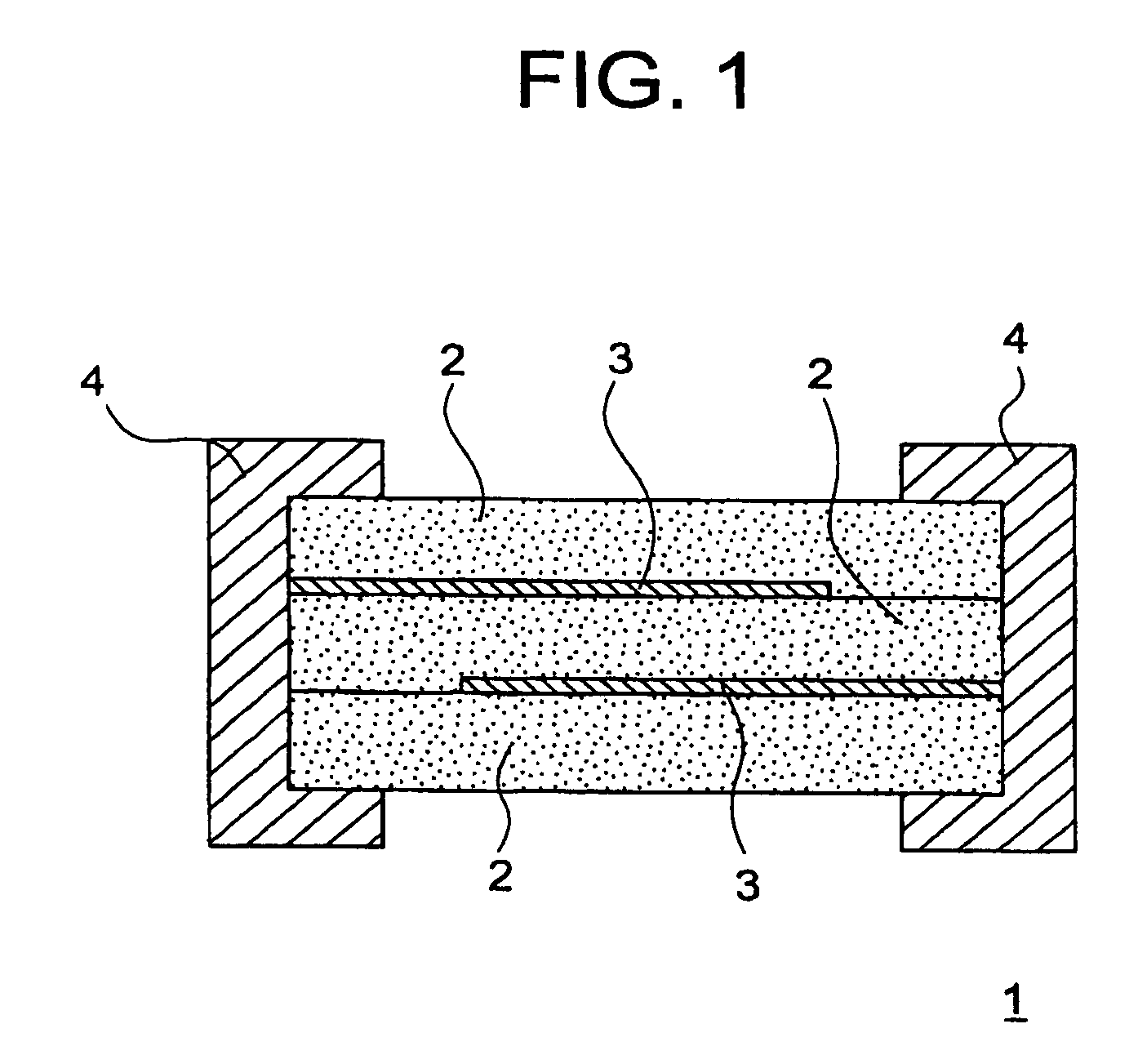
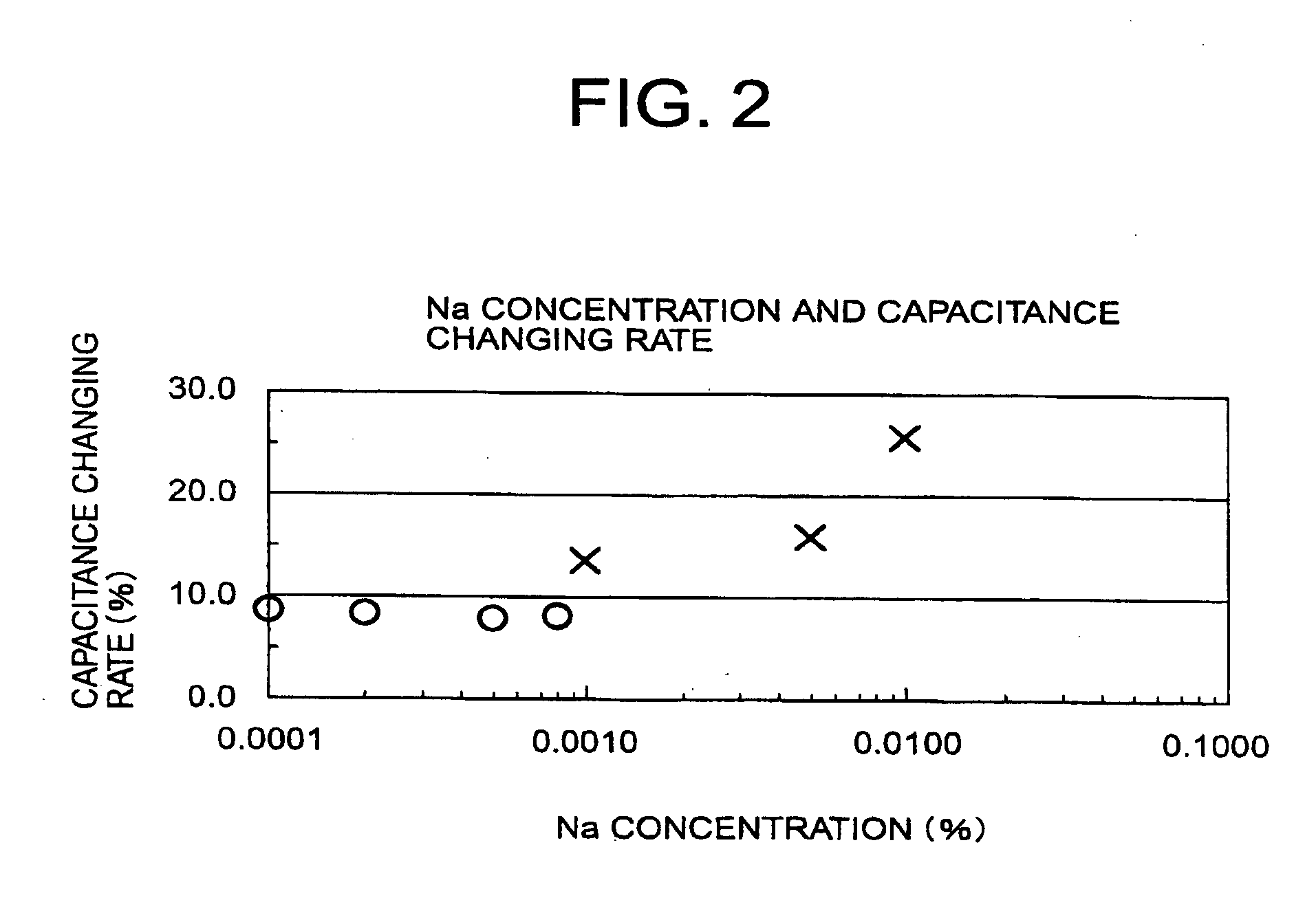
Voltage non-linear resistance ceramic composition and voltage non-linear resistance element
ActiveUS20080238605A1Small capacitance fluctuationEasy to changeCurrent responsive resistorsConductive materialCapacitanceMetallurgy
As for the voltage non-linear resistance element layer 2, sintered body (ceramics) having ZnO as main component is used. Said sintered body comprises Pr, Co, Ca and Na are added. Therefore, the ranges are 0.05 to 5.0 atm % of Pr, 0.1 to 20 atm % of Co, 0.01 to 5.0 atm % of Ca and 0.0001 to 0.0008 atm % of Na. When it is within the range, the capacitance changing rate at 85° C. with standard being 25° C. can be made to equal or less than 10%.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
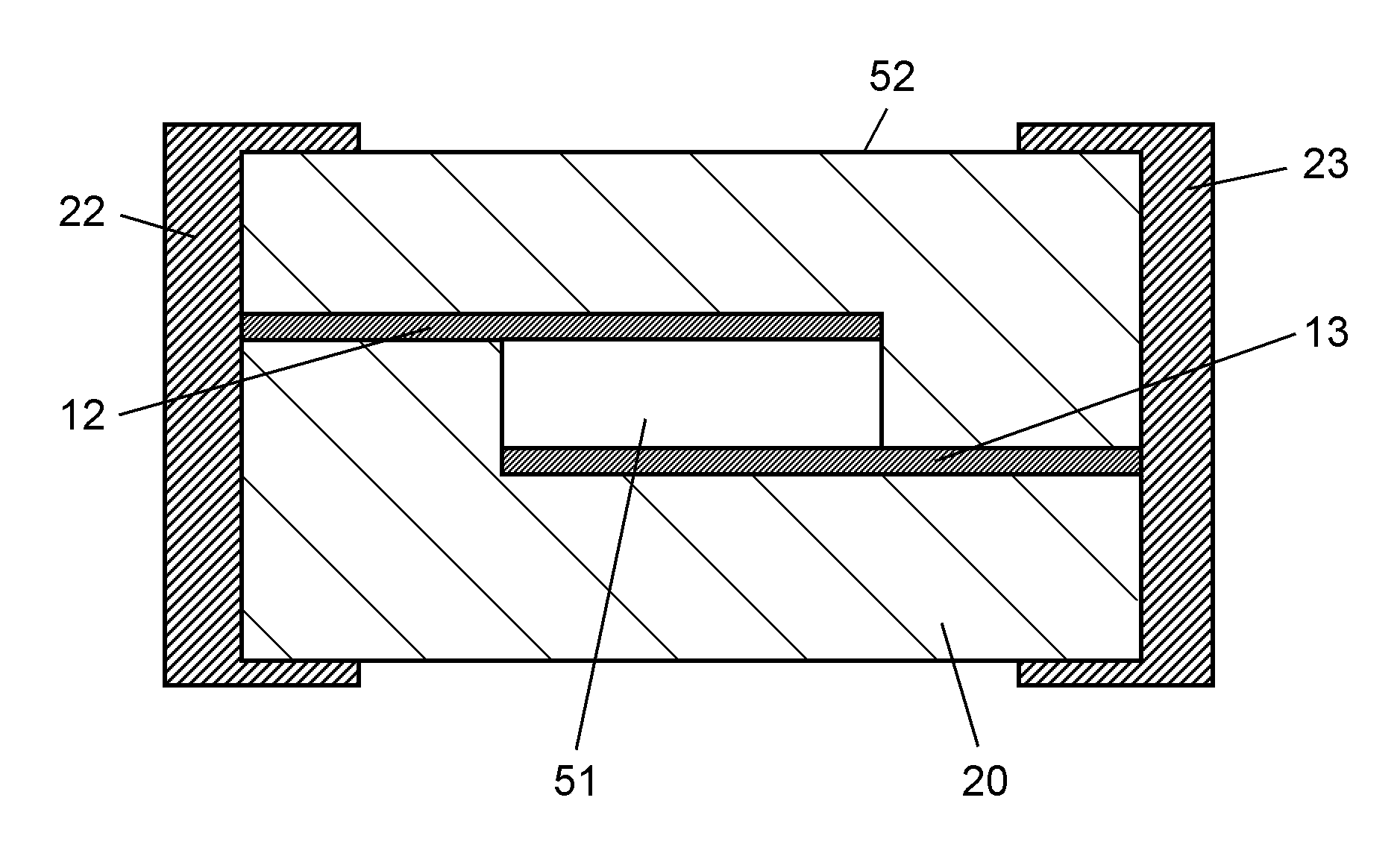
ESD protection device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120134059A1Discharge starting voltage and peak voltageNo characteristic degradationEnvelope/housing resistor manufacturePretreated surfacesGlass coverAuxiliary electrode
An ESD protection device includes a ceramic base material, a pair of opposed electrodes provided on a surface of or in the ceramic base material, and a discharge auxiliary electrode film arranged to connect the pair of opposed electrodes, wherein the discharge auxiliary electrode film is composed of a material containing, as its main constituents, metallic particles and glass covering the metallic particles. The discharge auxiliary electrode film is formed by providing an electrode paste containing glass-coated metallic particles that have an approximately 15% rate of increase in weight at about 400° C. for about 2 hours in air, a resin binder, and a solvent so as to connect the pair of opposed electrodes to each other, and then firing at a temperature of about 600° C. or more, higher than a softening point of glass of the glass-coated metallic particles, and not +200° C. higher than the softening point.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multilayer filter
ActiveUS20060261914A1Reduce flakingLikely can be stressedMultiple-port networksSolid-state devicesEngineeringVaristor
An object of the present invention is to provide a multilayer filter constructed so as to be less likely to suffer peeling between a varistor part and an inductor part. A multilayer filter 10 as a preferred embodiment has a structure in which a varistor part 20 and an inductor part are stacked. The varistor part 30 consists of a stack of varistor layers 31, 32 with internal electrodes 31a, 32a, and the varistor layers contain ZnO as a principal component, and contain at least one element selected from the group consisting of Pr and Bi, Co, and Al as additives. The inductor part 20 consists of a stack of inductor layers 21-24 with conductor patterns 21a-24a, and the inductor layers contain ZnO as a principal component and substantially contain neither Co nor Al.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Varistor and light-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS7705709B2Efficient heatingDeterioration of characteristicCurrent responsive resistorsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLight emitting device
A varistor comprises a varistor portion, a metal portion, and buffer portion. The varistor portion has a varistor element body exhibiting a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic and two electrode portions. The metal portion has a thermal conductivity higher than that of the varistor element body. The buffer portion is disposed between the varistor portion and metal portion so as to be bonded to each of the varistor portion and metal portion and mainly composed of glass. The two electrode portions are arranged in the varistor element body so as to be electrically insulated from each other while exposing at least a portion of each thereof from an outer surface of the varistor element body. The metal portion and varistor portion are joined firmly to each other. The heat transmitted to the varistor can efficiently be diffused from the metal portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multilayer chip varistor
ActiveUS20050276001A1Reduce capacitanceImprove the immunityCurrent responsive resistorsFixed capacitor dielectricDielectricEngineering
A multilayer chip varistor comprises a multilayer body and a pair of external electrodes formed on the multilayer body. The multilayer body has a varistor section and a pair of outer layer sections disposed so as to interpose said varistor section. The varistor section comprises a varistor layer developing a voltage nonlinear characteristic and a pair of internal electrodes disposed so as to interpose the varistor layer. The pair of external electrodes are connected to respective electrodes of the pair of internal electrodes. The relative dielectric constant of the outer layer sections is set lower than the relative dielectric constant of the region where the pair of internal electrodes in the varistor layer overlap each other.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Varistor
InactiveUS20100117782A1Avoid crackingJoint strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCurrent responsive resistorsEngineeringLight emitting device
A varistor having a favorable heat-dissipating property is provided.In the varistor, a composite part having a favorable heat-dissipating property formed by a composite material composed of ZnO and Ag is arranged between main faces of a varistor matrix. Therefore, the heat transmitted from a semiconductor light-emitting device to a varistor part through an outer electrode can rapidly be transferred toward a main face on the opposite side through the composite part. In this varistor, side faces excluding inner side faces are exposed at side faces of the varistor matrix. Such a structure yields a favorable heat-dissipating property.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Surge absorbing element
InactiveUS20110304946A1Little effectCurrent responsive resistorsEmergency protective arrangement detailsMaterials scienceAbsorbing element
A surge absorbing element has a first electrode, a second electrode, and a ceramic layer. The second electrode is opposed to the first electrode. The ceramic layer has a polycrystal structure including a plurality of crystal grains showing voltage nonlinearity, and is at least partially brought into contact with the first electrode and the second electrode. The ceramic layer has a void inside therein, and surface discharge is generated on surfaces, exposed to the void, of the crystal grains, whereby electric conduction is attained between the first and second electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Resistance memory element
ActiveUS8093682B2Fixed capacitor dielectricSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRare-earth elementHigh rate
A resistance memory element is provided which has a relatively high switching voltage and whose resistance can be changed at a relatively high rate. The resistance memory element includes an elementary body and a pair of electrodes opposing each other with at least part of the elementary body therebetween. The elementary body is made of a semiconductor ceramic expressed by a formula: {(Sr1-xMx)1-yAy}(Ti1-zBz)O3 (wherein M represents at least one of Ba and Ca, A represents at least one element selected from the group consisting of Y and rare earth elements, and B represents at least one of Nb and Ta), and satisfies 0<x≦0.5 and 0.001≦y+z≦0.02 (where 0≦y≦0.02 and 0≦z≦0.02); 0.5<x≦0.8 and 0.003≦y+z≦0.02 (where 0≦y≦0.02 and 0≦z≦0.02); or 0.8<x≦1.0 and 0.005≦y+z≦0.01 (where 0≦y≦0.02 and 0≦z≦0.02).
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
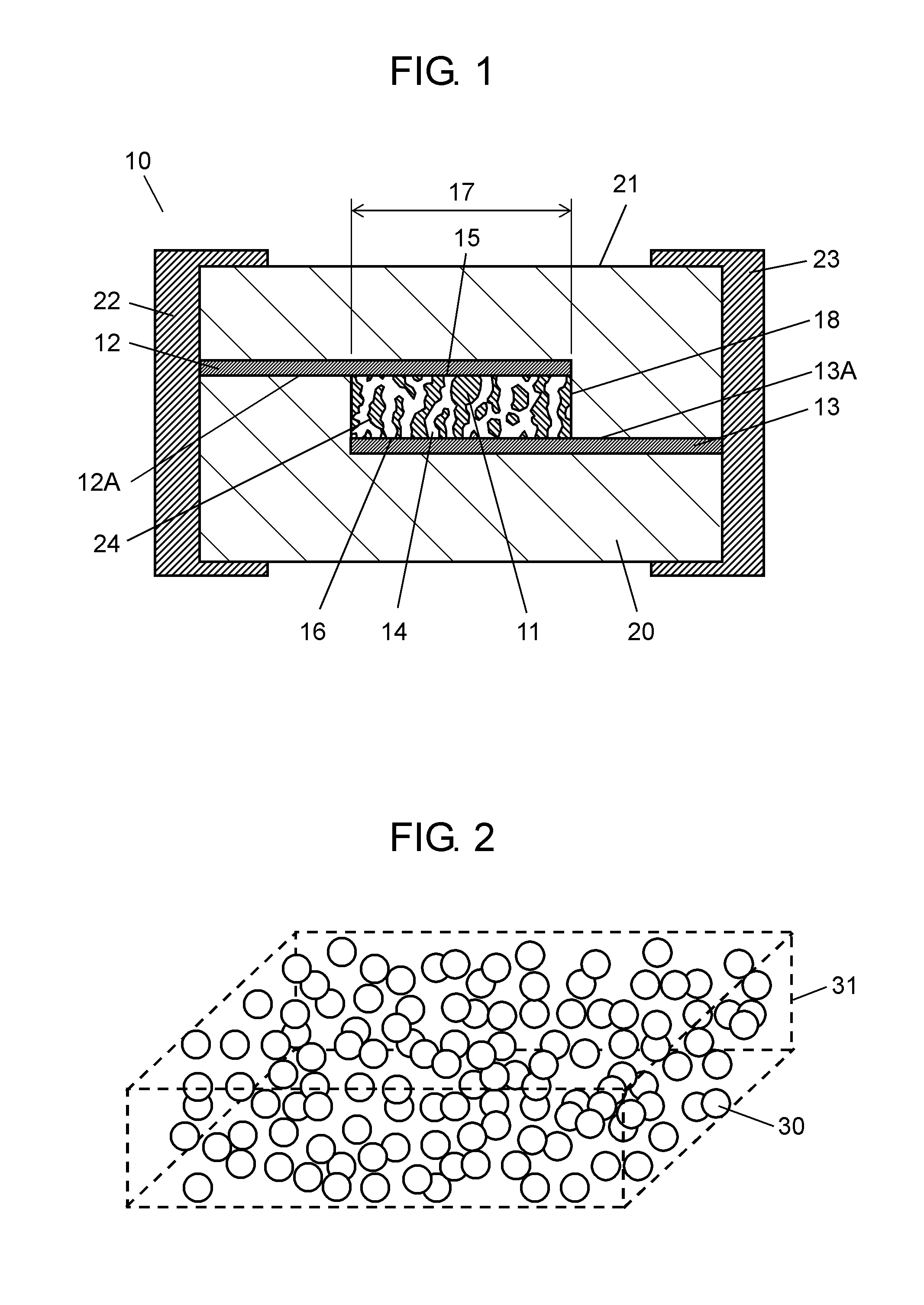
Method of manufacturing ESD protection component
InactiveUS20050141166A1Emergency protective arrangement detailsCeramic shaping apparatusCooking & bakingElectrical conductor
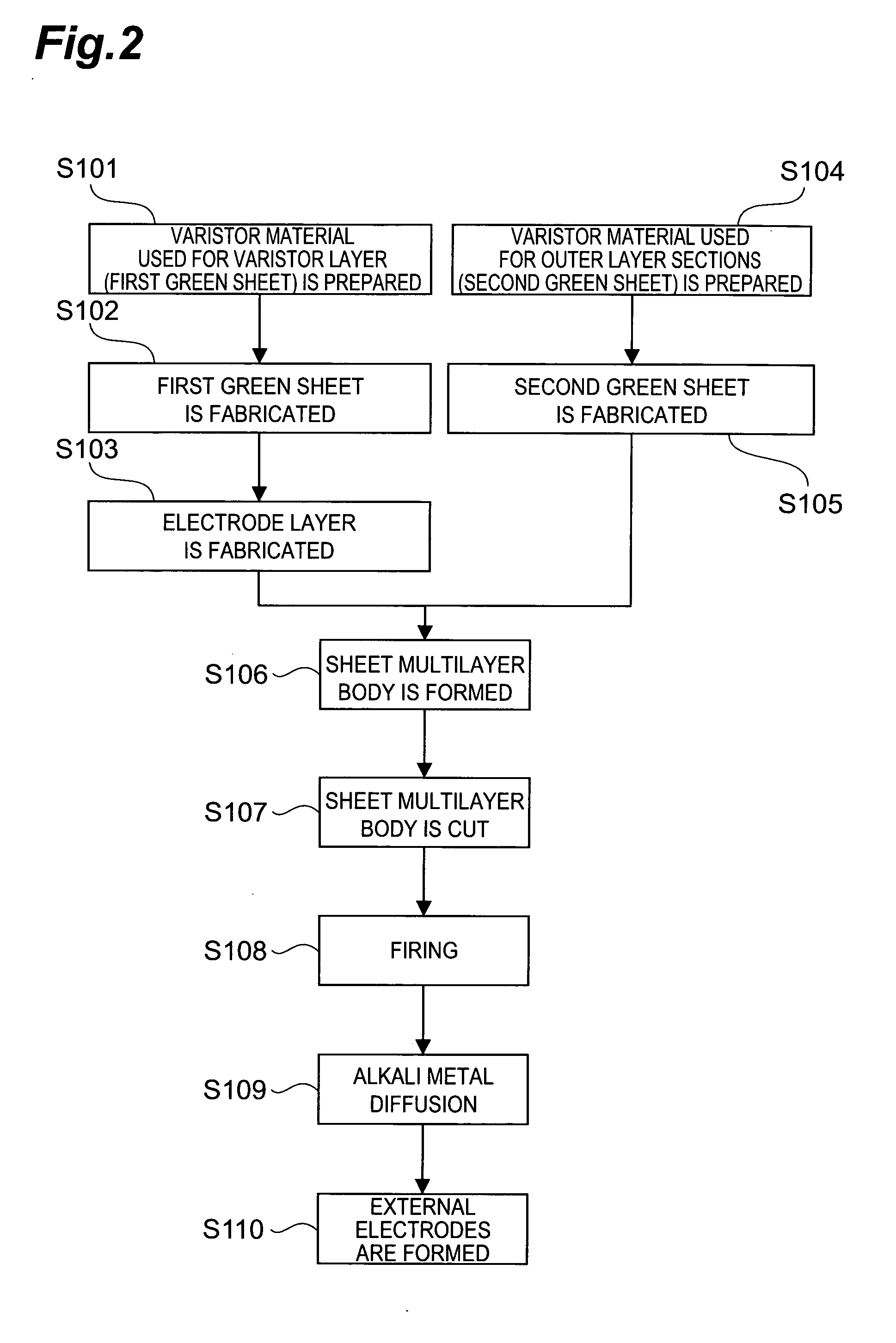
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing an ESD protection component, where the method includes at least a step of producing slurry including varistor particles and a resin binder; a step of producing a varistor green sheet from this slurry; a step of forming a conductor layer; a step of forming an adhesive layer on a ceramic substrate; a step of sticking a varistor green sheet on an adhesive layer; and a step of baking, providing a high-performance and uniform ESD protection component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
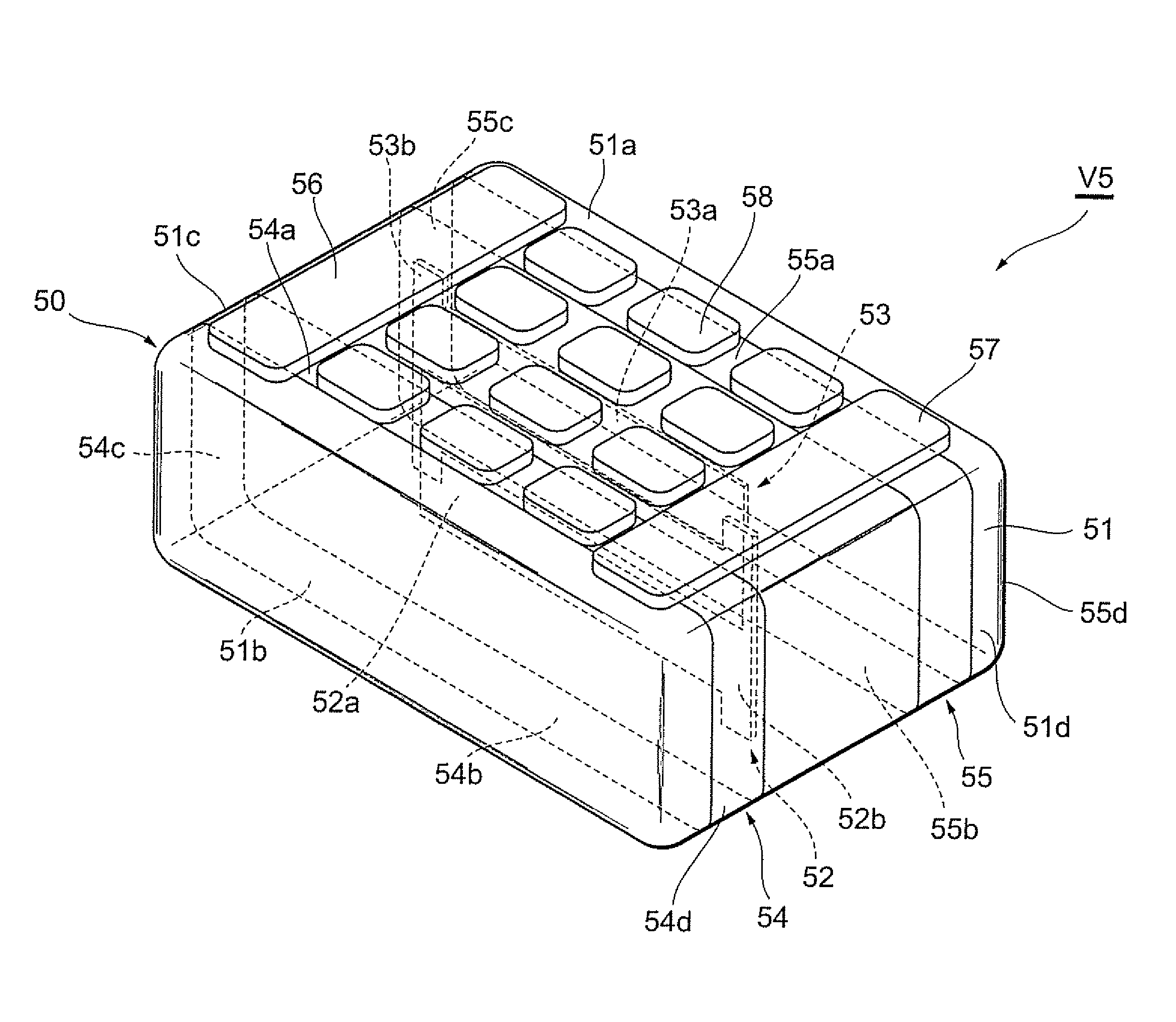
Ceramic component and method for producing a ceramic component
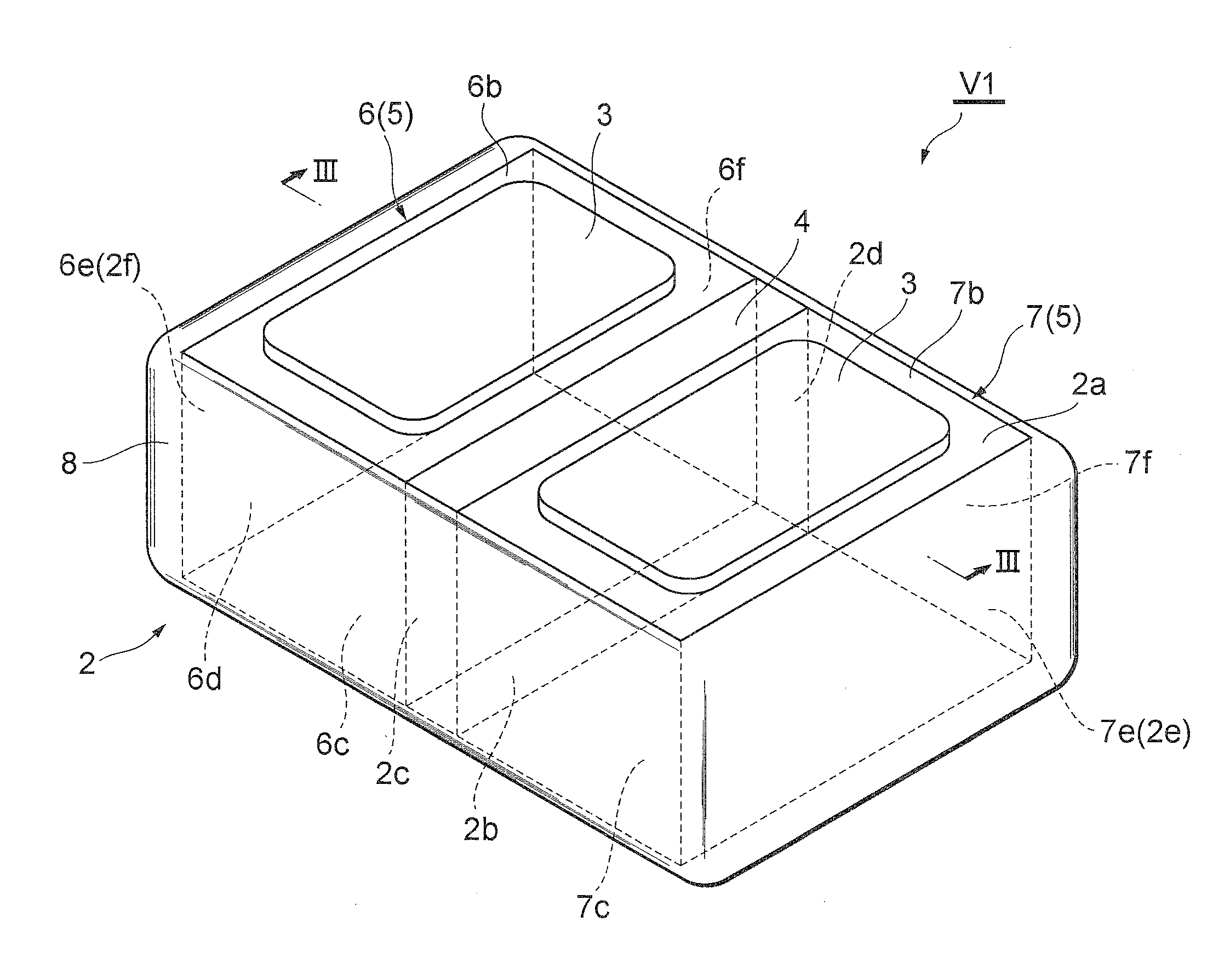
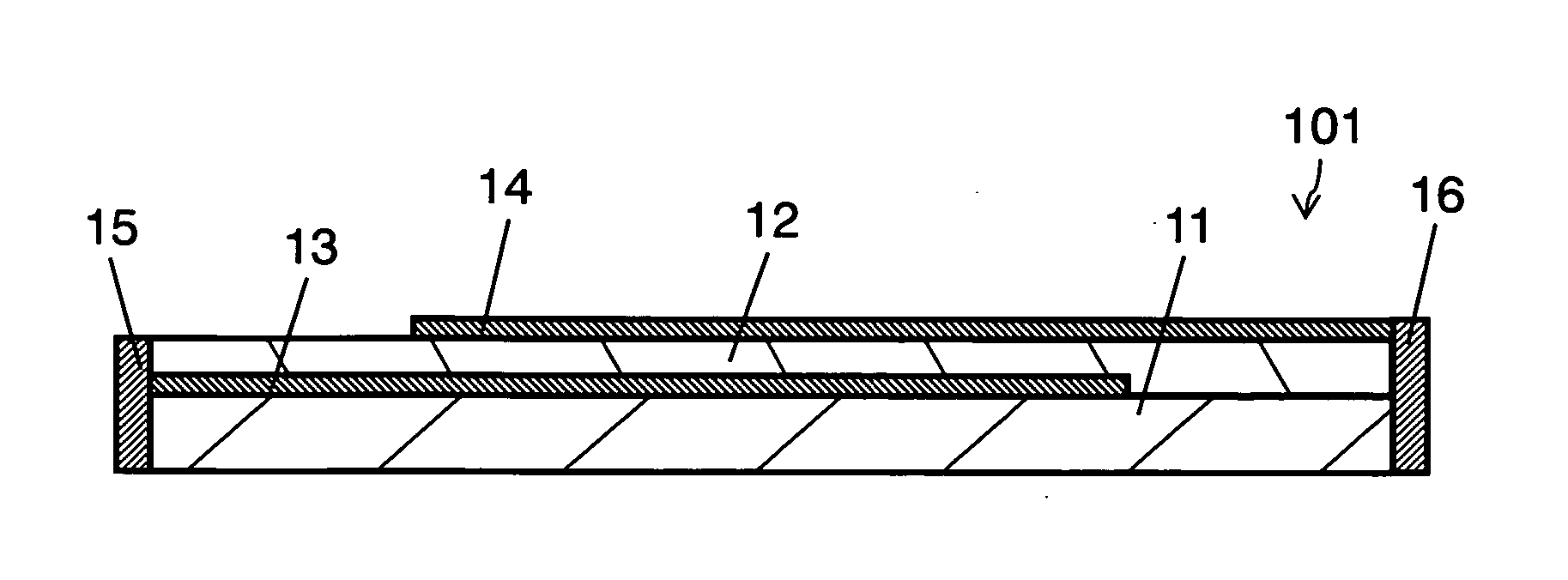
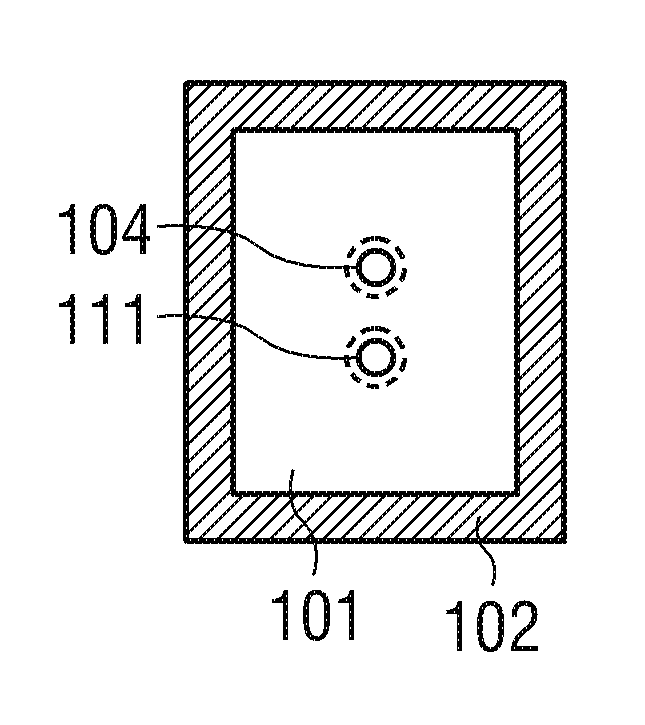
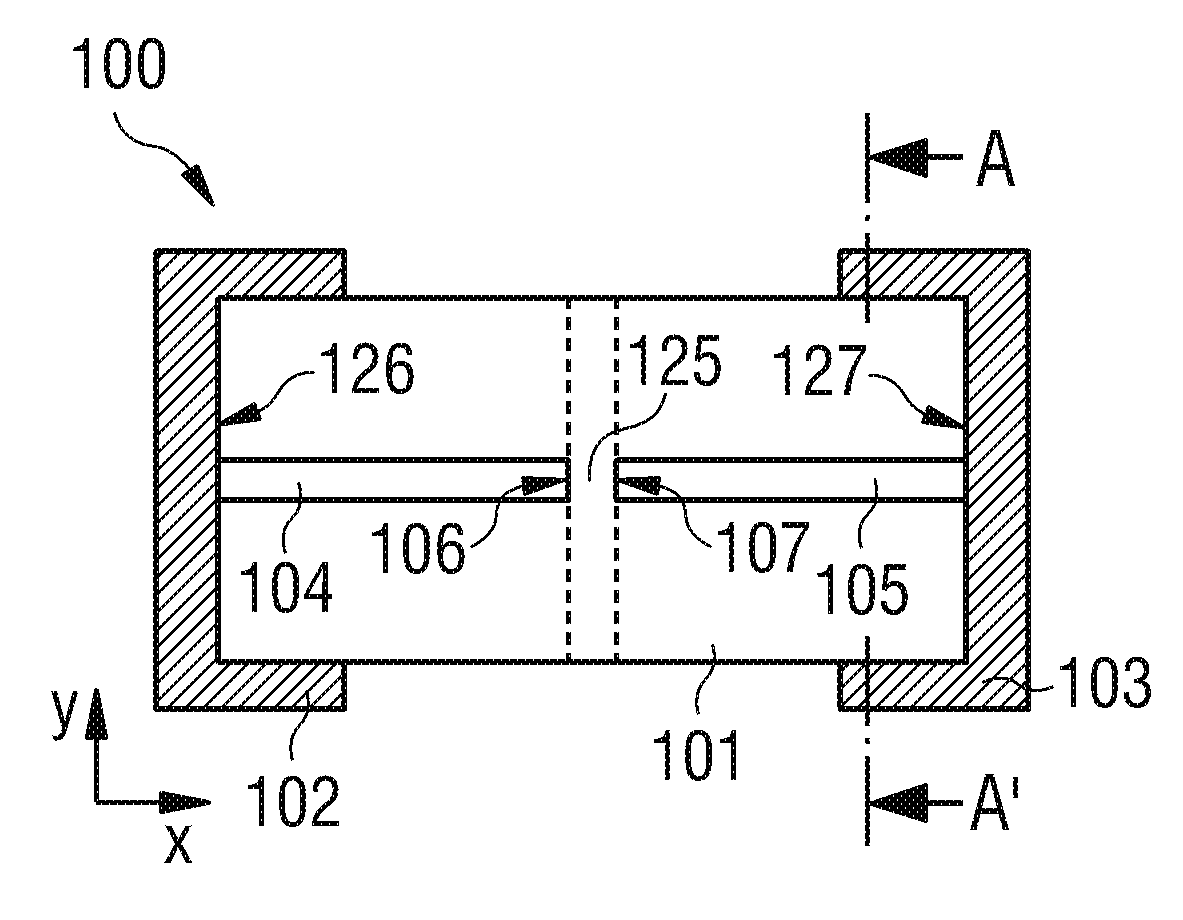
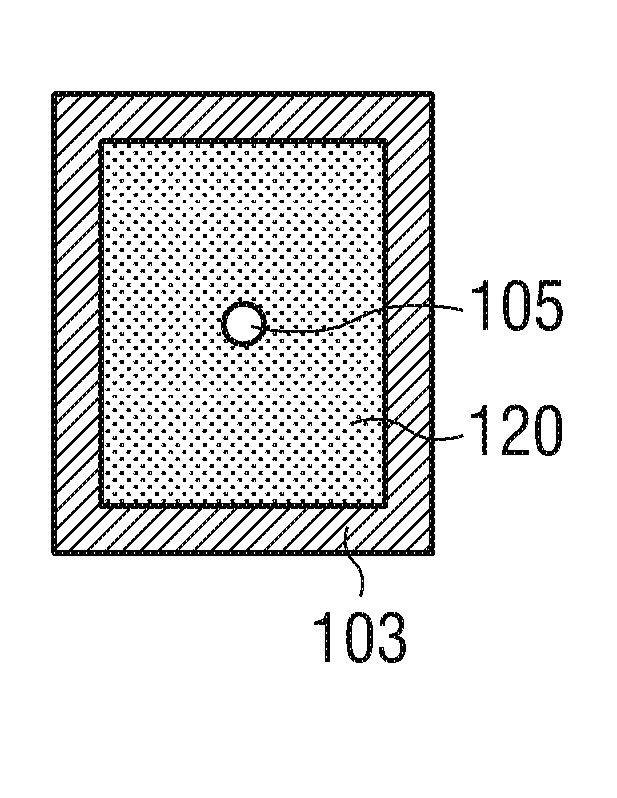
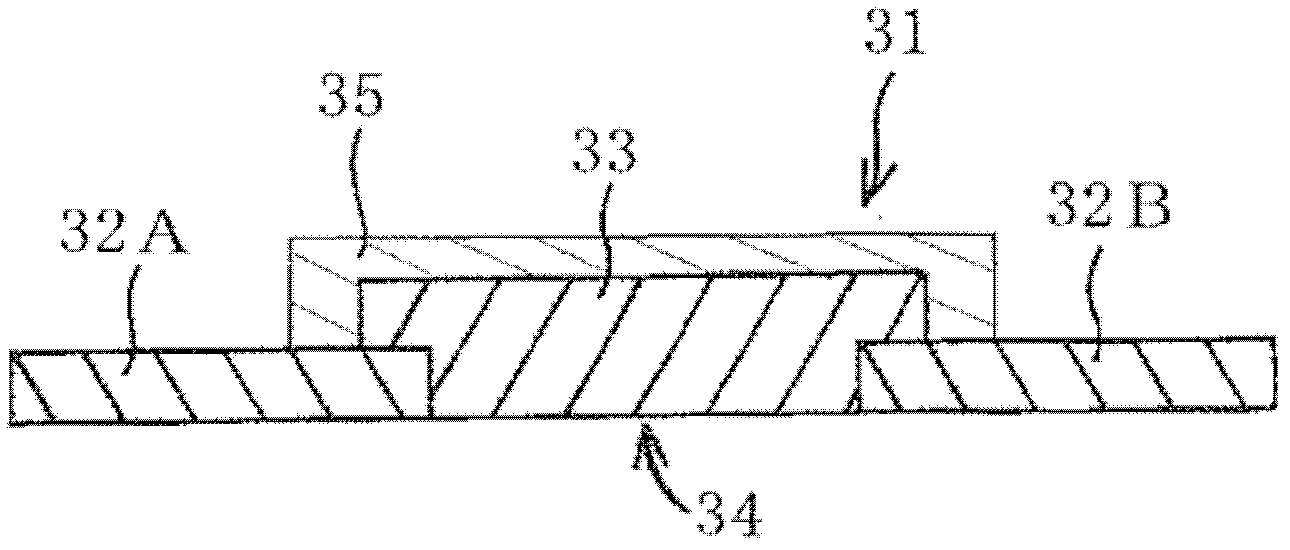
ActiveCN103210456AReduce capacitanceSmall capacitance settingThick film varistorsVaristor coresMaterials scienceElectrode
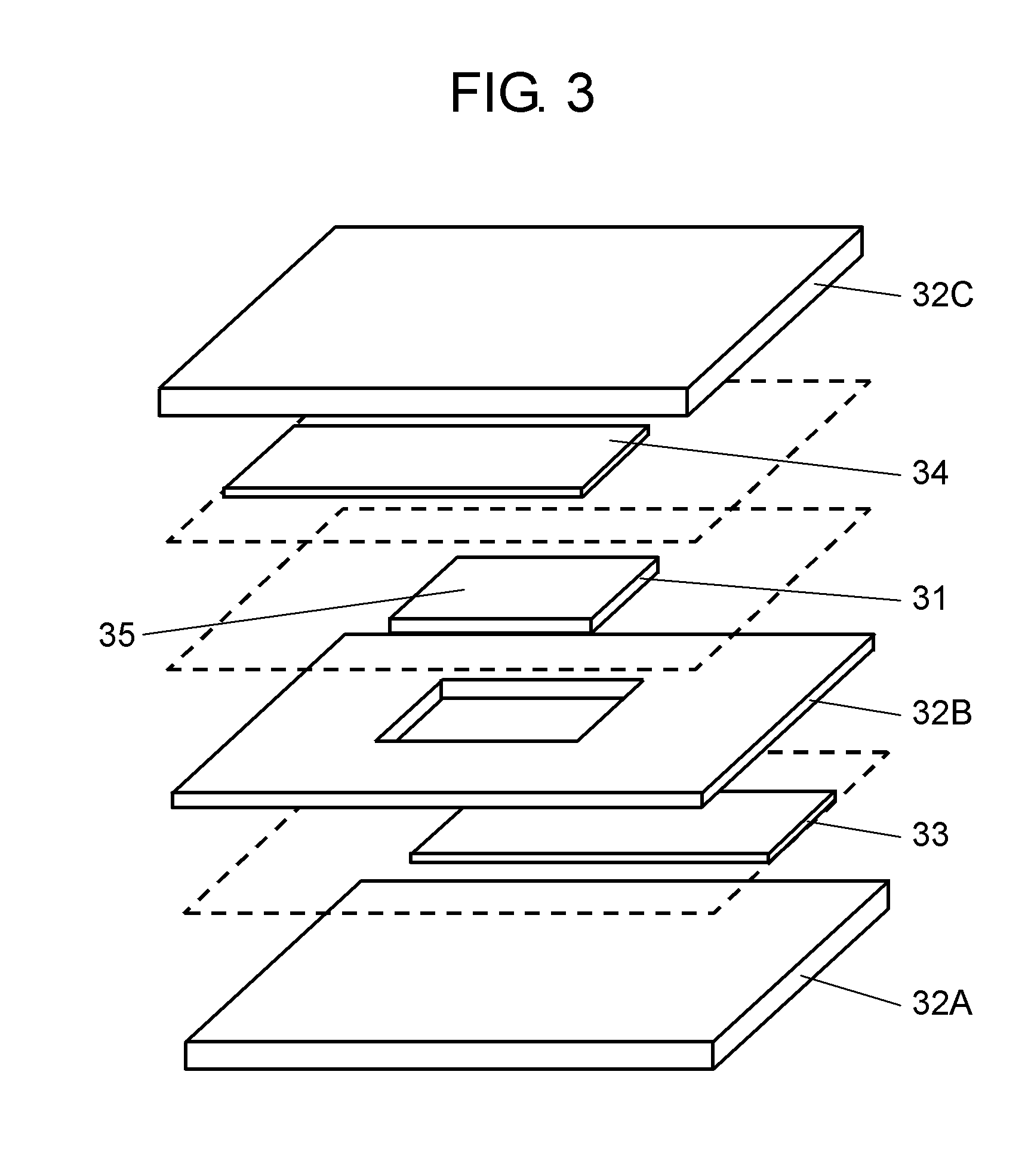
A ceramic component (100) comprises a basic body (101) with two connecting contacts (102, 103) fitted thereon. The component (100) has a first longitudinally extended via electrode (104) and a second longitudinally extended via electrode (105), said electrodes each being coupled to one of the connecting contacts (102, 103). The first via electrode (104) and the second via electrode (105) each have an extended area (106, 107) in projection in the longitudinal direction. For production purposes, a plurality of ceramic layers (117, 118, 119) is layered to form a layer stack, which forms the basic body (101), and the two via electrodes (104, 105) are introduced into the layer stack transversely to the layer sequence.
Owner:EPCOS AG
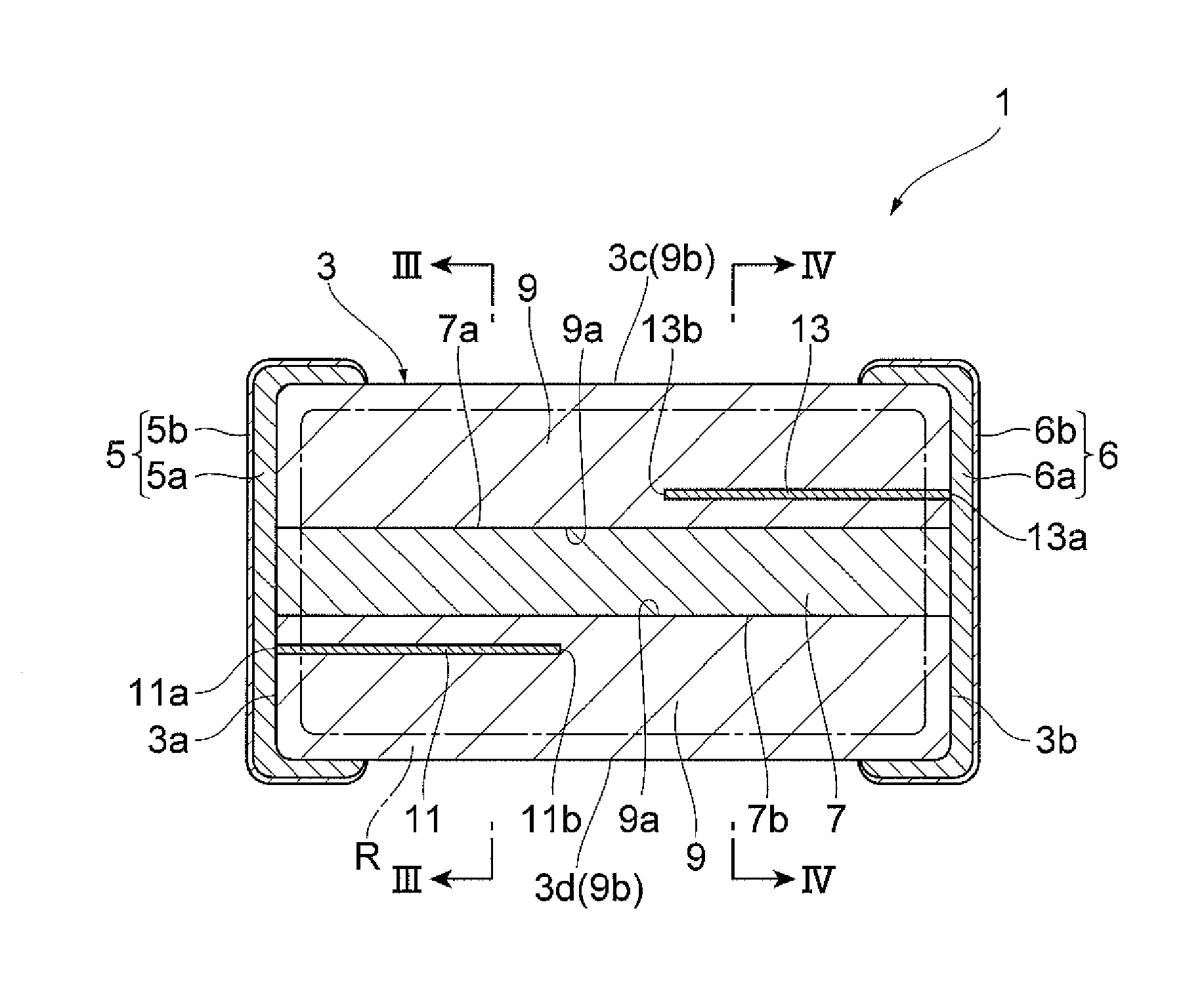
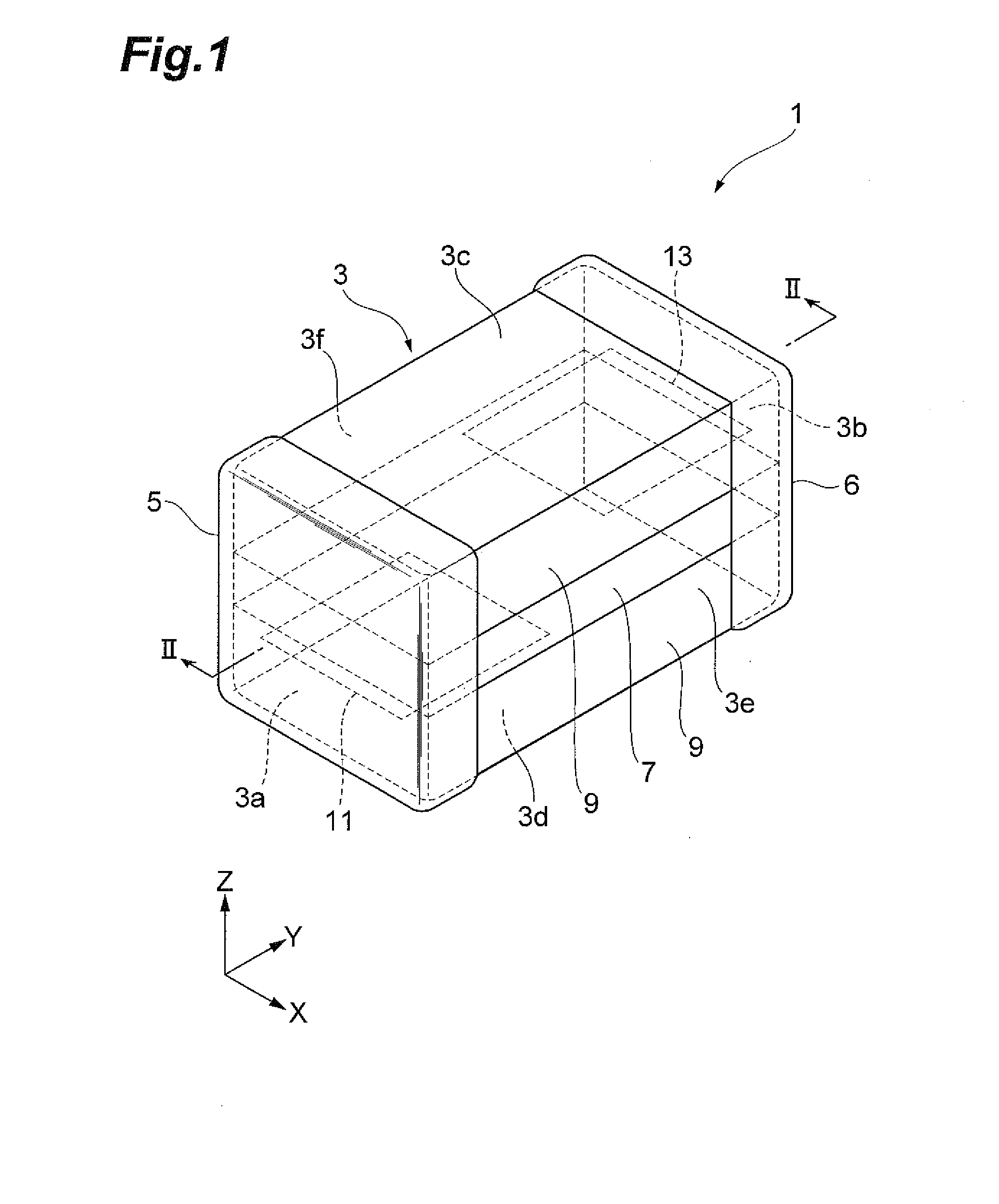
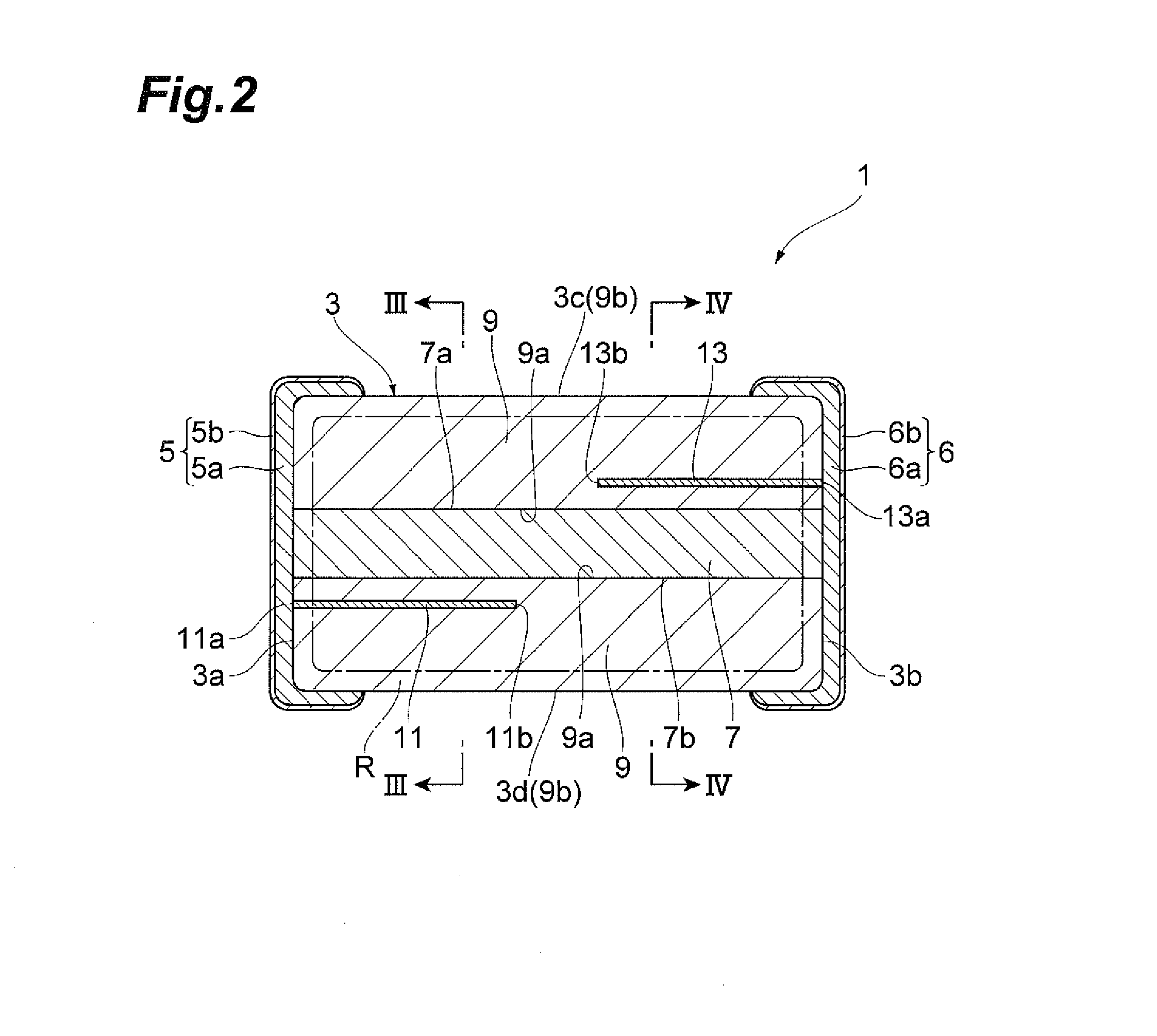
Multilayer chip varistor
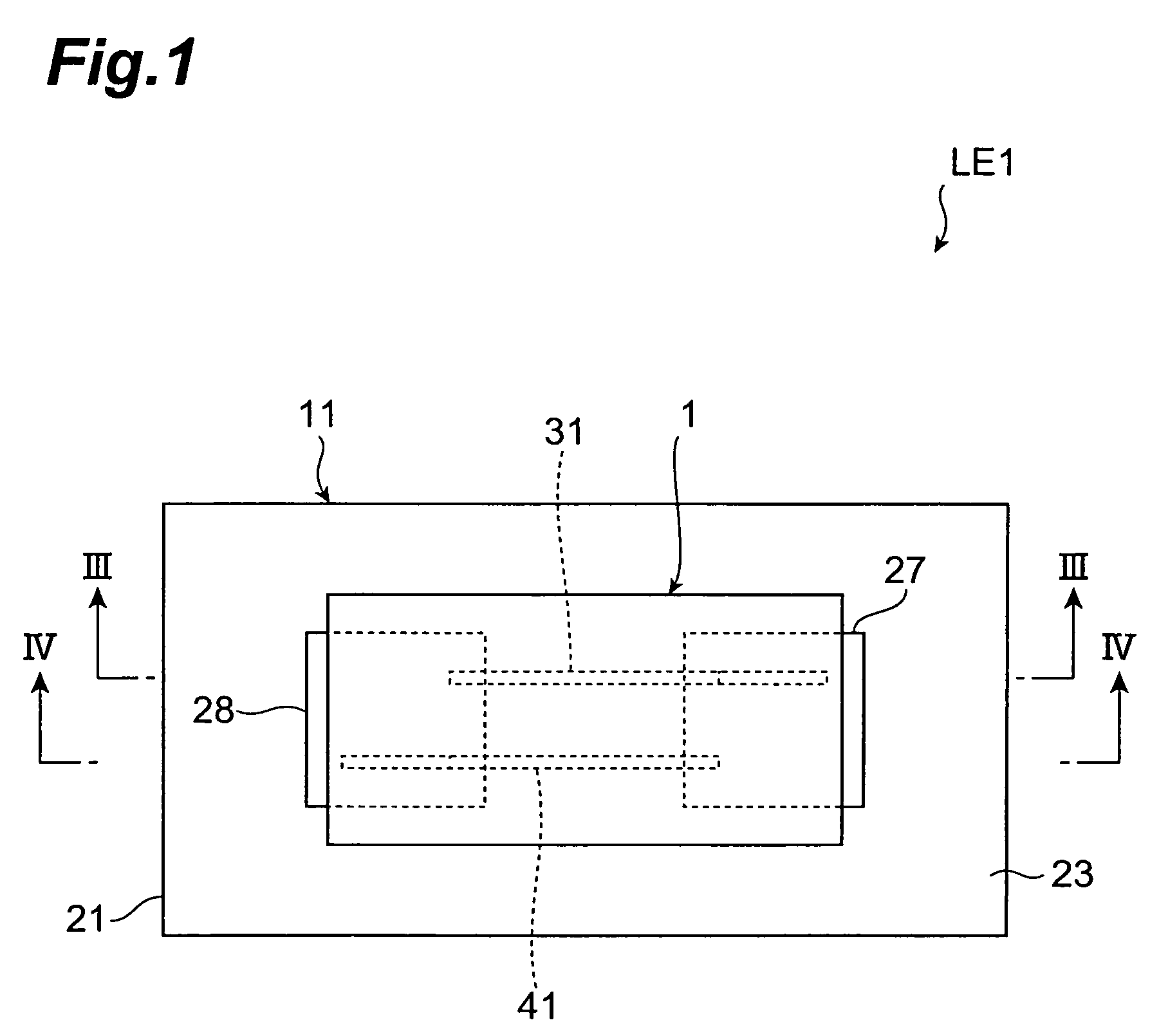
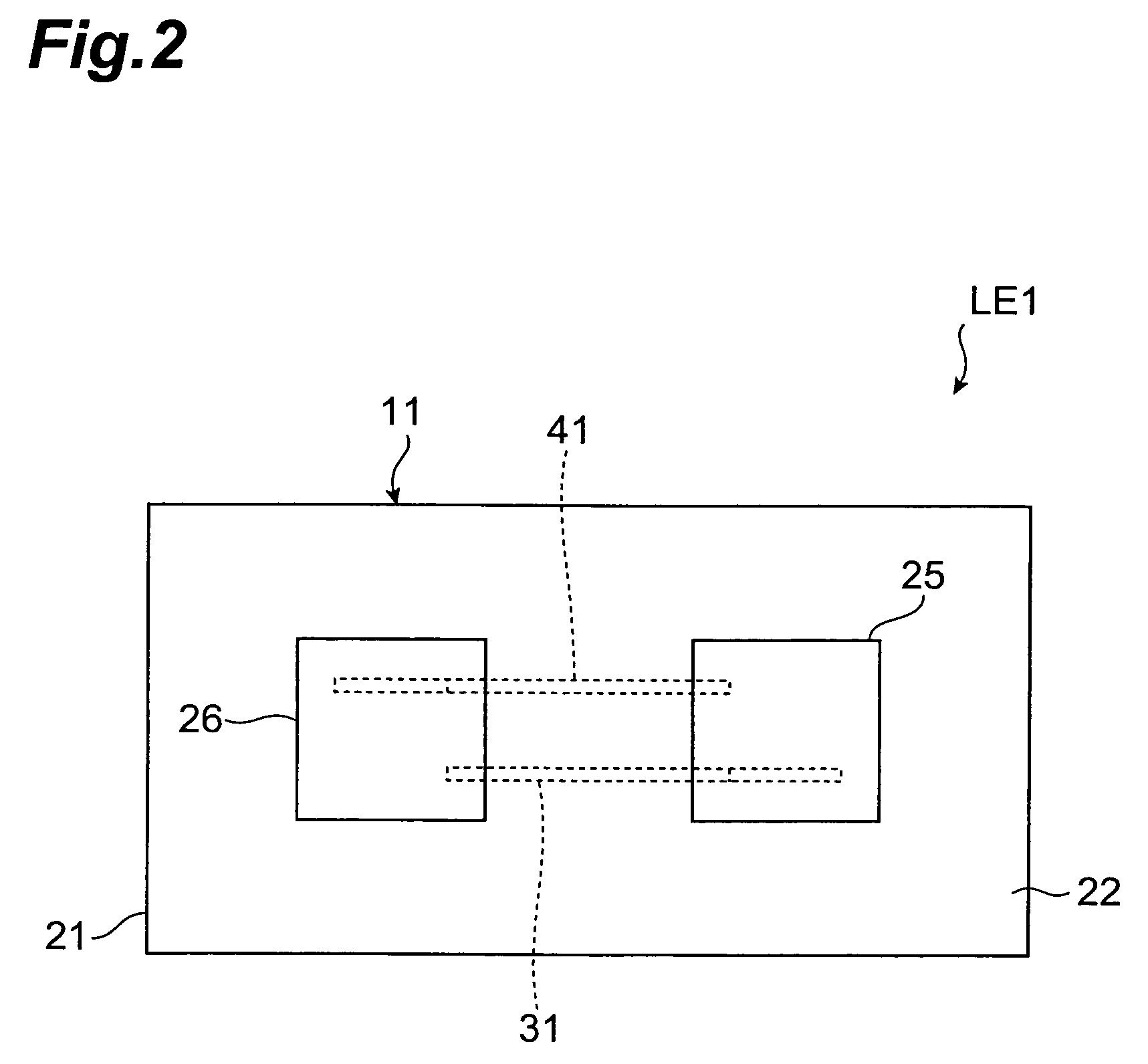
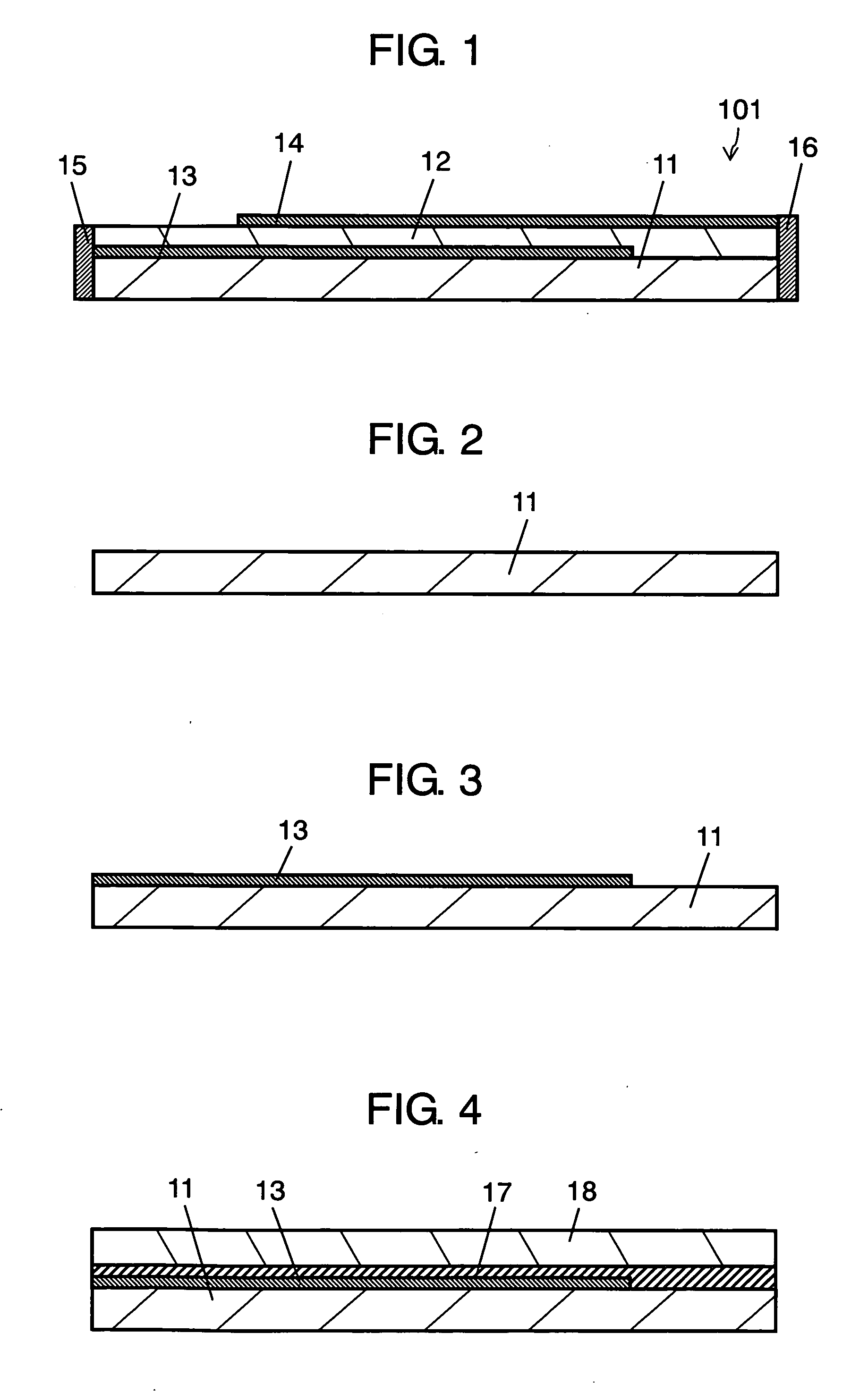
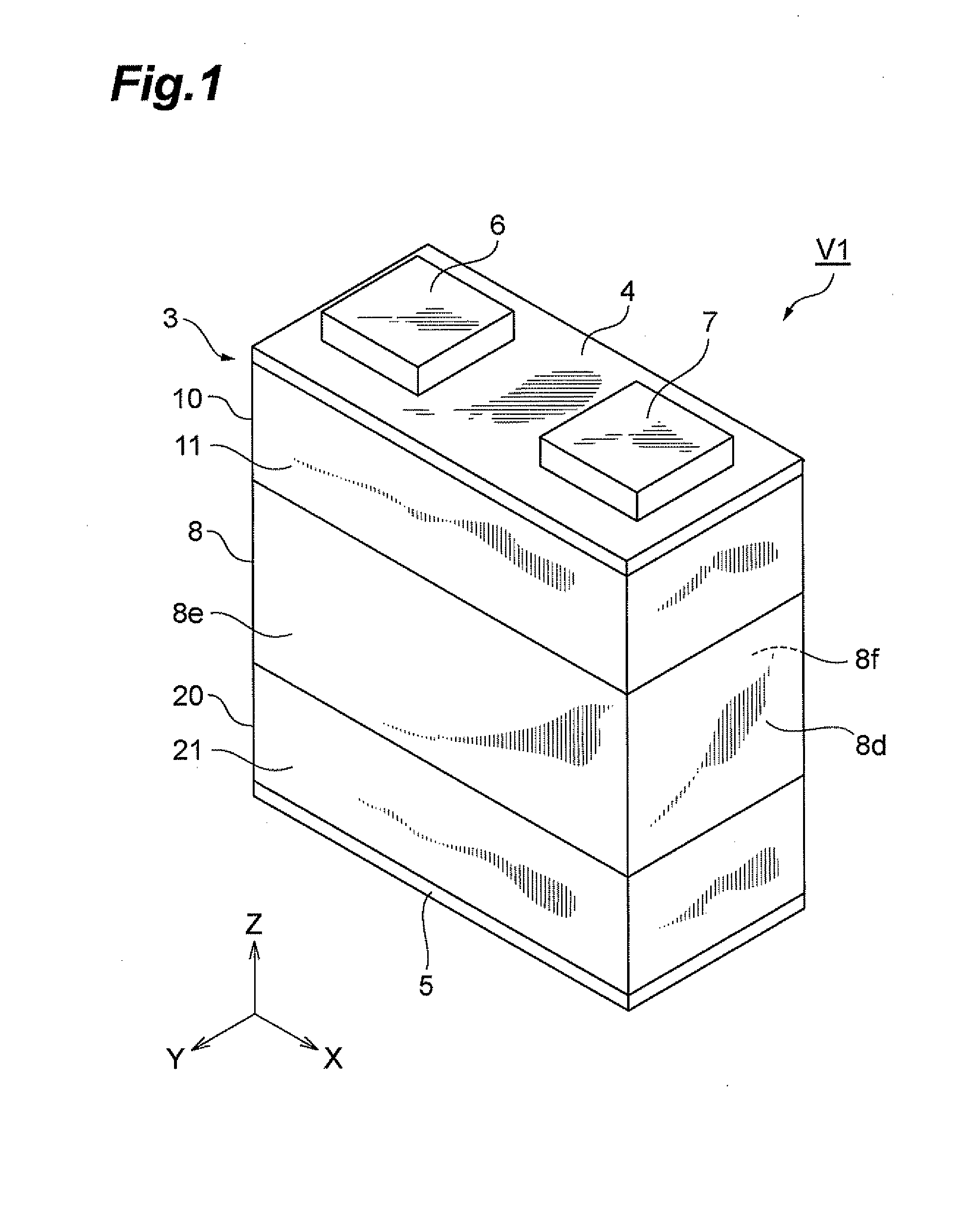
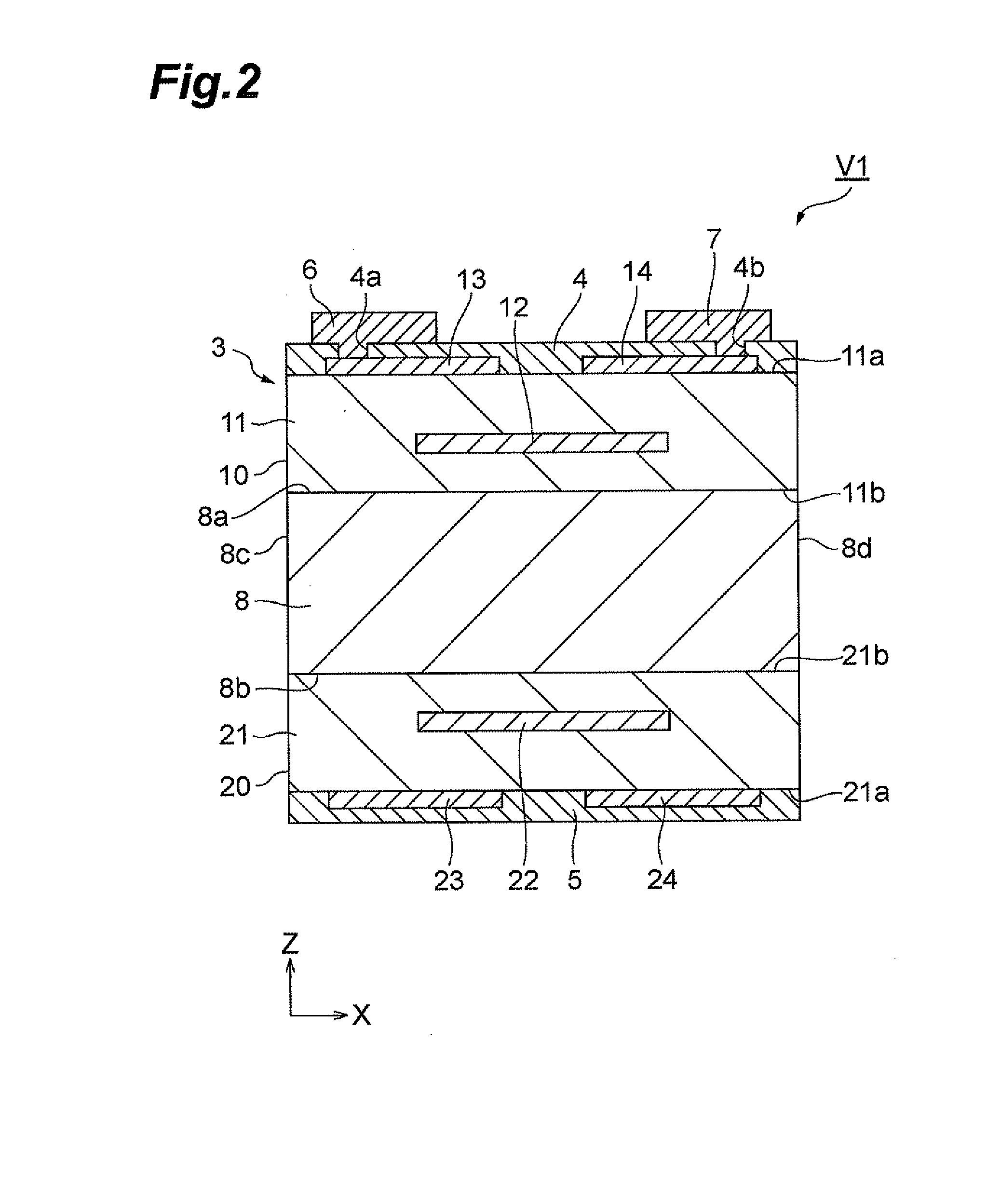
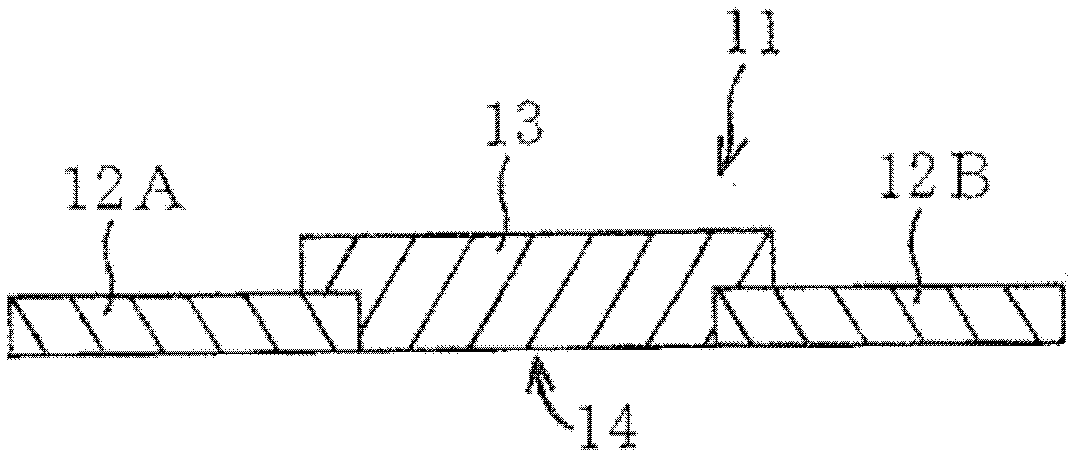
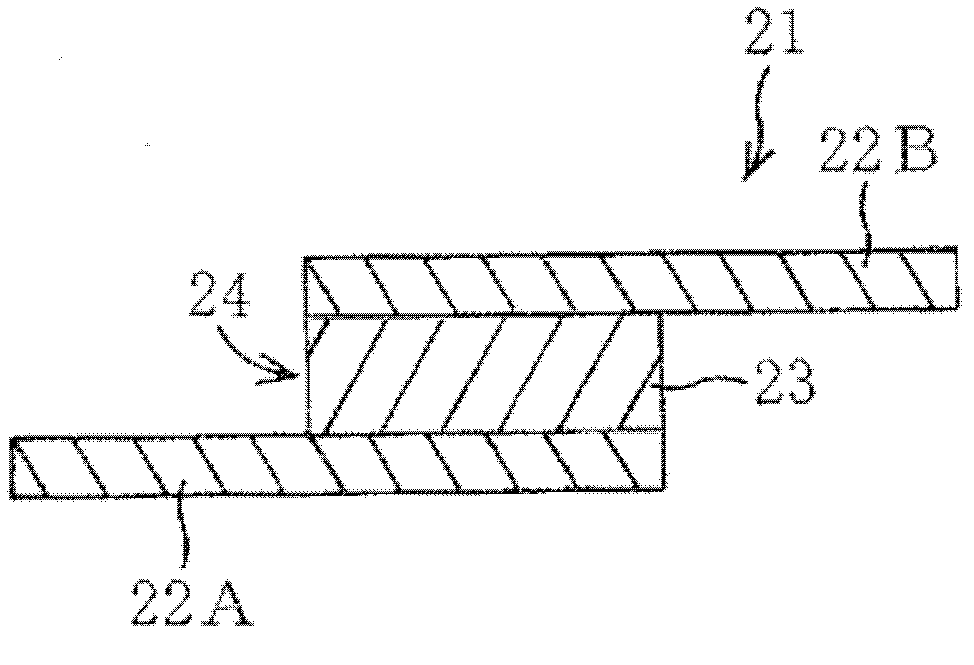
InactiveUS7649435B2Reduce areaEasy to installCurrent responsive resistorsThick film varistorsBiomedical engineeringVaristor
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Ceramic element
ActiveUS20090191418A1Avoid surface lossEffective controlFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsProtection layerMaterials science
A ceramic element, including: a ceramic body having an internal electrode layer and a ceramic layer; an external electrode having a base electrode which is provided on the outside of the ceramic body so as to be electrically connected with the internal electrode layer, and a plating layer covering the outer surface of the base electrode; and a protective layer for covering at least a portion of the outer surface of the ceramic layer other than the portion covered by the external electrode, wherein the protective layer includes a first layer that is an insulating layer containing an insulating oxide, and a second layer that is an insulating layer containing the same insulating oxide as the first layer and an element that is the same as at least one of elements forming the ceramic layer, and the first layer and second layer are formed in that order from the inside.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Varistor and light emitting device
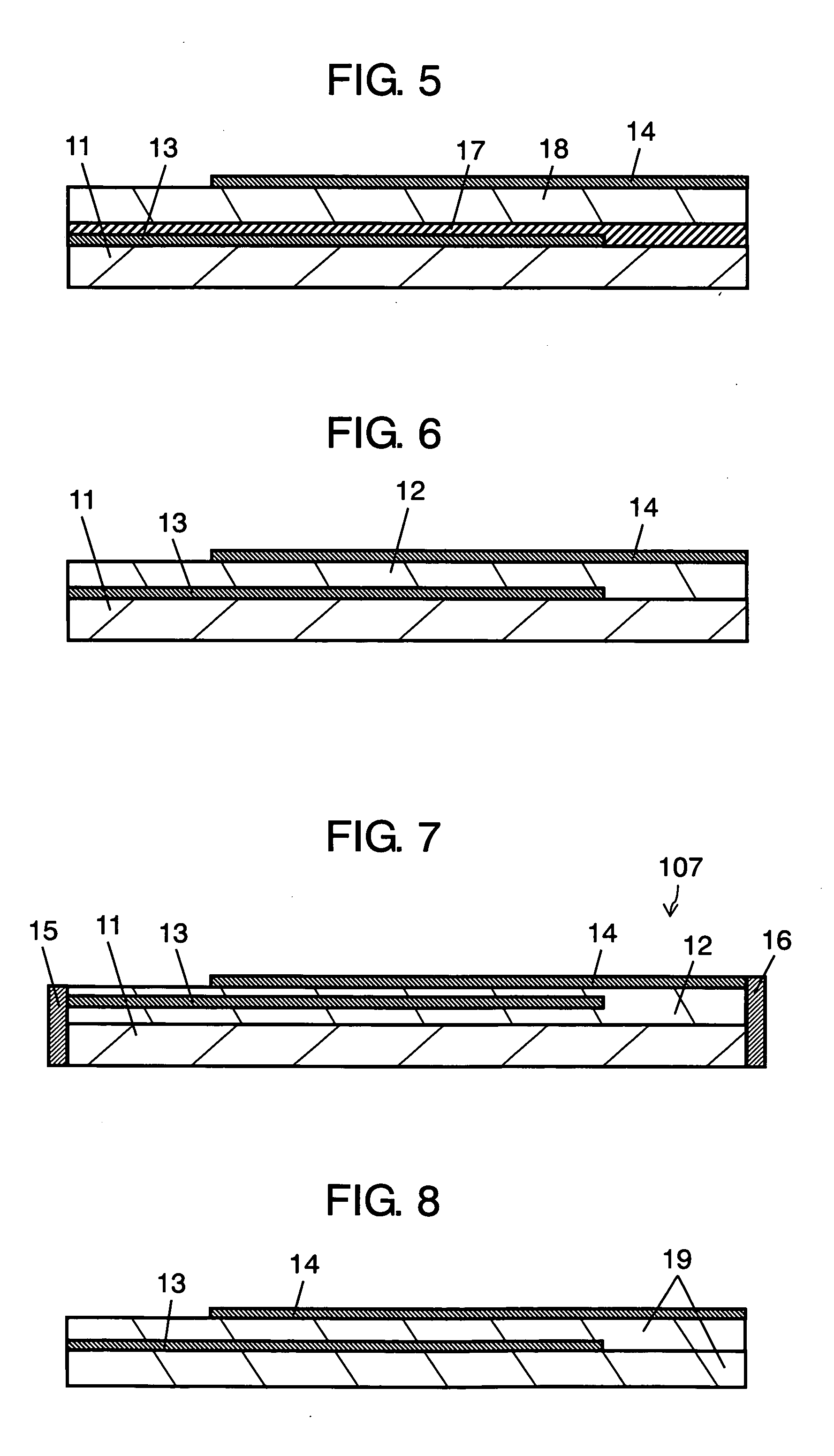
InactiveUS7932806B2Radiate generated heatDeterioration of characteristicResistor terminals/electrodesCurrent responsive resistorsElectrical resistance and conductanceThermal radiation
In a varistor, a heat radiating portion contains the same components as ZnO that is the main component of a varistor element body, as metal oxides, thereby, the structural components of the varistor element body and the heat radiating portion are caused to be common. During firing, Ag contained in the heat radiating portion diffuses into the grain boundaries of ZnO, near the interface between surfaces of the heat radiating portion and the varistor element body. Consequently, in the varistor, cracks hardly occur between the varistor portion and the heat radiating portion during firing (or during binder removal), thereby, ensuring sufficient bonding strength between the varistor portion and the heat radiating portion. Therefore, heat conducted to the varistor portion is radiated efficiently conducting through electrically conducted paths formed in the heat radiating portion from the surface facing the varistor element body to other three surfaces of the heat radiating portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Light emitting device
ActiveUS20060232373A1Easy to installReduce installation costsCurrent responsive resistorsSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
A light emitting device has a semiconductor light emitting element and a multilayer chip varistor. The multilayer chip varistor has a multilayer body with a varistor portion therein, and a plurality of external electrodes disposed on an outer surface of the multilayer body. The varistor portion has a varistor layer containing ZnO as a principal component and exhibiting nonlinear voltage-current characteristics, and a plurality of internal electrodes arranged to interpose the varistor layer between them. Each of the external electrodes is connected to a corresponding internal electrode out of the plurality of internal electrodes. The semiconductor light emitting element is disposed on the multilayer chip varistor. The semiconductor light emitting element is connected to corresponding external electrodes out of the plurality of external electrodes so as to be connected in parallel to the varistor portion.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Composition and method
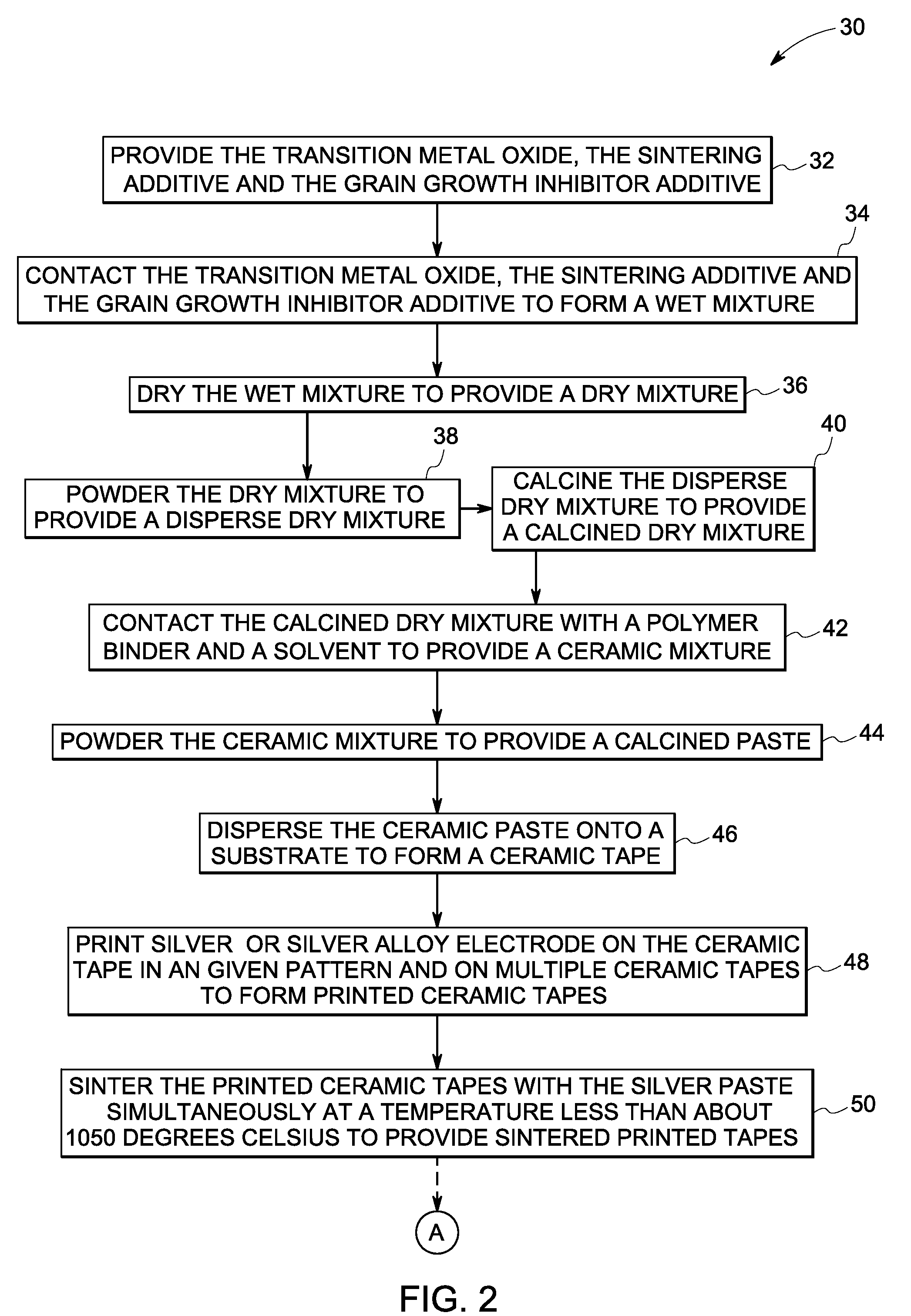
InactiveUS20090143216A1Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsGrain growthGrain boundary
A composition includes a sintered mass having a plurality of cores and a grain boundary layer disposed between each of the plurality of cores. The core includes a transition metal oxide, and grain boundary layer includes a sintering additive, a grain growth inhibitor additive and a grain boundary additive.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Aggregate substrate, production method of aggregate substrate, and varistor
ActiveUS20090189732A1Efficiently dissipatedAffect operationCurrent responsive resistorsCeramicsEngineeringVaristor
An aggregate substrate has a first varistor part, a second varistor part, and a heat dissipation layer The first varistor part includes a first varistor element layer to exhibit nonlinear voltage-current characteristics, and a plurality of first internal electrodes juxtaposed in the first varistor element layer. The second varistor part includes a second varistor element layer to exhibit nonlinear voltage-current characteristics, and a plurality of second internal electrodes juxtaposed in the second varistor element layer The heat dissipation layer is located between the first and second varistor parts and is in contact with the first and second varistor parts.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Composition for filling discharge gap and electrostatic discharge protection member
InactiveCN102341978AHigh adjustment accuracyElectrostatic discharge protectionResistor manufactureMiniaturizationOxide coating
Disclosed is an electrostatic discharge protection member which can be formed in an arbitrary shape and conveniently used for solving ESD problems in electronic circuit boards of various designs, shows excellent properties of highly accurately controlling working voltage, and enables downsizing and cost reduction. Also disclosed is a composition for filling a discharge gap which can be used in producing the aforesaid electrostatic discharge protection member. A composition for filling a discharge gap characterized by comprising a metal grain having an oxide coating (A), a stratiform substance (B) and a binder component (C); and an electrostatic discharge protection member which comprises the composition.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
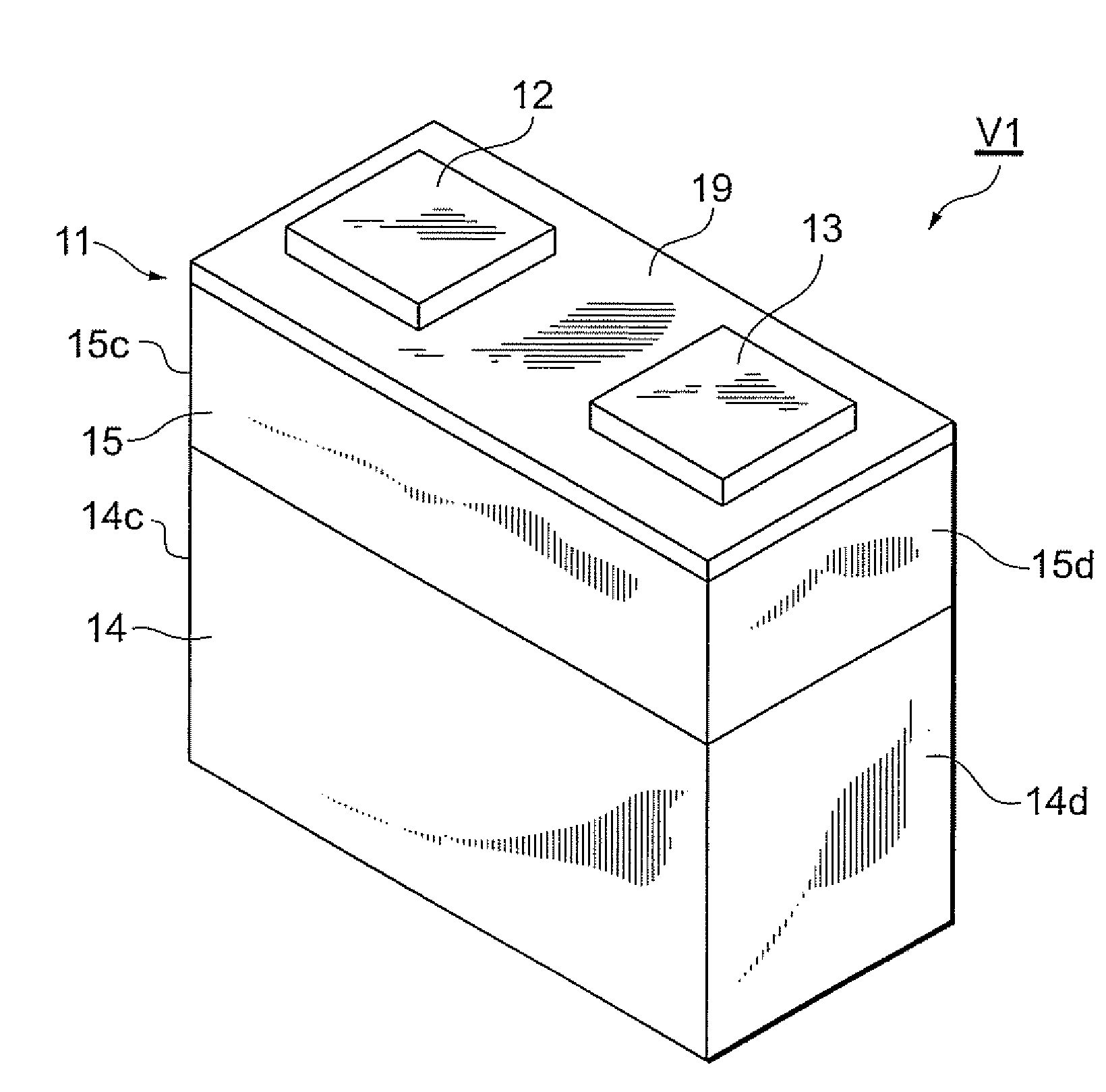
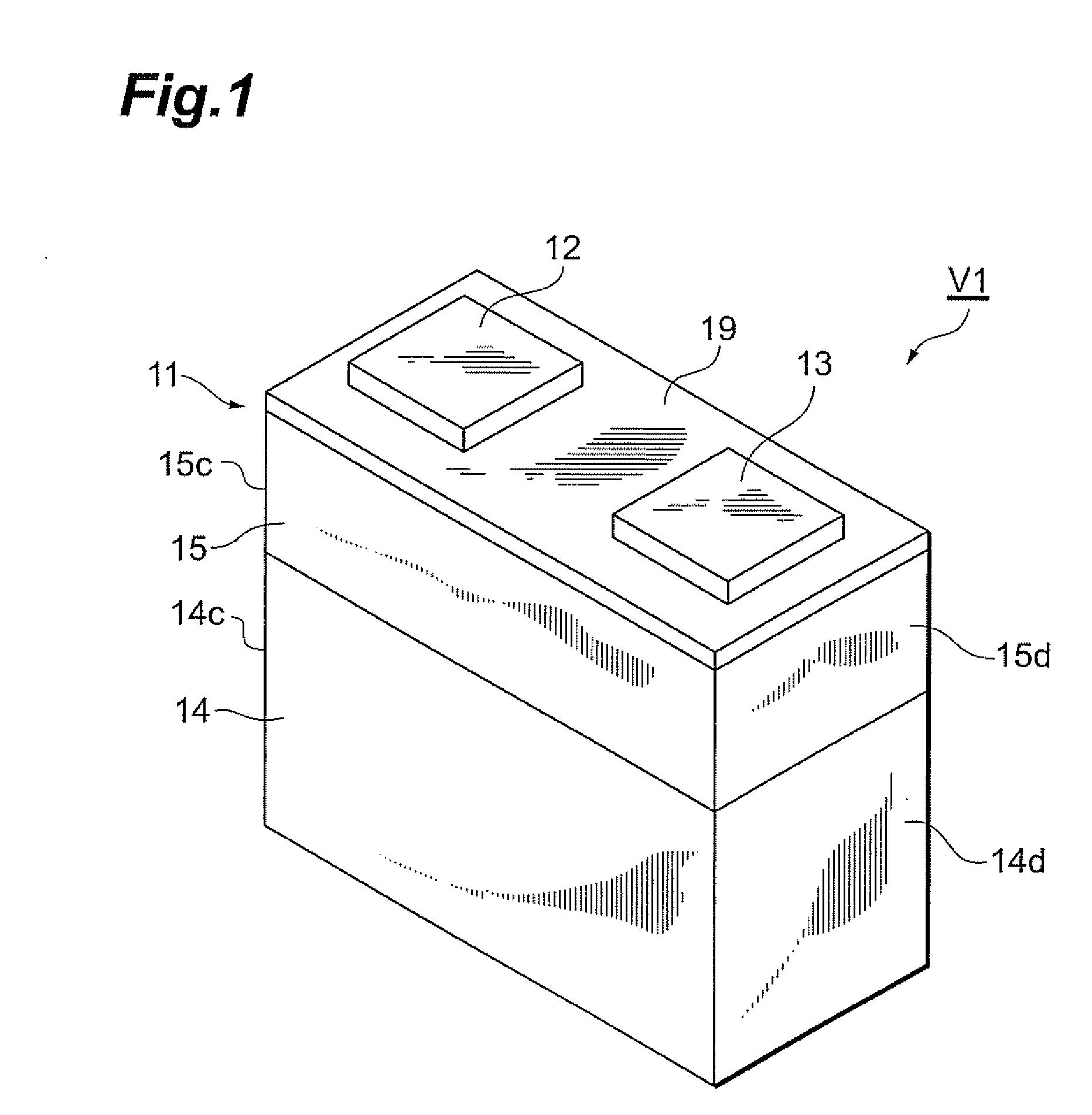
Chip varistor
ActiveUS20140167909A1Excellent clamp propertyMaintain good propertiesCurrent responsive resistorsThick film varistorsElectrical conductorEngineering
An element body has first and second faces opposed to each other. A first conductor has one end exposed in a first face and the other end located in the element body. The second conductor has one end exposed in a second face and the other end located in the element body. The element body has a first element body section having the nonlinear voltage-current characteristics and a second element body section in which an electric current is more likely to flow than in the first element body section. The first element body section is located at least in part between the first conductor and the second conductor, in a direction in which the first conductor and the second conductor are separated from each other. The other end of the first conductor and the other end of the second conductor are located in the second element body section.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
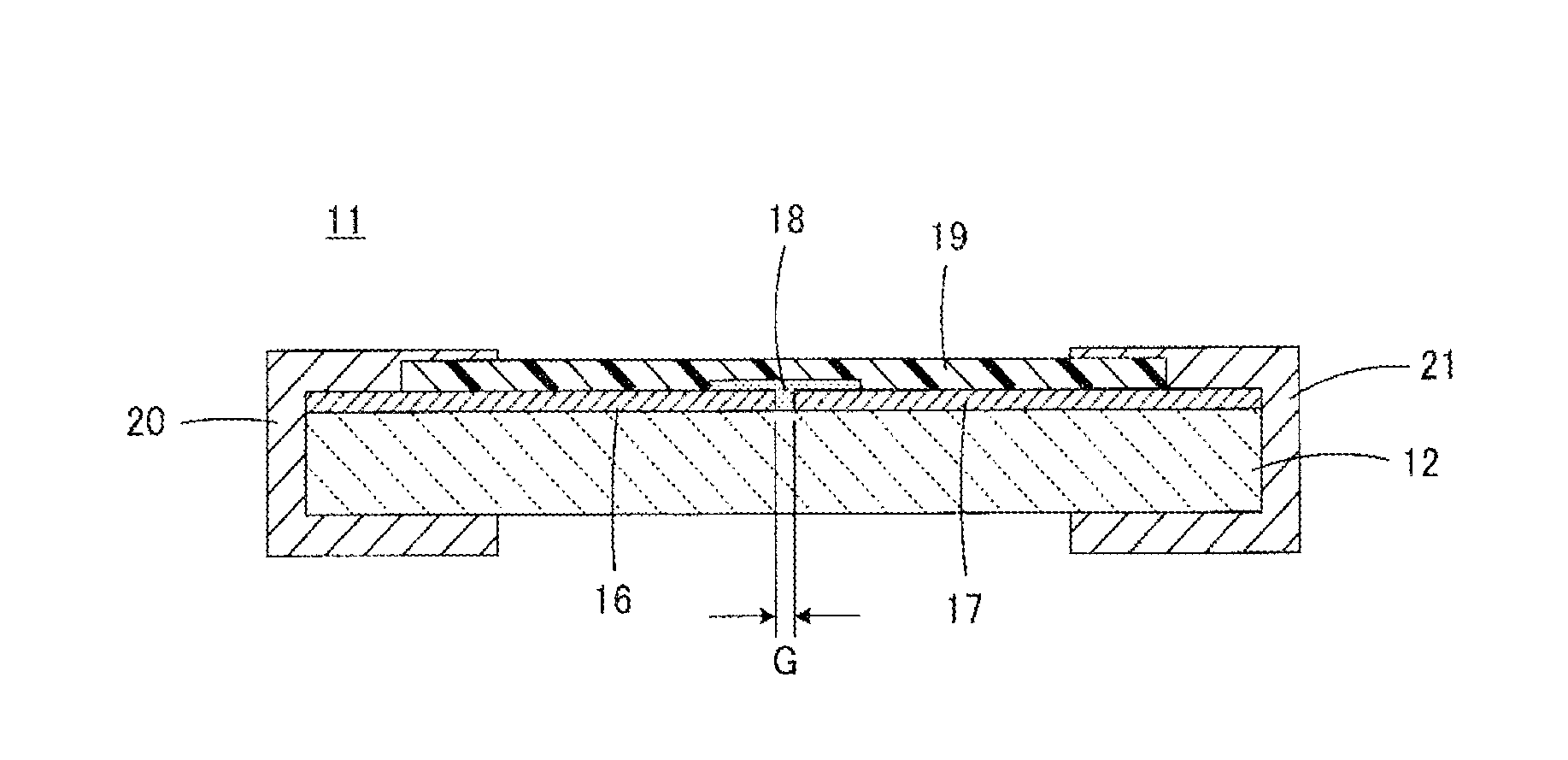
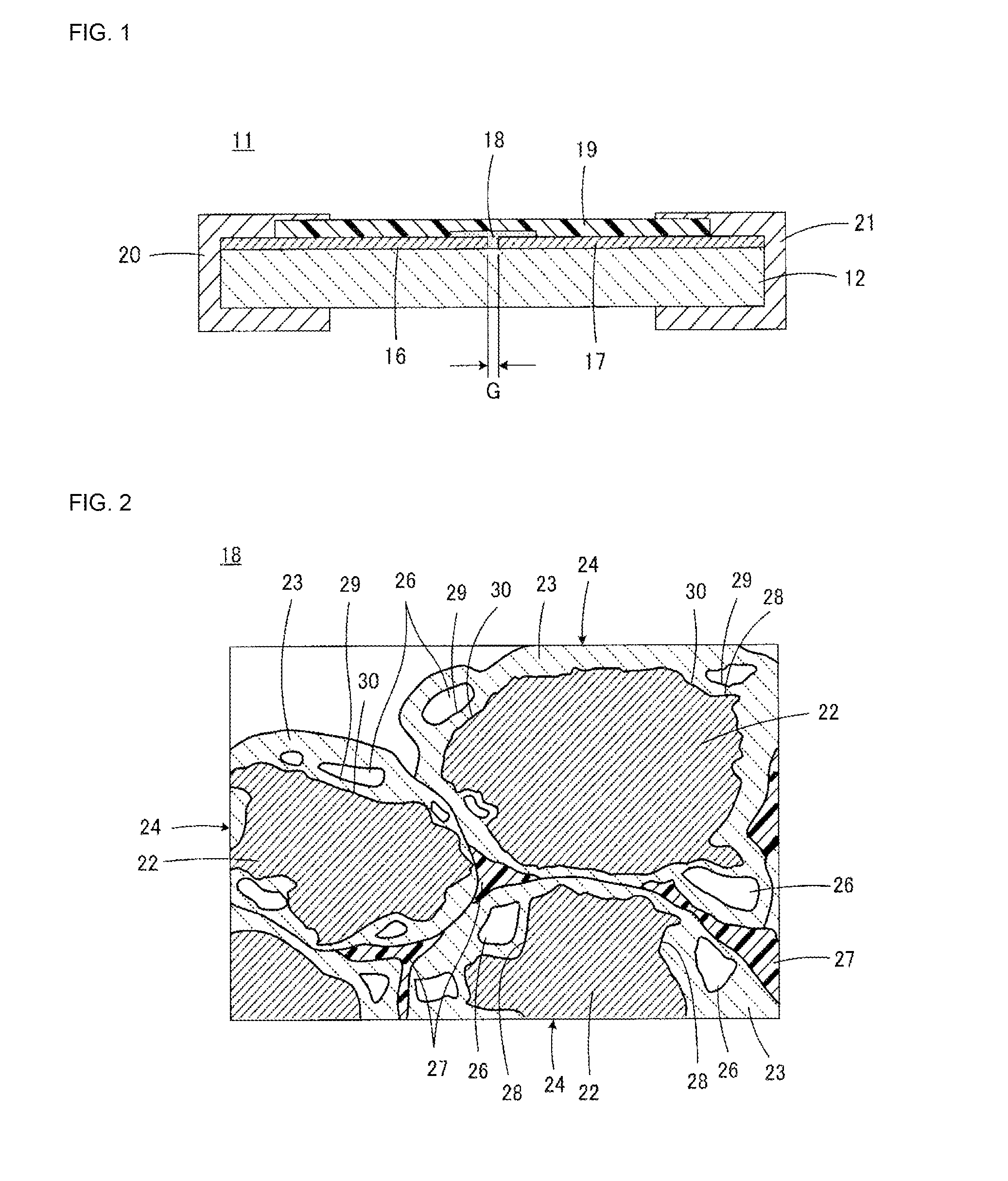
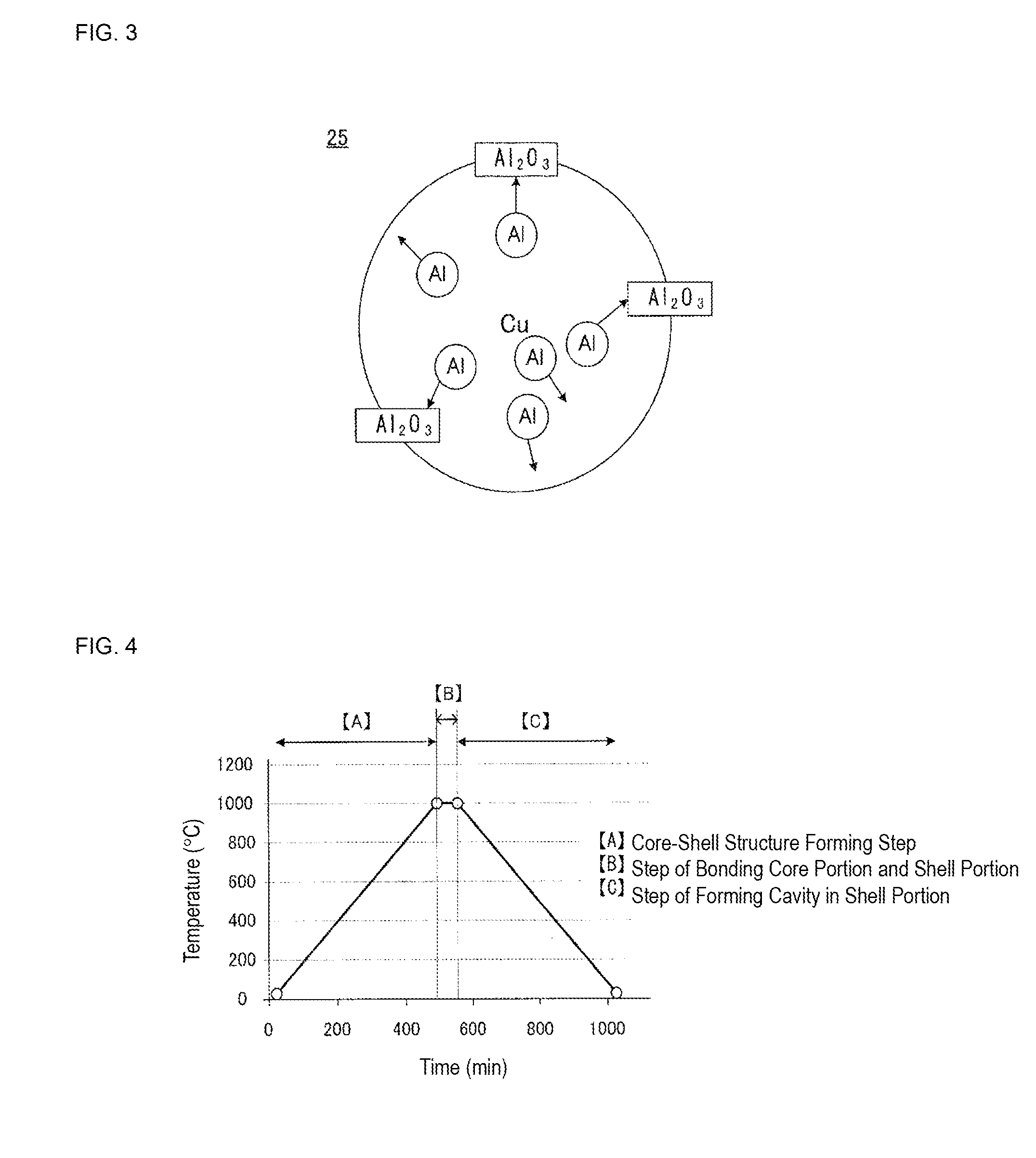
ESD protection device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150171618A1Improve insulation reliabilityImprove discharge characteristicsThick film varistorsSpecial surfacesAuxiliary electrodePhysics
An ESD protection device having high insulation reliability and excellent discharge characteristics is provided. In an ESD protection device including a first and a second discharge electrode disposed to face each other, a discharge auxiliary electrode (18) formed so as to bridge the first and second discharge electrodes, and an insulating substrate holding the first and second discharge electrodes and the discharge auxiliary electrode (18), the discharge auxiliary electrode (18) is formed of an aggregate of metal grains (24) each having a core-shell structure comprising a core portion (22) primarily formed of a first metal and a shell portion (23) primarily formed of a metal oxide containing a second metal, and the aggregate of metal grains (24) further includes an insulating resin (27) which bonds the metal grains (24) to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Popular searches
Fixed capacitor terminals Conductive pattern formation Overvoltage protection resistors Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current Resistor details Arrangements responsive to excess voltage Semiconductor devices Electric component structural association Adjustable resistors Fixed signal inductances
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com