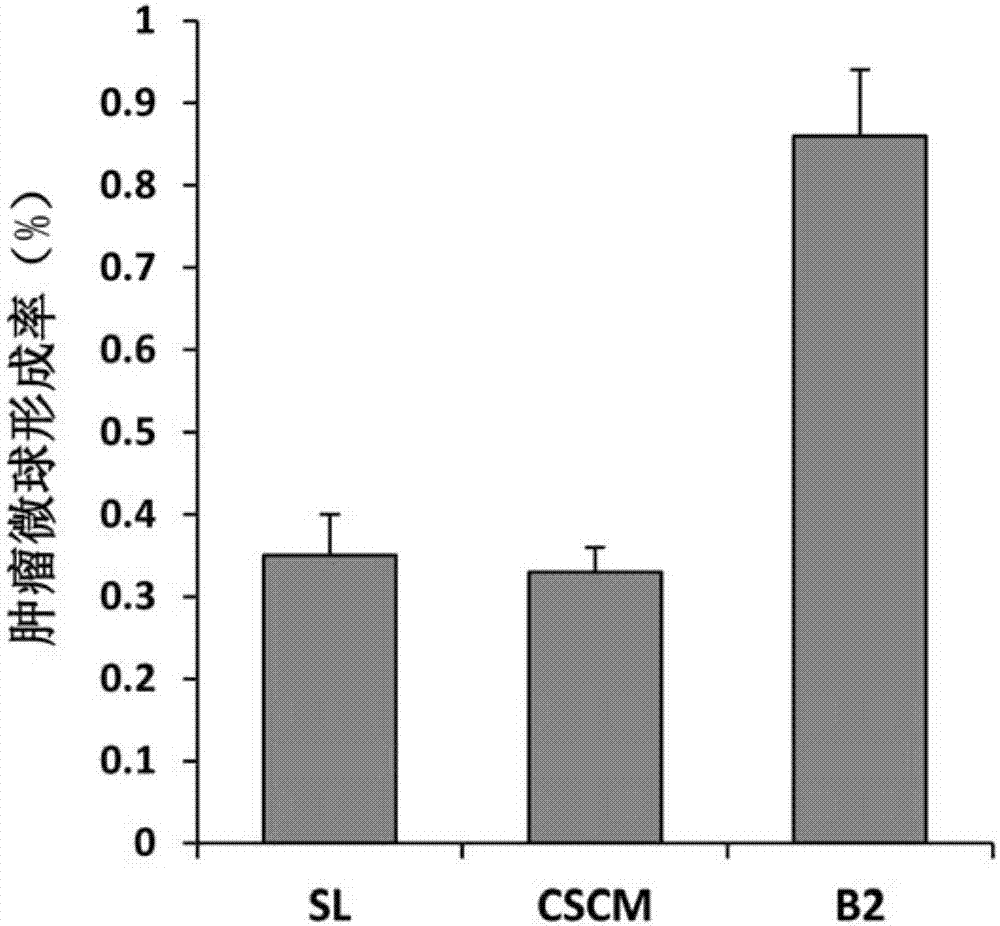
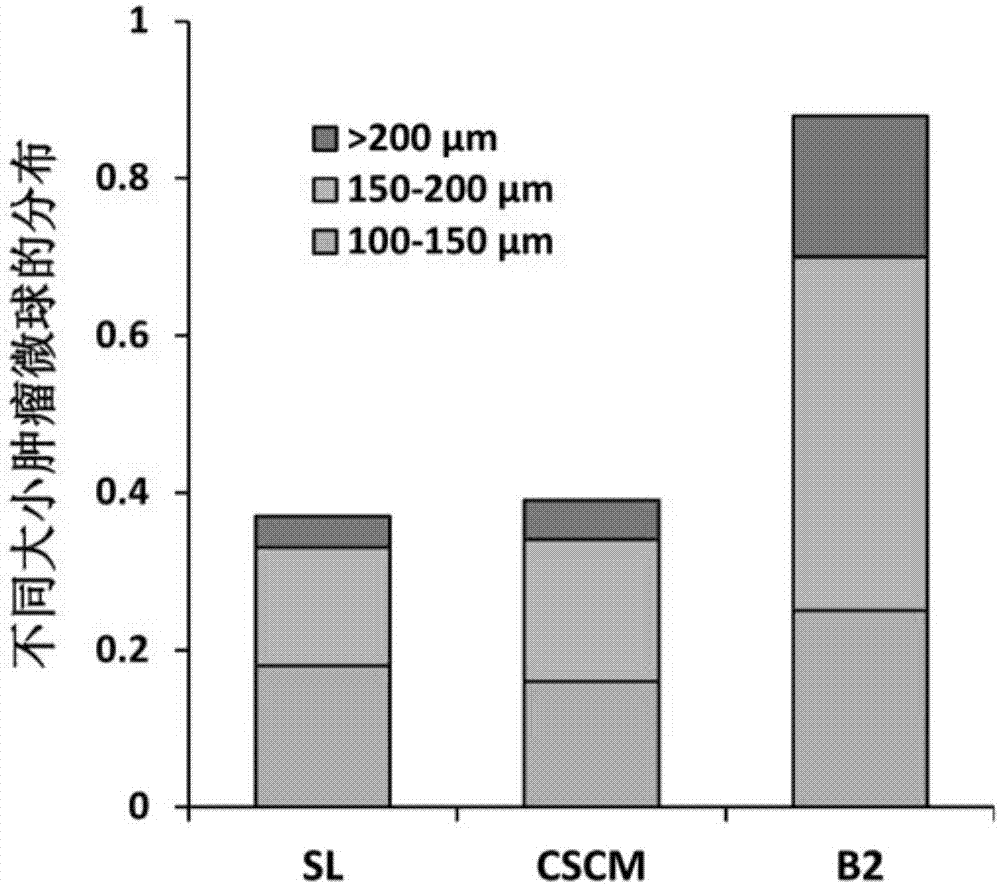
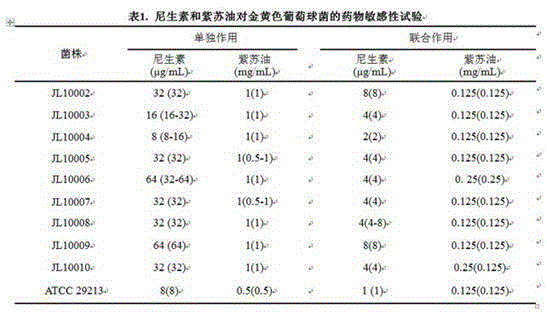
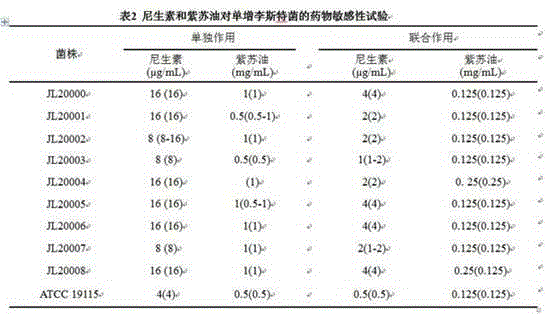
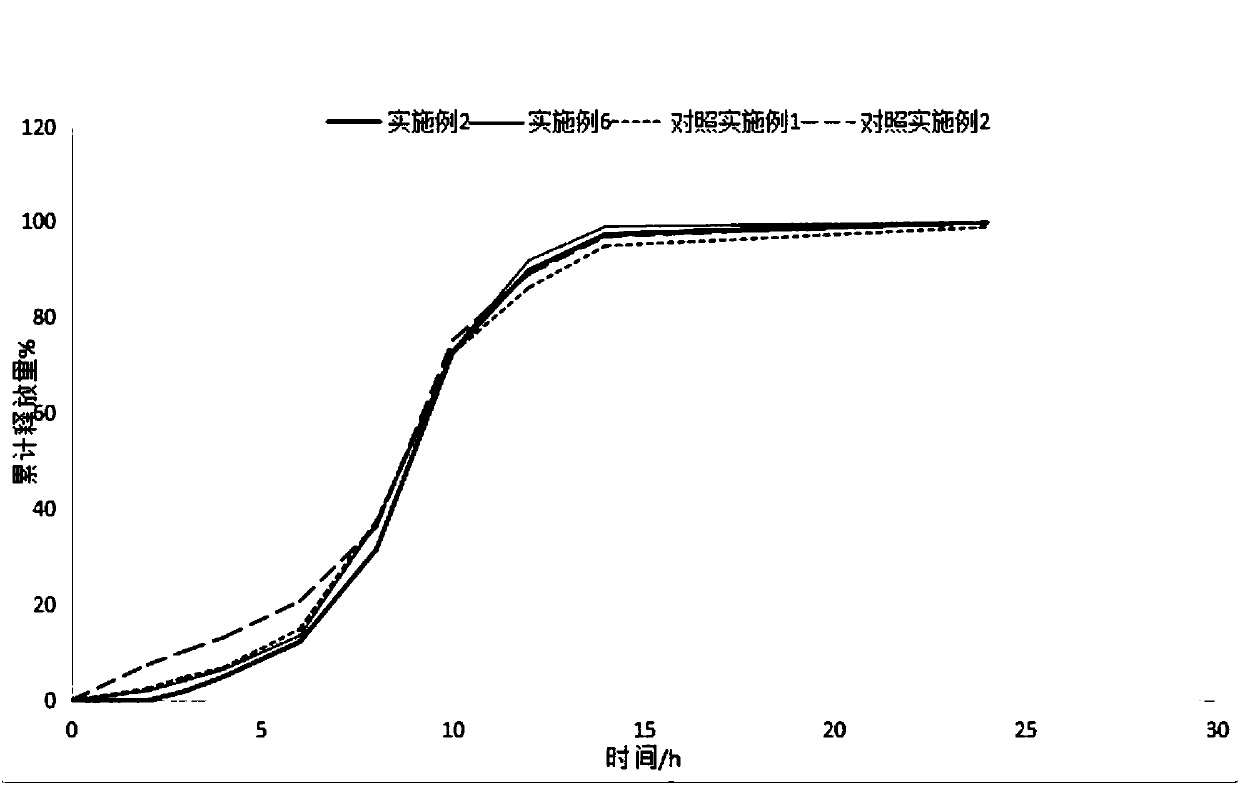
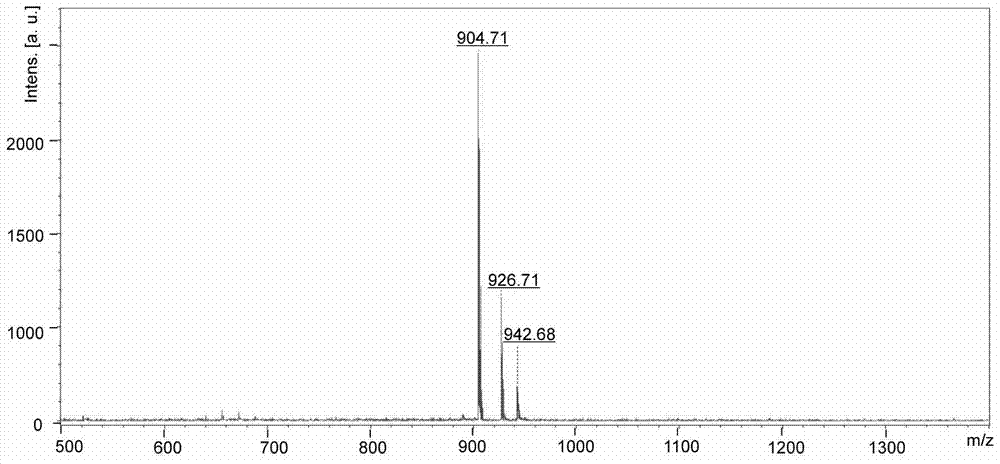
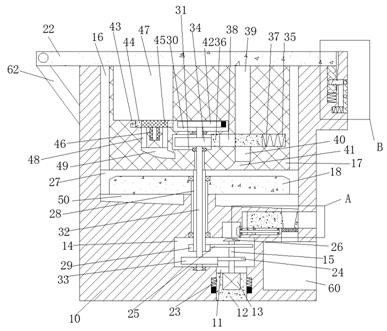
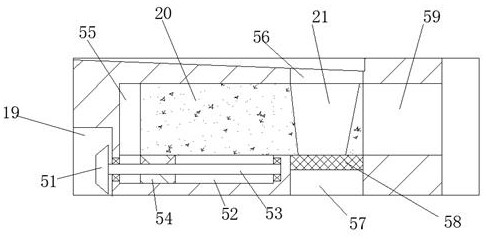
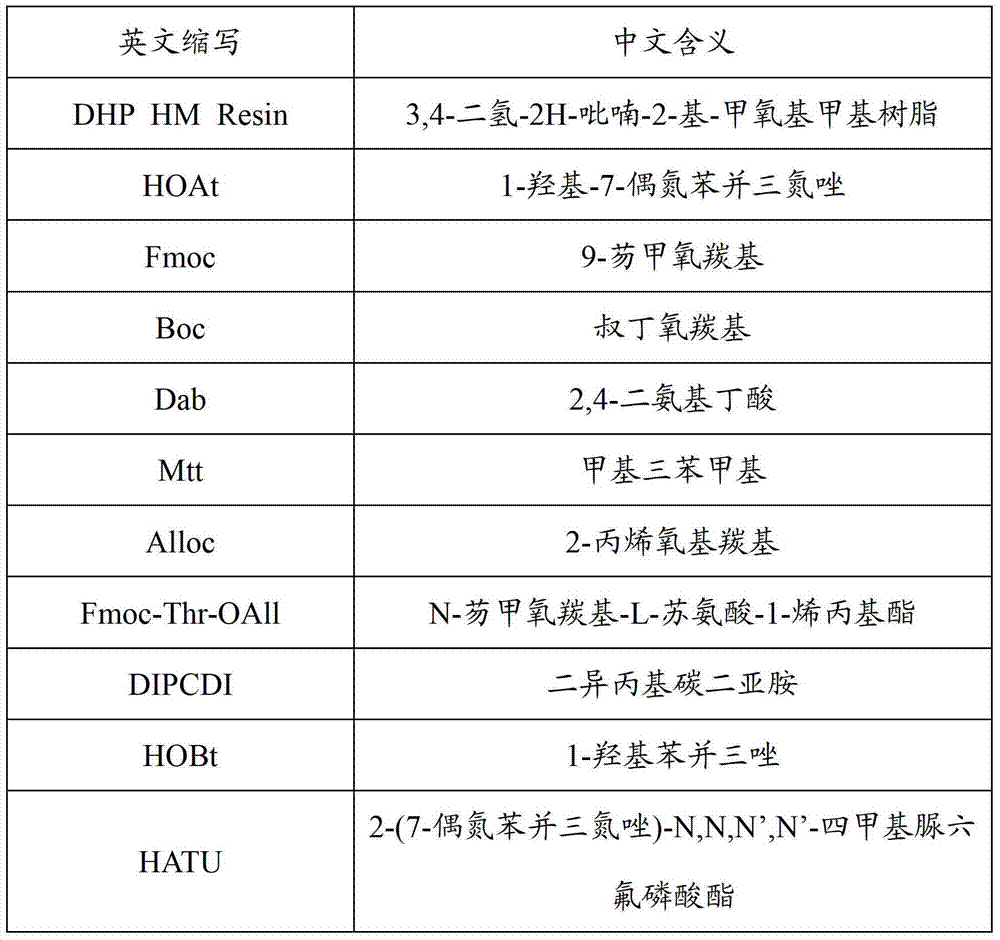
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Polypeptide antibiotic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polypeptide antibiotics are a chemically diverse class of anti-infective and antitumor antibiotics containing non-protein polypeptide chains. Examples of this class include actinomycin, bacitracin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Actinomycin-D has found use in cancer chemotherapy. Most other polypeptide antibiotics are too toxic for systemic administration, but can safely be administered topically to the skin as an antiseptic for shallow cuts and abrasions.
Method for producing polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide through fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating streptomyces actuosus to a slant culture medium for carrying out slant culture; inoculating an obtained slant with spores to a seed bottle to culture a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution to a fermentation culture medium for carrying out fermentation culture according to an inoculation quantity of 10 wt%; and further treating the fermented fermentation liquor to obtain nosiheptide crystals. The nosiheptide is produced by adopting a fermentation method. The method is simple and easy and is low in production cost. The polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide produced by adopting the method can be used as a safe, high-efficiency and environmental-friendly novel feed additive.
Owner:江西兴鼎科技有限公司
Method for producing polypeptide enramycin with zymotechnics
InactiveCN101245362AHigh potencyAchieve high density cultureMicroorganism based processesFermentationAntibiotic YBacterial strain
The invention relates to a method for producing polypeptide antibiotics enramycin by the fermentation method, which pertains to the fields of agricultural biotechnology, industrial biotechnology and the fermentation engineering. The method is as follows: (1) slant culture: a Streptomyces sp.NJWGY3665 bacterial strain is inoculated in a glucose nutrient culture medium to carry out the slant culture, the culture temperature is 28 to 37 DEG C and the culture time is 2 to 6 days; (2) seed culture: a spore which is cultured on a slant is produced into a single-spore suspension by using sterile water, which is also inoculated in a seed culture medium for culture, the temperature is 28 to 32 DEG C, the rotational speed is 200rpm and the culture lasts for 2 to 6 days; (3) fermentation culture: the seed liquid is inoculated in a fermentation culture medium for culture, the temperature is controlled at 28 to 37 DEG C, the pH is controlled at 6.0 to 9.0, the rotational speed is 180 to 220rpm, the fermentation lasts for 5 to 9 days, so as to obtain the Streptomyces sp., methanol or ethanol is used for the extraction and separation of mycelium through the method of centrifugal separation, then the resin method is adopted for carrying out refining, so as to obtain the peptide antibiotics enramycin.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Composite hydrogel wound dressing and preparation method thereof
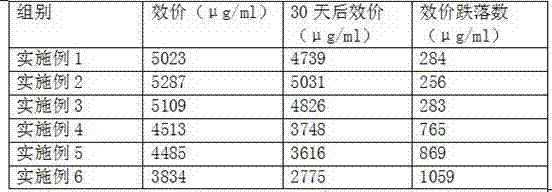
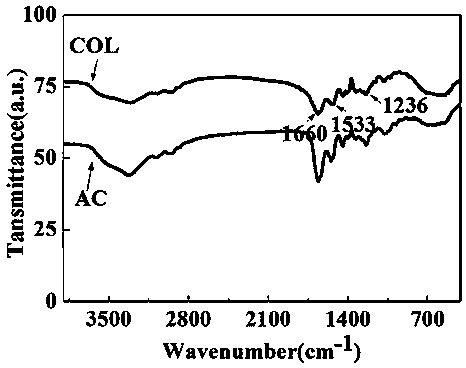
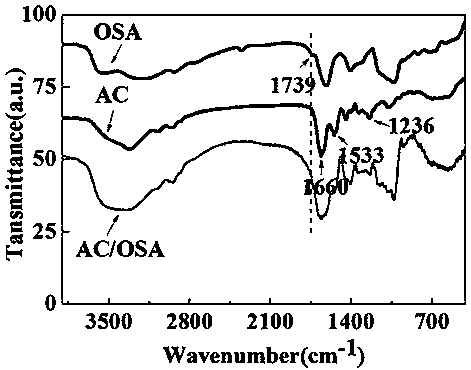
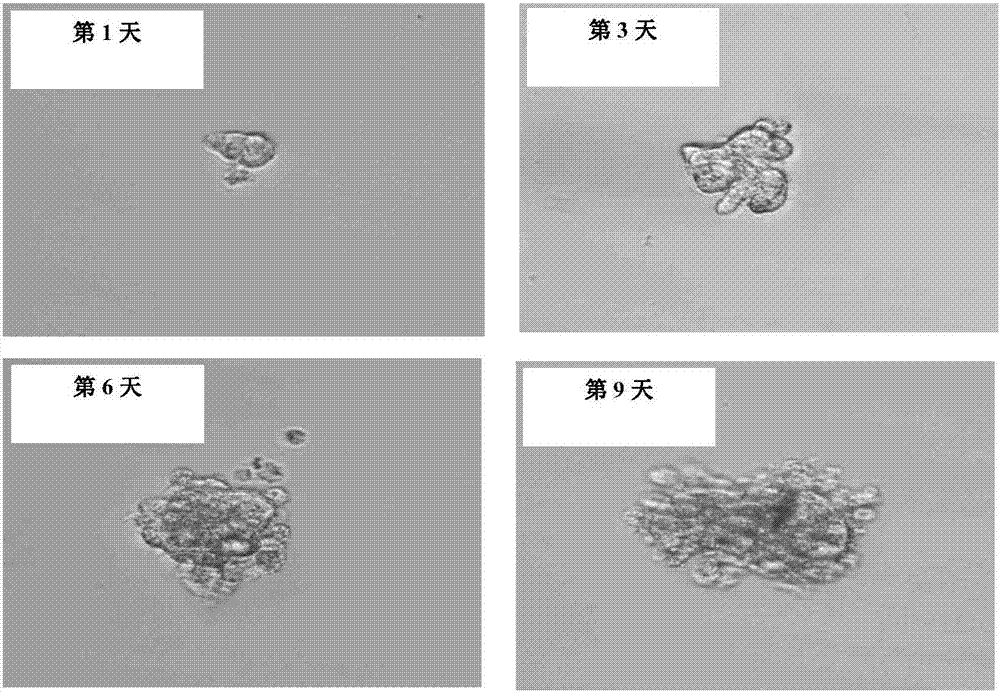
The invention provides a composite hydrogel wound dressing and a preparation method thereof. The aminated collagen and oxidized sodium alginate are used as base materials; two polypeptide antibiotics,namely polymyxin B sulfate and bacitracin are loaded; and the AC / OSA-PB composite hydrogel dressing is prepared through a Schiff base reaction. The preparation method is simple to operate; the requirements on reaction conditions are low; gel can be formed in a short time, large-scale production is facilitated, and the prepared wound dressing not only has a good bactericidal effect, but also can improve the HSF cell mobility and the HSF cell proliferation rate to the maximum extent, has excellent wound healing promoting capacity, and also has mechanical properties and mechanical properties suitable for skin wounds.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for biosynthesizing virginiamycin by streptomycete
ActiveCN102943102APromote growthReduction weakMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyVirginiamycin
The invention discloses a method for biosynthesizing virginiamycin by streptomycete, which comprises the following steps of: preparing a slope with spores of virginiamycin; inoculating the slope spores into a culture medium to obtain a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, adding a precursor substance at the early stage of fermentation so as to increase the yield of virginiamycin; and further processing the fermentation solution after fermentation to obtain virginiamycin crystals. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement, is stable in the fermentation result and low in production cost. The fermentation result is improved compared with the traditional process, and the highest yield of virginiamycin can reach 3500 mu g / ml. Virginiamycin is polypeptide antibiotic containing lactonic rings, has the characteristics of no toxicity, no accumulation, easiness in degradation, and no drug resistance, and is a new animal feed additive.
Owner:江西兴鼎科技有限公司
Composition for indolent wound healing and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS7879798B1Inhibition formationBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsWhite petrolatumIrritation
A topical ointment is described for use in the treatment of indolent wounds composed of fat-soluble vitamins, namely, vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and a subantimicrobial amount of polypeptide antibiotic, which, in turn, acts as a proteinase inhibitor. The active ingredients are combined with a pharmaceutically acceptable topical carrier of lanolin, white petrolatum, mineral oil, and admixtures thereof. In treating these difficult to heal wounds, the selection of the level of the antibiotic at near trace amounts was surprisingly found to be above the proteinase inhibiting threshold and below the wound irritation level. The formulation hereof produced unexpected healing results not found in vitamin-enriched ointments or in antibiotic ointments.
Owner:REGENICEL
Pure-solid-phase synthesis method of polypeptide antibiotic Colistin
InactiveCN103396475ASimplify the synthesis processSimple stepsPolymyxinsPeptide preparation methodsDrugs synthesisSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis, and discloses a method of pure-solid-phase synthesis of polypeptide antibiotic Colistin. By use of the method, the synthetic process and procedure of the Colistin are simplified, the synthesis time is shortened, and the use amount of solvents is reduced.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Serum-free tumor stem cell culture medium and application thereof
ActiveCN107365747AEfficient enrichmentStable growthCulture processCell culture active agentsSodium bicarbonateMetabolite
The invention discloses a serum-free tumor stem cell culture medium. The serum-free tumor stem cell culture medium is prepared from an MCDB153 basic culture medium, cell factors, protein polypeptides, antibiotics, epinephrine, selenium, sodium hydrogen carbonate, lipids and mangrove endophytic fungus metabolite 4(15)-eudesmene-5,7-dyhydroxyl-1-ketone. The tumor stem cell culture medium contains no serum, the formula compositions are definite, the safety is relatively high, the serum-free tumor stem cell culture medium can efficiently concentrate tumor stem cells from a malignant tumor cell line and tumor tissues, the tumor stem cells are enabled to grow stably, good cell activity and physiological property can be maintained, and the serum-free tumor stem cell culture medium is very applicable to the field of relevant researches for tumor cells and the tumor stem cells.
Owner:上海揽微赛尔生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing organic fertilizer from polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues
InactiveCN107522546AIncrease productionImprove the safety of useOrganic fertilisersAmmonium salt fertilisersPersulfateResource utilization
The invention provides a method for preparing organic fertilizer from polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues and relates to a harmless treatment and resource utilization method for the polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues in order to solve the problems that treatment cost of existing polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues is high, environmental risks still exist after treatment of the existing polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues and the like. The method comprises steps as follows: fresh polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues are subjected to oxidation treatment by utilizing persulfate as an oxidizing agent, wherein the residual quantity of polypeptide antibiotics in the fresh polypeptide antibiotic bacteria residues is 800-1500 mg / kg, and pH is 6.5-8.0; the treated bacteria residues are subjected to centrifugal treatment and then subjected to mixed granulation with auxiliary materials, and the organic fertilizer is prepared. The fertilizer preparation technology is simple, easy to operate and low in treatment cost; polypeptide antibiotic degradation efficiency is high, polypeptide antibiotic resistant bacteria in the bacteria residues can be effectively killed, and use safety of the fertilizer is high; one safe treatment and resource utilization method for the bacteria residues is provided for a pharmaceutical enterprise, and certain economic benefit is achieved by the enterprise through reduction of the treatment cost.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Synergist for improving gram-positive-bacterium-resistant effect of nisin
InactiveCN104605463AAdd lessEnhanced activity against Gram-positive bacteriaFood preservationBiotechnologyPerilla oil
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparing method for extracting polypeptide antibiotics from silkworm
InactiveCN1456574AEasy extractionHigh economic valueOrganic active ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsChemistryPolypeptide antibiotic
A process for extracting polypeptide antibiotic from bombxy mori includes such steps as including polypeptide antibiotic in young silkworm of pupa, preparing extracting liquid, separating and purifying. Its advantages are simple process, low cost, broad antibacterial spectrum, and high purity.
Owner:成都天创生物科技有限责任公司
Synthesis process of D-tryptophane
InactiveCN101020653ARaw materials are easy to getReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryEthyl acetateSolvent
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and application thereof
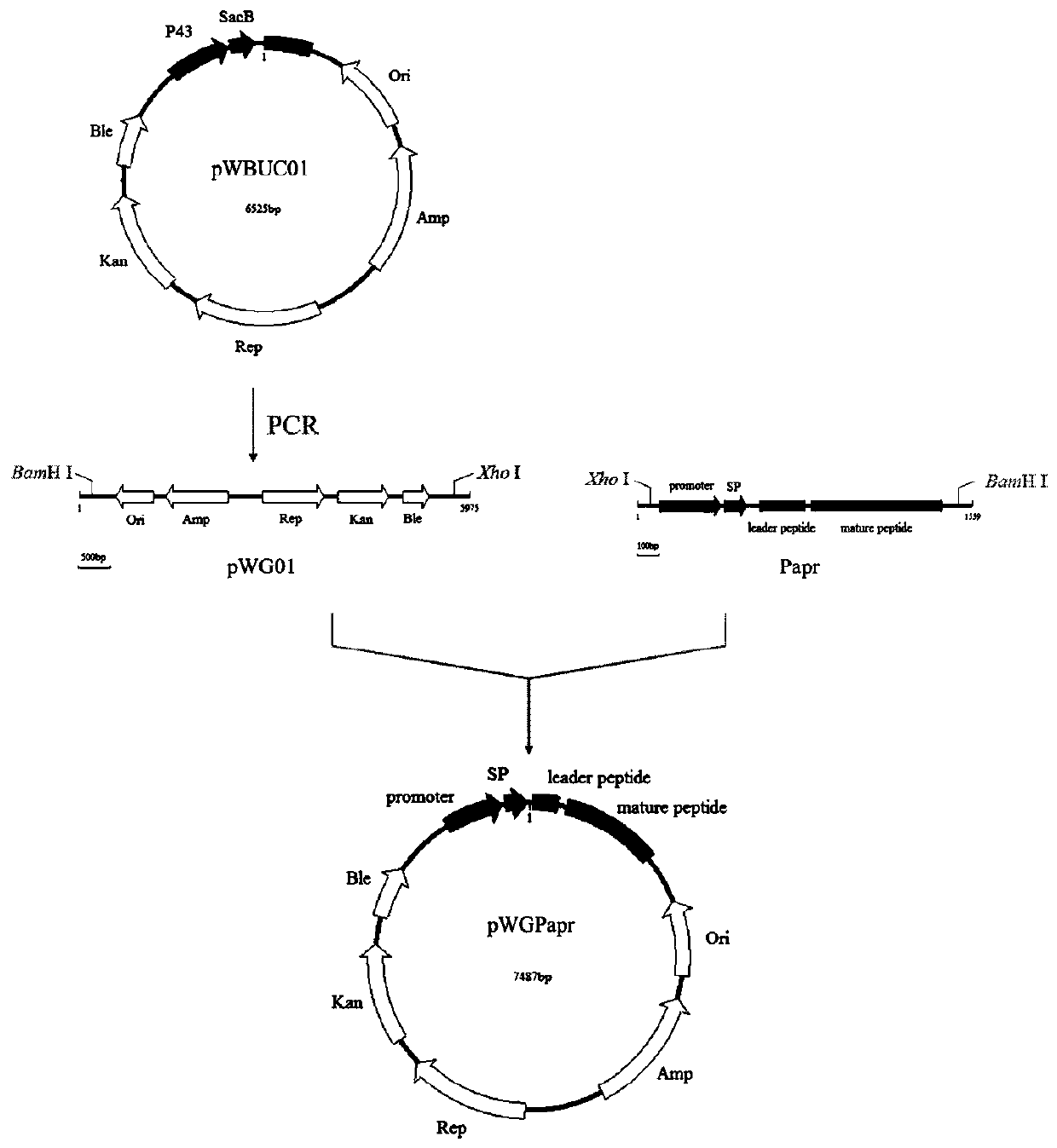
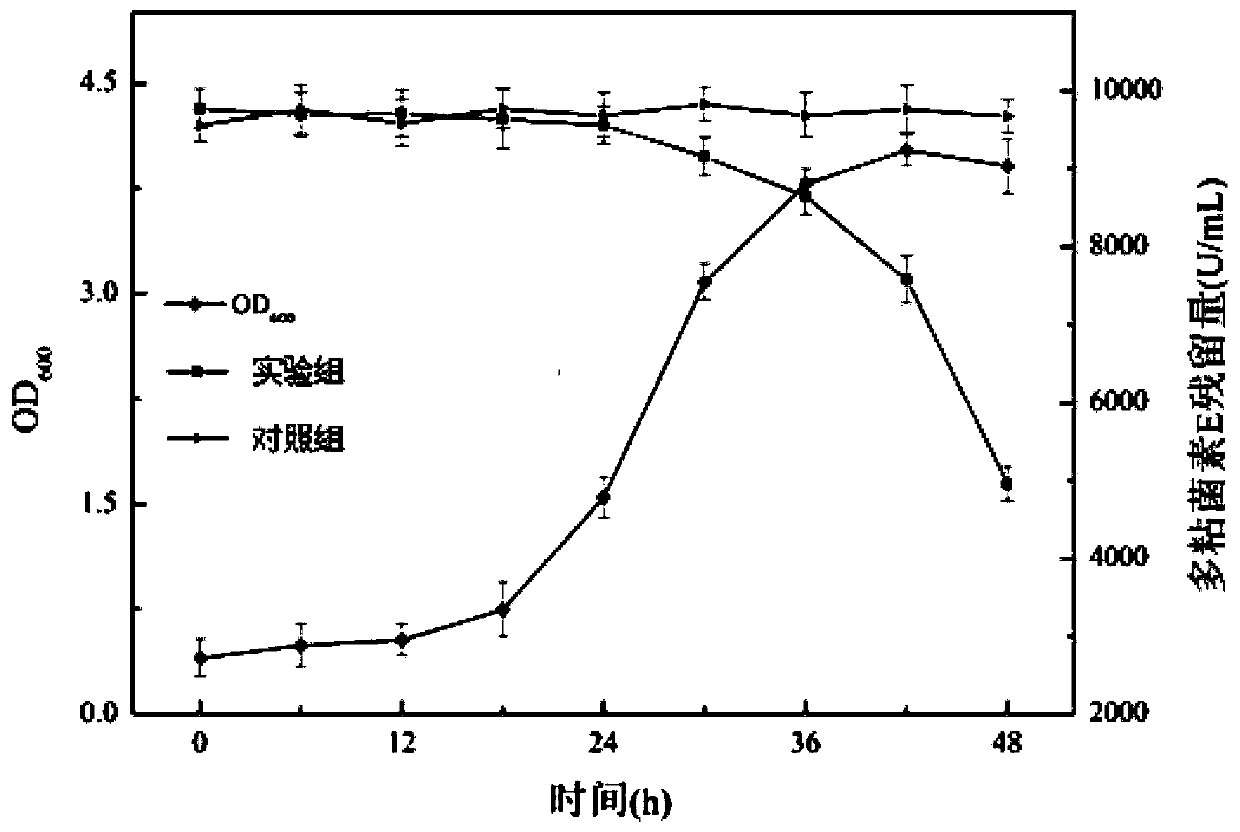
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis and application thereof in degradation of polypeptide antibiotics. The engineering bacteria are obtained by ligating a gene segment shown in SEQ ID No. 1 to a linearized pWBUC01 vector and then transferring into bacillus subtilis. The bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria for degrading the polypeptide antibiotics can effectively and quickly remove the polypeptide antibiotics in a water environment, and has the advantages of safety, high efficiency and energy conservation compared with the traditional chemical degradation and physical absorption. The bacillus subtilis WB800 / pWBUC01-apr provided by the invention can effectively degrade polymyxin residue in the contaminated sludge, and the 16000 U / mL polymyxin is basically degraded completely in 8 days; however, the polymyxin degradation rate of WB800 with no-loaded pWBUC01 is only about 38%.
Owner:浙江科峰生物技术有限公司
Antibiotics based upon bacteriophage lysis proteins
InactiveUS20050191628A1Slow onsetFunction increaseBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLysisAntibiotic Y
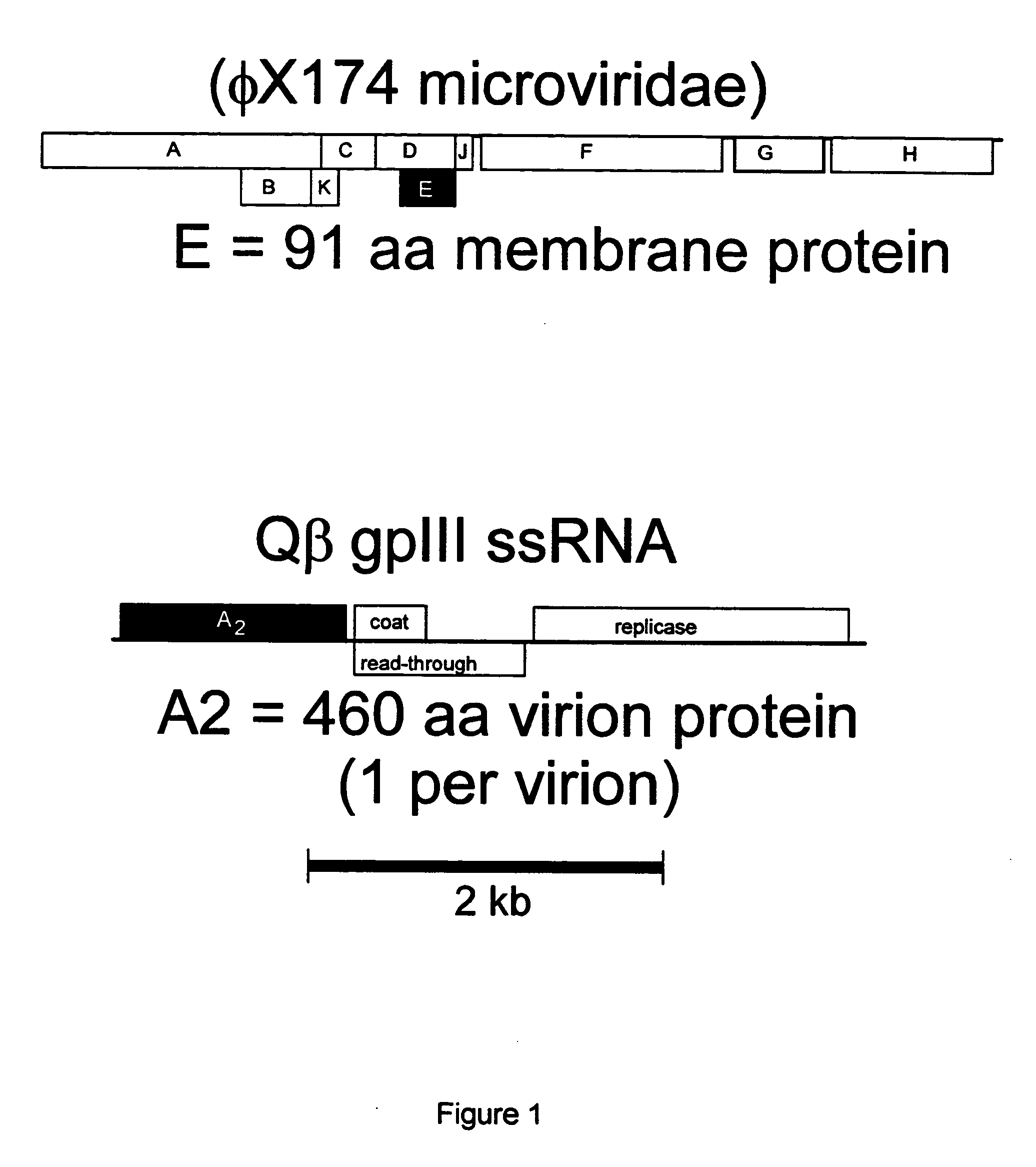
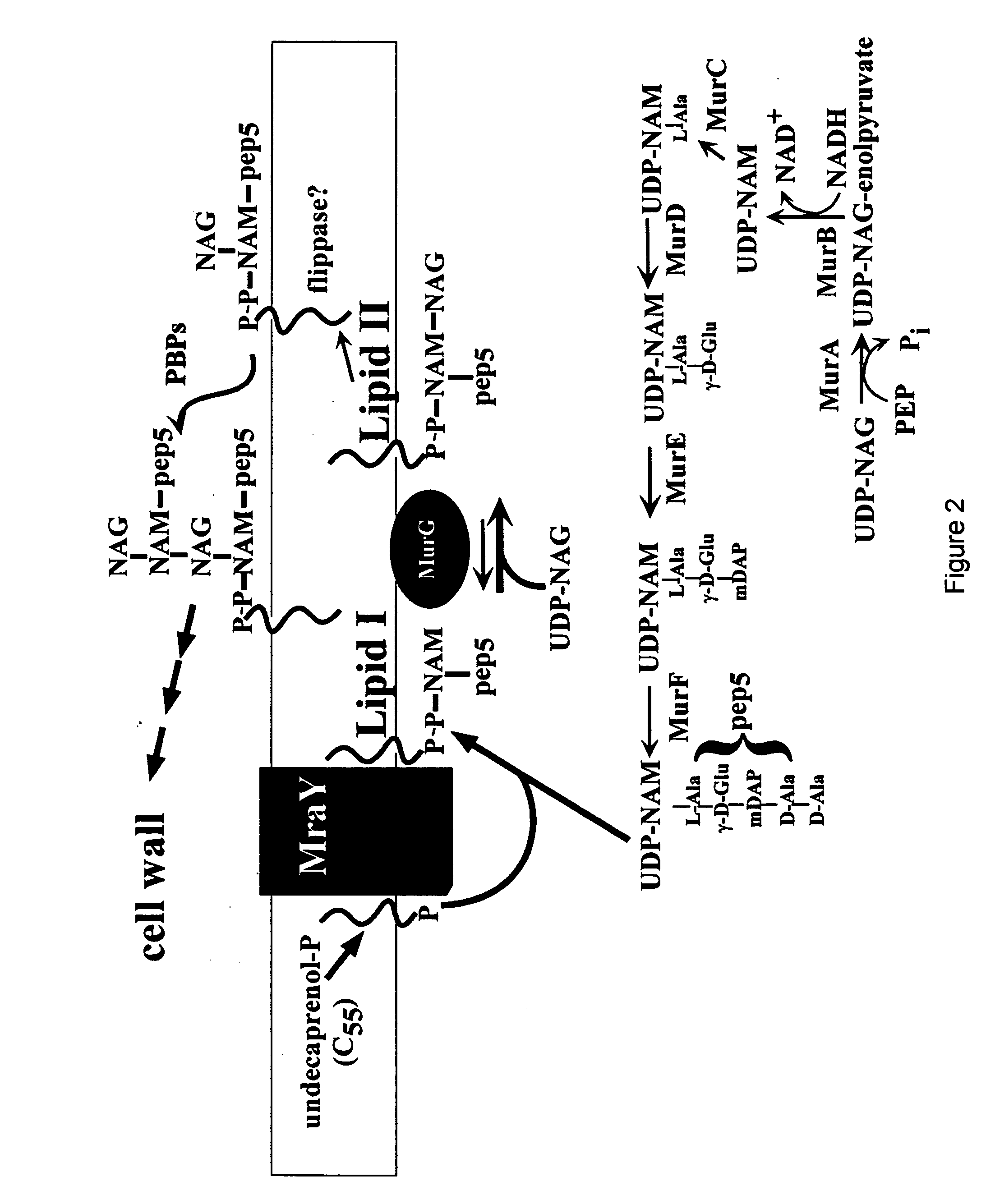
This invention relates to polypeptide antibiotics, including materials and methods related thereto, based upon the observation that bacteriophage elaborate proteins that cause host cell lysis by interfering with specific steps in cell wall biosynthesis. Examples of antibiotics based upon this invention include the bacteriophage φX174 gene E product and structurally and / or functionally related polypeptide and small protein antibiotics that interact with MraY, and the bacteriophage Qβ gene A2 product and structurally and / or functionally related polypeptide and small protein antibiotics that interact with MurA. This leads to the general model for obtaining new polypeptide antibiotics by using genetic approaches based on these findings to find polypeptide sequences which cause bacterial cell lysis.
Owner:YOUNG RYLAND +4
Method for producing polypeptide enramycin with zymotechnics
InactiveCN101245362BHigh potencyAchieve high density cultureMicroorganism based processesFermentationAntibiotic YBacterial strain
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
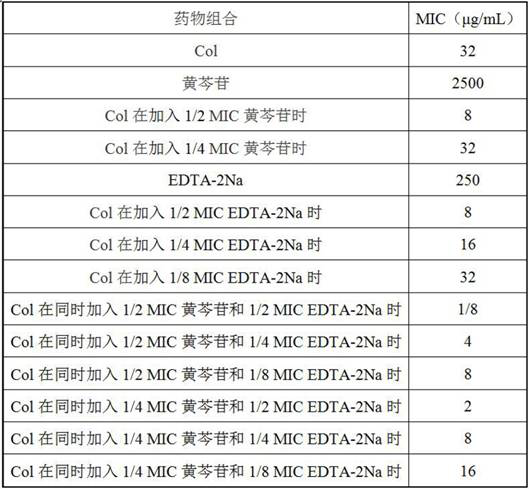
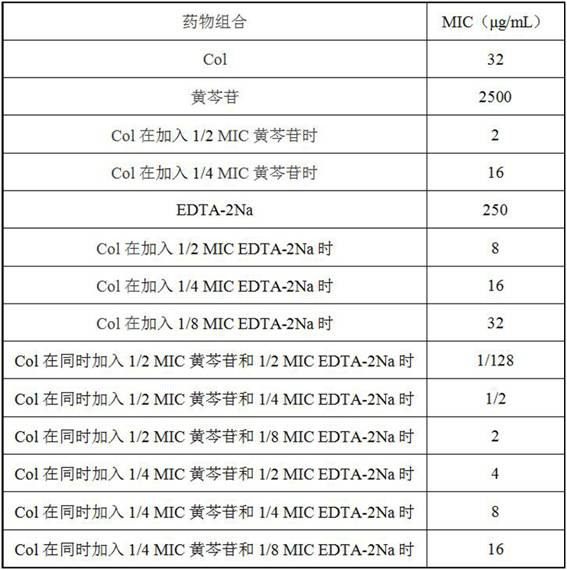
New application of scutellaria baicalensis flavonoid compounds and/or metal ion complexing agents in enhancement of polymyxin antibiotic antibacterial effect
ActiveCN112245566AEliminate side effectsReduce doseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPolymyxin AntibioticAntibacterial activity
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a new application of scutellaria baicalensis flavonoid compounds and / or metal ion complexing agents in enhancement of polymyxin antibiotic antibacterial effect. In-vitro tests prove that the scutellaria baicalensis flavonoid compounds and the metal ion complexing agents are combined with polymyxin antibacterialagents, so that the antibacterial activity of polymyxin antibiotics can be improved to different degrees, and the drug resistance of bacteria to the polypeptide antibiotics can be reversed. Therefore,a synergist of the polymyxin antibiotics can be used, and used for preparing a compound preparation. Under the conditions that the drug resistance of the clinical polymyxin antibiotics is increasingly common and the drug resistance degree is increasingly serious, the new application can recover the sensitivity of the drug-resistant bacteria to the polymyxin antibiotics, can reduce the dosage of the polymyxin antibiotics such as the colistin, improve the antibacterial treatment effect, and reduce the toxic and side effects, and has significant clinical application value.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and construction method and application thereof
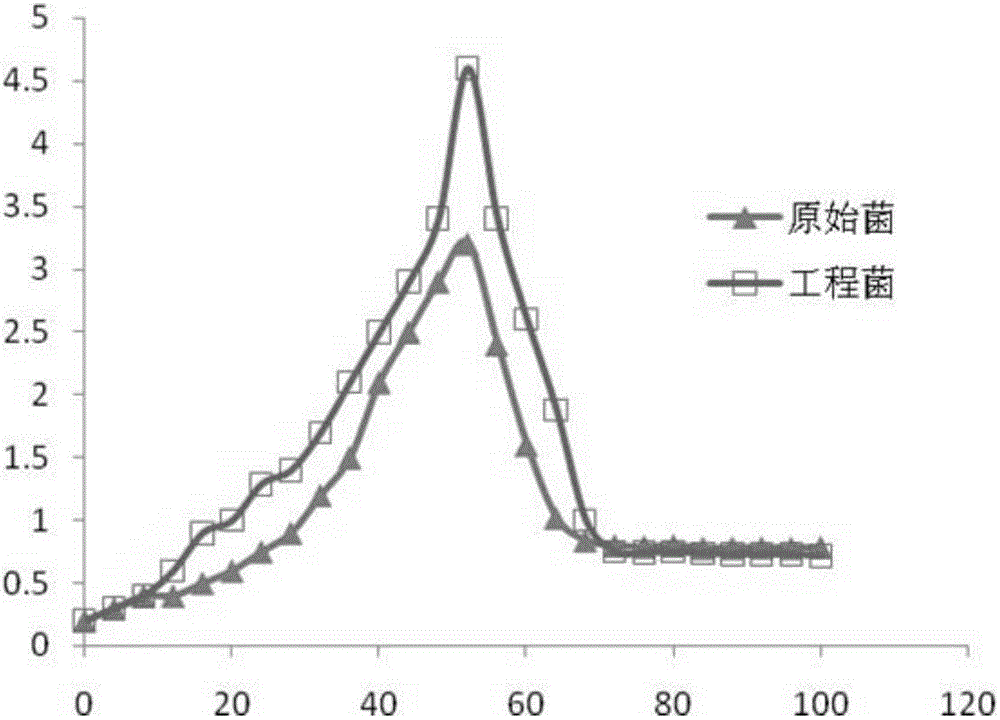
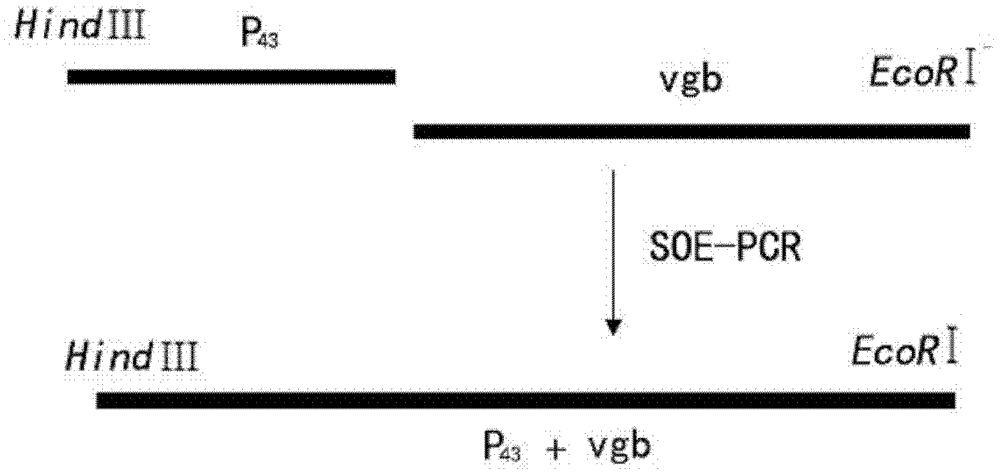
ActiveCN102776147AIncrease profitImprove liquidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEngineered geneticPromoter
The invention discloses a gene-engineered bacterium of gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and a construction method and application of the gene-engineered bacterium. Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus BC39 with vitreoscilla hemoglobin regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter is constructed by constructing a gene-recombination integrative vector with a peoriae paenibacillus LXH-B-1 strain as host bacteria. The gene-engineered bacterium of the gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus is capable of intracellularly expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, so that the utilization rate of oxygen by the peoriae paenibacillus, the cell biomass liveweight and the yield of catalysate polypeptide antibiotics can be improved; and the yield of the catalysate polypeptide antibiotics of the engineering strain is increased by 45% compared with that of the original strain; and therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the problem of insufficient oxygen supply in the cell culture and catalysis process of the peoriae paenibacillus.
Owner:杨凌静玥生物科技有限公司
Pulse-type administration preparation of anti-drug-resistant-bacteria antibiotic microspheres
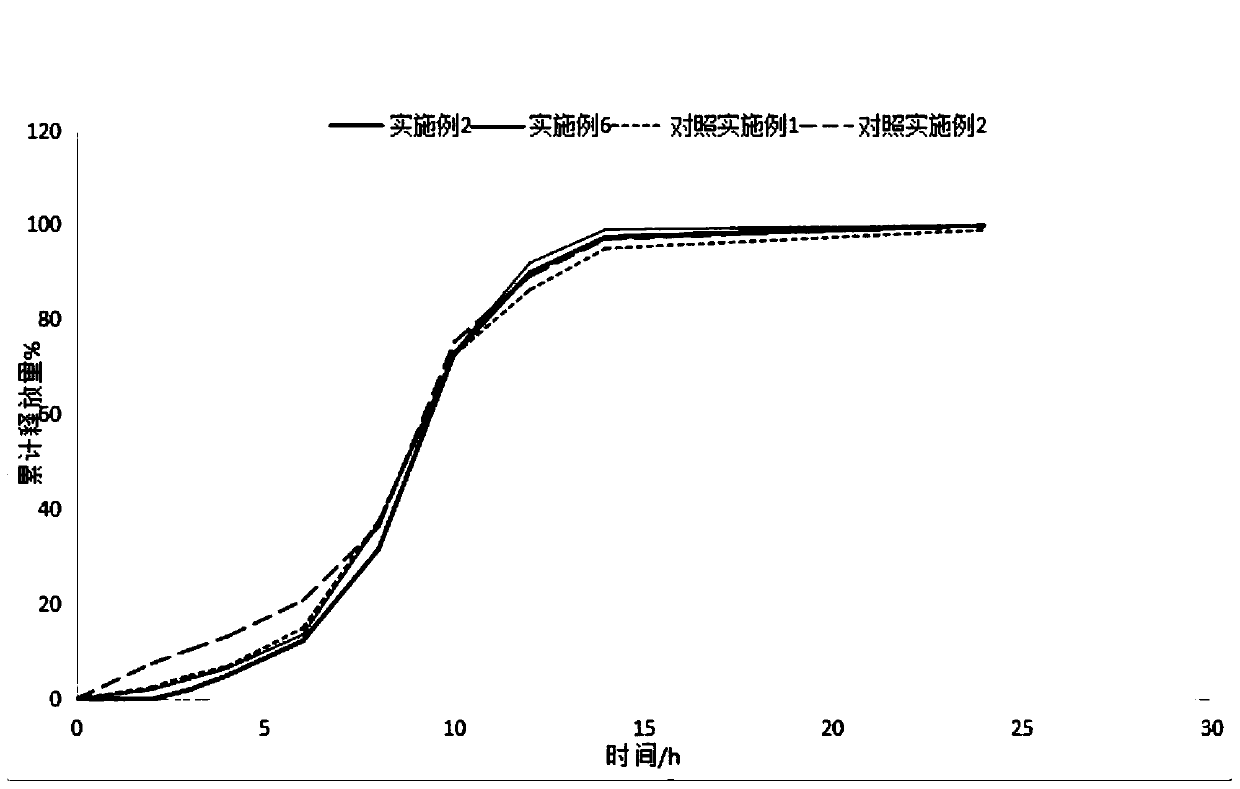
ActiveCN107582541AWith pulse release propertiesLittle side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The invention relates to a pulse-type administration preparation of anti-drug-resistant-bacteria antibiotic microsphere, wherein the preparation comprises three parts capable of achieving pulse slow release in three times. The three parts include: a quick release part, which contains a main drug core microsphere; an N-hour delaying part, which contains a main drug core microsphere, an inner-layermixture coating, and an outer-layer enteric polymer coating; and a 2N-hour delaying part, which contains a main drug core microsphere, an inner-layer mixture coating, and an outer-layer enteric polymer coating, wherein N is a natural number in a range of 2-6. The main drug is anti-drug-resistant-bacteria antibiotics, which includes carbapenem antibiotics, aminoglycoside antibiotics, and polypeptide antibiotics. The preparation has a pulse-type administration system that ensures conveying of a single medicine or a medicine association at the same time and a controller of pulse-type administration time for efficiently treating diseases, and has maximum patient compliance and minimum side effect.
Owner:BEIJING YUEKANGKECHUANG PHARM TECH CO LTD
A method for improving the antibacterial properties and stability of cationic short peptides
InactiveCN104672307BIncrease the strength of actionReduce exposureAntibacterial agentsPeptidesAntibiotic resistanceCell membrane
Owner:JILIN UNIV
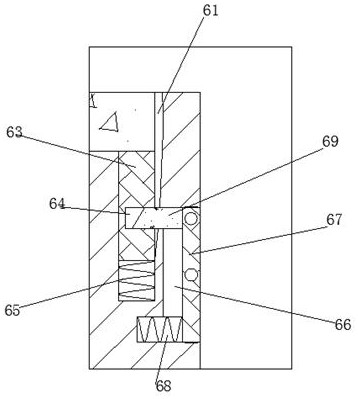
A kind of polypeptide antibiotic device
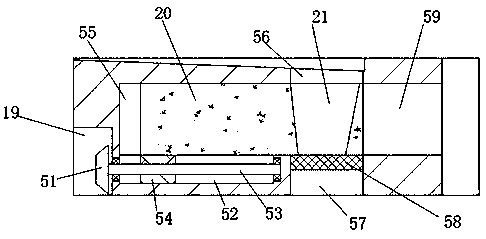
ActiveCN110078786BQuick grindingAvoid destructionPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a plypeptide antibiotic device, including a device man body and a function switching cavity provided in the device main body, wherein a function switching device is arranged inthe function switching cavity; the function switching device includes a switching button capable of moving up and down in the function switching cavity. The plypeptide antibiotic device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure and convenient operation. Through the device, rapid grinding of plant materials are achieved, damage to medical ingredients caused by high temperature and high pressure during traditional medicine grinding production is avoided, extraction efficiency and extraction effect of polypeptide antibiotics later are greatly improved. At the same time, an automatic discharging device is provided, residues and slag can be automatically discharged with one click, no manual power to clean residues and slag is needed, medicine preparation efficiency is greatly improved and the polypeptide antibiotic device is worth recommending and using.
Owner:重庆旺大生物科技有限公司 +1
A kind of polypeptide antibiotic and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111471093BImprove the bactericidal effectStable structureAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiofilmAntimicrobial peptides
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method for biosynthesizing virginiamycin by streptomycete
ActiveCN102943102BSusceptibility to drug resistanceNo drug resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyVirginiamycin
The invention discloses a method for biosynthesizing virginiamycin by streptomycete, which comprises the following steps of: preparing a slope with spores of virginiamycin; inoculating the slope spores into a culture medium to obtain a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation culture, adding a precursor substance at the early stage of fermentation so as to increase the yield of virginiamycin; and further processing the fermentation solution after fermentation to obtain virginiamycin crystals. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement, is stable in the fermentation result and low in production cost. The fermentation result is improved compared with the traditional process, and the highest yield of virginiamycin can reach 3500 mu g / ml. Virginiamycin is polypeptide antibiotic containing lactonic rings, has the characteristics of no toxicity, no accumulation, easiness in degradation, and no drug resistance, and is a new animal feed additive.
Owner:江西兴鼎科技有限公司
A kind of recombinant bacillus subtilis and its application
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis and application thereof in degradation of polypeptide antibiotics. The engineering bacteria are obtained by ligating a gene segment shown in SEQ ID No. 1 to a linearized pWBUC01 vector and then transferring into bacillus subtilis. The bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria for degrading the polypeptide antibiotics can effectively and quickly remove the polypeptide antibiotics in a water environment, and has the advantages of safety, high efficiency and energy conservation compared with the traditional chemical degradation and physical absorption. The bacillus subtilis WB800 / pWBUC01-apr provided by the invention can effectively degrade polymyxin residue in the contaminated sludge, and the 16000 U / mL polymyxin is basically degraded completely in 8 days; however, the polymyxin degradation rate of WB800 with no-loaded pWBUC01 is only about 38%.
Owner:浙江科峰生物技术有限公司
Pulse drug delivery formulation of antibiotic microspheres against drug-resistant bacteria
ActiveCN107582541BWith pulse release propertiesLittle side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseImmediate release
The invention relates to a pulse-type administration preparation of anti-drug-resistant-bacteria antibiotic microsphere, wherein the preparation comprises three parts capable of achieving pulse slow release in three times. The three parts include: a quick release part, which contains a main drug core microsphere; an N-hour delaying part, which contains a main drug core microsphere, an inner-layermixture coating, and an outer-layer enteric polymer coating; and a 2N-hour delaying part, which contains a main drug core microsphere, an inner-layer mixture coating, and an outer-layer enteric polymer coating, wherein N is a natural number in a range of 2-6. The main drug is anti-drug-resistant-bacteria antibiotics, which includes carbapenem antibiotics, aminoglycoside antibiotics, and polypeptide antibiotics. The preparation has a pulse-type administration system that ensures conveying of a single medicine or a medicine association at the same time and a controller of pulse-type administration time for efficiently treating diseases, and has maximum patient compliance and minimum side effect.
Owner:BEIJING YUEKANGKECHUANG PHARM TECH CO LTD
Polypeptide antibiotic device
ActiveCN110078786AQuick grindingAvoid destructionPeptide preparation methodsBiochemical engineeringSlag
The invention discloses a plypeptide antibiotic device, including a device man body and a function switching cavity provided in the device main body, wherein a function switching device is arranged inthe function switching cavity; the function switching device includes a switching button capable of moving up and down in the function switching cavity. The plypeptide antibiotic device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure and convenient operation. Through the device, rapid grinding of plant materials are achieved, damage to medical ingredients caused by high temperature and high pressure during traditional medicine grinding production is avoided, extraction efficiency and extraction effect of polypeptide antibiotics later are greatly improved. At the same time, an automatic discharging device is provided, residues and slag can be automatically discharged with one click, no manual power to clean residues and slag is needed, medicine preparation efficiency is greatly improved and the polypeptide antibiotic device is worth recommending and using.
Owner:重庆旺大生物科技有限公司 +1
A method for pure solid-phase synthesis of polypeptide antibiotic colistin
InactiveCN103396475BSimple stepsReduce usagePolymyxinsPeptide preparation methodsDrugs synthesisAntibiotic Y
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine synthesis, and discloses a method of pure-solid-phase synthesis of polypeptide antibiotic Colistin. By use of the method, the synthetic process and procedure of the Colistin are simplified, the synthesis time is shortened, and the use amount of solvents is reduced.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
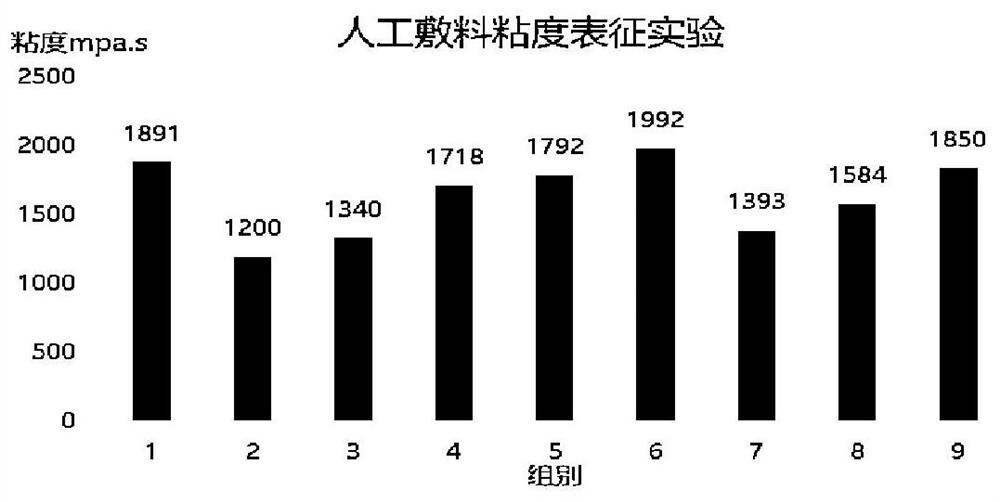
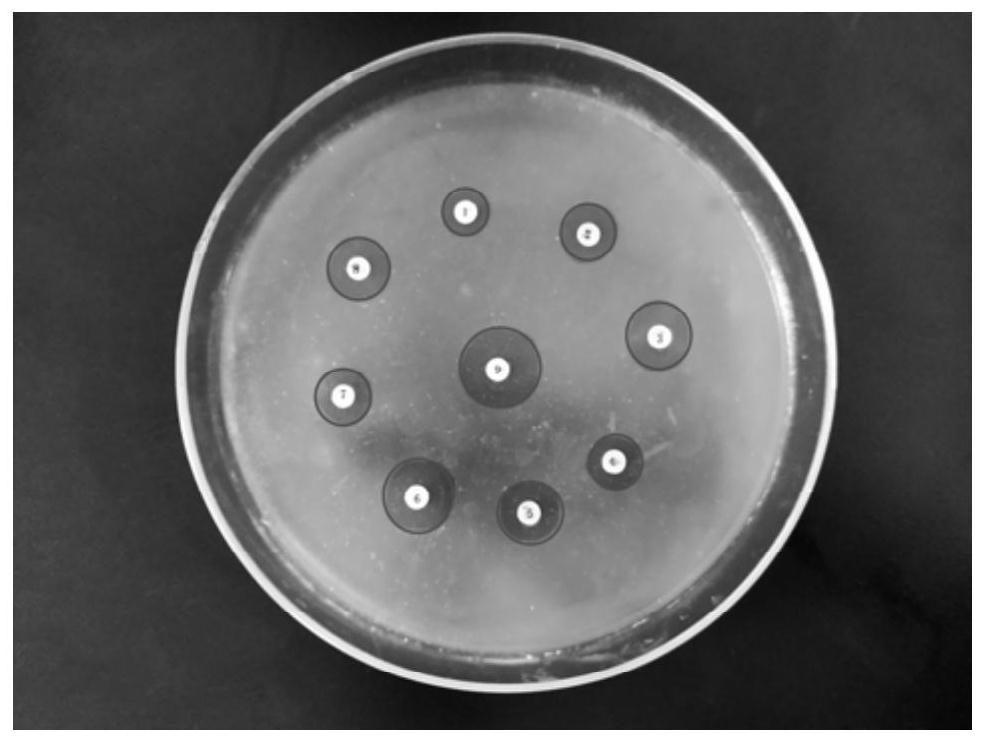
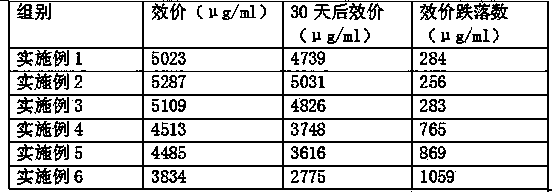
Development of polypeptide antibiotic antibacterial artificial dressing
The invention relates to development of a polypeptide antibiotic antibacterial artificial dressing. The dressing is composed of antibacterial peptide, a mixed solution and a substrate, wherein the substrate is composed ofthe following components in percentage by weight: 3-6% of chitosan, 0.3-0.9% of collagen, 0.1-0.3% of hyaluronic acid, and 3-6% of glycerin; the substrate is prepared by the following steps: adding 3-6% of chitosan into 80-100mL of 2% acetic acid solution, performing uniform swelling by using a stirrer at the rotating speed of 500 r / min, testing the pH value, and adjusting the pH value of the solution to 4.5-5 by using 1 mol / L of NaOH; and dissolving 0.3-0.9% of collagen peptide into the mixed solution at room temperature, adding 0.1-0.3% of hyaluronic acid into the mixed solution, and performing uniform swelling at the rotating speed of 500 r / min, wherein the mixed solution is prepared from 3-6% of glycerin, 1-3% of a polypeptide solution, 1% of a vitamin C solution and 11-13% of deionized water. The finally prepared novel polypeptide antibiotic-based antibacterial artificial dressing is light yellow non-transparent gel. The gel has good smearing performance, and can be directly applied to wounds to achieve antibacterial and healing-promoting effects.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide through fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating streptomyces actuosus to a slant culture medium for carrying out slant culture; inoculating an obtained slant with spores to a seed bottle to culture a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution to a fermentation culture medium for carrying out fermentation culture according to an inoculation quantity of 10 wt%; and further treating the fermented fermentation liquor to obtain nosiheptide crystals. The nosiheptide is produced by adopting a fermentation method. The method is simple and easy and is low in production cost. The polypeptide antibiotics nosiheptide produced by adopting the method can be used as a safe, high-efficiency and environmental-friendly novel feed additive.
Owner:江西兴鼎科技有限公司
Process for the purification of lipopolypeptide antibiotics
InactiveUS20210355160A1Great degreeConveniently removedPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingAnion-exchange chromatography
Disclosed is a process for the purification of lipopolypeptide antibiotics from culture broths which comprises: a) removal of the mycelium from the broth; b) anion-exchange chromatography of the solution resulting from stage a), eluting with di- or trivalent ions; c) optional concentration of the purified fraction resulting from stage b); d) hydrophobic interaction chromatography of the fraction resulting from stage b) or c), eluting with C1-C4 alcohols; e) cation-exchange chromatography of the desired lipopolypeptide-enriched fraction resulting from stage d), eluting at a pH equal to or greater than the isoelectric point of the lipopolypeptide; and f) dialysis, concentration and freeze-drying or spray-drying of the purified lipopolypeptide.
Owner:GNOSIS SPA
Gene recombined Paenibacillus russica and its construction method and application
ActiveCN102776147BIncrease profitImprove liquidityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic YGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a gene-engineered bacterium of gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus, and a construction method and application of the gene-engineered bacterium. Gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus BC39 with vitreoscilla hemoglobin regulated and controlled by a P43 strong promoter is constructed by constructing a gene-recombination integrative vector with a peoriae paenibacillus LXH-B-1 strain as host bacteria. The gene-engineered bacterium of the gene-recombined peoriae paenibacillus is capable of intracellularly expressing the vitreoscilla hemoglobin, so that the utilization rate of oxygen by the peoriae paenibacillus, the cell biomass liveweight and the yield of catalysate polypeptide antibiotics can be improved; and the yield of the catalysate polypeptide antibiotics of the engineering strain is increased by 45% compared with that of the original strain; and therefore, an effective way is provided for solving the problem of insufficient oxygen supply in the cell culture and catalysis process of the peoriae paenibacillus.
Owner:杨凌静玥生物科技有限公司
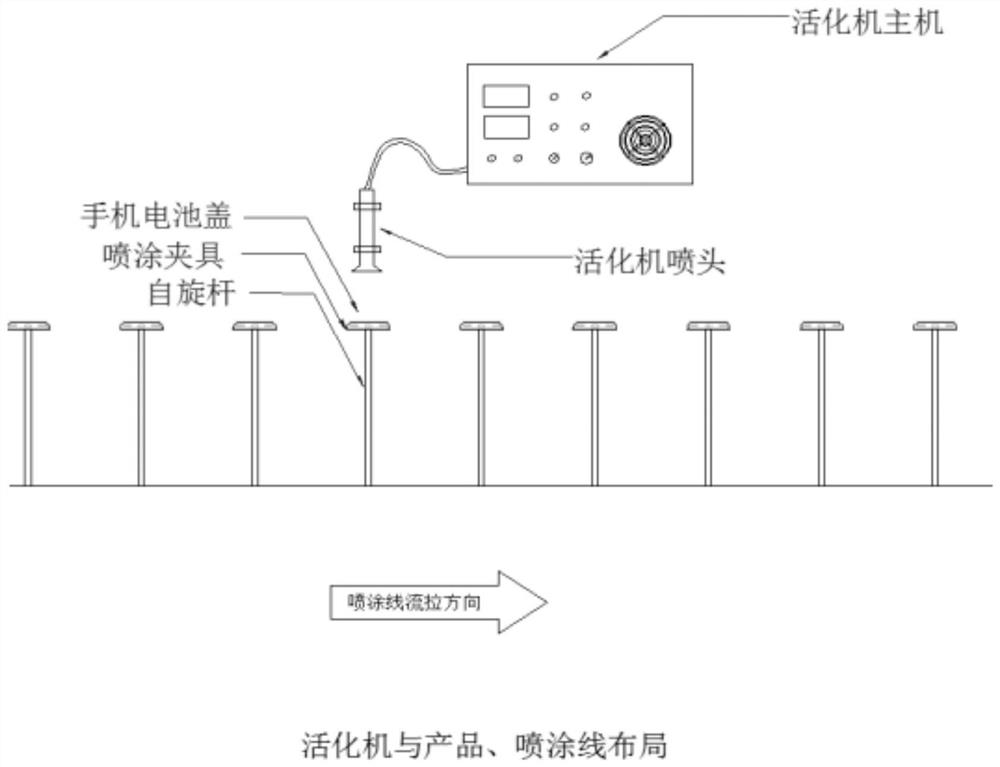
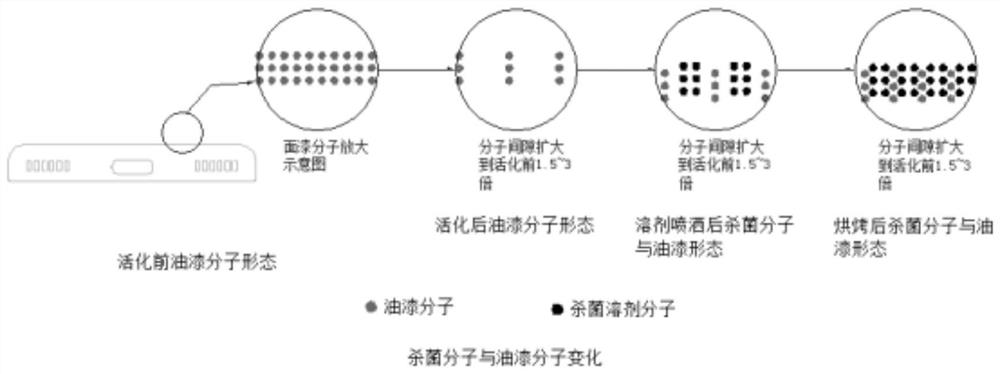
Mobile phone surface antibacterial coating and spraying process thereof
PendingCN113105788AStable structureGood removal effectAntifouling/underwater paintsConjugated diene hydrocarbon coatingsPhosphorous acidCell membrane
The invention discloses a mobile phone surface antibacterial coating, relates to the technical field of coatings, and aims at solving the problem that the surface of an existing mobile phone does not have antibacterial performance. The antibacterial emulsion disclosed by the invention is prepared from the following raw materials: gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, modified nano silicon dioxide, caprolactam, oxalic acid, tetrabutyl titanate, didecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide, dibasic lead phosphite, polyisoprene, polyamide wax micro powder and an antibacterial emulsion. The invention further discloses a spraying process of the mobile phone surface antibacterial coating. The antibacterial emulsion molecules adsorbed by the modified silicon dioxide in the antibacterial coating can secrete a polypeptide antibiotic, namely nisin, which can cause permeation of cell membranes, nutrient loss and reduction of membrane potential by interfering with normal functions of the cell membranes, so that cells of pathogenic bacteria and putrefying bacteria die, fungi / mould can be removed for a long time, and the effective rate of sterilization is greater than or equal to 99.9%.
Owner:安徽千鑫通讯科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com