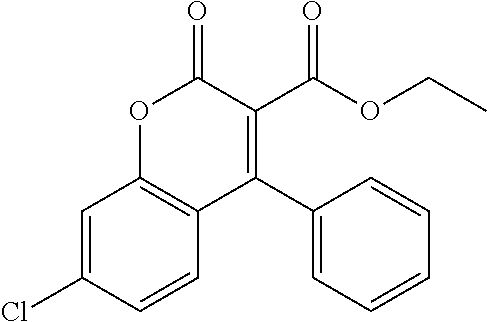
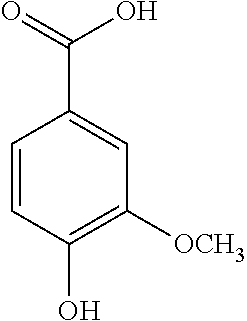
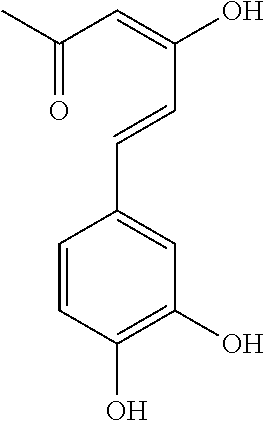
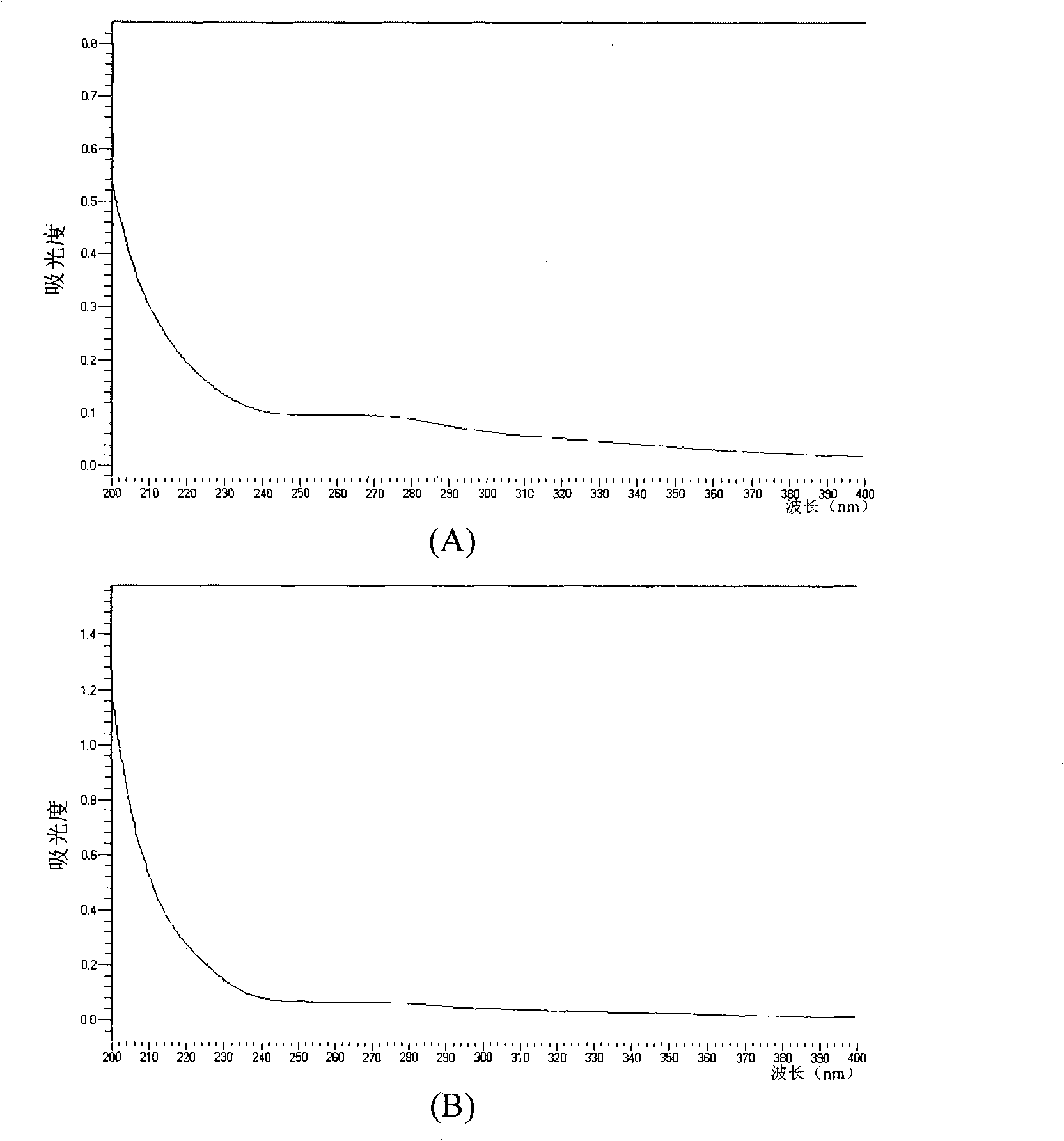
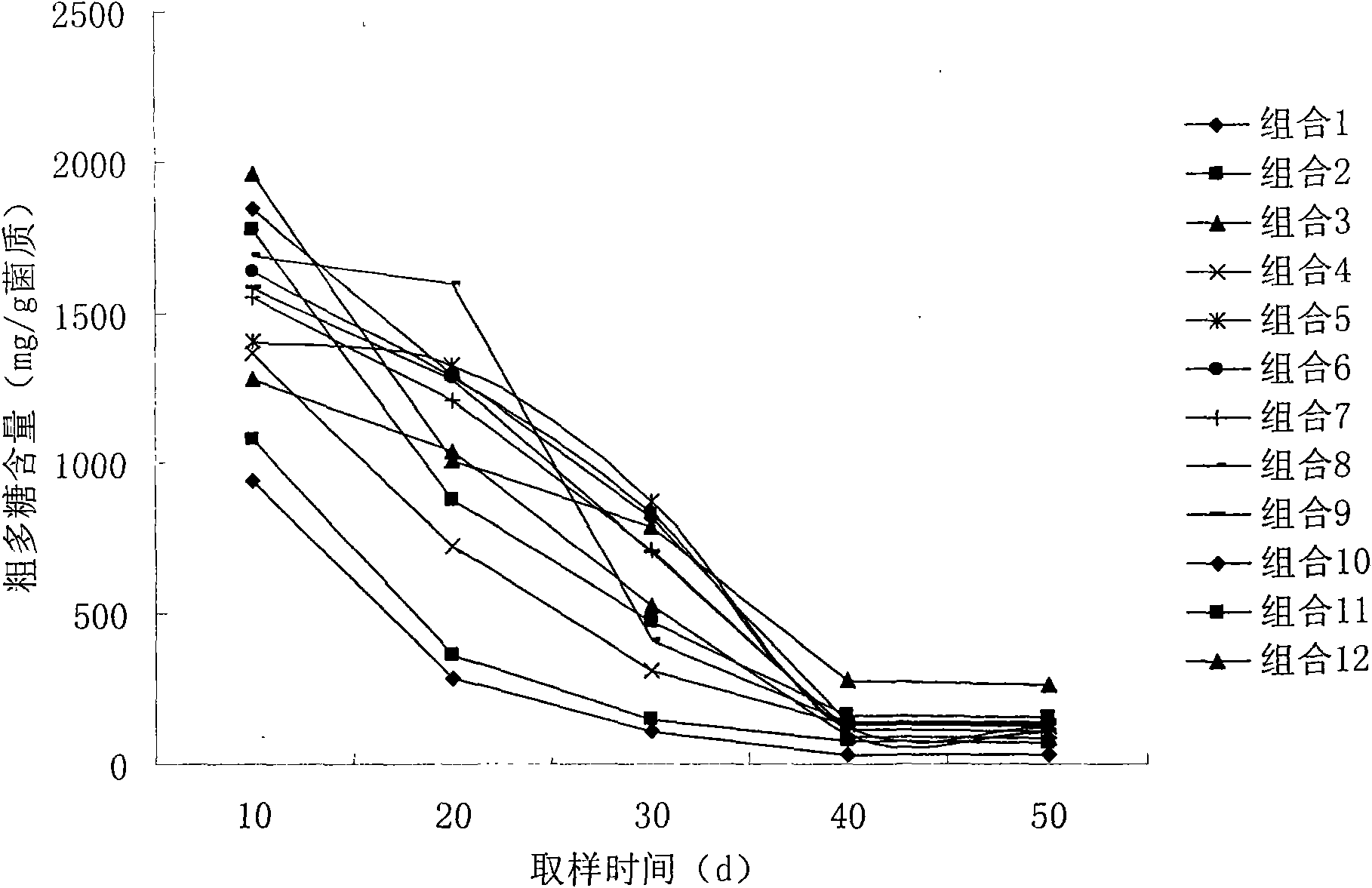
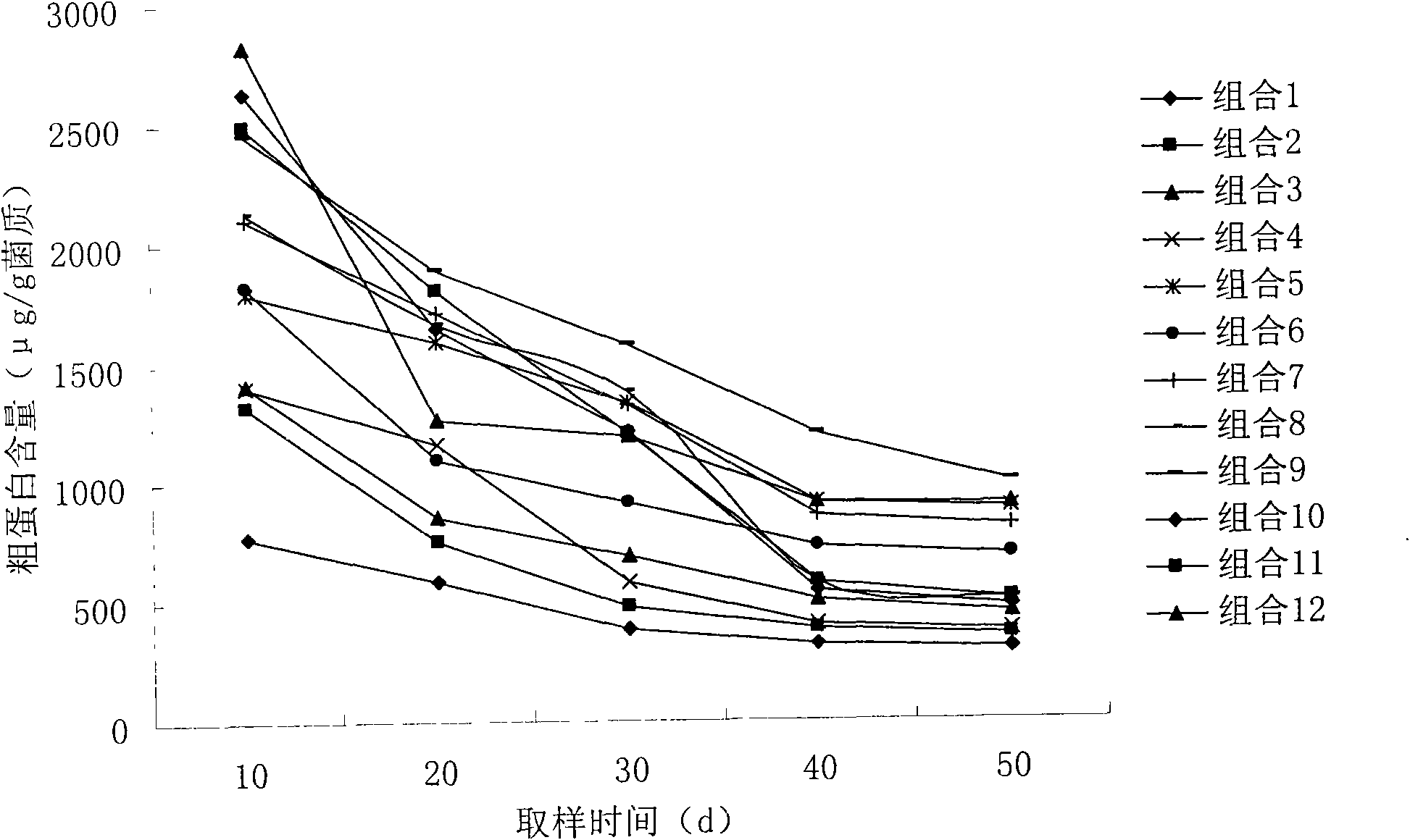
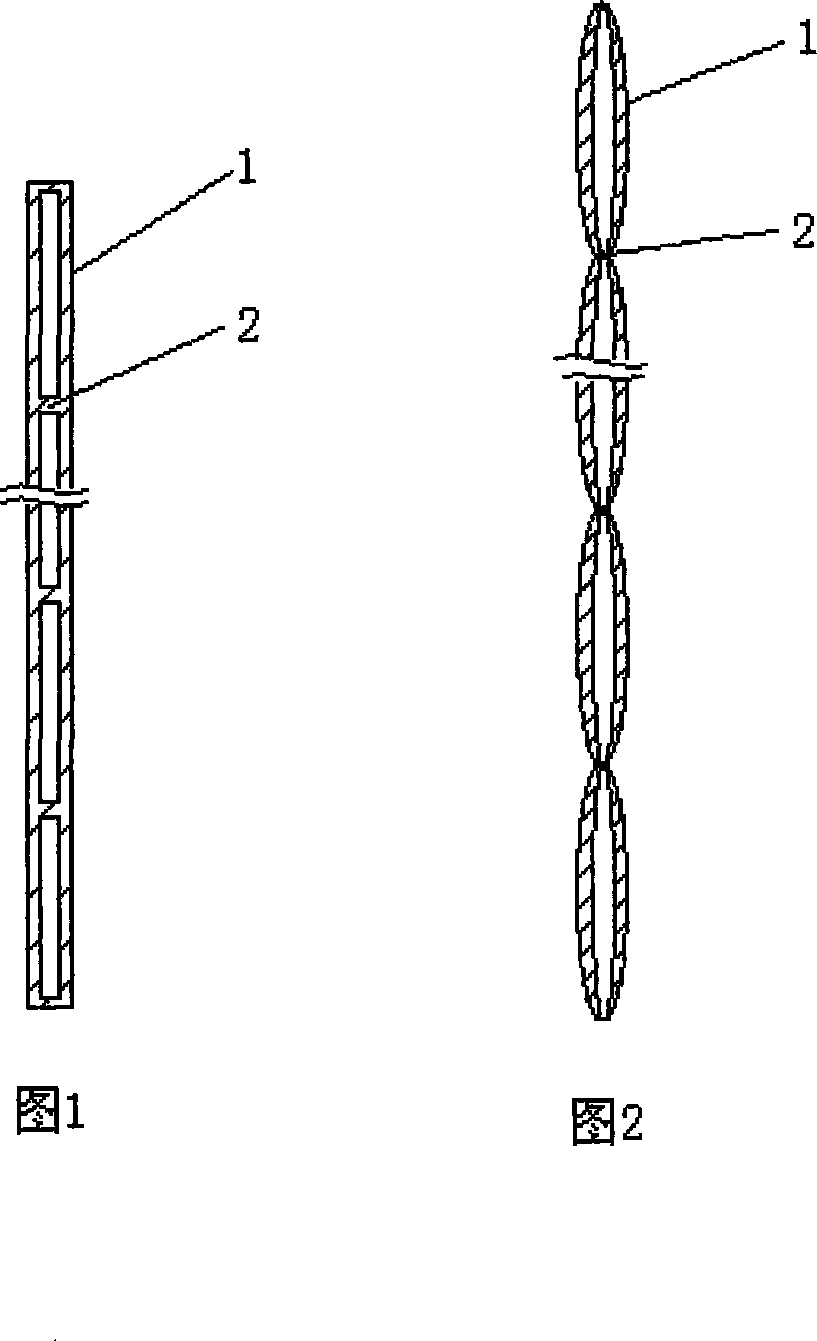
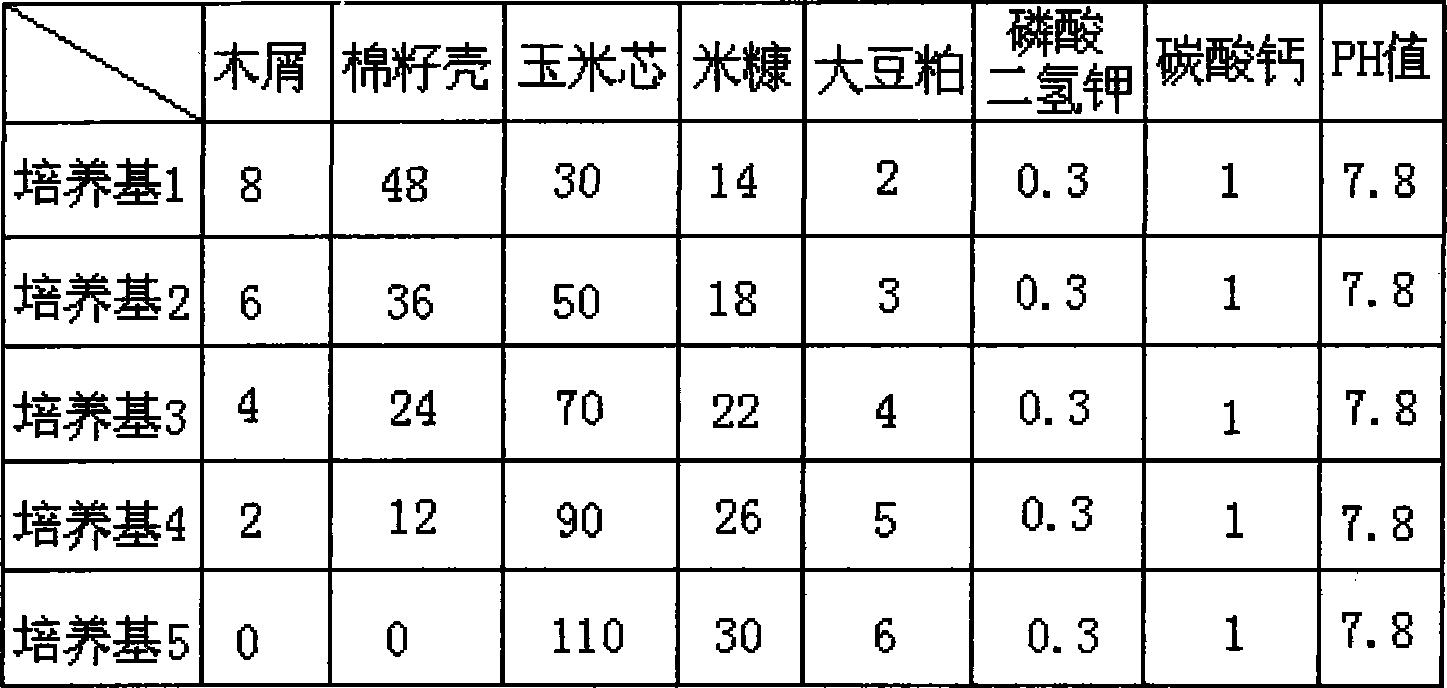
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1496 results about "Fungal mycelium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus or fungus-like bacterial colony, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi.
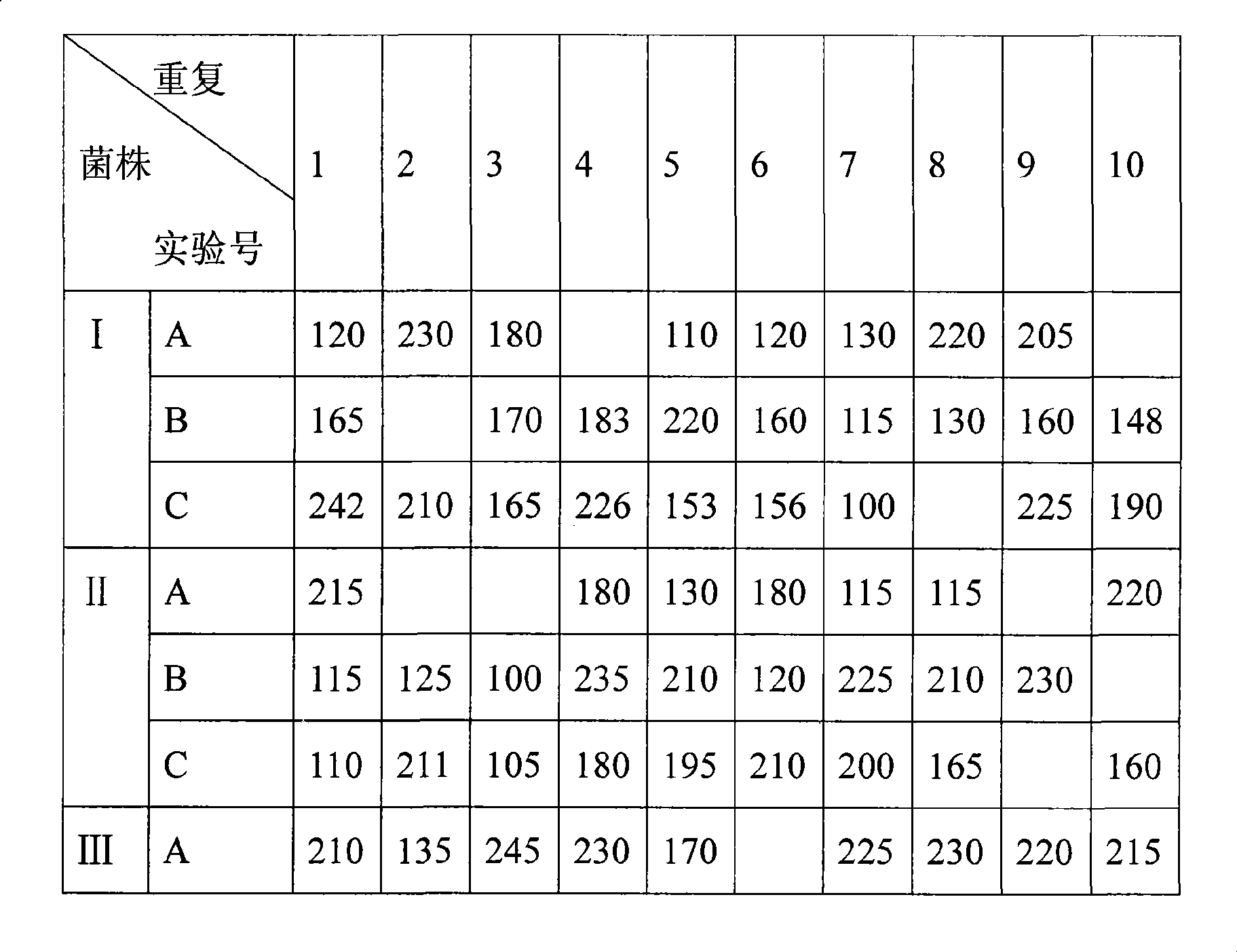
Clear-white gold needle mushroom cultivation method
InactiveCN101366346AAvoid pollutionNo diseaseBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a method for cultivating pure white needle mushrooms. The method comprises the following steps: a strain is prepared; a culture material is prepared; bagging and sterilization are carried out; inoculation is carried out; a mycelium is cultured; nutrition, humidity, temperature, light, air and other culture conditions are strictly controlled during a fruiting period; and harvesting is carried out in an optimum period. the formulation of the culture material is 0 to 32 percent of weed tree sawdust, 0 to 93 percent of cotton seed hulls or wheat straw, straw, corncob and other crop straw, 0 to 20 percent of wheat bran, 0 to 10 percent of corn meal, 0 to 10 percent of soybean meal, 0 to 1 percent of calcium carbonate, 0 to 0.2 percent of monopotassium phosphate, 0 to 0.2 percent of magnesium sulfate, 1 to 1.2 percent of sucrose, 0 to 10 percent of rice bran, 0 to 1 percent of plaster and 0 to 0.02 percent of urea. Quicklime and wettable carbendazim are added during the preparation of the culture material so as to prevent the pollution of undesired bacteria. The technical proposal aims to select proper breeds, popularize local large scale planting and improve cultivation benefit.
Owner:WUHU YESHULIN BIOTECH
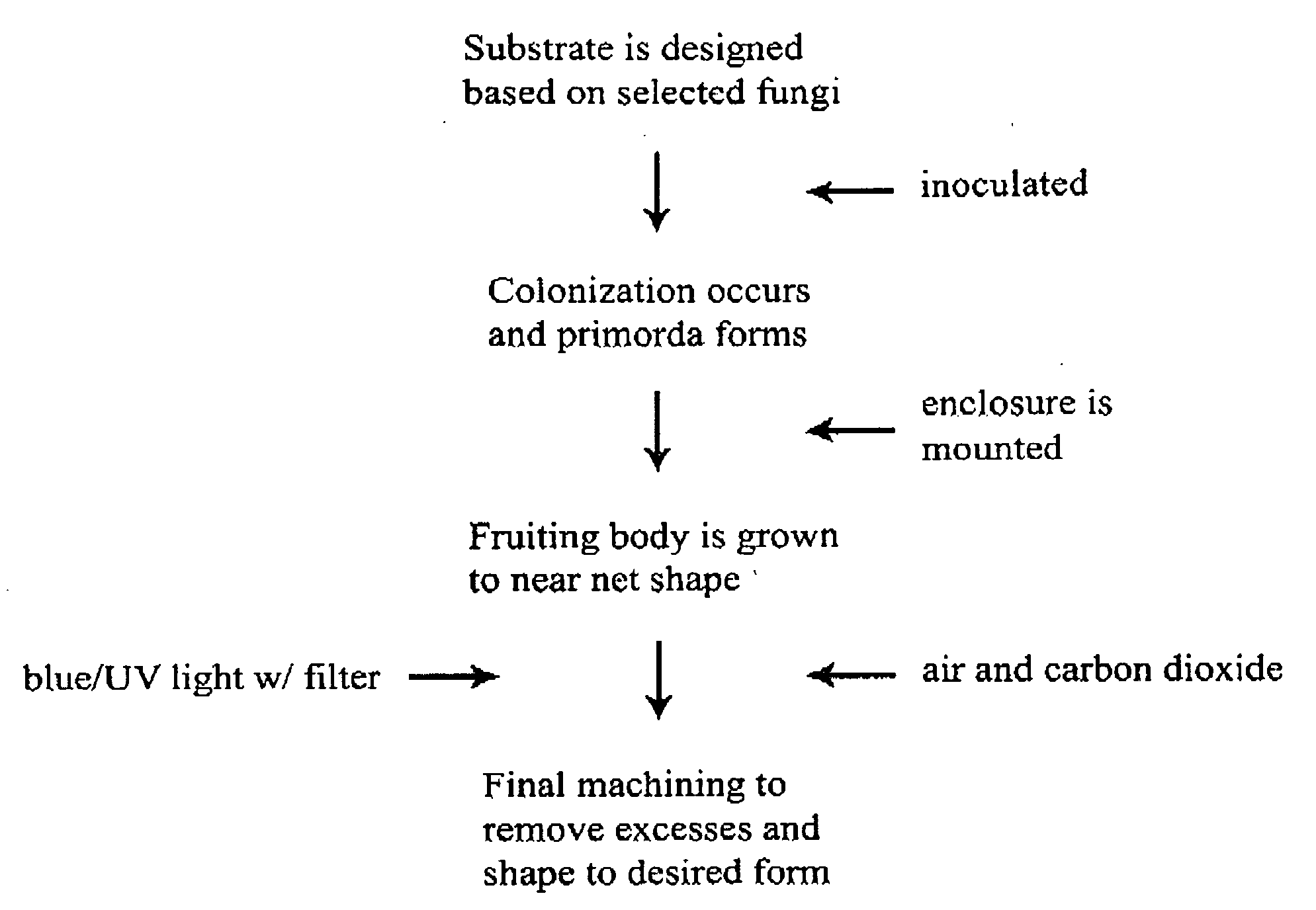
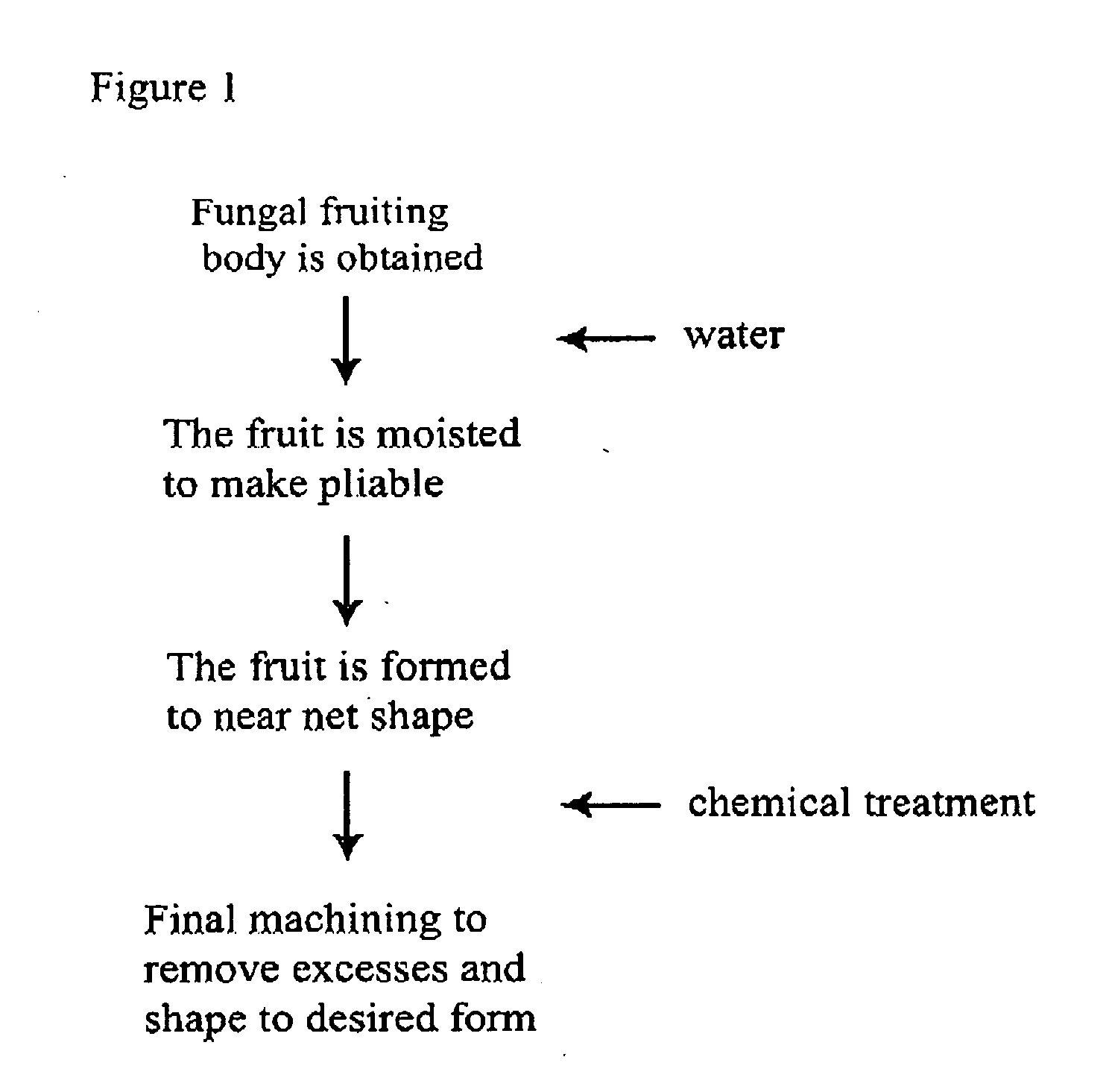
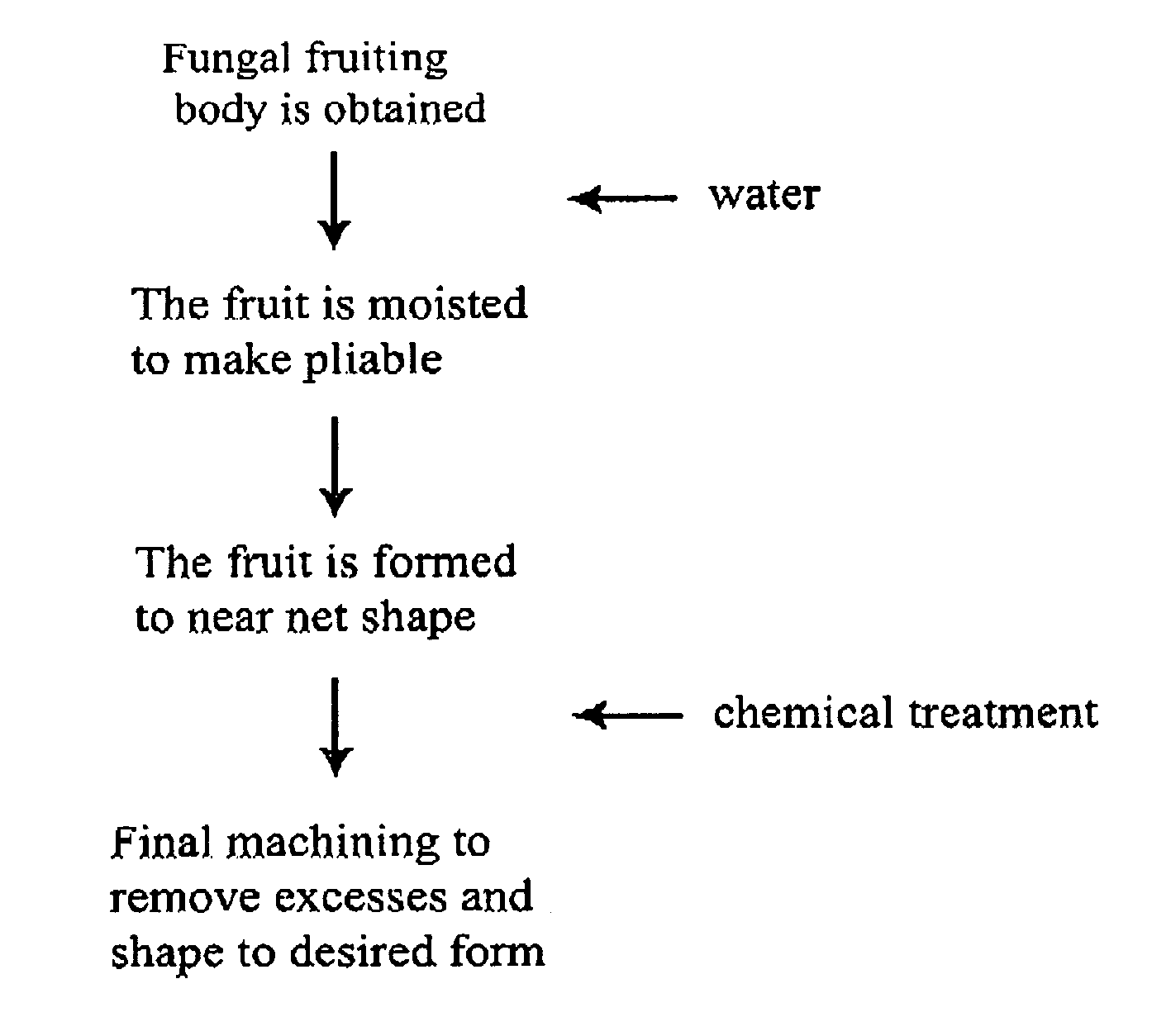
Method for producing rapidly renewable chitinous material using fungal fruiting bodies and product made thereby
ActiveUS20090307969A1Influence growth speedInfluence spore dispersionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyBiological body
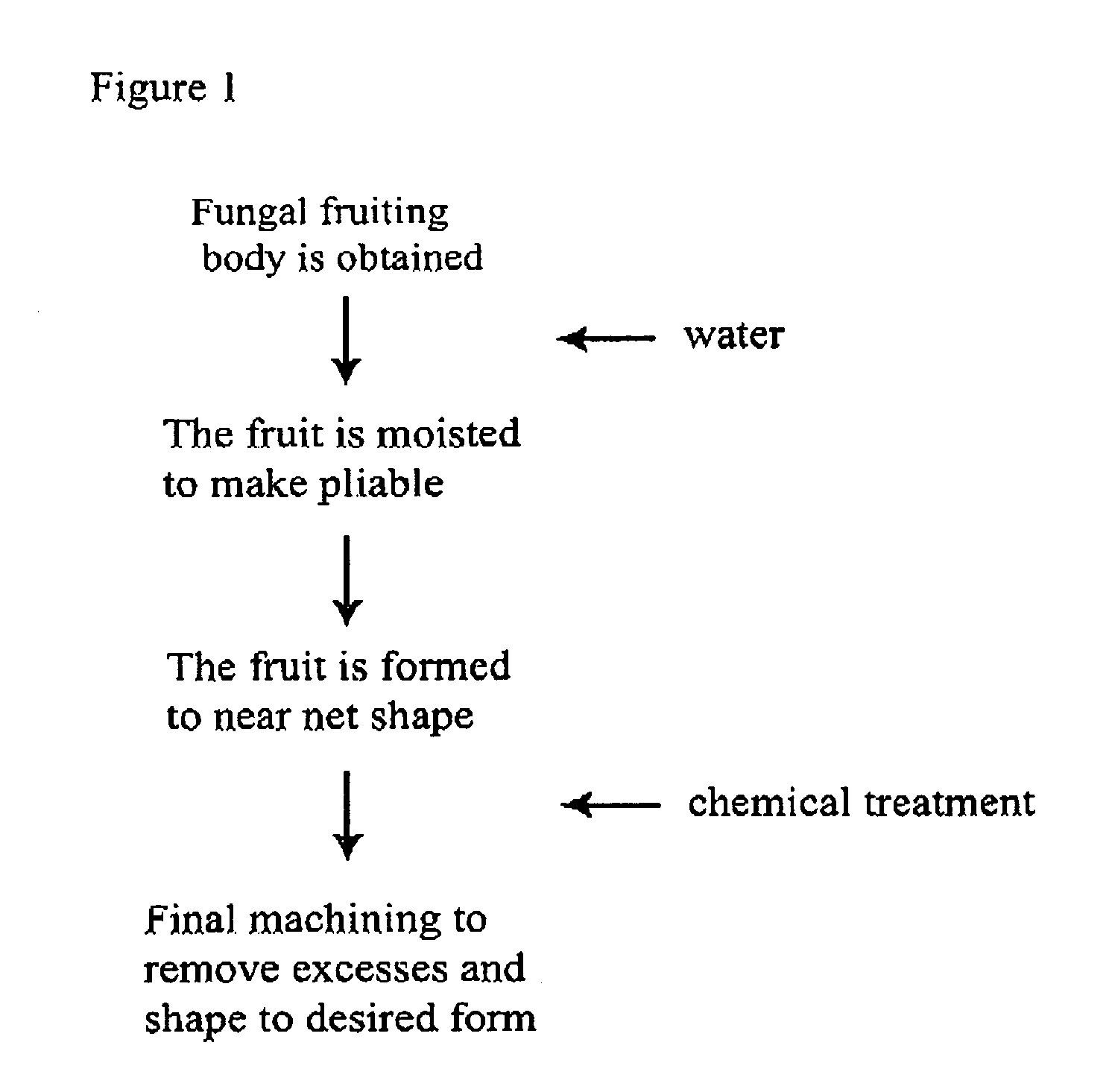
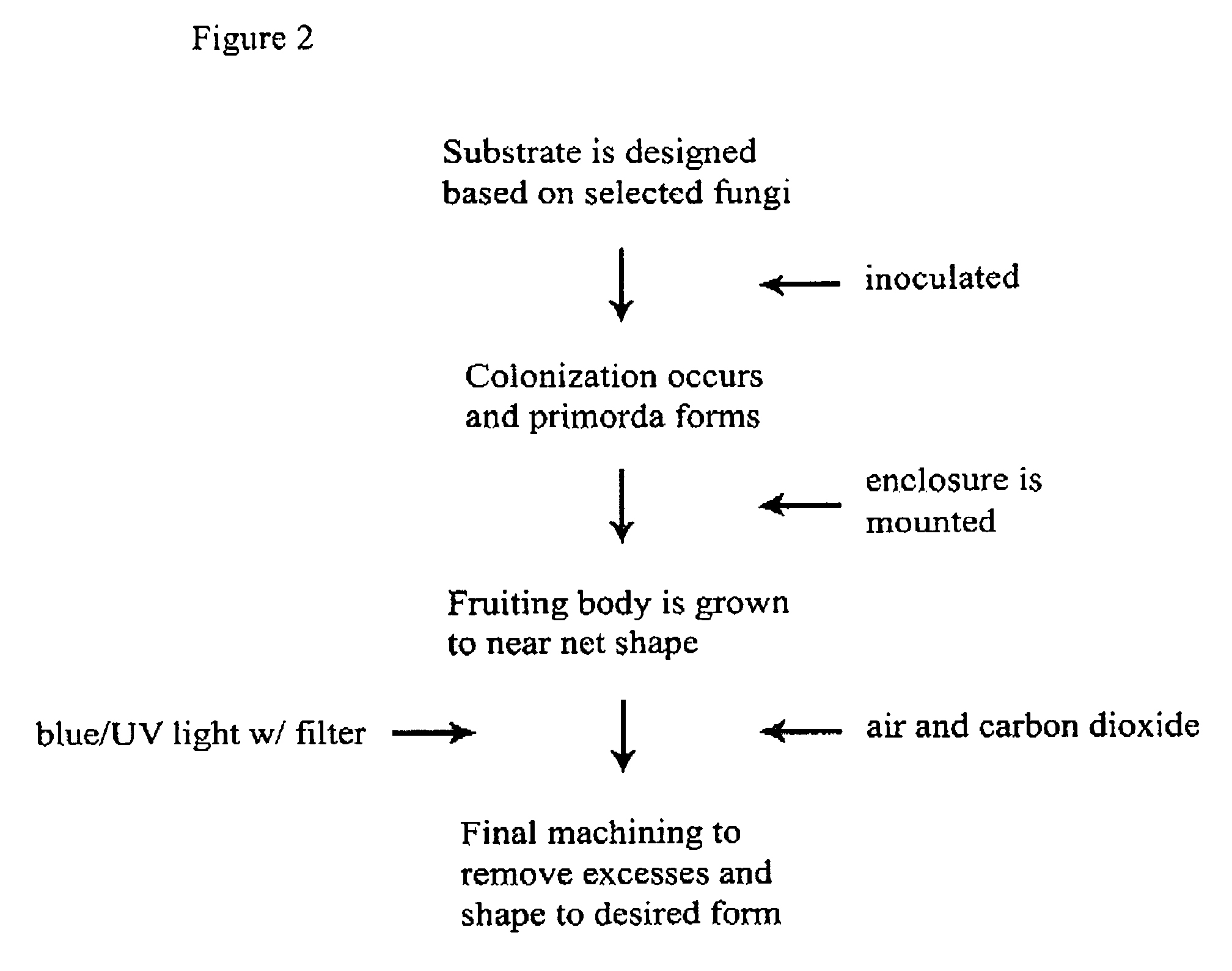
The method of growing a fungal fruiting body requires exposing a mycelium of a desired organism type to environmental conditions sufficient to induce fruiting of fungal primordium in the organism type followed by enclosing the fungal primordium within a mold of a designated shape representing a near net shape volume of a desired final product. The fungal primordium is allowed to grow and fill the mold to form a mass of fungal tissue equivalent in shape to the designated shape of the mold after which the mass of fungal tissue is removed from the mold and dried.
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
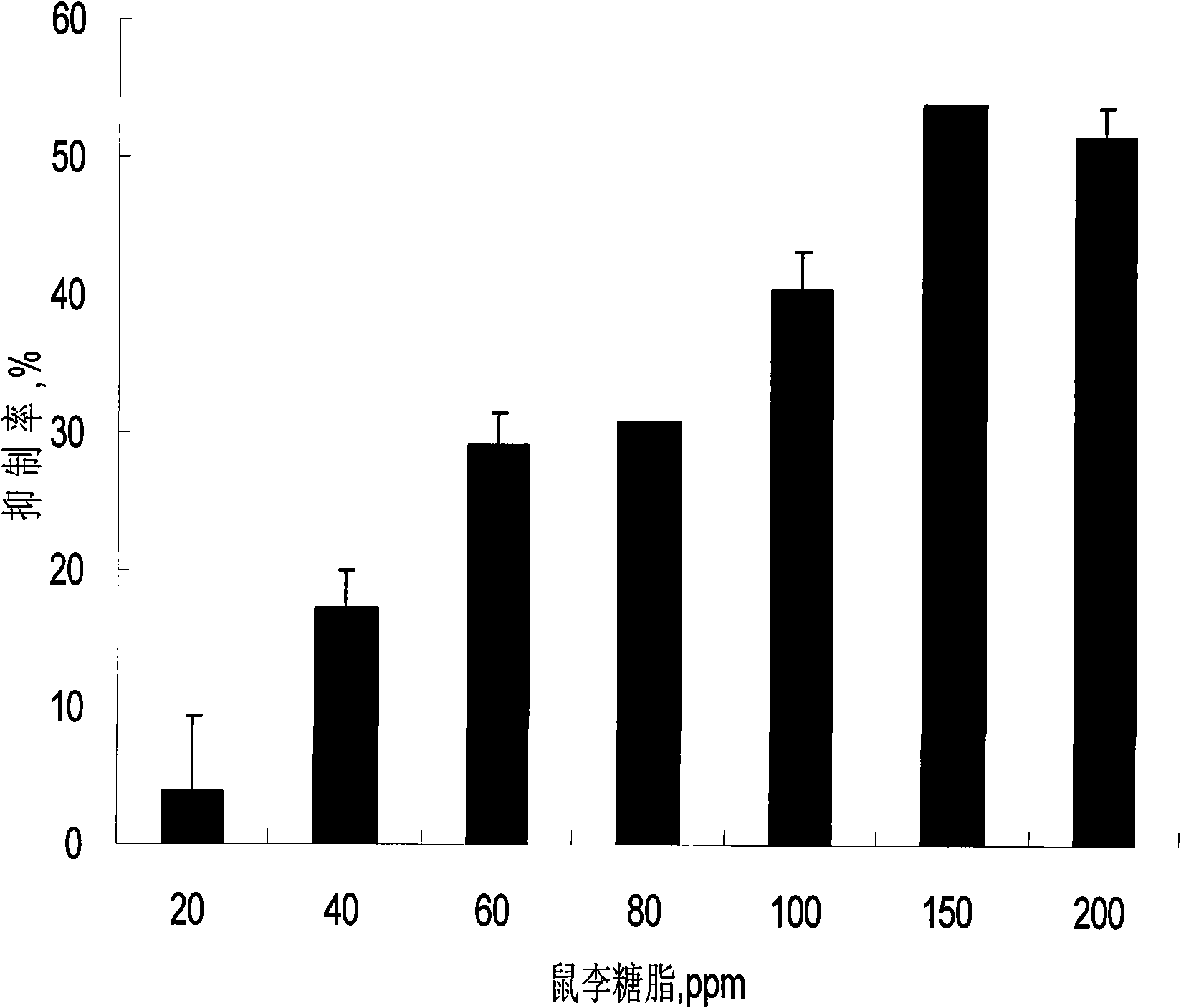
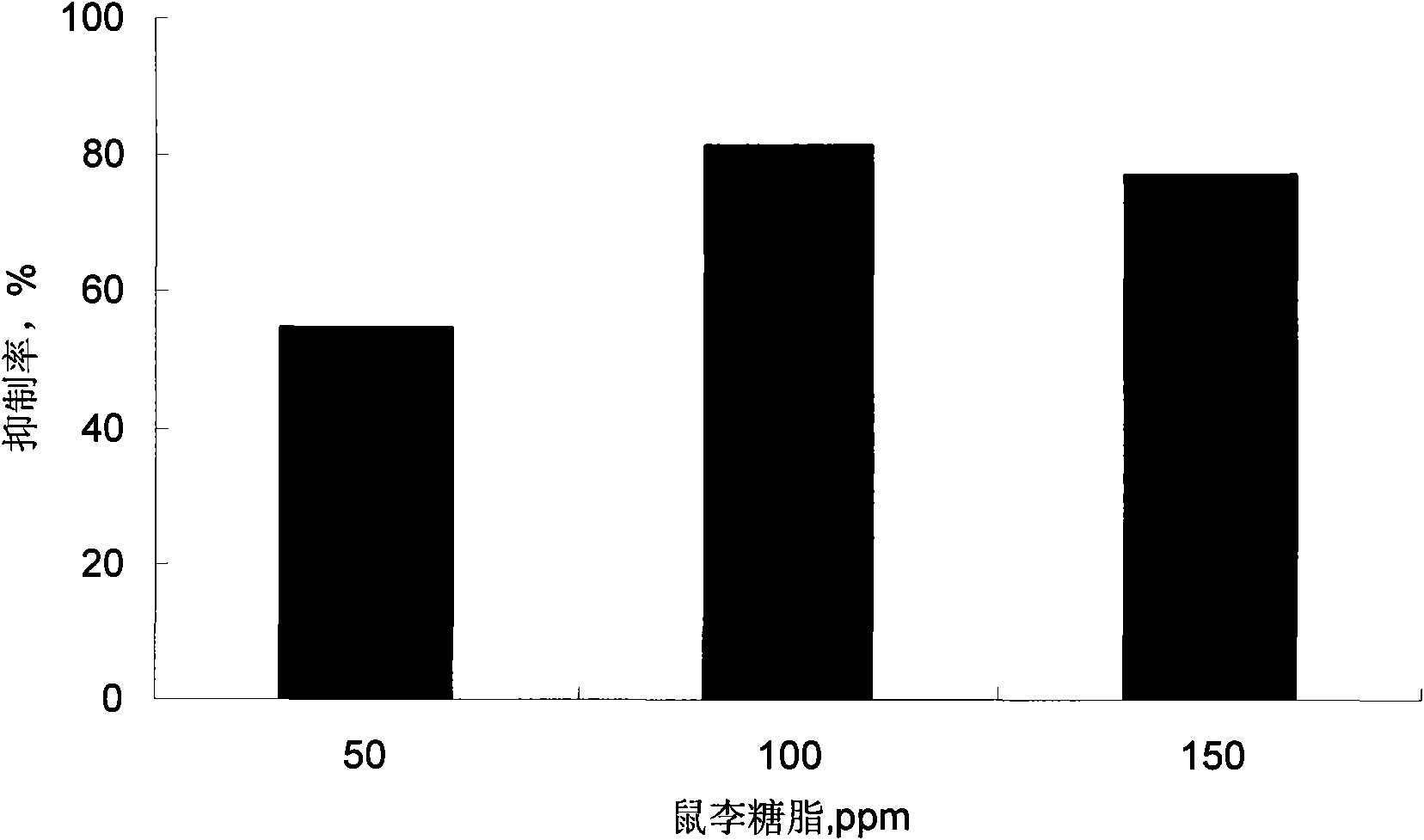
Preparation method and application of rhamnolipid
ActiveCN101845468AReduce manufacturing costLow costBiocideSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningDiseaseSpore germination
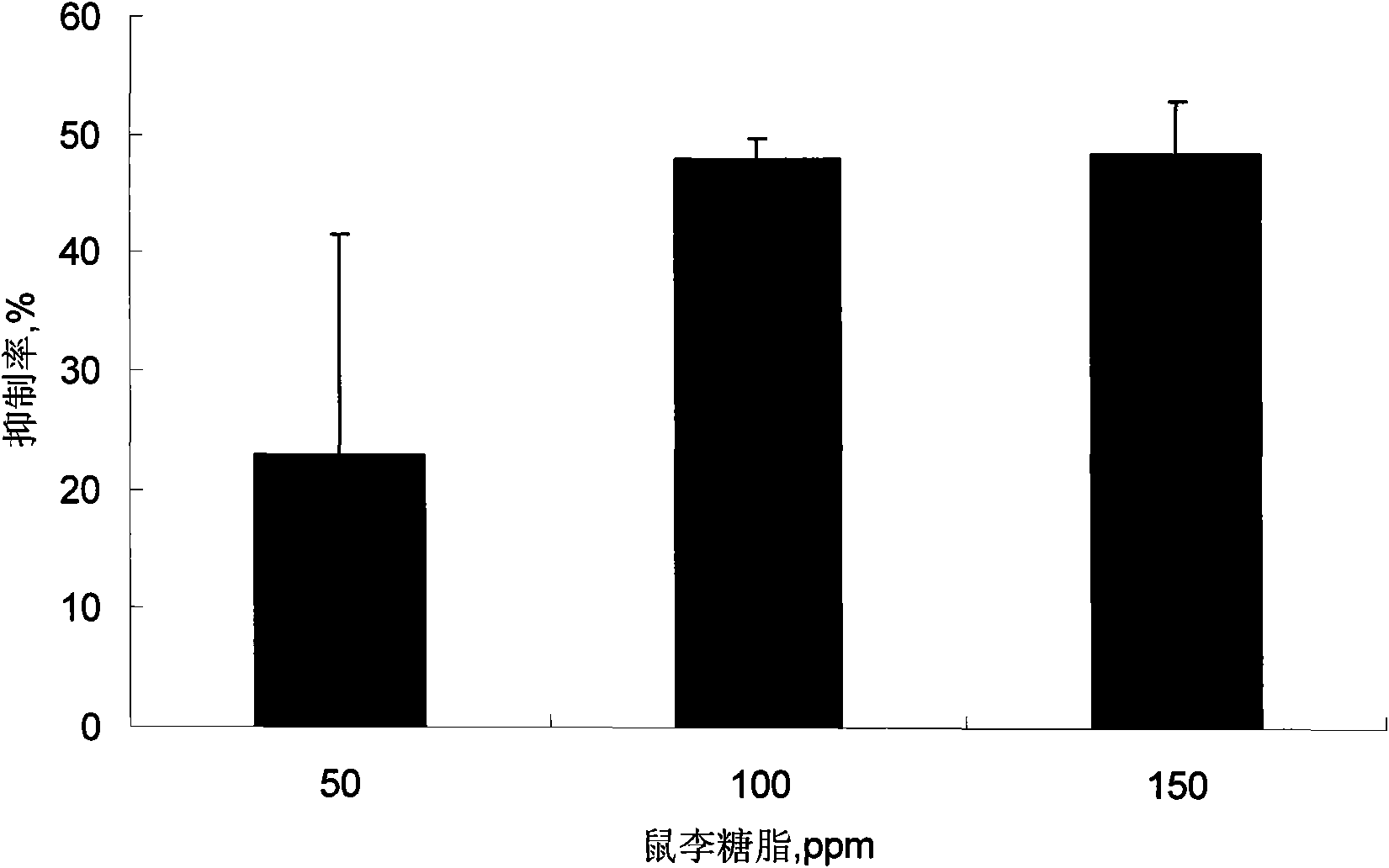
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of rhamnolipid. In the method, the rhamnolipid is produced by using waste grease as carbon source, and utilizing the fermentation of pseudomonas aeruginosa; and with the combination of the defoaming effect of ethanol, the yield of the rhamnolipid can reach 35 to 50 g / L and the cost is about 25 to 40 percent lower than that of the conventional method. When the solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid is used for processing plant disease fungus, the ratio of inhibiting disease fungal mycelium growth and spore germination can reach 40 to 90 percent and the plant fungal diseases can be effectively inhibited; the solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid has an obvious effect of killing cockroaches and aphids; and in addition, when the rhamnolipid is used as an aid of pesticide, fertilizer and feed and a dehydrating agent of oil-contained sludge by replacing a chemical surface active agent, the effect is obvious.
Owner:浙江圣达紫金生物科技有限公司
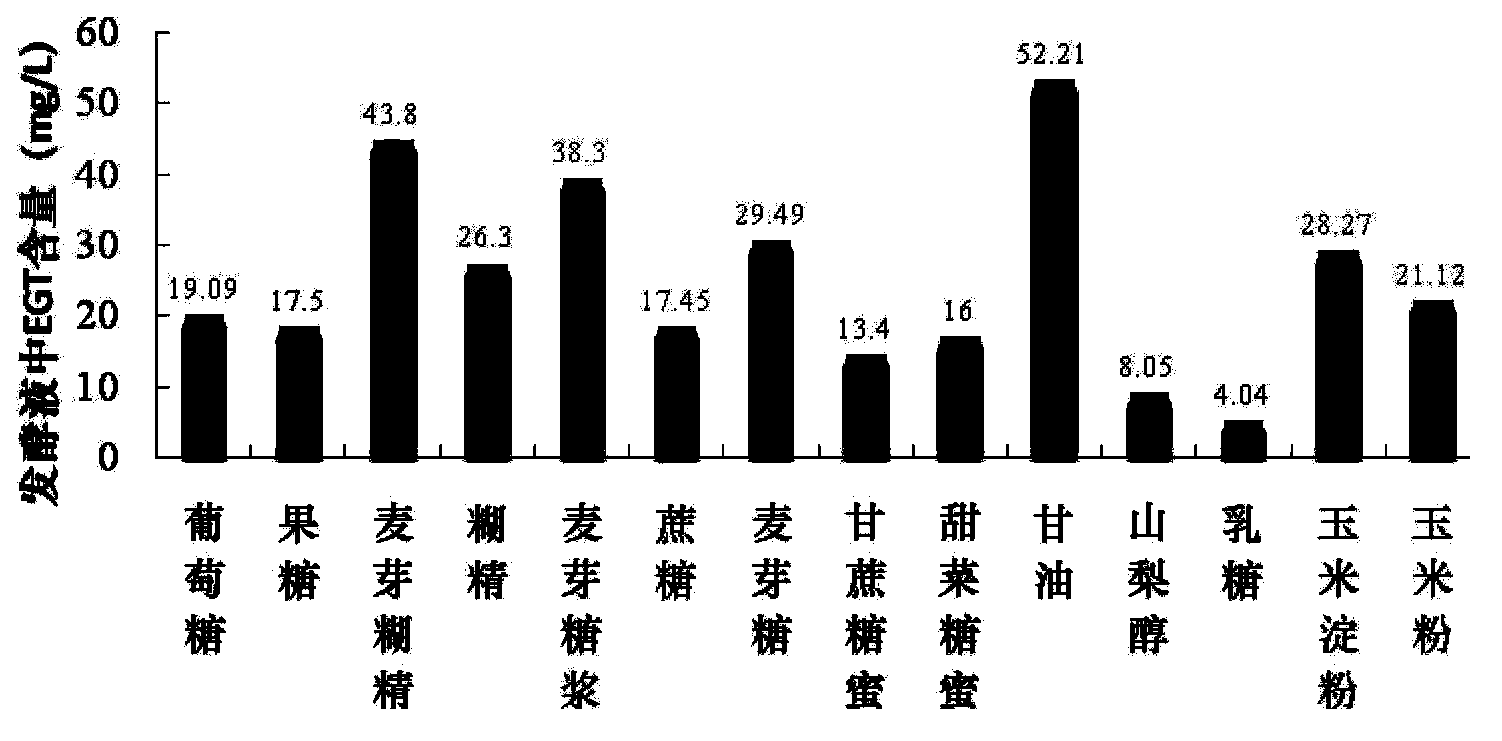
Bacterial strain producing L-erythrothioneine and method of preparing the L-erythrothioneine
ActiveCN103734022AIncrease contentRaw materials are cheap and easy to getFungi productsLichen productsMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a strain Pleurotus ostreatus TIB.BPE.10010 with the accession number being CGMCC No.6232. The invention also relates to a method of preparing L-erythrothioneine. The method comprises steps of culturing and fermenting the Pleurotus ostreatus CGMCC No.6232 to perform biosynthesis to form the L-erythrothioneine and extracting the L-erythrothioneine from mycelium cells.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Termitomyces albuminosus with black skin producing process
InactiveCN101218876ARealize large-scale artificial cultivationMeet the huge market demandHorticultureFertilizer mixturesMother cultureZoology
The invention discloses a method for producing Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum belonging to the fungus cultivating field. The process of the invention includes preparation of mother culture, preparation of stock, preparation of cultivar and artificial cultivation. The invention is characterized in that the mother culture is cultivated and prepared by combining an encarpium mycelium of the Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum and a rhizoid mycelium of the Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum. Compared with the prior art, the method for producing Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum of the invention has filled the gap of the artificial cultivation technology of the Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum in the prior art and has the advantages of low cost, easy realization, etc. The invention can be broadly applied to the large-scale artificial production of the Black Tremellodon Gelatinosum.
Owner:BEIJING HESHUN ECOLOGICAL AGRI
Method of liquid fermentation culturing flammulina velutipes mycelium rich in Se and Zn
InactiveCN101228830AHigh content of active ingredientsHigh active ingredient content, added valueFungiFood preparationFood additiveBiotechnology
A method for cultivating golden mushroom mycelia abundant in Se and Zn elements through liquid fermentation belongs to the field of biotechnology. The invention substantially comprises cultivation of strains, cultivation of liquid seed, namely the domestication of two elements, and enrichment, fermentation and cultivation of two elements in a deep liquid, and collecting, drying and smashing of mycelia. The dried golden mushroom mycelia abundant in organic Se and organic Zn obtained with the method of the invention has over 35Mug / g organic Se and 4.25mg / g organic Zn. The powder of the mycelia with suitable food can be used as food additives and made into functional food, which has great health care function for the people in sub-health state resulted from deficient intake of microelements of Se and Zn. The invention is high in technological content, high content in effective components of the products, high additive value, which is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mycoattractants and mycopesticides
InactiveUS7122176B2High recruitmentReduce consumptionBiocideLichen medical ingredientsCelluloseFreeze-drying
The present invention utilizes the pre-sporulation (preconidial) mycelial stage of entomopathogenic fungi as insect attractants and / or pathogens. The fungus can be cultivated on grain, wood, agricultural wastes or other cellulosic material, attracting the insect and optionally introducing insect-specific pathogenic fungi. More than one fungus and substrate can be used in combination. The matrix of preconidial fungi can optionally be dried, freeze-dried, cooled and / or pelletized and packaged and reactivated for use as an effective insect attractant and / or biopesticide. Attractant extracts of the preconidial entomopathogenic mycelium are disclosed.
Owner:MYCOSYS +1
Culture medium for cultivating agaricus bisporus and cultivating process thereof
InactiveCN101284750ALow costNot easy to stickSuperphosphatesBio-organic fraction processingCaladiumPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a culture medium used for cultivating bisporic mushrooms as well as the cultivating method thereof. Per 100 square meters of culture medium contain the following cultural materials: cotton seed hull 1800 to 3200 catties, waste cotton 0 to 1200 catties, corncobs 0 to 1200 catties, cottonseed meal 0 to 200 catties, cattle manure 2 to 4 cubic meters, chicken manure 0 to 1.2 cubic meters, urea 0 to 60 catties, quicklime 80 to 120 catties, plaster powder 0 to 120 catties, calcium superphosphate 0 to 120 catties, enzyme microorganisms 2 to 4 catties, and water of proper amount. The method includes the following steps: firstly, the cultural materials are mixed; secondly, the mixed cultural materials are composted and fermented; thirdly, the cultural materials are processed in a shed; fourthly, sowing is carried out; fifthly, the culture medium is distributed; sixthly, the soil is covered; seventhly, the mushrooms are obtained. The culture medium has low cost, the conglutination of the cultural materials is not easy to happen, and the cultural materials have easy pile-turning, thereby causing the composting and the fermentation to be laborsaving and timesaving; the enzyme microorganisms can not only speed up the fermentation of the cultural materials and improve the fermentation quality, but also facilitate the absorption and utilization of the culture medium by the mycelium of the bisporic mushrooms.
Owner:贾恩茂
Production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN101940127AAvoid pollutionBody hair bacteria fastClimate change adaptationBioloigcal waste fertilisersCaladiumAgaricus
The invention discloses a production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii. The agaricus bisporus consists of the following substances in percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of mushroom residues, 20 to 40 percent of corn straws, 10 to 30 percent of cow dung, 1 to 3 percent of urea, 1 to 3 percent of lime and 0.5 to 2.5 percent of calcium superphosphate. In the production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using the mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii, the routine production process for culturing agaricus bisporus is adopted, wherein the process comprises the following steps of: pre-wetting raw materials, piling the materials, turning over the piles, placing and laying the piled materials on a frame, fermenting the materials, seeding the materials, mycelium culture, earthing, taking out and managing the agaricus bisporus and harvesting fruit bodies. Because the mushroom residues for producing pleurotus eryngii are recycled to serve as the material for planting agaricus bisporus, environmental pollution is avoided and the aim of clean growth and environmental protection is fulfilled.
Owner:李文生
Liquid submerged fermentation culture method for hericium erinaceus
InactiveCN101971762AIncreased biomassIncrease productionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesSubmerged fermentationBearded tooth
The invention discloses a liquid submerged fermentation culture method for hericium erinaceus, and belongs to the field of culture methods for edible fungi. The culture method comprises the following steps of: activating hericium erinaceus strains on a slant culture medium, then performing primary strain culture on a liquid seed culture medium, performing secondary strain culture on a liquid fermentation culture medium, and finally performing amplified culture on the liquid fermentation culture medium to obtain hericium erinaceus mycelium. The invention also discloses hedgehog hydnum 1 in the hericium erinaceus strains, a seed culture medium and a fermentation culture medium for hericium erinaceus culture. The biological yield of the hericium erinaceus mycelium obtained by the culture method is high and can reach 12g / L which is over two times as much as the fermentation production level of the current factory; the hedgehog hydnum 1 in the hericium erinaceus strains has high growth speed which can reach 5.8 millimeters every day; and moreover, the liquid seed culture medium and the fermentation culture medium have good culture effect so that the hericium erinaceus mycelium has quick growth and high yield.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Antiviral Activity from Medicinal Mushrooms and their Active Constituents
ActiveUS20160000754A1Lack useImprove efficiencyBiocideSugar derivativesNatural productMedicinal mushroom
Compounds having unique antiviral properties found in mushroom mycelium and their analogs are extracted, concentrated, isolated or manufactured to create compositions useful in preventing the spread and proliferation of various viruses afflicting animals, particularly viruses harming humans, pigs, birds, bats and bees. Such compounds and compositions can be used individually or in combination with known medicines or natural products to improve health.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
Glossy ganoderma culturing process
The present invention relates to culturing and processing technology of medical and edible fungus in agricultural technology field and aims at providing practical, cheap and efficient culture medium. The culture medium with wheat as main component is suitable for glossy ganoderma to grow and suitable for industrial production and management. The present invention makes it possible to obtain fresh and dry primodium or sporophore as well as 100 % edible glossy ganoderma mycelium. The present invention features that fresh primodium in different shapes are collected and freeze dried to obtain new type of glossy ganoderma product with water content of 6-11 %. The present invention has wide application range, and the residual culture medium may be used as food material, so that the production process is eco-friendly.
Owner:蒋丹
Recombinant antibodies to sclerotinia antigens
The invention is directed to recombinant antibodies which bind to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigens and comprise a single chain variable fragment (scFv). The antigen may be selected from SSPG1d or a portion thereof, aspartyl protease or a portion thereof, or whole Sclerotinia sclerotiorum mycelium. The invention also provides an antibody linked to an anti-fungal polypeptide. The invention extends to nucleic acid sequences encoding the antibodies, and expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences. The invention is also directed to transgenic plants, seeds, tissues or cells transformed with the expression vectors. Methods for producing a transgenic plant that is resistant to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, and for detecting Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in a biological sample utilizing an antibody which binds to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum antigen, and immunoassay kit for same are also provided.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Formula of high-yield flammulina velutipes culture medium and producing technique thereof
InactiveCN101514130AVigorousIncrease productionOrganic fertilisersHorticultureAdditive ingredientTransformation efficiency
The present invention provides a formula of high-yield flammulina velutipes culture medium and a producing technique thereof. The invention relates to the technical filed of biological strain, and specially to the formula of high-yield flammulina velutipes culture medium and producing technique thereof. The corncob is used as main ingredient for replacing fir sawdust. The invention adopts 40-45% of corncob, 10-12% of bagasse, 25-30% of rice bran, 8-10% of bran, 4-6% of soybean hull and 2-3% of corn flour as the raw materials of flammulina velutipes culture medium. The method comprises the techniques of dry mixing, wet mixing, etc. The pH value is controlled between 7.0 and 7.5. The cultured flammulina velutipes has the advantages of strong activity of mycelium, high production volume, ordered mushroom generation, excellent commodity valve, ordered growing of sporphore, uniform magnitude of bonnet, white color, and no infection of foreign fungus. The unit production obtains 286-293grams / bottle. The dry object of each bottle is 260grams. The biological transformation efficiency reaches up to 110-113% and is increased for 30-40% compared with the common formula. The economic benefit is excellent.
Owner:韶关市星河生物科技有限公司 +2
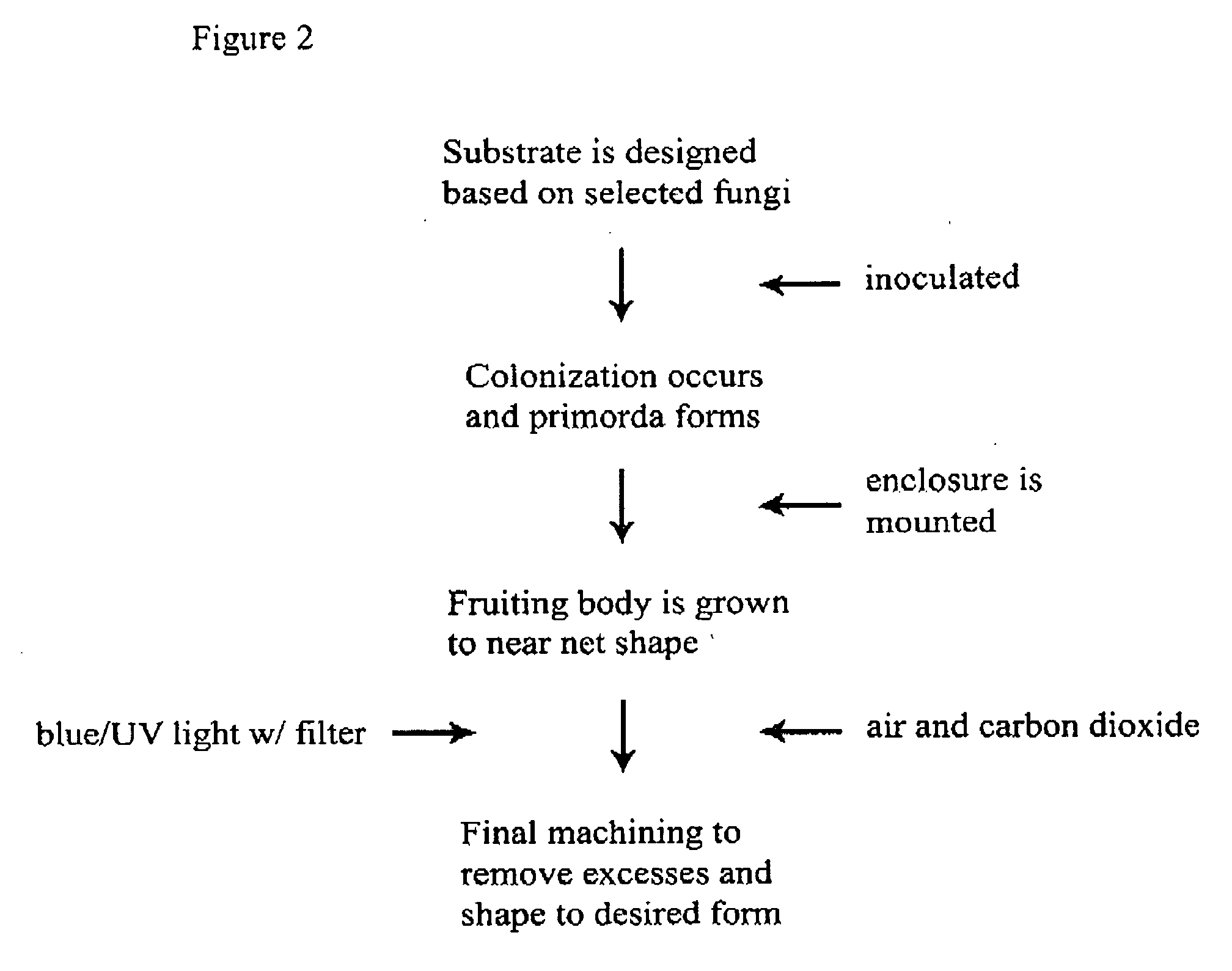
Method for producing rapidly renewable chitinous material using fungal fruiting bodies and product made thereby
The method of growing a fungal fruiting body requires exposing a mycelium of a desired organism type to environmental conditions sufficient to induce fruiting of fungal primordium in the organism type followed by enclosing the fungal primordium within a mold of a designated shape representing a near net shape volume of a desired final product. The fungal primordium is allowed to grow and fill the mold to form a mass of fungal tissue equivalent in shape to the designated shape of the mold after which the mass of fungal tissue is removed from the mold and dried.
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
Strain separation method of apricot ormer mushroom and cultivating method thereof
The invention discloses a strain separation method of apricot ormer mushroom and a cultivating method thereof. The cultivating method comprises the following step: cultivating strains which derive from apricot ormer mushroom-2 strains sold by Gaoyou Edible Fungi Institute of Science and has high yield and strong stress resistance; the cultivating process of the strains is as follows: preparing composts, bagging and sterilizing; inoculating; managing myceliums; opening the bag and leading the mushroom out; managing the mushroom; and harvesting properly. The invention not only achieves the strain scale plantation of the apricot ormer mushroom by selecting different culture media and different culture conditions, but also shortens the strain planting period of the apricot ormer mushroom, so that the apricot ormer mushroom to be planted has strong resistance, high biological efficiency, good quality and the like. By adopting the technical scheme, the biologic conversion rate of the apricot ormer mushroom achieves above 145%; the planting technology is easy to master; and the source of the culture media is wide. The invention is particularly suitable for the scale plantation in wide rural areas, thereby improving the planting efficiency.
Owner:许忠
Culture medium for producing winter worm summer herb mycelium
The invention discloses a culture medium to ferment and manufacture Cordyceps sinensis mycelium, which consists of bevel culture medium and fermentation culture medium, wherein different culture mediums are adopted in different stages to ensure plain growth of the Cordyceps sinensis and equal quality of fermented and natural Cordyceps sinensis, which modifies the product quality and improves the production with certain effect. The invention supports the character of nourishment with natural Cordyceps sinensis, which is fit for industrial manufacturing need.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHONGMEI HUADONG PHARMA +1
Bagged mushroom production method
InactiveCN102919054AImprove survival rateImprove product qualityHorticultureAgricultural scienceSucrose
The invention discloses a bagged mushroom production method which comprises the steps of strain making, nutrient preparation, bagging, sterilization, inoculation, mycelium culture, coloring, inducement to primordium of mushroom and harvesting. The method is characterized in that 1, in the nutrient preparation step, 78% of miscellaneous tree sawdust, 20% of wheat bran, 1% of sucrose and 1% of gypsum in percentage by weight are evenly mixed, then 55-58% of water is added, and blending is performed; 2, the nutrient is put in barrel bags within 4 hours; 3, the bags are piled in the shape of a well and are sterilized; 4, when the bags are cooled to 25-28 DEG C, inoculation is performed; 5, the mushroom bags are transferred into a mushroom growth room of 20-25 DEG C and subjected to mycelium culture, and puncturing ventilation is performed twice in the mycelium culture period; and 6, in the mushroom growth management period, artificially-aided inducement to primordium of mushroom, dry stimulation and other treatment operations are performed. According to the invention, large-scale bagged mushroom production can be realized, the mushroom survival rate is high, the deformed mushroom defective rate is below 5%, the cost can be reduced and the product quality is high.
Owner:SHAANXI CHUNTIAN AGRI INDZATION LTD
Hardened mycelium structure and method
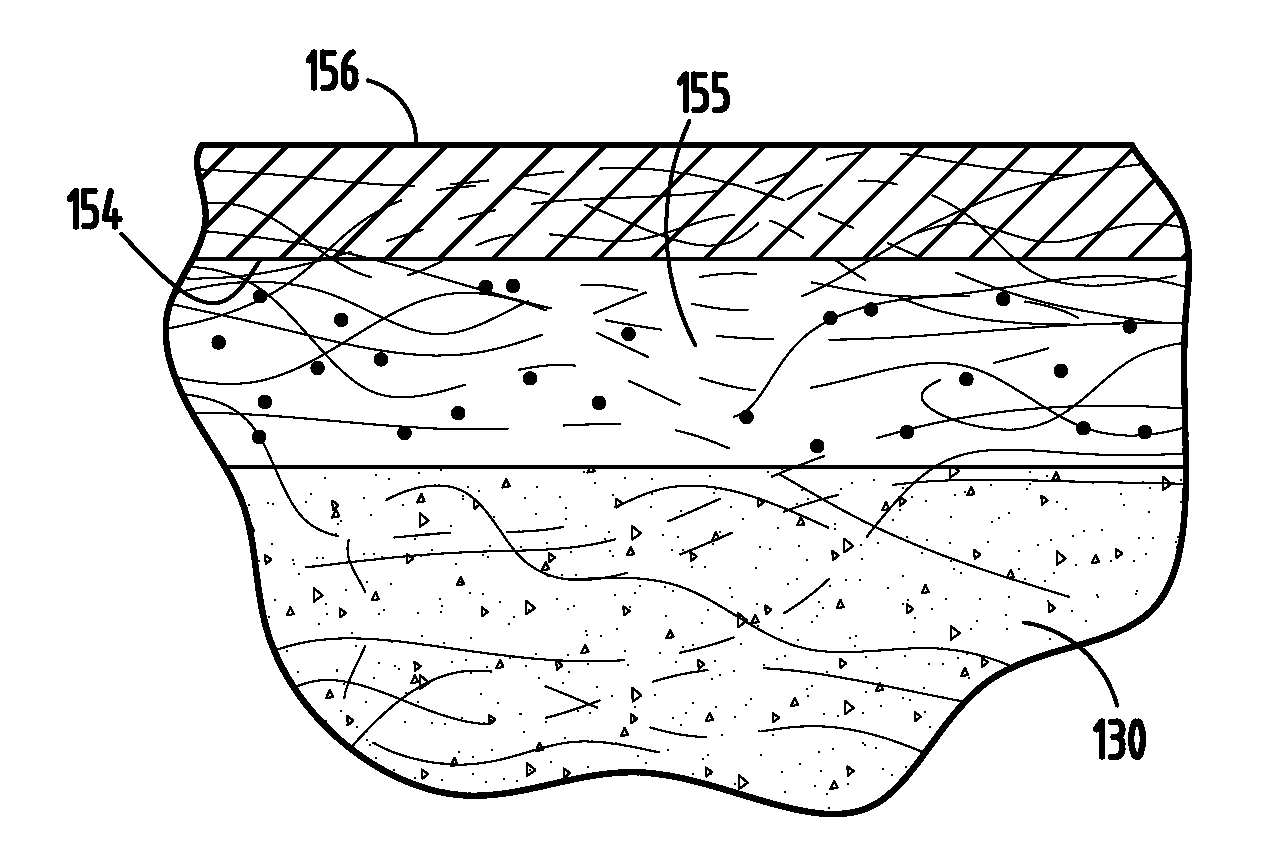
A method of preparing a mycelium component, including growing live mycelium from a fungal inoculum and a liquid aggregate. The live mycelium is cured to terminate further mycelium growth and form a mycelium structure. Moisture is applied to the mycelium structure such that the mycelium structure is nearly fully saturated. The mycelium structure is dried to form a hardened mycelium structure.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Biologically active compounds of Ganoderma pfeifferi DSM 13239
The present invention relates to novel biologically active compounds from fungi of the species Ganoderma pfeifferi DSM 13239, processes for their preparation, and their use. From the fruit body and mycelium of the species Ganoderma pfeifferi DSM 13239, extracts can be obtained which have antimicrobial activity and are suitable as preserving agents, for pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations, for controlling infections, and for use in fish breeding. Antimicrobially active substances called ganomycins having activity against multiresistant germs are isolated from the extracts. The total synthesis of the ganomycins and their derivatization enables their use an antibiotics.
Owner:ERNST MORITZ ARNDT UNIV GREIFSWALD
Controlling zoonotic disease vectors from insects and arthropods using preconidial mycelium and extracts of preconidial mycelium from entomopathogenic fungi
InactiveUS20120039976A1High recruitmentReduce consumptionBiocideLichen medical ingredientsCelluloseAgro waste
The present invention utilizes extracts of the pre-sporulation (preconidial) mycelial stage of entomopathogenic fungi as insect and arthropod attractants and / or pathogens and can be employed to limit the zoonotic diseases they transmit. The fungus can be cultivated on grain, wood, agricultural wastes or other cellulosic material and extracts can be made thereof. More than one fungus and substrate can be used in combination with one or more antimicrobial, antiprotozoal, antiviral, and genetically modified agents that result in reduced spread of contagions and lessens the damage they inflict on animals, and plants.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
Natural planting method of mushroom
InactiveCN102084782AQuality improvementIncrease productionHorticultureGround temperatureSecondary forest
The invention discloses a natural planting method of a mushroom, solving the problems of low quality and easiness of manual pollution because the traditional mushroom planting technology is limited in the room. The natural planting method comprises the following steps of: 1, culturing a strain: separating a field-planted sporocarp to obtain a patent seed, culturing the patent seed according to the conventional expanding propagation method, continuously culturing a breeder seed to obtain a planting strain; 2, culturing a mycelium; 3, selecting a natural environment for planting: selecting an original forest, a secondary forest and an artificial forest with the ground temperature of 4-15 DEG C, the air humidity of 42-88 percent, the soil pH value of 6-7 and the forest land and grassland canopy density of 0.3-0.7; and 4, managing fruiting. The mushroom is cultured and planted by using the natural environment, and the mushroom sporocarp grows and develops under a natural and wild condition to ensure that the growth environment of the mushroom is more excellent and the product quality is better.
Owner:XINZHOU CITY HUIHENG AGRI FORESTRY & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY OVERALL DEV
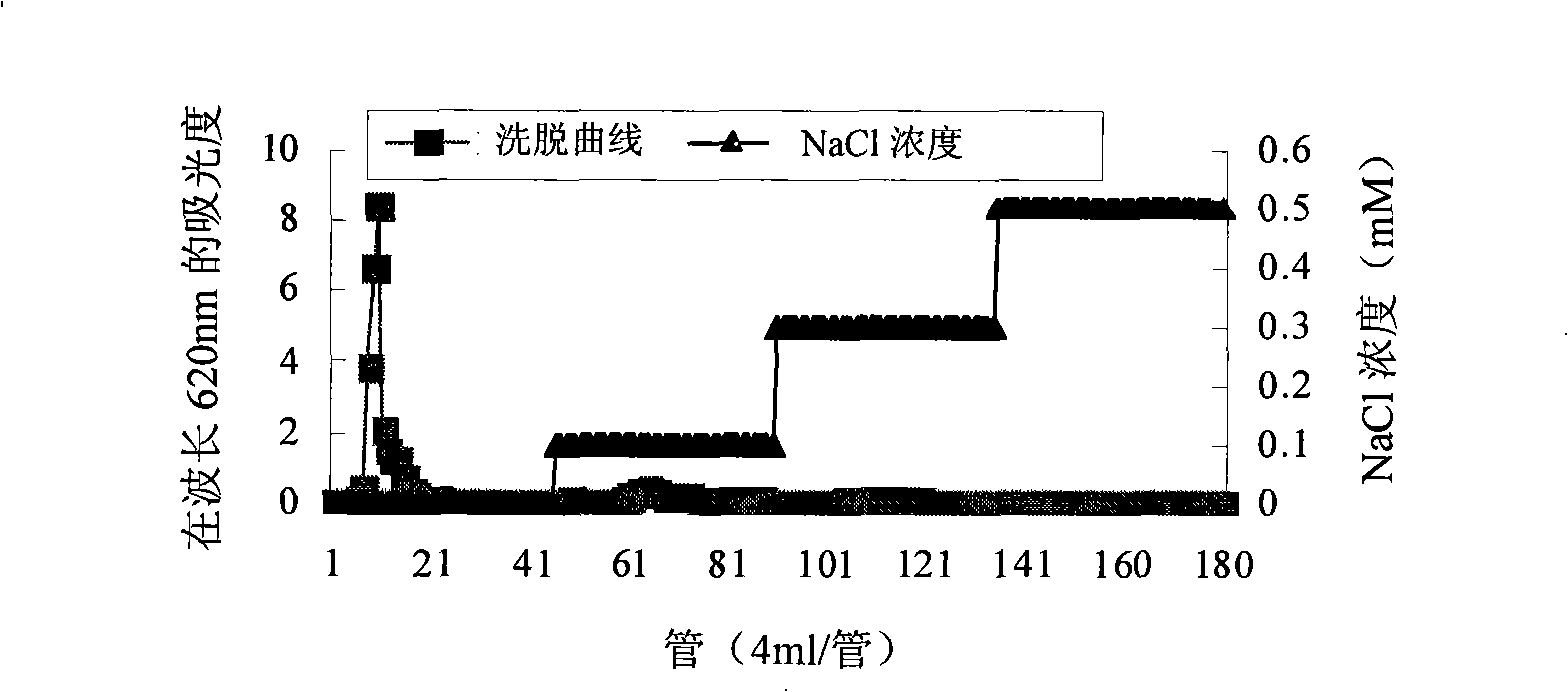
Process for abstracting mycelium polysaccharide by cordyceps fermentation
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying polysaccharide from a fermented mycelium of Cordyceps sinensis. The method comprises the following steps of: using the fermented mycelium of Cordyceps sinensis as a raw material to produce crude polysaccharide of the Cordyceps sinensis via degreasing, aqueous extraction, concentration and alcohol precipitation; then, redissolving the crude polysaccharide into distilled water, deproteinizing the crude polysaccharide by Sevag, decoloring the deproteinized crude polysaccharide by H2O2, dialyzing the decolored crude polysaccharide, and precipitating the dialyzed crude polysaccharide by alcohol to produce primarily purified polysaccharide; finally, purifying the primarily purified polysaccharide by ion-exchange chromatography, collecting different produced compositions stepwisely, dialyzing the compositions, precipitating the dialyzed compositions by alcohol, drying the precipitated compositions to produce the polysaccharide of the Cordyceps sinensis after the precipitated compositions are orderly washed by absolute ethyl alcohol, acetone, aether and so on. In the produced polysaccharide of the Cordyceps sinensis, MPS2 is identified to be homogeneous polysaccharide by ultraviolet absorption spectrum and gel chromatography, with high content of total sugar. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient extraction steps and low cost.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biofilm treatment of composite materials containing mycelium
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
Paecilomyces lilacinus and application
The invention discloses Paecilomyces lilacinus FZ07-9F-5 CGMCC No.2780, microbial inoculum and application thereof. The microbial inoculum is wireworm killing biological microbial inoculum with slow application function, which is prepared by the following steps: using a macromolecular material, namely sodium alginate as basic skeleton, using mycelium and spore mixture of P. lilacinus FZ07-9F-5 CGMCC No.2780 as active components, using infusorial earth as a carrier, and adopting a method of sodium alginate-calcium chloride reaction according to the characteristic of forming gel by the sodium alginate and polyvalent cations to be prepared into the microbial inoculum. Proved by experiments, the microbial inoculum has better wireworm killing efficacy, has control ratio up to between 50 and 60 percent, is comparatively stable, has no noxious chemical residues (innocuous and non-residue), does not pollute agricultural products and environment (does not react with other substances in the environment), and has the characteristics of high cost performance and convenient application. The microbial inoculum plays an important role in control of wireworm diseases of plant roots and knots, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:中农绿康(北京)生物技术有限公司
Production technology for cordyceps militaris mycelium
InactiveCN102612985ASimple ingredientsLow costCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationCordycepsCordyceps militaris
The invention discloses a production technology for cordyceps militaris mycelium. The production technology mainly comprises the procedures of preparation of a test tube stock culture, culture medium preparation and culturing mode of a liquid strain, culture medium preparation and culturing mode of mycelium, and the like. The defects of the materials adopted by a culture medium are complex, the manufacturing cost is high and the liquid strain culturing condition is high in the prior art are changed by adjusting a formula and a technology according to the invention; after the mycelium is cultured and subjected to color transfer, the main components and pharmacology of the mycelium are more approached to those of the natural cordyceps militaris; and the production technology has the advantages of simple method, low comprehensive production cost, capability of performing large-scale production, and higher developing value.
Owner:何寒 +1
Method for preparing beta-carotene through fermentation of Blakeslea trispora
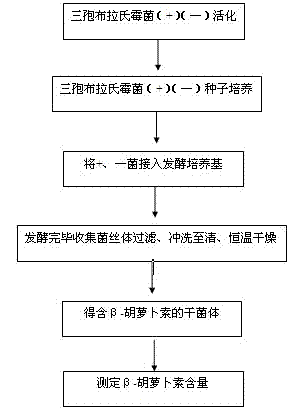
ActiveCN102757995ASignificantly progressiveSolid content reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBlakeslea trisporaBeta-Carotene
The invention discloses a method for preparing beta-carotene through fermentation of Blakeslea trispora. The method comprises the following steps of: after activating Blakeslea trispora ATCC14271 (+) and ATCC14272 (-), carrying out seed culture on the activated Blakeslea trispora; inoculating the Blakeslea trispora to a fermentation medium according to a certain inoculum concentration and inoculation ratio under an optimized fermentation process condition so as to ferment the Blakeslea trispora; and finally obtaining a mycelium with higher beta-carotene content. Through the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, a natural high-quality beta-carotene product with low cost and high titer can be obtained.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Cultivating method of tuckahoe
InactiveCN101578945AExpedited screeningGood yieldHorticultureFertilizer mixturesCuticleWolfiporia extensa
The invention discloses a cultivation method of tuckahoe, which comprises the steps of: (1) firstly, the epidermis of the tuckahoe is cut; the tuckahoe is superficially sterilized by 70 to 75% of ethanol and washed with sterile water; the water content of the tuckahoe is blotted up by disinfection cloth or a filter paper; in an aseptic inoculation box, an alcohol burner is lightened, the processed tuckahoe is sliced off by an abacterial knife near fire and the cross section is scraped into be cambered and successively scraped for twice; on the second scraping position, blocks like wheat size are connected on a pure strain culture medium, placed in a greenhouse, and cultured in the temperature of 25 to 30 DEG C till mycelial overgrows; the blocks which are white, are not infected by mixed bacterium, are villous, dense and craggy, vigorously and uniformly grow, secretes white milk pearl mycelium are pure strains; (2) a primary strain cultivation is carried out; (3) a second class strain cultivation is carried out; (4) a third class strain cultivation is carried out. The method is characterized by short production period of mycelium, excellent and stable tuckahoe quality and high yield.
Owner:贵州昌昊中药发展有限公司
Zymocyte mixture containing lucid ganoderma, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a zymocyte mixture containing lucid ganoderma. A mycoplasm mixture containing hypha and culture matrix components is obtained by fermenting the lucid ganoderma in a solid fermentation mode in a nutritional culture matrix which at least comprises a carbon source and a nitrogen source needed by the growth of fungi, wherein medical raw materials salvia miltiorrhiza are mixed in the culture matrix. A mycoplasm fermentation final product having both the effects of the salvia miltiorrhiza and the ganoderma fungi is obtained after bidirectional solid fermentation including influence of medical raw materials on the growth and metabolism process of ganoderma mycelium and transformation of a ganoderma fungal enzyme system on the medical materials compositions, and the invention can be applied to preparing a medicament and / or a cosmetic with the effects of promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis and antioxidation.
Owner:成都宇泽生物基因化妆品有限公司
Domestic fungus flour, noodle and method for preparing the same
The invention relates to a kind of edible mushroom flour and noodles and the preparation method. The raw material for edible mushroom and their proportion by weight are as follows: edible mushroom seed solution 2-8%, and edible grain granule 92-98%. The method comprises processes of spraying seed solution, bacteria growing, airing or drying and disintegrating. Said edible mushroom seed solution is one or mixture of hedgehog fungus, mushroom and lucid ganoderma. Said edible grain is one or mixture of wheat, soybean meal and pea meal. The raw material for noodle and their proportion are as follows: mycelium wheat powder 35-100%, one or mixture of mycelium soybean meal and mycelium pea meal 0-20%, and glutinous rice 0-10%. The process comprises mixing raw material and pressing. The invention selects optimal bacteria strain, then induces and cultures them to make them adapt to breeding condition for grain culture, and gets mycelium flour. The noodles and flour product are nutritious and healthy-care.
Owner:张嘉闻
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com