Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Hantaan virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The type species of the genus HANTAVIRUS infecting the rodent Apodemus agrarius and humans who come in contact with it. It causes syndromes of hemorrhagic fever associated with vascular and especially renal pathology.
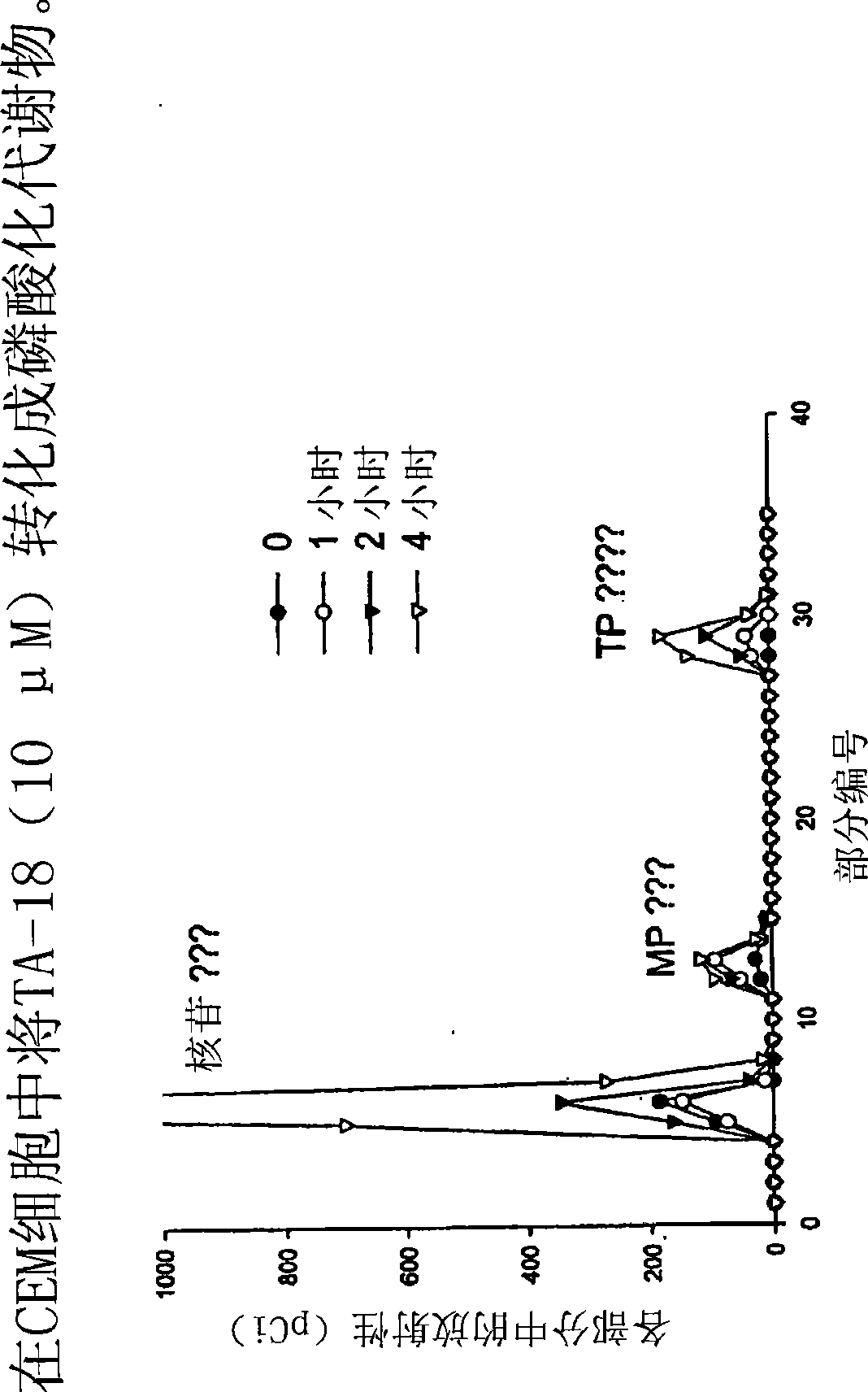
Azole nucleosides and use as inhibitors of RNA and DNA viral polymerases
InactiveUS20100129317A1Inhibition is effectivePrevent slippingBiocideSugar derivativesCrimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virusPolymerase L
Azole nucleosides represented by the formulae (I) and (II); wherein A=C or N B═C or N X═H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br and I; OH, NH2, NH—(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo); Z═H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br, I; OH NH2, NH—(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo; E=(CH2)HONHR; n is an interger from 0-6 and more typically 0-3; R1= aryl or heterocyclo; each of W, Y, R is individually selected from the group consisting of H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br, and I; O, OH, Oalkyl, Oaryl, NH2, NH(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo); provided that at least one of W, Y, and R is other than H and wherein both W and Y together can be ═O; and each D individually is OH, Oalkyl, Oaryl, FL and H; pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, prodrugs thereof and mixtures thereof are provided. Compounds of this disclosure are useful as inhibitors of viral RNA and DNA polymerases such as, but not limited to, Influenza, hantaan Virus, Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Polio, Coxsackie A and B, Rhino, Echo, orthopoxvirus (small pox), HIV, Ebola, and West Nile virus polymerases; and especially orthopoxvirus, HIV, and hepatitis B.
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
HTNV-NP (Hantaan virus nucleoprotein)-specific CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptides and application thereof
The invention discloses HTNV-NP (Hantaan virus nucleoprotein)-specific CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptides and application thereof. The CTL epitope peptides have amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1-12. Especially, HLA-I (human leucocyte antigen-I) molecule restricted epitope polypeptide in the HTNV-NP-specific CTL epitope peptides can induce CD8+T lymphocyte to generate strong cellular immune response and secrete high-level IFN-gamma. The HTNV-NP-specific CTL epitope peptides can be used for preparing CTL epitope peptide vaccines or for inducing the generation of CTL epitope peptide-specific CTL, or for preparing CTL epitope peptide-sensitized antigen presenting cells and have bright development and application prospects in the field of specific immunization therapy of HFRS (hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome).
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
RT-PCR method for testing hantavirus genome
InactiveCN101294226AImprove positive detection rateReduce False Negative TestsMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionHantavirus Infection
The invention discloses a method for detecting hantaan virus strain genome. The method has the following steps: (1) two pairs of hantaan virus general primers are designed; (2) the hantaan virus detection method comprises the following steps that: first, viral specific RNA extraction kit is utilized to extract the total RNA in a serum sample; second, a nucleic acid analyzer is adopted to detect the RNA content, and the RNA is taken to perform the RT-PCR reaction; third, RT-PCR:RT uses HV group-specific primers such as P0, PCR uses HV general primers such as P1P2 and P3P4; fourth, viral nucleic acid amplified results are observed through agarose gel electrophoresis, and a specific nucleic acid band appears. The method is intuitionistic and predominant, the sensibility is good, and the effects are good; the serum detection rate in recent ten years is 79.2 percent, and the serum detection rate in twenty years ago can still reach to 70.5 percent; the method is applied to the laboratory detection of hantaan virus infection and the molecular epidemiological survey.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation and application of hemorrhagic fever associated pathogen identifying gene chip
ActiveCN105087824APracticalShort detection cycleNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide chipOligonucleotide
The invention relates to a hemorrhagic fever associated pathogen identifying gene chip; the preparation method comprises preparation of a specific primer, preparation of a pathogen specific oligonucleotide probe, preparation of an oligonucleotide chip, establishment of an RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) system and establishment of a hybrid system and a signal detection method. The gene chip prepared by the invention can be used for simultaneously identifying 16 hemorrhagic fever associated pathogen microorganisms, including Zaire Ebola virus, Sudan Ebola virus, marburg virus, lassa virus, junin virus, Machupo virus, rift valley fever virus, Crimea-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, plasmodium, hantaan virus, SFTS (severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome) virus, dengue virus, yellow fever virus, Chikungunya virus, influenza A virus and influenza B virus. The gene chip has the characteristics of being rapid and accurate, high in throughput and high in sensitivity; and a new technological means is offered for the diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever pathogen, health supervision and the control and prevention of infectious diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION +1
Multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer, kit and method for quickly distinguishing 5 respiratory pathogens of mouse
ActiveCN107312873AAvoid crossbreedingGuaranteed temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
The invention discloses a multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer, kit and method for quickly distinguishing 5 respiratory pathogens of a mouse. The multi-liquid-phase gene chip detection primer is easy to operate; a target amplified fragment is obtained through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); an amplified product, fluorescence coded microspheres and streptavidin-phycoerythrin are hybridized; an MFI (Mean Fluorescence Intensity) value is read through a detector so as to distinguish different types of viruses. The method disclosed by the invention can detect a pneumonia virus, a hantaan virus, a sendai virus, a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and mycoplasma pulmonis of the mouse at the same time, and is high in specificity, high in sensitivity and high in repetitiveness. Compared with the conventional detection method, the method disclosed by the invention realizes simultaneous detection of various different target molecules in the same sample; the sample use amount is small; the operation is simple and quick; the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST
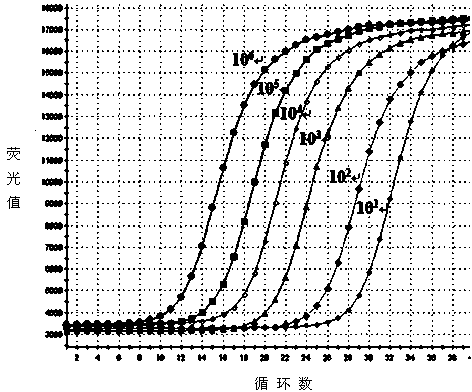
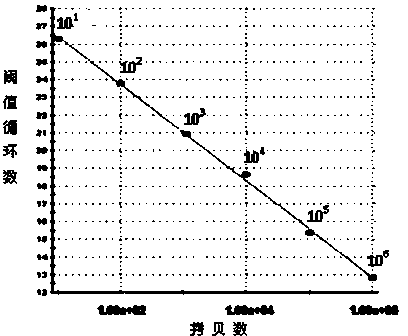
Method for quantitatively detecting hantaan virus load through one-step fluorescence probe real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
InactiveCN102634609AQuantitatively accurateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceSyndrome patient
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting hantaan virus load through one-step fluorescence probe real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. According to the method, the overall-length fragment of in vitro transcription S of the hantaan virus is utilized as a quantitative detection standard substance, a one-step fluorescence probe real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction method is established by the design of detecting a virus gene sequence primer and a prober and the selection of the method so as to quantitatively detect the hantaan virus load of the blood plasma or other body fluid and tissues of a hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome patient. Compared with a conventional PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method, the method has the advantages that the specimen detection and operation steps are few, the sensitivity is high, the linear relation is good, and the experiment shows that the detection method has good specificity and repeatability and provides a powerful tool for the scientific research and preventive treatment of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Murine original monoclonal antibody 3D8 identified hantaan virus glycoprotein neutralizing epitope peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN102731623ADirect determination of linear epitopesViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsViral glycoproteinProtein target
The invention discloses a neutralizing monoclonal antibody 3D8 identified HTNV-GP specific B cell epitope and key amino acid residue sequence of the epitope for treating hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by hantaan virus (HTNV) infection. The B cell epitope has an amino acid sequence of 882GFLCPEFPGSFRKKC896. The epitope peptide can be applied to study of mechanism of 3D8 neutralizing monoclonal antibody in treatment of HFRS, or preparation of drug for treating HFRS and preparation of novel vaccine strain aiming at hantaan virus 76-118, or development of novel diagnostic kitfor hantaan virus 76-118 as a target protein. The invention has good prospects of development and application in the field of HFRS specific immunotherapy.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Use of anti-hantavirus medicament arbidol
InactiveCN101461805AInhibition of replicationInduces antiviral state effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsSide effectMortality rate
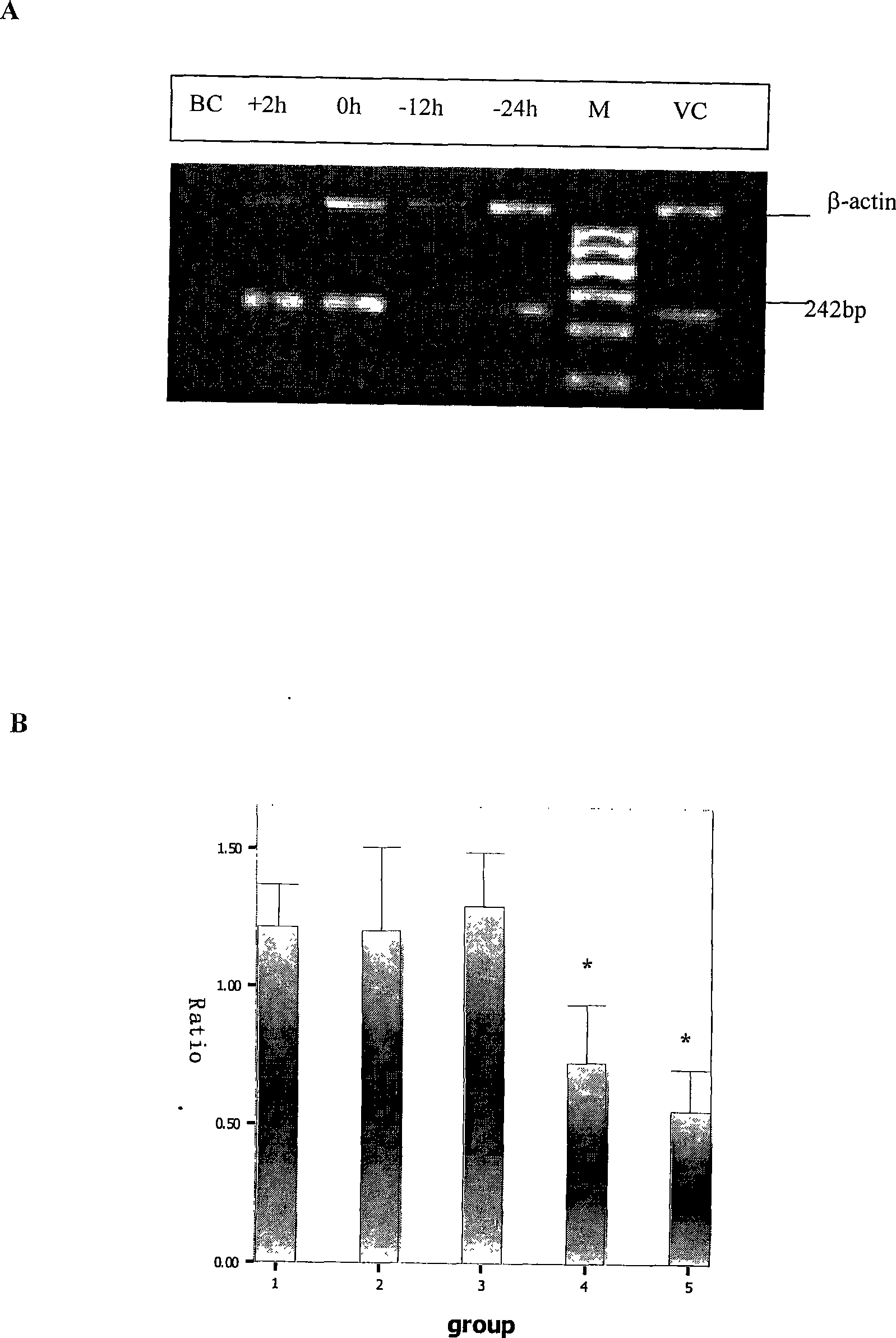
The invention discloses application of a medicine in resisting Hantaan viruses, namely arbidol. The arbidol has obvious effect of inhibiting the Hantaan viruses in vitro, and the antivirus effect of drug administration before the viruses enter a cell is stronger than that of the drug administration after the viruses enter the cell. The concrete embodiment comprises the following: the drug administration is performed before and after the infection, the positive rate of virus-infected cells and the fluorescence intensity are reduced along with the concentration increase, and the medicine has dosage effect; and the medicine can obviously reduce the positive rate of virus infection, and the mRNA expression of the viruses is reduced. The arbidol has protection and treatment effect on the infection of the Hantaan viruses on a suckling mouse, and the protection effect is stronger than the treatment effect. The drug administration is performed within 24h before the infection; and with the increase of the dosage of the medicine, the death rate of the mouse is reduced, and the average survival days are extended. The drug administration within 24h after the infection can not improve the survival rate of an animal, but can extend the average survival days of the animal. The arbidol has the effect of inhibiting the Hantaan viruses in a body of the animal. The drug administration within 24h before the infection can lighten the pathologic change of tissues (lung, kidney, and brain), and has treatment effect on HFRS. The medicine has prevention effect and also has treatment effect on patients with the hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by the Hantaan viruses, and no toxic side effect is found.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
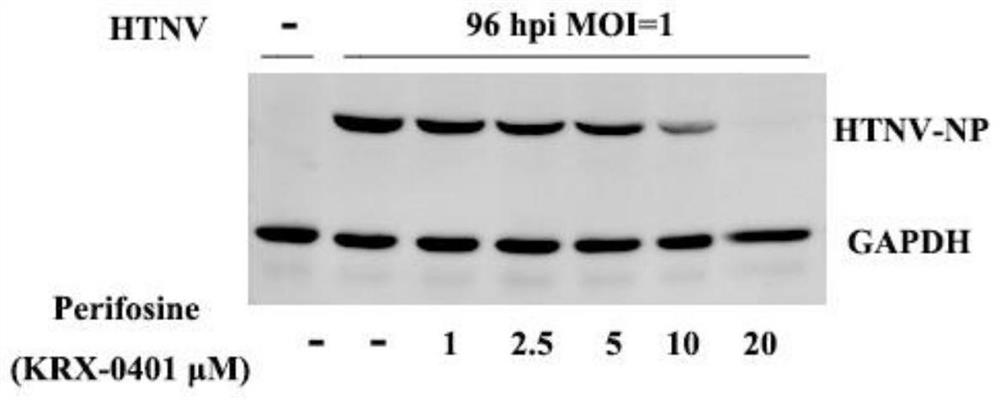
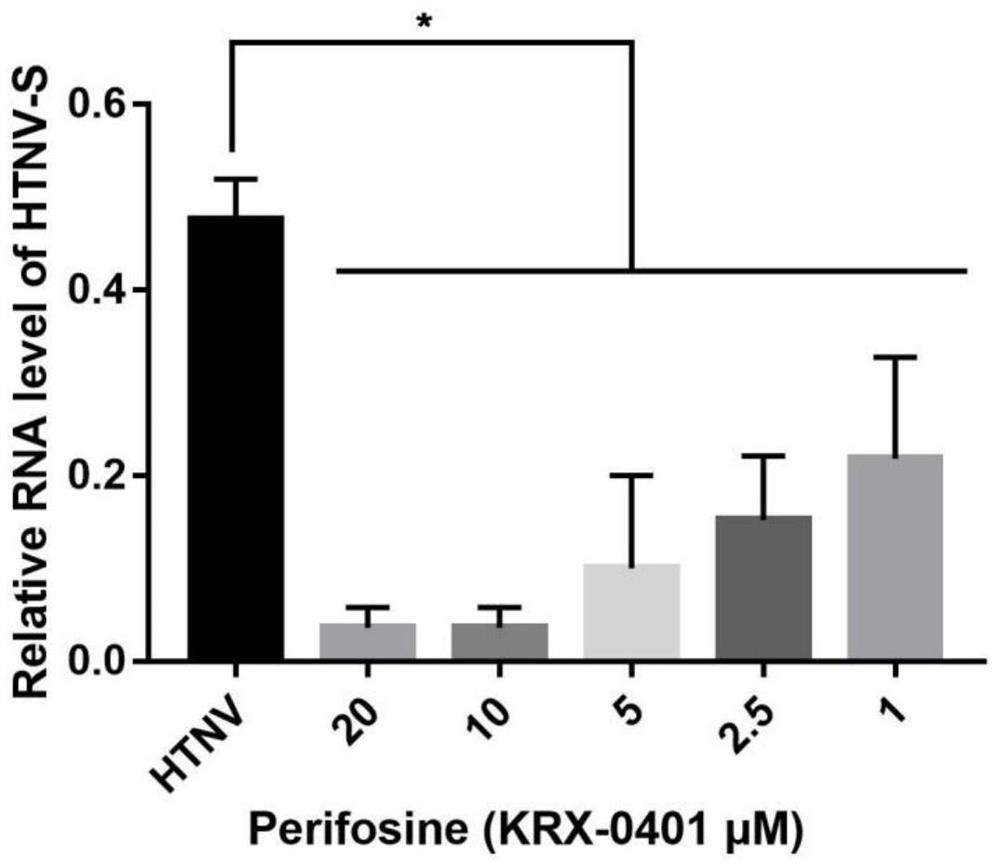
Application of Perifosine to preparation of anti-Hantaan virus drug
ActiveCN113813269AInhibition of replicationPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsInfected cellPharmaceutical Substances
The invention relates to an application of Perifosine to preparation of an anti-Hantaan virus drug. At present, no specific treatment drug aiming at a Hantaan virus infection exists, and the main clinical treatment means are still mainly supportive treatment, so that the research and development of the efficient and low-toxicity anti-Hantaan virus drug have extremely important clinical significance. The invention relates to application of the Perifosine to preparation of the anti-Hantaan virus drug, and the Perifosine is used for inhibiting replication and proliferation of Hantaan viruses. It is proved by experiments that after the Perifosine is added, a virus load in an infected cell is obviously reduced, a nucleic acid level is obviously reduced, and the compound has small influence on the cell activity under the concentration of playing an anti-virus effect and can be used as a high-efficiency and low-toxicity anti-Hantaan virus drug.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) nucleic acid detection primers and kit of Hantaan viruses
InactiveCN104946799ALow costReduce use costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionMicrobiology
The invention discloses RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) nucleic acid detection primers and a kit of Hantaan viruses and in particular relates to a group of primers for detecting Hantaan viruses, a kit containing the primers and a detection method of the Hantaan viruses. The primers comprise base sequences shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1 to a sequence table SEQ ID No.6. The kit has high sensitivity and strong specificity, is low in cost and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT +1
SYBR Green I Real-time PCR method for quickly detecting and indentifying Hantaan virus infection
InactiveCN103436637AAccurate detectionStrong contrastMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceConserved sequenceHaemorrhagic fever
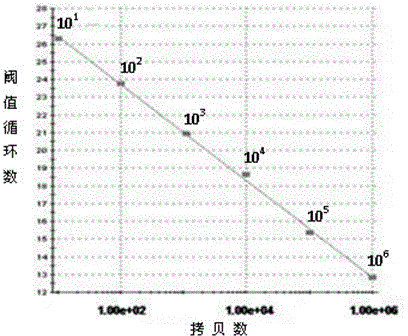
The invention discloses an SYBR Green I Real-time PCR (Real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction) method for quickly detecting and indentifying Hantaan virus infection. The method comprises the following steps: designing a pair of specific primers mainly according to a conserved sequence of an S gene in a GenBank database; using a positive plasmid subjected to 10-time gradient dilution as a standard product; optimizing a reaction condition; establishing the SYBR Green I Real-time PCR method used for detecting a Vero E6 cell, a mouse and a clinical patient, which are infected by Hantaan virus nucleic acids according to qRT-PCR specificity amplification, wherein a copy number of the detection sensitivity can reach 101, and sensitivity, repeatability and specificity of the Hantaan virus nucleic acids are detected. Compared with a conventional Hantaan virus detection method, the method has the advantages that types of detecting samples are rich, the application range is wide, the contrast is strong, operation steps are relatively few, convenience and quickness are realized, the sensitivity and the repeatability are high, the specificity is good, and a linear relationship is good, and can provide a strong experimental basis on clinical and laboratory detection of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome as well as studying of epidemiology.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Hantaan virus glucoprotein specific T cell epitope peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN102731617AStrong immune responseViral antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesCtl epitopeSpecific immunity
The invention discloses an HTNV-Gn / Gc specific T cell epitope peptide and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the HTNV-Gn / Gc specific T cell epitope peptide is one selected from SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO. 75. The HTNV-Gn / Gc specific T cell epitope peptide comprises CD4<+>T cell epitope and CTL epitope, and can respectively induce CD4<+>T cell and CD8<+>T cell to generate intensive cellular immunologic response and to secrete high-level IFN-gamma. The HTNV-Gn / Gc specific T cell epitope peptide can be used in the preparation of T cell epitope peptide vaccines, and can be used in inducing CD4<+>T cell or cytotoxicity T cell generating epitope peptide specificity. Therefore, the HTNV-Gn / Gc specific T cell epitope peptide has a good exploitation and application prospect in the field of HFRS specific immunotherapy.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid set, kit and detection method for detecting Hantaan viruses through RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification)
ActiveCN110373502ALower requirementShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesForward primerTrue positive rate
The invention relates to a nucleic acid set, a kit and a detection method for detecting Hantaan viruses through RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification). The nucleic acid set comprises a primer pairand a probe. The primer pair comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer, the sequence of the forward primer is SEQ ID NO. 2, the sequence of the reverse primer is SEQ ID NO. 3, and the sequenceof the probe is SEQ ID NO. 4. The kit comprises the nucleic acid set, and is applied to the detection method. Amplification can be realized at a temperature near to the body temperature, and visual discrimination of amplified products can be realized by a disposable nucleic acid detecting device. The nucleic acid set, the kit and the detection method have the advantages of high sensitivity and specificity, low requirement on hardware equipment, short reaction time, no complicated treatment on samples, suitability for on-site detection and the like, and are suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:中国人民解放军东部战区疾病预防控制中心
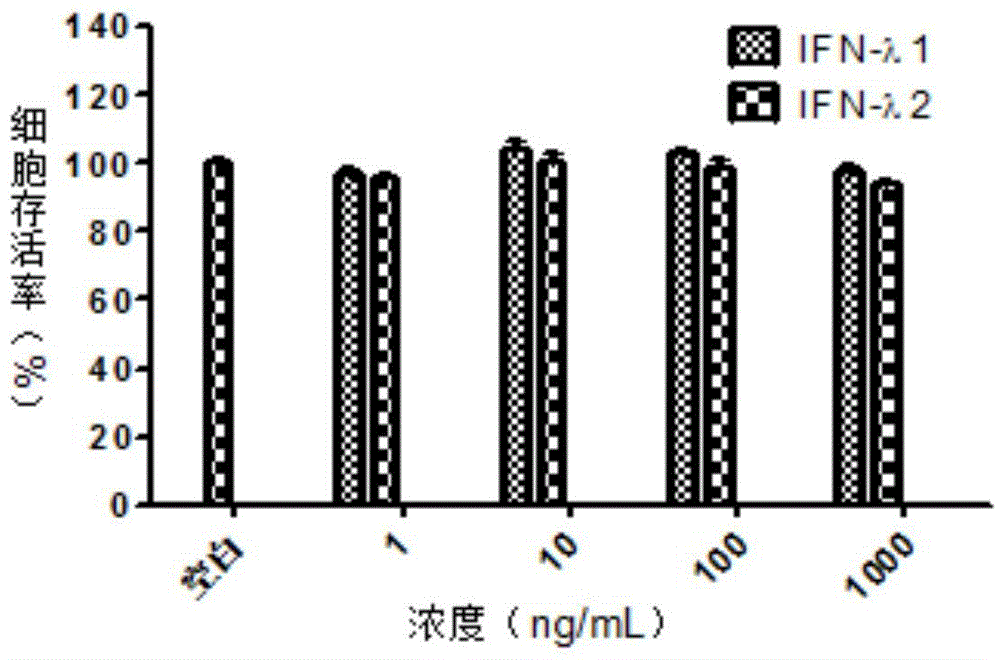
Application of lambda interferon to preparation of anti-Hantaan virus drugs
ActiveCN104784680AAlleviate pathological changesReduced expression levelPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAnti virusSide effect
The invention discloses an application of lambda interferon to the preparation of anti-Hantaan virus drugs and belongs to the field of anti-virus drugs. The invention discovers that lambda interferon can induce generation of various anti-virus factors and inhibit Hantaan virus infection in vitro and in vivo, does not have toxic or side effects, can protect cells from being infected with Hantaan viruses in vitro and increase the survival rate and mean survival days of animals infected with the Hantaan viruses in vivo, relieves pathological lesion of tissues, and reduces viral nucleic acid level. The discovery shows that lambda interferon can be used for preparing the anti-Hantaan virus drugs and also can be used for preparing drugs for treating and preventing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by the Hantaan viruses.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Recombinant interferon lambda 4 encoded cDNA sequence as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106222178ARealize industrializationOptimizing the induction temperatureBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a recombinant interferon lambda 4 encoded cDNA sequence which can be efficiently expressed in a prokaryotic expression system. The nucleotide sequence of the recombinant interferon lambda 4 encoded cDNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further provides application of the cDNA sequence in preparing a medicine for treating and / or preventing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by hantaan viruses. The invention provides a method and application of recombinant interferon lambda 4. Escherichia coli can be concerted and expression can be induced by using a prokaryotic expression vector containing human interferon lambda 4 encoded cDNA, the optimal induction temperature of a relatively large amount of dissoluble interferon lambda 4 is 18 DEG C, the bacterium shaking speed is 120rpm, the induction time is 4 hours, and the IPTG concentration is 0.1mM. By adopting the product prepared by using the preparation method, basis is made for study on biological activity and action mechanisms of human interferon lambda 4, and the product can be also applied to medicines for treating and / or preventing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by hantaan viruses.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Application of benzopyran compounds in preparation of anti-hantaan virus (HTNV) drug
ActiveCN110420206AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood in vitro activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBenzopyranMedicine
The invention discloses application of benzopyran compounds in preparation of an anti-hantaan virus (HTNV) drug. The invention finds that compounds with structure shown in a formula I have good in vitro activity and have higher inhibition effects on HTNV.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Detection method and detection reagent kit for nephrotic syndrome and hemorrhagic fever
InactiveCN1095545CQuick checkCorrect and easy detectionBiological testingNitrocelluloseAntibody conjugate
The invention provides a method for detecting hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome by a gold drop method and a detection kit. In this method, the anti-Hantavirus IgG antibody in the serum is used as the detection object, and it includes the steps of: (a) coating the purified Hantavirus nucleoprotein on a nitrocellulose membrane to form a coating in the sampling area. A nitrocellulose detection membrane with hantavirus nucleoprotein; (b) using non-human anti-human IgG antibody and colloidal gold as raw materials to prepare a conjugate of colloidal gold-anti-human IgG antibody; (c) the Serum sample is added dropwise on the spotting area of the detection membrane obtained in step (a); (d) washing the spotting area of the detection membrane of step (c); (e) colloidal gold-antihuman The conjugate of the IgG antibody is dropped on the spotting area; (f) washing the spotting area of the detection membrane in step (e). The method and kit can detect hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome rapidly, correctly and conveniently.
Owner:上海市南汇县南华医院
RT-PCR method for testing hantavirus genome
InactiveCN101294226BImprove positive detection rateReduce False Negative TestsMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionHantavirus Infection
The invention discloses a method for detecting hantaan virus strain genome. The method has the following steps: (1) two pairs of hantaan virus general primers are designed; (2) the hantaan virus detection method comprises the following steps that: first, viral specific RNA extraction kit is utilized to extract the total RNA in a serum sample; second, a nucleic acid analyzer is adopted to detect the RNA content, and the RNA is taken to perform the RT-PCR reaction; third, RT-PCR:RT uses HV group-specific primers such as P0, PCR uses HV general primers such as P1P2 and P3P4; fourth, viral nucleic acid amplified results are observed through agarose gel electrophoresis, and a specific nucleic acid band appears. The method is intuitionistic and predominant, the sensibility is good, and the effects are good; the serum detection rate in recent ten years is 79.2 percent, and the serum detection rate in twenty years ago can still reach to 70.5 percent; the method is applied to the laboratory detection of hantaan virus infection and the molecular epidemiological survey.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
SYBR Green I Real-time PCR method for quickly detecting and indentifying Hantaan virus infection
InactiveCN103436637BAccurate detectionStrong contrastMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHaemorrhagic feverEpidemiology
The invention discloses a SYBR GreenⅠReal-time PCR method for rapid detection and identification of Hantaan virus infection. The method mainly designs a pair of specific primers based on the sequence of the conserved region of the S gene in the GenBank database. The gradient diluted positive plasmid was used as the standard, the reaction conditions were optimized, and the specific amplification by qRT-PCR was used to establish the SYBR Green Ⅰ Real-time PCR method for the detection of Hantaan virus nucleic acid in infected Vero E6 cells, infected mice and clinical patients, and the detection sensitivity A copy number of 101 was reached and tested for sensitivity, reproducibility, and specificity. Compared with conventional Hantaan virus detection and identification methods, this method has the advantages of rich types of detection specimens, wide application range, strong contrast, few operation steps, convenient and fast, high sensitivity, high repeatability and specificity, and has good The advantage of a linear relationship. It provides a strong experimental basis for the clinical, laboratory detection and epidemiological research of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
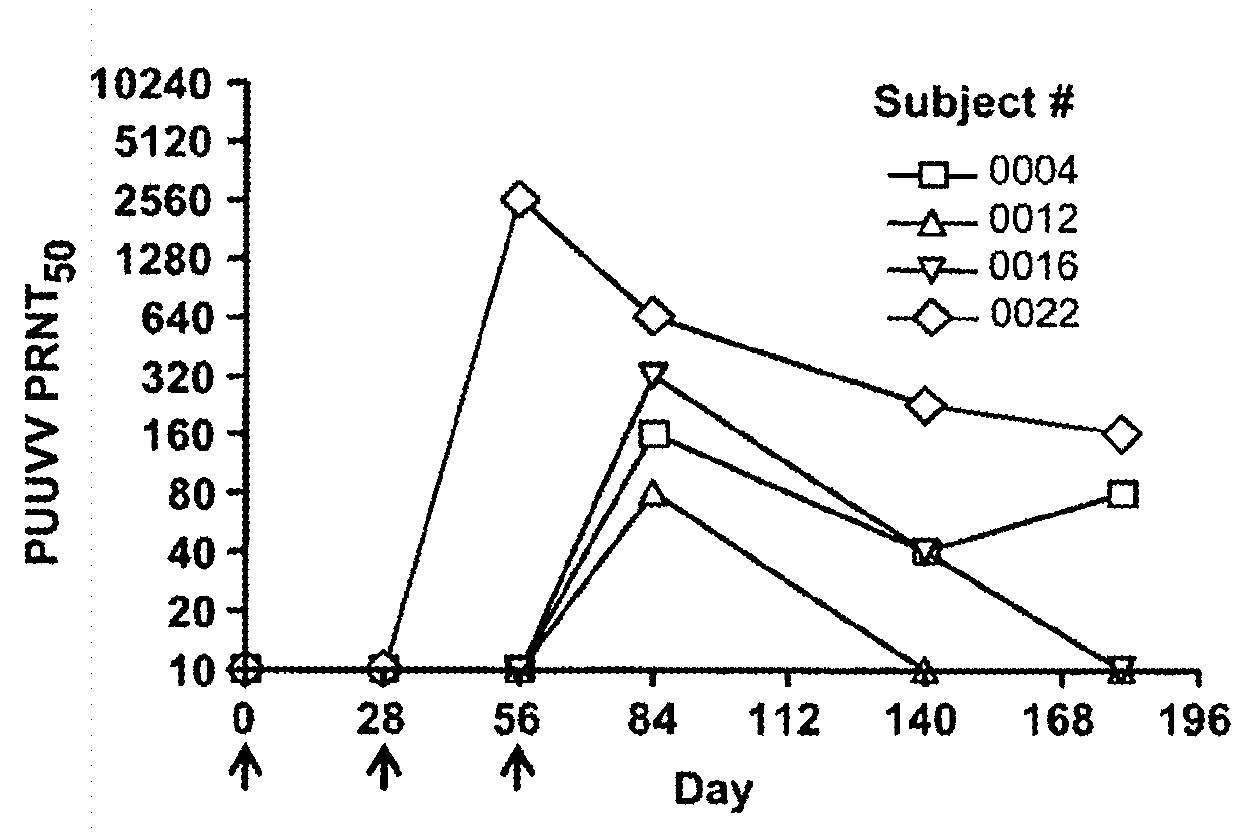
Gene Optimized Hantaan Virus M Segment DNA Vaccine For Hemorrhagic Fever With Renal Syndrome
ActiveUS20170112916A1Reduce efficacyLow immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryOpen reading frameNucleotide
A synthetic, codon-optimized Hantaan virus (HTNV) full-length M gene open reading frame that consists of a unique nucleotide sequence encoding HTNV proteins. This synthetic gene was cloned into a plasmid to form the first optimized HTNV full-length M gene that elicits neutralizing antibodies in animals when delivered in combination with a similarly optimized Puumala virus (PUUV) DNA vaccine. The invention obviates the need for an extraneous gene sequence that was previously required for expression of the non-optimized HTNV gene. The synthetic gene is engineered into a molecular vaccine system to prevent hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by infection with HTNV, SEOV, or DOBV. Alternatively, it can be combined with the optimized PUUV DNA vaccine to protect against HFRS caused by any hantavirus.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Azole nucleosides and use as inhibitors of rna and DNA varial polymerases
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
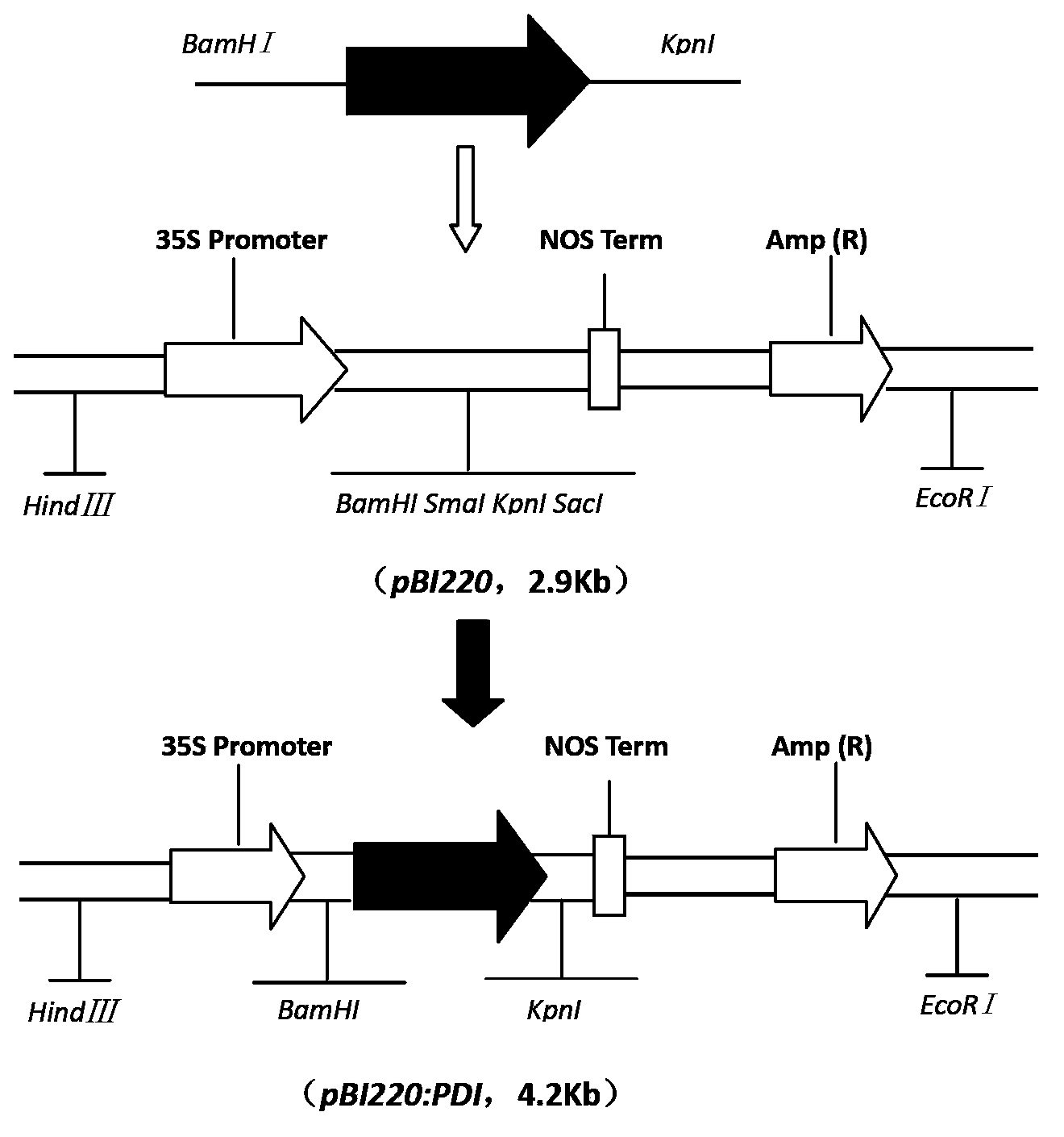
A Disulfide Isomerase Gene and Its Application
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and discloses a haynaldia villosa disulfide isomerase gene and an application thereof. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of Hv-PDI (Hantaan Virus-Protein Disulfide Isomerase) is SEQ ID NO. 1, and the encoded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO. 2. The gene derives from diploid haynaldia villosa (haynaldia villosa VV, 2n=14), is induced by powdery mildew in powdery mildew-resistant diploid haynaldia villosa, and is greatly expressed. Through transient expression, the gene is transformed to an infected wheat variety Yangmai 158, a result shows that excessive expression of Hv-PDI is capable of reducing the haustorium index of Yangmai 158. Therefore, the Hv-PDI is expectedly used for genetic engineering breeding, and the resistance of wheat to powdery mildew is hopefully improved when the Hv-PDI is introduced to wheat varieties susceptible to powdery mildew.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Murine original monoclonal antibody 3D8 identified hantaan virus glycoprotein neutralizing epitope peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN102731623BDirect determination of linear epitopesViral antigen ingredientsPeptidesProtein targetViral glycoprotein
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of benzopyrans in the preparation of anti-Hantaan virus drugs
ActiveCN110420206BEnhanced inhibitory effectGood in vitro activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBiochemistryPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses the application of benzopyran compounds for preparing anti-Hantaan virus drugs. It is found in the present invention that the structural compound represented by formula I has good in vitro activity, and has a strong inhibitory effect on anti-Hantaan virus.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
HTNV-NP (Hantaan virus nucleoprotein)-specific CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptides and application thereof
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Hantaan virus-like particle containing GM-CSF as well as preparation method and application of hantaan virus-like particle
InactiveCN104974990AEffectively exert immune enhancement effectIncrease production capacityViral antigen ingredientsInactivation/attenuationHantavirus InfectionVirus-like particle
The invention relates to a hantaan virus-like particle containing GM-CSF as well as a preparation method and application of hantaan virus-like particles. For the VLP (virus-like particle) composed of multiple proteins, baculoviruses for expressing all proteins are required to be prepared on the basis of an insect cell expression system, and then insect cells are co-infected according to different proportions, so that a lot of work for exploring a co-infection proportion is required, and in addition, a certain difficulty is brought to purification in a later period due to baculoviruses mixed in the product. According to the invention, on the basis of a mammalian cell expression system, by constructing a eukaryotic expression vector to co-transfect dhfr-CHO cells, and the hantaan virus-like particle containing GM-CSF is assembled. According to the invention, all components of the chimeric virus like particle can express, the constructed eukaryotic expression vector contains multiple selection markers, a cell strain for stably expressing chimeric virus like particles can be constructed through screening, mass production and preparation are facilitated and the hantaan virus-like particle can be used for preventing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which is caused by hantaan virus infection.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A high-throughput method for rapid detection of Hantaan virus neutralizing antibody titer
ActiveCN106706582BOptimizing the Optimal DoseOptimal TimeBiological material analysisFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetCytopathic effect
The invention discloses a high-flux method for quickly detecting hantaan virusneutralizing antibody titer. The method is characterized by utilizing an In-cell Western (ICW) method for simply, conveniently and intuitively detecting cells infected by HTNV (Hantaan Virus). The method is high in detection sensitivity (capable of detecting 5g of target protein), short in period (72 hours), objective in result interpretation, good in repetitiveness, high in flux, standardized in method, and convenient to inter-laboratory popularize, and can be particularly used for detecting the infectivity of acellular cytopathic effect virus. The invention also discloses application of the method in HTNV infectivity titration (TCID50), HTNV neutralizing antibody titration, anti-HTNV molecular screening and identification, human HTNV vaccine immunity protection evaluation and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gene optimized hantaan virus M segment DNA vaccine for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome
ActiveUS20160051659A1Reduce efficacyLow immunogenicityPowder deliveryVirusesOpen reading frameNucleotide
A synthetic, codon-optimized Hantaan virus (HTNV) full-length M gene open reading frame that consists of a unique nucleotide sequence encoding HTNV proteins. This synthetic gene was cloned into a plasmid to form the first optimized HTNV full-length M gene that elicits neutralizing antibodies in animals when delivered in combination with a similarly optimized Puumala virus (PUUV) DNA vaccine. The invention obviates the need for an extraneous gene sequence that was previously required for expression of the non-optimized HTNV gene. The synthetic gene is engineered into a molecular vaccine system to prevent hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) caused by infection with HTNV, SEOV, or DOBV. Alternatively, it can be combined with the optimized PUUV DNA vaccine to protect against HFRS caused by any hantavirus.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Hantavirus-like particles containing gm-csf, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104974990BEffectively exert immune enhancement effectIncrease production capacityViral antigen ingredientsInactivation/attenuationHantavirus InfectionHaemorrhagic fever
The invention relates to a hantaan virus-like particle containing GM-CSF as well as a preparation method and application of hantaan virus-like particles. For the VLP (virus-like particle) composed of multiple proteins, baculoviruses for expressing all proteins are required to be prepared on the basis of an insect cell expression system, and then insect cells are co-infected according to different proportions, so that a lot of work for exploring a co-infection proportion is required, and in addition, a certain difficulty is brought to purification in a later period due to baculoviruses mixed in the product. According to the invention, on the basis of a mammalian cell expression system, by constructing a eukaryotic expression vector to co-transfect dhfr-CHO cells, and the hantaan virus-like particle containing GM-CSF is assembled. According to the invention, all components of the chimeric virus like particle can express, the constructed eukaryotic expression vector contains multiple selection markers, a cell strain for stably expressing chimeric virus like particles can be constructed through screening, mass production and preparation are facilitated and the hantaan virus-like particle can be used for preventing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which is caused by hantaan virus infection.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Kidney syndrome hemorrhagic fever mucosa immune vaccines and method of preparing the same
The invention discloses a mucosa immune vaccine of hemorrhage fever syndrome and a preparation method thereof. The vaccine comprises inactivated virus and chitosan from hantaan virus which can cause hemorrhage fever syndrome in one or a plurality of types, wherein the chitosan exists in the form of micro-particles; the inactivated virus is covered inside the micro-particles of chitosan; furthermore, the vaccine can fruther comprise escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit with mucosa adjuvant activity; the result of the animal experiment shows that the vaccine of the invention can effectively excite the immune response of specific mucosa and the body fluid of the body anti-hantaan virus through nasal cavity and oral administration. The vaccine has statistical significance compared with the control group (p is less than 0.01) and has the advantages of safety, convenience, cost-effeciveness etc., compared with traditional hemorrhagic fever injected vaccine.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com