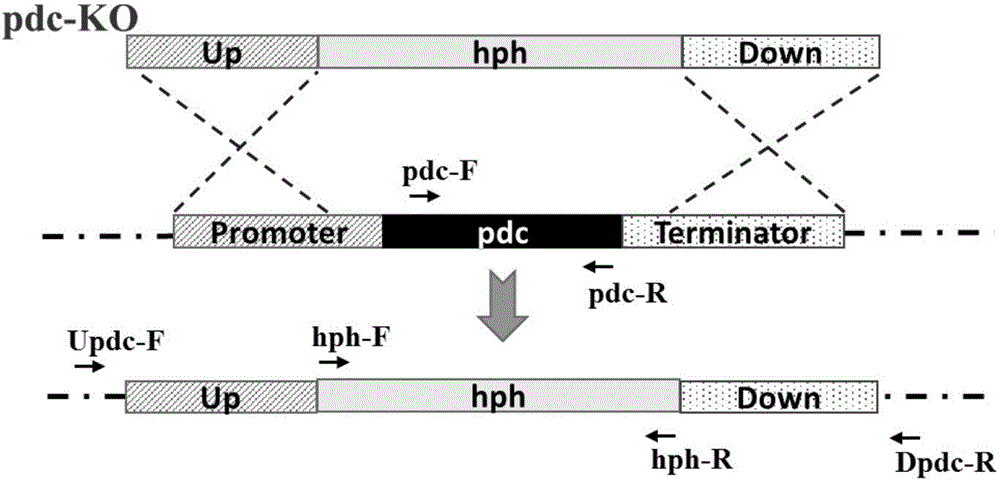
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
547 results about "Gene Deletions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is lost during DNA replication.
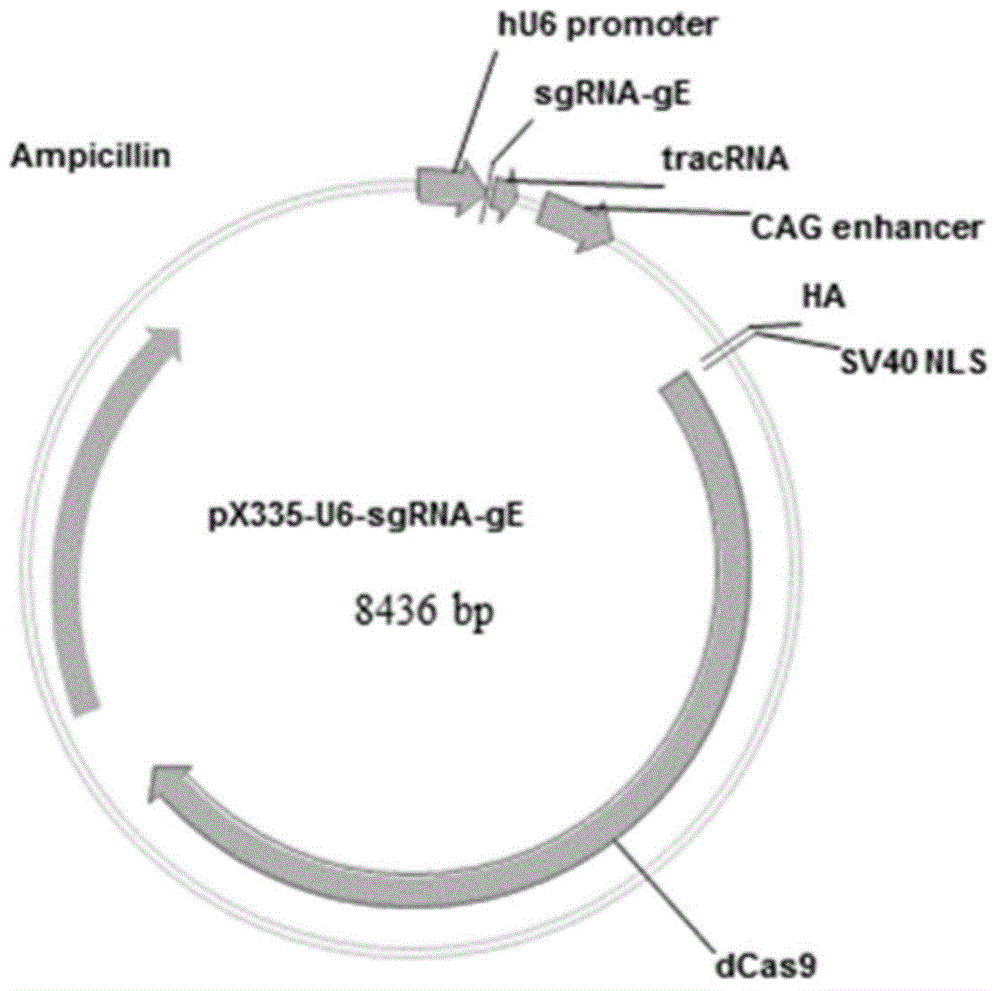
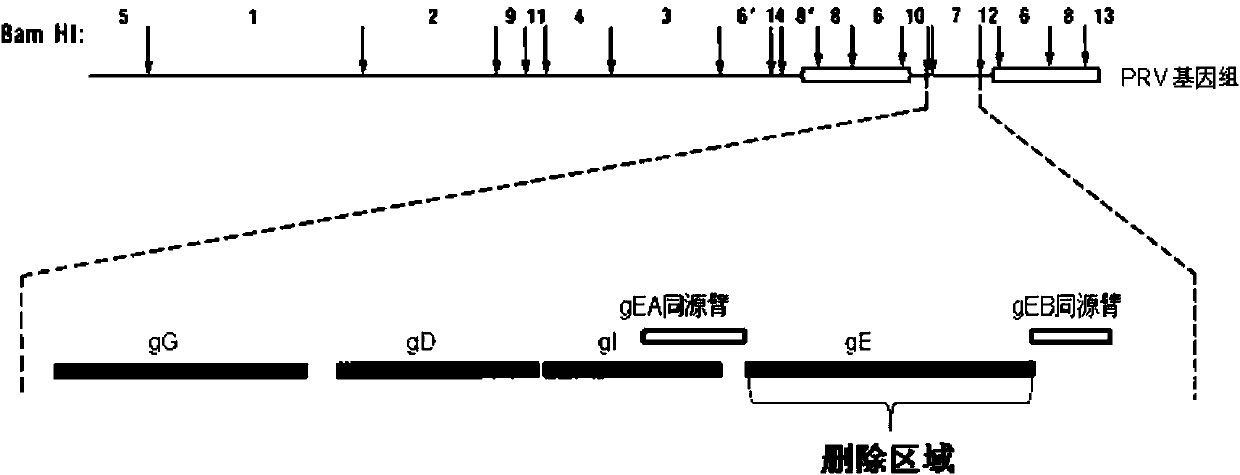
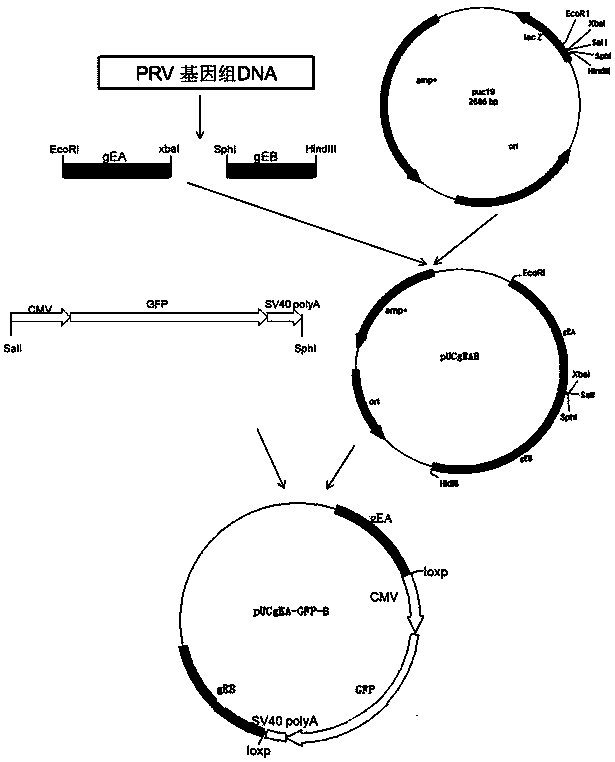
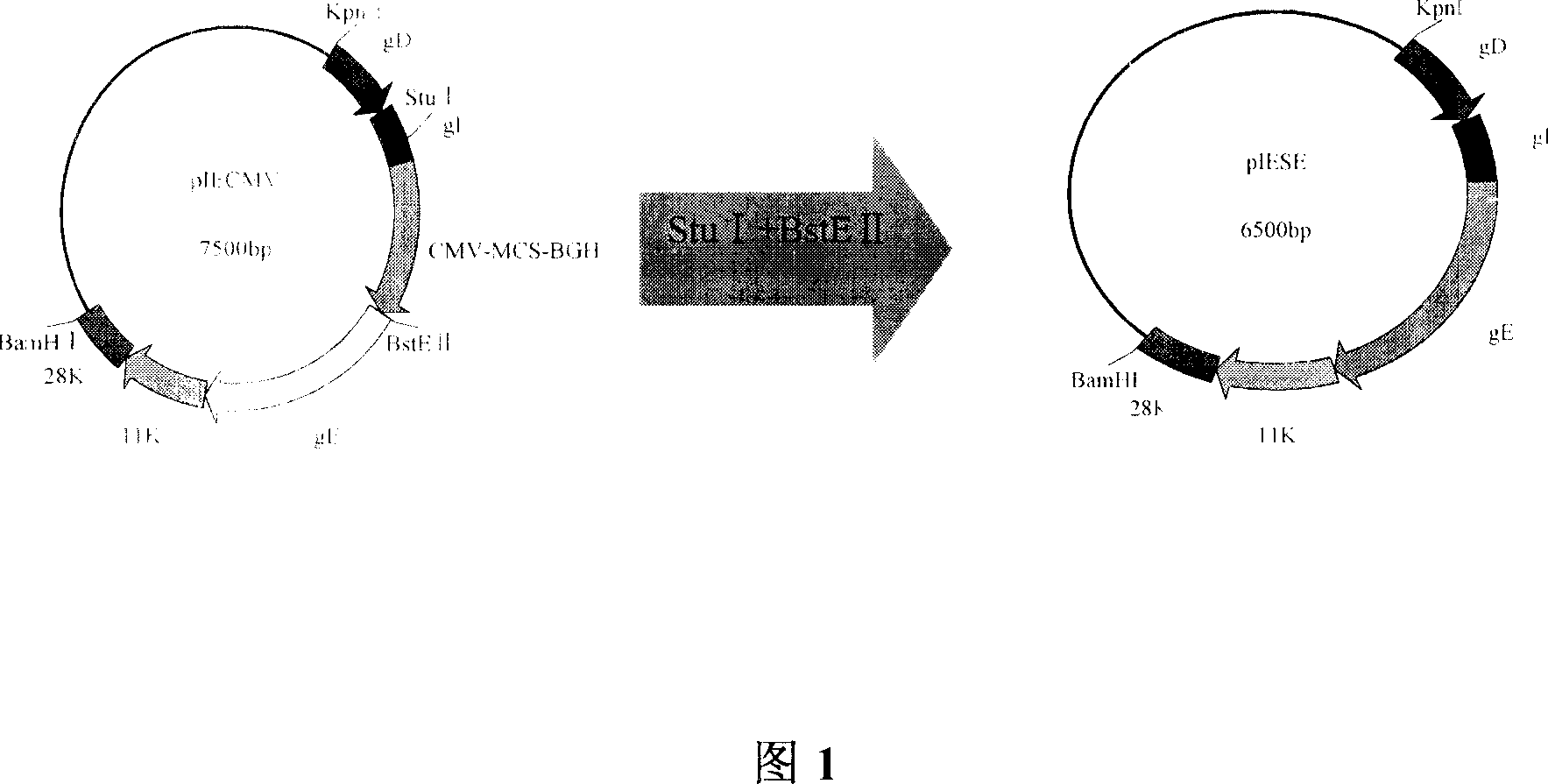
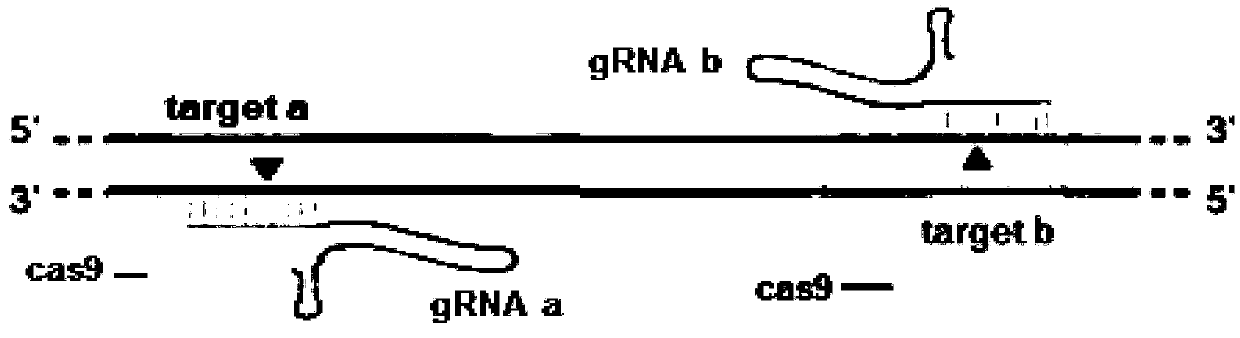
Method for preparing vaccine by editing pseudorabies virus genomes based on CRISPR/Cas9 and Cre/lox systems and application of method
ActiveCN104894075AReduce disease lossEasy to operateAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesMCherry fluorescent proteinBiology
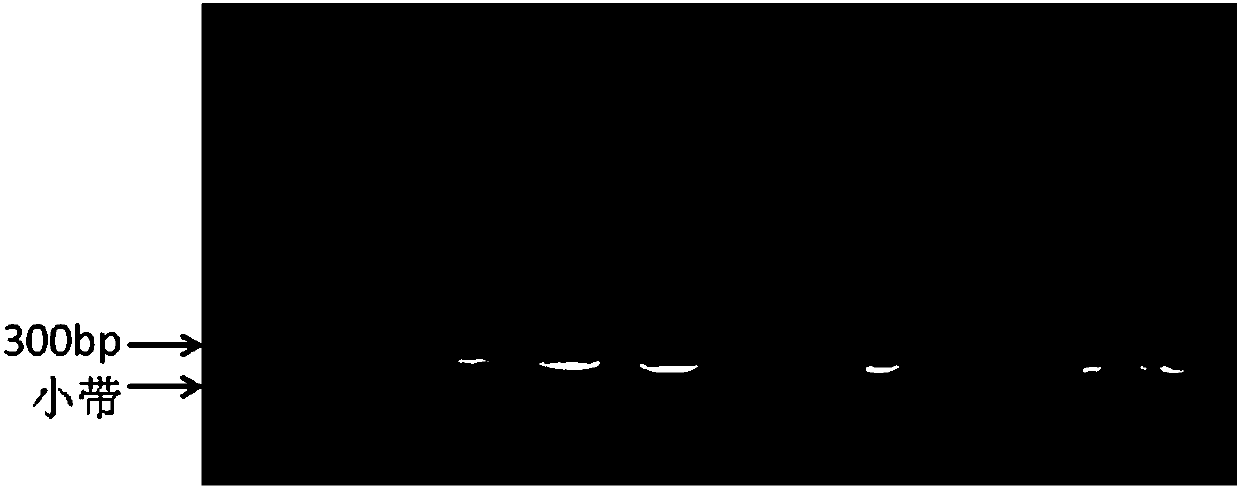
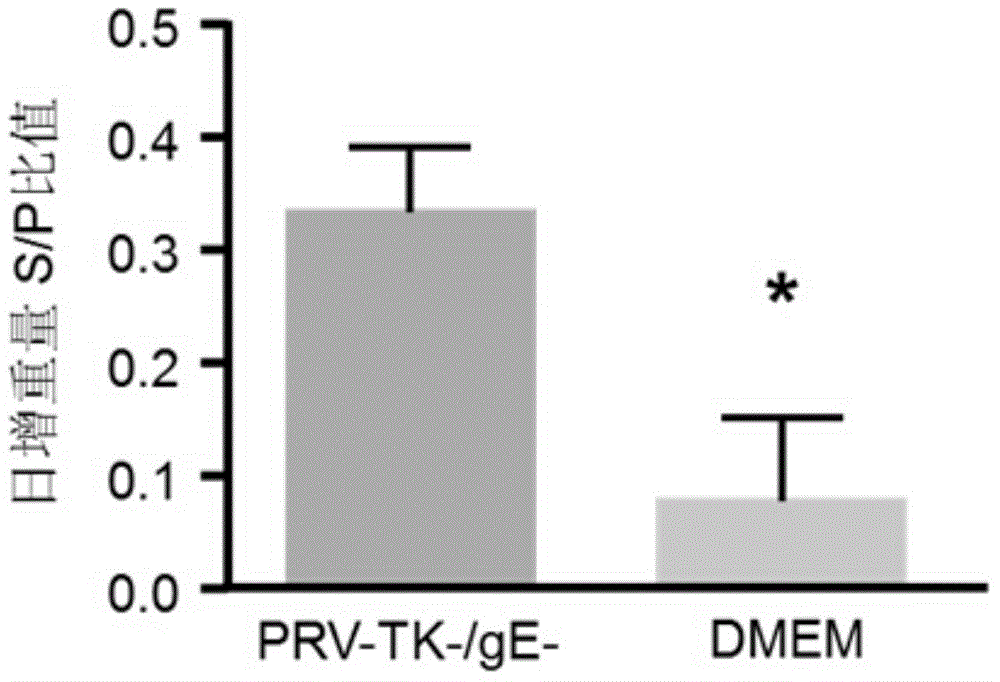
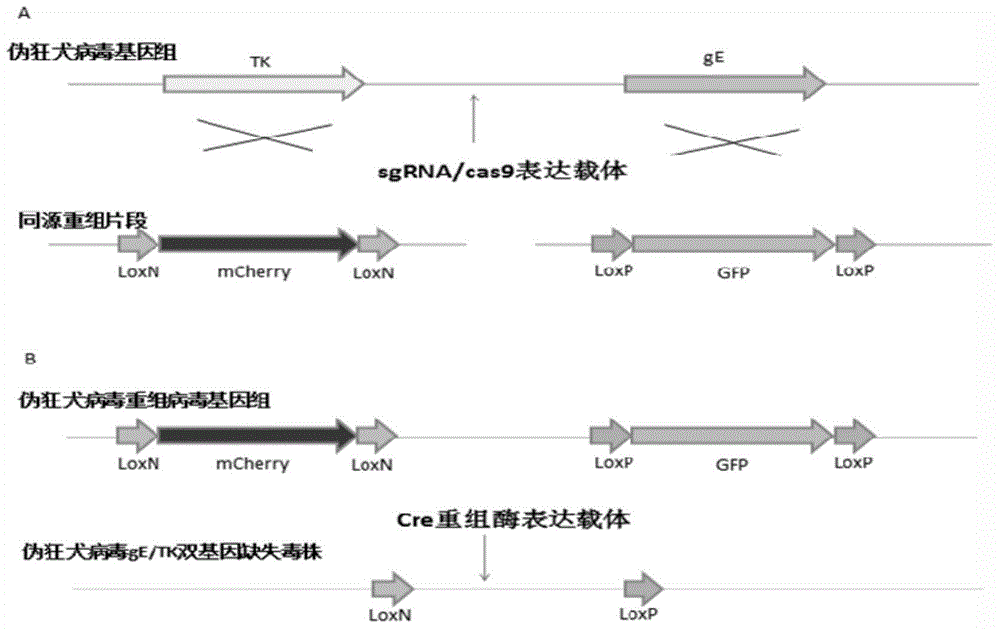
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing a vaccine by editing pseudorabies virus genomes based on a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system and a Cre / lox recombination system and an application of the method. According to the method, the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system is used for synchronously and efficiently recombining a GFP gene and a mCherry gene to a pseudorabies virus gE gene site and a TK gene site respectively to obtain conditional deletion strains of a gE gene and a TK gene; after purification, the Cre / lox system is used for cutting off extraneous GFP and mCherry genes in the pseudorabies virus recombinant virus genome so as to perform purification quickly to obtain a live pseudorabies virus vaccine lack of gE / TK genes; multiple genes are operated at the same time, so that multiple rounds of flows for knocking out multiple genes in the conventional method are reduced to one round; and meanwhile, the efficient edition of virus genes by using the CRISPR / Cas9 and Cre / lox systems simplifies about thirty generations of plaque purification processes into 3-4 generations, so that the preparation efficiency of the virus vaccine is greatly improved, and the method provides a strong guarantee for effectively preventing and controlling the larger-range popularization of variant pseudorabies viruses and reducing heavy economic losses.
Owner:武汉都为康生物科技有限公司
Porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN102994458AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and a gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof. The porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is named as HeN1, the microbial preservation number of the porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is CGMCC NO.6656, the deleted gE gene obtaines the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ on the basis of the virulent strain HeN1, and the microbial preservation number is CGMCC NO.6657. The virulent strain can be prepared into inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine), the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into activated vaccine or inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine) and the like, so that porcine pseudorabies can be effectively prevented or cured, or the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into a diagnosis reagent for diagnosing the porcine pseudorabies. The gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ has the advantages of being good in safety, high in protection efficiency, beneficial to differential diagnosis.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus and application thereof as vaccine
ActiveCN110093324AGood immune protectionFull Poison Attack ProtectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverGenetic engineering
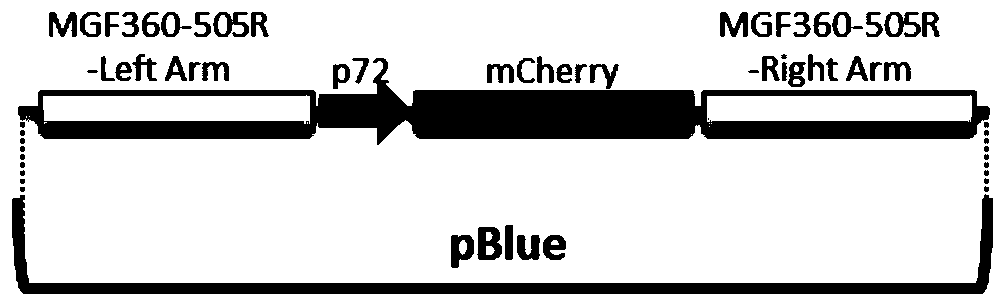
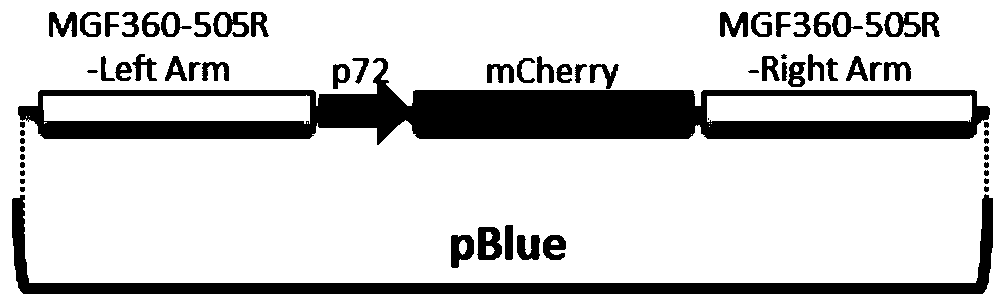
The invention relates to a gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus as a vaccine and the vaccine, and a construction method thereof. An African swine fever Chinese epidemic strain Pig / CN / HLJ / 2018 is adopted, a virulence gene of the African swine fever virus is deleted by a genetic engineering technology, and the gene deletion virus of MGF360-505R deletion and joint deletion of CD2V and MGF360-505R is obtained. Experiments show that the two virus strains can provide 100% immune protection against the African swine fever Chinese epidemic virulent strains, can be used as vaccines for safe and effective prevention and control of African swine fever in China, and have great social value.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
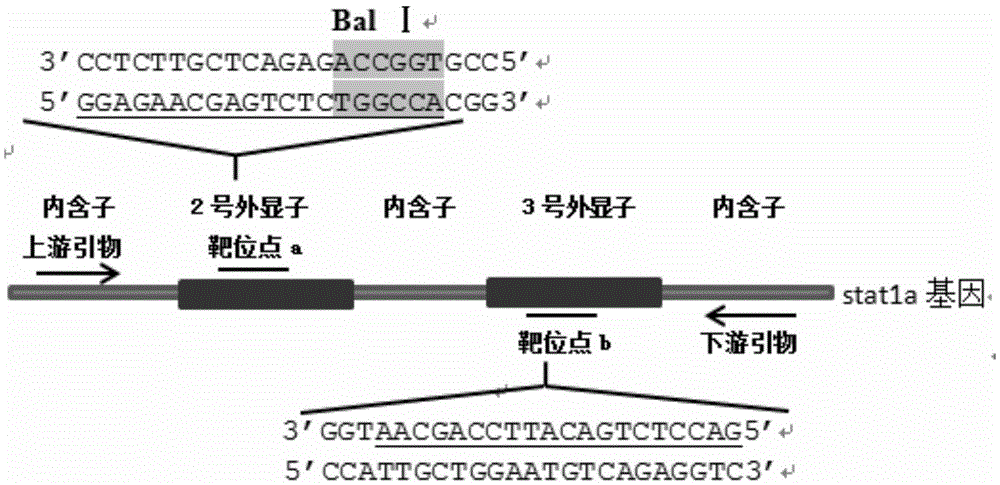
Statla gene deletion type zebra fish
InactiveCN105594664AInefficient shooting techniqueLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesFish embryoEmbryo
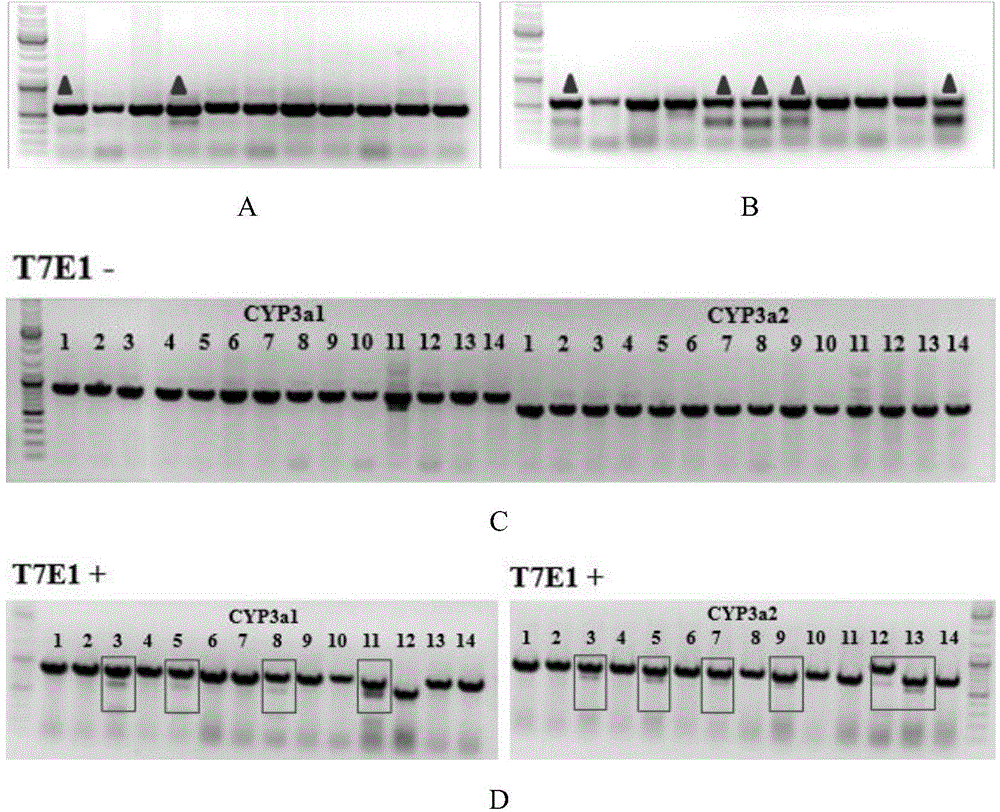
The invention provides statla gene deletion type zebra fish. After an experiment design region is knocked out, the sequence is represented as SEQ ID No.1; an experiment comprises the following steps: designing a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout target point: constructing a gRNA expression vector and synthesizing gRNA in vitro; carrying out micro-injection of zebra fish embryos; detecting the effectiveness of the target point by a T7E1 method and Sanger sequencing; two months after injection, carrying out tail shearing and identification and carrying out identification steps above; carrying out TA cloning of a target sequence; carrying out Sanger sequencing of plasmids; obtaining an F1 generation of descendible zebra fish mutants; obtaining F2 generation homozygotes of the zebra fish mutants; and carrying out F3 generation homozygous heredity of the gene deletion type zebra fish according to the method above to obtain a new zebra fish line.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
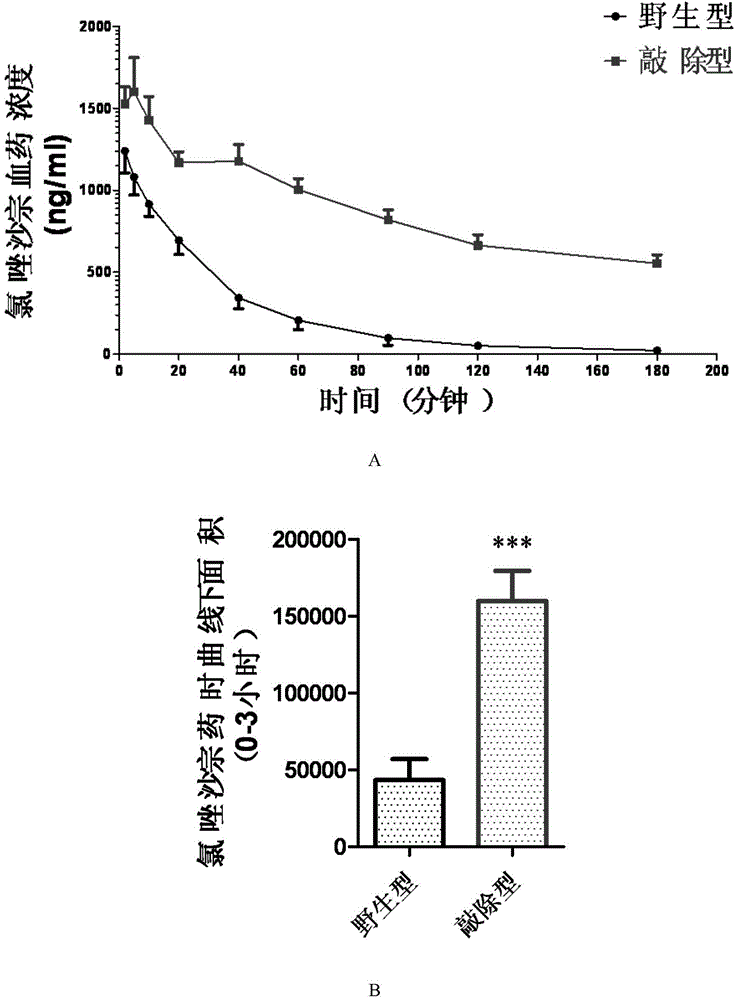
Cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and preparation method of liver microsome of the rats
ActiveCN106148416ADiverse in vitro modelsImprove transfer abilityMicroinjection basedFermentationHepaticaMicro injection
The invention provides a cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and a preparation method of liver microsome of the rats. The Cyp gene knock-out herein includes Cyp single gene knock-out and Cyp multiple gene knock-out. In the method, firstly a Cyp gene knocked-out rat is constructed by means of a CRISPR / Cas system, which includes selection of a knocked-out target site, in-vitro synthesis and transcription of sg RNA and Cas9m RNA, preparation of a pseudopregnant female rat, in-vitro micro-injection and transplanting of a single-cell embryo, and cultivation of the rat, and finally, a homozygote Cyp gene knocked-out rat can be cultured. Furthermore, the liver of the Cyp gene knocked-out rat is extracted and is subjected to homogenization and differential centrifugation to prepare the liver microsome of the rat in Cyp gene deletion. The invention also provides an application of the Cyp gene knocked-out rats and the liver microsome thereof in study on drug metabolism.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
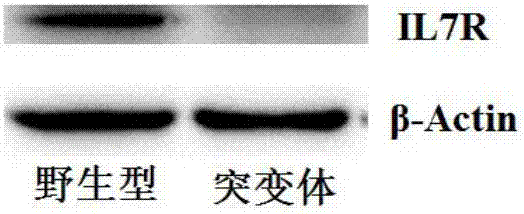
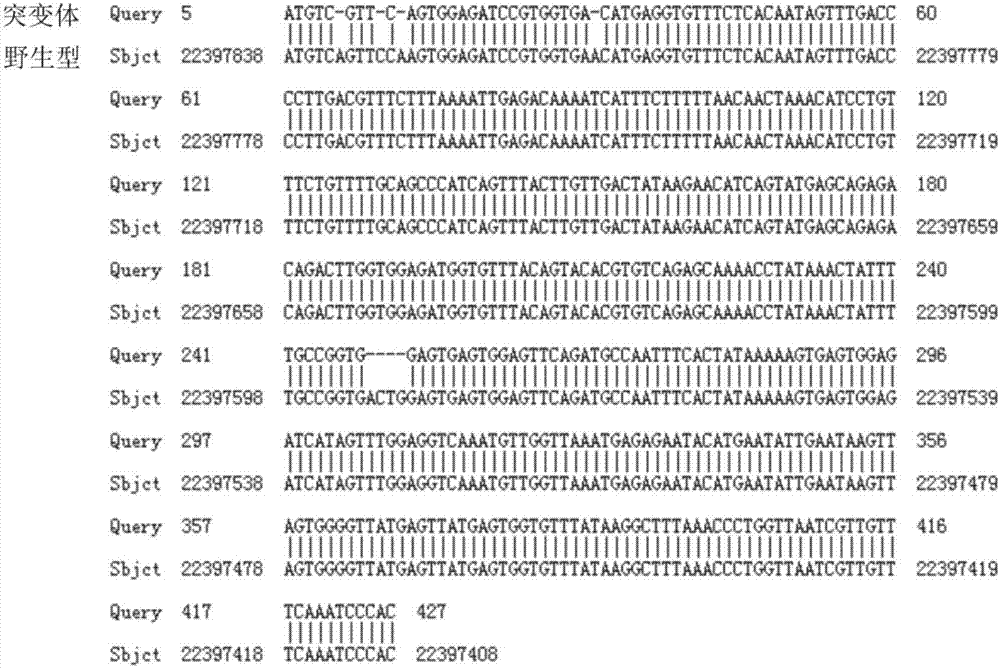
Preparation of IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107058320AConvenient for in vivo experimental researchGenetic stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesDeveloping nervous systemMutant
The invention discloses an IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant and a preparation method thereof. The construction of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant is realized through a CRISPR / Cas9 technology. Moreover, the invention also discloses application of the IL7R gene-deleted zebra fish mutant; a mutant model provided by the invention can be used for studying an effect of IL7R in the nervous system development and myelination.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
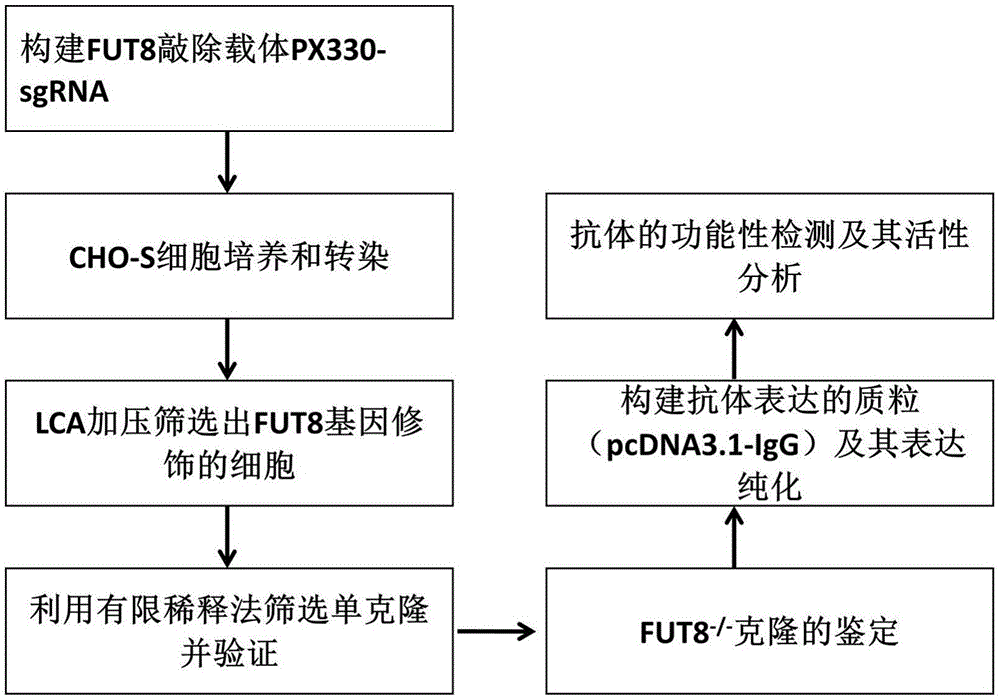
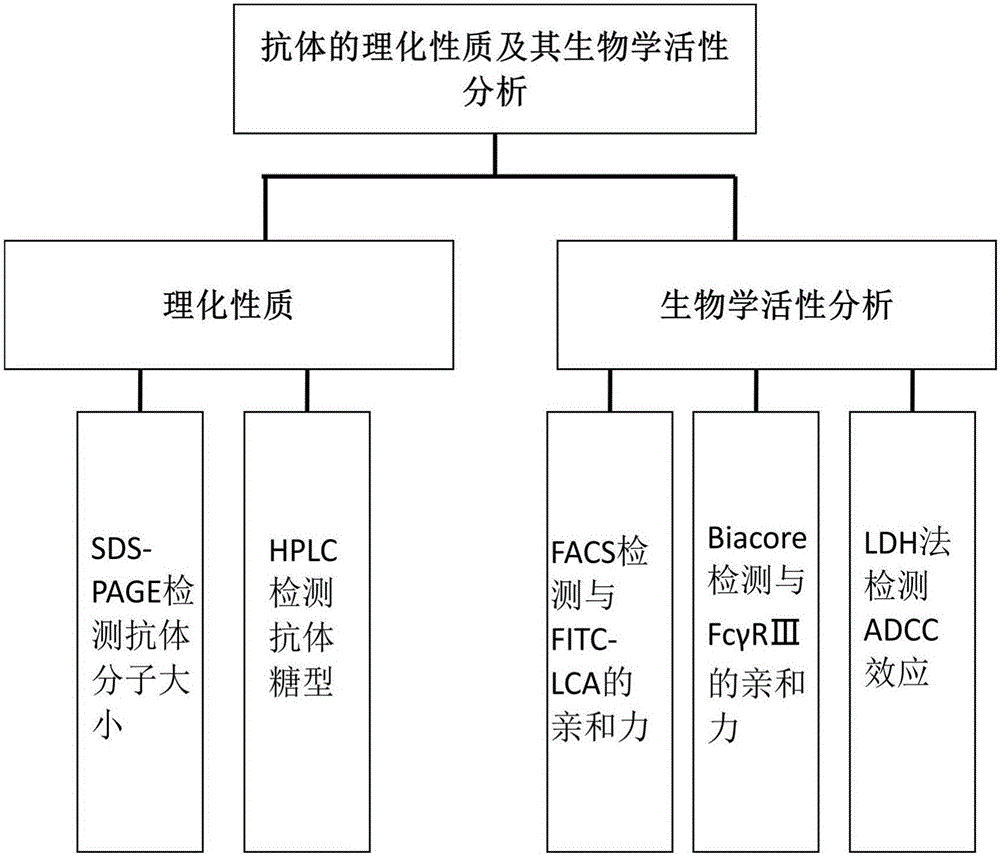
Establishment and application of CHO cell line for producing fucose-free monoclonal antibody
PendingCN106701823AEdit validSimple and fast operationNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsAntigenWild type
The invention discloses establishment and application of a CHO cell line for producing a fucose-free monoclonal antibody. A CRISPR / Cas9 technology is utilized to encode an FUT8 gene of a CHO cell to obtain the FUT8 gene silenced CHO cell line for stabilizing FUT8 gene deletion (hereinafter referred to as FUT8- / -cell line). By adopting physicochemical property and bioactivity detection of an FUT8- / -cell expressed antibody, a glycoform detection result indicates that fucose of the FUT8- / -cell expressed monoclonal antibody is completely eliminated, a fucose-containing monoclonal antibody expressed by a wild CHO cell serves as a contrast, the affinity with a Fcgamma RIIIa antigen of the fucose-free monoclonal antibody is improved by 7 times, and the ADCC effect is improved by 25 times.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
Four-gene-deletion weak-toxin strain for African swine fever viruses and application of four-gene-deletion weak-toxin strain
InactiveCN110551695AEasy to solveViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAfrican swine feverToxin
The invention discloses a four-gene-deletion weak-toxin strain for African swine fever viruses. The weak-toxin strain is the four-gene-deletion weak-toxin strain for an African swine fever virus SY18separation strain, and the following gene function protein is deleted: CD2v gene coding products and three multigene family genes( MGF360-12L, MGF360-13L and MGF360-14L ) coding products. The invention further discloses an application of the weak-toxin strain of the African swine fever viruses to preparation of vaccines for preventing or treating African swine fever. The weak-toxin strain of the African swine fever viruses can provide complete immunoprotection effect on attack of ASFV parent toxin strains, is high in safety, and is suitable for being used as vaccine candidate strains for preventing the African swine fever.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, vaccine composition, and preparation method and application of vaccine composition
ActiveCN103923884ASymptoms relieved or improvedMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsVirus antigenTGE VACCINE
The invention provides a porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain, a vaccine composition, and a preparation method and an application of the vaccine composition. The vaccine composition comprises an immunizing dose of an attenuated livetotivirus antigen and an inactivated totivirus antigen of the porcine pseudorabies virus gene deletion strain or its culture. The vaccine composition can effectively induce the antibody production, can effectively protect pigs, and can be used as a marking vaccine to effectively differentiate wild strains and vaccine strains.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
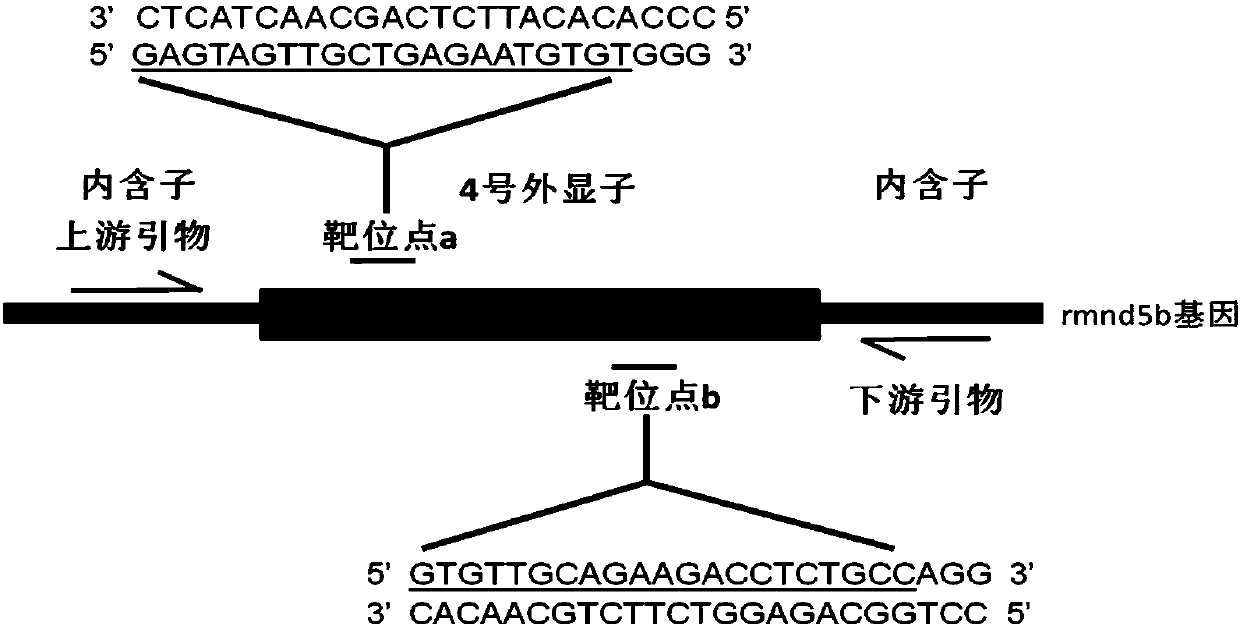
Method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN108018316AEasy to makeLow miss rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMeiotic nuclear divisionEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout and belongs to the field of gene knockout. According to the method, construction of a gRNA expression vector and gRNA in-vitro synthesis are performed through design of a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated 9) gene knockout target site, micro-injection is performed on an embryo of the zebra fish, the effectiveness of the target site is detected, tail cutting identification is performed, TA cloning is performed on a target sequence, plasmids are subjected to Sanger sequencing, an F1 generation of heritable zebra fish mutants is obtained, the same mutant female fish and male fish are picked from mutants of the F1 generation, hybridization is performed, an F2 generation of the zebra fish mutants is obtained, F2 generation homozygote is picked from the F2 generation of the zebra fishmutants, F3 generation pure-line inheritance is performed, and an rmnd5b gene deletion type zebra fish strain is obtained. The method is lower in off-target rate and has good medical research value inresearch of the correlation between rmnd5b gene deletion and development of other organs.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) systems and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7583379B2Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyOblique angle
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) systems and methods for detecting biomolecules of interest, such as a virus, bacterium, or other infectious agent, are provided. A spectroscopic assay based on surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) using a silver nanorod array substrate fabricated by oblique angle deposition has been developed that allows for rapid detection of trace levels of viruses or bacteria with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity. This novel and improved SERS assay can detect minor spectral differences within strains of a single virus type such as respiratory syncytial virus or influenza virus in the presence of biological media. The method provides rapid diagnostics for direct molecular and structural characterization of virus strains and virus gene deletion mutants generating reproducible viral spectra without viral manipulation.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
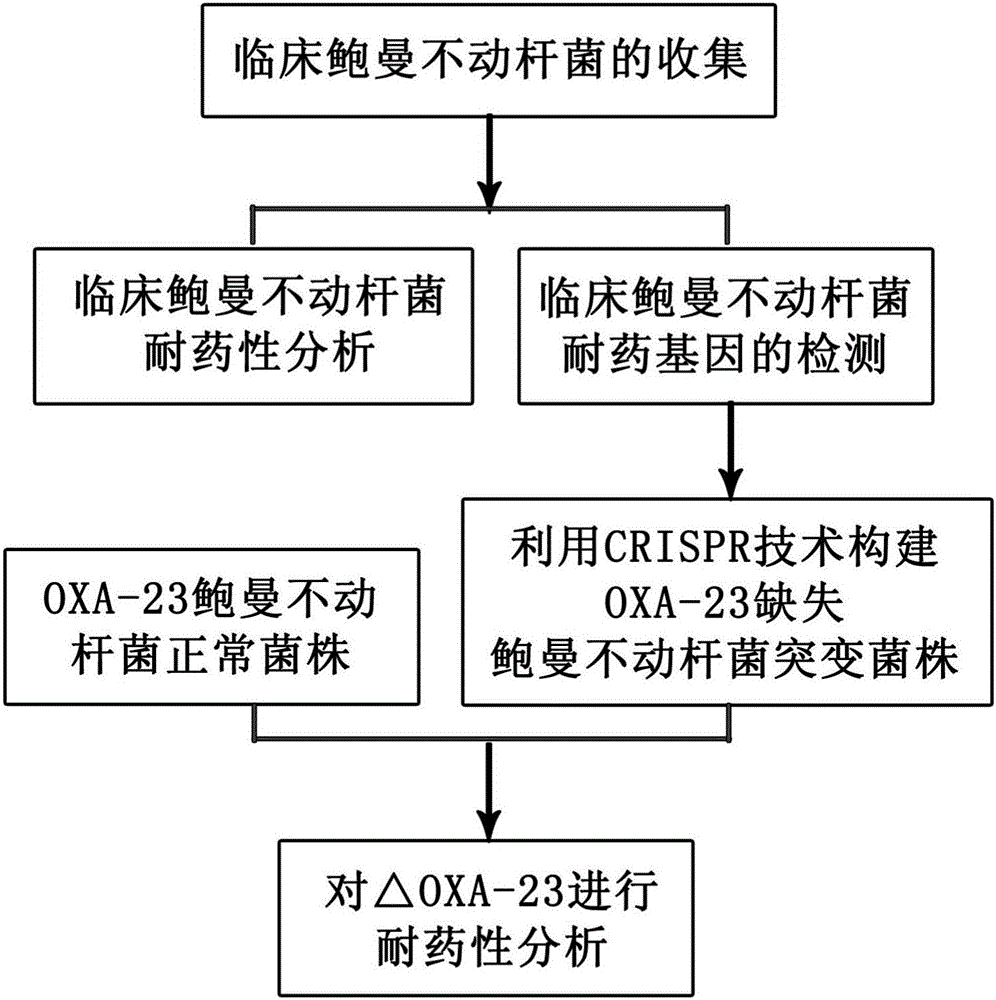
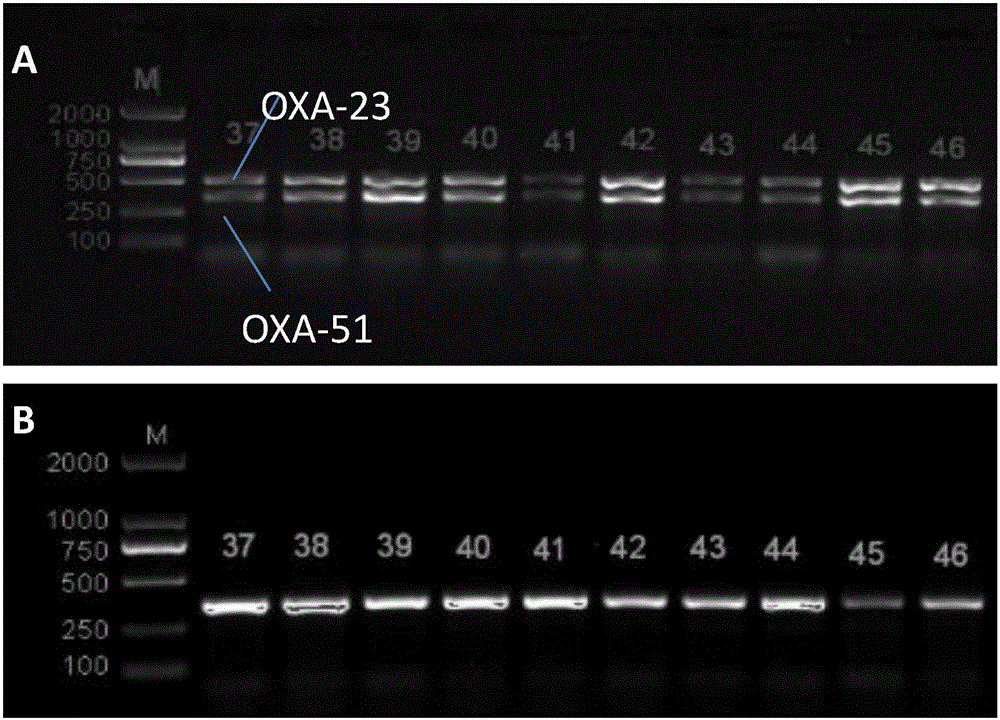
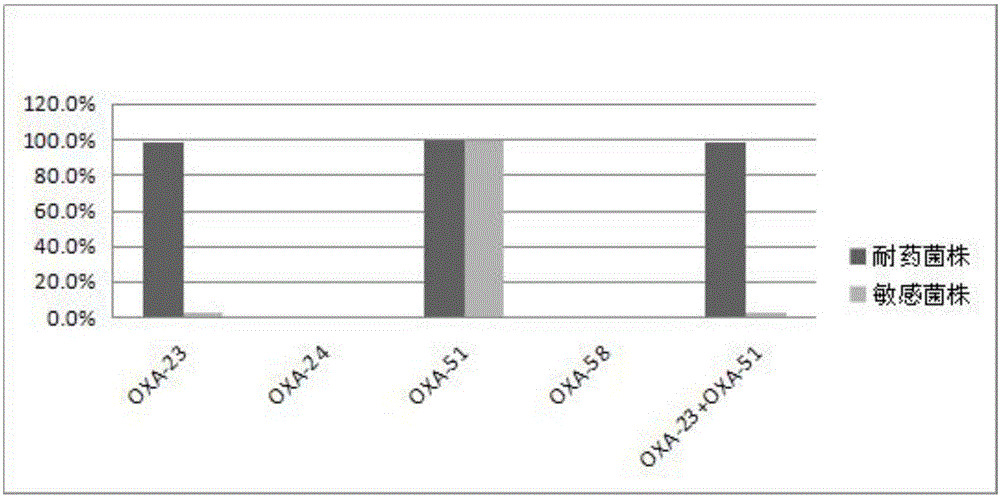
Method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN106544353ASensitivity reversalEasy to operateVectorsMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMulti drug resistant
The invention discloses a method for deleting drug resistant genes of acinetobacter baumannii (AB) through CRISPR-Cas9. The method comprises the steps that firstly, AB is collected clinically, and drug resistance analysis and statistics are conducted after the AB is subjected to drug resistance measurement through a drug sensitive slip method; secondly, the multi-drug resistant AB is subjected to DNA extraction through a lysis-boiling method, and then amplification analysis is conducted by mean of well designed drug resistant gene primers of the AB; and thirdly, according to drug resistant gene detection in the former step, the AB containing an OXA-23 gene is selected, CRISPR / Cas9 and sgRNA plasmids are established and transferred into the AB containing the OXA-23 gene, an OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain is established, and drug resistance analysis is conducted on the OXA-23 gene deletion AB mutant strain. The method is easy to operate and high in knocking-out efficiency, and a novel method and a novel concept are provided for preventing spreading of the drug resistant genes and treating drug resistant bacteria.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Goat TLR4 gene knock-out vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106755097AThe method is simple and fastHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention discloses a goat TLR4 gene knock-out vector and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, designing an sgRNA fragment of the TLR4 gene by adopting a CRISPR / cas9 system, synthesizing an sgRNA nucleotide sequence, constructing and simultaneously expressing the sgRNA and plasmid PYSY-sgRNA of Cas9 D10A, connecting and transforming to an Escherichia coli DH5 alpha competent cell, and verifying the transformant; and judging and proving by enzyme digestion and sequencing that the TLR4 gene knock-out vector is constructed correctly. The invention adopts the CRISPR / cas9 for constructing the vector, and provides a theoretical basis for subsequently acquiring a goat TLR4 gene deletion type alveolar epithelial cell system, and studying the immune response molecular mechanism of mycoplasma pneumonia infection.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
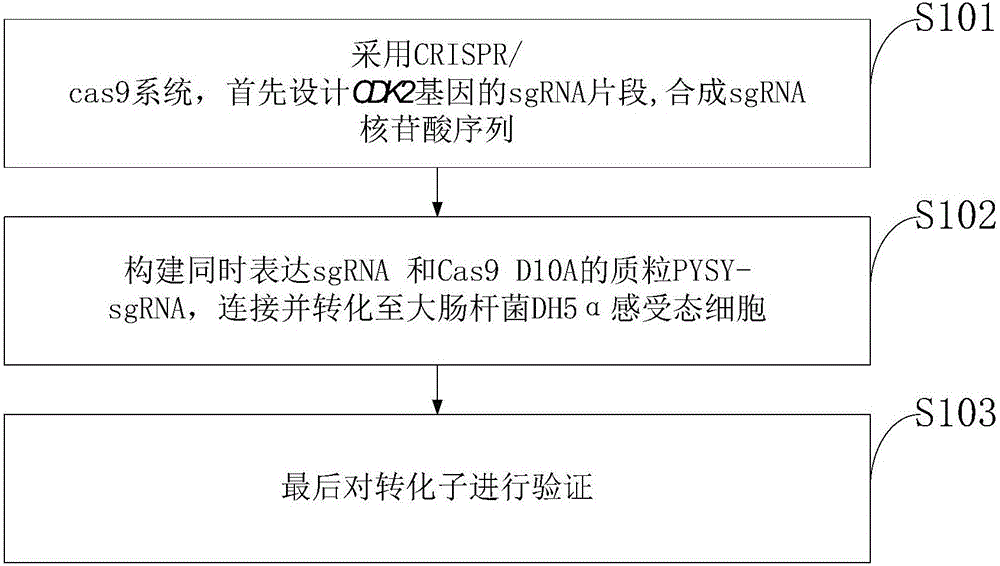
Goat CDK2 (Cyclin-dependent kinases 2) gene knockout vector and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106834347AThe method is simple and fastHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a goat CDK2 (Cyclin-dependent kinases 2) gene knockout vector and a construction method thereof. A CRISPR / Cas9 system is adopted; an SgRNA segment of a CDK2 gene is designed at first and an SgRNA nucleotide sequence is synthesized; a plasmid PYSY-sgRNA for expressing SgRNA and Cas9D10A at the same time is constructed; the plasmid PYSY-sgRNA is connected and transformed to an escherichia coli DH5alpha competent cell; finally, a transformant is verified; restriction enzyme digestion and sequencing identification prove that the construction of the CDK2 gene knockout vector is accurate. The vector constructed by CRISPR / Cas9 is adopted, and a theoretical basis is provided for subsequently obtaining a goat CDK2 gene deletion type cell line and researching a molecular mechanism of cell apoptosis molecules triggered by mycoplasma pneumonia infection.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
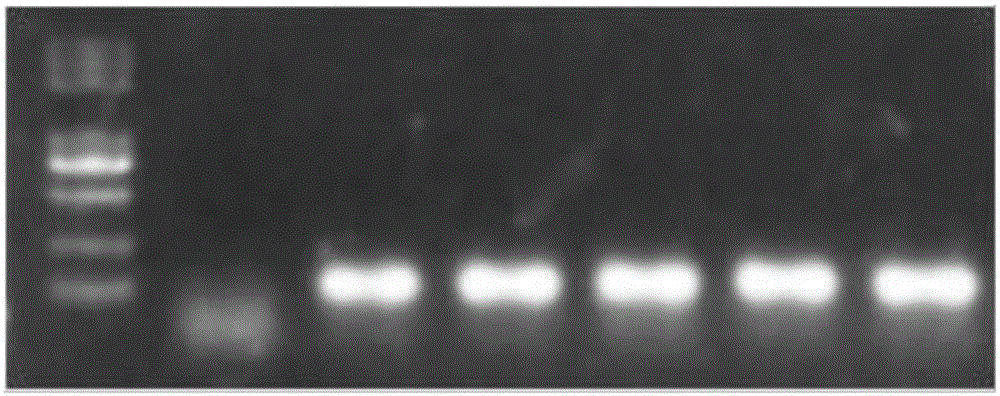
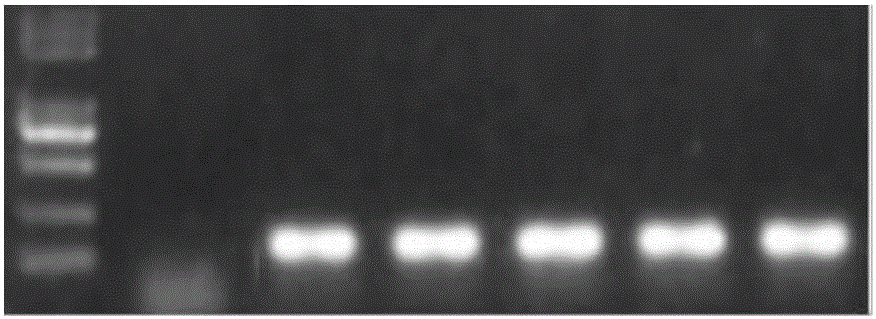
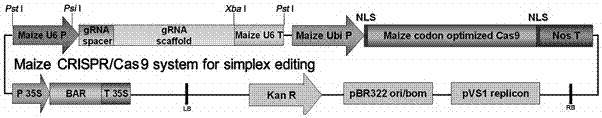
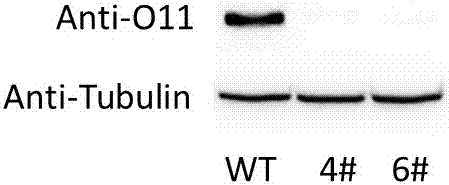
Corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and application thereof
The invention relates to a corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and an application of the corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167. A base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO (sequence identifier number): 1. A corn immature embryo is transformed by taking a gene segment SEQ ID NO: 2 of the sequential coding protein ZmbHLH167 as guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) by use of a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 technology, and a plant of a gene deletion mutant is obtained. Compared with a wild seed, a corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is smaller significantly, but a germination rate is not influenced. Biochemical analysis shows that a starch content of the corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is decreased obviously, a content of protein and total oil and fat is significantly increased, and a genetic resource is provided for creating high quality corn.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Pseudo-rabies gE/gI-gene loss poison strain, killed vaccine containing it and use
ActiveCN1940063AStrong targetingFacilitate chemical processingViral antigen ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesRabiesPseudorabies Virus PRV
A recombinant Pseudorabies virus PrV gene engineering strain WKQ-001, inactivated vaccine containing the poisonous strain and its use are disclosed. It can be used to discriminate and diagnose artificial immunity pig or natural infectious pig. It's safe and doesn't contain exogenous gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
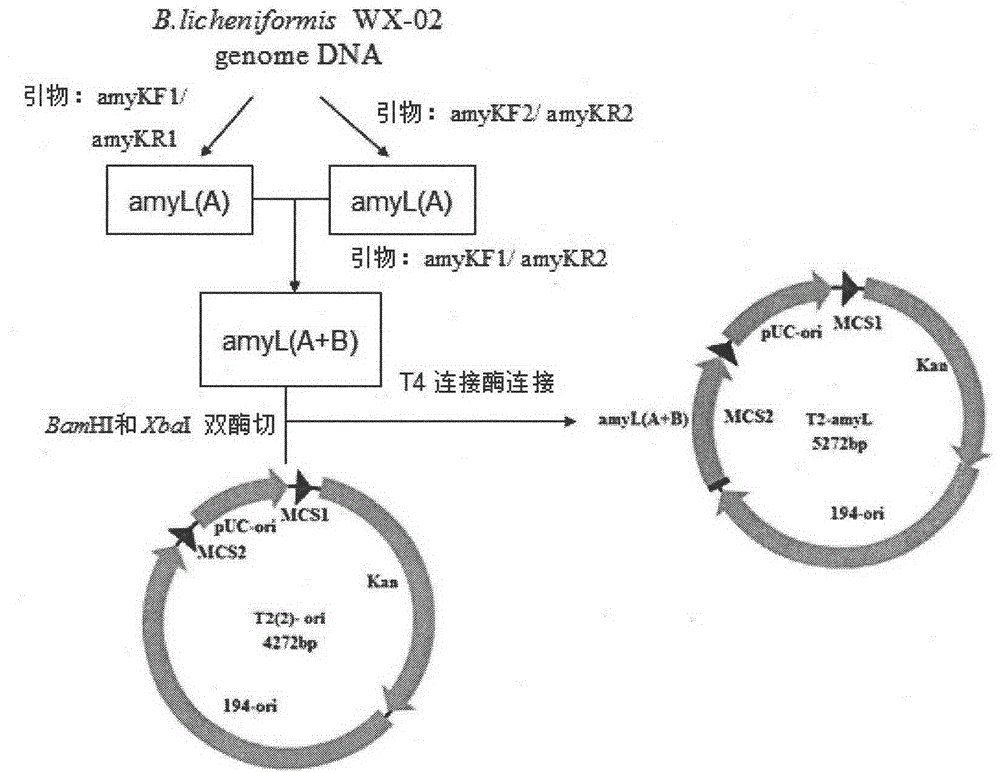
Bacillus licheniformis expression host
ActiveCN104630123AReduced activityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisProtein target
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis host bacterium BL10 with multiple gene deletion, the accession number of which is CCTCCNO:M2013400. The host bacterium derives from a bacillus licheniformis WX-02 which partially or completely has deletion of ten genes. The ten genes comprises eight protease genes (mpr encoding a metalloprotease; vpr encoding a serine protease; aprX encoding an intracellular serine protease; epr encoding a minimal extracellular protease; bpr encoding a bacillus peptidase F; wprA encoding a protease combined with cell walls; aprE encoding an extracellular alkaline serine protease; and bprA encoding a bacillus peptidase F) and two extracellular secretory protein genes (hag encoding flagellin; and amyL encoding alpha-amylase). The BL10 has completely no extracellular protease activity and can reduce the degradation effect of a protease on a target protein. When the target protein is expressed by the expression host, the expression level is higher, and the host bacterium benefits protein expression enhancement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method and application for improving application efficiency of gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus
ActiveCN104894165AHigh gene targeting efficiencyHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBinding siteLIG4
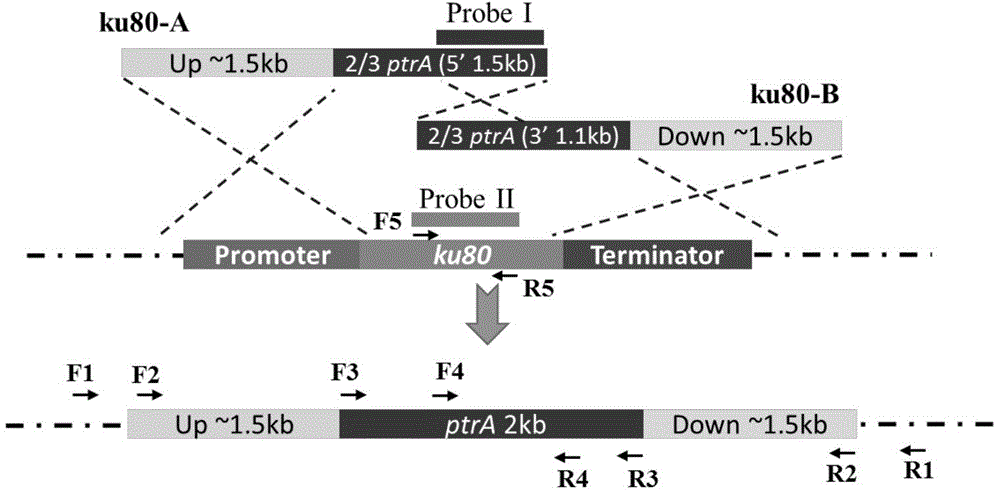
The invention discloses a method and application for improving application efficiency of a gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking Aspergillus terreus as an initial bacterium, knocking off a ku80 gene or an lig4 gene so as to increase the exogenous DNA homologous recombination probability of a strain; secondly, establishing a pyrG gene deletion uracil auxotroph stain, establishing a inheritance conversion system based on a pyrG gene as a screening tag; and finally, cutting off the screening tag by using a Cre / LoxP specific binding site recombinant system, thereby obtaining a uracil auxotroph stain which can be applied to genetic modification again. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, an efficient aspergillus terreus gene targeting platform can be established, the method has the advantages that high homologous recombination efficiency can be achieved, the bidirectional screening of the conversion system can be achieved, a screening tag cutting method is simple and feasible, the screening tag can be recycled, and the like, and basic support can be provided for efficient genetic modification of aspergillus terreus by using the gene targeting technique.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Biological product for preventing novel coronavirus
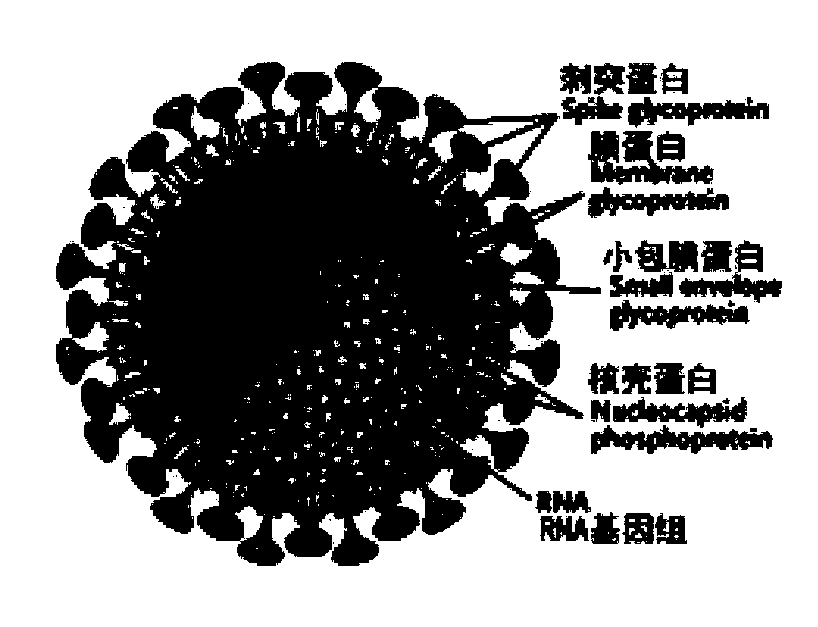
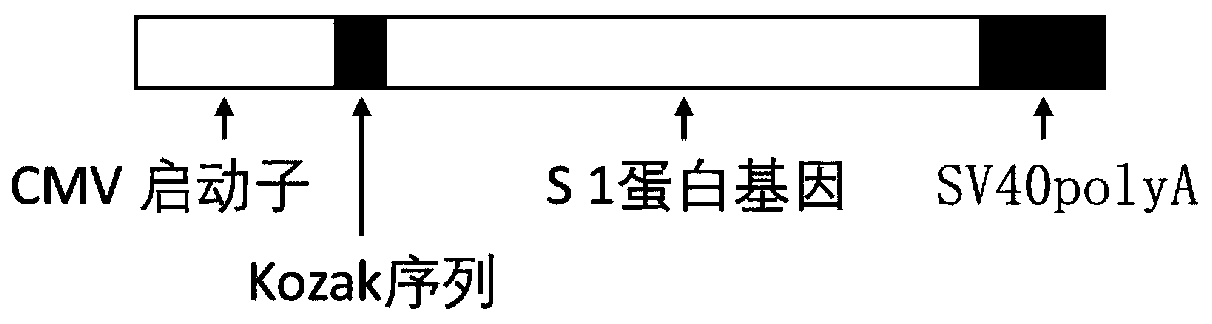
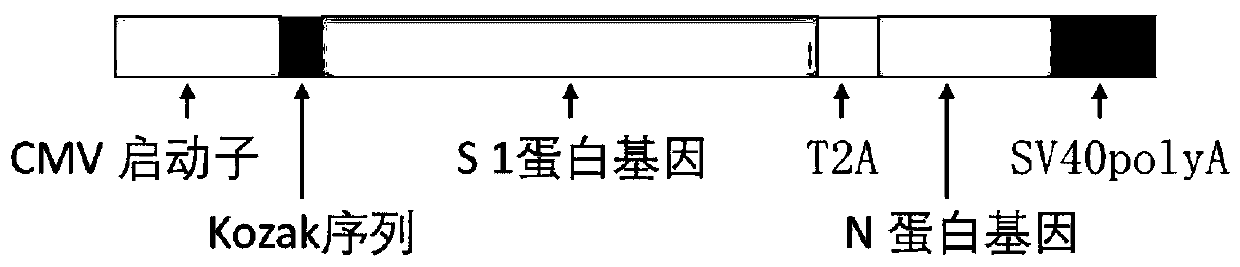
InactiveCN111228475ASsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsGenetic vaccineProtein antigen
The invention discloses a biological product for preventing novel coronavirus (COVID-19). The biological product can be a gene vaccine or gene medicine, wherein the gene vaccine adopts a human type-5adenovirus with deletion of E1 and E3 genes as a vector for carrying an S1 protein antigen for expressing a Spike S1 subunit of the novel coronaviruses or simultaneously carrying an S1 expression protein antigen and N protein antigen. Through in-vivo expression of antigen proteins, the immune reaction of a body upon the novel coronavirus can be stimulated, and the effect of preventing infection and propagation of the novel coronavirus.
Owner:SYNO SHENZHEN BIOMEDICAL RES CO LTD
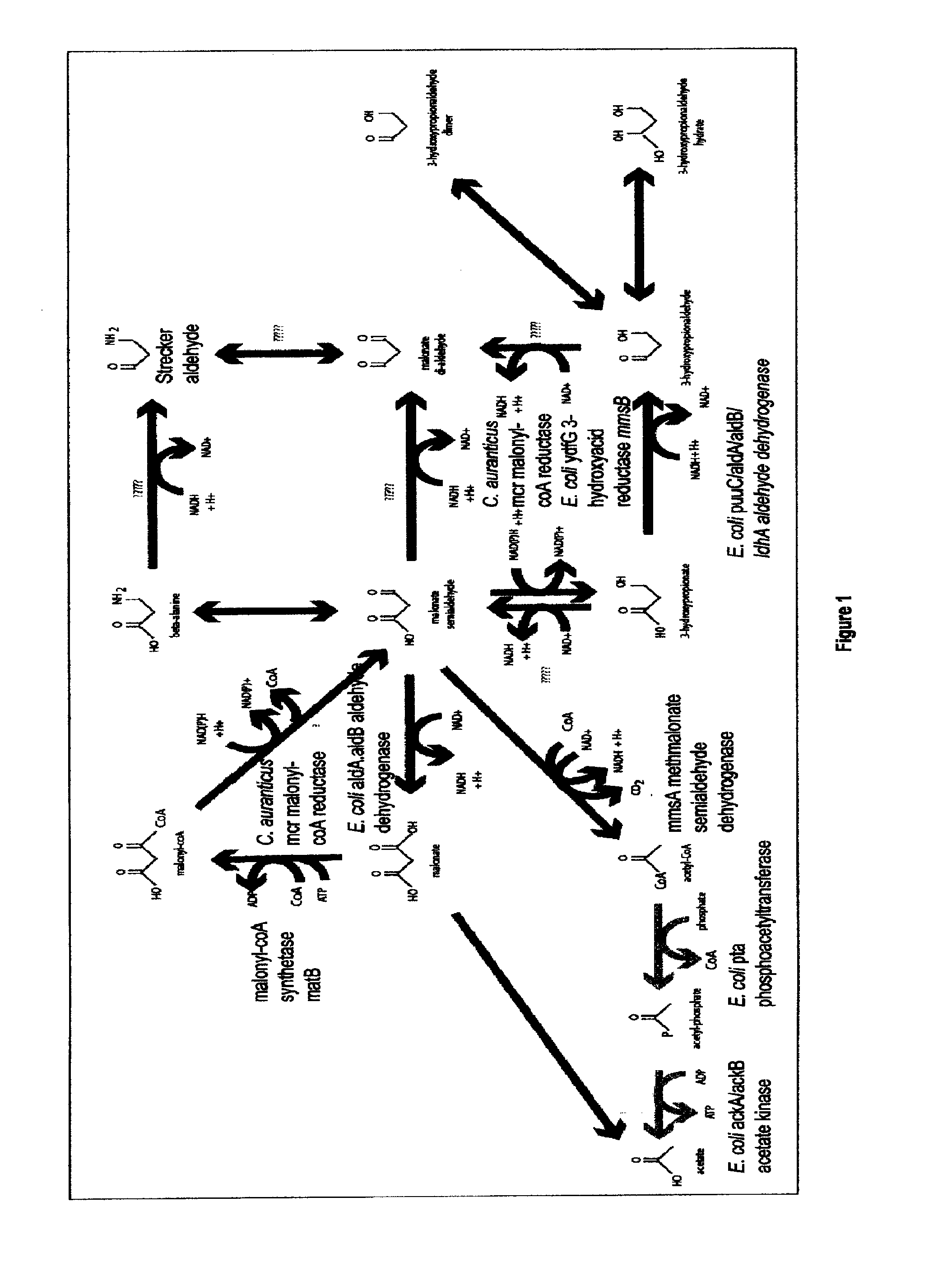
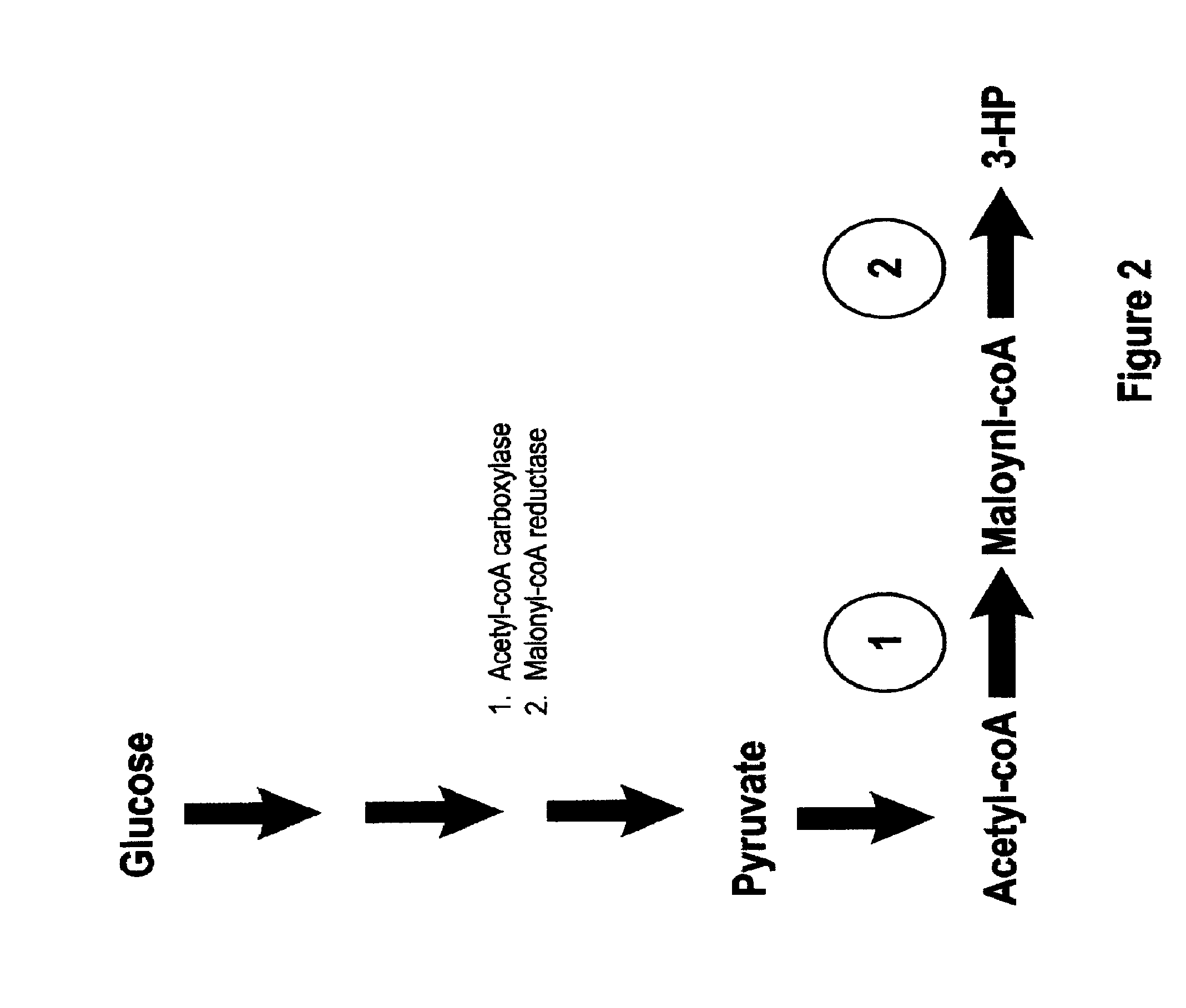
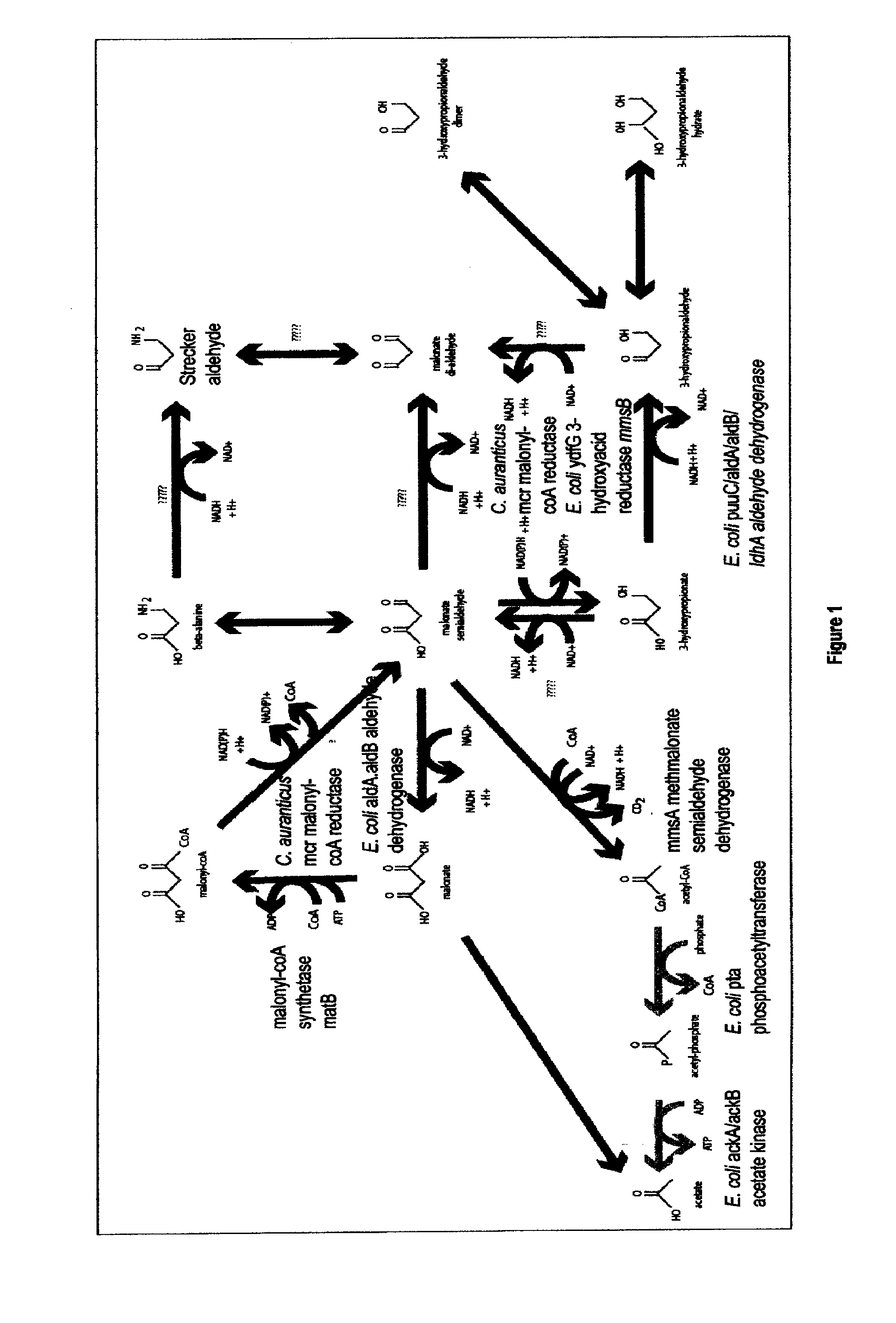
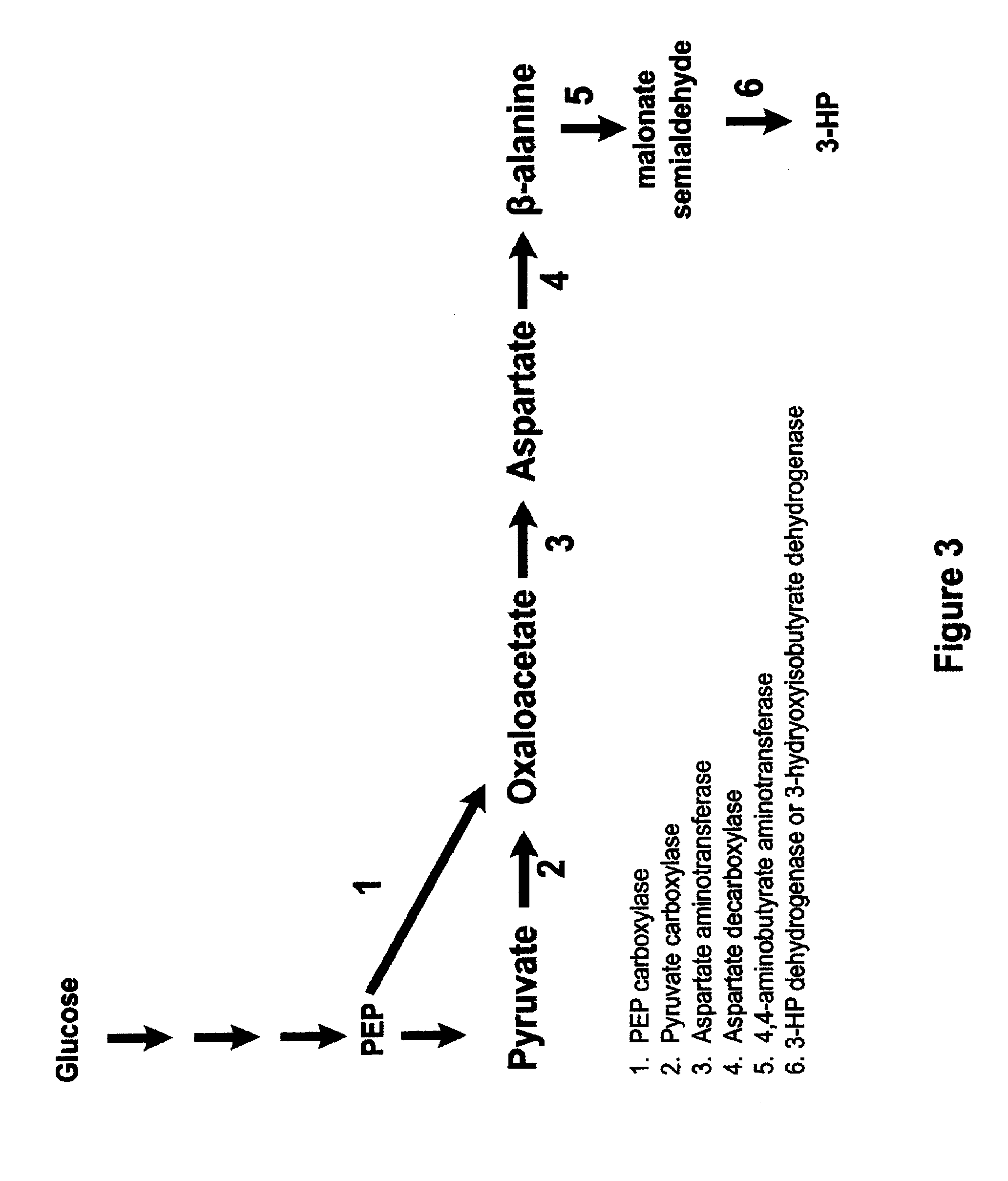
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
Owner:CARGILL INC
Double genes knockout Listeria monocytogenes attenuation mutant and constructing method
InactiveCN101139567AAchieve attenuationLow toxicityBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyBacterial strain
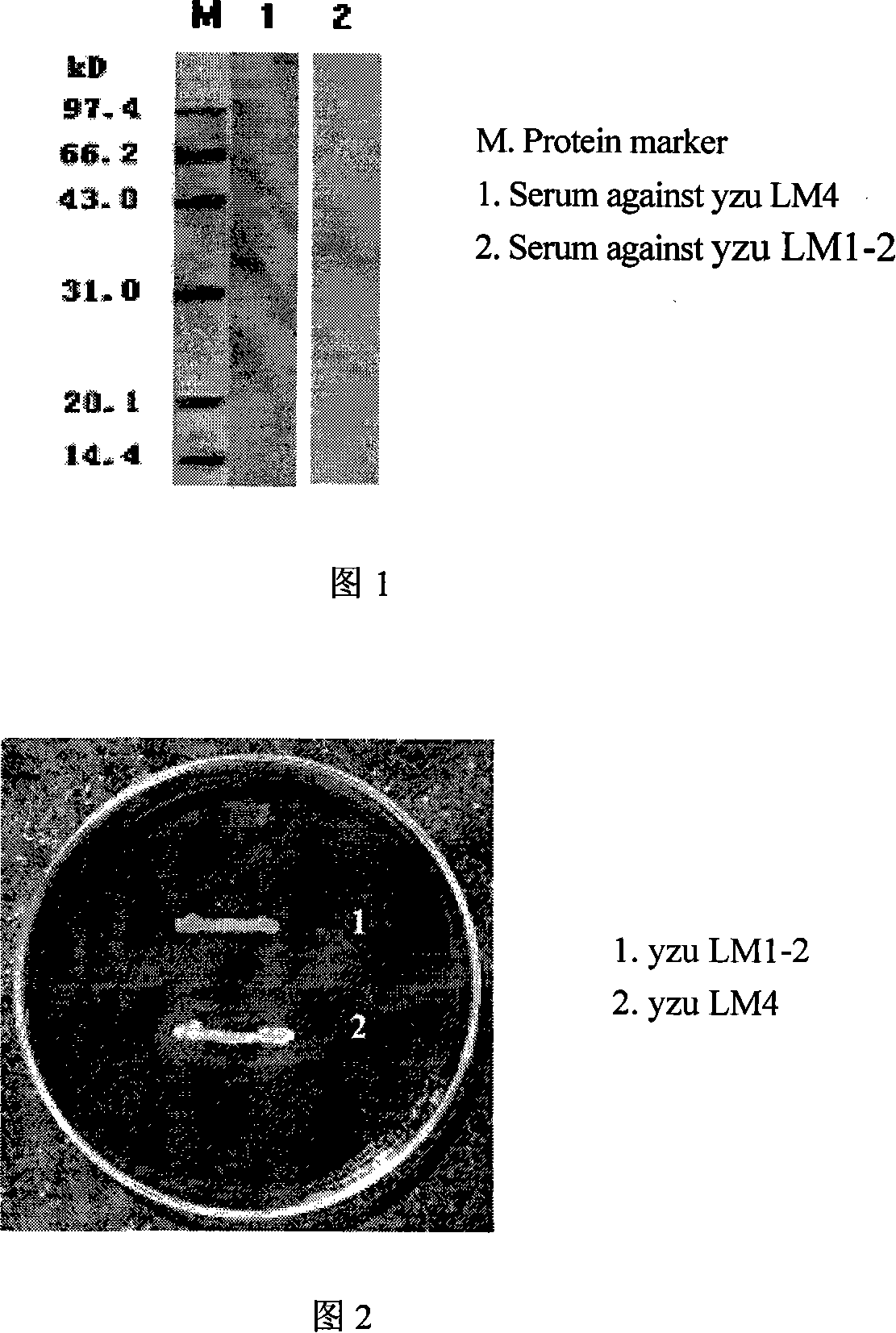
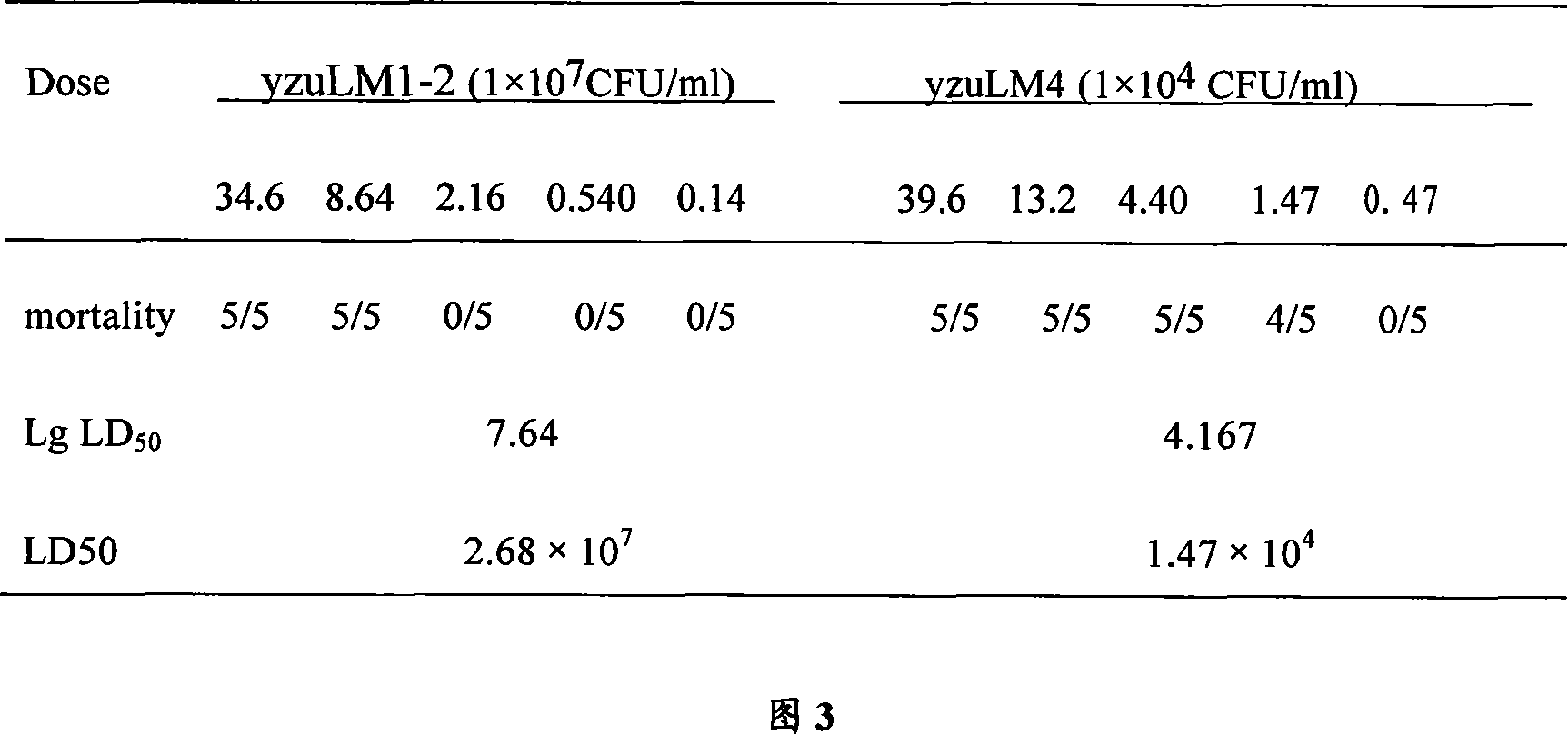
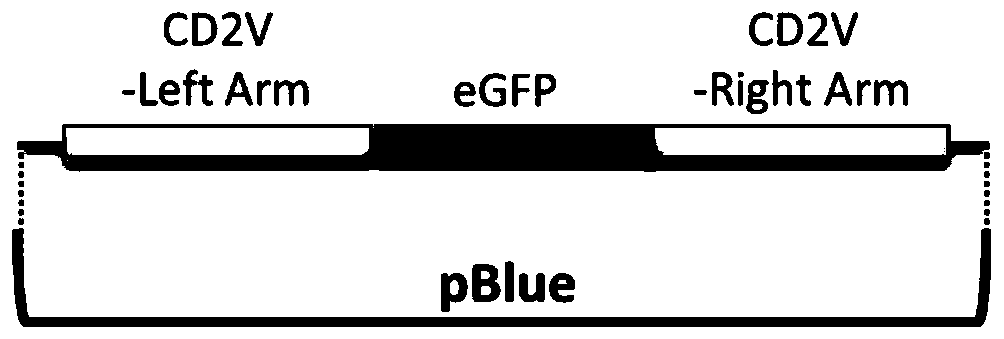
The invention relates to a construction way for toxic gene deletion of a wild Listeria monocytogenes (short as LM). After expanding homogenetic sectionsactA and plcB at two wings of the genes to be deleted, the actA and plcB are spliced by SOEing PCR method, inserted into a penetrating carrier pKSV7, introduced by electric transferring into Listeria monocytogenes, so as to get Listeria monocytogenes yzu LM1-2 with actA and pclB deleted, the preservation no. for the Listeria monocytogenes yzu LM1-2 is CCTCC NO: M206107. The invention solves the pathogen for human being and animals of Listeria monocytogenes, high death rate and pollution and harm of LM on food. The invention deletes actA and plcB, hence reduces the toxicity of the wild bacterial strain yzu LM4.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Attenuated African swine fever virus with gene deletion and its application as a vaccine
ActiveCN110093324BGood immune protectionFull Poison Attack ProtectionViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAfrican swine feverGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a gene deletion attenuated African swine fever virus as a vaccine and the vaccine, and a construction method thereof. An African swine fever Chinese epidemic strain Pig / CN / HLJ / 2018 is adopted, a virulence gene of the African swine fever virus is deleted by a genetic engineering technology, and the gene deletion virus of MGF360-505R deletion and joint deletion of CD2V and MGF360-505R is obtained. Experiments show that the two virus strains can provide 100% immune protection against the African swine fever Chinese epidemic virulent strains, can be used as vaccines for safe and effective prevention and control of African swine fever in China, and have great social value.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxyproplonic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
InactiveUS20130189787A1Lower metabolismDecrease microbial enzymatic conversionBacteriaUnicellular algaeEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, directed to achieve decreased microbial conversion of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) to aldehydes of 3-HP. In various embodiments this is achieved by disruption of particular aldehyde dehydrogenase genes, including multiple gene deletions. Among the specific nucleic acids that are deleted whereby the desired decreased conversion is achieved are aldA, aldB, puuC), and usg of E. coli. Genetically modified microorganisms so modified are adapted to produce 3-HP, such as by approaches described herein.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
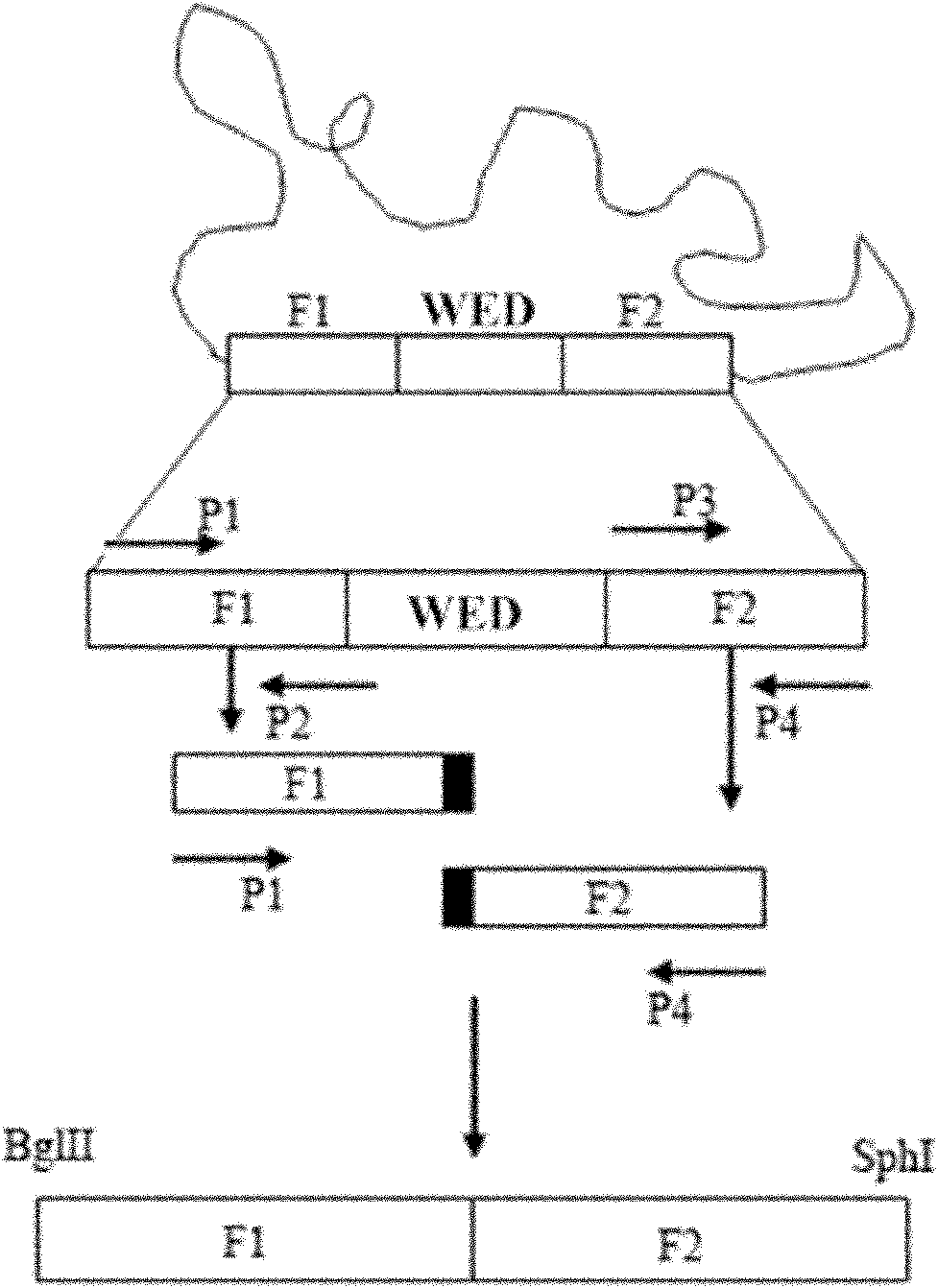
Marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of Edwardsiella tarda wild strain as well as relevant preparations and application thereof
ActiveCN101974472AGood control effectImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsChorismic acidAttenuated Live Vaccine
The invention relates to a marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of an Edwardsiella tarda wild strain. The marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain is an attenuated live vaccine of an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, which deletes the chorismic acid synthase gene aroC of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain, three types of secretion system response element genes of eseB, escA, eseC and eseD and an endogenous plasmid, preferably, the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain EIB202 with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M208068; the endogenous plasmid is a plasmid of pEIB202; and the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain of the Edwardsiella tarda virulent strain is an attenuated strain WED with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M2010278. The invention also provides relevant preparations and application of the marker-free gene deletion attenuated mutant strain. The attenuated mutant strain or relevant preparations eliminate the potential environment and safety risk of products existing in the traditional attenuated live vaccines generally and is a safe, effective and economic vaccine aiming at Edwardsiella tarda diseases of cultured fishes.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
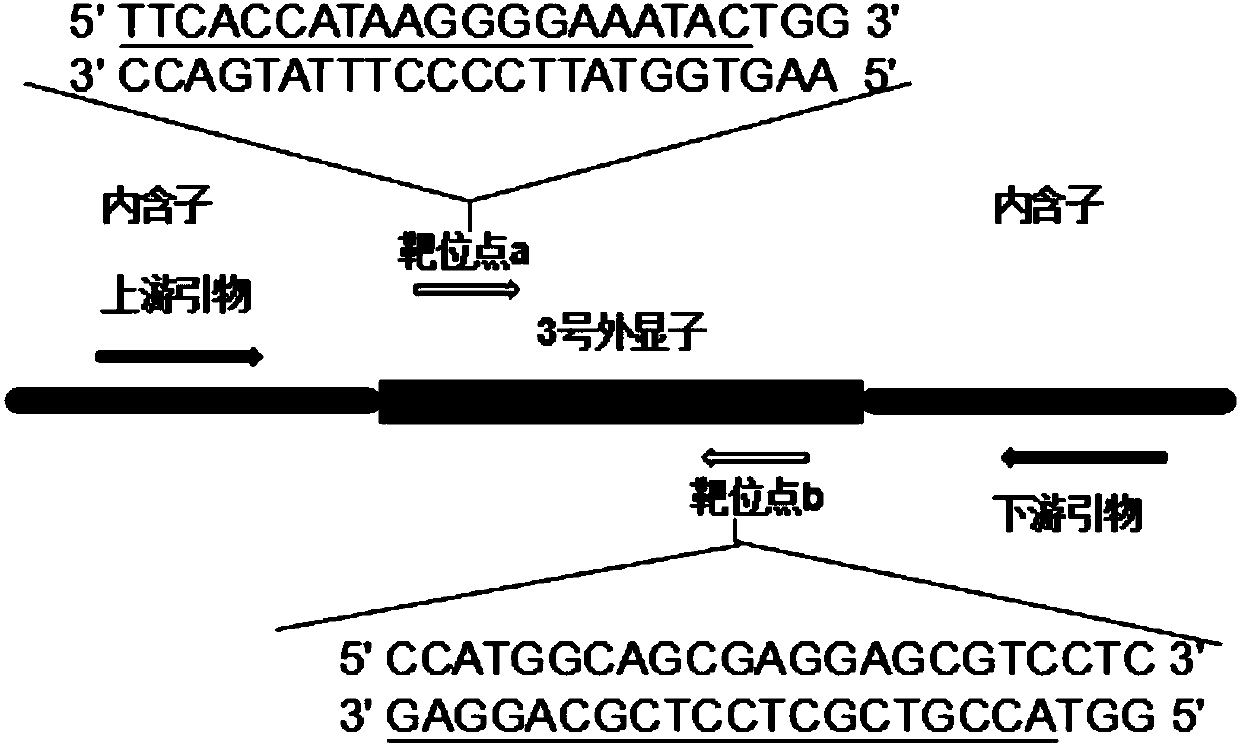
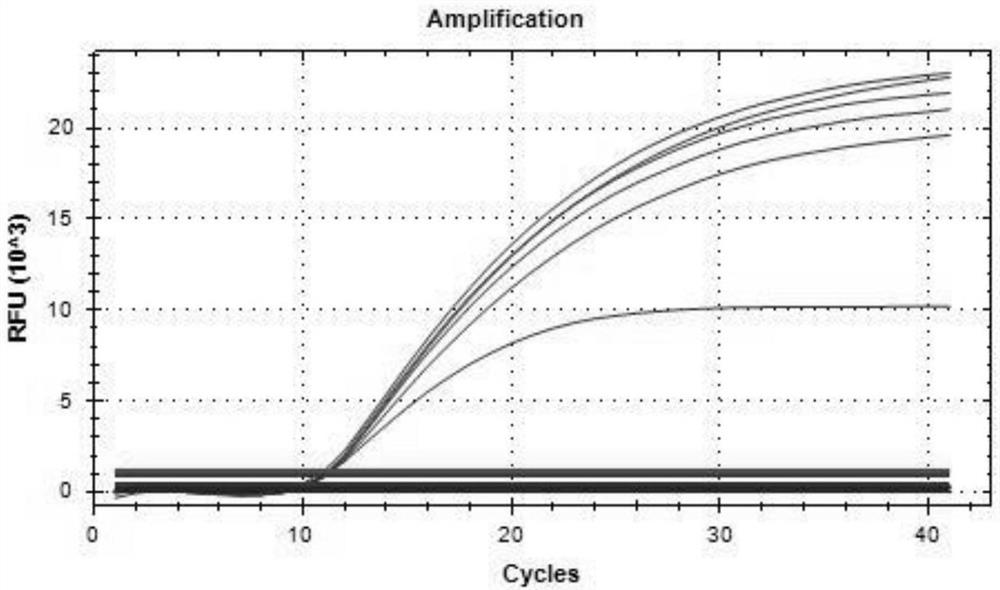
Triple real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR kit for detecting African swine fever wild strains and gene deletion strain
InactiveCN111020062AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationClassical swine fever virus CSFVAfrican swine fever
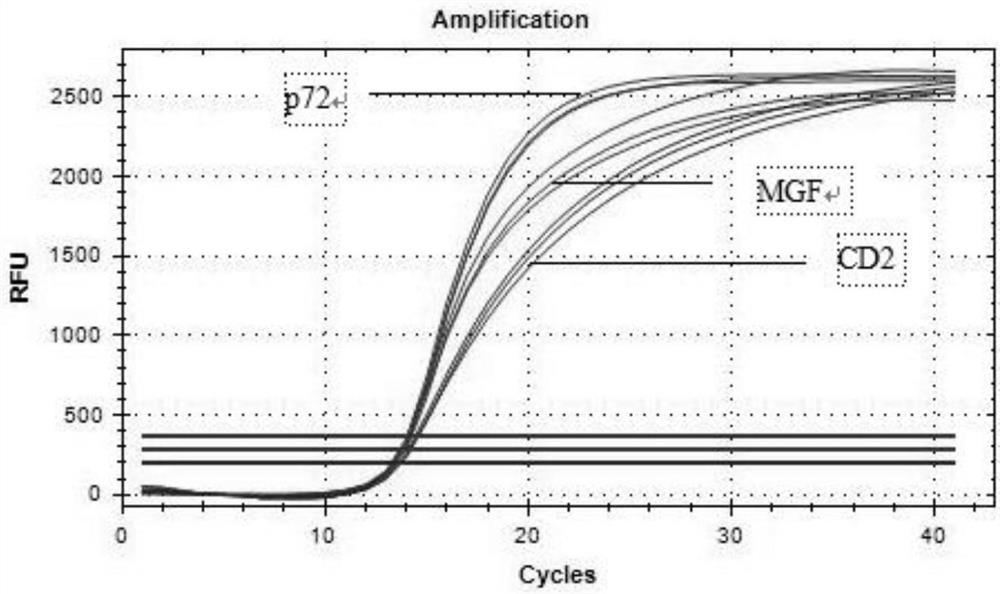
The invention provides a triple real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection primer for detecting an African swine fever wild strain and a gene deletion strain, and a kit and a detection method thereof. The triple fluorescent quantitative detection kit is developed and researched for three genes CD2V, VP72 and MGF-360 14L of the African swine fever virus by utilizing a multiple fluorescent PCRtest means, and whether a sample is infected with the African swine fever virus and whether gene deletion exists in the infected virus or not can be determined at the same time. The method can detecta large number of samples at the same time, provides an effective tool for scientifically and reasonably preventing and controlling African swine fever, guarantees the healthy development of the pigindustry, and has the advantages of convenience in operation, high sensitivity, strong specificity, short detection time and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
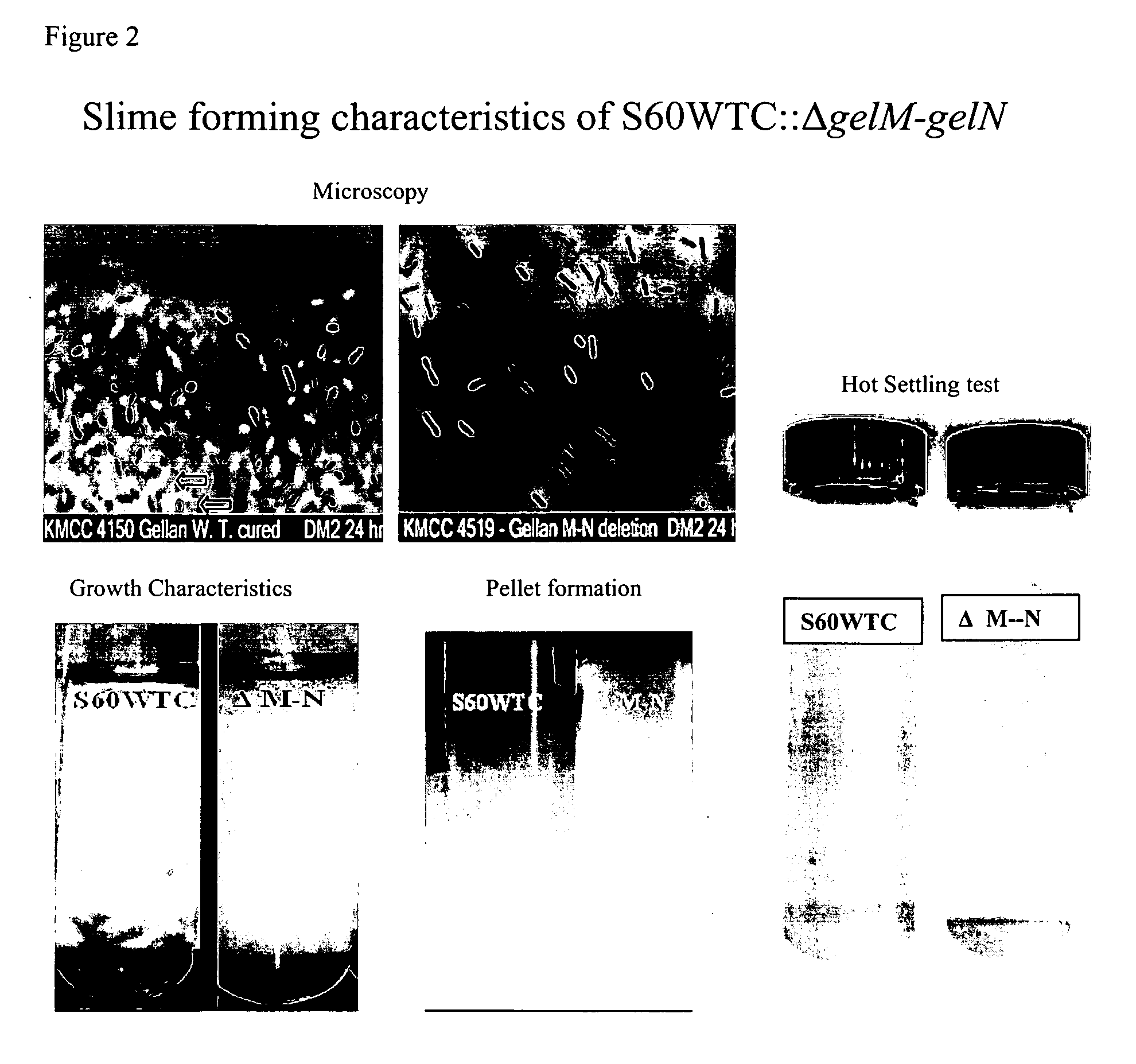
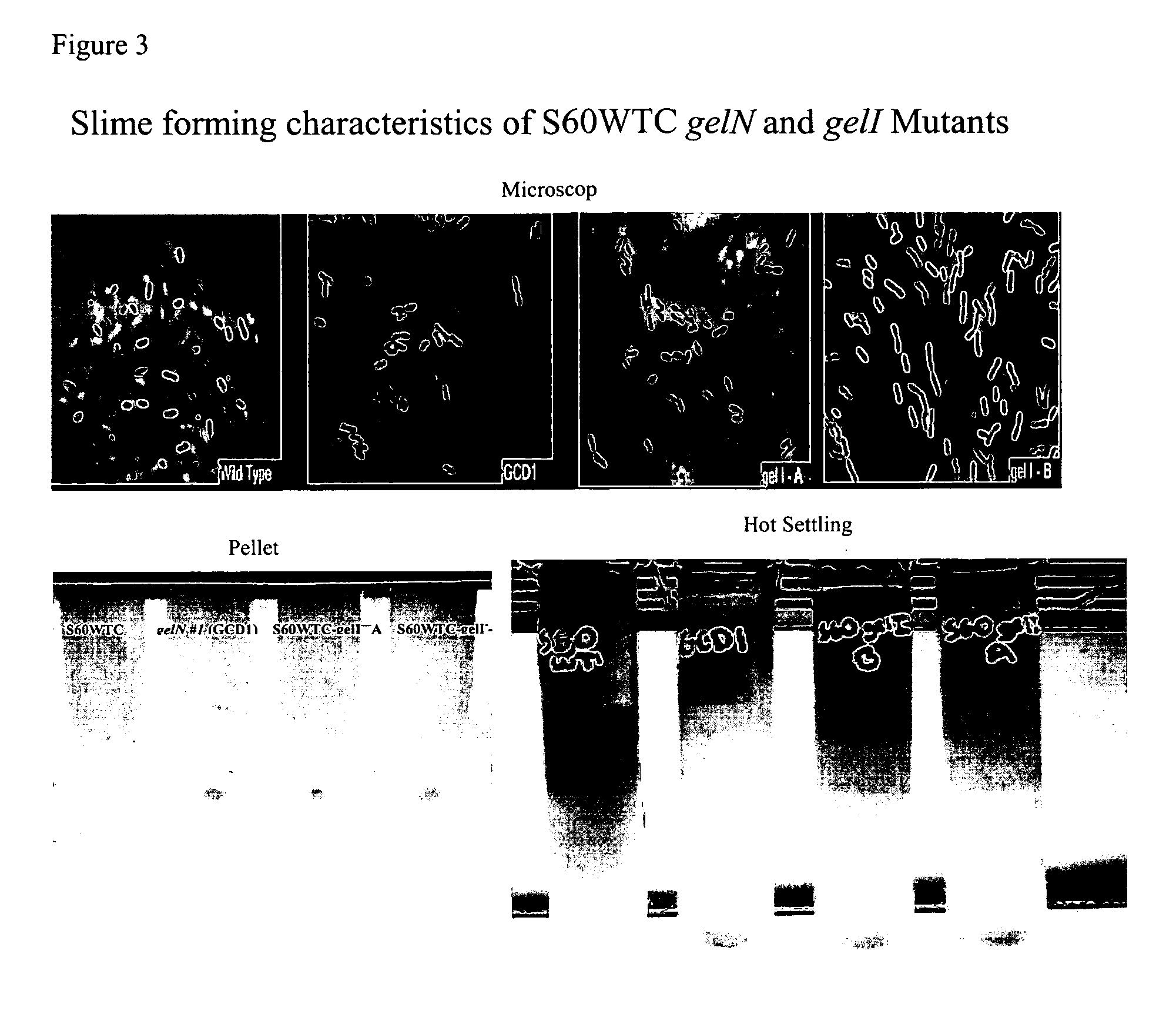
Targeted gene deletions for polysaccharide slime formers
Sphingomonas strains have extracellular polysaccharide (e.g., gellan, diutan) that is firmly attached to the cell surface. This attachment may limit polysaccharide production by impairing uptake of nutrients into the cell or due to limited sites for polysaccharide biosynthesis on the cell surface. Two genes for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelM and gelN in gellan-producing strains and dpsM and dpsN in diutan-producing strains, have been inactivated by deletion mutations and shown to produce polysaccharide that is not firmly attached to the cell surface, i.e., slime form. Another gene for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelI in gellan producing strains, was inactivated by insertion mutation and also shown to produce the slime phenotype. The homologous gene dpsi in the diutan producing strain should also be involved in the attachment of the polysaccharide to the cell surface. The slime characteristic was demonstrated by the ability of the cells to be centrifuged and the lack of cell clumping as seen under the microscope or in diluted suspensions. The diutan slime mutants had somewhat increased productivity and the recovered diutan product had significantly improved rheology. Gellan slime mutants had lower broth viscosity which facilitates mixing during fermentation; however, the recovered gellan product had lower gel strength than the gellan produced from a capsular strain. A deletion in a gene gelR, which encodes a protein with homology to surface proteins and outer membrane proteins and weak homology to proteins with polysaccharide degradation activity, was shown to restore higher gel strength to the slime form of gellan, and to produce gellan of higher gel strength than that of the capsular gellan producing strains.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Primer, probe and kit for fluorescent quantitative detection on genes of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
ActiveCN104480206AEasy to detectAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceSmn gene
The invention relates to the field of gene detection, and particularly relates to a primer, a probe and a kit for fluorescent quantitative detection on genes of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The kit comprises the primer and the probe for fluorescent quantitative detection on genes of SMA, wherein the primer includes 9 pairs of primers; the probe includes 15 probes. According to the primer, the probe and the kit for fluorescent quantitative detection on genes of SMA, a fluorescent quantitative PCR technology is utilized, common mutation site detection which is not found in existing patent technologies is added, so that, 16 types of SMA patients caused by SMN gene deletion, transformation and site mutation can be specifically detected in one time, and classification of SMA patients can be realized.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
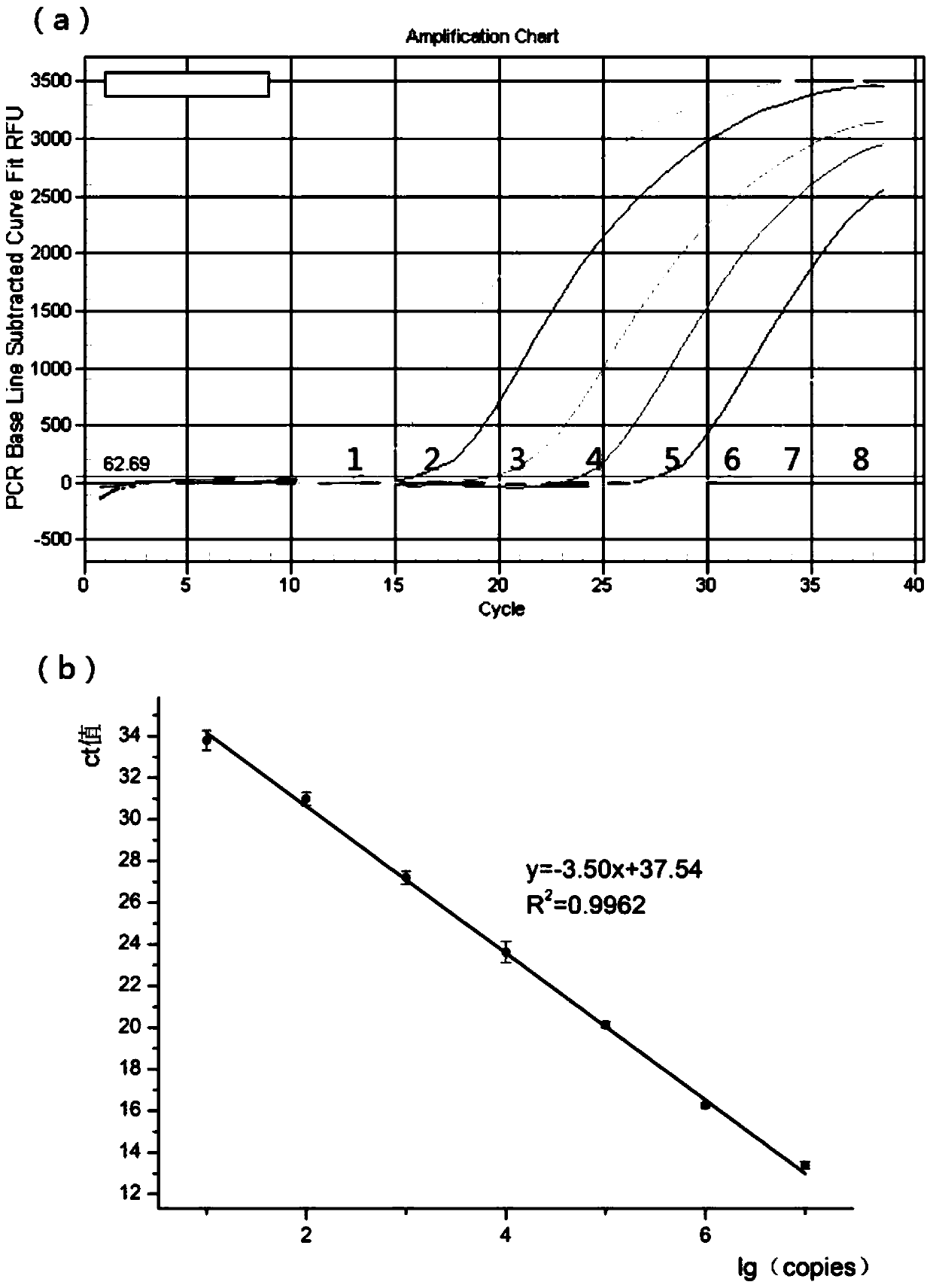
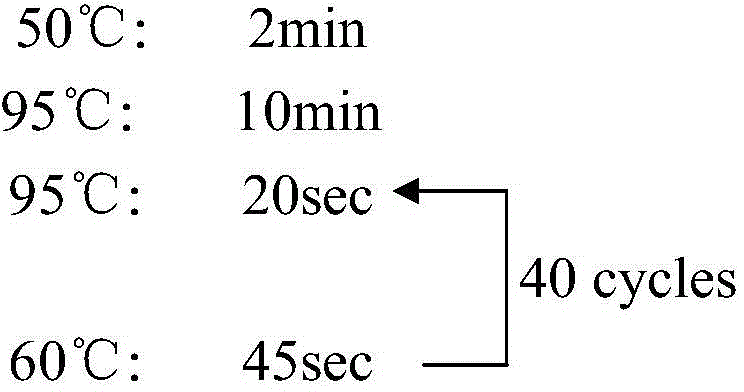
Quantitative detection method for gene copy number
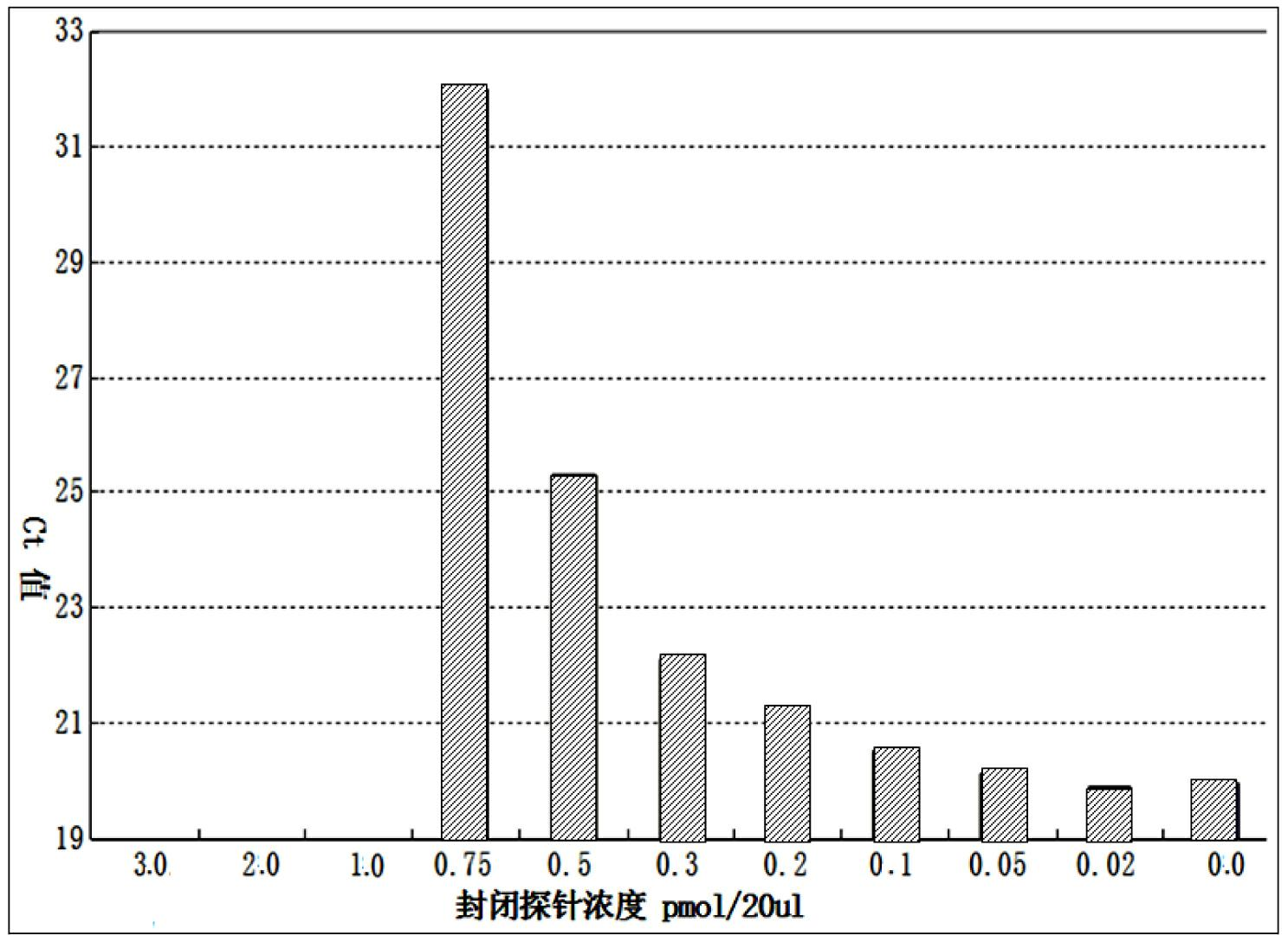
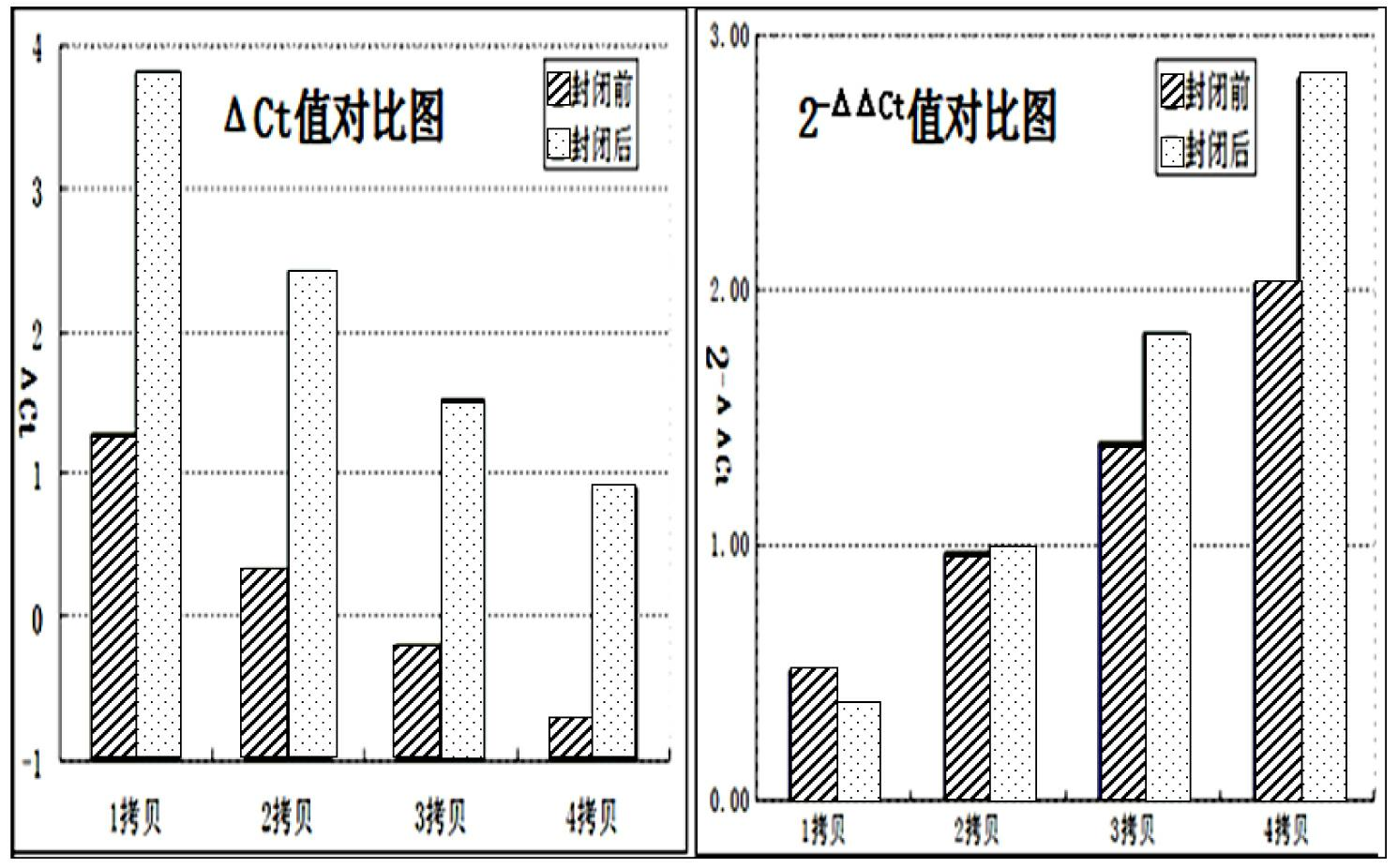
InactiveCN102618646ASync detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesReference sample
The invention discloses a quantitative detection method for a gene copy number. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively designing primers and fluorescence probes for target gene and reference gene amplification sequences, and designing a closed probe for the target gene amplification sequence; detecting a sample: performing multiple TaqMan fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on target genes and reference genes by using the DNA sample to be detected as a template, and respectively recording Ct values by using a DNA sample with known target gene copy number as a reference sample; and analyzing the result. By the method, the copy number of the functional genes can be directly and quantitatively detected, and deletion, deletion number and multiple copies (CNVs) of the detected genes are directly reflected, so that synchronous quick detection of gene deletion and multiple gene copies is realized; and the method is high in sensitivity, the synchronous quick detection of the gene deletion and the multiple gene copies can be finished only by a common fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument, and experiments prove that the method is accurate and reliable.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gene knockout method for breeding selection of fhl1b gene-deletion type zebra fish
InactiveCN108048486AEfficient and More Precise SilenceEasy to makeHydrolasesMicroinjection basedDiseaseGenotype Analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of gene knockout and particularly discloses a gene knockout method for breeding selection of a fhl1b gene-deletion type zebra fish. According to the method, by means of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technique, an appropriate target locus is designed on a fhl1b gene of the zebra fish, specific sgRNA and Cas9-mRNA which are synthesized outside the fish bodyare microscopically injected into one cell of the zebra fish, and 60 hours after embryo cultivation is carried out, by selecting embryos to conduct genotype analysis, the effectiveness of the selectedlocus is proved. The off-target rate is low, not only is the fhl1b gene removed by interference, but also more convenience is provided for further disclosing the whole process of generation of a heart shape and regulating and controlling a molecular mechanism of the process by adopting a genetic approach to studying the functions of the fhl1b gene, and the method has a significant meaning in understanding of medical pathology of heart diseases and research and development on new therapeutic schemes.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Primer group for simultaneously identifying wild strain and gene deletion strain of African swine fever based on multiple qPCR technology and test kit
InactiveCN111996191AReduce pollutionShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAfrican swine feverViral test
The invention provides a primer group for simultaneously identifying a wild strain and a gene deletion strain of African swine fever based on a multiple qPCR technology and a test kit, and belongs tothe technical field of virus detection. The primer probe group for simultaneously identifying the wild strain and the gene deletion strain of the African swine fever based on the multiple qPCR technology comprises a p72 gene specific primer probe, a CD2v gene specific primer probe and an MGF gene specific primer probe. The test kit comprises the primer probe group. Multiple qPCR detection is performed by adopting the test kit; p72 gene specific primers of a conserved gene of ASFV can amplify the wild strain and the gene deletion vaccine strain; specific primers of a CD2v gene and an MGF gene can only amplify the wild strain; and the three pairs of primers are combined for use, so that the wild strain and the gene deletion vaccine strain of the ASFV can be simultaneously identified. The primer group and the test kit have the advantages of accurate detection, sensitivity, high efficiency, low cost and the like, and have relatively high practical value for diagnosis of clinical samples and the breeding industry.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com