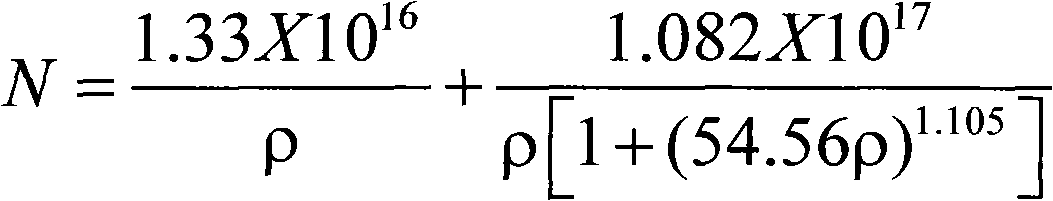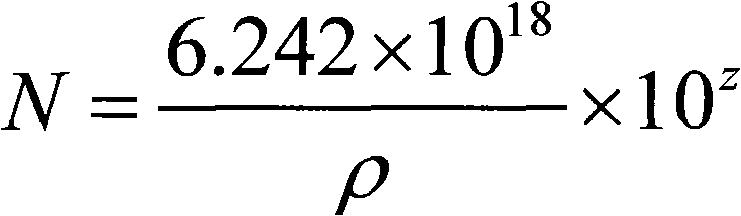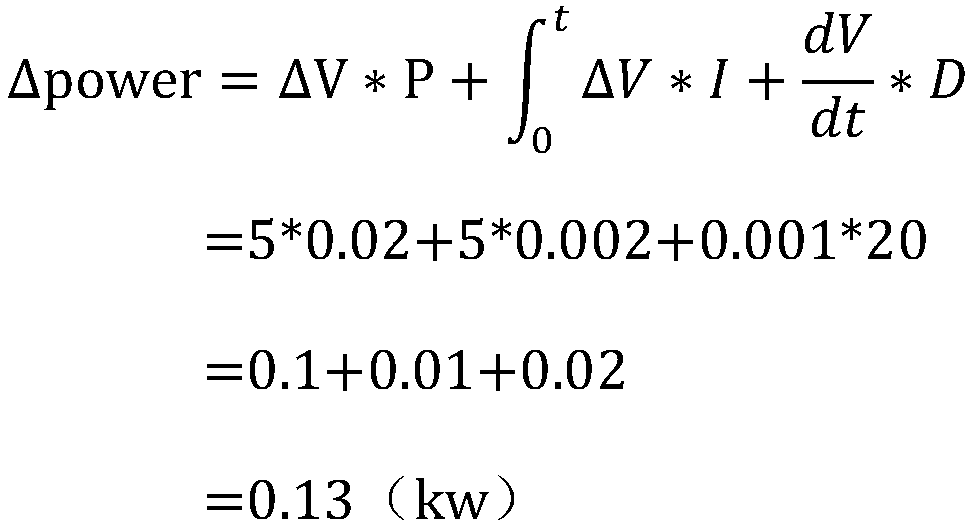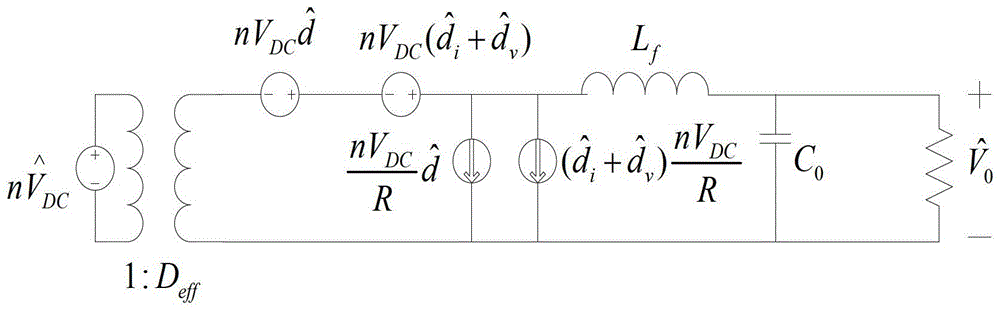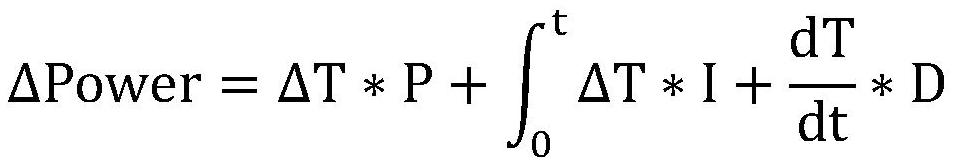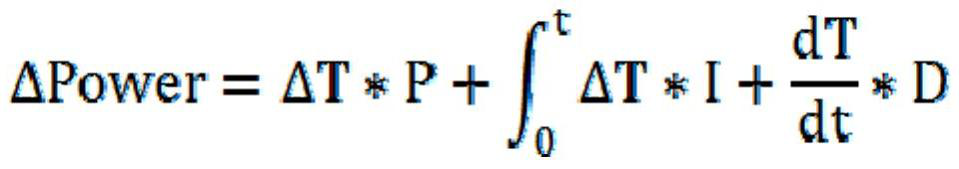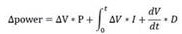Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Cz silicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
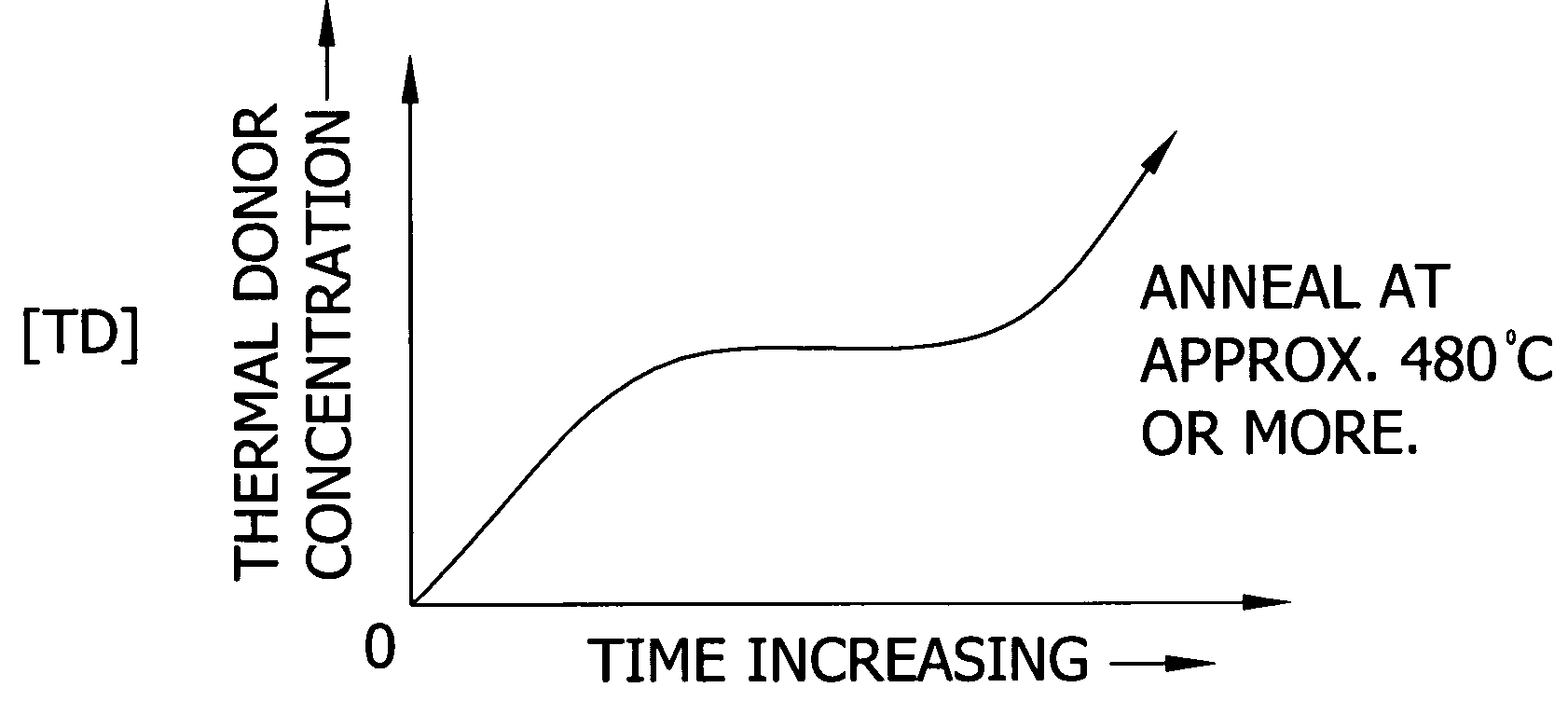
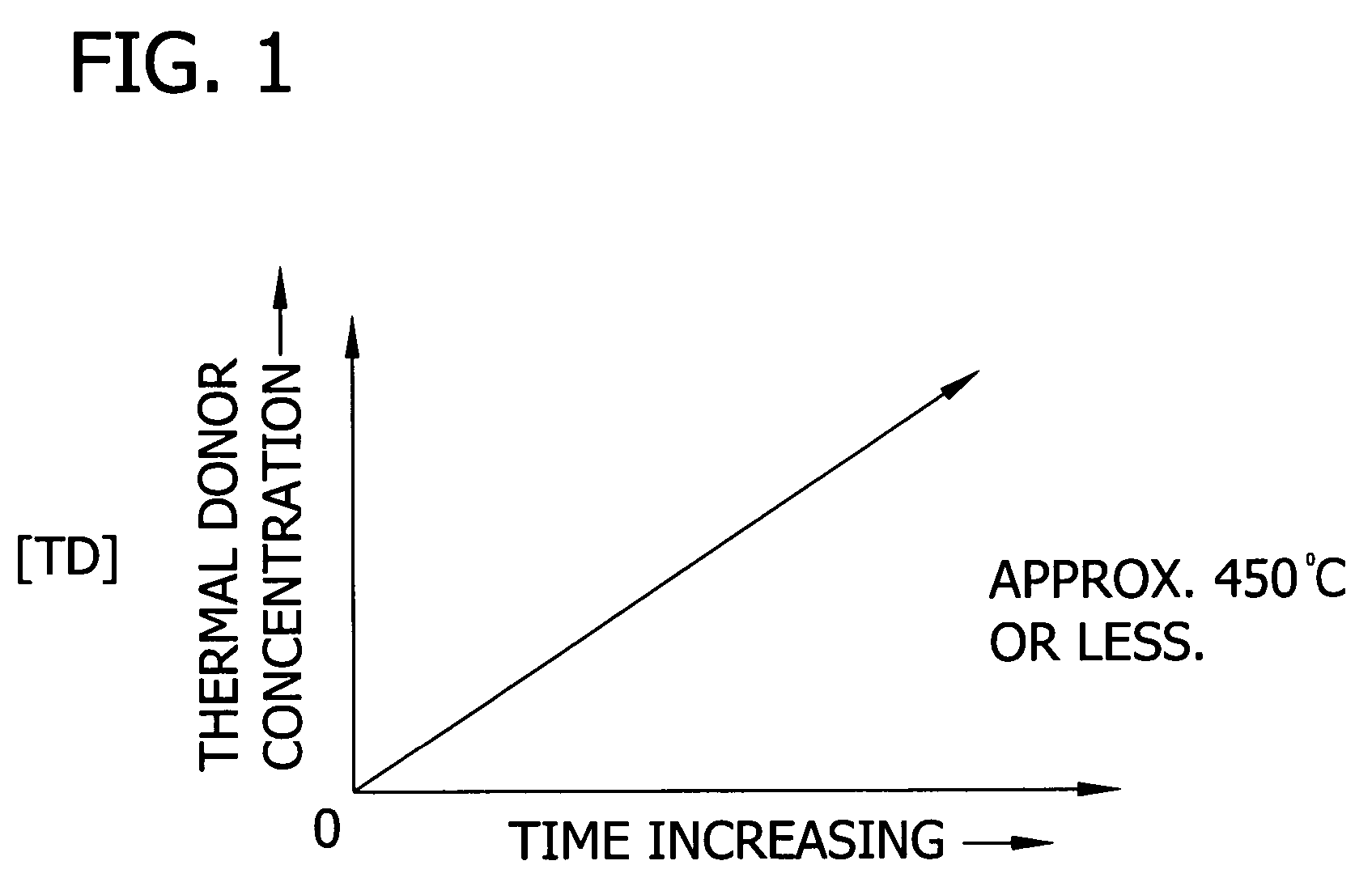
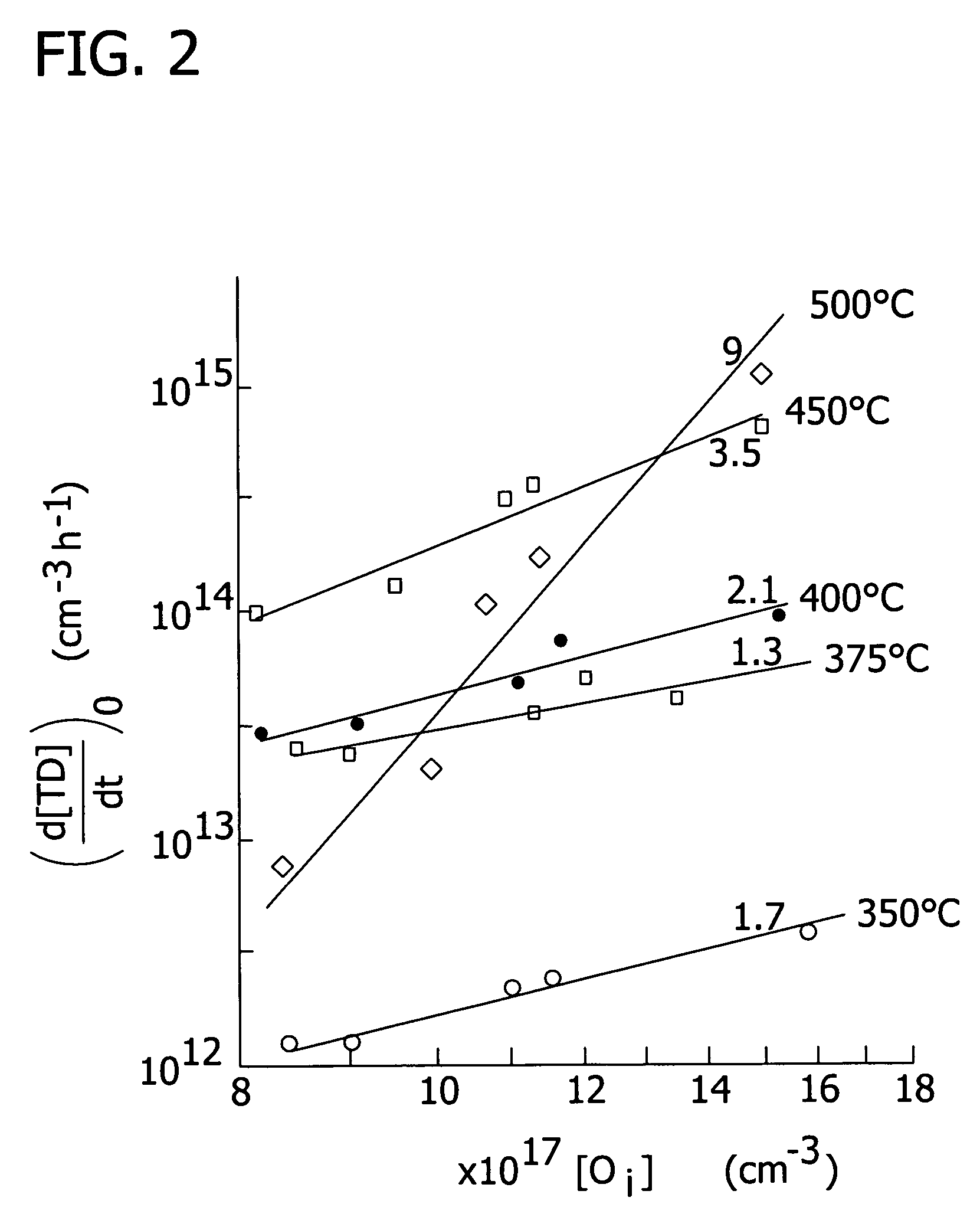
Control of thermal donor formation in high resistivity CZ silicon
InactiveUS20050158969A1After-treatment detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSurface layerSingle crystal
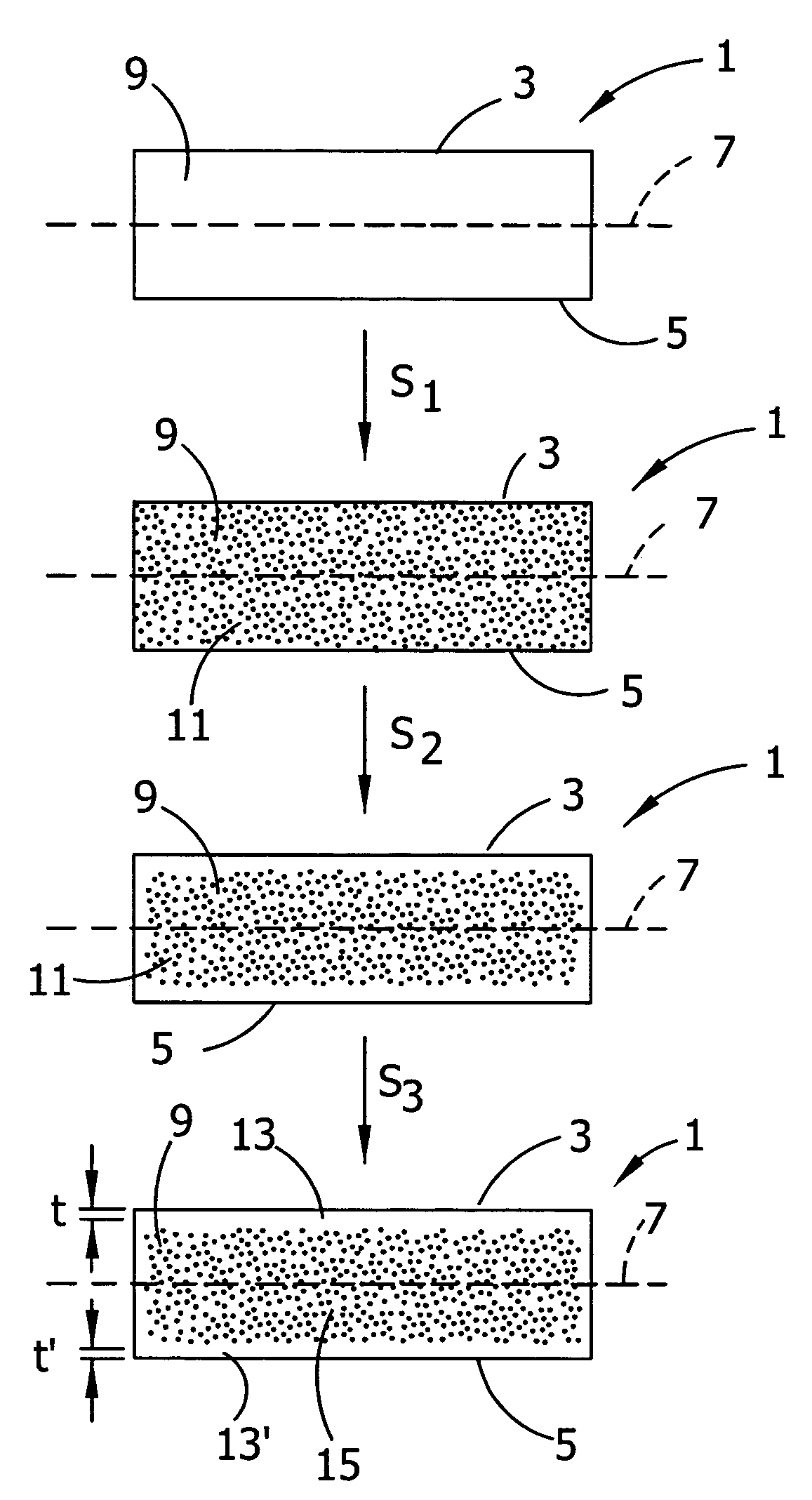
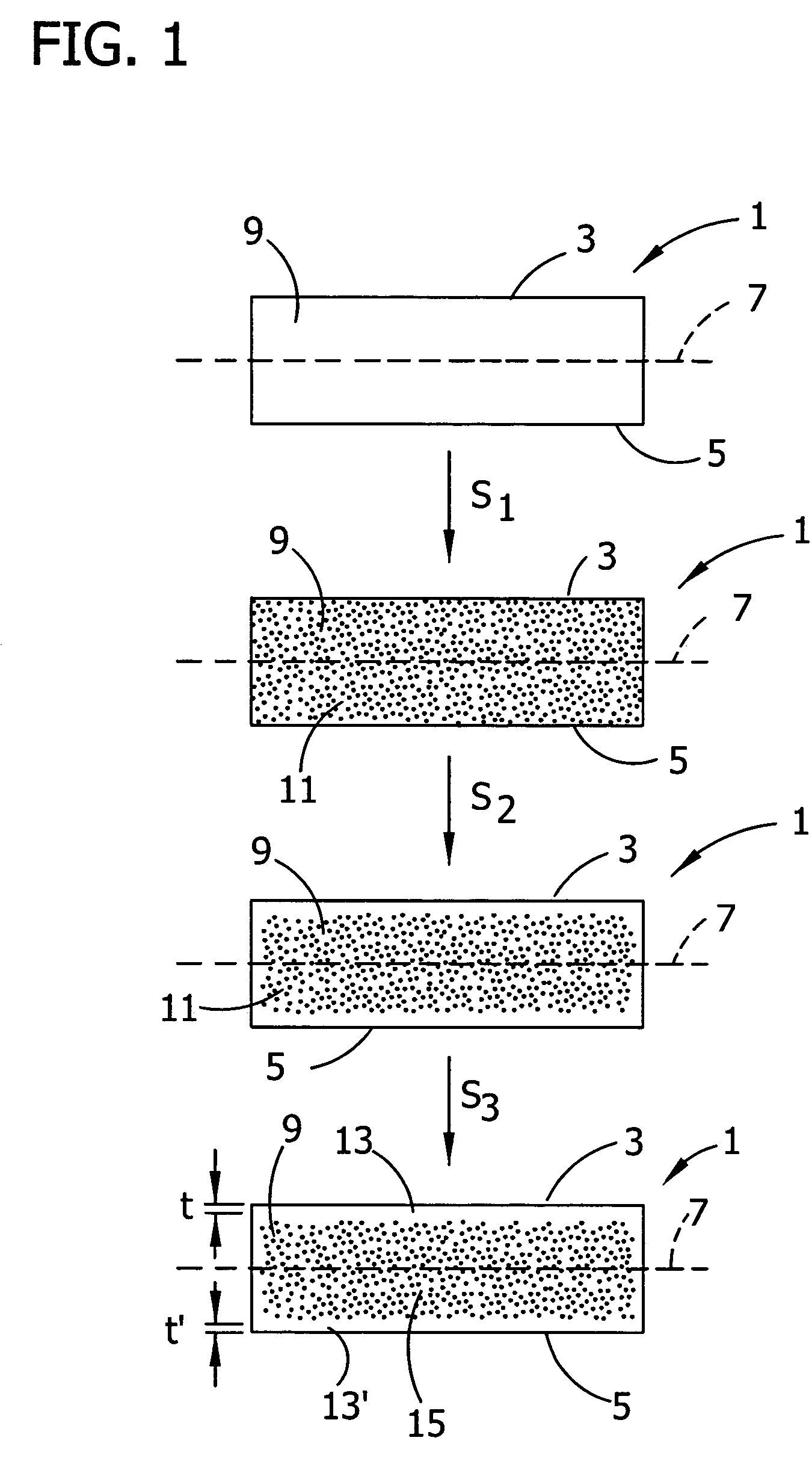
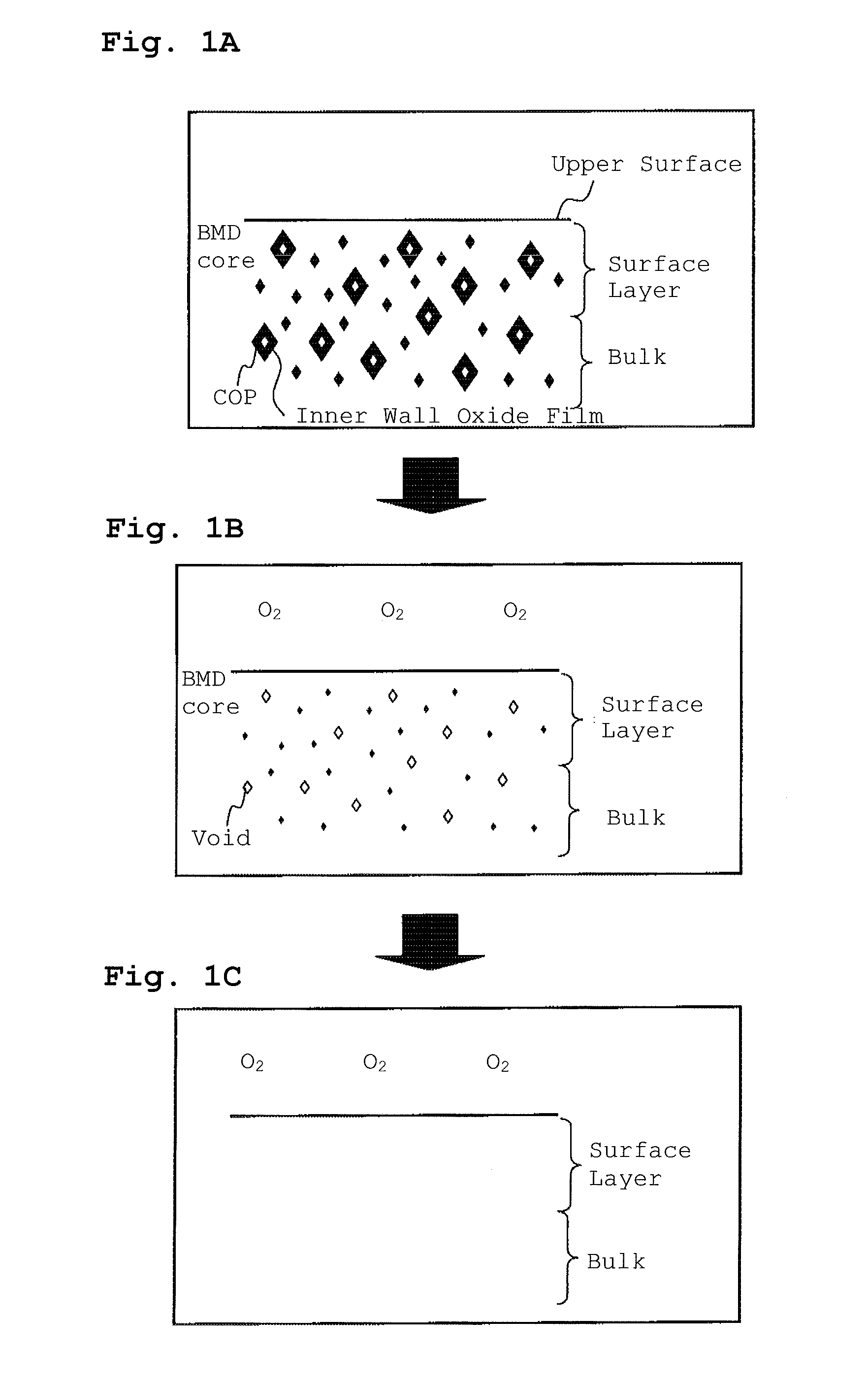
The present invention is directed to a single crystal Czochralski-type silicon wafer, and a process for the preparation thereof, which has at least a surface layer of high resistivity, the layer having an interstitial oxygen content which renders it incapable of forming thermal donors in an amount sufficient to affect resistivity upon being subjected to a conventional semiconductor device manufacturing process. The present invention further directed to a silicon on insulator structure derived from such a wafer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
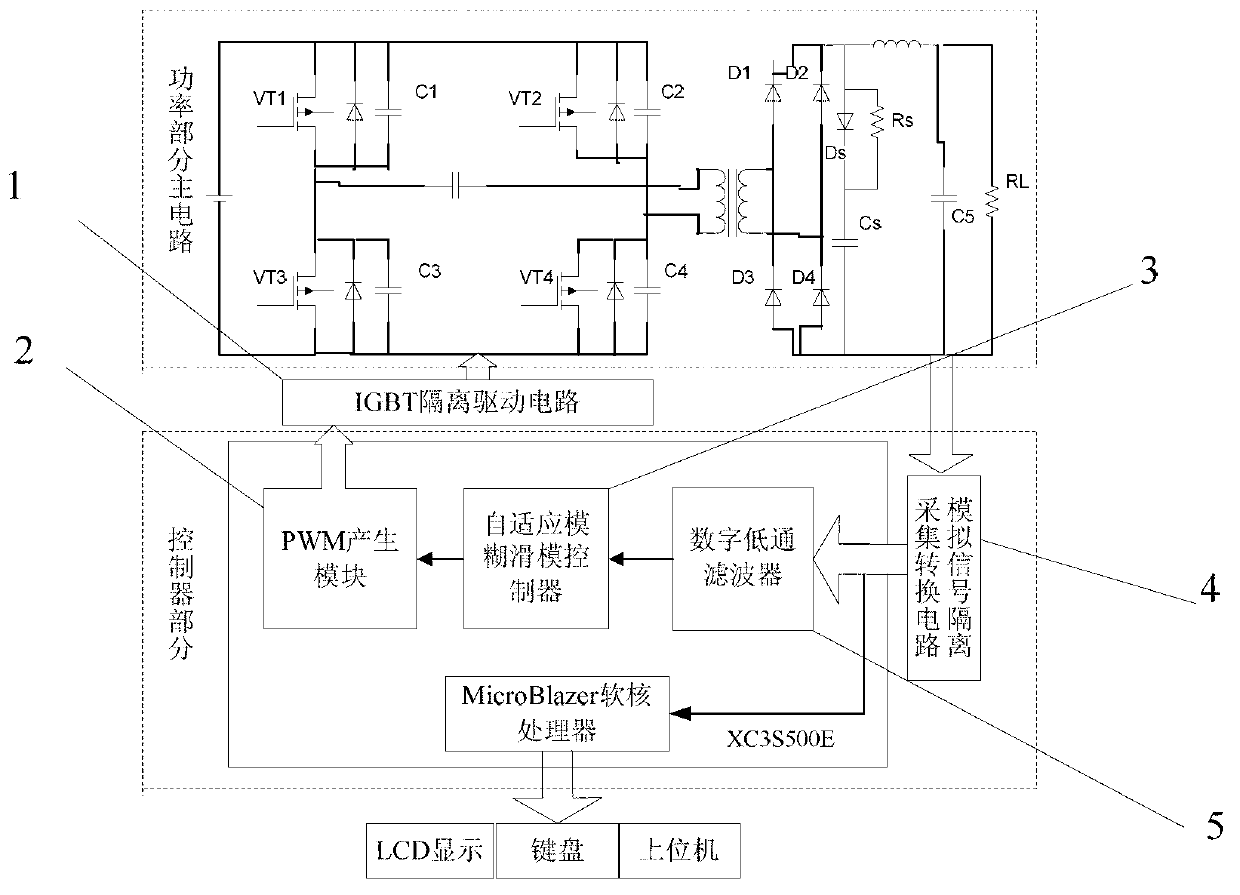
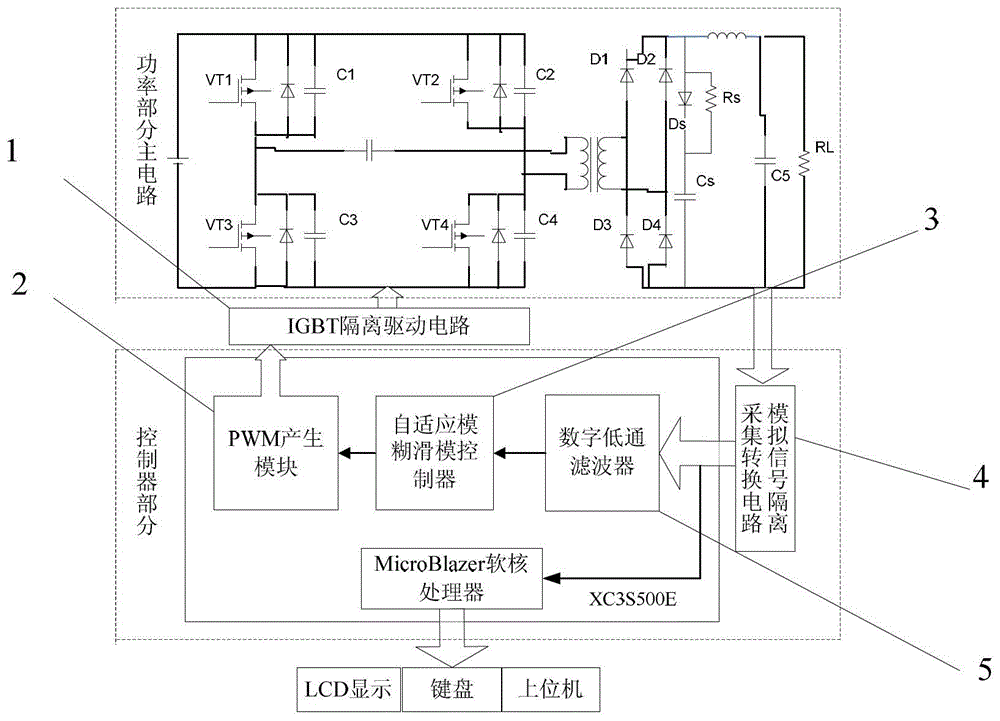
Control system of high frequency switching power supply for Cz silicon single crystal furnace and control method
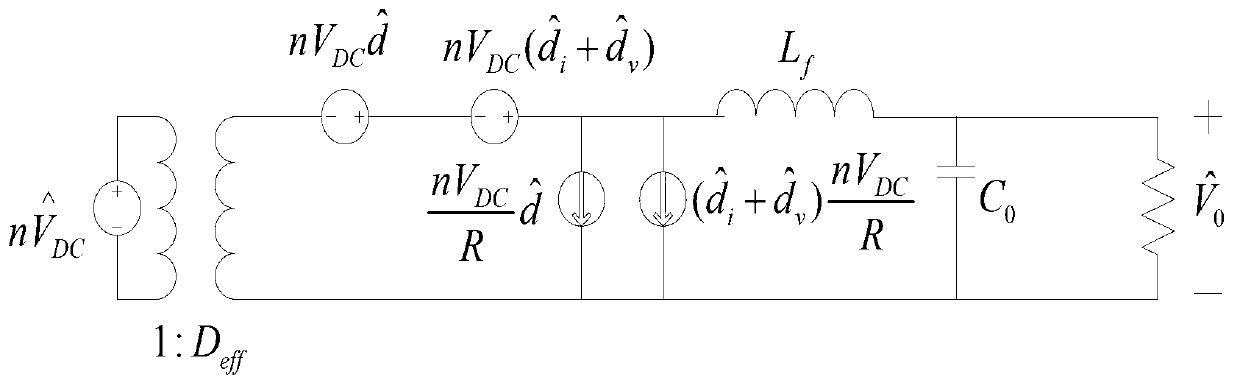
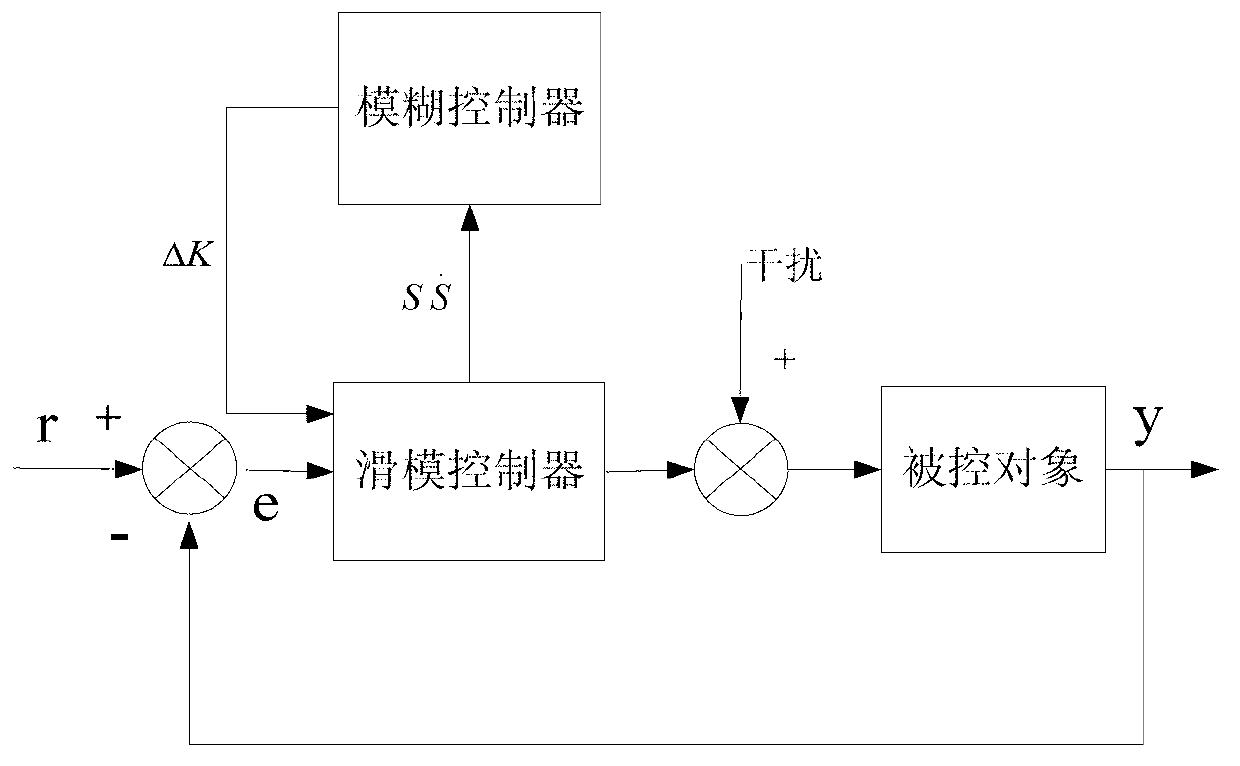
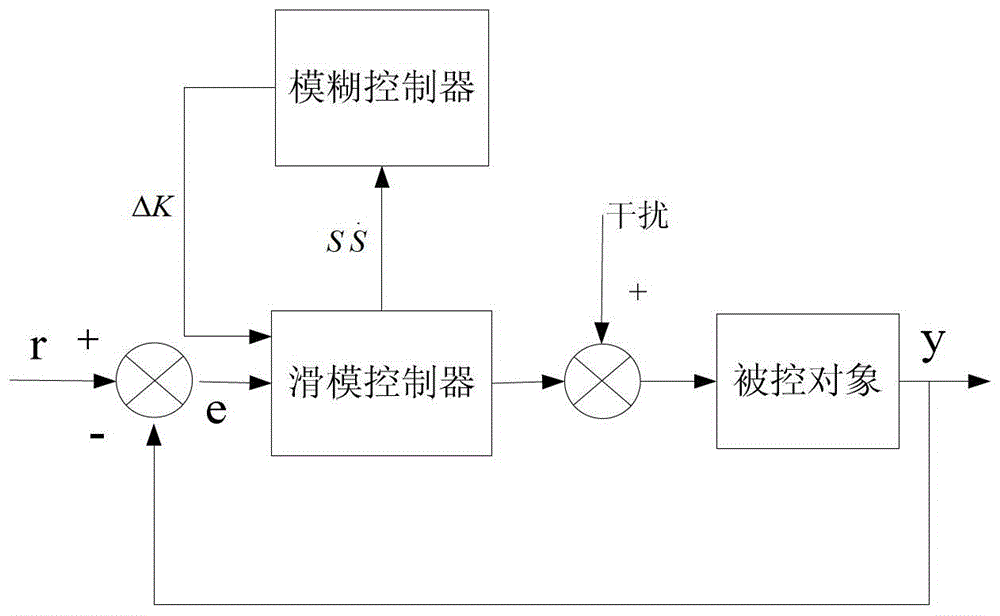
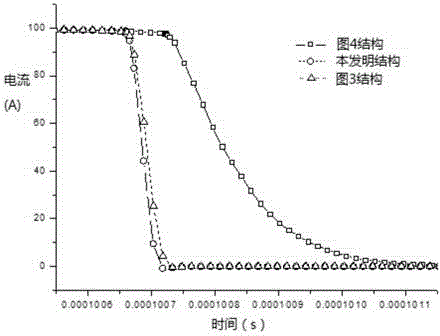
InactiveCN103346676AImprove robustnessImprove dynamic characteristicsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPower controllerControl system
The invention discloses a control system of a high frequency switching power supply for a Cz silicon single crystal furnace and a control method. The control method includes the steps of combining self-adaptive fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control, and aiming at a high-frequency switch heating electric power for the Cz silicon single crystal furnace to design a power controller based on a self-adaptive fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control method. The control system of the high frequency switching power supply for the Cz silicon single crystal furnace and the control method play respective advantages of fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control, further improve dynamic performance of the system, have good robustness for input voltage or load disturbance, and relieve or avoid vibration which generally happens to a sliding mode.
Owner:青海鑫诺光电科技有限公司
Control of oxygen precipitate formation in high resistivity CZ silicon
InactiveUS6897084B2Layer is highHigh resistivityAfter-treatment detailsSolid-state devicesSurface layerHigh resistivity
The present invention is directed to a single crystal Czochralski-type silicon wafer, and a process for the preparation thereof, which has at least a surface layer of high resistivity, the layer having an interstitial oxygen content which renders it incapable of forming thermal donors in an amount sufficient to affect resistivity upon being subjected to a conventional semiconductor device manufacturing process. The present invention further directed to a silicon on insulator structure derived from such a wafer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Method for controlling of thermal donor formation in high resistivity CZ silicon
The present invention is directed to a single crystal Czochralski-type silicon wafer, and a process for the preparation thereof, which has at least a surface layer of high resistivity, the layer having an interstitial oxygen content which renders it incapable of forming thermal donors in an amount sufficient to affect resistivity upon being subjected to a conventional semiconductor device manufacturing process. The present invention further directed to a silicon on insulator structure derived from such a wafer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Carbon-carbon composite guide cylinder of CZ silicon crystal growing furnace and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101717992AImprove performanceImprove insulation effectAfter-treatment apparatusBy pulling from meltFiberCarbon composites
The invention discloses a carbon-carbon composite guide cylinder of a CZ silicon crystal growing furnace and a preparation method thereof. The cylinder body of the carbon-carbon composite guide cylinder of the CZ silicon crystal growing furnace consists of a surface coating, a carbon-carbon composite layer and a carbon-carbon composite central layer. The preparation method of the carbon-carbon composite guide cylinder comprises the following steps: (1) designing and manufacturing a mold of the guide cylinder; (2) designing the shape and size of carbon fiber felt and cutting and blanking according to the size; (3) preparing a blank; (4) curing the blank; (5) performing CVD densification; (6) demolding the guide cylinder and polishing the surface of the guide cylinder; (7) performing secondary CDV densification; (8) machining the end parts of the guide cylinder and finishing the rest surface of the guide cylinder; (9) subjecting the finished guide cylinder to surface anti-oxidization, anti-erosion and anti-corrosion coating processing; and (10) subjecting the guide cylinder to drying and high-temperature purification processing. The guide cylinder product of the invention has the advantages of high service reliability, long service life and convenient replacing operation; and the preparation method can improve the rate of finished crystals and reduce the energy consumption of crystal pulling by about 10 percent.
Owner:HUNAN NANFANG BOYUN NOVEL MATERIAL
Silicon epitaxial wafer and production method for same
InactiveUS20090017291A1Sufficient IG effectImprove applicabilityPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureSingle crystalIngot
A silicon epitaxial wafer of the invention comprises a silicon single crystal wafer sliced from a CZ silicon ingot doped with carbon in a concentration range of not less than 5×1015 atoms / cm3 and not more than 5×1017 atoms / cm3 and an epitaxial layer consisting of a silicon single crystal epitaxially grown on a front surface of the silicon single crystal wafer. A polycrystalline silicon layer having a thickness of not less than 0.5 μm and not more than 1.5 μm is formed on a back surface of the silicon single crystal wafer.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
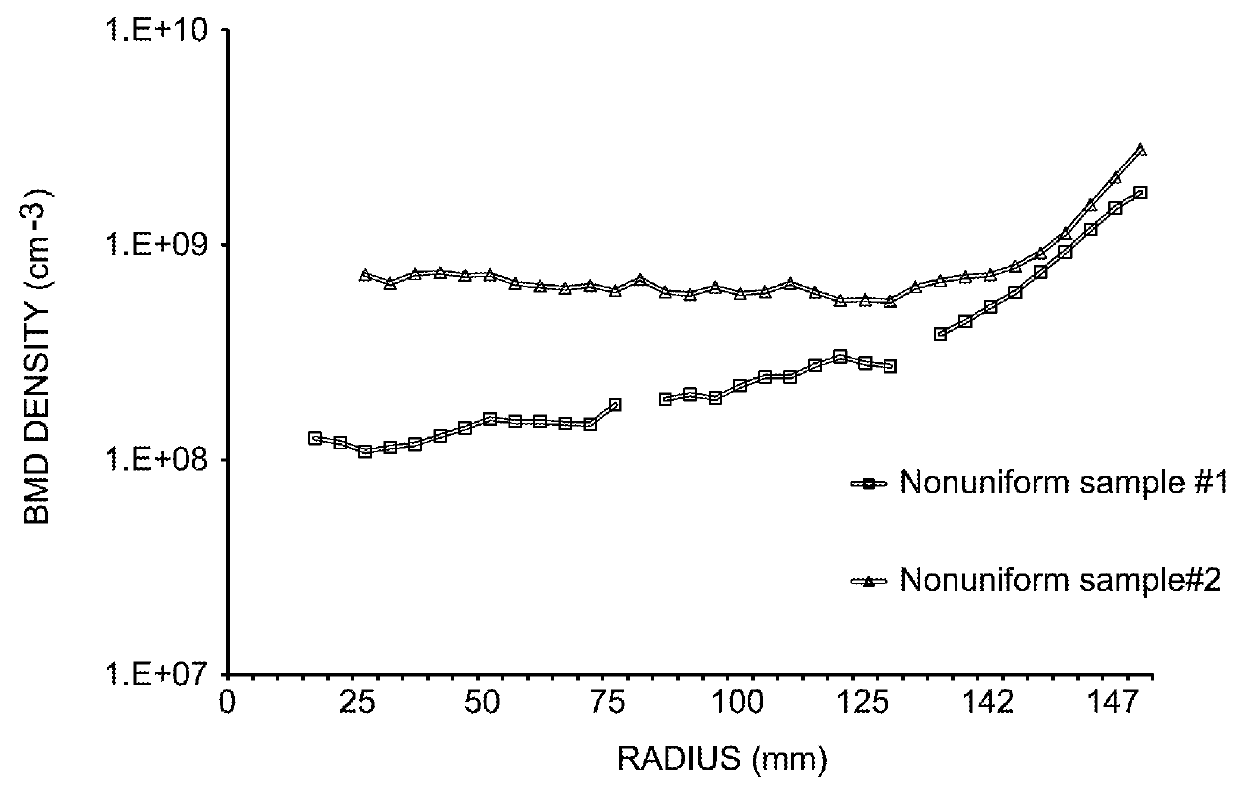
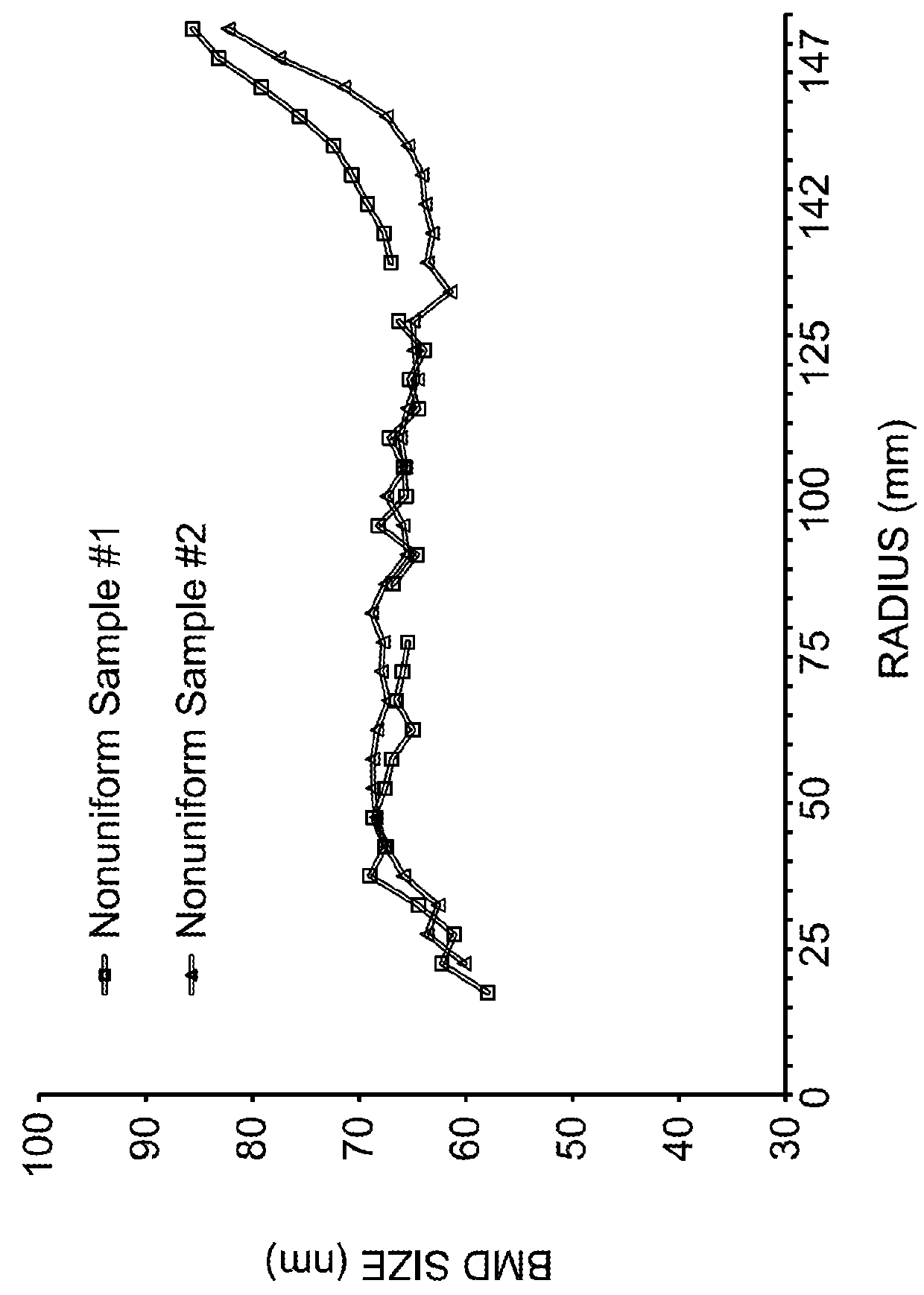
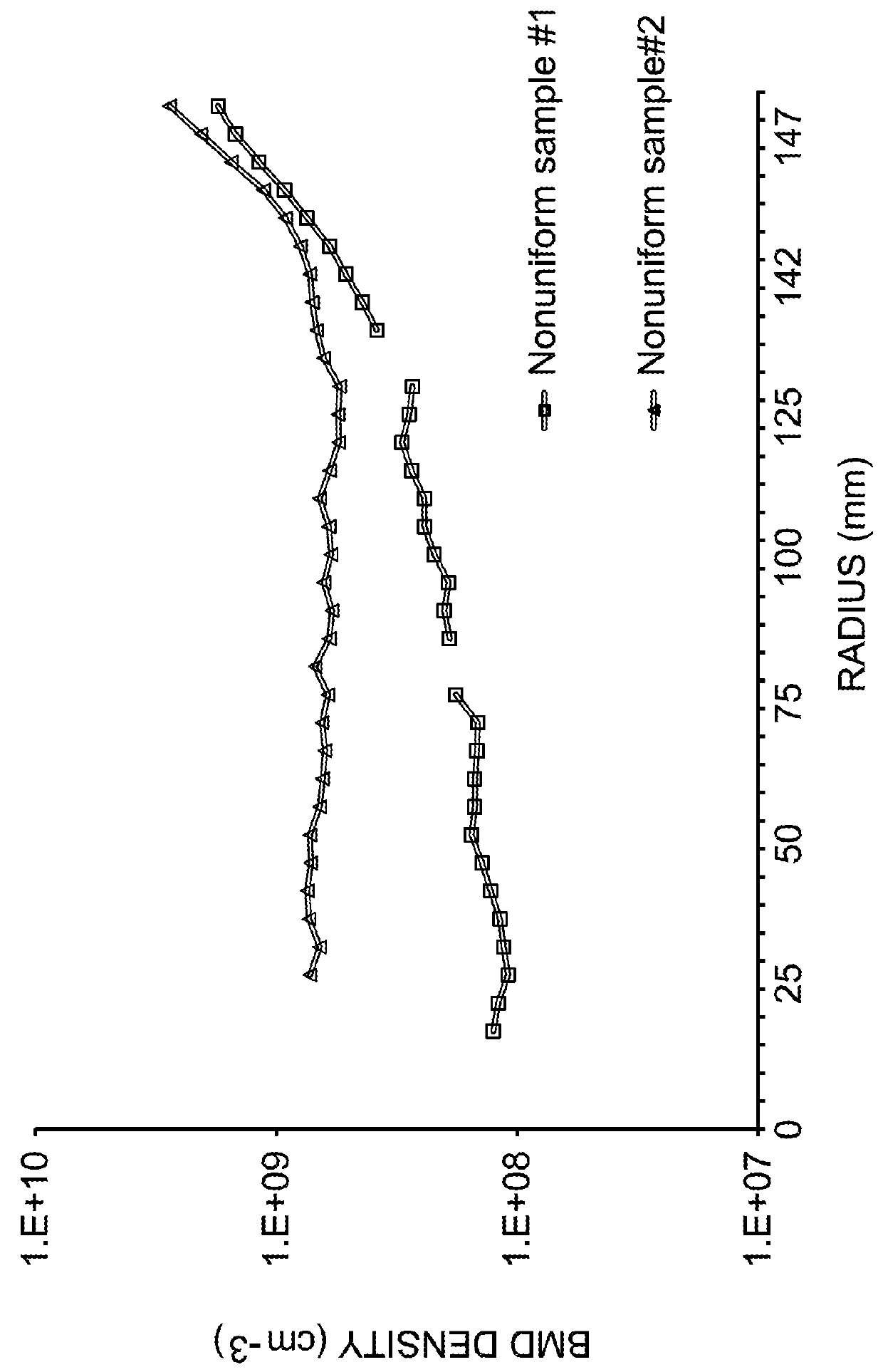
Nitrogen doped and vacancy dominated silicon ingot and thermally treated wafer formed therefrom having radially uniformly distributed oxygen precipitation density and size
ActiveUS20160032491A1Increase in radial bulk micro defect sizeImprove defect densityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWaferingDensity distribution
Nitrogen-doped CZ silicon crystal ingots and wafers sliced therefrom are disclosed that provide for post epitaxial thermally treated wafers having oxygen precipitate density and size that are substantially uniformly distributed radially and exhibit the lack of a significant edge effect. Methods for producing such CZ silicon crystal ingots are also provided by controlling the pull rate from molten silicon, the temperature gradient and the nitrogen concentration. Methods for simulating the radial bulk micro defect size distribution, radial bulk micro defect density distribution and oxygen precipitation density distribution of post epitaxial thermally treated wafers sliced from nitrogen-doped CZ silicon crystals are also provided.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
High resistivity silicon structure and a process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS7521382B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHigh resistivity siliconHigh resistivity
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Method for displaying and detecting void type defects in Czochralski silicon wafer
ActiveCN102768134AImprove the display effectMeet the actual needs of productionPreparing sample for investigationPreferential etchingCopper nitrate
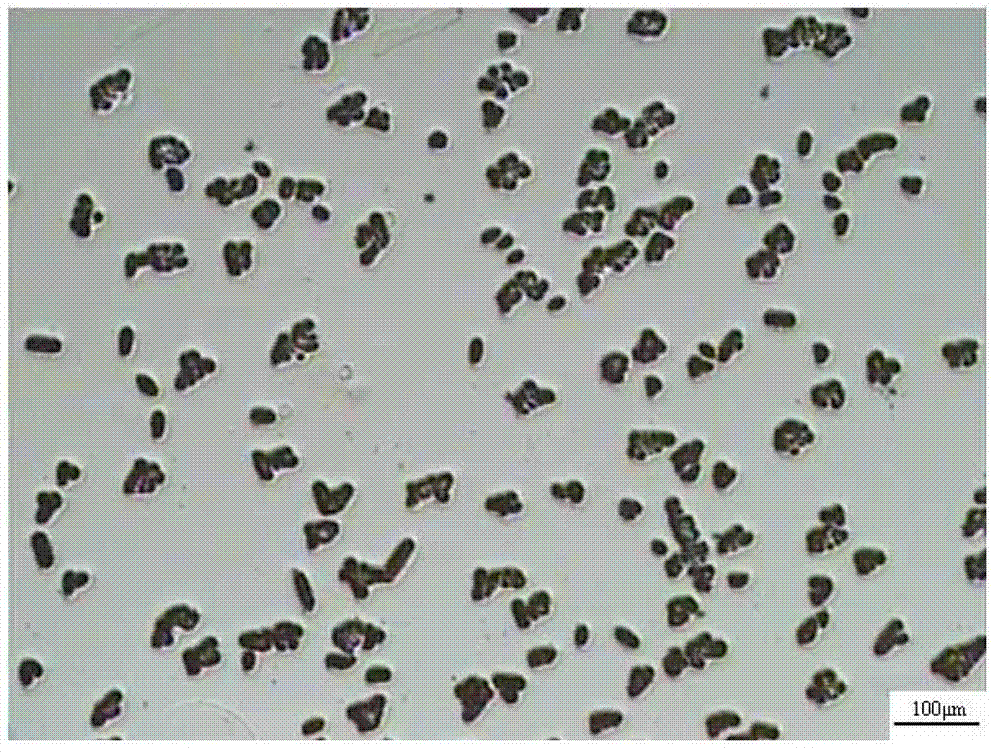
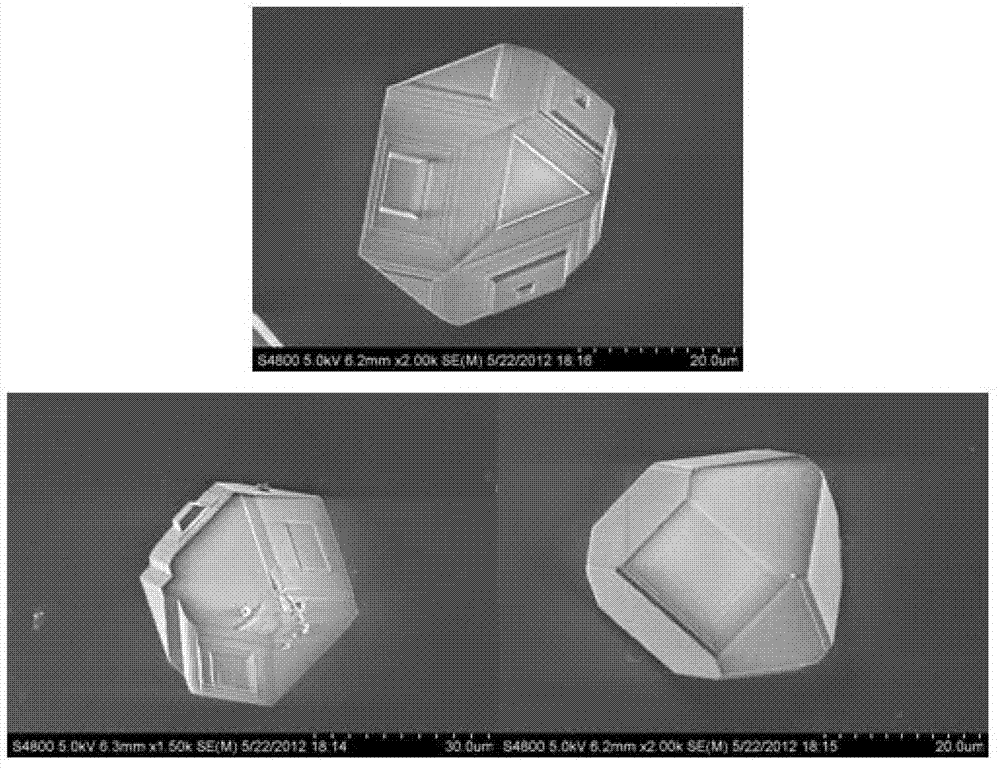
The invention provides a method for displaying and detecting void type defects in a Czochralski silicon wafer, and the void type defects are displayed by utilizing polyhedron copper precipitation. The method for displaying the void type defects in the Czochralski silicon wafer comprises the following steps of: immersing a polished silicon wafer into a copper nitrate solution for standing; rinsing the silicon wafer in deionized water, taking out and airing; performing heat treatment on the silicon wafer after copper precipitation and airing; quickly cooling the silicon wafer after heat treatment; and horizontally placing the silicon wafer after cooling in a preferential etching solution for etching. The invention further provides the method for detecting the void type defects in the Czochralski silicon wafer, and the method comprises the following steps of: preparing a silicon wafer sample according to the method; and directly observing the polished surface of the silicon wafer sample by an optical microscope or a scanning electron microscope. The polyhedron copper precipitation observed under the microscope corresponds to the void type defects. According to the method provided by the invention, the void type defects in the Czochralski silicon wafer can be clearly displayed within a shorter period of time, the observation can be conveniently performed by adopting the conventional optical microscope under common environments, and the method is suitable for detecting the void type defects in the Czochralski silicon wafer in industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
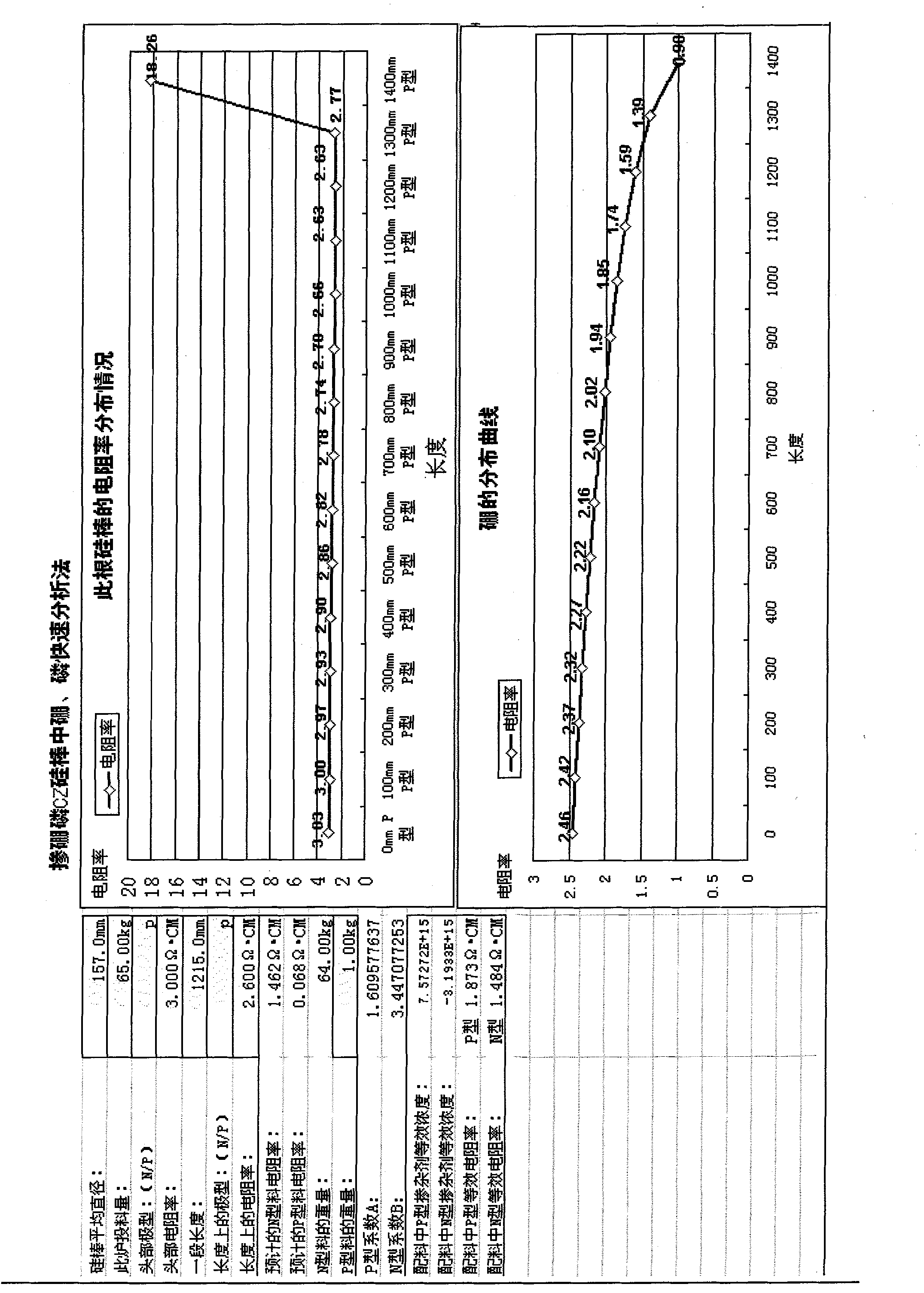
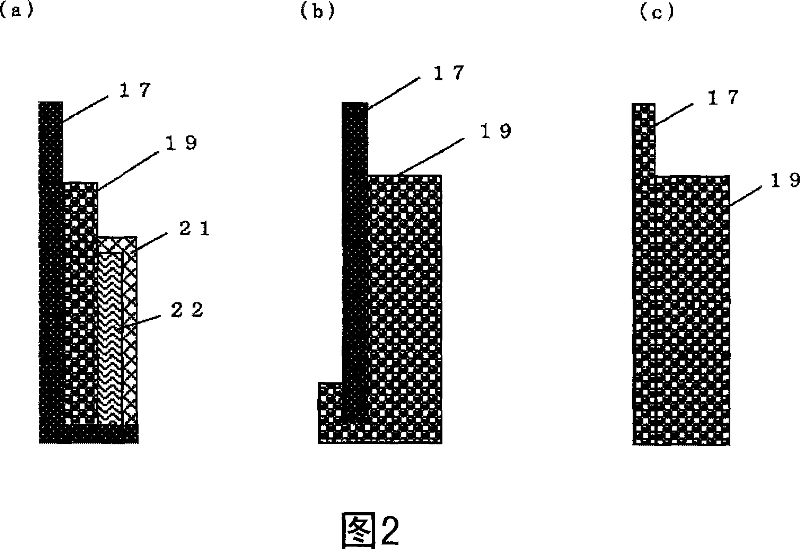
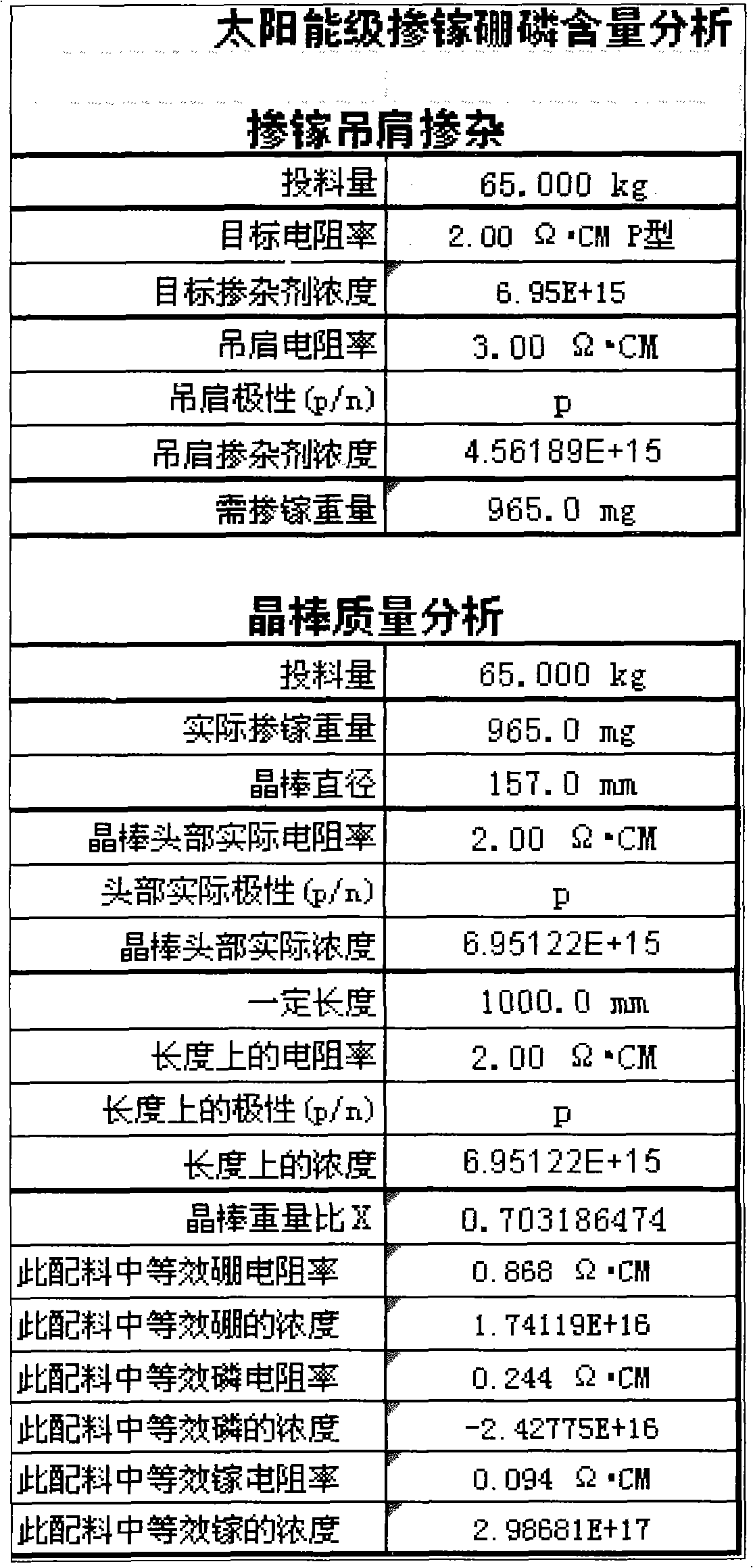
CZ (Czochralski) silicon rod doped with boron and phosphorus, and method for rapidly analyzing contents of boron and phosphorus in ingredients
InactiveCN102081063AReduce quality verification costsImprove craftsmanshipMaterial resistanceAdditive ingredientSingle crystal
The invention relates to a CZ (Czochralski) silicon rod doped with boron and phosphorus, and a method for rapidly analyzing the contents of boron and phosphorus in ingredients. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating the head doping concentration of the CZ silicon rod and the doping concentration in a certain length; deriving the contents of the boron and phosphorus in the ingredients of the CZ silicon rod according to the formulas (4), (5) and (6), and converting into the corresponding resistivity; and simultaneously, calculating the resistivity and equivalent resistivity caused by the content of the boron in any length on the silicon rod according to the formula (4). The invention has the advantage of accurate, convenient and rapid calculation, reduces the testing cost and expense of silicon materials, can be used in the aspects of quality identification of solar energy level CZ single crystals, quality identification of semiconductor CZ single crystals, quality identification of the silicon materials and the like, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:王正园
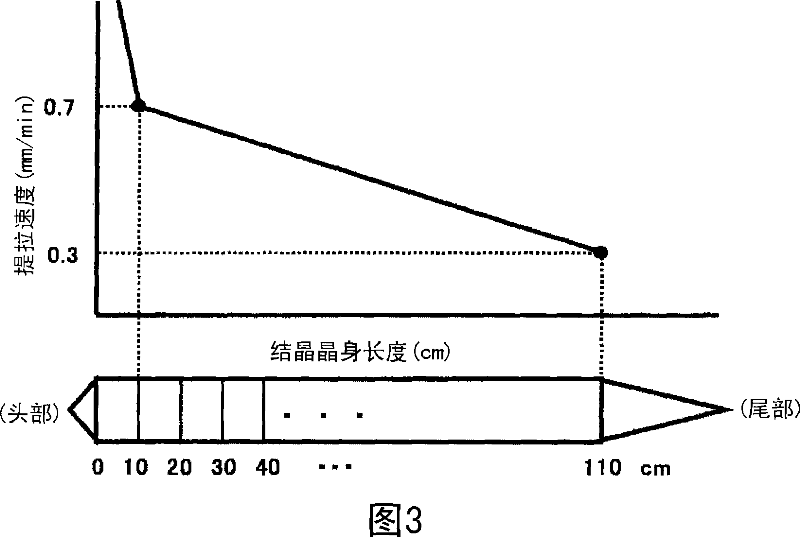
Solar-grade Czochralski (CZ) silicon single crystal thermal donor control process
InactiveCN101994151ASimple processing methodLow costPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSingle crystalCz silicon
The invention relates to a solar-grade Czochralski (CZ) silicon single crystal thermal donor control process. The technical problems to be solved are to control the thermal donor concentration at the head of a CZ silicon single crystal and reduce or avoid silicon wafers needing annealing treatment. The process comprises the following main steps of: 1, charging, dissolving, making residues fall, and doping or pre-doping; 2, volatilizing; 3, seeding, shouldering, turning a shoulder, ensuring equal diameter and closing; and 4, closing, catching, lifting the crystal and cooling. Compared with the process in the conventional industry, the process can reduce the thermal donor concentration by 60 to 75 percent, effectively reduces the silicon wafers needing the annealing treatment, reduces cost and improves quality.
Owner:王正园
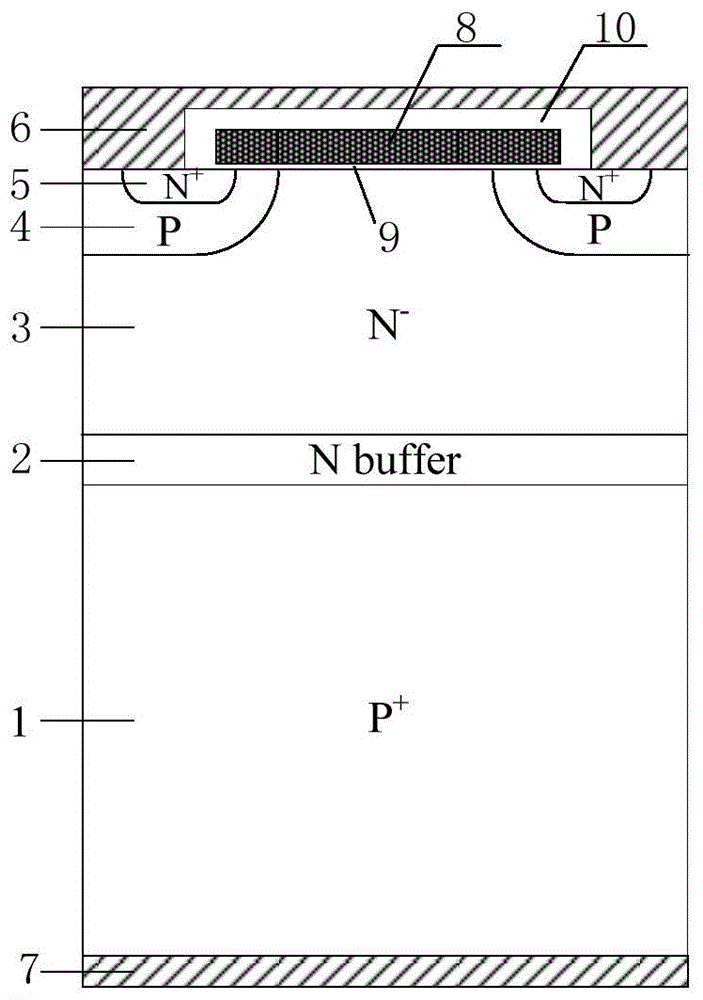
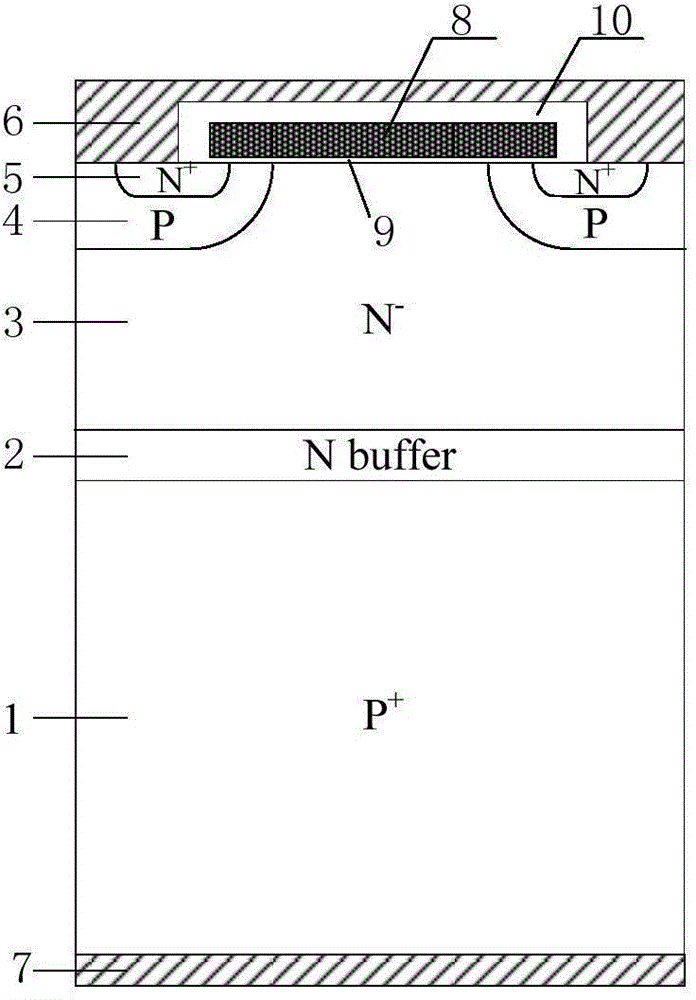
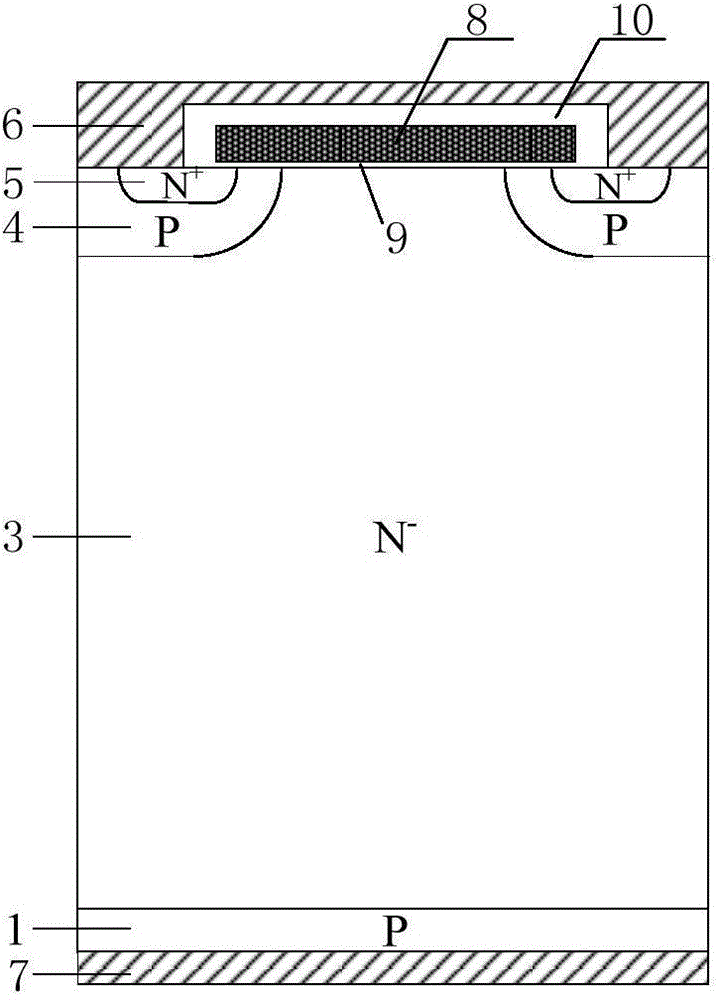
Preparation method of FS-IGBT (Field Stop-Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator)
ActiveCN104681433AForward voltage dropReduced turn-off lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow voltageSurface structure
The invention provides a preparation method of an FS-IGBT (Field Stop-Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator), which is used for solving the problems caused by a thin silicon wafer during a preparation process of a medium / low-voltage FS-IGBT that the preparation technology is complicated, the difficulty is large, the thin silicon wafer warps and deforms and is segmented, the size of the thin silicon wafer (a wafer) is limited, the yield is low, the cost is high, and industrialization is difficult to realize and overcoming the huge technical challenge caused by the thin silicon wafer in follow-up scribing of the wafer and encapsulating of a chip. The preparation method comprises the steps of selecting light-doped N-type FZ silicon as a first silicon wafer and heavy-doped N-type or P-type CZ silicon or FZ silicon as a second silicon wafer; firstly, making an N-type FS layer of the FS-IGBT on the back surface of the first silicon wafer, and then, depositing an oxidation layer; bonding the first silicon wafer and the second silicon wafer; making a front-surface structure after thinning the thickness of an original first silicon wafer; etching after thinning the thickness of the second silicon wafer; preparing a P-type transparent collecting zone through a groove; finally, forming a collector electrode through metal depositing and chemical-mechanical polishing; obtaining the FS-IGBT.
Owner:苏州翠展微电子有限公司
N-type czochralski silicon with uniform doping resistivity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102560627AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltPhotovoltaic industryCzochralski method
The invention discloses an N-type czochralski silicon with a uniform doping resistivity and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing a polycrystalline silicon material, a phosphorus doping agent and gallium; fusing; and growing a silicon monocrystal by using a czochralski method. According to the N-type czochralski silicon with the uniform doping resistivity prepared by using the method, the resistivity of a whole crystal of the N-type czochralski silicon can be controlled in the range of 1.0-2.0 omega.cm, therefore, the utilization rate of the N-type silicon crystal in the process of manufacturing a solar cell is effectively improved, the manufacturing cost of the solar cell is remarkably lowered, the preparation method is simple to operate and easy to popularize and use in the photovoltaic industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Phosphorus, arsenic and antimony co-doped N-type heavily-doped Czochralski silicon single crystal and silicon epitaxial wafer thereof
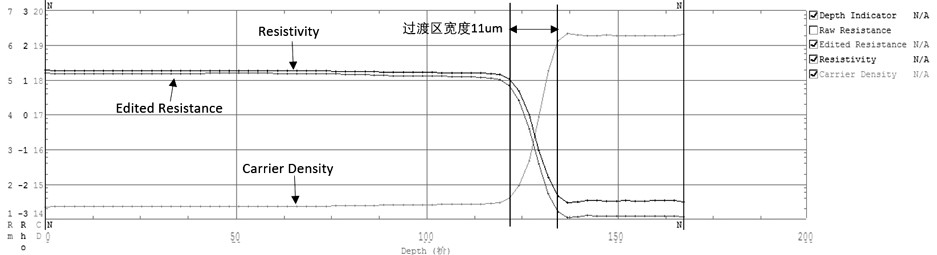
ActiveCN104711675ANo problems with widening of the transition zoneNo widening problemPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltDopantLattice mismatch
The invention discloses a phosphorus, arsenic and antimony co-doped N-type heavily-doped Czochralski silicon single crystal and a silicon epitaxial wafer thereof. The phosphorus, arsenic and antimony co-doped N-type heavily-doped Czochralski silicon single crystal takes phosphorus as the main doping element, and either or both of arsenic and antimony as auxiliary doping elements, the concentration of phosphorus is larger than or equal to 4.6*10<19> / cm<3>, phosphorus accounts for more than or equal to 60% of the doping elements, and the auxiliary doping elements accounts for 0.1-40% of the doping elements. The phosphorus, arsenic and antimony co-doped N-type heavily-doped Czochralski silicon single crystal can eliminate or remarkably reduce slip lines caused by lattice mismatching in the silicon epitaxial wafer, and can effectively reduce or eliminate mismatched dislocation lines generated when an epitaxial layer is grown on a polished wafer formed by processing of the N-type heavily-doped Czochralski silicon single crystal with high doping concentration; while the problems are solved, widening of a transition zone in a semi-conductor device after a high-temperature process is prevented; the industry practice that two or more of phosphorus, arsenic and antimony in a silicon single crystal cannot serve as dopants at the same time is changed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG QL ELECTRONICS
Single-crystal production apparatus
InactiveCN101040068AImprove insulation effectEfficient manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltIn planeCzochralski method
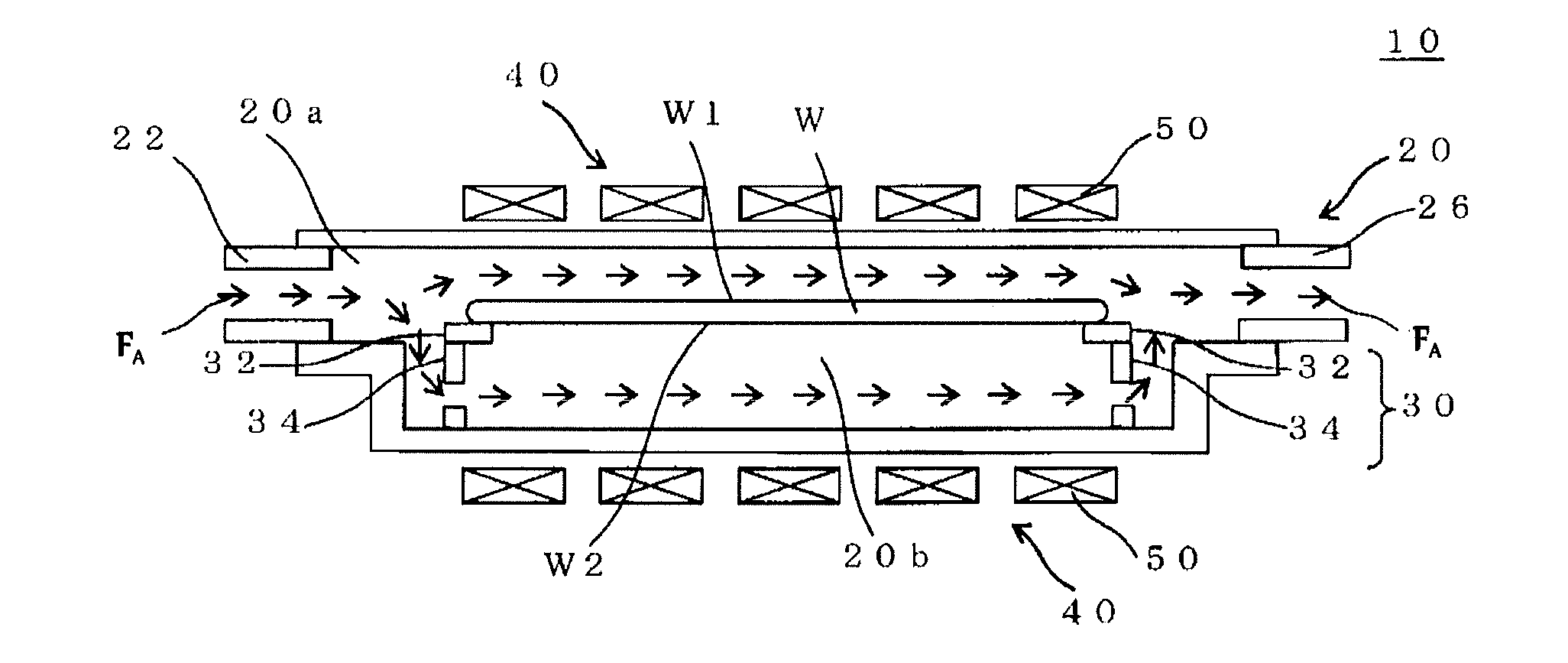
A single-crystal production apparatus for growing of a silicon single-crystal according to the Czochralski method, characterized by having at least a gas rectifier tube disposed so as to surround a silicon single-crystal in a chamber for carrying out the single-crystal growing and capable of aligning the stream of gas introduced in the chamber, the gas rectifier tube having a foamed quartz material disposed thereinside. Thus, in the growing of CZ silicon single-crystal, constantly controlling of single-crystal in-plane radial F / G at a given value can be accomplished to thereby enable efficient production of a silicon single-crystal having in-plane uniform desirable defect regions. Further, any Fe and Cu impurity contamination can be avoided to thereby provide a single-crystal production apparatus capable of production of a high-quality silicon single-crystal.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
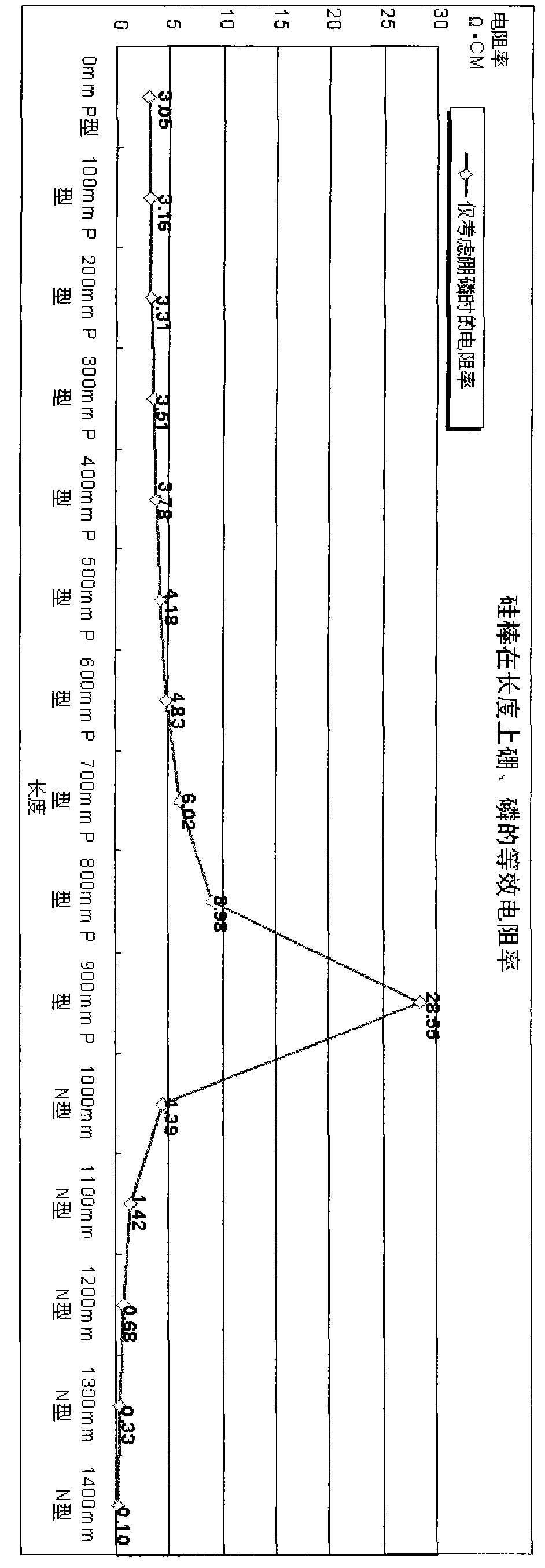
Analysis method of boron and phosphor in Ga-doped CZ silicon rod and ingredients
InactiveCN102087239AReduce quality verification costsImprove craftsmanshipMaterial resistanceAdditive ingredientPhosphor
Disclosed is an analysis method of boron and phosphor in Ga-doped CZ silicon rod and ingredients. In the method Ga doping concentrations at the head part of the silicon rod and at a certain length of the silicon rod, and doping concentrations at the head part of the CZ silicon rod and at a certain length of the CZ silicon rod when only boron and phosphor are considered are calculated first; boron and phosphor contents in Ga-doped CZ silicon rod ingredients are deduced by formulas (5) and (6), and converted to corresponding resistivity; and an excel data table is created. The invention is a necessary quality control method for Ga-doped solar grade CZ silicon single crystal. Through the invention, the production of solar energy silicon chip is controllable, and product quality and enterprise competitiveness are enhanced.
Owner:王正园
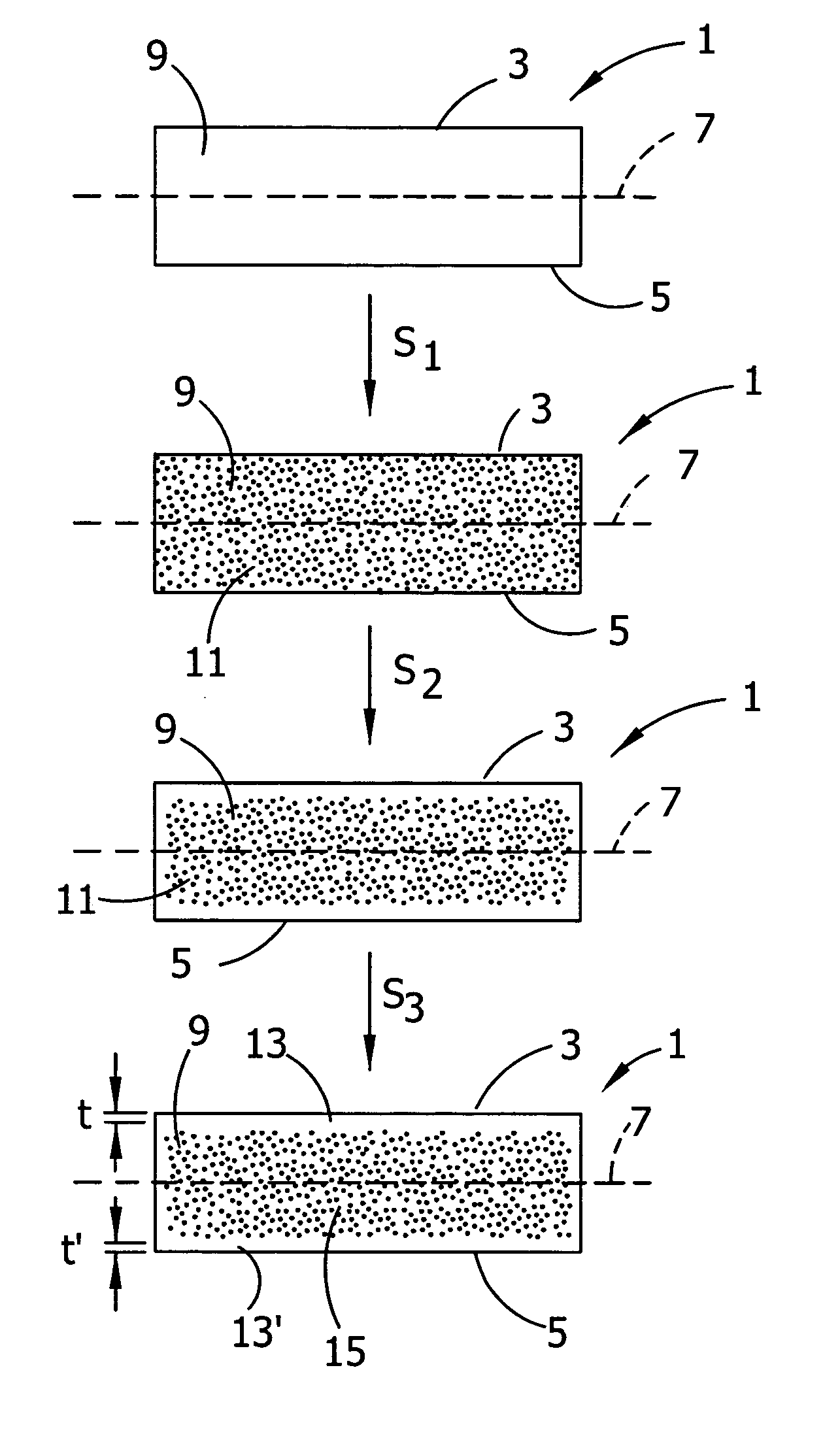
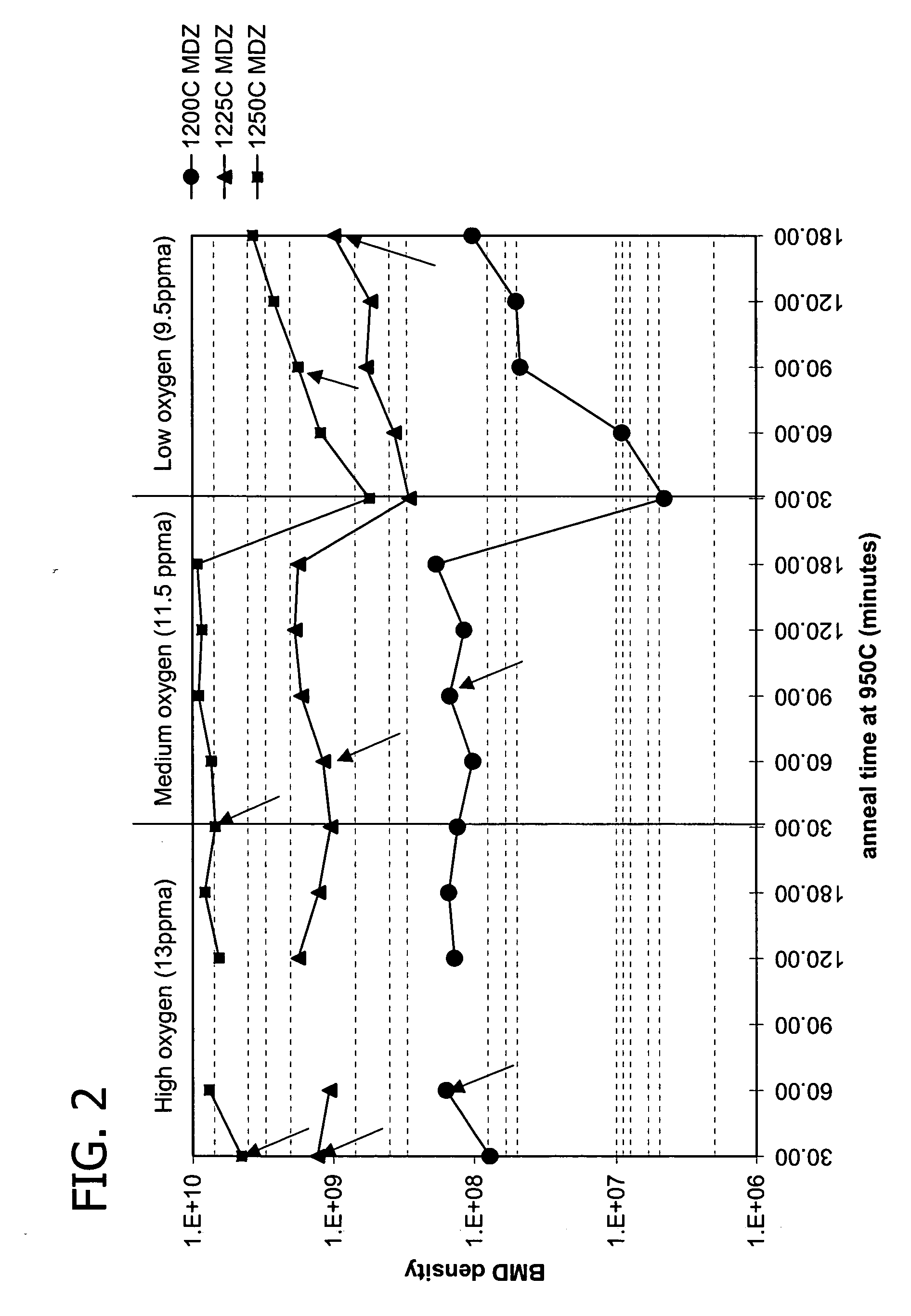
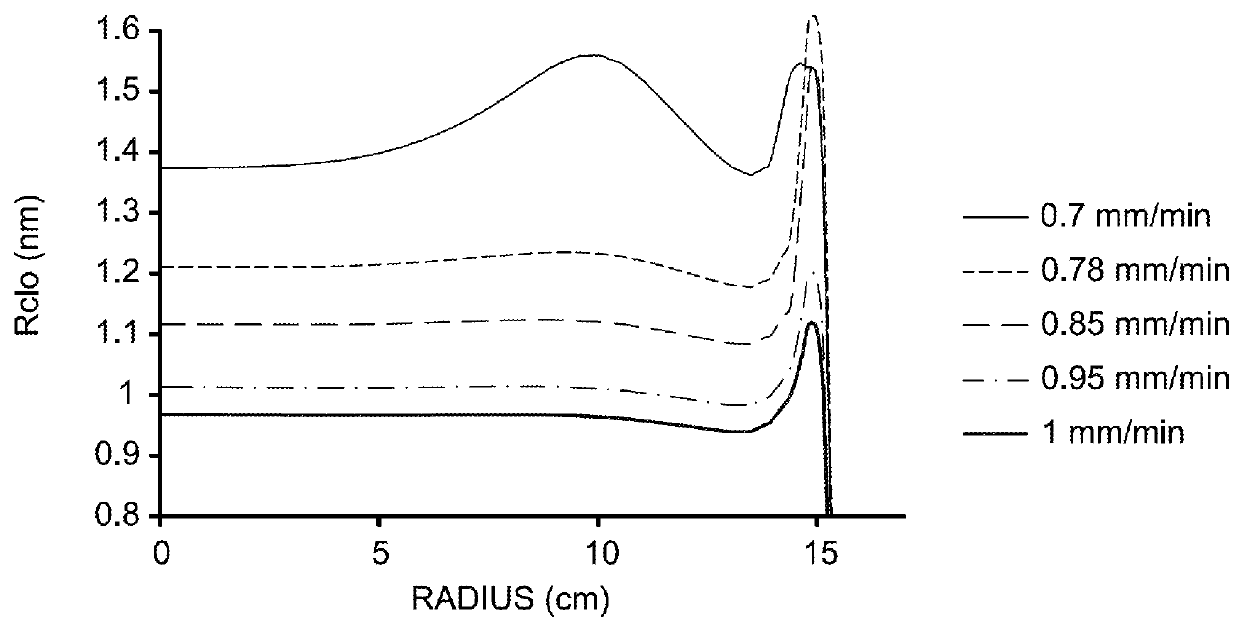
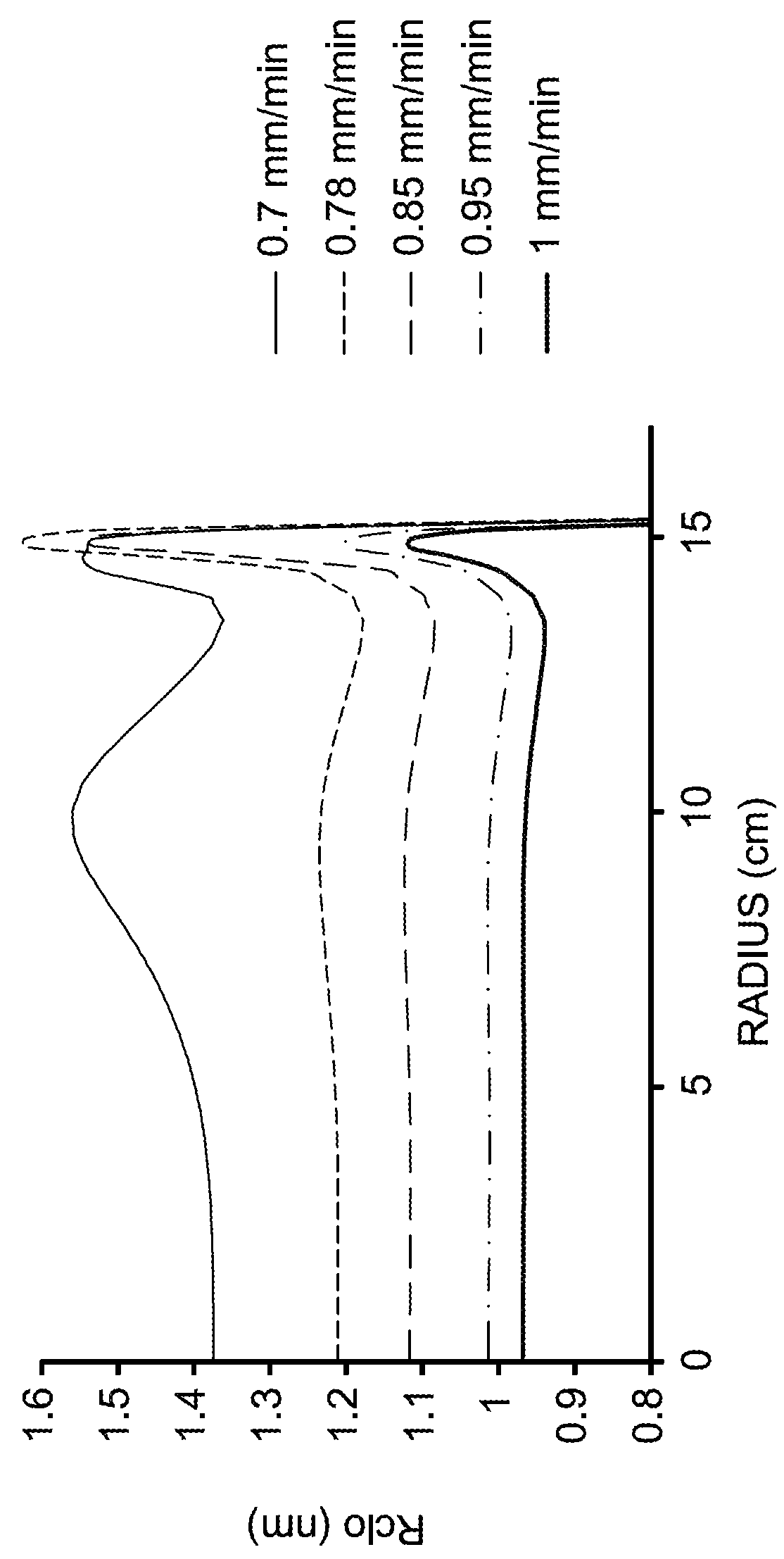
Method for heat-treating silicon wafer
InactiveUS20130078588A1Improve in-plane uniformityDecreasing COPsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationIn planeSurface layer
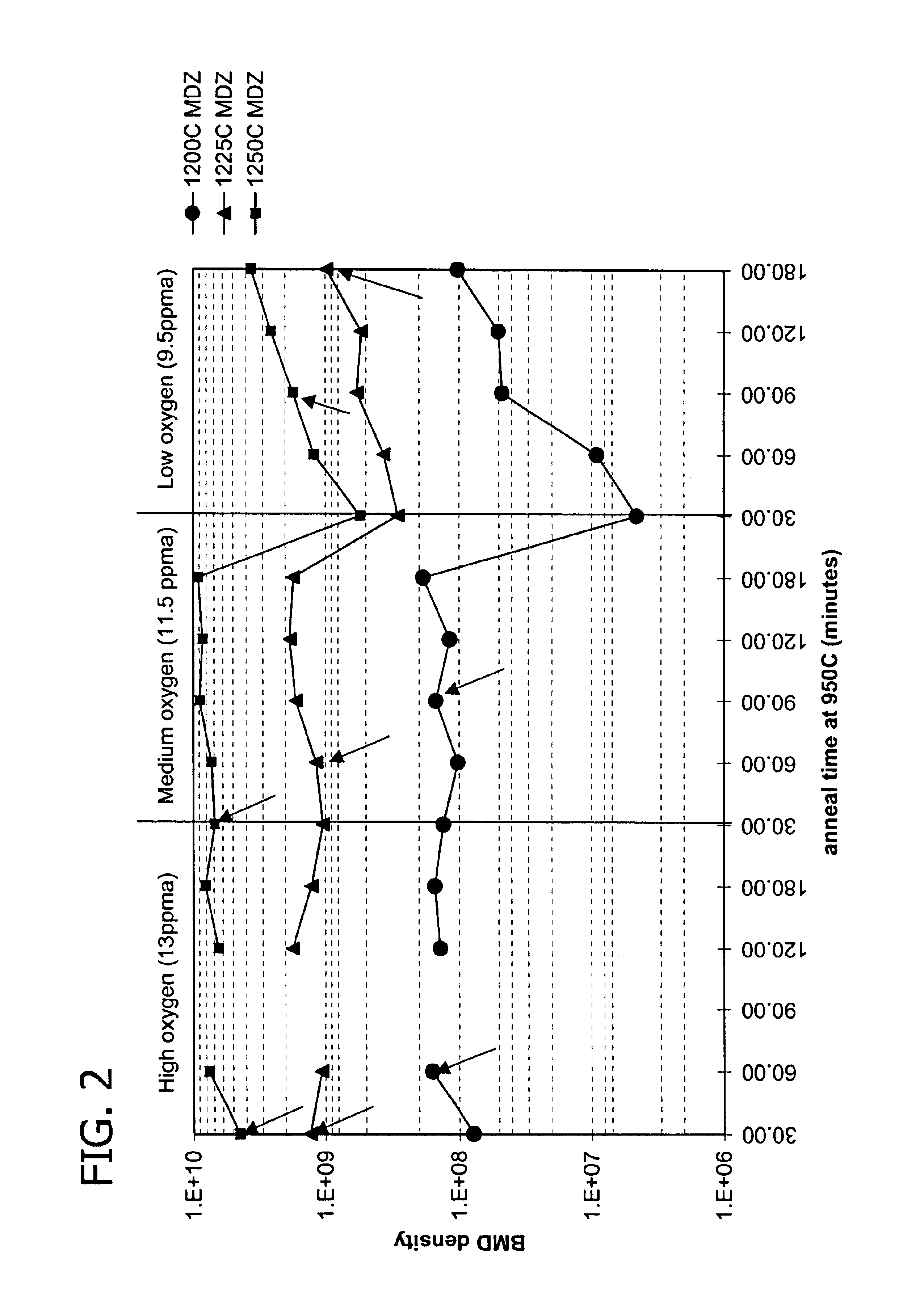
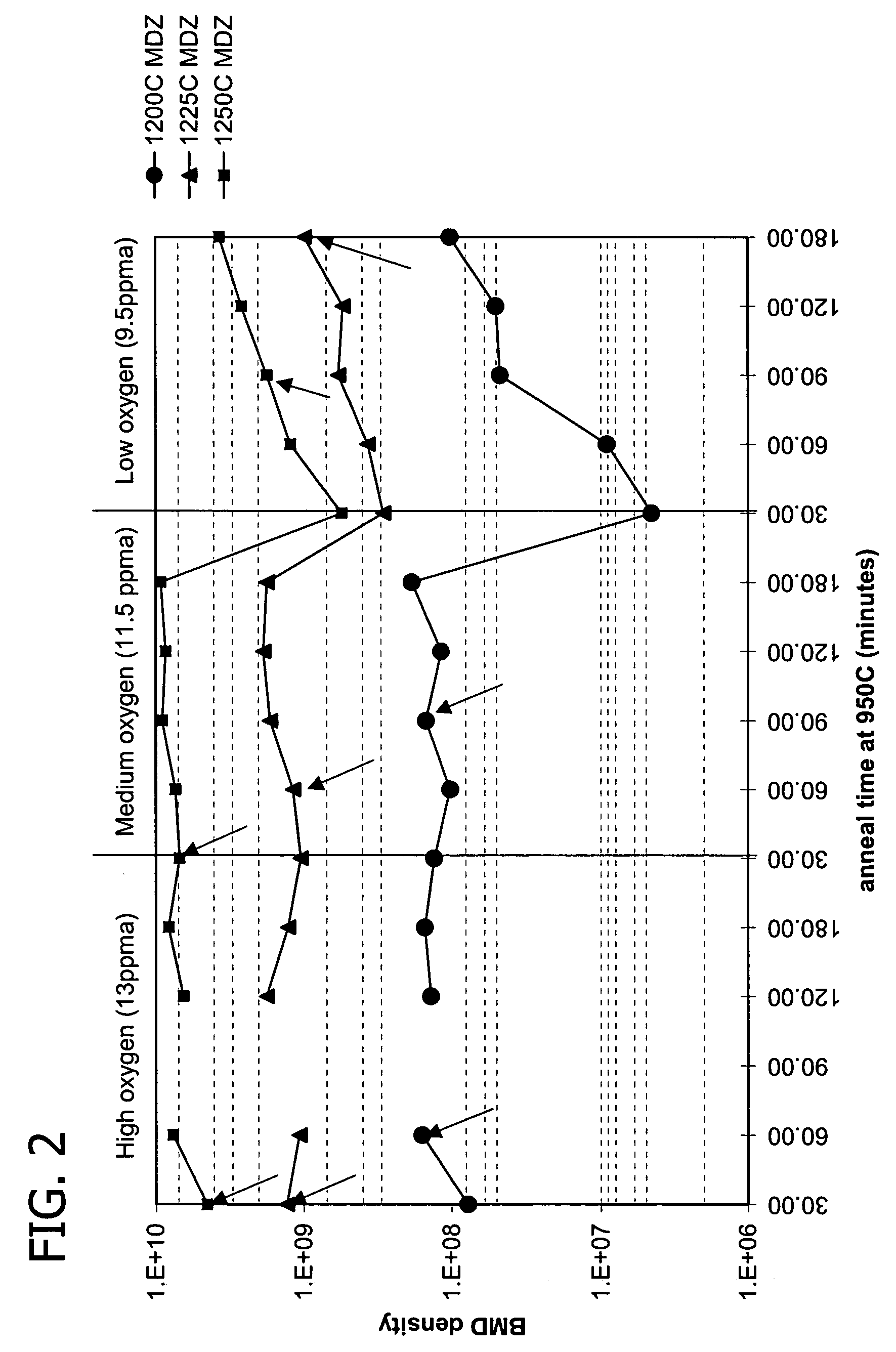
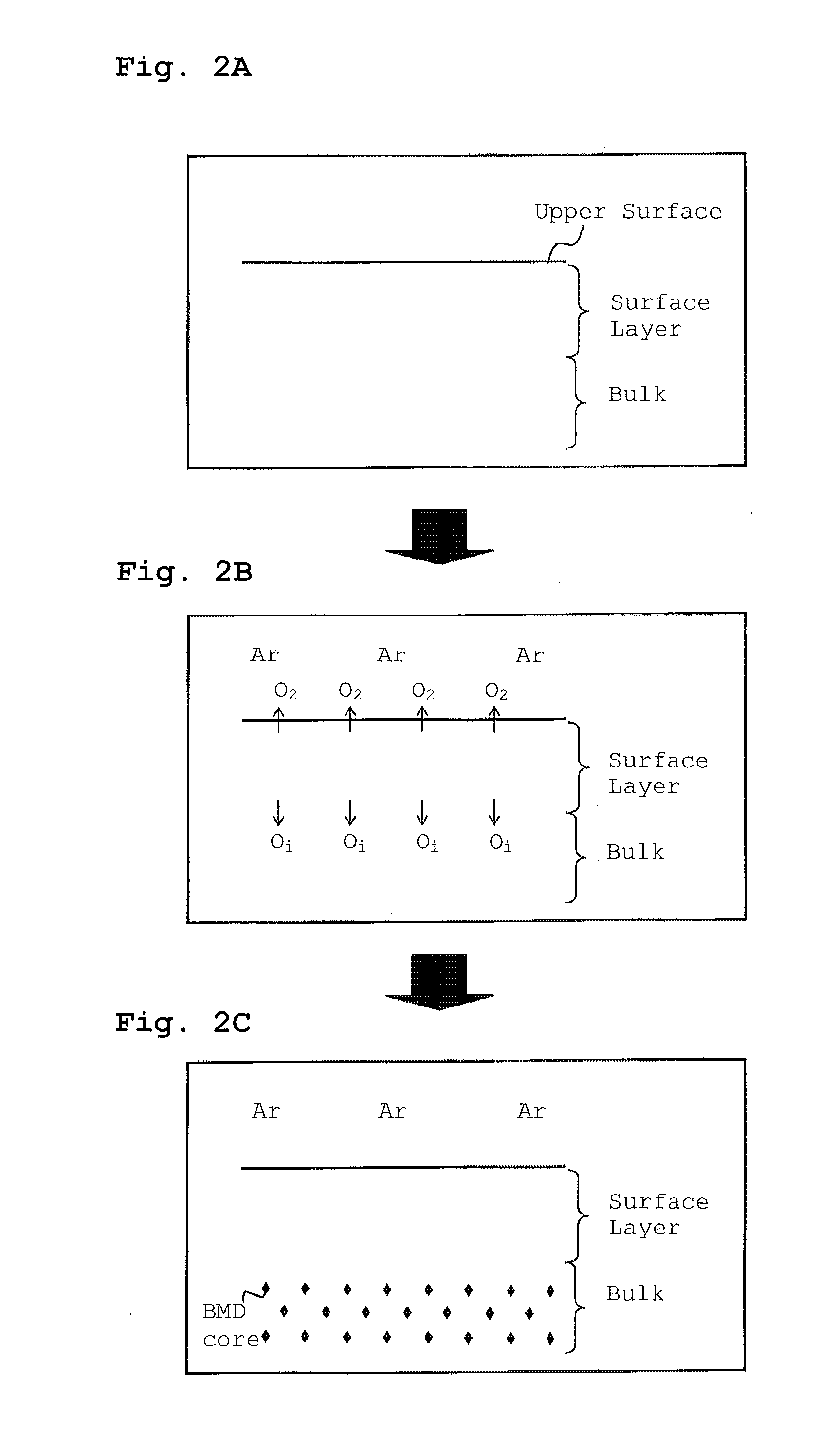
A method for heat-treating a silicon wafer is provided in which in-plane uniformity in BMD density along a diameter of a bulk of the wafer grown by the CZ process can be improved. Further, a method for heat-treating a silicon wafer is provided in which in-plane uniformity in BMD size can also be improved and COP of a surface layer of the wafer can be reduced. The method includes a step of a first heat treatment in which the CZ silicon wafer is heated to a temperature from 1325 to 1400° C. in an oxidizing gas atmosphere, held at the temperature, and then cooled at a cooling rate of from 50 to 250° C. / second, and a step of a second heat treatment in which the wafer is heated to a temperature from 900 to 1200° C. in a non-oxidizing gas atmosphere, held at the temperature, and then cooled.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS JAPAN
Charging method and device of straight-pull silicon single crystals
InactiveCN102653882AReduce manufacturing costImprove working environmentPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltWorking environmentAlloy
The invention relates to a charging method and device of straight-pull silicon single crystals. The method comprises the following steps: preparation before charging, charging, cover closing, vacuumizing, charging into a crystal pulling furnace, dismounting of a quartz crucible cover, and furnace closing. The device comprises a quartz crucible, a quartz crucible cover, an O-ring seal and a charging car. When charging, the quartz crucible is arranged on the charging car, the O-ring seal is put on the opening of the quartz crucible after charging the silicon single crystals and mother alloy, the quartz crucible cover is closed, a suction pump is connected for vacuumizing, and the quartz crucible is suspended. The straight-pull silicon single crystal charging technique can be independently carried out in a clean room, thereby avoiding pollution in the polysilicon material charging process, improving the work environment of charging and lowering the labor intensity of charging; the charging technique, furnace dismounting and thermal field cleaning can be performed at the same time, thereby greatly shortening the furnace mounting and dismounting time, enhancing the production efficiency and crystal pulling furnace utilization ratio, and lowering the production cost of the silicon single crystals.
Owner:TDG HLDG CO LTD
Seeding method and manufacturing method of czochralski silicon single crystal
ActiveCN110528068ASolve technical problems of uncertaintyReduce technical proficiency dependencyPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltAgricultural engineeringSingle crystal
The invention discloses a seeding method of a Czochralski silicon single crystal. A seeding temperature is regulated by seeding speed deviation, and the seeding speed deviation is a difference value between an average seeding speed and a set seeding speed in a seeding temperature regulation period. If the seeding speed deviation is positive, positive fine adjustment is performed on the seeding temperature; and if the seeding speed deviation is negative, negative fine adjustment is performed on the seeding temperature. According to differences of the diameter shrinkage process, the seeding temperature regulation and control mode comprises the steps that only one continuous diameter shrinkage process is performed in the whole seeding process, regulation and control are conducted in the wholeprocess, and the fine adjustment amount of the seeding temperature is set according to a power regulation coefficient; or the seeding process is a non-continuous diameter shrinkage process and comprises a first diameter shrinkage process, an equal grain refinement process and a second diameter shrinkage process, a target diameter of diameter shrinkage is achieved through the second diameter shrinkage process, once seeding temperature regulation and control is carried out in the equal grain refinement process, and the fine adjustment amount of the seeding temperature is set according to the power regulation coefficient. The invention also discloses a production method of the czochralski silicon single crystal by adopting the seeding method. The temperature is accurately adjusted through seeding, and the yield of single crystals is increased.
Owner:LONGI GREEN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Auxiliary machine for czochralski silicon single crystal furnace thermal field disassembling and cleaning
ActiveCN112658659AImprove disassembly efficiencyAvoid burnsFinal product manufactureMetal working apparatusEngineeringSingle crystal
The invention provides an auxiliary machine for czochralski silicon single crystal furnace thermal field disassembling and cleaning. The auxiliary machine comprises a supporting frame, a first driving assembly, supporting stand columns, clamping assemblies and tray assemblies, wherein the plurality of supporting stand columns are fixedly installed on the supporting frame, under driving force of the first driving assembly, the telescopic supporting stand columns do lifting motion in the vertical direction, the clamping assemblies are rotationally fixed to the supporting stand columns, the plurality of tray assemblies are rotationally installed on the supporting stand columns, and the clamping assemblies clamp a device in a single crystal furnace and places the device on the tray assemblies. The auxiliary machine is used for disassembling the single crystal furnace in a high-temperature state, so that time required for cooling is saved, and the problem of scalding the personnel is avoided; and in the process of disassembling the single crystal furnace, the rotatable clamping assemblies and the tray assemblies are small in occupied area, the pollution degree to the surrounding environment is reduced, the cleanliness of a workshop is guaranteed, the disassembling efficiency of the single crystal furnace is improved, and potential safety hazards of the workshop are reduced.
Owner:曲靖晶龙电子材料有限公司
Control system and control method of high frequency switching power supply for cz silicon single crystal furnace
InactiveCN103346676BImprove robustnessImprove dynamic characteristicsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPower controllerControl system
The invention discloses a control system of a high frequency switching power supply for a Cz silicon single crystal furnace and a control method. The control method includes the steps of combining self-adaptive fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control, and aiming at a high-frequency switch heating electric power for the Cz silicon single crystal furnace to design a power controller based on a self-adaptive fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control method. The control system of the high frequency switching power supply for the Cz silicon single crystal furnace and the control method play respective advantages of fuzzy control and sliding mode variable structure control, further improve dynamic performance of the system, have good robustness for input voltage or load disturbance, and relieve or avoid vibration which generally happens to a sliding mode.
Owner:青海鑫诺光电科技有限公司
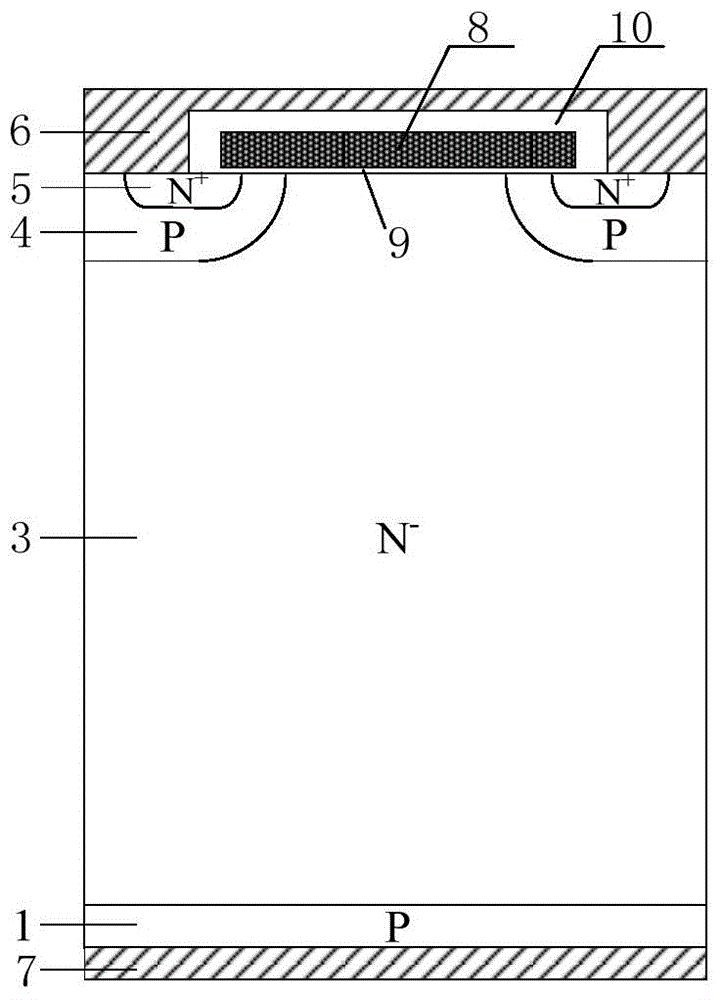
Preparation method of FS-IGBT
InactiveCN104681434AForward voltage dropReduced turn-off lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLow voltageSurface structure
The invention provides a method for preparing an FS-IGBT (Field Stop-Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator) on a silicon wafer, which is used for solving the problems caused by a thin silicon wafer during a preparation process of a medium / low-voltage FS-IGBT that the preparation technology is complicated, the difficulty is large, the thin silicon wafer warps and deforms and is segmented, the size of the thin silicon wafer (a wafer) is limited, the yield is low, the cost is high, and industrialization is difficult to realize and overcoming the huge technical challenge caused by the thin silicon wafer in follow-up scribing of the wafer and encapsulating of a chip. The preparation method comprises the steps of selecting light-doped FZ silicon as a first silicon wafer and heavy-doped CZ silicon or FZ silicon as a second silicon wafer; firstly, making an N-type FS layer and a P-type transparent collecting zone on the back surface of the first silicon wafer; then, bonding the first silicon wafer and the second silicon wafer; making a front-surface structure by thinning the thickness of the first silicon wafer; finally, thinning the second silicon wafer; forming a collector electrode through etching, metal depositing and chemical-mechanical polishing; obtaining the FS-IGBT.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nitrogen Doped and Vacancy Dominated Silicon Ingot and Thermally Treated Wafer Formed Therefrom Having Radially Uniformly Distributed Oxygen Precipitation Density and Size
ActiveUS20180266016A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsOxygen precipitatesNitrogen doped
Nitrogen-doped CZ silicon crystal ingots and wafers sliced therefrom are disclosed that provide for post epitaxial thermally treated wafers having oxygen precipitate density and size that are substantially uniformly distributed radially and exhibit the lack of a significant edge effect. Methods for producing such CZ silicon crystal ingots are also provided by controlling the pull rate from molten silicon, the temperature gradient and the nitrogen concentration. Methods for simulating the radial bulk micro defect size distribution, radial bulk micro defect density distribution and oxygen precipitation density distribution of post epitaxial thermally treated wafers sliced from nitrogen-doped CZ silicon crystals are also provided.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
N/n+ silicon epitaxial wafer with high metal impurity absorption capacity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103094316APromote generationQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStacking faultMetal impurities
The invention provides a n / n+ silicon epitaxial wafer with a high metal impurity absorption capacity, and the n / n+ silicon epitaxial wafer with the high metal impurity absorption capacity includes that a light-doped n-type silicon is an epitaxial layer, defect density of the stacking fault and dislocation is less than or equal to 0.05 / cm2, nitrogen-doped heavy-doped n-type czochralski silicon is a substrate, and the resistivity of the substrate is less than or equal to 0.005 omega cm; the substrate contains a stable oxygen precipitation nucleation center, and the generated density of oxygen precipitation is more than or equal to 1 * 109 / cm3. The invention further provides a preparation method of the n / n+ silicon epitaxial wafer, and the steps of the preparation method include that the heavy-doped n-type czochralski silicon is carried out a high temperature rapid heat treatment under N2 atmosphere, and the light-doped n-type silicon epitaxial layer grows on the heat-treated heavy-doped n-type czochralski silicon. The n / n + silicon epitaxial wafer is acquired through two steps of heat treatment including a low temperature heat treatment and a high temperature heat treatment. The n / n+ silicon epitaxial wafer with a high metal impurity absorption capacity and the preparation method of the n / n+ silicon epitaxial wafer solve the problem that an oxygen precipitation with a high density is hard to generate in the n / n + silicon epitaxial wafer heavy-doped n-type czochralski silicon substrate, and have a good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
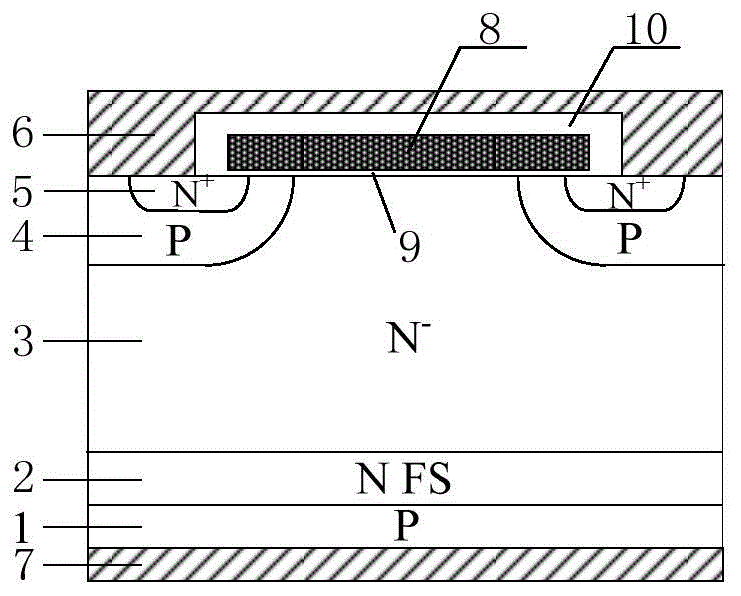
Method for manufacturing high-voltage VDMOS by adopting silicon-silicon bonding process
PendingCN111900198AQuality improvementNarrowing of the transition zoneSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBonding processMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a high-voltage VDMOS by adopting a silicon-silicon bonding process. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a support substrate and a bonding substrate; carrying out silicon-silicon bonding on the support substrate and the bonding substrate, and carrying out high-temperature annealing and curing; carrying out a corrosion treatment onthe edge chamfers of the bonded support substrate and the bonding substrate; thinning the bonding substrate to a required thickness; and polishing the bonding substrate. The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for manufacturing a high-voltage VDMOS by adopting a silicon-silicon bonding process. The silicon-silicon bonding process is used; a silicon-silicon bonding sheet is prepared by bonding conventional CZ silicon substrate materials with different resistivity to replace an existing thick-film epitaxial wafer, a high-quality silicon substrate sheet meeting customer requirements isobtained, the production efficiency is improved, the production cost is reduced, a transition region of the obtained high-voltage VDMOS device is obviously narrowed, and the consistency of product parameters is better.
Owner:杭州华芯微科技有限公司
Substrate for an electronic device and method for producing the same
PendingUS20220367188A1Cheap productionGood substratePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWaferingCrystal orientation
The present invention is a substrate for an electronic device, including a nitride semiconductor film formed on a joined substrate including a silicon single crystal, where the joined substrate has at least a bond wafer including a silicon single crystal joined on a base wafer including a silicon single crystal, the base wafer includes CZ silicon having a resistivity of 0.1 Ωcm or lower and a crystal orientation of <100>, and the bond wafer has a crystal orientation of <111>. This provides a substrate for an electronic device, having a suppressed warp.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
A kind of automatic temperature regulation method of Czochralski silicon single crystal
ActiveCN110528069BReduce instabilityImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltTemperature controlPhysical chemistry
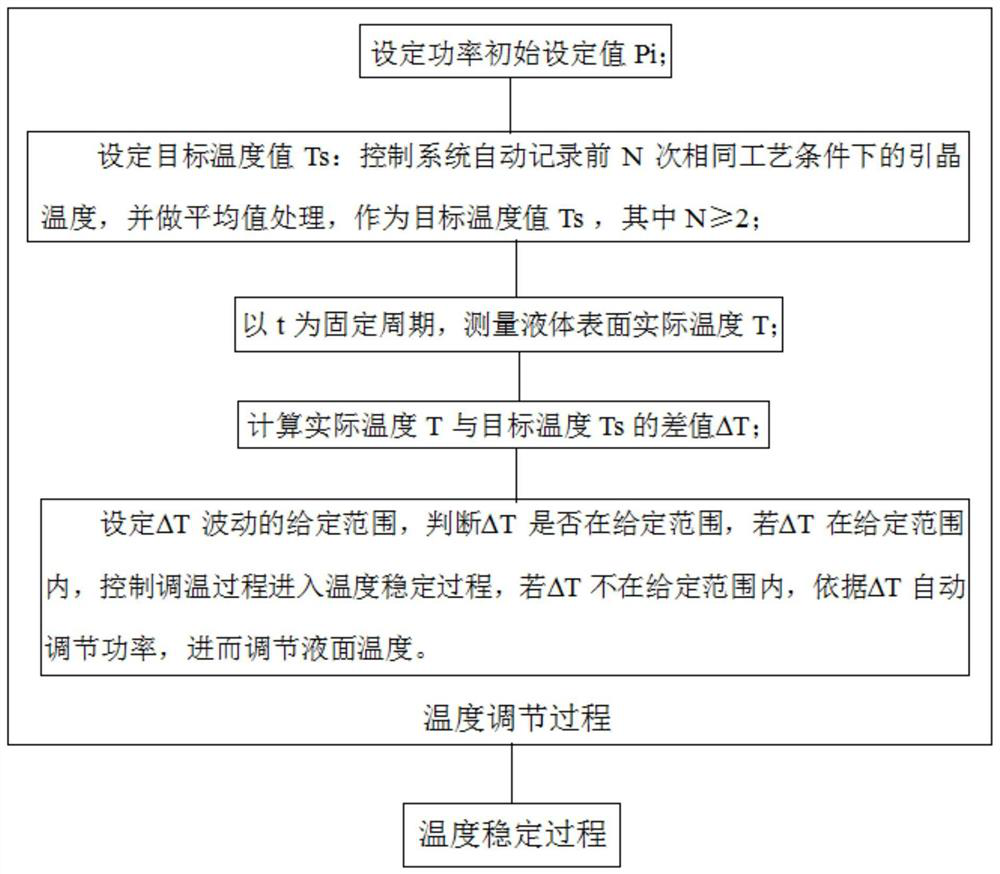
The automatic temperature adjustment method for Czochralski silicon single crystal disclosed by the present invention is used for automatic adjustment of the liquid surface temperature, comprising the following steps: setting the target liquid surface temperature value Ts, measuring the actual liquid surface temperature value T, and taking t as the fixed cycle time Calculate the difference ΔT between the actual liquid surface temperature T and the target liquid surface temperature Ts; judge whether ΔT is within a given range; if yes, enter the temperature stabilization process, if not, perform the temperature adjustment process; The value ΔT is calculated to obtain the power adjustment amount ΔPower and the power setting value Pr, the output power setting value Pr, and then adjust the temperature of the silicon melt surface. The present invention cancels the control that SP participates in, eliminates unstable factors, improves the stability of the system control temperature, improves the uniformity of temperature adjustment, improves the yield and reduces the production cost.
Owner:LONGI GREEN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Modeling method for czochralski silicon single crystal pulling speed-crystal diameter identification model
ActiveCN110009094ASimplify the reverse training processThe solution accuracy is not highPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltModel methodSingle crystal
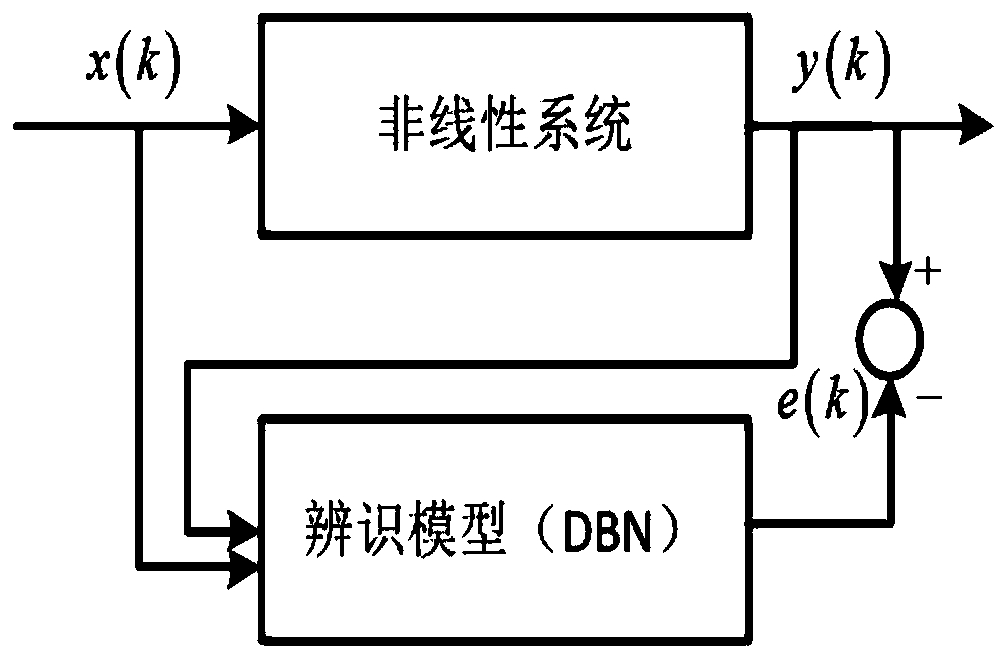
The invention provides a modeling method for a czochralski silicon single crystal pulling speed-crystal diameter identification model. The method specifically comprises the following steps: step 1, sampling for multiple times, recording the pulling speeds and crystal diameters of a czochralski silicon single crystal at different sampling moments k, and forming a plurality of groups of data pairs at different sampling moments k; step 2, determining to obtain a specific discrete time nonlinear system model expression about the pulling speed and the crystal diameter of the czochralski silicon single crystal; step 3, training the DBN network; step 4, taking trained DBN network as a czochralski silicon single crystal pulling speed-crystal diameter identification model. According to the modelingmethod of the Czochralski silicon single crystal pulling speed-crystal diameter identification model, the defects existing in training by adopting a DBN network in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Seeding method and manufacturing method of Czochralski silicon single crystal
ActiveCN110528068BSolve technical problems of uncertaintyReduce technical proficiency dependencyPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltTemperature controlSingle crystal
The invention discloses a crystal seeding method for Czochralski silicon single crystal. The seeding temperature is regulated by the seeding speed deviation, and the seeding speed deviation is the difference between the average seeding speed and the set seeding speed in the seeding temperature adjustment period. . If the seeding speed deviation is positive, the seeding temperature is fine-tuned positively; if the seeding speed deviation is negative, the seeding temperature is fine-tuned negatively. According to the difference in the diameter reduction process, the seeding temperature control methods include: the entire seeding process has only one continuous diameter reduction process, which is regulated throughout the process, and the seeding temperature fine-tuning amount is set according to the power adjustment coefficient; or the seeding process is a non-continuous process. The diameter reduction process includes the first diameter reduction process, the equal grain reduction process and the second diameter reduction process. After the second diameter reduction process, the target diameter of diameter reduction is achieved. During the equal grain reduction process, the seeding temperature is adjusted once. The amount of fine adjustment is set according to the power adjustment coefficient. The invention also discloses the production method of the Czochralski silicon single crystal adopting the above seeding method. The invention can accurately regulate the temperature of the seeded crystal, thereby improving the yield of single crystal.
Owner:LONGI GREEN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Storage bag for polycrystalline silicon ingot, method for packing polycrystalline silicon ingot, and method for producing CZ silicon single crystal
ActiveUS10266964B2Easy to cleanPolycrystalline material growthSiliconLinear low-density polyethyleneAntioxidant
In the present invention, as a bag to store polycrystalline silicon ingots, there is used a bag in which the concentration of paraffinic hydrocarbons in a concentrate of solvent-soluble components obtained by Soxhlet extraction using acetone as a solvent is lower than 300 ppmw as a value measured by GC-MS method; the concentration of antioxidants, lower than 10 ppmw; the concentration of ultraviolet absorbents, lower than 5 ppmw; and the concentration of antistatic agents and surfactants, lower than 50 ppmw. Then, when the polycrystalline silicon ingots are packed, preferably, the polycrystalline silicon ingots are put in the storage bag; thereafter, the storage bag is sealed; further, the storage bag is put and sealed in a linear low-density polyethylene bag containing an antistatic agent or a surfactant added in the bag material.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com