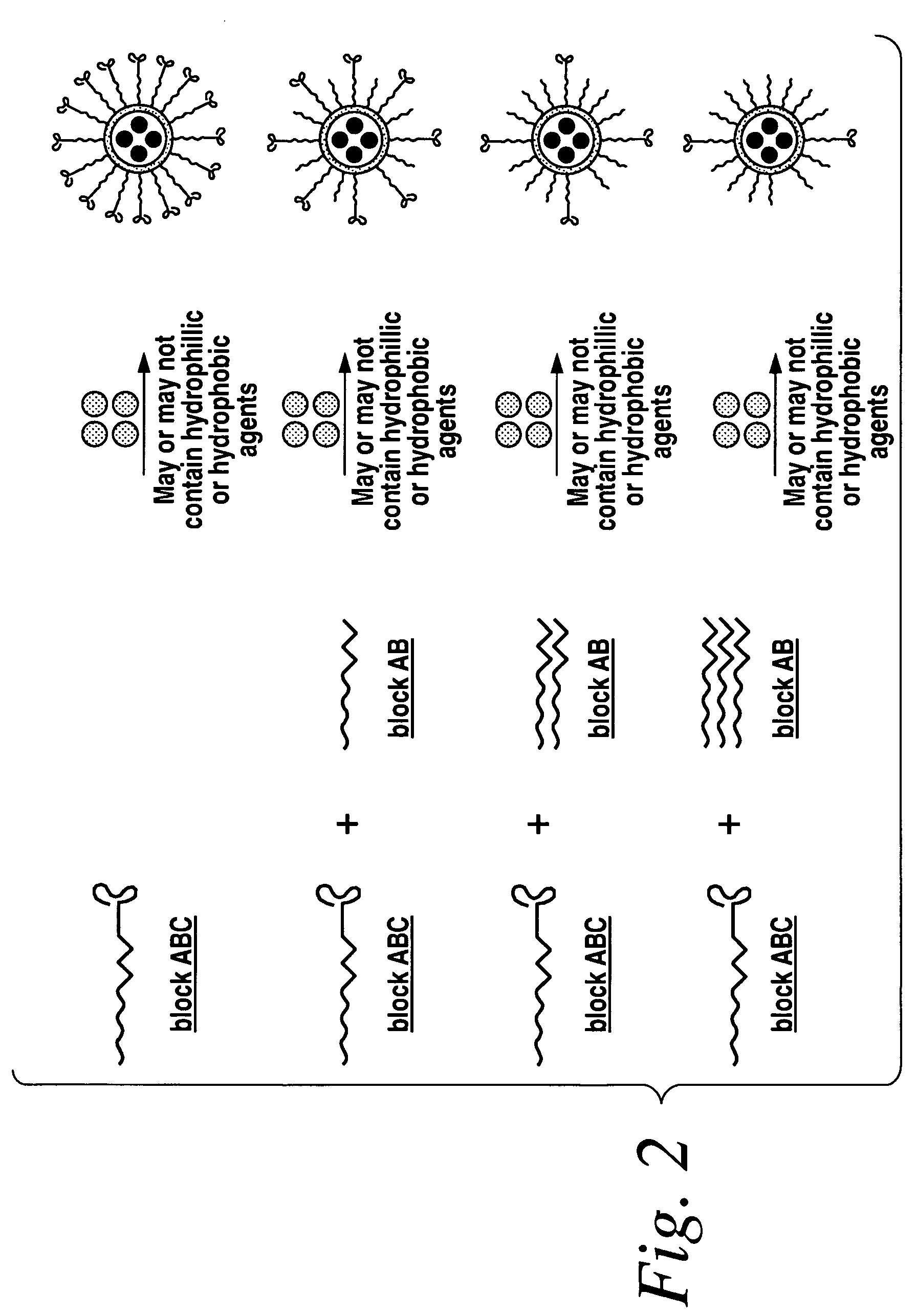
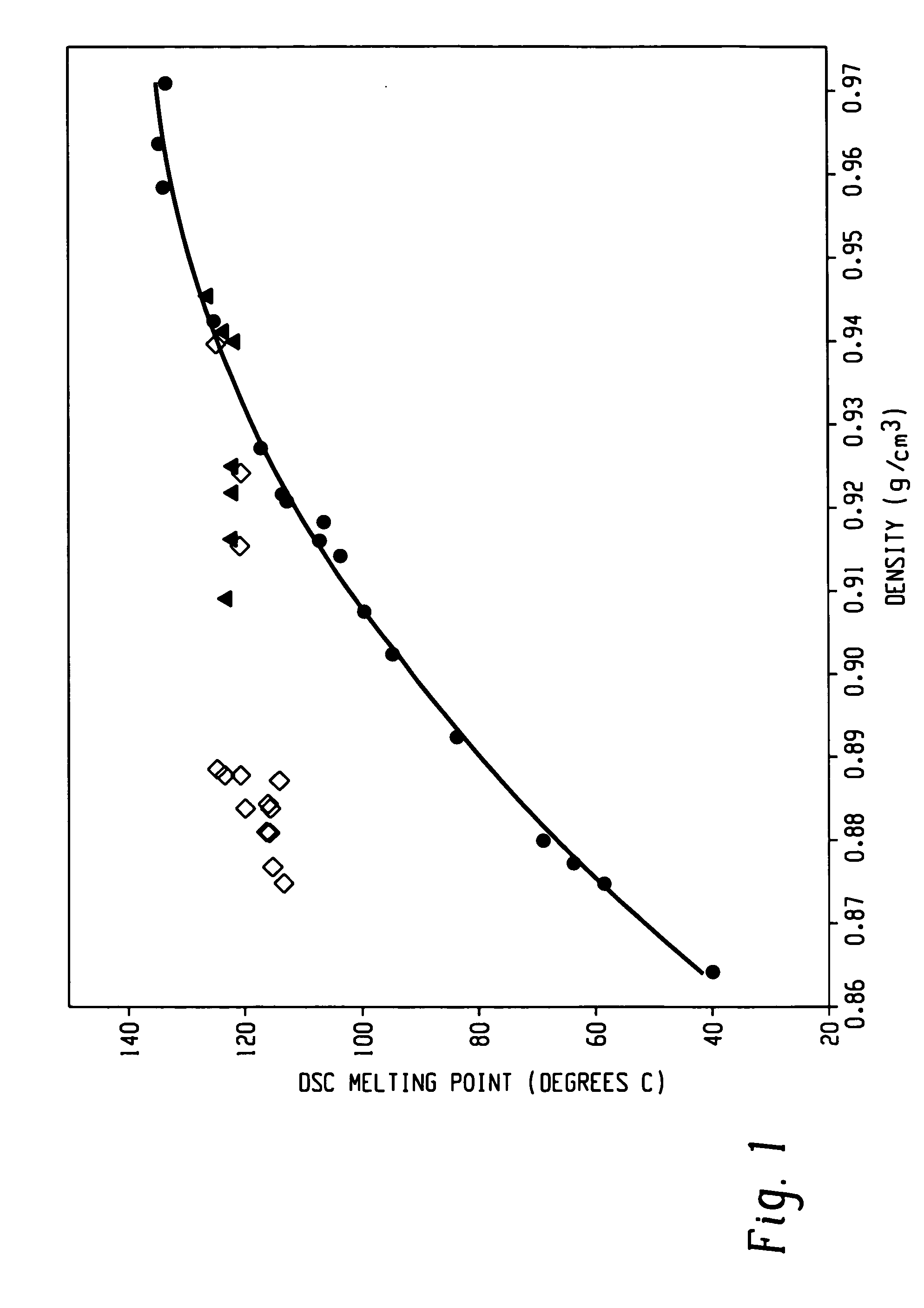
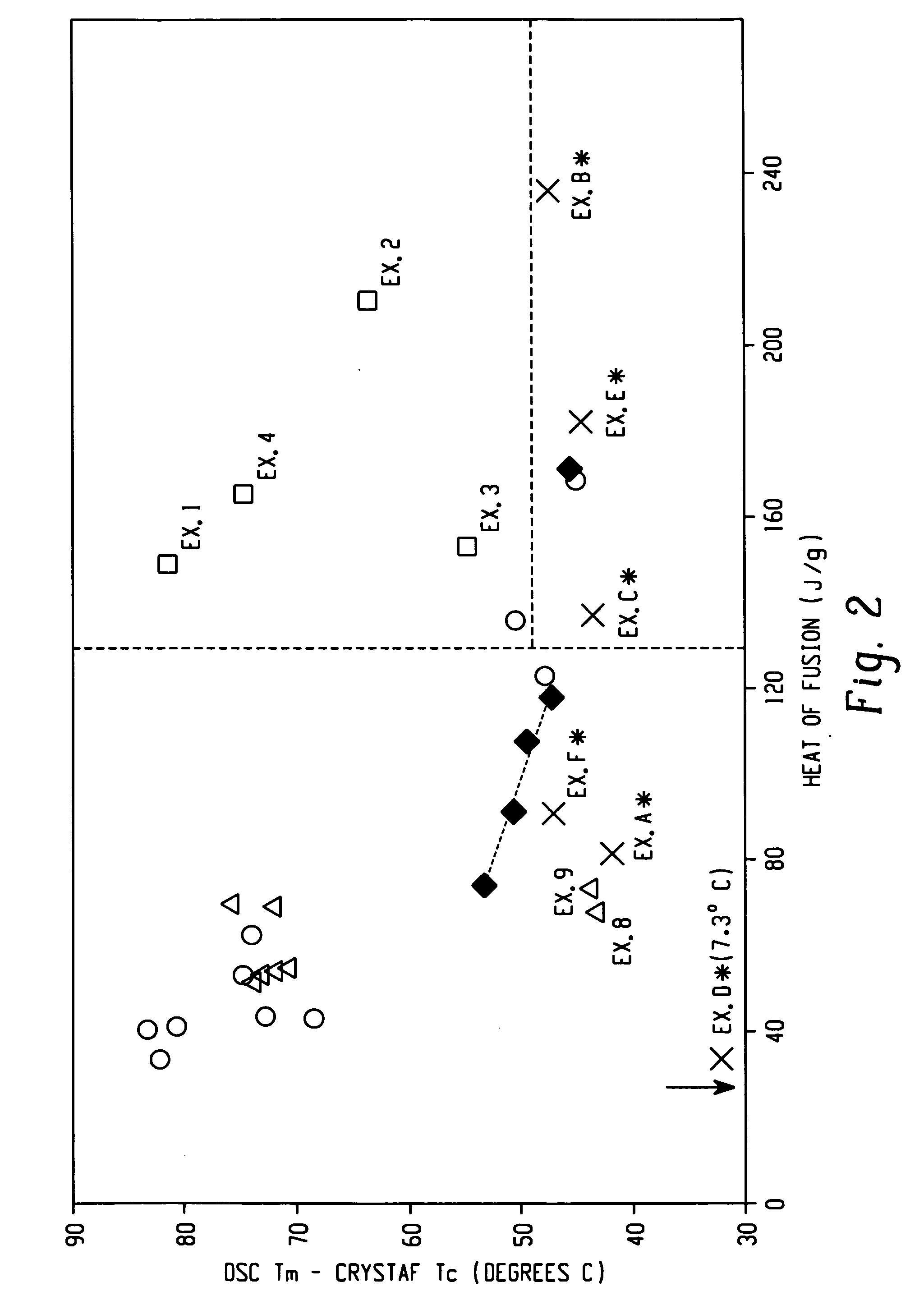
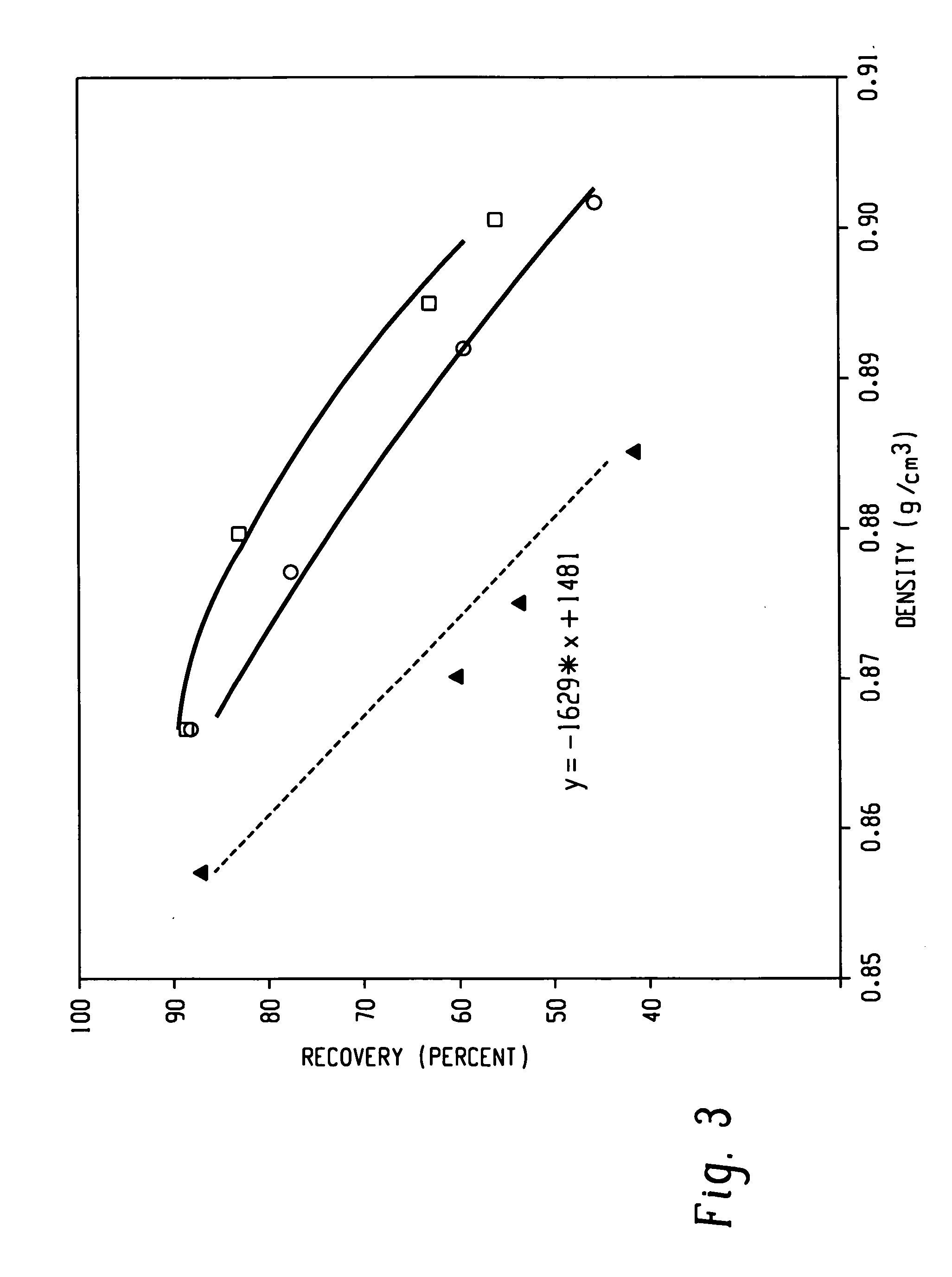
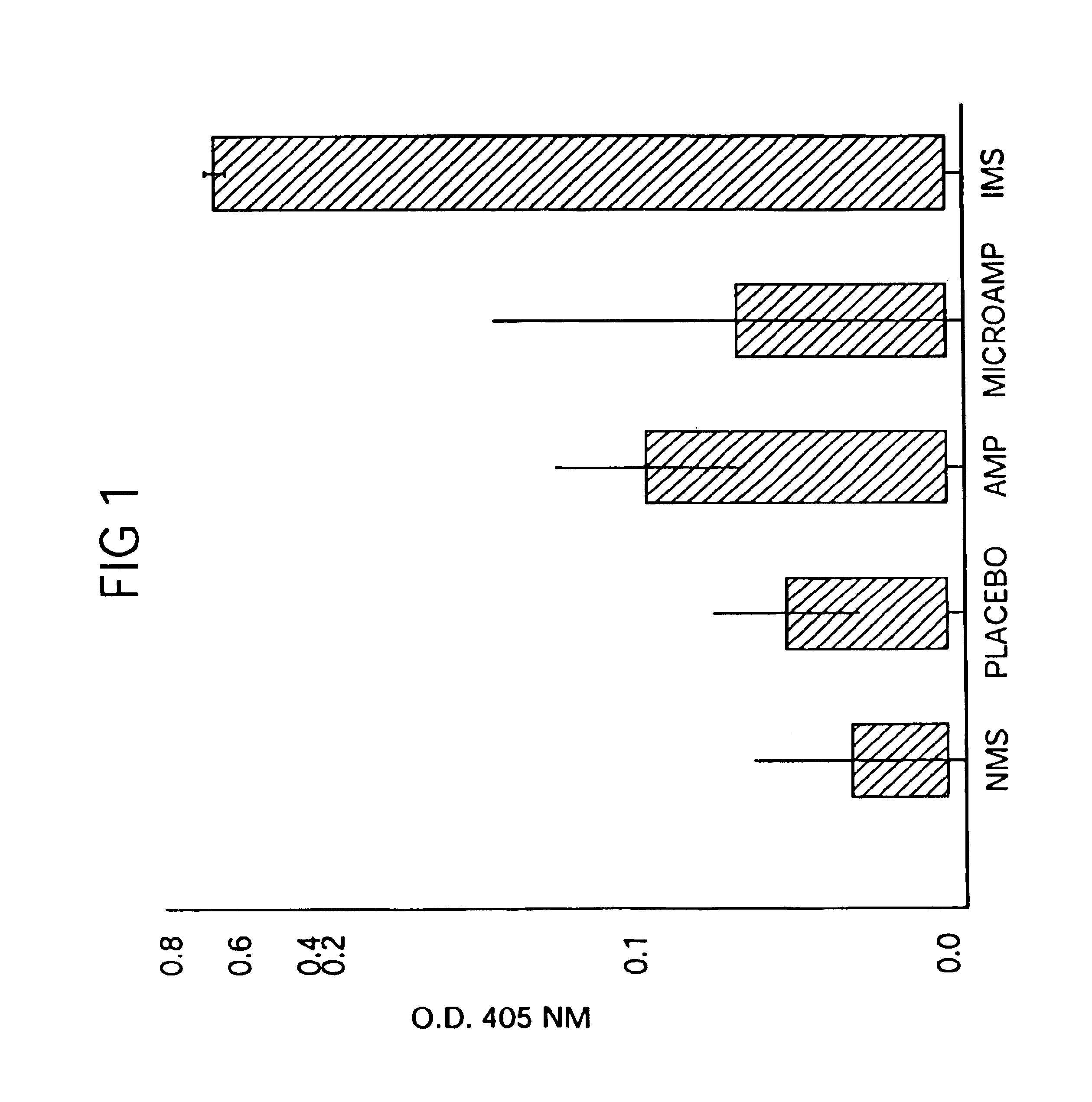
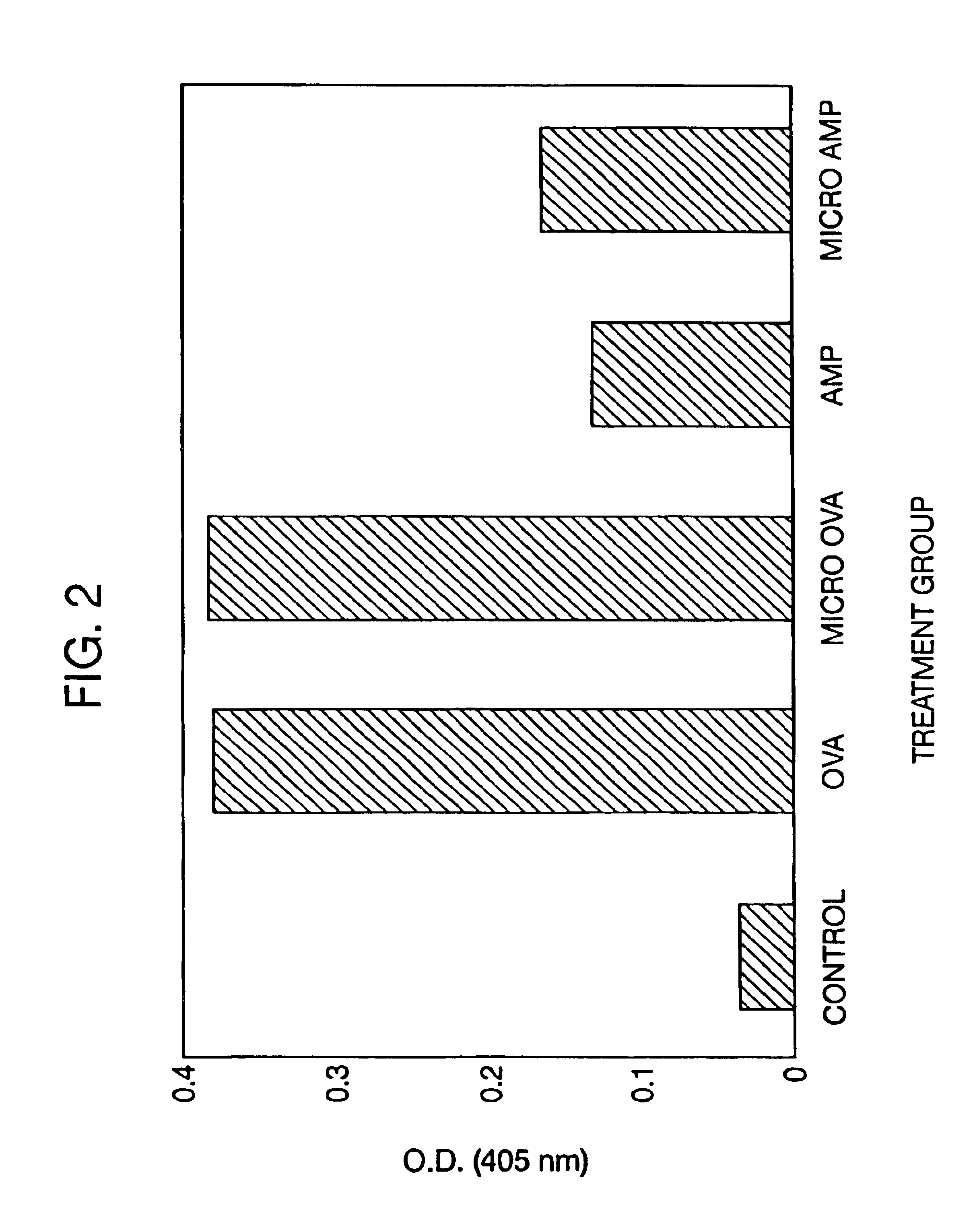
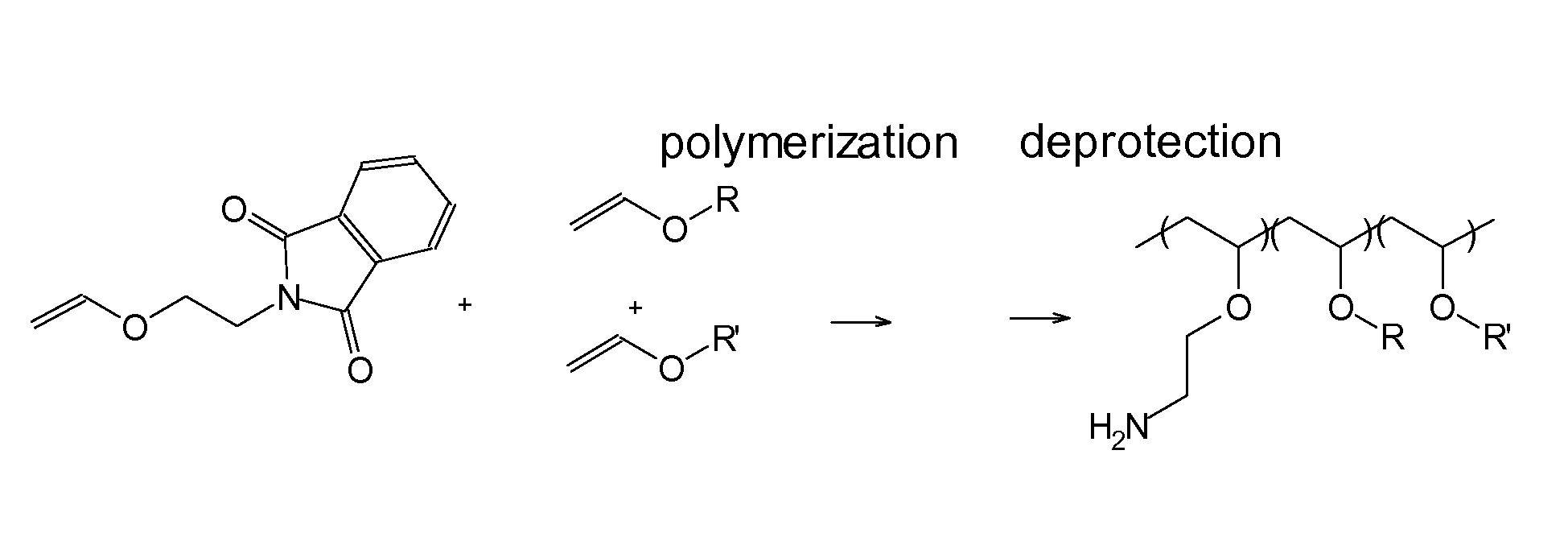
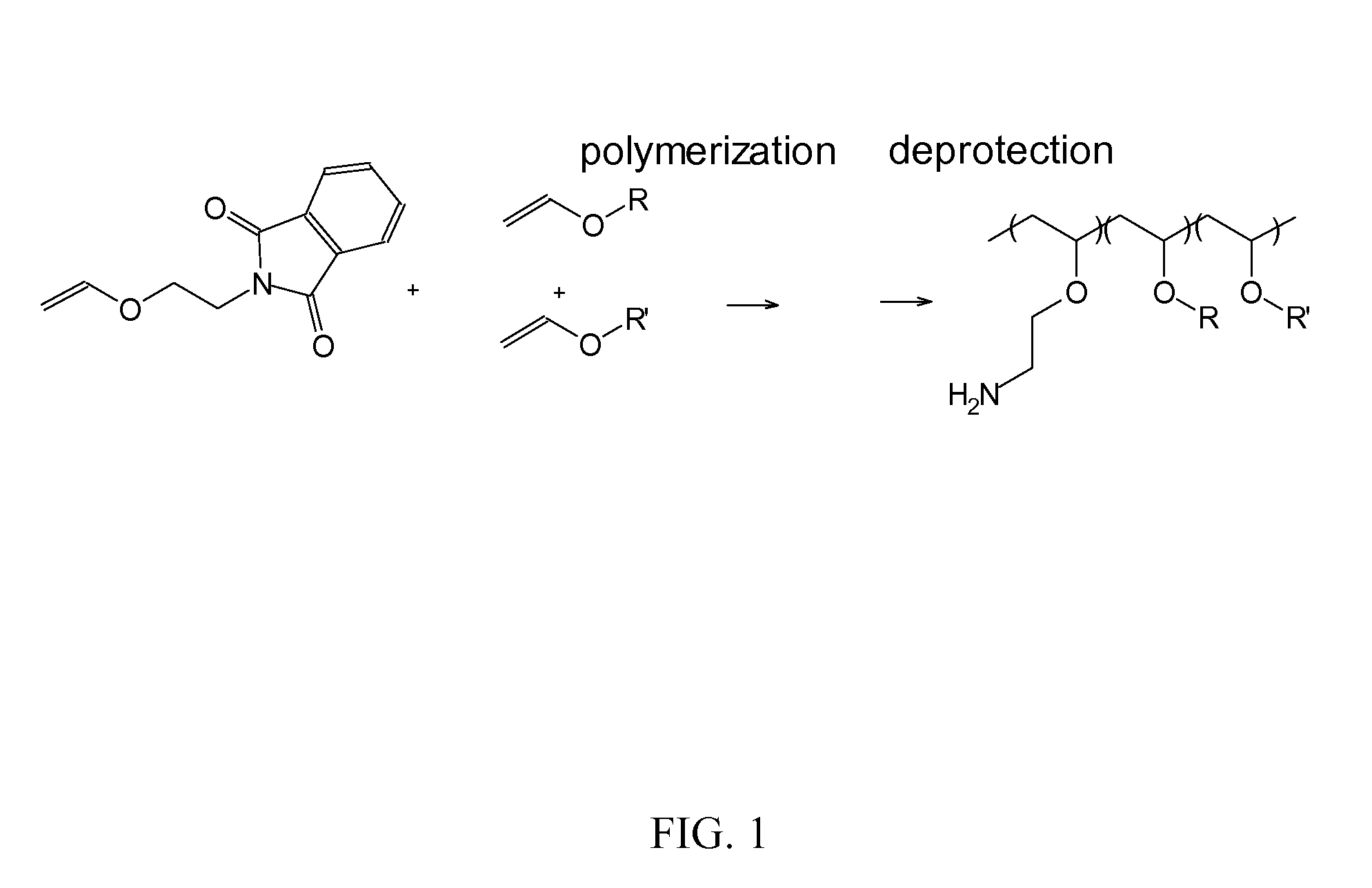
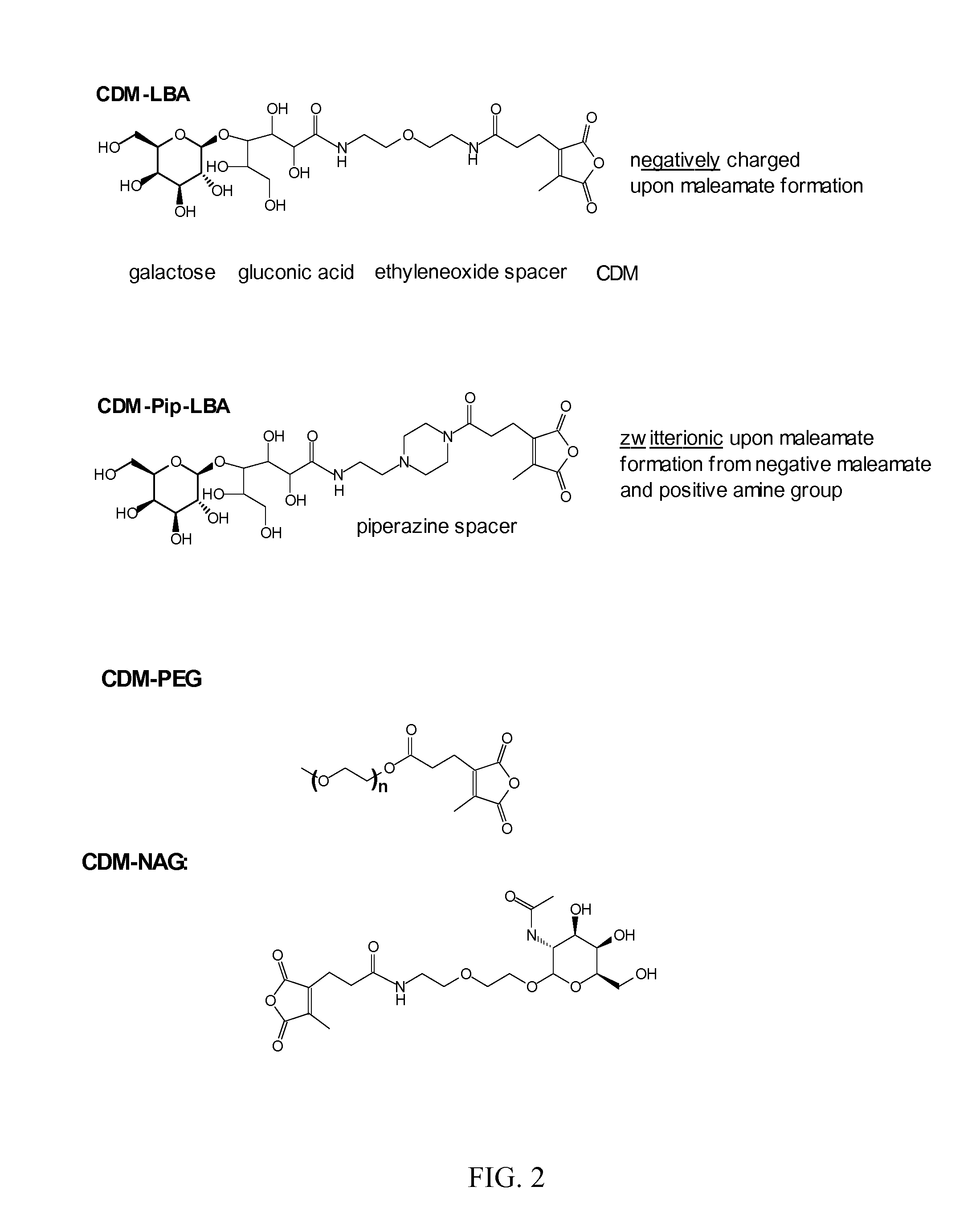
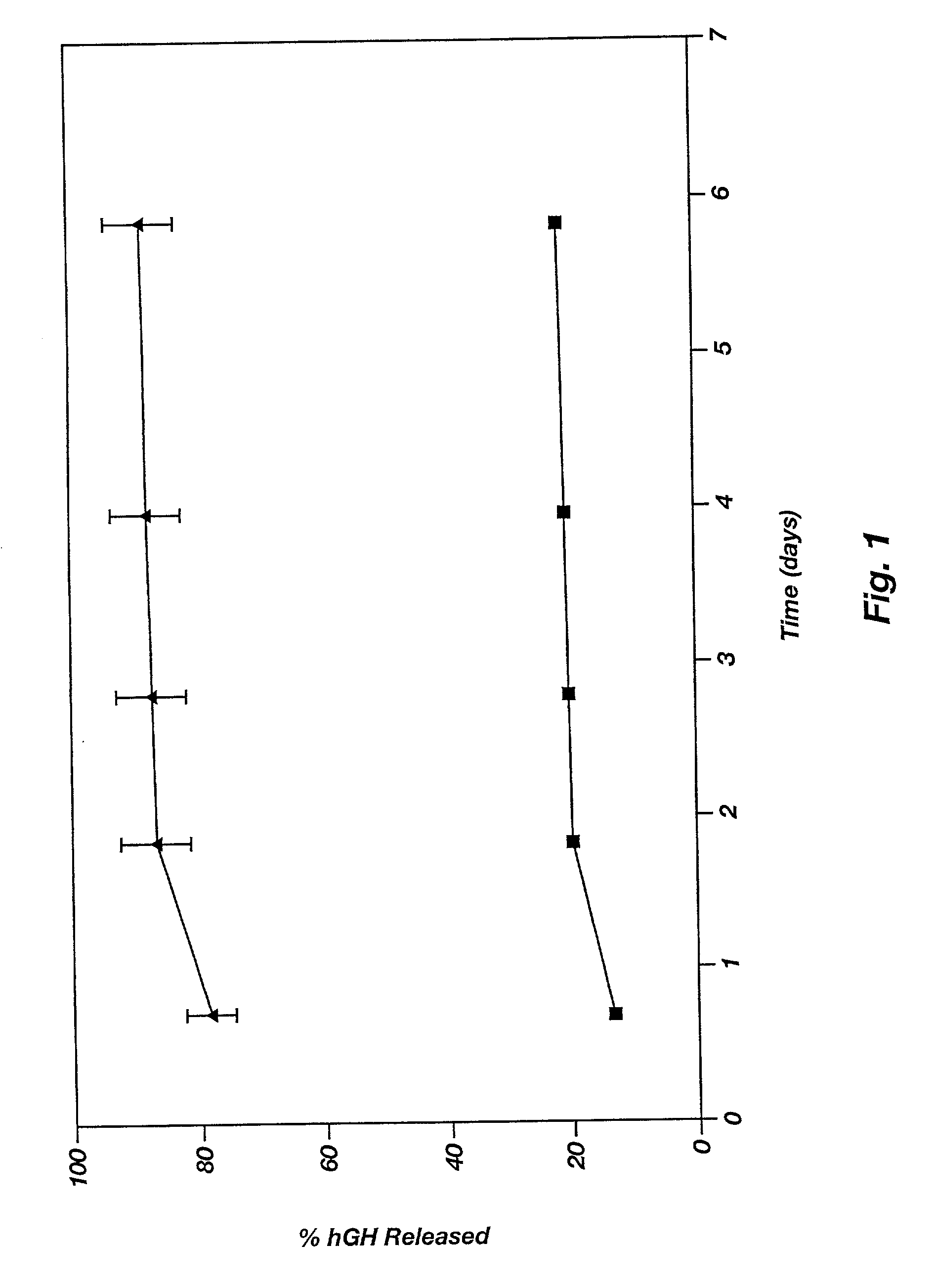
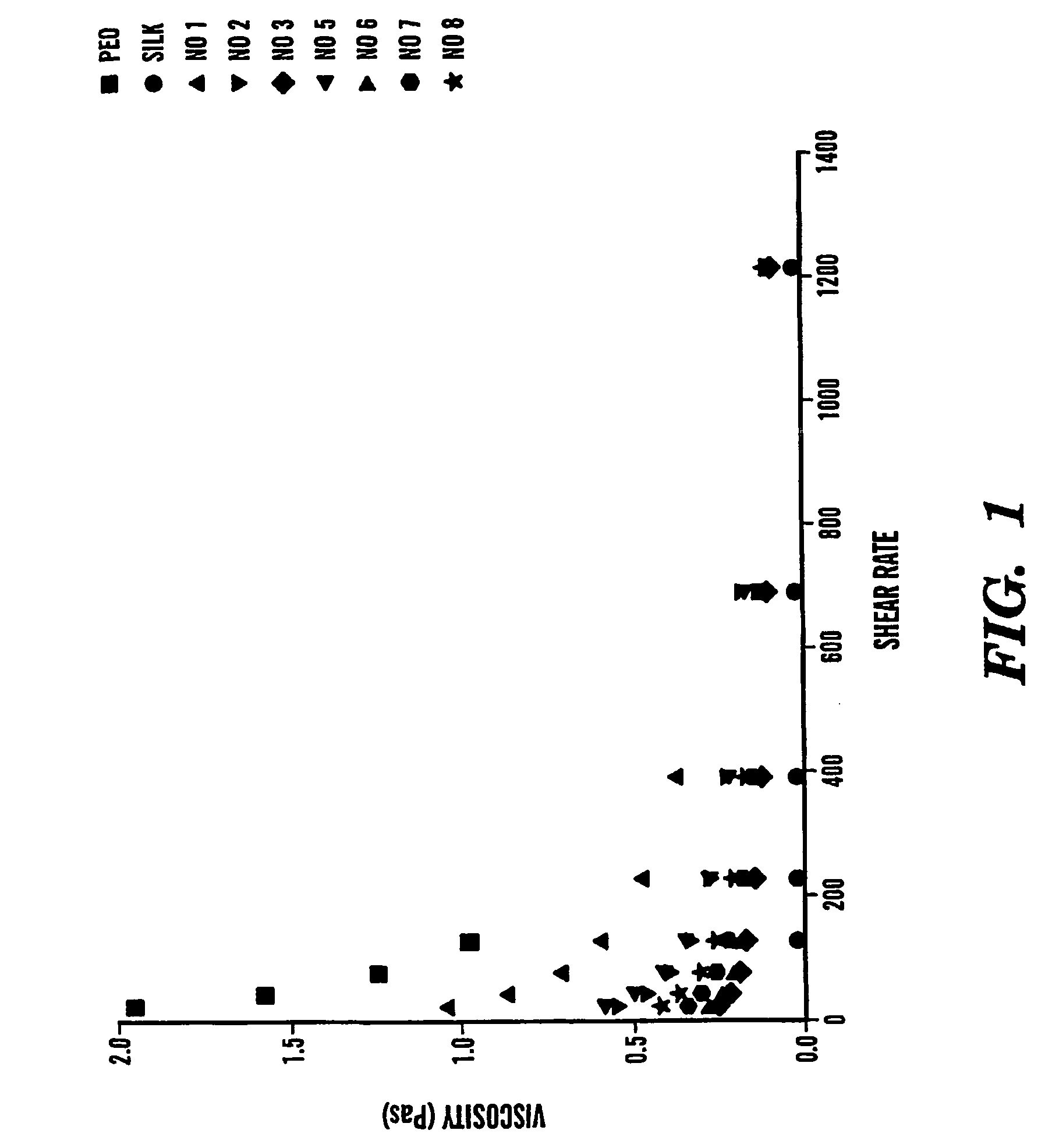
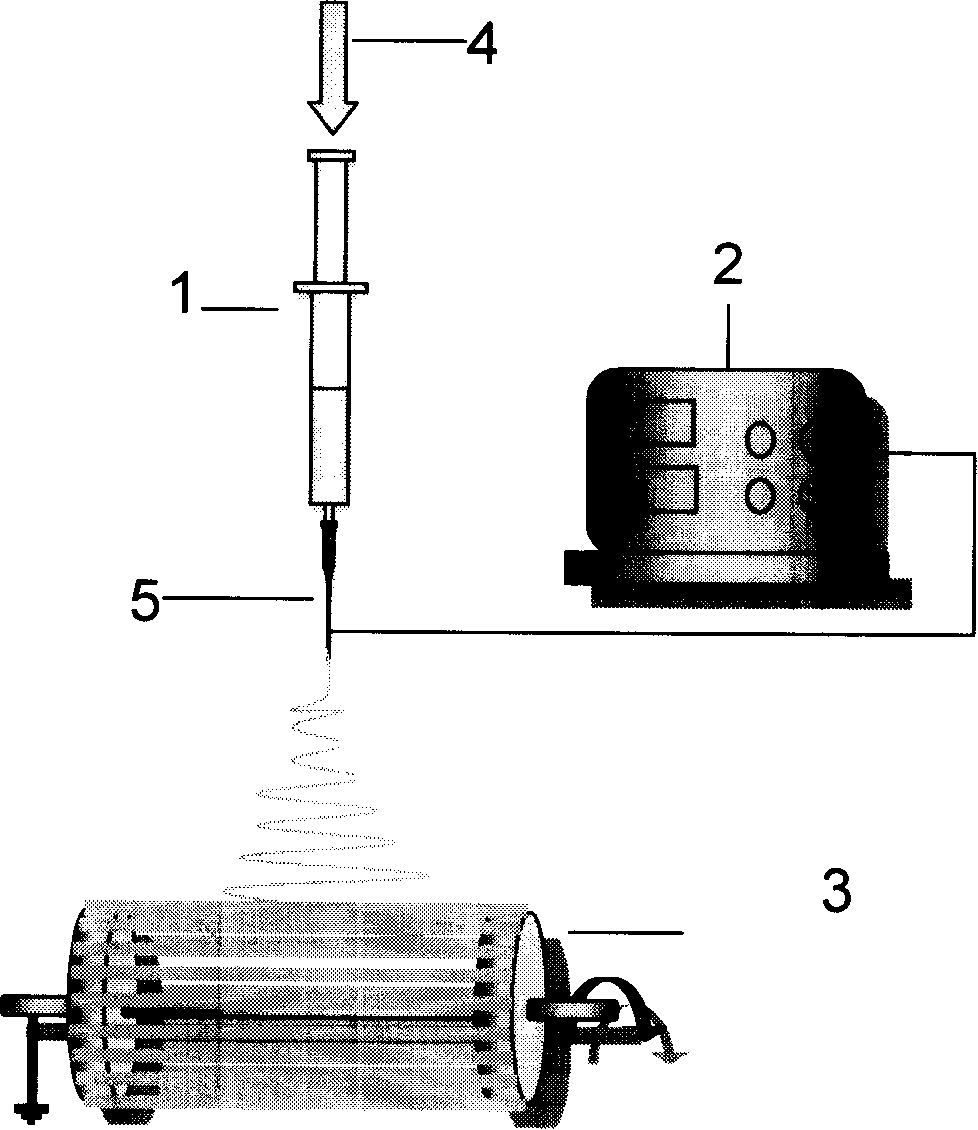
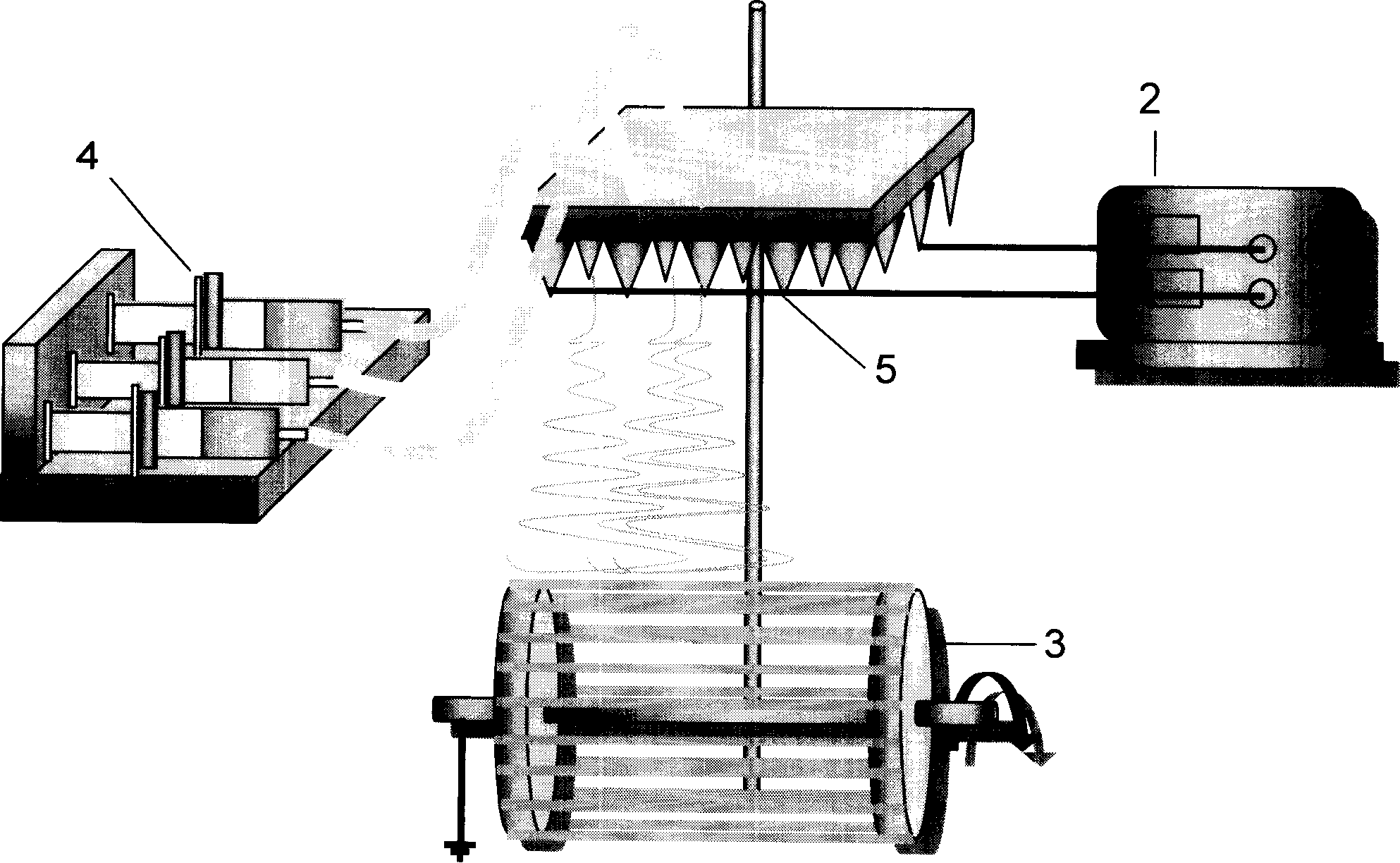
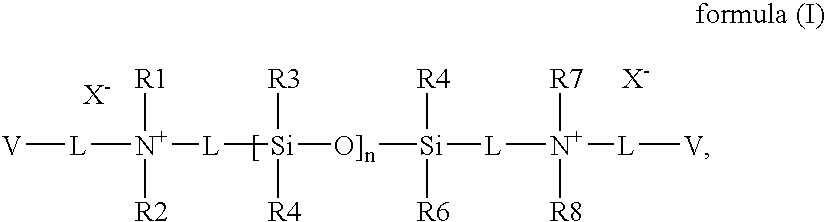
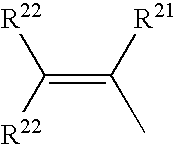
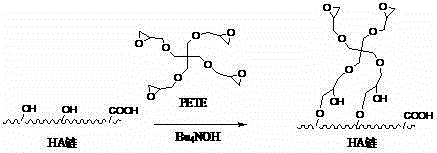
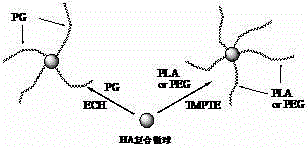
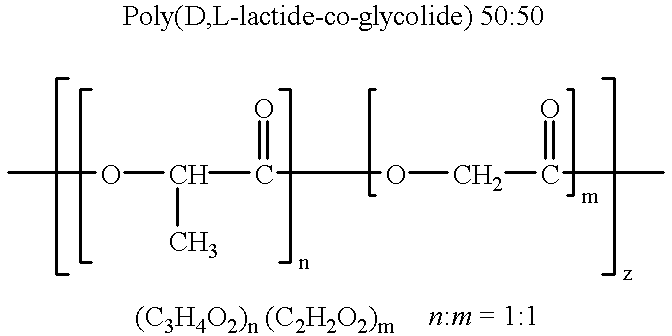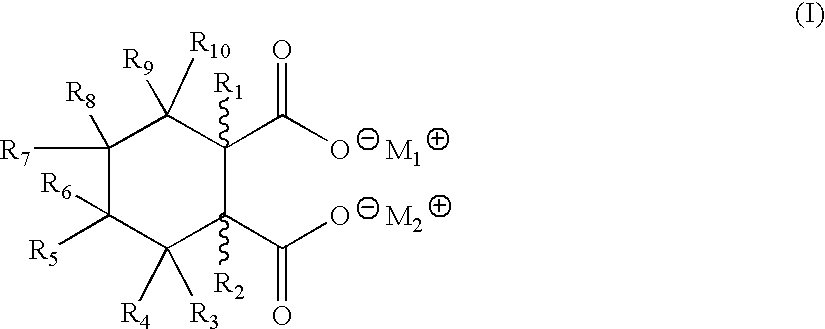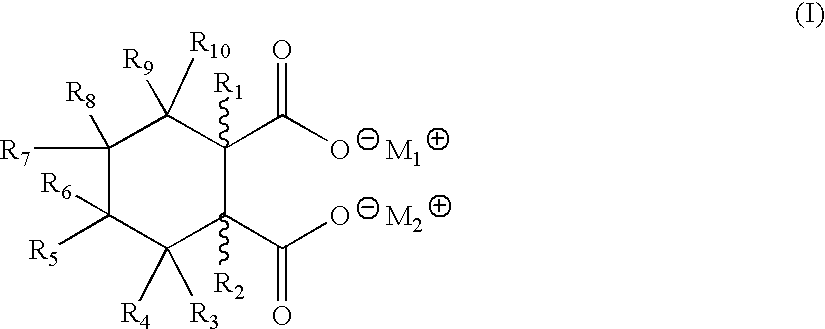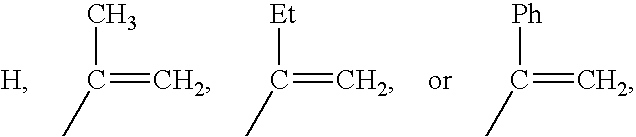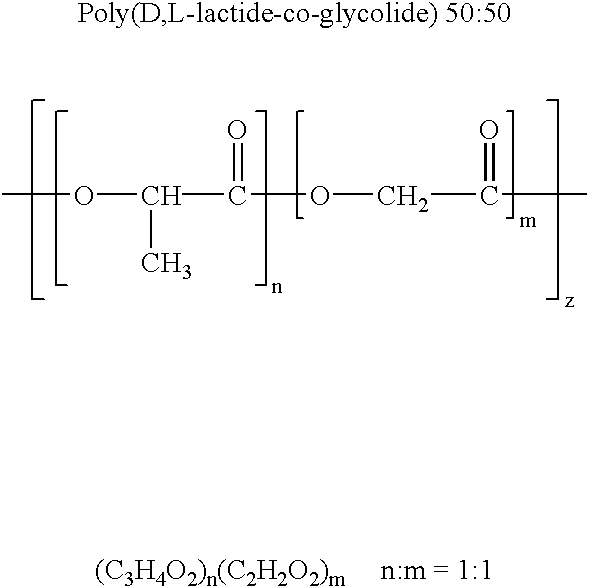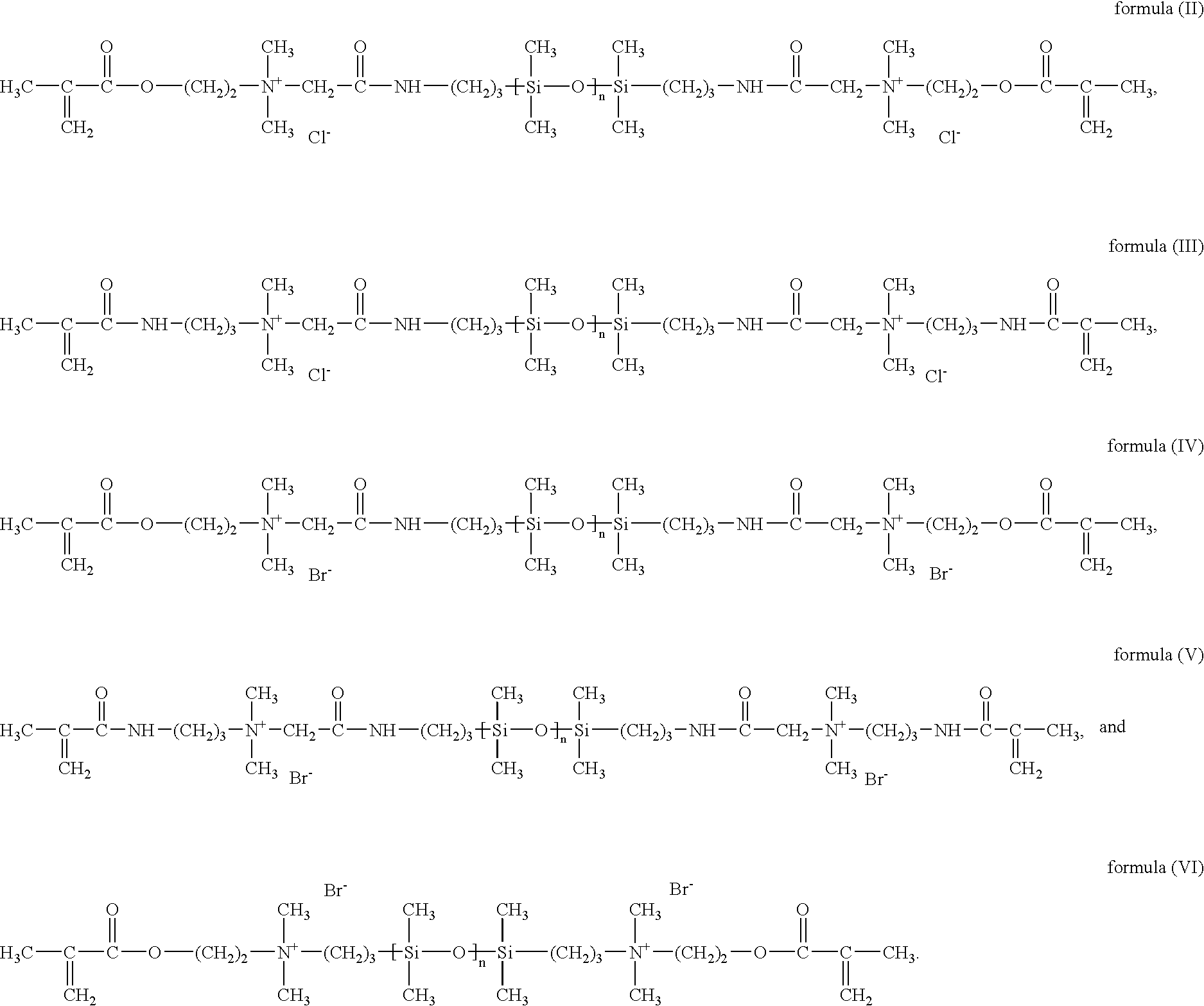Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13564 results about "Compatibilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
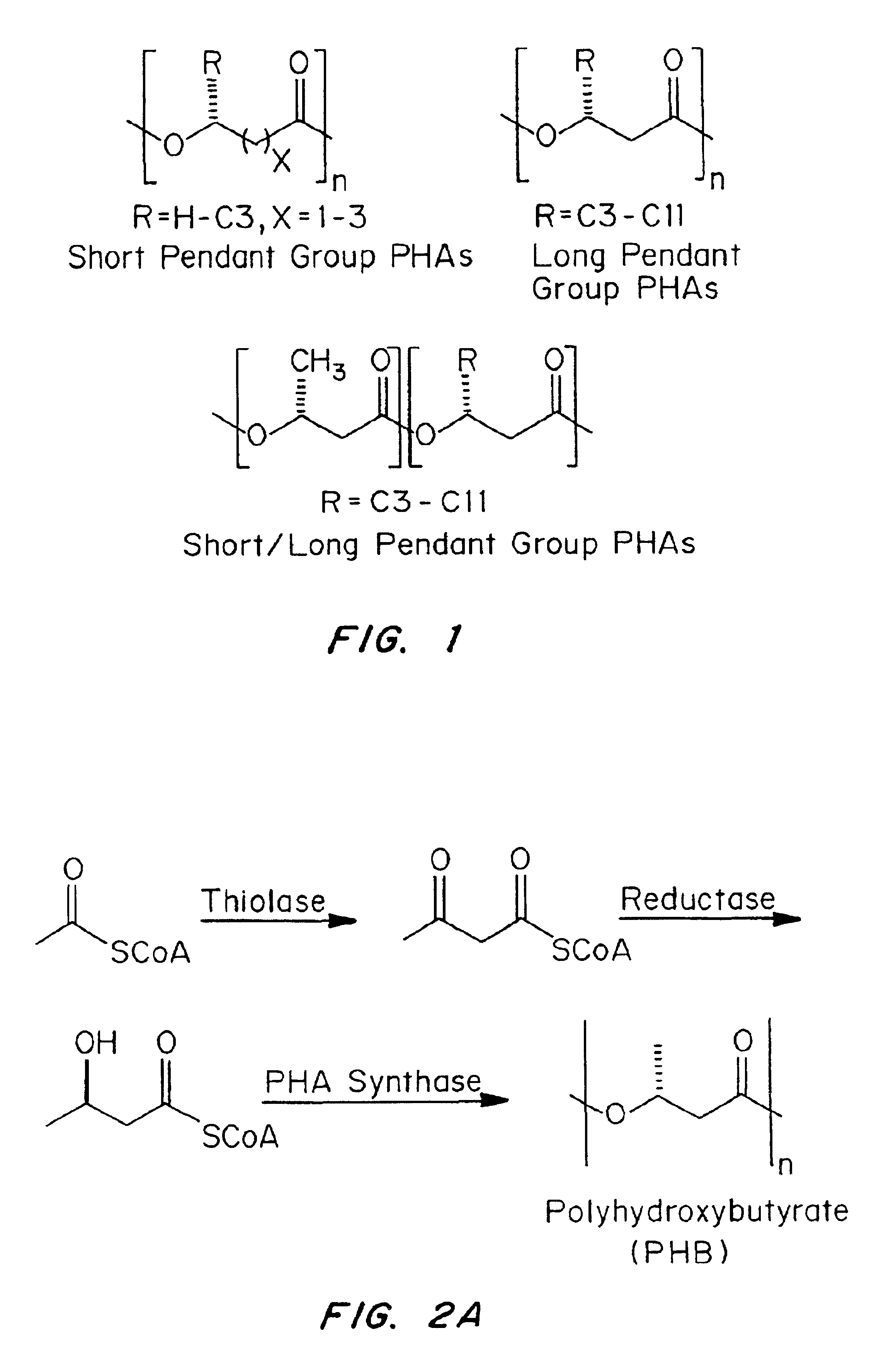
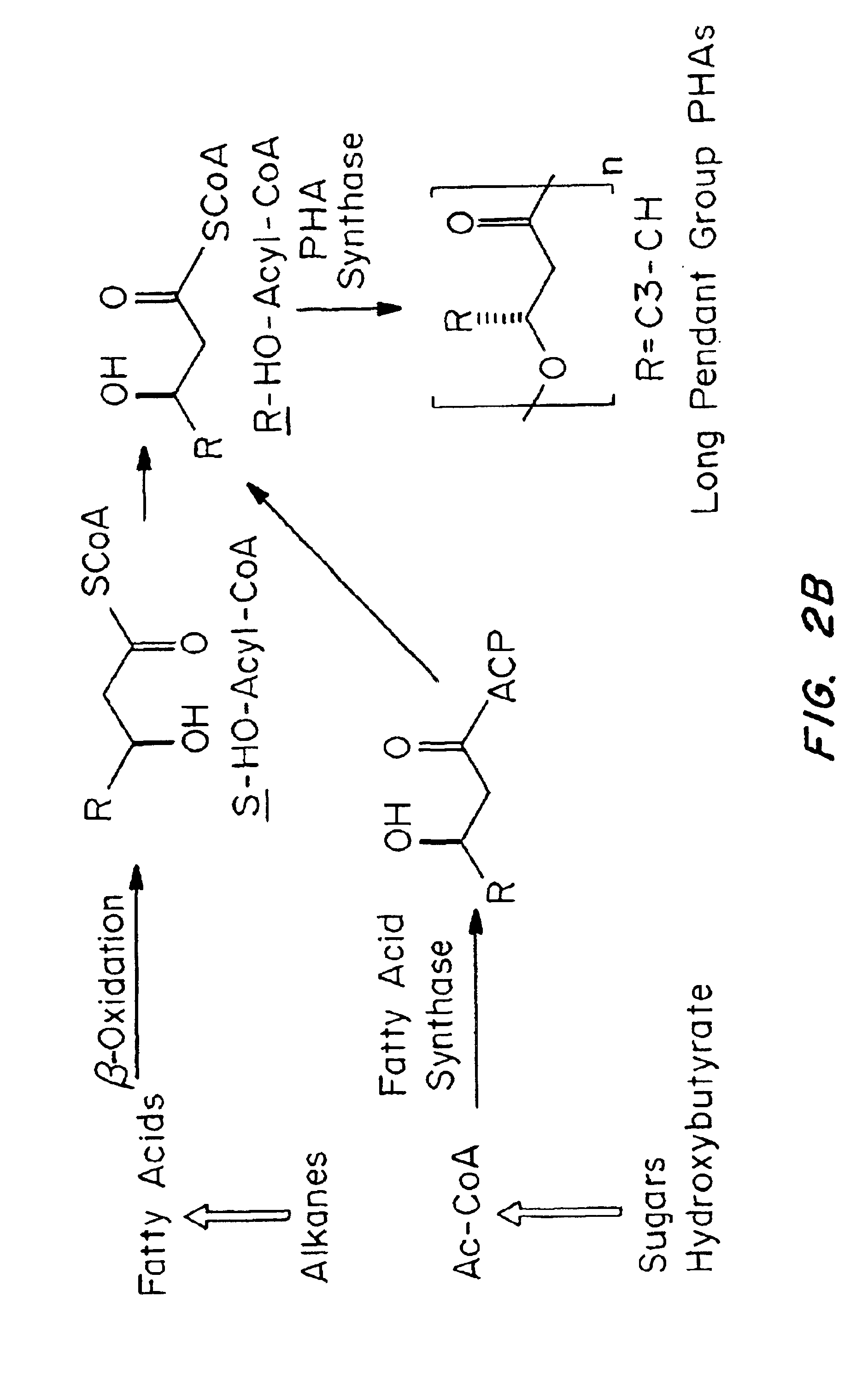
Compatibilization in polymer chemistry is the addition of a substance to an immiscible blend of polymers that will increase their stability. Polymer blends are typically described by coarse, unstable phase morphologies. This results in poor mechanical properties. Compatibilizing the system will make a more stable and better blended phase morphology by creating interactions between the two previously immiscible polymers. Not only does this enhance the mechanical properties of the blend, but it often yields properties that are generally not attainable in either single pure component.
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
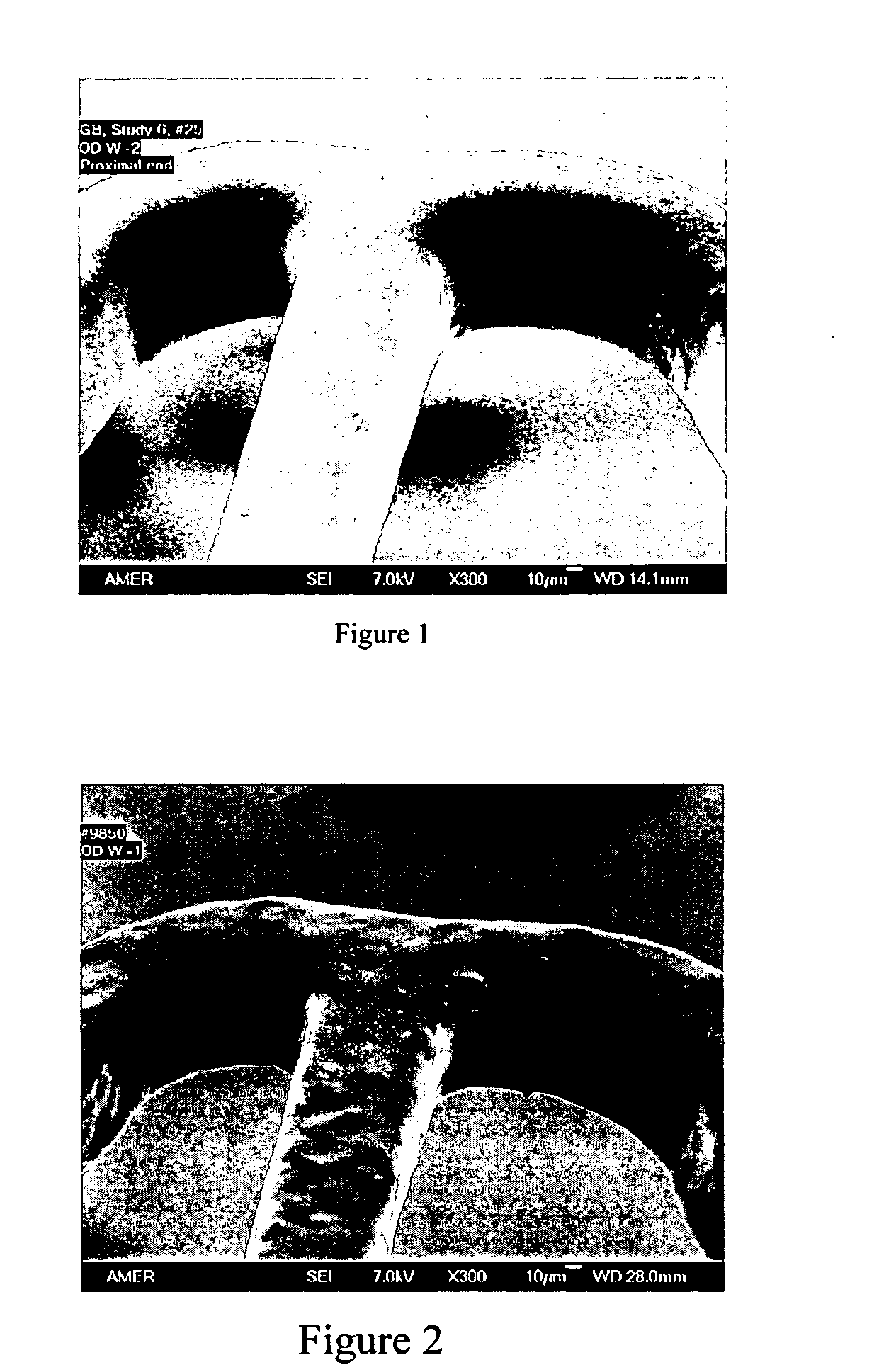
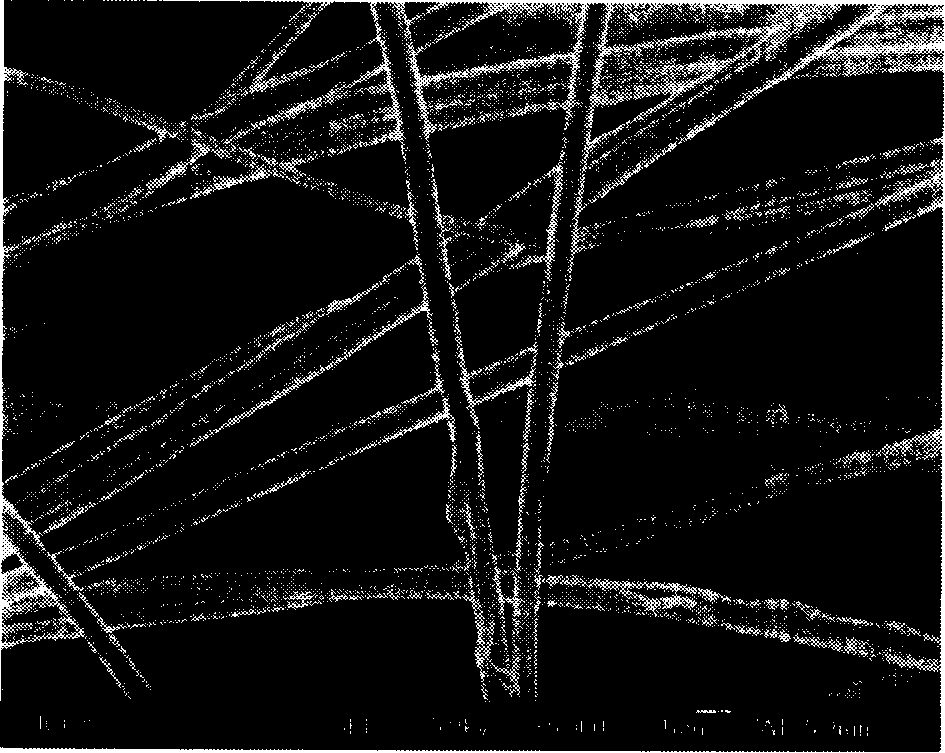
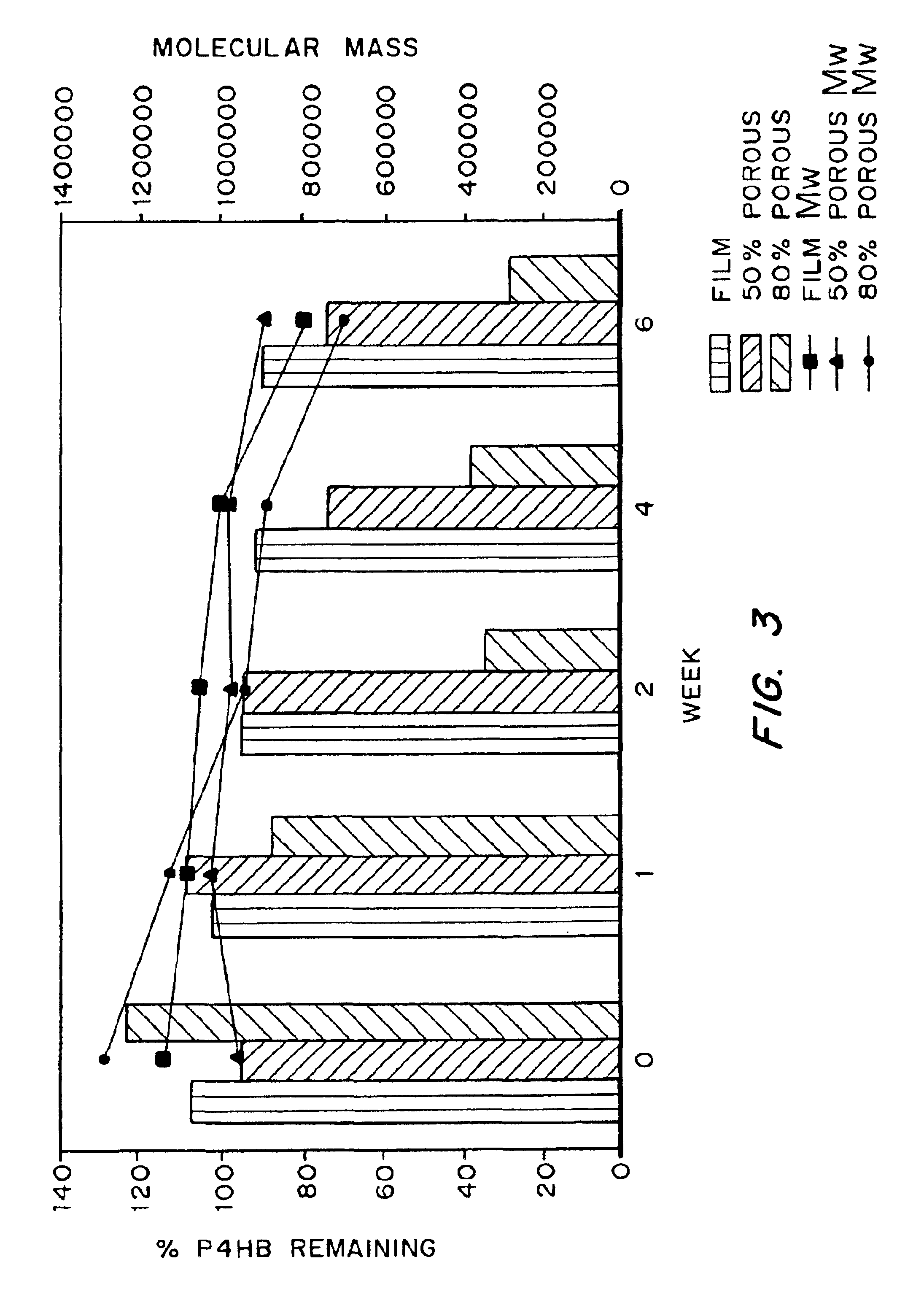
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional biopolymeric materials and methods
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional cross-linked proteinaceous biopolymeric materials that may be implanted in vivo, and methods of making such materials are disclosed. The biopolymeric materials most preferably include reinforcing media, such as biocompatible fibrous or particulate materials. In use, the preformed, shaped biopolymeric materials may be applied to tissue in need of repair and then sealed around its edges with a liquid bioadhesive. In such a manner, repaired tissue which is capable of withstanding physiological pressures may be provided.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
Medical film
InactiveUS7718556B2Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthSuture equipmentsBiocideGelatin filmThin membrane
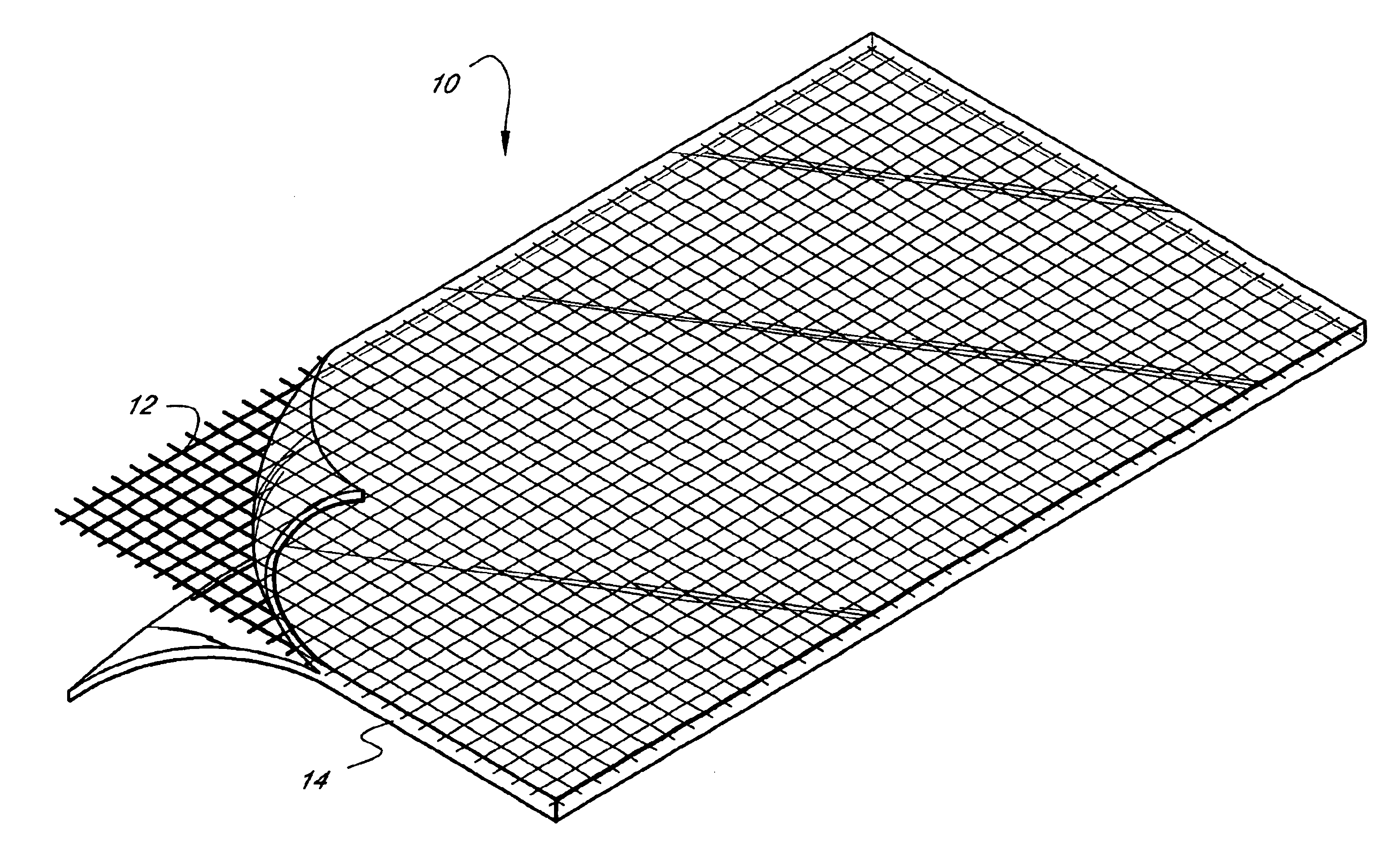
A medical film that is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has an excellent strength in suturing and bonding is provided. A reinforcing material 12 made of a biodegradable polymer is placed in a gelatin solution so as to allow the solution to infiltrate in the reinforcing material 12 and then the gelatin is dried. This allows the gelatin that has infiltrated entirely in an internal part of the reinforcing material 12 to gel, thereby forming a gelatin film 11. Thus, a medical film 1 in which the reinforcing material 12 and the gelatin film 11 are integrated is obtained. The gelatin film 11 preferably is a cross-linked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Adhesive formulations
ActiveUS8349987B2Organic non-macromolecular adhesiveSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsArylPolymer science
The disclosure relates to biocompatible components useful for forming compositions for use as medical / surgical synthetic adhesives and sealants. Biocompatible components of the present disclosure may include a polymeric polyol core, which may be treated with a nitroaryl compound to form a nitro ester. The resulting nitro ester groups may be reduced to form amino groups which, in turn, may be treated to form isocyanate groups. The resulting isocyanate may then be reacted with a second component to form adhesive and / or sealant compositions.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Therapeutic treatment and prevention of infections with a bioactive materials encapsulated within a biodegradable-biocompatible polymeric matrix
InactiveUS6309669B1Sustained release of active agent over timeEfficient and effective usePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantEnd-group
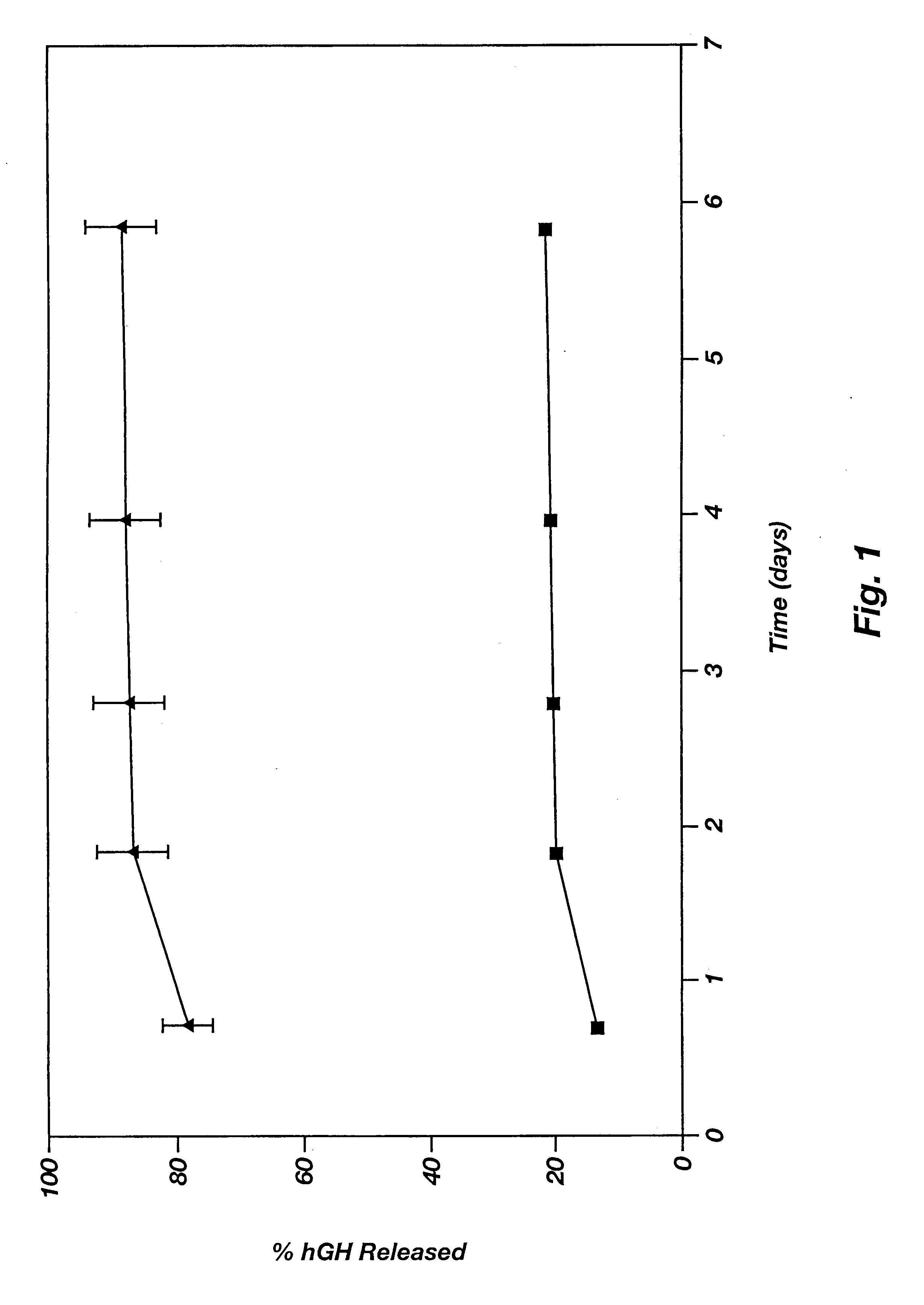
Novel burst-free, sustained release biocompatible and biodegrable microcapsules which can be programmed to release their active core for variable durations ranging from 1-100 days in an aqueous physiological environment. The microcapsules are comprised of a core of polypeptide or other biologically active agent encapsulated in a matrix of poly(lactide / glycolide) copolymer, which may contain a pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvant, as a blend of upcapped free carboxyl end group and end-capped forms ranging in ratios from 100 / 0 to 1 / 99.
Owner:ARMY GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Bioactive agent delivering system comprised of microparticles within a biodegradable to improve release profiles
InactiveUS6589549B2Improve stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentEngineering
A composition and method for releasing a bio-active agent or a drug within a biological environment in a controlled manner is disclosed. The composition is a dual phase polymeric agent-delivery composition comprising a continuous biocompatible gel phase, a discontinuous particulate phase comprising defined microparticles and an agent to be delivered. A microparticle containing a bio-active agent is releasably entrained within a biocompatible polymeric gel matrix. The bioactive agent release may be contained in the microparticle phase alone or in both the microparticles and the gel matrix. The release of the agent is prolonged over a period of time, and the delivery may be modulated and / or controlled. In addition, a second agent may be loaded in some of the microparticles and / or the gel matrix.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Isoelastic prosthetic filet stitch fabric
This knit is produced on the basis of a biocompatible polymer material monofilament, whose pattern is defined by a front lap and a rear lap of yarns knitted together and determines a plurality of cells each having a substantially polygonal shape. The pattern gives the knit a multidirectional tensile behavior such as obtained by a front lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1 / 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 and by a rear lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 / 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
Biocompatible crosslinked coating and crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating
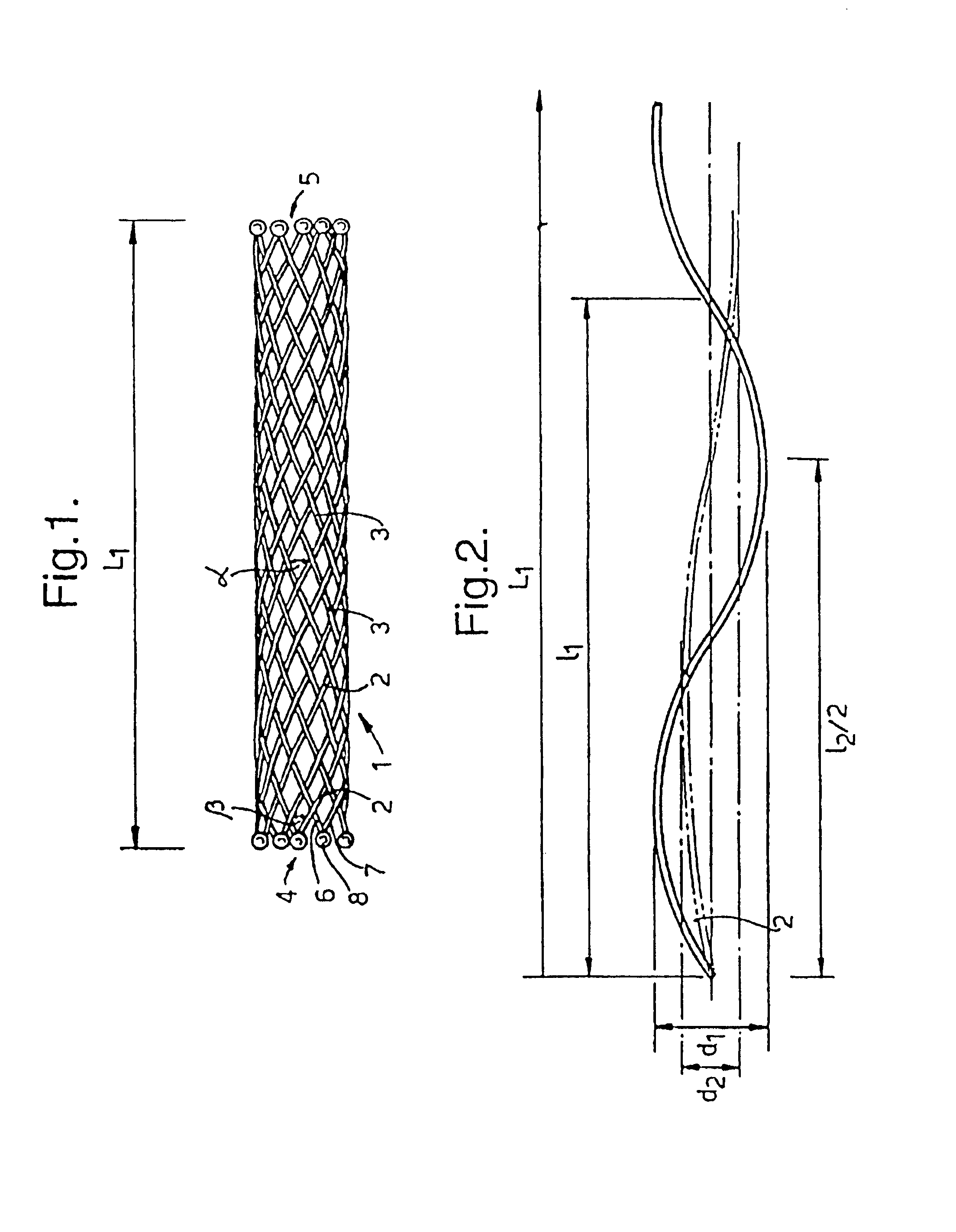
A braided stent (1) for transluminal implantation in body lumens is self-expanding and has a radial expanded configuration in which the angle α between filaments is acute. Some or all of filaments (6,7) are welded together in pairs at each end (4,5) of the stent to provide beads (8), thereby strengthening the stent and assisting its deployment from a delivery device. The stent is preferably completely coated using a biocompatible polymeric coating, said polymer preferably having pendant phosphoryl choline groups. A method of making the stent by braiding and welding is described as well as a delivery device for deploying the device.The present invention provides a biocompatible crosslinked coating and a crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating. The biocompatible crosslinked coating may be formed by curing a polymer of 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate. The crosslinkable coating polymer may include 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate.<?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Poly(amino acid) targeting moieties
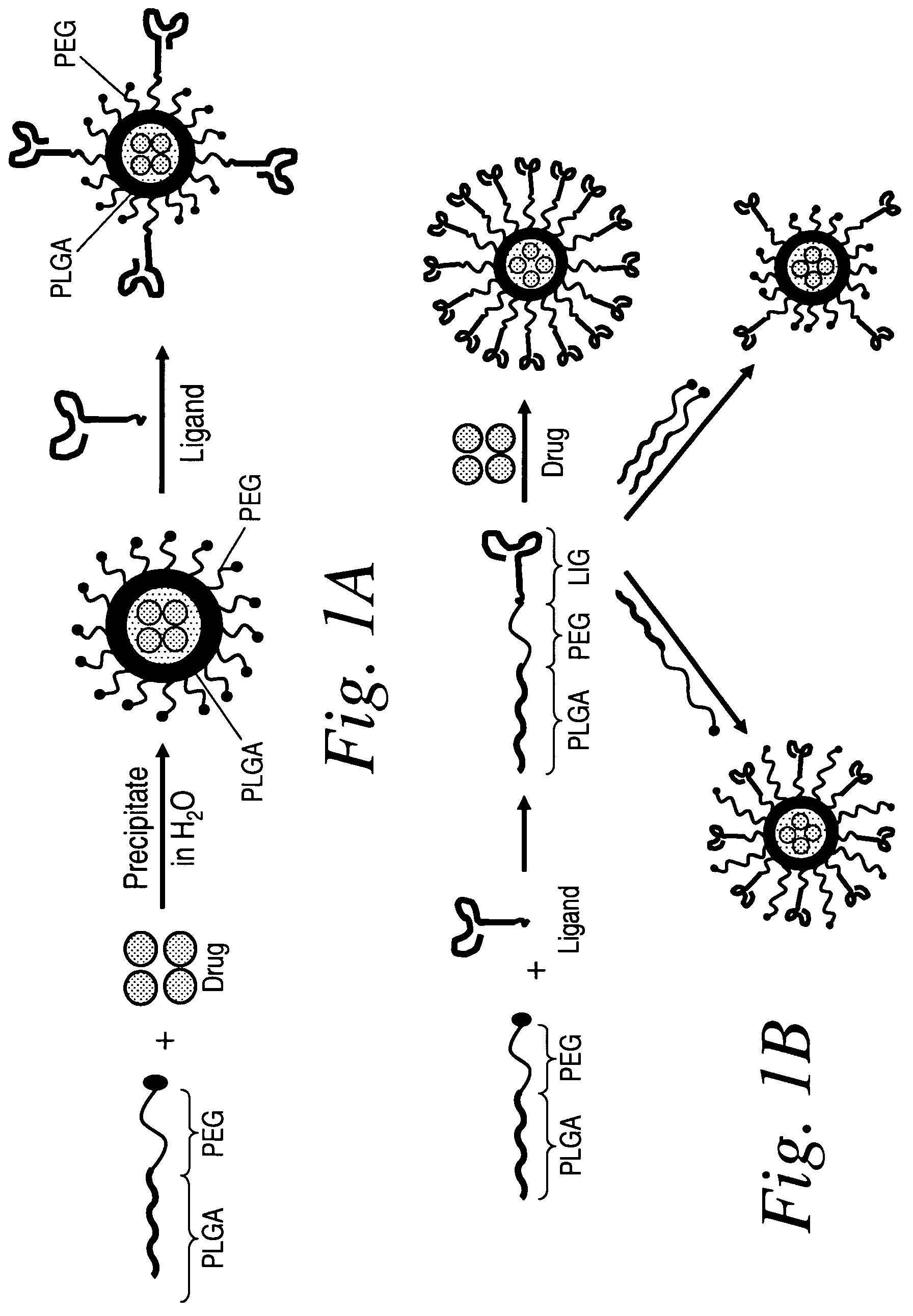
The present invention generally relates to polymers and macromolecules, in particular, to polymers useful in particles such as nanoparticles. One aspect of the invention is directed to a method of developing nanoparticles with desired properties. In one set of embodiments, the method includes producing libraries of nanoparticles having highly controlled properties, which can be formed by mixing together two or more macromolecules in different ratios. One or more of the macromolecules may be a polymeric conjugate of a moiety to a biocompatible polymer. In some cases, the nanoparticle may contain a drug. Other aspects of the invention are directed to methods using nanoparticle libraries.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC +1
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefin with improved compatibility
Disclosed herein are polymer blends comprising at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and two different polyolefins which can be homopolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. In some embodiments, the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer can function as a compatibilizer between the two polyolefins which may not be otherwise compatible. Methods of making the polymer blends and molded articles made from the polymer blends are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Metal salts of hexahydrophthalic acid as nucleating additives for crystalline thermoplastics
InactiveUS6599971B2Excellent calcium stearate compatibilityExcellent high peak crystallization temperatureOrganic compound preparationFibre treatmentThermoplasticScavenger
Compounds and compositions comprising specific metal salts of hexahydrophthalic acid (HHPA) in order to provide highly desirable properties within thermoplastic articles are provided. The inventive HHPA derivatives are useful as nucleating and / or clarifying agents for such thermoplastics, are practical and easy to handle. Such compounds provide excellent crystallization temperatures, stiffness, and acid scavenger compatibility within target polyolefins. Also, such compounds exhibit very low hygroscopicity and therefore excellent shelf stability as powdered or granular formulations. Thermoplastic additive compositions and methods of producing polymers with such compounds are also contemplated within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Therapeutic treatment and prevention of infections with a bioactive material(s) encapuslated within a biodegradable-bio-compatable polymeric matrix
InactiveUS6902743B1Induce productionSustained release of active agent over timePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic treatmentActive agent
Novel burst-free, sustained release biocompatible and biodegrable microcapsules which can be programmed to release their active core for variable durations ranging from 1-100 days in an aqueous physiological environment. The microcapsules are comprised of a core of polypeptide or other biologically active agent encapsulated in a matrix of poly(lactide / glycolide) copolymer having a molar composition of lactide / glycolide from 90 / 10 to 40 / 60, which may contain a pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvant, as a blend of uncapped free carboxyl end group and end-capped forms ranging to ratios from 100 / 0 to 1 / 99.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Reversibly Masked Polymers
InactiveUS20080281041A1Reduce aggregationGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesLinkage conceptActive polymer
The present invention is directed to reversibly inactivation of membrane active polymers useful for cellular delivery of compounds. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery conjugates. The use of multiple reversible linkages connecting component parts provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
Elastic blends comprising crystalline polymer and crystallizable polymers of propylene
Improved thermoplastic polymer blend compositions comprising an isotactic polypropylene component and an alpha-olefin and propylene copolymer component, said copolymer comprising crystallizable alpha-olefin sequences. In a preferred embodiment, improved thermoplastic polymer blends are provided comprising from about 35% to about 85% isotactic polypropylene and from about 30% to about 70% of an ethylene and propylene copolymer, wherein said copolymer comprises isotactically crystallizable propylene sequences and is predominately propylene. The resultant blends manifest unexpected compatibility characteristics, increased tensile strength, and improved process characteristics, e.g., a single melting point.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Bioactive agent delivering system comprised of microparticles within a biodegradable to improve release profiles
InactiveUS20020076441A1Improve stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentPharmaceutical drug
A composition and method for releasing a bio-active agent or a drug within a biological environment in a controlled manner is disclosed. The composition is a dual phase polymeric agent-delivery composition comprising a continuous biocompatible gel phase, a discontinuous particulate phase comprising defined microparticles and an agent to be delivered. A microparticle containing a bio-active agent is releasably entrained within a biocompatible polymeric gel matrix. The bioactive agent release may be contained in the microparticle phase alone or in both the microparticles and the gel matrix. The release of the agent is prolonged over a period of time, and the delivery may be modulated and / or controlled. In addition, a second agent may be loaded in some of the microparticles and / or the gel matrix.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Silk biomaterials and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7674882B2Avoid problemsReduce usagePeptide/protein ingredientsFilament/thread formingFiberIn vivo
The present invention provides an all-aqueous process and composition for production of silk biomaterials, e.g., fibers, films, foams and mats. In the process, at least one biocompatible polymer, such as poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) (a well-documented biocompatible material), was blended with the silk protein prior to processing e.g., electrospinning. We discovered that this step avoids problems associated with conformational transitions of fibroin during solubilization and reprocessing from aqueous solution which lead to embrittled materials. Moreover, the process avoids the use of organic solvents that can pose problems when the processed biomaterials are exposed to cells in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Medical device having a coating layer with structural elements therein and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060025848A1Efficient methodCounteracting forceStentsSurgeryInsertion stentCompressibility
The invention pertains to coated medical devices, such as stents and balloon catheters, for delivering a biologically active material to body tissue of a patient. The medical device has a coating layer comprising a biocompatible polymer, non-polymer material, or biologically active material disposed on its surface, and at least one structural element embedded within the coating layer. The structural elements reduce the compressibility of the coating layer. The structural element may be any shape or configuration. A biologically active material may be dispersed within the coating layer or structural elements. Methods for making such medical devices are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fluoroligomer surface modifiers for polymers and articles made therefrom
InactiveUS6127507AGood compatibilityImprove stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPharmaceutical containersPolymer scienceMedical device
A composition comprising in admixture with a polymer, preferably a polyurethane, and a compatible surface-modifying macromolecule having (i) a central portion of a segmented block oligomeric copolymer comprising at least one polar hard segment, and (ii) PROPORTIONAL - omega terminal polyfluoro oligomeric groups, in a surface modifying enhancing amount. The composition is of use in providing articles having improved surface properties, particularly, medical devices having improved resistance to enzyme degradation with acceptable blood compatibility.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOLOGICS INC
Prosthetic bone filler and process for the production of the same
InactiveUS6203574B1Preventing good bio-compatibilityPromote resultsIon-exchange process apparatusImpression capsCeramic particleLiving body
A prosthetic bone filler including ceramic granules for use in a living body, the ceramic granules being bonded to each other with a polymeric substance, and having ventilation pores produced as a result of the presence of gaps between the adjacent granules. The prosthetic bone filler is produced by adding the polymeric substance in two portions to the ceramic granules. In addition to good flexibility, the prosthetic bone filler exhibits excellent bio-compatibility.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Advanced compatible polymer wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6210792B1Improve compatibilityGood material compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsThermoplasticFiber
The invention relates to a composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer, the fiber or both can be modified to increase compatibility. The wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Biopolymer nano tunica fibrosa material capable of being biological degraded and absorbed, preparing method and uses of the same
InactiveCN101172164AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationSurgeryFilament/thread formingFiberCellulose
The invention relates to compound millimicron fibrous membrane material of cellulose and cellulose matrix which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption and a preparation method thereof and an industry and medical purpose, and belongs to the biological macro-molecule non woven fabric material field which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption. Electrostatic spinning equipment is used to obtain the fibrous membrane material which can perform the biological degradation and the biological absorption, the weight of the cellulose is taken as basic reference, the component of the material comprises cellulose more than 0 and less than or equal to 100 weight parts, other biomacromolecule more than and equal to 0 and less than 100 weight parts, 0 to 10 weight parts of curative drug or 0 to 50 weight parts of inorganic catalyzer and / or 0 to 50 weight parts of inorganic strengthening agent. The material of the invention has good biological compatibility, biological degradation property and degradation absorptivity, and can be used for haemostasia material, wound cladding material, organization engineering supporting rack material, the transportation and release of medicine, artificial skin and blood vessel, and postoperation anti blocking material, beauty material and catalyzer carrier, filtering membrane and radiation protection material and so on.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silicon-containing monomers end-capped with polymerizable cationic hydrophilic groups
InactiveUS20070142584A1High oxygen permeabilityDesirable biocompatibilitySilicon organic compoundsIntraocular lensEndcappingOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to polymeric compositions useful in the manufacture of biocompatible medical devices. More particularly, the present invention relates to certain cationic monomers capable of polymerization to form polymeric compositions having desirable physical characteristics useful in the manufacture of ophthalmic devices. Such properties include the ability to extract the polymerized medical devices with water. This avoids the use of organic solvents as is typical in the art. The polymer compositions comprise polymerized silicon-containing monomers end-capped with polymerizable cationic hydrophilic groups.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Hyaluronan and biodegradable high polymer modified material and preparation method
The invention relates to a hyaluronan and biodegradable high polymer modified material and a preparation method, in particular to a method for complex crosslinking and grafting of the hyaluronan and a derivative thereof with a biodegradable high polymer with active functional groups through a crosslinking agent. The method comprises the steps of taking the hyaluronan and the biodegradable high polymer as raw materials, conducting complex crosslinking or grafting reaction of a hyaluronan aqueous solution and at least one biodegradable high polymer solution with the presence of the crosslinking agent, and removing a solvent. According to the method, plural gel, an amphiphilic polymer, a graft polymer, a star polymer and a microsphere can be prepared. The method has the advantages that the reaction condition is simple, the utilization ratio of the crosslinking agent is high, the residual quantity of the crosslinking agent is small, and the gel is higher in thermostability and good in biological compatibility. The method is applicable to the fields of cosmetics, tissue filling and repair, biological stents, ophthalmonogy, sustained-release delivery and targeted drug delivery and the like, and has a wider application prospect.
Owner:IMEIK TECH DEV CO LTD
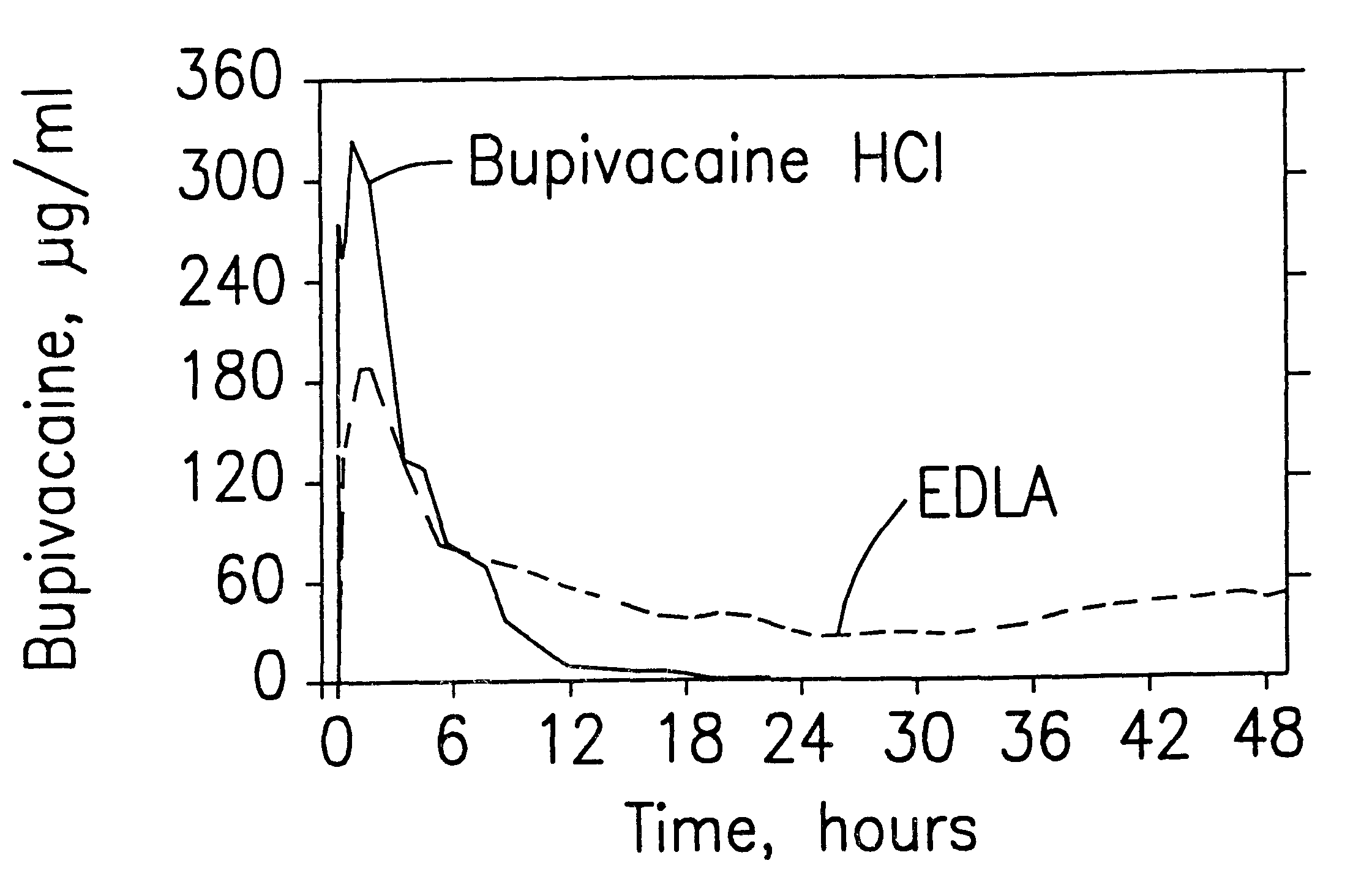
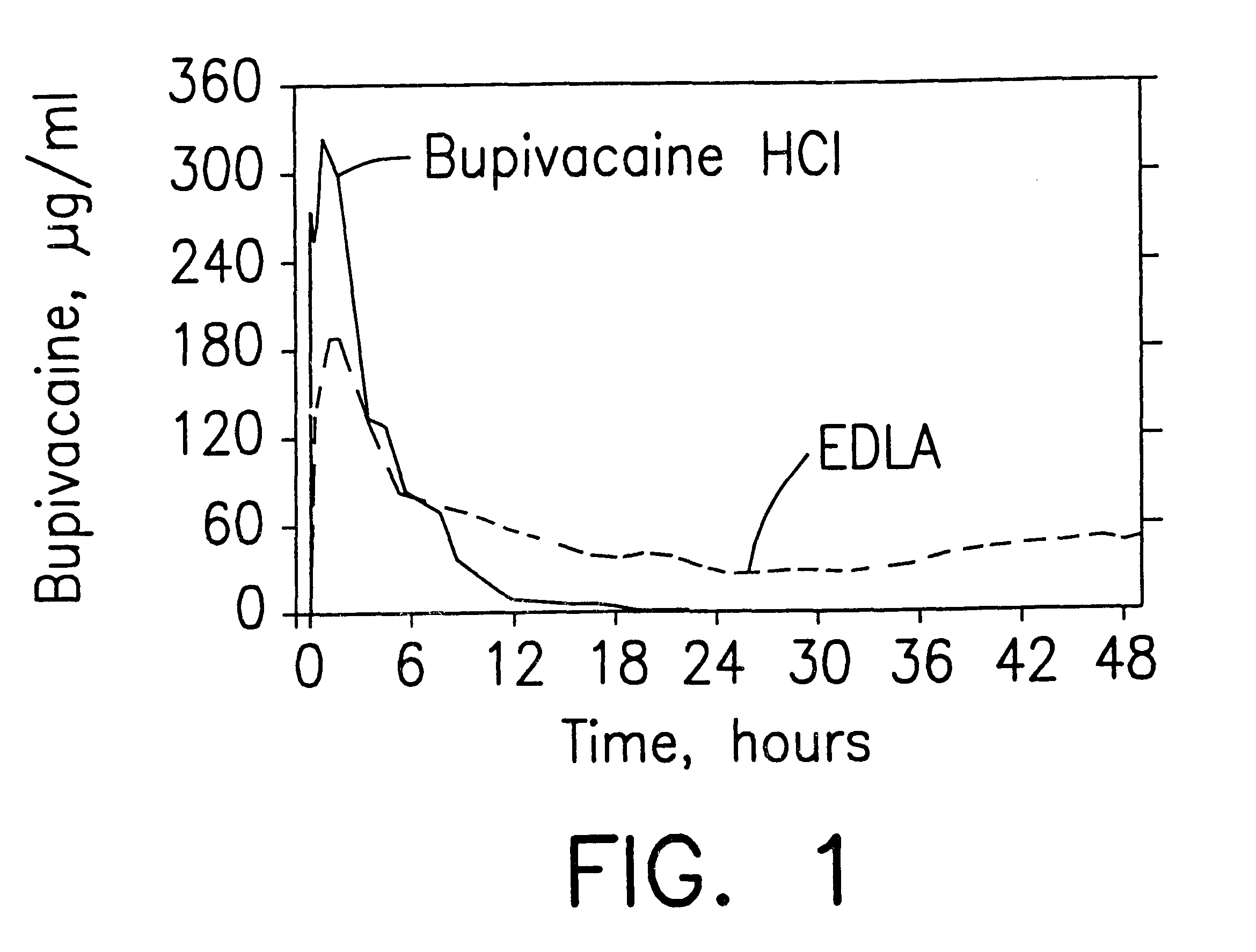
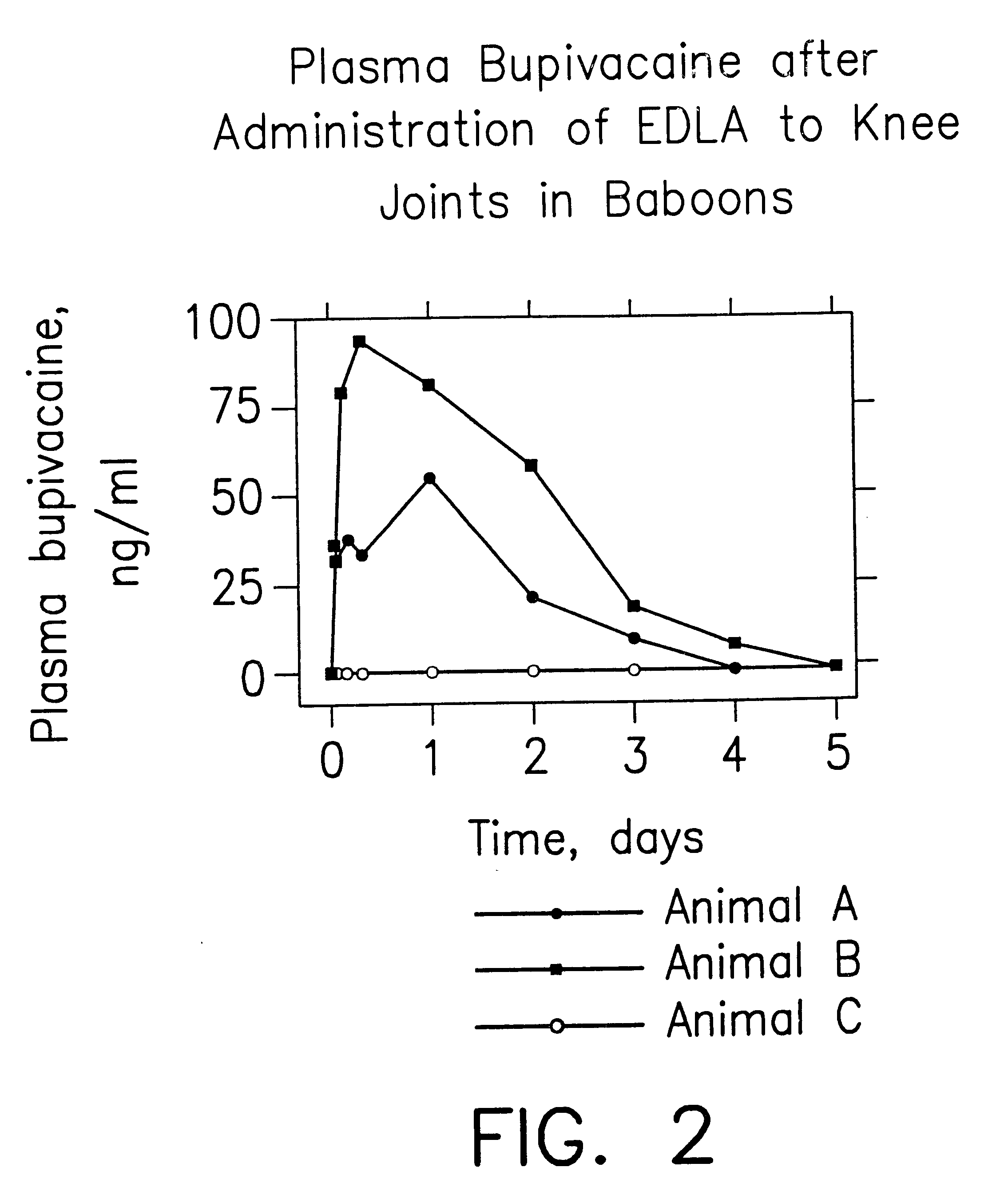
Formulations and methods for providing prolonged local anesthesia
InactiveUS6451335B1Slow in-vitro releaseRelease the local anestheticAnaesthesiaGranular deliveryControlled releaseAnesthetic Agent
A formulation for inducing sustained regional local anesthesia in a patient comprising a substrate comprising a local anesthetic and an effective amount of a biocompatible, biodegradable, controlled release material prolonging the release of the local anesthetic from the substrate to obtain a reversible local anesthesia when implanted or injected in a patient, and a non-toxic augmenting agent effective to prolong the duration of the local anesthesia for a time period longer than that obtainable from the substrate without the augmenting agent. In preferred embodiments, the controlled release material is a low molecular weight, acid-terminated polymer. A further aspect of the invention is directed to such formulations which release the local anesthetic in two phases, the first a rapid "bolus" to initiate anesthesia and a second, slower release to maintain anesthesia.
Owner:EURO-CELTIQUE SA
Method for preparing complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body
InactiveCN102335742ADesign personalizationHigh dimensional accuracyIncreasing energy efficiencyProsthesisNatural boneMetallic materials
The invention provides a method for preparing a complexly shaped biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body and belongs to the technical field of biomedical porous metallic material preparation. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a mixture of titanium and molybdenum metallic element powder and organic polymer powder as raw materials, and then preparing the biomedical porous titanium molybdenum alloy implant body by adopting the processes, such as three-dimensional modeling, selective laser-firing rapid forming, thermal de-greasing, vacuum sintering, and the like. The processing steps are simple, the period is short, the use ratio of materials is high, the cost is low, any complexly shaped porous titanium alloy implant body can be conveniently manufactured, and the method has efficiency and economic advantages in individual design and rapid manufacturing of the implant body. A titanium molybdenum alloy material prepared by using the method has the advantages that pore space is uniform, adjustment scopes of porosity, aperture ratio and aperture are wide, elasticity modulus and compression strength are in close proximity to natural bone, and the demand on biomechanical compatibility required by a biomedical material is met.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Isolatable, water soluble, and hydrolytically stable active sulfones of poly(ethylene glycol) and related polymers for modification of surfaces and molecules
A poly(ethylene glycol) derivative is disclosed that is activated with a sulfone moiety for selective attachment to thiol moieties on molecules and surfaces. The activated PEG is water soluble, hydrolytically stable for extended periods, and forms hydrolytically stable linkages with thiol moieties. The linkages generally are not reversible in reducing environments. The PEG derivative is useful for modifying the characteristics of substances including modifying biologically active molecules and surfaces for biocompatibility. Methods for synthesizing the active PEG and for preparing conjugates of the active PEG and other substances, including biologically active substances, are also disclosed.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
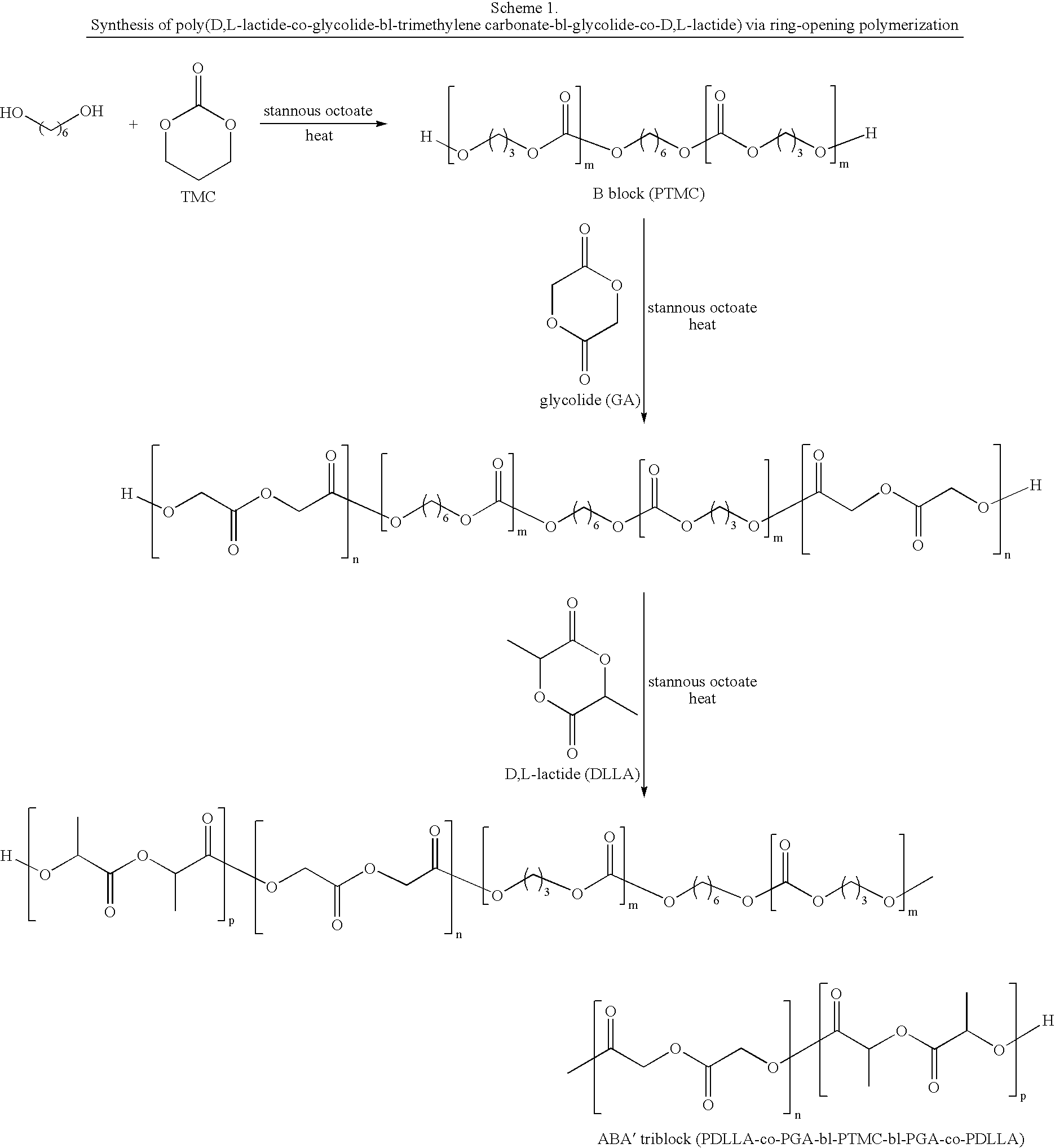
Biodegradable triblock copolymers for implantable devices
InactiveUS20090004243A1Reduce adverse effectsImprove mechanical propertiesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDevice formBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention is directed to polymeric materials made of biodegradable, bioabsorbable triblock copolymers and implantable devices (e.g., drug-delivery stents) containing such polymeric materials. The polymeric materials may also contain at least one therapeutic substance. The polymeric materials are formulated so as to improve the mechanical and adhesion properties, degradation, biocompatibility and drug permeability of such materials and, thus, implantable devices formed of such materials.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
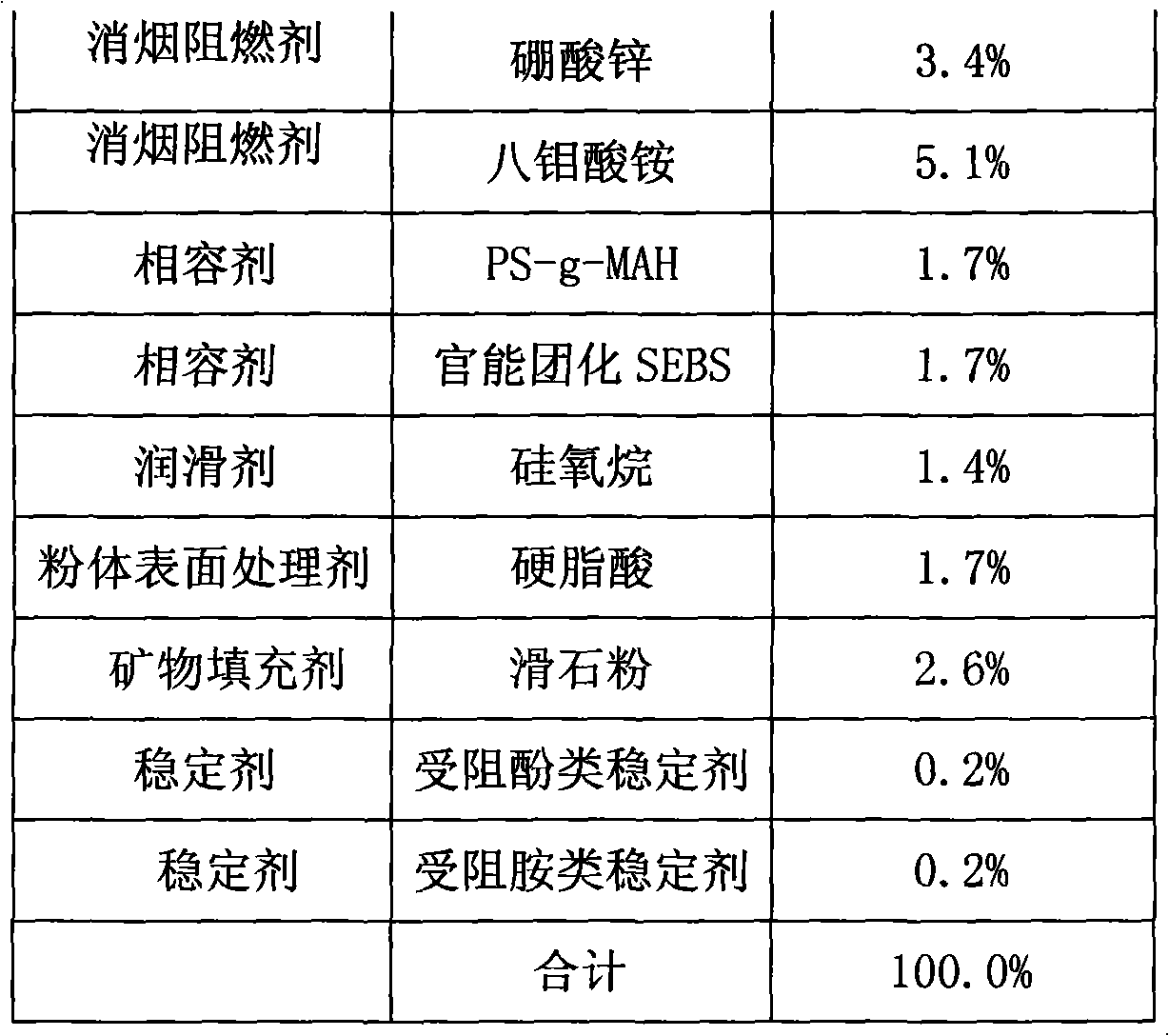
Halogen-free flame-retardant thermoplastic elastomer electrical cable material using polyphenylene ether as base material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101358028AGood compatibilityReduce stratificationInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsElastomerPolyphenylene oxide
The invention discloses a halogen-free flame-retardant thermoplastic elastomer cable material with polyphenylether as the base materials and a preparation method thereof. The raw material of the cable material contains the components with the following weight percentage: 10 to 35 percent of matrix resin A; 5 to 15 percent of matrix resin B; 10 to 25 percent of elastomer; 5 to 25 percent of softening plasticizer; 8 to 15 percent of flame-retardant plasticizer; 20 to 40 percent of smoke-suppression flame retardant; 3 to 10 percent of compatilizer; 1 to 5 percent of lubricant; 1 to 5 percent of powder surface conditioner; 0 to 10 percent of mineral filler; 0.1 to 1 percent of stabilizing agent. The invention adds matrix resin, polyphenylether of strong polarity and functional group of styrene-ethylene / butylene-styrene segmented copolymer, which effectively improves the compatibility of non-polar elastomer with polyphenylether; the invention also adds plasticizer, which reduces the hardness of the material and increases the flexibility; and through the optimization and interaction of the softening plasticizer and the flame-retardant plasticizer, the invention reduces the hardness and improves the tactility of the material, and the flame retardant performance is excellent.
Owner:NINGBO SHIP PLASTIC CO LTD
Method for preparing medical porous tantalum implant material
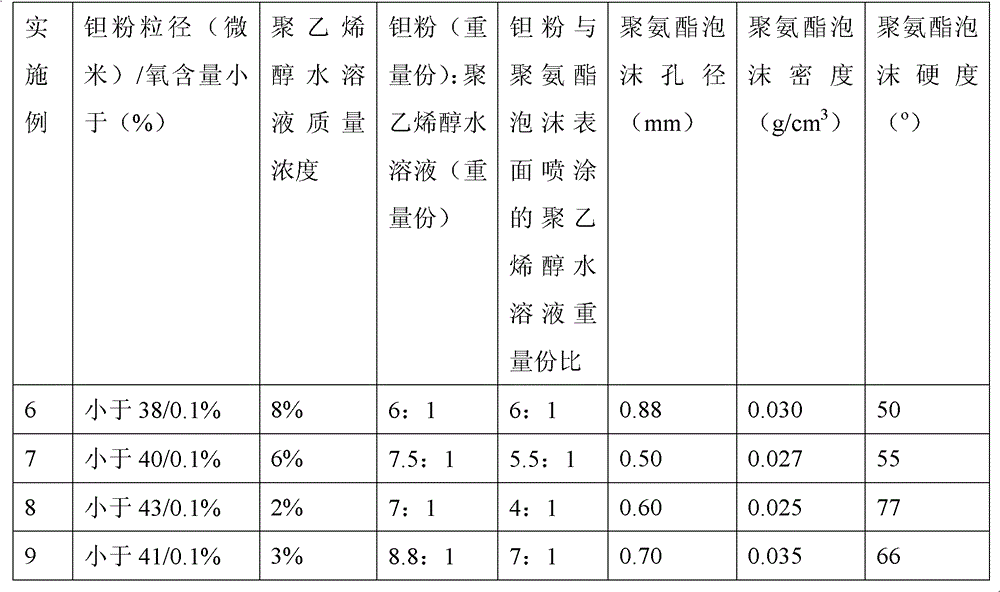
ActiveCN102796894AReduce contentImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisPolyvinyl alcoholBiocompatibility Testing
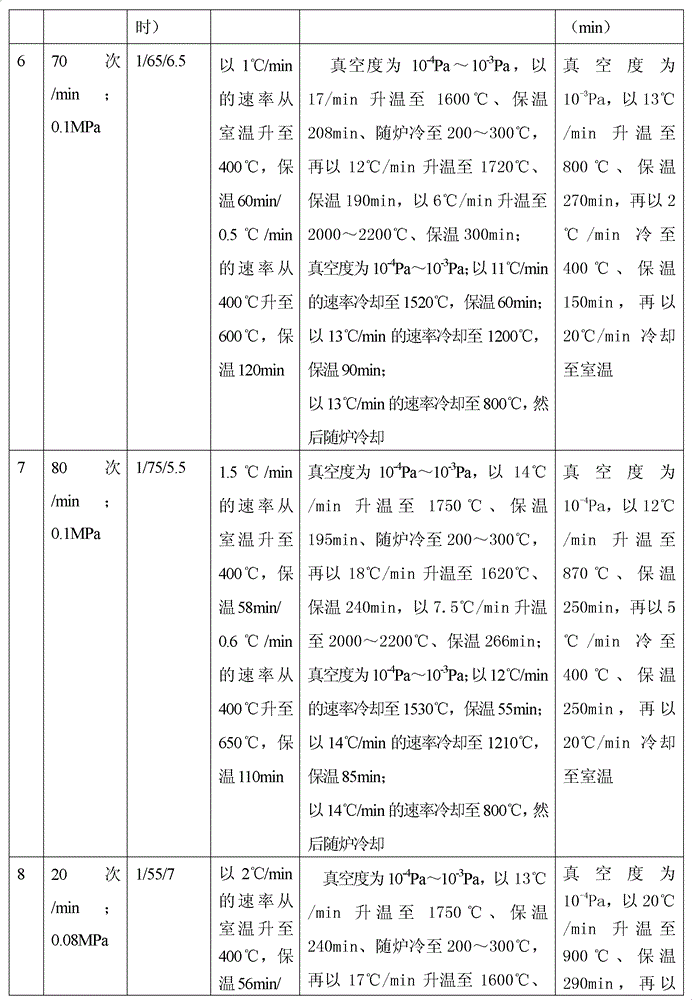
The invention discloses a method for preparing a medical porous tantalum material. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a poly ethanol aqueous solution and tantalum powder to obtain slurry, wherein the mass concentration of the poly ethanol aqueous solution is 2 to 8 percent; injecting the slurry into an organic foam by vibrating and pressurizing, wherein the vibrating frequency is 20 to 80 times / min; drying; degreasing; sintering, namely raising temperature to 1,500 to 1,800 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min under the vacuum degree of 10<-4> to 10<-3>Pa, preserving heat for 120 to 240 minutes, cooling to 200 to 300 DEG C along with a furnace, raising temperature to 1,500 to 1,800 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min again, preserving heat for 180 to 240 minutes, raising temperature to 2,000 to 2,200 DEG C at the speed of 5 to 10 DEG C / min, and preserving heat for 120 to 360 minutes; cooling; and performing thermal treatment, namely raising temperature to 800 to 900 DEG C at the speed of 10 to 20 DEG C / min under the vacuum degree of 10<-4> to 10<-3> Pa, preserving heat for 240 to 480 minutes, cooling to 400 DGE C at the speed of 2 to 5 DGE C / min, preserving heat for 120 to 300 minutes, and cooling to room temperature along with the furnace. The porous tantalum prepared by the method is very suitable to be used for the medical implant material for replacing bearing bone tissues, and biocompatibility and the mechanical property can be guaranteed simultaneously.
Owner:CHONGQING RUNZE PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com