Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110results about How to "Reduce water vapor content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
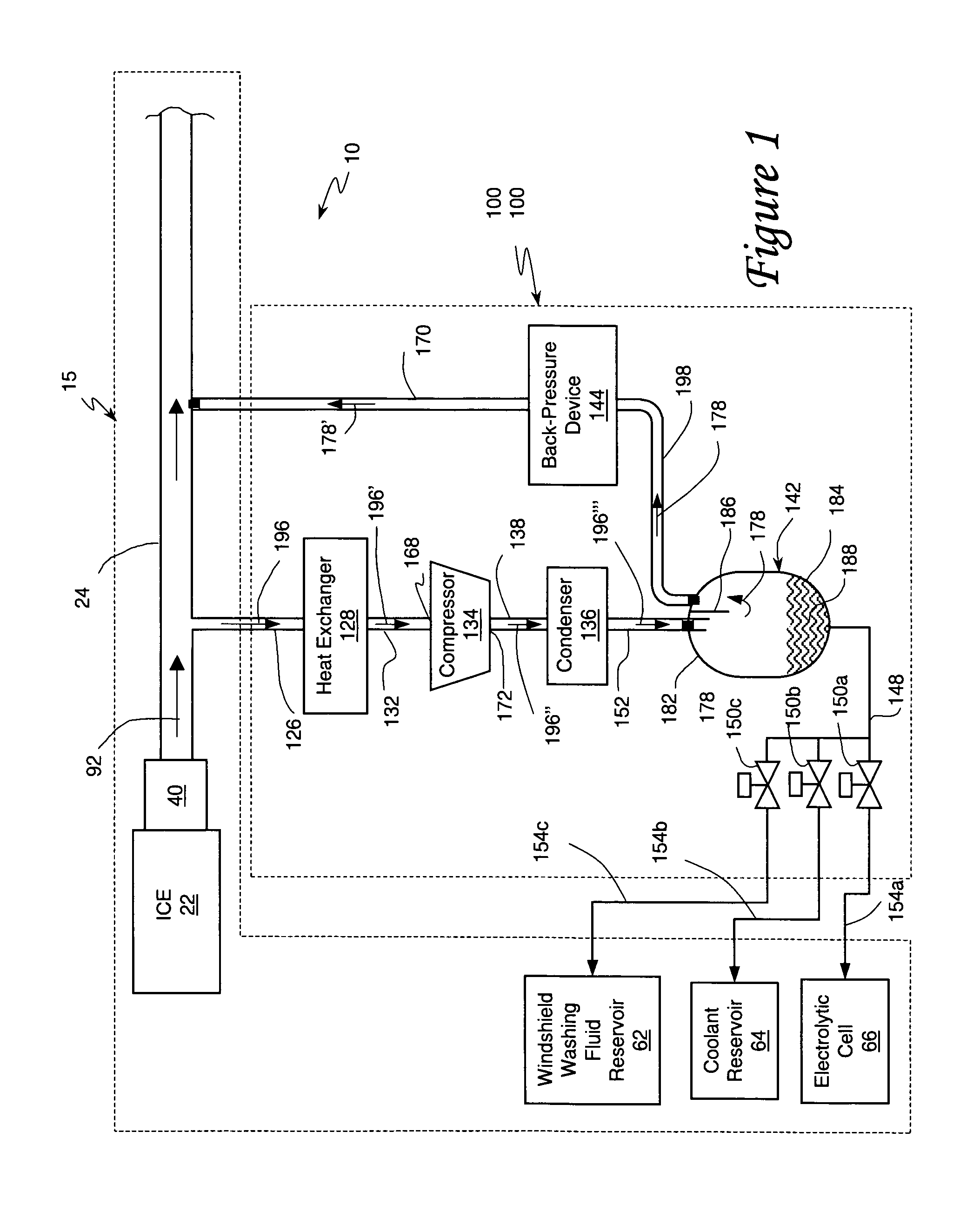
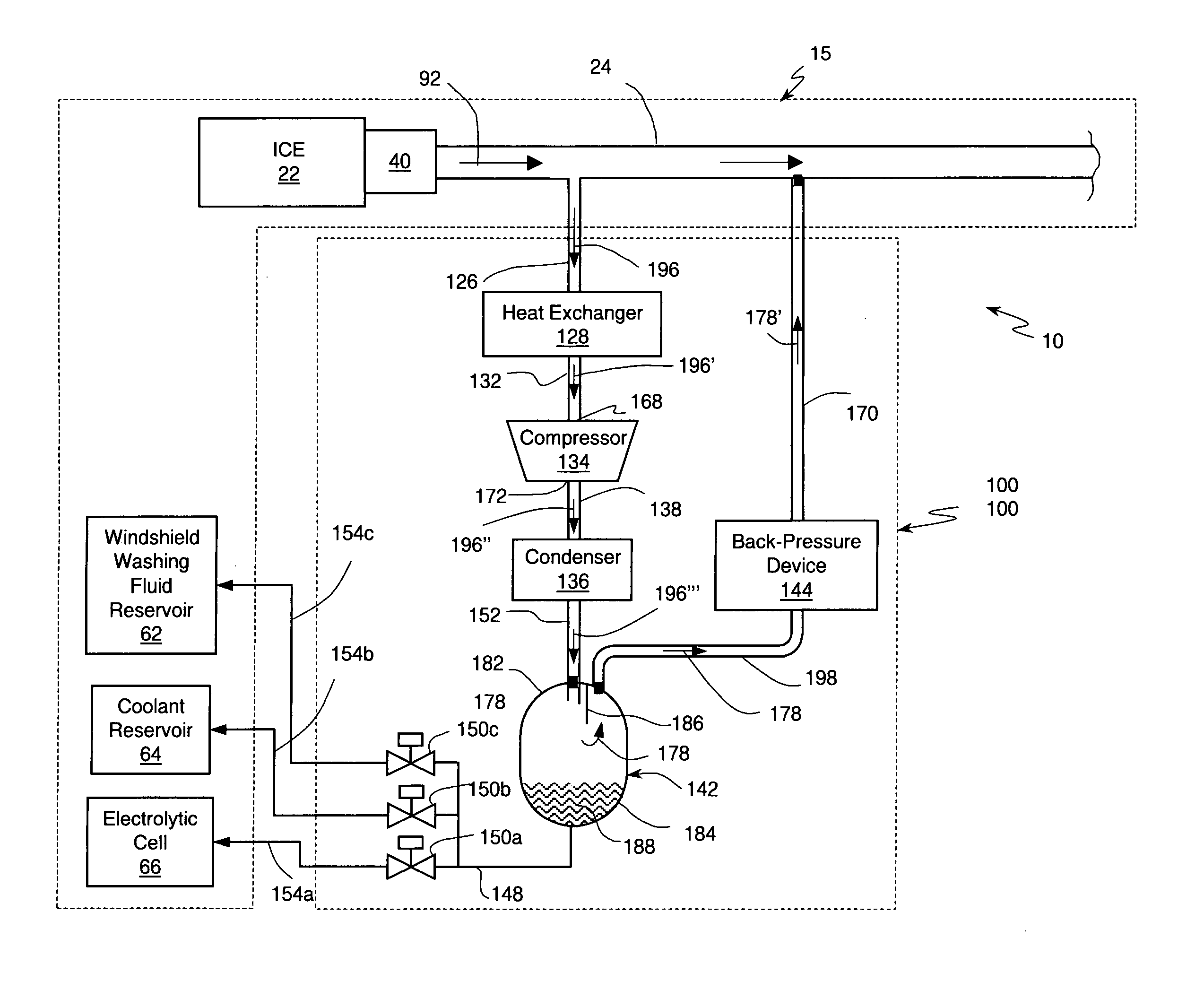
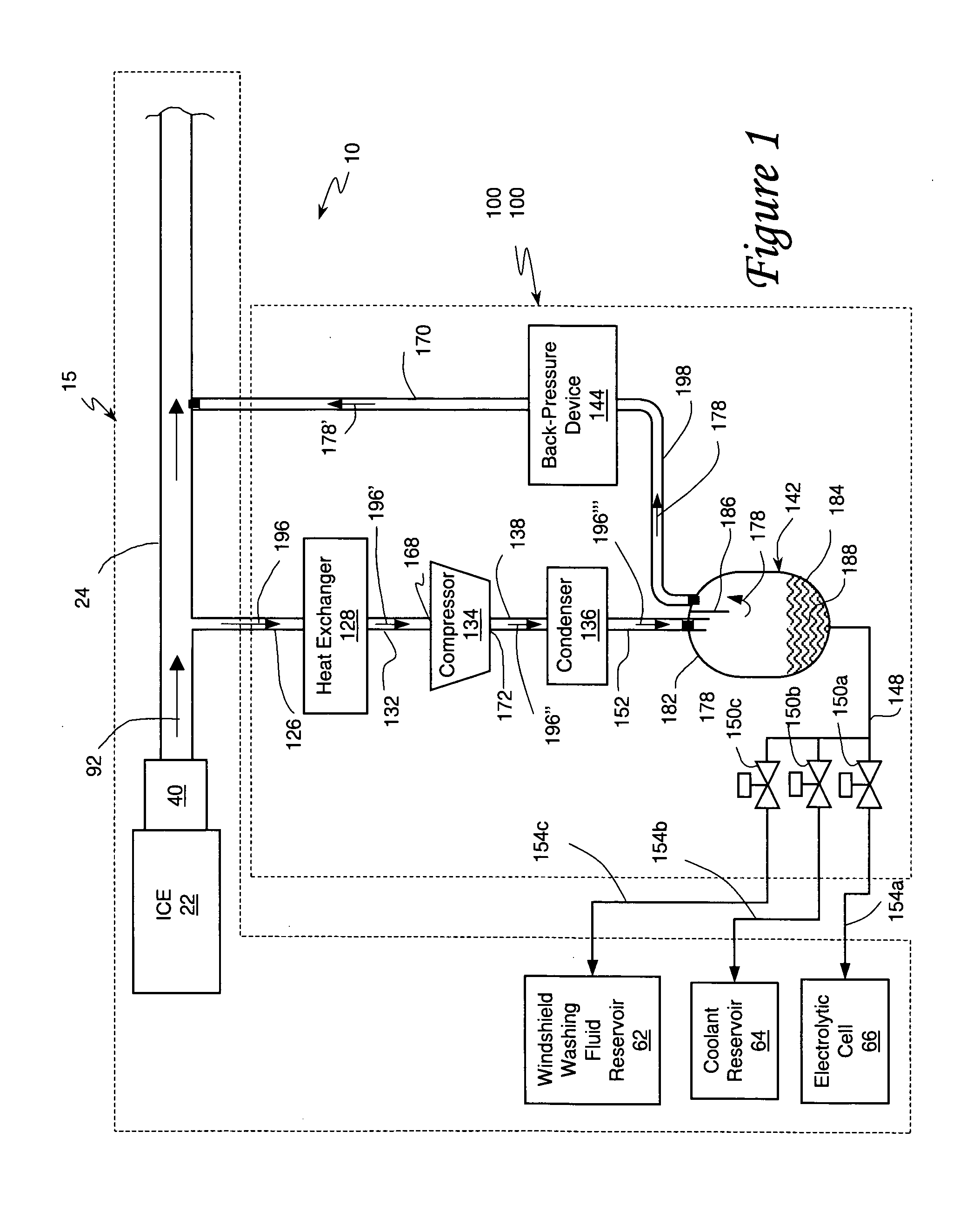
Internal combustion engine/water source system
InactiveUS7302795B2Increase pointsSimple and reliable processNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineWater source
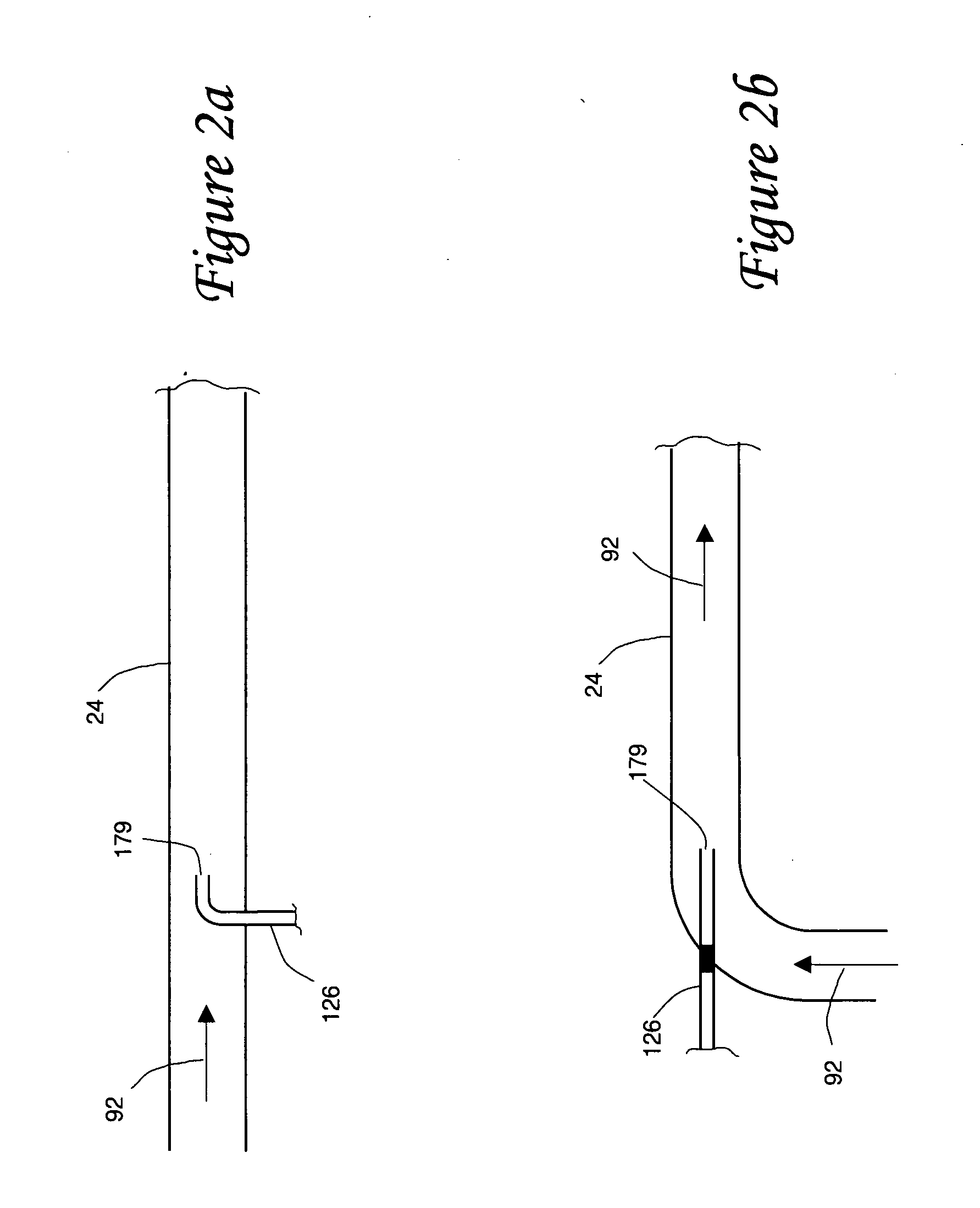
An internal combustion engine system for automotive vehicle wherein liquid water is produced by cooling a portion of exhaust gases at elevated pressure to induce condensation. The use of elevated pressure allows condensation to occur at a higher dew point which is easier to realize with cooling by ambient air. Liquid water condensate is collected and provided to an electrolytic cell for electrolysis into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen gas generated by the cell is used by the internal combustion engine to reduce internal combustion engine wear and to reduce exhaust pollutants especially during start-up. Alternate uses of the liquid water include a replenishment of engine coolant and window washing fluid.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
Internal combustion engine/water source system
InactiveUS20070006571A1Reliable generationSuitable for mass productionNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesWater sourceLiquid water
An internal combustion engine system for automotive vehicle wherein liquid water is produced by cooling a portion of exhaust gases at elevated pressure to induce condensation. The use of elevated pressure allows condensation to occur at a higher dew point which is easier to realize with cooling by ambient air. Liquid water condensate is collected and provided to an electrolytic cell for electrolysis into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen gas generated by the cell is used by the internal combustion engine to reduce internal combustion engine wear and to reduce exhaust pollutants especially during start-up. Alternate uses of the liquid water include a replenishment of engine coolant and window washing fluid.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
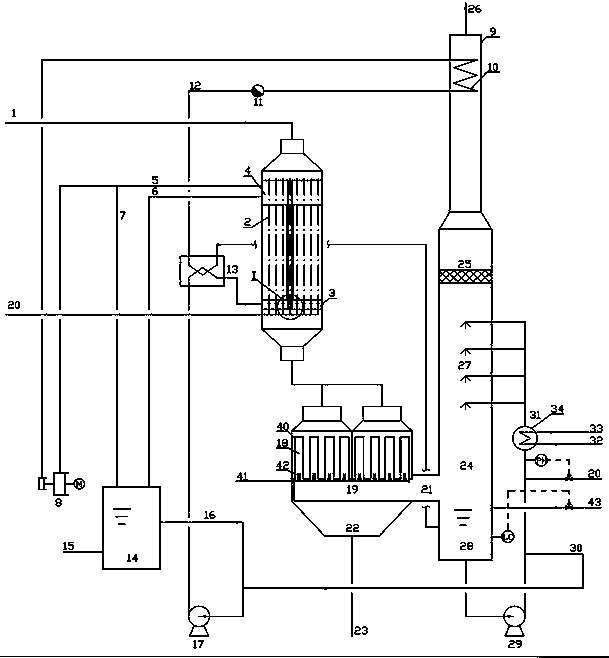
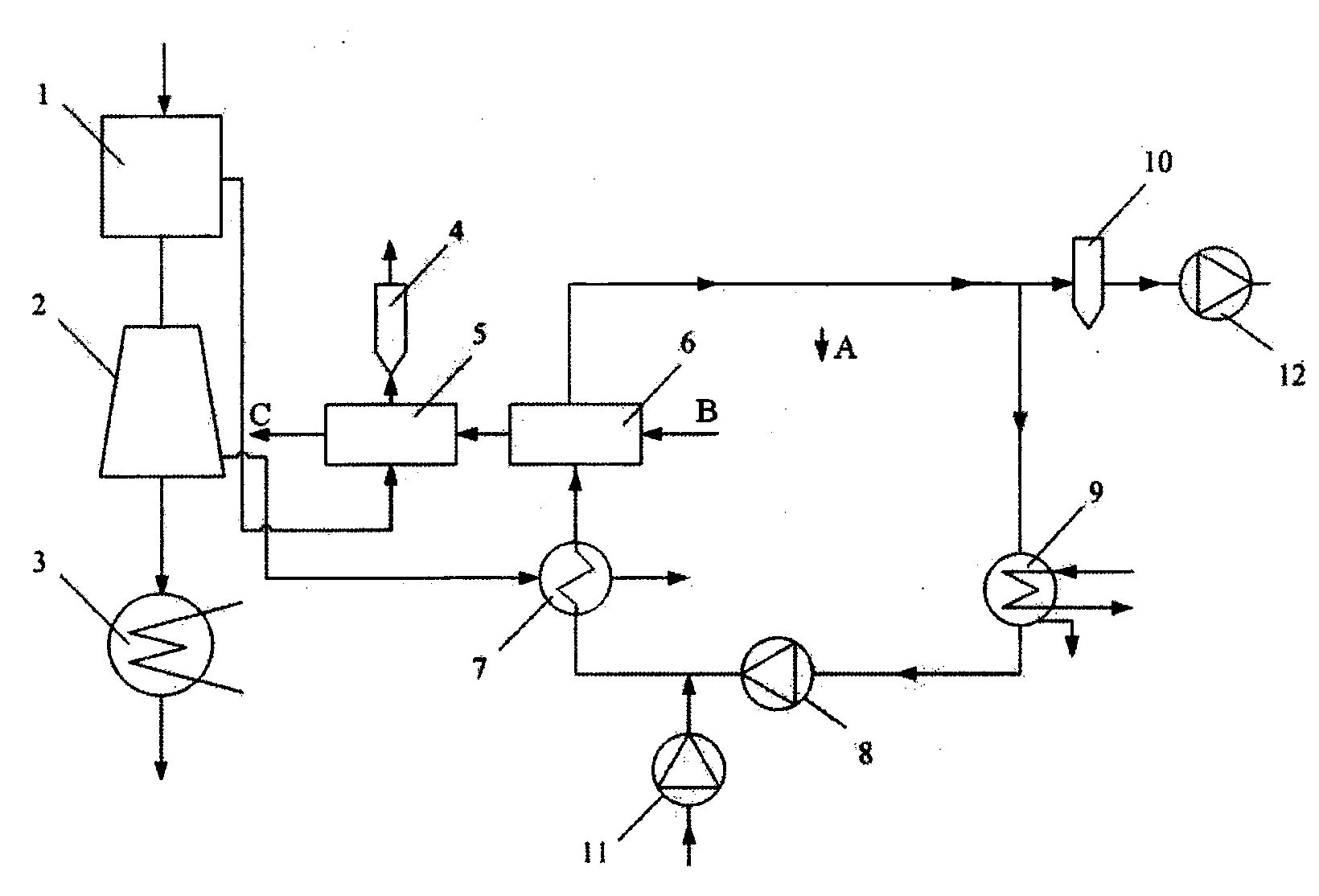
System and method for recycling flue gas waste heat and water while white fog of coal-fired power station chimney is eliminated
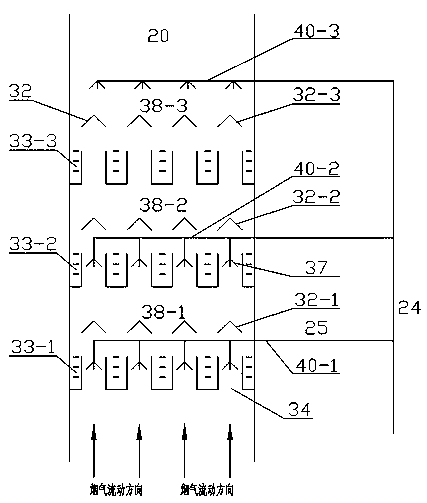
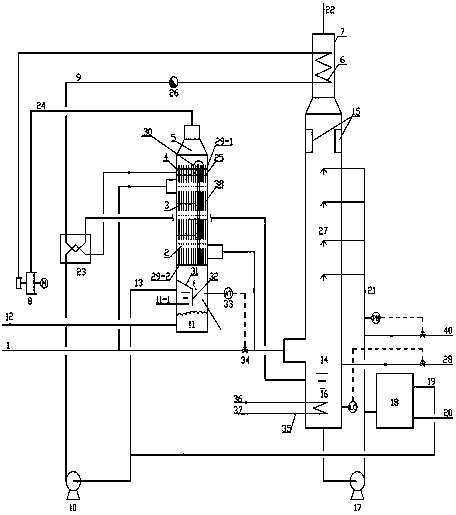
ActiveCN106500122AIncrease superheatReduce water vapor contentEnergy efficient heating/coolingClimate change adaptationFlue gasWater vapor
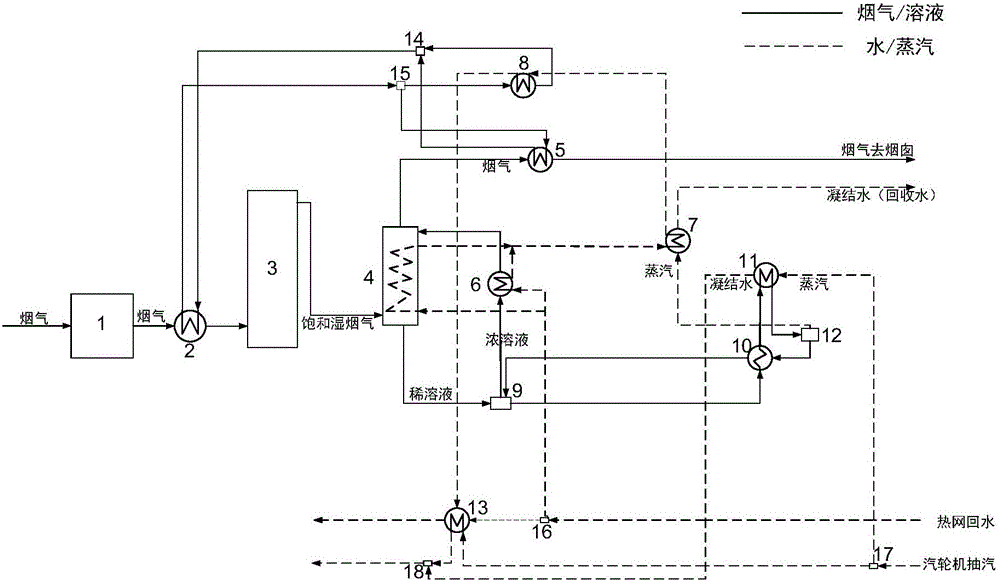
The invention provides a system and method for recycling flue gas waste heat and water while white fog of a coal-fired power station chimney is eliminated. The system comprises an absorber absorbing water vapor in flue gas through a salt solution, a solution reproducer, a corresponding heat recycling system and an integrated system for flue gas heat recycling before wet desulphurization. By means of the system and method, white fog of the wet desulphurization coal-fired power station chimney can be eliminated, especially, white fog in winter is eliminated, waste heat and water of flue gas can be recycled, the energy utilizing efficiency of a power station is improved, and consumed water of the power station is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for producing high-purity magnesium oxide and co-producing industrial concentrated hydrochloric acid through partially hydrated magnesium chloride fluidization pyrolysis
InactiveCN105197968AReduce water vapor contentTake advantage ofChemical industryMagnesiaExhaust gasMagnesium
The invention provides a method and device for producing high-purity magnesium oxide and co-producing industrial concentrated hydrochloric acid through partially hydrated magnesium chloride fluidization pyrolysis. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a partially hydrated magnesium chloride solid material is subjected to fluidization pyrolysis in a fluidized bed pyrolysis furnace and subjected to gas-solid separation, and rough magnesium oxide and pyrolysis tail gas are obtained; secondly, the rough magnesium oxide is cooled and subjected to aftertreatment, and high-purity magnesium oxide is obtained; thirdly, the pyrolysis tail gas is used for preparing the industrial concentrated hydrochloric acid. The method can be used for producing the high-purity magnesium oxide and co-producing the industrial concentrated hydrochloric acid; besides, the resource utilization rate of the method is high, little three wastes are generated, heat efficiency in the process is high, production cost is low, product purity is high, quality is stable, and the method is particularly suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compressed air drying device based on vortex tube refrigeration technology and working method of compressed air drying device
InactiveCN104174261AReduce moisture contentAvoid wastingDispersed particle separationLiquid storage tankAir compressor
The invention discloses a compressed air drying device based on a vortex tube refrigeration technology, belonging to the technical field of air drying. The compressed air drying device comprises an air compressor, an air-liquid heat exchanger, an air cooler, a high-pressure air storage tank, a high-pressure dehumidifier, a first control valve, a nozzle, a pore plate, a vortex tube, a second control valve, a high-pressure liquid storage tank, a first throttling valve, an intermediate heat exchanger, a solution heater, a normal-pressure regenerator, a normal-pressure liquid storage tank, a high-pressure solution pump, a solution cooler, a third control valve and a dry air outlet. The invention further discloses a working method of the drying device. The drying device has the following beneficial effects of improving the energy utilization efficiency of the compressed air drying system, enhancing humidifying and regenerating effects, effectively reducing the moisture content of a compressed air outlet, and improving the refrigerating efficiency and the energy utilization rate of the vortex tube. The working method of the compressed air drying device based on the vortex tube regeneration technology is simple in steps and is energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Process and apparatus for producing iron carbide
InactiveUS20010048913A1Reduce methane concentrationIncrease production capacityFluidised-bed furnacesGas emission reductionHigh pressureQuenching
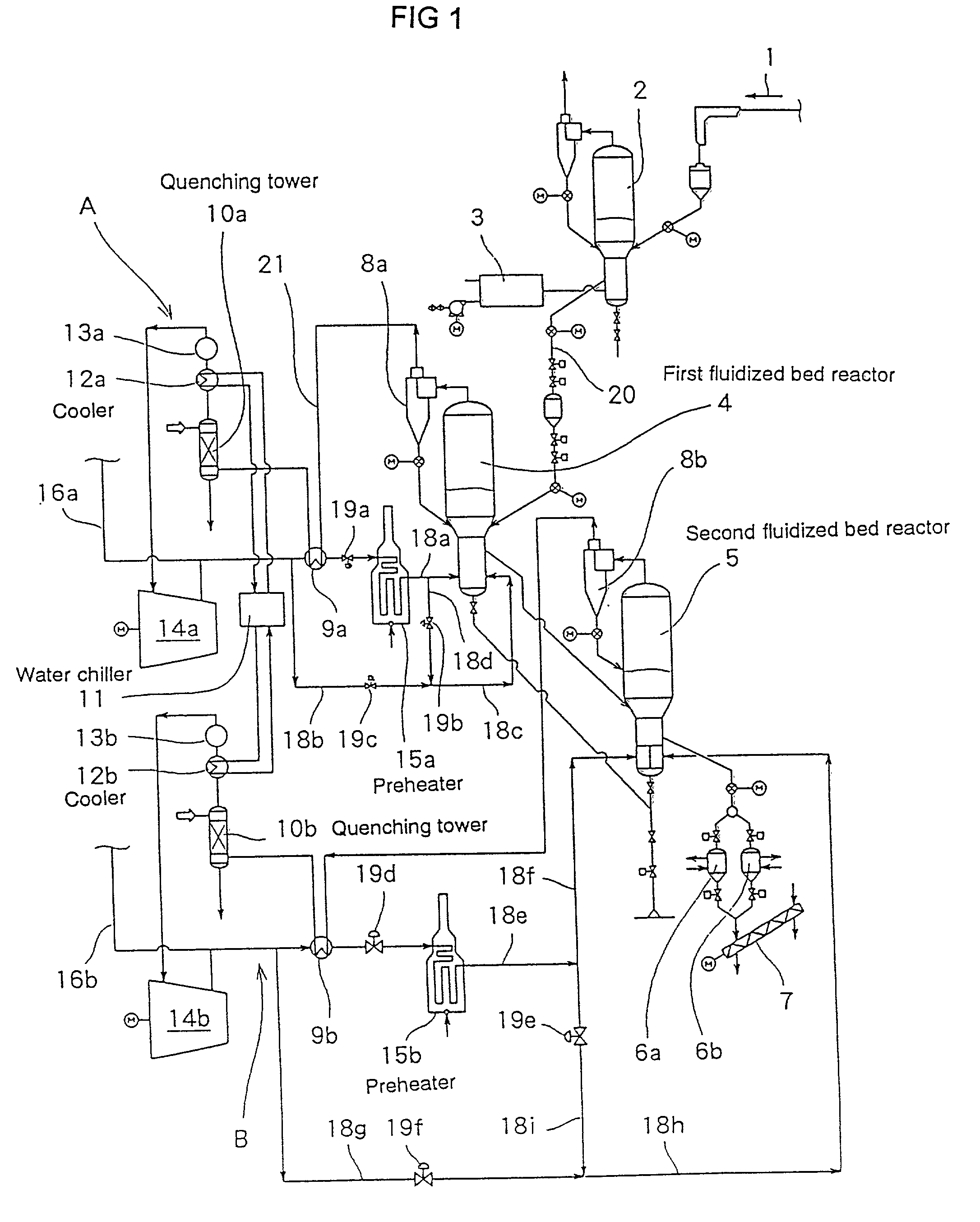
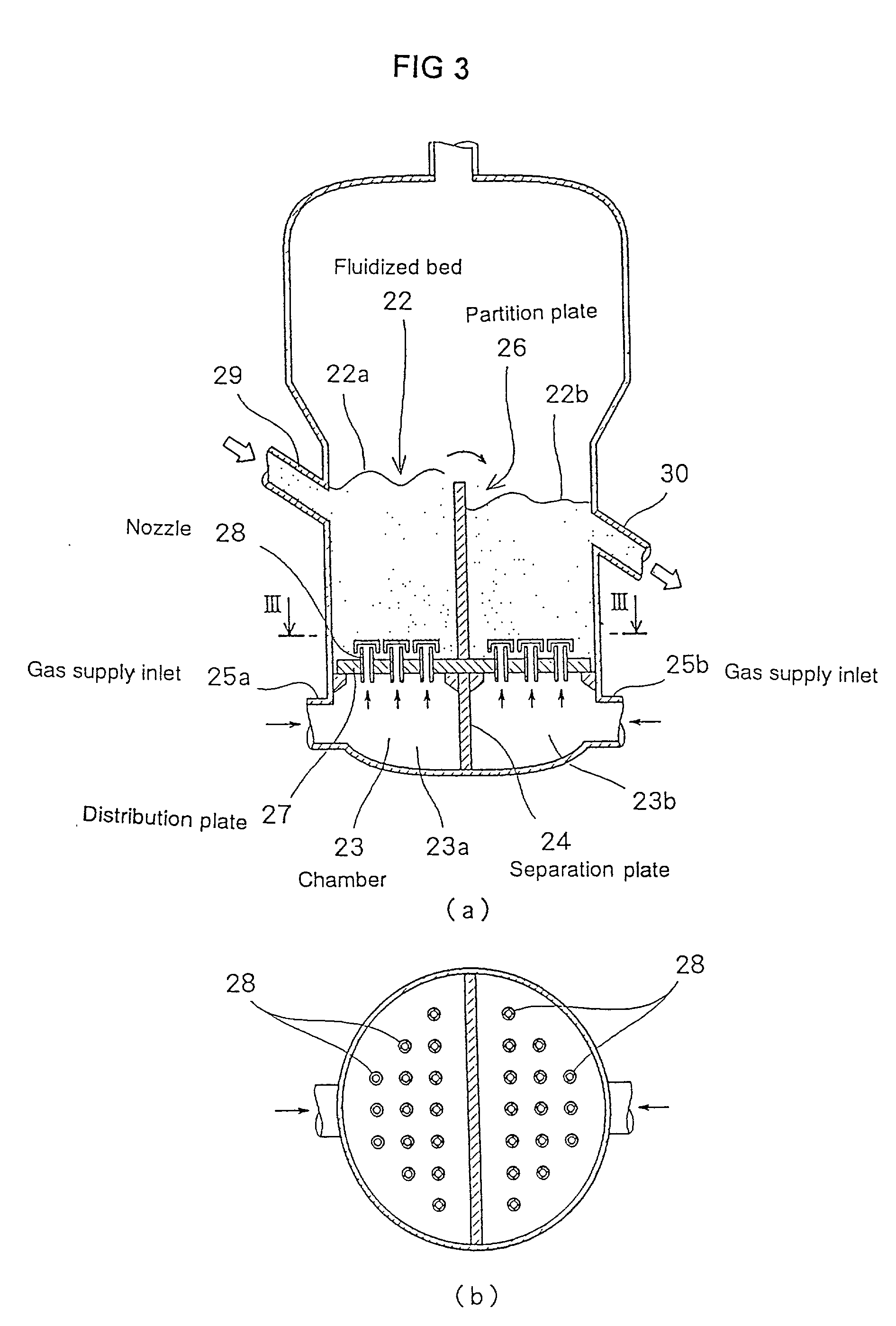
Iron carbide is produced by an apparatus comprising first fludized bed reactor 4 and second fluidized bed reactor 5, wherein the charged grainy iron oxide is reduced and carburized by the high temperature and high pressure gas being introduced from the bottom of the reactor. Both fluidized bed reactors comprise chamber 23 for introducing gas into the reactor, distribution plate 27 having multiple gas-introducing nozzles 28, partition plate 26 partitioning the fulidized bed into plural division rooms, and gas supply inlet 25a, 25b arranged on chamber 23 for supplying gas to specific division room respectively. Each gas supply inlet is connected to gas supply line having a gas flow control valve for controlling gas pressure or gas flow rate. There is provided with a gas circulation loop having a quenching tower 10a,10b and cooler 12a, 12b which eliminate dust contained in the exhaust gas of the reactor, and having a preheater 15a, 15b for heating the gas, wherein the exhaust gas is returned to the chamber by way of quenching tower, cooler and preheater. Using the above apparatus, a grainy iron oxide is reacted with gas and iron carbide is produced by the steps of; charging a grainy iron oxide from a side wall of fluidized bed reactor 4, 5; reducing and carburizing the grainy iron oxide under floating and fluidizing by high temperature and high pressure gas being introduced from the bottom of the reactor; transferring the grainy iron oxide from the division room of the upstream side to the division room of the downstream side via a communication space located at either upper or lower part of the partition plate under fluidizing; discharging produced iron oxide from the final division room.
Owner:JP STEEL PLANTECH +1
Method for drying ceramic blank and energy-saving rapid drying kiln used in method
ActiveCN103868340AAvoid crackingSmall temperature differenceDrying gas arrangementsMaterials scienceWater vapor
The invention discloses a method for drying ceramic blank. The method comprises the steps of leading a thermal medium to a drying kiln, mixing the thermal medium with steam, and mixing the steam with the thermal medium before the thermal medium enters the drying kiln. After optimization, humidity of the thermal medium is adjustable; and the humidity of the thermal medium is decreased progressively along with the drying degree of the ceramic blank. The invention further discloses the energy-saving rapid drying kiln used in the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG JUMPER THERMAL TECH
System and method for treating sintered flue gas desulfurization and denitrification and wastewater
ActiveCN108706784AAchieve recyclingReduce water vapor contentSludge treatmentWater contaminantsLiquid wasteFiltration
The invention relates to a system and a method for treating sintered flue gas desulfurization and denitrification wastewater, belonging to the technical field of environmental protection. The method comprises the steps of carrying out precipitation reaction by virtue of Ca<+> in desulfurizing tower waste liquid and SO4<2-> in a denitrification tower, conveying reacted slurry to a gypsum pressure filtration system, carrying out pressure filtration so as to obtain gypsum, returning filtrate to a mixing tank, mixing concentrated flue gas condensate water from a chimney inlet with an upper-layer mixed solution in the mixing tank, conveying the mixed solution to a sintered material mixing process site to participate in mixing formation of a sintered material, and generating reduction reaction by virtue of the mixed material, nitrate and nitrite in water in the mixed material from the mixing tank and coke powder and coal powder in the sintered material under the effect of an iron base, so asto realize denitrification. The cyclic utilization and the harmless wastewater treatment are realized in the whole treatment process; and compared with the prior art, the desulfurization and denitrification wastewater is treated, and meanwhile, white smoke can be eliminated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Water-saving and fog-clearing crossflow type cooling tower
InactiveCN105605940AReduce the amount of waterReduce water vapor contentTrickle coolersDistribution systemAerospace engineering
The invention discloses a water-saving and fog-clearing crossflow type cooling tower which comprises a cooling tower body, wherein a left air inlet and a right air inlet are formed in the cooling tower body; an air duct is arranged on the upper end face of the cooling tower body; a first filler device is arranged at the left air inlet; a second filler device is arranged at the right air inlet; a water distribution system is arranged in the cooling tower body; the first filler device and / or the second filler device comprise a plurality of independent filler modules; each filler module consists of a filler frame and filler in the filler frame; a first air inlet is formed in one side of each filler frame, and a first air outlet is formed in the other opposite side; a water inlet is formed in the top face of each filler frame; louver type shading structures are mounted at the water inlets of the odd or even numbered filler frames longitudinally in sequence from front to back; opening or closing of the louver type shading structures is controlled to make the water inlets open or close. The water-saving and fog-clearing crossflow type cooling tower can achieve a fog clearing structure, and has the characteristic of good water-saving effect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LAXUN TECH DEV CO LTD
Flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization wastewater treatment method and flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization wastewater treatment apparatus
ActiveCN108686478AIncrease unsaturationDissipate in timeGas treatmentDispersed particle filtrationGas phaseTreatment costs
The invention relates to a flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization wastewater treatment method. According to the flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization wastewater treatment method, a flue gas pre-treatment tower comprises a flue gas / desalted water heat exchanger and a spraying unit; liquid-state desalted water is converted into gas-state desalted water by using flue gas in the flue gas / desalted water heat exchanger, and the gas-state desalted water enters a gas-liquid separator and is separated; the gas phase is compressed, the compressed gas phase enters the gas discharge cylinderon the top of a desulfurization tower to heat and purify the flue gas; the spraying unit is used for spraying a NaOH solution to reduce the flue gas temperature to below the dew point temperature of an acid, the cooled flue gas enters a bag type dust removing device and is treated, and the treated flue gas enters the desulfurization tower; and on the bottom of the desulfurization tower, a proper amount of desulfurization wastewater is subjected to spraying drying by using the flue gas, and the flue gas enters a desulfurization zone and is subjected to desulfurization purification. The invention further relates to a treatment apparatus of the treatment method. With the method and the apparatus of the present invention, the purified flue gas meets the discharge requirement, and the zero discharge of the flue gas desulfurization wastewater is achieved, the white smoke and the blue smoke are simultaneously eliminated, and the flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization wastewater comprehensive treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Treating method and treating apparatus for waste liquid produced in flue gas desulfurization
ActiveCN108117210AAvoid cloggingSmall footprintWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater treatment parameter controlFlue gasTreatment costs
The invention relates to a treating apparatus for waste liquid produced in sodium-process flue gas desulfurization. The treating apparatus mainly comprises a flue gas / desulfurization waste liquid heatexchanger, a dust-removal and desulfurization tower, a solid-liquid separator, a plate heat exchanger and a steam compressor, wherein the flue gas / desulfurization waste liquid heat exchanger is divided into an upper heat exchange zone and a lower crystallization zone; the upper heat exchange zone comprises a steam chamber, an upper tube plate, a partition plate, a heat exchange tube and a lower tube plate from top to bottom; a desulfurization waste liquid feeding box is arranged between the upper tube plate and the partition plate; a liquid film former is arranged at the heat exchanger tube end of the desulfurization waste liquid feeding box; the lower crystallization zone is provided with an inclined drainage plate, a sealing plate and a crystallization tank; and the sealing plate is inserted into a position located below the liquid level of the crystallization tank. Through adoption of the specific treating apparatus and a specific treating method, the dual purposes of allowing purified flue gas to meet emission requirements and realizing zero discharge of waste liquid produced in flue gas desulfurization are achieved on the basis of full use of the waste heat of flue gas; and in particular, the supplementation amount of fresh water for a flue gas desulfurization system is reduced, and overall treatment cost of flue gas desulfurization and desulfurization waste liquid is lowered.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Flue gas and flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment method and device
ActiveCN108619871AIncrease water vapor contentRaise the acid dew pointCombination devicesGas treatmentLiquid wasteSteam condensation
The invention relates to a flue gas and flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment method and device. The flue gas is used to exchange heat and raise the temperature of desulfurization wastewater in a flue gas / desulfurization wastewater heat exchanger, a spray nozzle is arranged in a flue gas outlet to spray an NaOH solution, the temperature of the flue gas is reduced to the temperature of theacid dew point, then the flue gas enters a bag filter to remove dust and a sulfate / sulfuric acid liquid drop and then falls into a desulfurizing tower; the flue gas is desulfurized, purified and heated and the temperature is raised in the desulfurizing tower, the wastewater part at the bottom part of the desulfurizing tower serves as a circulating absorption liquid, other wastewater enters a plateheat exchanger in the form of desulfurization wastewater; and the plate heat exchanger uses steam condensation water produced in a heating coil in an exhaust funnel to preheat the desulfurization wastewater, and the preheated wastewater enters the flue gas / desulfurization wastewater heat exchanger. The double purposes of purifying the flue gas and meeting the emission requirement and achieving zero emission of the flue gas desulfurization waste liquid are achieved on the basis that the waste heat of the flue gas is fully used, meanwhile, the white smoke and the blue smoke are eliminated, andthe comprehensive treatment costs for the flue gas desulfurization and the desulfurization waste liquid are reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Sludge drying system and method
ActiveCN104176898AGuaranteed uptimeAvoid pollutionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningHigh concentrationSludge
The invention relates to a sludge drying system and method. A flue gas discharged from a boiler is used as fluidized gas of a drying device of a fluidized bed to dry wet sludge, discharged exhaust gas with high concentration of oxygen is introduced into the boiler for carrying out incineration treatment, the hot flue gas discharged from the boiler is used for supplementing the fluidized gas such that the temperature of the fluidized gas is higher than the dew point temperature and the concentration of oxygen in the fluidized gas keeps away from an explosion limit. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the sludge drying system comprises a boiler, wherein one path of a flue gas exhaust outlet of the boiler is connected with a chimney, the other path of the flue gas exhaust outlet of the boiler is connected with a first gas inlet of a 1# mixer with a three-way structure, a gas exhaust outlet of the 1# mixer is connected with a gas inlet of the drying device of the fluidized bed, a gas exhaust outlet of the drying device of the fluidized bed is connected with a gas inlet of a 2# mixer with a three-way structure, a first gas exhaust outlet of the 2# mixer is connected with a gas inlet of a condenser, a gas outlet of the condenser is connected with a second gas inlet of the 1# mixer, and a second gas exhaust outlet of the 2# mixer is connected to a gas inlet of the boiler; boiler tube bundles are arranged inside a boiler hearth and the boiler tube bundles are communicated with heating tubes of the drying device of the fluidized bed.
Owner:凤阳县经济发展投资有限公司
Bag-type dust removal device with water vapor treatment function
PendingCN107648944AReduce the temperatureReduce water vapor contentAuxillary pretreatmentDispersed particle filtrationWater vaporDust control
Disclosed is a bag-type dust removal device with a water vapor treatment function. The device comprises a dust removal chamber and supporting legs arranged at the bottom of the dust removal chamber, the dust removal chamber is internally divided into a dust removal area and an air purification area by a clapboard, the dust removal area is provided with an air inlet, a water removal pipe is installed at the air inlet and is of an inversely U-shaped structure, one side of the water removal pipe is communicated with the air inlet, the other side of the water removal pipe is provided with an air inlet pipe, the exterior of the water removal pipe is spirally wounded with a heat exchange pipe, the bottom of the water removal pipe is connected with a water accumulation tank through a conical structure, one end of the heat exchange pipe is provided with a water inlet, and the other end of the heat exchange pipe is provided with a water outlet. The bag-type dust removal device overcomes deficiencies in the prior art, the air inlet of the bag-type dust removal device is provided with a circulating water condensing device, and the temperature of smoke is reduced by utilizing circulating water, so that water vapor in the smoke gathers and flows into the water accumulation tank, the content of water vapor in the dust removal chamber is effectively reduced, the working capability and servicelife of a bag cage are ensured, partial heat energy is recycled indirectly at the same time, and the bag-type dust removal device saves energy and protects the environment.
Owner:合肥合意环保机电装备制造有限公司
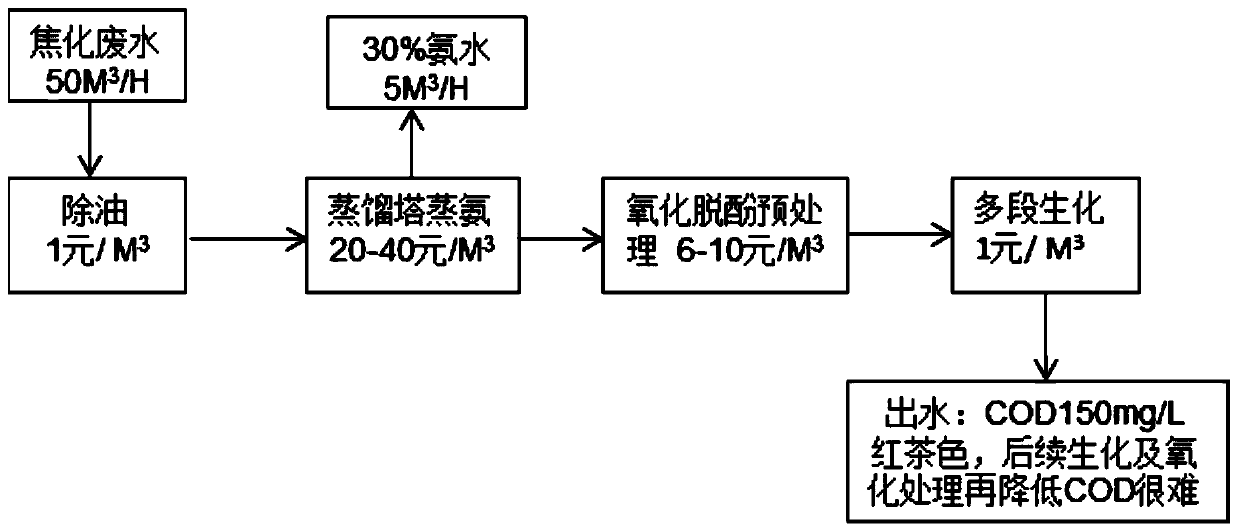
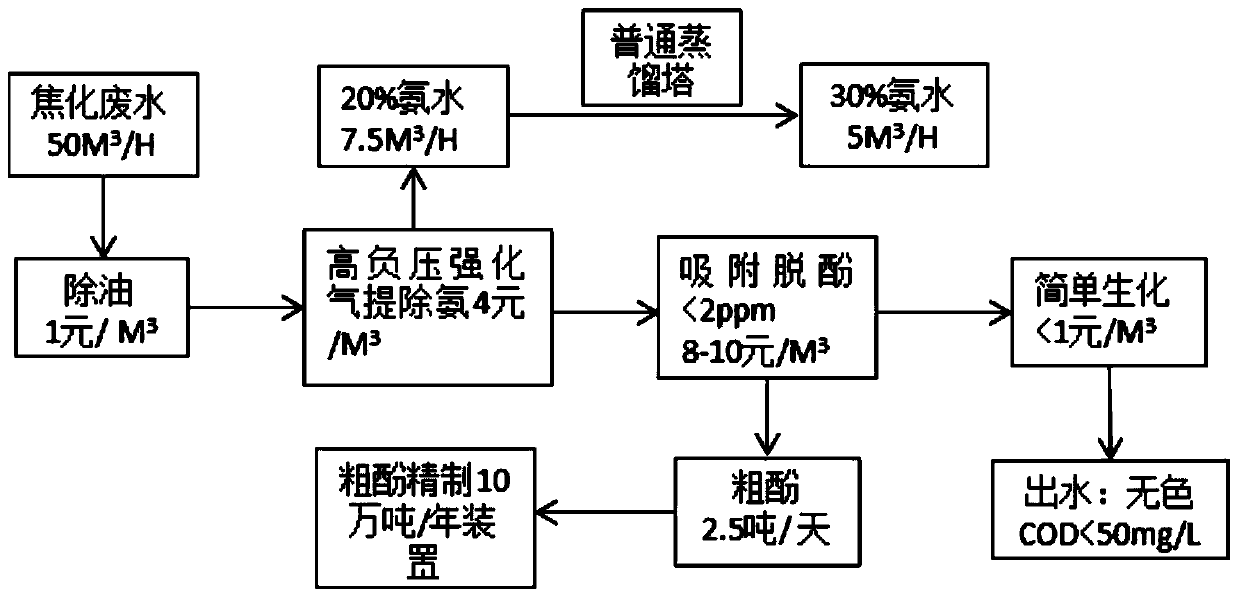
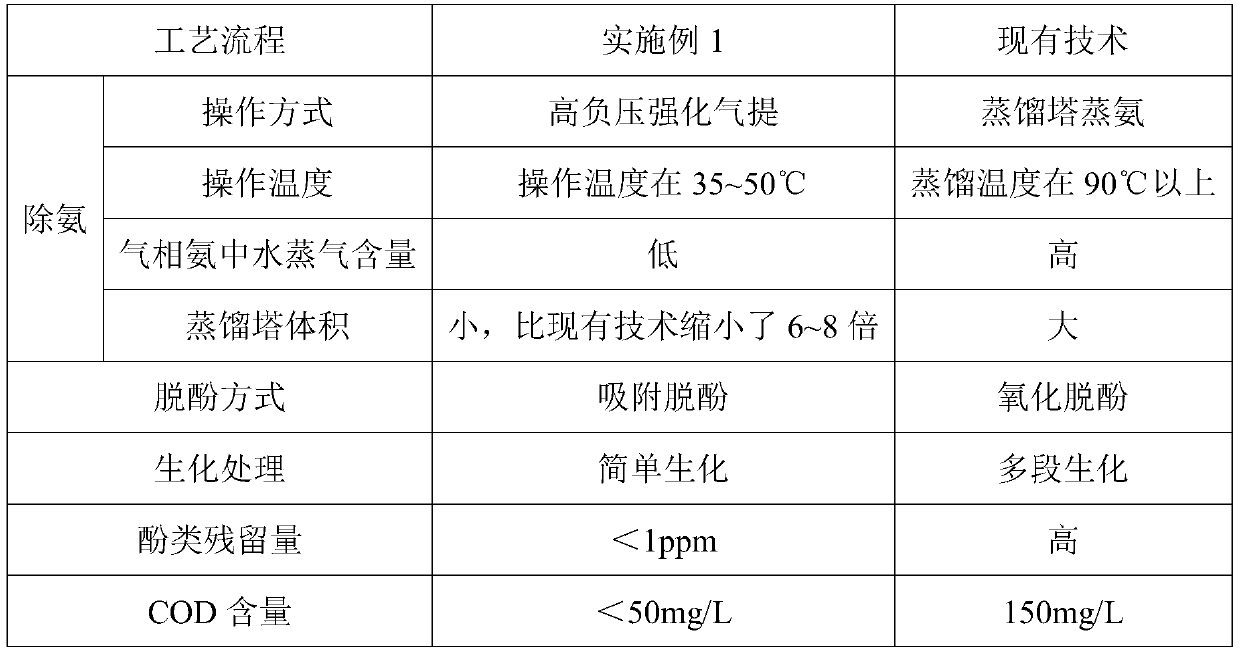
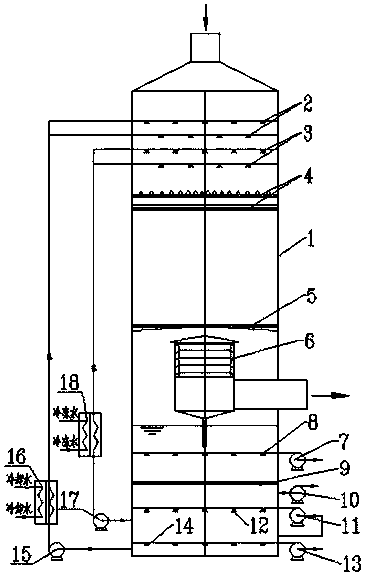
Low-cost and high-efficiency treatment technology for coking and semi-coke wastewater
PendingCN110498564AReduce processing costsReduce water vapor contentFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSpecific water treatment objectivesGas phaseSorbent
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and provides a low-cost and high-efficiency treatment technology for coking and semi-coke wastewater. The technology comprises thefollowing steps: S1, deoiling: removing coal tar and large-particle suspended oil and suspended matters in the coking and semi-coke wastewater to obtain deoiled coking and semi-coke wastewater; S2,performing high negative pressure enhanced gas stripping ammonia removal: carrying out high negative pressure enhanced gas stripping on the deoiled coking and semi-coke wastewater obtained in step S1 under -0.08 to -0.03 MPa at 35-50 DEG C in order to obtain gas phase ammonia and liquid phase wastewater; S3, performing adsorbing dephenolization: performing adsorbing dephenolization on the liquid phase wastewater obtained in step S2 by adopting an adsorbent to adsorb phenols in the wastewater in order to obtain dephenolized wastewater; and S4, biochemically treating effluent: biochemically treating on the dephenolized wastewater obtained in step S3, and discharging the treated water after reaching standards. The technology solves the problems of high cost and poor treatment effect of the coking and semi-coke wastewater in the prior art.
Owner:石家庄惠洁科技有限公司
High-efficiency flue gas downstream dust removal, desulfurization and whitening method and device
PendingCN109289475AEasy to removeImprove removal efficiencyGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentVapor–liquid separatorMulti pollutant
The invention discloses a high-efficiency flue gas downstream dust removal, desulfurization and whitening device comprising a spray scrubbing tower, high-level spray layers, low-level spray layers, adownstream Venturi gas-liquid uniform distributor, a rotational flow gas-liquid separator, a downstream tower type demister, oxidizing fans, an oxidizing air distribution device, a flow-equalizing pore plate, slurry disturbance pumps, a slurry turbulence distributor, slurry feeding pumps, a slurry feeding distributor, cooling slurry circulating pumps, cooling water heat exchangers, freezing slurrycirculating pumps, freezing water heat exchangers and slurry discharge pumps. The upper part of a tower body of the spray scrubbing tower is provided with a flue gas inlet, and a flue gas outlet is arranged in the middle of the tower body; an absorption liquid enters the tower from the upper spray layers and falls into a lower slurry pool, the absorption liquid flows in the same direction as fluegas, and a downstream flow is formed. Integrated effective removal of multiple pollutants is achieved by downstream spraying, and the device is suitable for dust removal, desulfurization (acid removal) and whitening treatment of flue gas and tail gas, and can be widely applied in the fields of air pollution prevention and control of thermal power, steel, non-ferrous metals and the like.
Owner:上海翰忠环保有限公司
Landfill leachate anaerobic biogas purification method
ActiveCN104909456AReduce water vapor contentImprove purification efficiencyGaseous fuelsWaste based fuelLiquid waterChemistry
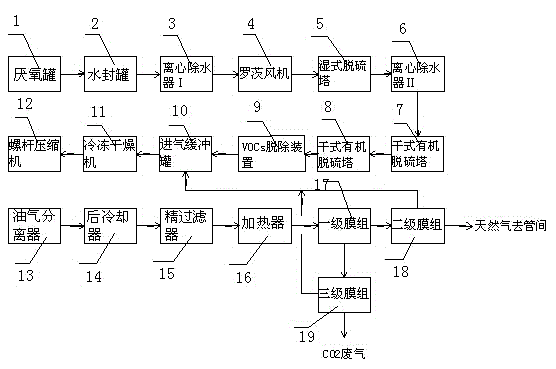
The invention relates to the field of biogas purification, and discloses a landfill leachate anaerobic biogas purification method. The method comprises the steps of gas liquid water dust removing, hydrogen sulfide rough removing, hydrogen sulfide fine removing, gas organic sulfur removing, biogas VOCs removing, freeze-drying machine processing, biogas purification system processing, and three-stage membrane separation system processing. With the method, water vapor content in biogas can be effectively reduced, such that subsequent compressor and membrane assemblies are protected, and a purification efficiency is high. After purification, a biogas concentration can be higher than 99.9%. CO2 / CH4 high-efficiency separation membrane reflux gas can be reutilized, wherein a recovery rate can be higher than 99.0%.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENGYUE NEW ENERGY TECH
Moisture-removal and white-smoke-elimination device for boiler exhaust gas
InactiveCN107388272AReduce water vapor contentSolve the phenomenon of white smokeIndirect heat exchangersCombustion technology mitigationAir preheaterWater discharge
A moisture-removal and white-smoke-elimination device for boiler exhaust gas comprises a gas duct which is provided with a boiler exhaust gas connecting opening, and an exhaust gas outlet is formed in the tail end of the gas duct. An air preheater used for mainly absorbing the sensible heat in the exhaust gas so as to reduce the exhaust smoke temperature of the exhaust gas is arranged in the gas duct, and a condenser used for mainly absorbing the latent heat of the water vapor in the exhaust gas so as to further reduce the temperature of the exhaust gas is arranged in the gas duct; the air preheater is a heat pipe type air preheater, wherein the liquid phase heat exchange section of the heat pipe type air preheater is arranged in the portion, in front of the condenser, of the gas duct, and the gas phase heat exchange section of the heat pipe type air preheater is arranged in the portion, behind the condenser, of the gas duct; the condenser is a water circulation condenser which adopts circulating water to cool the exhaust gas, and a condensate water discharging outlet is formed in the water circulation condenser. The moisture-removal and white-smoke-elimination device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the use is convenient and reliable, the content of the water vapor in the boiler exhaust gas can be reduced, and the problem that the exhaust gas emits white smoke is solved.
Owner:LIJU THERMAL EQUIP TECH
Method and system for recycling smoke waste heat through absorption type heat pump
PendingCN107655021AImprove waste heat recovery efficiencyReduce system power consumptionHeat recovery systemsLighting and heating apparatusSpray towerProcess engineering
A system for recycling smoke waste heat through an absorption type heat pump comprises a spraying tower, a wet desulphurization smoke inlet is formed in the bottom of the spraying tower, a cooled smoke outlet is formed in the top of the spraying tower, a spraying water inlet is formed in the upper portion of the spraying tower, and a spraying water outlet is formed in the lower portion of the spraying tower. The spraying water outlet is connected with a heating medium inlet of a plate heat exchanger, and the spraying water inlet is connected with a heating medium outlet of the plate heat exchanger. A loop is formed by a refrigerant outlet and inlet port of the plate heat exchanger and the cold end of the heat pump, and a loop is formed by the heat end of the heat pump and heat net return water. After smoke is heated, the smoke is sent to the bottom of the spraying tower and runs upwards to exchange heat with downward spraying water, heat is transmitted to the spraying water, and the cooled smoke is discharged from the top of the spraying tower. For the spraying water with the increased temperature, heat is transmitted to the cold end of the absorption type heat pump through the plate heat exchanger, under driving of a drive heat source, the heat pump recycles heat from the cold end for heating the heat net return water at the heat end, and the beneficial effects of high recycling efficiency, low energy consumption and environment friendliness are achieved.
Owner:HUANENG CLEAN ENERGY RES INST
Device and method for co-producing yellow phosphorus and synthesis gas by reducing phosphate ore through pressurized gasification of phosphorus coal
PendingCN111363591AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityHuman health protectionHydrogen separationSyngasPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a device for co-producing yellow phosphorus and synthesis gas by reducing phosphate ore through pressurized gasification of phosphorus coal. The device is characterized by comprising a grinding and pelletizing unit, an air separation unit, a phosphorus coal gasification reduction unit and a separation and purification unit, wherein the grinding and pelletizing unit is usedfor grinding a part of the raw materials into powder and preparing phosphorus pellets; the air separation unit is used for separating air components and preparing oxygen; the phosphorus coal gasification reduction unit is used for realizing the gasification reduction reaction of each material in the device to obtain phosphorus-containing furnace gas; the separation and purification unit is used for separating and purifying the phosphorus-containing furnace gas to obtain yellow phosphorus and clean synthesis gas; the grinding and pelletizing unit is used for supplying the obtained phosphorus pellets to the phosphorus coal gasification reduction unit; the air separation unit is used for supplying a gas material to the phosphorus coal gasification reduction unit; and the phosphorus-containingfurnace gas generated after a reaction in the phosphorus coal gasification reduction unit enters the separation and purification unit so as to obtain synthesis gas and yellow phosphorus. The method is an efficient and advanced technology for co-producing yellow phosphorus and synthesis gas.
Owner:贵州航天迈未科技有限公司
Treatment method for sulfur-containing industrial waste gases
InactiveCN107876011ALarge specific surface areaWell-developed pore structureGas treatmentOther chemical processesWater vaporPhosphate
The invention discloses a treatment method for sulfur-containing industrial waste gases, and belongs to the technical field of waste gas treatment and preparation. According to the method provided bythe invention, a series of modification such as acid washing, catalysis with a heavy metal salt solution and activation are performed on activated carbon, since the activated carbon has a large specific surface area and a developed pore structure, the activated carbon has good adsorption performance, thereby facilitating adsorption of sulfur-containing gases in the waste gases; a self-prepared mixed liquid obtained by mixing of an anaerobic thiobacillus denitrificans bacterial suspension liquid, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium nitrate, sucrose and deionized water is added, so that the adsorption capacity of the activated carbon to the sulfur-containing gases is enhanced; condensation is performed through chilled water, and an ''ice split'' principle is utilized, so that the water vapor content in the waste gases is reduced and the activity of the activated carbon is prevented from being destroyed by the water vapor; since the activated carbon adsorption is an exothermic reaction, waste gases with a lower temperature enter an adsorption tower, adsorption of the sulfur-containing gases in the waste gases by the activated carbon is facilitated; and the treatment method for theindustrial waste gases not only recovers the sulfur-containing gases, but also has no pollution to the environment.
Owner:吴亚琴
System and method for pre-drying brown coal by utilizing waste heat of power station
ActiveCN103822439AReduce the risk of fire and explosionImprove securityDrying solid materials with heatHearth type furnacesFlueBrown coal
The invention provides a system for pre-drying brown coal by utilizing the waste heat of a power station. The system comprises two stages of drying systems, wherein the first-stage drying system comprises a first-stage dryer, a circulating fan is connected with the first-stage dryer through an air heater, the first-stage dryer is connected with a first dust collector and a dehumidifier, the first dust collector is connected with an induced draft fan, the dehumidifier is connected with the circulating fan, a forced draft fan is connected with the circulating fan, and the second-stage drying system comprises a second-stage dryer which is connected with an extracting opening of a boiler rear smoke channel and a second dust collector. The invention also provides a method for pre-drying the brown coal by utilizing the waste heat of the power station. The device provided by the invention overcomes the defects in the prior art and can be used for performing classification drying on the brown coal for effectively removing internal water and external water of the brown coal, the drying is complete, smoke waste heat is directly utilized, the heat recovery and utilization efficiency is high, and the safety of the brown coal drying process and the power generating efficiency of the brown coal power station are effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOILER WORKS +1
Recovery system and method for desulfurizing agent in desulfurized gas of catalytic-cracking regeneration waste gas
ActiveCN107837681ALower dew pointReduce water vapor contentGas treatmentDispersed particle separationWater vaporProduct gas
The invention relates to a recovery system and method for a desulfurizing agent in a desulfurized gas of a catalytic-cracking regeneration waste gas. The recovery system comprises a desulfurizing tower, a condensing heat exchanger, a mechanical separation purifier, a heating heat exchanger and a filter, wherein a gas outlet of the desulfurizing tower is communicated with a gas inlet of the mechanical separation purifier through a first pipeline; the condensing heat exchanger is mounted in the first pipeline; the heating heat exchanger is mounted in a gas exhaust pipeline of the mechanical separation purifier; the condensing heat exchanger and the mechanical separation purifier are communicated with the filter respectively through second pipelines. The recovery system can be used for effectively decreasing the dew point of an outlet gas from the desulfurizing tower, is used for decreasing water vapor content and the particle concentrations of entrained desulfurizing agent and catalyst in the outlet gas, can be used for recovering most of the desulfurizing agent, and is used for decreasing the discharge loss of the desulfurizing agent, decreasing a running cost and meanwhile reducingenvironment pollution; through arranging the heating heat exchanger, an exhausted gas can be prevented from entering an environment of which temperature is lower than the temperature of the gas so that a liquid drop can be still immediately condensed and the formation of a rime fog is prevented.
Owner:BEIJING CREDITCONGRUITY ENERGY TECH CO LTD
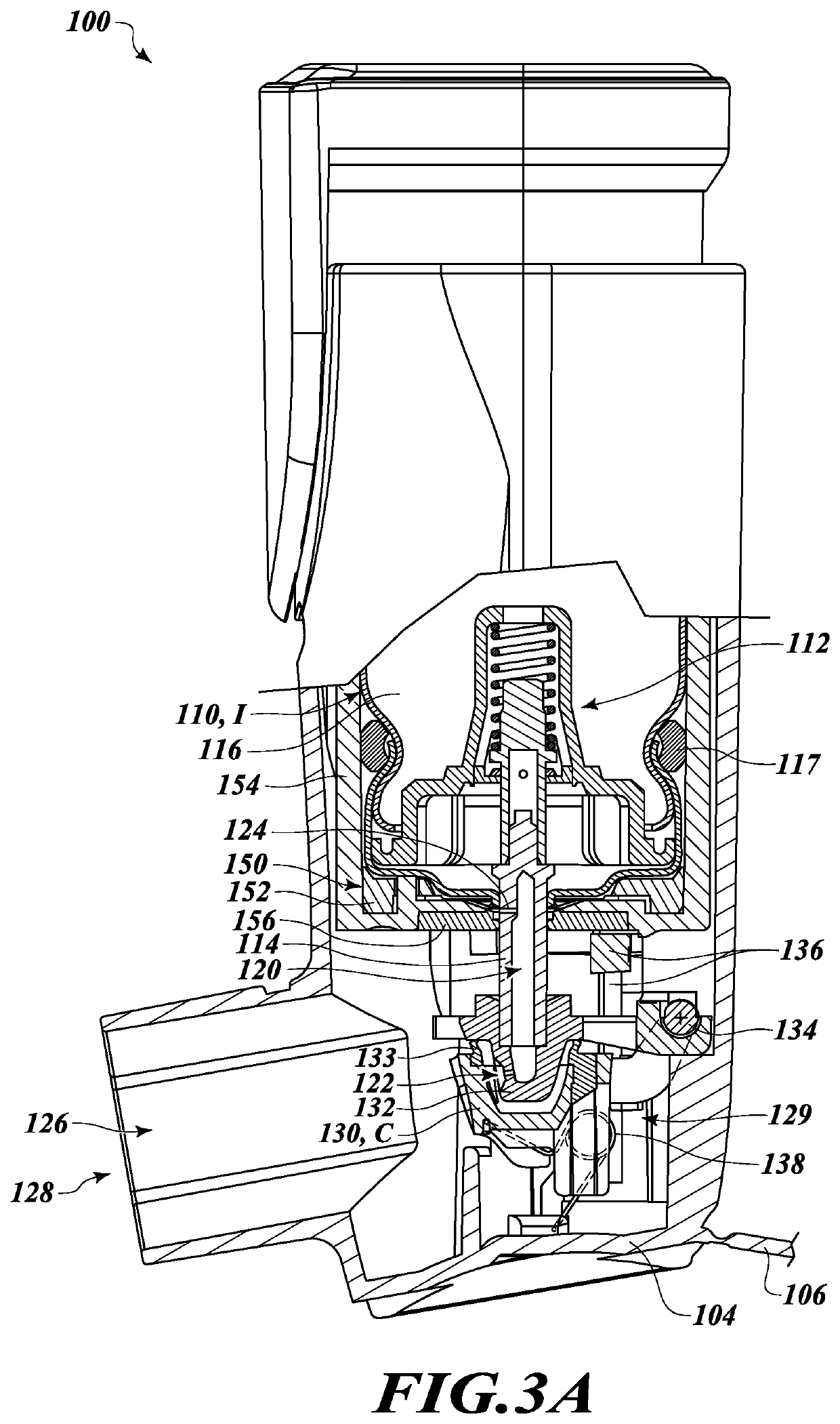
Drug delivery systems and related methods
PendingUS20200353185A1Reduce contentEliminate and significantly reduce depositionPowder deliveryDispensing apparatusDesiccantInhalation
Systems and methods for isolating and / or desiccating a portion of a drug delivery tract of a drug delivery apparatus to reduce water vapor content therein are provided. For example, there is provided a metered dose inhaler for delivering aerosolized medicament or other matter to a user. The aerosolized medicament or other matter may be discharged from a discharge passageway within the inhaler into an inhalation passageway for inhalation by a user, and the inhaler may comprise a seal member operative to selectively isolate the discharge passageway from the inhalation passageway and external environment during inactivity. The inhaler may further comprise a desiccant material arranged to withdraw moisture from the isolated discharge passageway. In other instances, desiccant material may be arranged to withdraw moisture from the discharge passageway of the inhaler without isolating the discharge passage during inactivity.
Owner:PEARL THERAPEUTICS
Modified processing method of electrolytic manganese bioxide for lithium battery
InactiveCN1933218AImprove electrochemical activityFully contactedElectrode manufacturing processesManganese oxides/hydroxidesElectrolysisElectrical battery
This invention discloses a modified process method for electrolyte MnO2 used in Li batteries, which processes electrolyte MnO2 powder under the temperature of 370-380deg.C for 10-24 hours and inlets inert gas for protection in process.
Owner:广州微宏电源科技有限公司
Pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106810410AReduce addLow hygroscopicityInorganic oxygen-halogen salt explosive compositionsNitrated explosive compositionsOrganic solventWater vapor
The invention relates to a pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of gas generating agent compositions. The pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition is composed of 3, 4-dinitrofurazanofuroxan, Fe2O3, CuO, oxidant, catalyst, cooling agent and binder. The preparation method includes: sufficiently mixing the oxidant, 3, 4-dinitrofurazanofuroxan, the catalyst and the cooling agent, and then sieving to obtain well-mixed powder; dissolving the binder in an organic solvent, adding into the powder for granulation, and drying to obtain solid particles; tabletting the obtained solid particles to obtain the pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition. The pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition is high in gas generating efficiency, generated gas is pure and free of environment pollution, content of water vapor generated by burning the generated gas is extremely low, using safety is improved, and the pyrotechnic gas generating agent composition has great application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Laser scanning mirror plane cleaning device for material field
InactiveCN110153130AAvoid stickingReduce dust contentGas treatmentDispersed particle separationControl signalWater vapor
The invention discloses a laser scanning mirror plane cleaning device for a material field. The laser scanning mirror plane cleaning device is arranged on a protective cover on the outer side of a laser scanner and comprises an air heating component for heating water vapor in the air outside the protective cover, an air purging component for purging dust in the air outside the protective cover, amirror plane cleaning component for washing and brushing the outer wall of the protective cover, and a controller, wherein the air heating component and the air purging component are mounted on the outer wall of the protective cover; the mirror plane cleaning component is movably arranged on the outer wall of the protective cover; and the control terminals of the air heating component, the air purging component and the mirror plane cleaning component are electrically connected with the control signal output end of the controller. The laser scanning mirror plane cleaning device solves the technical problem that a laser for scanning coal in a power plant can be shielded by dust easily and cannot carry out scanning operation normally.
Owner:HUANENG LAIWU POWER GENERATION CO LTD +1
Stack package plate for preventing condensation in fuel cell stack
InactiveCN102945973AAvoid poolingAvoid short circuitFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesInsulation layerFuel cells
The invention discloses a stack package plate for preventing the condensation in a fuel cell stack, comprising a water accepting layer, a supporting layer and a heat insulation layer, wherein the water accepting layer, the supporting layer and the heat insulation layer are fixedly connected in order. According to the invention, the structure of the stack package plate is improved by taking insulation measure to reduce the water vapor content in the stack package to the greatest extent and absorbing the water vapor or water that seeps through the outside by the water accepting layer, thus the formation of the condensation in the fuel cell stack is reduced, and the security threats brought by short circuit caused by water ingress in the stack are effectively prevented.
Owner:SUNRISE POWER CO LTD
Radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal and anti-condensation method
PendingCN111520847AReduce excess spaceReduce installation difficultyMechanical apparatusCondensate preventionCapillary networkIndoor air quality
The invention discloses a radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal and an anti-condensation method and belongs to the field of radiation air conditioner terminals. The radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal comprises an air processing box, a capillary pipe radiation face and a control system. The radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal can utilize a capillary radiation plate to conduct radiation heat exchange treatment on indoor air and can also conduct air return circulating dehumidification heat exchange on the indoor air, theradiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal can also introduce fresh air and guarantee the indoor air quality, and the overall heat exchange amount and the heat exchange efficiencyof the radiation plate are improved; installation is easy; the radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal can well solve the problems that in the prior art, a capillary network radiation plate is prone to condensation, the cooling capacity is limited, and transformation is complicated, and the radiation and fresh air integrated anti-condensation terminal has broad market application prospect.
Owner:BUILDING & MOUNTING ENG CO LTD NO 12 BUREAU MINIST OF RAILWAYS +2
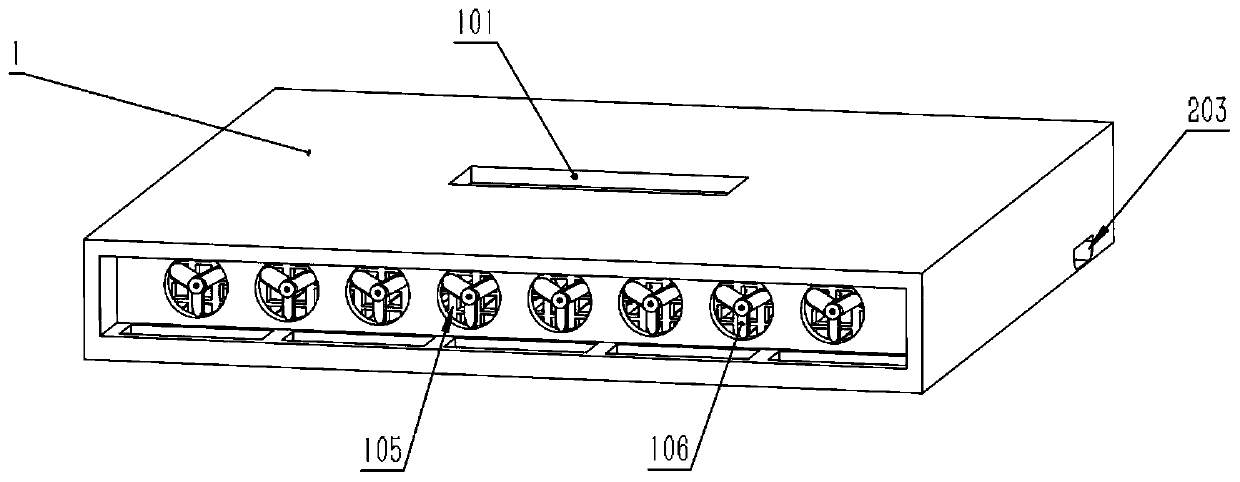
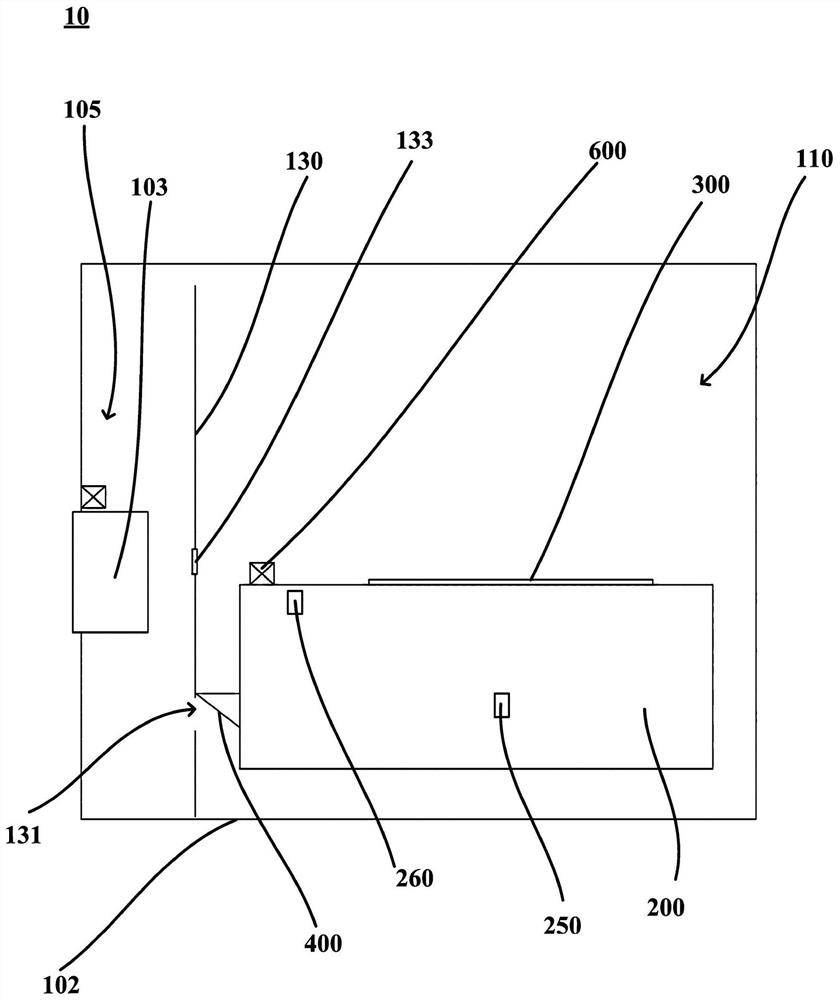
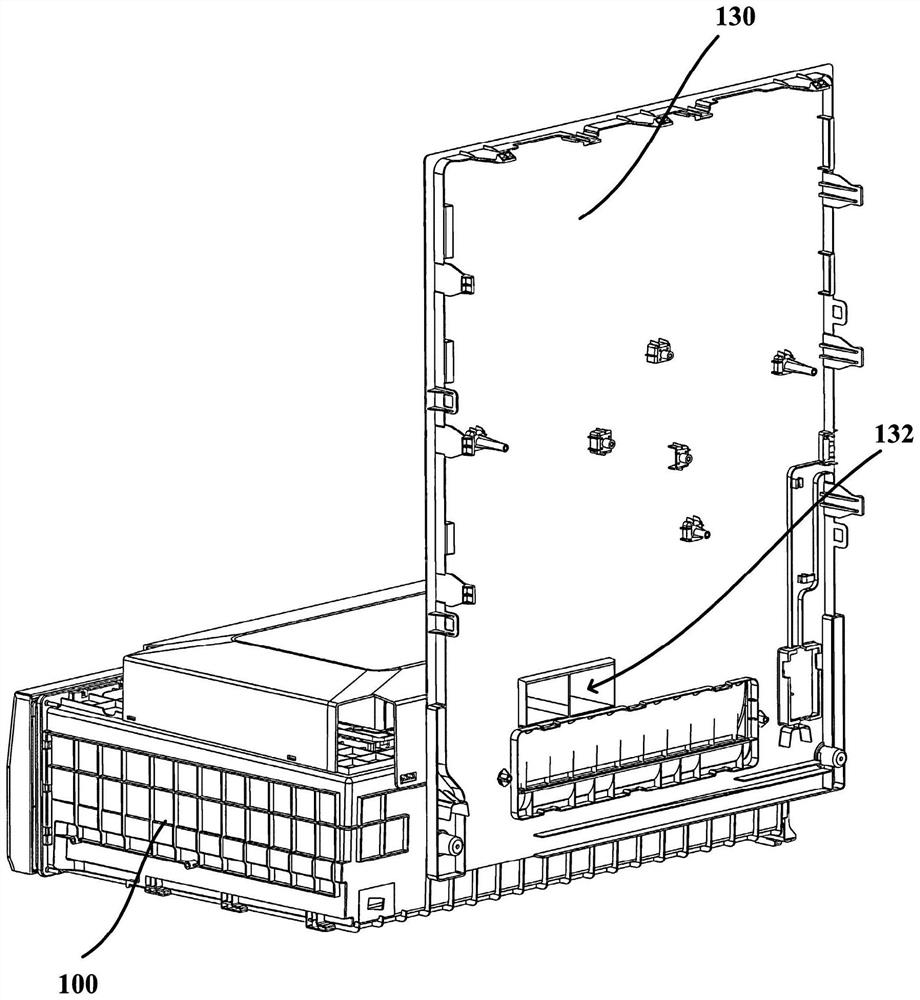
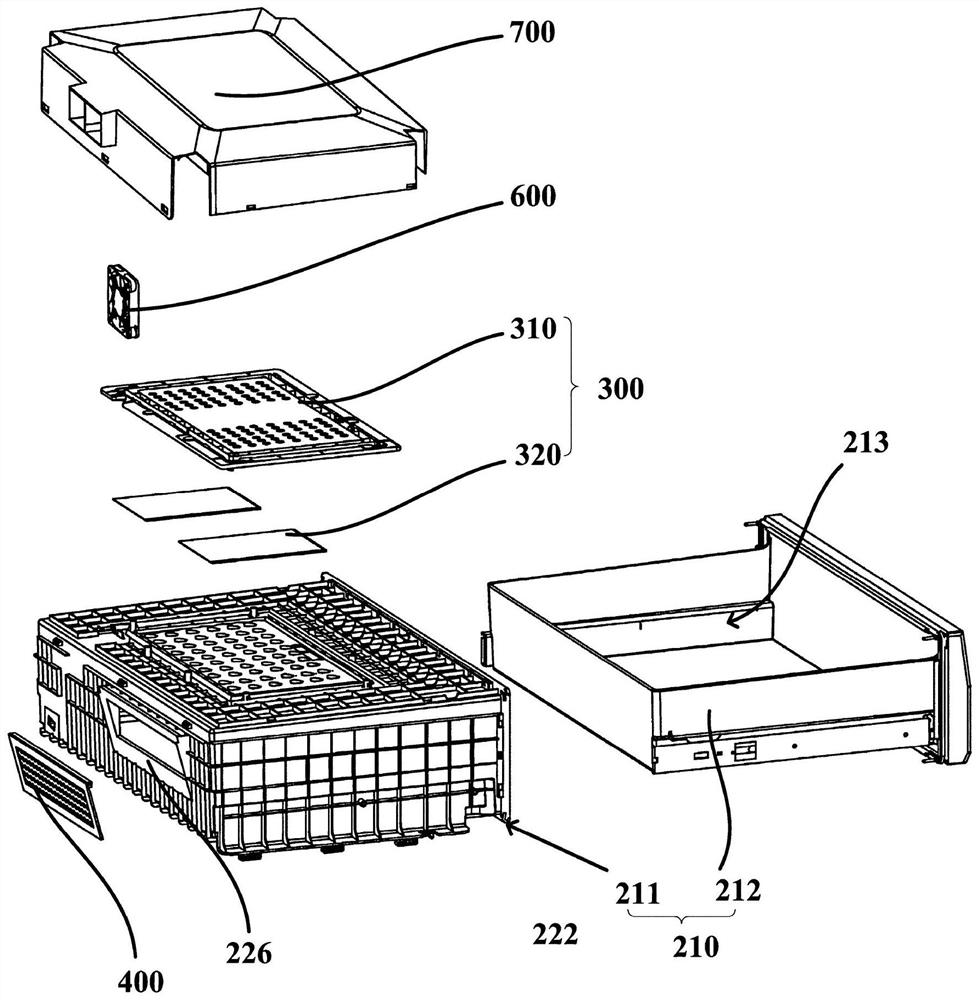
Refrigerator
InactiveCN112747528AReduce condensationReduce drippingLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsElectrochemical responseElectrolysis
The invention provides a refrigerator, which comprises an inner container, a storage compartment is formed in the inner container, and an air supply duct is formed on the rear side of the storage compartment; a storage container arranged in the storage compartment; an oxygen removal assembly arranged on the storage container and provided with an oxygen consumption part facing the interior of the storage container and used for consuming oxygen through an electrochemical reaction and an electrolysis part facing the exterior of the storage container and used for electrolyzing water vapor outside the storage container through the electrochemical reaction; a moisture-permeable assembly arranged on the storage container, the moisture-permeable assembly and the deoxidizing assembly are arranged at an interval, and the moisture-permeable assembly is configured to allow the water vapor in the storage container to seep out; and an air inducing opening for supplying air to the moisture-permeable assembly is arranged on the air supply duct, and the air inducing opening is configured to allow airflow in the air supply duct to enter the storage compartment and flow through the face, back to the interior of the storage container, of the moisture-permeable assembly in a moisture-permeable mode, so that a dry environment is formed outside the storage container, and the moisture-permeable efficiency of the moisture-permeable assembly is improved. and therefore, the phenomenon of condensation or water dripping in the storage container is reduced or avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER REFRIGERATOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com