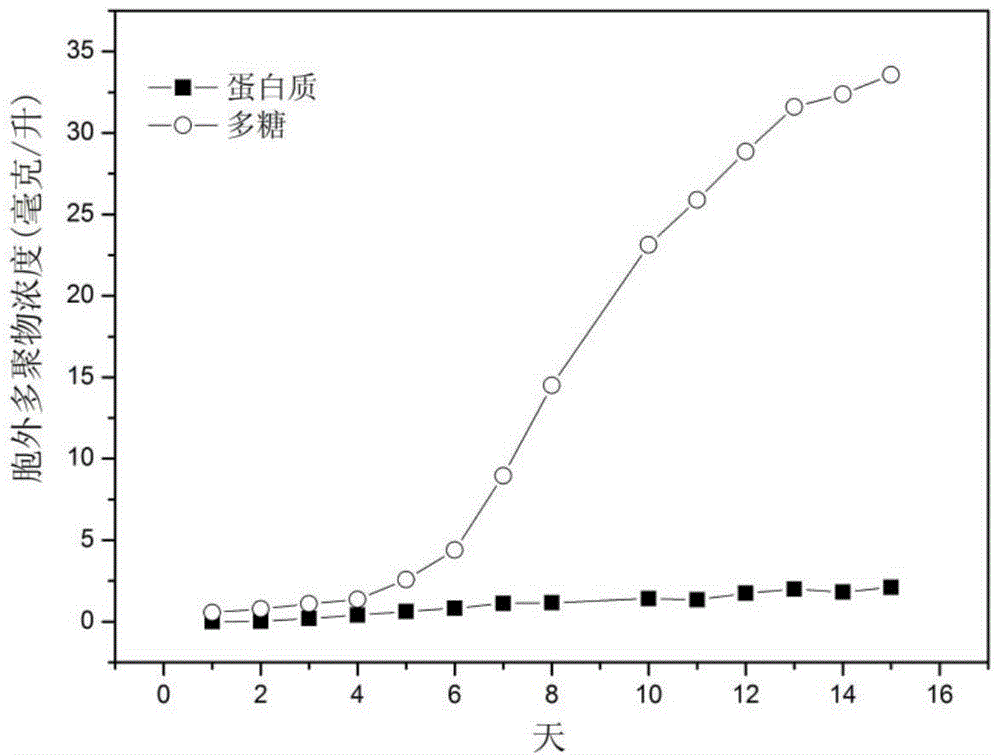
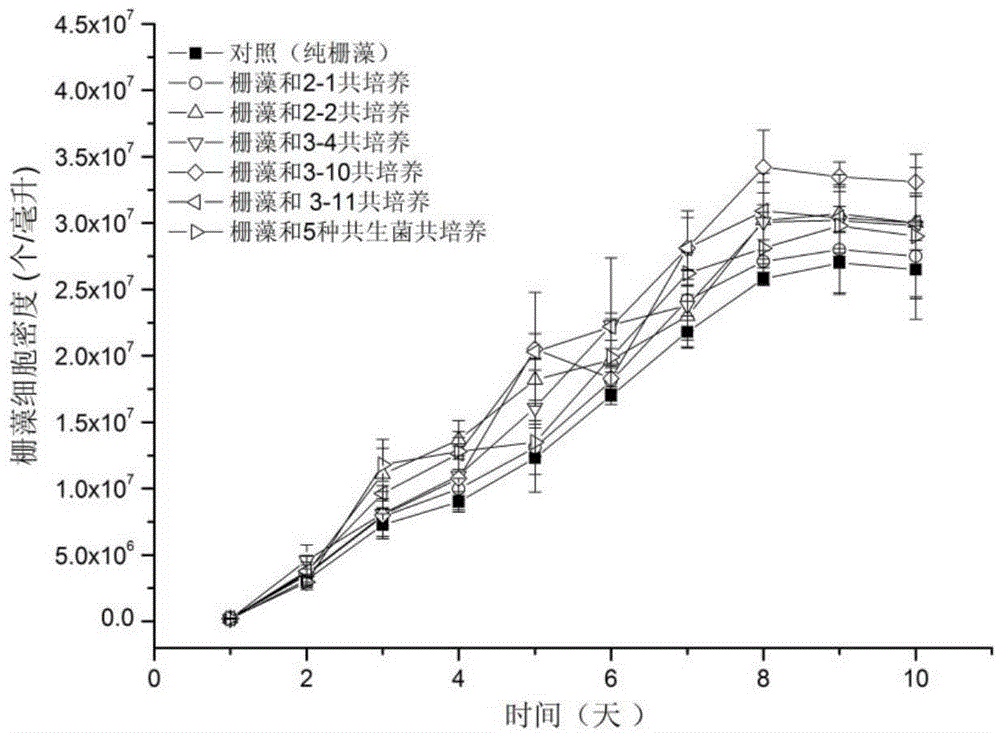
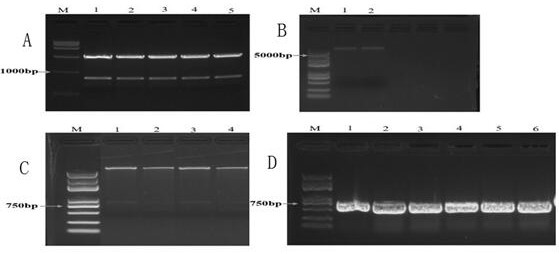
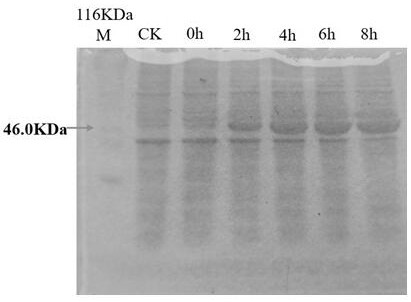
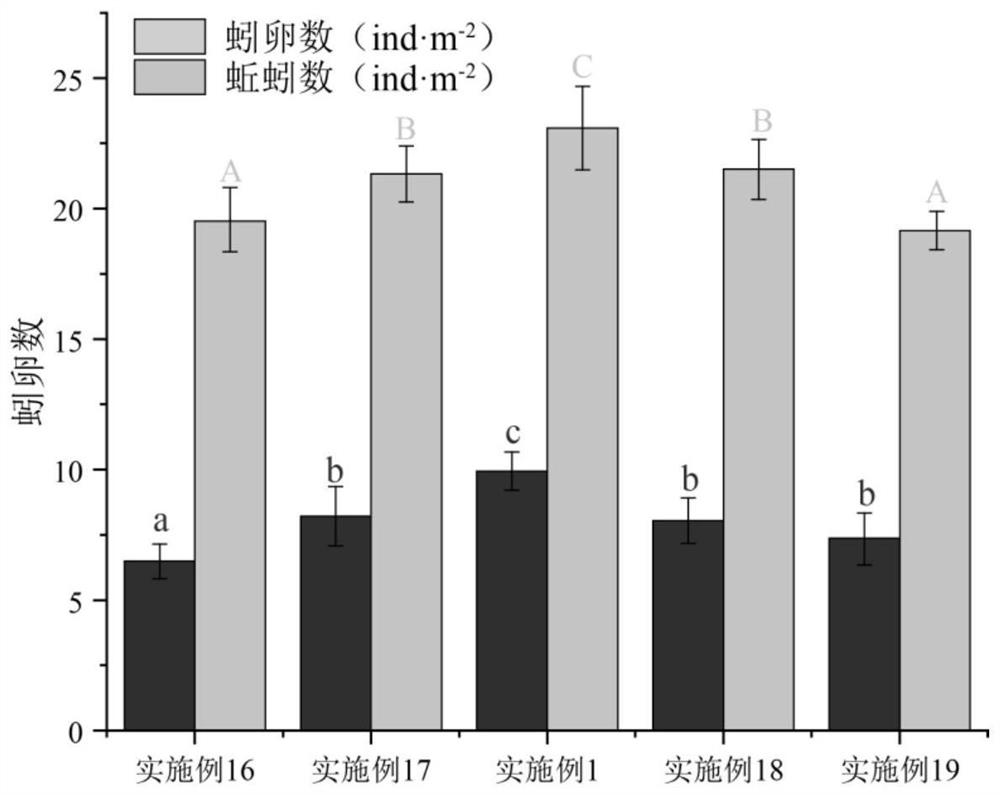
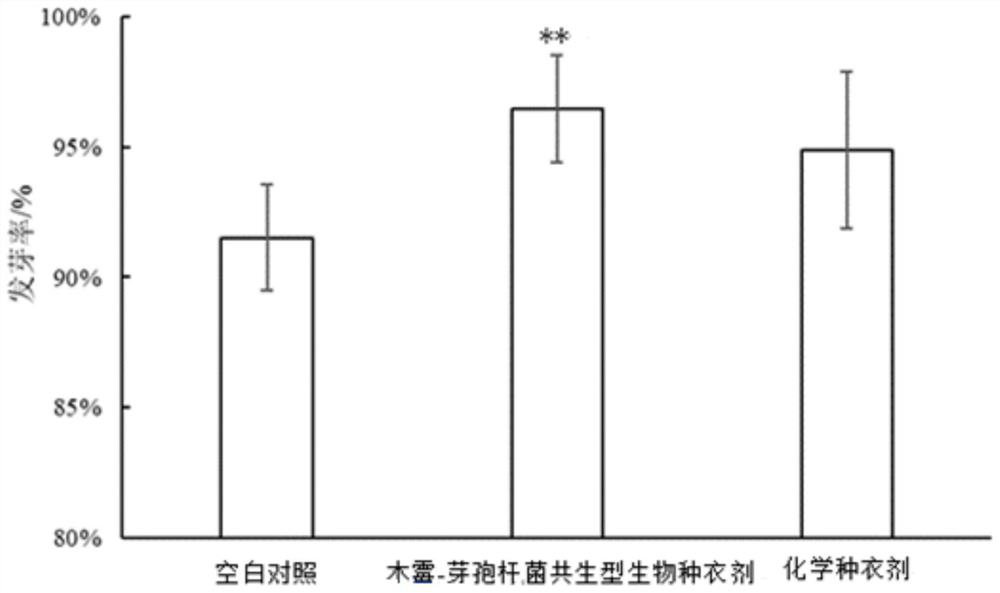
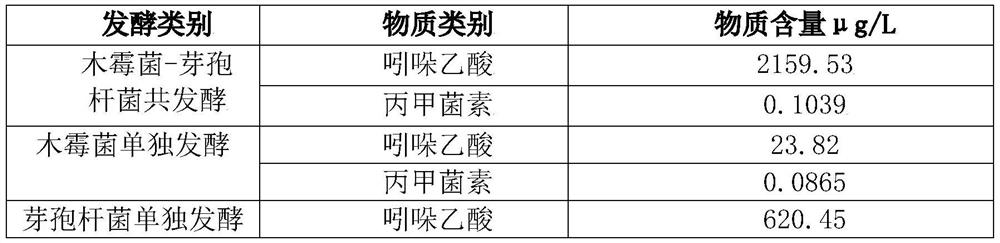
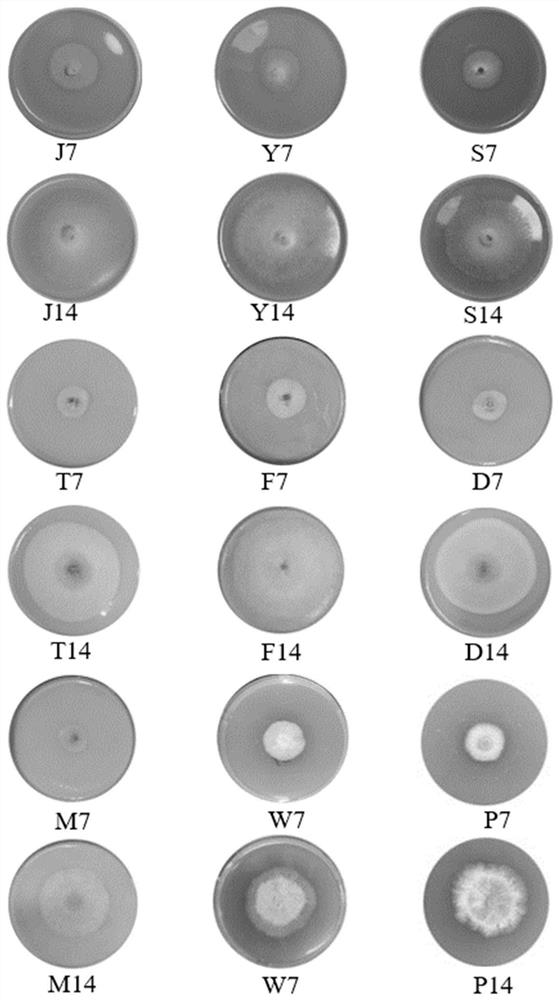
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Xenorhabdus sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
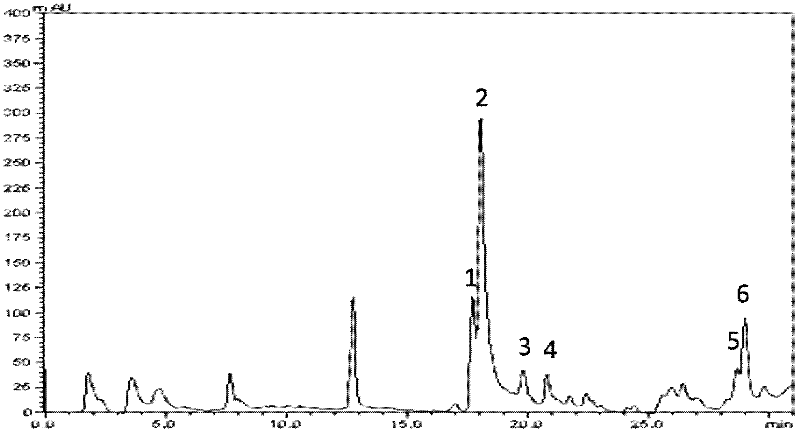
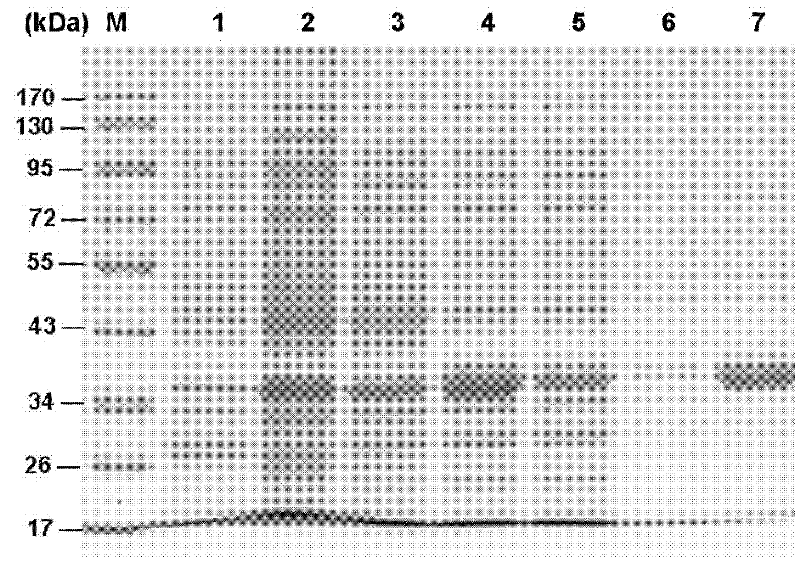
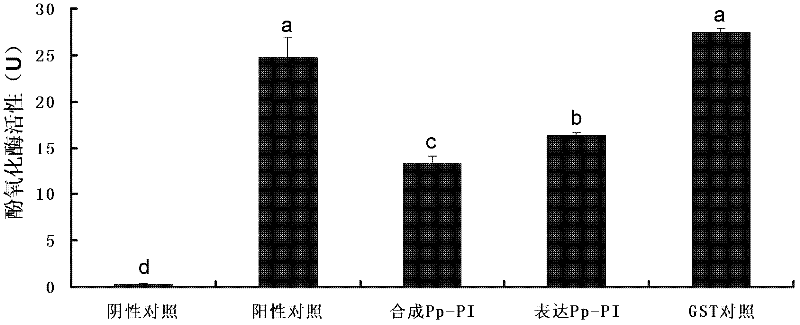
Serine protease inhibitor pp-pi polypeptide from chrysalis chrysalis chrysalis venom and its application
ActiveCN102260348AMicroorganism based processesRecombinant DNA-technologySerine Protease InhibitorsSymbiotic bacteria
The invention discloses a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide which has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. At the same time, the invention also discloses a gene for encoding the Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide. The gene has a nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has at least 70% homology with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1; or the gene has a nucleotide sequence which can hybridize with the nucleotide sequence from the 126th nucleotide to the 290th nucleotide in SEQ ID NO: 1 at 40-55 DEG C. The Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor Pp-PI polypeptide can be used to prepare a Pteromalus puparum venom serine protease inhibitor for genetically modifying crops or altering plant symbiotic bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
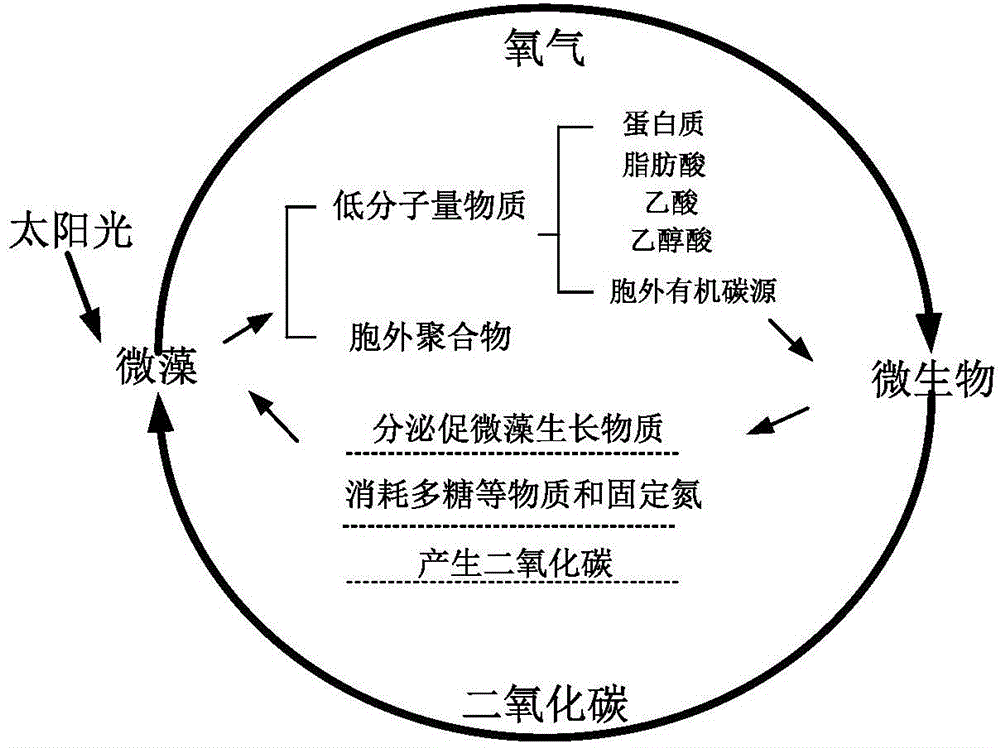
Symbiotic bacterium system for increasing biomasses of scenedesmus obliquus and improving quality of grease and application of symbiotic bacterium system
ActiveCN105296376APromote growthPromote material exchangeBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiomassCarbon dioxide
The invention relates to the field of micro-alga biotechnologies, in particular to a symbiotic bacterium system for increasing biomasses of scenedesmus obliquus and improving the quality of grease and the stability of culture systems and application of the symbiotic bacterium system. The symbiotic bacterium system comprises the scenedesmus obliquus and symbiotic bacteria. The symbiotic bacteria include one type or a plurality of types of brevunmdimonas sp., rhizobium sp., pseudomonas sp. and acidovorax sp. The symbiotic bacterium system and the application have the advantages that the symbiotic bacteria and mixed floras of the symbiotic bacteria are applied to scenedesmus obliquus culture procedures, extracellular substances and oxygen which are generated by the scenedesmus obliquus can be consumed by each single type of symbiotic bacteria and the mixed floras, carbon dioxides can be generated to be utilized by the scenedesmus obliquus, micro-environments favorable for growth of the scenedesmus obliquus can be created, and accordingly substance exchange and metabolism of the scenedesmus obliquus, the symbiotic bacteria and the mixed floras can be promoted.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gastrodia elata superoxide dismutase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113528551AReduce incubation timeImprove resistance to low temperature stressFungiMicroorganism based processesDismutaseNucleotide
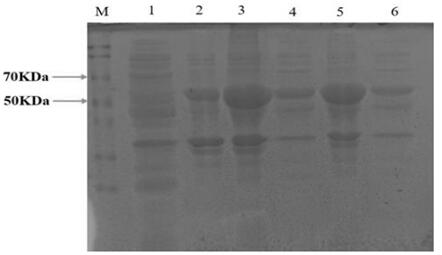
The invention discloses a gastrodia elata superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gastrodia elata superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; 239 amino acid residues are encoded; a prokaryotic expression vector of the gastrodia elata SOD gene is constructed, prokaryotic expression analysis shows that the gastrodia elata SOD gene is soluble protein, and the molecular weight of the gastrodia elata SOD gene is about 47.4 kDa; an eukaryotic overexpression vector of the gastrodia elata SOD gene is constructed, gastrodia elata symbiotic bacteria armillaria mellea is transfected through an agrobacterium method to obtain gastrodia elata SOD transfected armillaria mellea, the SOD transfected gene engineering armillaria mellea is cultured at 13 DEG C, the growth vigor is better than that of wild armillaria mellea, and the growth speed is high; therefore, the gastrodia elata superoxide dismutase gene is beneficial to shortening the culture time of the armillaria mellea and improving the cold-resistant growth of the armillaria mellea, and an experimental basis for enhancing the cold resistance of the gastrodia elata, expanding the planting distribution range of the gastrodia elata and improving the yield of the gastrodia elata is provided. meanwhile, experiments also prove that the gastrodia elata superoxide dismutase gene can promote the growth of arabidopsis thaliana.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Isolated culture method for nilaparvata lugens in-vivo yeast-like symbiotic bacteria and special culture medium
InactiveCN102010834ACompatibility is reasonableReasonable designFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses an isolated culture method for nilaparvata lugens in-vivo yeast-like symbiotic bacteria and a special culture medium, and belongs to the technical field of microculture. The special culture medium comprises 31 nutrient substances needed by nilaparvata lugens in-vivo yeast-like symbiotic bacteria, and the culture method comprises the following steps of: feeding adult nilaparvata lugen; treating ovaries of nilaparvata lugens; preparing culture solution, performing isolated culture and the like. By employing the culture method, two yeast-like strains are isolated from the nilaparvata lugens in vivo so as to provide basis for further researching genetic background of the yeast-like symbiotic bacteria and the interavailable nutrient relation between the yeast-like symbiotic bacteria and host nilaparvata lugens, and modifying the symbiotic bacteria to control the harm of the nilaparvata lugens. Meanwhile, the special culture medium is reasonable in components and provides necessary nutrition basis for isolated subculture of the nilaparvata lugens in-vivo yeast-like symbiotic bacteria. The method also provides technical support for isolated culture of other homoptera insect in-vivo yeast-like symbiotic bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Large-scale entomopathogenic nematode production method and entomopathogenic nematode
The invention belongs to the production field of entomopathogenic nematodes and relates to a large-scale entomopathogenic nematode production method and entomopathogenic nematodes. The production method comprises the steps that the entomopathogenic nematodes in an infection period are inoculated onto greater wax moths for infection, and the entomopathogenic nematodes are collected to prepare an entomopathogenic nematode suspension after the greater wax moths die; separated entomopathogenic nematodes are utilized to infect greater wax moths, then the entomopathogenic nematodes are separated from died greater wax moth bodies for single bacterium culture, and the entomopathogenic nematodes cultured based single bacteria are separated for production and propagation; the entomopathogenic nematodes in the infection period are utilized to infect living greater wax moth bodies, then died greater wax moth hemolymphs are collected, and a symbiotic bacterium solution for production is obtained through culture, authentication, adaption, fermentation and symbiotic bacterium propagation; the obtained symbiotic bacterium solution is firstly inoculated to breeding bags of a shared culture medium,and then the obtained entomopathogenic nematodes are inoculated into the breeding bags of the shared culture medium for culture. The large-scale entomopathogenic nematode production method is convenient to operate, capable of making product quality good and higher in yield and efficiency and makes factory-like large-scale breeding easy to achieve.
Owner:吉林省怡科农业生物科技有限公司 +1
Novel method for preventing and controlling brown planthopper
The invention relates to the technical field of biological prevention and control, in particular to a novel method for preventing and controlling brown planthopper. Trifloxystrobin-tebuconazole water dispersible granule (the mass percentage of effective components is 75 percent, wherein the mass percentage of trifloxystrobin is 25 percent, and the mass percentage of tebuconazole is 50 percent) is used for preventing and controlling brown planthopper filial generations. The most remarkable characteristic of the novel method is that yeast-like symbiotes are prevented or inhibited from entering ovarian tissues from the hemolymph of brown planthopper female adults through a trifloxystrobin-tebuconazole sterilizing agent, so that the reproductive systems of the brown planthopper is influenced, the egg laying amount is reduced, and the hatching rate of the laid eggs is remarkably lowered due to the lack of symbiotic bacteria. Thus, the generation of brown planthopper filial generations is effectively controlled.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
DsRNA of gene of symbiotic bacterium of aphids and application thereof to inhibition of growth of aphids
The invention discloses dsRNA of a gene of a symbiotic bacterium of aphids and an application thereof to inhibition of growth of aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids is obtained; the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids can be inhibited or silenced, impaired growth and development of the wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
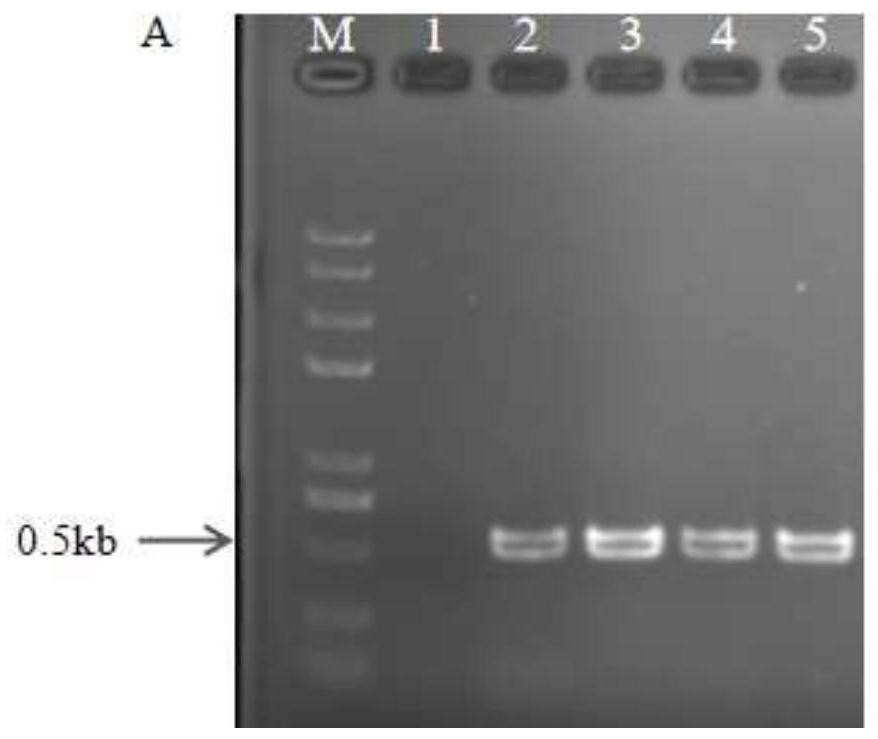
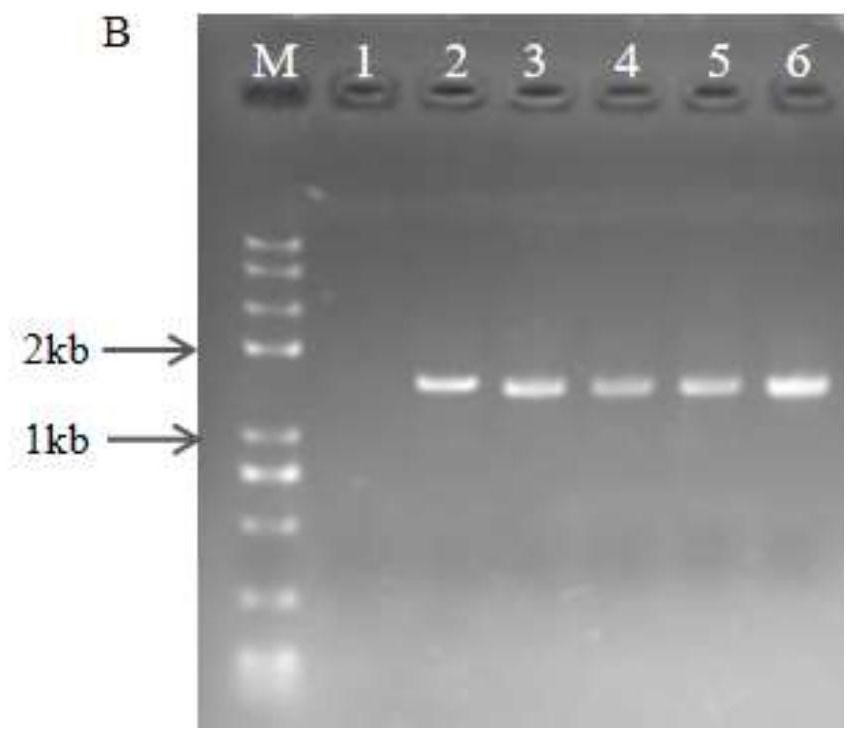
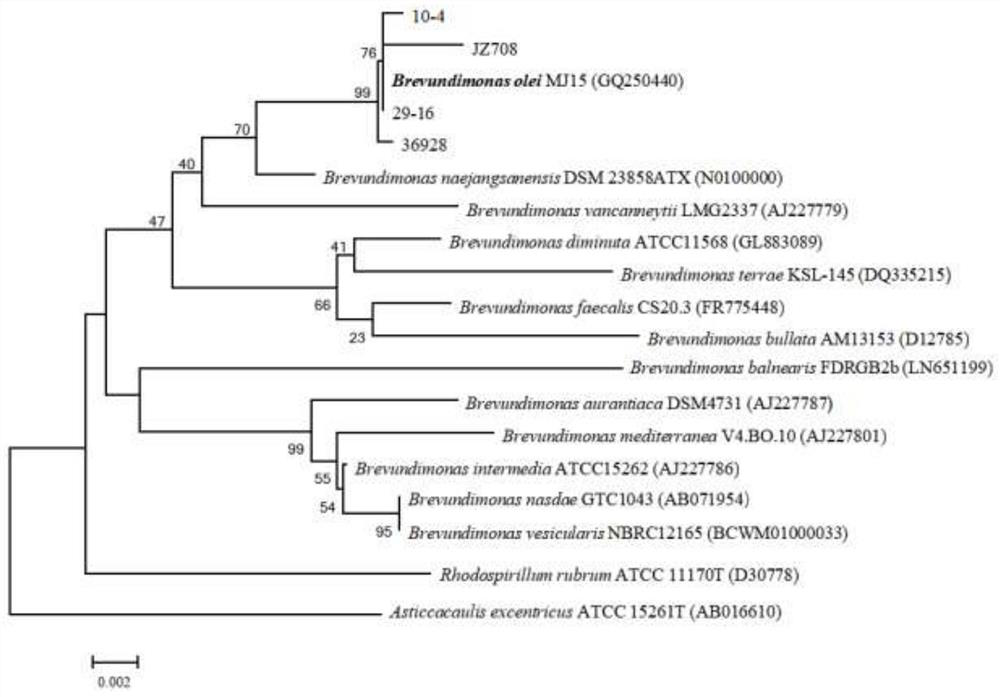
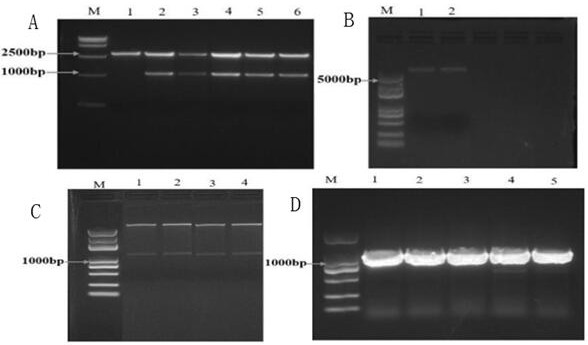
Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei and application thereof
ActiveCN112175887AHigh antibacterial rateProduce inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyXenorhabdus sp.
The invention discloses Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei and application thereof. The Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei is named as Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei, and the preservation number of the Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei is CCTCC NO: M 2020392. The strain is determined to be Brevundimonas olei dahliae olei through morphological identification and diversity sequencing analysis, and the influence of B.olei fermentation liquor on growth of the Brevundimonas oleei and microsclerosis is explored through a co-culture experiment. Through scanning electron microscope observation, as the culture time and the concentration of the fermentation liquor increase, formation of conidia of the Brevundimonas oleei is reduced, the hypha morphology is expanded, broken and deformed, the microsclerosisis gradually reduced and disappears, and it is proved through the research that the symbiotic B.olei has good bacteriostatic activity on the Brevundimonas olei.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113564184AReduce incubation timeImprove resistance to low temperature stressFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideXenorhabdus sp.
The invention discloses a gastrodia elata Glutamine Synthetase (GS) gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; and 342 amino acid residues are encoded; a prokaryotic expression vector of the gastrodia elata GS gene is constructed, and prokaryotic expression analysis shows that the gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene is soluble protein, and the molecular weight of the gene is about 59.94kDa. The eukaryotic overexpression vector of the gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene is constructed, gastrodia elata symbiotic bacteria armillaria mellea is transfected through an agrobacterium method, the armillaria mellea transfected with the gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene is obtained, the GS genetically engineered armillaria mellea is cultured at 13 DEG C and 28 DEG C, the growth vigor of the GS genetically engineered armillaria mellea is better than that of wild type armillaria mellea, and the growth speed is high. Therefore, the gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene is beneficial for shortening the culture time of the armillaria mellea and improving the cold resistance and high-temperature growth resistance of the armillaria mellea. The gastrodia elata glutamine synthetase gene provides an experimental basis for enhancing the cold resistance of gastrodia elata, expanding the planting distribution range of gastrodia elata, enhancing the nitrogen metabolism capacity of gastrodia elata and increasing the yield of gastrodia elata.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Construction method and application of phenanthrene and pyrene combined aerobic degradation symbiotic flora
PendingCN112708580AHigh molecular weightNo accumulationBacteriaWater treatment compoundsBiotechnologyEcological environment
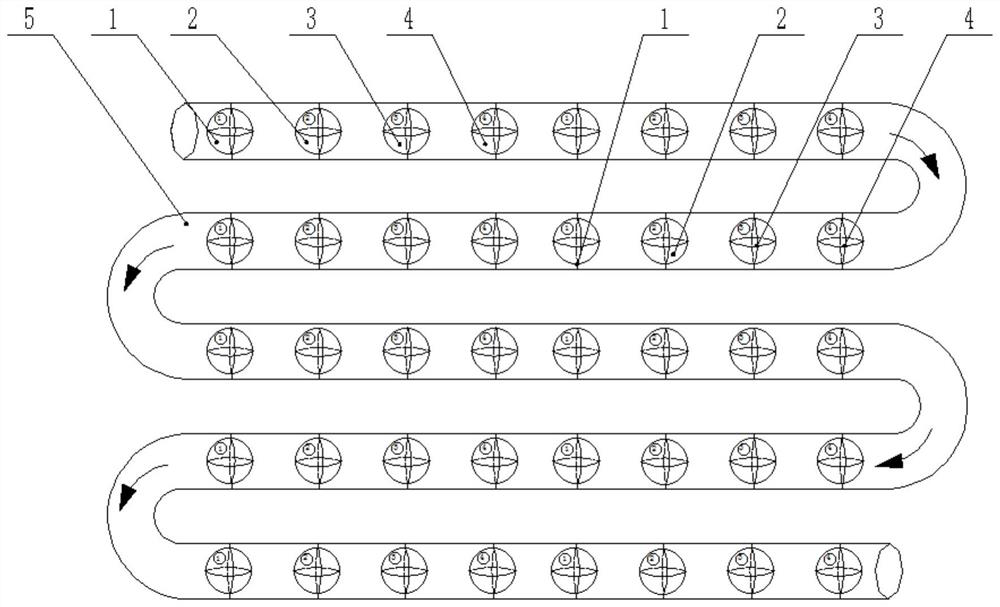
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a phenanthrene and pyrene combined aerobic degradation symbiotic flora, and the phenanthrene and pyrene combined aerobic degradation symbiotic flora uses four strains, namely Pseudomonas.sp,GenBank:GCA_000006765.1, Bacillus.sp,GenBank:AY881640.1, Sphingomonas.sp,GenBank:AB000106.1 and achromobacter.sp,GenBank:GCA_004296055.1. The construction method comprises an amplification culture method of each strain, an enhanced medium formula, culture conditions and operation methods, wherein the phenanthrene and pyrene combined aerobic degradation symbiotic flora is applied to biological extracellular polymers in a reactor device, the reactor device comprises a pipeline and a microbial inoculum ball group, and the biological extracellular polymers prepared from four strains are loaded in the microbial inoculum ball group. The method has the advantages that biodegradation of phenanthrene and pyrene in the chemical wastewater is achieved in an aerobic environment, secondary pollution is avoided in the treatment process, resources can be saved, the ecological environment can be protected, and finally, the purpose of treating degradation-resistant organic matter namely the phenanthrene and the pyrene is achieved.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
Symbiotic bacterium composition, preparation method thereof and microalgae culture method
PendingCN113278557AMitigate the risk of pests and diseasesHarm reductionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyRhodotorula
The invention relates to the technical field of microalgae culture, in particular to a symbiotic bacterium composition, a preparation method thereof and a microalgae culture method. The symbiotic bacterium composition consists of marine clostridium butyricum, marine rhodotorula benthica and marine purple non-sulfur bacteria. Through the symbiotic effect of the three probiotics including the marine clostridium butyricum, the marine rhodotorula benthica and the marine purple non-sulfur bacteria, the risk of diseases and pests in the seawater chlorella culture process is effectively inhibited, the harm of the diseases and pests is reduced, and the capacity and yield of chlorella factory culture are effectively improved.
Owner:HAINAN GREEN ALGAE WORLD BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
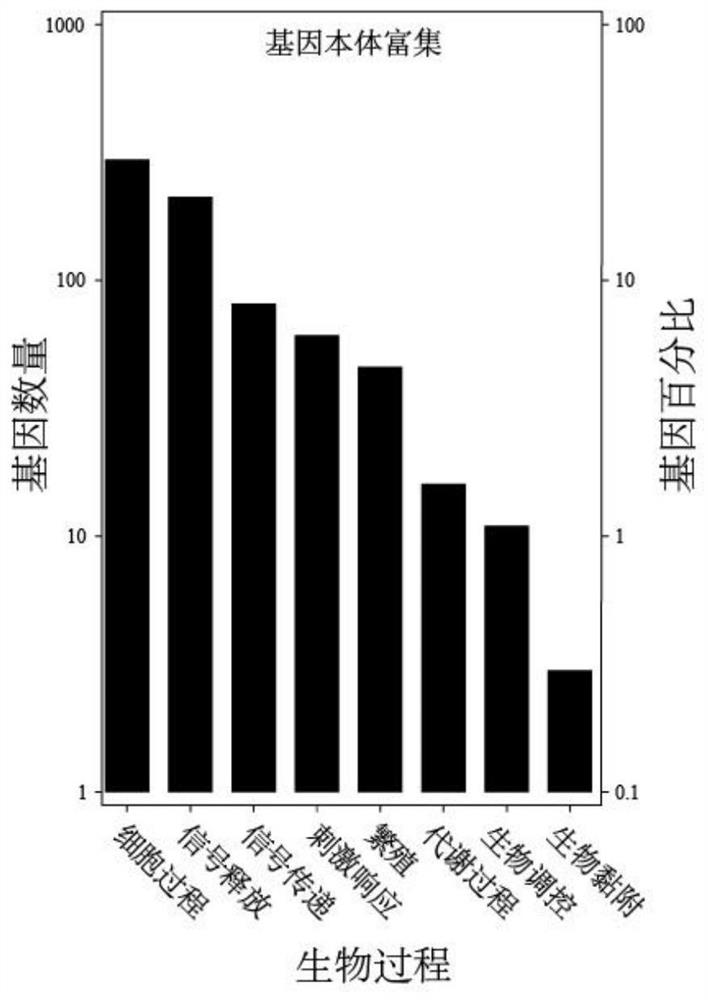
Xenorhabdus sp. genome sequences and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110167520A1High expressionSugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsXenorhabdus sp.ADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from Xenorhabdus and, in particular, to genomic DNA sequences, and to the insecticidal Xenorhabdus strain Xs85816. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins, fragments of proteins, tRNA's, fragments of tRNA's, rRNA's and fragments of rRNA's. In addition, proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins are encompassed by the present invention. The invention also relates to methods of using the disclosed nucleic acid molecules, proteins, fragments of proteins, RNA's, and antibodies, for example, for gene identification and analysis, and preparation of constructs.
Owner:CORBIN DAVID R +7
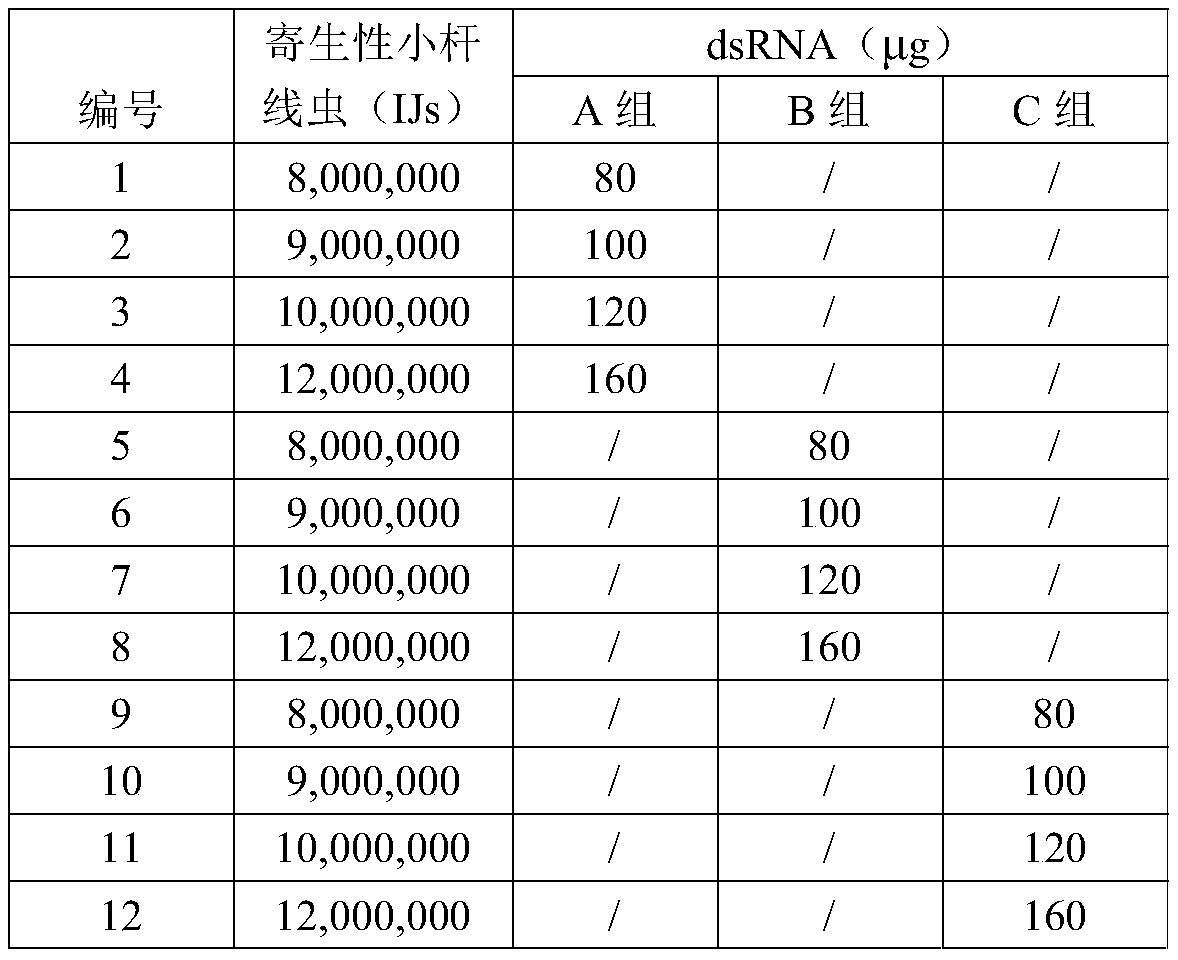
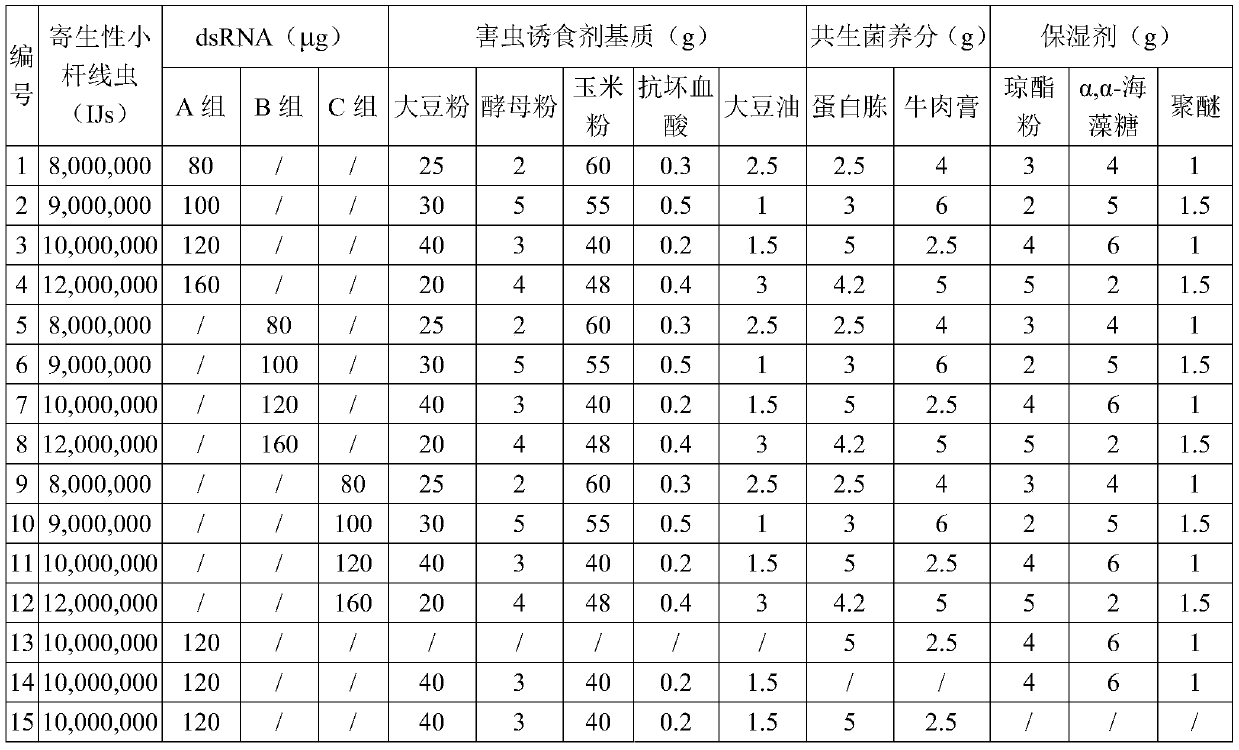
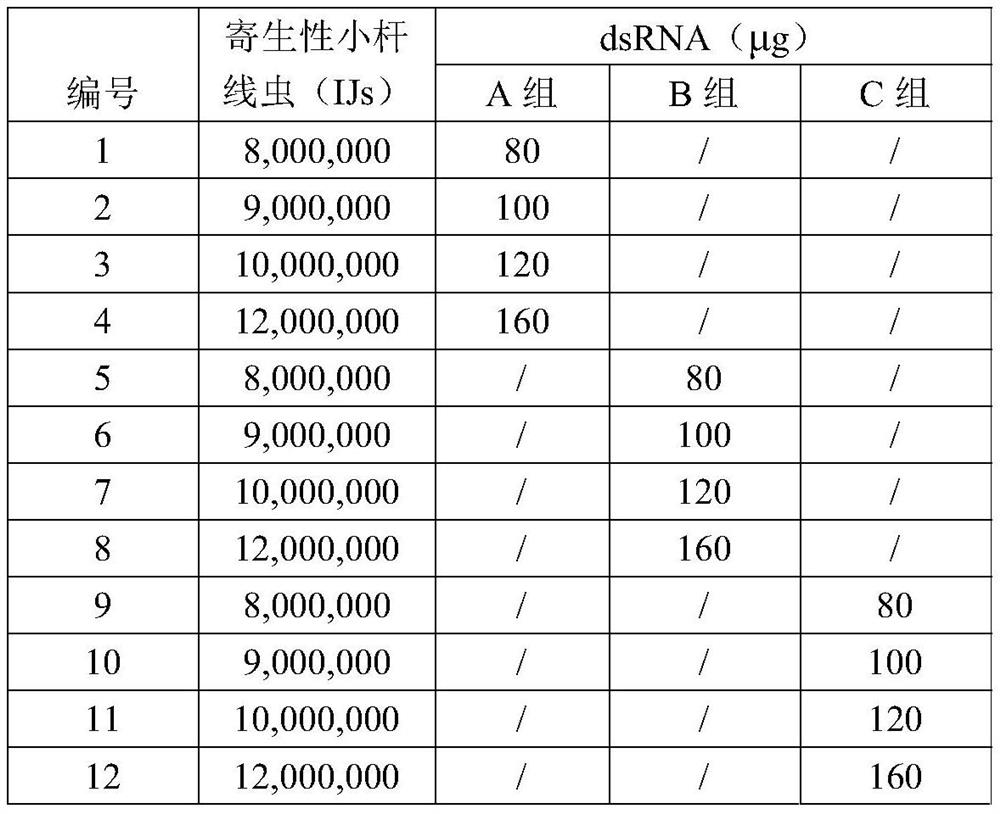
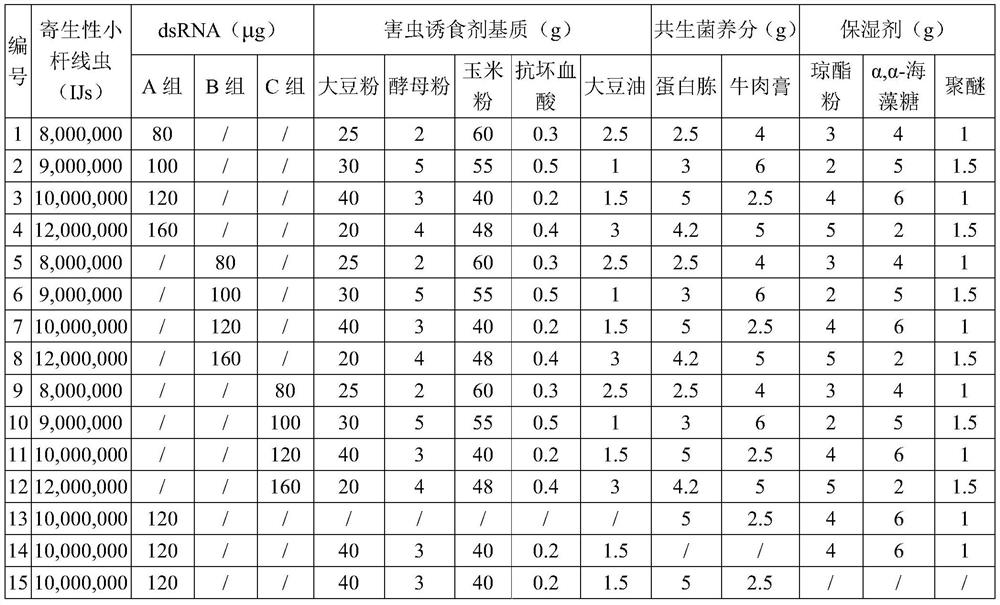
Parasitic small-stem nematode preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111543437ARapid infectionGood killing effectBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyXenorhabdus sp.
The invention discloses a parasitic small-stem nematode preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of biopesticides, and solves the problems oflow biocontrol quick-acting property and incapability of efficiently and quickly killing grassland spodoptera litura in the prior art. The parasitic small-stem nematode preparation comprises parasitic small-stem nematodes and RNA fragments interfering with polyphenol oxidase PO gene expression of the grassland spodoptera litura, the preparation also comprises an insect pest attractant matrix, a nematode humectant and nematode symbiotic bacteria nutrients. The invention creatively starts from the aspects of inducing, infecting, saprophytic, adding dsRNA to inhibit the immune response of pestsand the like, and the killing effect of the nematodes on the grassland spodoptera litura is effectively improved under the combined actions.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
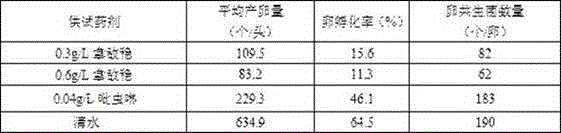
Application of nativo to control over filial generations of brown planthopper
InactiveCN104823767AReduce spawningReduce egg hatch rateBiocideFungicidesWater dispersibleSymbiotic bacteria
The invention relates to the technical field of biological control, in particular to application of nativo to control over filial generations of brown planthopper. Native water dispersible granule (with 75 % mass percent of active ingredients including 25 % mass percent of trifloxystrobin and 50% mass percent of tebuconazole) is utilized by the invention for control over filial generations of brown planthopper.The most salient feature of the invention is described in that nativo, as bactericide, helps to prevent of inhibit yeast-like endosymbiote from entering ovarian tissues from hemolymph of female adults of brown planthopper such that a genital system of brown planthopper is affected and the egg laying amount is reduced; and the hatching rate is greatly decreased because produced eggs lack symbiotic bacteria so that generation of the filial generations of brown planthopper is effectively controlled.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Preparation method and product of earthworm breeding companion soil remediation agent
PendingCN113881437AShorten the fermentation cyclePromote secretionOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsAntibiosisSoil remediation
The invention provides a preparation method and a product of an earthworm breeding companion soil remediation agent. The soil remediation agent is used for soil remediation by taking earthworm biomass improvement as a target, a rotten earthworm glandula accessoria ion stress matrix is used as a substrate, an antibacterial earthworm fiber skeleton is filled, an annulata earthworm cocoon synthesis promoting agent benefiting earthworm cocoon, an earthworm symbiotic bacterium agent and an artificial earthworm cocoon barrier are matched, so that the remediation agent is formed. The biomass of the soil earthworm cocoons and earthworms can be increased by 4.40 and 2.9.
Owner:天津天丰泽田生物科技有限公司 +1
Biological seed coating agent based on trichoderma-bacillus sequential inoculation symbiotic culture fermentation liquor and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113444649AOvercome antagonismOvercoming is a competitive effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyTrichoderma sp.
The invention discloses a biological seed coating agent based on trichoderma-bacillus sequential inoculation symbiotic culture fermentation liquor and a preparation method of the biological seed coating agent. According to a synthetic biology principle, a symbiotic bacterium solution is prepared from trichoderma having the characteristics of inducing disease resistance, stress resistance and the like, bacillus having the characteristics of antagonizing pathogenic bacteria, promoting crop growth and the like through a staged inoculation co-fermentation technology; and meanwhile, the symbiotic bacterium solution not only meets the balance of the contents of two types of spores, but also contains components for mutual action and specific induction of two types of microorganisms. The symbiotic bacterium liquid is mixed with diatomite and brassinolide in proportion to prepare the powder type biological seed coating agent, the biological seed coating agent contains high-content spores, antagonistic substances, growth promoting substances and the like, the growth, disease resistance and stress resistance of crops such as corn, wheat, rice and the like are obviously improved, and the technology is a new technology for beneficial bacteria treatment of food crop seeds.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Culture medium for Amylostereum areolatum and culture method thereof
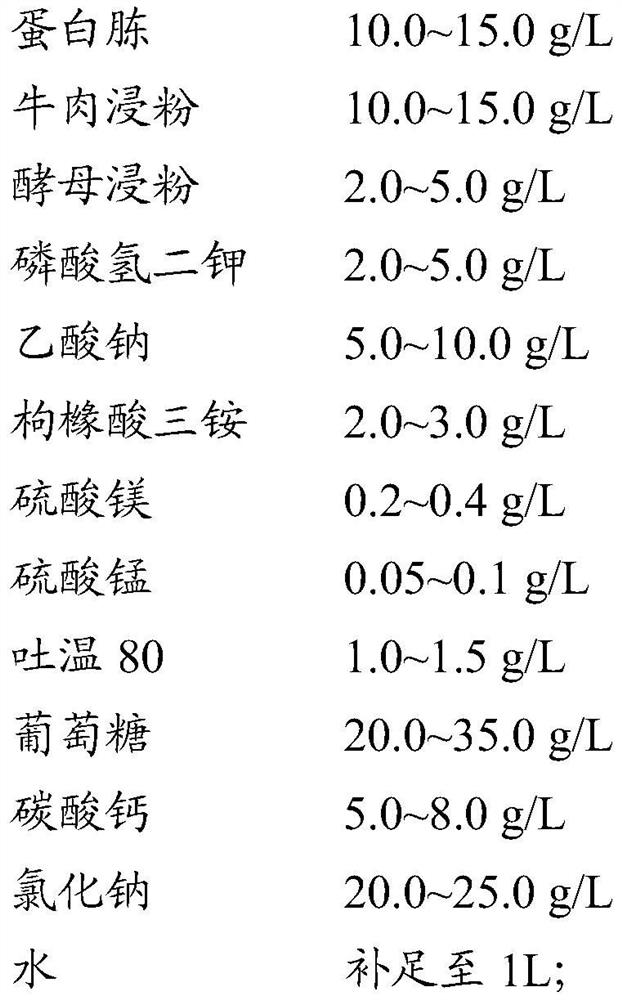
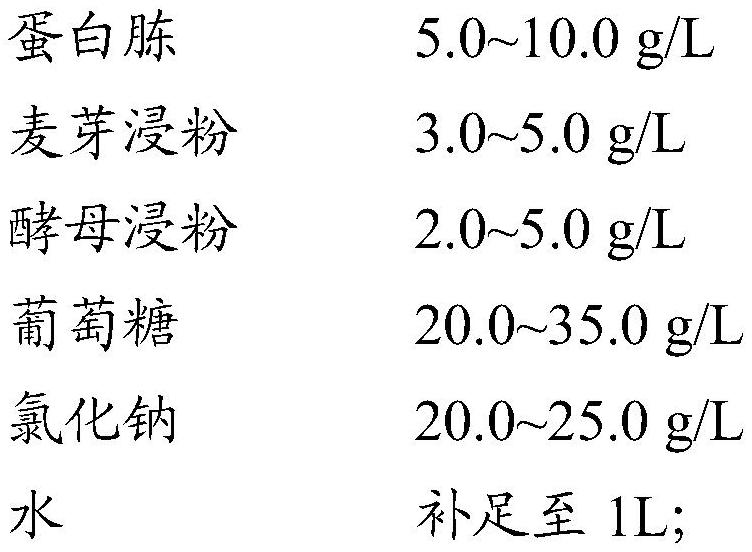
PendingCN113475312AFast growthScientific and reasonable ingredientsCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyXenorhabdus sp.
The invention provides a culture medium for Amylostereum areolatum and a culture method thereof. The culture medium comprises healthy pine wood flour, malt extract and yeast extract. The culture medium for Amylostereum areolatum provided by the invention has the advantages that the components and the proportion of the culture medium are scientific and reasonable, the growth speed of the cultured Amylostereum areolatum is higher, part of the Amylostereum areolatum can grow sporocarp, the Amylostereum areolatum is not easy to be polluted, and a foundation is laid for further research of symbiotic bacteria of pine bees and even prevention and control of the pine bees.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Xenorhabdus SP. Genome Sequences and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence from Xenorhabdus that encodes a GroEL protein. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins, fragments of proteins, tRNA's, fragments of tRNA's, rRNA's and fragments of rRNA's. In addition, proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins are encompassed by the present invention. The invention also relates to methods of using the disclosed nucleic acid molecules, proteins, fragments of proteins, RNA's, and antibodies, for example, for gene identification and analysis, and preparation of constructs.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
A kind of Phalaenopsis single bud propagation method using symbiotic bacterial agent
ActiveCN111758567BShorten the timeShort reproductive cycleAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyAxillary bud
The invention provides a single bud propagation method of Phalaenopsis phalaenopsis, comprising the following steps: S1, taking a pedicel stem section that grows robustly in spring and full with axillary buds as explants and carries out disinfection treatment; S2, cutting the explants with axillary buds into pieces Grow 1.5cm and receive it into the bud induction medium for axillary bud induction; S3, when the axillary bud grows to 2cm in step S2, cut the sprouts and transfer them to the proliferation medium for proliferation culture; S4, when the proliferation culture sprouts > 2cm , when it grows to 3-4 leaves, remove weak seedlings and ineffective seedlings less than 2 cm, select seedlings > 2 cm to carry out rooting culture of strong seedlings; S5, move the culture bottle seedlings to 25-30 ℃ temperature conditions to strengthen seedlings for 10- After 15 days, the rooted seedlings can be taken out of the culture bottle, the residual medium attached to the roots is washed with running tap water and dried until no water drips, and then transplanted into the pre-prepared mixed matrix and pressed. If it is planted, it should be watered for the first time after planting, and then every 4-6 days after that. The method has the advantages of short reproductive cycle, strong seedlings, strong adaptability and good quality.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Bacteria strain (X-7 strain) for culturing bait eelworm and its eelworm culture method
Owner:GUANGDONG ENTOMOLOGICAL INST
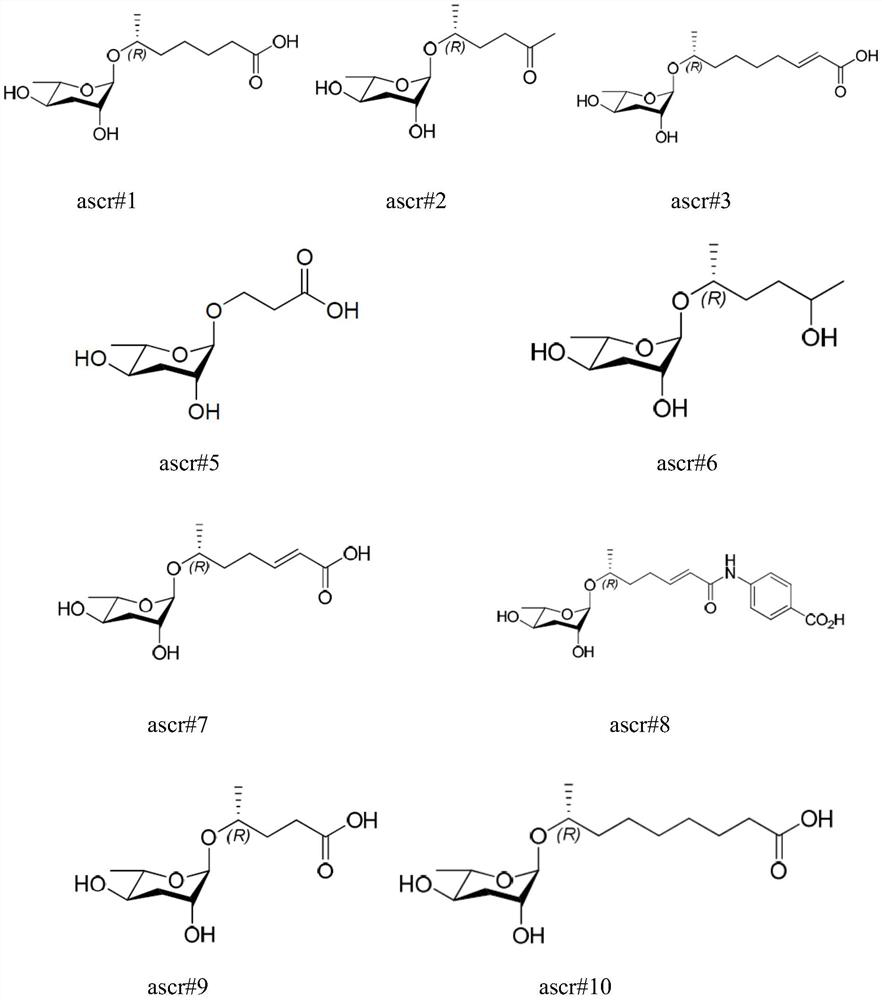
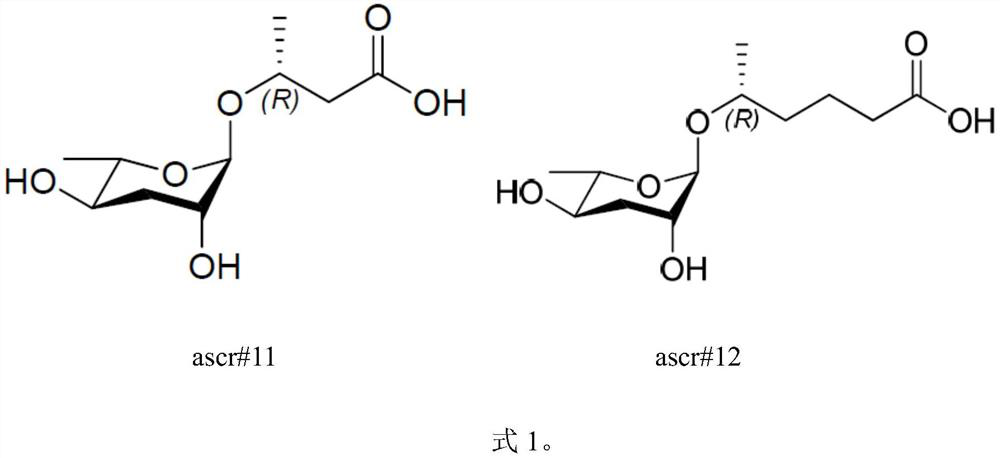
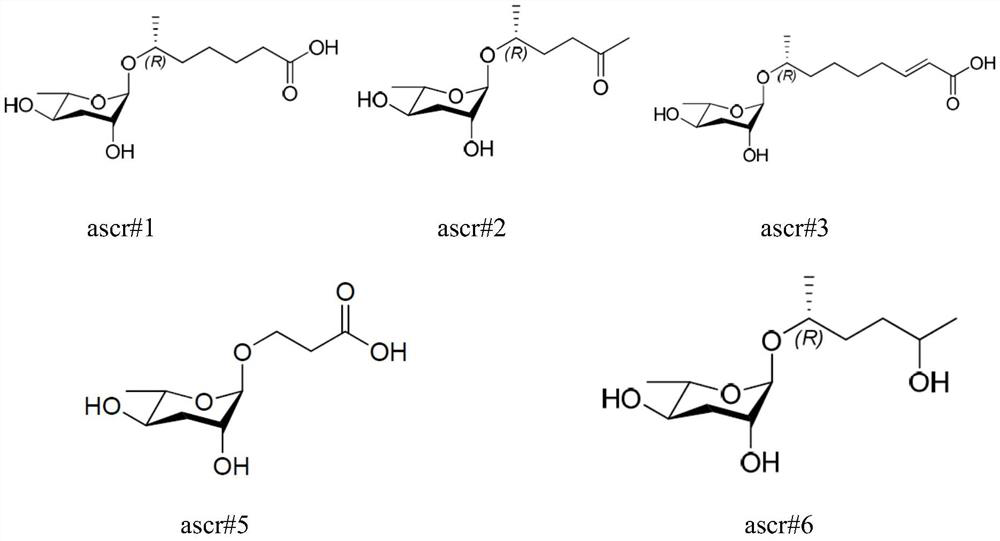
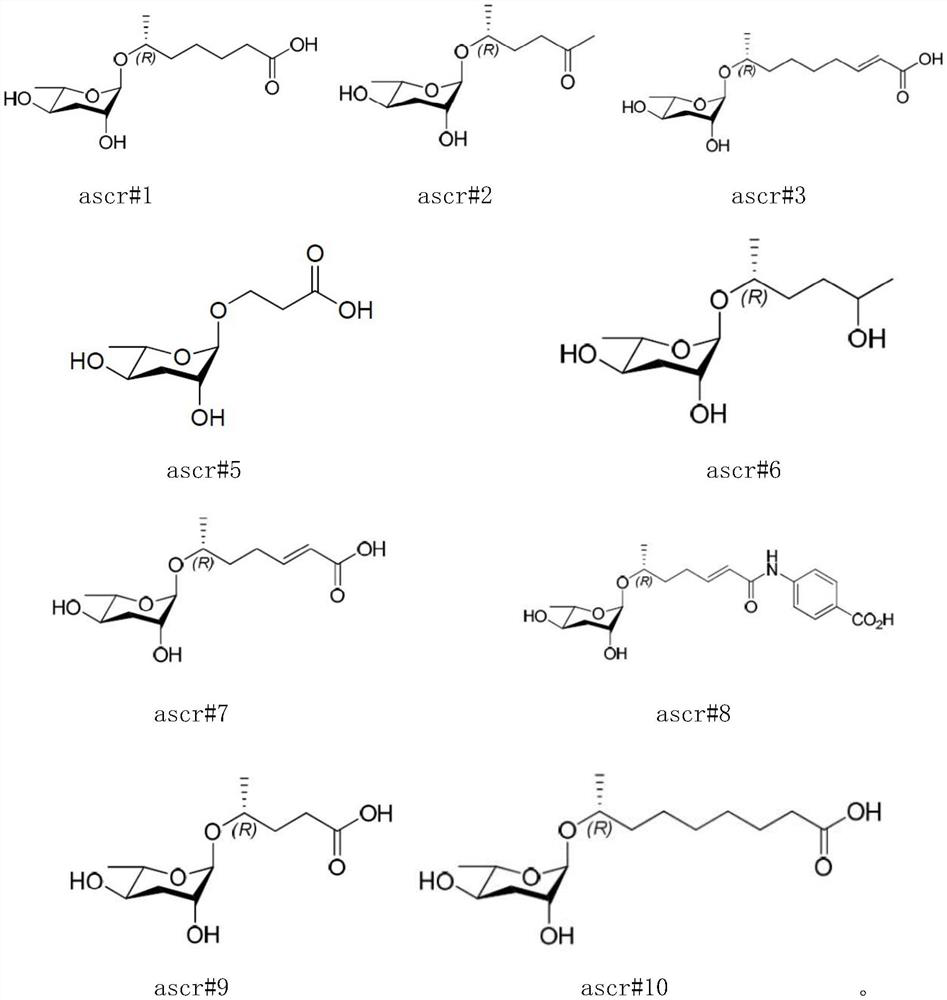
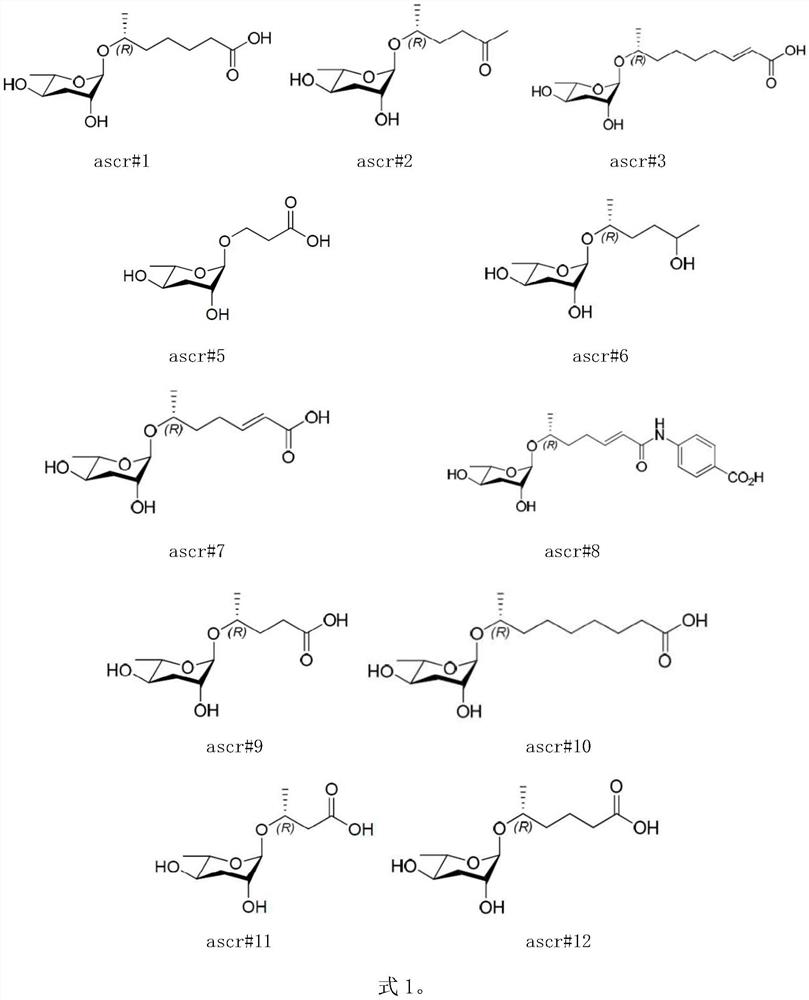
Application of ascaroside in preparation of preparation for promoting development recovery of nematodes in Steinernema carpocapsae All infection period
The invention discloses an application of ascaroside in the preparation of a preparation for promoting the development recovery of nematodes in a Steinernema carpocapsae All infection period. According to the application disclosed by the invention, compared with a symbiotic bacteria liquid supernatant as a control, the ascaroside can be used for remarkably promoting the development recovery of the nematodes in the S.carpocapsae All infection period. Therefore, in the mass culture process of the nematodes, the ascaroside can be used for inducing the nematodes in the S.carpocapsa All infection period to recover development, and a core technology is provided for commercialized production of the S.carpocapsa All nematodes with cost advantages.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Extraction and purification method of anoectochilus roxburghii symbiotic bacteria
ActiveCN111471618AStrong seedlingsShorten the production cycleBacteriaMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyXenorhabdus sp.
The invention discloses an extraction and purification method of anoectochilus roxburghii symbiotic bacteria. The extraction and purification method comprises the following steps: S1, removing mixed bacteria of anoectochilus roxburghii; S2, separating mother strains of the symbiotic bacteria; S3, purifying and culturing the symbiotic bacteria; and S4, expanding culture of the symbiotic bacteria. The method is used for producing the symbiotic bacteria in the anoectochilus roxburghii tissue culture and planting industry, the growth period of the anoectochilus roxburghii can be obviously shortened by adding the symbiotic bacteria into an anoectochilus roxburghii tissue culture sterile culture medium or an anoectochilus roxburghii planting culture medium, leaves of plants are more stretched, golden lines of the leaves are more obvious, stem nodes are shortened, and single plant quality is improved by 20% in average; in addition, the pollution rate of the culture medium added with the symbiotic bacteria is reduced by 30%, and the requirement of the anoectochilus roxburghii tissue culture industry for symbiotic bacteria additive products can be met; meanwhile, the preparation process issimple, operation is easy, the symbiotic bacteria can be added for co-culture in tissue culture seedlings of anoectochilus roxburghii produced in factories, the quality and yield of anoectochilus roxburghii seedlings are improved, and the survival rate and environmental adaptability of later underground cultivation of the anoectochilus roxburghii are facilitated.
Owner:厦门乐莲乐生物科技有限公司
Method for direct seeding and seedling raising of pleione bulbocodioides by using symbiotic bacteria
PendingCN114868617ALow costHigh survival rate in the wildFlowers cultivationGrowth substratesPiriformosporaPleione bulbocodioides
The invention provides a method for direct sowing and seedling raising of pleione bulbocodioides by utilizing symbiotic bacteria, which comprises the following steps: mixing piriformospora indica into a culture medium, sowing pleione bulbocodioides seeds, and performing symbiotic culture to obtain symbiotic pleione bulbocodioides seedlings. The method is simple and convenient to operate, the symbiotic bacteria and pleione bulbocodioides seeds are directly sown for seedling raising for the first time, after 10-15 days, most of the seeds appear green, after 30 days, a large number of protocorms appear native meristem, after 45 days, the protocorms grow first leaves, after 2 months, seedlings form 2-3 leaves and grow roots, and the seedlings can be transplanted to a nursery garden.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Portable biological crust seed source and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114574474APromote formationOther chemical processesClimate change adaptationEndocarponSeeds source
The invention discloses a portable biological crust seed source and a preparation method of the portable biological crust seed source, and the portable biological crust seed source comprises a biological crust seed source small ball prepared from a stone coat symbiotic bacterium (Endocarpon bacillus) F07020, a stone coat symbiotic alga (Diplosphaera chodatii) A07020 and a forming culture medium. The method is favorable for forming a seed source of the lichens which are collected in a state closer to a natural state, can be applied to desertification land control engineering on a large scale, and is favorable for promoting the formation of artificial biological crust.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of ascaroside in preparation of preparation for development recovery of nematodes in H.bacteriophora H06 infection stage
The invention discloses application of ascaroside in the preparation of a preparation for promoting the development recovery of nematodes in a Heterorhabditis bacteriophora H06 infection stage. According to the application disclosed by the invention, compared with a contrast symbiotic bacterium liquid supernatant, the ascaroside can be used for remarkably promoting the development recovery of the nematodes in the H.bacteriophora H06 infection stage, and the ascaroside can be used for inducing the development recovery of the nematodes in the H.indica LN2 infection stage. Therefore, in the mass culture process of the nematodes, the ascaroside is added into a culture medium added with the H.bacteriophora H06 infection stage nematodes containing corresponding symbiotic bacteria, and the nematodes in the infection stage are induced to recover development and growth. The core technology is provided for commercially producing the H.indica LN2 nematodes with a cost advantage.
Owner:YUXI TABACOO COMPANY OF YUNNAN PROVINCE +1
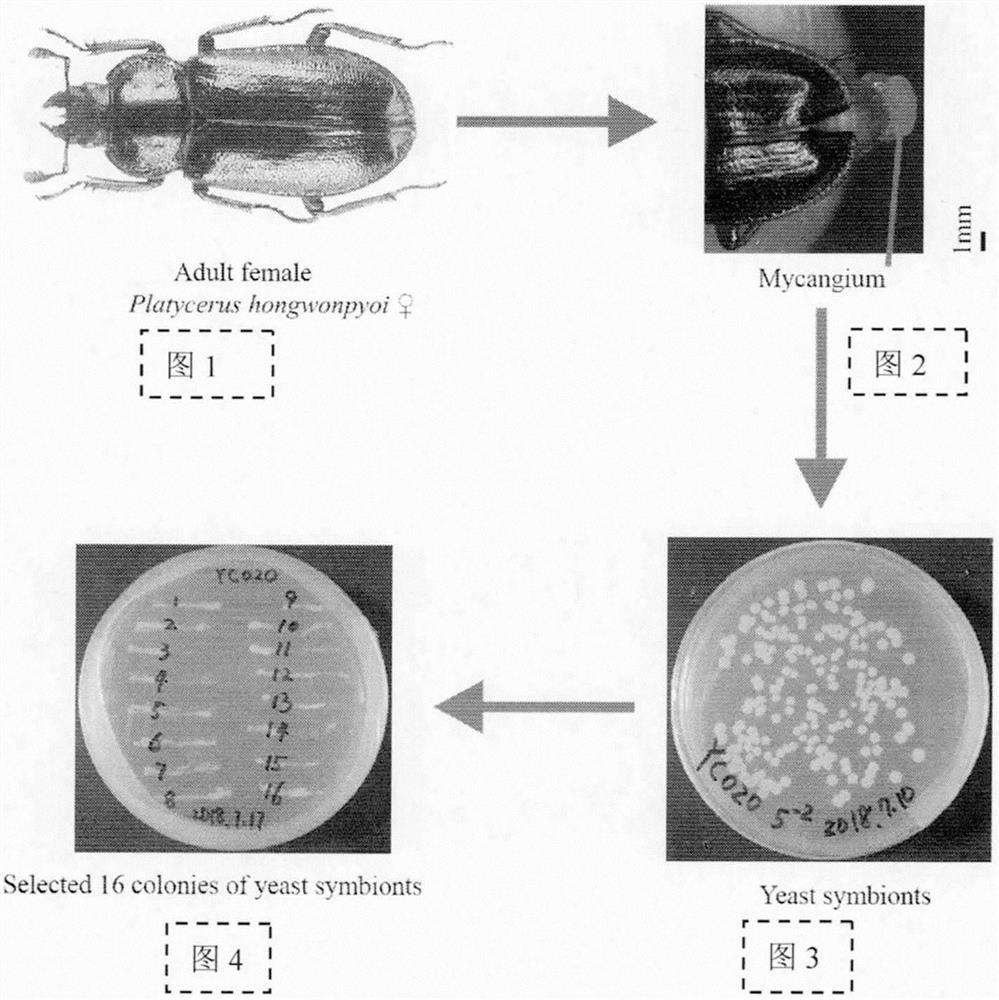
Method for extracting symbiotic microorganisms in coleopteran insects
The invention relates to a method for extracting symbiotic microorganisms in coleopteran insects, which comprises the following steps of: selecting a plurality of sexually mature female coleopteran insects, enabling the bellies of the female coleopteran insects to face upwards, and extruding the middle and rear sections of the bellies to extend out of symbiotic bacterium sacs (one ellipse has a small cyst type structure, and the interiors of the symbiotic bacterium sacs are mostly yellow or white tissues); the method comprises the following steps: completely picking off the tissue with tweezers under a microscope, immersing the tissue into a vessel containing a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) with a certain concentration, grinding the tissue with a grinding rod to fully dissolve the content in the solution, carrying out concentration dilution, transferring the tissue into a culture dish containing YNB, placing the culture dish in a constant temperature box with a proper temperature (25 DEG C), culturing for 2-3 days, and if white dot-shaped or strip-shaped tissue appears, taking out the tissue. And comparing with the known symbiotic bacteria gene sequence, and if the symbiotic bacteria belong to the same clade, indicating that the symbiotic microorganisms in the coleopteran insects are successfully extracted.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of parasitic small rod nematode preparation and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111543437BGood killing effectSuppress humoral immune responseBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyNematode
The invention discloses a parasitic small rod nematode preparation and its preparation method and application, belonging to the technical field of biological pesticides, solving the problem of low quick-acting biocontrol in the prior art, and unable to efficiently and quickly kill Spodoptera frugiperda The problem. The parasitic small rod nematode preparation of the present invention comprises: parasitic small rod nematodes, an RNA segment that interferes with the expression of the polyphenol oxidase PO gene of Spodoptera frugiperda; also includes a pest attractant matrix, a nematode moisturizing agent, and nematode symbiotic bacteria nutrients . The invention creatively starts from various aspects such as attracting, infecting, saprophytic, and adding dsRNA to suppress the immune response of pests, and works together to effectively improve the killing effect of nematodes on Spodoptera frugiperda.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of dsRNA of aphid symbiont gene and its application in inhibiting the growth of aphid
The invention discloses dsRNA of a gene of a symbiotic bacterium of aphids and an application thereof to inhibition of growth of aphids. DsRNA provided by the invention is double-stranded RNA formed by a nucleotide shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table and a nucleotide shown in an inverse complementary sequence of the sequence 2. Experiments prove that the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids is obtained; the gene of the endotrophic symbiotic bacterium hamiltonella defensa 28469 of wheat aphids can be inhibited or silenced, impaired growth and development of the wheat aphids can be caused and lethal effects can be generated by adopting the method of feeding dsRNA in vitro.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bletilla striata direct seeding and seedling raising method using symbiotic bacteria
PendingCN113207590AImprove the germination rate of natural live broadcastFast growthMicroorganismsGrowth substratesBiotechnologyBletilla striata
The invention discloses a bletilla striata direct seeding and seedling raising method using symbiotic bacteria. The method specifically comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring of the symbiotic bacteria of bletilla striata: culturing a bletilla striata explant to obtain a strain of the symbiotic bacteria of bletilla striata for later use; S2, direct sowing and seedling raising of bletilla striata: mixing pretreated bletilla striata seeds and the symbiotic bacteria of bletilla striata in the step S1, and then sowing the seeds in a seedbed; S3, sowing later-period management: after the sown seeds germinate and emerge, carrying out fertilization and seedling hardening treatment, and then transplanting. The symbiotic bacteria of bletilla striata and bletilla striata seeds are uniformly mixed, direct seeding is performed, then seedling hardening treatment is performed, due to the fact that the symbiotic bacteria of bletilla striata are added in the germination process of the bletilla striata seeds, the direct seeding germination rate of the bletilla striata seeds is as high as 86%, a Huabao leaf fertilizer is sprayed in the later-period management process, and the seedling growth speed is high. Compared with a tissue culture seedling raising method, the method has the advantages that the production cost and labor consumption are greatly reduced, the cultured bletilla striata seedlings are vigorous and uniform in growth vigor, and the transplanting survival rate reaches up to 99%.
Owner:INST OF DAFENG MARINE IND NANJING UNIV OF TECH
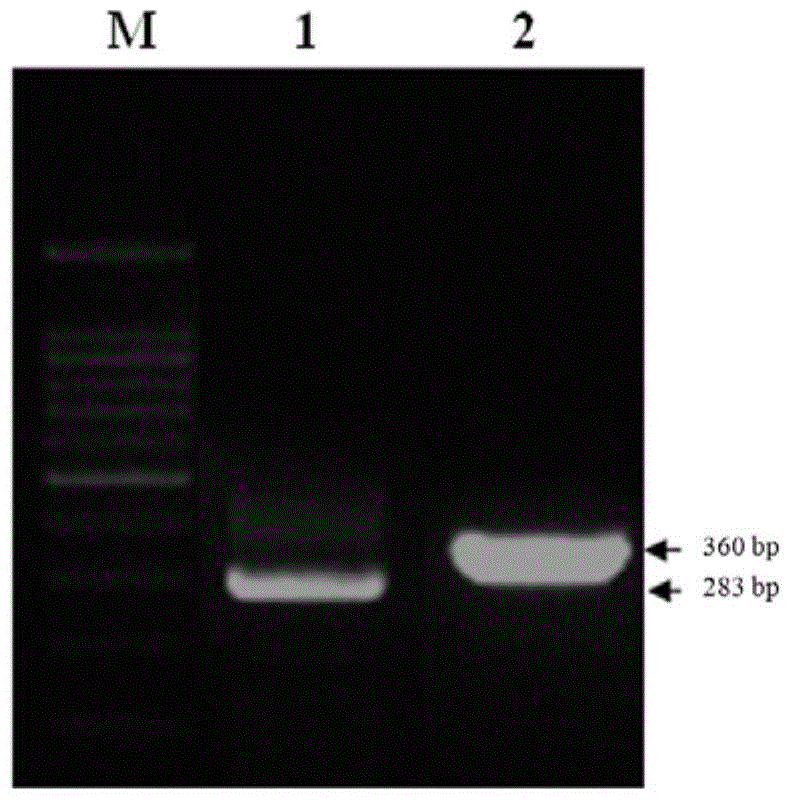
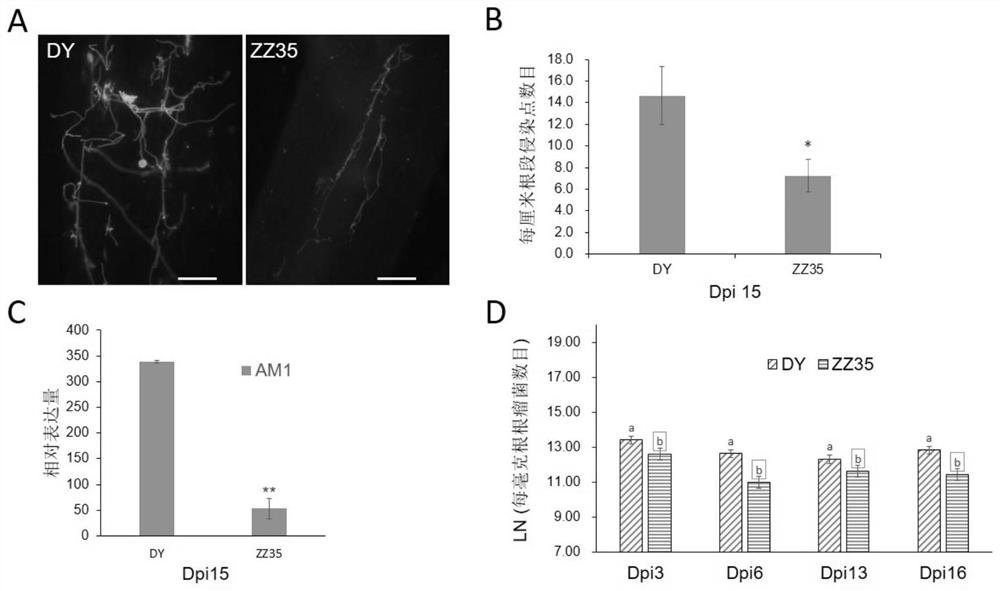
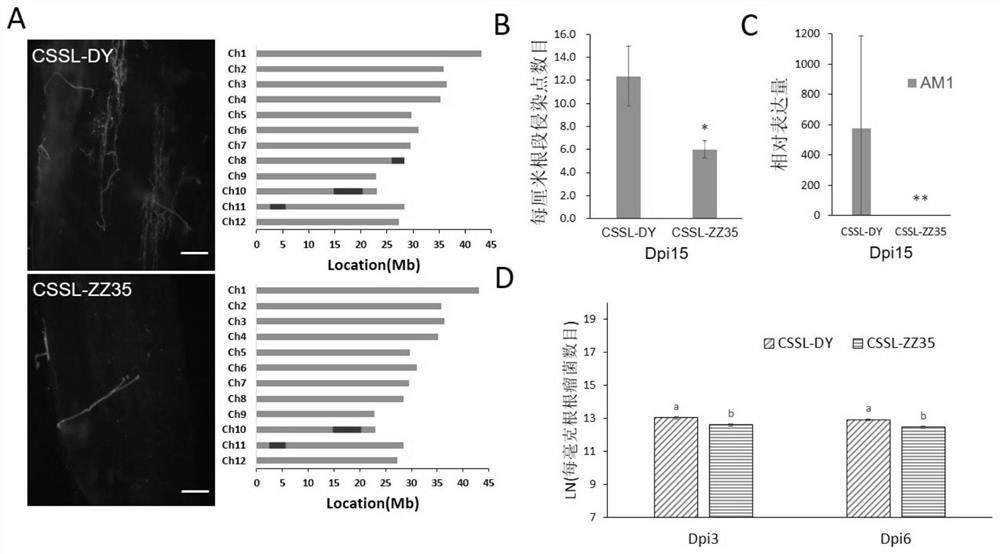
Protein for promoting symbiosis between plant root system and symbiotic bacteria, isolated nucleic acid molecule and application cultivation method thereof
The invention discloses a protein for promoting symbiosis of a plant root system and symbiotic bacteria, a separated nucleic acid molecule and an application and cultivation method thereof, which relate to the technical field of plant symbiosis. Compared with SEQ ID NO.6, the amino acid sequence of the protein disclosed by the invention has at least one of the following mutations: I118T and S121T.The protein can enable the plant root system to be more easily infected by symbiotic bacteria, is high in infection efficiency, and can quickly and efficiently establish a symbiotic relationship withthe symbiotic bacteria. The protein can be used for cultivating a plant variety which is easy to form a symbiotic relationship with the symbiotic bacteria.
Owner:江西省农业科学院水稻研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com