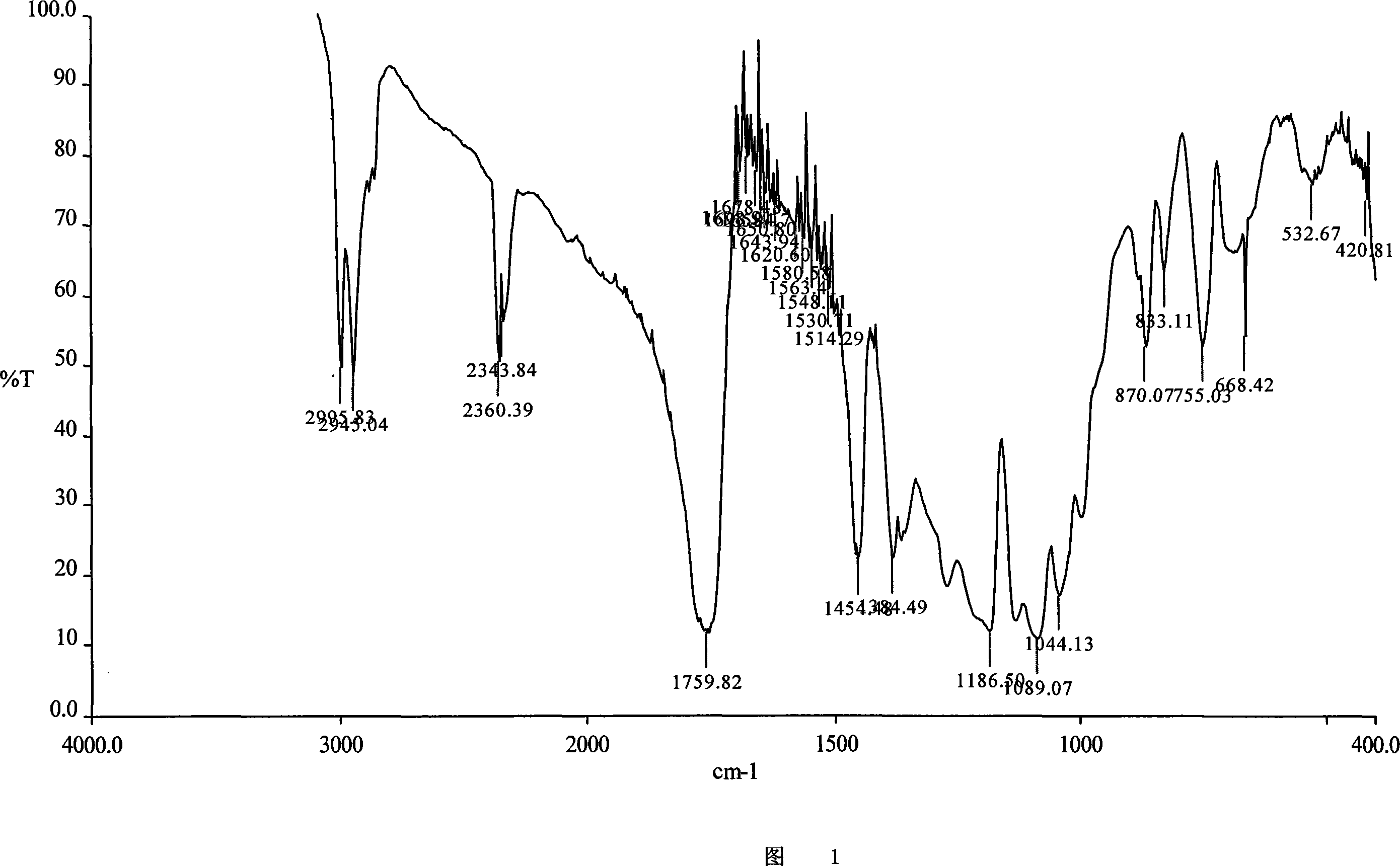
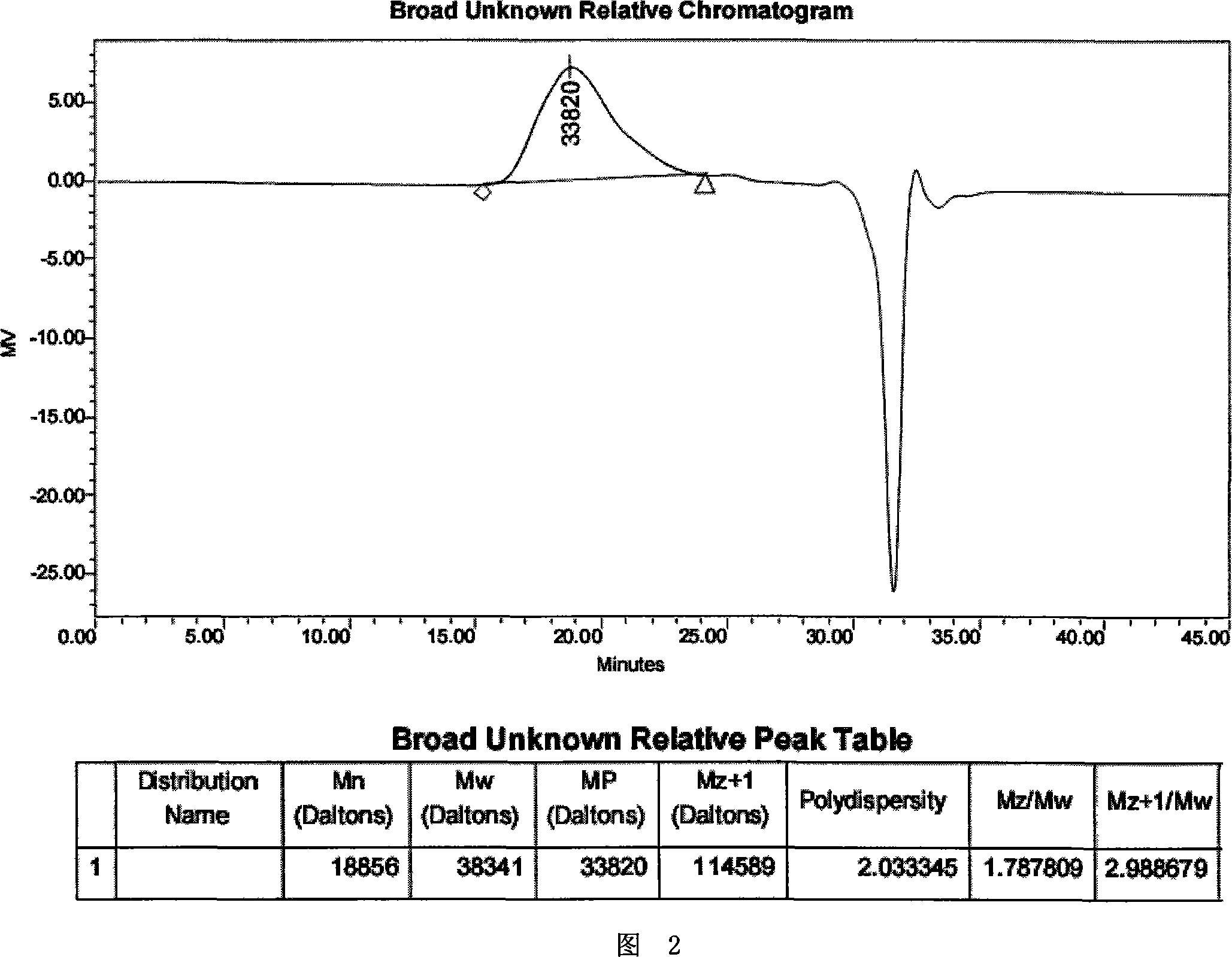
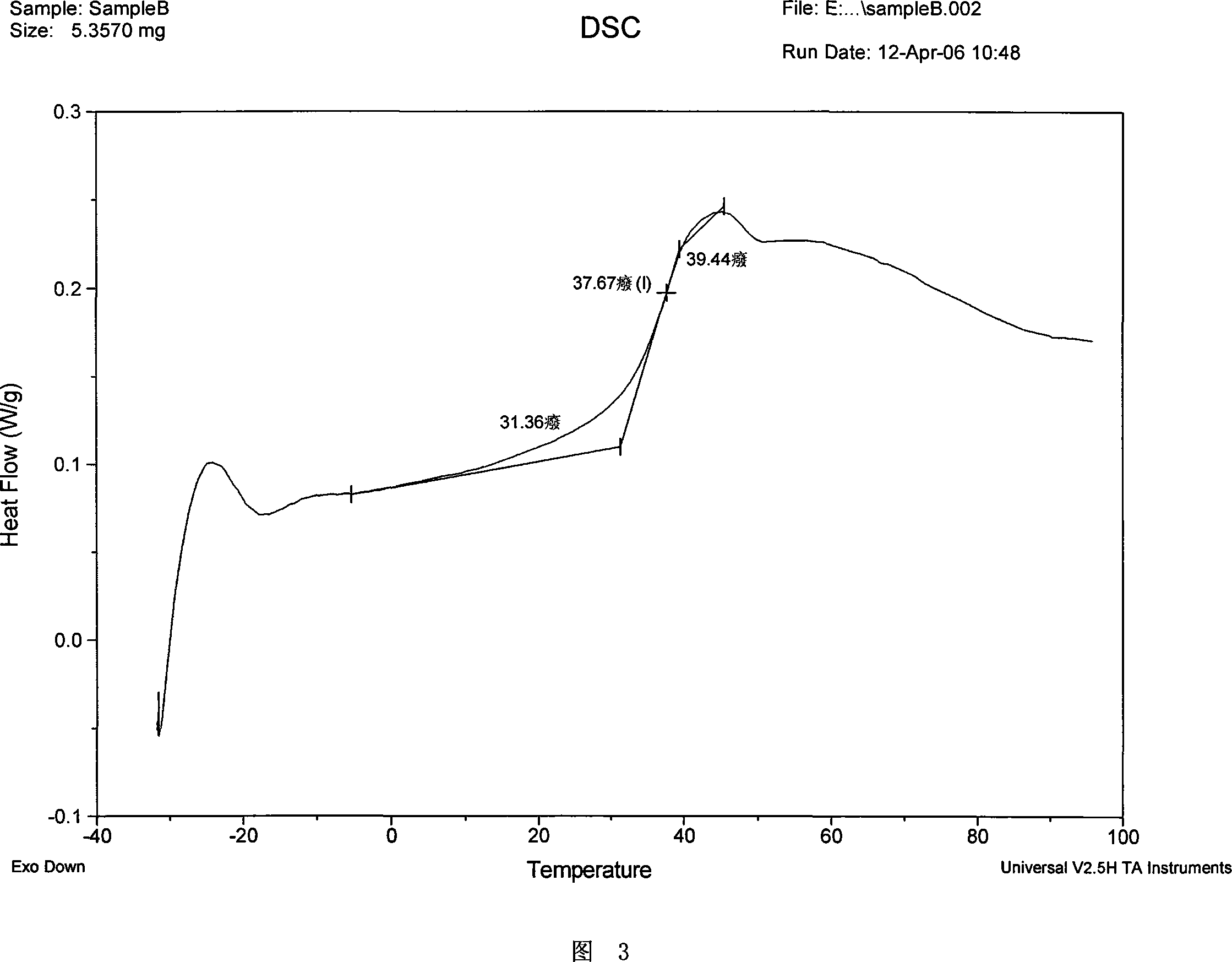
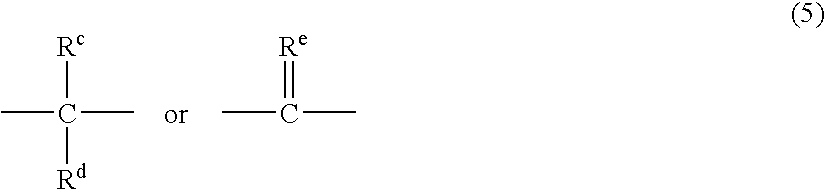Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "PLLA polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
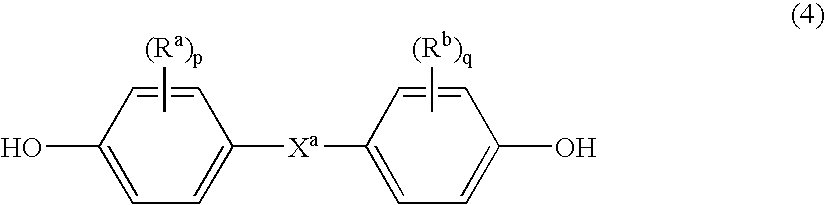
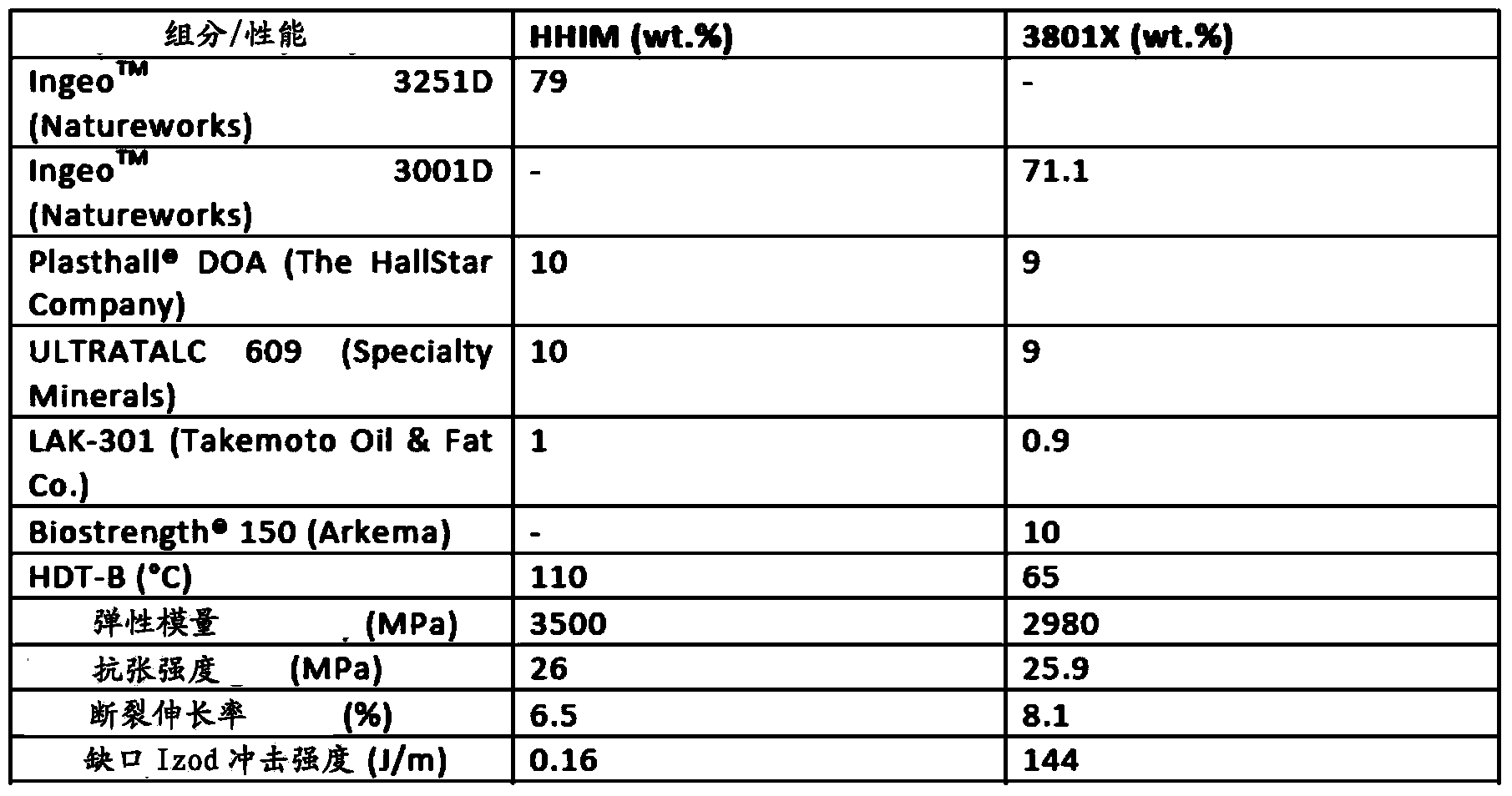
Thermoplastic polycarbonate/polyester blend compositions with improved mechanical properties
Disclosed is a thermoplastic composition comprising a mixture of from 10 to 98 weight % of a polycarbonate polymer, from 2 to 90 weight % of a polyester polymer comprising structures derived from a diol compound having the structure (A) HO-Z-OH, wherein Z is a C1 to C36 linear aliphatic radical, a C3 to C36 branched aliphatic or cycloaliphatic radical, a C6 to C36 aryl radical, or a C7 to C36 alkylaryl radical, and a diacid compound having the structure (B) HOOC—CH2CH2—COOH, from 0 to 5 weight % of a polylactic acid polymer, wherein the sum of the polycarbonate polymer, the polyester polymer, and the polylactic acid polymer is equal to 100 weight %. The thermoplastic composition has improved mechanical properties.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Ternary mixture of biodegradable polyesters and products obtained therefrom
InactiveUS6841597B2RapidityImproves UV stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPaper coatingPolymer scienceBiodegradable polyester
The invention relates to a mixture of biodegradable polyesters comprising: (A) a polyhydroxy acid of the poly-ε-caprolactone type and its copolymers, (B) aliphatic polyester, and (C) a polymer of polylactic acid, in which the concentration of (A) varies with respect to (A+B) in the range between 40 and 70% by weight, and the concentration of (C) with respects to (A+B+C) lies between 2 and 30%.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Thermoplastic resin composition and molded article comprising the same
ActiveUS7589151B2Increase resistanceHigh transparencyDyeing processPolymer scienceMethacrylate methyl
A thermoplastic resin composition comprising a polylactic acid polymer (A), an acrylic polymer (B) containing units of methyl methacrylate monomer, and a graft copolymer (C) obtained by graft-polymerizing a vinyl monomer onto a rubbery polymer, wherein the refractive index, Rc, of the graft copolymer (C) and the total refractive index, Rab, of the polylactic acid polymer (A) and the acrylic polymer (B) satisfy the following formula (1)−0.004≦Rc−Rab≦+0.008 (1).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
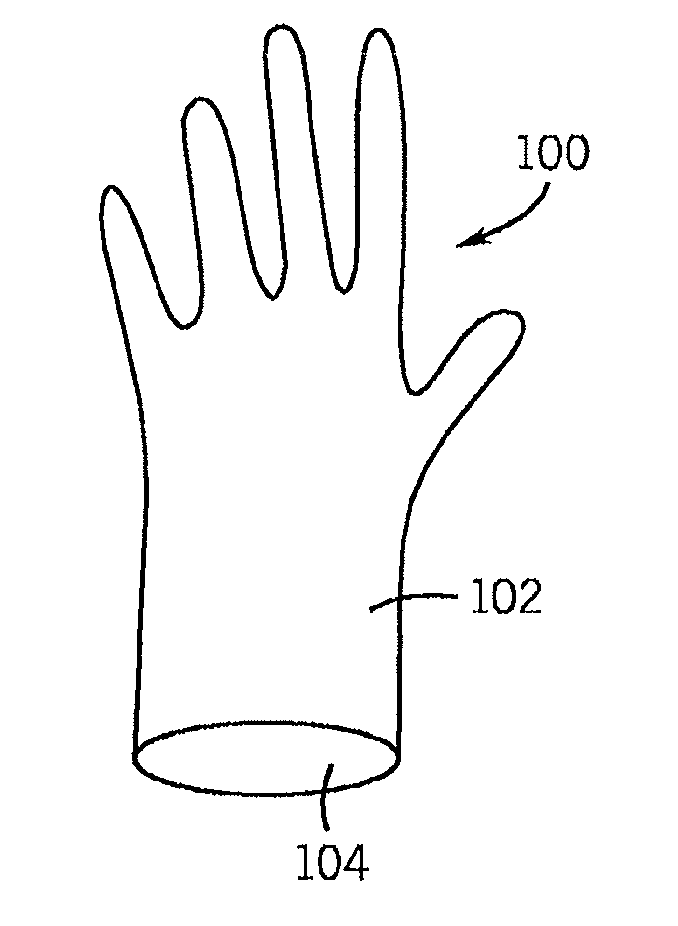
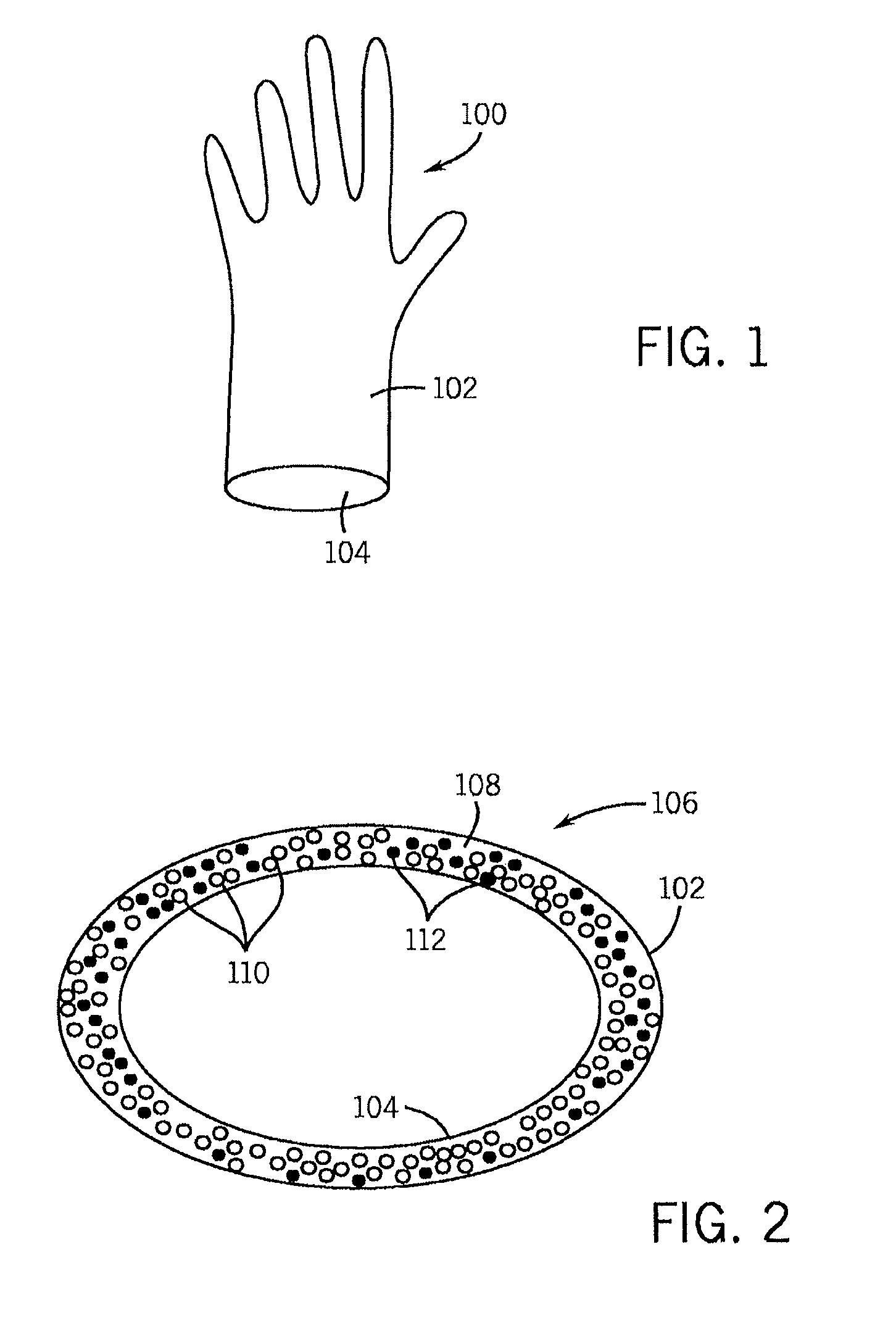
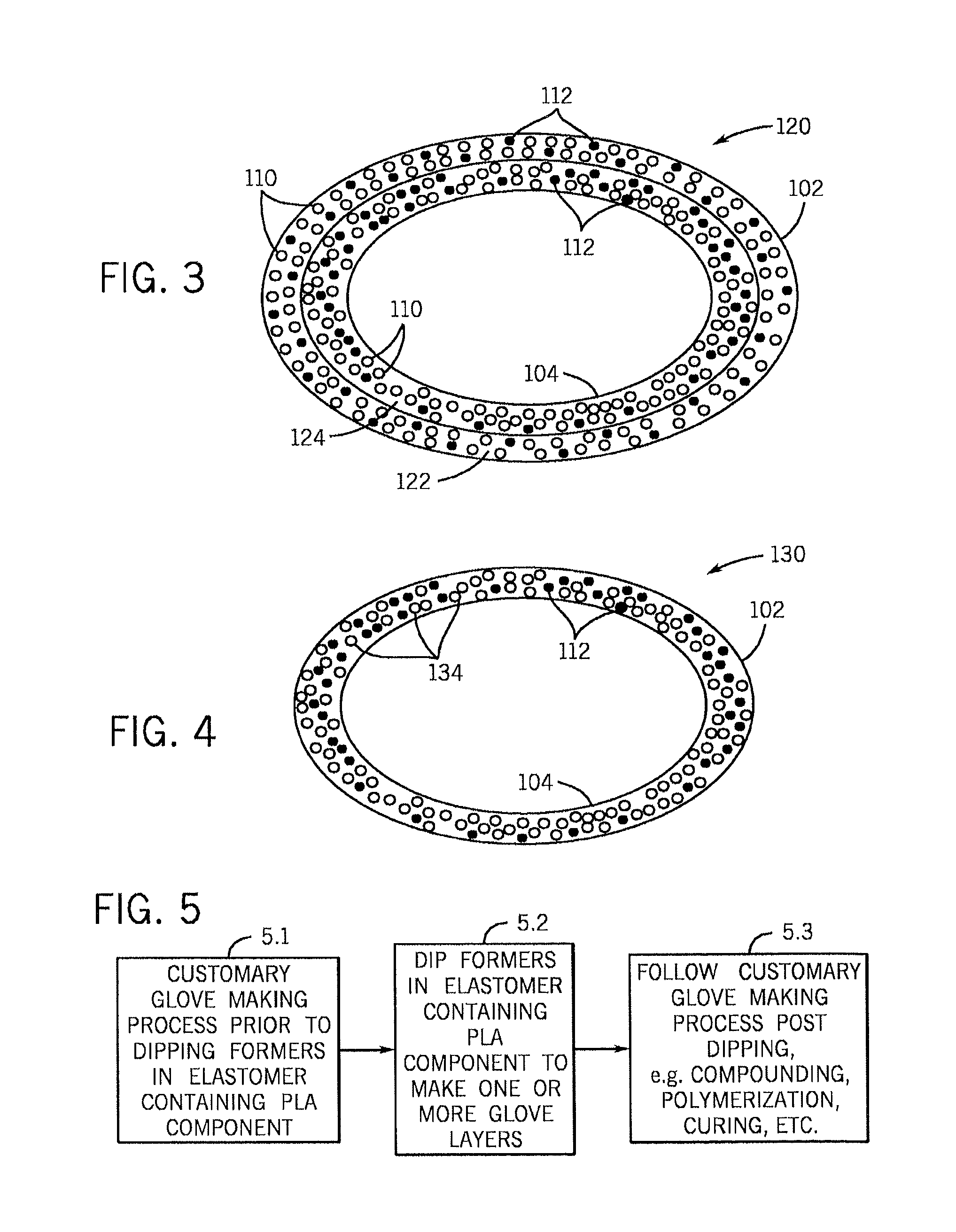
Polylactic acid gloves and methods of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20100257657A1Enhance their market appealBroad possible marketGarment special featuresSurgeryElastomerPolymer science
Biodegradable disposable gloves and methods of manufacturing the same are disclosed in which the elastomeric material used to manufacture the gloves includes a polylactic acid polymer component in combination with a biodegradable plasticizer.
Owner:SMARTHEALTH
Ternary mixture of biodegradable polyesters and products obtained therefrom
InactiveUS6787613B2Shorten speedImprove propertiesFlexible coversWrappersBiodegradable polyesterPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to a mixture of biodegradable polyesters which includes an aromatic-aliphatic polyester (A), an aliphatic polyester (B) and a polyactic acid polymer (C) in which the concentration of A varies, with respect to (A+B) in the range between 40 and 70% by weight, and the concentration of C with respect to (A+B+C) is of between 6 and 30% by weight.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Polylactic acid resin composition, process for producing the same, biaxially stretched polylactic acid film, and molded articles thereof
A resin composition contains poly(lactic acid) and a cellulosic ester, a resin composition excellent in transparency, mechanical properties, and thermostability; a biaxially drawn film containing poly(lactic acid) and at least one compound selected from cellulosic esters, poly(meth)acrylates, and polyvinyl compounds having a glass transition temperature of 60° C. or higher; and a biaxially drawn film excellent in transparency, mechanical properties, and thermostability. The resin composition is obtained by melt-kneading a poly(lactic acid) polymer with a weight average molecular weight of 50,000 or higher and a cellulosic ester; a resin composition excellent in transparency and having luminous transmittance of 40% or higher for visible light with 400 nm; a molded article and a film made of the resin composition; a poly(lactic acid) biaxially drawn film containing a poly(lactic acid) polymer with a weight average molecular weight of 50,000 or higher and at least one compound selected from cellulosic esters, poly(meth)acrylates, and polyvinyl compounds having a glass transition temperature of 60° C. or higher; a poly(lactic acid) biaxially drawn film excellent in transparency and having film haze of 10% or lower.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Low molecular weight polymers
InactiveUS20050238618A1Reduce molecular weightLow polydisperse polymersPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSolventPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to a procedure for purifying low molecular weight polylactic acid polymers by use of reduced temperature liquid-liquid phase separation of the polymers in methanol, ethanol or isopropanol based solvents, compositions comprising the polymers and methods of using the same.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and polylactic acid polymer compsns. for laminates and films
InactiveCN1500114APersonal careSynthetic resin layered productsPoly l lactic acidPolylactic acid polymer
Environmentally degradable films comprising a blend of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and a polylactic acid polymer or copolymer are disclosed. Laminates having a first layer comprising a PHA copolymer and a second layer comprising a PLA polymer or copolymer are also disclosed. Disposable articles comprising the environmentally degradable films or laminates are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polylactic acid filament nonwoven fabric and production method thereof
A nonwoven fabric formed of composite filaments by a spunbond method is disclosed. The composite filament includes a polylactic acid polymer having a melting point of 160° C. or higher and an aliphatic polyester polymer having a melting point lower, by 50° C. or more, than the melting point of the polylactic acid polymer. The aliphatic polyester polymer forms at least a portion of the filament surface. The aliphatic polyester polymer includes as the constituent components thereof 1,4-butanediol and succinic acid, and at the same time, includes 0.1 to 1% by mass of an amide wax.
Owner:UNITIKA LTD
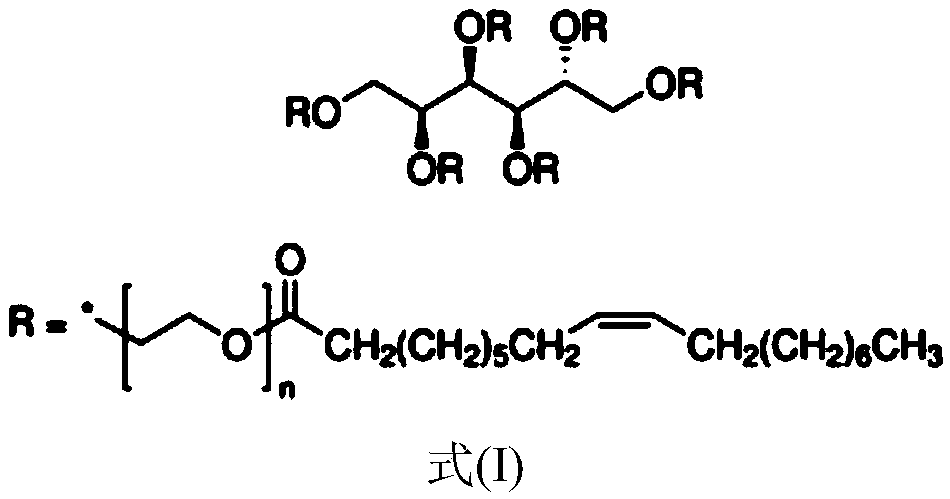
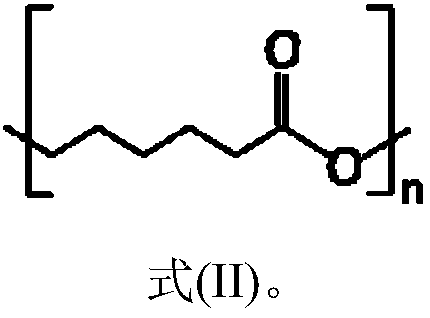
Compound comprising PLLA and PDLA
Owner:PURAC BIOCHEM
Ternary mixture of biodegradable polyesters and products obtained therefrom
The invention relates to a mixture of biodegradable polyesters comprising: (A) a polyhydroxy acid of the poly-ε-caprolactone type and its copolymers, (B) aliphatic polyester, and (C) a polymer of polylactic acid, in which the concentration of (A) varies with respect to (A+B) in the range between 40 and 70% by weight, and the concentration of (C) with respects to (A+B+C) lies between 2 and 30%.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Biodegradable injectable filler as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111617315AImprove cell affinityImprove performanceSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAllergic reactionHydrolysis
The invention provides a biodegradable injectable filler as well as a preparation method and application thereof, particularly provides an injectable implant composition and a preparation method thereof. The composition contains biodegradable polymer particles and hyaluronic acid with the content not higher than 0.1%. The hyaluronic acid can significantly improve the hydrophobic property of the surface of a PLLA polymer scaffold, promote adhesion and growth of collagen cells on the surface of the PLLA polymer scaffold, significantly improve a filling effect or a fulling effect of the composition, remove wrinkles, enhance attractiveness of facial skin, improve the suspension stability of the PLLA particles after freeze-drying redissolution, reduce hydrolysis and degradation of PLLA ester bonds, and reduce adverse reactions such as swelling, inflammation and allergic reaction possibly caused by acid degradation products.
Owner:MEIYAN SPACE (HEBEI) BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
Polylactic acid elastic non-woven material beneficial to tissue regeneration and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112210888APromote wound healingGood treatment effectAbsorbent padsTissue regenerationFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a polylactic acid elastic non-woven material beneficial to tissue regeneration and a preparation method thereof. The nano-micron polylactic acid elastic non-woven material is of an integrated structure composed of polylactic acid nano-micron fibers serving as a main body and polyolefin elastic filaments serving as a framework. The preparation method comprises the followingsteps of carrying out in-situ spray molding on a modified polylactic acid polymer and a polyolefin elastic framework to obtain a laminated fiber web, and carrying out water jet composite processing onthe laminated fiber web to form an integrated structure, and carrying out single-side lustring on the fiber net with the integrated structure to obtain a nano-micron elastic light patch and the preparation method thereof. The non-woven material prepared by adopting the method has an integrated structure, is not layered, has a relatively good anti-adhesion effect, also has excellent elasticity andflexibility, and can be applied to multiple fields of hernia patches, medical dressings, medical bandages and the like. The preparation method of the non-woven patch has the characteristics of shortprocess flow, high production speed and low cost, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE +1
Method for removing an ester from a vapor mixture
ActiveUS9700840B2Increase ratingsIncrease productivityDispersed particle separationLactideAqueous solution
A method for the removal of an ester (3′) from a vapor mixture (5′) containing the ester (3′) is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of by bringing the vapor (5) mixture (5′) into contact with an aqueous solution (6′) containing the acid (4′) corresponding to the ester (3′), wherein a portion of the ester (3′) is dissolved in or otherwise transferred to the aqueous solution (6′), and the aqueous solution (6′) is after the contact led in a circulation (73), the aqueous solution (6′) is processed in the circulation (73) in a process comprising: a heating step (240), a (10) reaction step (250) having a residence time and a temperature, a cooling step (260), wherein the heating step (240) precedes the reaction step (250), the reaction step (250) precedes the cooling step (260), and the residence time and the temperature in the reaction step (250) are sufficient to substantially reduce the content of the ester (3′) in the aqueous solution (6′). The invention further (15) relates to an apparatus (1) for carrying out said process. The present invention further relates also to the use of the apparatus (1) in the method of the invention, preferably in the production of a lactide (13′) or a polylactic acid polymer (12′).
Owner:SULZER MANAGEMENT AG
Biodegradation polymer and its preparing process and application
ActiveCN101125916APredictable release kineticsLong validity periodPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPolymer scienceDocetaxel
The invention relates to a polylactic polymer with organic phosphate bond in the main chain of biological degradation, which can change into innocuity residue by internal degradation. The solidity and hydrophobicity of lactic acid or glycollic acid prepolymer are strengthened by adding a circularity compound that potentially improves the final polymer Tg containing phosphorus, redudeces the need of high molecular weight prepolymer, and the internal degradation time is quickened by using low molecular weight preolymer and improving organic phosphate contents, which improves the encapsulating ratio between polymer and a plurality of aquosity medicines (such as paclixtel or docetaxel). Finally, practical matrices formed by medicine and polymer have much better mixing compatibleness without phenomena of medical phasic demixing and independent crystallization.
Owner:TIANDA PHARMA ZHUHAI
Modified polylactic acid material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113583412AEfficient degradationDegradation can be adjustedSurgeryPolymer sciencePLLA polymer
The invention discloses a modified polylactic acid material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The modified polylactic acid material comprises polylactic acid, a polymer and a block polymer, wherein the mass ratio of the polylactic acid to the full-degradable polymer to the block polymer is (0.3-0.7): (0.2-0.5): (0.03-0.1). The modified polylactic acid material can effectively solve the problem that an existing polylactic acid material is poor in compatibility, degradability and mechanical property.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fast-crystallization and high-crystallinity polylactic acid modification method
PendingCN110760172ALower activation energyReduce the free energy of whitening flourCarbon fibersCrystallinity
The invention discloses a fast-crystallization and high-crystallinity polylactic acid modification method which comprises the following steps: 1, performing melting extrusion on carbon fiber, L-polylactic acid, D-polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid and starch through a twin screw extruder so as to obtain a nucleating agent; 2, in parts by weight, putting semi-crystalline polylactic acid, a polymertype crystal accelerator, the nucleating agent and a plasticizer into a container according to a ratio, adding a dichloromethane solvent, performing stirring with a magnetic stirrer, and performing volatilization at room temperature to remove the solvent so as to obtain a lactic acid premix; and 3, melting and blending the polylactic acid premix with polyvinylidine according to a ratio, so as to obtain a polylactic acid complex. The method has the beneficial effects that a molding process is improved, the polymer type crystal accelerator is added to reduce activation energy required for formation of lattice of polylactic acid, the difficulty of crystallization can be reduced, and the crystallization rate can be increased.
Owner:BENGBU COLLEGE
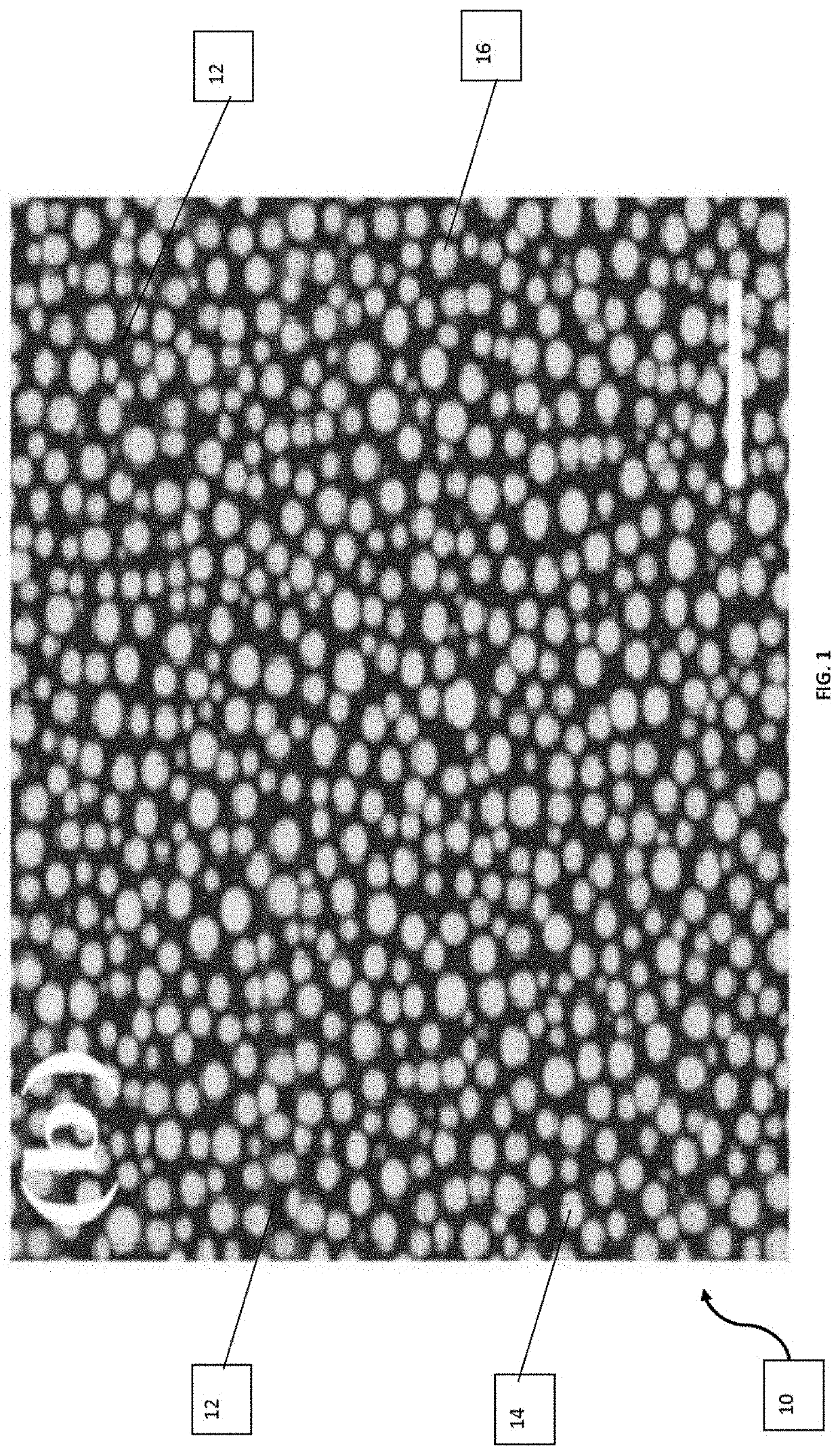
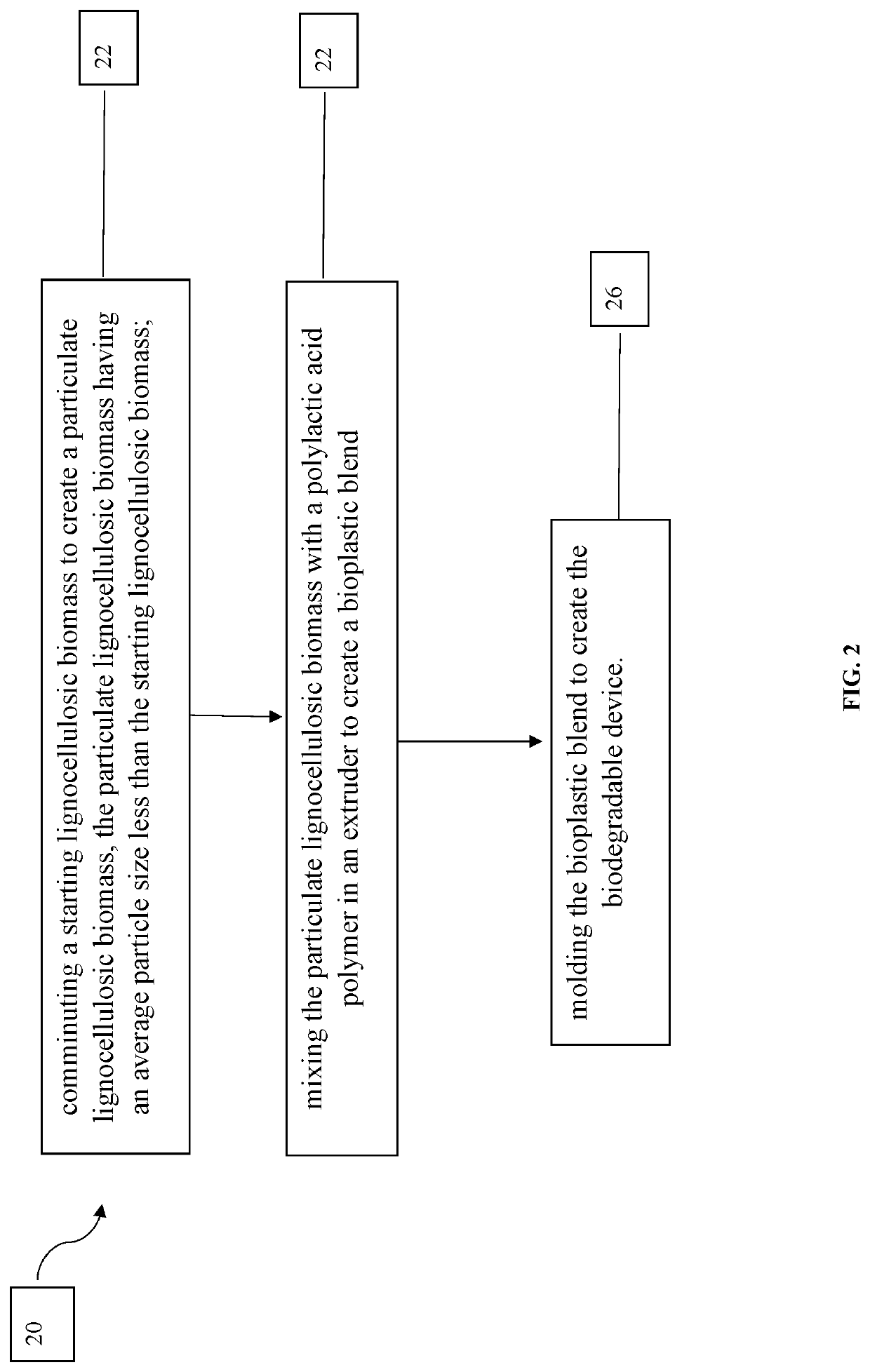
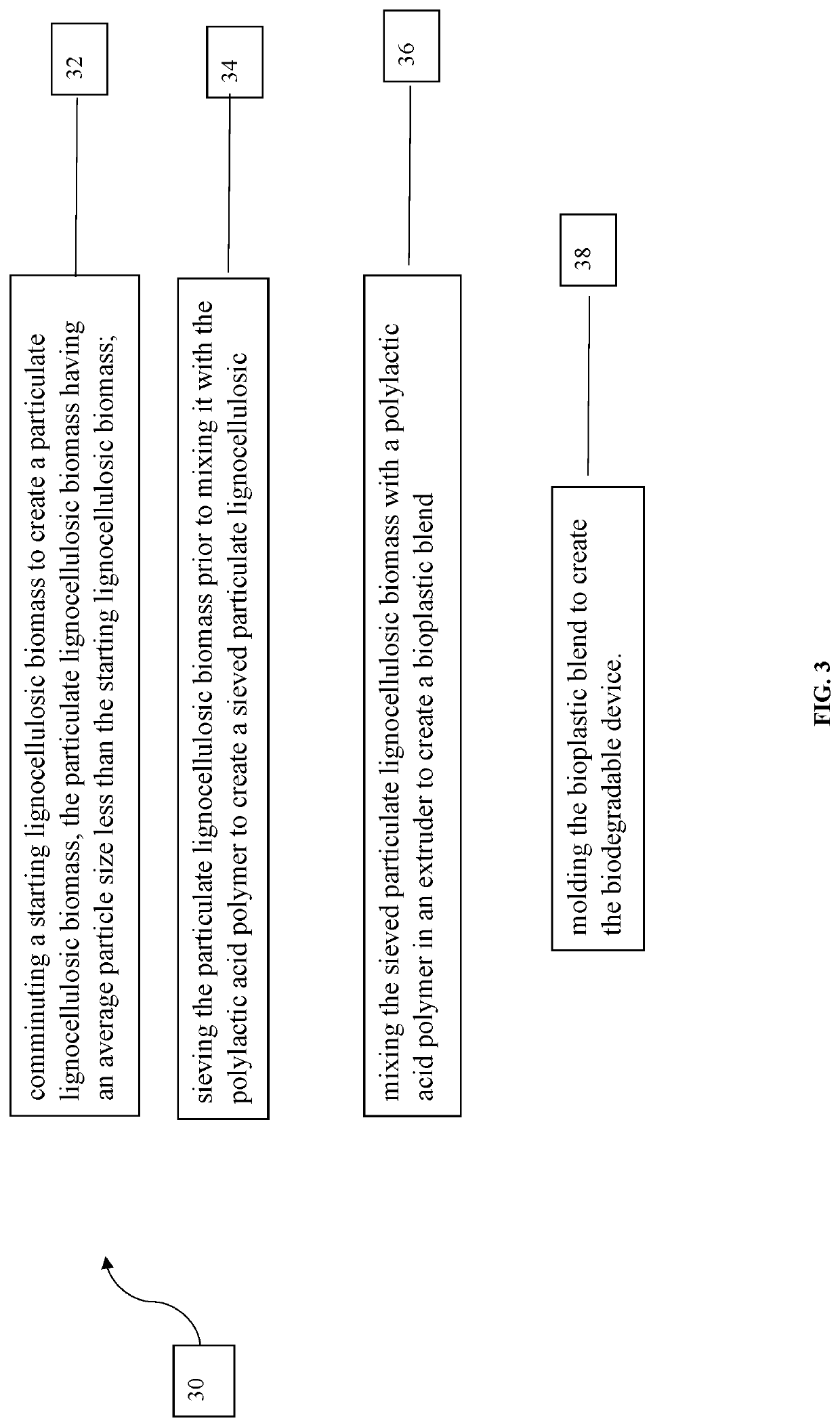
Biodegradgradable devices, and methods of making the same
A bioplastic blend is disclosed. The bioplastic blend may comprise a polylactic acid polymer and a lignocellulosic biomass. The lignocellulosic biomass may be a particulate and have an average particle size that is less than or equal to 60 micrometers, or less than or equal to 50 micrometers. The lignocellulosic biomass may be a particulate and comprise greater than or equal to 50 percent by weight of the bioplastic blend, or greater than or equal to 60 percent by weight of the bioplastic blend. In addition, the bioplastic blend may comprise a plasticizer.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Novel bionic 3D printing bioactive fusion cage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110327491AMulti-parameter fine-tuningResolve fractureAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationFreeze-dryingPLLA polymer
The invention discloses a novel bionic 3D printing bioactive fusion cage and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the fusion cage comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a 1,4-dioxane solution of PLLA polymer; (2) mixing n-HA with the PLLA polymer solution to obtain a basic solution; (3) 3D-printing a porous anatomical fusion cage, and removing organic solvent to obtain a porous anatomical fusion cage; (4) preparing loading PLGA / rhBMP-2 nanoparticles; (5) dissolving the PLGA / rhBMP-2 nanoparticles in 10ml of distilled water; (6) soaking the porous anatomic fusion cagein the PLGA / rhBMP-2 nanoparticle solution, and coating meshes of the porous anatomic fusion cage with the PLGA / rhBMP-2 nanoparticles; and (7) freeze-drying and forming the porous anatomical fusion cage. The novel fusion cage prepared by the method with three-dimensional physiological anatomical space conformation, controllable degradation and controlled release realizes the optimization of mechanical property, has controllable degradation and bone function promotion, and solves the problems of fracture and collapse of OLIF operation endplate and displacement of a fusion cage.
Owner:SHENZHEN HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
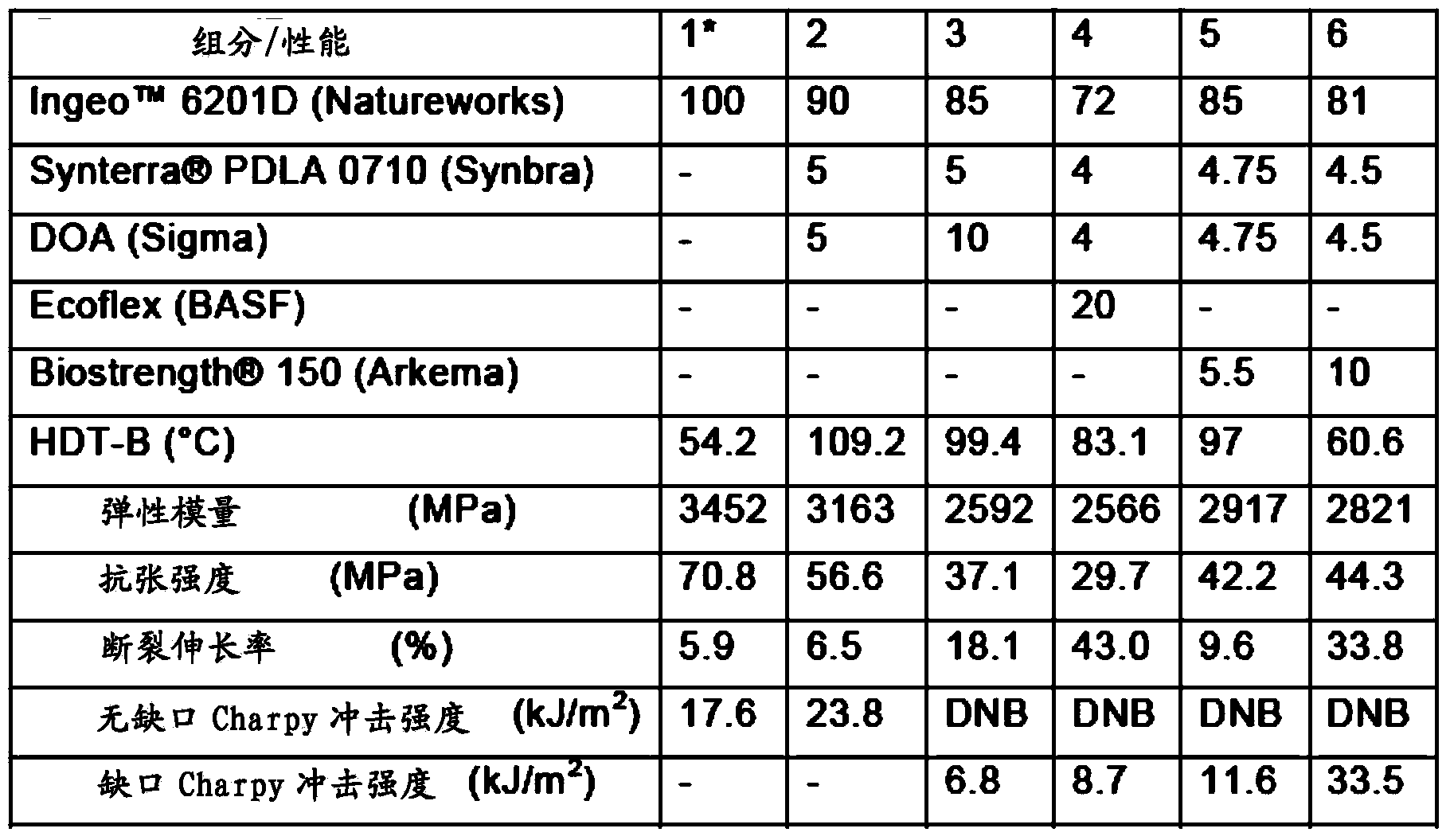
Biodegradable polymer
The present invention provides a biodegradable polymer composition having an elongation-at-break of at least 200 percent comprising a polylactic acid-based polymer and a mechanical performance modifier, wherein addition of the mechanical performance modifier to the biodegradable polymer increases the elongation-at-break to at least 200 percent while retaining at least 75 percent of the tensile strength of unmodified polylactic acid polymer and wherein the melting temperature of the biodegradable polymer is within 5 degrees Celsius of the melting temperature of unmodified polylactic acid polymer. In one embodiment, the mechanical performance modifier is poly(ethylene glycol) sorbitol hexaoleate. In another embodiment, the mechanical performance modifier is polycaprolactone.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Method for producing porous three-dimensional material by enzymatic degradation of PCL/PLLA polymer
PendingCN112144176AEasy to operateEffective resizingFibre typesElectro-spinningPolymer scienceSpinning
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering carrier materials, and particularly discloses a method for producing a porous three-dimensional material through enzymatic degradation ofa PCL / PLLA polymer. The method comprises the following steps of dissolving PCL and PLLA in a mixed solvent of dichloromethane and N,N-dimethylformamide to obtain a PCL / PLLA solution; carrying out electrostatic spinning on the solution to obtain a PCL / PLLA fibrous membrane; and placing the fibrous membrane in a PBS buffer solution added with esterase to be degraded, so that the porous three-dimensional PCL / PLLA fibrous membrane with the mechanical property not obviously reduced is obtained. The porous three-dimensional PCL / PLLA fibrous membrane is expected to serve as a high-quality raw material for preparing a porous tissue engineering scaffold or water / air treatment. According to the method, by adjusting the concentration and degradation time of the esterase, the purpose of controlling the size and number of micropores in the surface of the PCL / PLLA fibrous membrane can be achieved, and a new thought is provided for preparing porous materials with high porosity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Poly(aliphatic ester)-polycarbonate copolymer/polylactic acid blend
The present invention is directed to a blended composition comprising one or more polycarbonates wherein at least one of the polycarbonates is a polyesterpolycarbonate having at least one unit derived from a soft block ester unit, e.g., sebacic acid, and at least one unit derived from bisphenol A, and a polylactic polymer wherein the composition has an overall biocontent of at least 10% according to ASTMD6866.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Polylactic acid elastic nonwoven material beneficial to tissue regeneration and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112210888BPromote wound healingGood treatment effectAbsorbent padsTissue regenerationFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a polylactic acid elastic non-woven material beneficial to tissue regeneration and a preparation method thereof. The nano-micron polylactic acid elastic non-woven material is an integrated structure composed of polylactic acid nano-micron fibers as the main body and polyolefin elastic filaments as the skeleton. Its preparation method is as follows: the modified polylactic acid polymer and the polyolefin elastic skeleton are subjected to in-situ injection molding to obtain a laminated fiber web, and then the laminated fiber web is subjected to water jet composite processing to form an integrated structure, and then the integrated structure A fiber web is ironed on one side to obtain a nano-micron elastic lightweight patch and a preparation method thereof. The non-woven material prepared by this method has an integrated structure, no delamination and good anti-adhesion effect. At the same time, the non-woven material also has excellent elasticity and flexibility, and can be used for hernia patch, medical dressing, medical bandage, etc. multiple fields. The preparation method of the non-woven patch has the characteristics of short process flow, high production speed and low cost, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE +1
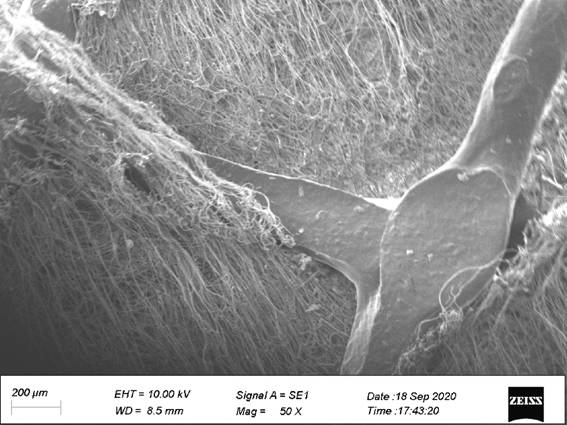
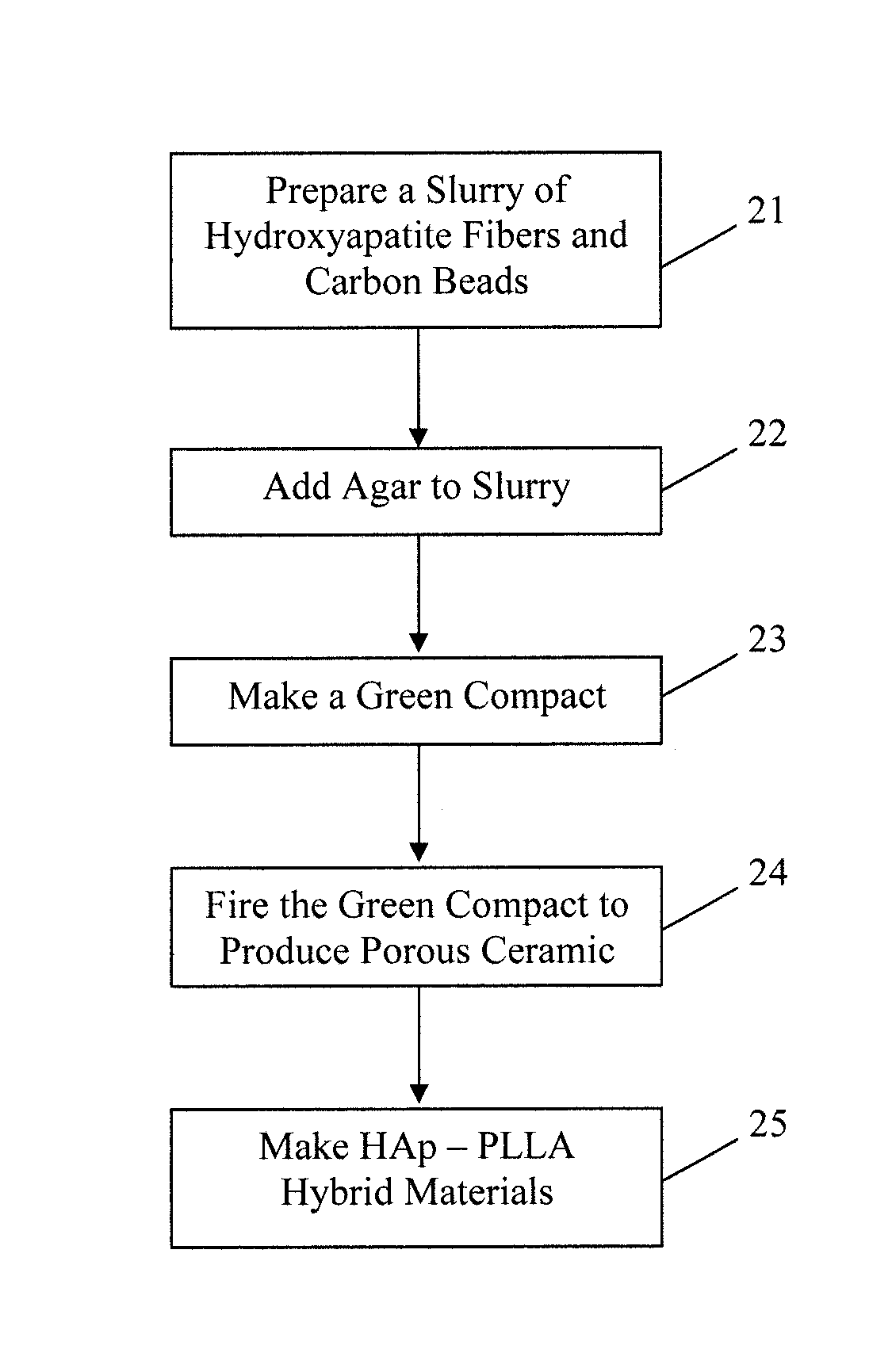
Biocompatible ceramic-polymer hybrids
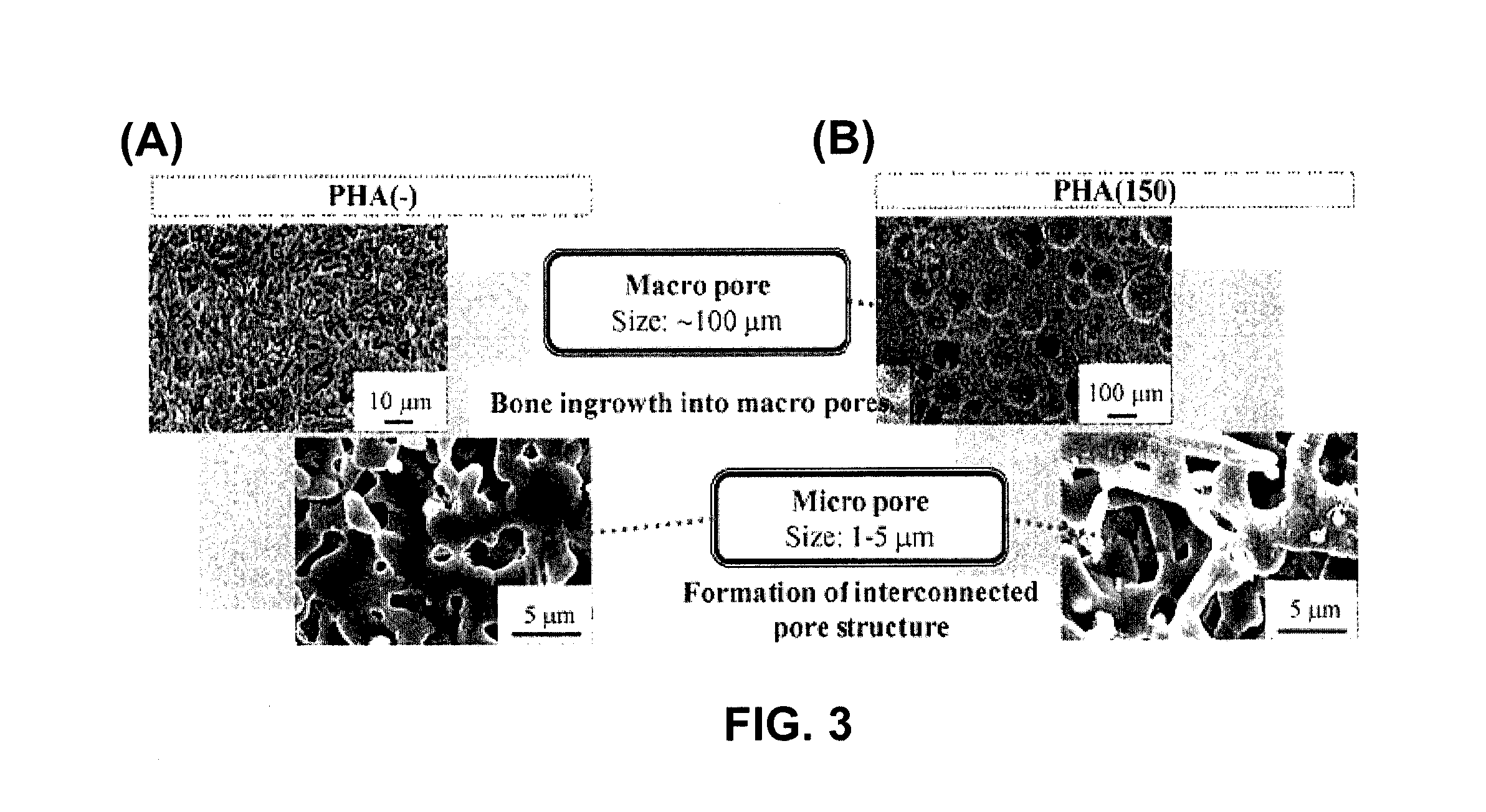
A hydroxyapatite ceramic hybrid material includes a hydroxyapatite ceramic structure having pores therein and a biodegradable polymer included in the pores in the hydroxyapatite ceramic structure. The biodegradable polymer can be a poly L-lactic acid polymer. A method for preparing a hydroxyapatite ceramic-biodegradable polymer hybrid material includes preparing a porous hydroxyapatite ceramic containing pores having an average pore diameter of 10 μm or larger; and forming a biodegradable polymer in the pores of the porous hydroxyapatite ceramic. The porous hydroxyapatite ceramic may be prepared by: preparing a slurry comprising hydroxyapatite fibers and heat-degradable particles in a selected solvent; filtering the slurry to obtain a paste; preparing a molded body using the paste; compacting the molded body to produce a green compact; and firing the green compact at a temperature at least 1000° C. to produce a porous hydroxyapatite ceramic structure.
Owner:SHOWA IKA KOHGYO
Oral matrix film and preparation method thereof
Owner:GUANGZHOU HONGJIAN BIOMEDICAL PROD TECH CO LTD
A kind of polyoxymethylene/polylactic acid SERS polymer substrate and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106498716BFast crystallization rateEffective control of apertureFibre typesRaman scatteringComposite filmRhodamine 6G
The invention discloses a polyoxymethylene / polylactic acid (POM / PLLA) SERS polymer substrate and its preparation method and use. The POM / PLLA SERS polymer substrate comprises a POM / PLLA composite film and metal nanoparticles carried by the surface of the POM / PLLA composite film. The POM / PLLA composite film has a micron-order spherocrystal structure. After an aminolysis reaction, the ring-banded spherulitic structure has nanoscale holes. The POM / PLLA melt blended film and an amino group modifier undergo a reaction so that an amino functional group is introduced and simultaneously, POM / PLLA blended film porous formation is realized. The POM / PLLA SERS polymer substrate can be used in rhodamine 6G and glucose detection. Compared with the existing detection limit, the sensitivity of the polymer substrate is high and the rhodamine 6G detection limit of the polymer substrate can reach 10-19mol / L.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Germ-repellent elastomer
The present invention provides a germ-repellent elastomer comprising: a base polymer selected from latex, synthetic rubber, thermoplastic elastomers, or copolymers or mixtures thereof; and at least one germ-repelling modifier selected from one or more polyethoxylated non-ionic surfactants such that a highly hydrophilic moiety is imparted from the at least one germ-repelling modifier to the base polymer either by physical or reaction extrusion.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Methods and Compositions for Preparing Particle Boards
ActiveUS20210023739A1Low viscosityReduce weightFlat articlesDomestic articlesPolymer scienceParticle board
An amorphous polylactic acid polymer having a weight average molecular weight in the range of about 35,000 to 180,000 is described. The polylactic acid polymer composition can be hammer milled without cryogenics result in the form of particles wherein 90% of the particles have particle size of about 250 μm or less and the material has a glass transition temperature of between about 55° C. to about 58° C. and a relative viscosity of about 1.45 to about 1.95 centipoise. The polymer composition can be used to form an aqueous suspension. The material is ideally suited for use in preparing particleboard. A method is disclosed for preparing such polylactic acid polymers. The method involves obtaining an amorphous polylactic acid polymer having a weight average molecular weight of between about 115,000 to about 180,000. Treating the polylactic acid polymer to reduce the molecular weight to between about 35,000 to 45,000 such that it has a glass transition temperature of between about 55° C. and 58° C. and a relative viscosity of about 1.45 to about 1.95. Material can be formed into particles in a commercial hammer mill with bypass such that 90% of the initial mass results in the particles which can pass thru a sieve having a pore size of about 250 μm. During particle board formation the temperature of around 140-140 C being reached to optimally activate the adhesive; Bond strengths and throughput rates of resulting particle boards can be controlled thereafter, with variable combination of particle sizes, adhesive loading and initial moisture content.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
High impact resistant poly(lactic acid) blends
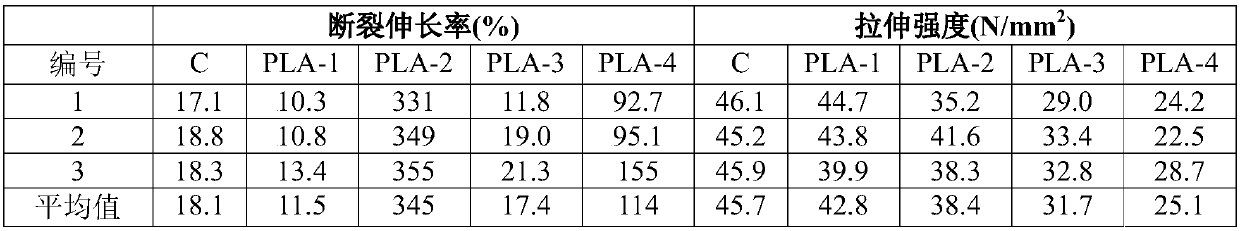
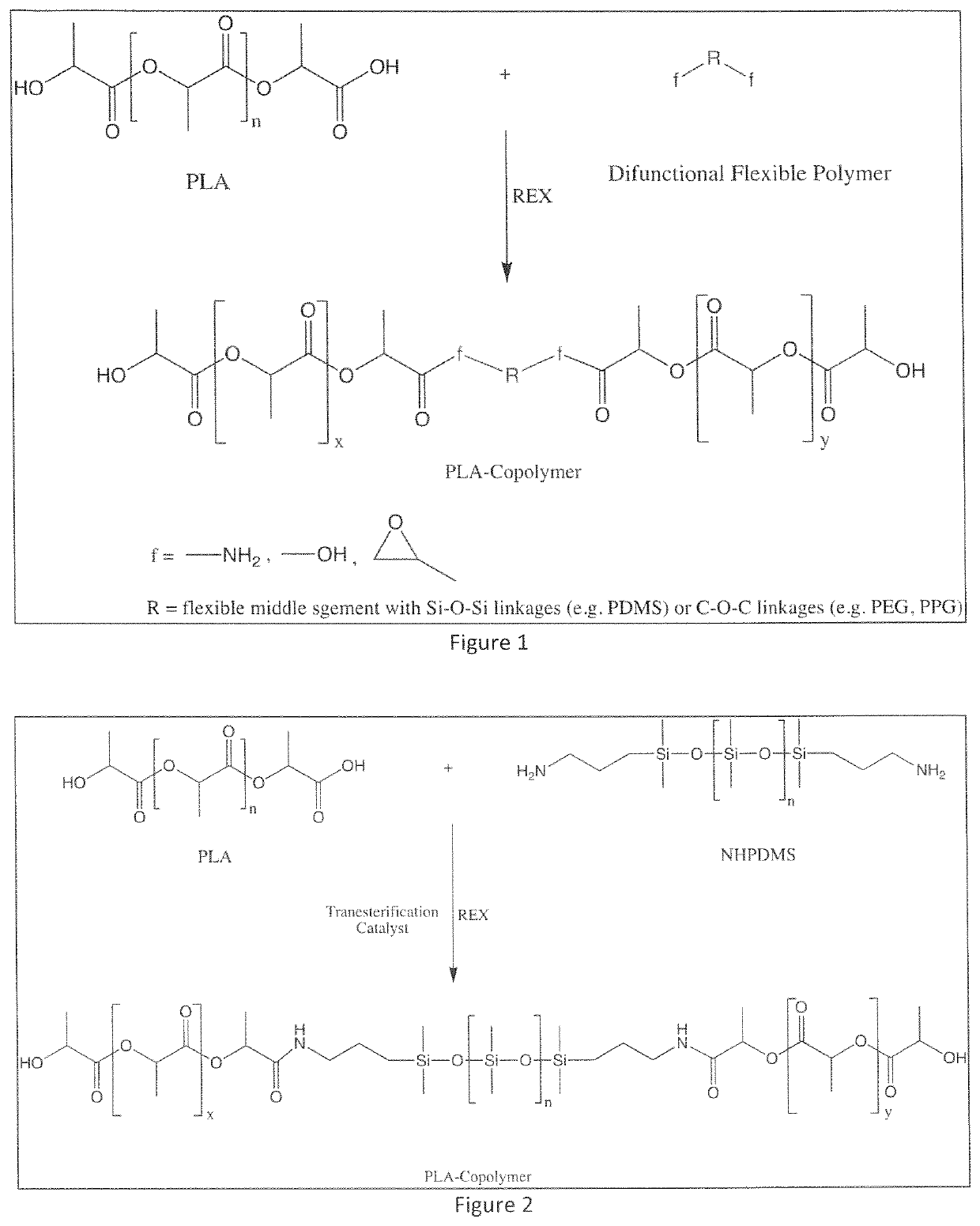
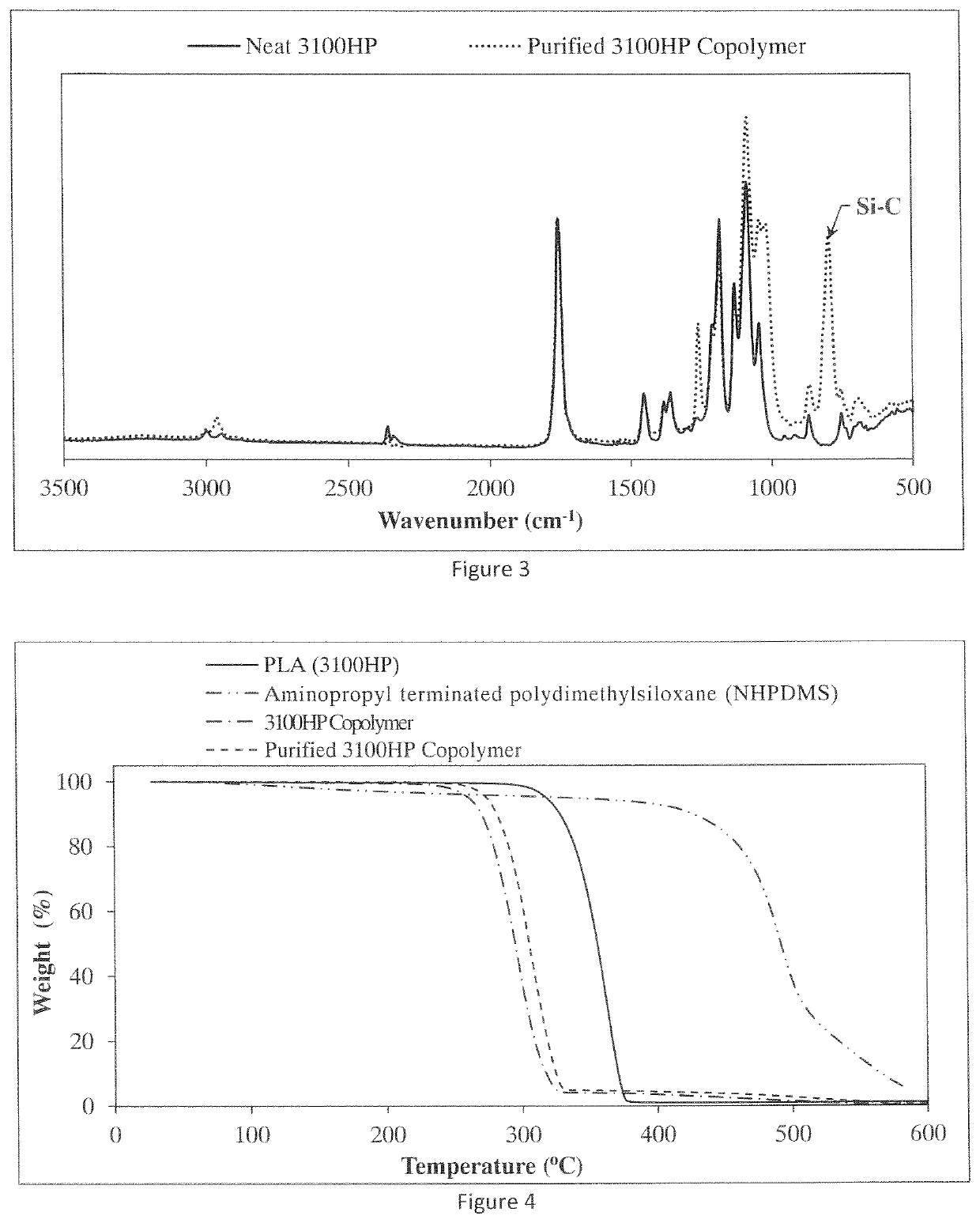
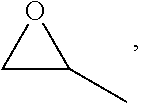
ActiveUS20210253849A1Eliminate separation stepImprove strength propertiesPolymer sciencePLLA polymer
The notched Izod impact toughness and tensile elongation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)-homopolymers are increased by about 2 to about 4 times by blending therewith a PLA-copolymer having a difunctional flexible middle segment such as a polysiloxane or a polyether from about 0.6 wt. % to about 20 wt. %. The PLA-homopolymer-PLA-copolymer blend having a difunctional flexible polymer from about 0.5 wt. % to about 10 wt. % is thermally annealed to provide impact toughness of at least about 5 kJ / m2 and tensile elongation of greater than 12%. This exceptional improvement observed in the PLA blend is a synergistic effect of the addition of the difunctional flexible polymer of the copolymer and thermal annealing. The improvement observed in the mechanical properties with high PLA homopolymer content above about 90 to about 98 wt. % is unusual and results in an increased scope of molding and thermoforming applications. The annealed PLA-copolymers having a difunctional flexible middle segment have also been found to have improved notched Izod impact properties.
Owner:NORTHERN TECH INT CORP
Methods and compositions for preparing particle boards
ActiveUS10843372B1Reduce molecular weightDegrade moleculeLayered productsFlat articlesPolymer scienceRelative viscosity
An amorphous polylactic acid polymer having a weight average molecular weight in the range of about 35,000 to 180,000 is described. The polylactic acid polymer composition can be hammer milled without cryogenics result in the form of particles wherein 90% of the particles have particle size of about 250 μm or less and the material has a glass transition temperature of between about 55° C. to about 58° C. and a relative viscosity of about 1.45 to about 1.95 centipoise.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com