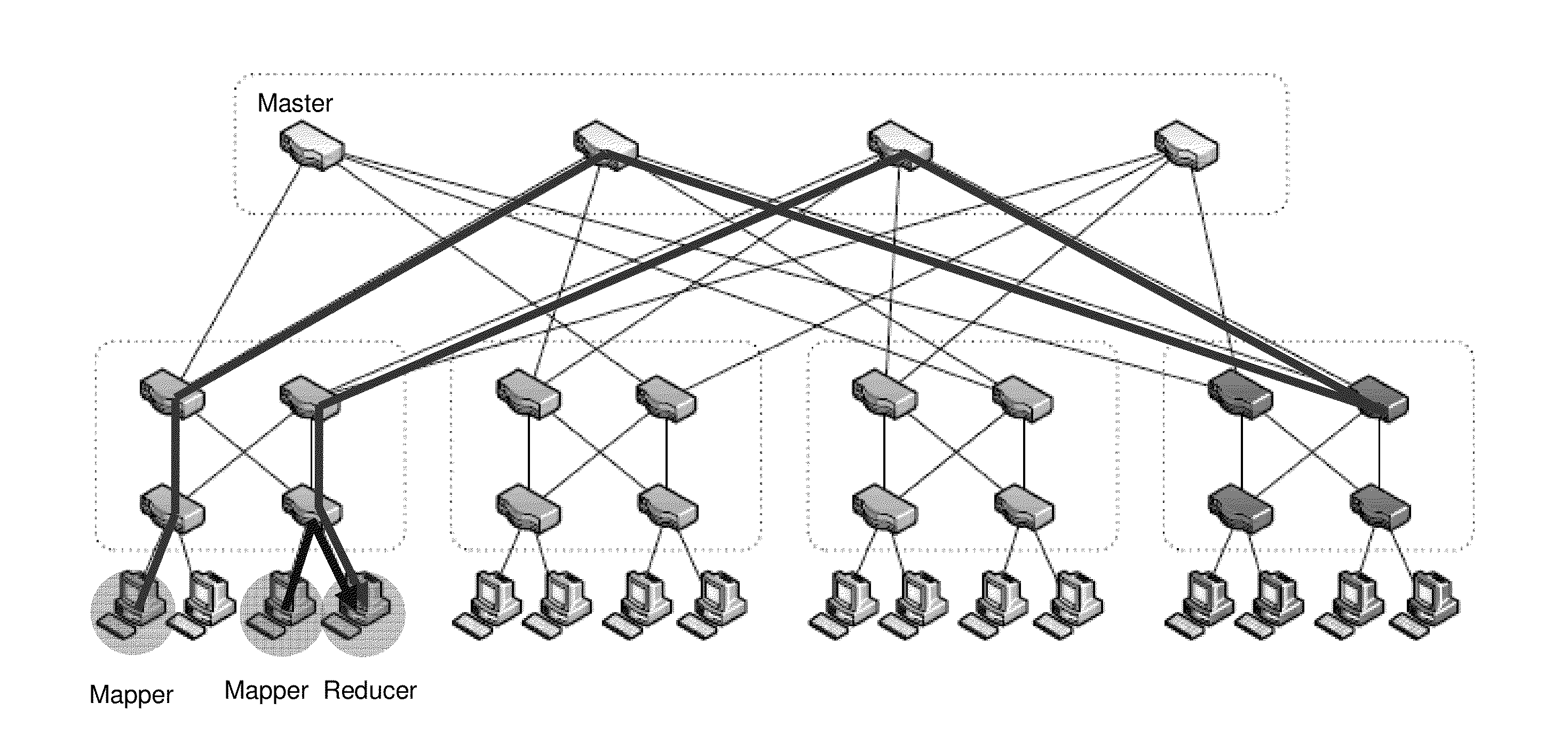
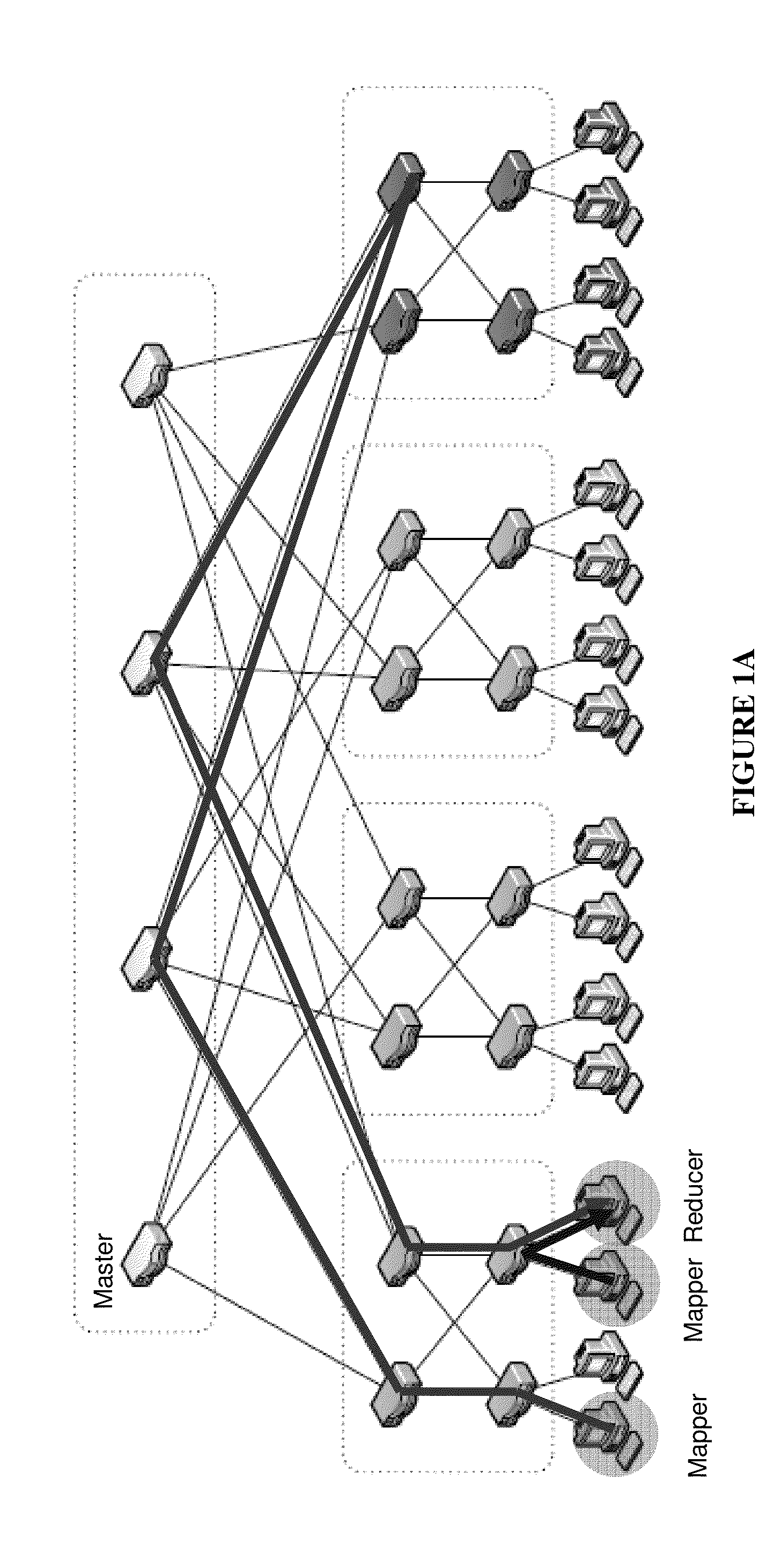
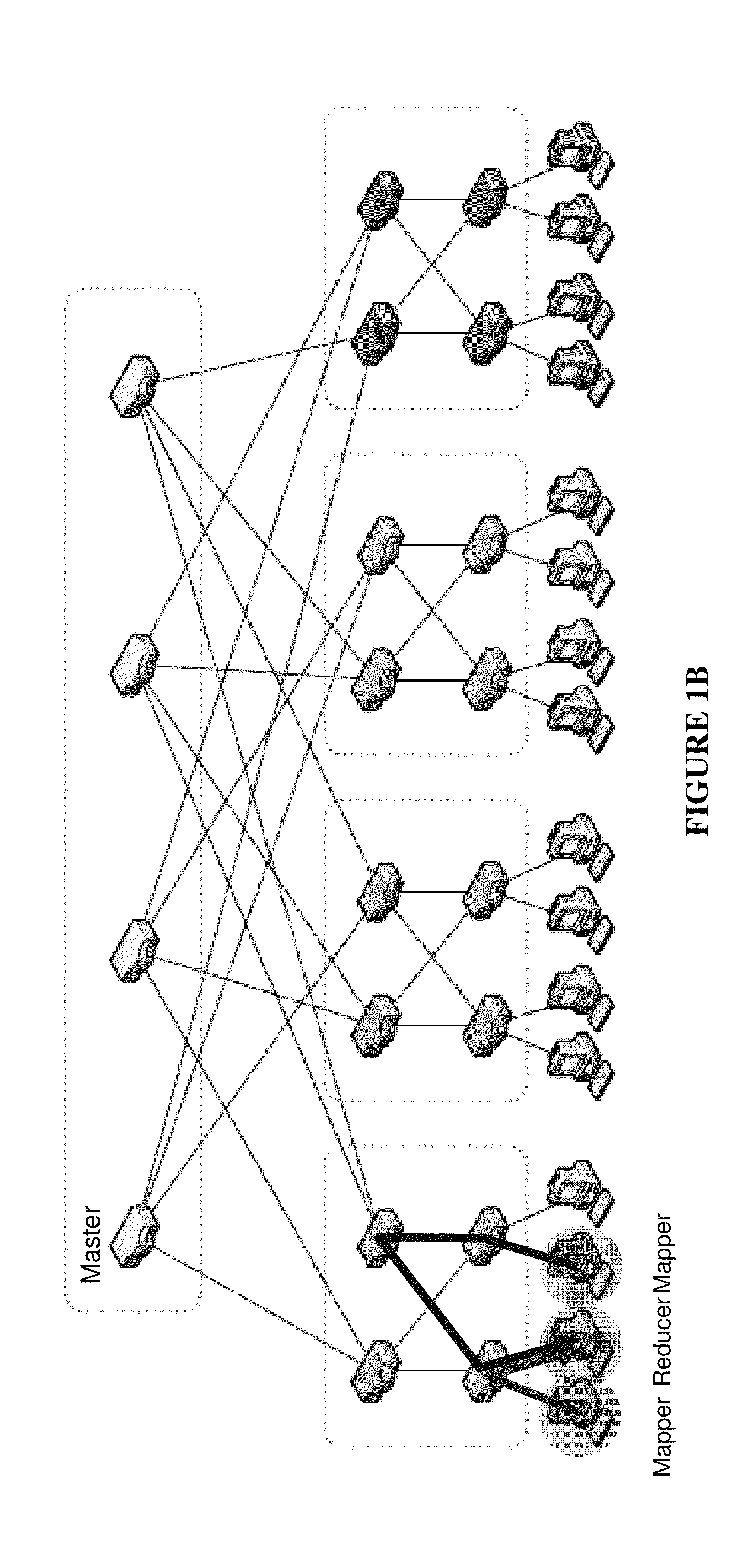
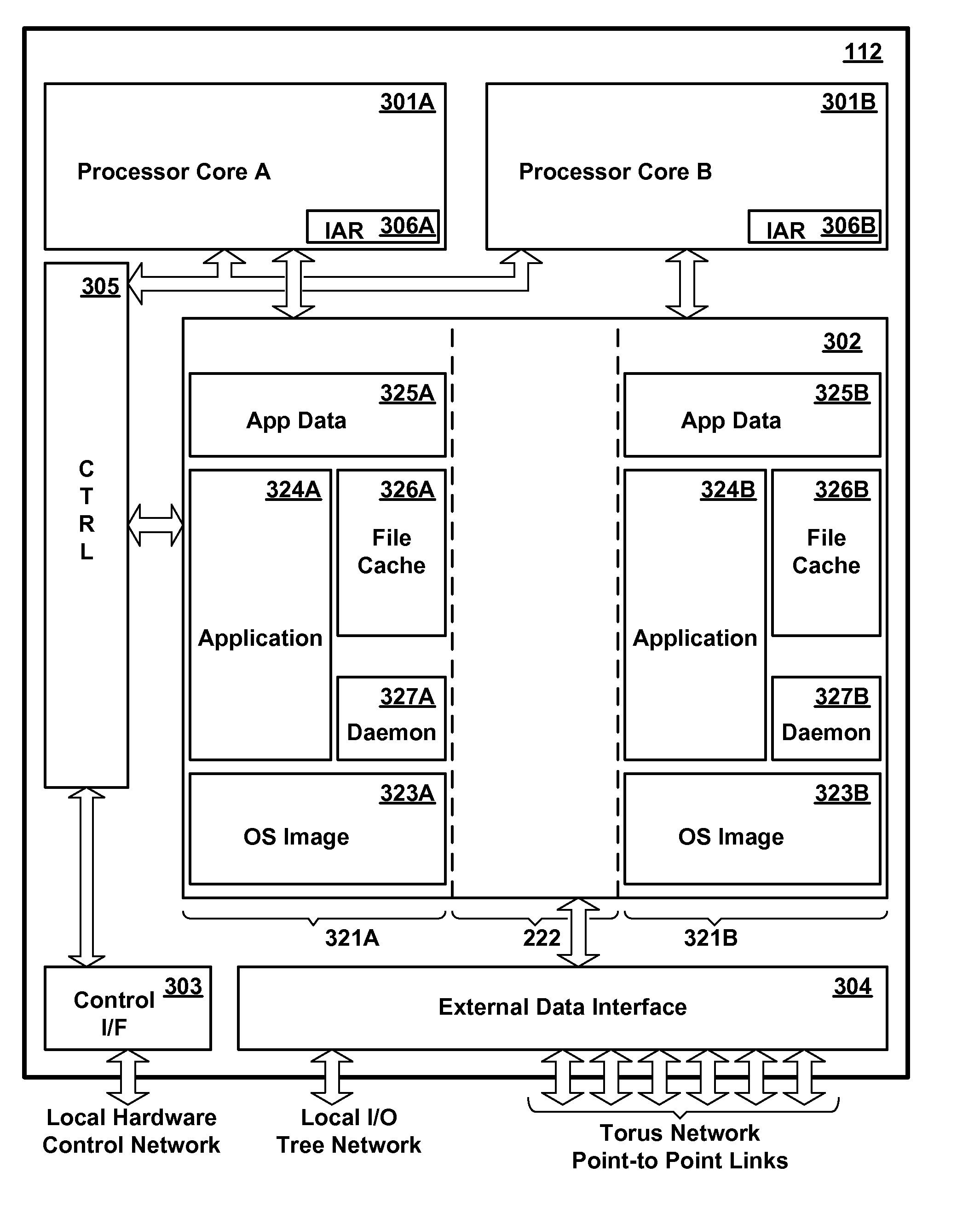
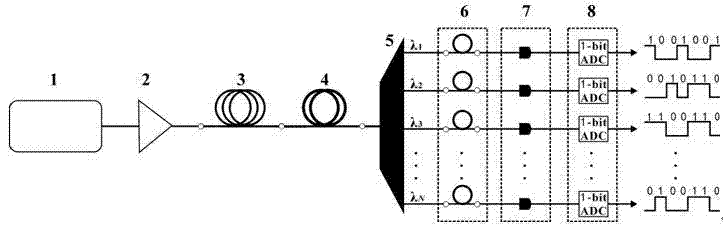
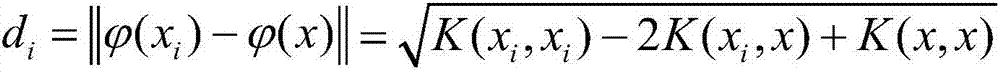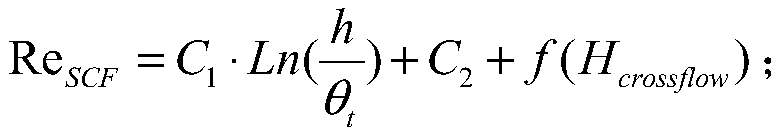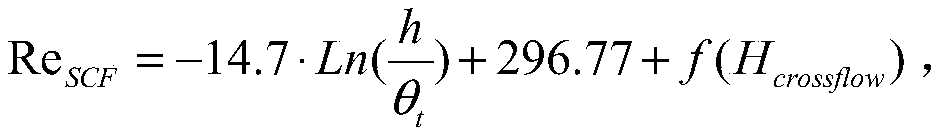Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Massively parallel computation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
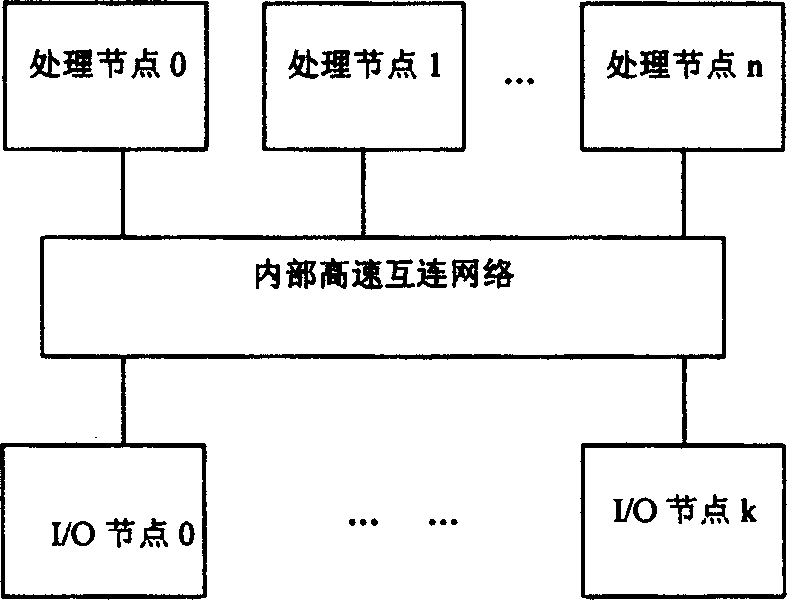
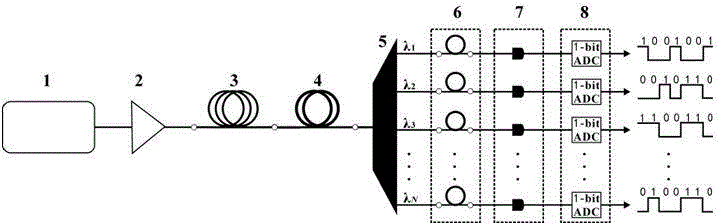
In computing, massively parallel refers to the use of a large number of processors (or separate computers) to perform a set of coordinated computations in parallel (simultaneously). In one approach, e.g., in grid computing the processing power of a large number of computers in distributed, diverse administrative domains, is opportunistically used whenever a computer is available.
Method and system of network transfer adaptive optimization in large-scale parallel computing system
ActiveUS20130144973A1Separate controlLittle overheadError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsAdaptive optimizationMassively parallel computation
A method and system for performing network transfer adaptive optimization in a large-scale parallel computing system. The method of network transfer adaptive optimization includes forming a message to be transferred through the network based on obtained information related to a task executed by computing nodes, wherein the message includes identification information of the computing nodes to perform data transfer and corresponding sink nodes, and an amount of data the computing nodes to transfer to the corresponding sink nodes; transferring the message to a network layer; and forming a new data transfer pattern for data transfer between the computing nodes and the corresponding sink nodes in accordance with the received message.
Owner:IBM CORP
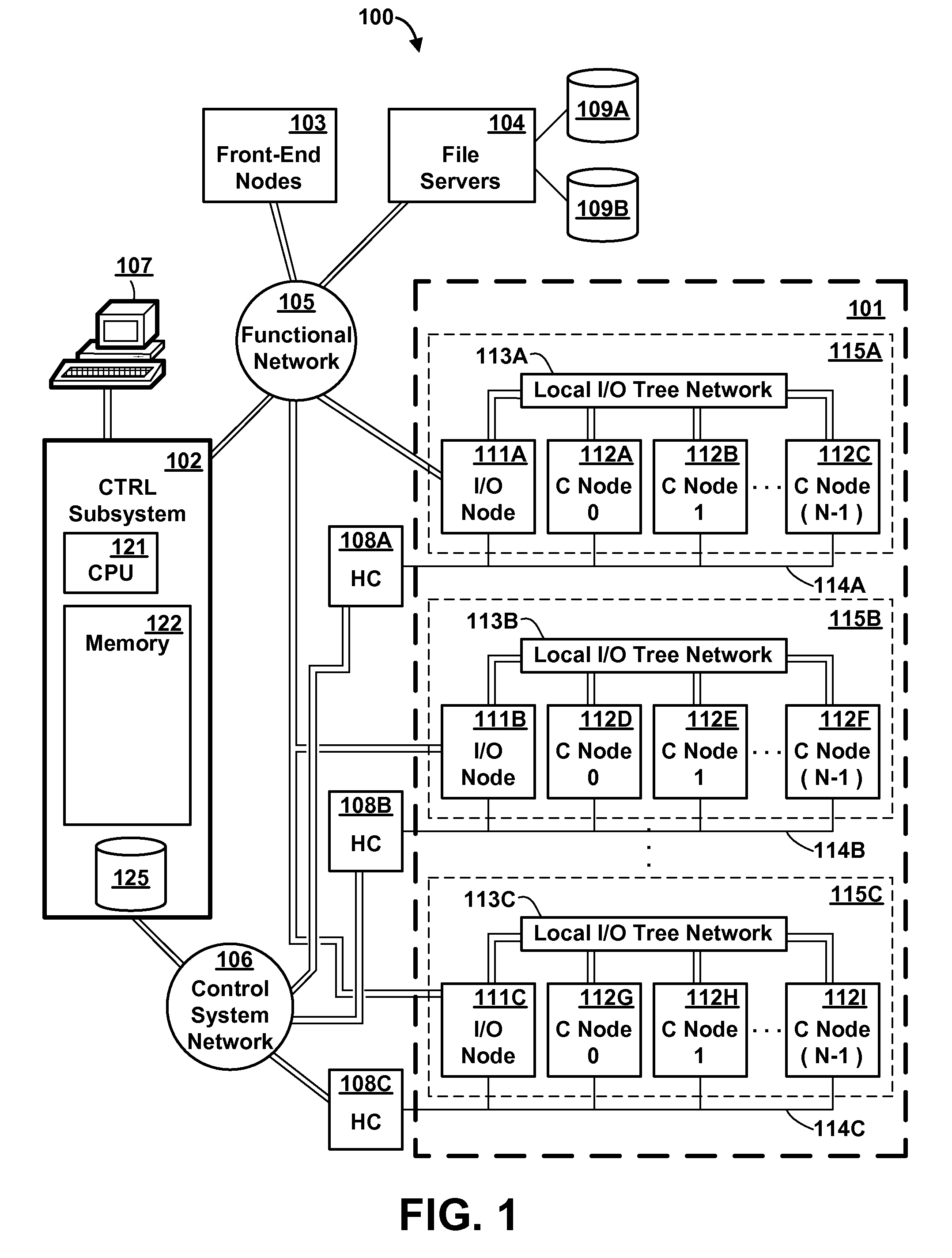
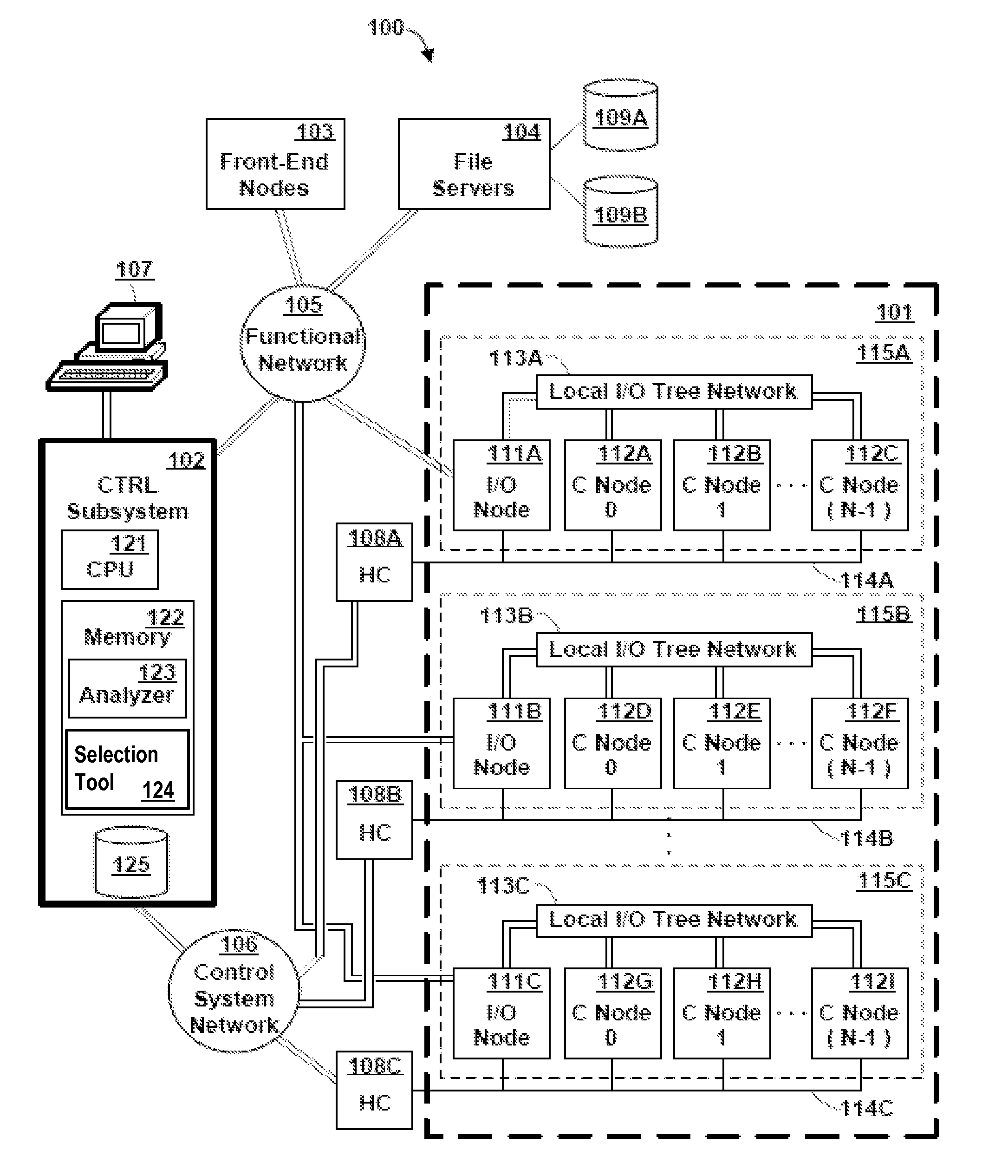
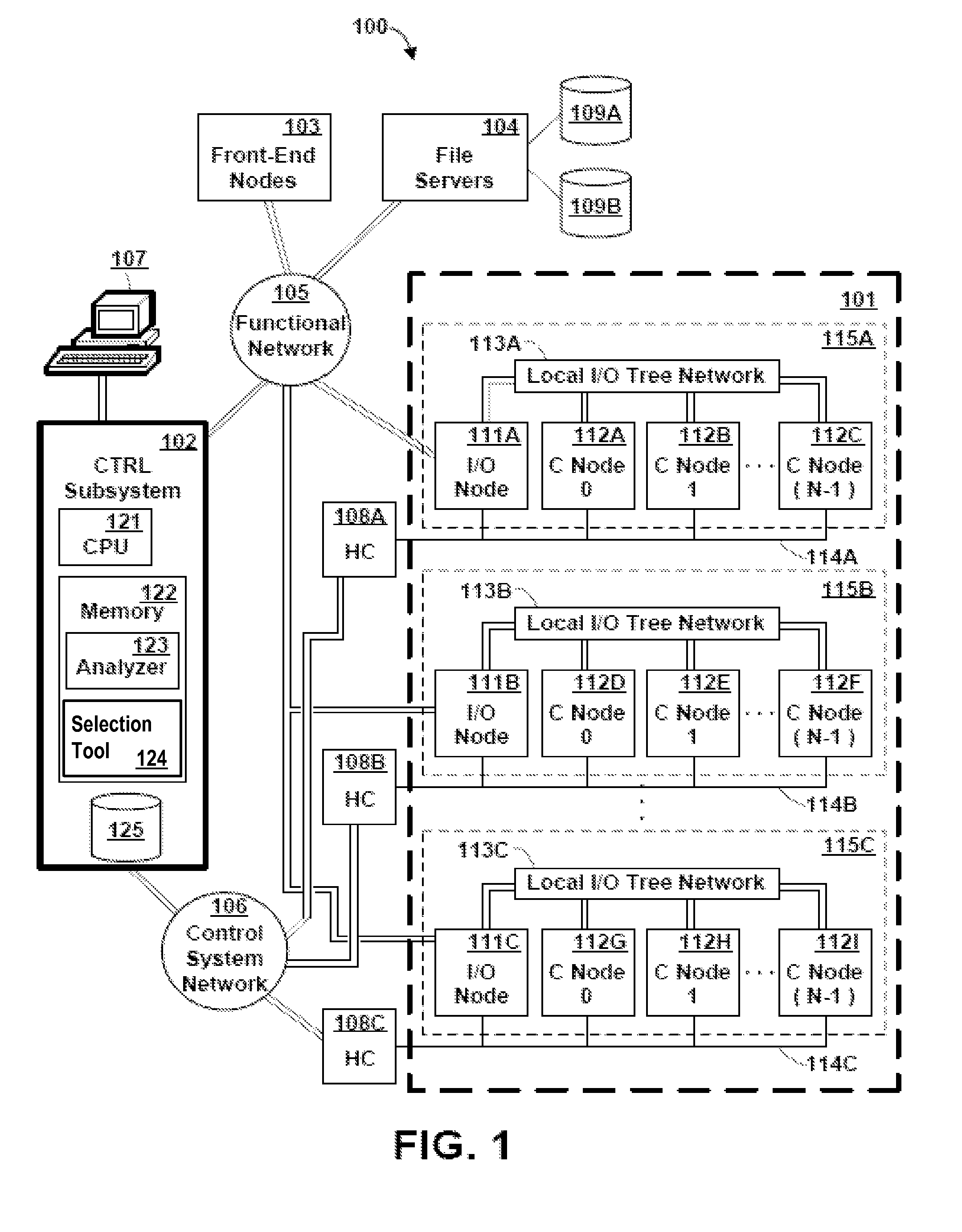
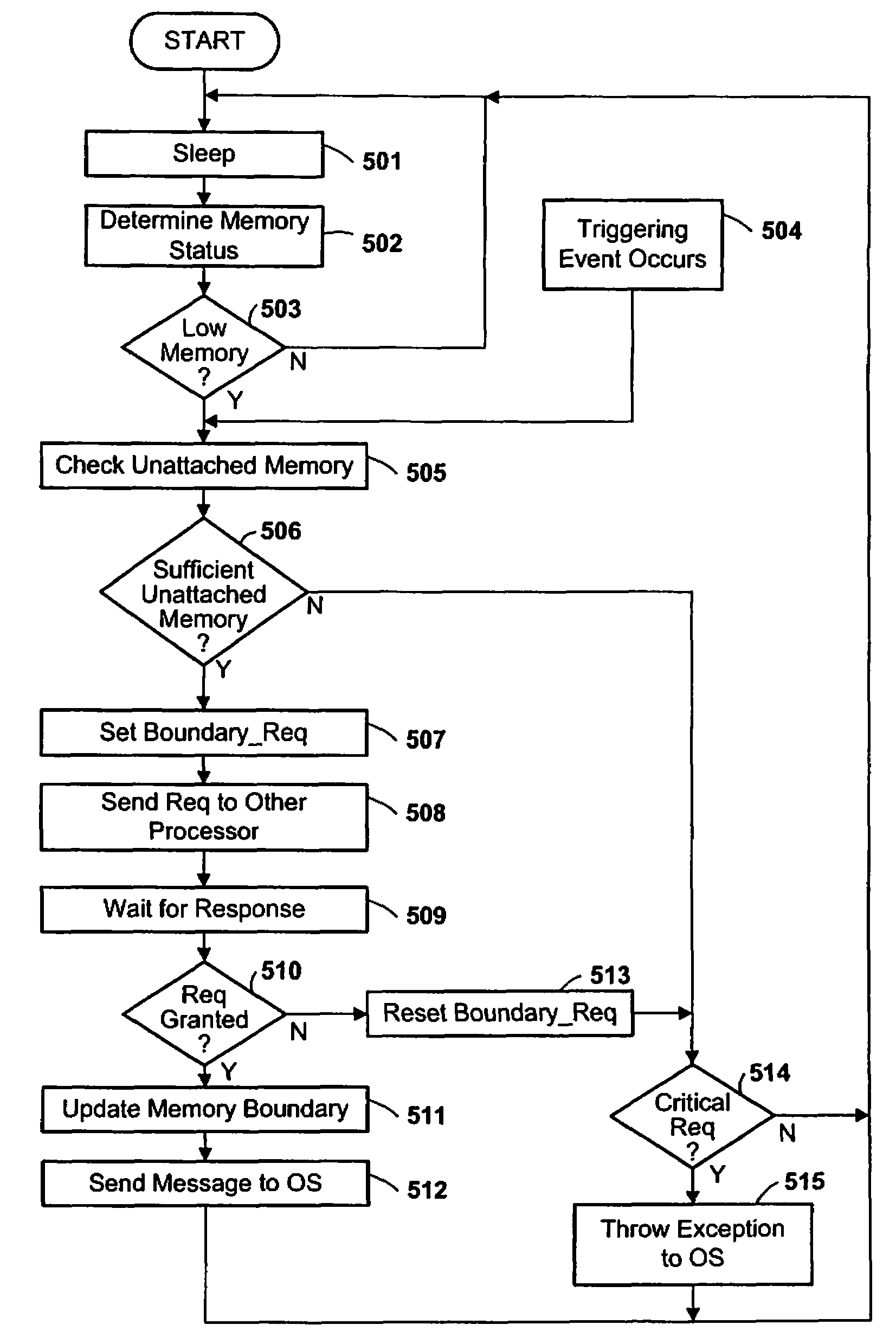
Memory Request/Grant Daemons in Virtual Nodes for Moving Subdivided Local Memory Space from VN to VN in Nodes of a Massively Parallel Computer System
InactiveUS20080270731A1Little overhead to implementEfficient use ofMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerComputer architectureEngineering
A memory management mechanism a nodal having multiple processors in a massively parallel computer system dynamically configures nodal memory on demand. A respective variable-sized subdivision of nodal memory is associated with each processor in the node. A processor may request additional memory, and the other processor(s) may grant or veto the request. If granted, the requested memory is added to the subdivision of the requesting processor. A processor can only access memory within its own subdivision. Preferably, each subdivision contains a daemon which monitors memory usage and generates requests for additional memory.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Analysis and selection of optimal function implementations in massively parallel computer
InactiveUS7954095B2Error preventionTransmission systemsParallel computingMassively parallel computation
An apparatus, program product and method optimize the operation of a parallel computer system by, in part, collecting performance data for a set of implementations of a function capable of being executed on the parallel computer system based upon the execution of the set of implementations under varying input parameters in a plurality of input dimensions. The collected performance data may be used to generate selection program code that is configured to call selected implementations of the function in response to a call to the function under varying input parameters. The collected performance data may be used to perform more detailed analysis to ascertain the comparative performance of the set of implementations of the function under the varying input parameters.
Owner:IBM CORP
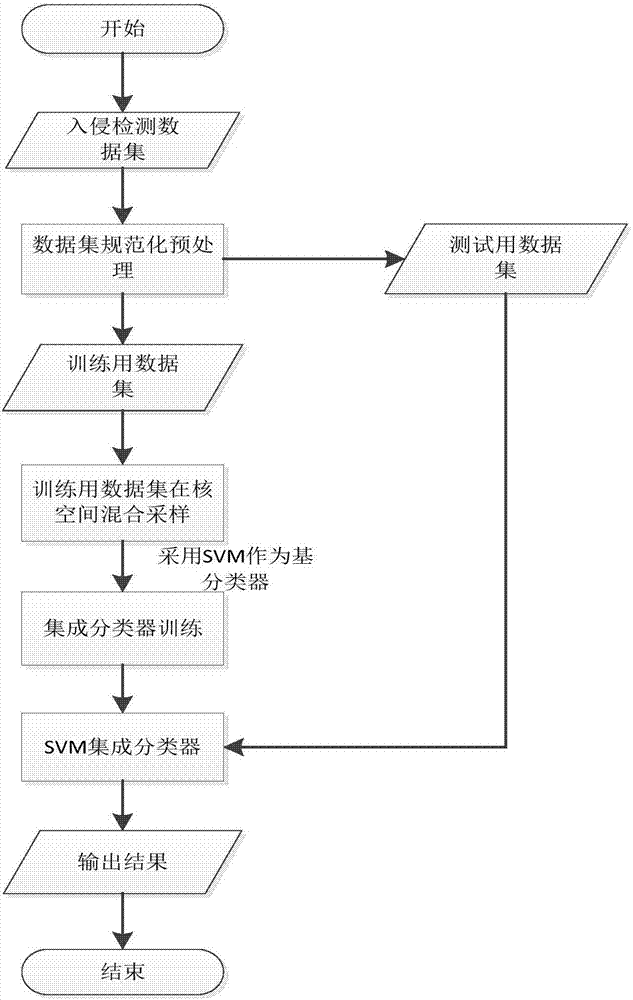
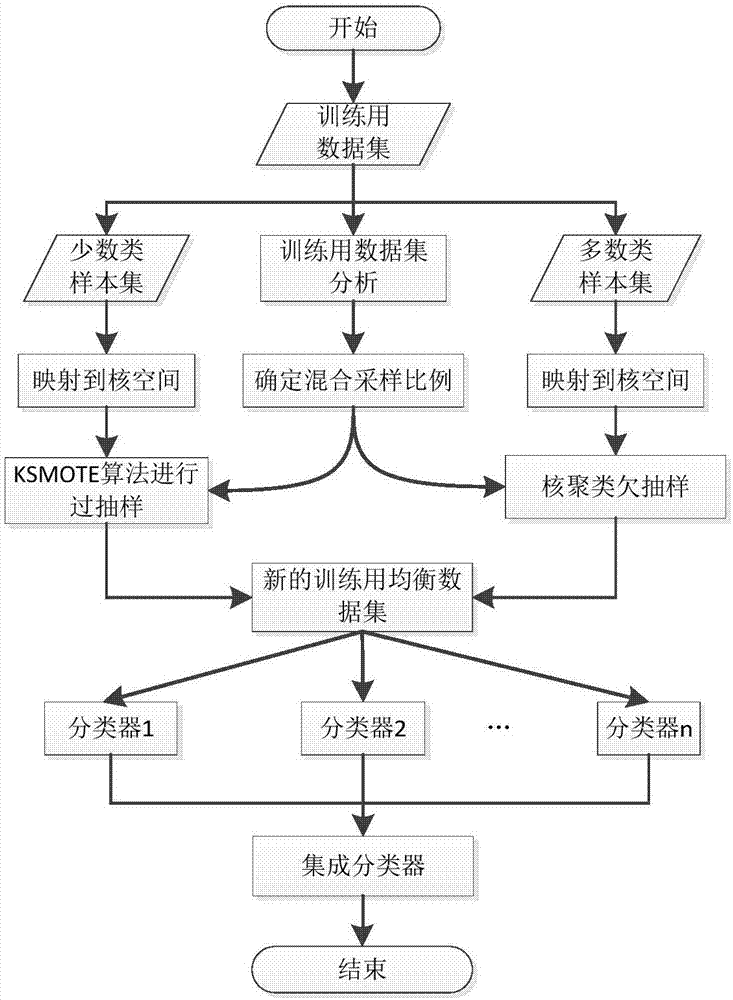
Classification method applicable for intrusion detection
The invention discloses a classification method applicable for intrusion detection. The method is characterized in that according to the characteristics of the SVM classification algorithm that the sensitivity to unbalanced classes of data sets is high and classification is carried out in a kernel space, through a mixed sampling mode, in which oversampling based on kernel SMOTE is carried out on minority sample sets in training sample sets, and undersampling based on kernel fuzzy C-means clustering is carried out on majority sample sets in the training sample sets, a balancing preprocessing of the unbalanced training data sets is achieved; and training is then carried out newly obtained training sample sets through the Bagging ensemble learning method to obtain an SVM-based ensemble classifier. The method has the advantages that a model obtained through the training can effectively solve the defects of unsatisfactory intrusion data identification effects and a high misjudgment rate for normal data of the traditional SVM intrusion detection model, and the adopted Bagging ensemble algorithm is applicable for large-scale parallel computing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
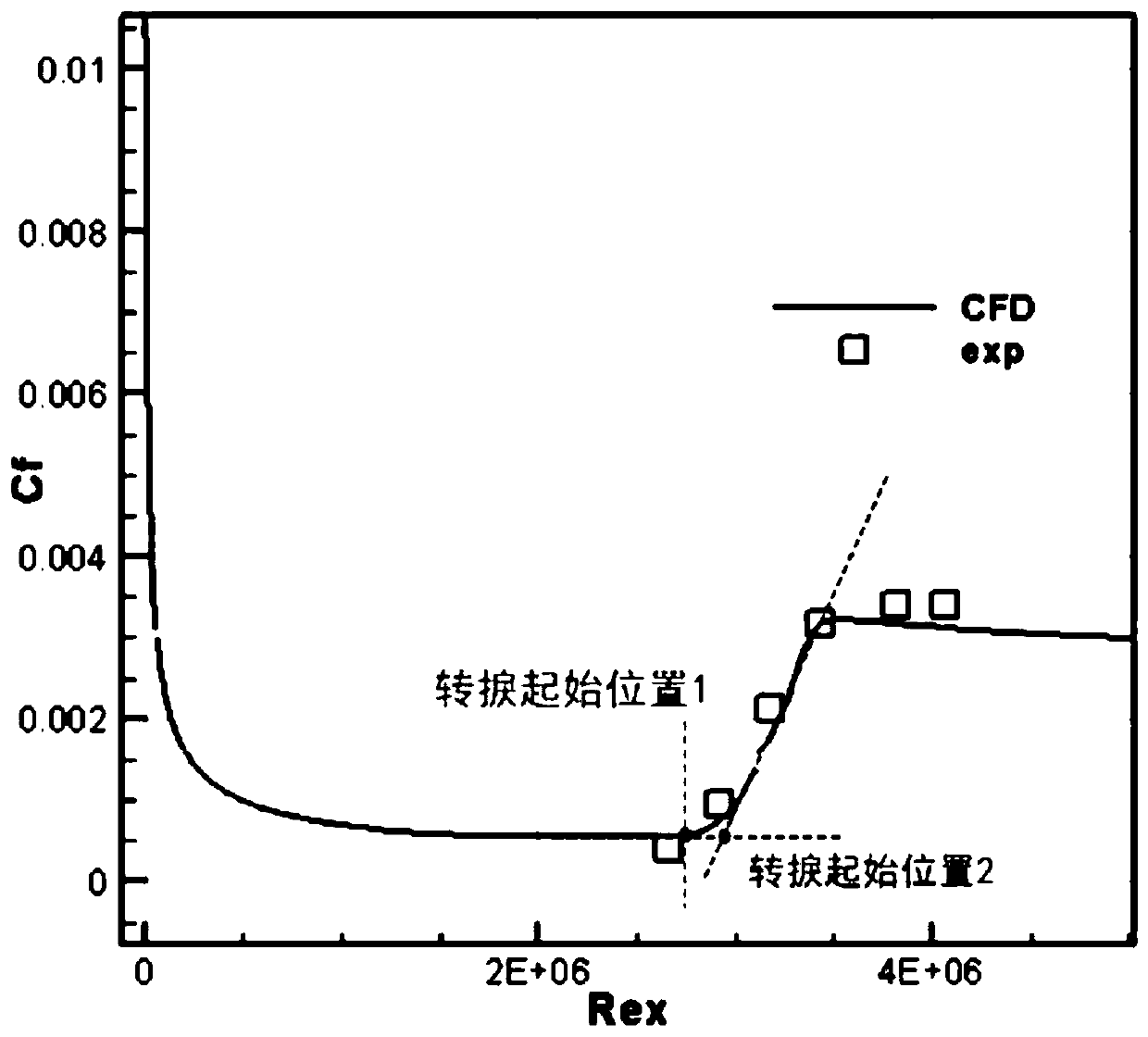
Hypersonic transverse flow transition prediction method considering surface roughness effect
ActiveCN110702356AFully localizedAerodynamic testingDesign optimisation/simulationMassively parallel computationLeast squares
The invention discloses a hypersonic transverse flow transition prediction method considering a surface roughness effect. The hypersonic transverse flow transition prediction method is based on the fact that a critical transverse flow Reynolds number and surface roughness meet a logarithmic relationship, and based on hypersonic wind tunnel experimental data, transition critical momentum thicknessReynolds numbers of different roughness under a hypersonic condition are obtained through CFD layer solution, a least square method is adopted to solve a relation coefficient, a criterion relational expression is obtained, and prediction of transverse flow transition is achieved by adding a transverse flow source item DSCF into an existing gamma-Retheta t transition model momentum thickness transport equation. Due to the fact that a gamma-Retheta t transition model is a localization model, the transverse flow criterion ReSCF is obtained through iteration, the momentum thickness Reynolds numberdoes not need to be solved through integration, and localization is achieved. Therefore, the method does not relate to calculation or calling of non-local amount, the prediction technology achieves complete localization, and the method is suitable for large-scale parallel calculation.
Owner:AERODYNAMICS NAT KEY LAB
Parallel computation dispatch method in heterogeneous environment
ActiveCN103500123AGood technical effectImprove resource utilizationResource allocationArray data structureResource utilization
The invention relates to the field of parallel computation, and discloses a parallel computation dispatch method in the heterogeneous environment. According to the method, a plurality of JVM task slots having different internal storages, and idle task slot sets are built, tasks in the parallel computation are divided into I / O intensities and CPU intensities, the tasks are appointed to suitable task slots for calculation, and parallel calculation efficiency in the heterogeneous environment is optimized. The parallel computation dispatch method has the advantages that the sizes and the types of the internal storages required by the tasks are determined dynamically, resource using efficiency of heterogeneous clusters is improved, total operation time of the parallel calculation work is shortened, and the situation that the internal storages overflow in a task operation process is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Large-scale parallel computer system sectionalized parallel starting method
InactiveCN1664784AImprove start-up efficiencyReduce startup timeProgram loading/initiatingStart timeComputerized system
This invention discloses a large scale parallel computer system sectionalizing starting method for solving the technology problem of how to reducing starting time based on large scale of parallel computer system with CC_NUMA structure. Technology project is characterized by the following steps: dividing all nodes into groups, setting a sort of node controller to control them to choose BSP in parallel and by stages in Firmware and their initialization and allocation, including three steps of start namely choosing BSP, LBSP and GBSP. The invention has the advantages of reducing system starting time, improving system usability and getting conducive to expanding the system structure.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
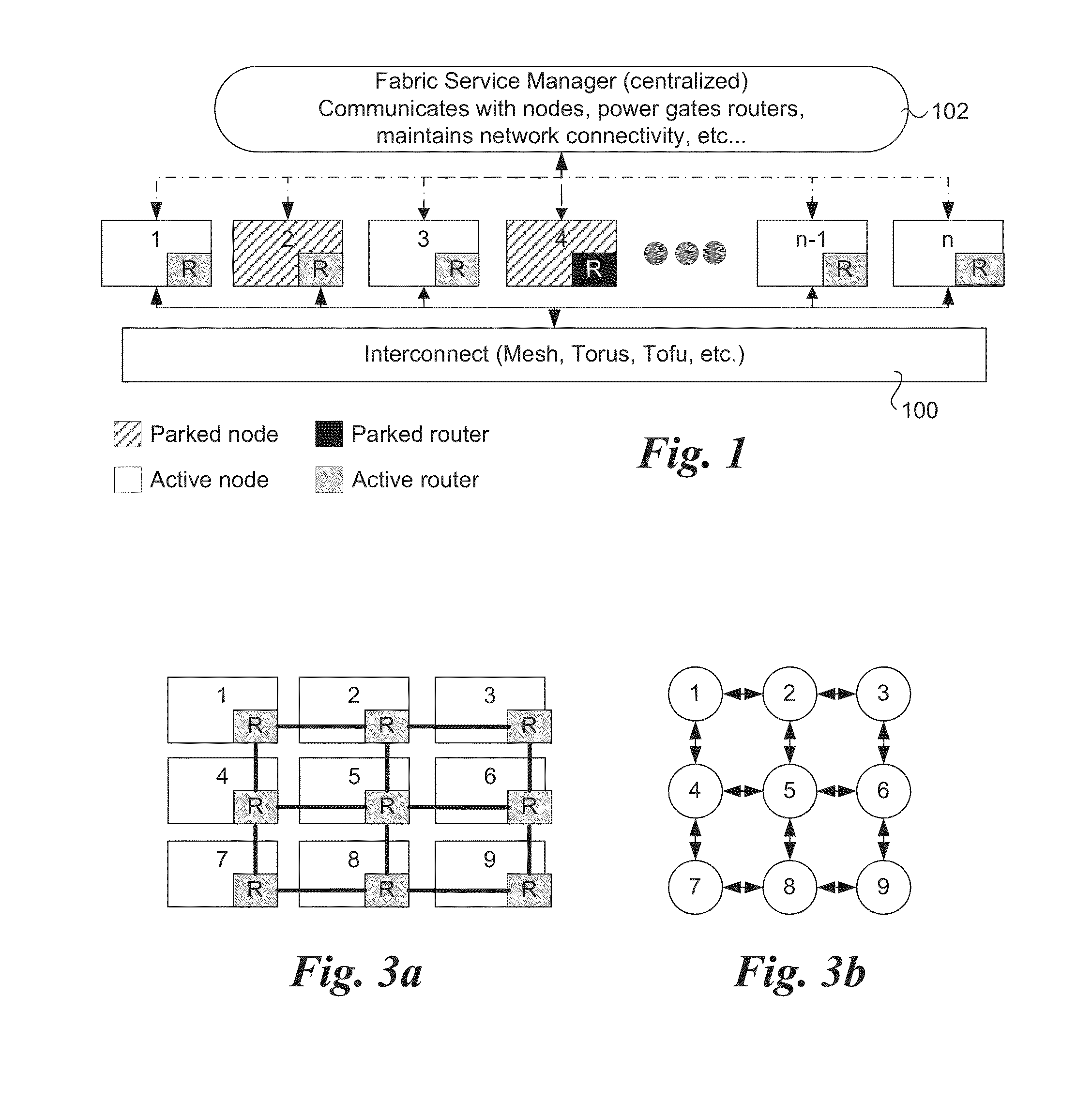
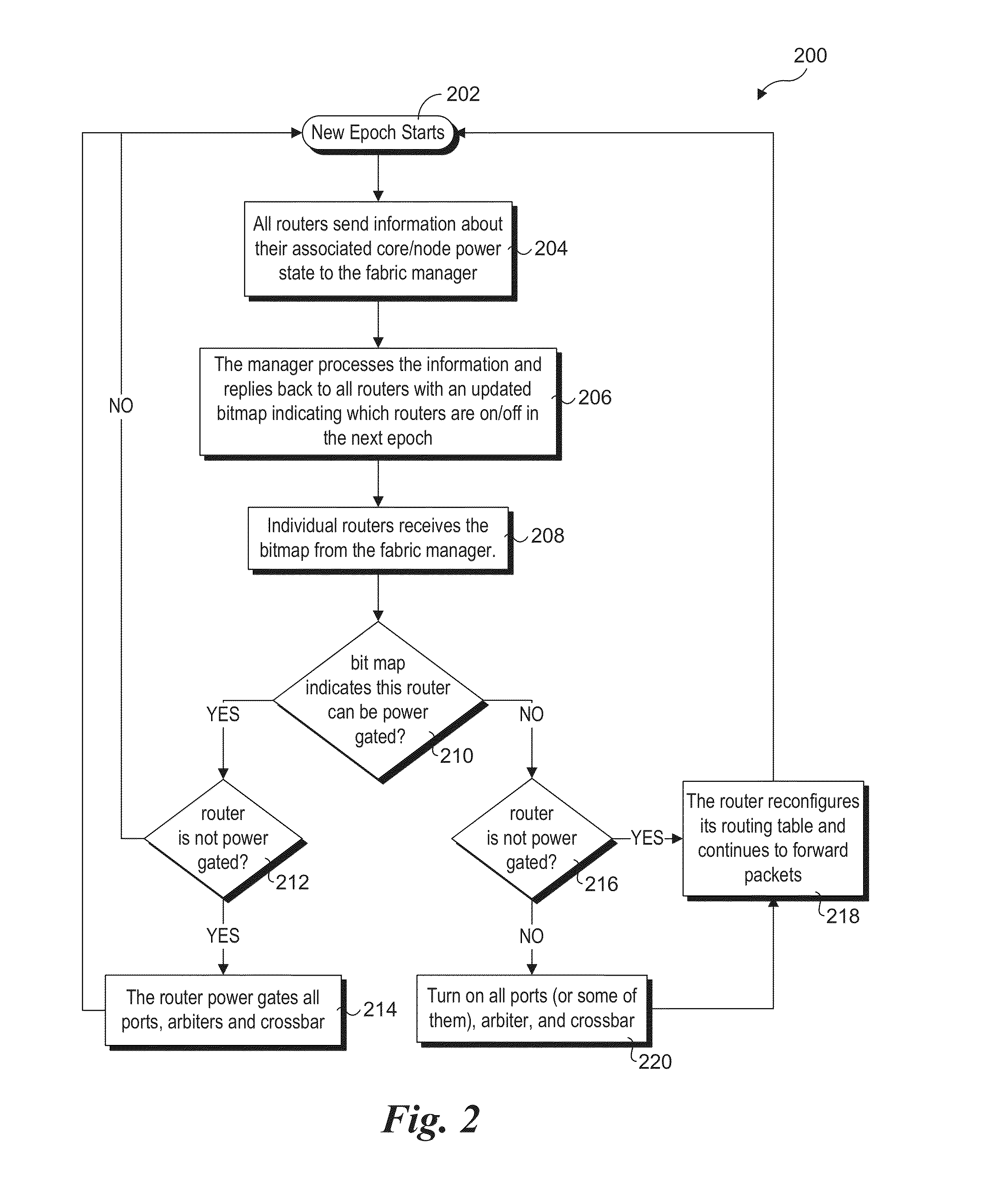
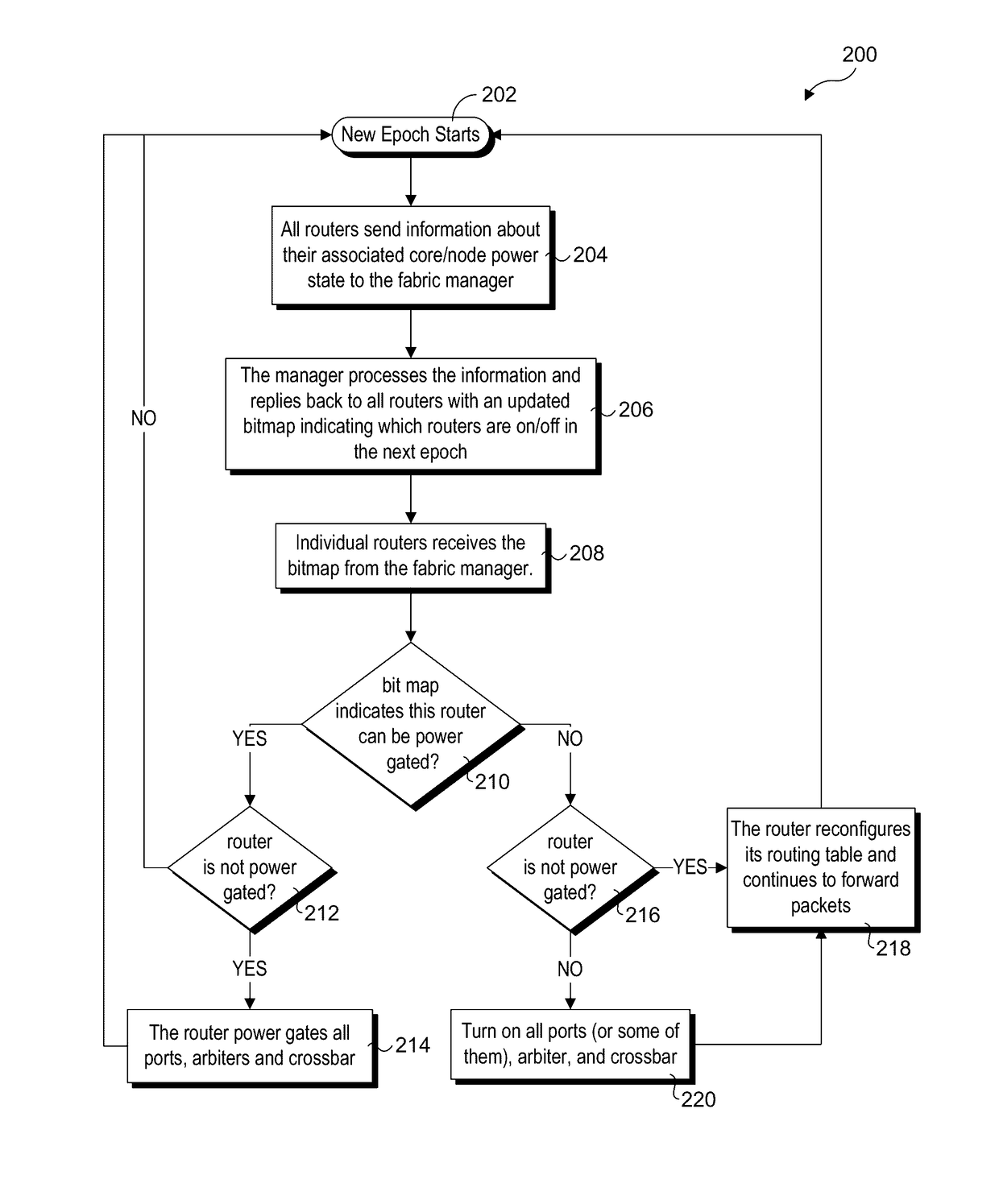
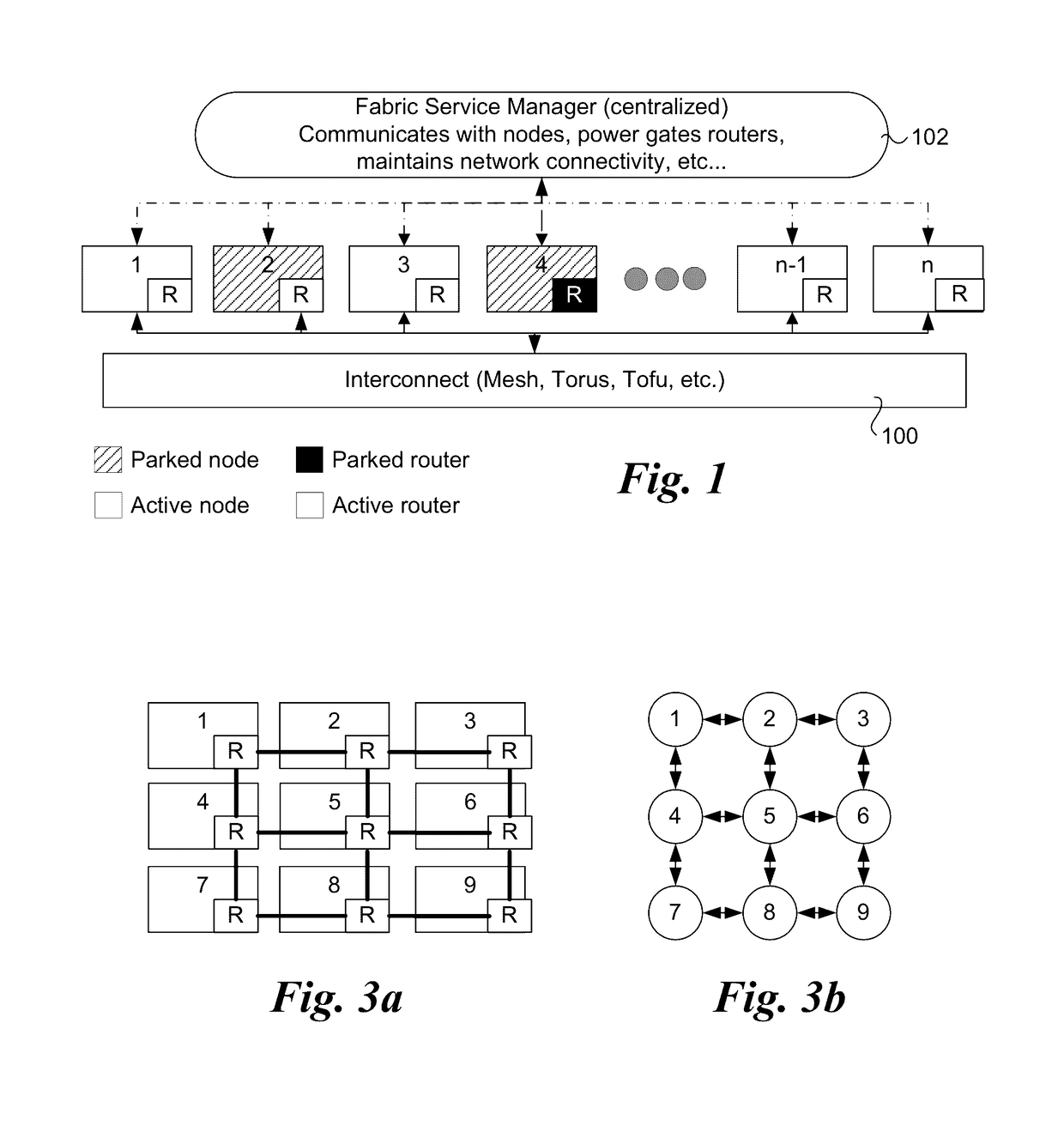
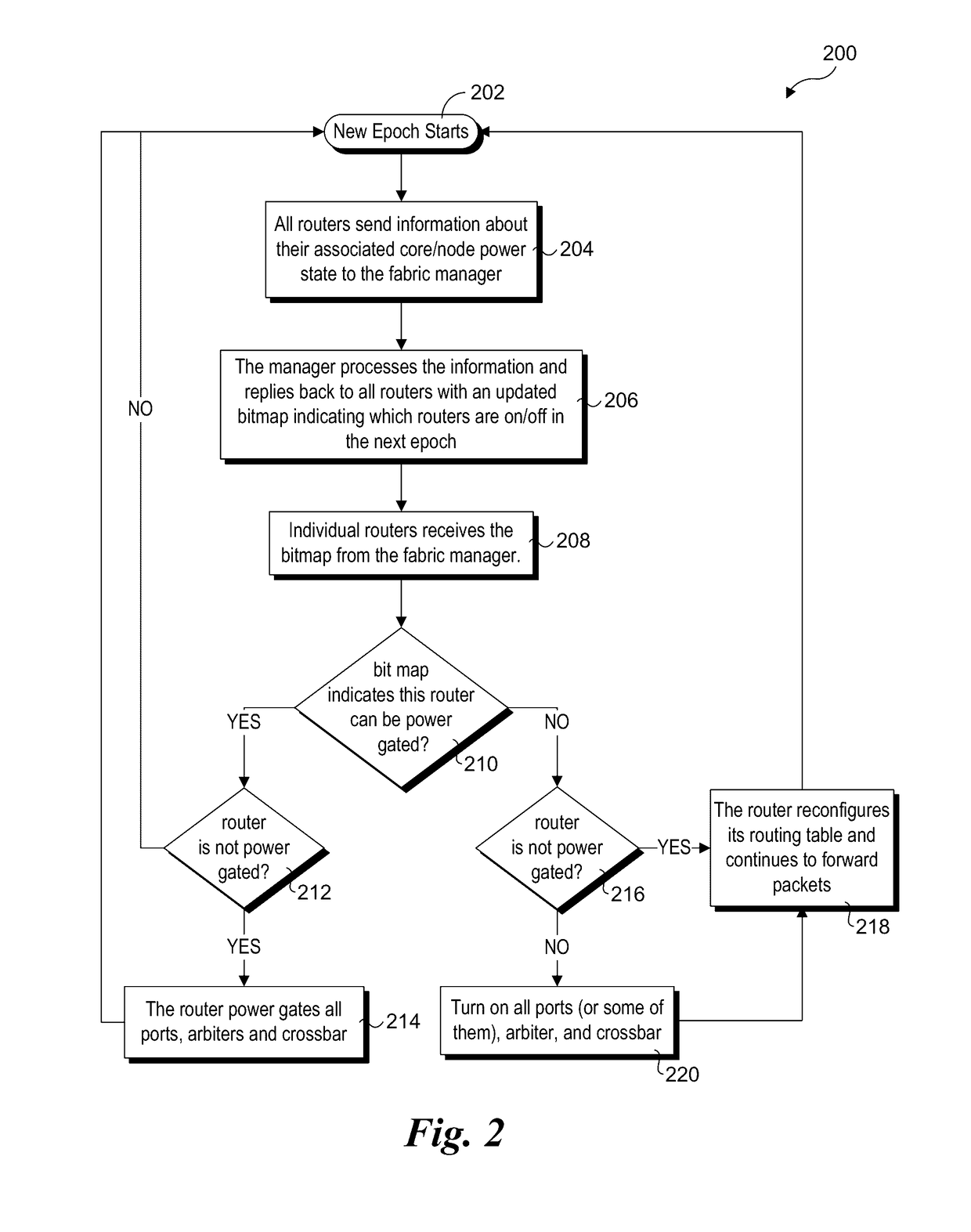
Router parking in power-efficient interconnect architectures
ActiveUS20140149766A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingQuality of servicePower efficient
A method and apparatus for selectively parking routers used for routing traffic in mesh interconnects. Various router parking (RP) algorithms are disclosed, including an aggressive RP algorithm where a minimum number of routers are kept active to ensure adequate network connectivity between active nodes and / or intercommunicating nodes, leading to a maximum reduction in static power consumption, and a conservative RP algorithm that favors network latency considerations over static power consumption while also reducing power. An adaptive RP algorithm is also disclosed that implements aspects of the aggressive and conservative RP algorithms to balance power consumption and latency considerations in response to ongoing node utilization and associated traffic. The techniques may be implemented in internal network structures, such as for single chip computers, as well as external network structures, such as computing clusters and massively parallel computer architectures. Performance modeling has demonstrated substantial power reduction may be obtained using the router parking techniques while maintaining Quality of Service performance objectives.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Thermal-expandability three-dimensional parallel cooling integration method, namely, on-chip system key technology for massively parallel computation
InactiveCN102243668ASignificant thermal scalabilityIncrease the amount of squareSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMassively parallel computationThermal expansion
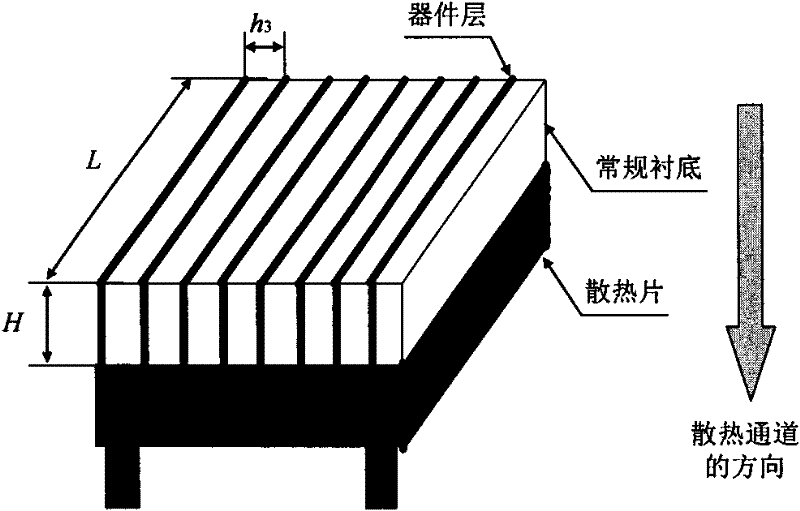
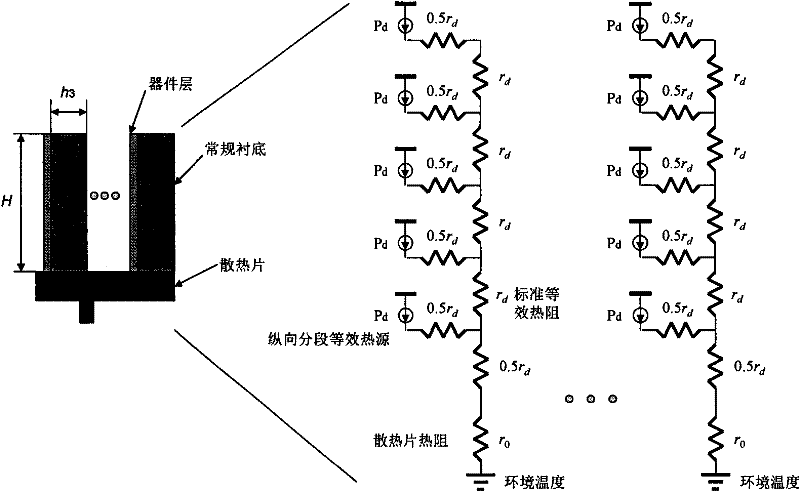
The invention belongs to the field of integrated circuit design, and in particular relates to a thermal-expandability three-dimensional parallel cooling integration method. The three-dimensional vertical integration technology proposed at present has disability in thermal expansion. The invention provides a thermal-expandability three-dimensional parallel cooling integration method. In the figure 1 described in the specification, all device layers are parallel with a cooling direction, each device layer is in a shape of a strip, short sides of the strip are parallel to the cooling device, and long sides of the strip are vertical to the cooling device, therefore each device layer is ensured to obtain an independent and shorter cooling channel by virtue of a high-thermal-conductivity silicon substrate (instead of thermal-conducting through holes) installed on the device layer and the fact that the highest temperature of a thermal-expandability three-dimensional parallel cooling integrated chip has no relation with the number of overlapped device layers is ensured. The invention also provides an analysis model for calculating the highest substrate temperature of the thermal-expandability three-dimensional parallel cooling integrated chip, and an analytic expression of the highest substrate temperature of a three-dimensional chip is derived, therefore the thermal expandability of the method disclosed by the invention can be proved theoretically. The method can be widely applied to a three-dimensional integration scheme-based massively parallel computation on-chip system needing good cooling performance urgently.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Transient, dynamic stabilization aid decision-making automatic searching method based on parallel calculation
ActiveCN101436779AEnsure safetyGuaranteed reliabilityData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesTransient state
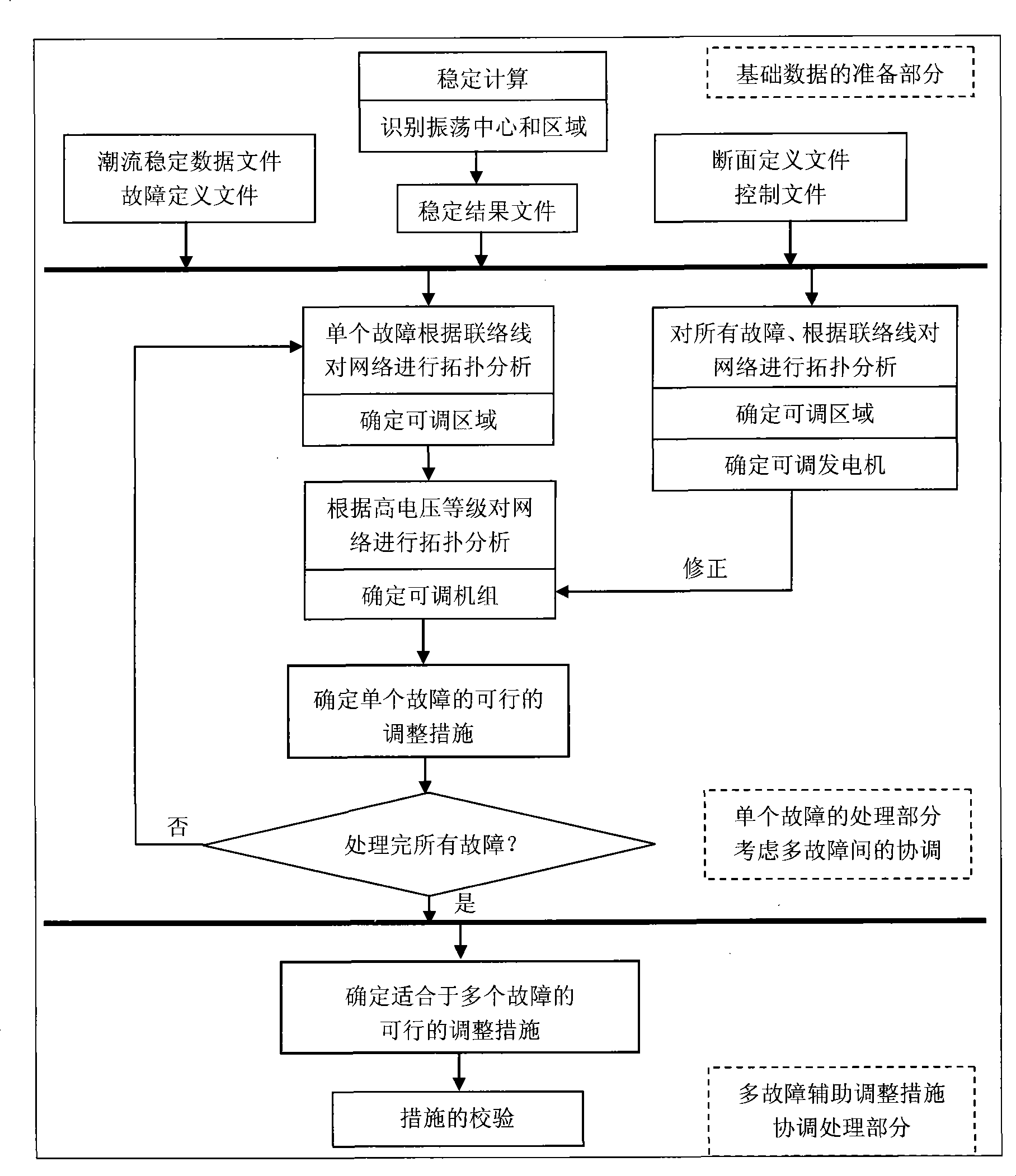
The invention relates to a method for automatically searching assistant decisions for transient and dynamic stability based on parallel computation. Based on power flow and stability data of a power grid and aimed at the problems of transient stability and dynamic stability, the method adopts large-scale parallel computation processing technology as well as human experience and a specific computation method to realize automatic identification of adjusting elements and automatic search of feasible adjustment methods, so as to achieve off-line transient stability analysis of an auxiliary electric power system and actual operation instruction.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
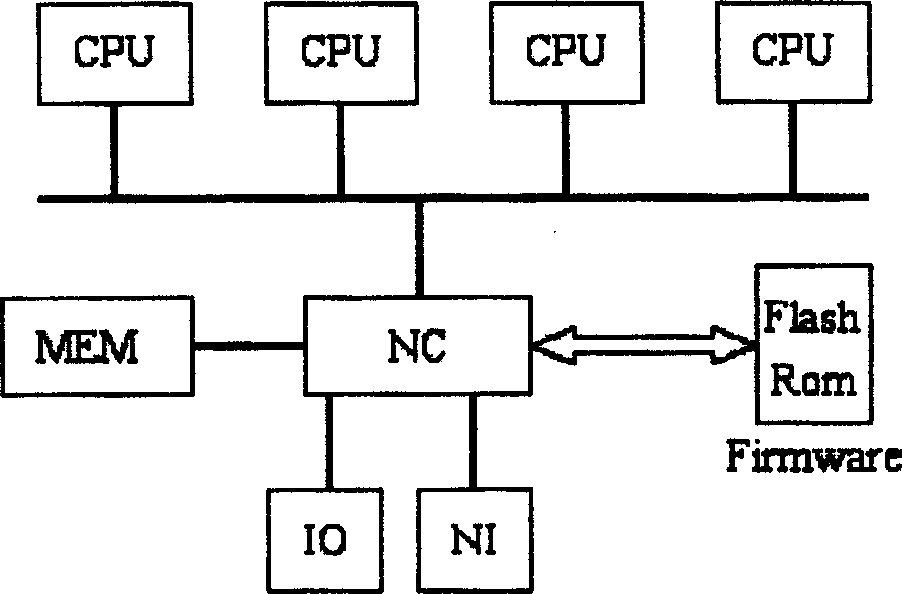
Method and Apparatus for Subdividing Local Memory in Nodes of a Massively Parallel Computer System
InactiveUS20080040561A1Little overhead to implementEfficient use ofGeneral purpose stored program computerProgram controlLocal memoriesOn demand
A memory management mechanism a nodal having multiple processors in a massively parallel computer system dynamically configures nodal memory on demand. A respective variable-sized subdivision of nodal memory is associated with each processor in the node. A processor may request additional memory, and the other processor(s) may grant or veto the request. If granted, the requested memory is added to the subdivision of the requesting processor. A processor can only access memory within its own subdivision. Preferably, each subdivision contains a daemon which monitors memory usage and generates requests for additional memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
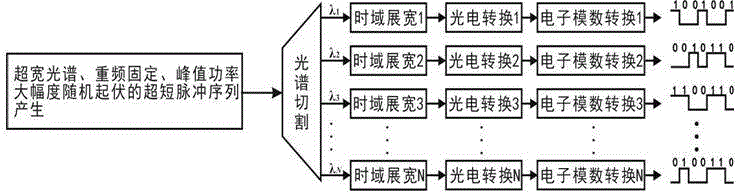
Method for generating high-speed parallel true random numbers with ultra-high scalability
ActiveCN104615406AOvercome the limitations of inherent periodicityImprove scalabilityRandom number generatorsElectric pulse generator circuitsConvertersConcurrent computation
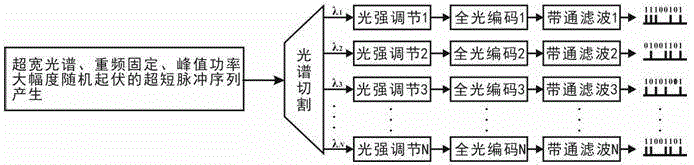
The invention provides a method for generating high-speed parallel true random numbers with an ultra-high scalability. The method comprises the steps that firstly, spectrum cutting is conducted on an ultra-short pulse sequence generated by an optical device, so that N paths of ultra-narrow-band ultras-short pulse sequences are obtained; secondly, time domain widening is conducted, so that large-pulse-width narrow-band short pulse sequences are obtained and then converted into electrical signals; thirdly, the signals enter an analog-digital converter to be converted into corresponding high and low levels, and therefore N paths of independent true random numbers with the repetition frequency being f are generated. The high-speed parallel true random number sequence generated through the method does not have periodicity, the code rate of each path can reach the magnitude order of 10 Gbps, at least 1000 paths of independent parallel true random numbers can be output at the same time, the scalability of an existing parallel true random number generator is improved at least 3-4 magnitude orders, and the modern large-scale parallel computing and high-speed secretive network communication demands can be met to a large extend.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Optimized scalable network switch
InactiveUS20080091842A1Lower latencyImprove throughputError preventionProgram synchronisationExtensibilityData pack
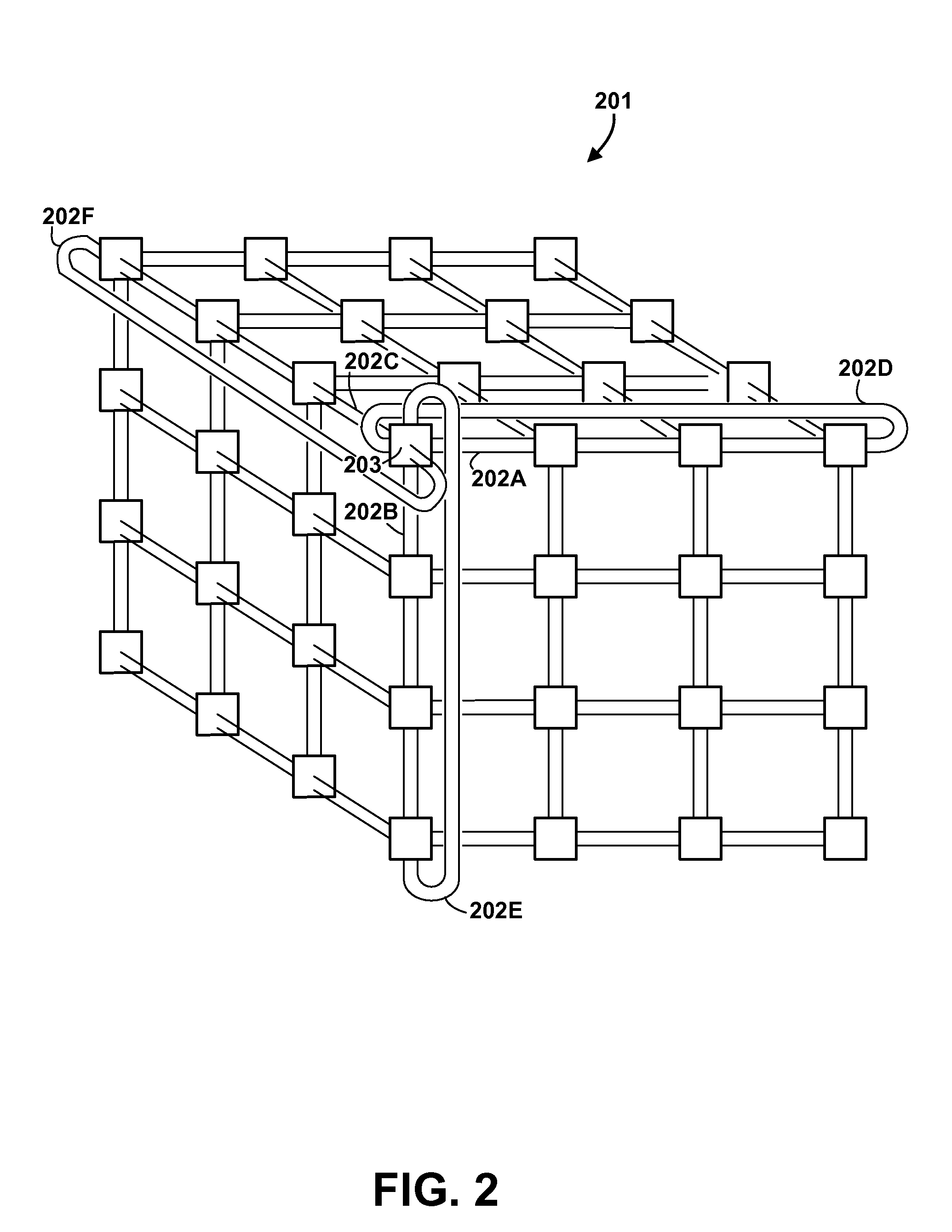
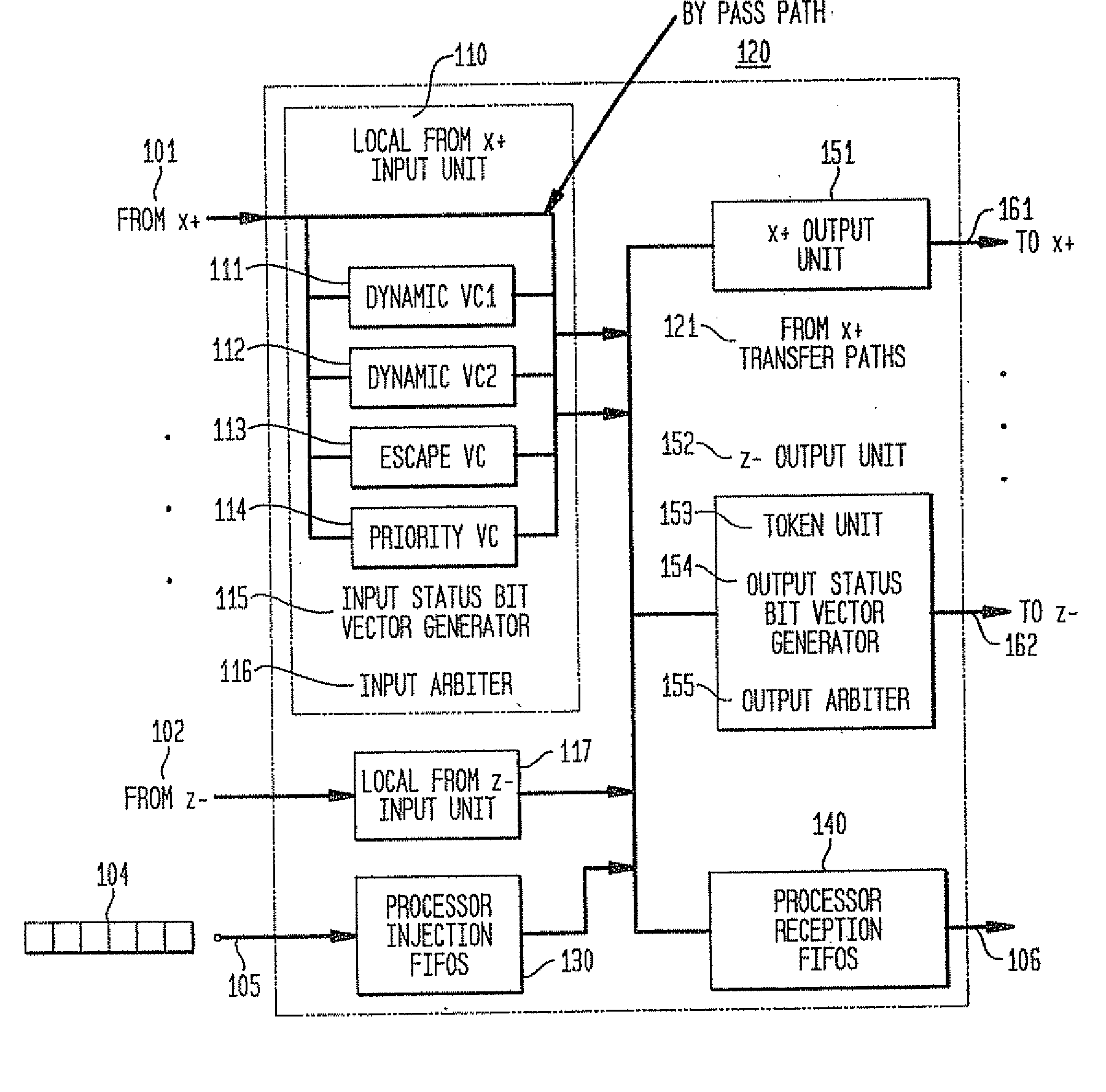
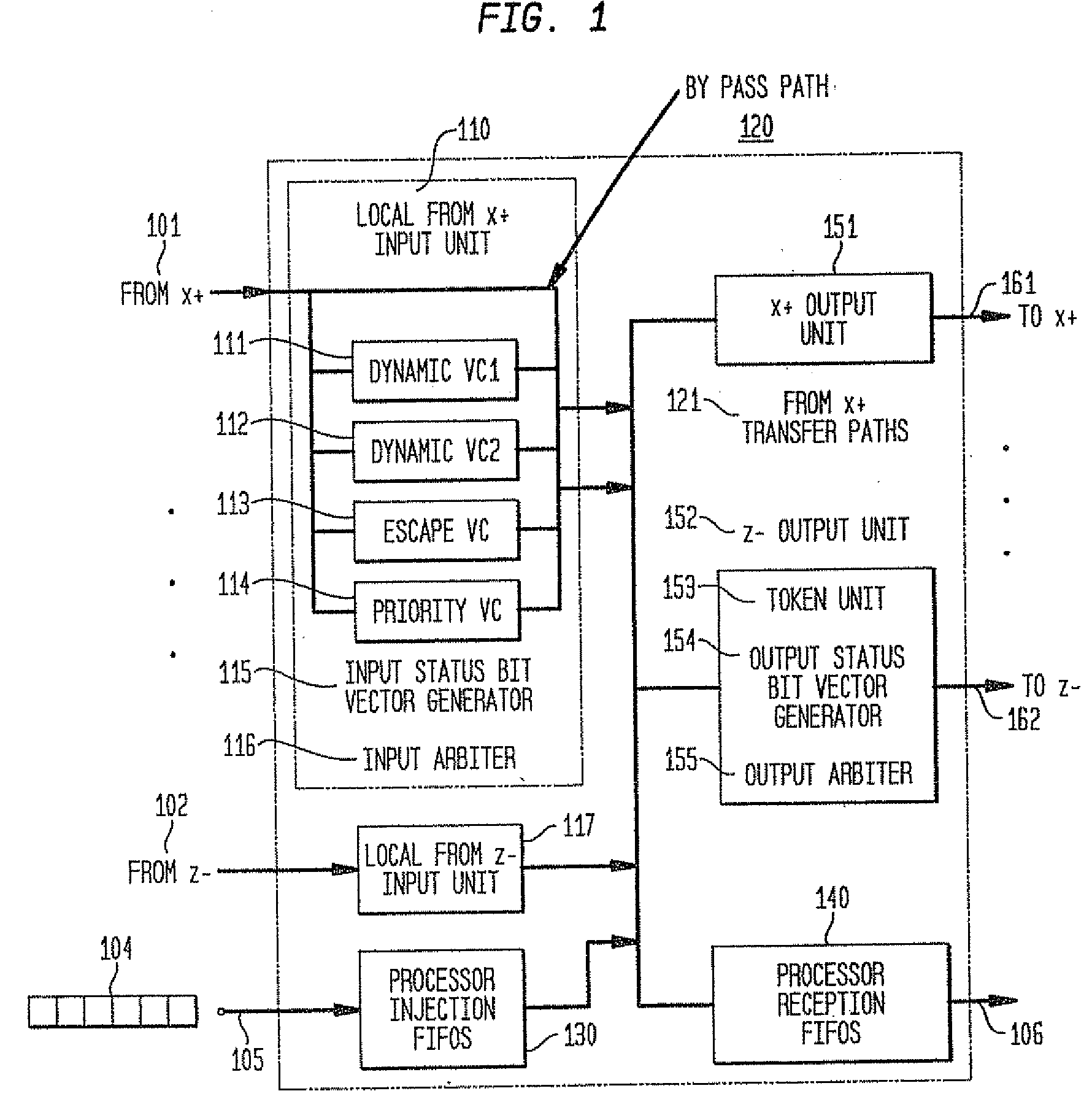
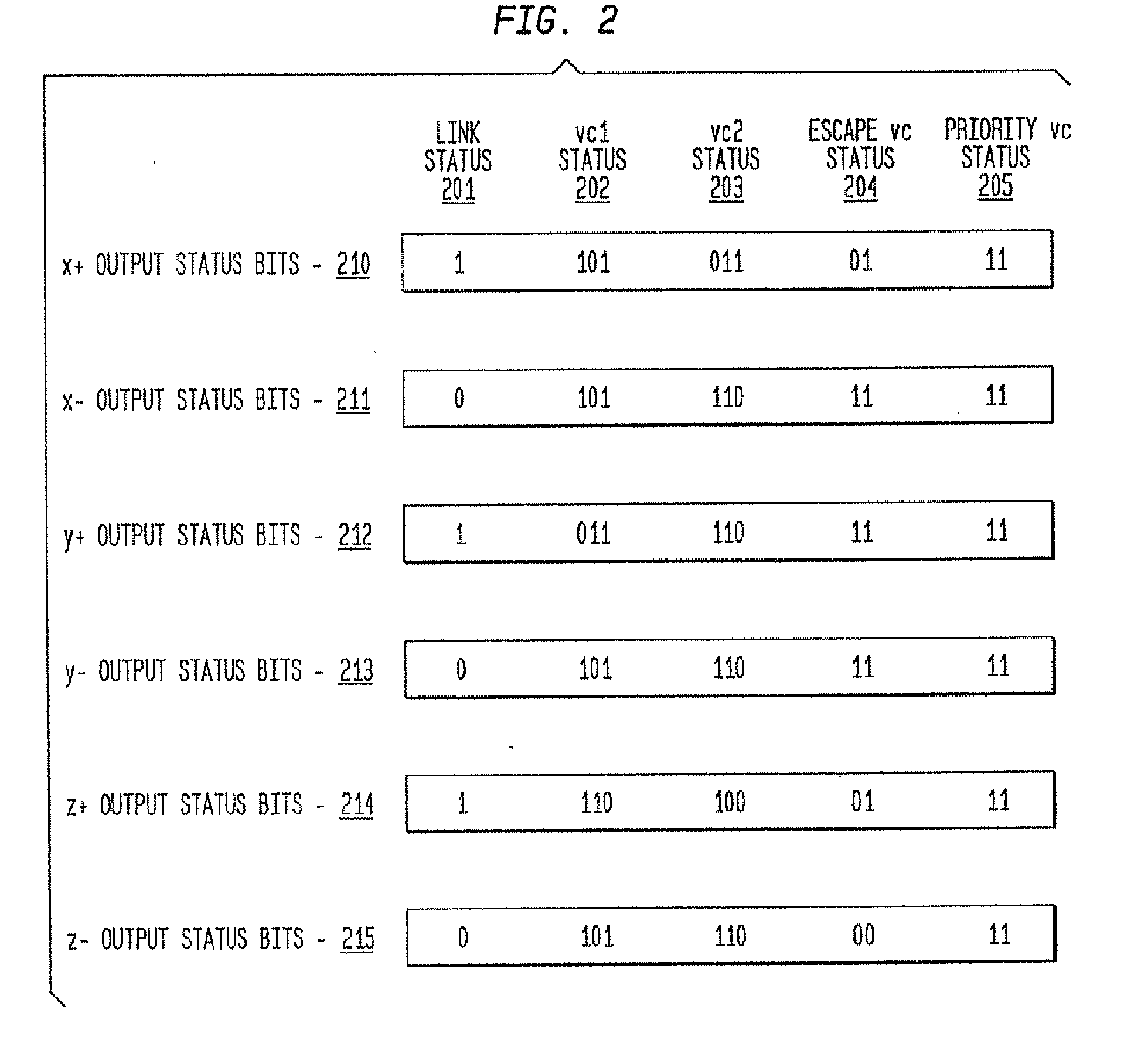
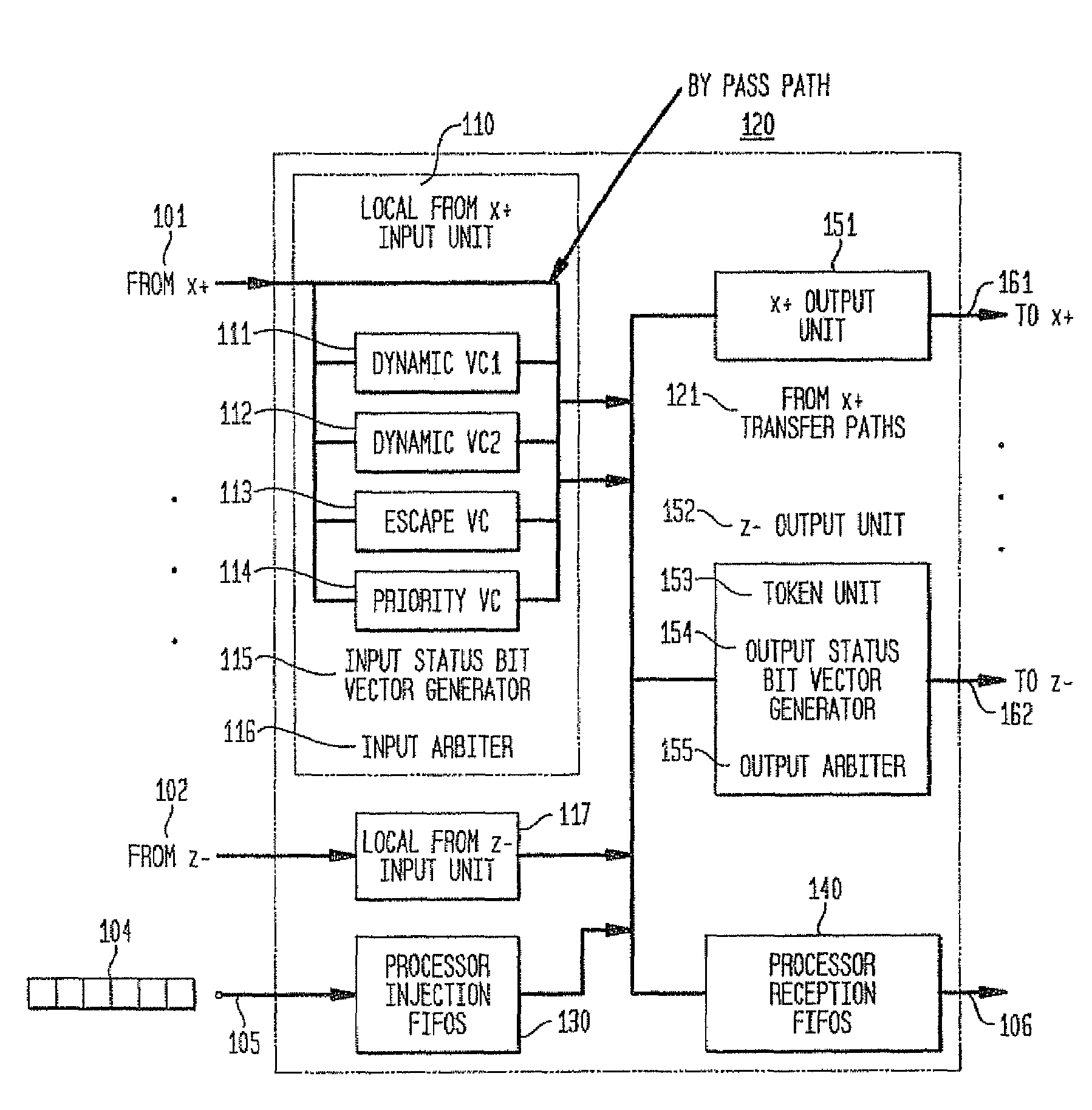
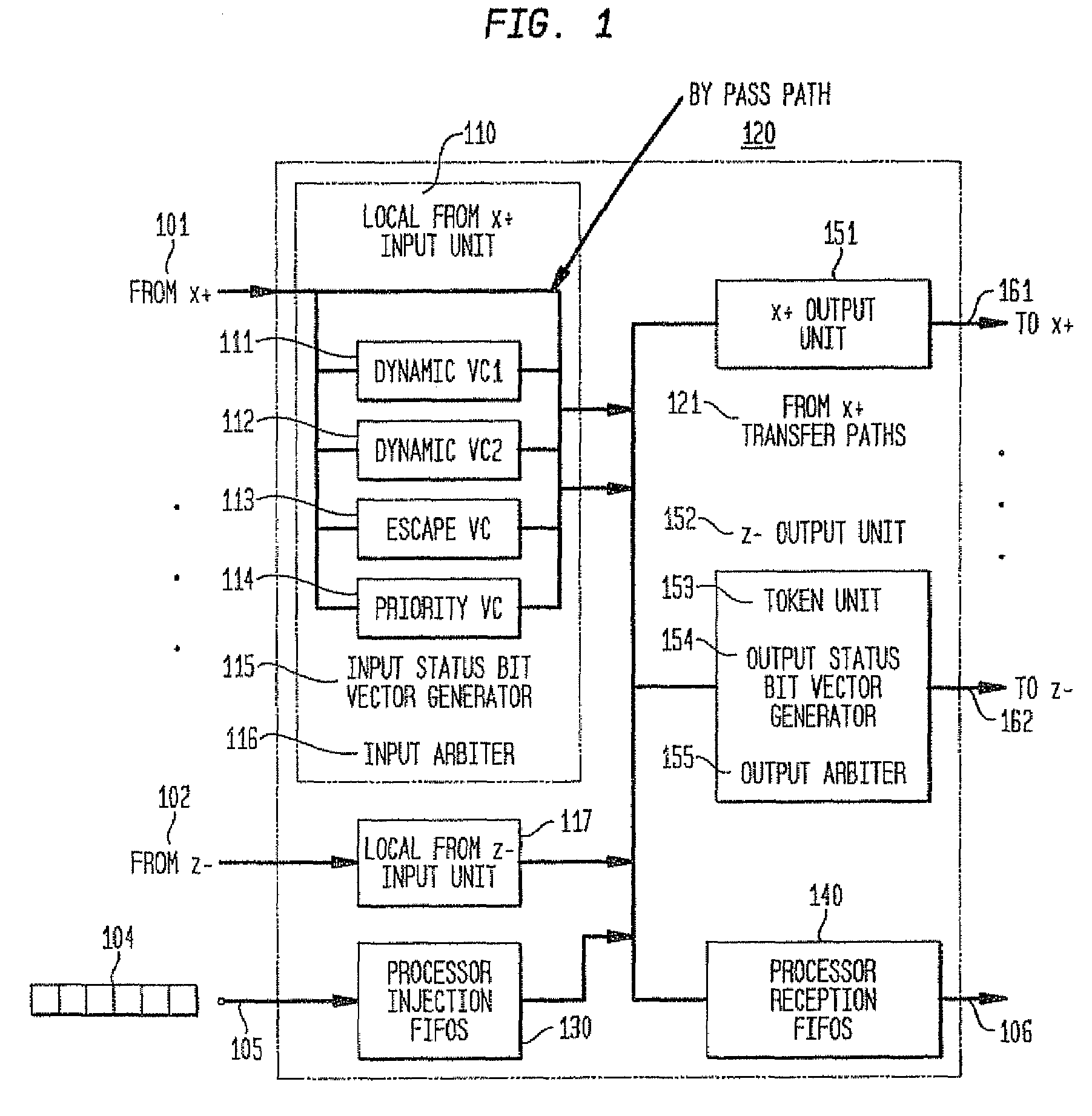
In a massively parallel computing system having a plurality of nodes configured in m multi-dimensions, each node including a computing device, a method for routing packets towards their destination nodes is provided which includes generating at least one of a 2 m plurality of compact bit vectors containing information derived from downstream nodes. A multilevel arbitration process in which downstream information stored in the compact vectors, such as link status information and fullness of downstream buffers, is used to determine a preferred direction and virtual channel for packet transmission. Preferred direction ranges are encoded and virtual channels are selected by examining the plurality of compact bit vectors. This dynamic routing method eliminates the necessity of routing tables, thus enhancing scalability of the switch.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
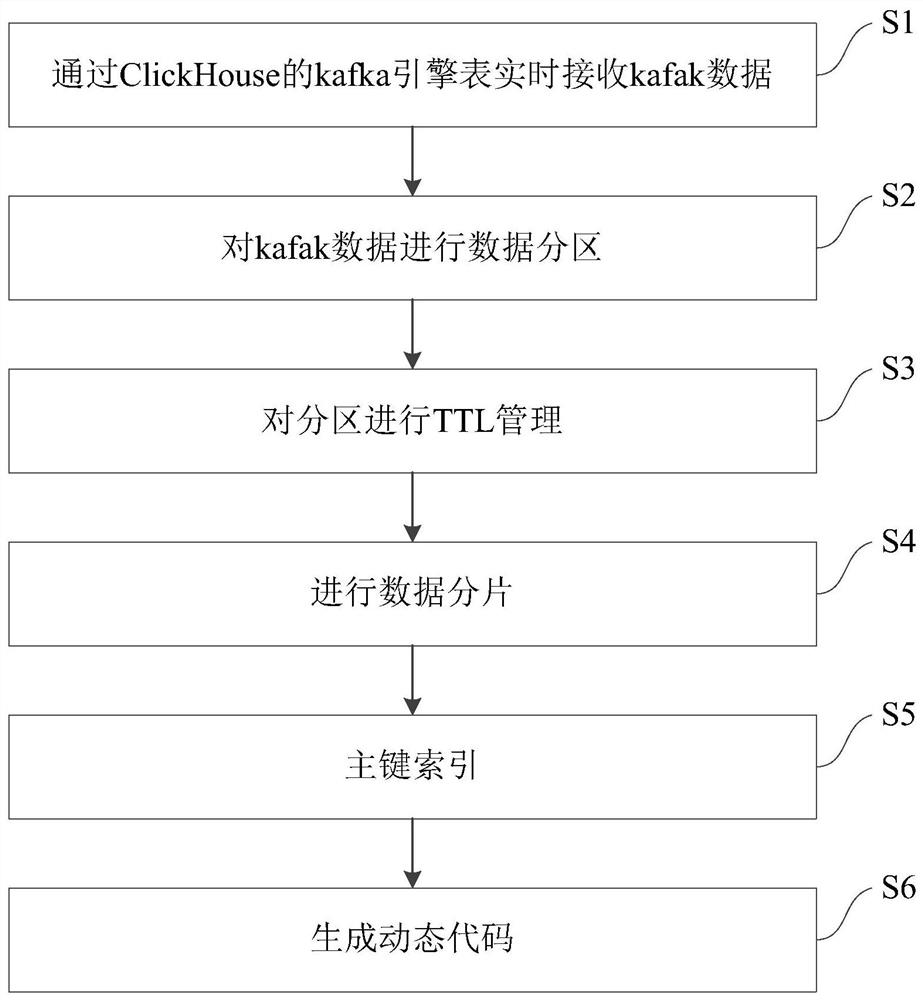
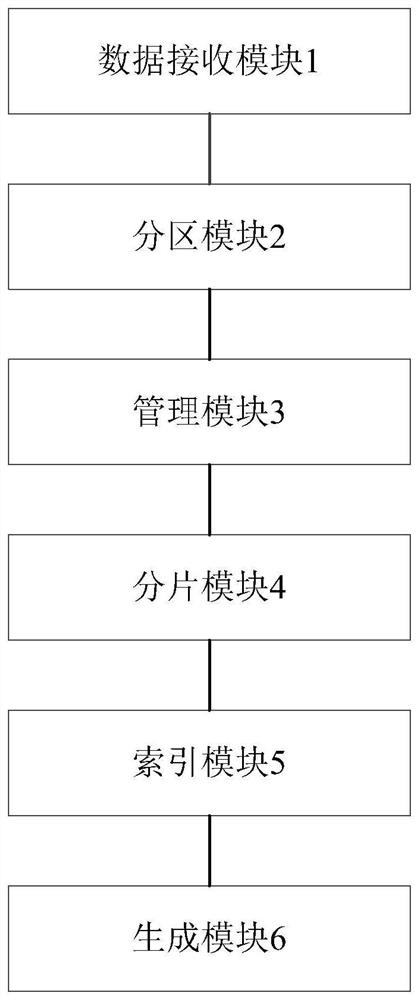
Method and device for realizing OLAP analysis based on ClickHouse
InactiveCN112163048ASolve the wavesIncrease massively parallel computing capabilitiesDatabase distribution/replicationMulti-dimensional databasesConcurrent computationMassively parallel computation
Owner:CHANGZHOU MICROINTELLIGENCE CO LTD
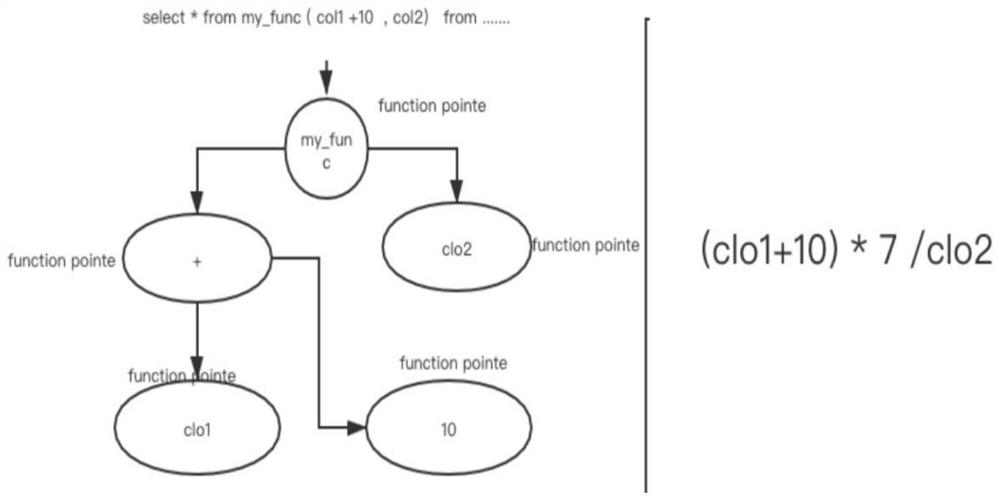
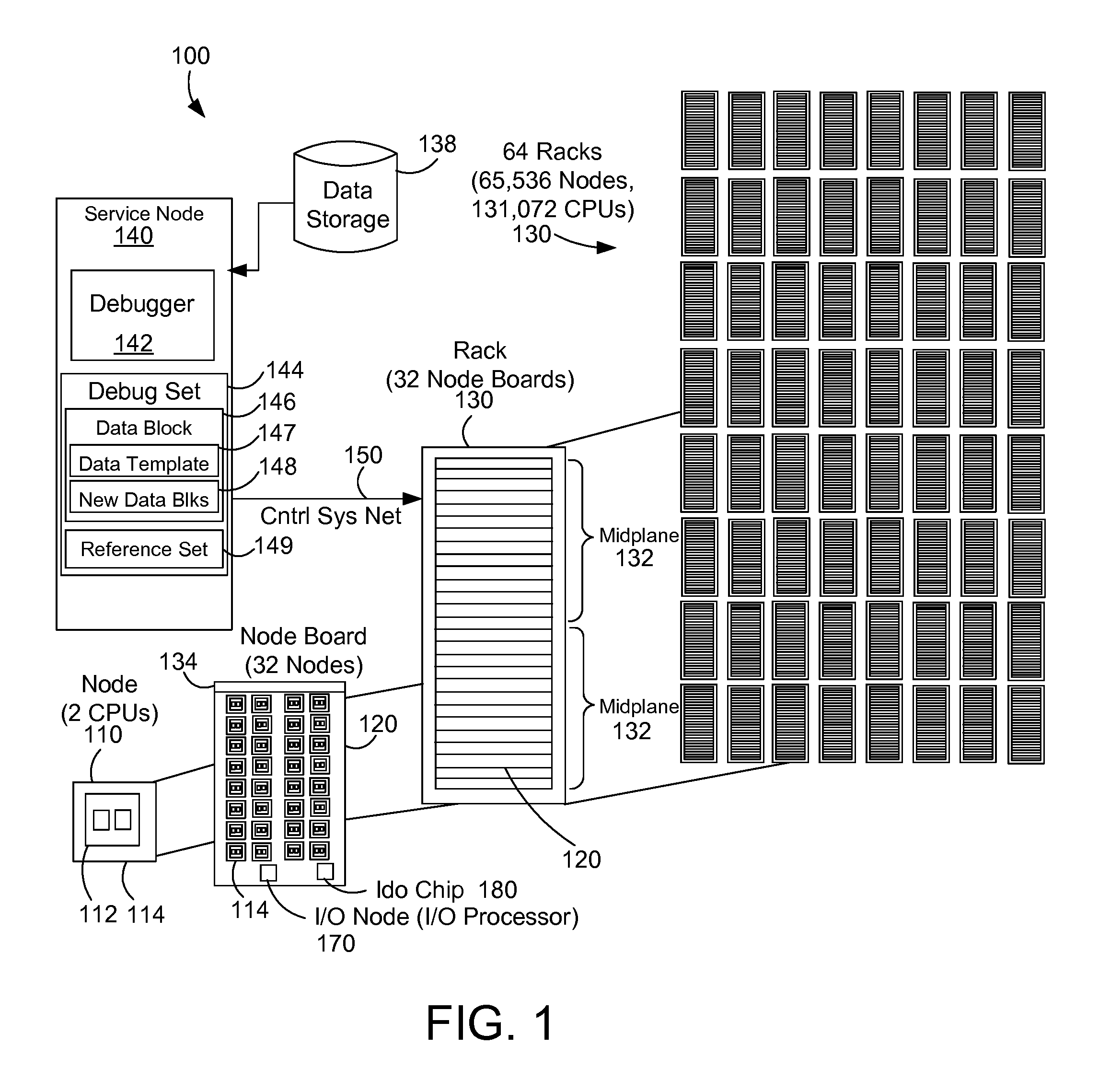
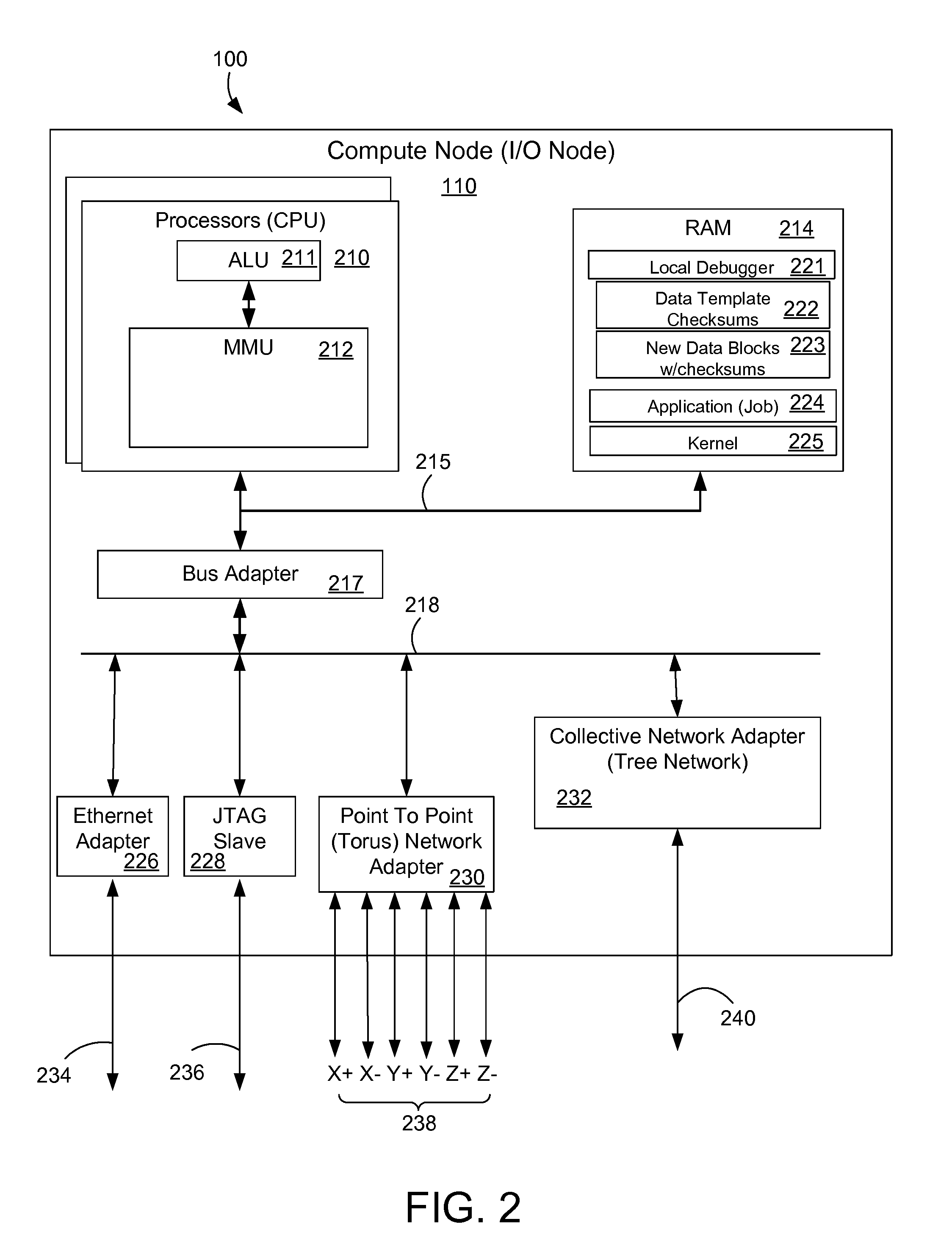
Parallel debugging in a massively parallel computing system
InactiveUS20110191633A1Easy to debugReduce the amount requiredError detection/correctionMassively parallelTemplate matching
A method and apparatus is described for parallel debugging on the data nodes of a parallel computer system. A data template associated with the debugger can be used as a reference to the common data on the nodes. The application or data contained on the compute nodes diverges from the data template at the service node during the course of program execution, so that pieces of the data are different at each of the nodes at some time of interest. For debugging, the compute nodes search their own memory image for checksum matches with the template and produces new data blocks with checksums that didn't exist in the data template, and a template of references to the original data blocks in the template. Examples herein include an application of the rsync protocol, compression and network broadcast to improve debugging in a massively parallel computer environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
Parallel computing system facing to particle method
InactiveCN1851683AImprove execution efficiencyReduce complexityDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingParallel computingParticle method
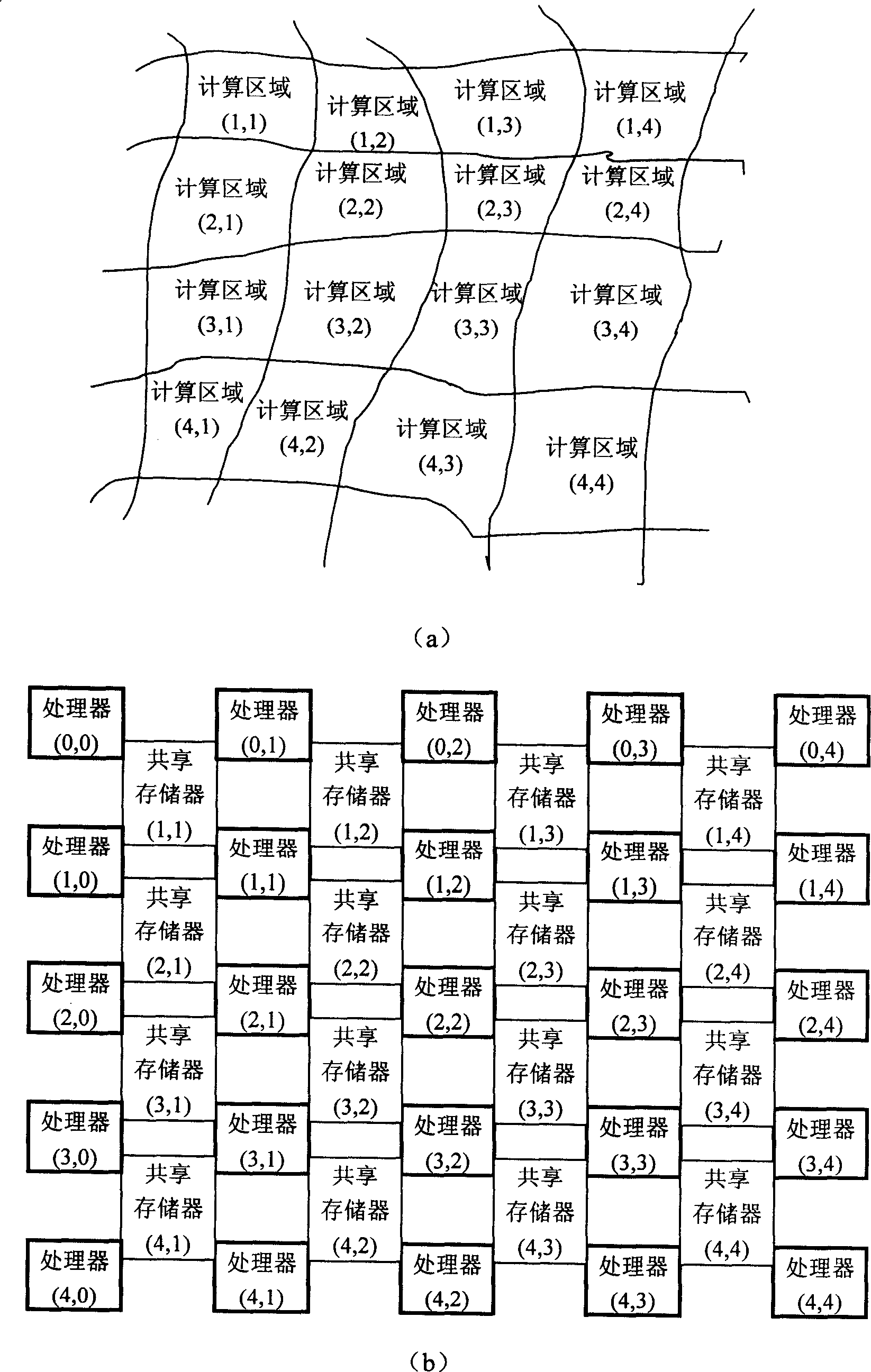
The present invention includes plurality of calculation nodes and plurality of storage nodes, wherein said plurality of calculation nodes arranged in periodicity distributed calculation node array in logic; said plurality of storage nodes arranged in periodicity distributed storage node array in logic; said calculation node array and said storage node array alternative arrangement and common forming periodicity distributed array. Each storage node is connected with and shared by plurality of neighboring calculation nodes; each calculation node is connected with plurality of neighboring storage nodes and to process data in said plurality of neighboring storage nodes. Said invention has advantages of comprehensive application area, very high software execution efficiency, greatly reducing massively parallel computation complexity.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Data processing method, system and device and storage medium
InactiveCN110334070AImprove synchronization efficiencyImprove acceleration performanceDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationData synchronizationFault tolerance
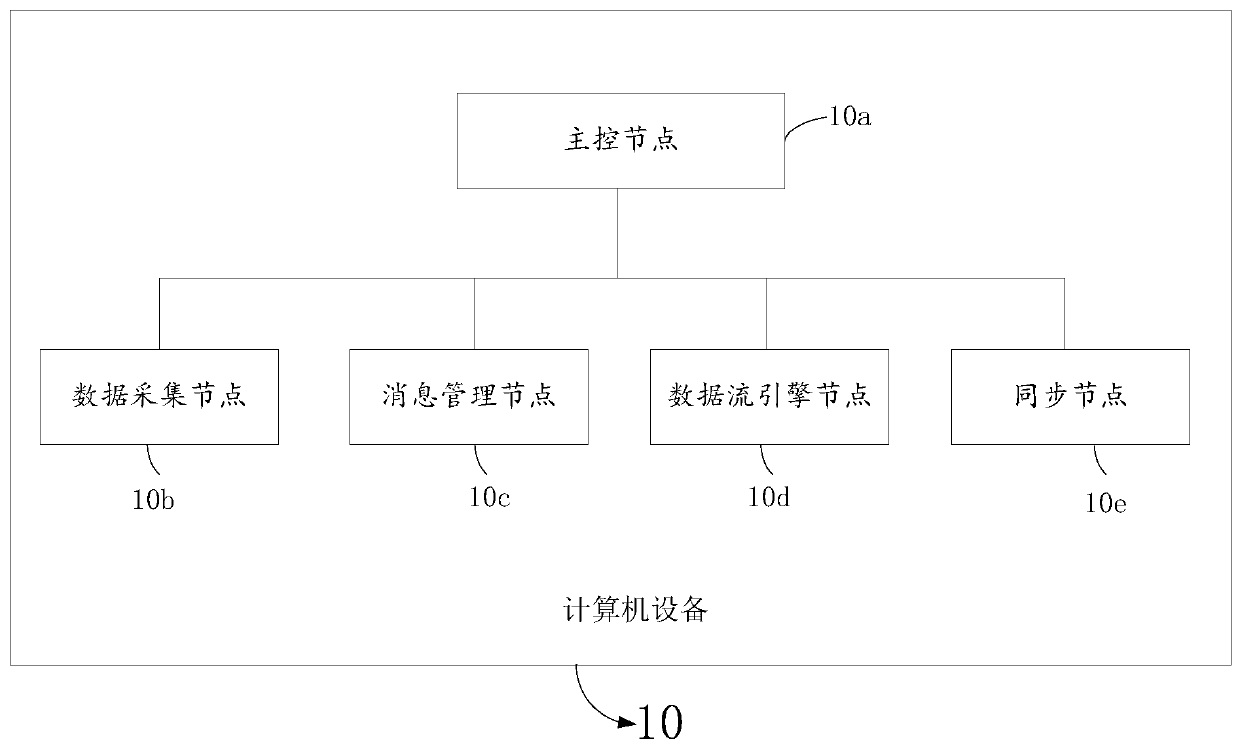
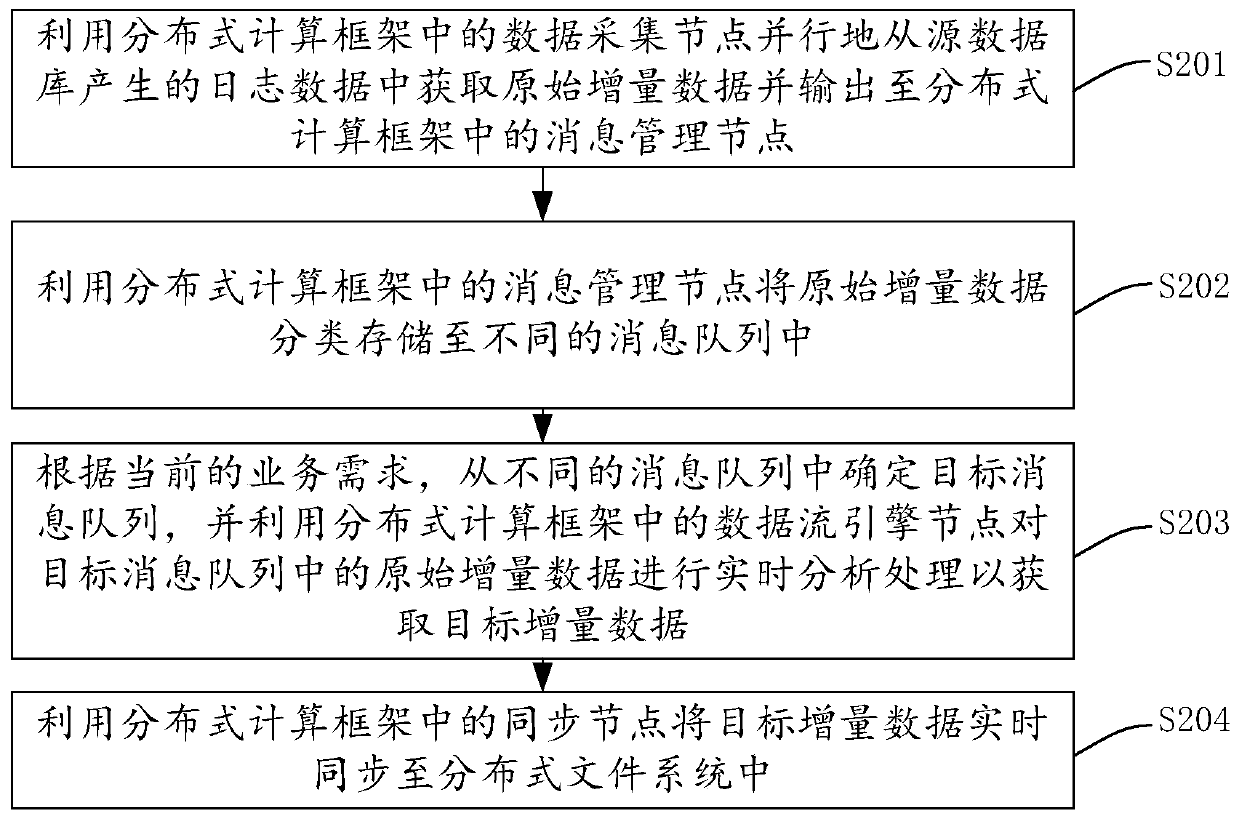
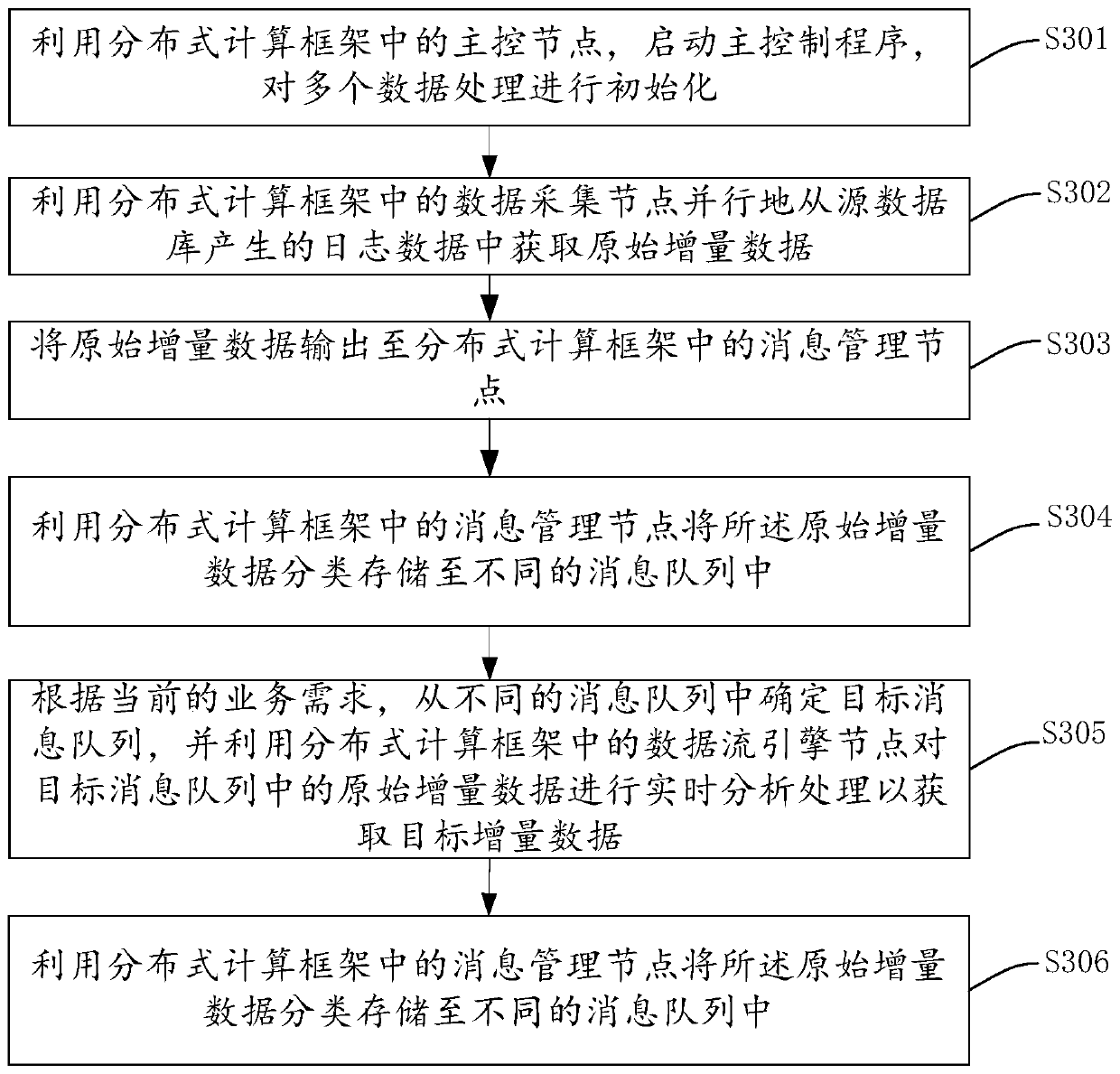
The embodiment of the invention provides a data processing method, system and device and a storage medium. In some embodiments of the invention, a distributed computing framework is deployed on a plurality of computer devices, and the distributed computing framework comprises a master control node, a data acquisition node, a message management node, a data flow engine node and a synchronization node. Under the control of the main control node, the data acquisition node, the message management node, the data flow engine node and the synchronization node process the data in real time, so that the data synchronization efficiency is improved, and the data processing expansibility and fault tolerance are improved. According to the method for processing the data stream by adopting the distributed computing framework, the data accuracy can be ensured under the condition of data disorder or delayed loading. Under the condition that a fault occurs, data recovery processing is carried out from alast completed check point through a check point mechanism, it is ensured that one-time state semantics are kept in an application program, large-scale parallel computing is supported, and good throughput and low delay are achieved.
Owner:PEOPLE'S INSURANCE COMPANY OF CHINA
High-speed parallel true random number generator with extra-strong scalability
ActiveCN104516714AOvercome the limitations of inherent periodicityImprove scalabilityRandom number generatorsConcurrent computationGrating
A high-speed parallel true random number generator with extra-strong scalability is characterized in that a pulse sequence is inputted to an array waveguide grate by a super-continuous spectrum entropy source, is cut into N narrow-band sub optical pulse sequences, enters a dispersion compensation fiber array generation time domain for spreading, is further inputted to a photoelectric detector array through another N polarization-preserving fibers, is transformed into corresponding electric pulse sequences, finally enters an analog-digital converter array and is quantized into N independent high-speed parallel true random number sequences. The single-channel code rate can reach +Gbps magnitude, at least N=1000 independent parallel true random numbers can be simultaneously outputted, the scalability of an existing parallel true random number generator is increased by at least three to four orders of magnitude, and requirements of modern large-scale parallel computing and high-speed secure network communication can be greatly met.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Global medium-term numerical forecast GRAPES_GFS
ActiveCN110703357AImprove stabilityMitigation of calculation errorsData processing applicationsWeather condition predictionConcurrent computationEngineering
The invention discloses global medium-term numerical forecast GRAPES_GFS. The global medium-term numerical forecast GRAPES_GFS is characterized in that in the aspect of large-scale parallel computing,the improvement of an existing framework is proposed for the shortcomings of an existing semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian integration scheme in terms of computational efficiency and scalability, and a solving algorithm with high efficiency and high performance is proposed based on the semi-implicit integral scheme and linearization system. The non-equidistant difference is adopted to improve the calculation accuracy of the background temperature profile and solve the problem of large errors of the background temperature profile at the level of drastic change of model vertical stratification thickness. The digital filtering module is reconstructed and optimized to improve the stability and computational efficiency of digital filtering. A 3D-Var integrated single-point test system is established.
Owner:NATIONAL METEOROLOGICAL CENTRE
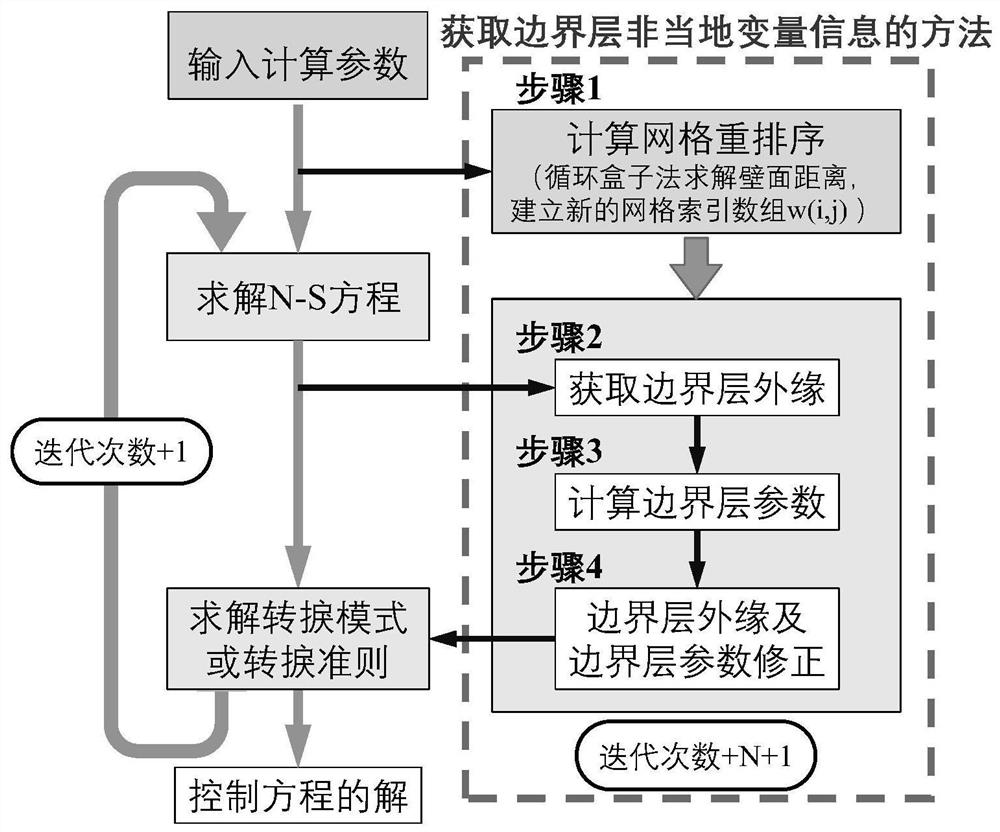
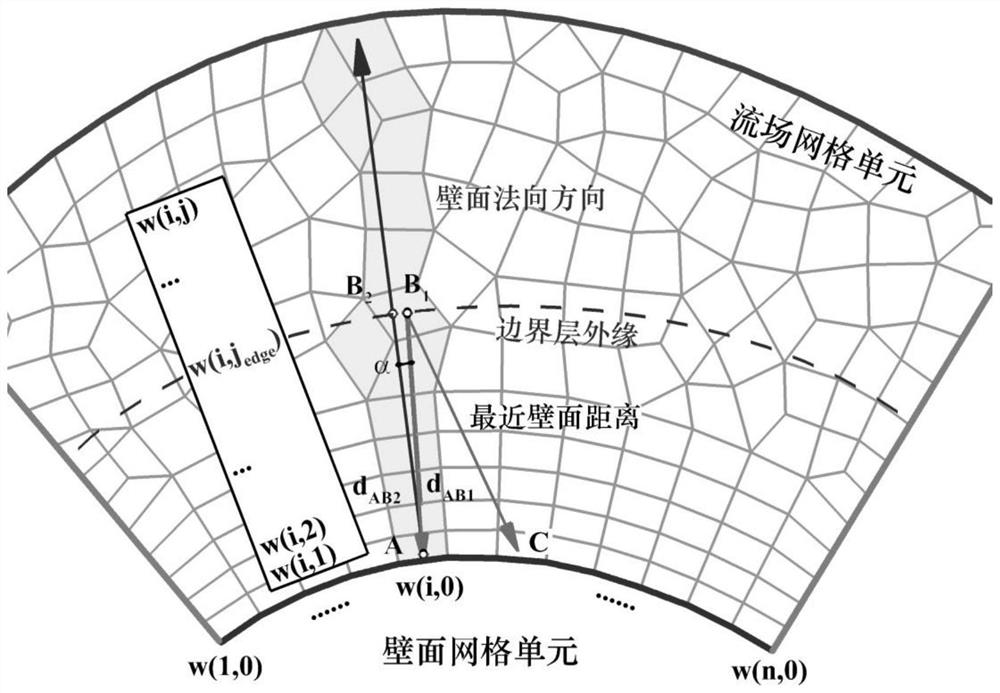
Method for acquiring non-local variable information of boundary layer of unstructured grid
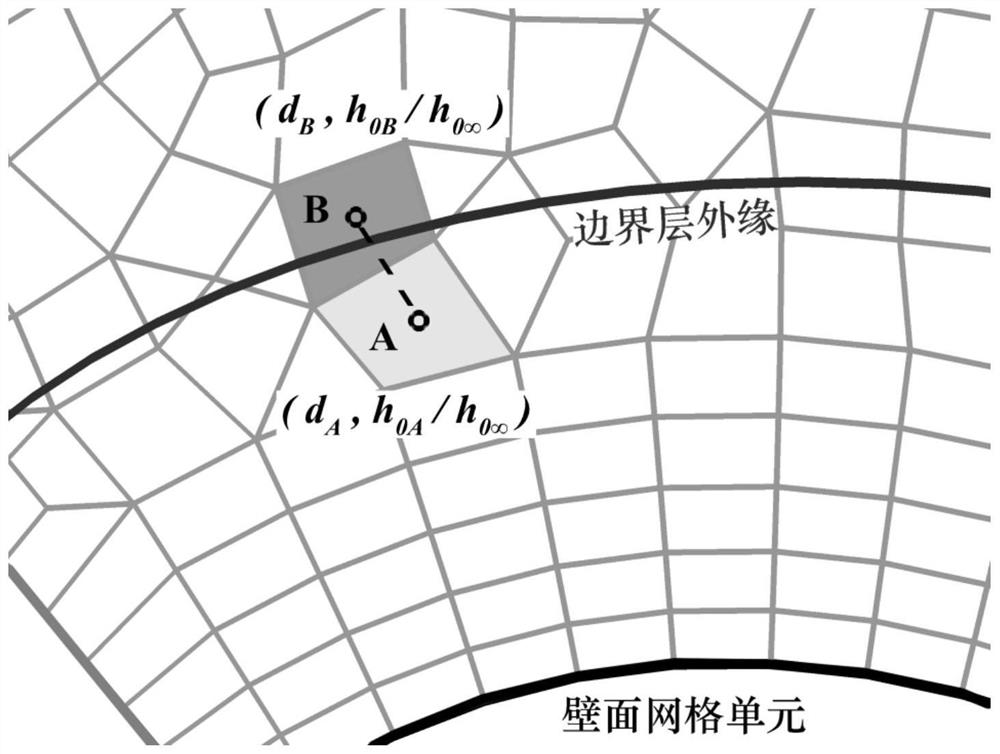
ActiveCN112818573AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computationLocal variable
The invention relates to a method for acquiring non-local variable information of a boundary layer of an unstructured grid, and belongs to the technical field of boundary layer transition prediction in fluid mechanics. According to the method, firstly, grids are preprocessed, all calculations for acquiring boundary layer information are completed in the w(i, j) array, and the i representing wall grid units in the w(i, j) array is independent from one another, so that large-scale parallel calculation can be performed, and the method is suitable for a modern CFD calculation method. The nearest wall surface distance is searched by adopting a circulating box method, and the reordering of the grids is completed on the basis, so that the calculation efficiency is relatively high. As the w(i, j) array is basically along the normal direction of the wall surface, and wall surface distance correction, boundary outer edge and boundary layer non-local variable parameter correction are carried out, the obtained result has high precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Fault recovery on a massively parallel computer system to handle node failures without ending an executing job
ActiveCN101589370ADigital computer detailsData resettingConcurrent computationMassively parallel computation
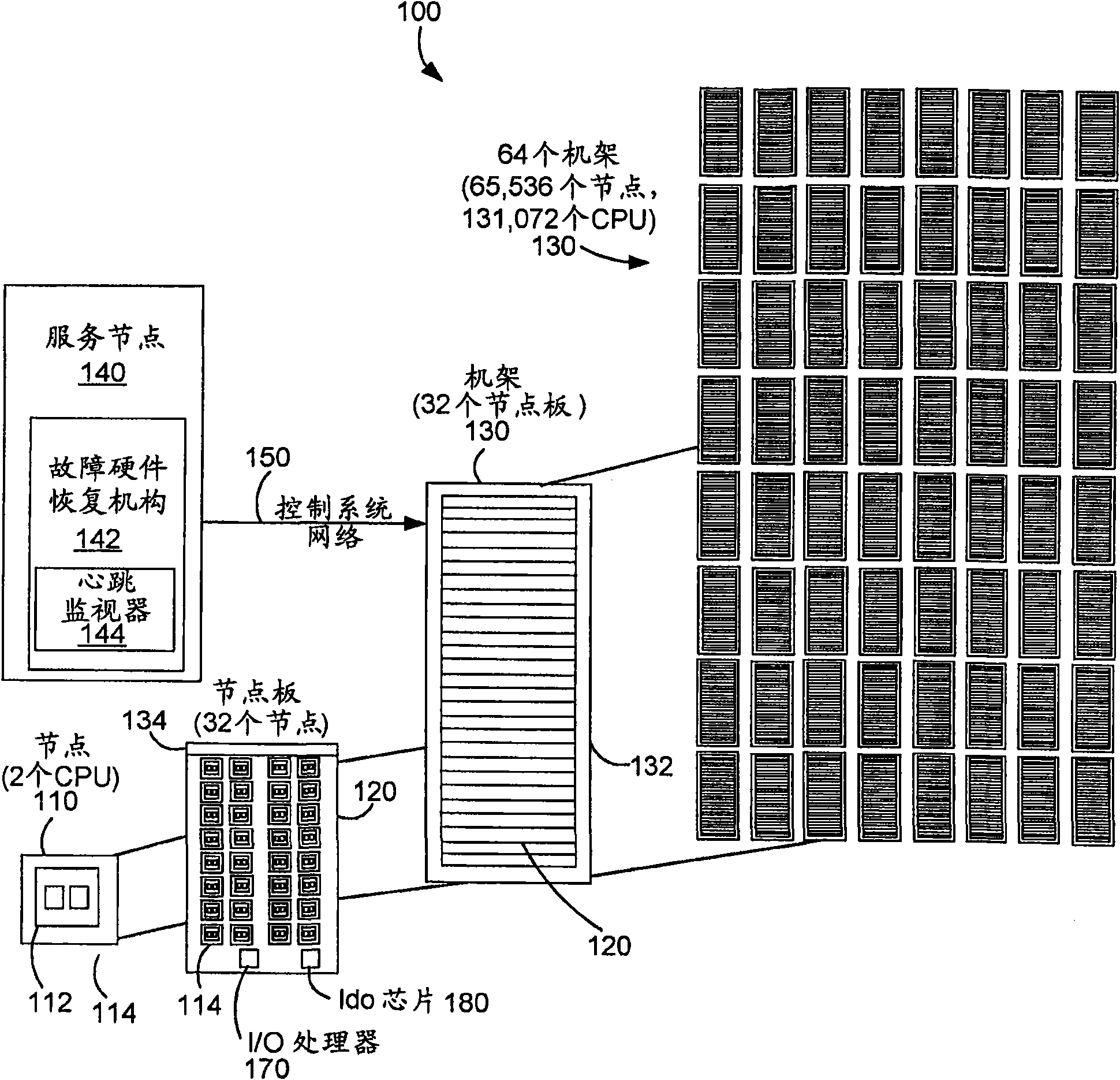
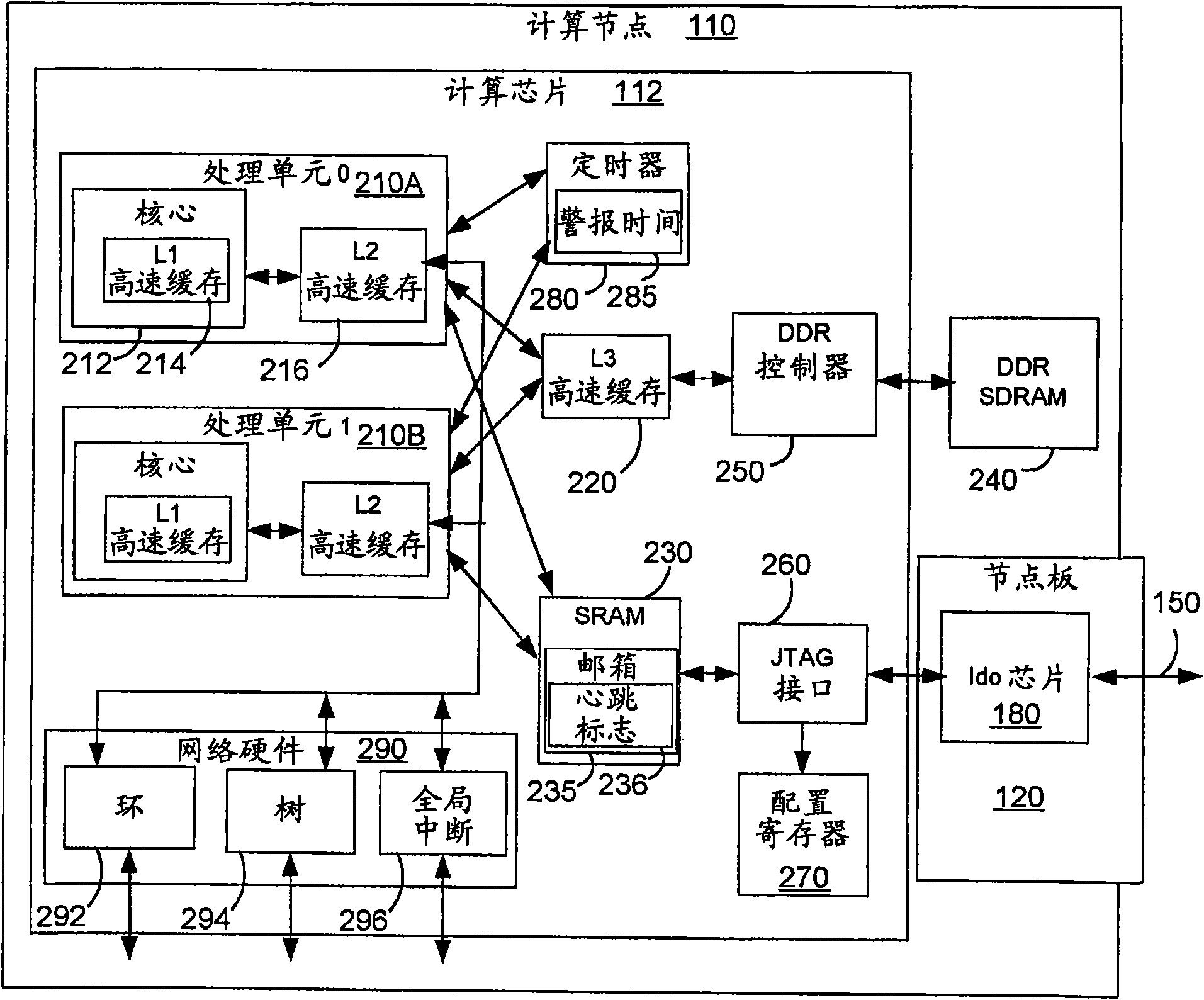
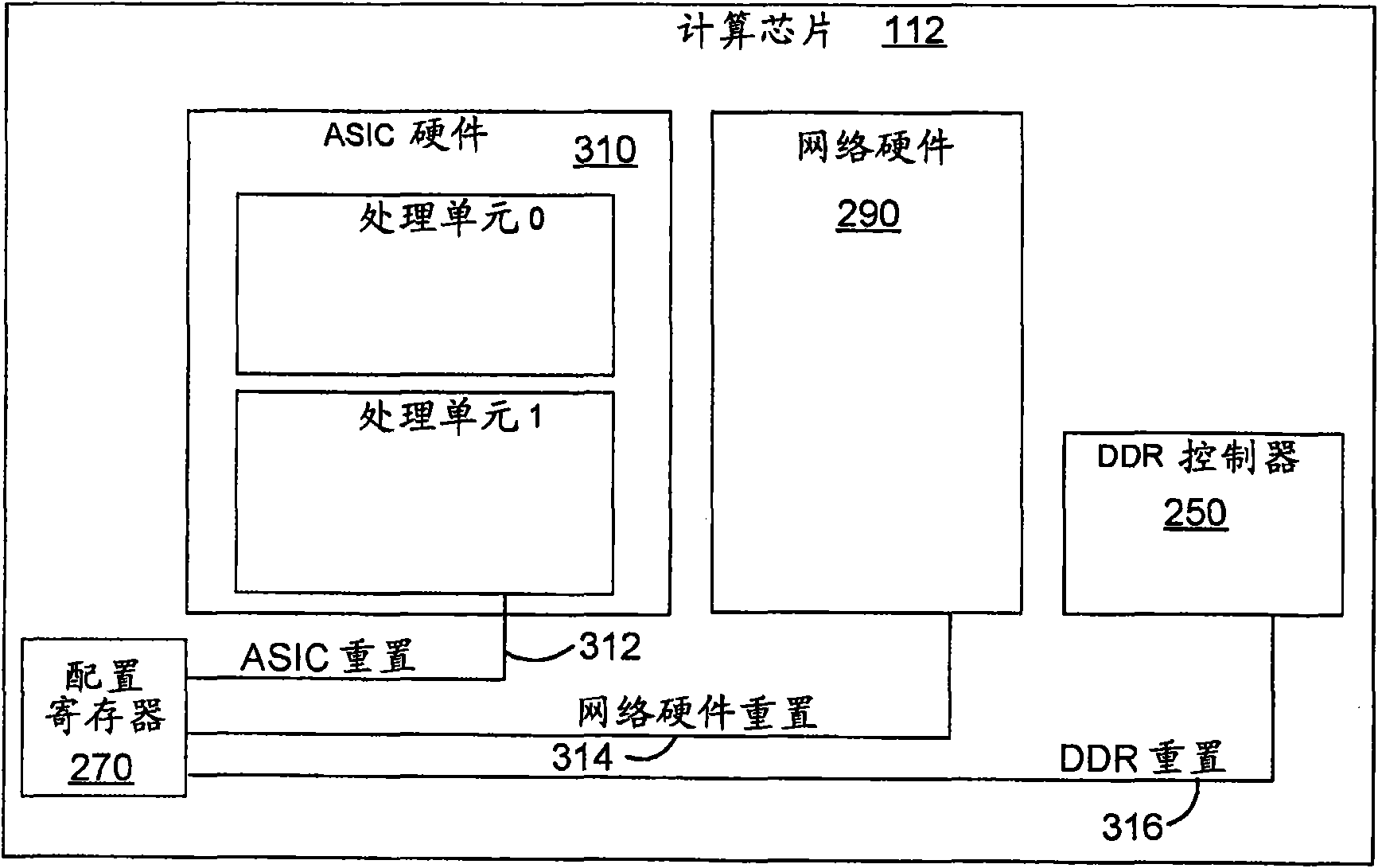
A method and apparatus for fault recovery of on a parallel computer system from a soft failure without endingan executing job on a partition of nodes. In preferred embodiments a failed hardware recovery mechanism on a service node uses a heartbeat monitor to determine when a node failure occurs. Where possible, the failed node is reset and re-loaded with software without ending the software job being executed by the partition containing the failed node.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Optimized scalable network switch
InactiveUS7668970B2Reduce latencyImprove throughputError preventionProgram synchronisationData packConcurrent computation
In a massively parallel computing system having a plurality of nodes configured in m multi-dimensions, each node including a computing device, a method for routing packets towards their destination nodes is provided which includes generating at least one of a 2m plurality of compact bit vectors containing information derived from downstream nodes. A multilevel arbitration process in which downstream information stored in the compact vectors, such as link status information and fullness of downstream buffers, is used to determine a preferred direction and virtual channel for packet transmission. Preferred direction ranges are encoded and virtual channels are selected by examining the plurality of compact bit vectors. This dynamic routing method eliminates the necessity of routing tables, thus enhancing scalability of the switch.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Tbps all-optical parallel true random number producing method having ultra-strong scalability
ActiveCN104461456AOvercome the limitations of inherent periodicitySingle channel speed increaseRandom number generatorsBandpass filteringConcurrent computation
A tbps all-optical parallel true random number producing method having ultra-strong scalability comprises the steps of utilizing an optical device to produce an ultra-short pulse sequence, conducting spectrum cutting on the obtained ultra-short pulse sequence to obtain N narrow-band ultra-short pulse sequences, then conducting power adjustment on the N narrow-band ultra-short pulse sequences to enable average powers of the sequences to equal, converting randomly fluctuating peak powers into different pulse states, encoding the peak powers as 1 if the peak powers are larger than pulse output of the average powers, encoding the peak powers as 0 if the peak powers are lower than pulse-free output of the average powers, achieving repeated-frequency N all-optical parallel true random number production and filtering out random numbers through N optical band pass filter elements. According to the tbps all-optical parallel true random number producing method, the limitation of inherent periodicity of a parallel pseudo random number generator is overcome, meanwhile at least 10000 independent parallel true random numbers are output, the scalability of an existing parallel true random number generator is improved by 3 to 4 magnitudes, and the demands for large-scale parallel computing and high-speed secure network communication are met.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
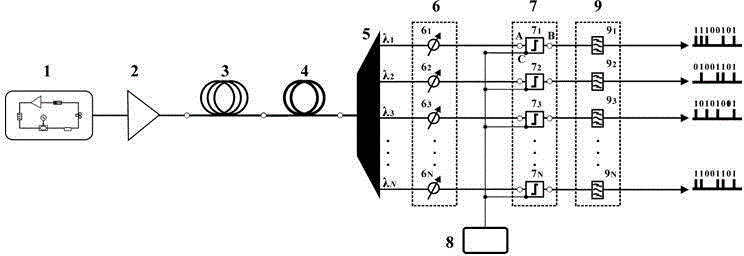
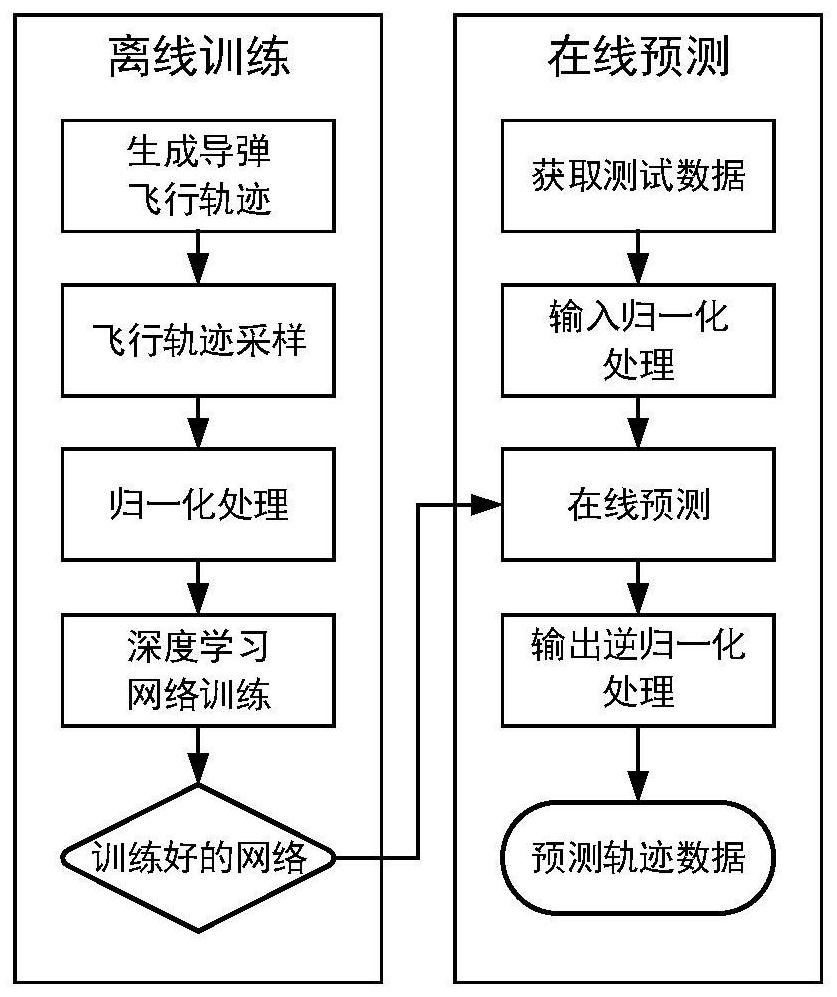
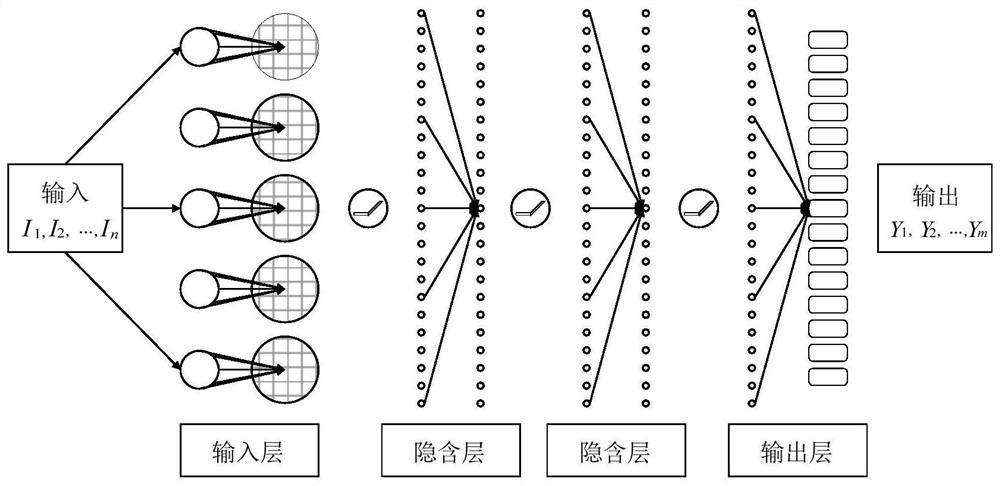
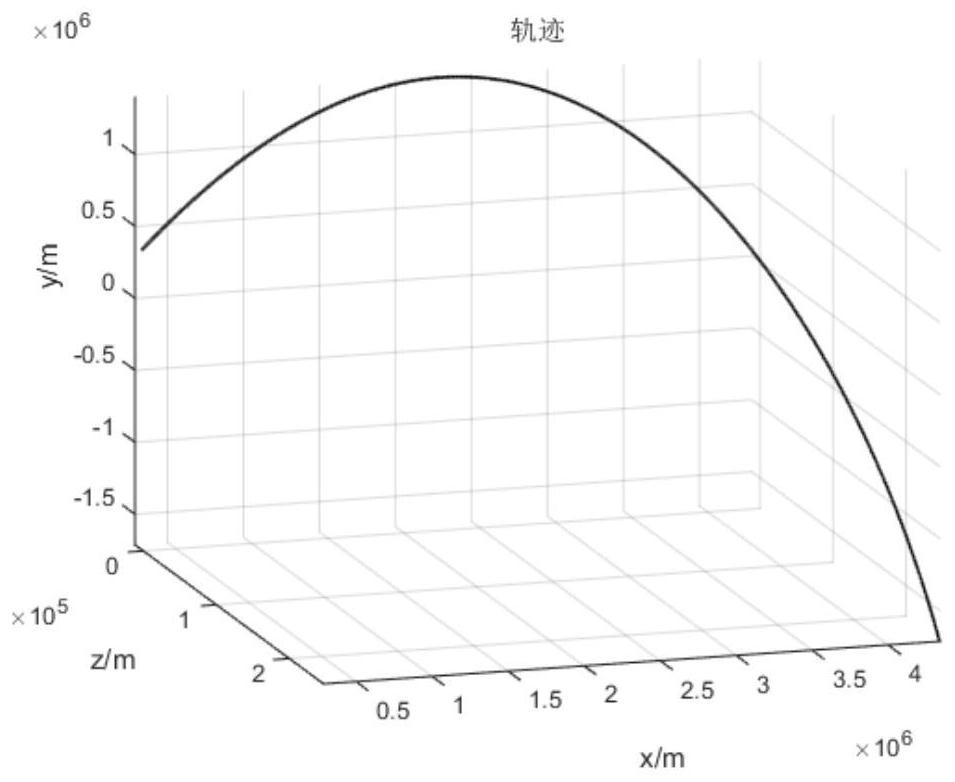
Missile flight path prediction method based on deep learning
PendingCN112348223AHigh feasibilityImprove accuracyForecastingNeural architecturesOffline learningState prediction
The invention discloses a missile flight path prediction method based on deep learning, and relates to the technical field of state prediction. The method aims to solve the problems that an existing numerical integration method is low in speed and large in occupied calculation resource during flight path calculation. The missile flight path prediction method based on deep learning is composed of two sub-modules, namely offline learning training and online path prediction, is high in prediction precision and high in calculation speed, does not depend on a numerical integration method needing alarge amount of repeated calculation, has online real-time calculation capacity, and the feasibility and accuracy of simultaneously calculating a large amount of flight path data are improved. Meanwhile, the prediction of the flight path of the missile can be accurately realized in different missile prediction initial states, the calculation consumption of the algorithm is low, the online realization can be realized, and besides, the method has the capability of large-scale parallel calculation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Router parking in power-efficient interconnect architectures
ActiveUS9619006B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingQuality of servicePerformance objective
A method and apparatus for selectively parking routers used for routing traffic in mesh interconnects. Various router parking (RP) algorithms are disclosed, including an aggressive RP algorithm where a minimum number of routers are kept active to ensure adequate network connectivity between active nodes and / or intercommunicating nodes, leading to a maximum reduction in static power consumption, and a conservative RP algorithm that favors network latency considerations over static power consumption while also reducing power. An adaptive RP algorithm is also disclosed that implements aspects of the aggressive and conservative RP algorithms to balance power consumption and latency considerations in response to ongoing node utilization and associated traffic. The techniques may be implemented in internal network structures, such as for single chip computers, as well as external network structures, such as computing clusters and massively parallel computer architectures. Performance modeling has demonstrated substantial power reduction may be obtained using the router parking techniques while maintaining Quality of Service performance objectives.
Owner:INTEL CORP
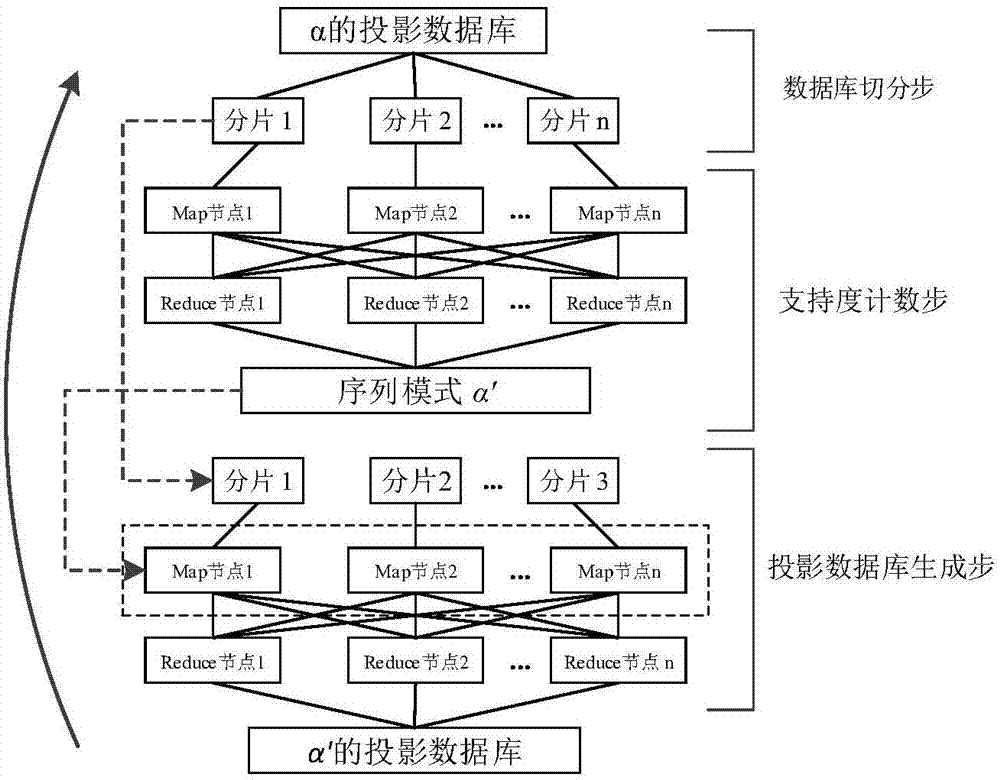
Parallel sequence pattern mining method based on Spark cloud computing platform
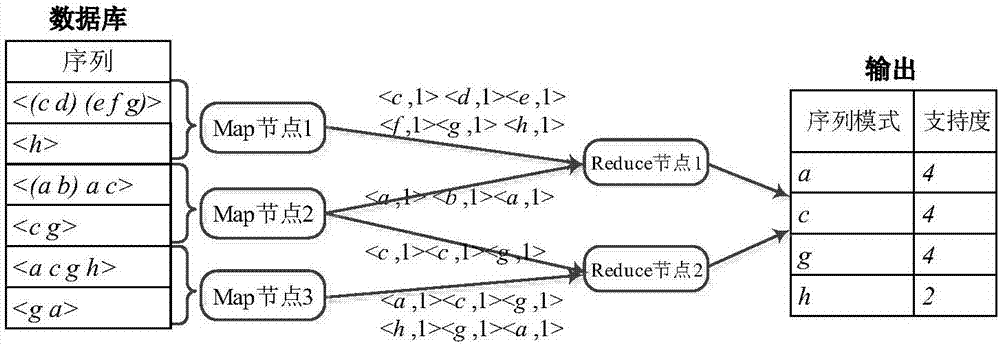
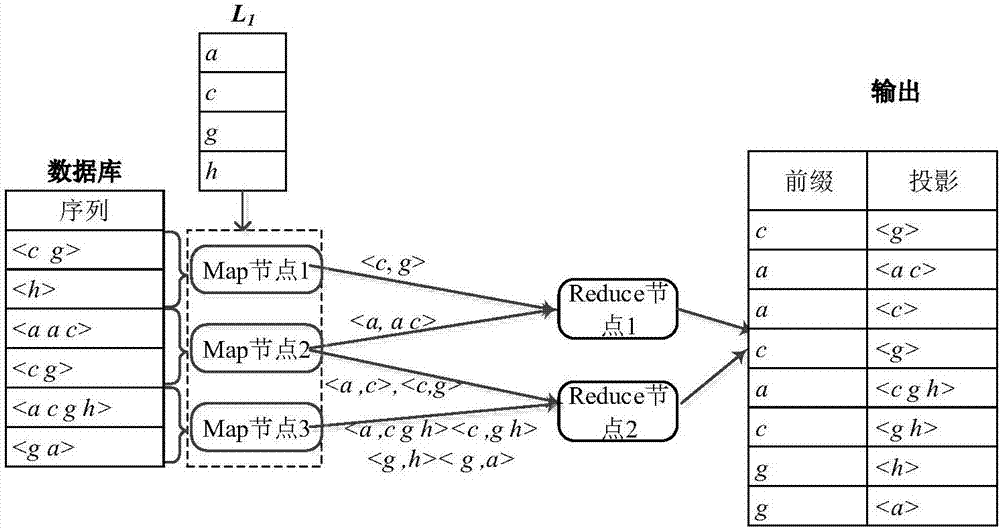
InactiveCN107346331AImprove digging efficiencySolve the problem of load imbalanceSpecial data processing applicationsSequence databaseSerialization
The invention discloses a parallel sequence pattern mining method based on a Spark cloud computing platform. For the problems that the existing serialization sequence pattern mining algorithm has low-effective algorithm capacity during processing mass data and the existing parallel sequence pattern mining algorithm based on Hadoop has high IO overhead and imbalanced loading, the invention designs a reasonable projection sequence database splitting strategy, so that the problem of imbalanced loading can be solved to maximum. On the basis, parallelization on an original PrefixSpan algorithm can be realized according to the characteristic of a MapReduce programming frame, so that the mass data sequence pattern mining efficiency can be improved by utilizing the massive parallel computing capacity of the Spark cloud computing platform. The technical scheme provided by the invention has the characteristics of easiness, and rapidness and can better improve the efficiency of sequence pattern mining.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
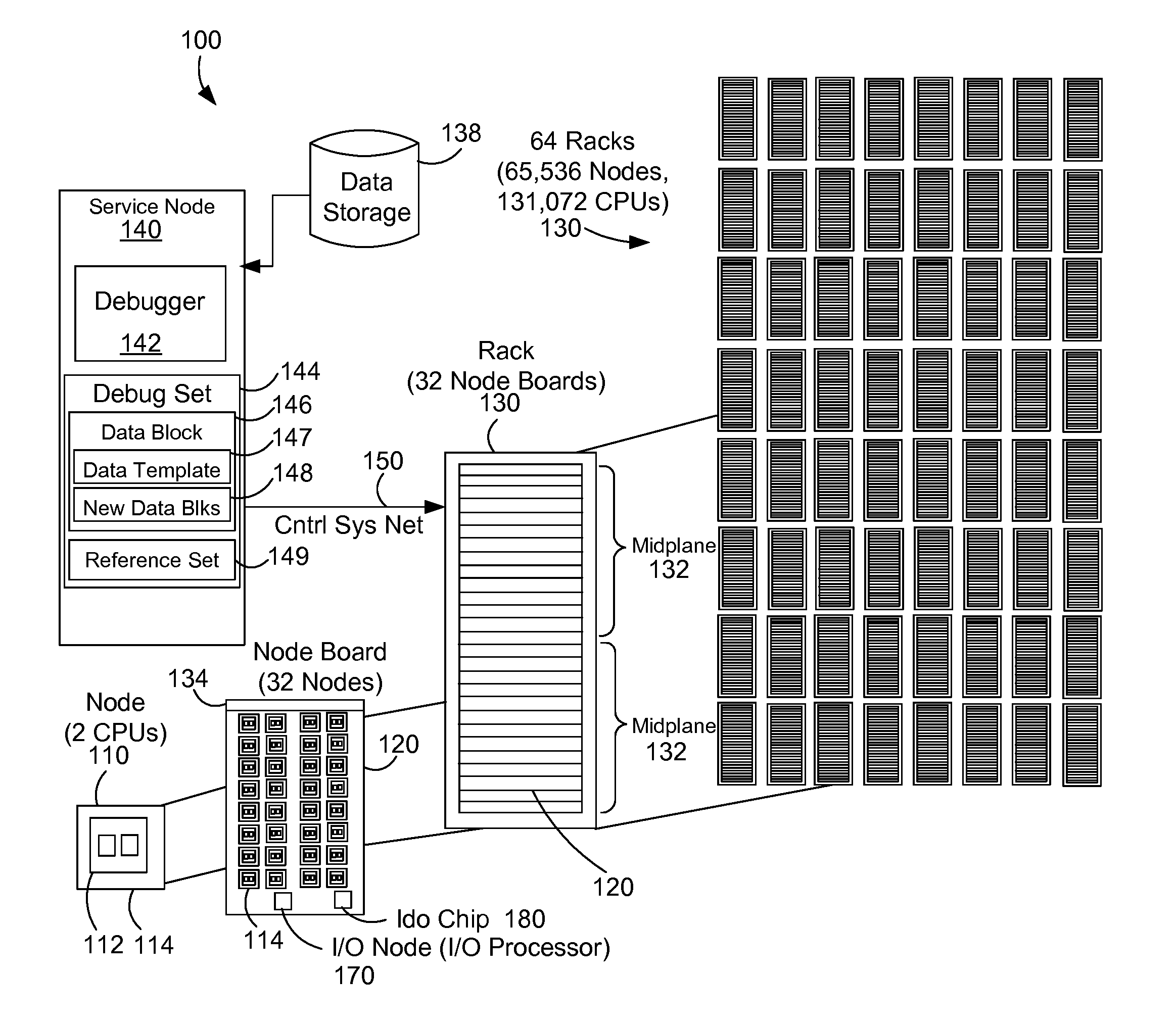
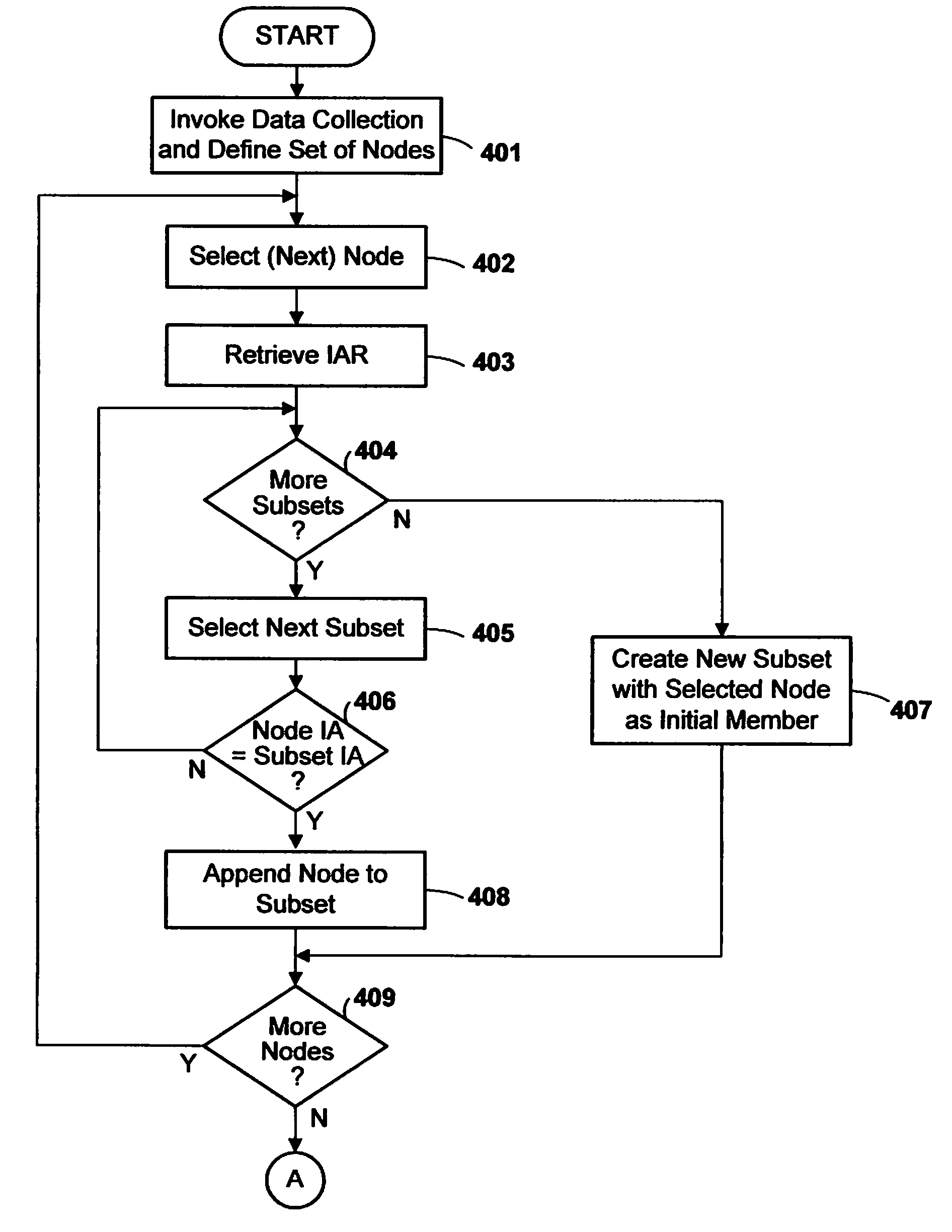
Method and apparatus for obtaining stack traceback data for multiple computing nodes of a massively parallel computer system
InactiveUS7673182B2Improve trustError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsComputational scienceTheoretical computer science
A data collector for a massively parallel computer system obtains call-return stack traceback data for multiple nodes by retrieving partial call-return stack traceback data from each node, grouping the nodes in subsets according to the partial traceback data, and obtaining further call-return stack traceback data from a representative node or nodes of each subset. Preferably, the partial data is a respective instruction address from each node, nodes having identical instruction address being grouped together in the same subset. Preferably, a single node of each subset is chosen and full stack traceback data is retrieved from the call-return stack within the chosen node.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
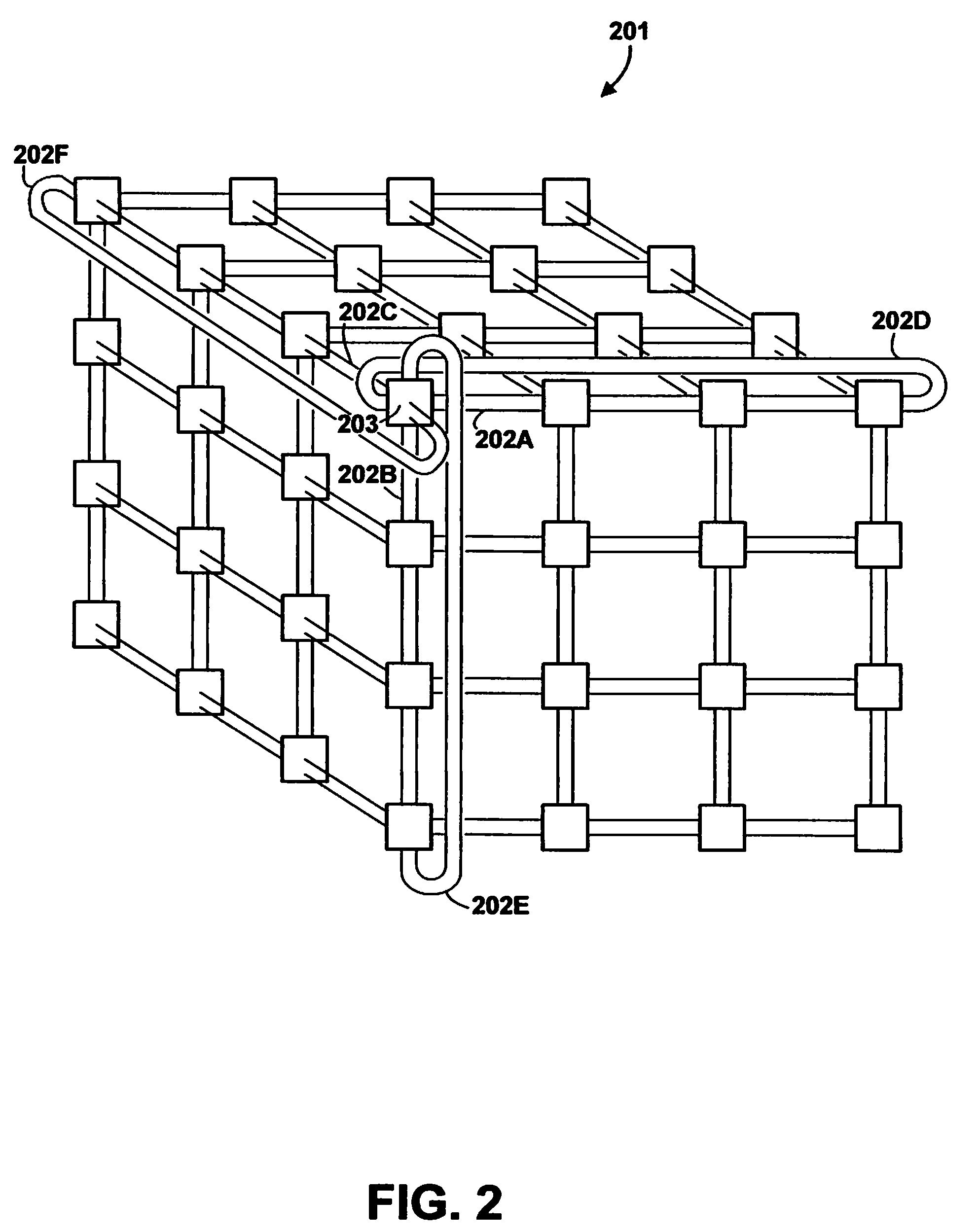
Method and apparatus for routing data in an inter-nodal communications lattice of a massively parallel computer system by routing through transporter nodes
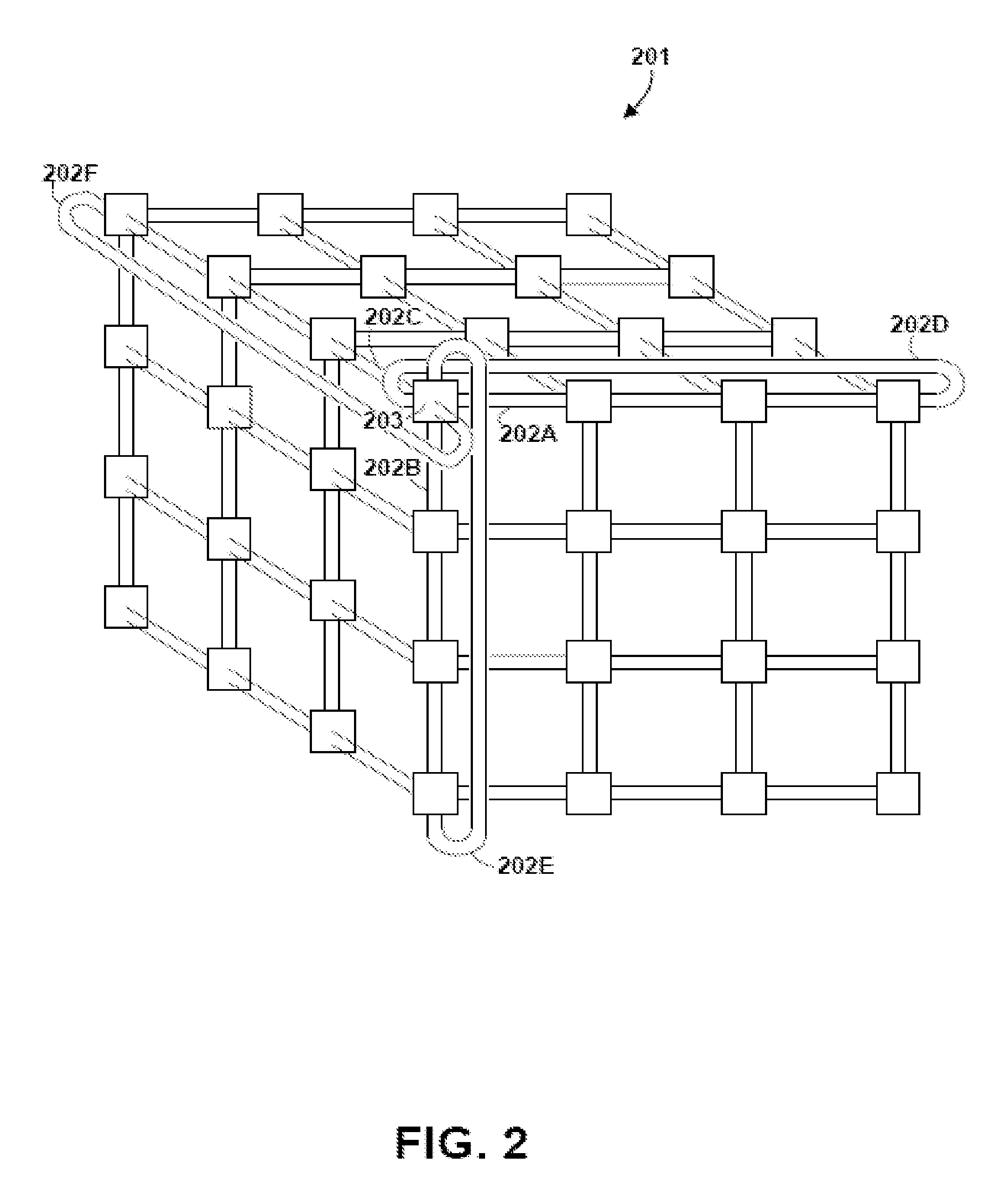
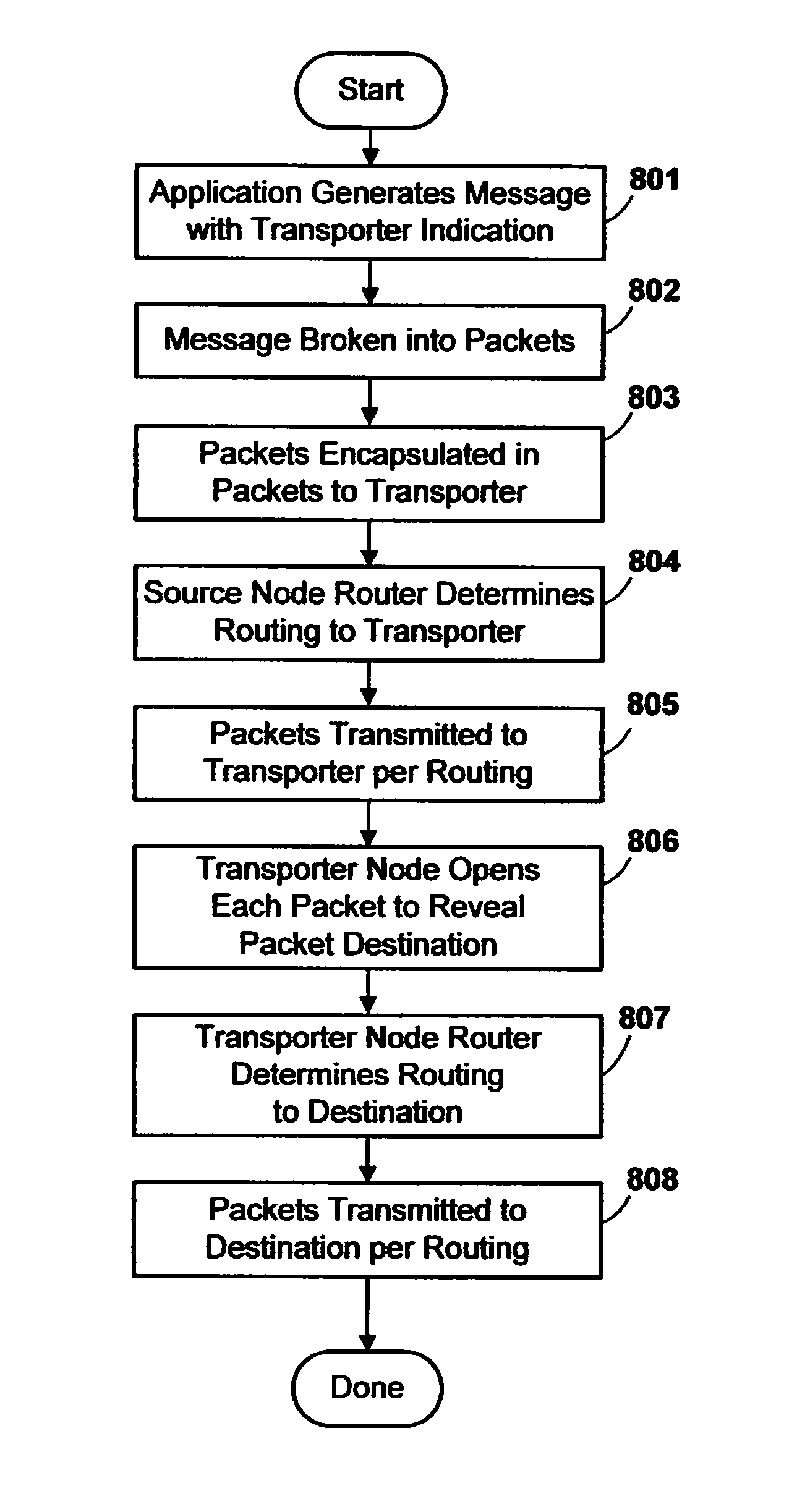
InactiveUS7835284B2Improve network efficiencyEasy to routeMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionAutomatic routingDistributed computing
A massively parallel computer system contains an inter-nodal communications network of node-to-node links. An automated routing strategy routes packets through one or more intermediate nodes of the network to reach a destination. Some packets are constrained to be routed through respective designated transporter nodes, the automated routing strategy determining a path from a respective source node to a respective transporter node, and from a respective transporter node to a respective destination node. Preferably, the source node chooses a routing policy from among multiple possible choices, and that policy is followed by all intermediate nodes. The use of transporter nodes allows greater flexibility in routing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
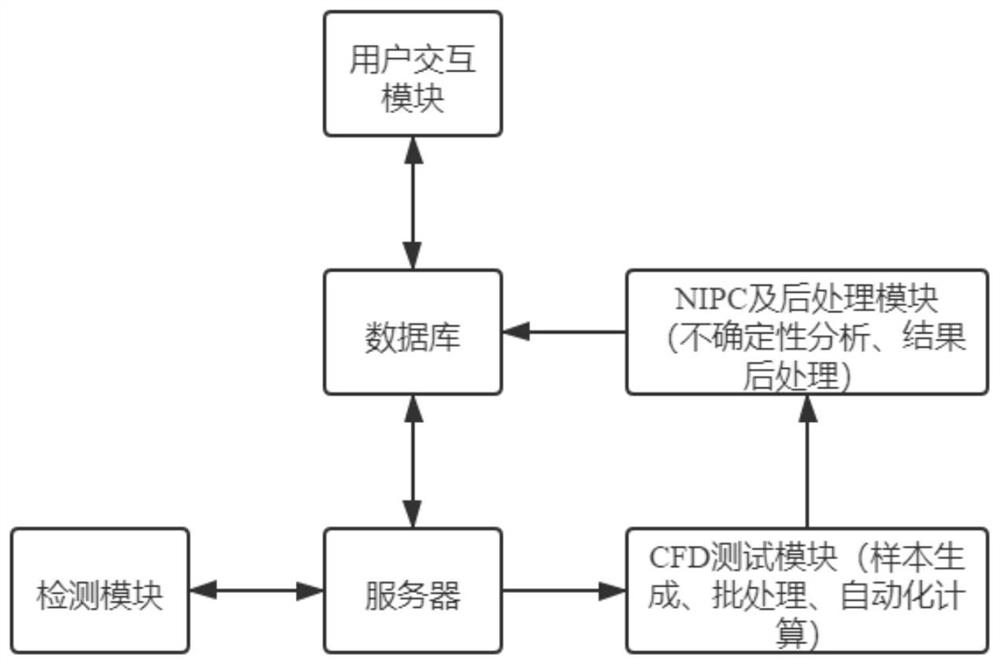
Automatic uncertainty analysis platform and method based on large-scale CFD parallel computing software
PendingCN114239428AImprove scalabilityWith analysis functionDesign optimisation/simulationBatch processingConcurrent computation
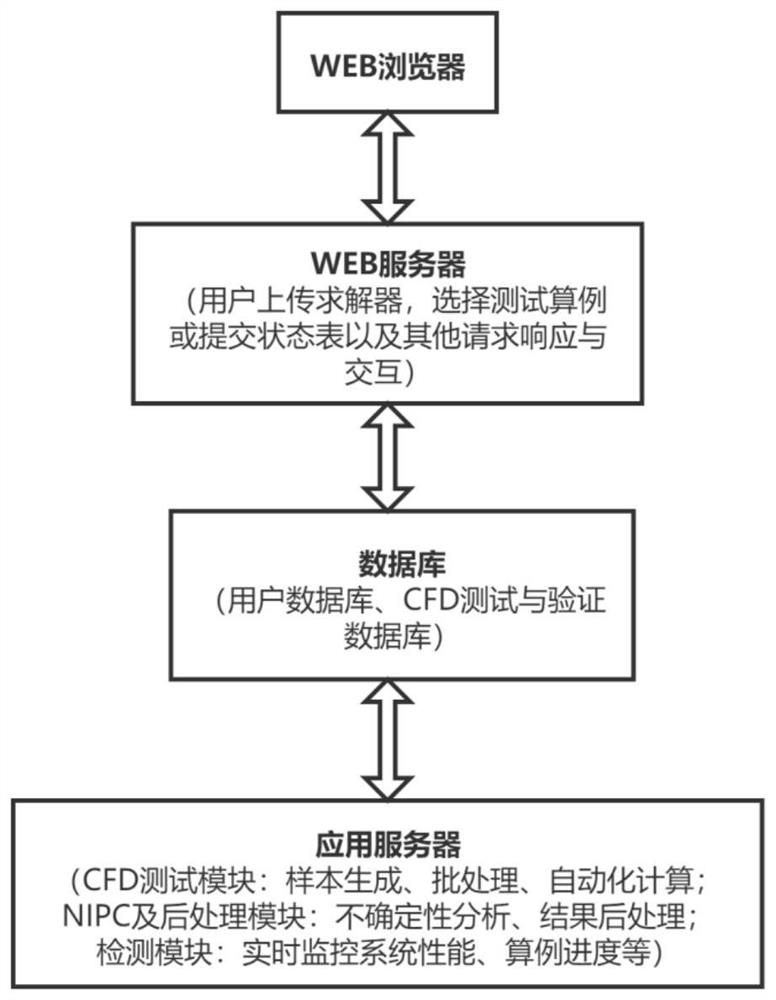
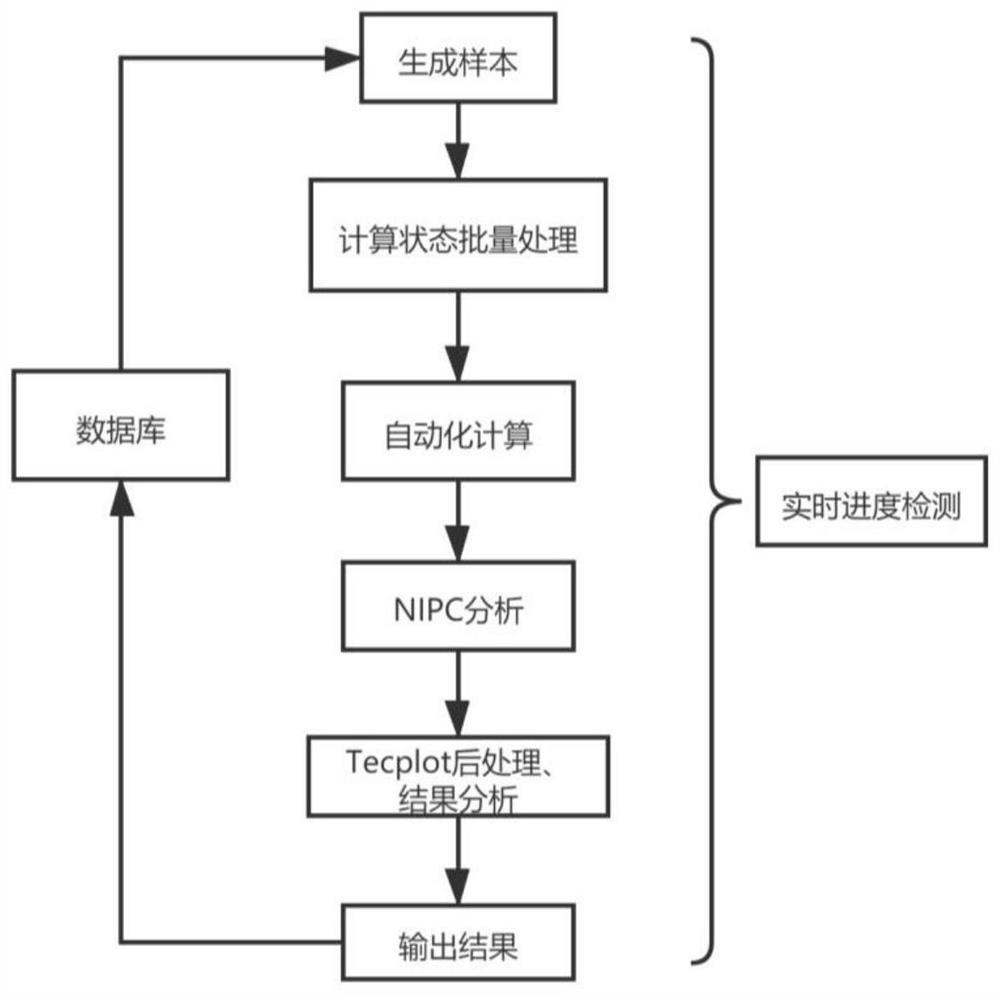
The invention provides an automatic uncertainty analysis platform and method based on large-scale CFD parallel computing software. The automatic uncertainty analysis platform comprises a user interaction module, a database, a server, a CFD test module, an NIPC, a post-processing module and a monitoring module. The database is connected with the user interaction module and the server, the server module is connected with and controls the CFD test module, the monitoring module and the NIPC and post-processing module, the CFD test module comprises sample generation, batch processing and automatic calculation, and finally a plurality of calculation results are output to the NIPC and post-processing module. And after uncertainty analysis and result post-processing, an analysis result and original data are returned to a database and finally returned to the user interaction module. According to the method, automatic uncertainty analysis of large-scale CFD software is completed through the processes of network access, automatic example and sample loading, cluster calculation submission, real-time progress monitoring, NIPC uncertainty analysis, automatic post-processing and the like, and experimental comparison diagrams, analysis reports, summary reports and the like are provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Large-scale DSP parallel computing device
PendingCN112631986AImprove computing powerSave computing powerResource allocationDigital computer detailsConcurrent computationControl cell
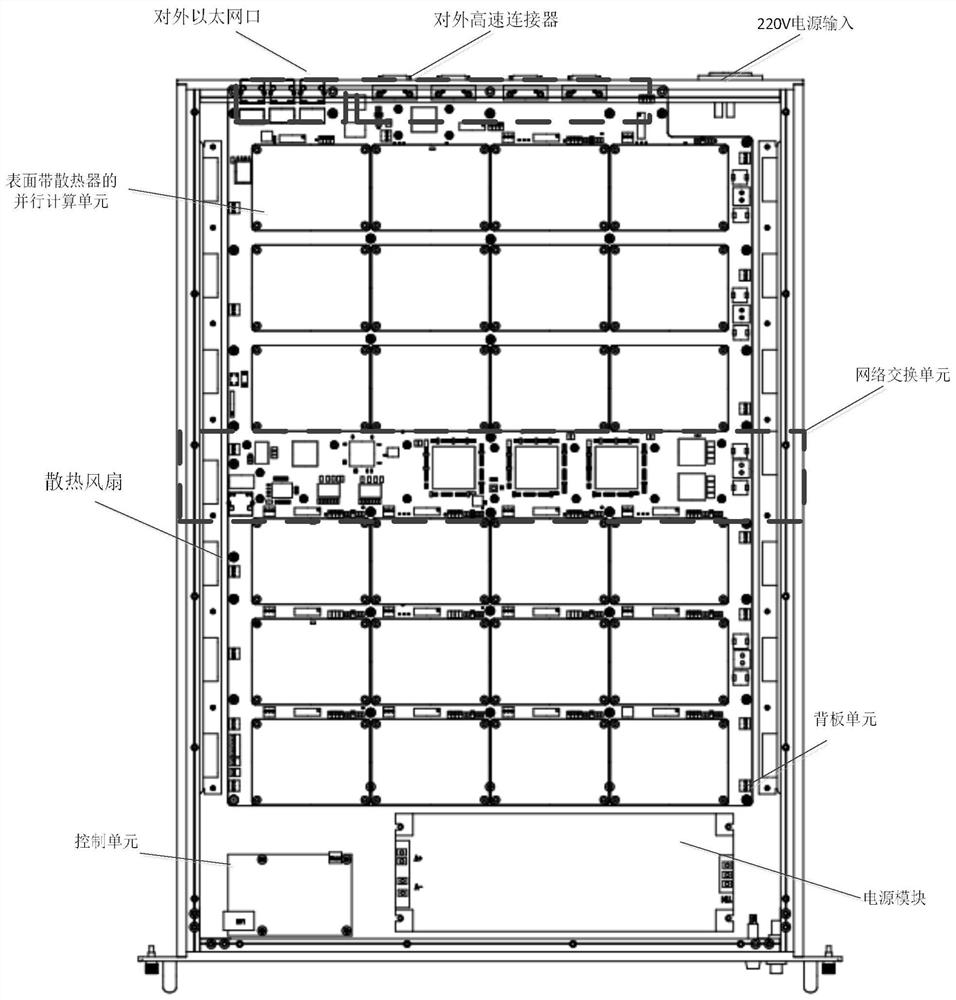
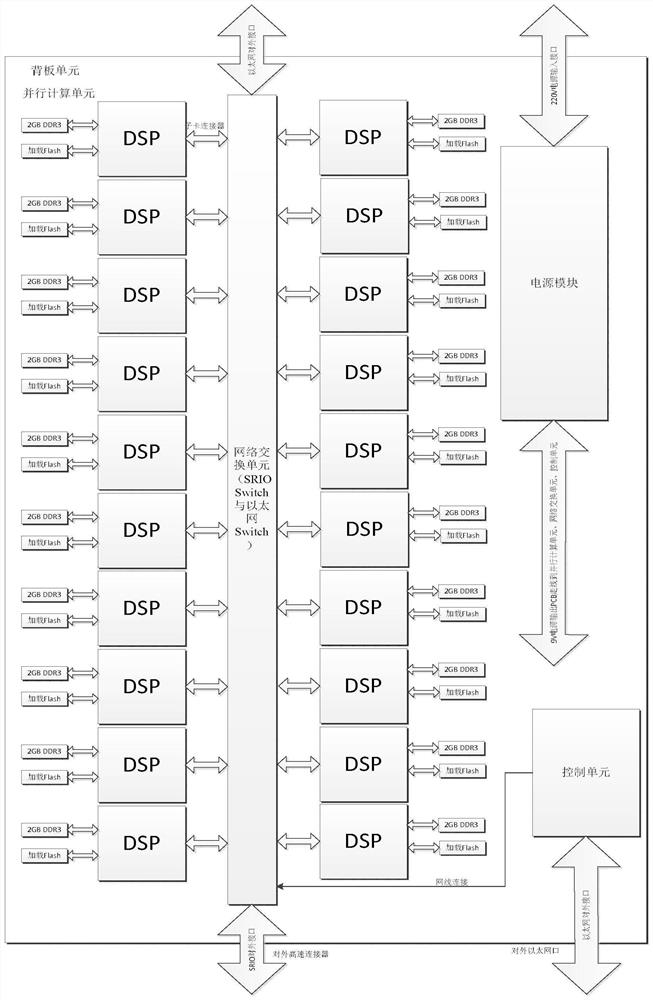
The invention discloses a large-scale DSP parallel computing device, and aims to provide a DSP parallel computing device which is simple in development environment, good in transportability, safe and reliable. According to the technical scheme, a backboard unit utilizes a high-speed printed circuit board (PCB) wiring technology to lead out an RIO network of an installation slot to be connected with a network switching unit, and each DSP chip sub-card board carries a DDR3 chip and cooperates with a loading FLASH chip and an EEPROM chip array to achieve a parallel computing unit. The DSP chips are symmetrically distributed and connected to the two sides of the network switching unit in a linear array manner; a control unit is connected with the network switching unit through a network cable, completes network routing, dynamically distributes sub-tasks based on measurement point calculation to each calculation node, automatically distributes calculation resources to newly established tasks, automatically distributes DSP calculation resources by receiving the calculation tasks issued by a user, and completes all iterative calculations by adopting different processes or the same process.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com