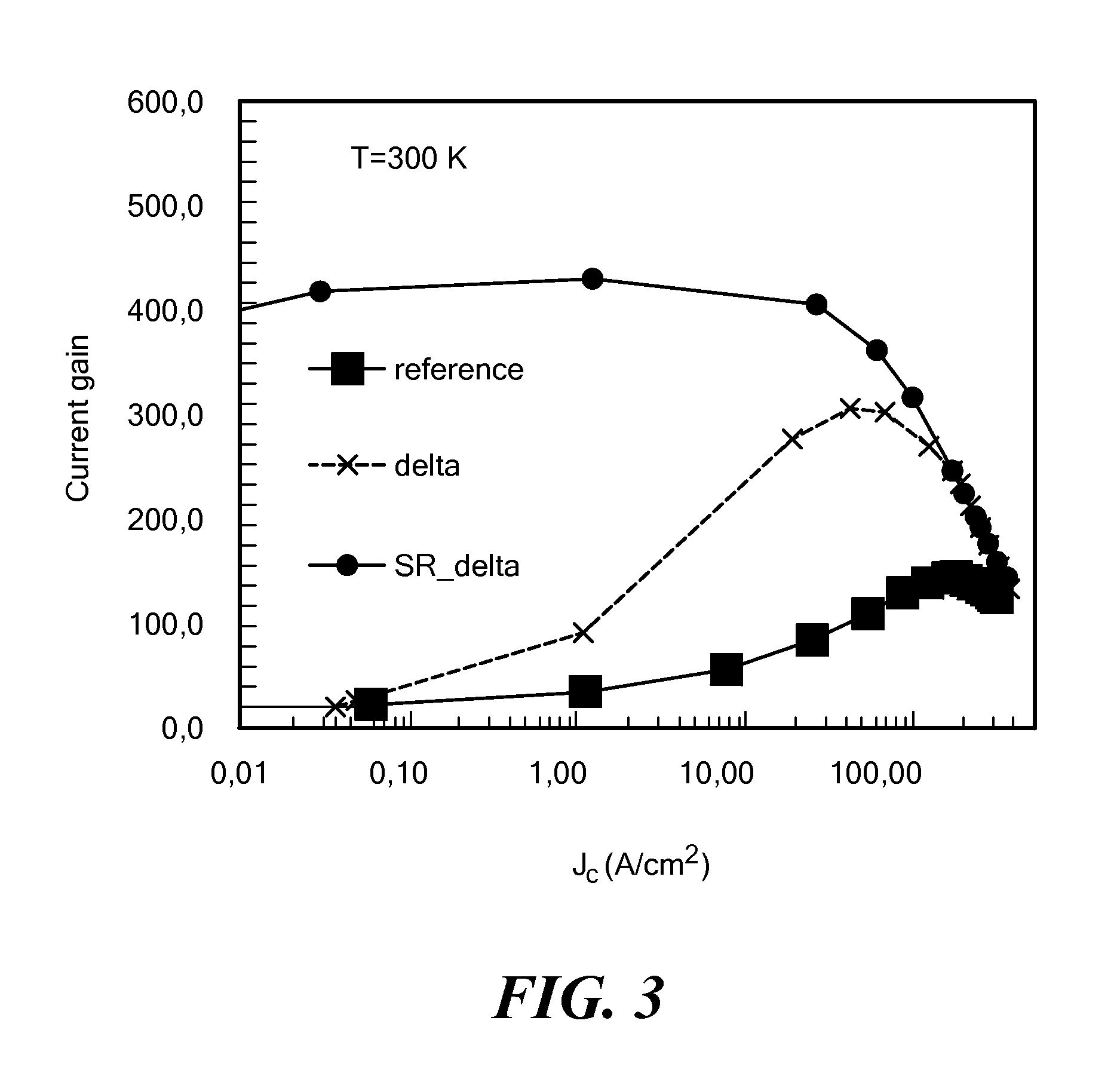
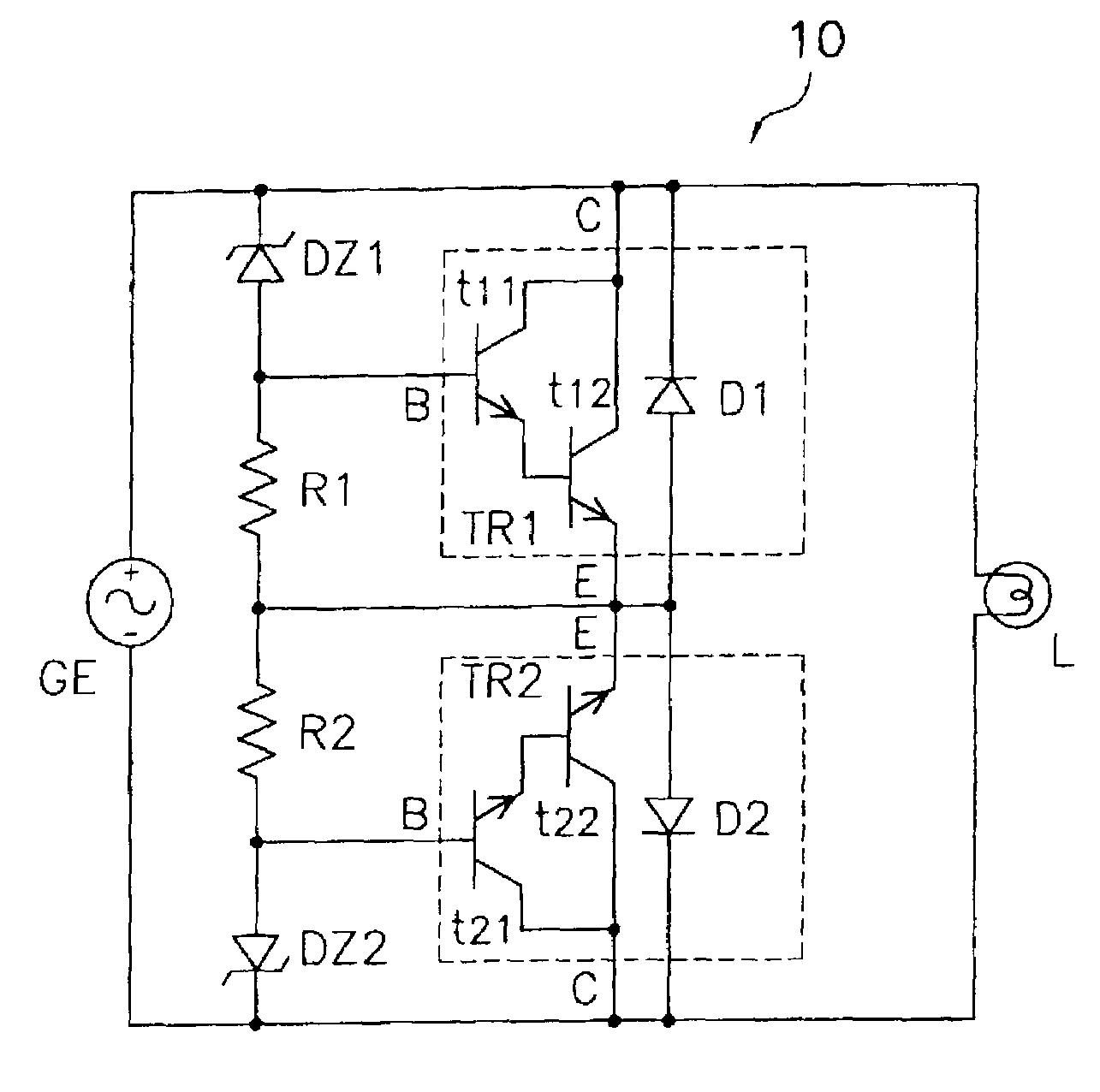
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "High current gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
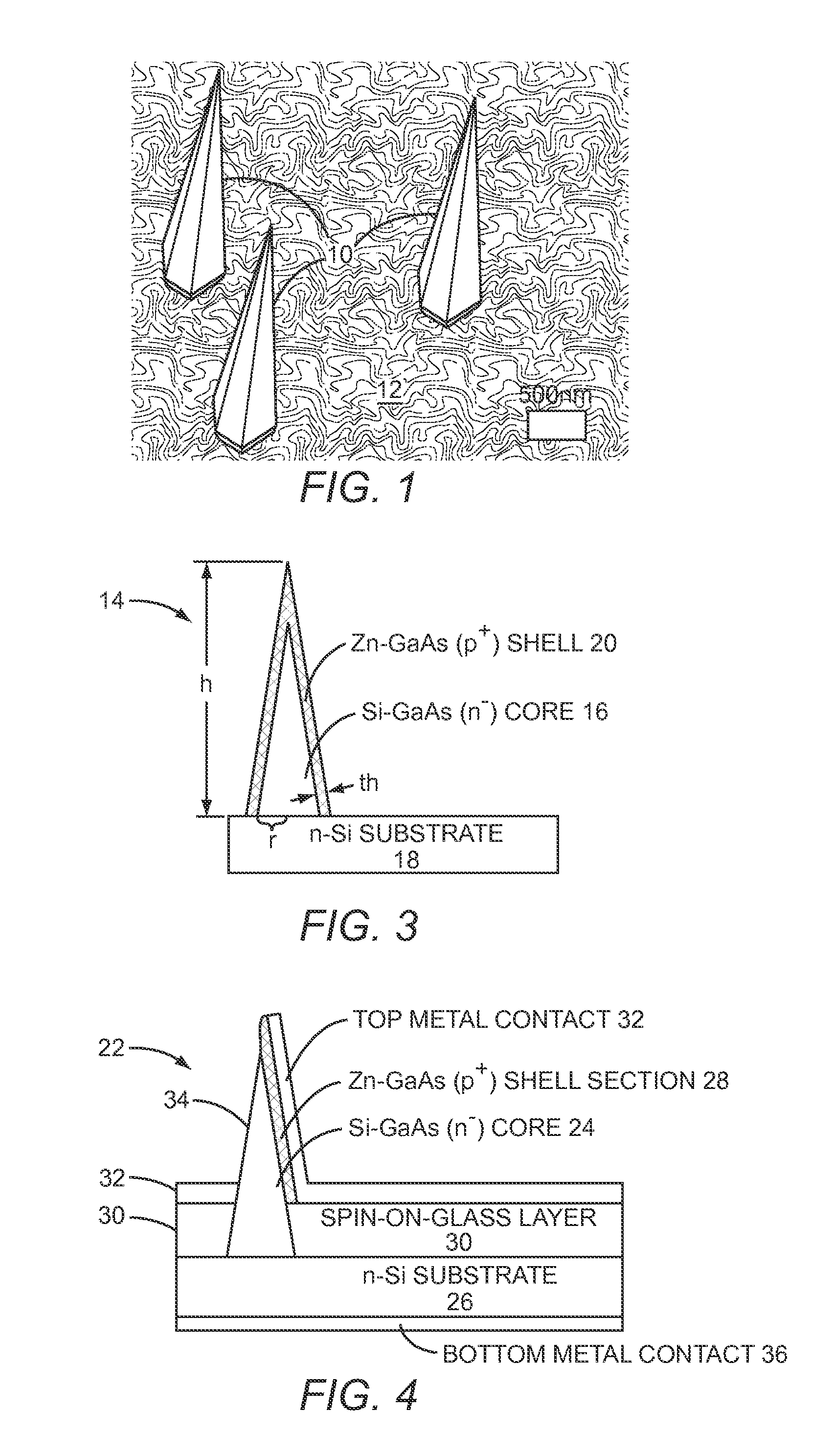
Nanoneedle plasmonic photodetectors and solar cells
InactiveUS20110146771A1Improve device performanceImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanosensorsPhotodetectorSolar cell
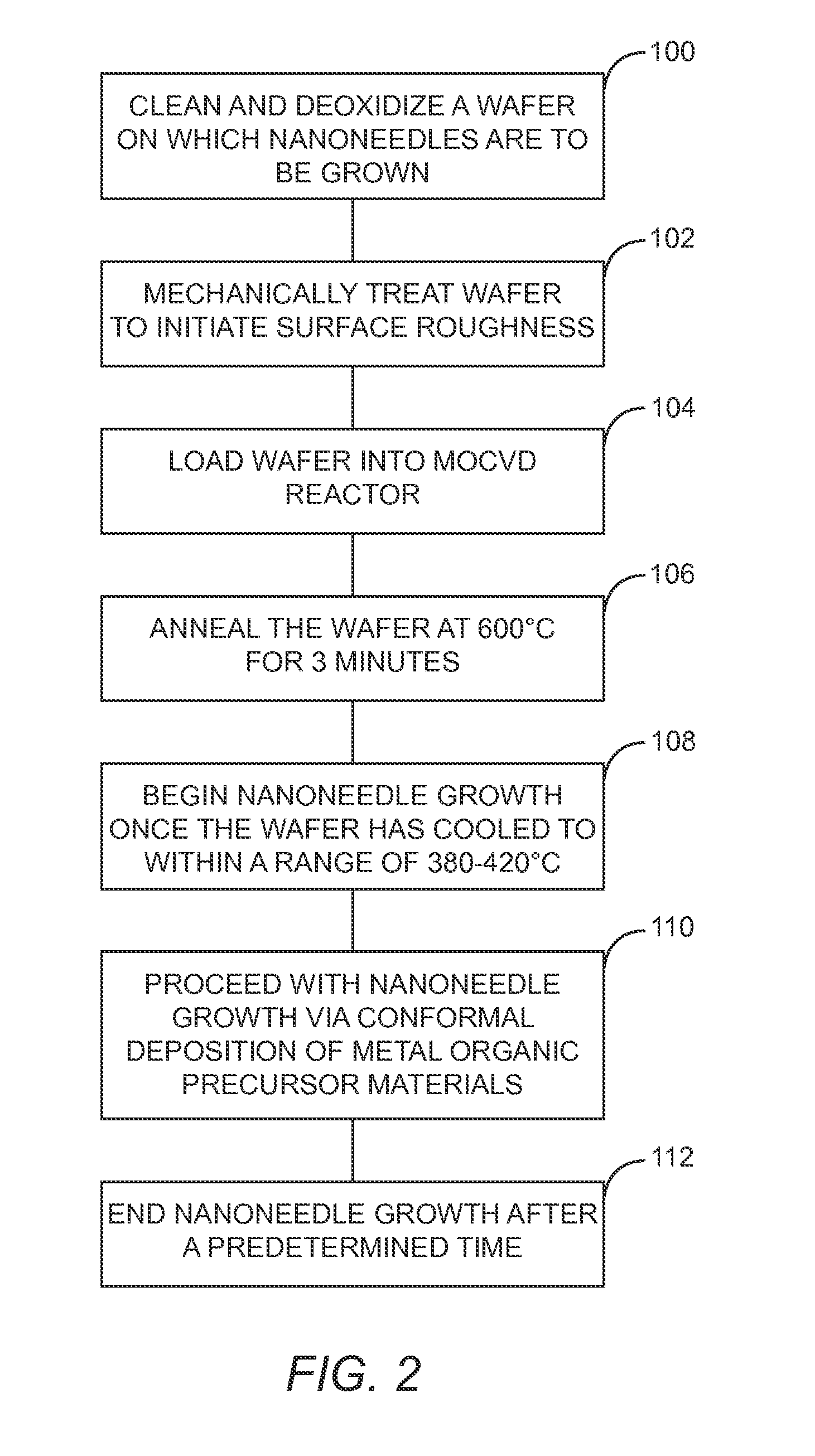
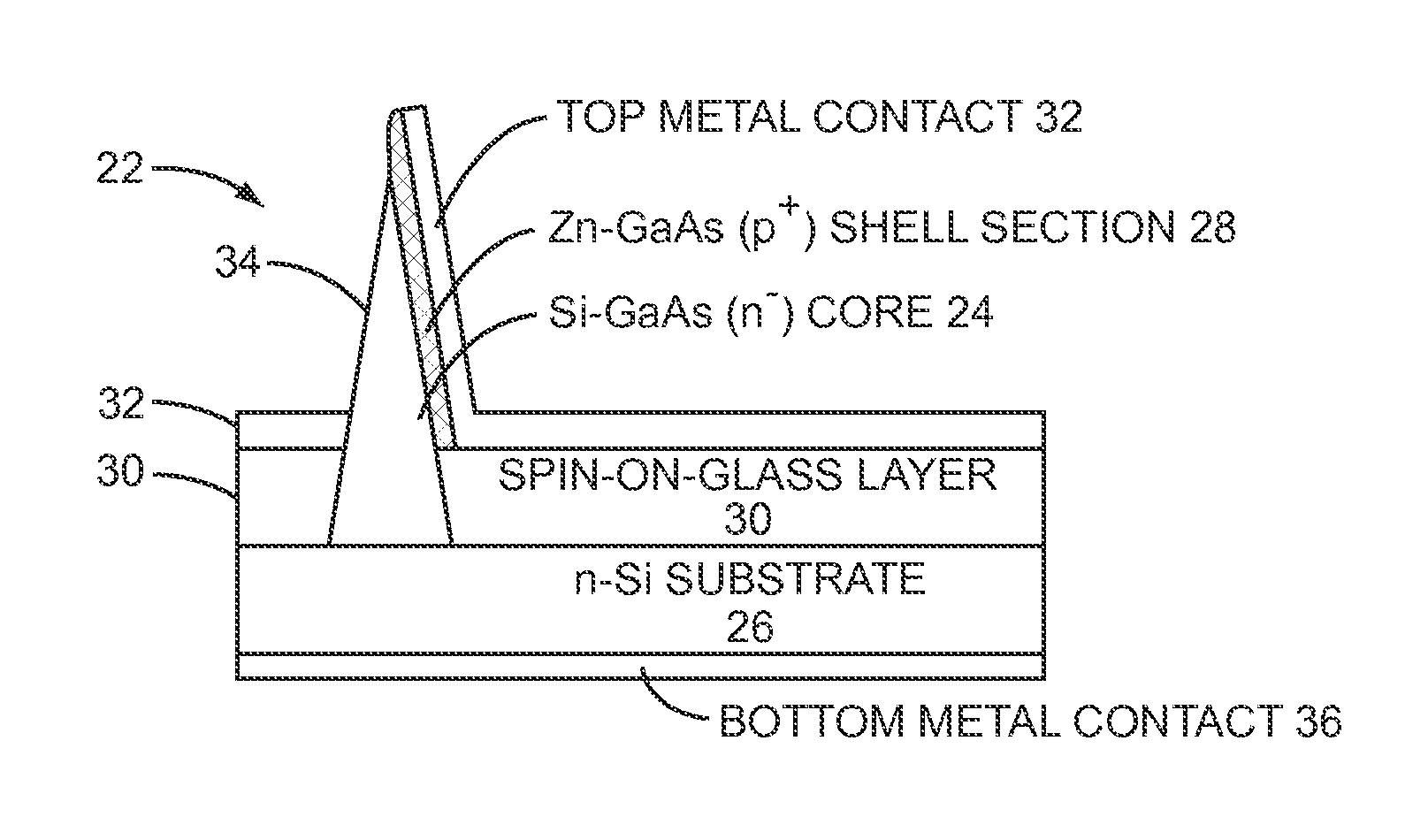
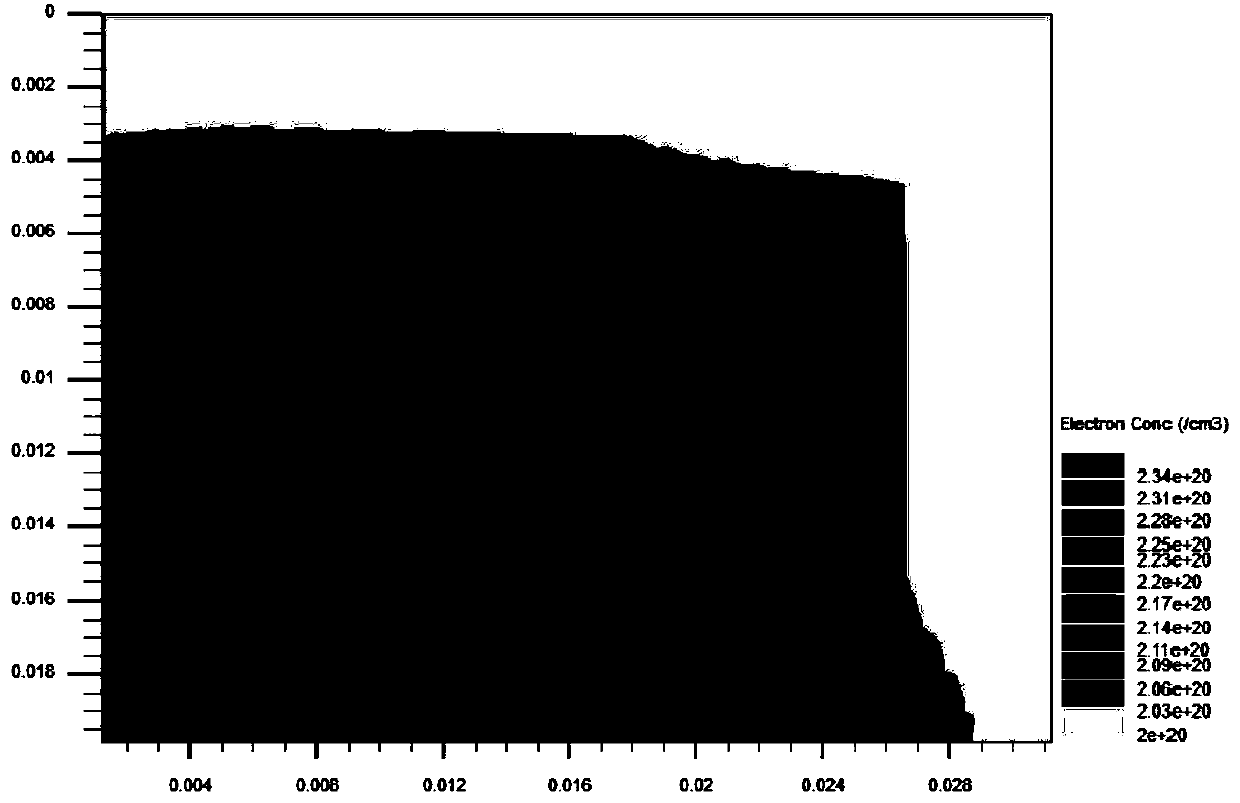
The present disclosure provides a catalyst-free growth mode of defect-free Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)-based nanoneedles on silicon (Si) substrates with a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible growth temperature of around 400° C. Each nanoneedle has a sharp 2 to 5 nanometer (nm) tip, a 600 nm wide base and a 4 micrometer (μm) length. Thus, the disclosed nanoneedles are substantially hexagonal needle-like crystal structures that assume a 6° to 9° tapered shape. The 600 nm wide base allows the typical micro-fabrication processes, such as optical lithography, to be applied. Therefore, nanoneedles are an ideal platform for the integration of optoelectronic devices on Si substrates. A nanoneedle avalanche photodiode (APD) grown on silicon is presented in this disclosure as a device application example. The APD attains a high current gain of 265 with only 8V bias.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High Voltage High Current Regulator
ActiveUS20120081097A1Minimized size requirementPreventing internal electrical short circuitAnti-noise capacitorsElectrode assembly support/mounting/spacing/insulationHigh voltage igbtControl signal
High voltage high current regulator circuit for regulating current is interposed between first and second terminals connected to an external circuit and comprises at least one main-current carrying cold-cathode field emission electron tube conducting current between the first and second terminals. First and second grid-control cold-cathode field emission electron tubes provide control signals for first and second grids of the at least one main-current carrying cold-cathode field emission electron tube for positive and negative excursions of voltage on the first and second terminals, respectively. The current regulator circuit may be accompanied by a voltage-clamping circuit that includes at least one cold-cathode field emission electron tube. At least two cold-cathode field emission electron tubes, configured to operate at high voltage and high current, are preferably contained within a single vacuum enclosure and are interconnected to provide a circuit function, so as to form a high voltage high current vacuum integrated circuit.
Owner:ADVANCED FUSION SYST LLC
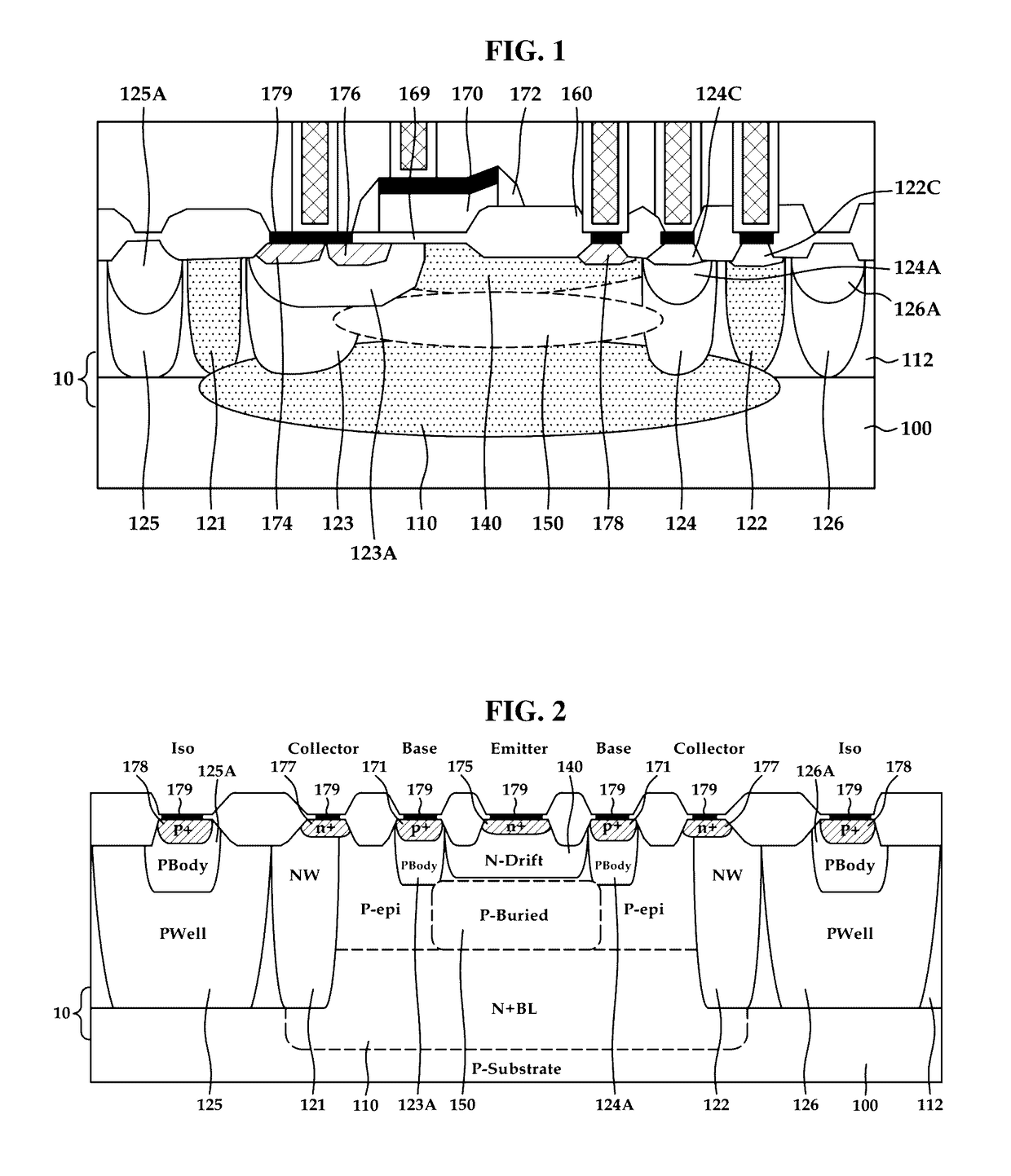
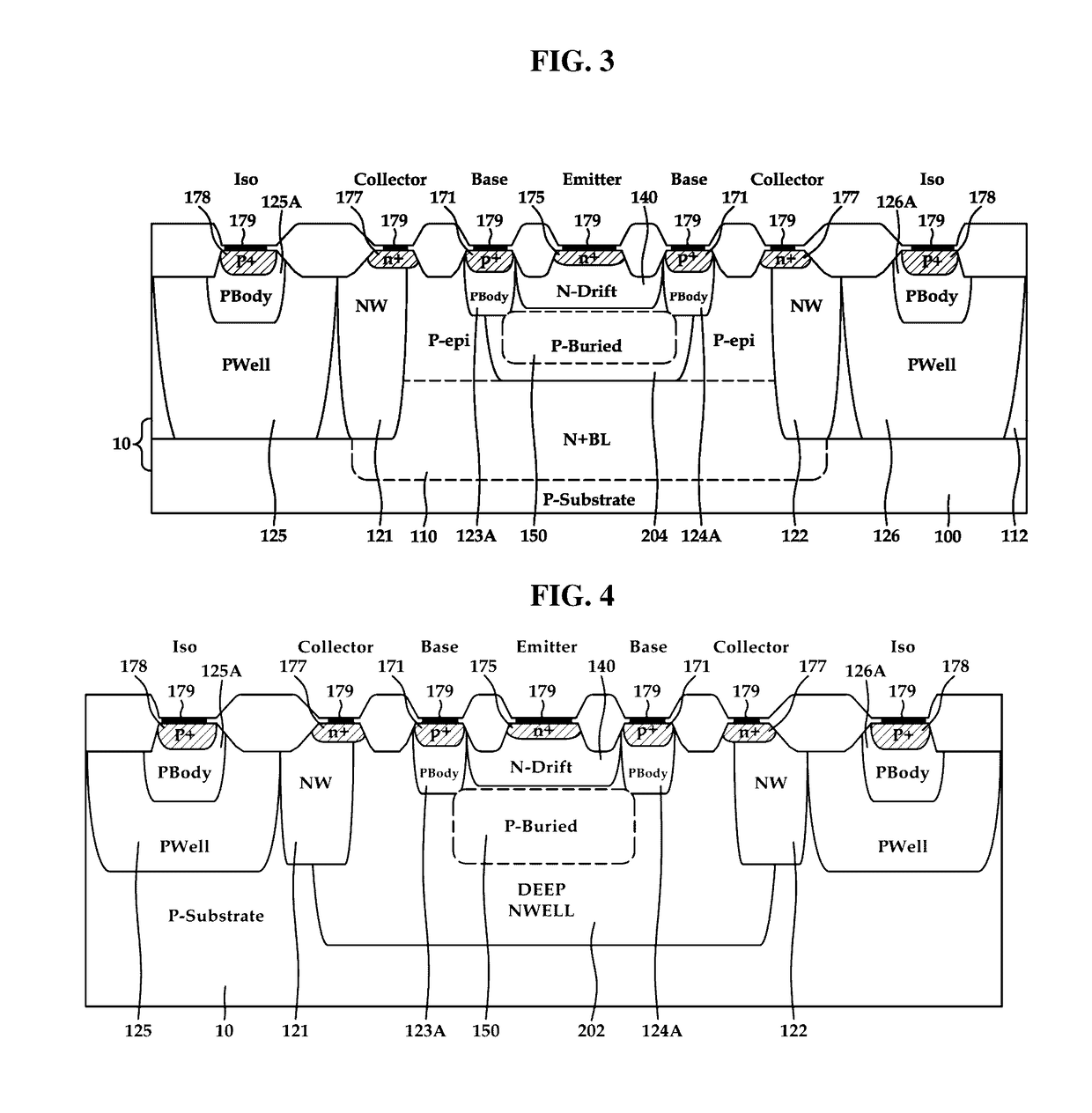
Vertical bipolar junction transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20150243770A1Well formedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationPower flow
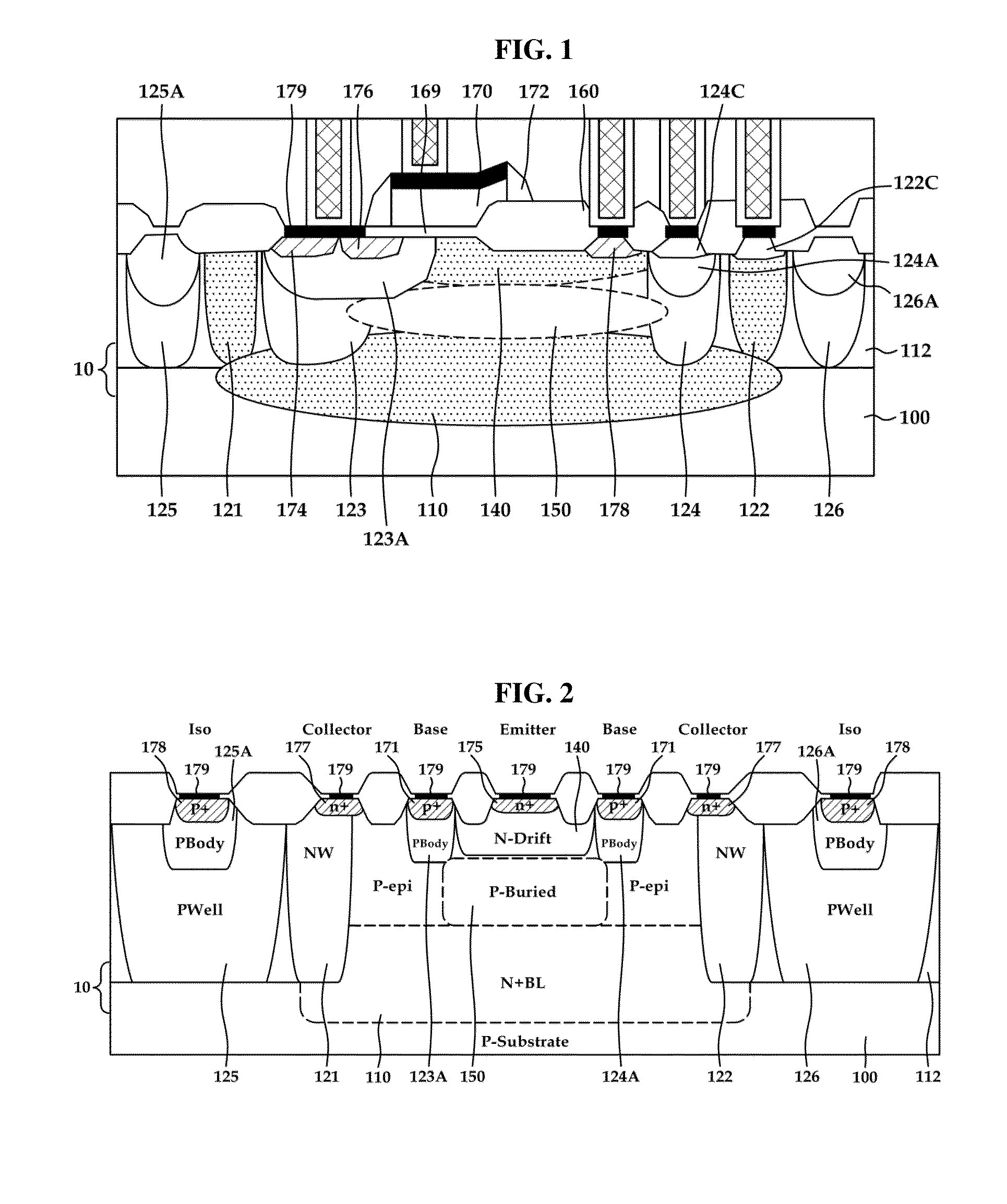
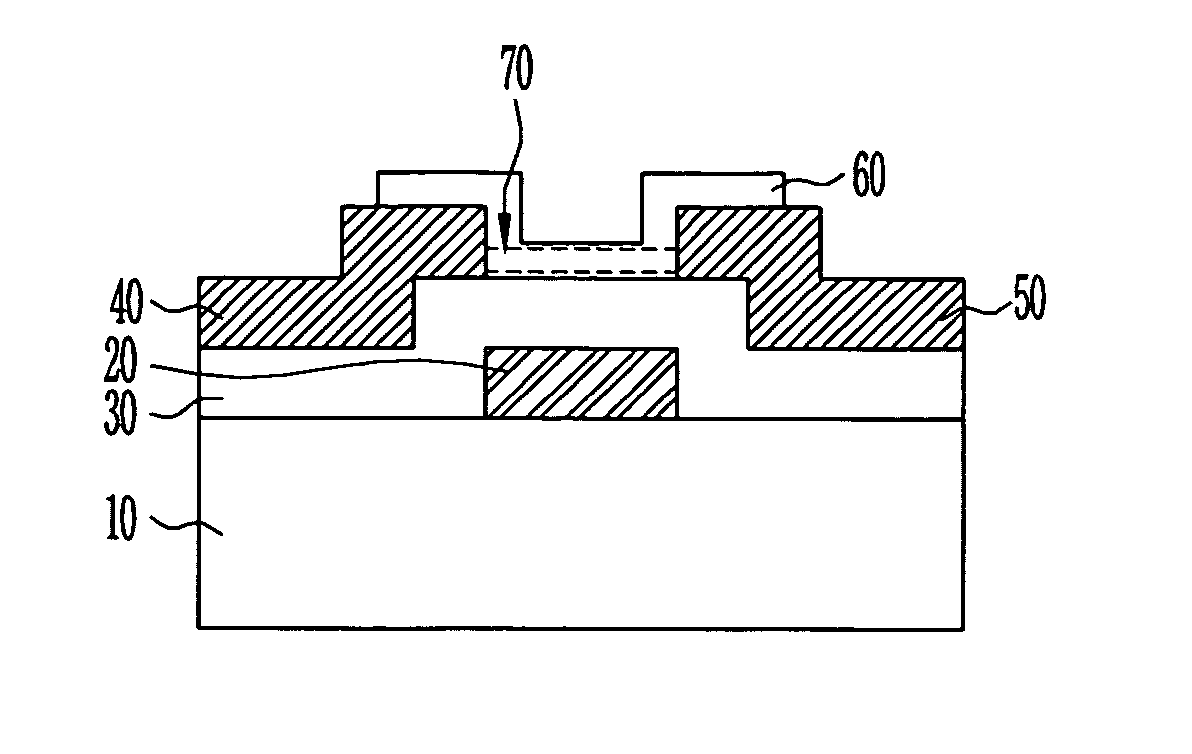
The present disclosure relates to a vertical bipolar junction transistor. A vertical bipolar junction transistor includes a high concentration doping region emitter terminal disposed on a semiconductor substrate; a high concentration doping region collector terminal disposed on a semiconductor substrate; a high concentration doping region base terminal disposed between the emitter terminal and the collector terminal; a drift region having a first doping concentration surrounding the emitter terminal and being deeper than either the base terminal or the collector terminal; a base layer disposed below the drift region; a collector layer in contact with the base layer, the collector layer having a second doping concentration higher than the first doping concentration. The manufacturing cost of the vertical bipolar junction transistor can be lowered and a current gain can be elevated using a low-cost BCD process.
Owner:KEY FOUNDRY CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7378325B2Improve pressure resistanceReduced injection efficiencyThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolumetric Mass DensityHigh pressure
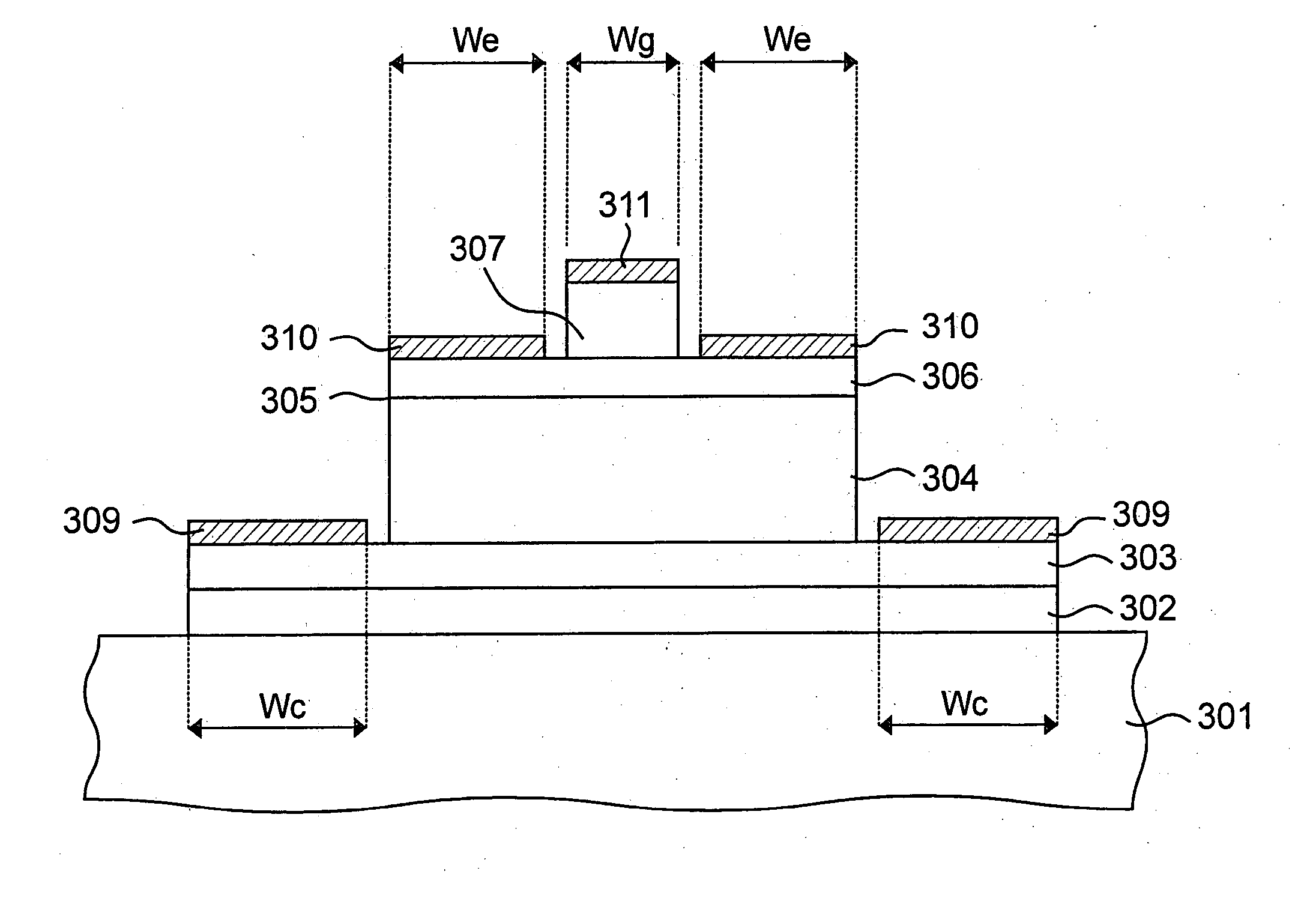
A high voltage semiconductor device having a high current gain hFE is formed with a collector region (20) of a first conduction type, an emitter region (40) of the first conduction type, and a base region (30) of a second conduction type opposite to the first conduction type located between the collector region and the emitter region. The free carrier density of the base region (30) where no depletion layer is formed is smaller than the space charge density of a depletion layer formed in the base region (30).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Metal-insulator transition switching transistor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7408217B2Small sizeHigh current gain characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal–insulator transitionSilicon
Provided is a metal-insulator-transition switching transistor with a gate electrode on a silicon substrate (back-gate structure) and a metal-insulator-transition channel layer of VO2 that changes from an insulator phase to a metal phase, or vice versa, depending on a variation of an electric field, and a method for manufacturing the same, whereby it is possible to fabricate a metal-insulator-transition switching transistor having high current gain characteristics and being stable thermally.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Bipolar junction transistor
InactiveCN101425536AImprove transportation capacityIncrease common emitter current gainTransistorDc dc converterSemiconductor
A bipolar junction transistor relates to the technical field of a semiconductor power device. The transistor comprises an underlay, a collecting region, an emitting region, a base region, an emitting electrode, a base electrode and a collecting electrode. The transistor is characterized in that a floating buried layer is arranged inside the base region; and the materials of the floating buried layer are different from that of the base region. The invention has the advantages of both good direct current characteristic and breakdown characteristic, namely both high current gain and higher breakdown voltage, and can be widely applied to the field of high-power converters (such as DC-DC converter and inverter).
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Semiconductor transistor element and its production
ActiveCN101030541AIncrease current gainEasy to operateTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSemiconductor
The invention is concerned with the method of making metal oxide semiconductor (MOS)transistor element, the characteristic is: the back-etching step that uses the silicon nitride covering layer with different stress and the superfluity shallow gully insulating layer, the field effect transistor element of N or P metal oxide semiconductor can with higher current gain, improves the operating efficiency of the semiconductor transistor element.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Metal-insulator transition switching transistor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070069193A1Small sizeHigh current gain characteristicSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesThermal stabilityMetal–insulator transition
Provided is a metal-insulator-transition switching transistor with a gate electrode on a silicon substrate (back-gate structure) and a metal-insulator-transition channel layer of VO2 that changes from an insulator phase to a metal phase, or vice versa, depending on a variation of an electric field, and a method for manufacturing the same, whereby it is possible to fabricate a metal-insulator-transition switching transistor having high current gain characteristics and being stable thermally.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Electrostatic discharge clamp circuit
InactiveUS20050002139A1Avoid troubleTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringDrain current
An ESD clamp circuit includes an ESD detecting unit and a discharge circuit with a longitudinal BJT. The longitudinal BJT is formed on a P-type substrate and includes a deep N-well formed on the P-type substrate, a P-well formed on parts of the deep N-well, a N-well formed on the deep N-well surrounding the P-well, a first N+ region formed on parts of the P-well and electrically coupled to a first voltage, a P+ region formed on the P-well surrounding the first N+ region and electrically coupled to a trigger signal, and a second N+ region formed on the N-well and electrically coupled to a second voltage. In the structure of the longitudinal BJT, the leakage current can be decreased, the current gain can be increased, and the dimension of the ESD clamp circuit can be reduced.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Nanoneedle plasmonic photodetectors and solar cells
InactiveUS8809672B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanosensorsPhotodetectorSolar cell
The present disclosure provides a catalyst-free growth mode of defect-free Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)-based nanoneedles on silicon (Si) substrates with a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible growth temperature of around 400° C. Each nanoneedle has a sharp 2 to 5 nanometer (nm) tip, a 600 nm wide base and a 4 micrometer (μm) length. Thus, the disclosed nanoneedles are substantially hexagonal needle-like crystal structures that assume a 6° to 9° tapered shape. The 600 nm wide base allows the typical micro-fabrication processes, such as optical lithography, to be applied. Therefore, nanoneedles are an ideal platform for the integration of optoelectronic devices on Si substrates. A nanoneedle avalanche photodiode (APD) grown on silicon is presented in this disclosure as a device application example. The APD attains a high current gain of 265 with only 8V bias.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
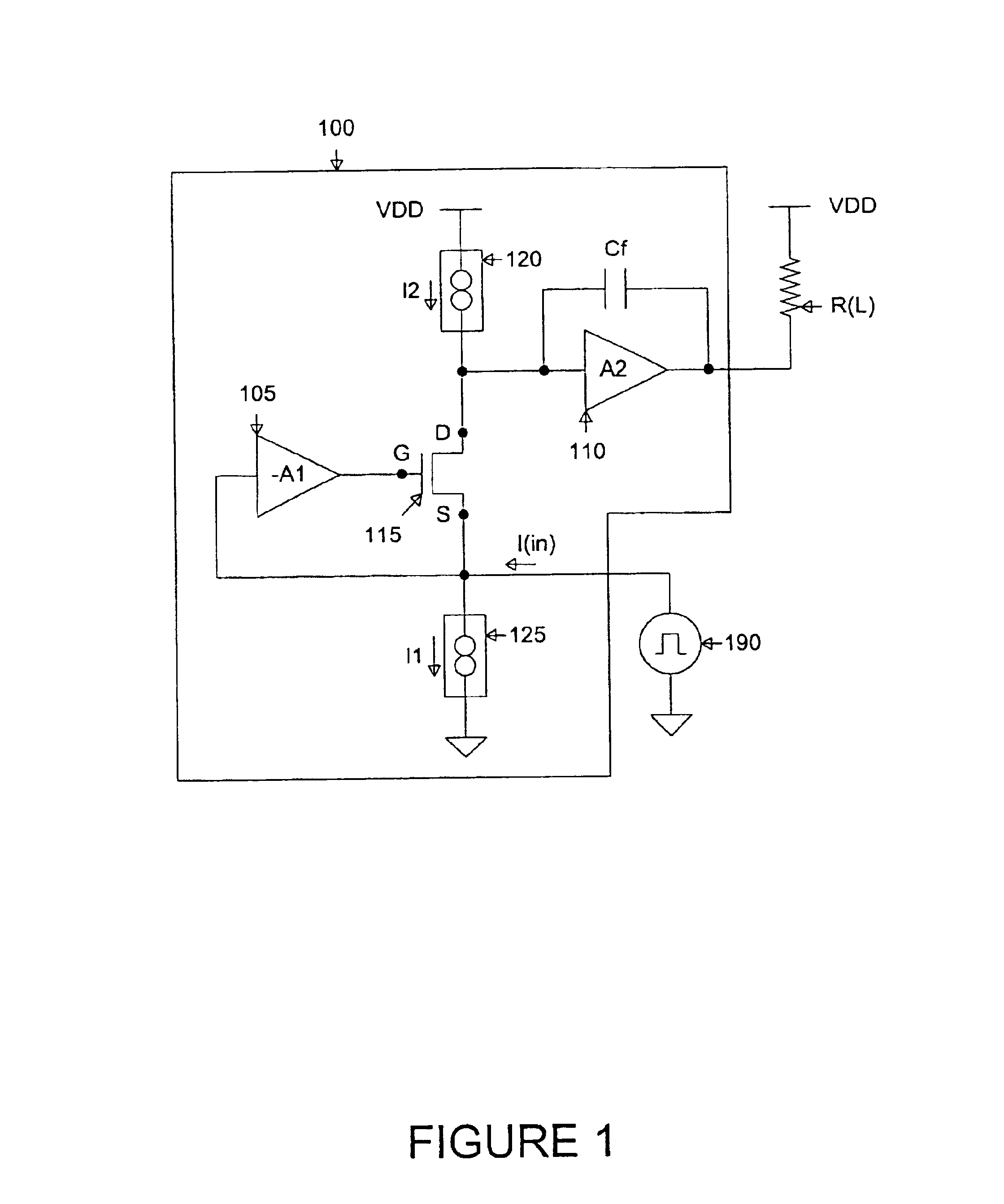
High speed high current gain operational amplifier
InactiveUS6937104B1Low impedance inputIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
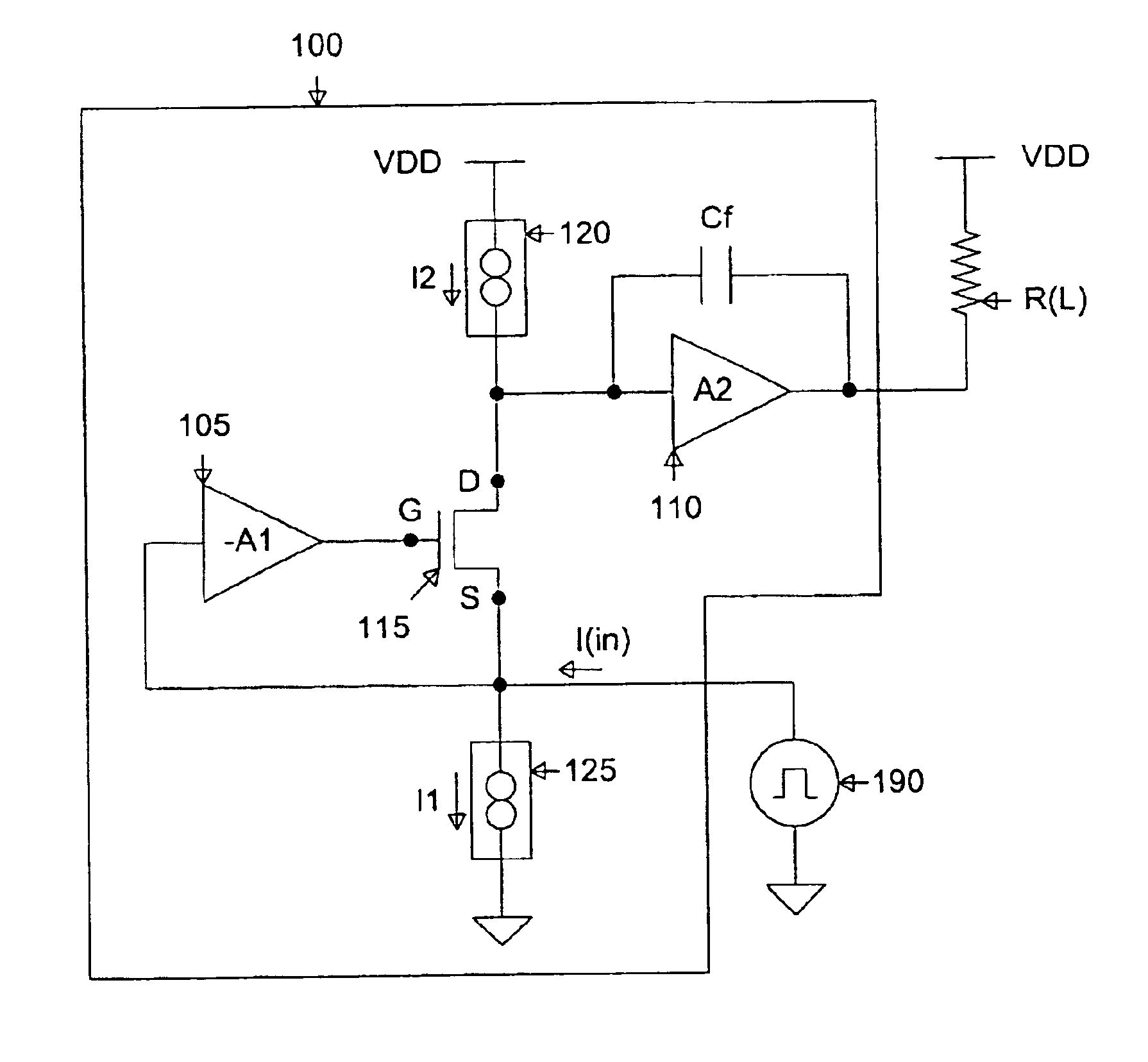
An operational amplifier having a low impedance input and a high current gain output. The operational amplifier comprises: 1) a first N-channel transistor having a source coupled to the low impedance input of the operational amplifier; 2) a first constant current source coupled between the source of the first N-channel transistor and ground; 3) a first amplifier stage having an input coupled to the first N-channel transistor source and an inverting output coupled to a gate of the first N-channel transistor; 4) a second amplifier stage having an input coupled to a drain of the first N-channel transistor and an output coupled to the high current gain output of the operational amplifier; and 5) an internal compensation capacitor coupled between the input and the output of the second amplifier stage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Vertical bipolar junction transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS9666700B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a vertical bipolar junction transistor. A vertical bipolar junction transistor includes a high concentration doping region emitter terminal disposed on a semiconductor substrate; a high concentration doping region collector terminal disposed on a semiconductor substrate; a high concentration doping region base terminal disposed between the emitter terminal and the collector terminal; a drift region having a first doping concentration surrounding the emitter terminal and being deeper than either the base terminal or the collector terminal; a base layer disposed below the drift region; a collector layer in contact with the base layer, the collector layer having a second doping concentration higher than the first doping concentration. The manufacturing cost of the vertical bipolar junction transistor can be lowered and a current gain can be elevated using a low-cost BCD process.
Owner:KEY FOUNDRY CO LTD
Amplifier with improved, high precision, high speed and low power consumption architecture
InactiveUS6281752B1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierIntermediate stage
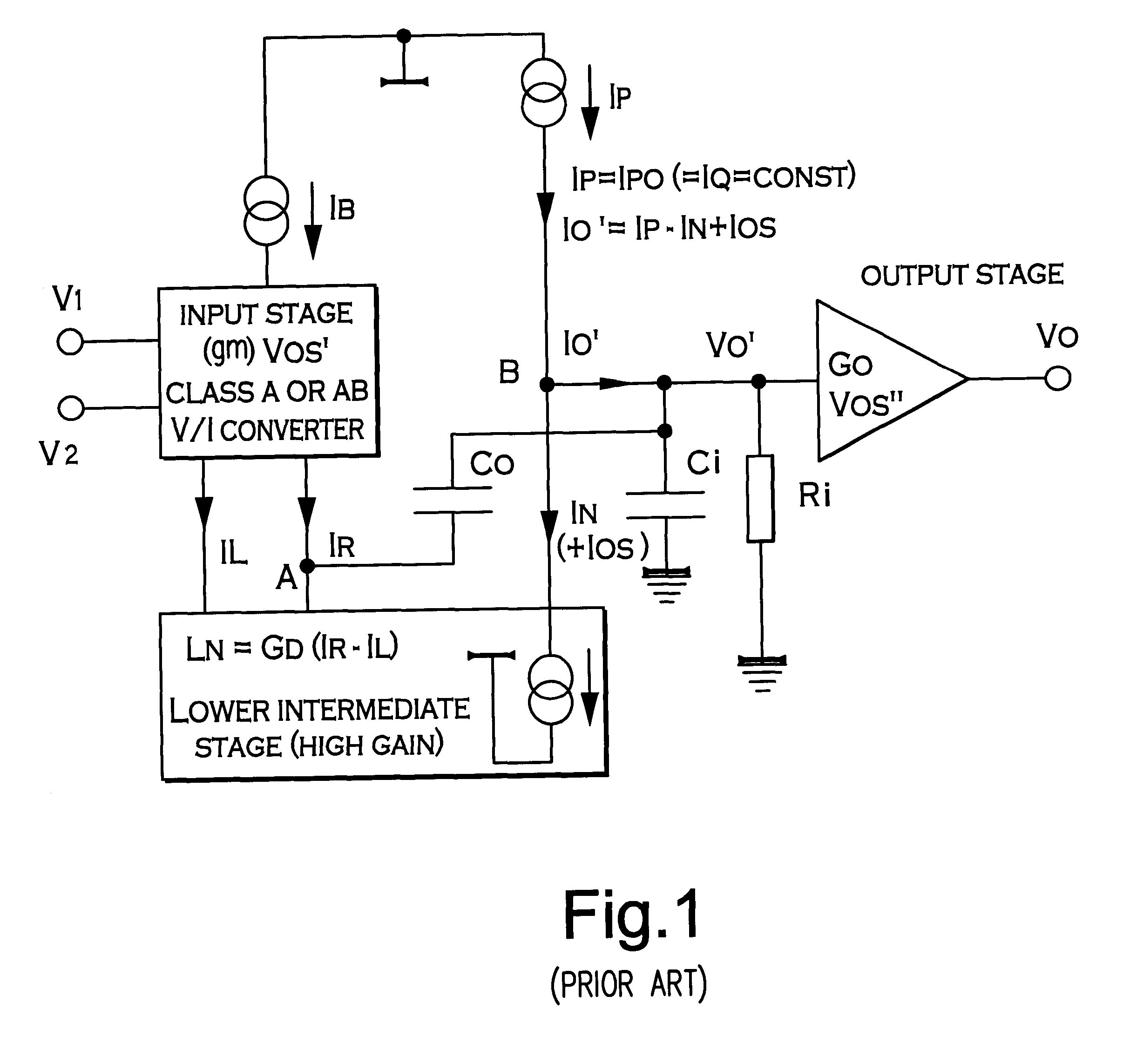
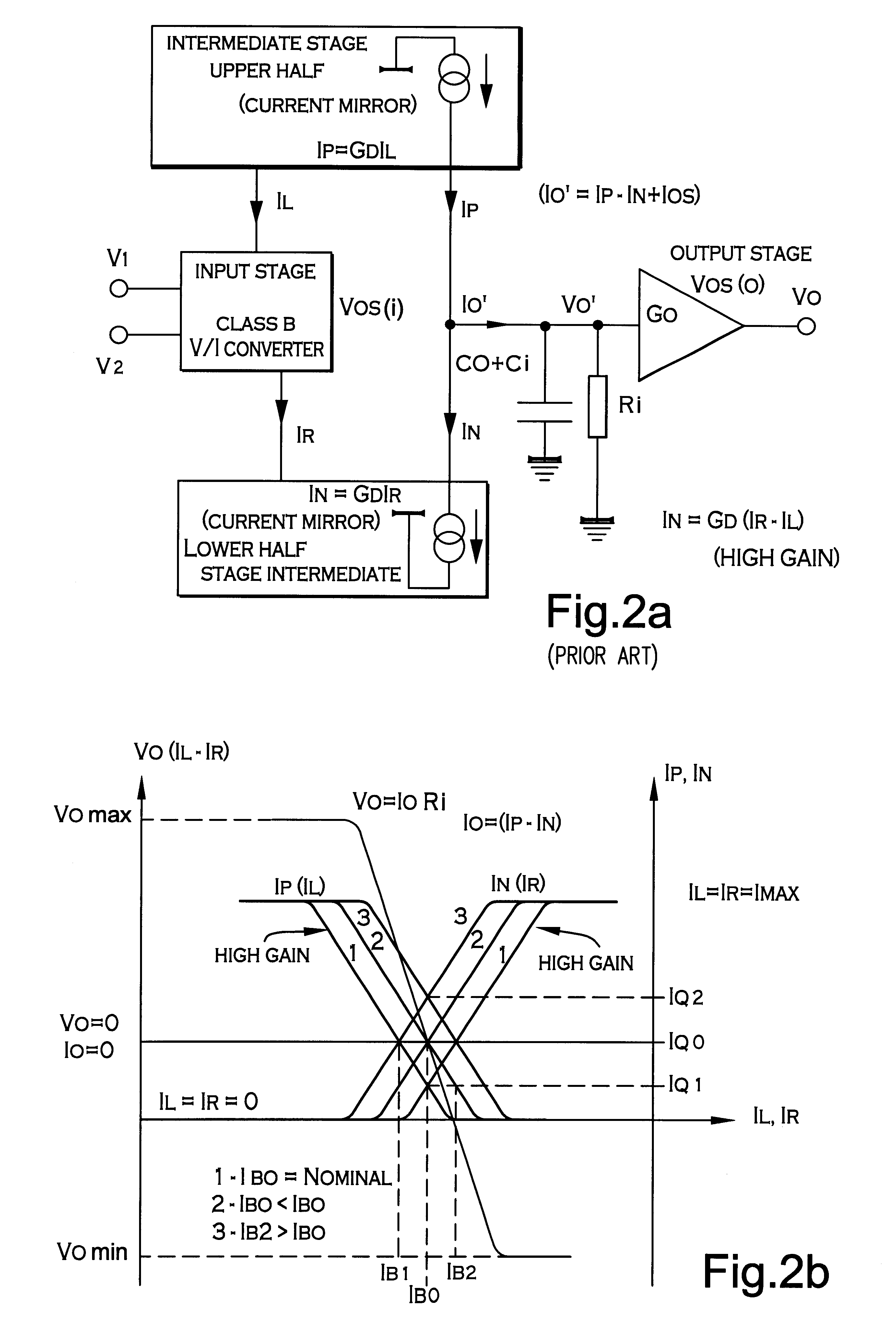
In an amplifier with improved, high precision, high speed and low power consumption architecture, comprising an input stage (1), an intermediate stage (2) and an output stage (3), the intermediate stage (2) is provided by combining two complementary class AB operating halves (2a, 2b) which are driven by a complementary input stage, which is, in turn, class AB operating, one of said halves having a low limited current gain (GU), conveniently but not necessarily controlled, and the other one having a high or very high current gain (GD) which can, but not necessarily, be controlled. Suitably the input class AB operating input stage (1) of this amplifier provides two pairs or one pair of antiphase output currents (IR and IL), apt to be used to feed both halves (2a, 2b) of the intermediate stage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor with composite metal gate
ActiveCN103474455AInhibition-lowering (DIBL) effectAvoid mechanical propertiesSemiconductor devicesIndiumGallium nitride
The invention relates to a gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor with a composite metal gate. The gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor comprises a substrate, a gallium nitride buffer layer, an aluminum nitride inserting layer, an aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer, and a source electrode, a drain electrode and a grid electrode on the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer, wherein the source electrode and the drain electrode form ohmic contact with the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer; the grid electrode and the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer form Schottky contact; the grid electrode on the aluminum-indium-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer is formed by connecting more than two metals with different work functions. Through the utilization of the influence of a step barrier shielding drain potential formed between the grid metals with different work functions on device channels, the Drain Induced Barrier Lowering (DIBL) effect is inhibited, and the SCEs (Short Channel Effects) of deep submicron gallium nitride based high electron mobility transistor are improved, thus the current gain cut-off frequency fT is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bipolar transistor
InactiveUS20050116319A1Increase current gainReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorHigh current gain
A bipolar transistor of the present invention comprises a collector layer made of an n-type semiconductor and an emitter layer made of an n-type semiconductor provided on this collector layer. A gate layer for injecting p-type carriers (holes) into the emitter layer is provided on the emitter layer. A p-type carrier retaining layer is formed between the collector layer and the emitter layer. The p-type carrier retaining layer temporarily retains the p-type carriers that are injected from the gate layer into the emitter layer and diffused in the emitter layer and reach the p-type carrier retaining layer. The bipolar transistor has a structure whose performance is not influenced by sheet resistance of the base layer, and is able to exhibit a high current gain even in a high-frequency region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Vertical-channel SiC junction gate bipolar transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106711207AReduce processing difficultyImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesJFETProcessing cost
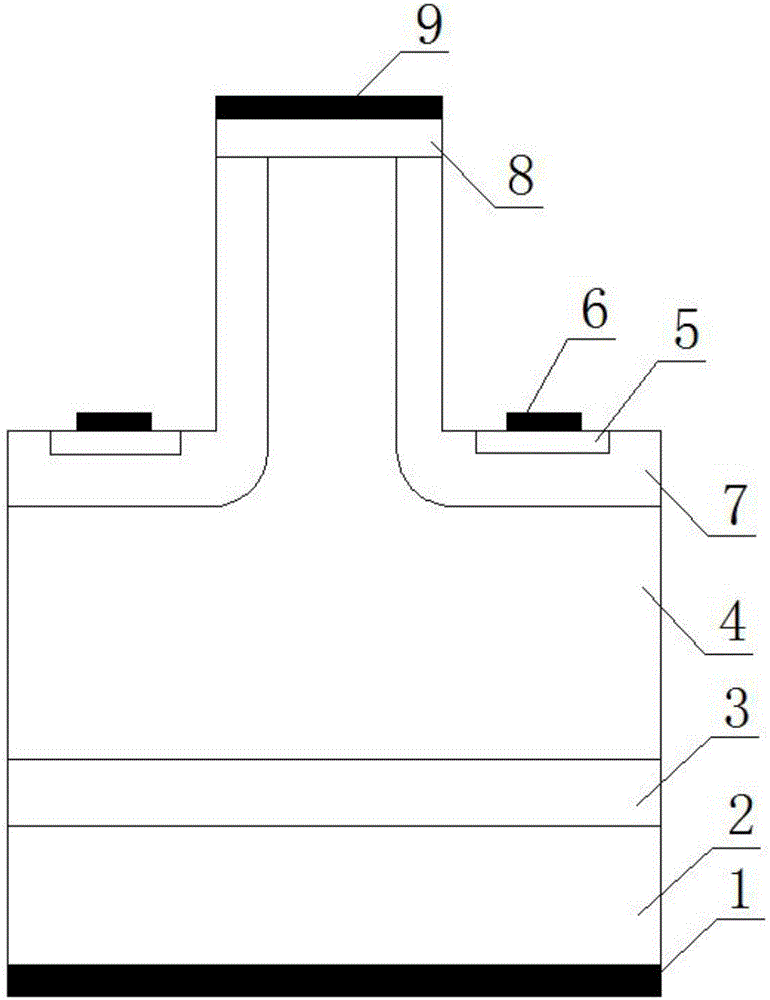
The invention provides a vertical-channel SiC junction gate bipolar transistor and a preparation method, mainly solves a problem of interface states brought about by an oxide layer of a SiC IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) device in the prior art, avoids a possibly occurring latch-up effect, reduces processing steps and saves the processing cost at the same time. The characteristics are that a channel structure of a vertical-channel JFET (Junction Field-Effect Transistor) is adopted in a P- drift region to replace an upper structure of the traditional IGBT device, and the width of a channel region of the device is 1-4 microns. The vertical-channel SiC junction gate bipolar transistor provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low cost, high current gain and the like, and can be applied to a stabilized switching power supply, electric energy conversion, automobile electronics, oil drilling equipment and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060208261A1Improve pressure resistanceReduced injection efficiencyThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialVolumetric Mass Density
A high voltage semiconductor device having a high current gain hFE is formed with a collector region (20) of a first conduction type, an emitter region (40) of the first conduction type, and a base region (30) of a second conduction type opposite to the first conduction type located between the collector region and the emitter region. The free carrier density of the base region (30) where no depletion layer is formed is smaller than the space charge density of a depletion layer formed in the base region (30).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
High-gain X ray detector based on double-heterojunction HEMT
ActiveCN105679859AIncrease current gainMake up for the problem of low absorption efficiencySemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionElectron current
The invention discloses a high-gain X ray detector based on a double-heterojunction HEMT. The high-gain X ray detector comprises an AlGaN barrier layer, a GaN channel layer, an AlGaN back barrier buffer layer, a substrate, a Si3 N4 passivation layer, a grid electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode. Cavity accumulation in the irradiation process happens to the interface between the channel layer and the back barrier buffer layer in the detector structure, so that the barrier height is lowered, the electron current of a channel changes, and finally an extremely high current gain is generated. The X ray detector is based on a GaN-based material system, the ionising radiation resistance is high, and the current gain is extremely high, so that the defect that the absorption rate of the GaN material to X rays is low is overcome, and the problem that the response time of a conventional GaN schottky X ray detector is solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
High speed, high current gain voltage buffer and method
ActiveUS20080174369A1Increase conversion rateHigh currentPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
An amplifying circuit which may be useful in a diamond buffer amplifier or operational amplifier includes an input transistor including an emitter, a collector, and a base coupled to receive an input voltage. An adjustable current source circuit is coupled between a first reference voltage and the emitter of the input transistor. A current source is coupled between a second reference voltage and the collector of the input transistor. An isolation resistor has a first terminal coupled to an output terminal of the adjustable current source circuit and a second terminal coupled to the emitter of the input transistor. A current follower circuit is coupled between the collector of the input transistor and an input terminal of the adjustable current source circuit. A feed-forward capacitor is coupled between the collector of the input transistor and the first terminal of the isolation resistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
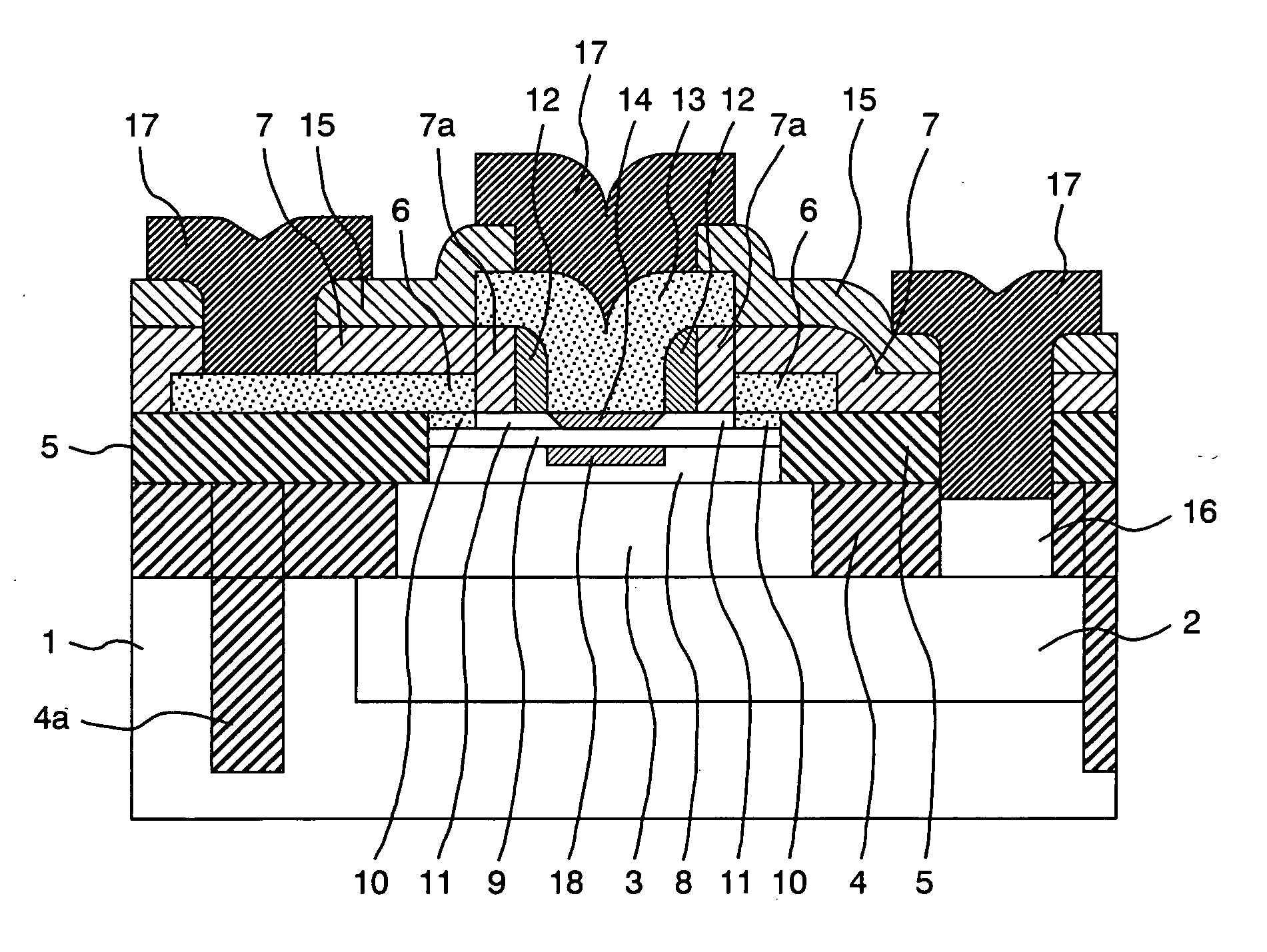
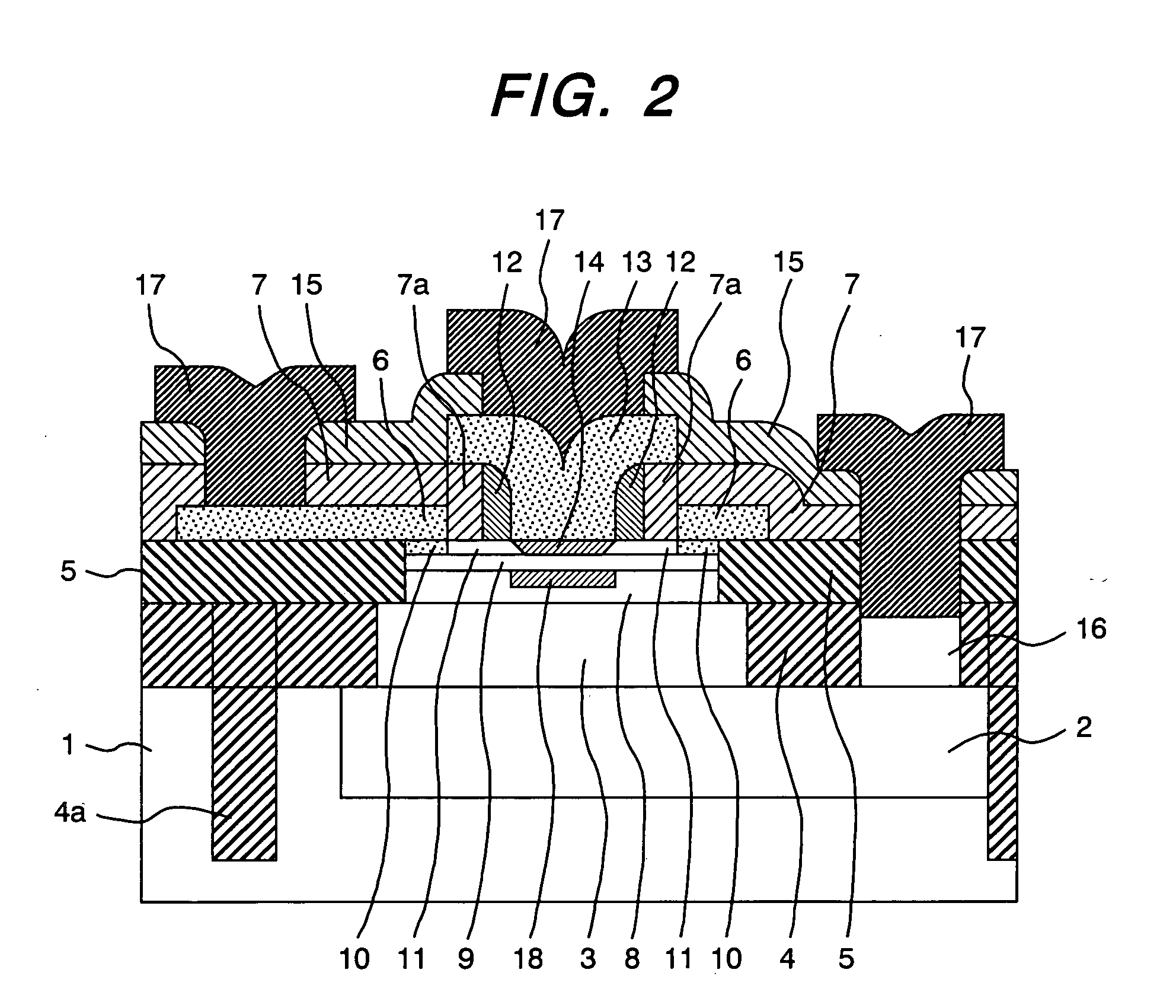
InactiveUS7214973B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorPeak value
A bipolar type semiconductor device capable of attaining high current gain and high cut-off frequency and performing a satisfactory transistor operation also in a high current region while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance, as well as a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device, are provided. In a collector comprising a first semiconductor layer and a second semiconductor layer narrower in band gap than the first semiconductor layer, an impurity is doped so as to have a peak of impurity concentration within the second collector layer and so that the value of the peak is higher than the impurity concentration at any position within the first collector layer. It is preferable to adjust the concentration of the doped impurity in such a manner that a collector-base depletion layer extends up to the first collector layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7071536B2Improve pressure resistanceReduced injection efficiencyTransistorThyristorHigh pressureFree carrier density
A high voltage semiconductor device having a high current gain hFE is formed with a collector region (20) of a first conduction type, an emitter region (40) of the first conduction type, and a base region (30) of a second conduction type opposite to the first conduction type located between the collector region and the emitter region. The free carrier density of the base region (30) where no depletion layer is formed is smaller than the space charge density of a depletion layer formed in the base region (30).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
High speed, high current gain voltage buffer and method
ActiveUS7394316B1Increase conversion rateHigh currentPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplifying circuit which may be useful in a diamond buffer amplifier or operational amplifier includes an input transistor including an emitter, a collector, and a base coupled to receive an input voltage. An adjustable current source circuit is coupled between a first reference voltage and the emitter of the input transistor. A current source is coupled between a second reference voltage and the collector of the input transistor. An isolation resistor has a first terminal coupled to an output terminal of the adjustable current source circuit and a second terminal coupled to the emitter of the input transistor. A current follower circuit is coupled between the collector of the input transistor and an input terminal of the adjustable current source circuit. A feed-forward capacitor is coupled between the collector of the input transistor and the first terminal of the isolation resistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Power semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120097974A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A method and apparatus for achieving high current gain, and low on-resistance, from a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) in high temperature and high power applications are disclosed. In some embodiments, a thin doped delta layer is inserted at the base emitter junction but inside the base layer. In addition, in some embodiments, a surface recombination layer is inserted between the emitter-base regions of the device. In some embodiments, use of an ion implantation step is avoided to achieve simplicity and low cost of manufacture.
Owner:UNIVSSENTERET PA KJELLER
Voltage clamping circuit for a bicycle dynamo
InactiveUS7245171B2Minimal degradationAccurate speedAc-dc conversion without reversalPulse automatic controlVoltage clampDynamo
A voltage clamping circuit comprises a first high current gain circuit adapted to receive current from the first line; and a first switching circuit that turns on the first high current gain circuit to flow current away from the first line when the first switching circuit senses a first voltage from the first line above a clamping voltage, and turns off the first high current gain circuit when the first switching circuit senses the first voltage below the clamping voltage.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Bipolar transistor
InactiveCN1655363AReduce power consumptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierSemiconductor
A bipolar transistor of the present invention comprises a collector layer made of an n-type semiconductor and an emitter layer made of an n-type semiconductor provided on this collector layer. A gate layer for injecting p-type carriers (holes) into the emitter layer is provided on the emitter layer. A p-type carrier retaining layer is formed between the collector layer and the emitter layer. The p-type carrier retaining layer temporarily retains the p-type carriers that are injected from the gate layer into the emitter layer and diffused in the emitter layer and reach the p-type carrier retaining layer. The bipolar transistor has a structure whose performance is not influenced by sheet resistance of the base layer, and is able to exhibit a high current gain even in a high-frequency region.
Owner:SHARP KK
Transverse SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor with adjustable doping concentration
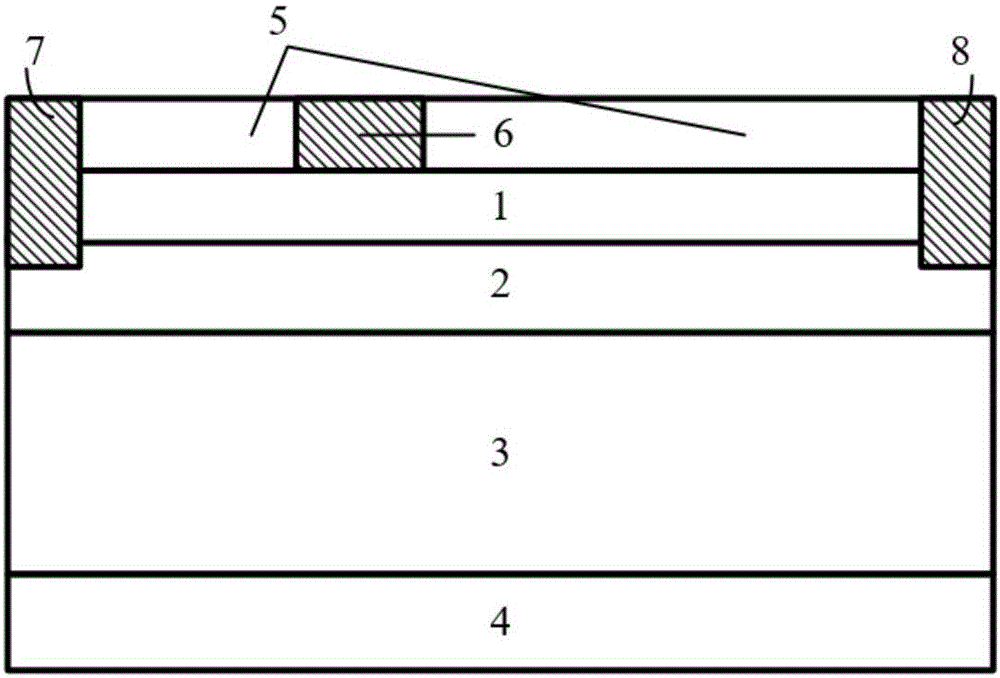
ActiveCN110556420AExtended microwave power operating rangeRaise the eigenfrequencySemiconductor devicesPower flowCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a transverse SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor with adjustable doping concentration. The transverse SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor is an NPN type or PNP type transverse SiGe HBT (Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor). By applying a positive voltage to a substrate electrode below an emitter region and a base region of an NPN type device (or applying a negative voltage to a substrate electrode below an emitter region and a base region of a PNP type device), the doping concentration of the emitter region can be increased, the doping concentration of the base region can be reduced, and meanwhile, the current gain and the characteristic frequency can be improved. By applying a negative voltage to a substrate electrode below a collector region of the NPN type device (or applying a positive voltage to a substrate electrode below a collector region of the PNP type device), the doping concentration of the collector region can be reduced, and the breakdown voltage can be improved. Compared with a conventional transverse SiGe HBT, the doping concentrations of the three regions can be independently adjusted by changing the external voltages applied to the substrate electrodes below the emitter region, the base region and the collector region, so that the characteristic frequency, the current gain and the breakdown voltage are synchronously improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Voice coil motor control method and system
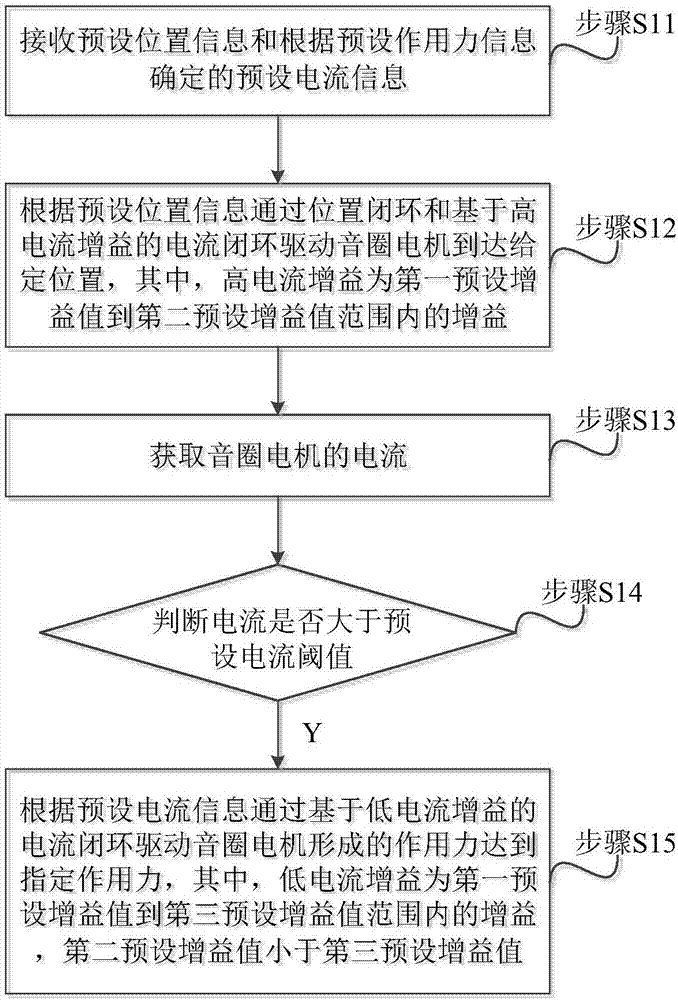
The invention discloses a voice coil motor control method and system. The method comprises the steps of receiving preset position information and preset current information determined according to preset acting force information; driving a voice coil motor to reach a given position through a position closed loop and a current closed loop based on a high current gain according to the preset position information, wherein the high current gain is a grain within a range from a first preset gain value to a second preset gain value; acquiring a current of the voice coil motor, and determining whether the current is greater than a preset current threshold; if yes, driving an acting force formed by the voice coil motor to reach a specified acting force through a current closed loop based on a lowcurrent gain according to the preset current information, wherein the low current gain is a gain within a range from the first preset gain value to a third preset gain value, and the second preset gain value is smaller than the third preset gain value. According to the voice coil motor control method and system, different requirements at the position control stage and the force control stage can be met simultaneously, the voice coil motor can complete a complicated process, and the application range of the voice coil motor is greatly widened.
Owner:广东阿达智能装备有限公司
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060043418A1Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorDevice material
A bipolar type semiconductor device capable of attaining high current gain and high cut-off frequency and performing a satisfactory transistor operation also in a high current region while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance, as well as a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device, are provided. In a collector comprising a first semiconductor layer and a second semiconductor layer narrower in band gap than the first semiconductor layer, an impurity is doped so as to have a peak of impurity concentration within the second collector layer and so that the value of the peak is higher than the impurity concentration at any position within the first collector layer. It is preferable to adjust the concentration of the doped impurity in such a manner that a collector-base depletion layer extends up to the first collector layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
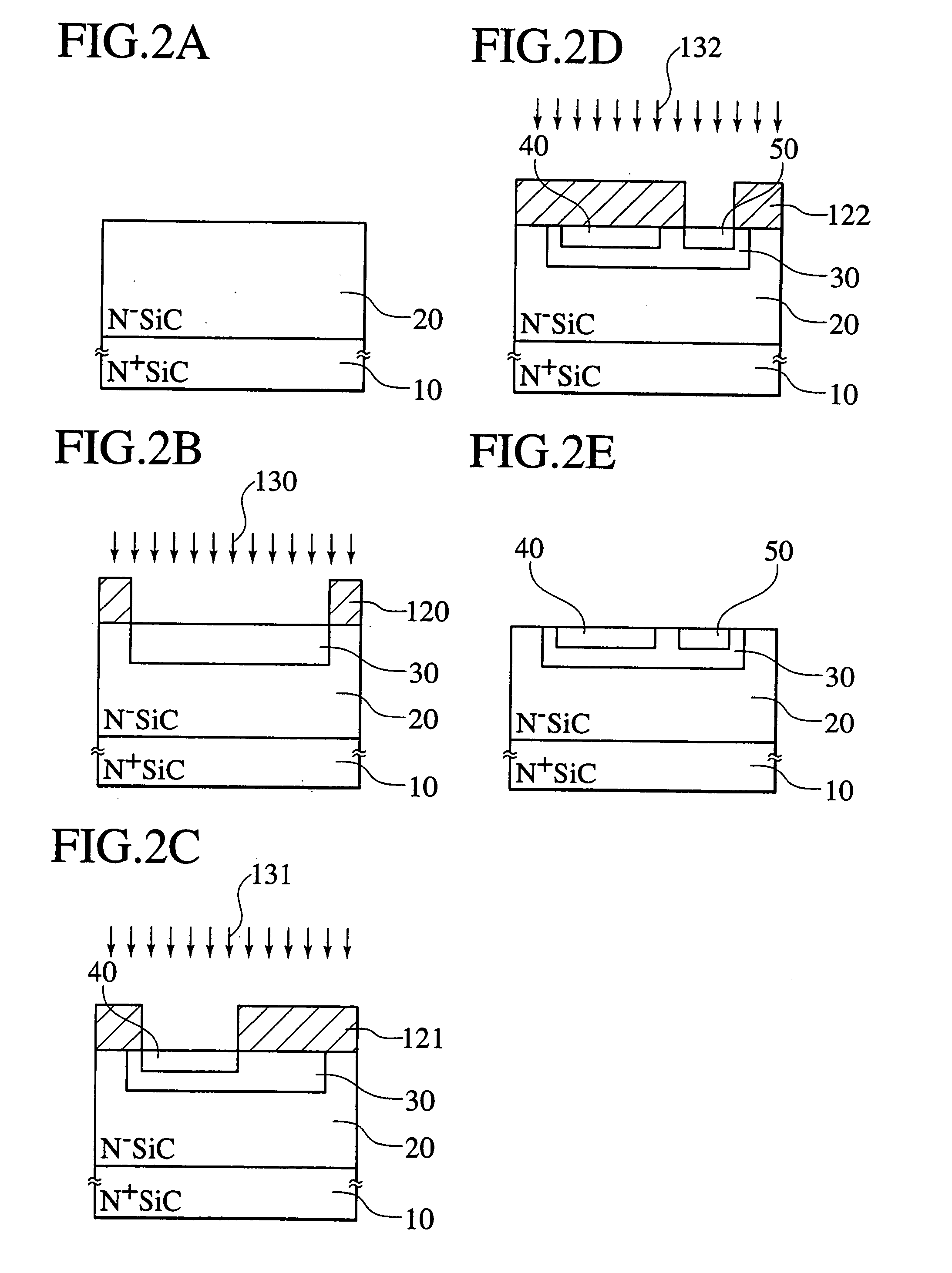
InactiveUS20160211332A1Increase current gainEasy constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesChemical treatmentDevice material
A silicon carbide semiconductor device capable of achieving a high current gain with a simplified construction is provided. A silicon carbide layer includes a collector region, a base region, and an emitter region. The silicon carbide layer is provided with a trench having a sidewall surface reaching the base region from a first main surface through the emitter region. The sidewall surface includes a region macroscopically having an angle not smaller than 50° and not greater than 70° with respect to a {000-1} plane. A manufacturing method includes the step of forming a trench. The step of forming a trench includes the step of chemically treating the first main surface of the silicon carbide layer for forming the region.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
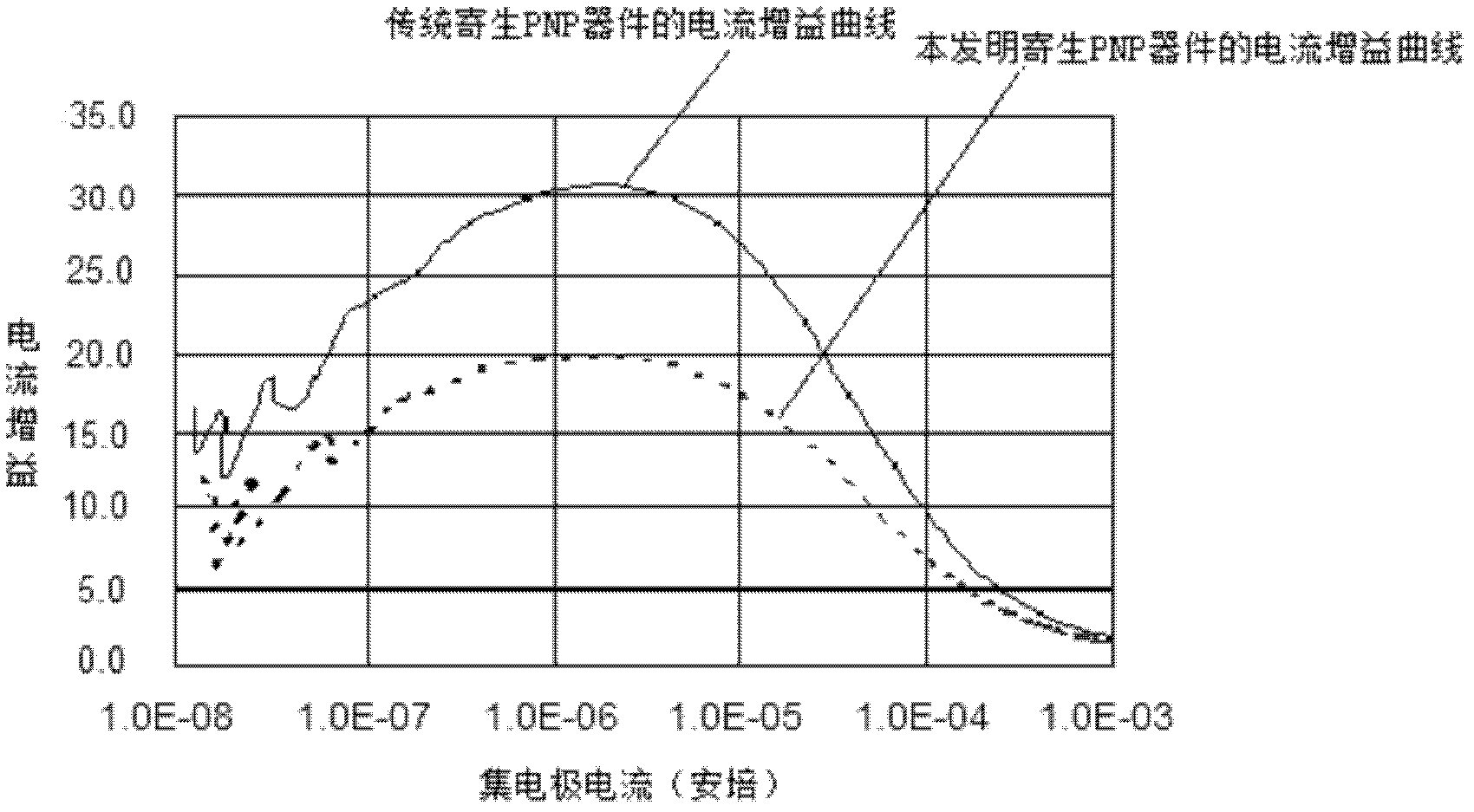
Parasitic plug-and-play (PNP) component structure and manufacturing method thereof in a silicon germanium (SiGe) heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) process
ActiveCN103107188AIncreasing the thicknessAvoid formingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal silicideSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses a parasitic plug-and-play (PNP) component structure in a silicon germanium (SiGe) heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) process. The parasitic PNP component structure in a SiGe HBT process comprises a base region which is formed above a collector region, an N-shaped buried layer and a shallow groove separation, and wherein the shallow groove separation is located above the N-shaped buried layer; metal silicides which are formed on the collector region are connected with metal connecting wires through contact holes; the N-shaped buried layer guides and connects the metal connecting wires through deep contact holes; an emitter region is formed above the base region and the shallow groove separation, and the metal silicides are formed above the emitter region; wherein the metal silicides which are located above the emitter region are located at the bilateral sides above the emitter region, and the metal silicides guides and connects the metal connecting wires through the contact holes; a silica medium layer is located above the emitter region, and an N-shaped polycrystalline silicon layer is located above the silica medium layer. Compared with a conventional parasitic PNP component, the parasitic PNP component structure has the advantages of enhancing the current gain effect, and using as a high speed, high gain output component in a radio frequency circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com