Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Improved breakdown voltage performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
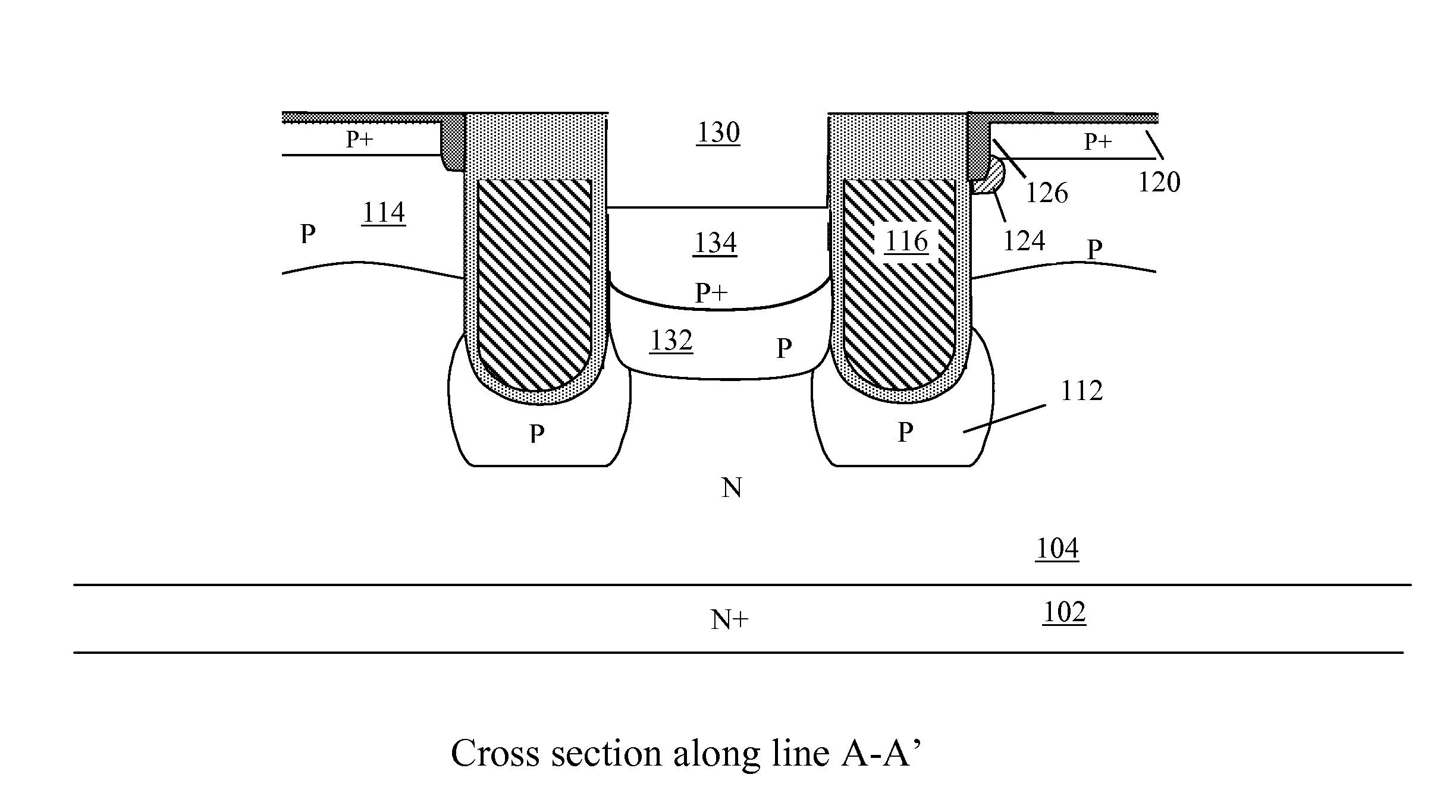
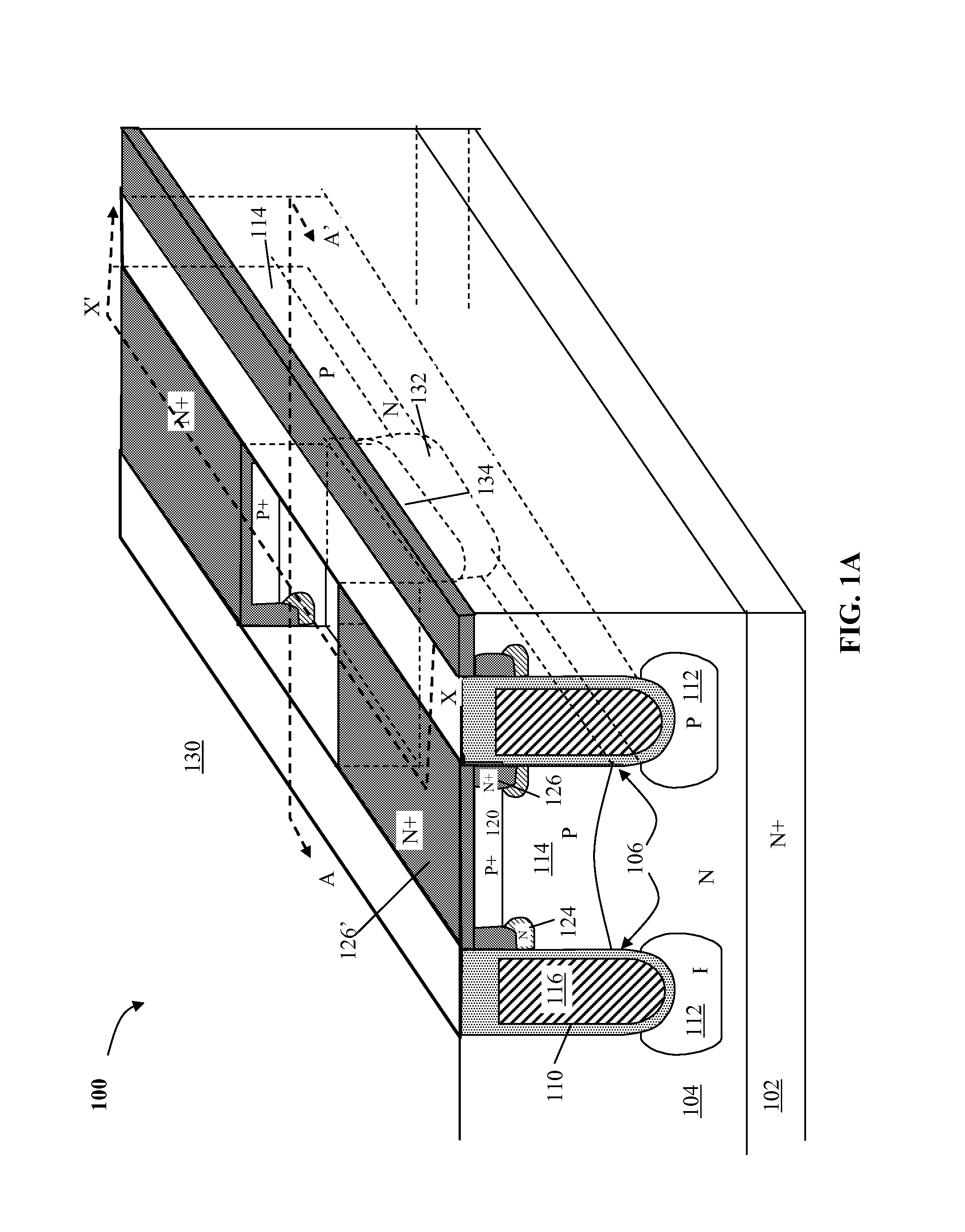
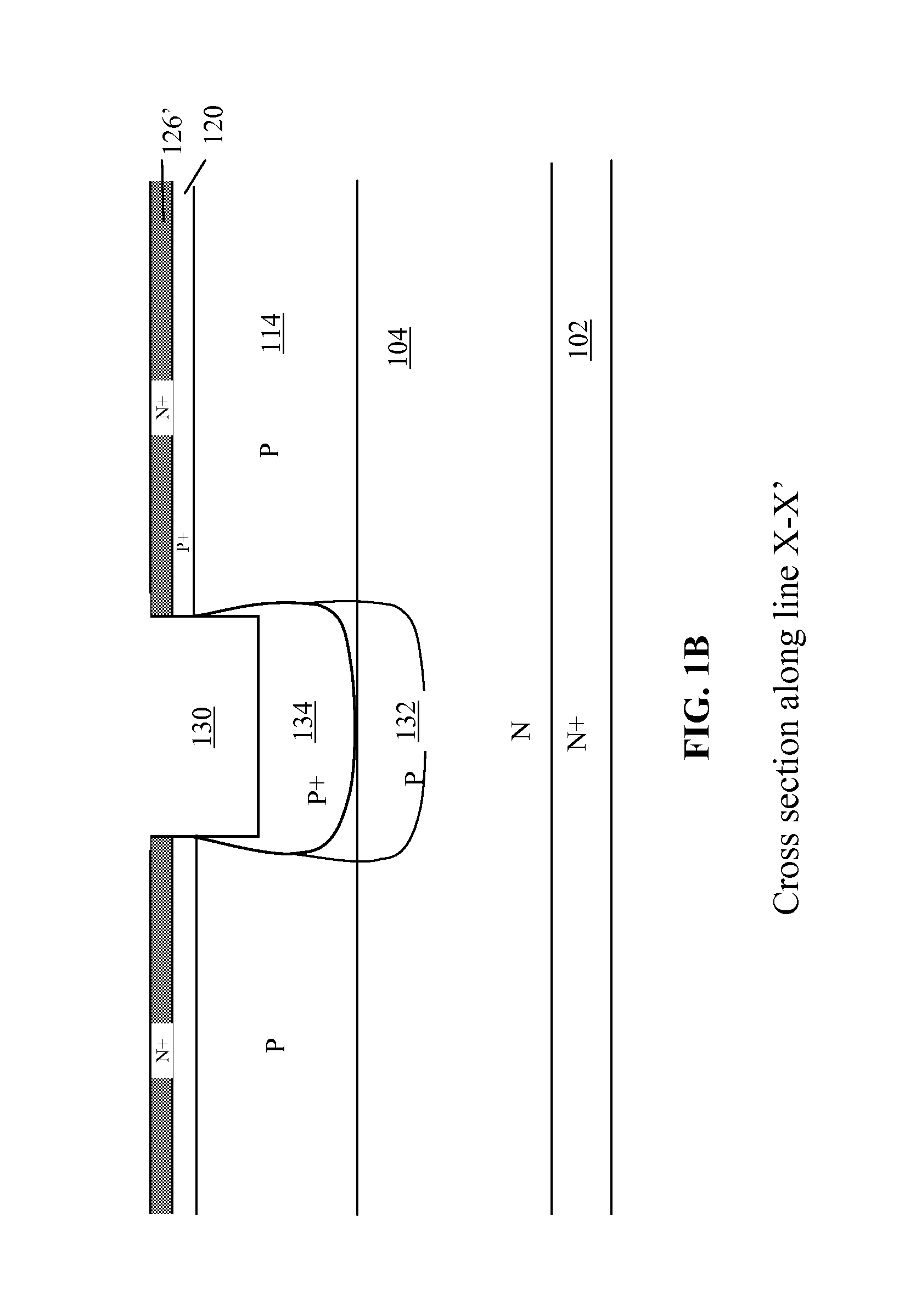
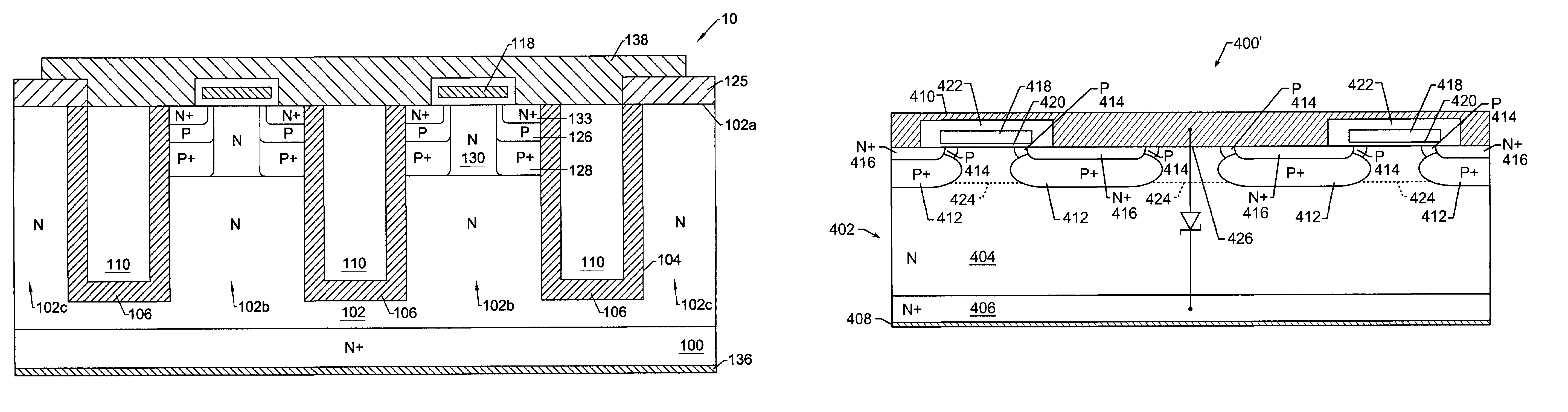
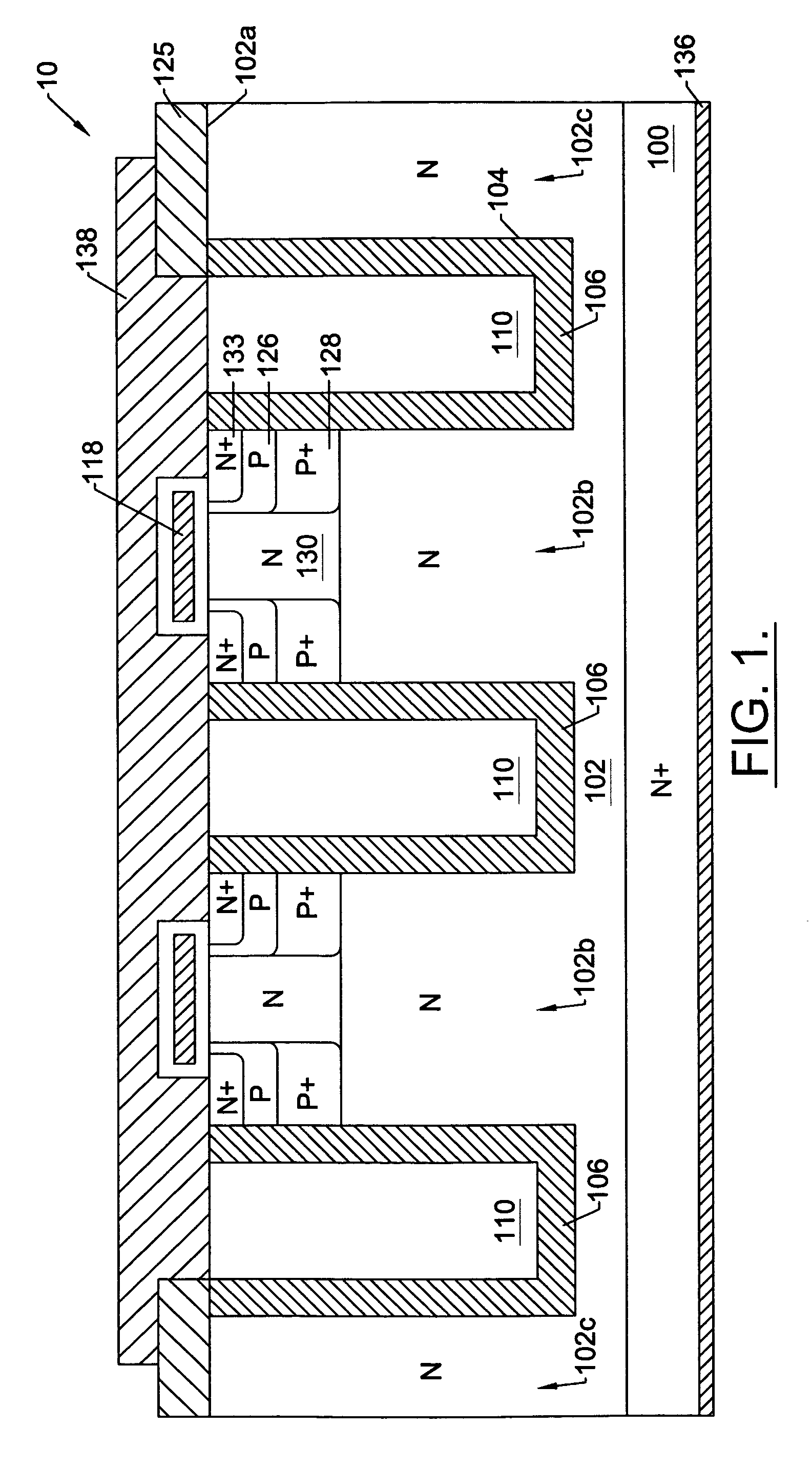
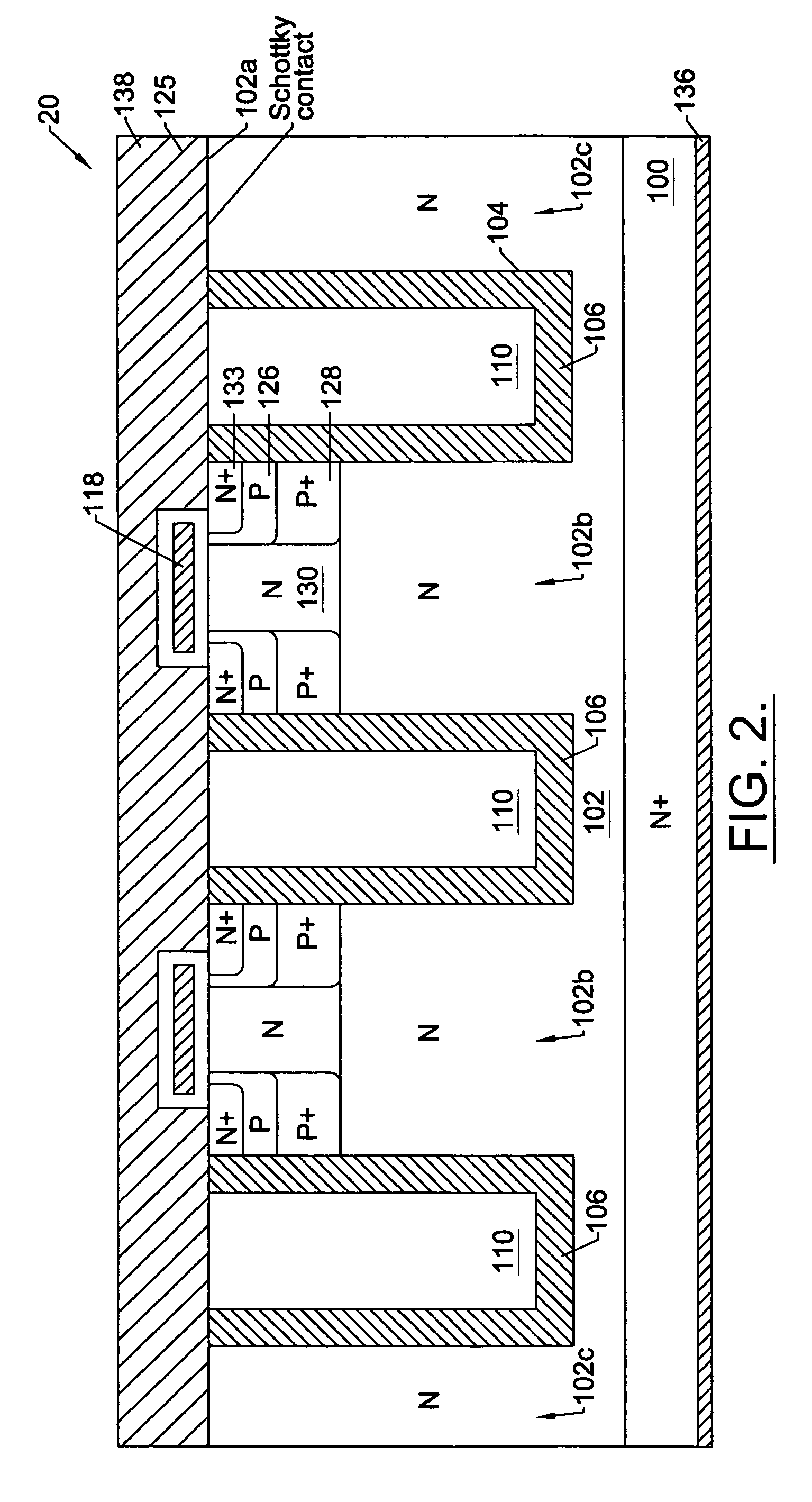
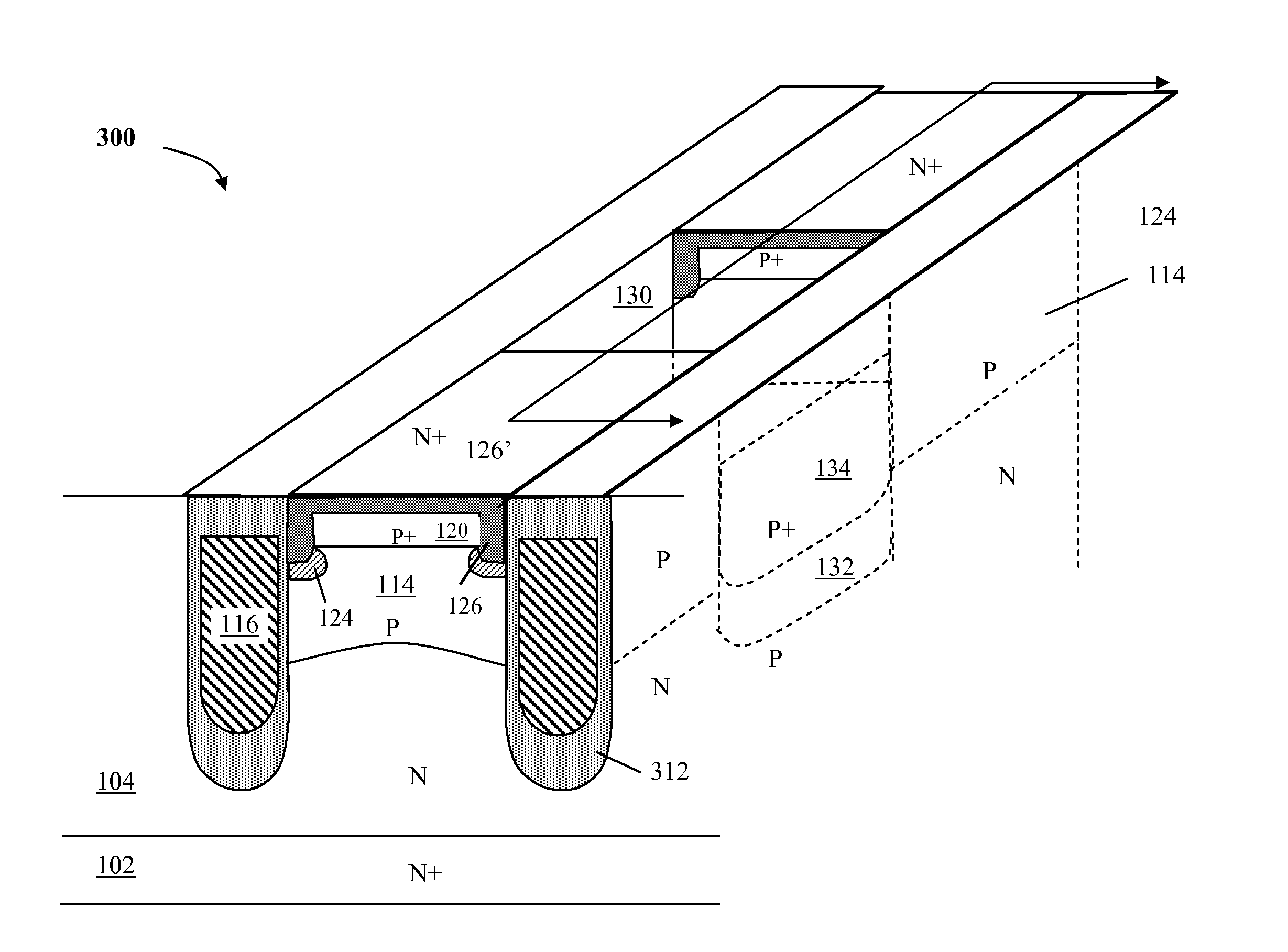
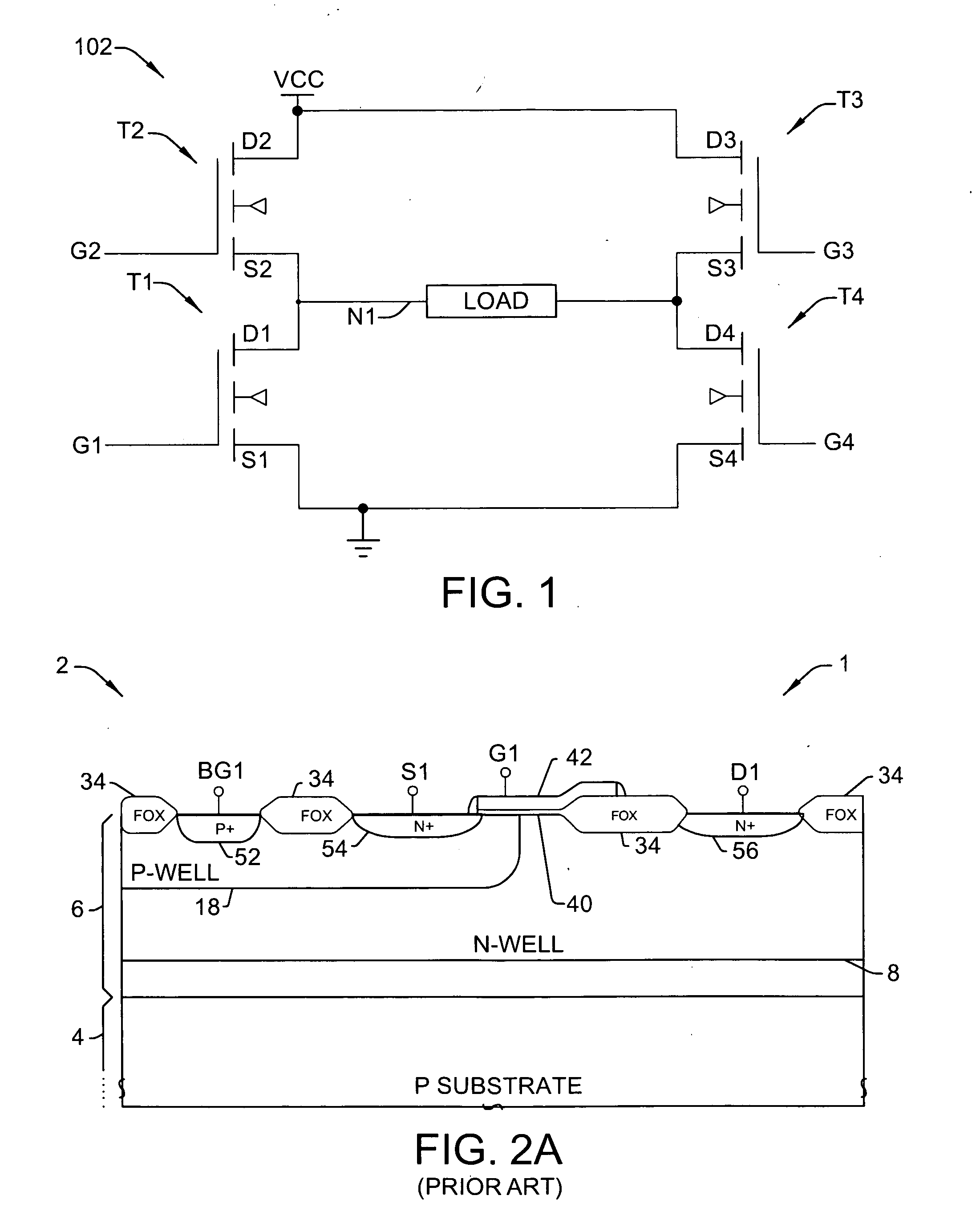
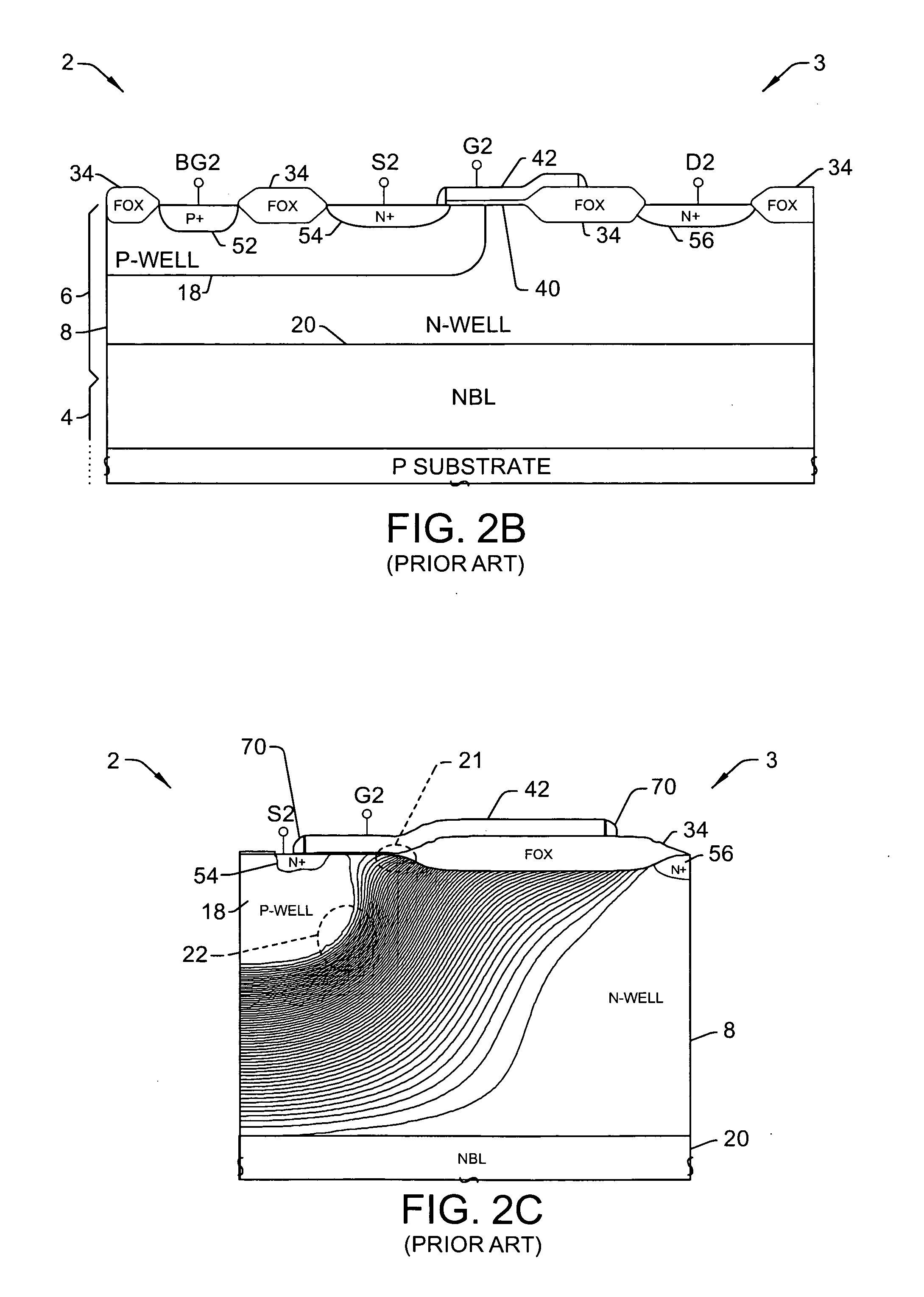
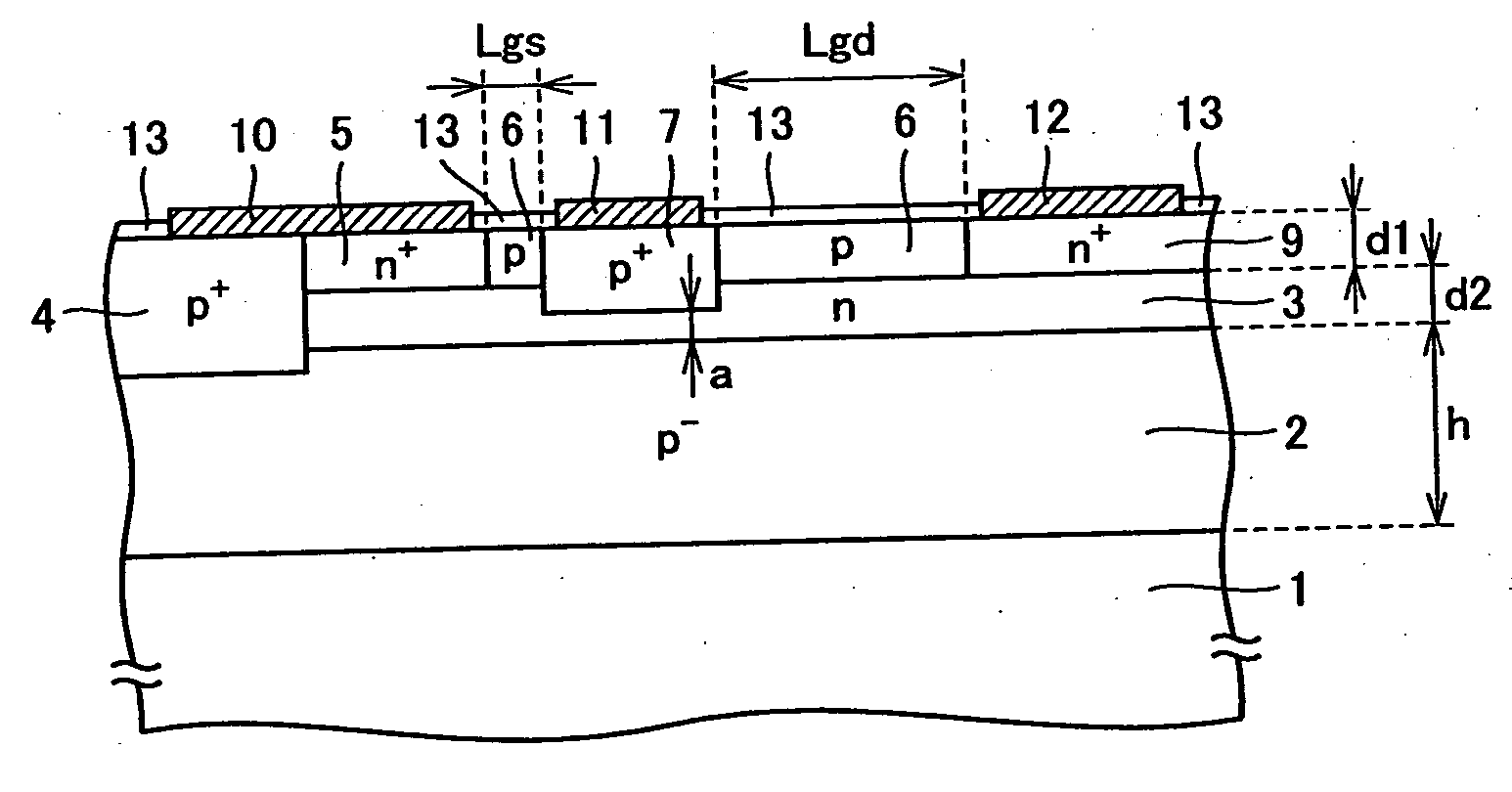
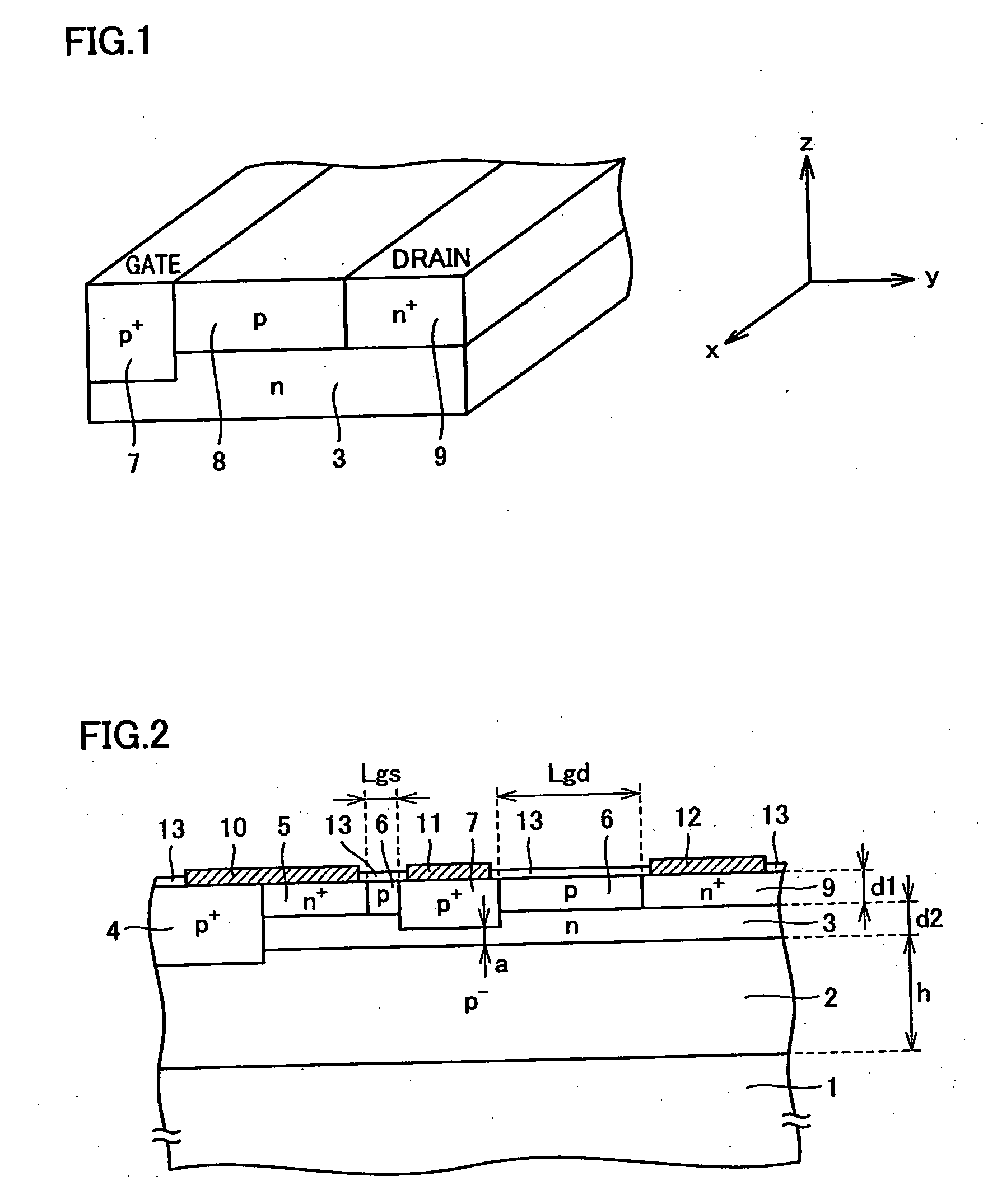
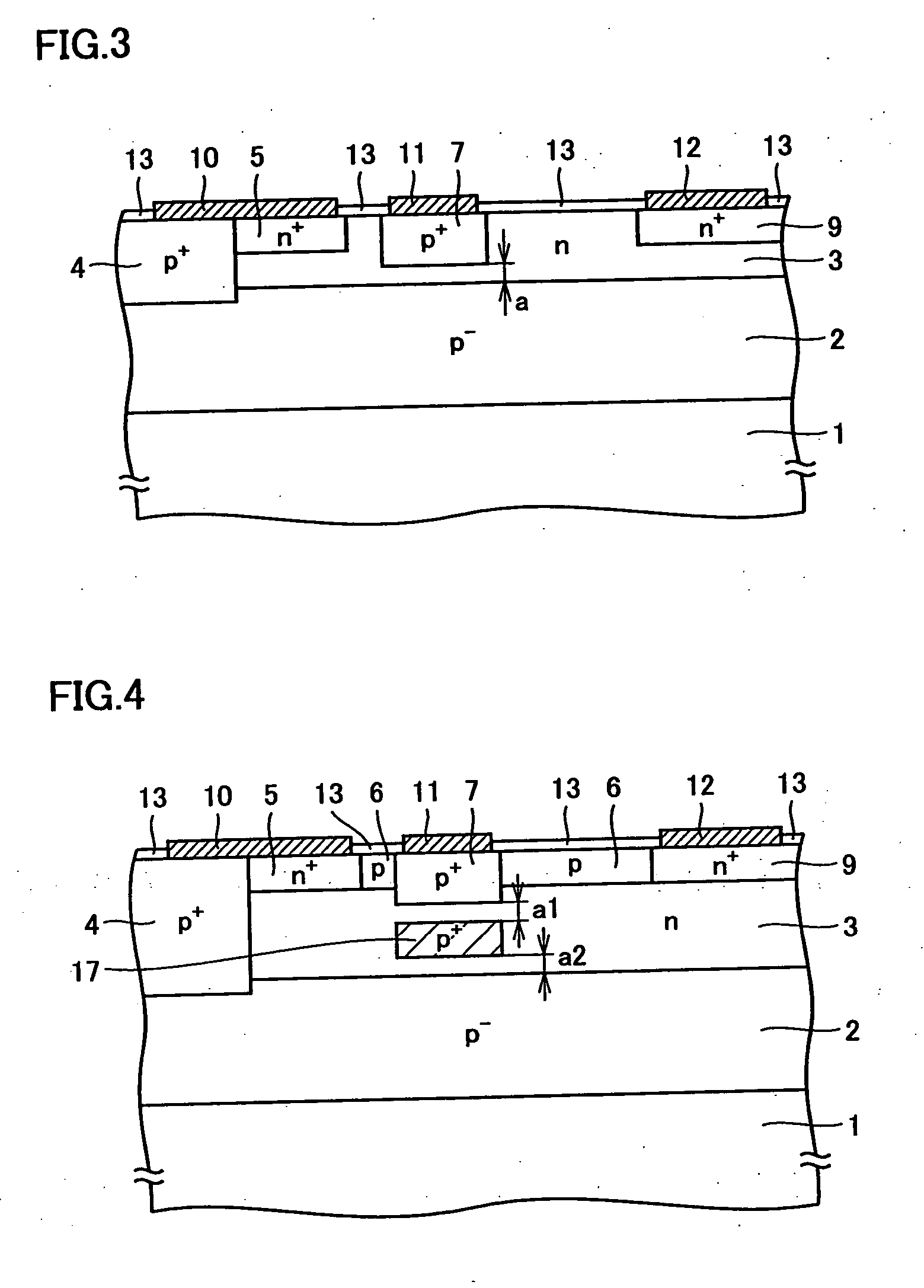
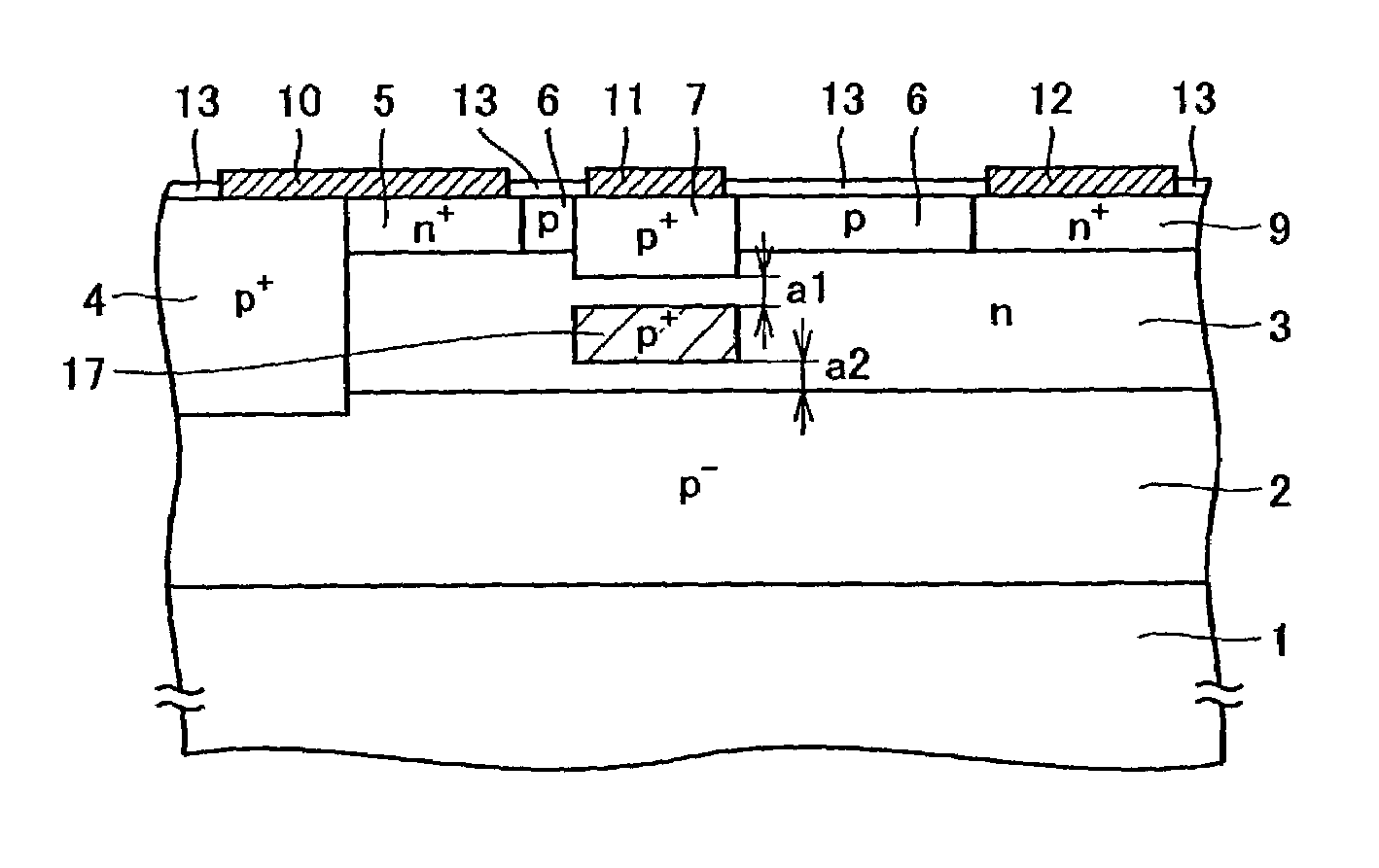
Nano mosfet with trench bottom oxide shielded and third dimensional p-body contact
A semiconductor power device may include a lightly doped layer formed on a heavily doped layer. One or more devices are formed in the lightly doped layer. Each device may include a body region, a source region, and one or more gate electrodes formed in corresponding trenches in the lightly doped region. Each of the trenches has a depth in a first dimension, a width in a second dimension and a length in a third dimension. The body region is of opposite conductivity type to the lightly and heavily doped layers. The source region is formed proximate the upper surface. One or more deep contacts are formed at one or more locations along the third dimension proximate one or more of the trenches. The contacts extend in the first direction from the upper surface into the lightly doped layer and are in electrical contact with the source region.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Semiconductor device
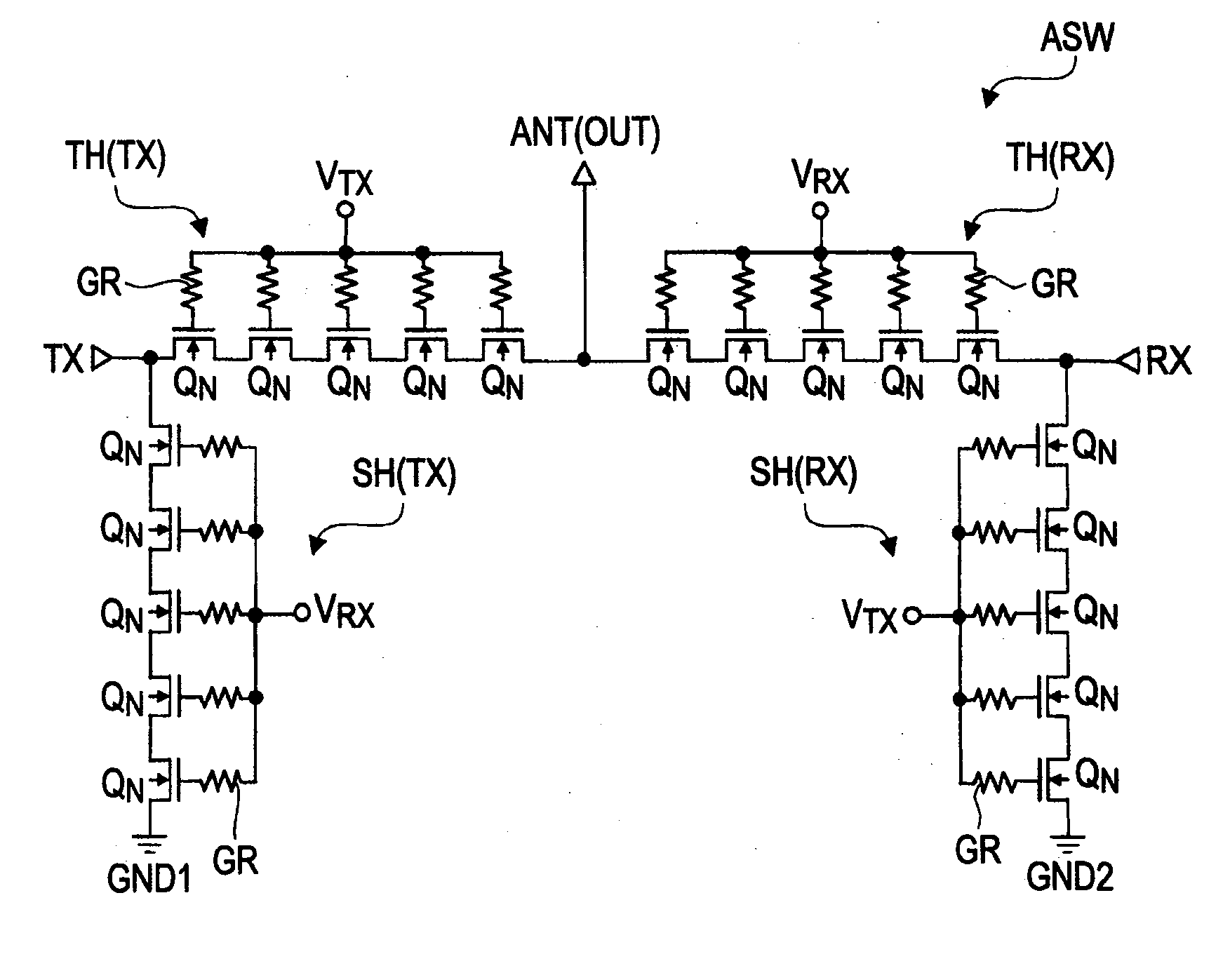
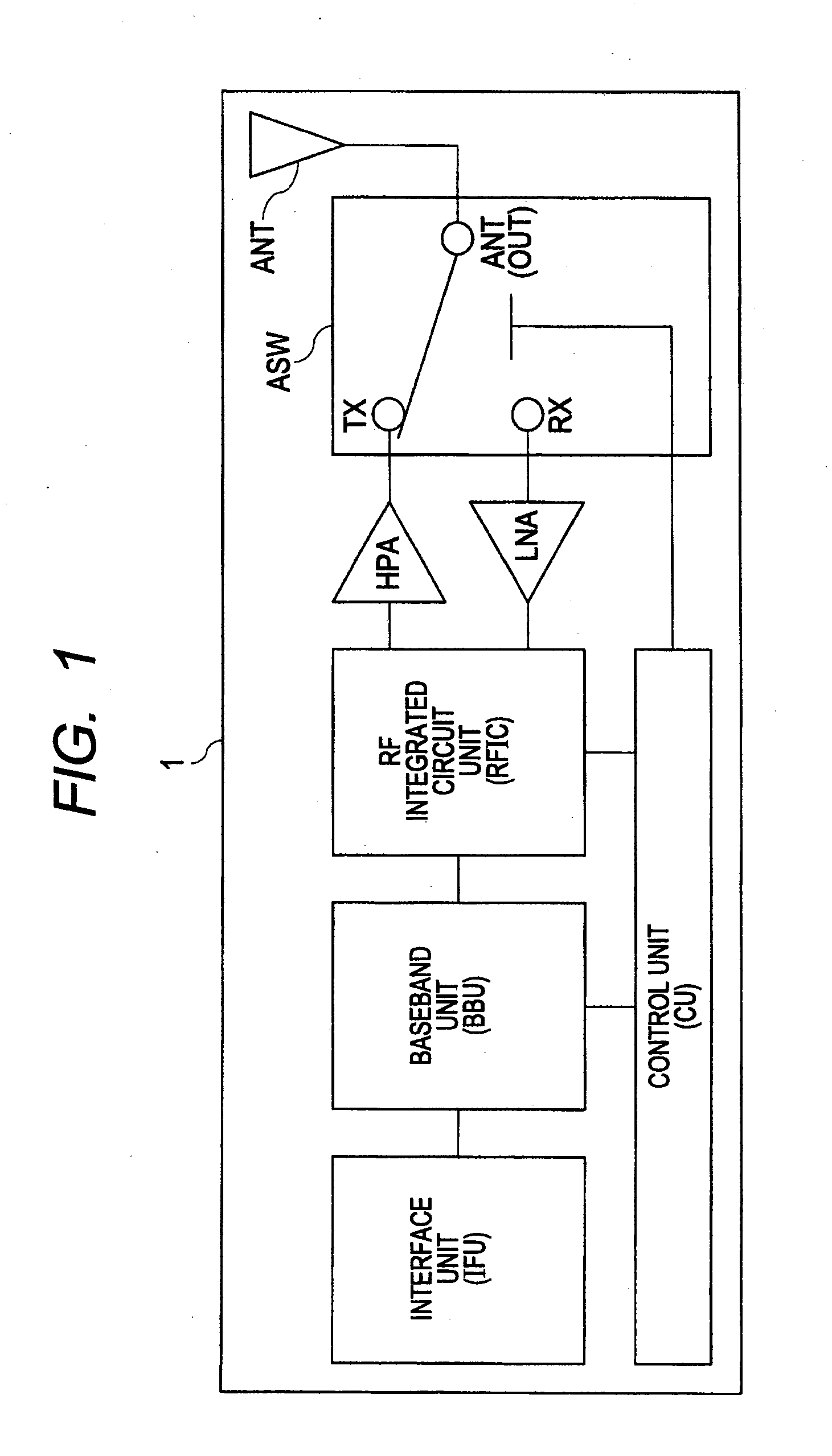
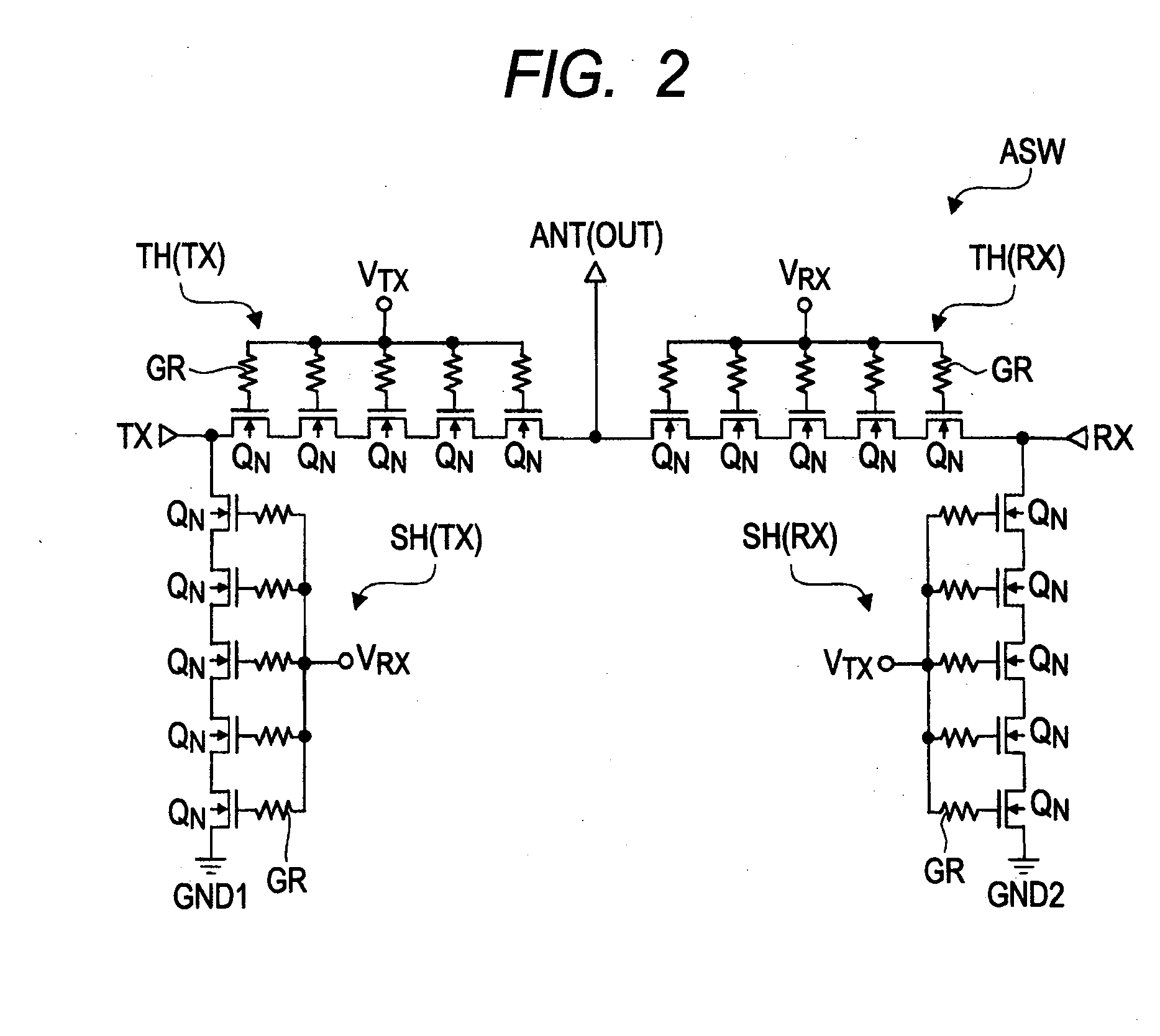
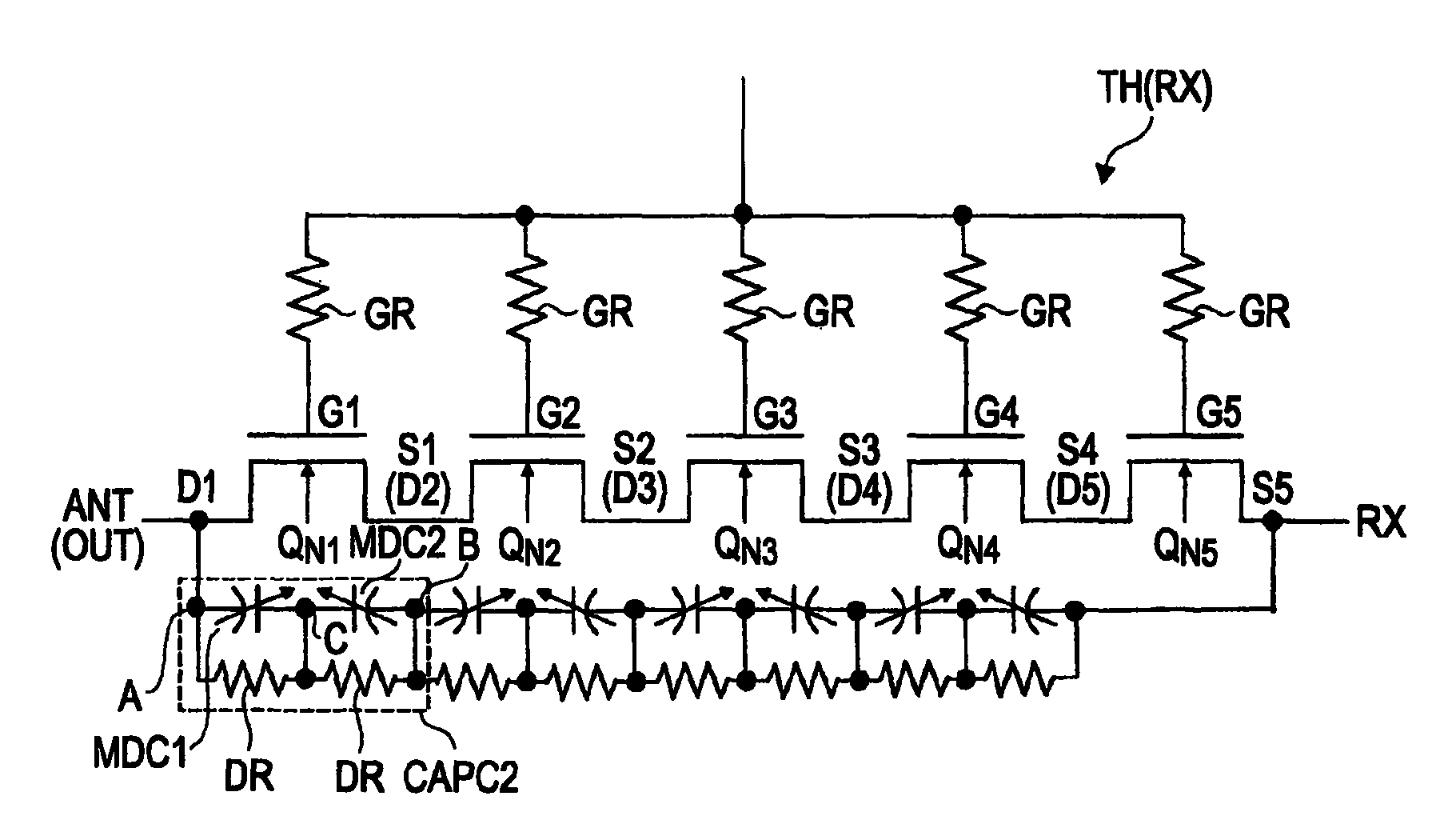
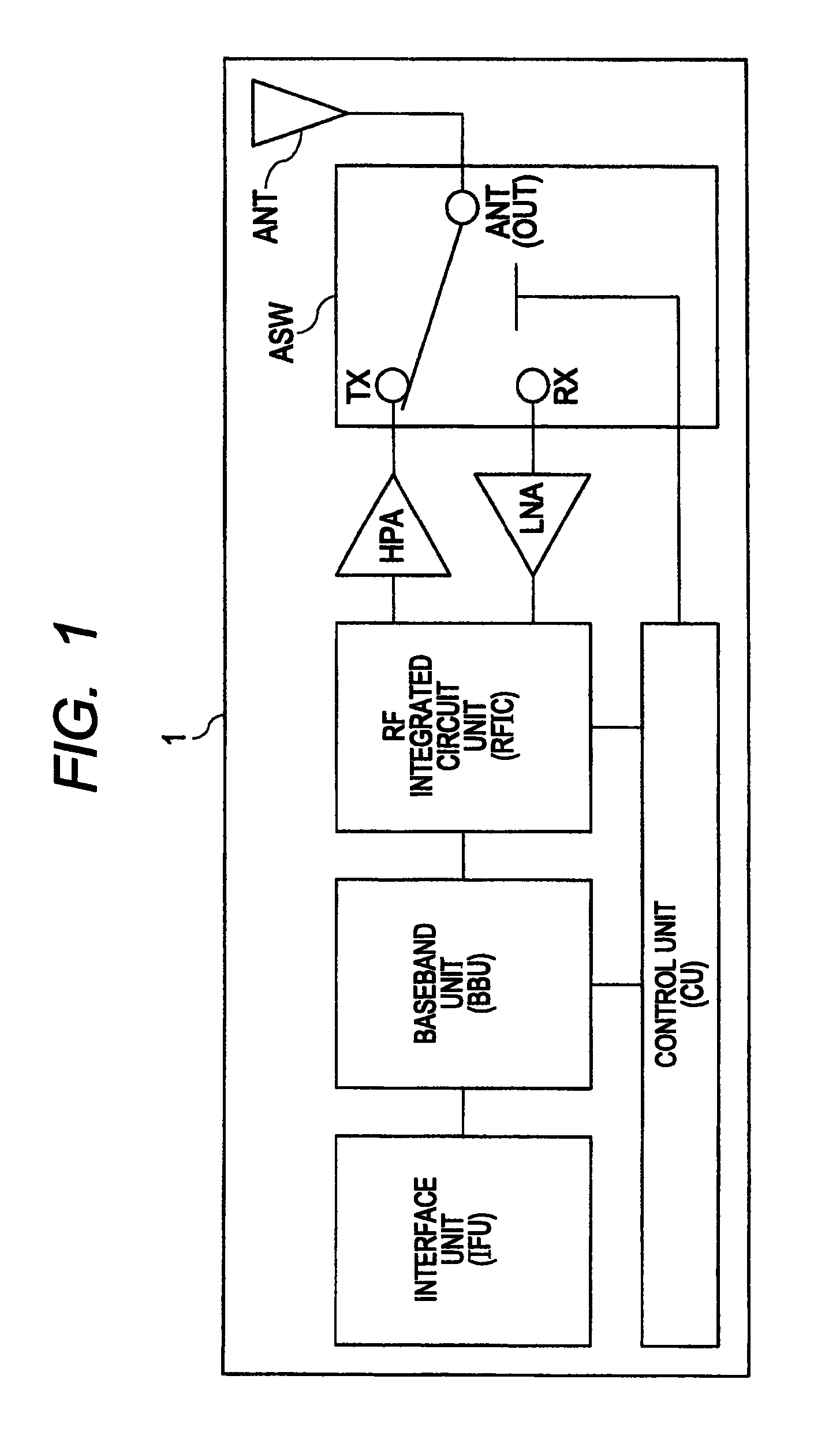
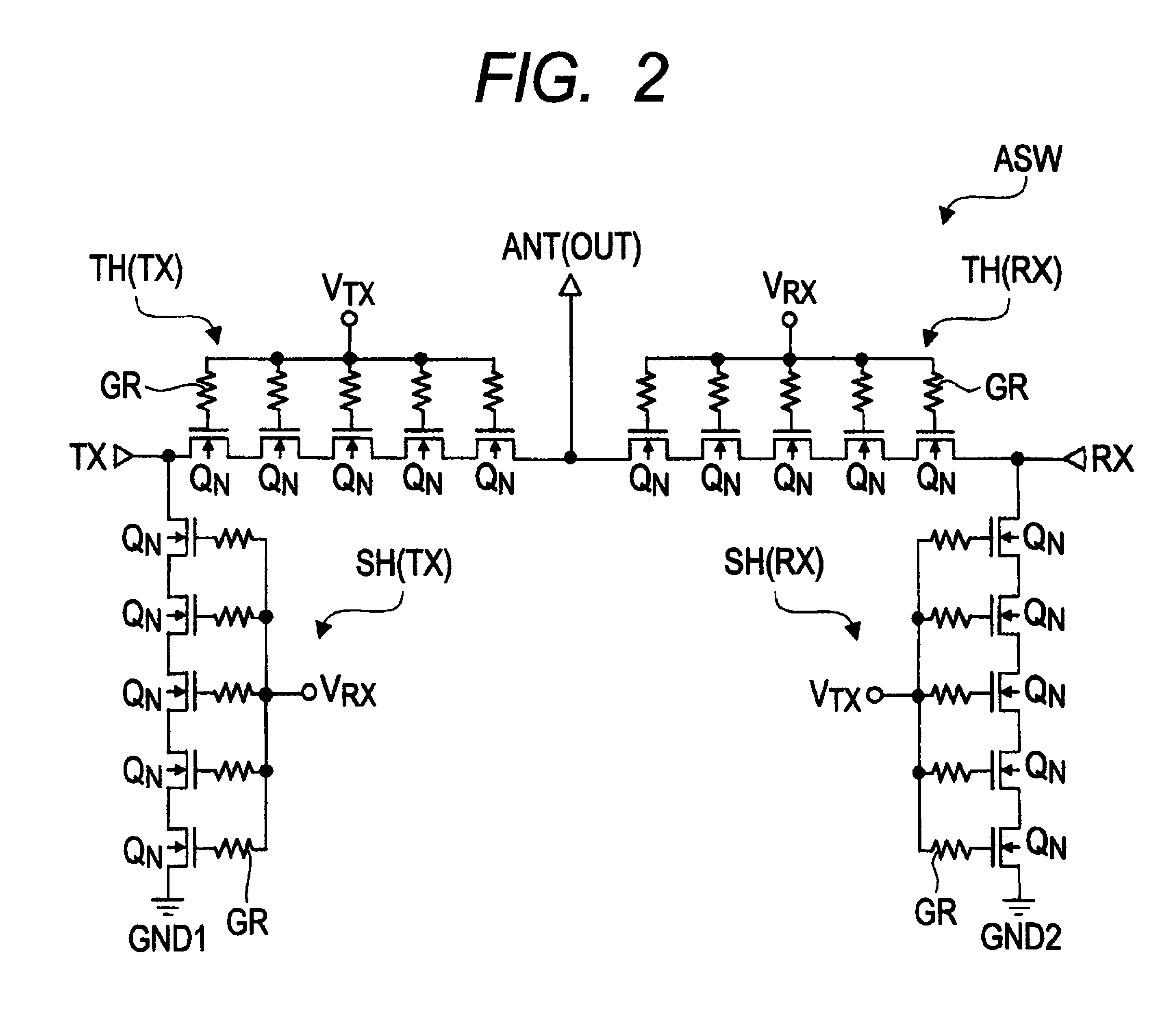
ActiveUS20110316062A1Lower Antenna CostsMinimizing harmonic distortionTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTotal harmonic distortion
In terms of achieving a reduction in the cost of an antenna switch, there is provided a technology capable of minimizing harmonic distortion generated in the antenna switch even when the antenna switch is particularly formed of field effect transistors formed over a silicon substrate. Between the source region and the drain region of each of a plurality of MISFETs coupled in series, a distortion compensating capacitance circuit is coupled which has a voltage dependency such that, in either of the cases where a positive voltage is applied to the drain region based on the potential of the source region and where a negative voltage is applied to the drain region based on the potential of the source region, the capacitance decreases to a value smaller than that in a state where the potential of the source region and the potential of the drain region are at the same level.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device
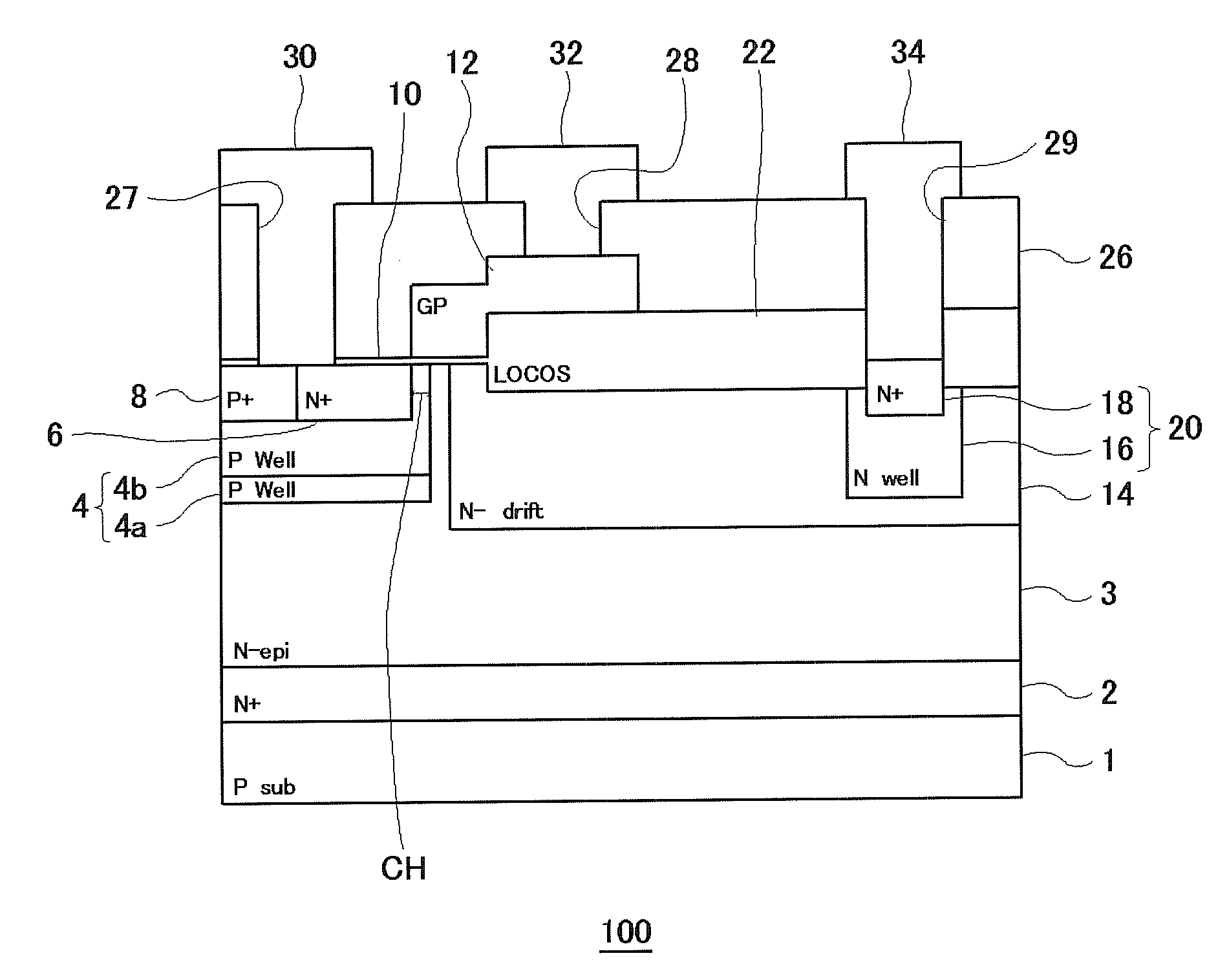
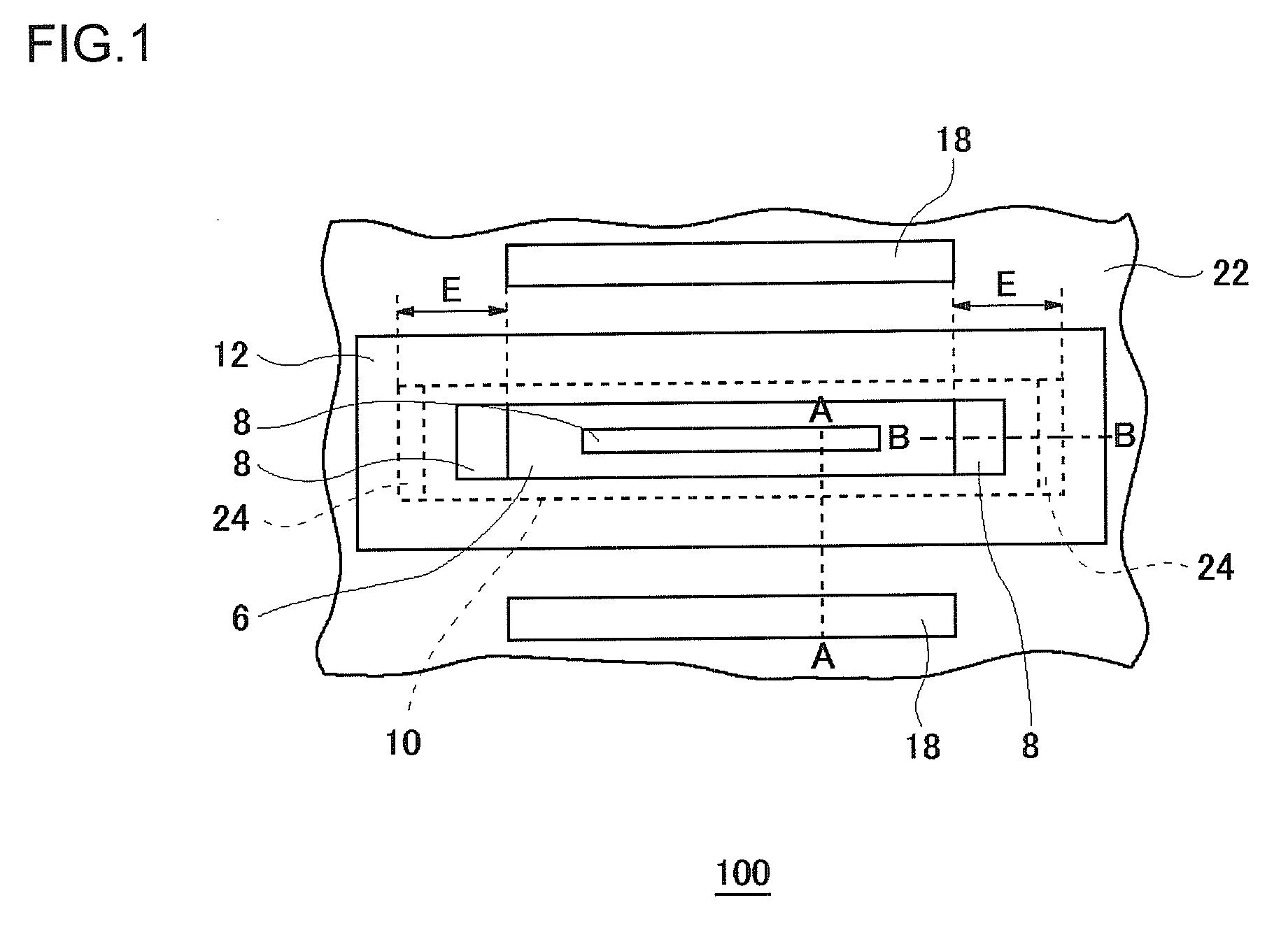
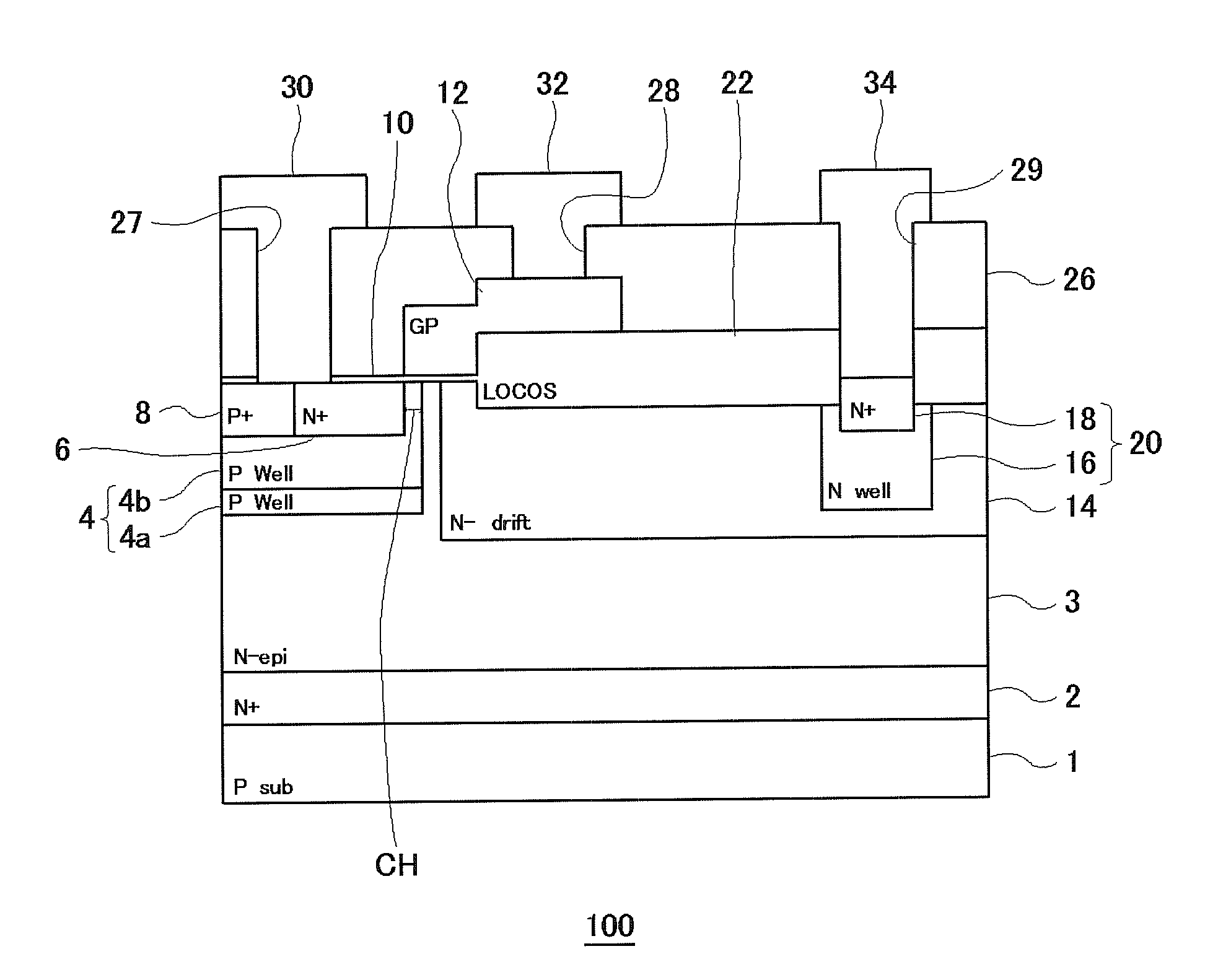
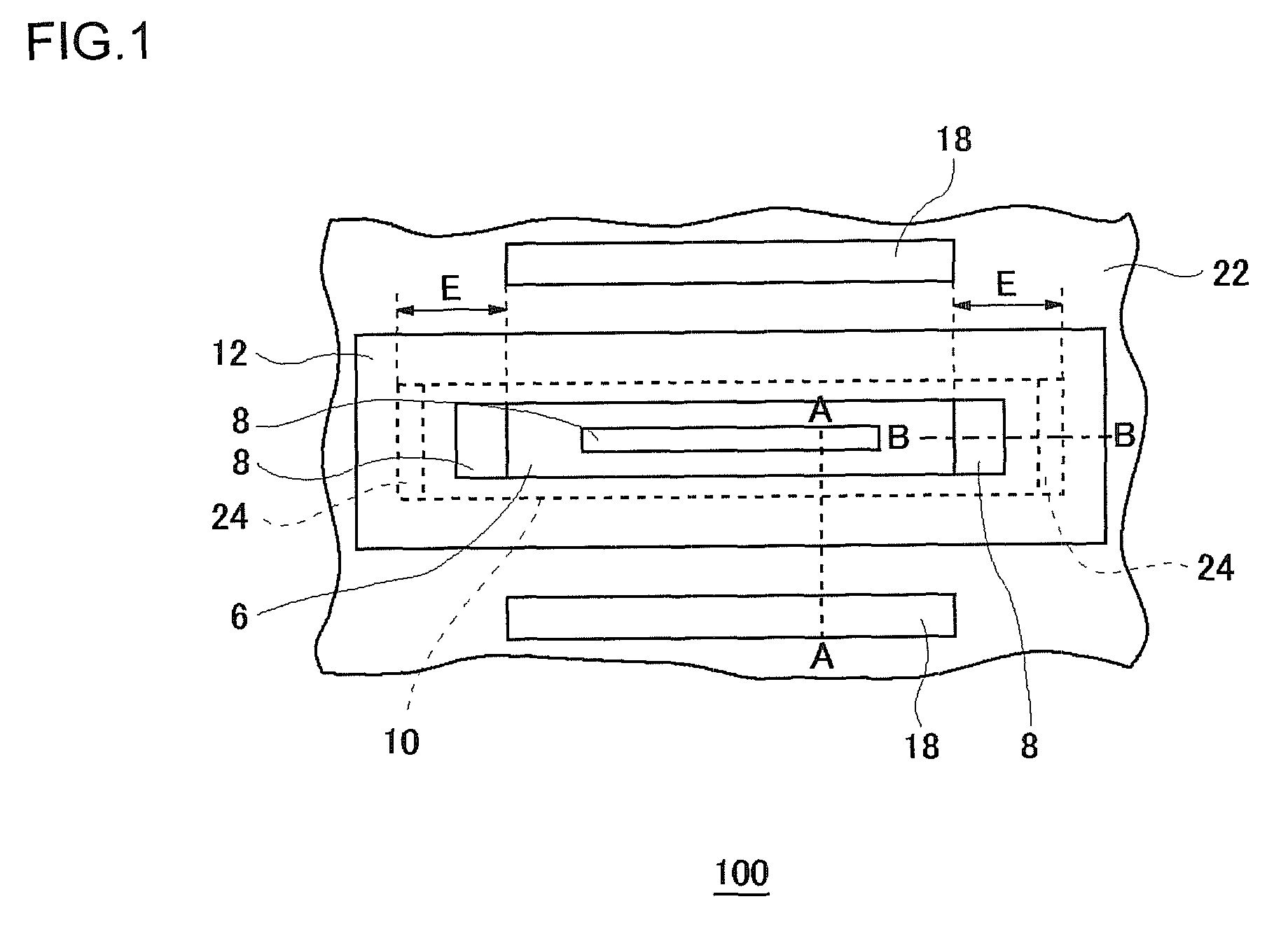
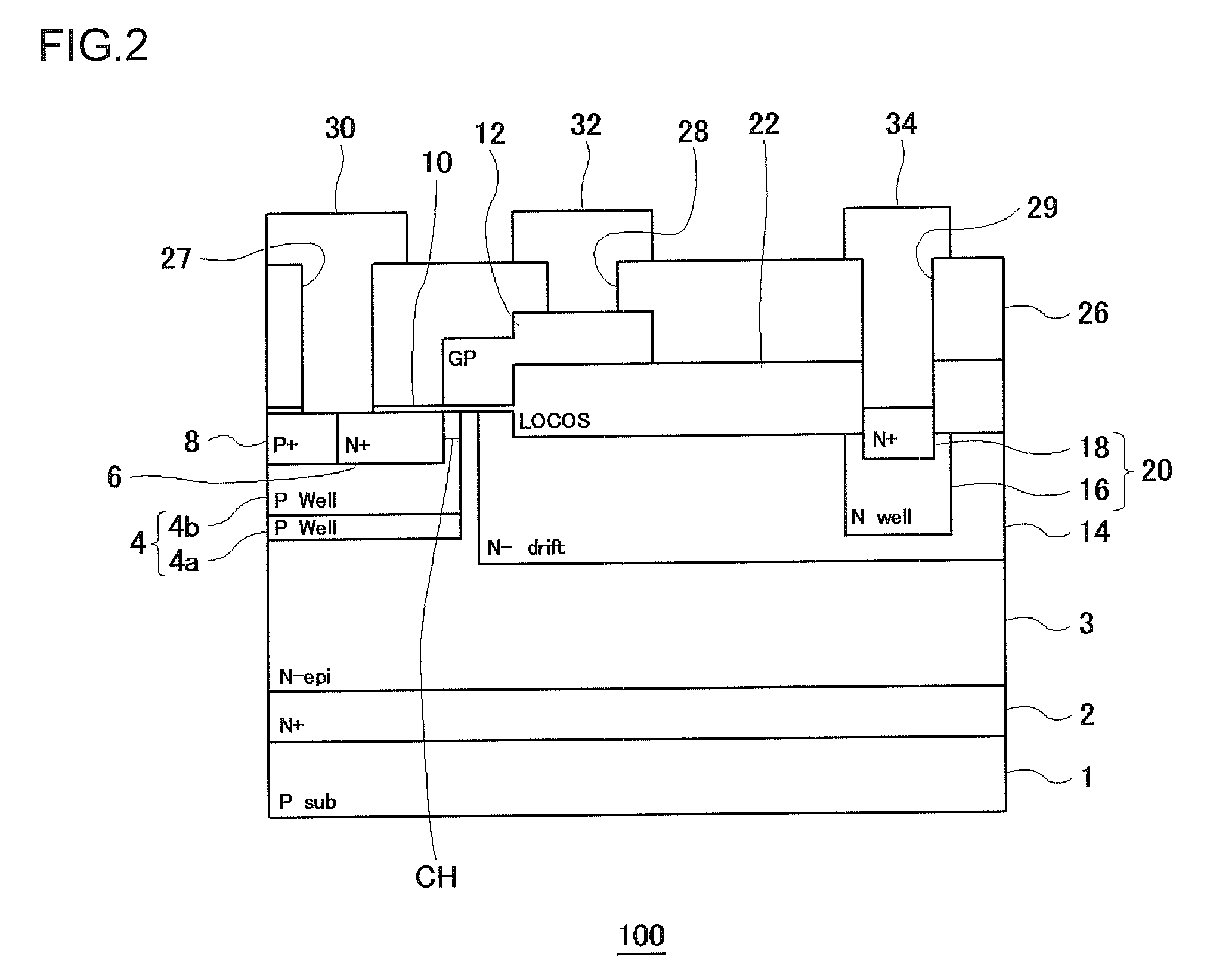
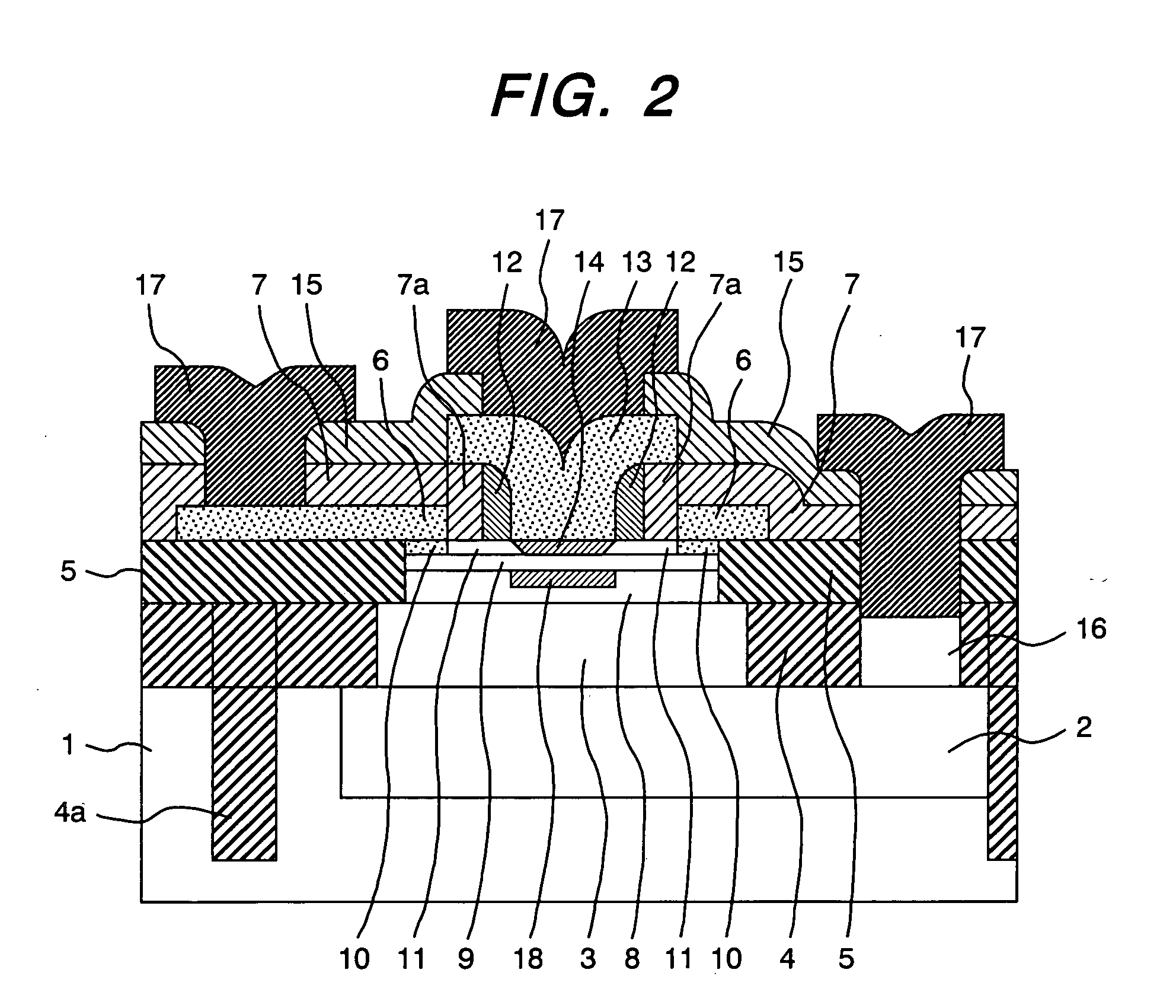
ActiveUS20090242981A1High breakdown voltage performanceImproved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysicsSemiconductor
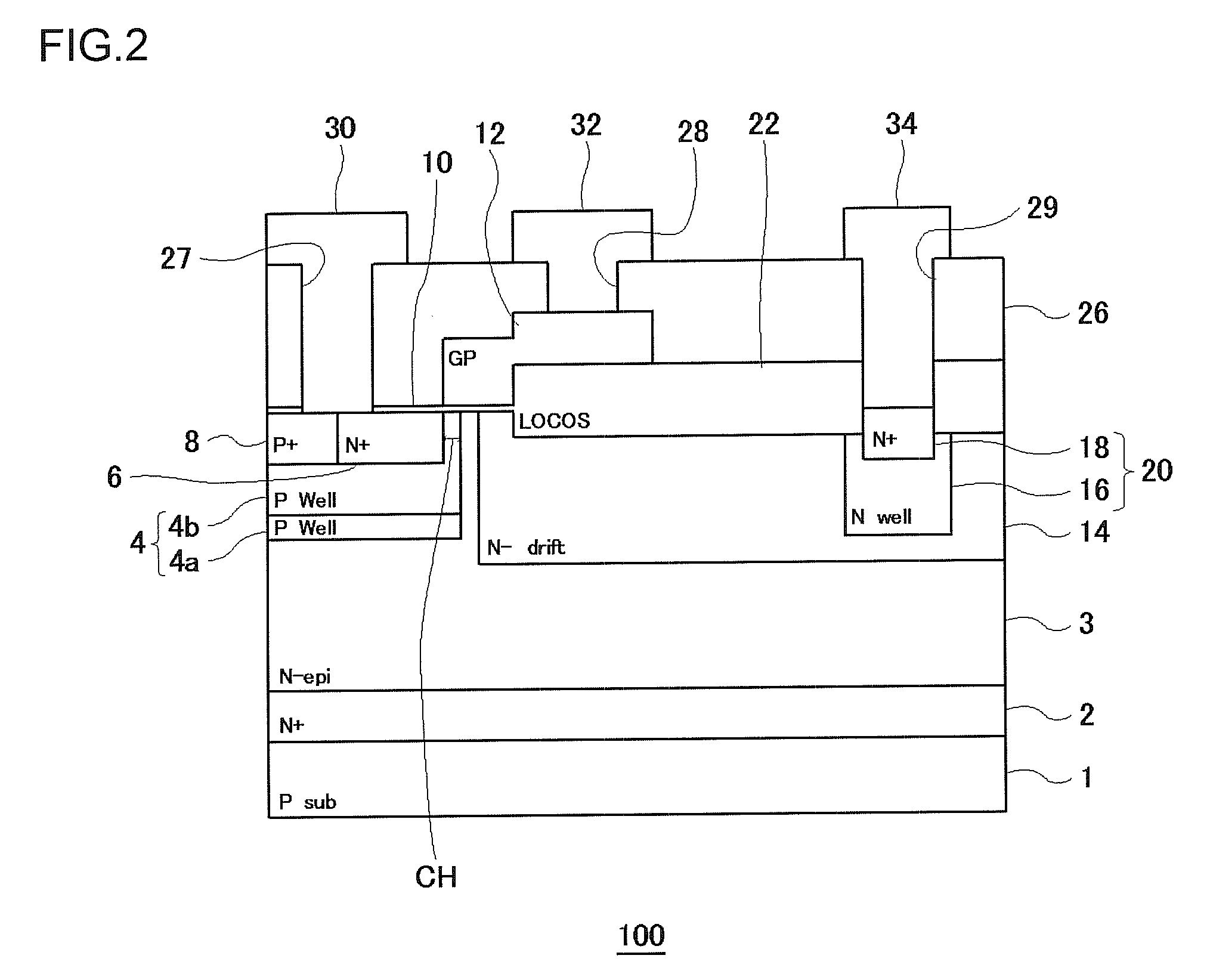
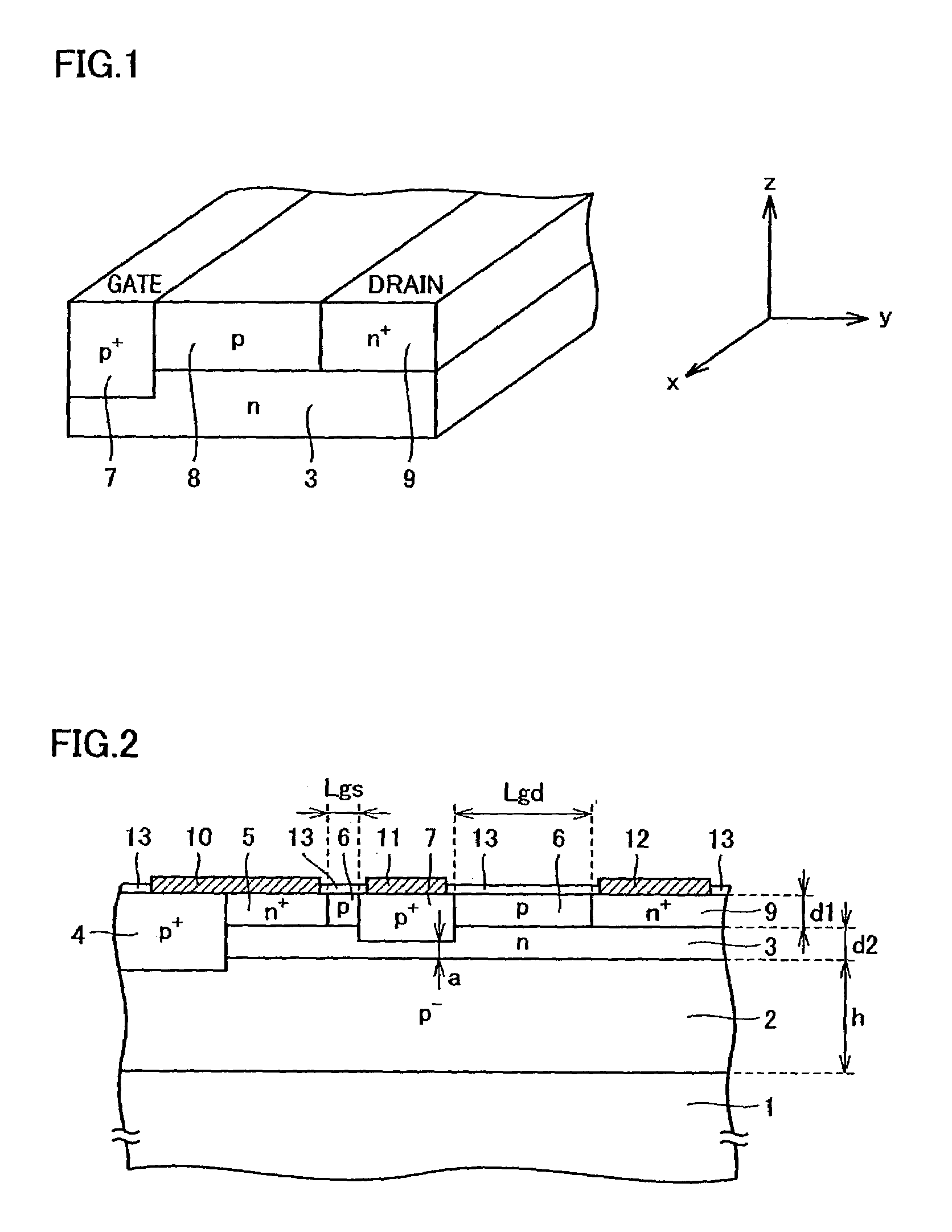
A semiconductor device includes: an epitaxial layer; a body layer, formed in the epitaxial layer, which includes a channel region; a source layer disposed in superposition on the body layer; a gate insulator, formed on the epitaxial layer, which is in a ring shape surrounding the source layer; a gate electrode formed through the gate insulator; a drift layer, formed in the epitaxial layer, which is in a ring shape surrounding the body layer; and a drain layer formed in the surface of the epitaxial layer and disposed opposite to the source layer. The body layer is disposed such that the boundary surface at an end in the gate-width direction is in contact with the undersurface of the gate insulator. The gate insulator has a thick film portion thicker than a part above the channel region in the gate-length direction at least in a part where the gate insulator is in contact with the boundary surface of the body layer at the end in the gate-width direction.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
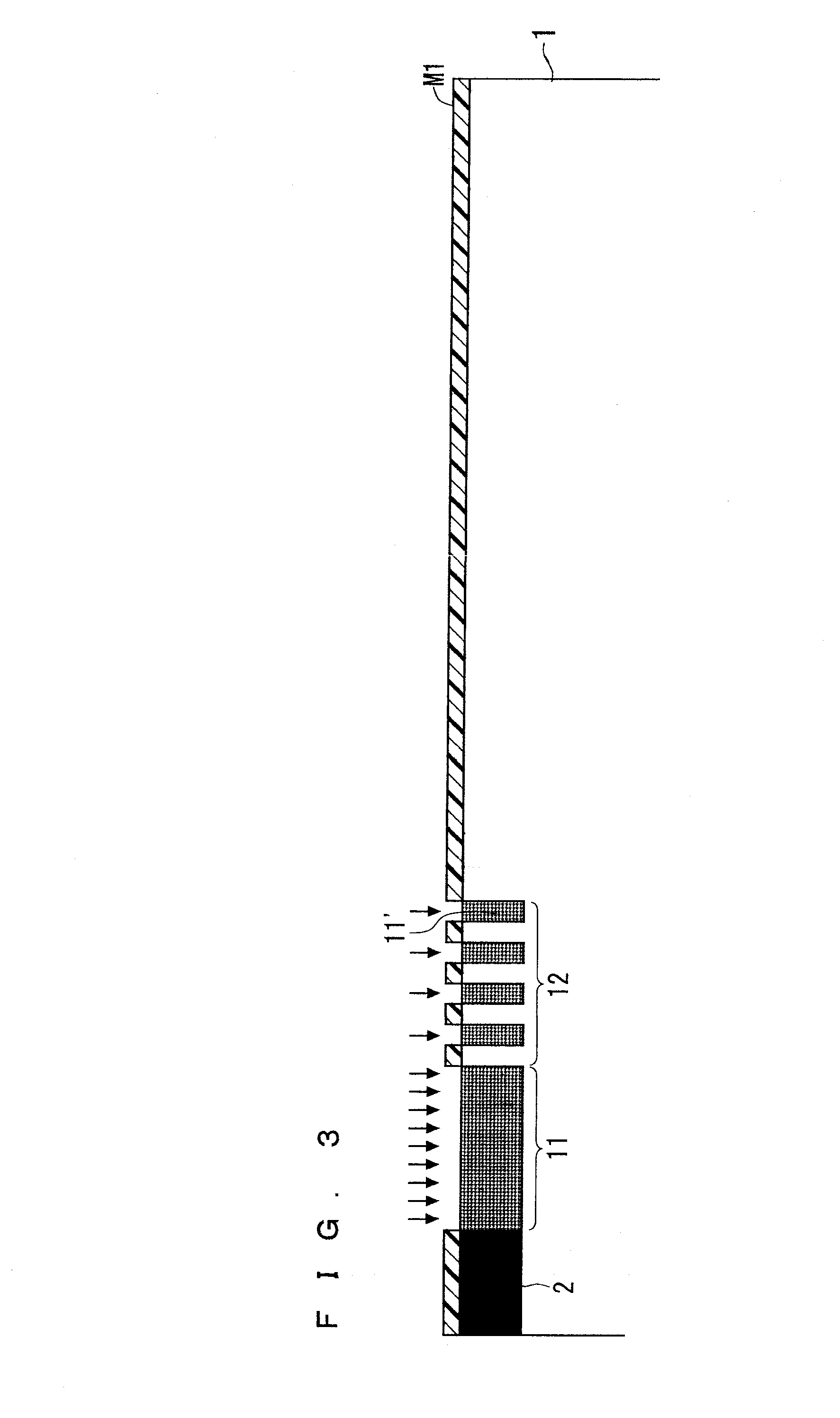
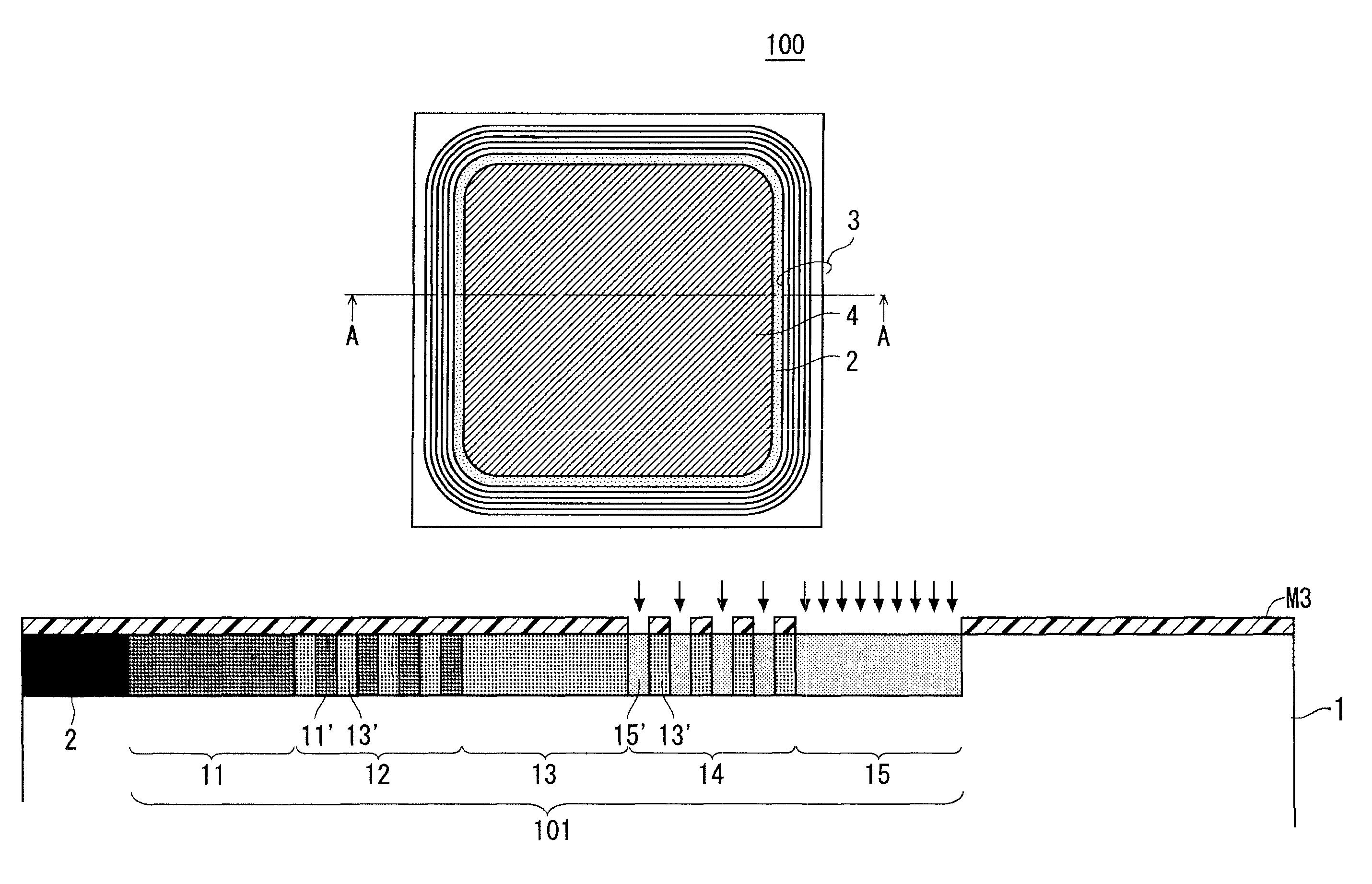
ActiveUS20130140582A1Improved breakdown voltage performanceLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpuritySemiconductor
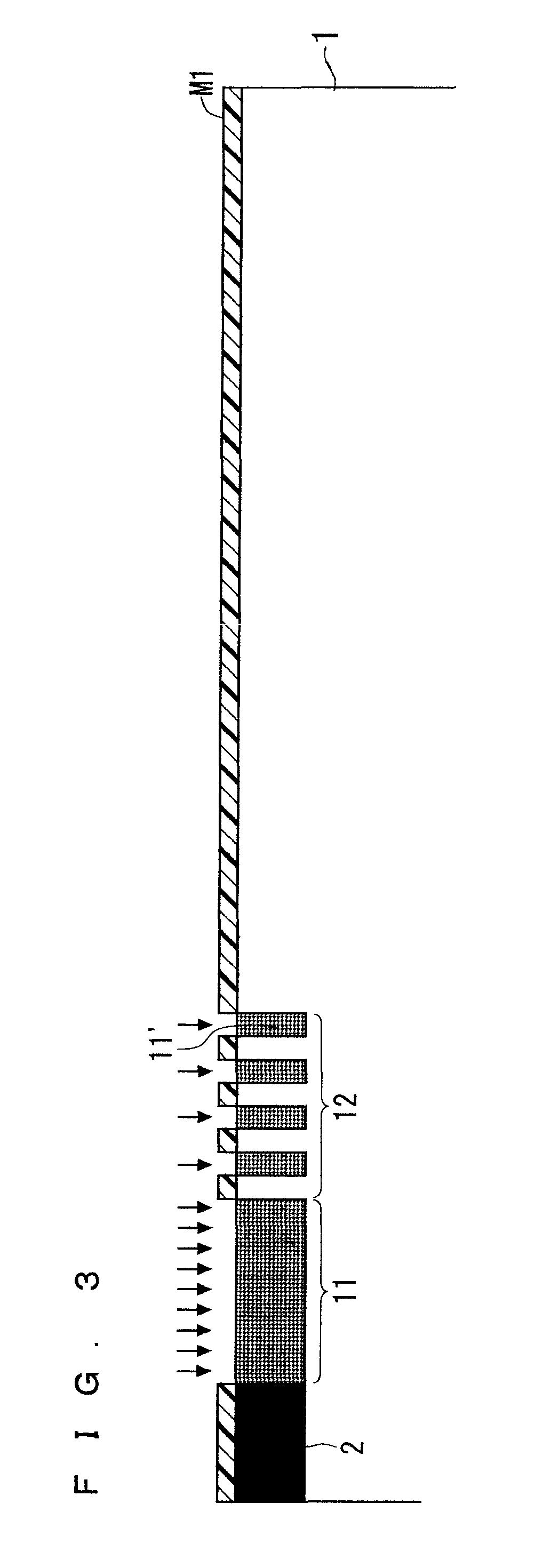
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. A RESURF layer (101) including a plurality of P-type implantation layers having a relatively low concentration of P-type impurity is formed adjacent to an active region (2). The RESURF layer (101) includes a first RESURF layer (11), a second RESURF layer (12), a third RESURF layer (13), a fourth RESURF layer (14), and a fifth RESURF layer (15) that are arranged sequentially from the P-type base (2) side so as to surround the P-type base (2). The second RESURF layer (12) is configured with small regions (11′) having an implantation amount equal to that of the first RESURF layer (11) and small regions (13′) having an implantation amount equal to that of the third RESURF layer (13) being alternately arranged in multiple. The fourth RESURF layer (14) is configured with small regions (13′) having an implantation amount equal to that of the third RESURF layer (13) and small regions (15′) having an implantation amount equal to that of the fifth RESURF layer (15) being alternately arranged in multiple.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Methods of forming power semiconductor devices having laterally extending base shielding regions
InactiveUS7041559B2Avoiding characteristicHigh dopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePower semiconductor deviceDopant
Methods of forming power semiconductor devices include forming a semiconductor substrate having a drift region of first conductivity type therein and a transition region of first conductivity type that extends between the drift region and a first surface of the semiconductor substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the first surface. Base and base shielding region dopants are implanted into the transition region using the gate electrode as an implant mask. A plurality of annealing steps are performed so that the base shielding region dopants are driven in laterally and vertically to substantially their full and final depth within the substrate and thereby define first and second base shielding regions that constrict a neck of the transition region to a minimum width.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Nano MOSFET with trench bottom oxide shielded and third dimensional P-body contact
ActiveUS8785278B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceMore manufacturableTransistorThyristorBody regionSemiconductor
A semiconductor power device may include a lightly doped layer formed on a heavily doped layer. One or more devices are formed in the lightly doped layer. Each device may include a body region, a source region, and one or more gate electrodes formed in corresponding trenches in the lightly doped region. Each of the trenches has a depth in a first dimension, a width in a second dimension and a length in a third dimension. The body region is of opposite conductivity type to the lightly and heavily doped layers. The source region is formed proximate the upper surface. One or more deep contacts are formed at one or more locations along the third dimension proximate one or more of the trenches. The contacts extend in the first direction from the upper surface into the lightly doped layer and are in electrical contact with the source region.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Drain-extended MOS transistors and methods for making the same
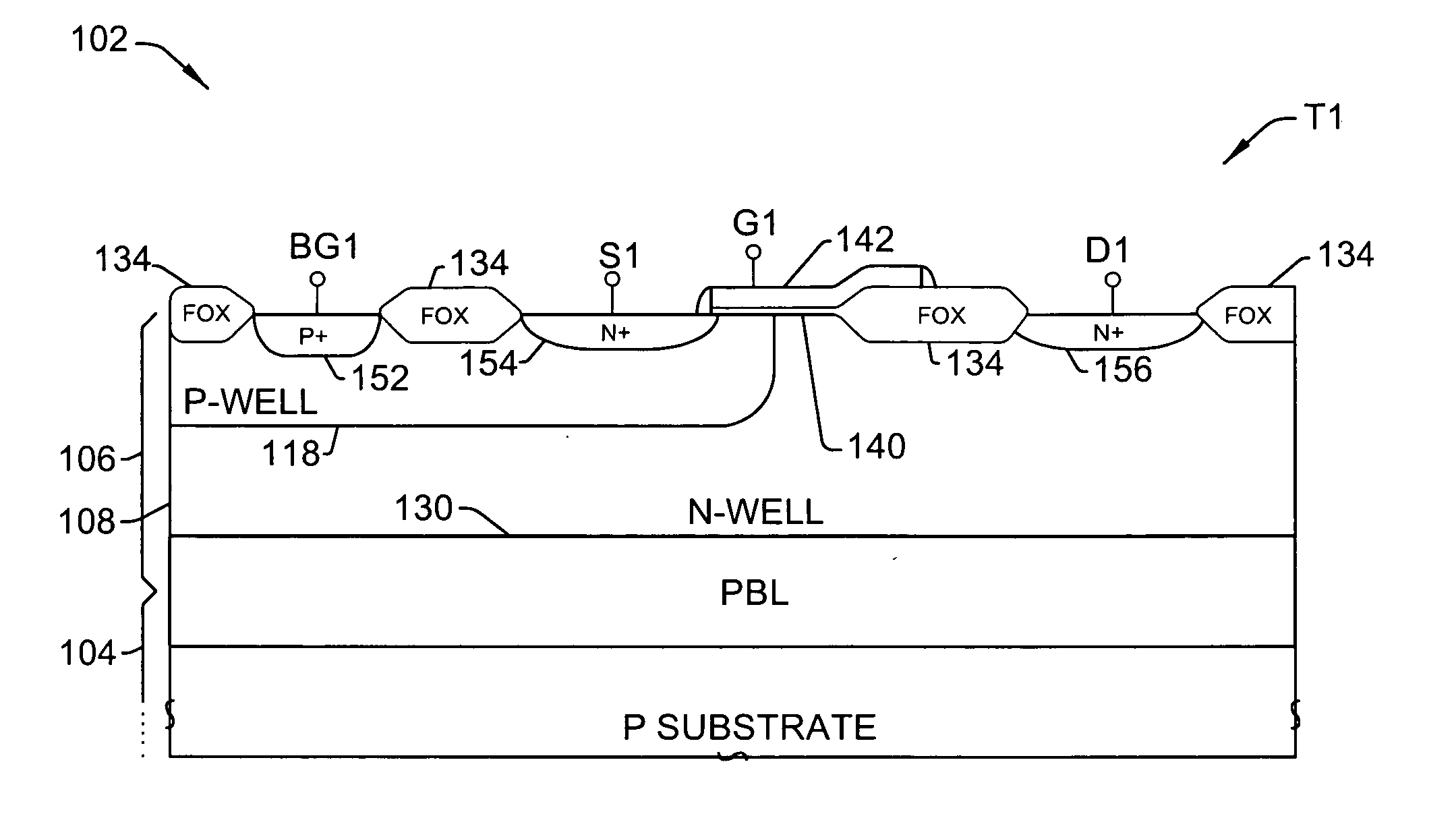
ActiveUS20060001102A1Improve off-stateImprove transient breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
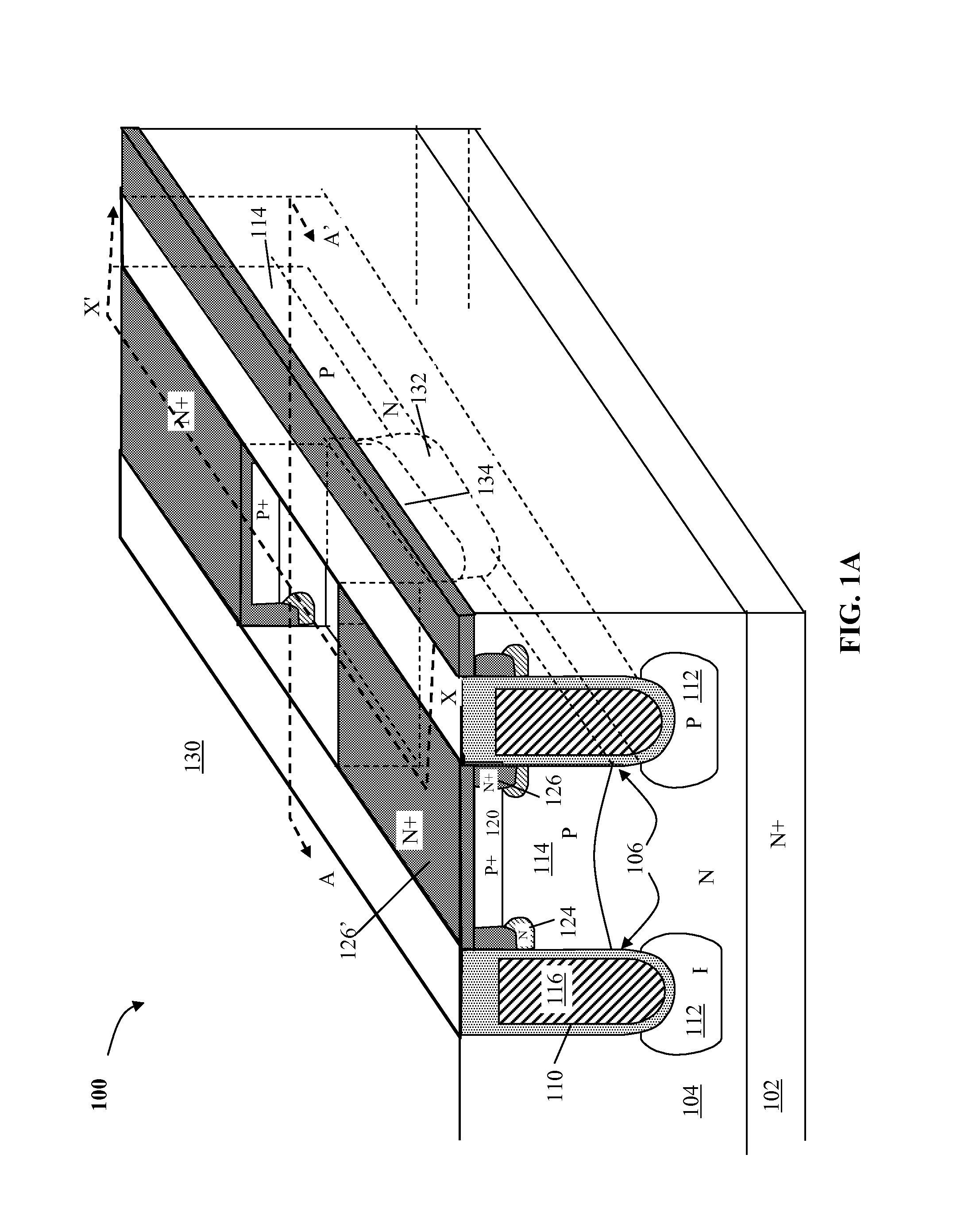
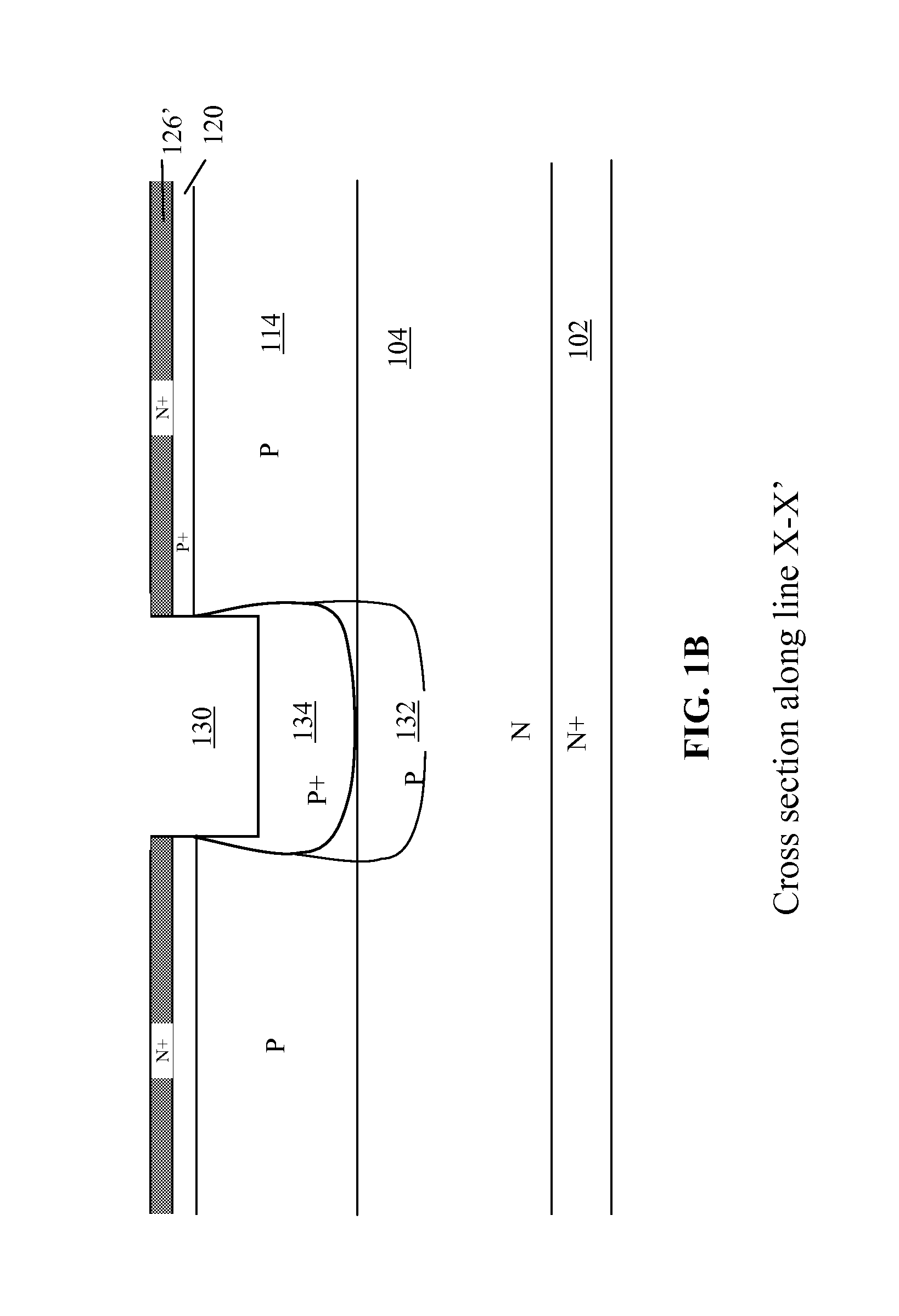
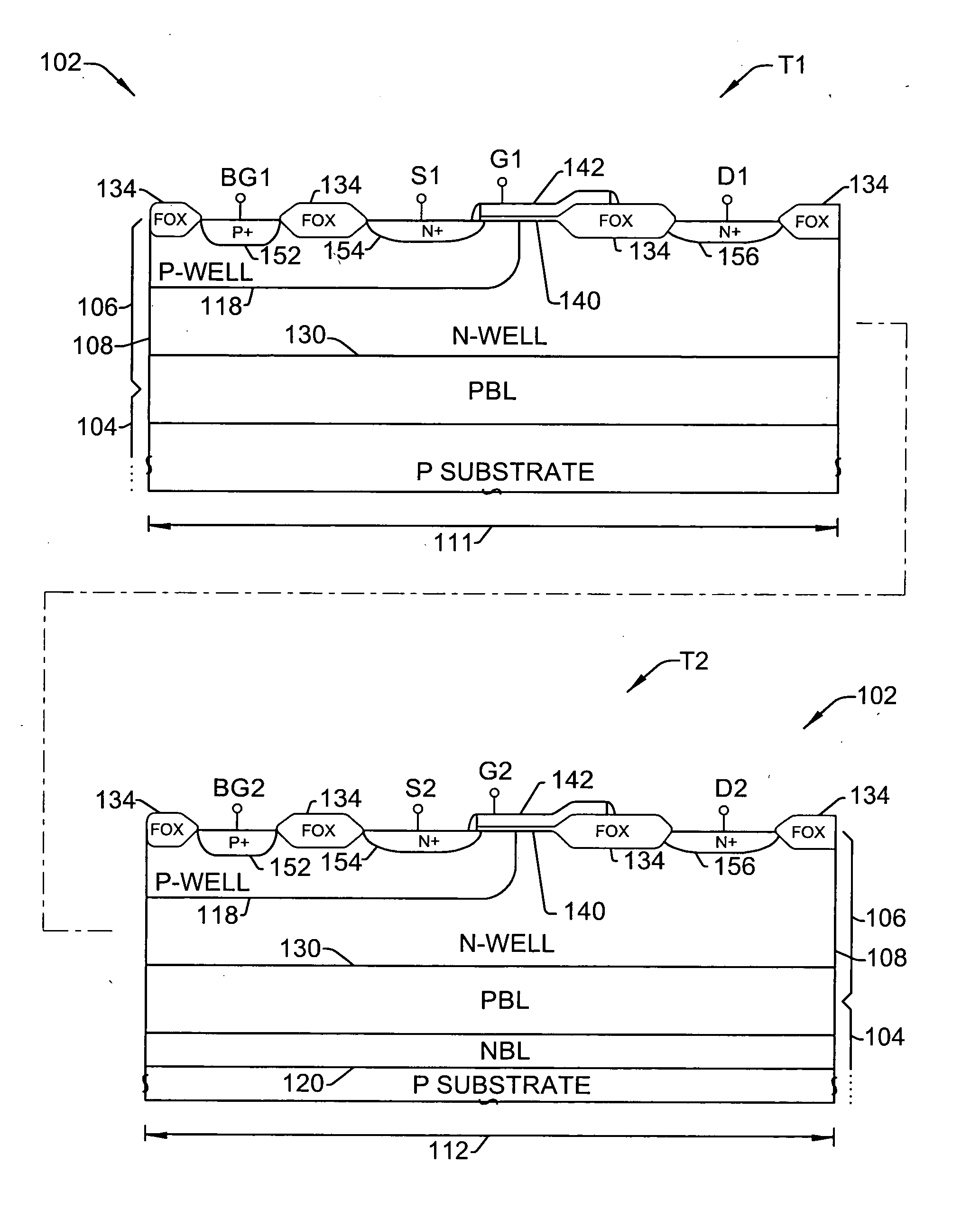
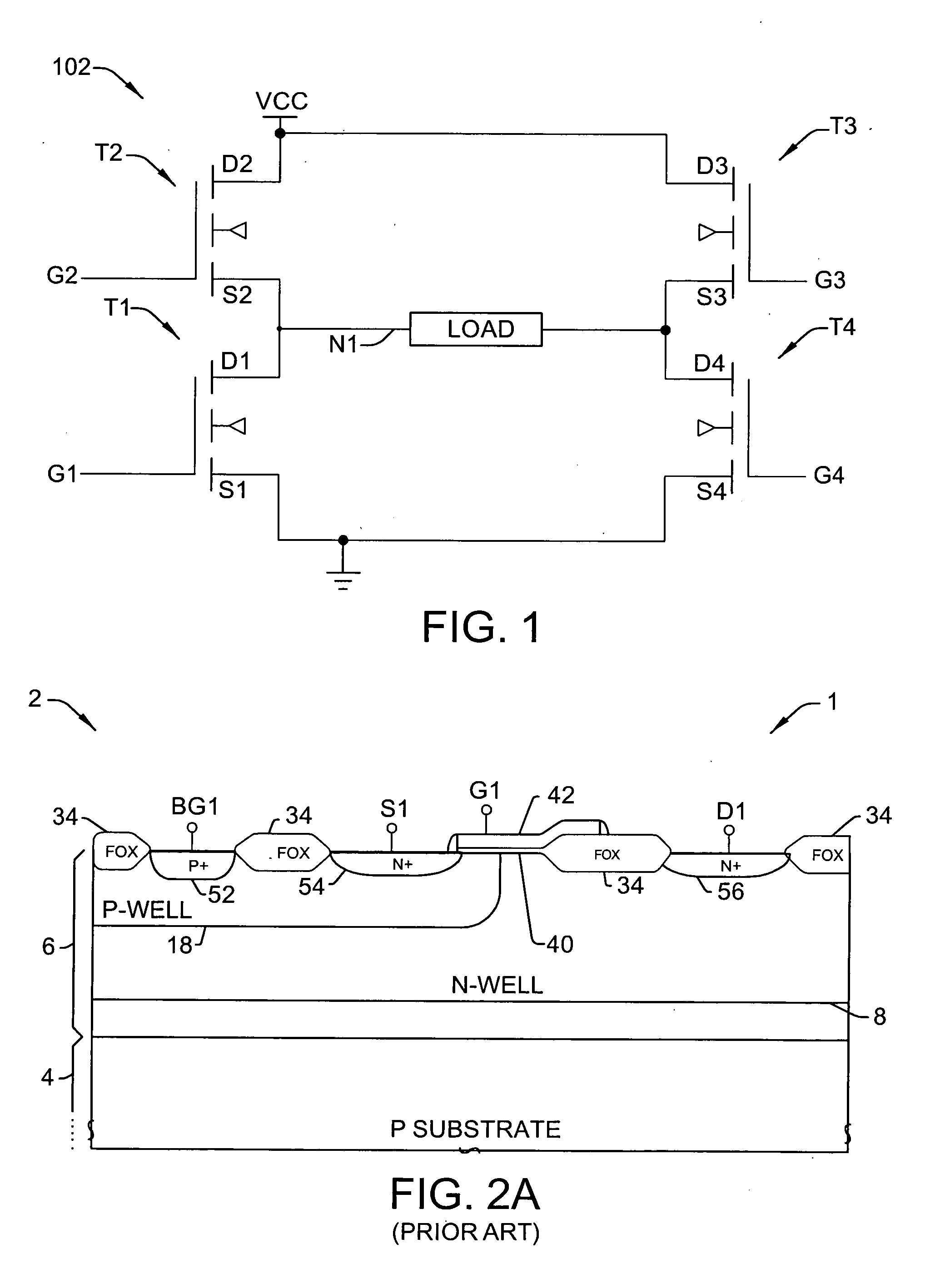
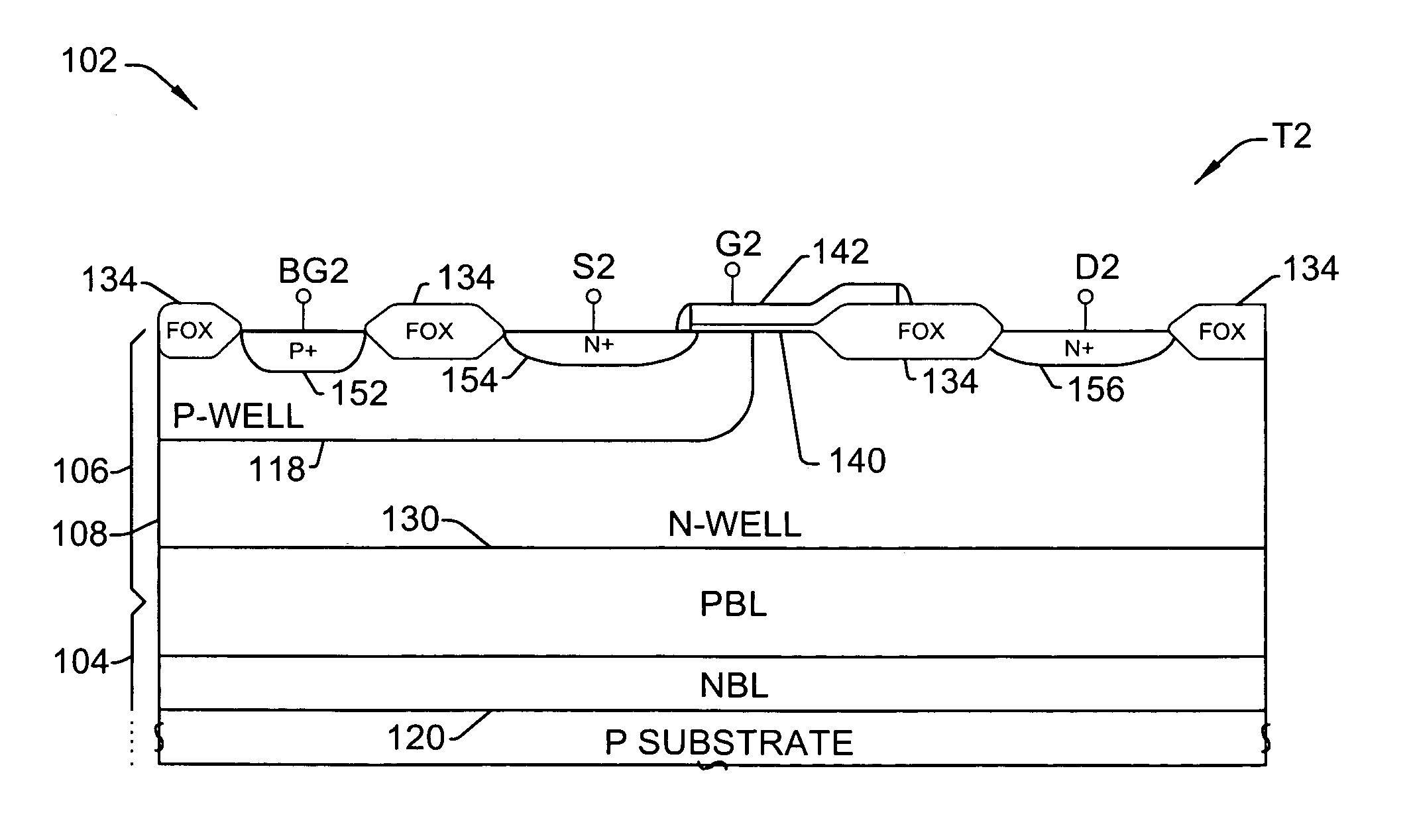
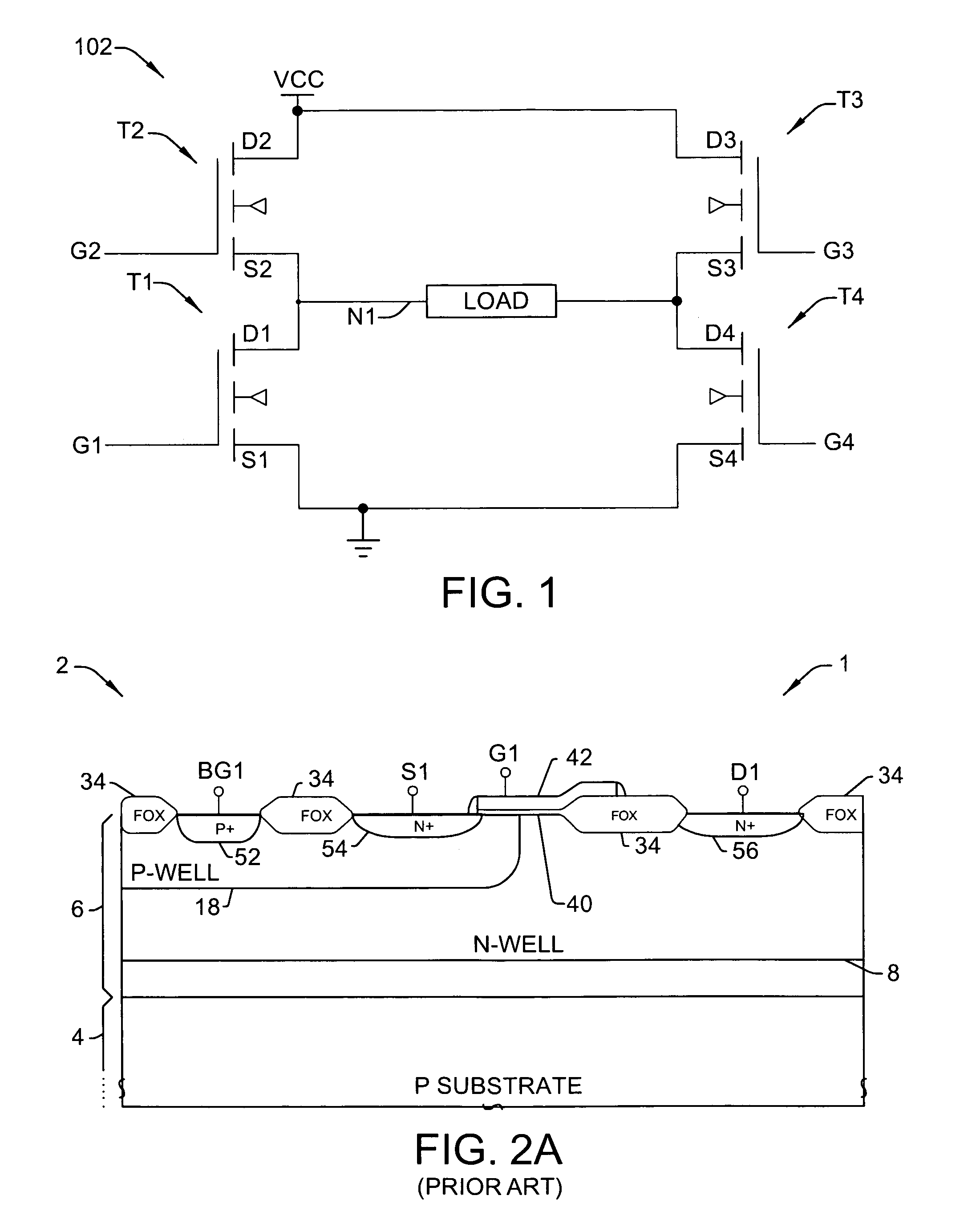
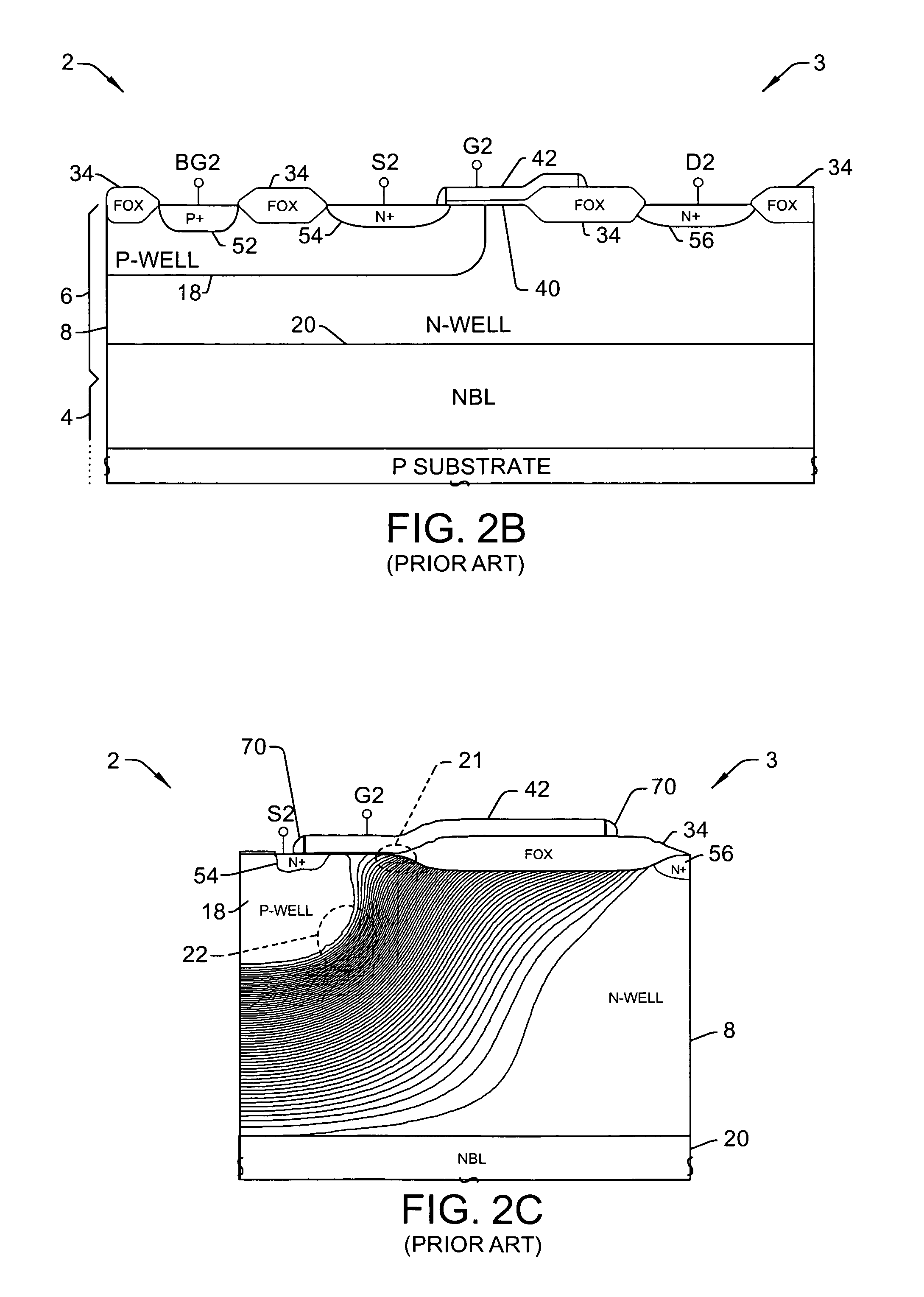
Drain-extended MOS transistors (T1, T2) and semiconductor devices (102) are described, as well as fabrication methods (202) therefor, in which a p-buried layer (130) is formed prior to formation of epitaxial silicon (106) over a substrate (104), and a drain-extended MOS transistor (T1, T2) is formed in the epitaxial silicon layer (106). The p-buried layer (130) may be formed above an n-buried layer (120) in the substrate (104) for high-side driver transistor (T2) applications, wherein the p-buried layer (130) extends between the drain-extended MOS transistor (T2) and the n-buried layer (120) to inhibit off-state breakdown between the source (154) and drain (156).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8786002B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceQuality improvementTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTotal harmonic distortion
In terms of achieving a reduction in the cost of an antenna switch, there is provided a technology capable of minimizing harmonic distortion generated in the antenna switch even when the antenna switch is particularly formed of field effect transistors formed over a silicon substrate. Between the source region and the drain region of each of a plurality of MISFETs coupled in series, a distortion compensating capacitance circuit is coupled which has a voltage dependency such that, in either of the cases where a positive voltage is applied to the drain region based on the potential of the source region and where a negative voltage is applied to the drain region based on the potential of the source region, the capacitance decreases to a value smaller than that in a state where the potential of the source region and the potential of the drain region are at the same level.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device
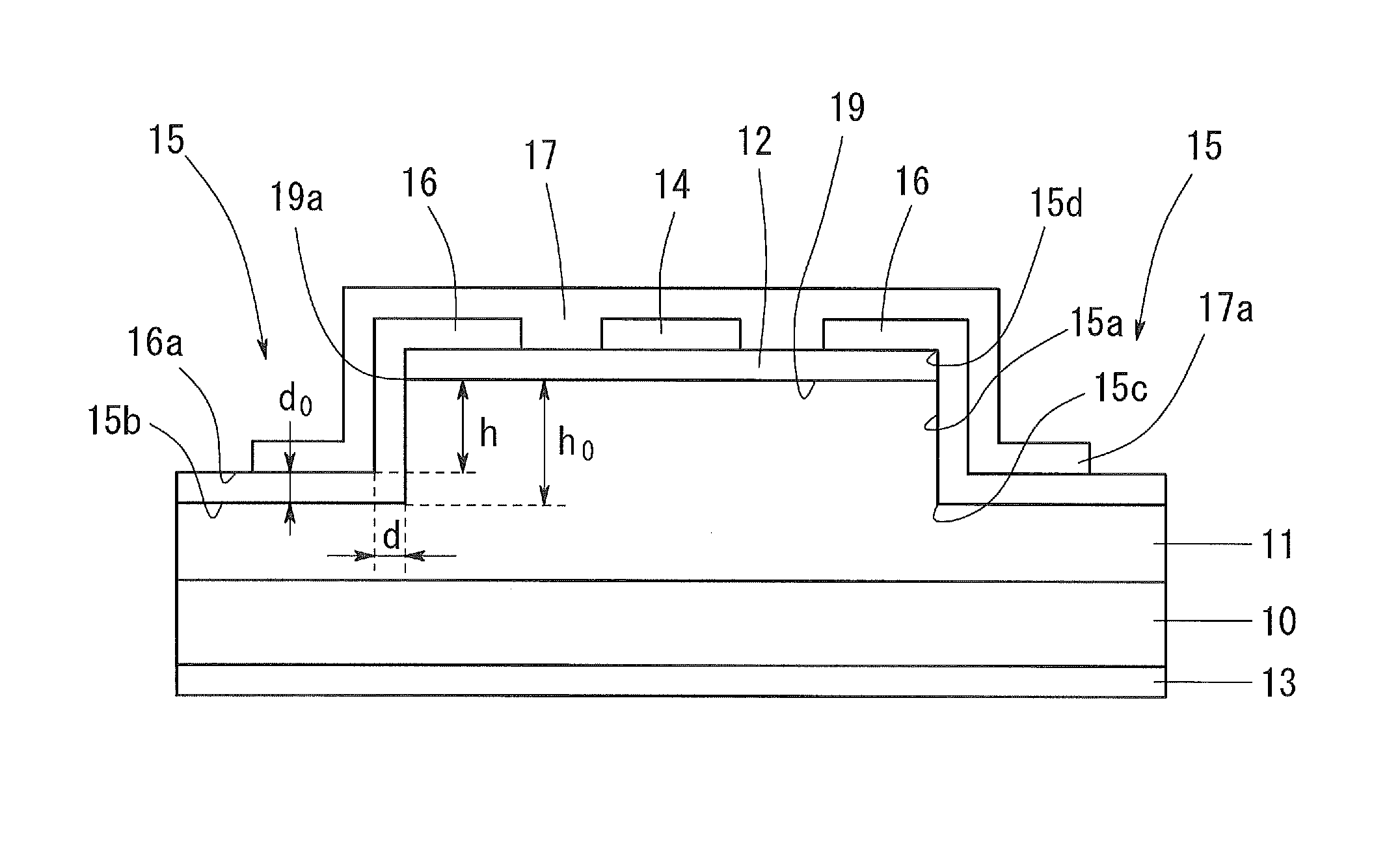
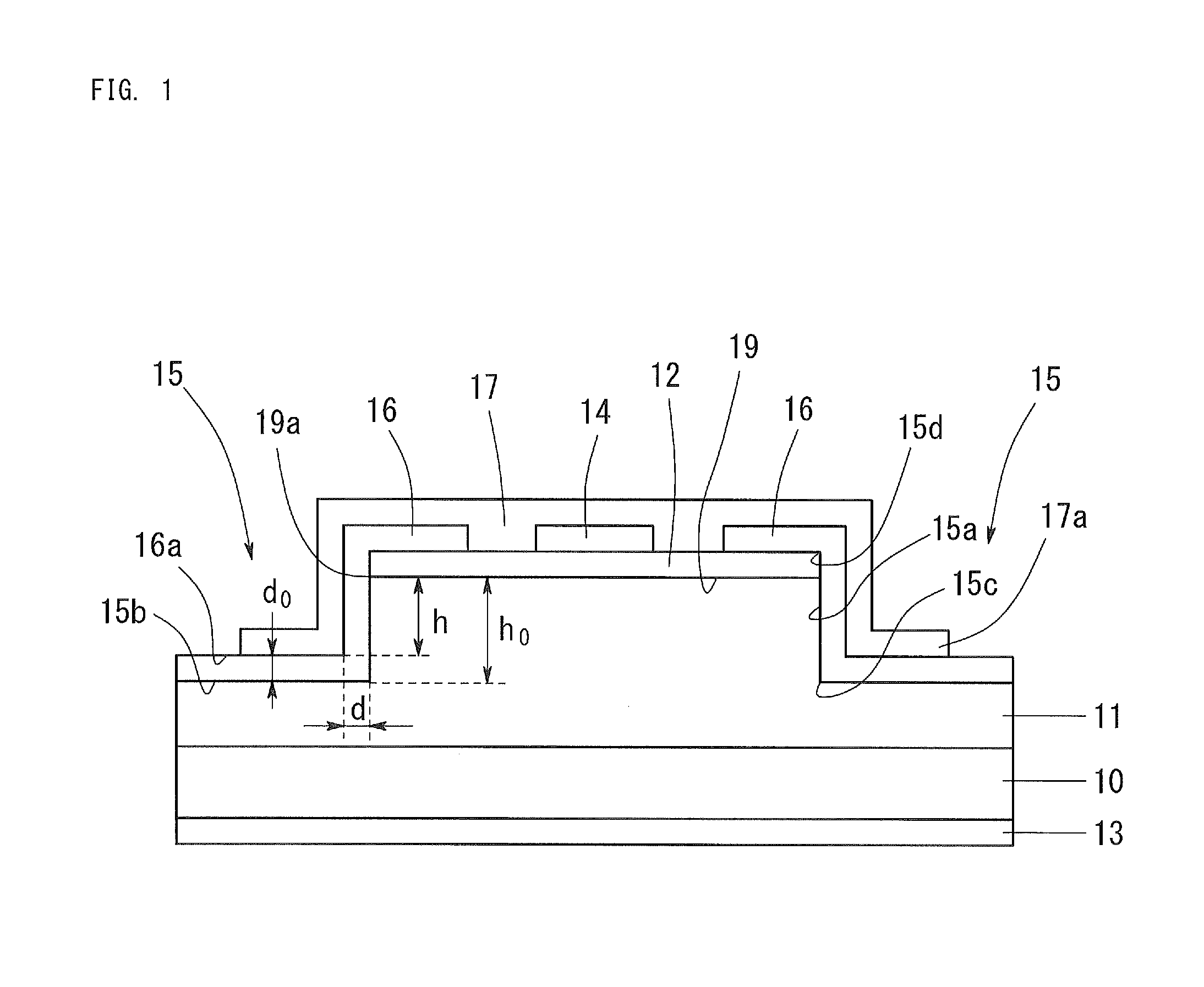
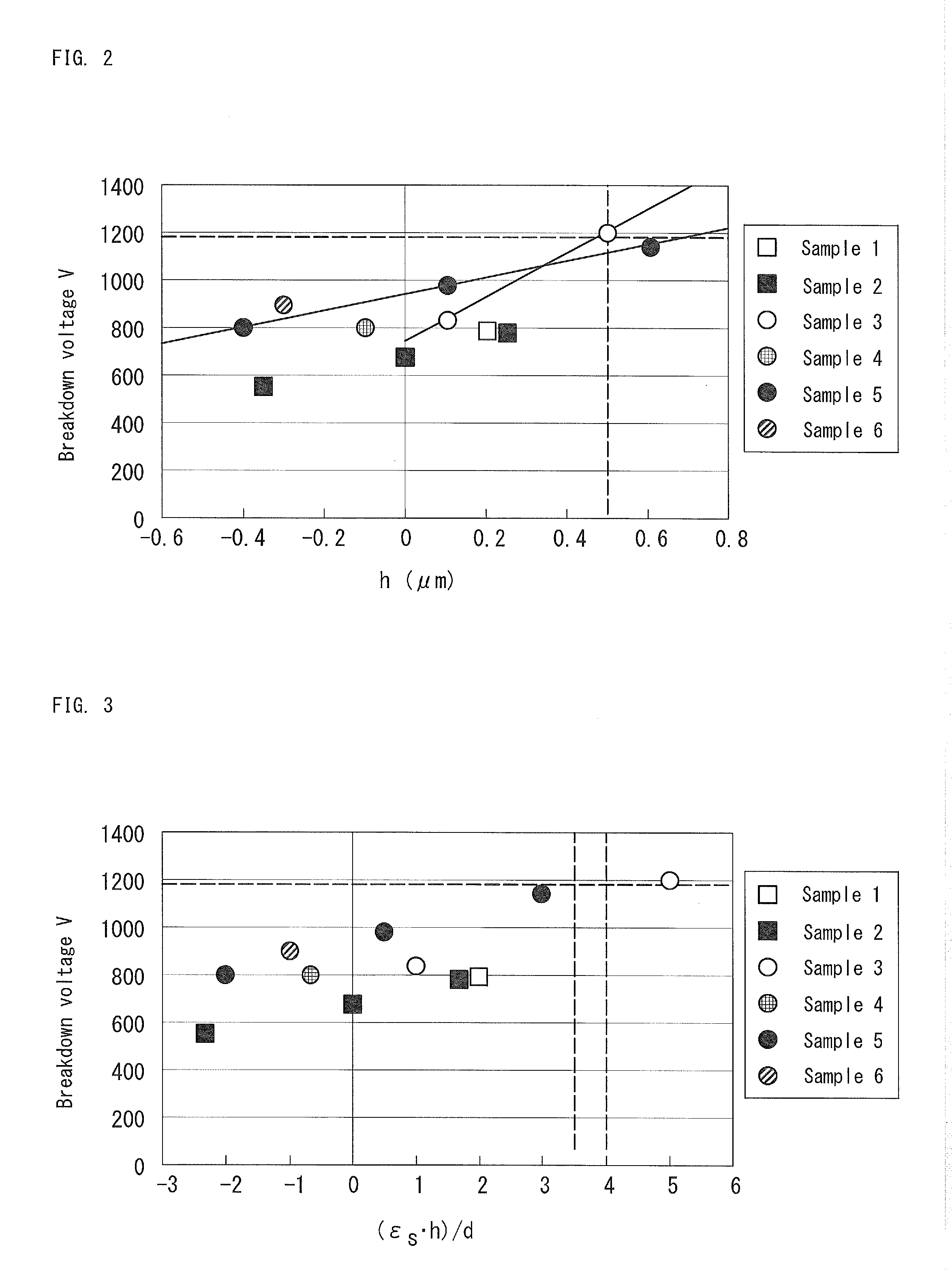
ActiveUS20130328120A1Large electric field relaxing regionImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesTectorial membraneSemiconductor
A device comprises a substrate, an n-layer and a p-layer, an n-electrode, and a p-electrode. A step is formed at an outer circumference of the device. A protective film is formed so as to continuously cover a side surface and a bottom surface of the step. A field plate electrode connected with the p-electrode is formed on the protective film. When a distance from the pn junction interface to the surface of the protective film on the bottom surface of the step is defined as h (μm), a dielectric constant of the protective film is defined as ∈s, and a thickness of the protective film at the pn junction interface on the side surface of the step is defined as d (μm), (∈s·h) / d is 4 or more, and ∈s / d is 3 (1 / μm) or more.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Drain-extended MOS transistors and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20060001086A1Improve off-stateImprove transient breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
Drain-extended MOS transistors (T1, T2) and semiconductor devices (102) are described, as well as fabrication methods (202) therefor, in which a p-buried layer (130) is formed prior to formation of epitaxial silicon (106) over a substrate (104), and a drain-extended MOS transistor (T1, T2) is formed in the epitaxial silicon layer (106). The p-buried layer (130) may be formed above an n-buried layer (120) in the substrate (104) for high-side driver transistor (T2) applications, wherein the p-buried layer (130) extends between the drain-extended MOS transistor (T2) and the n-buried layer (120) to inhibit off-state breakdown between the source (154) and drain (156).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8716717B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A RESURF layer including a plurality of P-type implantation layers having a low concentration of P-type impurity is formed adjacent to an active region. The RESURF layer includes a first RESURF layer, a second RESURF layer, a third RESURF layer, a fourth RESURF layer, and a fifth RESURF layer that are arranged sequentially from the P-type base side so as to surround the P-type base. The second RESURF layer is configured with small regions having an implantation amount equal to that of the first RESURF layer and small regions having an implantation amount equal to that of the third RESURF layer being alternately arranged in multiple. The fourth RESURF layer is configured with small regions having an implantation amount equal to that of the third RESURF layer and small regions having an implantation amount equal to that of the fifth RESURF layer being alternately arranged in multiple.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Drain-extended MOS transistors and methods for making the same
ActiveUS7176091B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Drain-extended MOS transistors (T1, T2) and semiconductor devices (102) are described, as well as fabrication methods (202) therefor, in which a p-buried layer (130) is formed prior to formation of epitaxial silicon (106) over a substrate (104), and a drain-extended MOS transistor (T1, T2) is formed in the epitaxial silicon layer (106). The p-buried layer (130) may be formed above an n-buried layer (120) in the substrate (104) for high-side driver transistor (T2) applications, wherein the p-buried layer (130) extends between the drain-extended MOS transistor (T2) and the n-buried layer (120) to inhibit off-state breakdown between the source (154) and drain (156).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Lateral junction field-effect transistor
InactiveUS20060118813A1Improved breakdown voltage performanceReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsJFET
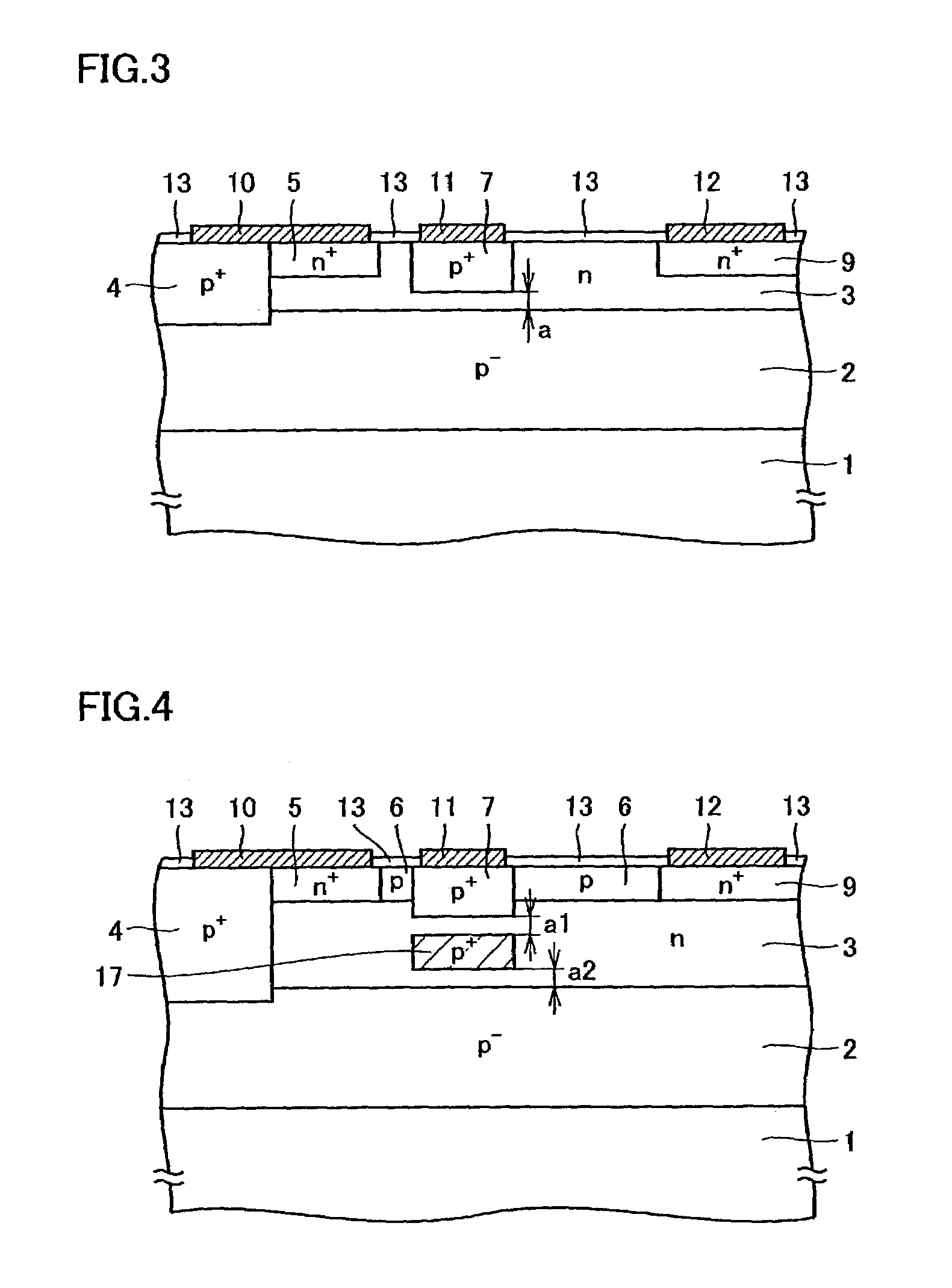
A lateral JFET has a basic structure including an n-type semiconductor layer (3) formed of an n-type impurity region and a p-type semiconductor layer formed of a p-type impurity region on the n-type semiconductor layer (3). Moreover, in the p-type semiconductor layer, there are provided a p+-type gate region layer (7) extending into the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and containing p-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and an n+-type drain region layer (9) spaced from the p+-type gate region layer (7) by a predetermined distance and containing n-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3). With this structure, the lateral JFET can be provided that has an ON resistance further decreased while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Lateral junction field-effect transistor
InactiveUS7023033B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsJFET
A lateral JFET has a basic structure including an n-type semiconductor layer (3) formed of an n-type impurity region and a p-type semiconductor layer formed of a p-type impurity region on the n-type semiconductor layer (3). Moreover, in the p-type semiconductor layer, there are provided a p+-type gate region layer (7) extending into the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and containing p-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and an n+-type drain region layer (9) spaced from the p+-type gate region layer (7) by a predetermined distance and containing n-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3). With this structure, the lateral JFET can be provided that has an ON resistance further decreased while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Capacitor having improved surface breakdown voltage performance and method for marking same
InactiveUS7667949B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceImprove capacitor performanceAnti-noise capacitorsFeed-through capacitorsSurface breakdownExact location
A capacitor having improved surface breakdown voltage performance and a method for applying laser marking to capacitors which does not reduce capacitor surface breakdown voltage, can be applied using existing laser marking technologies and apparatus, and which results in a mark that is legible and clear, is disclosed. In a first exemplary embodiment a capacitor includes a laser mark which is located near one of the capacitor terminals. The exact location is not critical as long as the mark does not make physical contact with the terminal. Conventional laser marking technologies and apparatus may be used to fix the mark in the new location. In a second embodiment the laser mark is oriented so that a flat portion of the mark is is oriented closest to the adjacent terminal.
Owner:MAXWELL JOHN
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7968941B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate insulatorSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes: an epitaxial layer; a body layer, formed in the epitaxial layer, which includes a channel region; a source layer disposed in superposition on the body layer; a gate insulator, formed on the epitaxial layer, which is in a ring shape surrounding the source layer; a gate electrode formed through the gate insulator; a drift layer, formed in the epitaxial layer, which is in a ring shape surrounding the body layer; and a drain layer formed in the surface of the epitaxial layer and disposed opposite to the source layer. The body layer is disposed such that the boundary surface at an end in the gate-width direction is in contact with the undersurface of the gate insulator. The gate insulator has a thick film portion thicker than a part above the channel region in the gate-length direction at least in a part where the gate insulator is in contact with the boundary surface of the body layer at the end in the gate-width direction.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
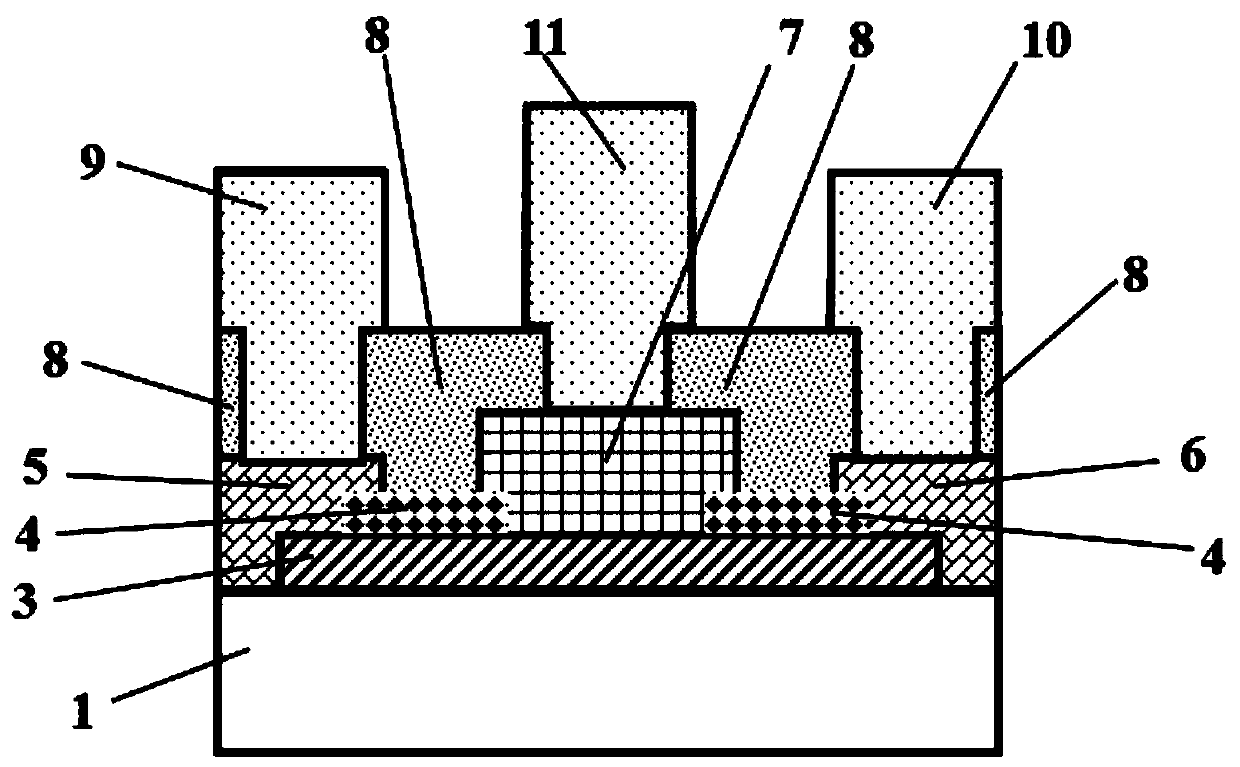
Method for enhancing self-aligning contact hole breakdown voltage and polysilicon gate construction
ActiveCN101452814AIncrease distanceImproved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitridePolysilicon gate
The invention discloses a method for improving breakdown voltage for a self-aligning contact hole, which comprises the following steps: 1, depositing polycrystalline silicon, an oxidation film layer and a hard mask layer on an oxide layer on a silicon substrate in turn; 2, etching the hard mask layer, the oxidation film layer and the polycrystalline silicon from the top down in turn to form a polycrystalline silicon gate, and making a top angle at the top of the polycrystalline silicon become circular; 3, growing an oxidation film layer on the lateral surface of the polycrystalline silicon gate; 4, growing a side wall; and 5, etching the self-aligning contact hole. A polycrystalline silicon structure comprises a polycrystalline silicon layer, the oxidation film layer and the hard mask layer from the bottom up in turn. The oxidation film layer as a polycrystalline silicon gate structure is arranged between the hard mask layer and the polycrystalline silicon layer, the top angle at the top of the polycrystalline silicon gate is made to be circular, and the thicker oxidation film and nitride film are formed at the top angle of the top of the grate, so as to improve the breakdown voltage performance for the self-aligning contact hole.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
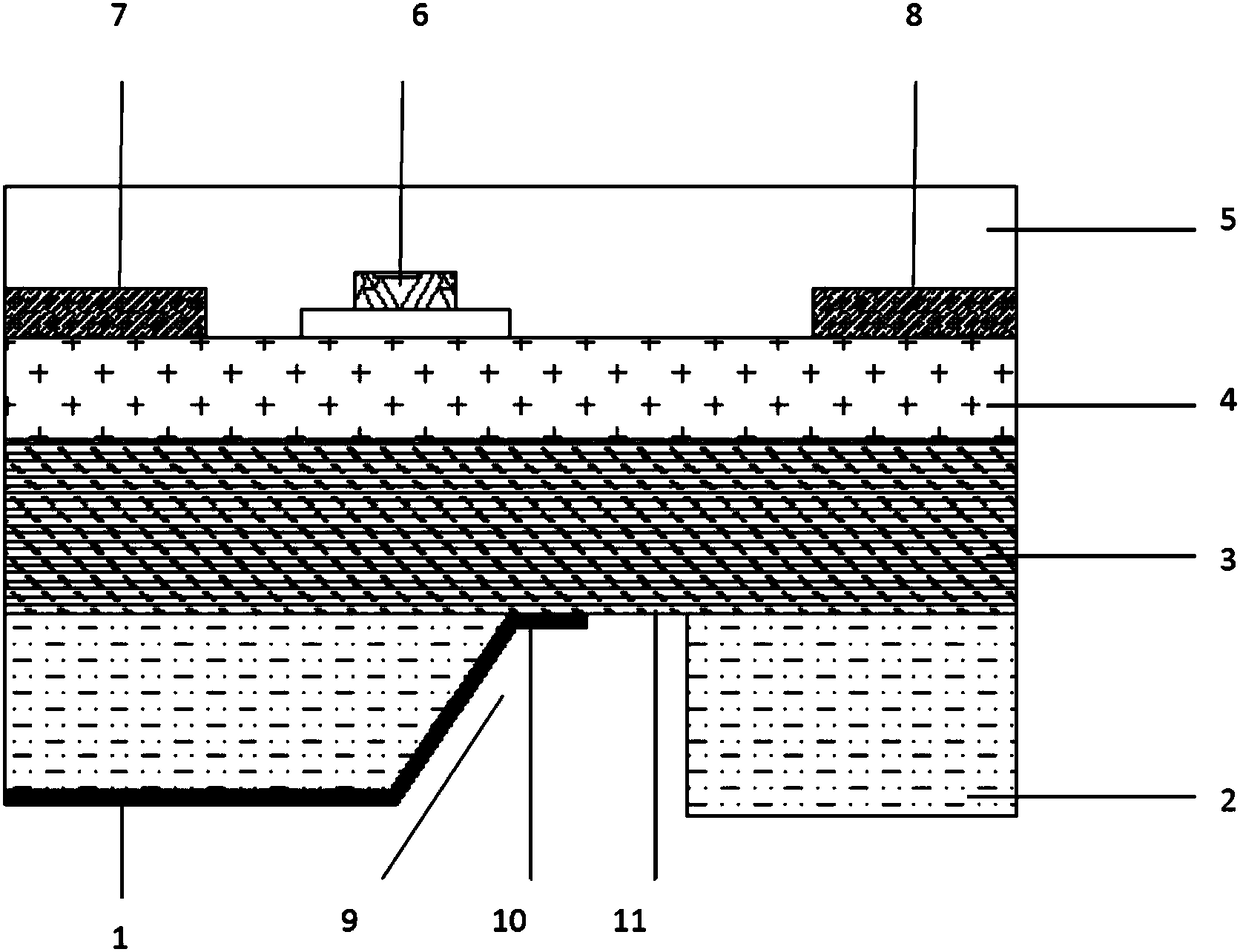
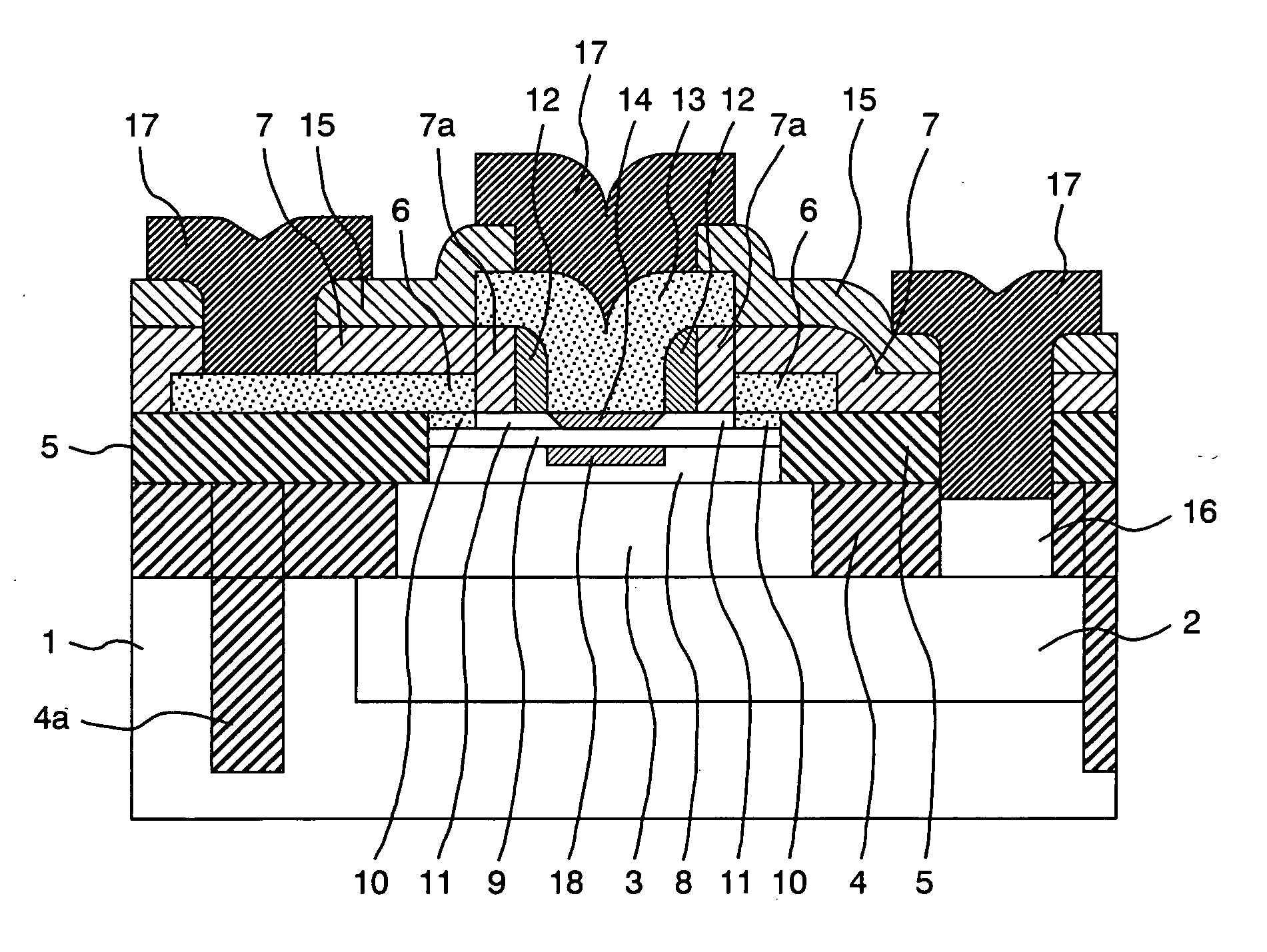
Semiconductor device
A semiconductor device according to the present invention includes, in a termination region, a p− type breakdown voltage holding region that is an impurity region formed in a predetermined depth direction from a substrate surface of an n− type substrate, a first insulating film formed on the n− type substrate so as to cover at least the p− type breakdown voltage holding region, a first field plate formed on the first insulating film, a second insulating film formed so as to cover the first field plate and the first insulating film, and a second field plate formed on the second insulating film. The first insulating film is thicker in a corner portion than in an X-direction straight portion and a Y-direction straight portion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
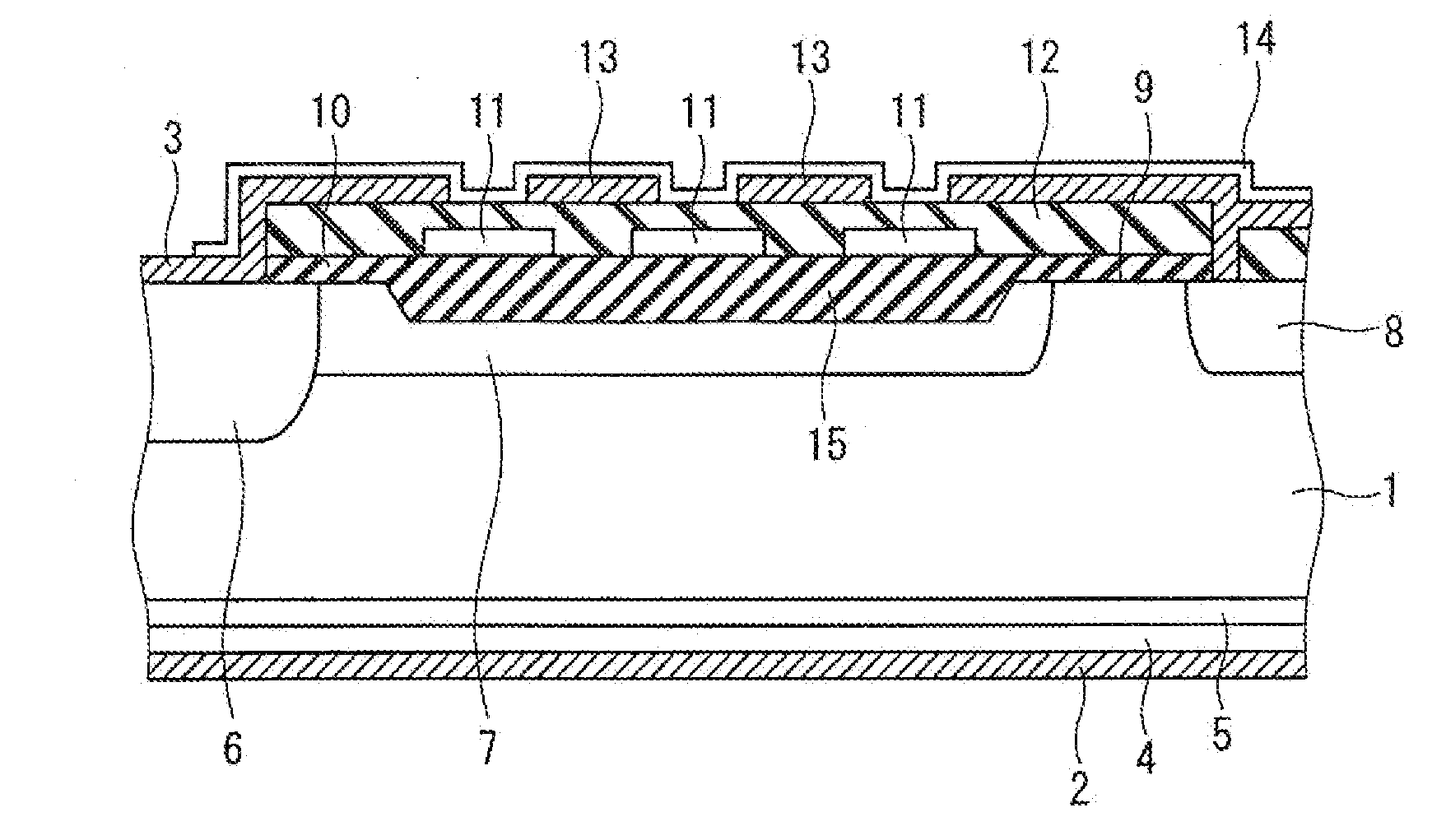
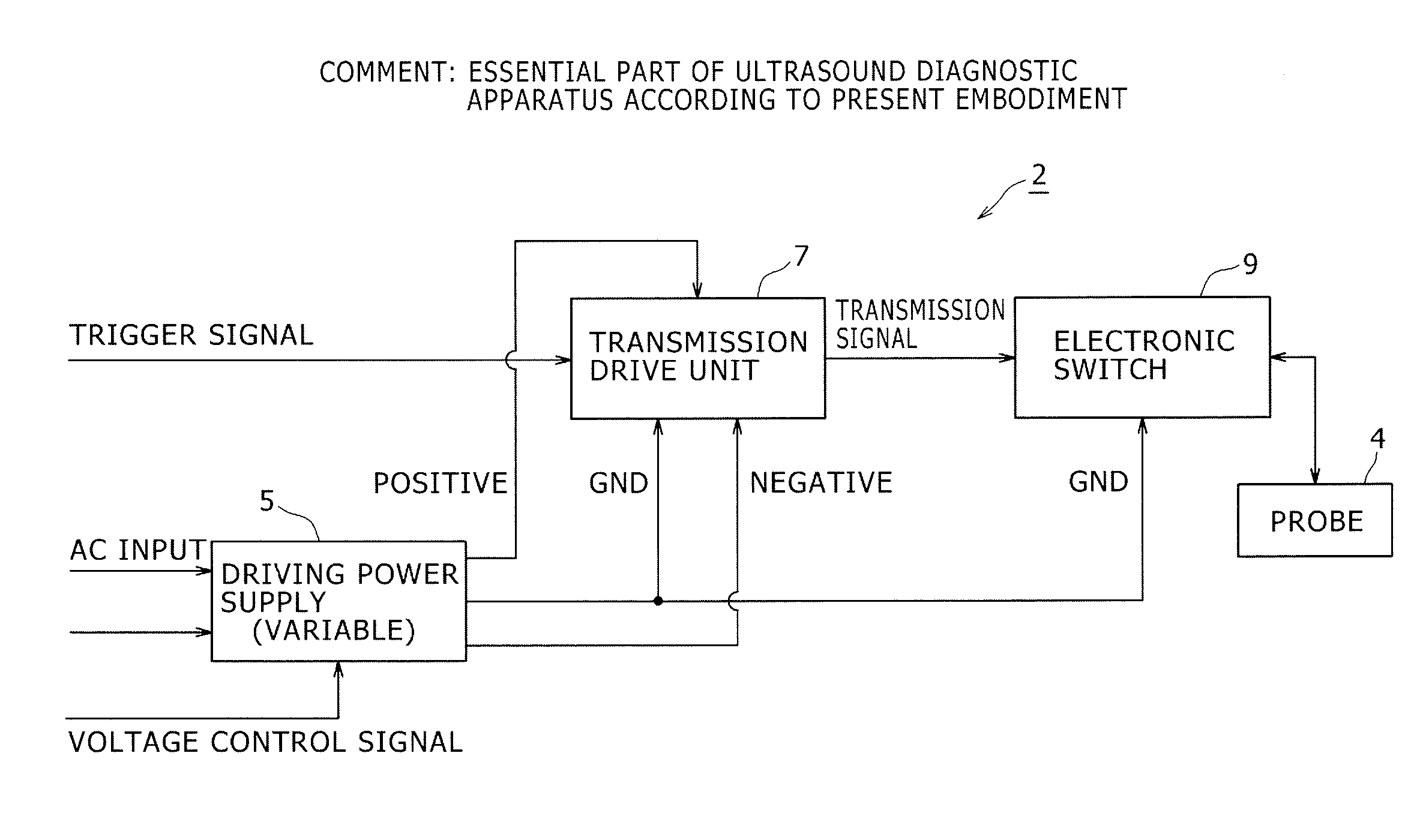
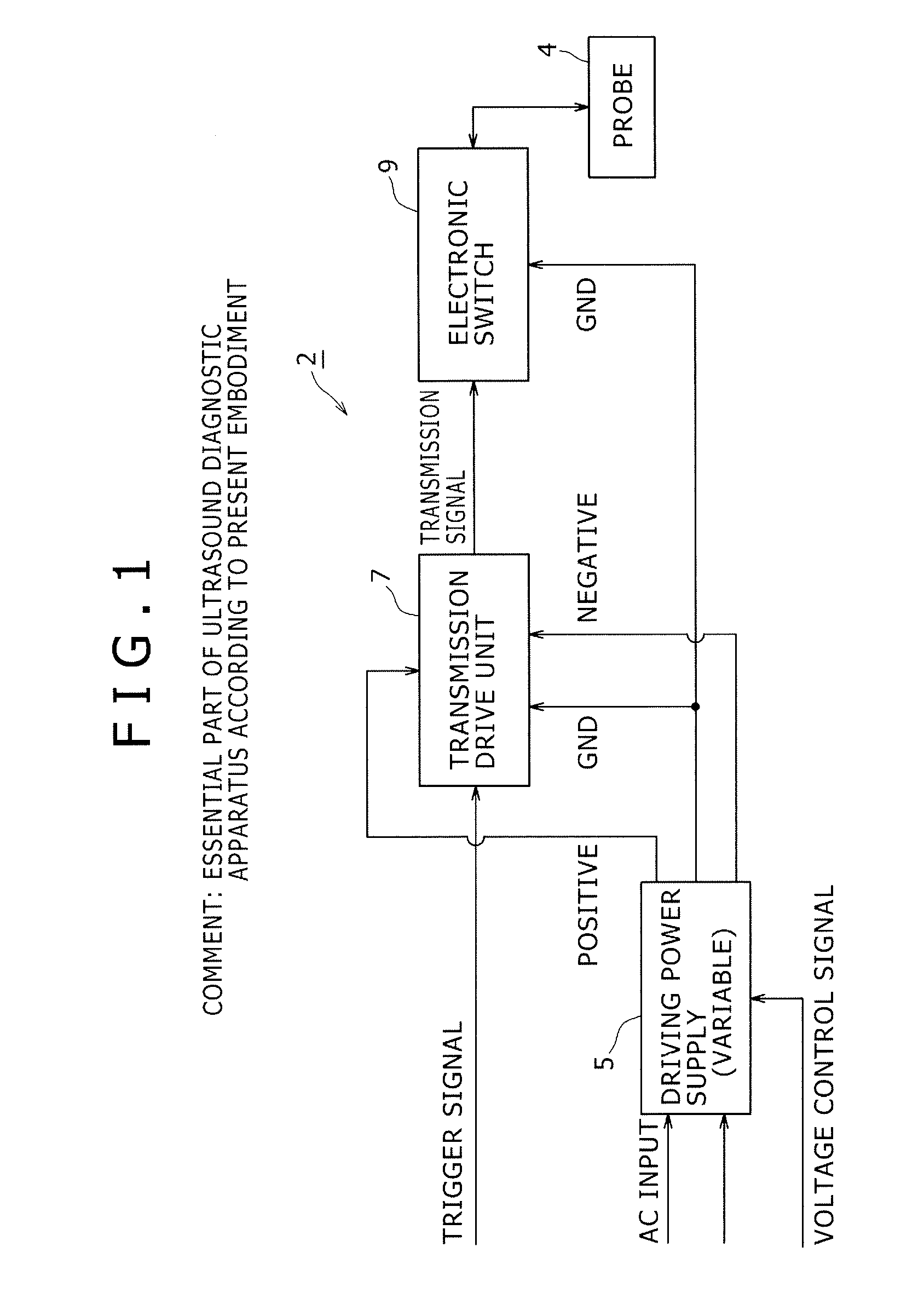
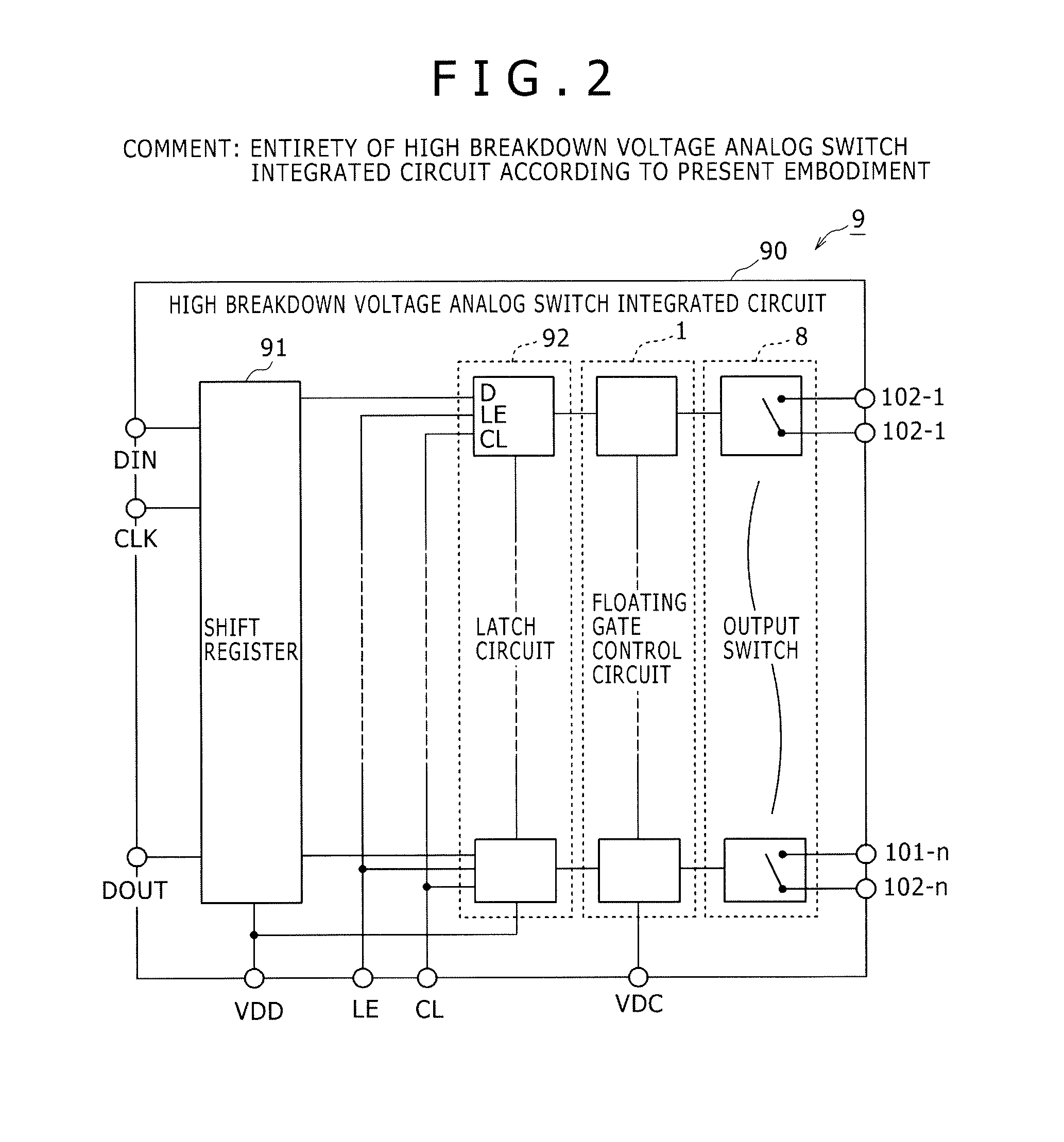
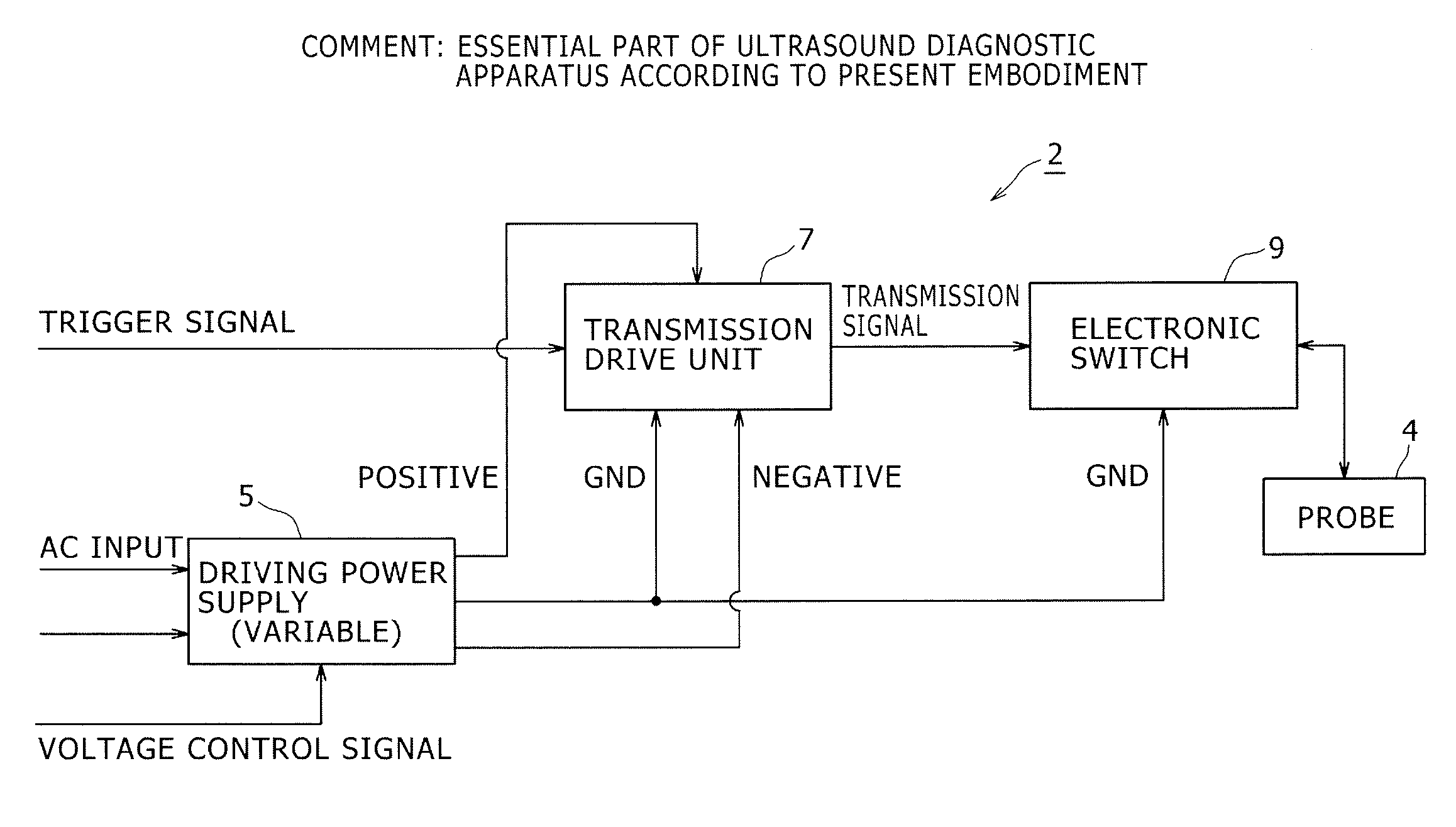
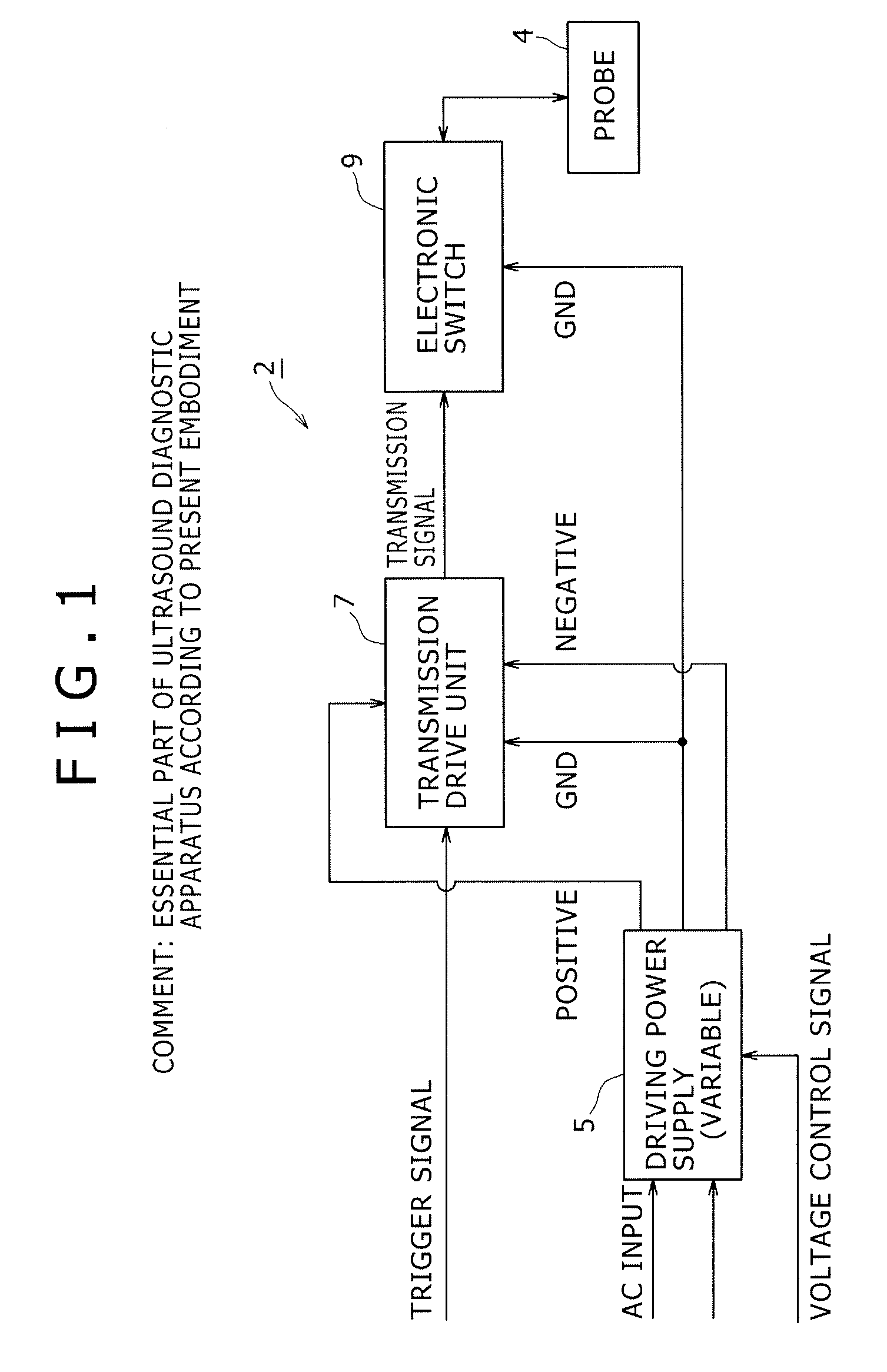
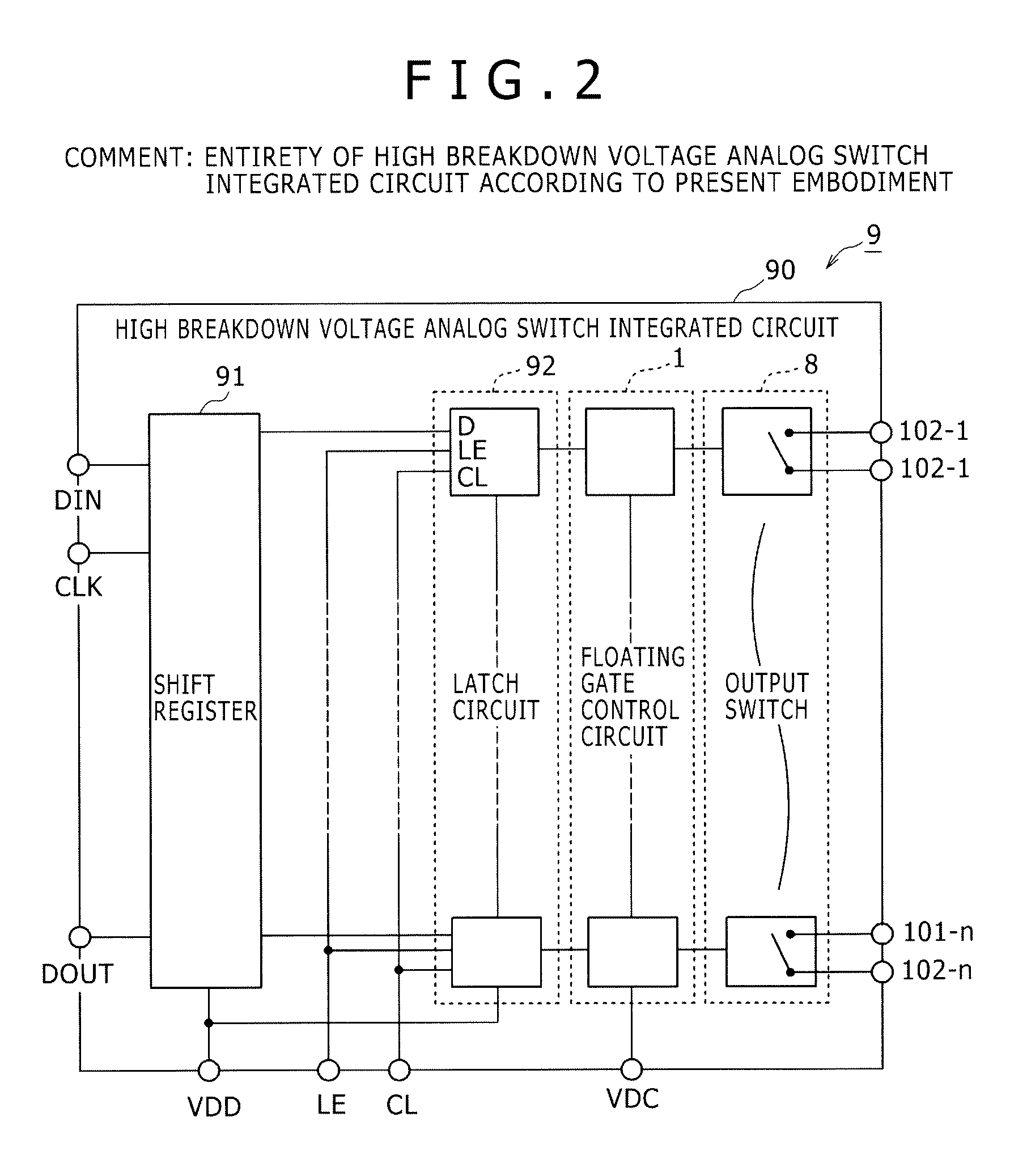
Semiconductor switch circuit, signal processing apparatus, and ultrasound diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS20150087990A1Low insertion lossImproved breakdown voltage performanceTransistorUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMOSFETZener diode
A semiconductor switch circuit comprises: a first switch pair including two MOSFETs having gates connected one another and sources connected to one another, and a zener diode reversely connected between the gates and sources of the MOSFETs; a second switch pair including two MOSFETs having gates connected one another and sources connected to one another, and a zener diode reversely connected between the gates and sources of the MOSFETs; and a third switch pair comprising two MOSFETs having gates connected to one another and sources connected to one another. The first switch pair and the second switch pair are connected in series between two input / output terminals through a connecting node. The third switch pair is connected to the connecting node between the first switch pair and the second switch pair.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
N-type diamond-doped field effect transistor with field plate structure
PendingCN109768081ANot prone to hard breakdownImprove withstand voltage characteristicsSemiconductor devicesSingle crystalMESFET
The present invention discloses a n-type diamond-doped field effect transistor with a field plate structure. The field effect transistor comprises a diamond substrate; a mesa formed by n-type monocrystal diamond-doped epitaxial film is laid on the diamond substrate; two strip-shaped dielectric layers are deposited on the mesa; a drain and a source are respectively laid along the outer edges of each dielectric layer and the mesa; a gate is laid between the two dielectric layers; and the dielectric layers, the drain, the source and the gate constitute a field plate structure. A source extractionelectrode, a drain extraction electrode and a gate extraction electrode are respectively deposited on the source, the drain and the gate; and the source extraction electrode, the drain extraction electrode and the gate extraction electrode are completely separated from each other by a passivation layer. The invention introduces the field plate structure at the edges of the source, gate and drainelectrodes of the diamond MESFET, effectively reduces the electric field concentration effect, increases the breakdown characteristics of the device, effectively reduces the electric field concentration phenomena at the edges of the source, the gate and the drain of the device and improves the breakdown voltage of the device.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Lateral junction field-effect transistor
InactiveUS7528426B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceReduce resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJFETImpurity
A lateral JFET has a basic structure including an n-type semiconductor layer (3) formed of an n-type impurity region and a p-type semiconductor layer formed of a p-type impurity region on the n-type semiconductor layer (3). Moreover, in the p-type semiconductor layer, there are provided a p+-type gate region layer (7) extending into the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and containing p-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3) and an n+-type drain region layer (9) spaced from the p+-type gate region layer (7) by a predetermined distance and containing n-type impurities of an impurity concentration higher than that of the n-type semiconductor layer (3). With this structure, the lateral JFET can be provided that has an ON resistance further decreased while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
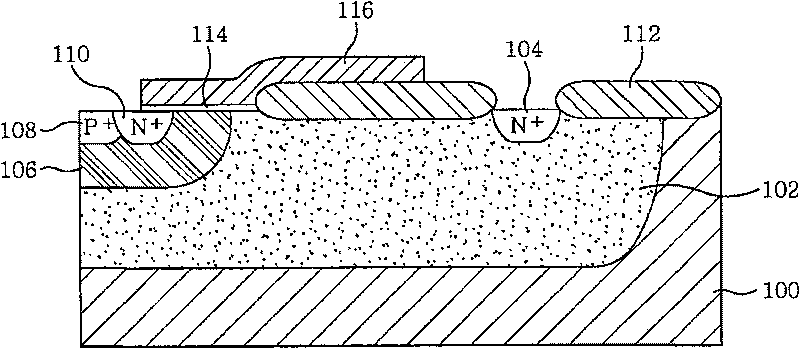
InactiveUS7214973B2Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorPeak value
A bipolar type semiconductor device capable of attaining high current gain and high cut-off frequency and performing a satisfactory transistor operation also in a high current region while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance, as well as a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device, are provided. In a collector comprising a first semiconductor layer and a second semiconductor layer narrower in band gap than the first semiconductor layer, an impurity is doped so as to have a peak of impurity concentration within the second collector layer and so that the value of the peak is higher than the impurity concentration at any position within the first collector layer. It is preferable to adjust the concentration of the doped impurity in such a manner that a collector-base depletion layer extends up to the first collector layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
HEMT (high electron mobility transistor) device with back field plate structure and preparation method of HEMT device
PendingCN108231882ALower working temperatureExtended service lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPeak valueGallium nitride
The invention discloses an HEMT (high electron mobility transistor) device with a back field plate structure. The HEMT device comprises a silicon substrate, a GaN epitaxial layer, an AlGaN barrier layer and an Si3N4 passivated protection layer sequentially from bottom to top; a gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode are arranged on the AlGaN barrier layer; a groove with the crosssection in a right trapezoid shape is formed in the silicon substrate; the groove opens downwards, and the top of the groove is the lower surface of the AlGaN barrier layer; a back field plate structure is arranged on part of lower surface of the silicon substrate, the slope of the groove and part of top of the groove. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the HEMT device adoptingthe back field plate structure. By use of substrate isolation and back field plate technologies, substrate breakdown of the device is avoided, the breakdown voltage of the GaN HEMT device is increased, the field intensity peak value of the drain side of the gate electrode is reduced, the cooling performance of the device is improved, and the HEMT device has important significance in realizing high-performance and high-reliability gallium nitride based devices.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
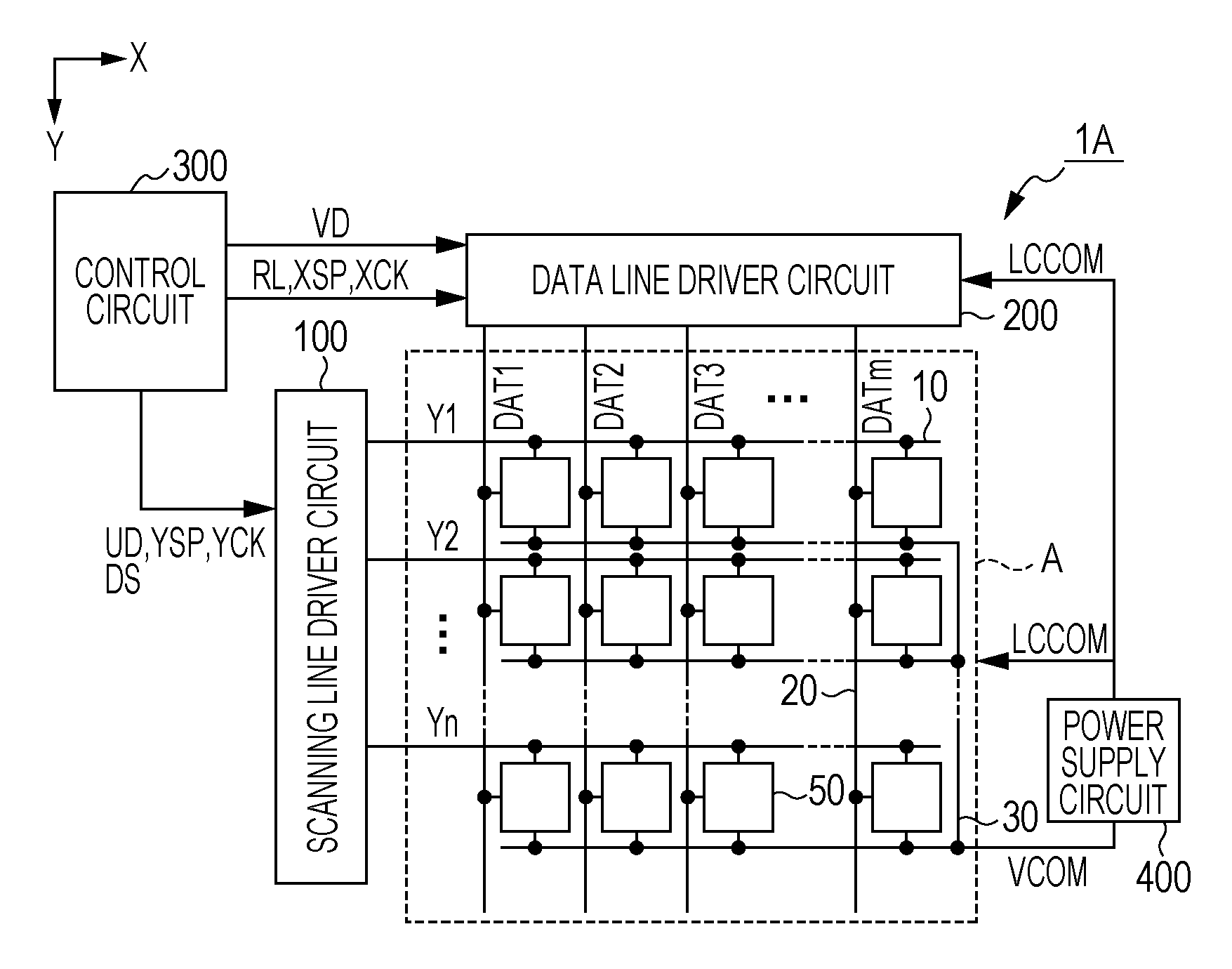
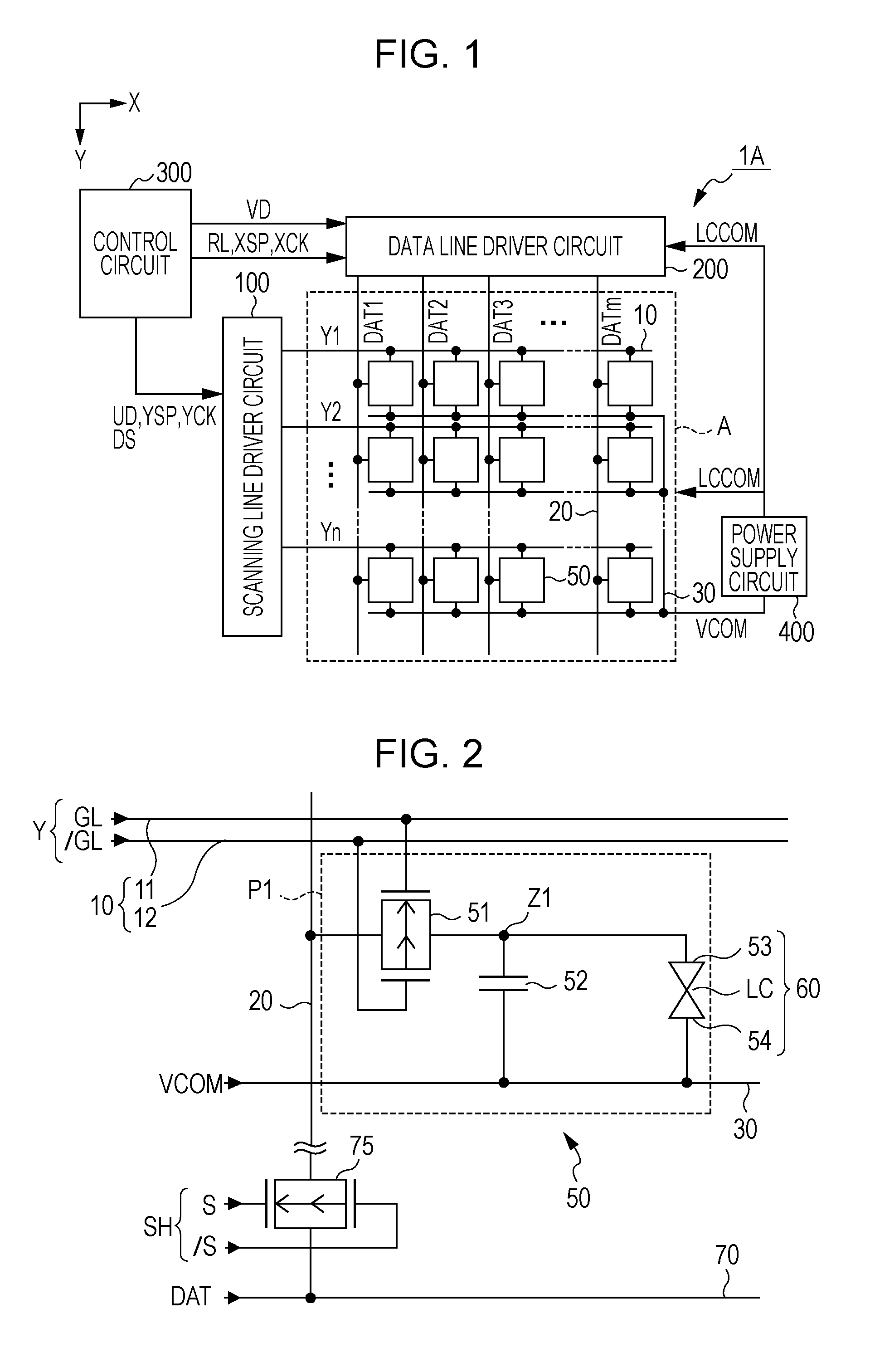
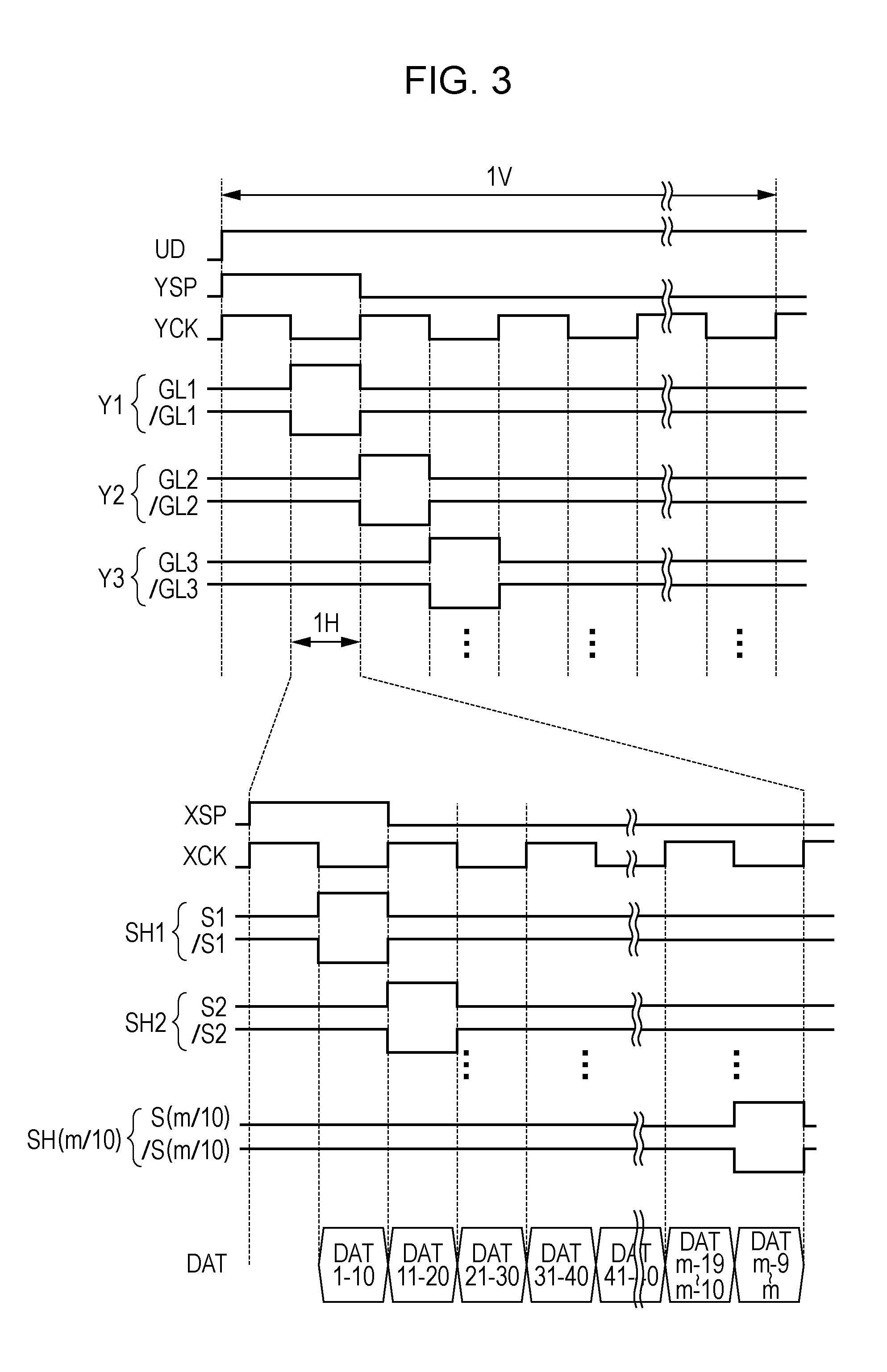
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20120062532A1Quality improvementImproved breakdown voltage performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriver circuitElectrical polarity
The electro-optical device includes a first electrode for inverting a polarity, a second electrode opposite to the first electrode, and liquid crystals interposed between these electrodes. Before a polarity inversion timing, the scanning line driver circuit simultaneously selects two or more scanning lines of the plural scanning lines, and the data line driver circuit outputs an offset potential with the polarity opposite to that of the potential of the first electrode thereafter, to a data line. On the other hand, after the polarity inversion timing, the scanning line driver circuit individually selects each of the plural scanning lines, and the data line driver circuit outputs the data potential corresponding to the potential polarity of the first electrode thereafter, to the data line.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor switch circuit, signal processing apparatus, and ultrasound diagnostic apparatus
ActiveUS9531368B2Low insertion lossImproved breakdown voltage performanceTransistorUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMOSFETZener diode
A semiconductor switch circuit comprises: a first switch pair including two MOSFETs having gates connected one another and sources connected to one another, and a zener diode reversely connected between the gates and sources of the MOSFETs; a second switch pair including two MOSFETs having gates connected one another and sources connected to one another, and a zener diode reversely connected between the gates and sources of the MOSFETs; and a third switch pair comprising two MOSFETs having gates connected to one another and sources connected to one another. The first switch pair and the second switch pair are connected in series between two input / output terminals through a connecting node. The third switch pair is connected to the connecting node between the first switch pair and the second switch pair.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
Process for machining mesa diode
InactiveCN109585569AImproved breakdown voltage performanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrofluoric acidAcetic acid
The invention discloses a process for machining a mesa diode. The process comprises the following steps of producing a diffusion sheet; photoetching a trench; corroding a circular trough mesa; growingsilicon dioxide film on the circular trough mesa and performing a cleaning treatment; coating glass powders; baking glass powders; performing glass passivation; and performing surface corrosion and cleaning. The process is characterized by preparing a mixed acid etching solution by mixing nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and glacial acetic acid in a volume ratio of 5:3:1; then etching the photoetched silicon wafer into the mixed acid etching solution to obtain the PN-junction mesa trench of each chip; and etching the mesa diode PN-junction into a circular shape. The circular shape has a smoothcurved surface and can have the highest breakdown voltage so as to improve the breakdown voltage effect of a device.
Owner:嘉兴实新企业服务有限公司
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060043418A1Improved breakdown voltage performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorDevice material
A bipolar type semiconductor device capable of attaining high current gain and high cut-off frequency and performing a satisfactory transistor operation also in a high current region while maintaining a high breakdown voltage performance, as well as a method of manufacturing the semiconductor device, are provided. In a collector comprising a first semiconductor layer and a second semiconductor layer narrower in band gap than the first semiconductor layer, an impurity is doped so as to have a peak of impurity concentration within the second collector layer and so that the value of the peak is higher than the impurity concentration at any position within the first collector layer. It is preferable to adjust the concentration of the doped impurity in such a manner that a collector-base depletion layer extends up to the first collector layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Bidirectional transient voltage suppressor and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN109768076AImprove the ability to withstand breakdown voltageLow application costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransient voltage suppressorOptoelectronics
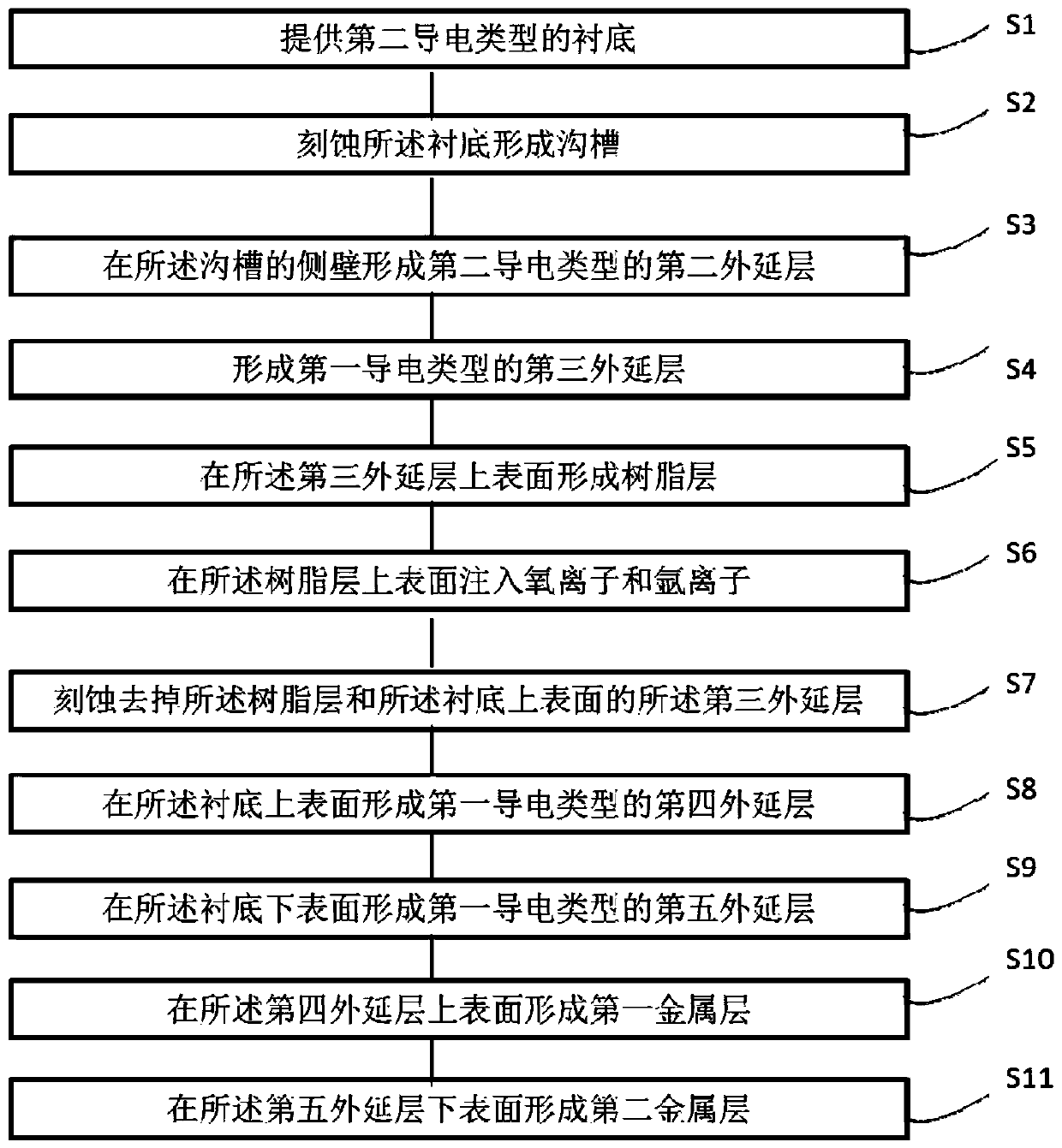
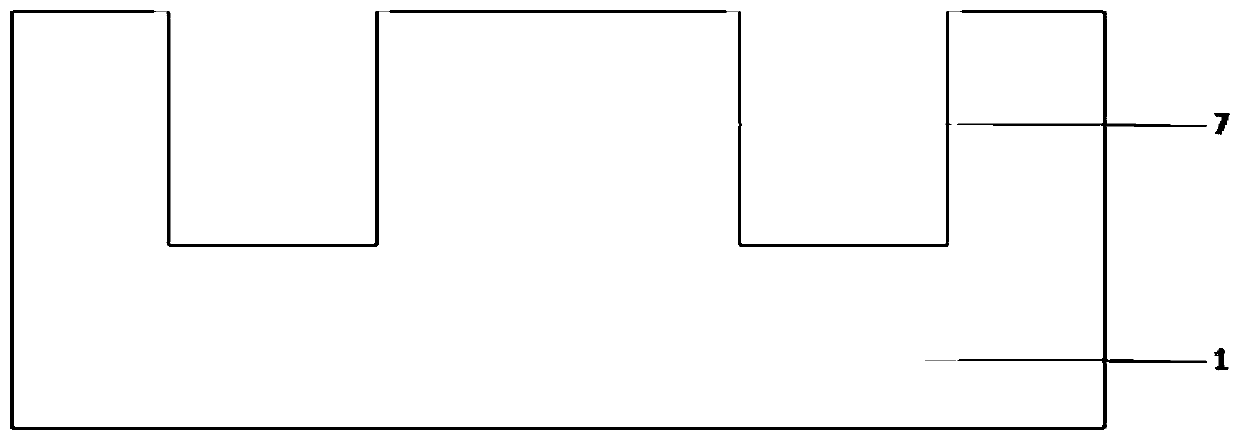
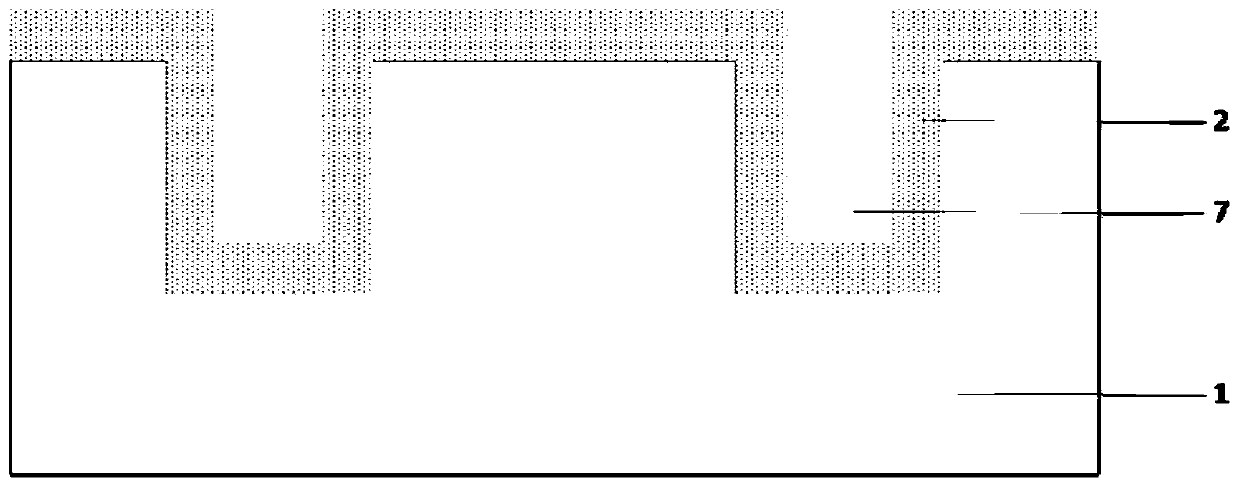
The invention provides a bidirectional transient voltage suppressor and a manufacture method thereof. The manufacture method comprises steps of providing a substrate of a second conductive type, etching the substrate so as to form a ditch, forming a second epitaxial layer and a third epitaxial layer of the second conductive type on the side wall of the ditch, forming a forth epitaxial layer of a first conductive type on the upper surface of the substrate, forming a fifth epitaxial layer of the first conductive type on the lower surface of the substrate, forming a first metal layer on the uppersurface of the fourth epitaxial layer, and forming a second metal layer on the lower surface of the fifth epitaxial layer. The anti-breakdown voltage capability of the bidirectional transient voltagesuppressor is improved through multiple groups of PN junctions; the bidirectional transient voltage suppressor has a multi-path bidirectional function so as to protect multiple circuits simultaneously in use, and application cost of the power device is lowered. The bidirectional transient voltage suppressor requires etching for only once, so that the manufacture cost is lowered.
Owner:泉州臻美智能科技有限公司
Annular isolation structure in high-voltage BCD structure, and manufacturing method thereof
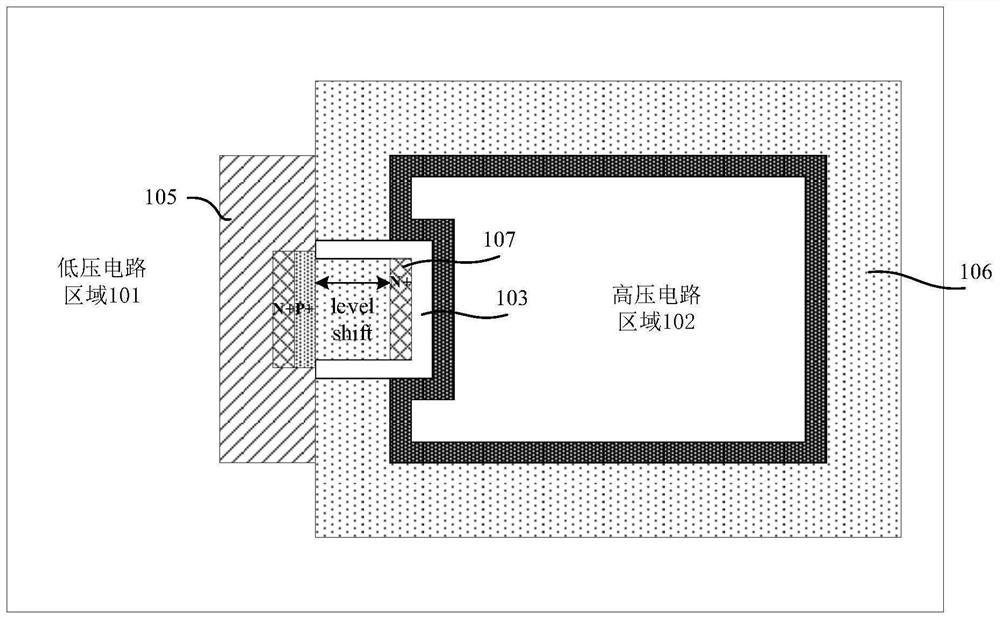
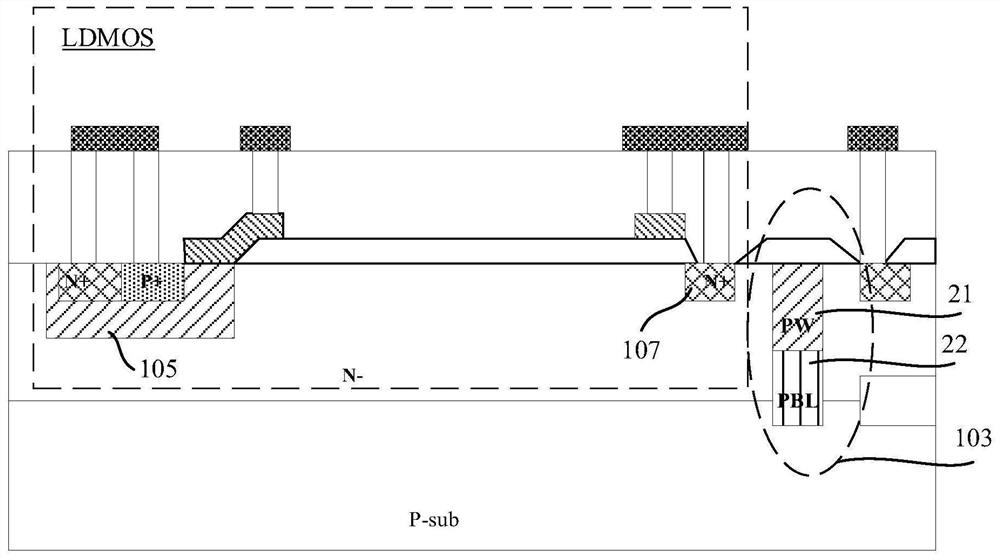
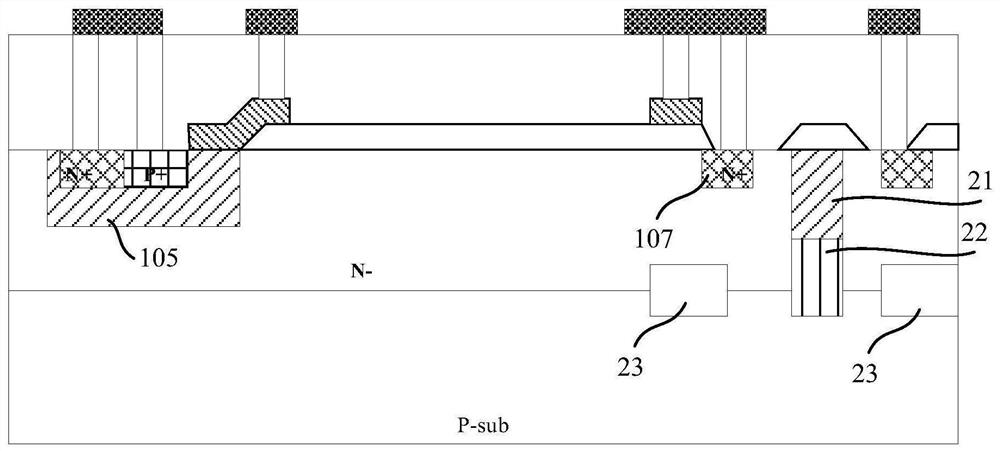
PendingCN113921458AImprove concentration distributionImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsLithography process
The invention discloses an annular isolation structure in a high-voltage BCD structure, and a manufacturing method thereof, and relates to the field of semiconductor manufacturing. The manufacturing method of the annular isolation structure in the high-voltage BCD structure comprises the following steps: forming the annular isolation structure between a high-voltage circuit region and a low-voltage circuit region, wherein the annular isolation structure is composed of a first-type well region and a first-type buried layer; defining second-type buried layer patterns on two sides of the annular isolation structure through a photoetching process, wherein the left side of the annular isolation structure comprises at least two second-type buried layer patterns with different widths; and forming second-type buried layers in the substrate corresponding to the second-type buried layer patterns through an ion implantation process. The problem that a buried layer on the left side of an existing annular isolation structure is prone to breakdown is solved. The effects of improving the concentration distribution of the buried layers on the two sides of the annular isolation structure and improving the breakdown voltage of the annular isolation structure are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Lateral dmos device structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101308797BImprove operating speedAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeEngineeringBody region
A lateral DMOS device having a structure that prevents breakdown of a semiconductor device while enhancing the breakdown voltage property. The lateral DMOS device can include a body diode region having a second conduction type well region formed in a first conduction type semiconductor substrate, the second conduction type well region including a first conduction type body region and a drain region each formed in the second conduction type well region, a first conduction type impurity region formed in the first conduction type body region, a source region formed in the first conduction type body region, and a gate insulating film and a gate electrode formed on the first conduction type semiconductor substrate, wherein the first conduction type body region and the second conduction type well region compose a body diode; and a protective diode region in which the first conduction type impurity region is formed at a prescribed interval, wherein the first conduction type body region and the second conduction type well region compose a protective diode.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com