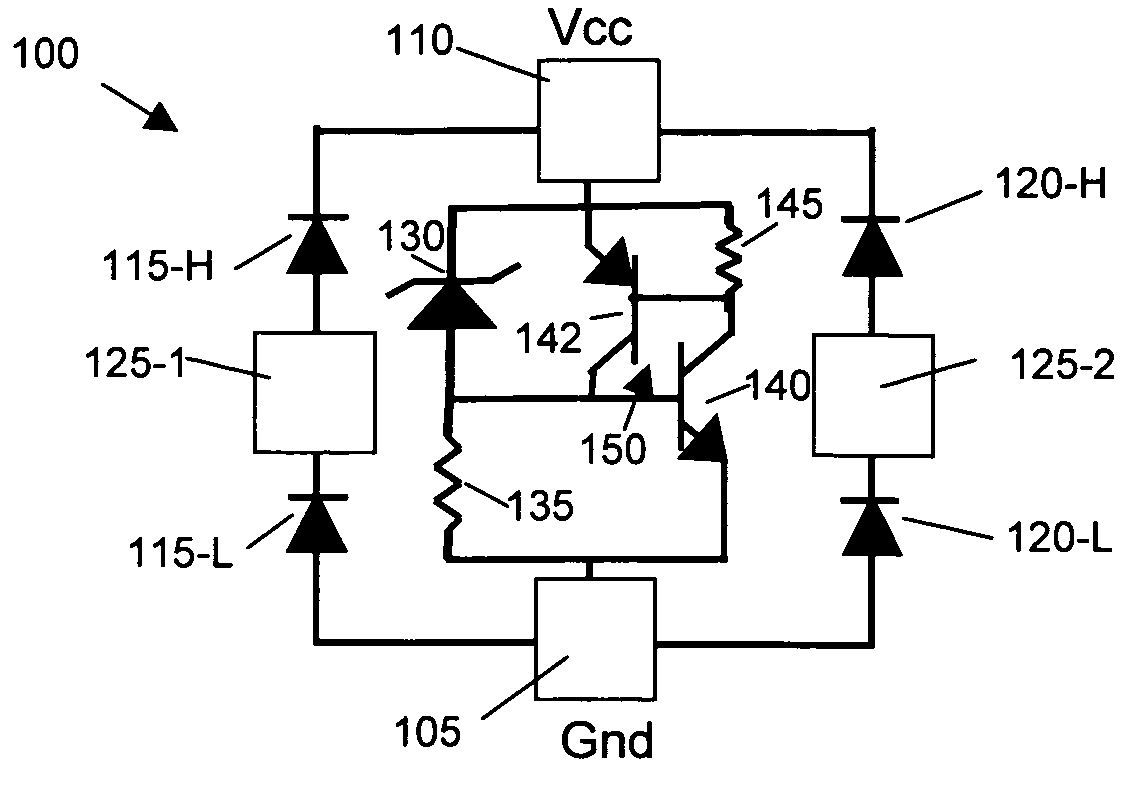
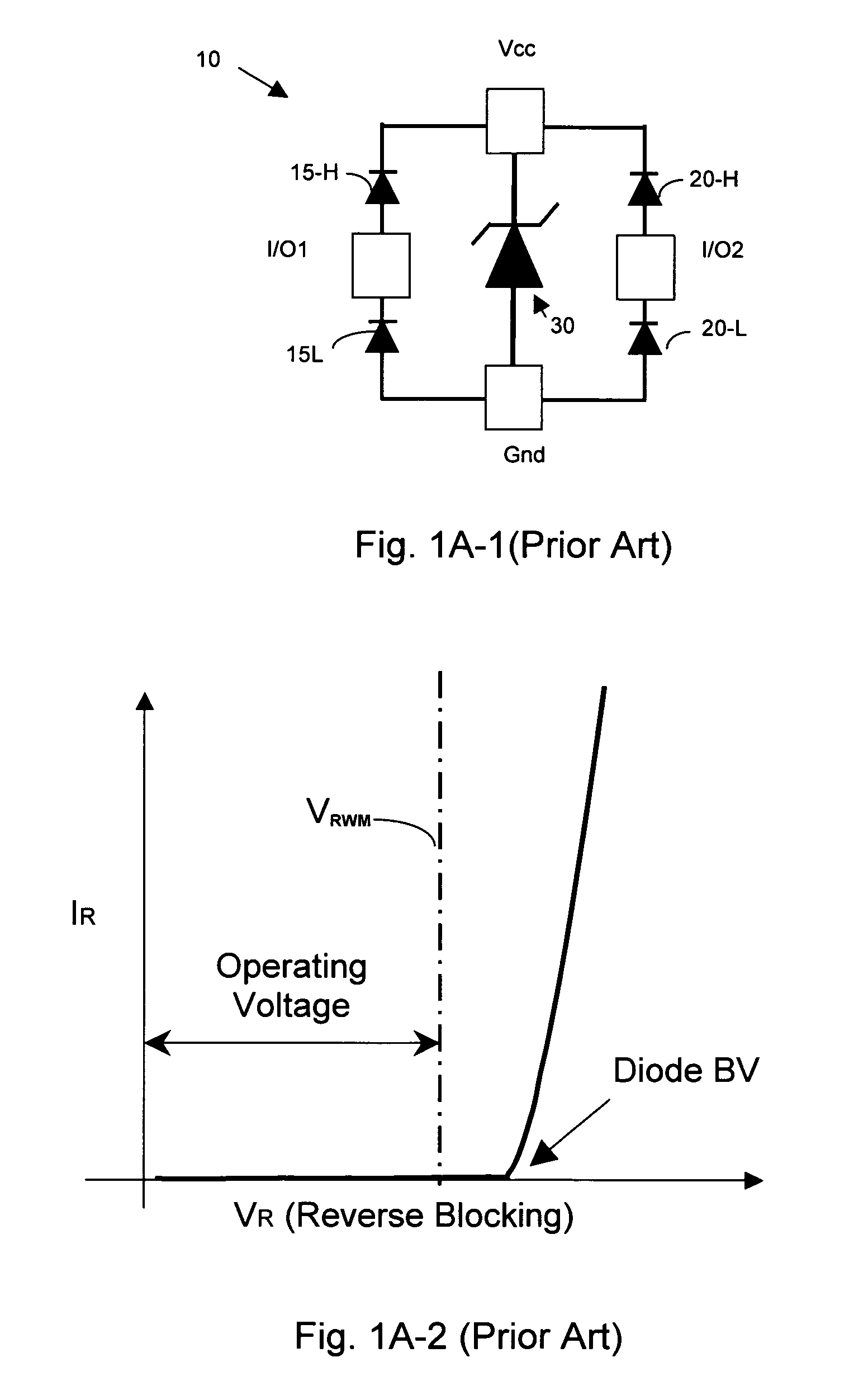
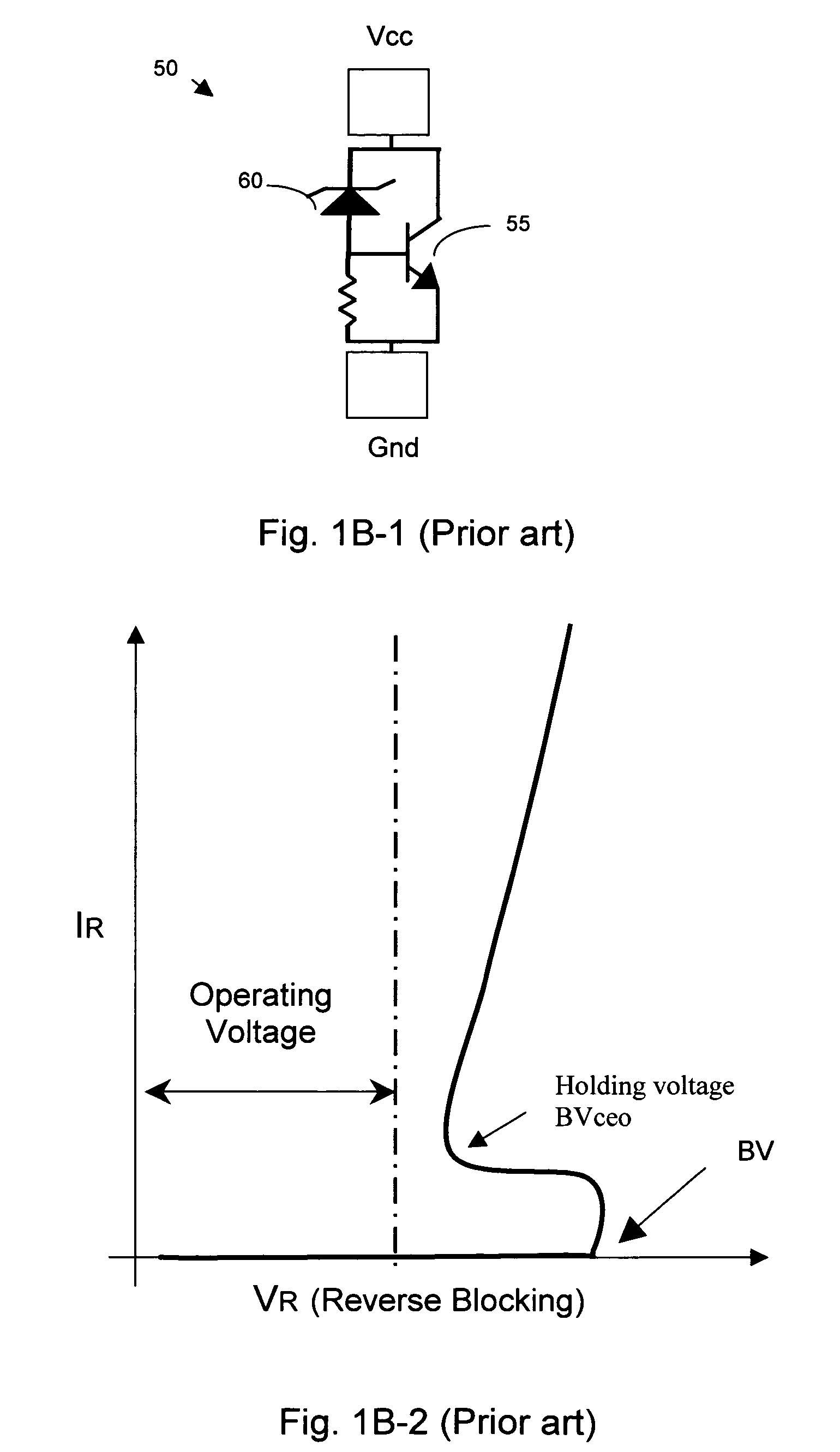
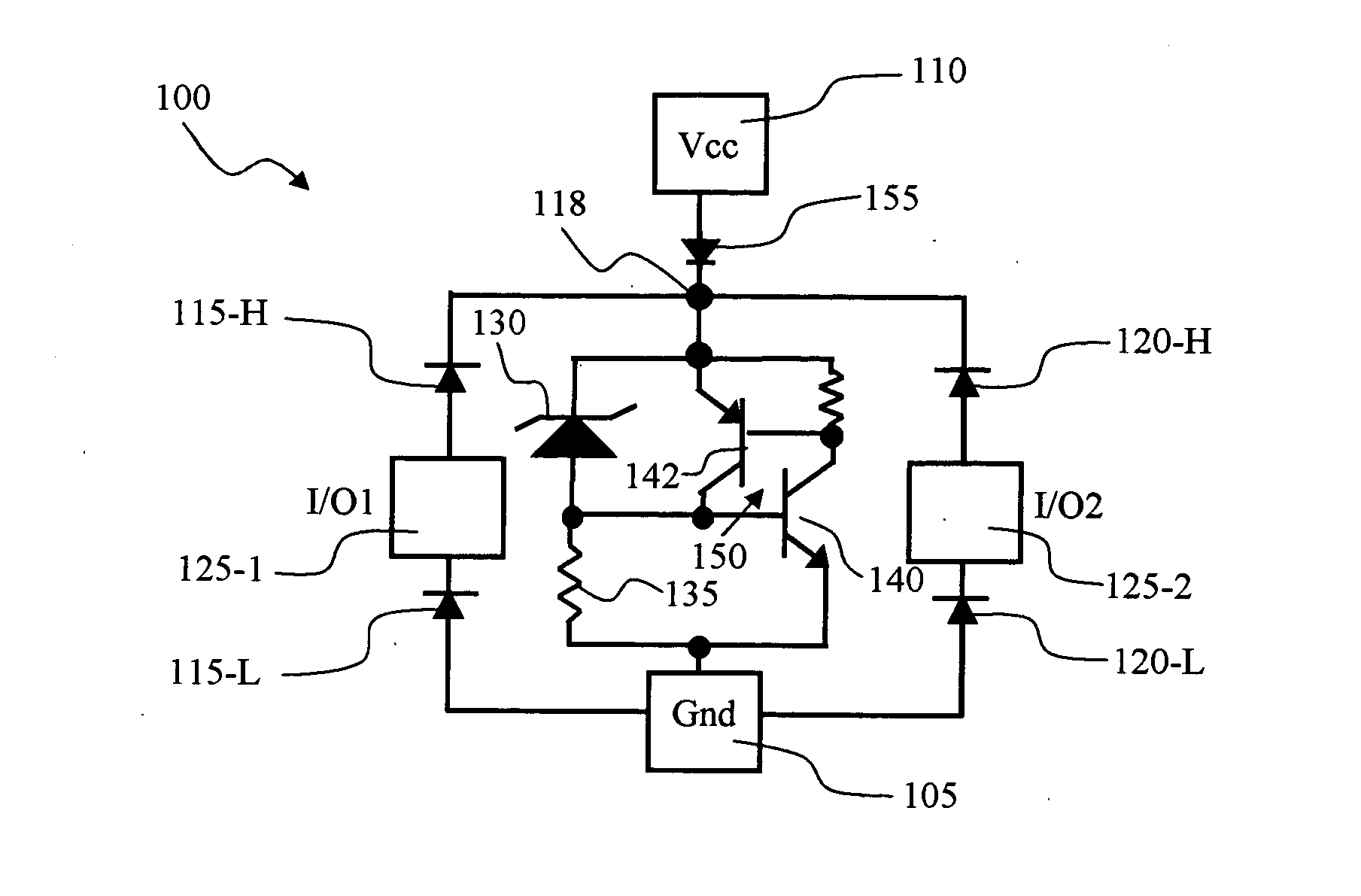
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
751 results about "Transient voltage suppressor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
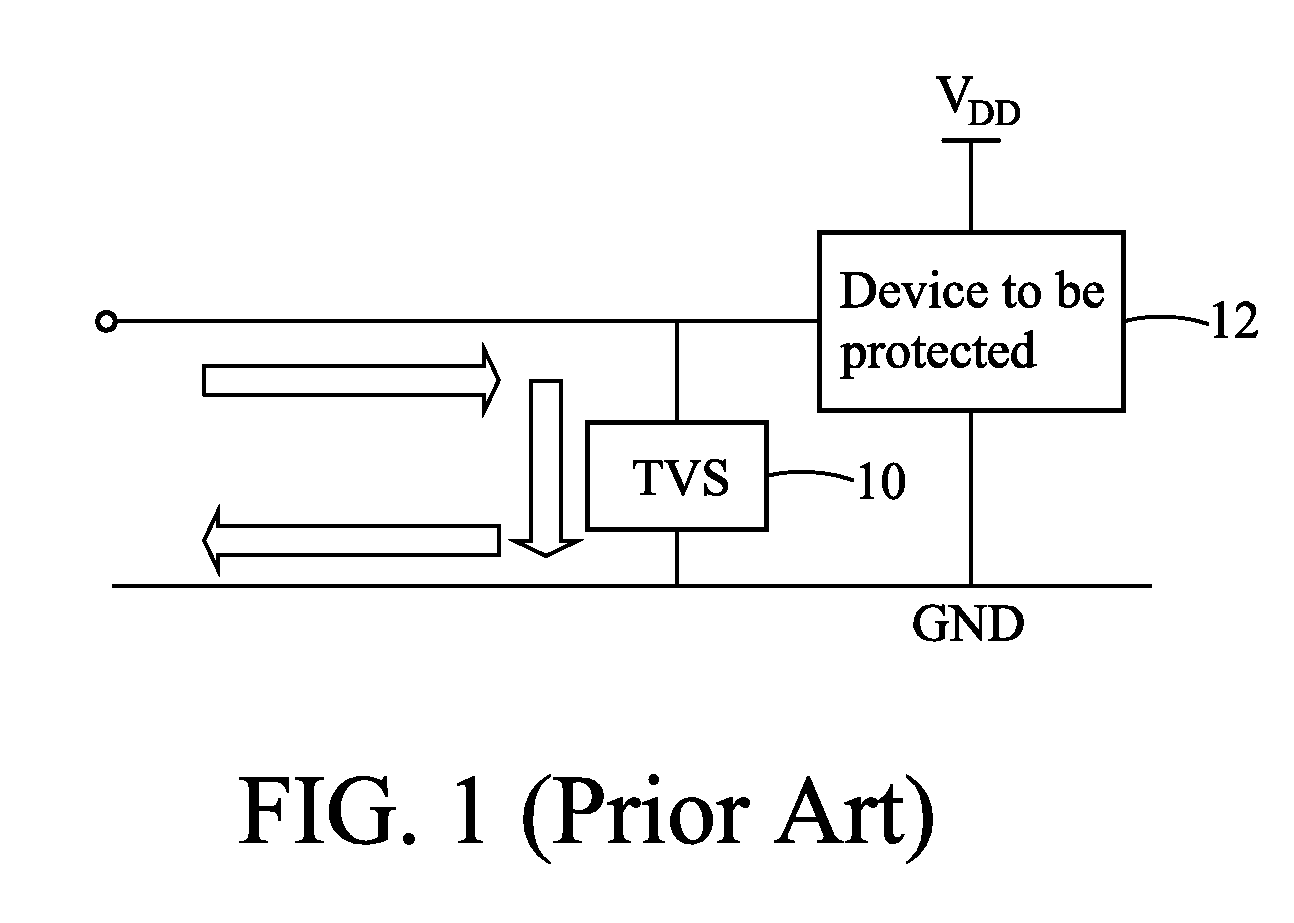
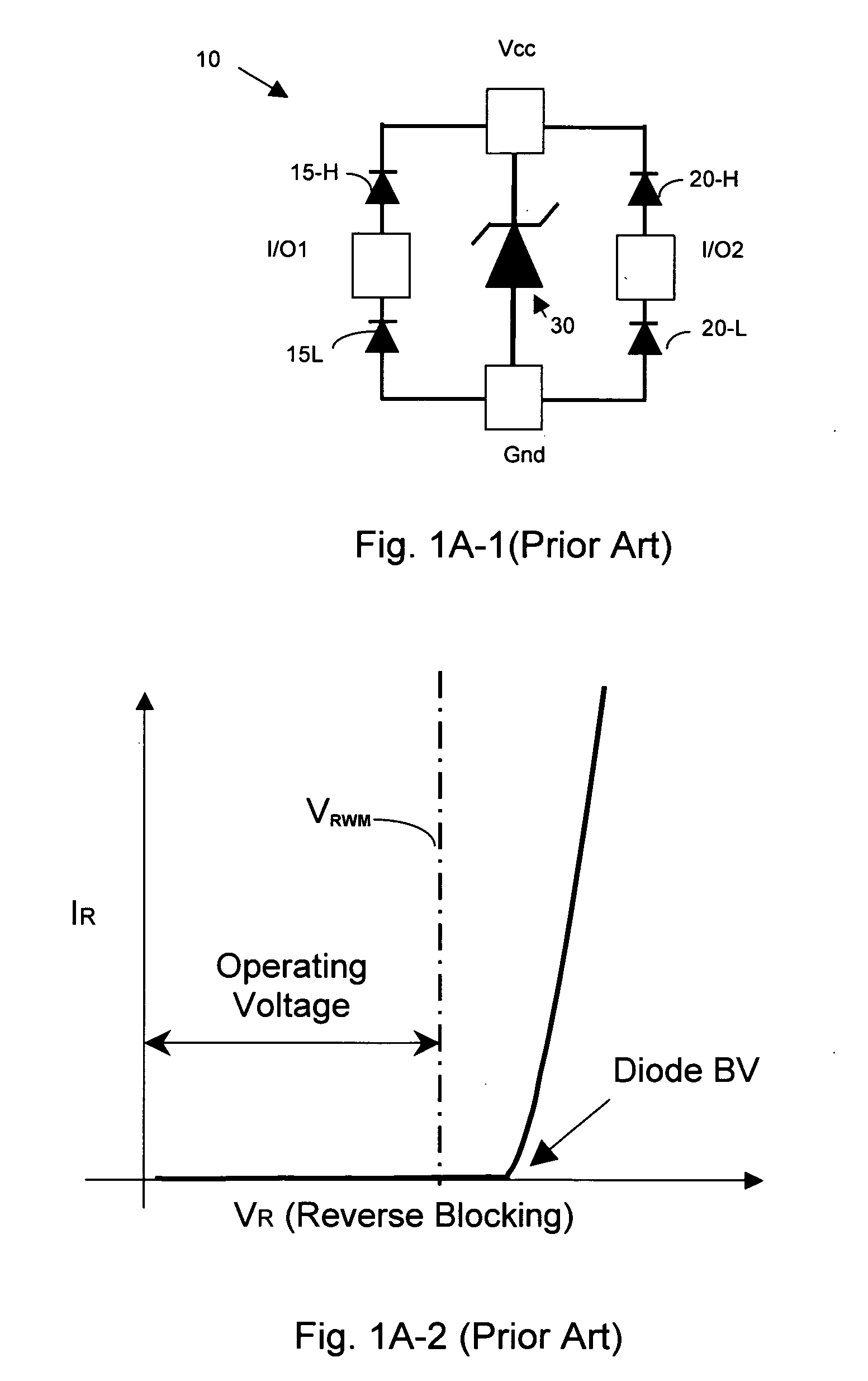
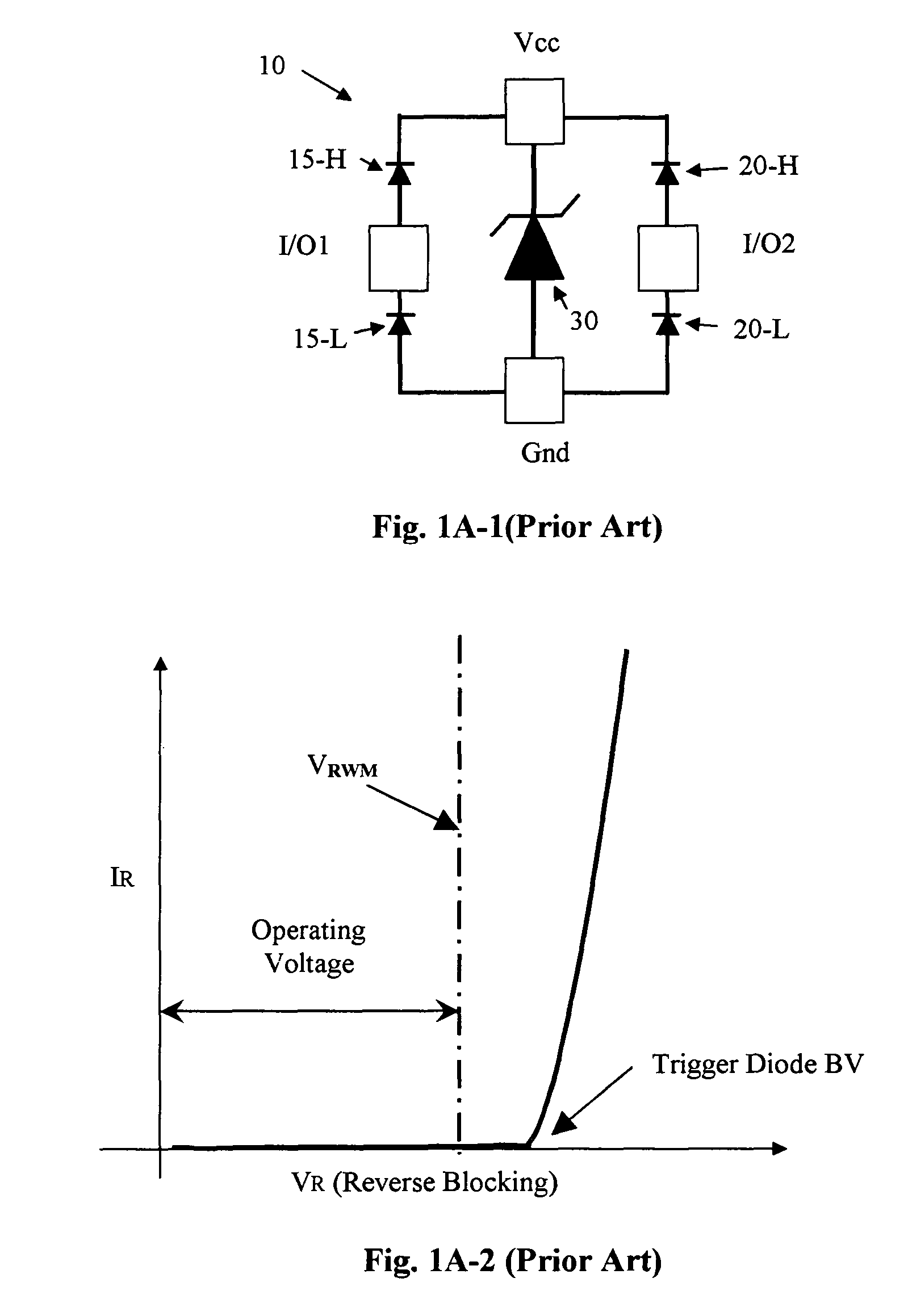
A transient voltage suppressor or TVS is a general classification of an array of devices that are designed to react to sudden or momentary overvoltage conditions. One such common device used for this purpose is known as the transient voltage suppression diode that is simply a Zener diode designed to protect electronics device against overvoltages. Another design alternative applies a family of products that are known as metal-oxide varistors (MOV) that protect electronic circuits and electrical equipment.
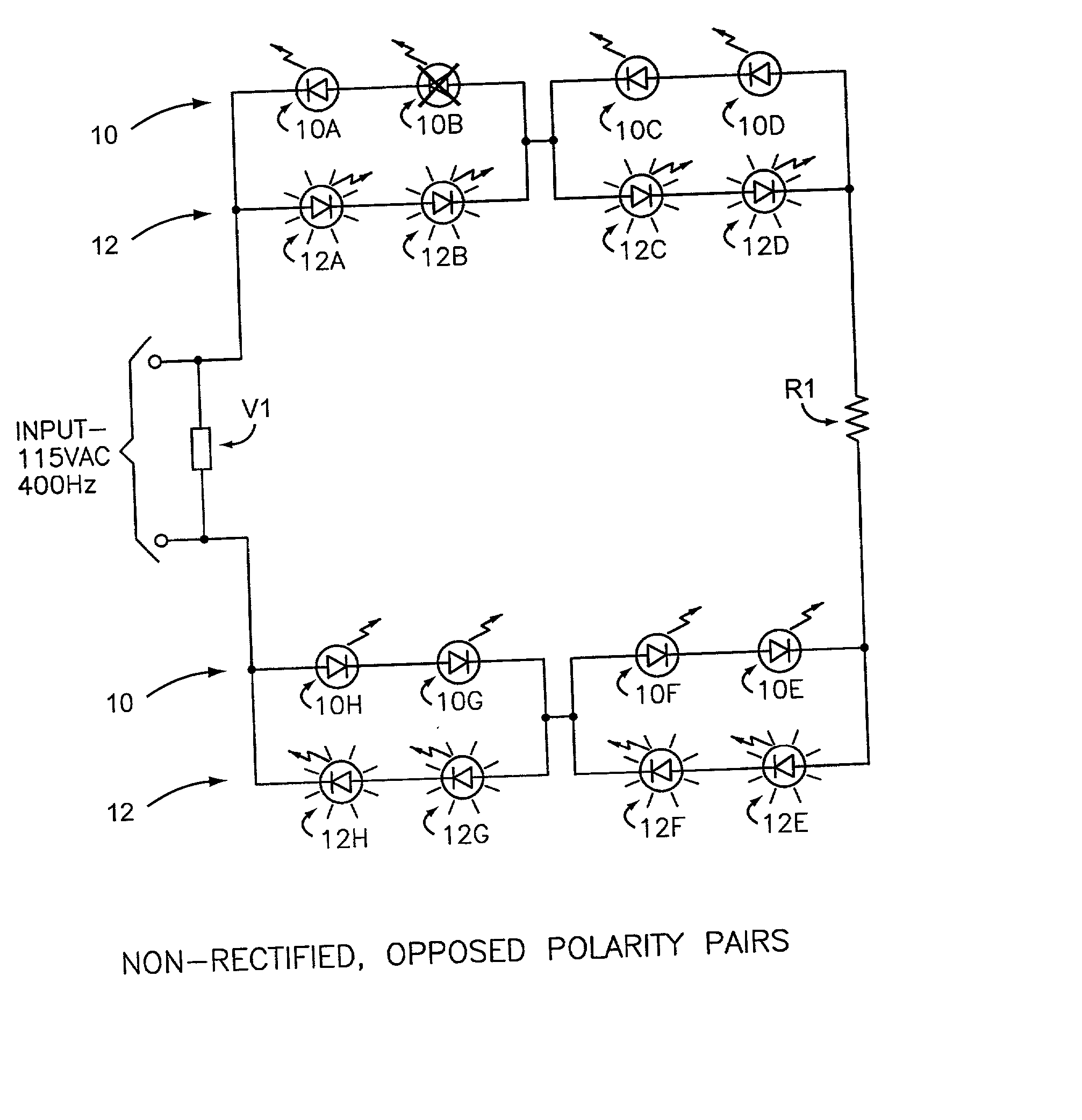
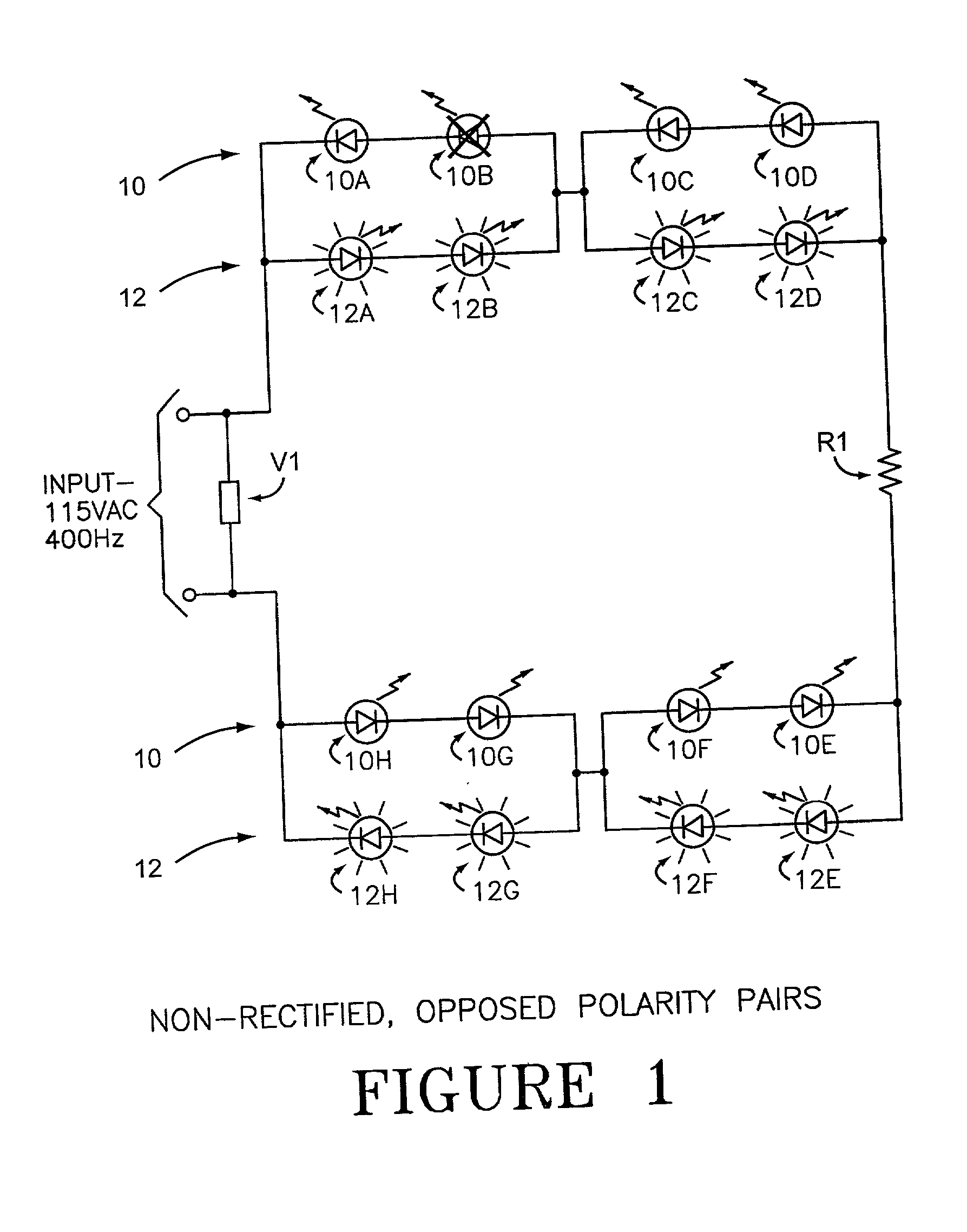
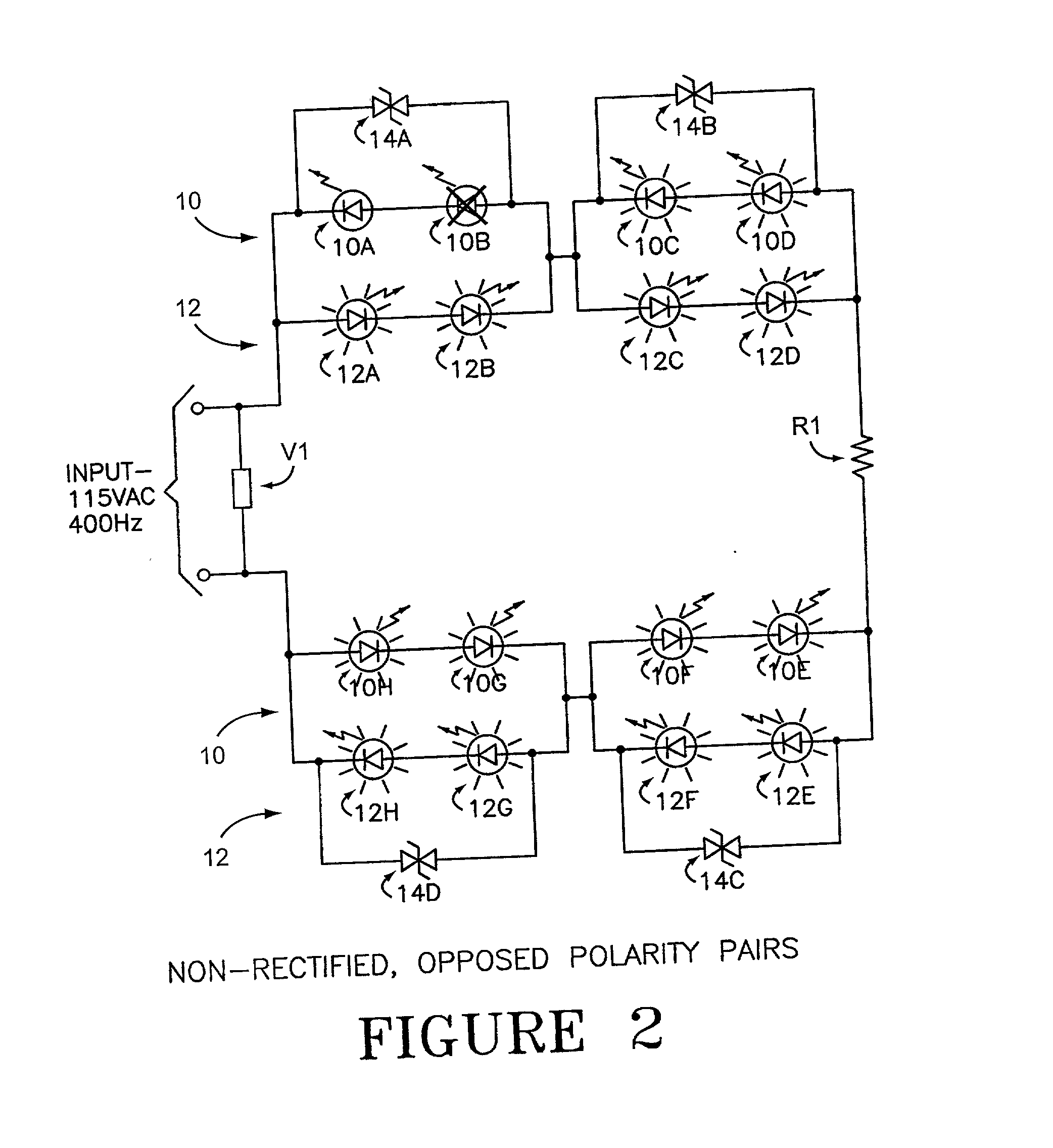
LED array primary display light sources employing dynamically switchable bypass circuitry
InactiveUS20020043943A1Reduce heat outputEasy burn-out element replacementElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBlack outEffect light
The invention comprises use of Dynamically Switchable Bypass (DSB) elements in association with one or more Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in arrays for illumination circuits to provide rugged, reliable lighting. The DSBs are selected from Transient Voltage Suppressors, including Silicon, Metal Oxide Varistors, and Multi Layer Varistors as well as Zener Diodes. The DSBs are not used as circuit protecting devices, but rather as alternative paths for electric current to bypass failed LEDs. Bi-directional TVSs are used as alternative electric paths for circuits using Alternating Current (AC) and parallel LED arrays that light on both phases of AC. Zener Diodes are used in parallel to, but in the opposite polarity orientation to, one or more LEDs in DC or rectified AC circuits. The inventive paired DSB / LED elements overcomes the black-out problems of prior series LED illumination systems, making possible the use of robust LEDs in illumination systems where reliability, long life, low power consumption, low heat output, resistance to shock, vibration, and humidity, and self-diagnosis are important. The DSB elements have breakdown voltages slightly higher than the LED(s) they support, so that when an LED fails, the conduction through the DSB begins. Because the conduction voltage of the DSB so nearly matches the conduction voltage of the LED(s), the remainder of the circuit continues to function as normal. The system is self-diagnostic in that any LED failure presents itself as a dark LED rather than as a whole string of dark LEDs. DSBs may be used with incandescent bulbs.
Owner:IDD AEROSPACE
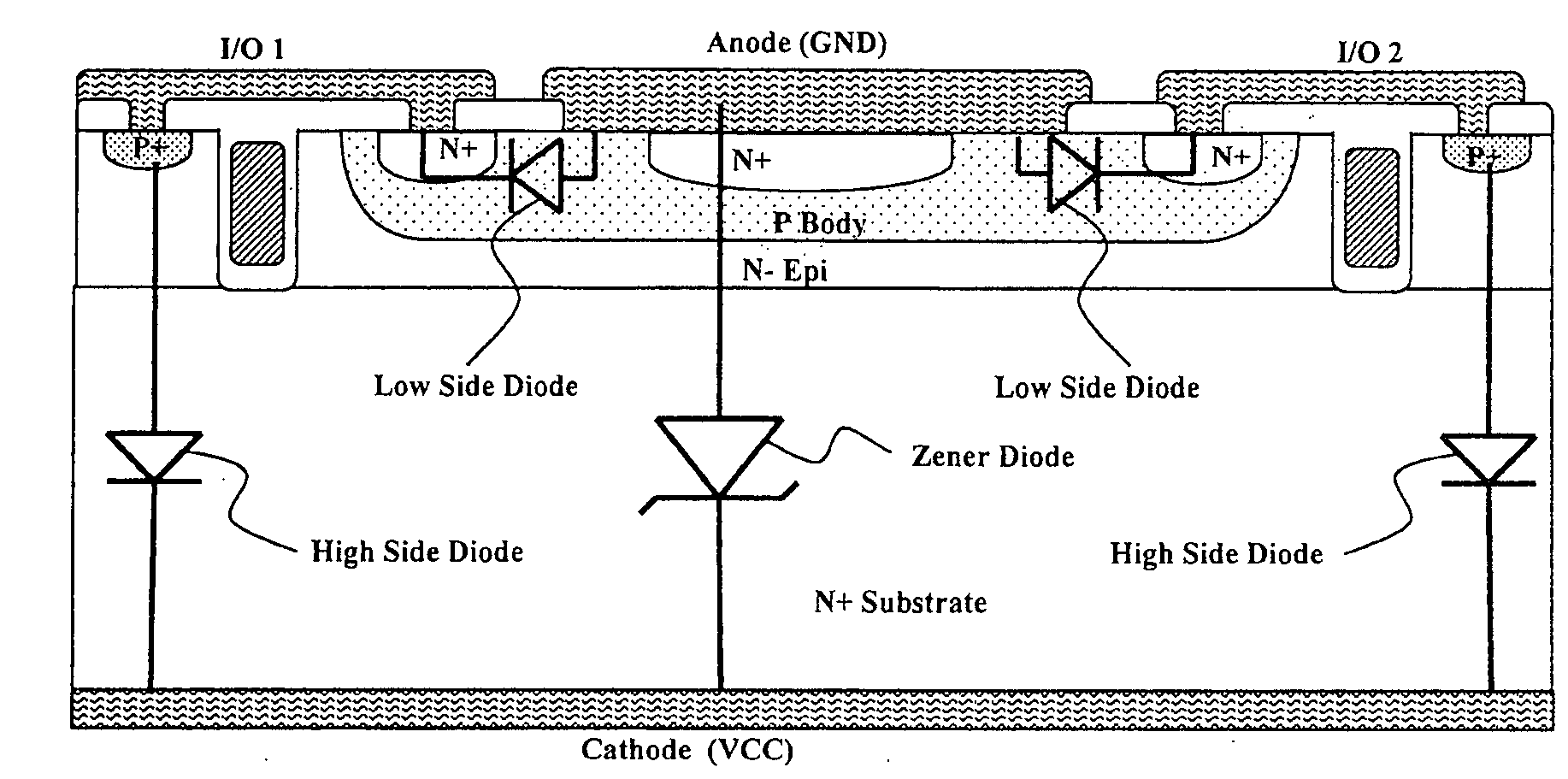
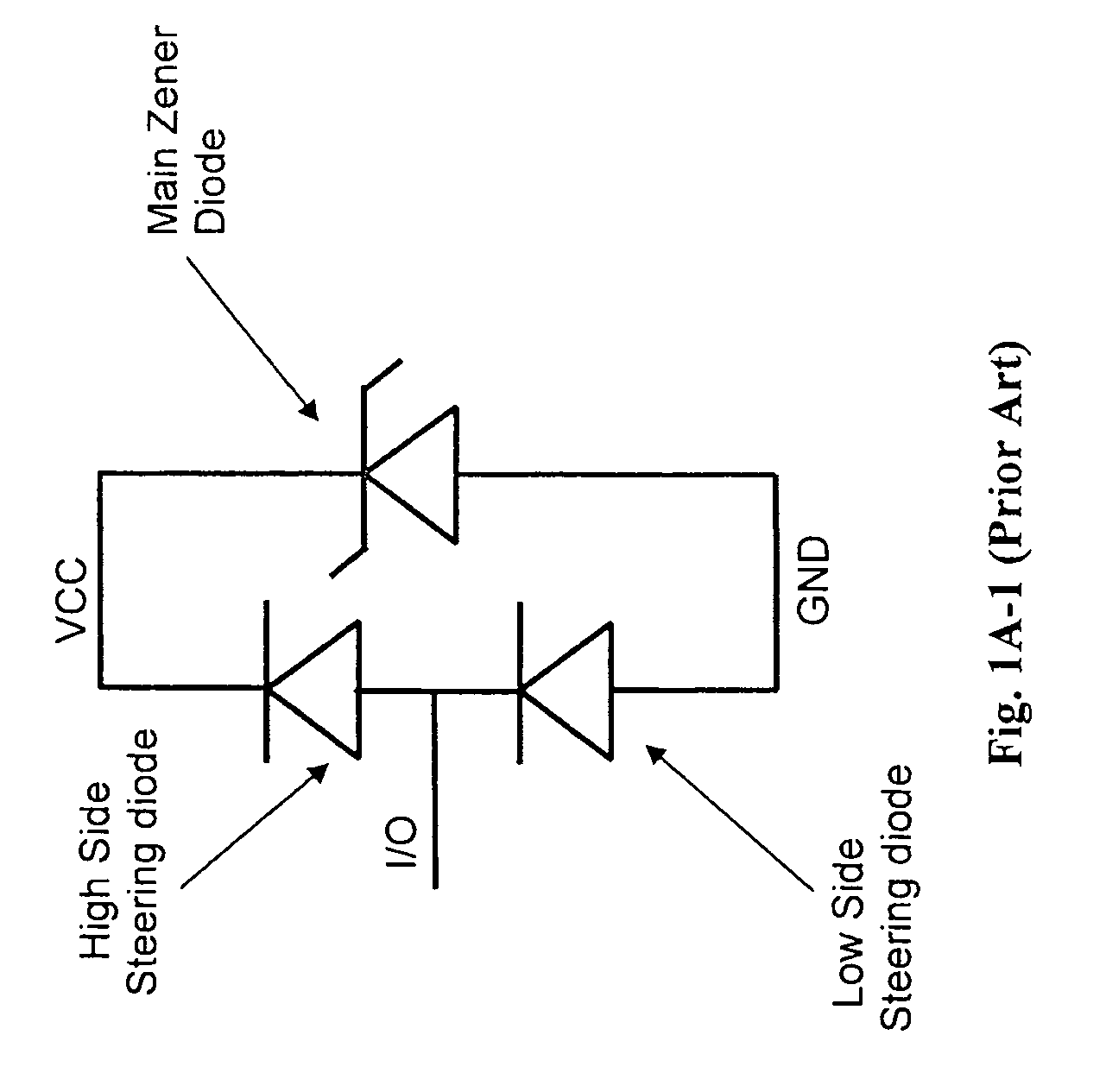
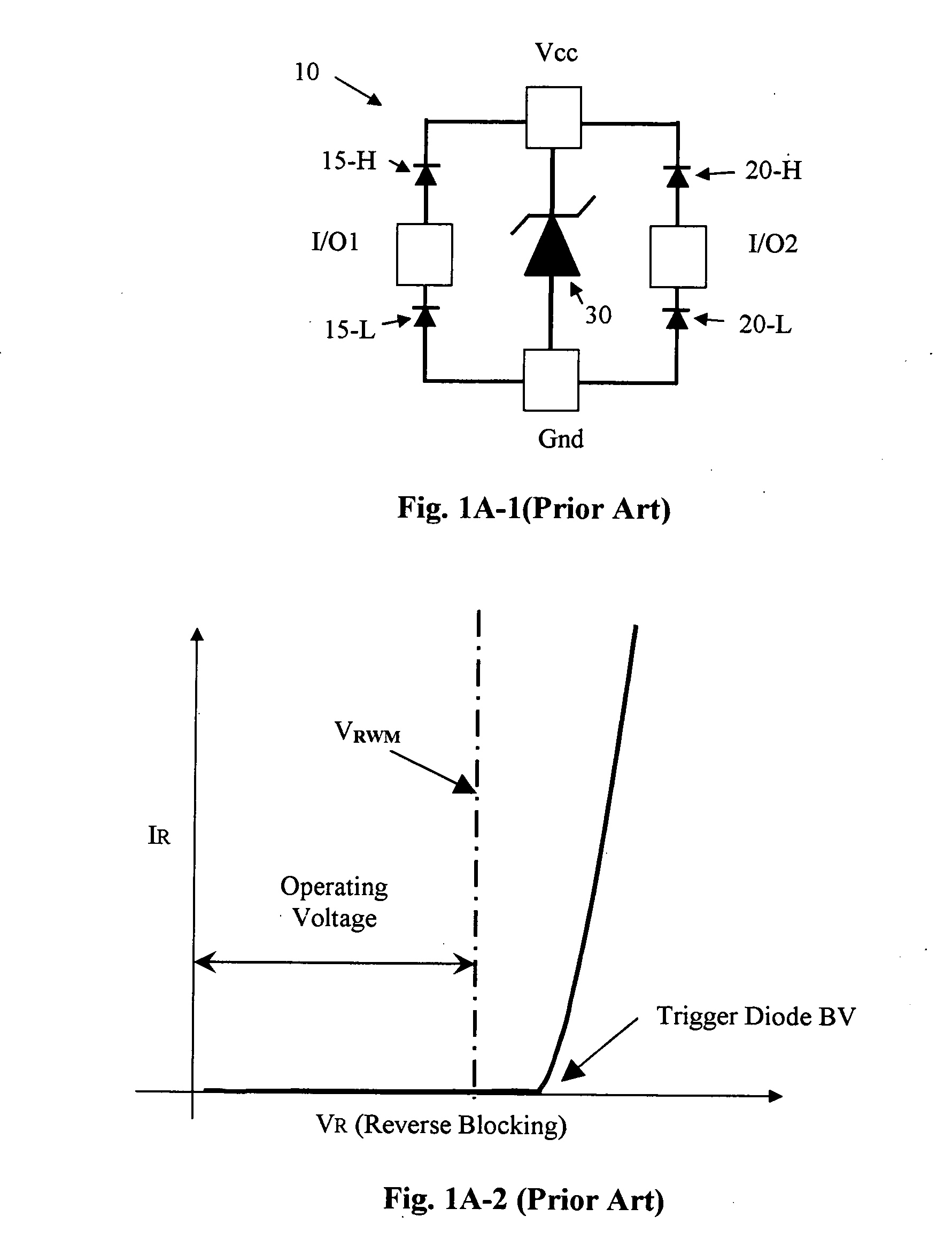
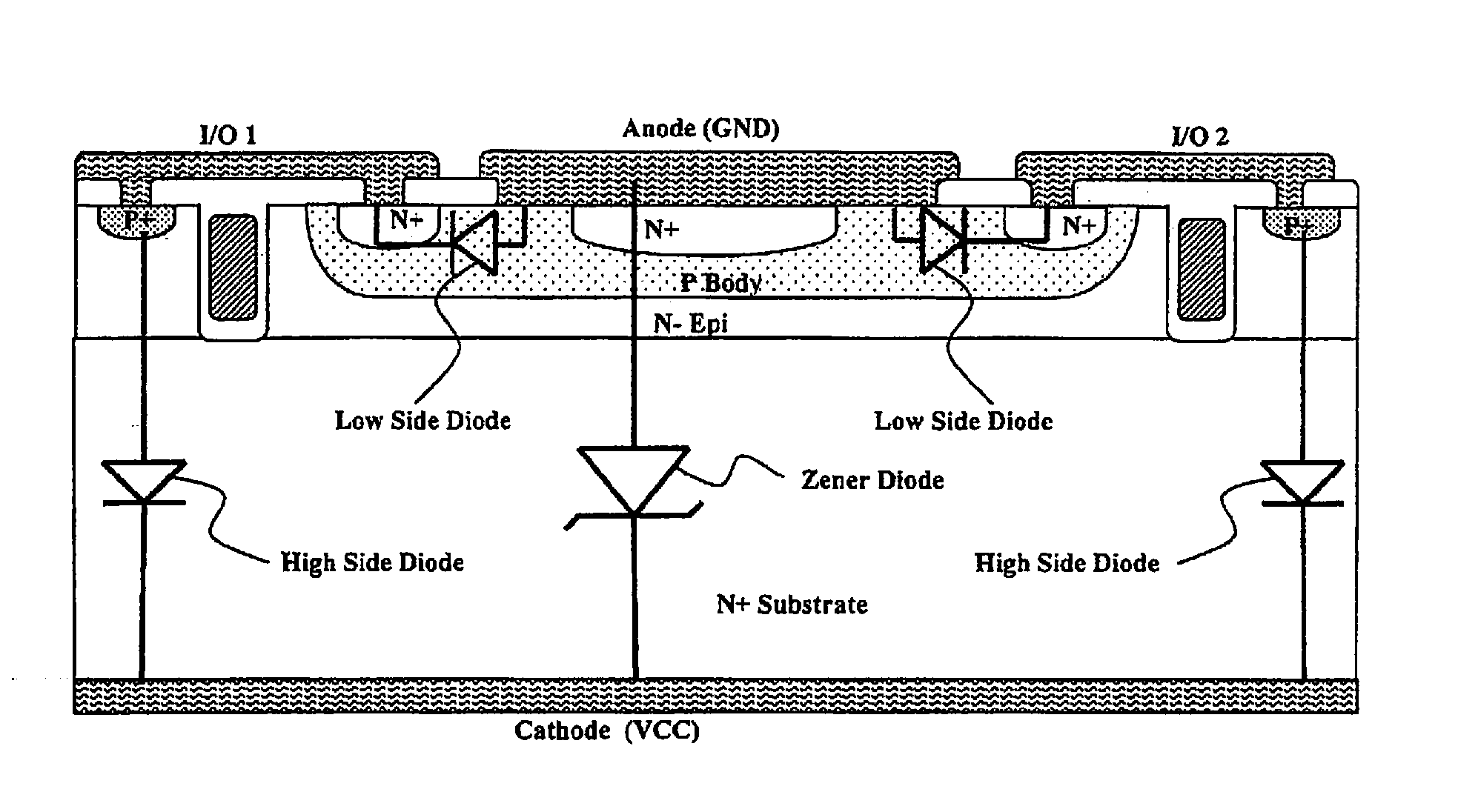
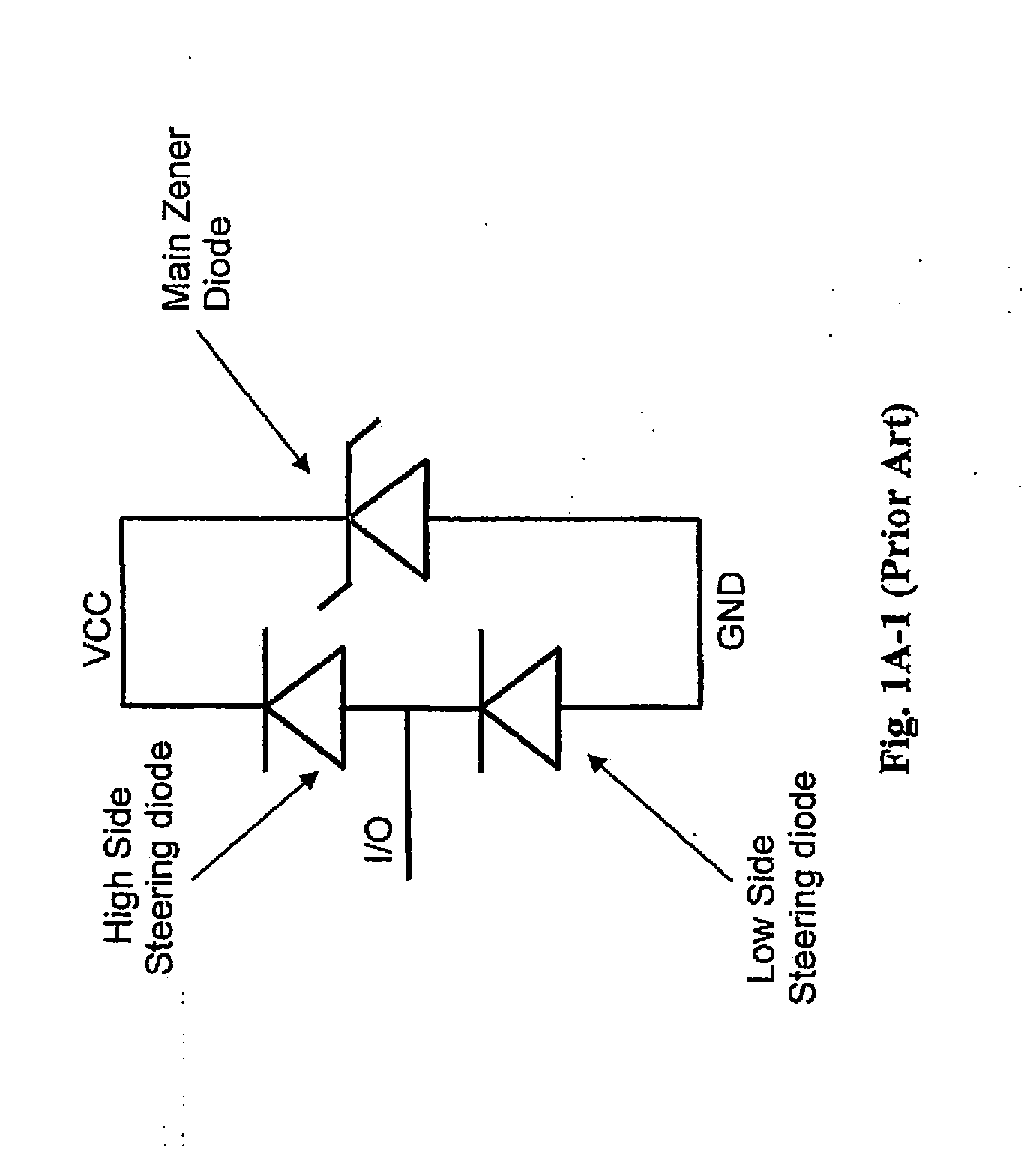
Optimized configurations to integrate steering diodes in low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20090045457A1Reduced lateral areaReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceZener diode
A transient-voltage suppressing (TVS) device disposed on a semiconductor substrate including a low-side steering diode, a high-side steering diode integrated with a main Zener diode for suppressing a transient voltage. The low-side steering diode and the high-side steering diode integrated with the Zener diode are disposed in the semiconductor substrate and each constituting a vertical PN junction as vertical diodes in the semiconductor substrate whereby reducing a lateral area occupied by the TVS device. In an exemplary embodiment, the high-side steering diode and the Zener diode are vertically overlapped with each other for further reducing lateral areas occupied by the TVS device.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
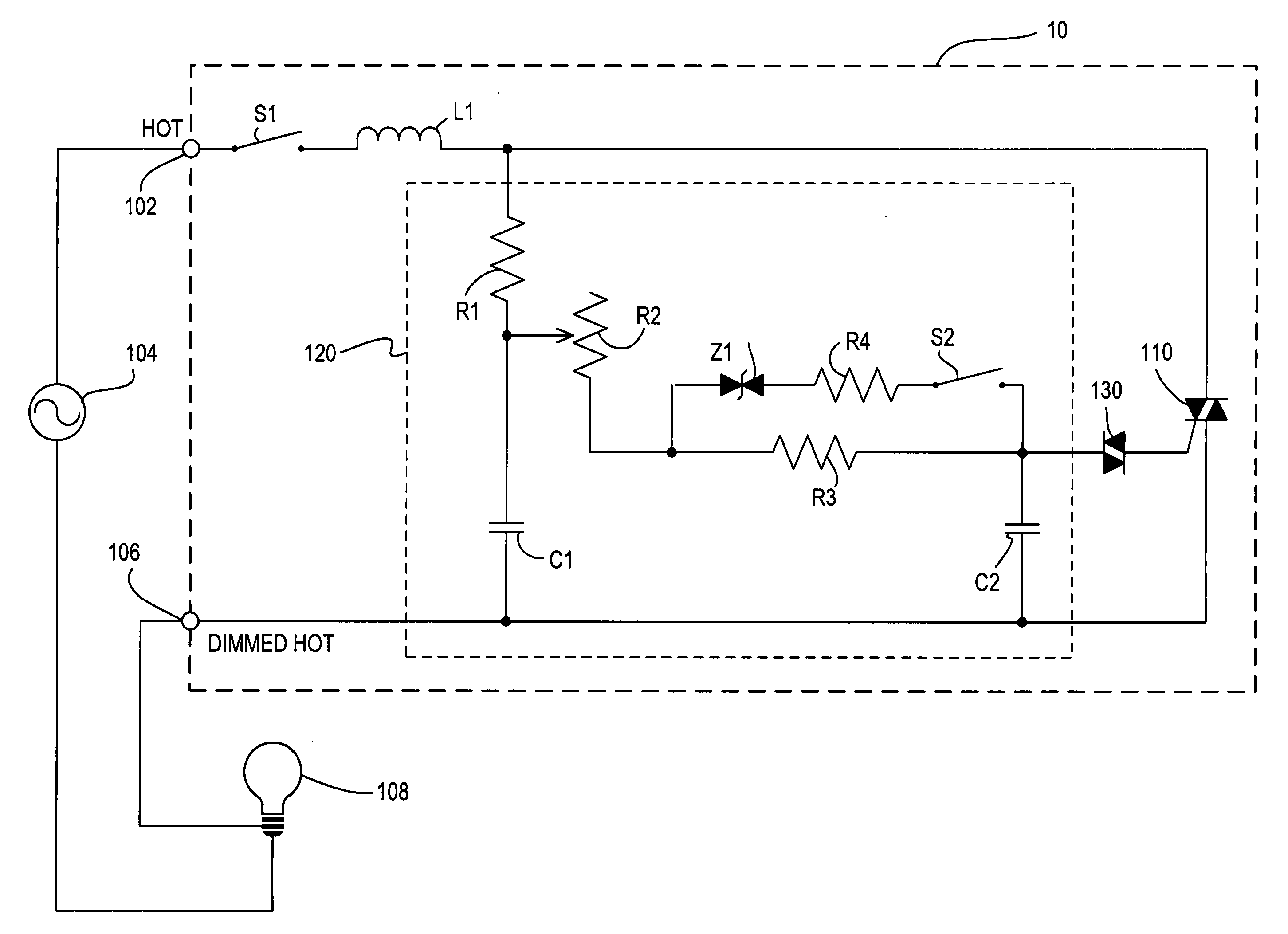
Dimmer switch with adjustable high-end trim
InactiveUS20070285027A1Reducing high-end trimReducing having substantially no affectElectric ignition installationSwitch power arrangementsMinimum timeTRIAC
A dimmer switch has a user adjustable high-end trim. The dimmer switch includes a bidirectional semiconductor switch, such as a triac, for controlling the amount of power delivered from a source of alternating current power to a lighting load, such as an electric lamp. A user-adjustable timing circuit controls the conduction time of the triac from a minimum time to a maximum time. The maximum possible conduction time of the triac is the high-end trim. The minimum possible conduction time of the triac is the low-end trim. The timing circuit includes a user-accessible switch that allows a user to reduce the high-end trim from a first nominal level to a second reduced level, lower than the first level, without substantially affecting the low-end trim. The switch allows a user to switch a transient voltage suppressor into and out of parallel connection with a resistor that is part of an RC timing circuit for the triac. The dimmer switch advantageously uses less energy and the lifetime of the lamp is extended when the second reduced level of the high-end trim is selected.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Transient voltage/current protection system for electronic circuits associated with implanted leads
A transient voltage / surge current protection system is provided for electronic circuits associated with implanted leads. In particular, a transient voltage suppressor such as a diode, a zener diode, a transorb, a surge protector, varistor components or the like, is placed in parallel with the electronic circuits to thereby divert harmful surge current and bypass the electronic circuit during an external defibrillation event or during an applied therapeutic shock, such as from an ICD.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter
ActiveUS20080121988A1Small footprintLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceTransient voltage suppressor
A vertical TVS (VTVS) circuit includes a semiconductor substrate for supporting the VTVS device thereon having a heavily doped layer extending to the bottom of substrate. Deep trenches are provided for isolation between multi-channel VTVS. Trench gates are also provided for increasing the capacitance of VTVS with integrated EMI filter.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter
ActiveUS7781826B2Small footprintImproved TVS and EMI filter circuitSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
A vertical TVS (VTVS) circuit includes a semiconductor substrate for supporting the VTVS device thereon having a heavily doped layer extending to the bottom of substrate. Deep trenches are provided for isolation between multi-channel VTVS. Trench gates are also provided for increasing the capacitance of VTVS with integrated EMI filter.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
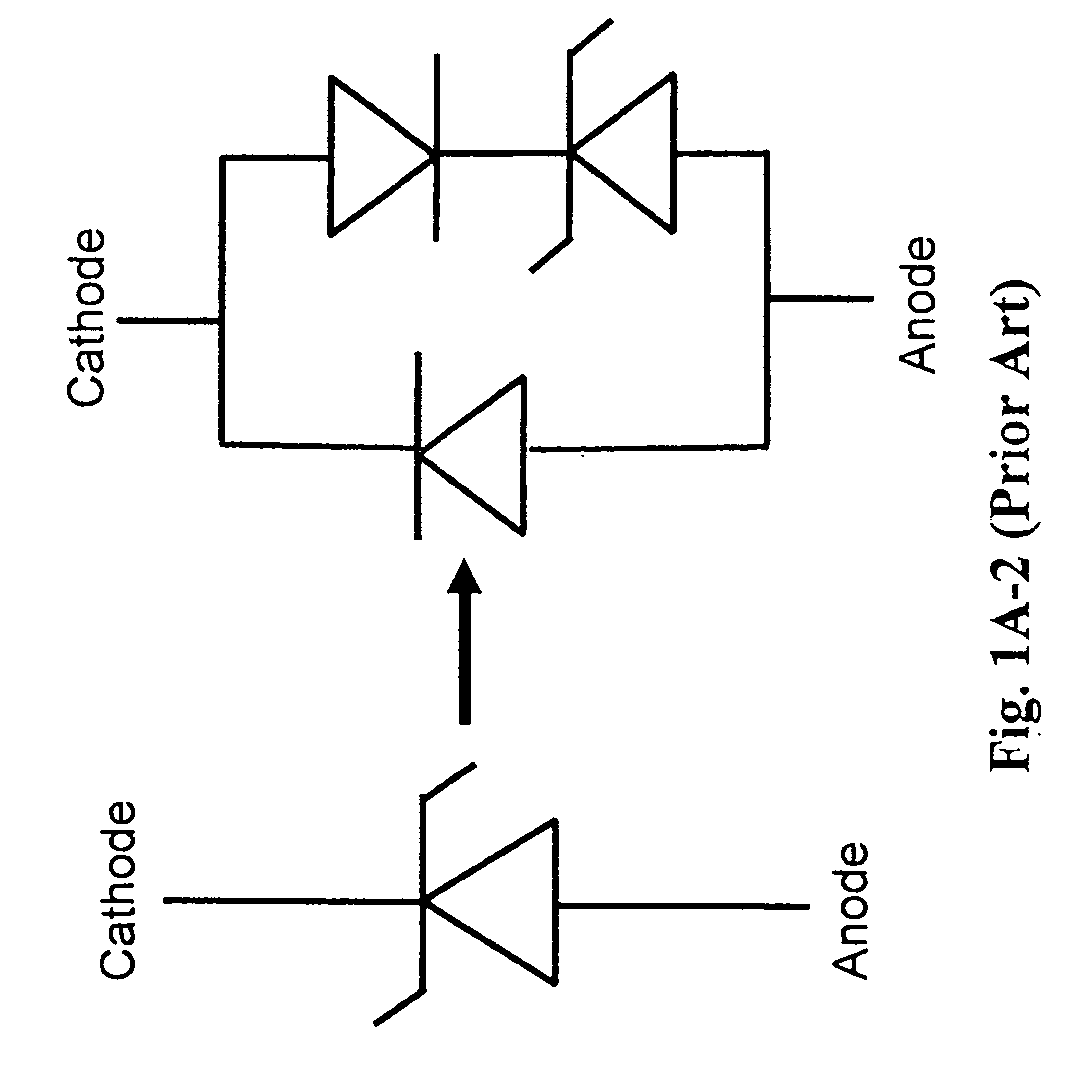
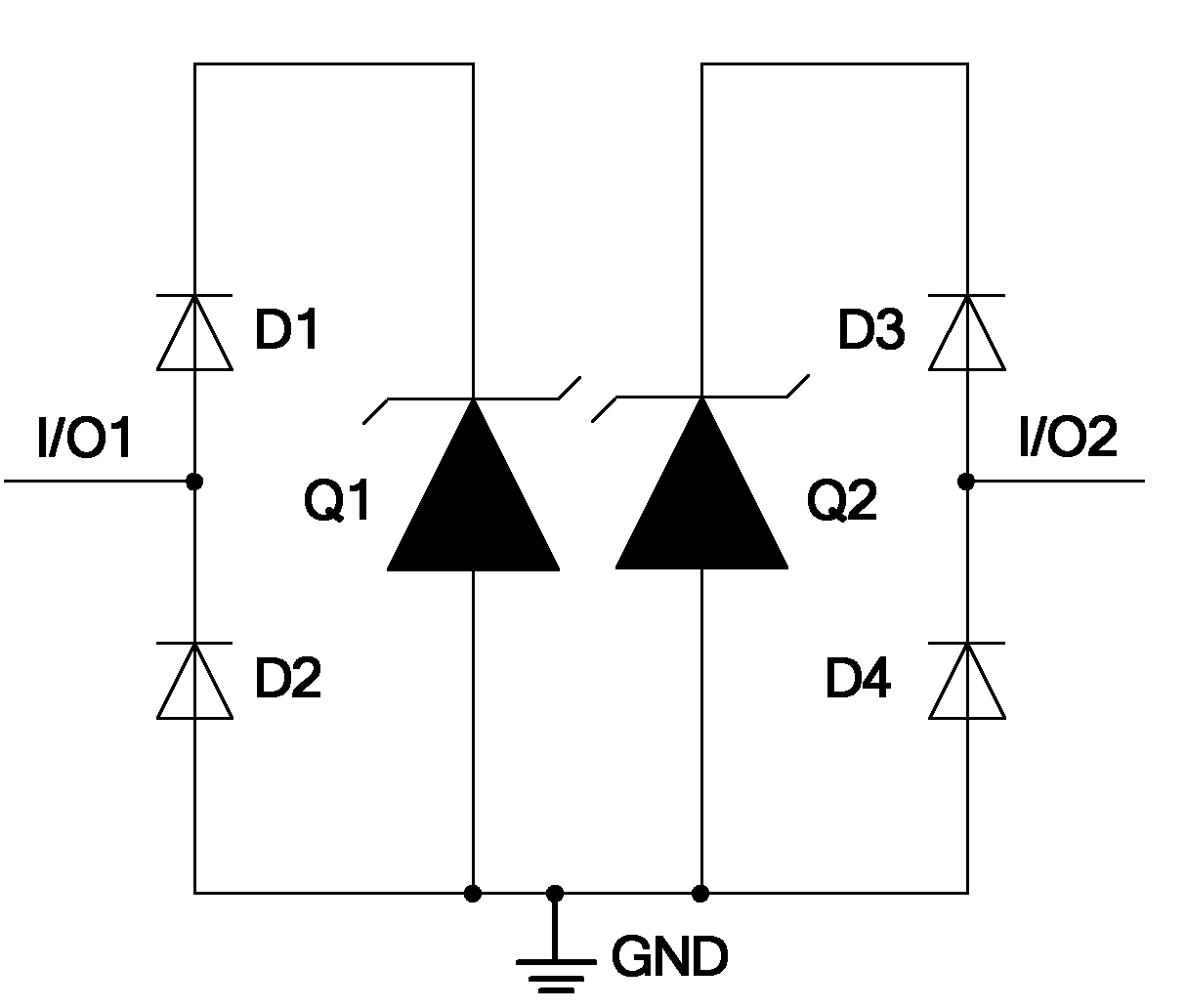
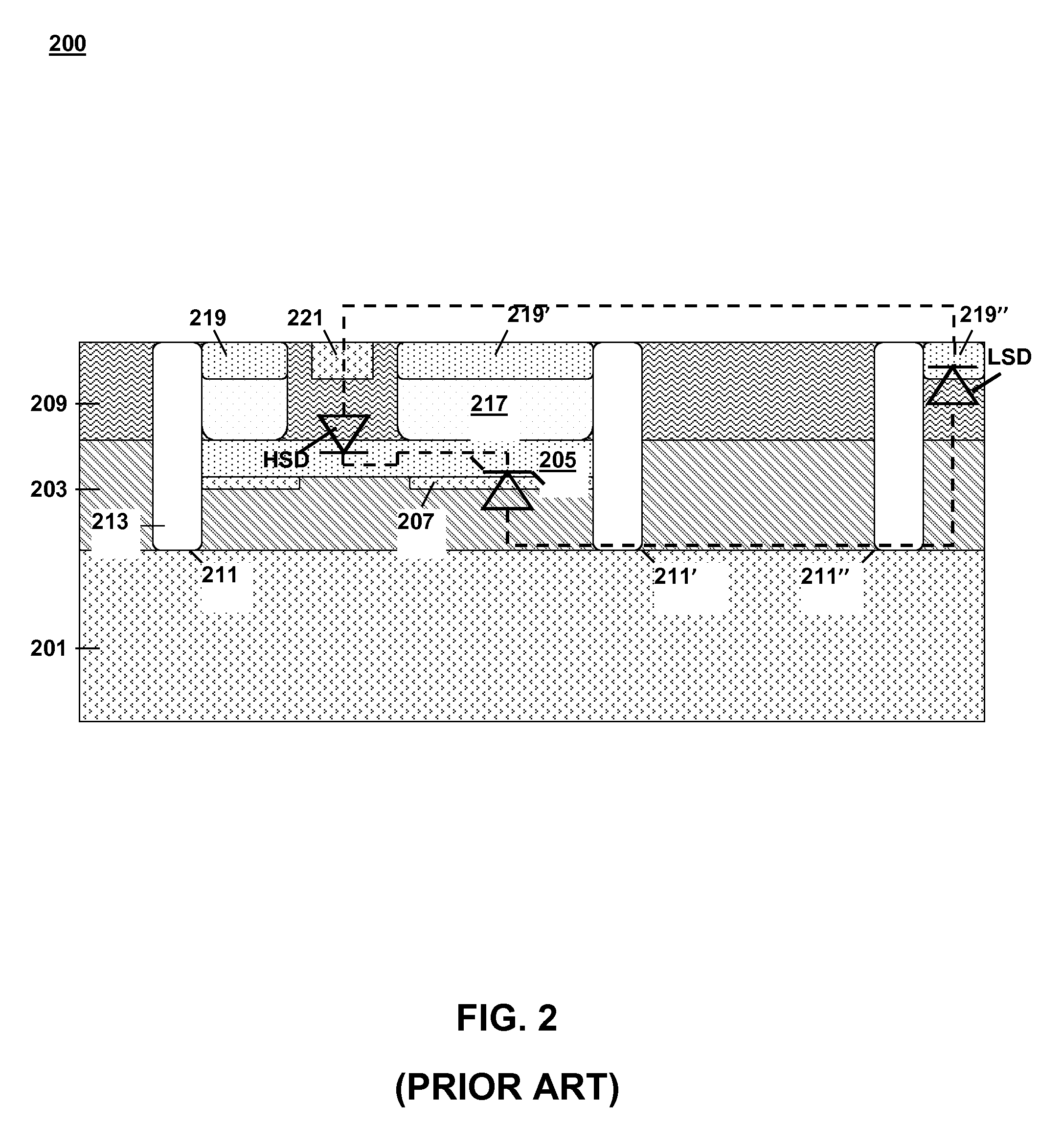
Transient voltage suppression device
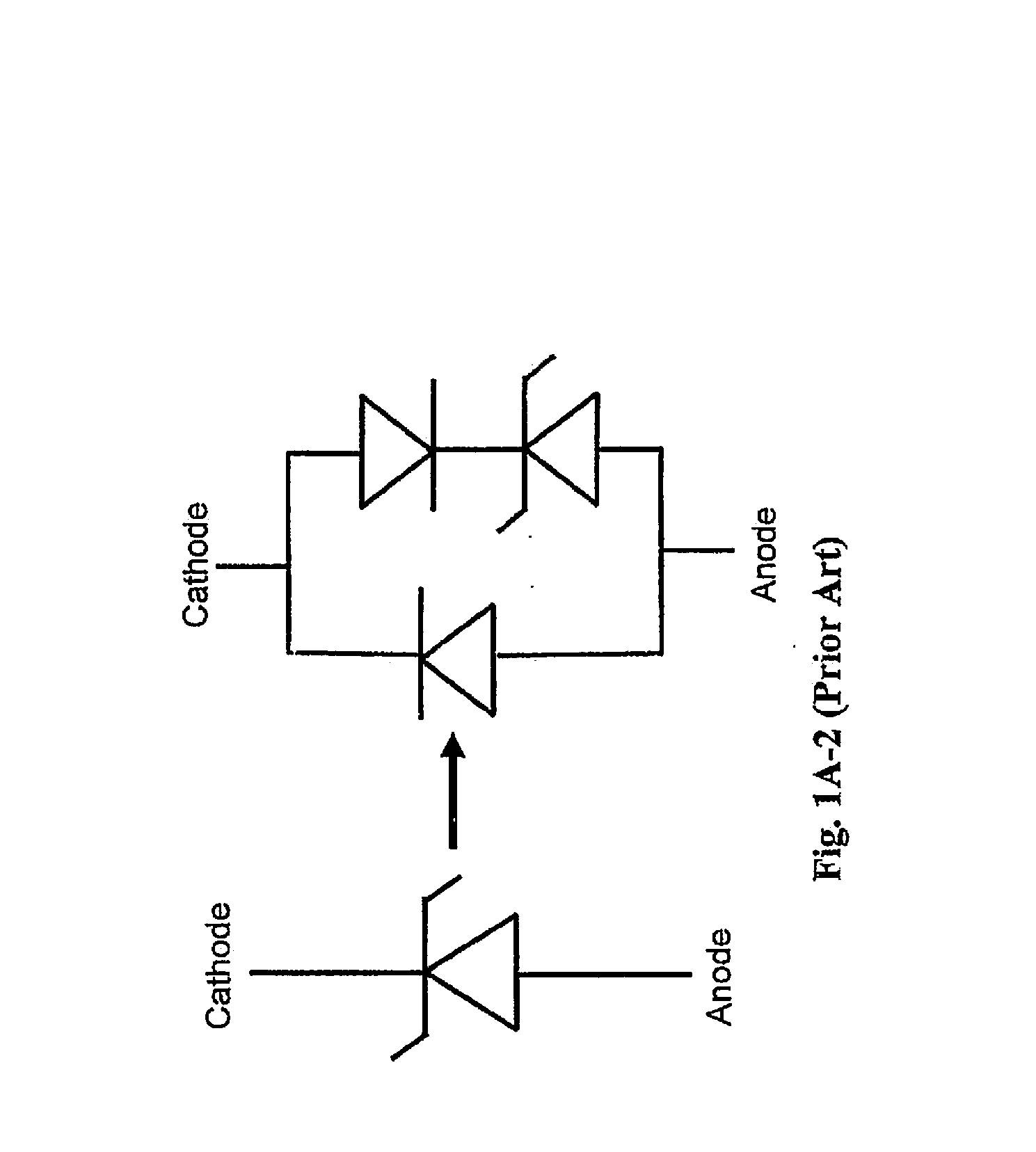
InactiveUS6867436B1Lower clamping voltageOvercome disadvantagesThyristorSolid-state devicesRectifier diodesHigh resistivity
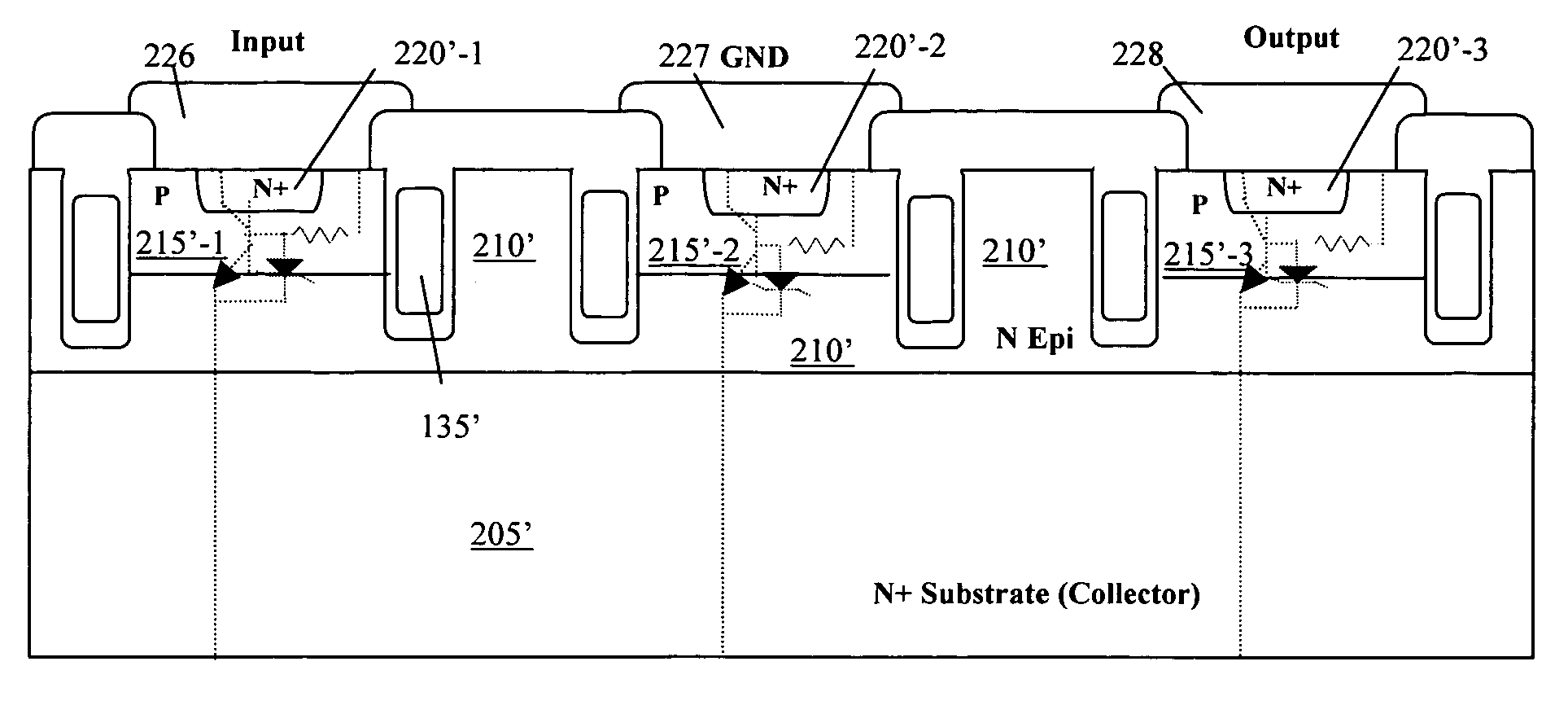
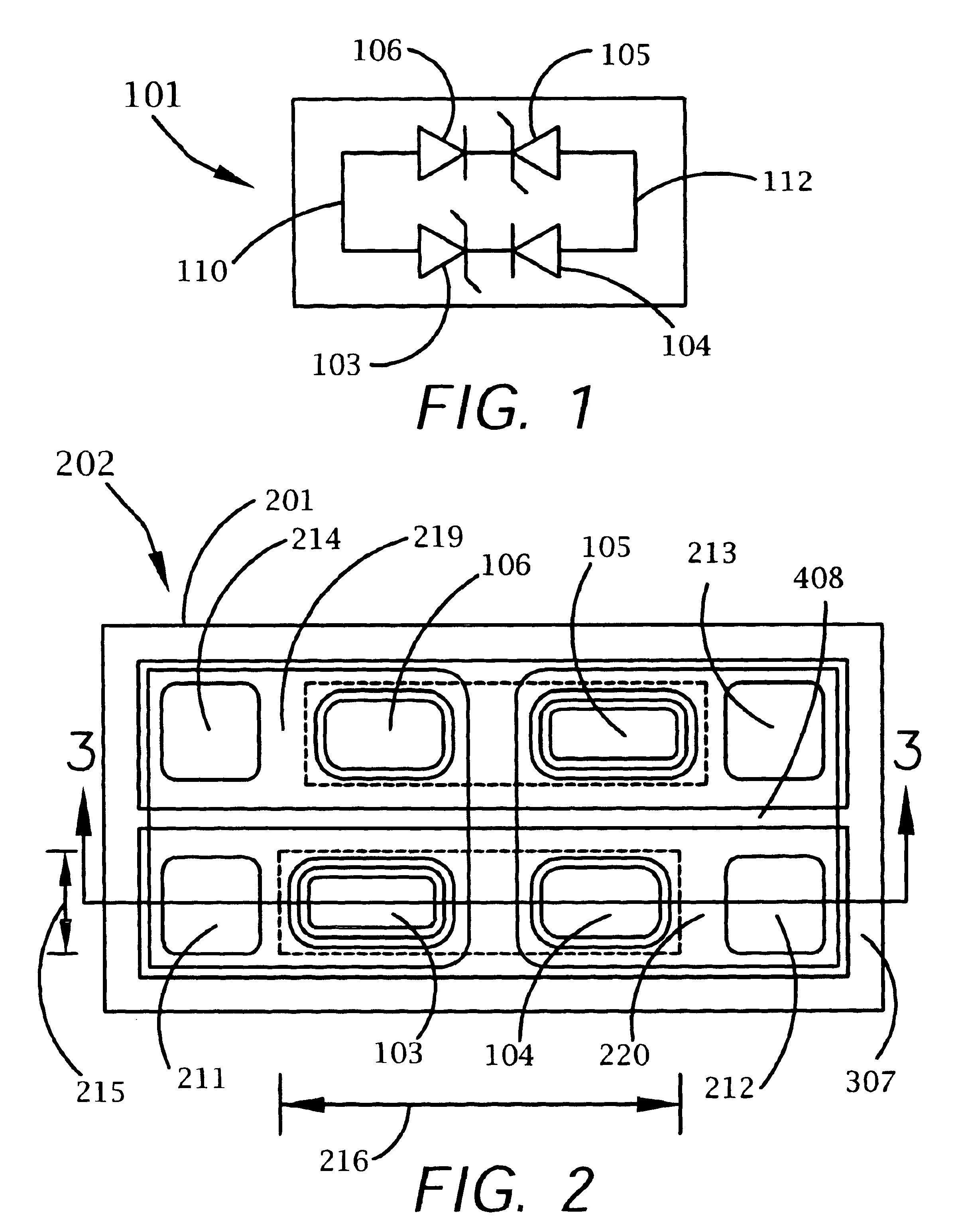
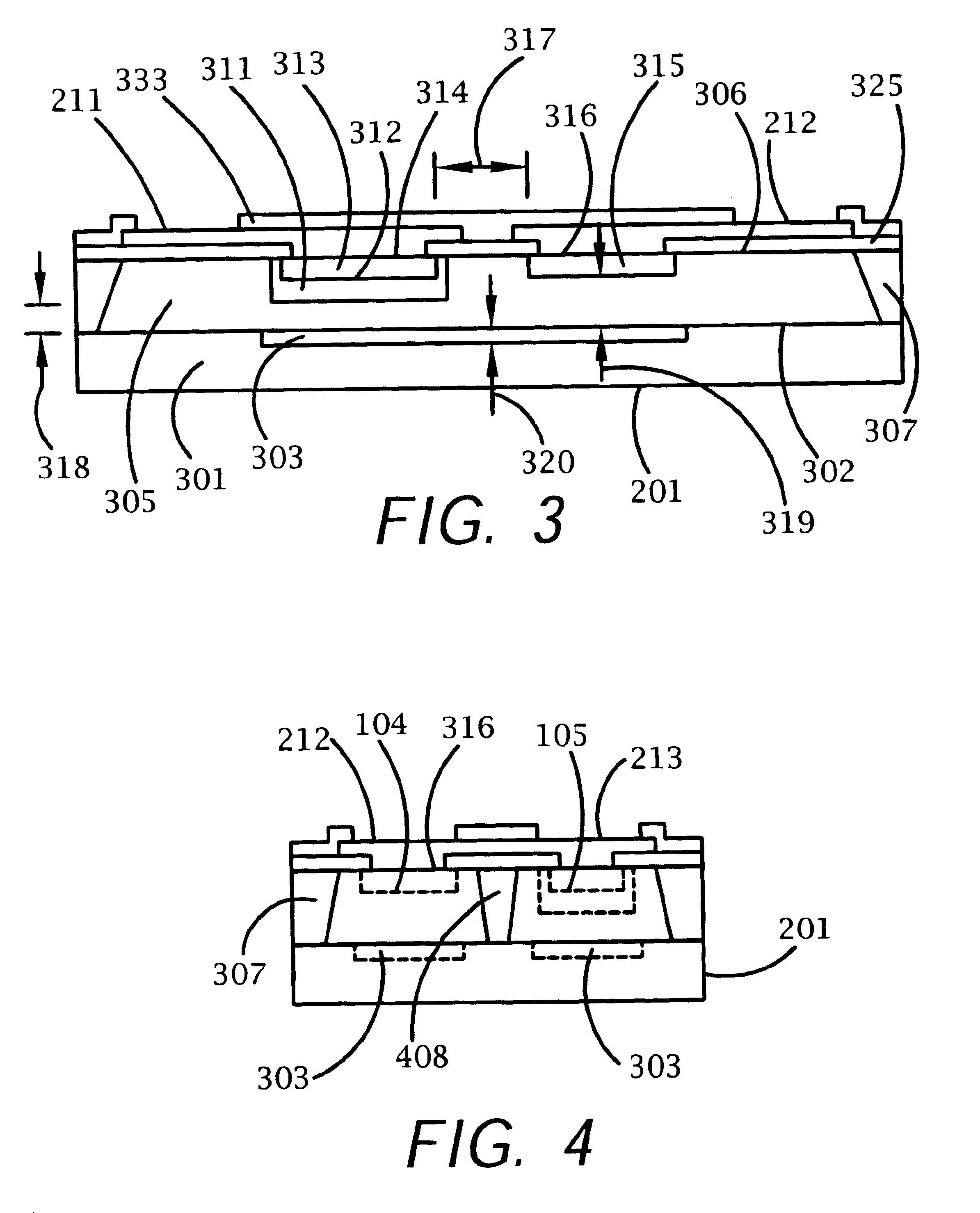
A bi-directional transient voltage suppression (“TVS”) device (101) includes a semiconductor die (201) that has a first avalanche diode (103) in series with a first rectifier diode (104) connected cathode to cathode, electrically coupled in an anti-parallel configuration with a second avalanche diode (105) in series with a second rectifier diode (106) also connected cathode to cathode. All the diodes of the TVS device are on a single semiconductor substrate (301). The die has a low resistivity buried diffused layer (303) having a first conductivity type disposed between a semiconductor substrate (301) having the opposite conductivity type and a high resistivity epitaxial layer (305) having the first conductivity type. The buried diffused layer shunts most of a transient current away from a portion of the epitaxial layer between the first avalanche diode and the first rectifier diode, thereby reducing the clamping voltage relative to the breakdown voltage. The TVS device is packaged as a flip chip (202) that has four solder bump pads (211-214). The abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims pursuant to 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b).
Owner:PROTEK DEVICES
MOS transistor triggered transient voltage supressor to provide circuit protection at a lower voltage
ActiveUS20080218922A1Reduce leakageSuppress the I/O-to-I/O latch-upTransistorWave amplification devicesLow voltageDevice form
An electronic device formed as an integrated circuit (IC) wherein the electronic device further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit. The TVS circuit includes a triggering MOS transistor connected between an emitter and a collector of a first bipolar-junction transistor (BJT) coupled to a second BJT to form a SCR functioning as a main clamp circuit of the TVS circuit. The TVS circuit further includes a triggering circuit for generating a triggering signal for the triggering MOS transistor wherein the triggering circuit includes multiple stacked MOS transistors for turning into a conductive state by a transient voltage while maintaining a low leakage current.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
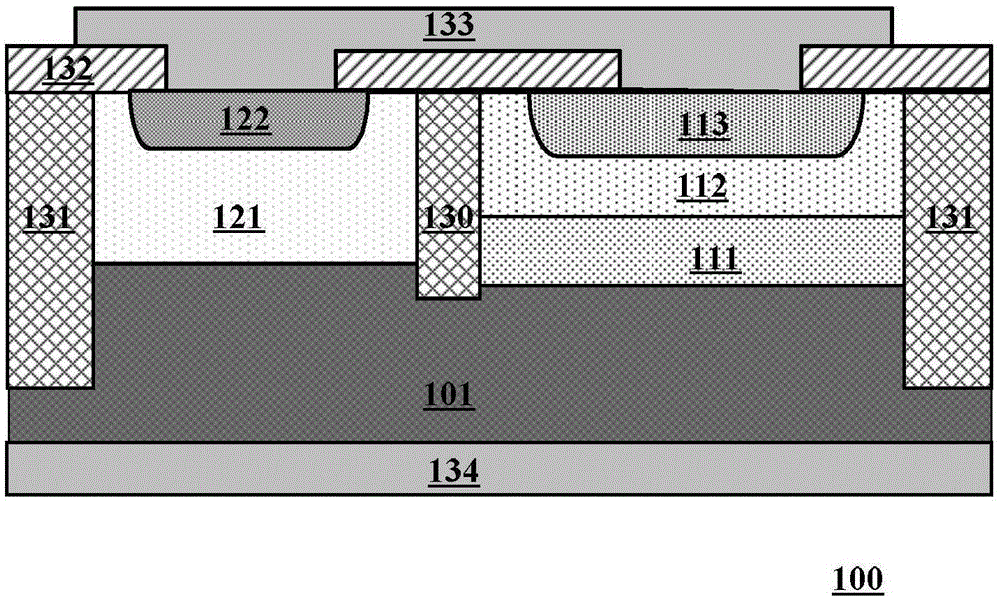
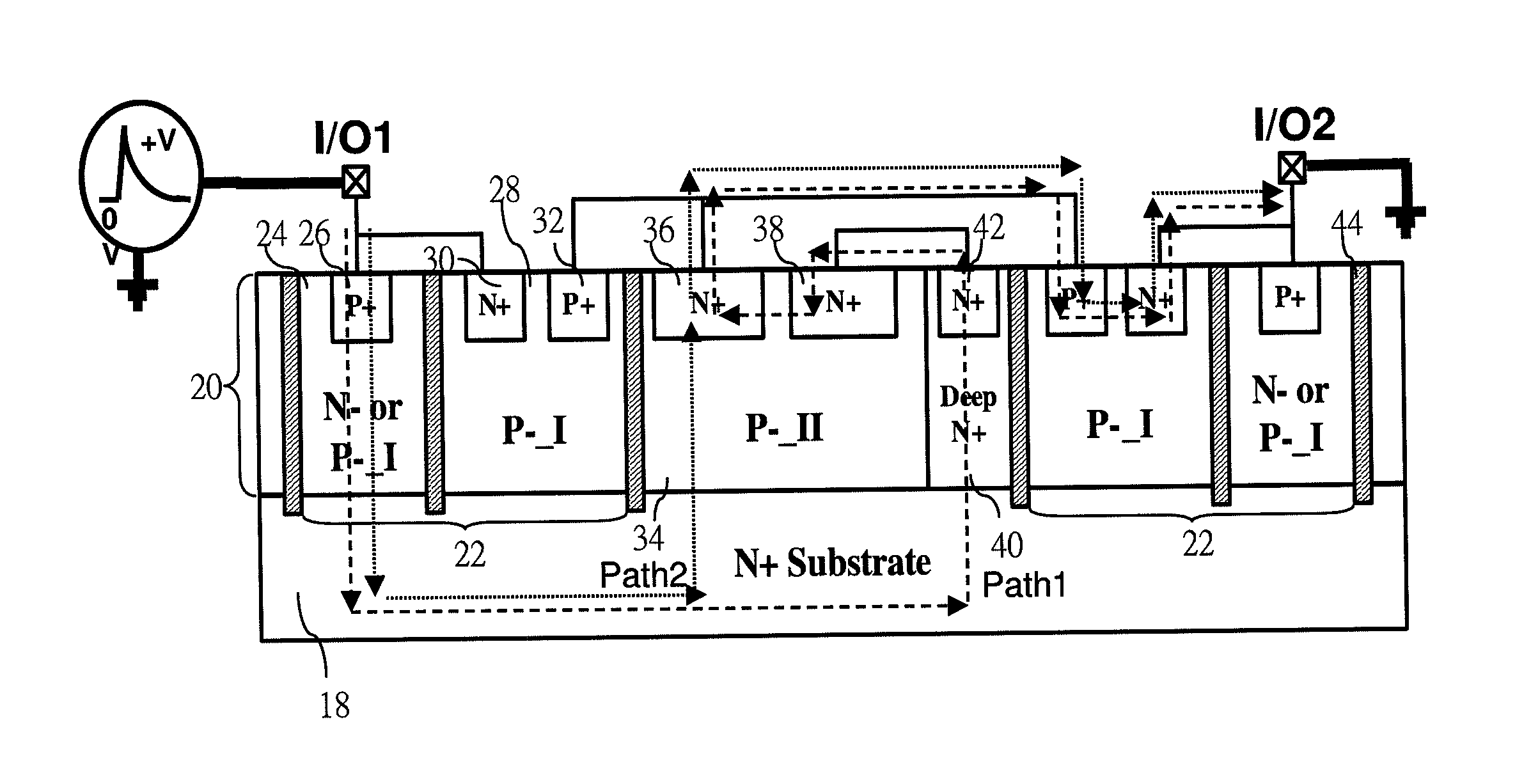
Transient voltage suppressor manufactured in silicon on oxide (SOI) layer
InactiveUS20090115018A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceAvoid latchSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerMicrometer
A transient voltage-suppressing (TVS) device supported on a semiconductor substrate is applied to protect an electronic device from a transient voltage. The TVS device includes a clamp diode functions with a high-side and a low side diodes for clamping a transient voltage disposed on a top layer of the semiconductor substrate insulated by a insulation layer constituting a TVS on silicon-on-insulator (SOI) device. In an exemplary embodiment, the insulator layer further includes a thick body oxide (BOX) layer having a thickness in the range of 250 Angstroms to 1 micrometer to sustain an application with a breakdown voltage higher than 25 volts. In another exemplary embodiment, the clamp diode further surrounded by a P-well and the P-well is formed on top of a P− / P+ substrate layer disposed above the insulator layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Transient voltage suppressors
ActiveUS20120068299A1Improve efficiencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransient voltage suppressorPhysics
The present invention relates a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) for directional ESD protection. The TVS includes: a conductivity type substrate; a first type lightly doped region, having a first type heavily doped region arranged therein; a second type lightly doped region, having a second type heavily doped region and a third type heavily doped region arranged therein; a third type lightly doped region, having a fourth type heavily doped region arranged therein; a plurality of closed isolation trenches, arranged on the conductivity type substrate, wherein at least one of the plurality of closed isolation trenches is neighbored one of the type lightly doped regions; and a first pin. Accordingly, the TVS of present invention may adaptively provide effective ESD protection under positive and negative ESD stresses, improve the efficiency of ESD protection within the limited layout area.
Owner:AMAZING MICROELECTRONICS
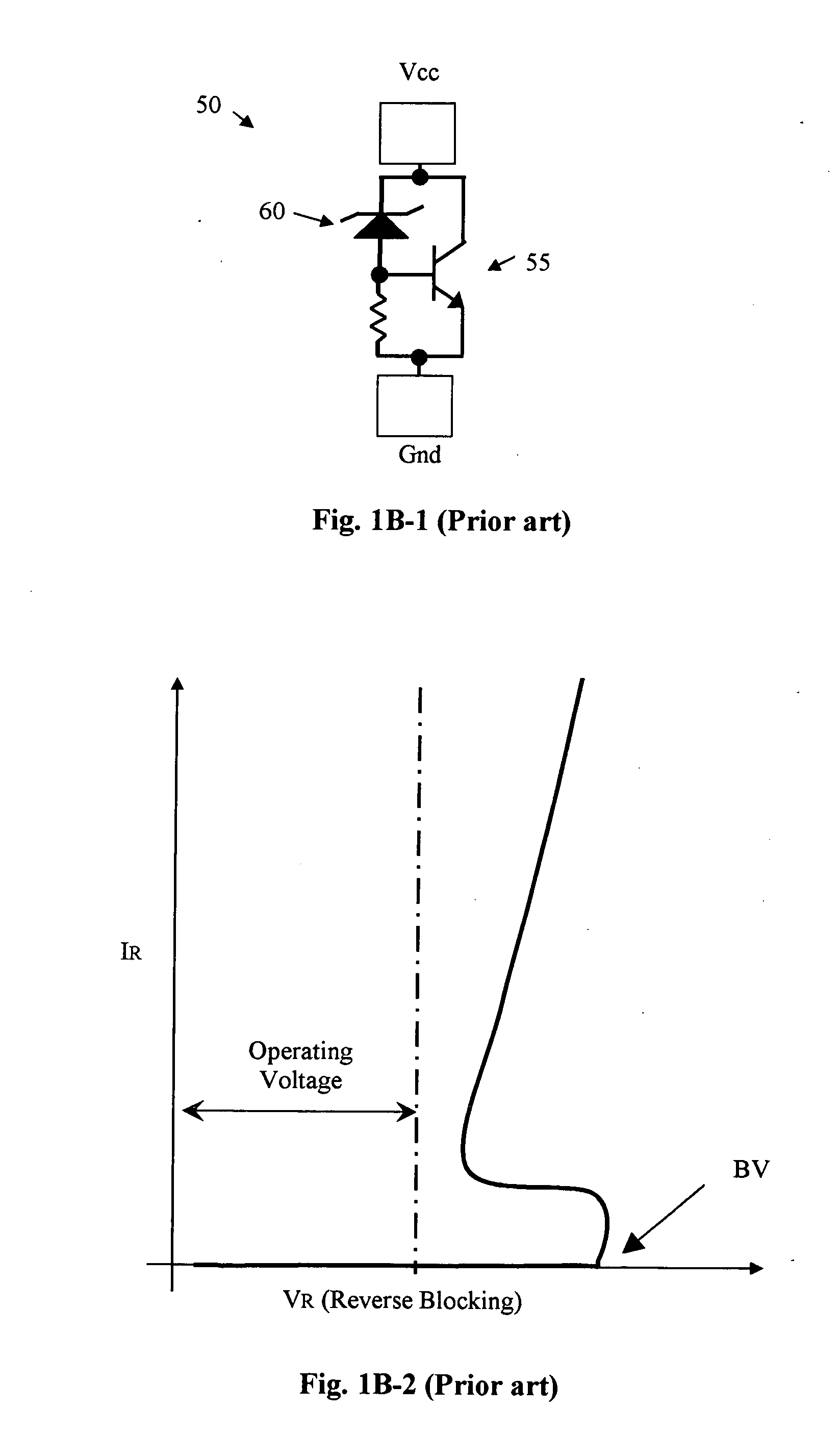
Circuit configurations to reduce snapback of a transient voltage suppressor
ActiveUS20070279824A1Reduce voltage dropEasy clampingTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice formZener diode
This invention discloses an electronic device formed as an integrated circuit (IC) wherein the electronic device further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit. The TVS circuit includes a triggering Zener diode connected between an emitter and a collector of a bipolar-junction transistor (BJT) wherein the Zener diode having a reverse breakdown voltage BV less than or equal to a BVceo of the BJT where BVceo stands for a collector to emitter breakdown voltage with base left open. The TVS circuit further includes a rectifier connected in parallel to the BJT for triggering a rectified current through the rectifier for further limiting an increase of a reverse blocking voltage. In a preferred embodiment, the triggering Zener diode, the BJT and the rectifier are formed in a semiconductor substrate by implanting and configuring dopant regions of a first and a second conductivity types in a N-well and a P-well whereby the TVS can be formed in parallel as part of the manufacturing processes of the electronic device.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Circuit configurations to reduce snapback of a transient voltage suppressor
ActiveUS7538997B2Reduce voltage dropEasy clampingTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice formZener diode
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
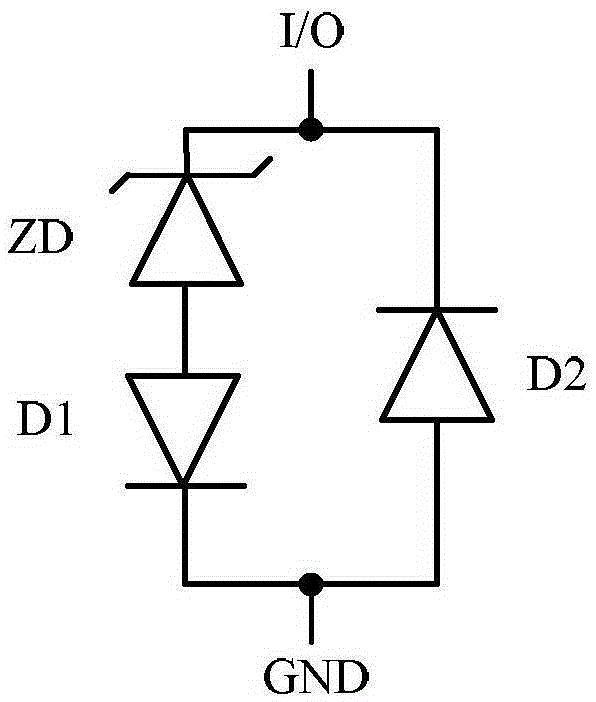
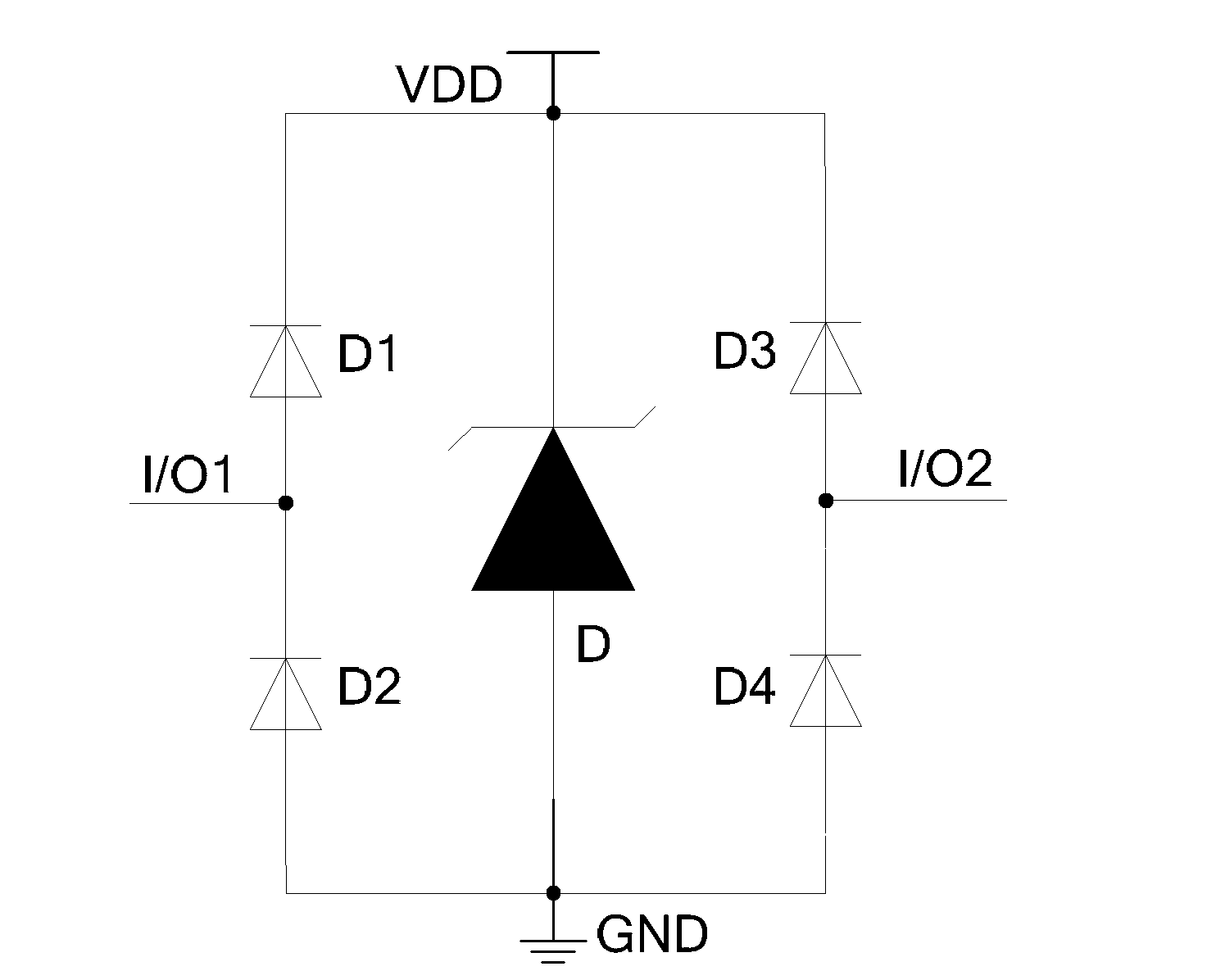
Transient voltage suppression circuit for an implanted RFID chip
A transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit includes an implantable RFID chip, an antenna associated with the RFID chip, and a transient voltage suppressor electrically connected in parallel to both the RFID chip and the antenna. The transient voltage suppressor may be formed of an array of diodes, such as back-to-back diodes, at least one Zener diode, or back-to-back or series opposing Zener diodes. In preferred embodiments, the antenna is formed of a biocompatible material suitable for long-term exposure to body tissue and body fluids, and the RFID chip and the transient voltage suppressor are disposed within a hermetically sealed biocompatible container.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Transient voltage suppressor (TVS) with improved clamping voltage
ActiveUS20090268361A1Reduce reboundImprove clamping effectTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentDevice formZener diode
This invention discloses an electronic device formed as an integrated circuit (IC) wherein the electronic device further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit for suppressing a transient voltage. The transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit includes a Zener diode connected between a ground terminal and a node for triggering a snapback circuit. In one embodiment, this node may be a Vcc terminal. The TVS device further includes a snapback circuit connected in parallel to the Zener diode for conducting a transient voltage current with a snapback current-voltage (I-V) characteristic upon turning on of the snapback circuit And, the TVS device further includes a snapback suppressing circuit connected in series with the snapback circuit for conducting a current with an I-V characteristic complementary to the snapback-IV characteristic for clamping a snapback voltage.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Optimized configurations to integrate steering diodes in low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20140319598A1Reduced lateral areaReduce areaTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceZener diode
A transient-voltage suppressing (TVS) device disposed on a semiconductor substrate including a low-side steering diode, a high-side steering diode integrated with a main Zener diode for suppressing a transient voltage. The low-side steering diode and the high-side steering diode integrated with the Zener diode are disposed in the semiconductor substrate and each constituting a vertical PN junction as vertical diodes in the semiconductor substrate whereby reducing a lateral area occupied by the TVS device. In an exemplary embodiment, the high-side steering diode and the Zener diode are vertically overlapped with each other for further reducing lateral areas occupied by the TVS device.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
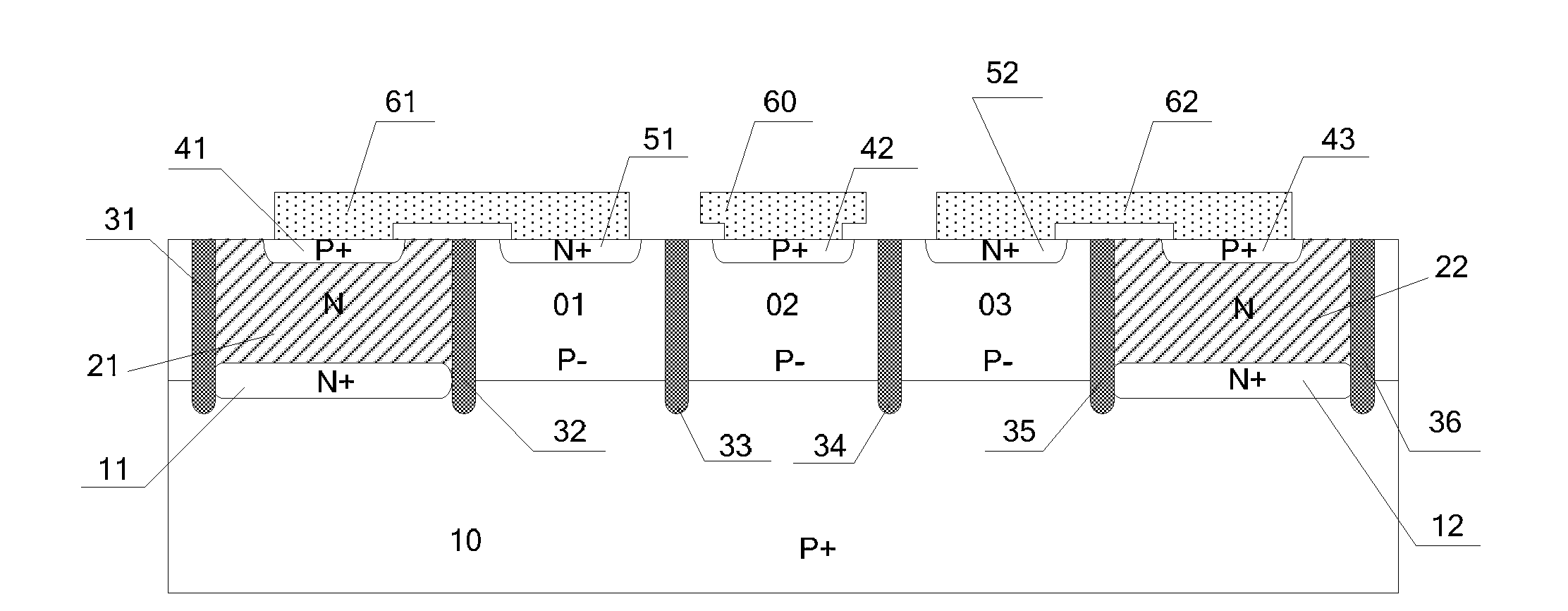
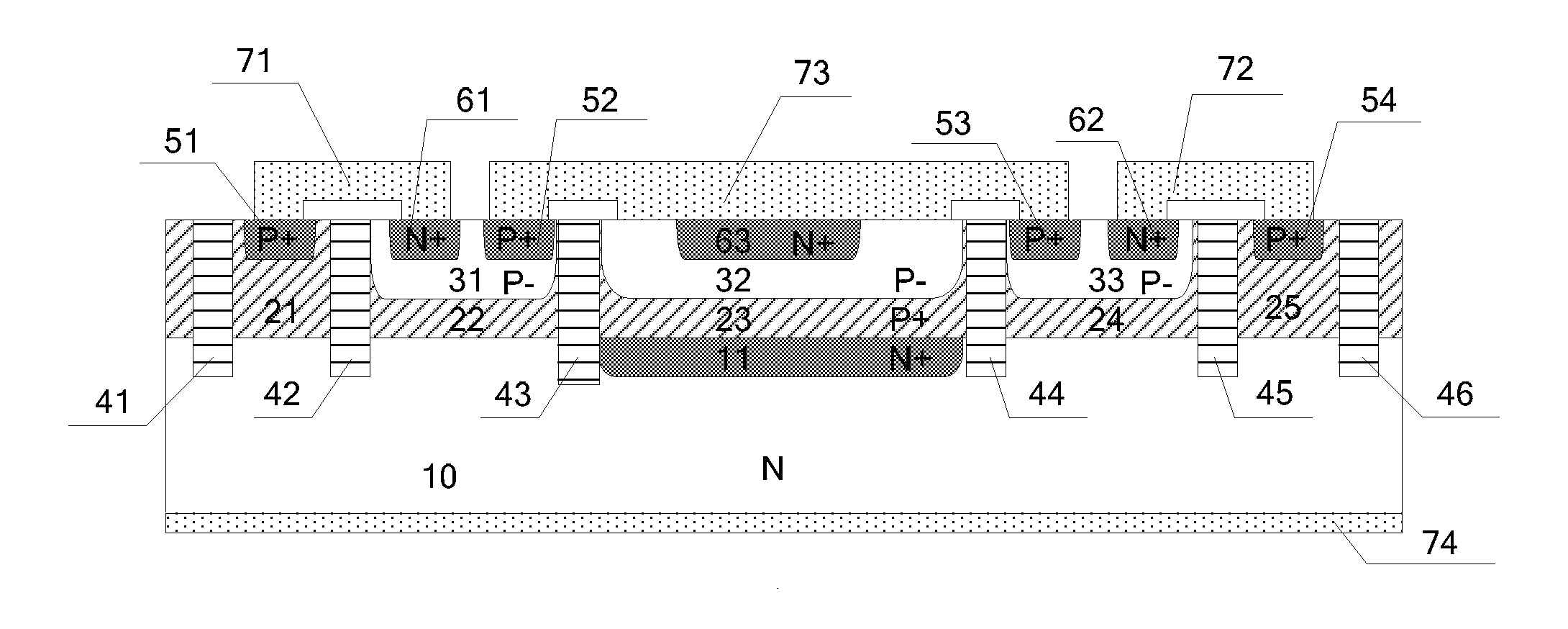
Transient voltage suppressor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105261616AReduce usageImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransient voltage suppressorSemiconductor
Disclosed are a transient voltage suppressor and a manufacturing method thereof. The transient voltage suppressor comprises a semiconductor substrate. On the semiconductor substrate, a first buried layer of a first doping type is formed. A second buried layer of a second doping type is formed with the first region of the first buried layer. A first epitaxial region is formed on the second buried layer and a second epitaxial region is formed on the second region of the first buried layer. The first epitaxial region and the second epitaxial region are of the second doping type and the first doping type, respectively. A first doped region and a second doped region are respectively located in the first epitaxial region and the second epitaxial region. The first doped region and the second doped region are respectively of the first doping type and the second doping type. An electrically conductive channel is configured to extend from the surface of the second epitaxial region to the first buried layer. A first electrode, a second electrode and a third electrode are respectively in contact with the electrically conductive channel, the first doped region and the second doped region. By means of the transient voltage suppressor, a multi-channel one-way or two-way device can be formed on a single chip.
Owner:NANJING SILERGY SEMICON TECH CO LTD
Bidirectional dual-channel transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
InactiveCN102306649AShort response timeHigh surge absorption capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesParasitic capacitanceTransient voltage suppressor
The invention discloses a bidirectional dual-channel transient voltage suppressor (TVS), which comprises a P+ substrate layer, wherein a first N+ buried layer, a first P- epitaxial region, a second P- epitaxial region, a third P- epitaxial region and a second N+ buried layer are sequentially arranged on the P+ substrate layer from left to right; a first N injection region and a second N injection region are arranged on the first N+ buried layer and the second N+ buried layer respectively; a first N+ active injection region and a second N+ active injection region are arranged on the first P- epitaxial region and the third P- epitaxial region respectively; and a first P+ active injection region, a second P+ active injection region and a third P+ active injection region are arranged on the first N injection region, the second P- epitaxial region and the second N injection region respectively. Due to the adoption of a combined structure of a Zener voltage-regulator tube and a low-capacitance diode, the parasitic capacitance of the TVS is further reduced, on resistance is reduced, and the clamp characteristic of the TVS is improved; and the TVS can be widely applied to static electricity protection of certain portable equipment and high-speed interfaces.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Applying trenched transient voltage suppressor (TVS) technology for distributed low pass filters
ActiveUS20090261897A1Improved filtering configurationImprove filtering effectTransistorMultiple-port networksLow-pass filterInductor
An electronic circuit includes a filtering circuit implemented with a distributed inductor-and-capacitor (LC) network that includes metal oxide effect (MOS) trenches opened in a semiconductor substrate filled with dielectric material for functioning as capacitors for the distributed LC network. The electronic circuit further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit integrated with the filtering circuit that functions as a low pass filter wherein the TVS circuit includes a bipolar transistor triggered by a diode disposed in the semiconductor substrate. The distributed LC network further includes metal coils to function as inductors disposed on a top surface of the semiconductor electrically contacting the MOS trenches.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Low capacitance transient voltage suppressor
ActiveUS20120241903A1Lower resistanceReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceSuppressor
A low capacitance transient voltage suppressor is disclosed. The suppressor comprises an N-type heavily doped substrate and an epitaxial layer formed on the substrate. At least one steering diode structure formed in the epitaxial layer comprises a diode lightly doped well and a first P-type lightly doped well, wherein a P-type heavily doped area is formed in the diode lightly doped well and a first N-type heavily doped area and a second P-type heavily doped area are formed in the first P-type lightly doped well. A second P-type lightly doped well having two N-type heavily doped areas is formed in the epitaxial layer. In addition, an N-type heavily doped well and at least one deep isolation trench are formed in the epitaxial layer, wherein the trench has a depth greater than or equal to depths of all the doped wells, so as to separate at least one doped well.
Owner:AMAZING MICROELECTRONICS
Flip-chip packaged SMD-type LED with antistatic function and having no wire bonding
ActiveUS20060012053A1Good static control effectAvoid problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface mountingLead bonding
A flip-chip packaged SMD-type (surface-mount device) light emitting diode is provided. The light emitting diode chip is packaged in flip chip packages and is connected with an electrostatic protection device such as a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or a Zener diode. The electrostatic protection device is attached with a substrate so as to form a flip-chip packaged SMD-type light emitting diode. The light emitting diode chip is connected to a lead frame of the substrate by a high electrical and heat conductive component thus the device needs no wire bonding. Due to the electrostatic protection device, the device has static control effect.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Transient Voltage Suppressor Having Symmetrical Breakdown Voltages
ActiveUS20100276779A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyTransient voltage suppressor
A vertical transient voltage suppressing (TVS) device includes a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type where the substrate is heavily doped, an epitaxial layer of the first conductivity type formed on the substrate where the epitaxial layer has a first thickness, and a base region of a second conductivity type formed in the epitaxial layer where the base region is positioned in a middle region of the epitaxial layer. The base region and the epitaxial layer provide a substantially symmetrical vertical doping profile on both sides of the base region. In one embodiment, the base region is formed by high energy implantation. In another embodiment, the base region is formed as a buried layer. The doping concentrations of the epitaxial layer and the base region are selected to configure the TVS device as a punchthrough diode based TVS or an avalanche mode TVS.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Circuit configuration and manufacturing processes for vertical transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and EMI filter
ActiveUS20140167218A1Small footprintLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceManufacturing technology
A vertical TVS (VTVS) circuit includes a semiconductor substrate for supporting the VTVS device thereon having a heavily doped layer extending to the bottom of substrate. Deep trenches are provided for isolation between multi-channel VTVS. Trench gates are also provided for increasing the capacitance of VTVS with integrated EMI filter.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Bottom source NMOS triggered zener clamp for configuring an ultra-low voltage transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20100321840A1Easy clampingReduce voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETBody contact
A low voltage transient voltage suppressing (TVS) device supported on a semiconductor substrate supporting an epitaxial layer thereon. The TVS device further includes a bottom-source metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (BS-MOSFET) comprises a trench gate surrounded by a drain region encompassed in a body region disposed near a top surface of the semiconductor substrate wherein the drain region interfaces with the body region constituting a junction diode and the drain region encompassed in the body region on top of the epitaxial layer constituting a bipolar transistor with a top electrode disposed on the top surface of the semiconductor functioning as a drain / collector terminal and a bottom electrode disposed on a bottom surface of the semiconductor substrate functioning as a source / emitter electrode. The body regions further comprises a surface body contact region electrically connected to a body-to-source short-connection thus connecting the body region to the bottom electrode functioning as the source / emitter terminal. The gate may be shorted to the drain for configuring the BS-MOSFET transistor into a two terminal device with a gate-to-source voltage equal to a drain-to-source voltage. The drain / collector / cathode terminal disposed on top of the trench gate turns on the BS-MOSFET upon application of a threshold voltage of the BS-MOSFET thus triggering the bipolar transistor for clamping and suppressing a transient voltage substantially near a threshold voltage of the BS-MOSFET.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Transient voltage suppressor (TVS) with improved clamping voltage
ActiveUS8218276B2Reduce reboundImprove clamping effectTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentDevice formCurrent voltage
This invention discloses an electronic device formed as an integrated circuit (IC) wherein the electronic device further includes a transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit for suppressing a transient voltage. The transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit includes a Zener diode connected between a ground terminal and a node for triggering a snapback circuit. In one embodiment, this node may be a Vcc terminal. The TVS device further includes a snapback circuit connected in parallel to the Zener diode for conducting a transient voltage current with a snapback current-voltage (I-V) characteristic upon turning on of the snapback circuit And, the TVS device further includes a snapback suppressing circuit connected in series with the snapback circuit for conducting a current with an I-V characteristic complementary to the snapback-IV characteristic for clamping a snapback voltage.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
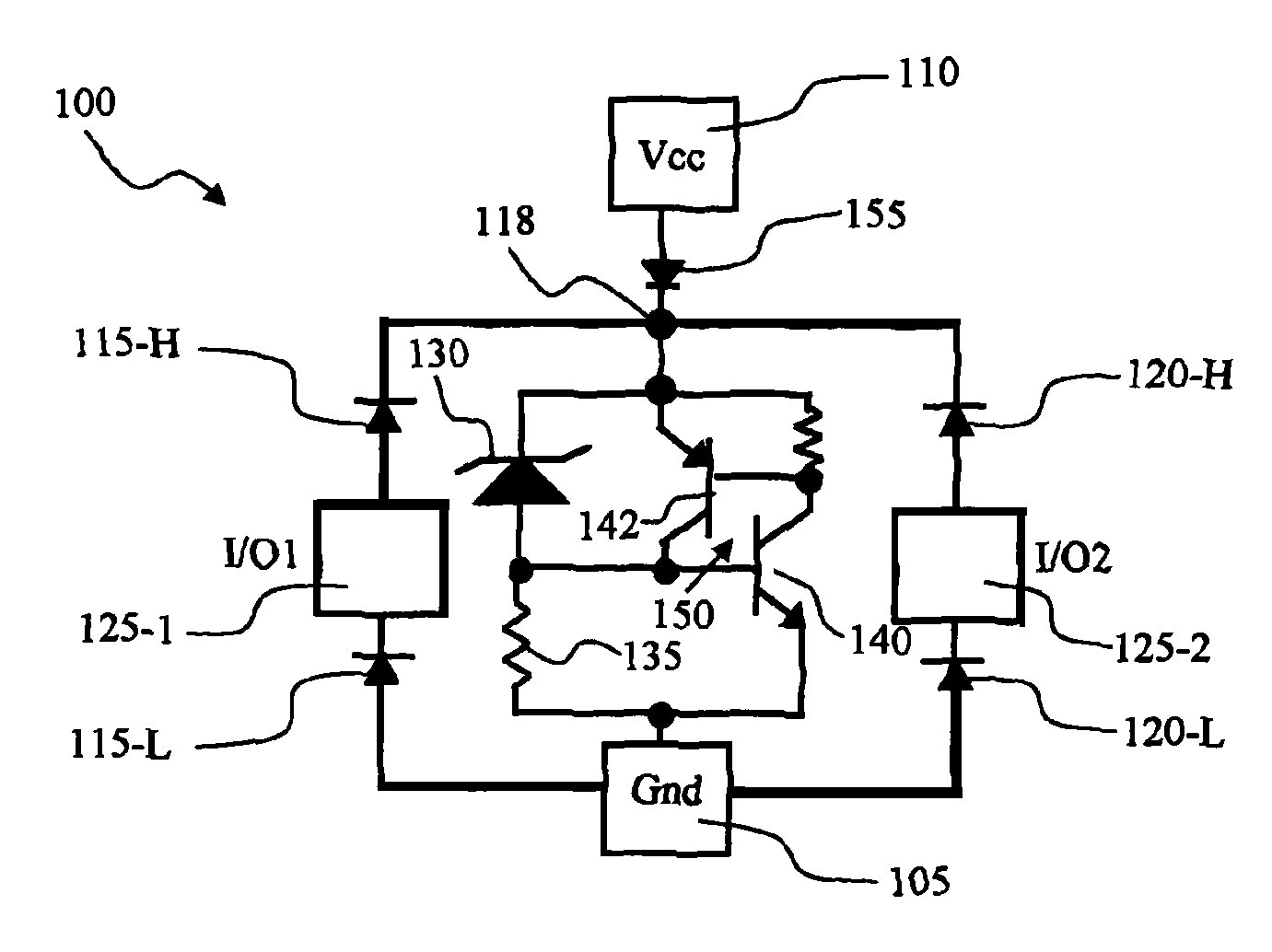
Symmetric blocking transient voltage suppressor (TVS) using bipolar transistor base snatch
A symmetrical blocking transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit for suppressing a transient voltage includes an NPN transistor having a base electrically connected to a common source of two transistors whereby the base is tied to a terminal of a low potential in either a positive or a negative voltage transient. The two transistors are two substantially identical transistors for carrying out a substantially symmetrical bi-directional clamping a transient voltage. These two transistors further include a first and second MOSFET transistors having an electrically interconnected source. The first MOSFET transistor further includes a drain connected to a high potential terminal and a gate connected to the terminal of a low potential and the second MOSFET transistor further includes a drain connected to the terminal of a low potential terminal and a gate connected to the high potential terminal.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Symmetric blocking transient voltage suppressor (TVS) using bipolar transistor base snatch
A symmetrical blocking transient voltage suppressing (TVS) circuit for suppressing a transient voltage includes an NPN transistor having a base electrically connected to a common source of two transistors whereby the base is tied to a terminal of a low potential in either a positive or a negative voltage transient. The two transistors are two substantially identical transistors for carrying out a substantially symmetrical bi-directional clamping a transient voltage. These two transistors further include a first and second MOSFET transistors having an electrically interconnected source. The first MOSFET transistor further includes a drain connected to a high potential terminal and a gate connected to the terminal of a low potential and the second MOSFET transistor further includes a drain connected to the terminal of a low potential terminal and a gate connected to the high potential terminal.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
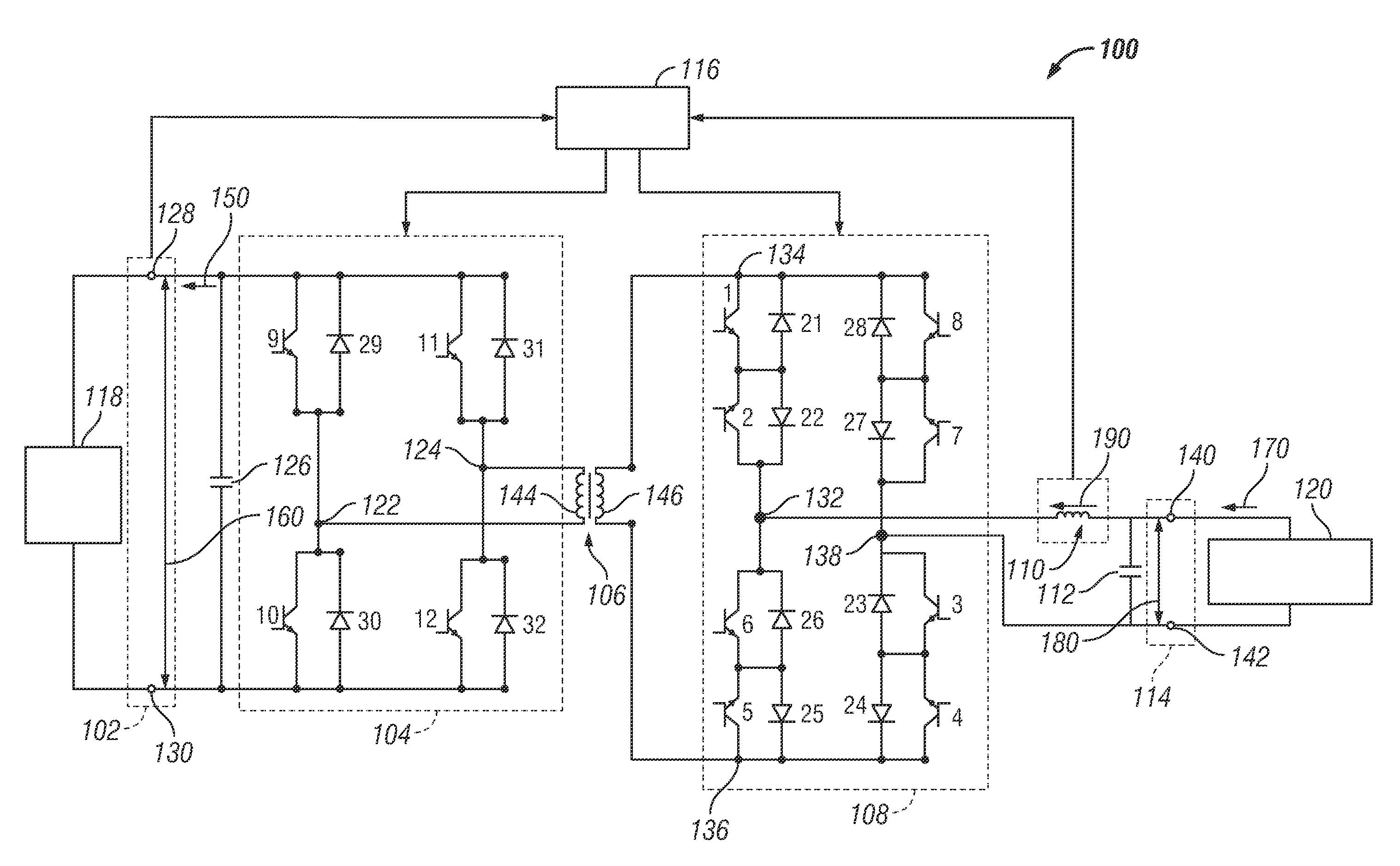
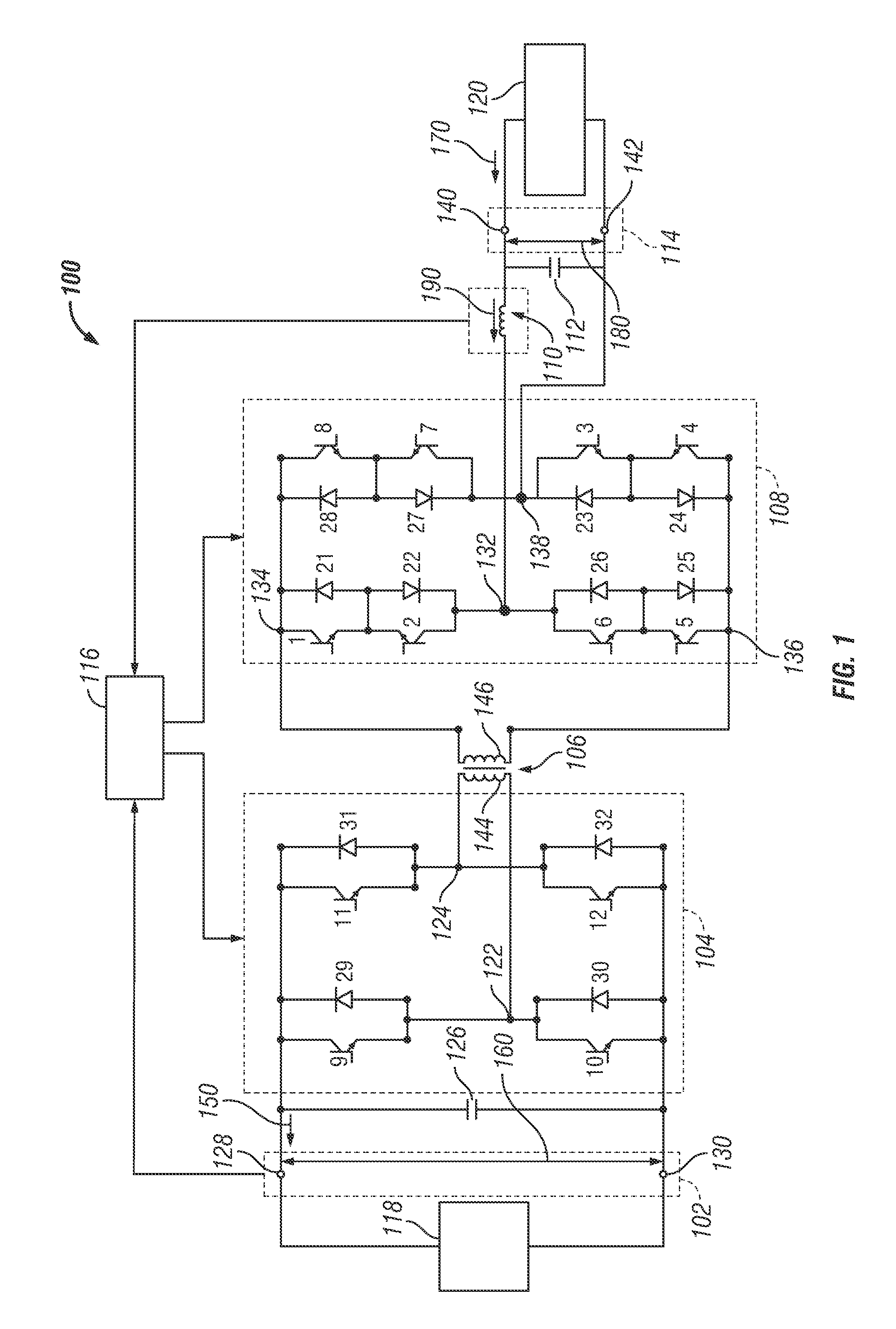
Systems and methods for reducing transient voltage spikes in matrix converters
Systems and methods are provided for delivering energy using an energy conversion module that includes one or more switching elements. An exemplary electrical system comprises a DC interface, an AC interface, an isolation module, a first conversion module between the DC interface and the isolation module, and a second conversion module between the AC interface and the isolation module. A control module is configured to operate the first conversion module to provide an injection current to the second conversion module to reduce a magnitude of a current through a switching element of the second conversion module before opening the switching element.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
A Transient Voltage Suppressor Based on Zener Diode
InactiveCN102290419AShort response timeHigh surge absorption capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesZener diodeParasitic capacitance
The invention discloses a transient voltage suppressor based on a Zener diode, which comprises an N substrate layer, wherein a first P+ epitaxial region, a second P+ epitaxial region, an N+ buried layer, a four P+ epitaxial region and a fifth P+ epitaxial region are sequentially arranged on the N substrate layer from left to right; a first P- well and a third P- well are respectively arranged on the second P+ epitaxial region and the fourth P+ epitaxial region; a third P+ epitaxial region, a second P- well and a third N+ active injection region are sequentially arranged on the N+ buried layerfrom bottom to top; a first P+ active injection region and a fourth P+ active injection region are respectively arranged on the first P+ epitaxial region and the five P+ epitaxial region; and an N+ active injection region and a P+ active injection area are respectively arranged on the first P-well and the third P-well in a corresponding manner. According to the transient voltage suppressor, the parasitic capacitance of the TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) is further reduced by adopting a composite structure of the Zener diode and a low capacity diode; and therefore, the transient voltage suppressor can be widely applied to certain portable equipment and high-speed interfaces for static electricity protection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-voltage transient voltage suppressor chip and production process
ActiveCN102543722AImprove pressure resistanceImprove anti-surge performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to a high-voltage transient voltage suppressor chip and a production process. The high-voltage transient voltage suppressor chip is of a chip structure with increased auxiliary puncture diffusion junctions, a main junction of the chip enables the puncture voltage to reach 250V-400V, the puncture voltage of an auxiliary PN (positive-negative) junction designed in a region nearby a chip mesa trench is higher than that of the main junction so that the main junction is punctured firstly, leakage current is distributed in a main junction region, and the auxiliary junction region is not punctured. Therefore, the problems of high electricity leakage, low puncture voltage and easiness in damage when a high-voltage chip is produced by a single diffusion junction structure are solved, voltage resistance of a high-voltage transient voltage suppressor is improved, and anti-surge capacity and reliability of the transient voltage suppressor are enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGHUAN SEMICON CO LTD
Low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS) with reduced clamping voltage
ActiveUS8698196B2Improve clamping effectReduce capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceEngineering
A low capacitance transient voltage suppressor with reduced clamping voltage includes an n+ type substrate, a first epitaxial layer on the substrate, a buried layer formed within the first epitaxial layer, a second epitaxial layer on the first epitaxial layer, and an implant layer formed within the first epitaxial layer below the buried layer. The implant layer extends beyond the buried layer. A first trench is at an edge of the buried layer and an edge of the implant layer. A second trench is at another edge of the buried layer and extends into the implant layer. A third trench is at another edge of the implant layer. Each trench is lined with a dielectric layer. A set of source regions is formed within a top surface of the second epitaxial layer. The trenches and source regions alternate. A pair of implant regions is formed in the second epitaxial layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com