Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Differential heating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Differential heating. [‚dif·ə′ren·chəl ′hēd·iŋ] (metallurgy) A thermal gradient caused as heating takes place; can result in a distribution of stress in a material.
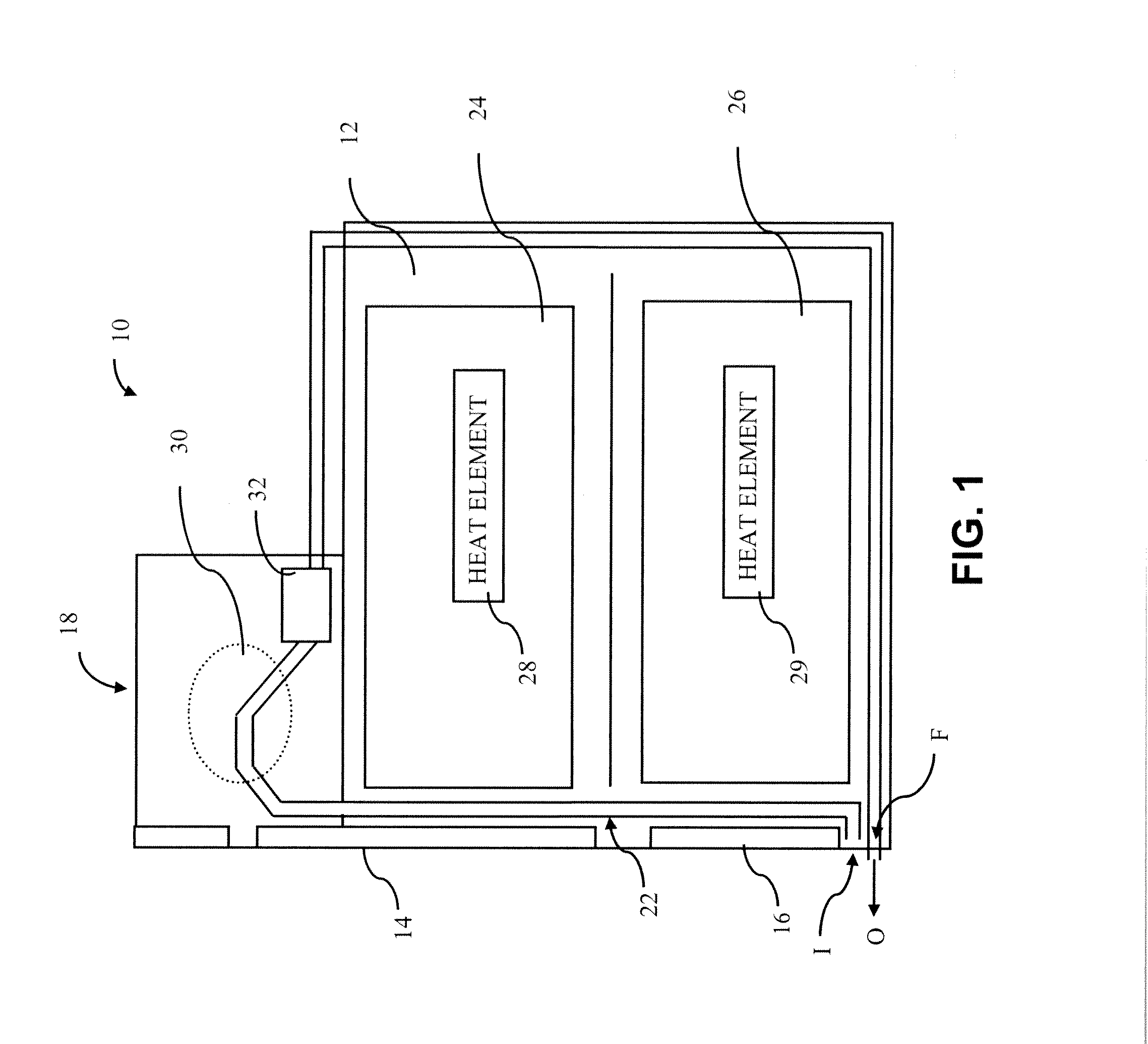
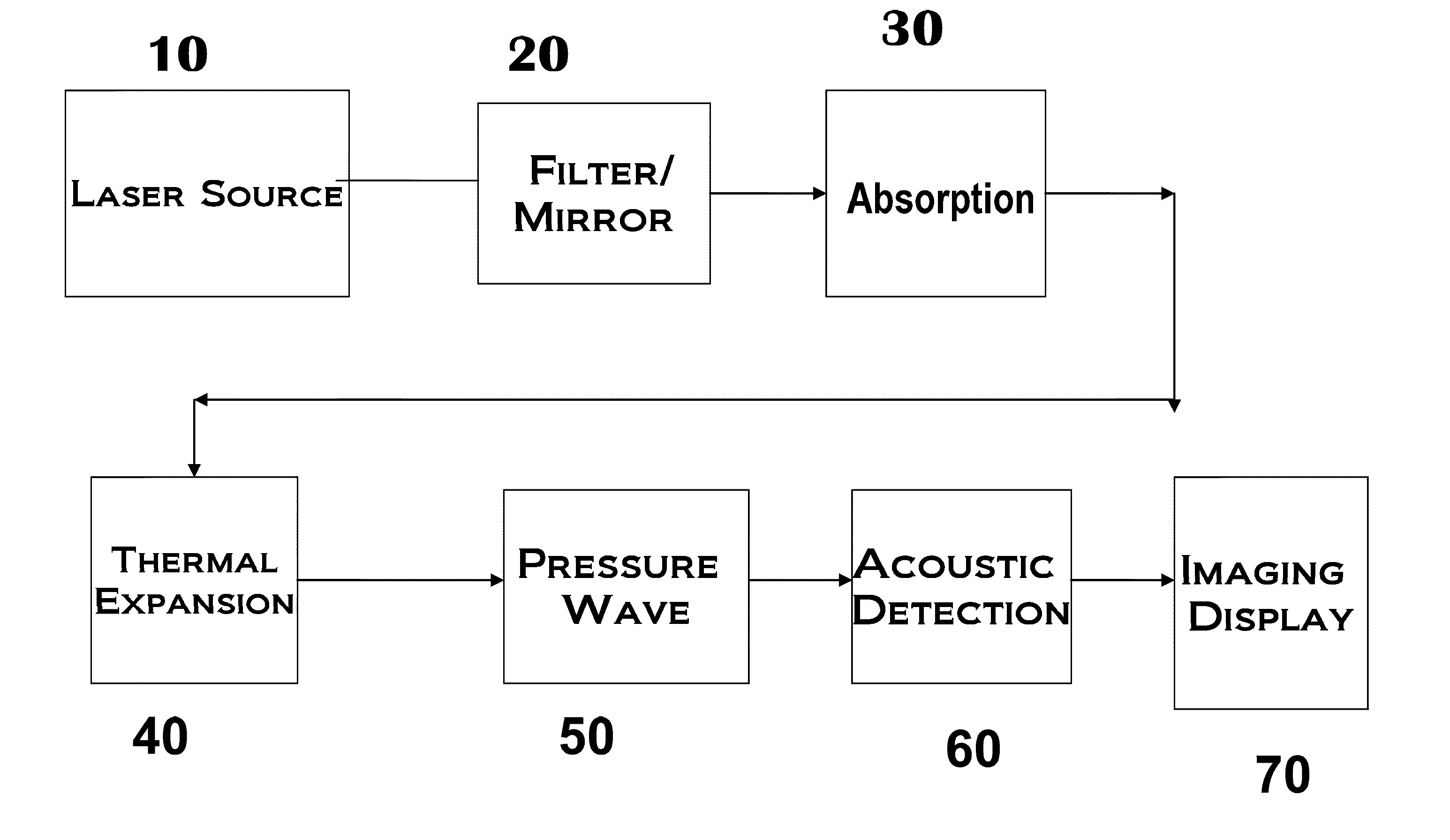
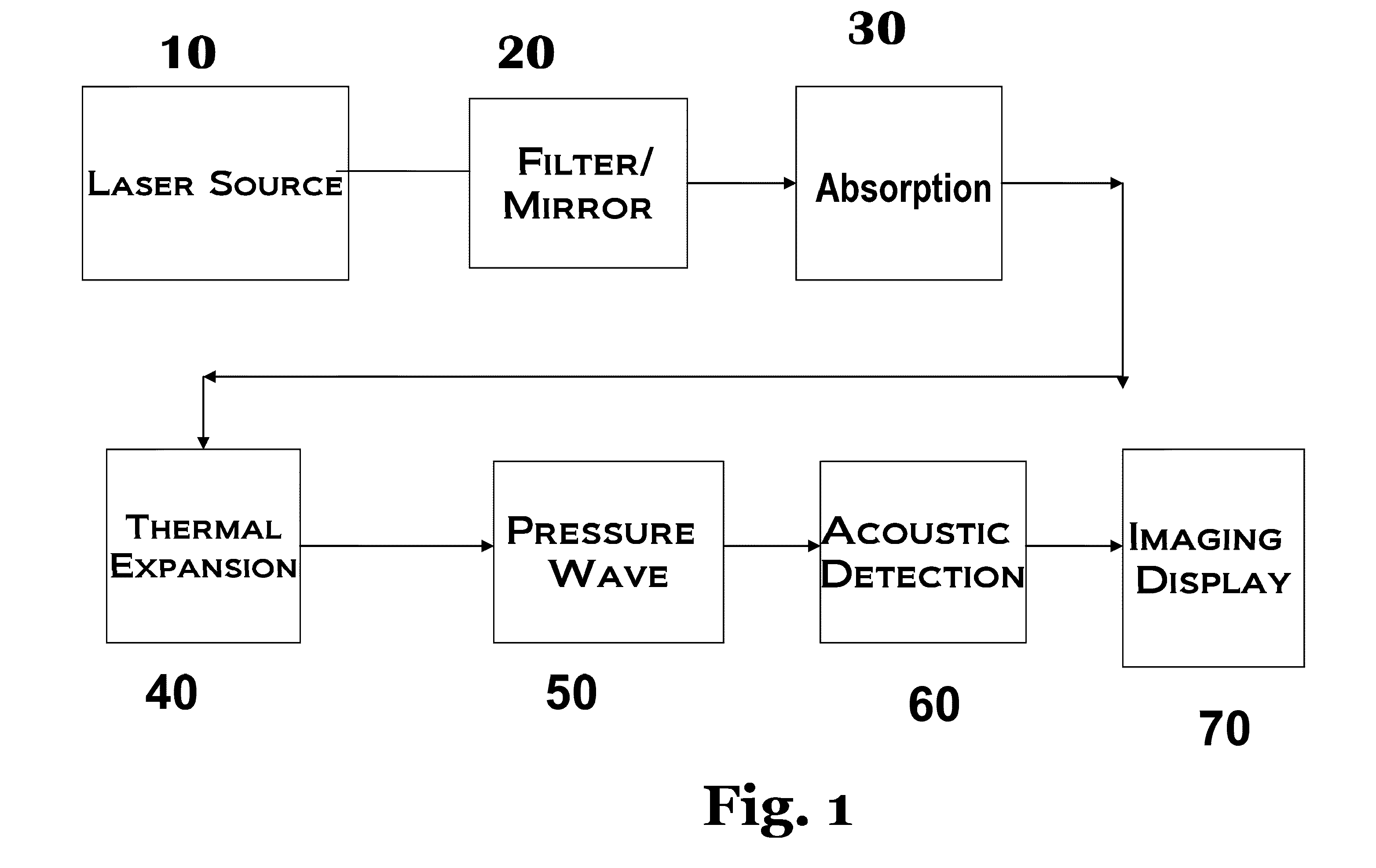
Method for measuring thermal properties using a long-wavelength infrared thermal image
InactiveUS7171328B1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionSingle imageLongwave
A method for estimating the thermal properties of surface materials using long-wavelength thermal imagery by exploiting the differential heating histories of ground points in the vicinity of shadows. The use of differential heating histories of different ground points of the same surface material allows the use of a single image acquisition step to provide the necessary variation in measured parameters for calculation of the thermal properties of surface materials.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for producing iridescent solid nanocrystalline cellulose films incorporating patterns
A new method to produce solid nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) films containing patterns by differential heating of aqueous suspensions of NCC has been discovered. When acid-form NCC suspensions are dried by heating to temperatures above 50° C., darkening of the NCC can occur, while neutral forms of NCC can produce iridescent chiral nematic films by heating to temperatures up to 105° C. Placing materials of different thermal conductivity beneath the container containing an evaporating NCC suspension results in watermark-like patterns of different iridescent color imprinted within the film structure. Other colloidal rod-like particles can be employed in place of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC), for example chitin or chitosan.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Nanoparticle-enhanced phase change materials (NEPCM) with great potential for improved thermal energy storage
InactiveUS20090236079A1Increased heat release rateFunction increaseMaterial nanotechnologyHeat storage plantsThermal energyThermal energy storage
Improved functionality of phase change materials (PCM) through dispersion of nanoparticles is described. The resulting nanoparticle-enhanced phase change materials (NEPCM) exhibit enhanced thermal conductivity in comparison to the base material. Starting with steady state natural convection within a differentially-heated square cavity that contains a nanofluid (water plus copper nanoparticles), the nanofluid is allowed to undergo solidification. Partly due to increase of thermal conductivity and also lowering of the latent heat of fusion, higher heat release rate of the NEPCM in relation to the conventional PCM is observed. The predicted increase of the heat release rate of the NEPCM is a clear indicator of its great potential for diverse thermal energy storage applications.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Tissue processor
Owner:GENERAL DATA
Frequency selected, variable output inductor heater system
InactiveUS6316754B1Rapid temperature changeMaintain temperatureCoil arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonanceInductor
An induction heating systems using a plurality of zones in a coil provides selective heating control for better uniformity especially for semiconductor and other thin film processing applications. By arranging the zones to have different resonance frequencies, the power supply may control the various zones by altering its frequency output. The power supply may also act to control the differential heating by switching among zones in conjunction with the frequency control, by sweeping through a variety of frequencies, by simultaneously providing power over different frequencies, by altering the residence time at each frequency, or by outputting different powers to each frequency or the like. Each zone may thus be tuned as appropriate to achieve the desired induction heating characteristic.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
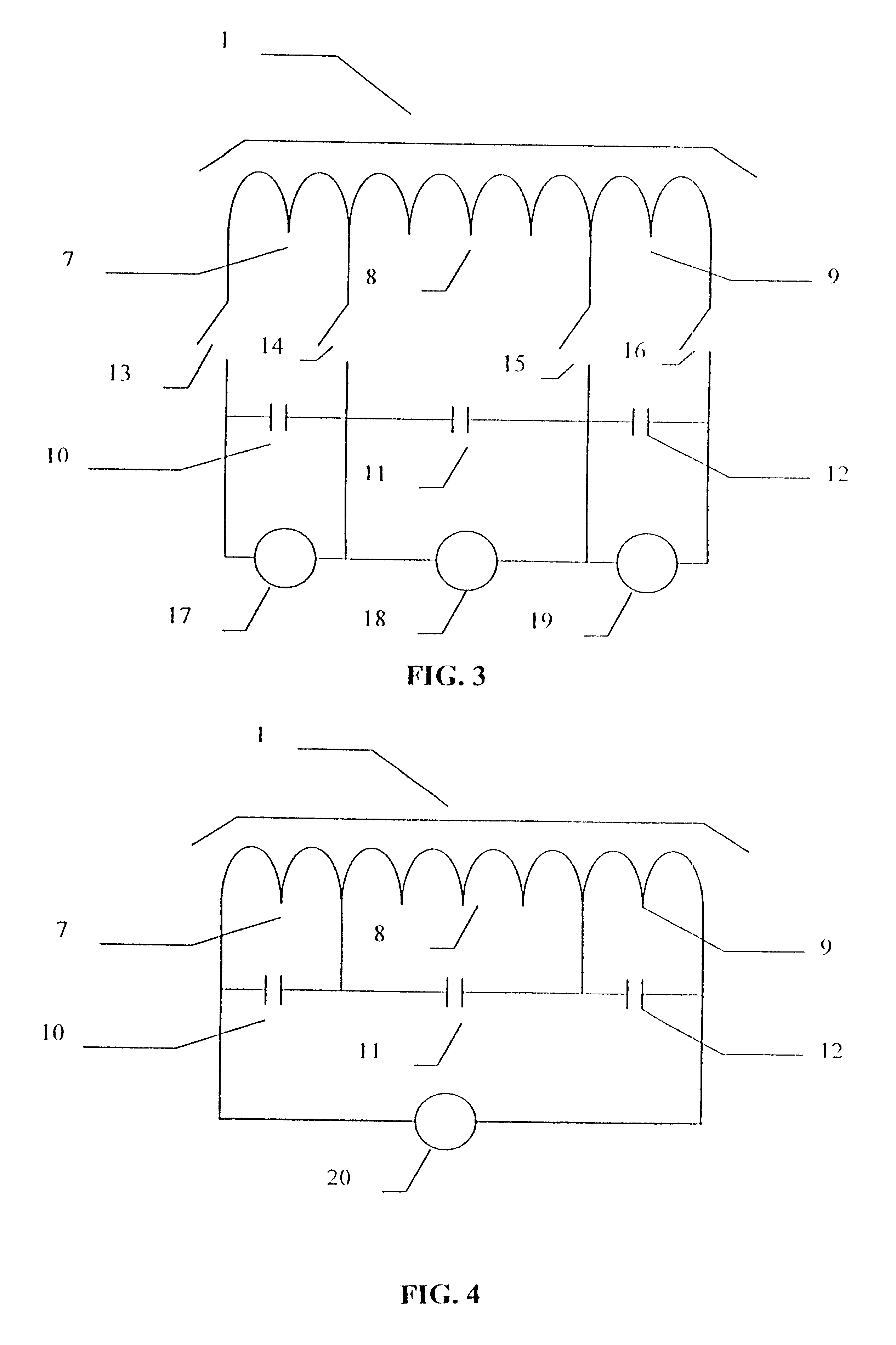
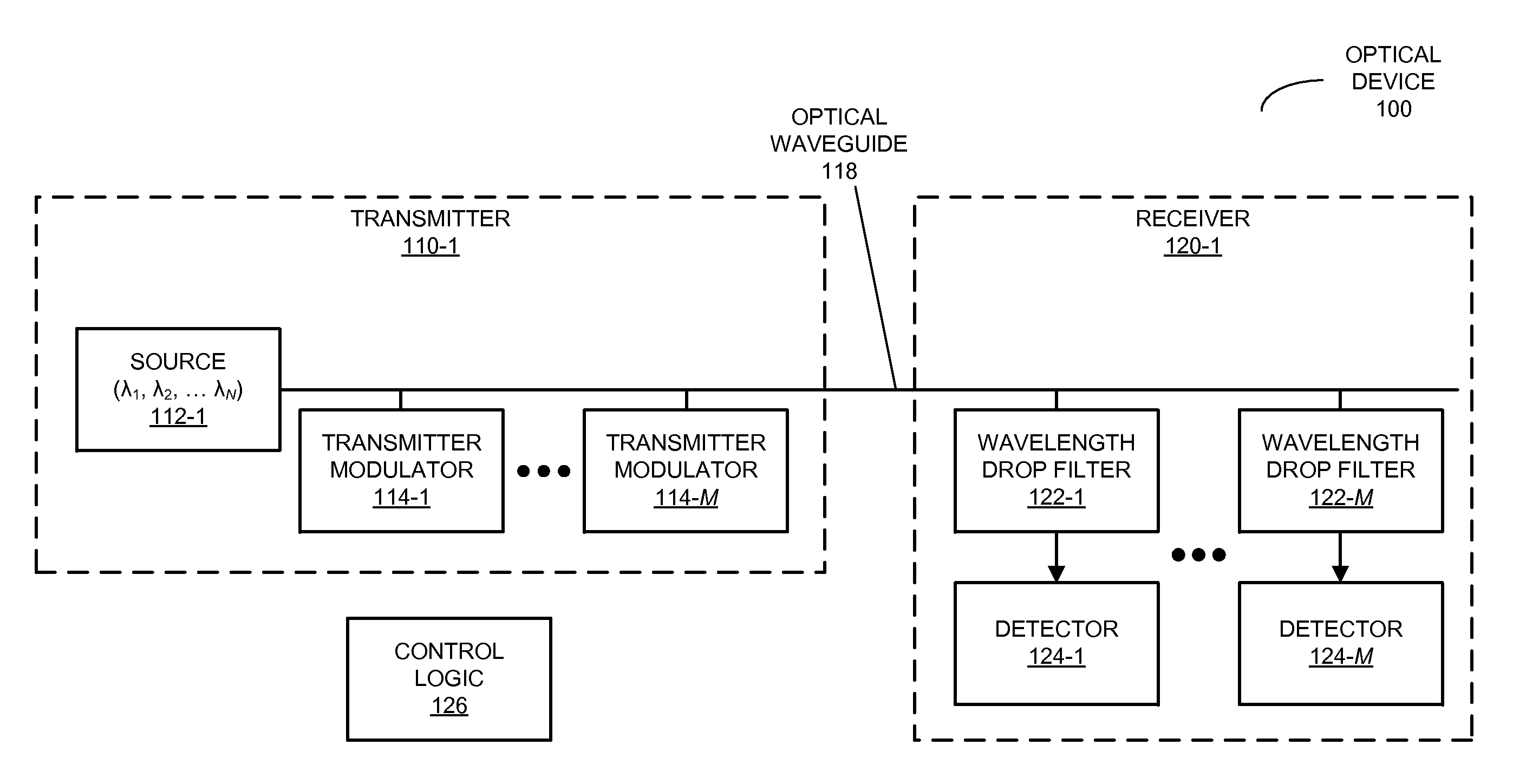
Optical device with reduced thermal tuning energy
ActiveUS20100329685A1Weaken energyEasy thermally tuneWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersCarrier signalEngineering
An optical device that includes multiple optical modulators having actual operating wavelengths at a given temperature is described. Because of differences between the actual operating wavelengths and target operating wavelengths of the optical modulators, heating elements may be used to thermally tune the optical modulators so that the actual operating wavelengths match corresponding carrier wavelengths in a set of optical signals. Furthermore, control logic in the optical device may assign the optical modulators to the corresponding carrier wavelengths based at least on differences between the carrier wavelengths and the actual operating wavelengths, thereby reducing an average thermal tuning energy associated with the heating elements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Quenching method for integral cast steel supporting roll
ActiveCN101698902ALow tensile strengthHigh hardnessFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlSlow rotationHardness
The invention relates to a quenching method of an integral cast steel supporting roll, which is an improvement of the quenching method of the working layer of the integral cast steel supporting roll, and the method is characterized in that the integral heating of the supporting roll comprises the following steps: first, heating the quenched and tempered supporting roll according to a heating rate of less than or equal to 20 DEG C / h to the temperature which is 50-100 DEG C below the cotectic curve temperature, and keeping temperature for 13D-20D; transferring the supporting roll into a differential heating furnace, quickly heating the supporting roll according to the heating rate of greater than or equal to 250 DEG C / h under slow rotation until the surface temperature is greater than or equal to the quenching temperature, and keeping temperature until the thermoosmosis thickness is greater than or equal to the required depth of the hardening layer; transferring the roll into a water quenching machine, carrying out rotating water spray quenching when the surface temperature is greater than or equal to 850 DEG C at the cooling rate of greater than or equal to 2 DEG C / s for the spray quenching of the roll, and stopping spraying water when the surface temperature is less than or equal to 220 DEG C; and transferring the roll into a heating furnace for tempering treatment to obtain the roll of which the surface hardness is 55-75HSD, the uniformity of the surface hardness is less than or equal to + / -1HSD, the radial hardness drop of the hardening layer is less than or equal to 0.5HSD / cm, and the tensile strength of the hardening layer is greater than or equal to 1200MPa. Compared with the prior art, the invention has high hardness of the working layer, good hardness uniformity, good hardening capacity, controllable depth of the hardening layer and small radial hardness drop.
Owner:JIANGSU GONGCHANG ROLL
Polishing pad and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20070042693A1Avoid contactPrevent materialOther chemical processesAbrasion apparatusBiomedical engineeringPolymer
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a polishing pad with embedded polymeric capsules useful for planarizing a substrate in a CMP process using a polishing composition. The method reduces non-uniformity of the polishing pad due to capsule floating, differential heating and capsule expansion by the use of novel capsule materials. The method also increases the efficiency of the manufacturing process by reducing the number of defective products and reducing waste.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Flip chip assembly method employing post-contact differential heating
InactiveUS20120217287A1Improve integritySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/cutting media/materialsRoom temperatureThermal expansion
A first substrate mounted to a bonder head and a second substrate mounted to a base plate are held at different elevated temperatures at the time of bonding that provide a substantially matched thermal expansion between the second substrate and the first substrate relative to room temperature. Further, the temperature of the solder material portions and the second substrate is raised at least up to the melting temperature after contact. The distance between the first substrate and the second substrate can be modulated to enhance the integrity of solder joints. Once the distance is at an optimum, the bonder head is detached, and the bonded structure is allowed to cool to form a bonded flip chip structure. Alternately, the bonder head can control the cooling rate of solder joints by being attached to the chip during cooling step.
Owner:IBM CORP
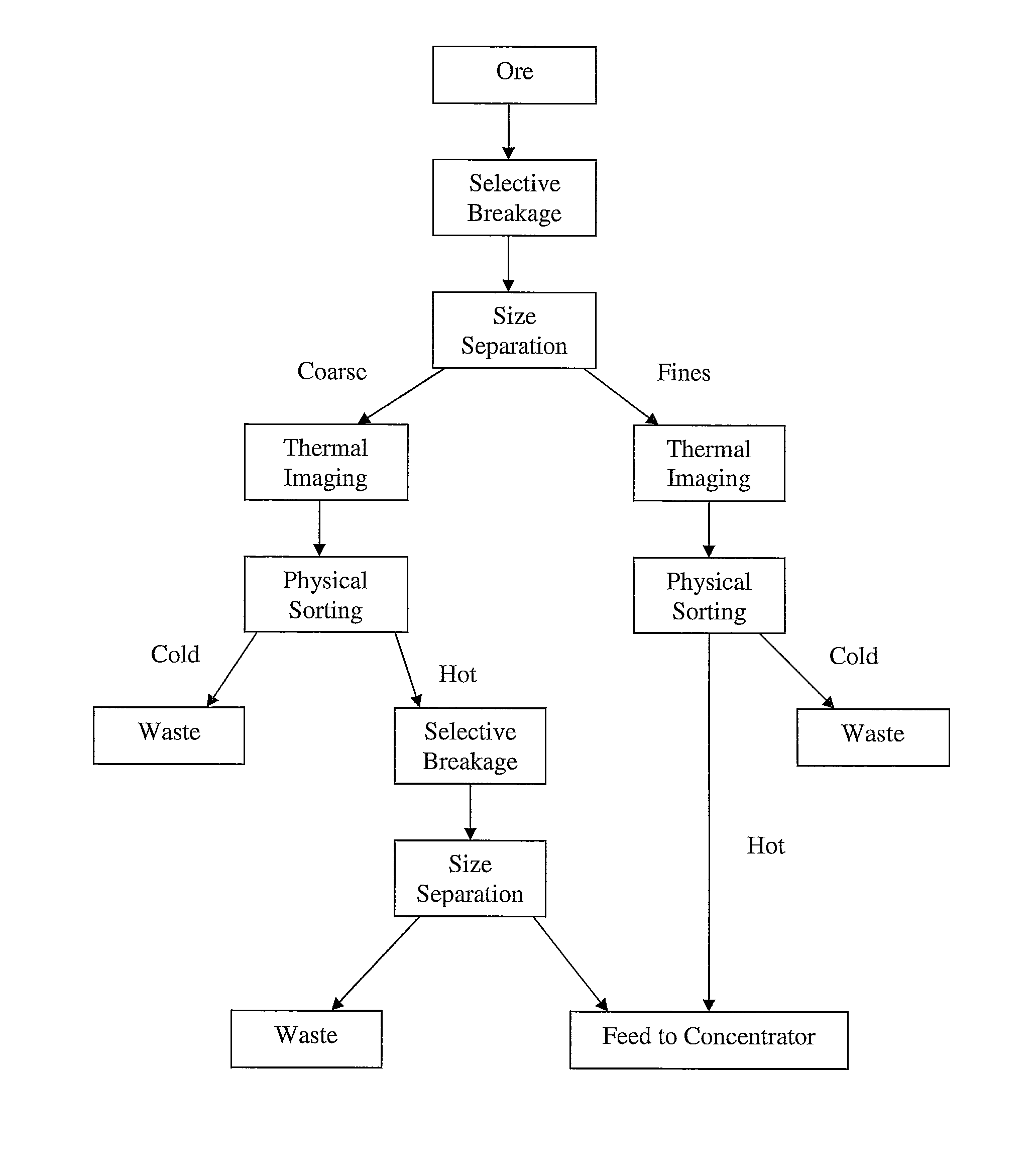
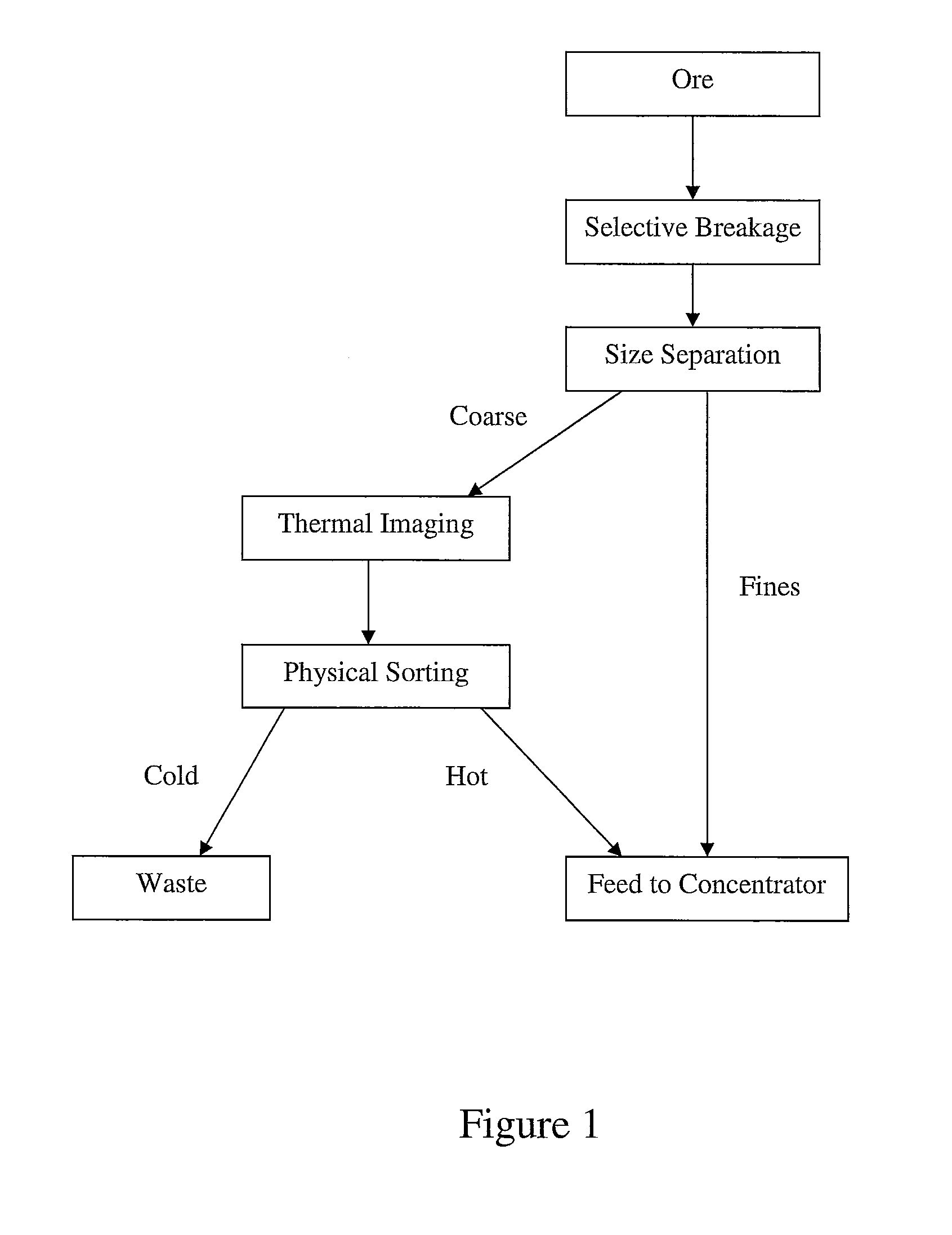
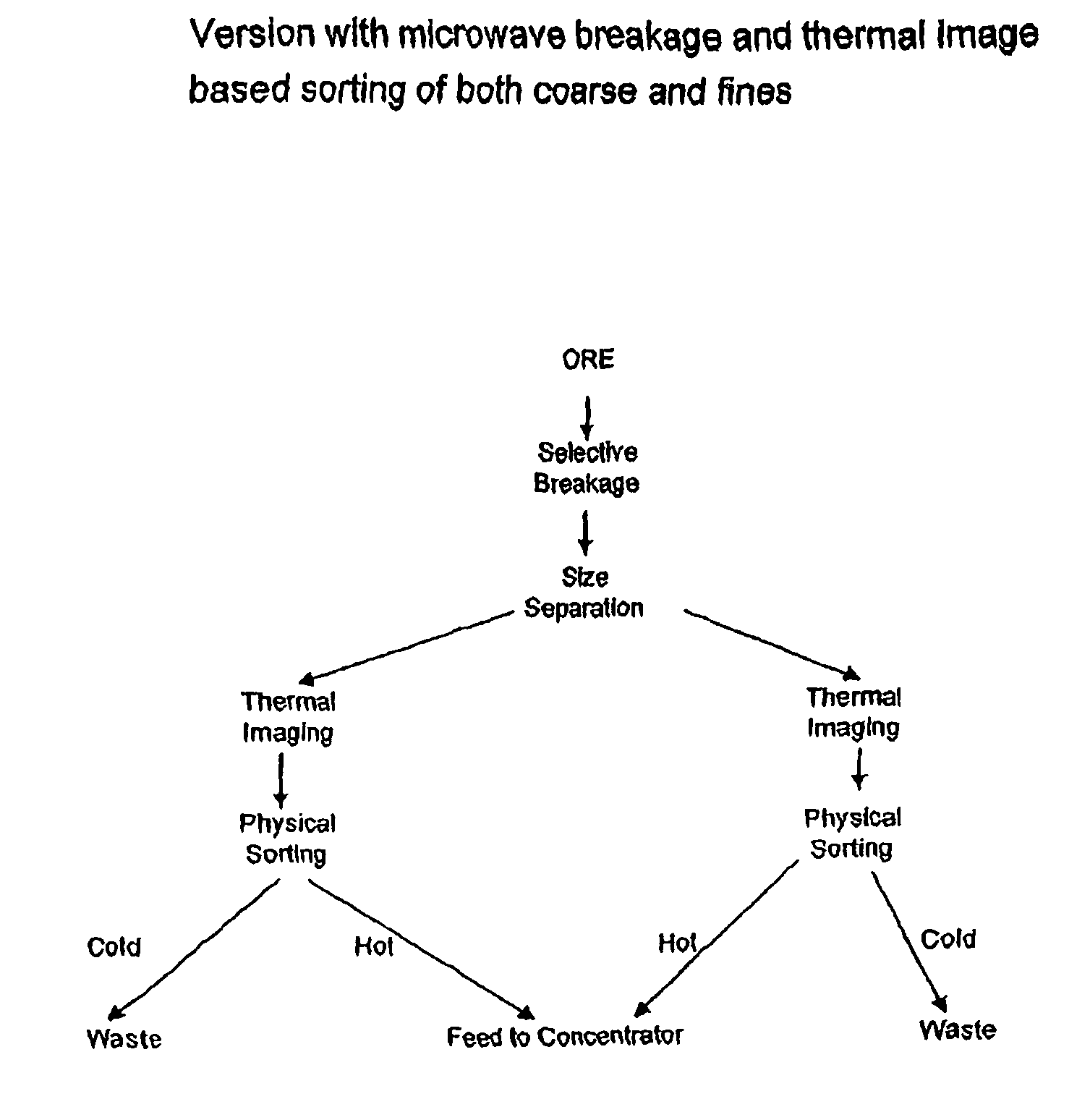
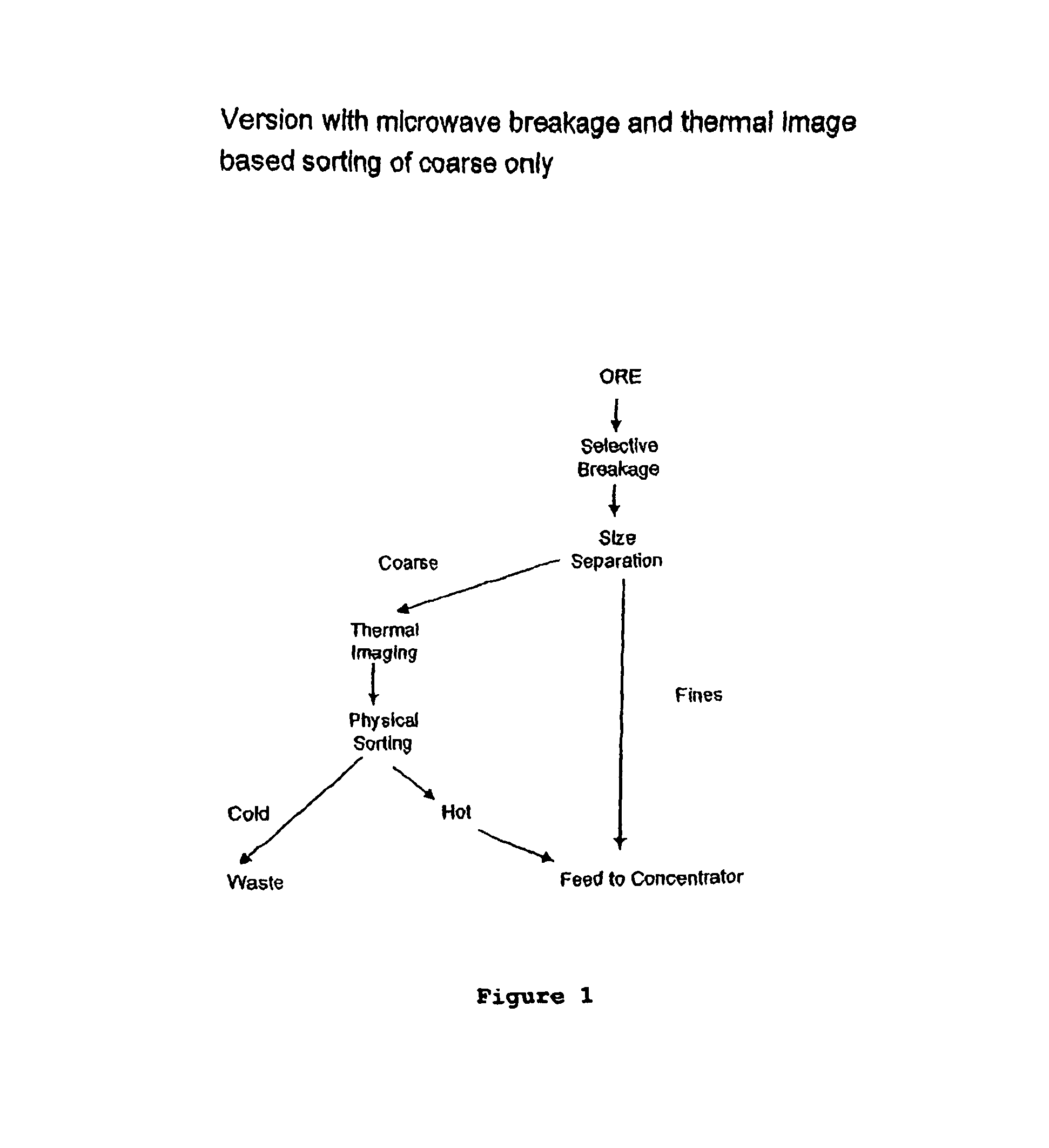
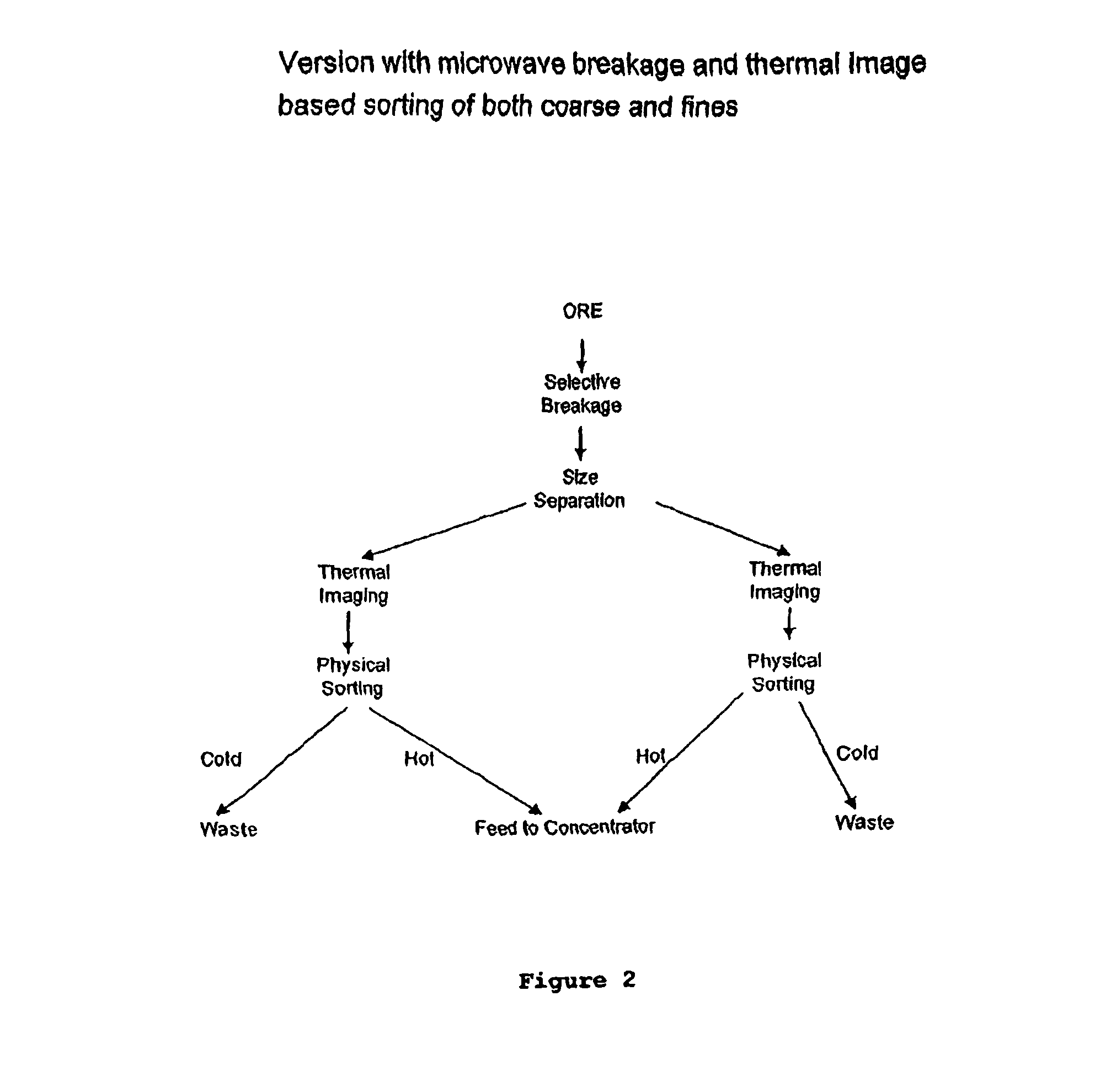
Sorting mined material
ActiveUS8820533B2Reduce the amount requiredMore capacityEarth material testingDifferential sedimentationMechanical engineeringThermography
A method of sorting mined material for subsequent processing to recover valuable material, such as valuable metals, from the mined material is disclosed. The method includes a combination of selective breakage of mined material, for example, by using microwaves and / or high pressure grinding rolls, subsequent size separation, and then particle sorting of a coarse fraction of the separated material based on differential heating and thermal imaging.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
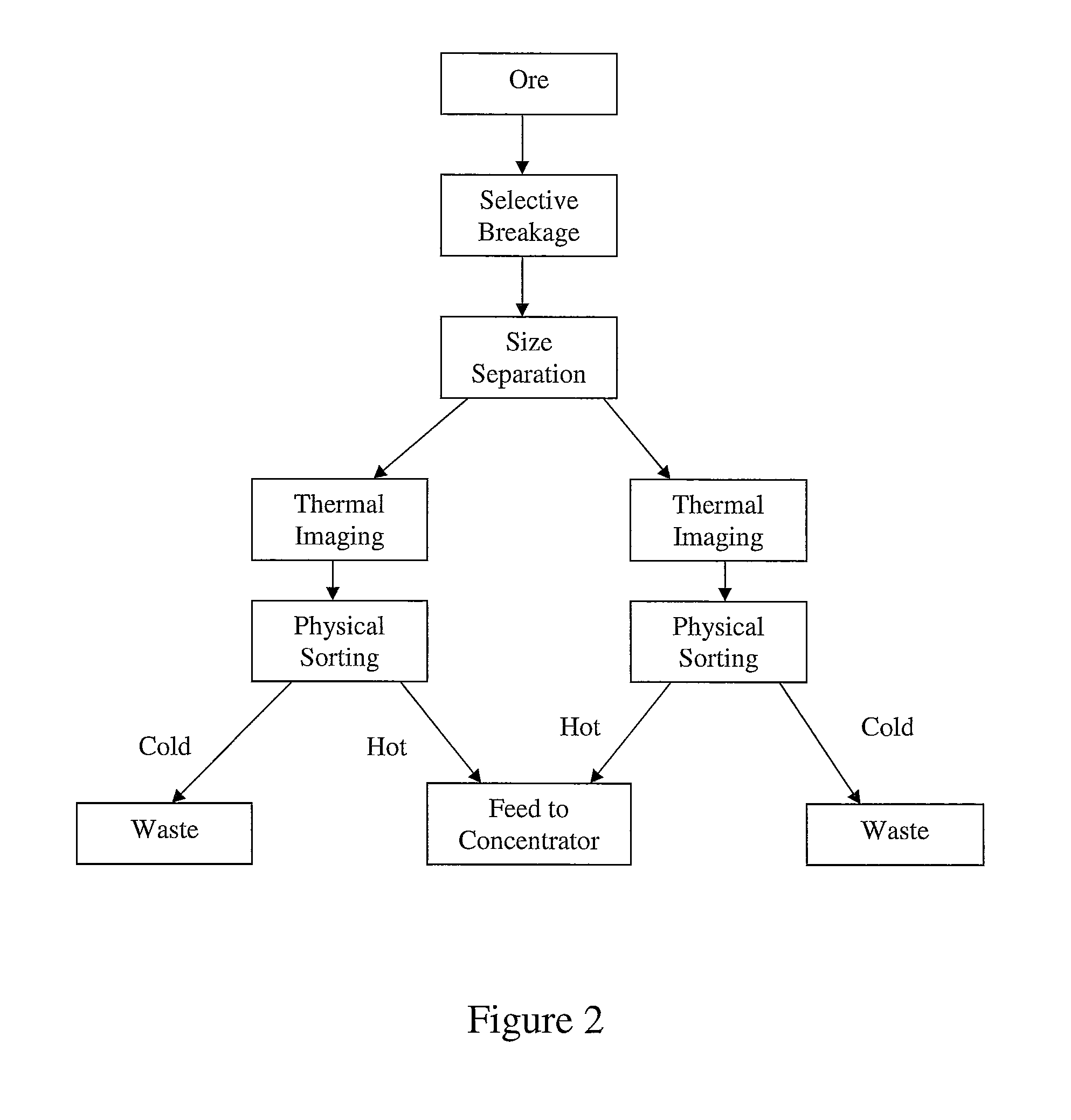
Sorting mined material
ActiveUS8240480B2Minimize powerMaximises thermal cyclingRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsEarth material testingMicrowaveParticle sorting
A method of sorting mined material for subsequent processing to recover valuable material, such as valuable metals, from the mined material is disclosed. The method includes a combination of selective breakage of mined material, for example, by using microwaves and / or high pressure grinding rolls, subsequent size separation, and then particle sorting of a coarse fraction of the separated material based on differential heating and thermal imaging.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
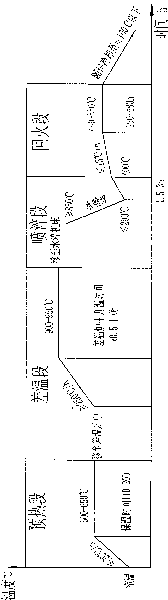
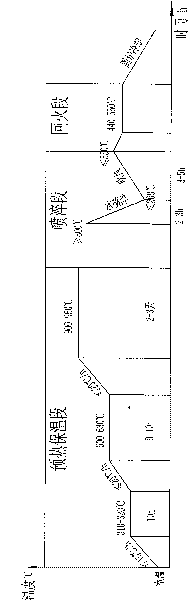
Differential temperature heat treatment method of minor-diameter high chromium cast-iron roll
ActiveCN103436679AImprove the heating effectHeat stableFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesFurnace temperatureAir–fuel ratio
The invention discloses a differential temperature heat treatment method of a minor-diameter high chromium cast-iron roll, which comprises the steps of roll neck bush welding, heat pretreatment, differential heating, precooling treatment, quenching & cooling, tempering treatment, roll neck bush removal and the like for the minor-diameter roll to achieve differential temperature heat treatment production of the minor-diameter roll. The method is simple and reasonable in technology; the roll is equipped with a roll neck bush, and an air-fuel ratio of a differential temperature furnace burner is adjusted, so that the heating capacity of a furnace is adaptive to the minor-diameter roll; the furnace temperature fluctuation range is greatly reduced; the heating and heat preservation stability is improved; and the heat treatment quality of the minor-diameter roll is improved.
Owner:SINOSTEEL XINGTAI MACHINERY & MILL ROLL
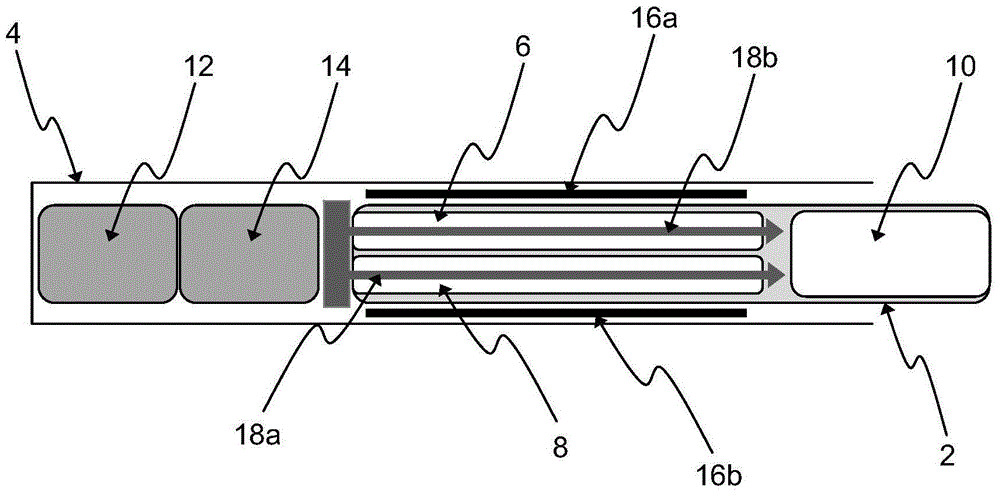
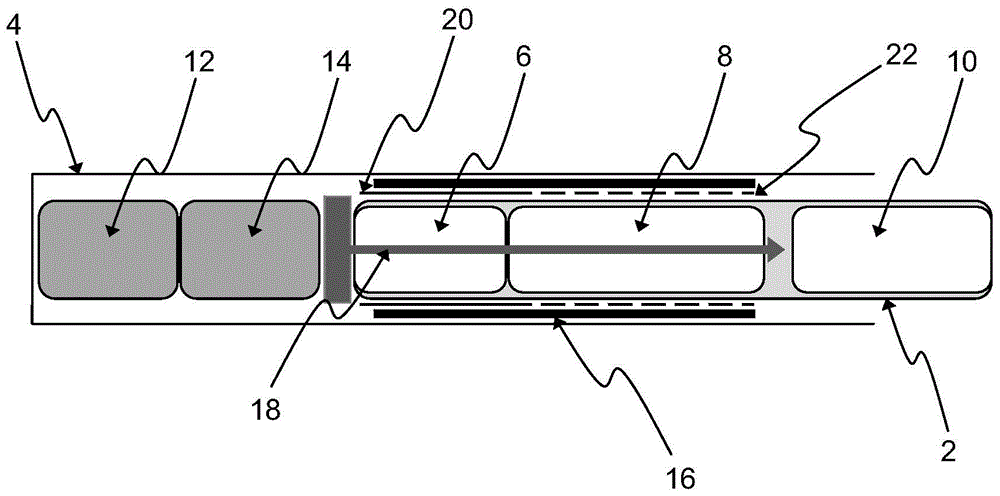
Aerosol-generating system with differential heating
ActiveCN104994757AImprove formation efficiencyThickenMedical devicesTobacco devicesDifferential heatingAerosol
An aerosol-generating system comprises an aerosol-generating article (2) and an aerosol-generating device (4). The aerosol-generating article (2) comprises: a first compartment (6) comprising a first one of a volatile delivery enhancing compound source and a medicament source; and a second compartment (8) comprising a second one of the volatile delivery enhancing compound source and the medicament source. The aerosol-generating device (4) comprises: a cavity configured to receive the first compartment (6) and the second compartment (8) of the aerosol-generating article (2); and an external heater (16, 16a, 16b) positioned about a perimeter of the cavity. The aerosol-generating device (4) is configured to heat the first compartment (6) and the second compartment (8) of the aerosol-generating article (2) so that first compartment (6) of the aerosol-generating article (2) has a lower temperature than the second compartment (8) of the aerosol-generating article (2).
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Heating arrangements for humidification systems
ActiveUS20150265796A1High price of raw materialSolve the real problemLighting and heating apparatusRespiratory masksPlastic materialsRespiratory humidifier
An electrically conductive plastic (ECP) material can be used to heat water in a reservoir of a respiratory humidifier to encourage heating and / or humidification of gases passing through the respiratory humidifier. The electrically conductive plastic material can at least in part overmould the base and / or walls of the chamber and / or the reservoir of the respiratory humidifier. The reservoir can also partially or fully be formed from the electrically conductive plastic material. Furthermore, the humidification system can be configured to create substantially equal or differential heating of water in the reservoir.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Heat actuated steering mount for maintaining frequency alignment in wavelength selective components for optical telecommunications
A simple and robust heat actuated steering device for use with mirrors and other optical components of optical telecommunications equipment is described, together with systems which implement such devices. The device uses differential heating between two legs of a flexured mount to allow tilting that can be used to steer an optical beam. Disturbances in the optical alignment, caused by temperature changes, of an optical device containing this component can be compensated by measuring the device temperature and using this to determine a command signal, for example as provided through a lookup table, to correct for device misalignment. Techniques for calibrating the device and establishing the correction data are also disclosed.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
Rolling mill support roll steel and heat treatment technology thereof
ActiveCN102796965AImproved accident resistanceImprove fatigue resistanceFurnace typesIncreasing energy efficiencyManganeseQuenching
The invention discloses a rolling mill support roll steel and a heat treatment technology of the rolling mill support roll steel. The steel comprises carbon, silicon, manganese, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, sulphur, phosphorus and the balance of iron and impurity not capable of being removed. The heat treatment technology of the rolling mill support roll steel comprises the following steps of: firstly, transporting a support roll into a car bottom furnace to be wholly preheated; clamping the support roll in an induction heating machine set, and driving a workpiece to rotate; arranging an inductor in the induction heating machine set, and spirally winding the inductor by a purple copper pipe; carrying out quick differential heating on the support roll by the inductor by controlling the control inductor; exactly controlling the temperature at a set temperature in the process of heating; when a roll body reaches to the set heating depth and temperature, quickly lifting the support roll into a spraying and quenching system from the induction heating machine set; and when the temperature of the support roll is reduced at 80-150 DEG C, lifting the support roll out of the spraying and quenching system. According to the heat treatment technology, the mechanical property of the support roll can be observably improved, and the service life of the support roll can be prolonged.
Owner:JIANGYIN RUNYUAN MACHINERY
Composite forming die and method for titanium alloy deep-cavity component
The invention provides a composite forming die and method for a titanium alloy deep-cavity component. The forming method includes the following steps that a hot-drawing forming die and a superplasticforming die are designed and machined according to the titanium alloy deep-cavity component, and the size of a round blank is determined; the hot-drawing forming die is mounted and positioned on a forming machine; aqueous graphite is sprayed to the flange position where an upper drawing die and a blank holder make contact with each other and the position where the round blank and a flange make contact with each other; differential heating of the hot-drawing forming die and preheating of the round blank are performed; die closing and drawing are performed on the hot-drawing forming die, and a preform is obtained; and the preform is placed in the superplastic forming die, and superplastic forming of deep-cavity component is performed. According to the composite forming die and method, through optimized design of the forming die and technological parameters, in combination with the unique technological process, precise forming of the titanium alloy specially-shaped deep-cavity component is realized, so that existing deep-cavity component forming technology bottlenecks are broken through, the defects of wrinkling and cracking are eliminated, the wall thickness uniformity is optimized,the product quality and yield are effectively increased, and the manufacturing and application requirements for specially-shaped components are met.
Owner:BEIJING HANGXING MACHINERY MFG CO LTD
Zone heating of specimen carriers
InactiveUS6949725B2Reduce resistanceLess heatBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringAlternating current
The present invention relates to heating of samples in specimen carriers, and more particularly to the heating of zones of a specimen carrier for differential heating of samples in a specimen carrier, including a specimen carrier in the form of a metallic sheet, in which a matrix of sample wells is incorporated, apparatus for applying electrical heating current through the carrier, having a plurality of electrical current sources, each connected in series across the carrier and together providing a variety of different possible current flow paths whereby localised regions of the carrier may be selectively heated. The current applied is either alternating current, or direct current.
Owner:BJ'S WHOLESALE CLUB
Flip chip assembly method employing post-contact differential heating
InactiveUS8381966B2Improve integritySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/cutting media/materialsRoom temperatureThermal expansion
A first substrate mounted to a bonder head and a second substrate mounted to a base plate are held at different elevated temperatures at the time of bonding that provide a substantially matched thermal expansion between the second substrate and the first substrate relative to room temperature. Further, the temperature of the solder material portions and the second substrate is raised at least up to the melting temperature after contact. The distance between the first substrate and the second substrate can be modulated to enhance the integrity of solder joints. Once the distance is at an optimum, the bonder head is detached, and the bonded structure is allowed to cool to form a bonded flip chip structure. Alternately, the bonder head can control the cooling rate of solder joints by being attached to the chip during cooling step.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thermal distortion compensation for laser mirrors
InactiveUS20090034577A1Deteriorating distortionLess concaveMirrorsOptical resonator shape and constructionCopperSolar mirror
A laser mirror assembly is disclosed with improved pointing stability. An elongated mirror includes a concave reflecting portion. A pair of elongated planar portions extend parallel to the concave reflecting portion on either side thereof. The planar portions are stepped down from the reflecting portion. The mirror is formed from copper. A pair of stainless steel strips are connected to planar portions. The bimetallic effect between the copper mirror and the stainless steel strips operates to counteract the warping of the mirror due to differential heating effects which arise during operation. In an alternate embodiment, a pair of aluminum strips are mounted on the rear surface of the mirror.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Appliance airflow detection using differential heating of electronic devices
ActiveUS20130025364A1Power dissipationContinuous operationTobacco treatmentVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringThermistor
Apparatus and methods are disclosed to measure airflow within a chassis-cooling pathway of an appliance. The rate of airflow is determined based on the differential heating among a pair of sensor devices, such as thermistors, transistors, diodes or resistive thermal devices operating at distinctly different power levels. The appliance utilizes the calculated airflow rate to perform safety-related tasks, such as de-energizing heating elements when low or no airflow is detected.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
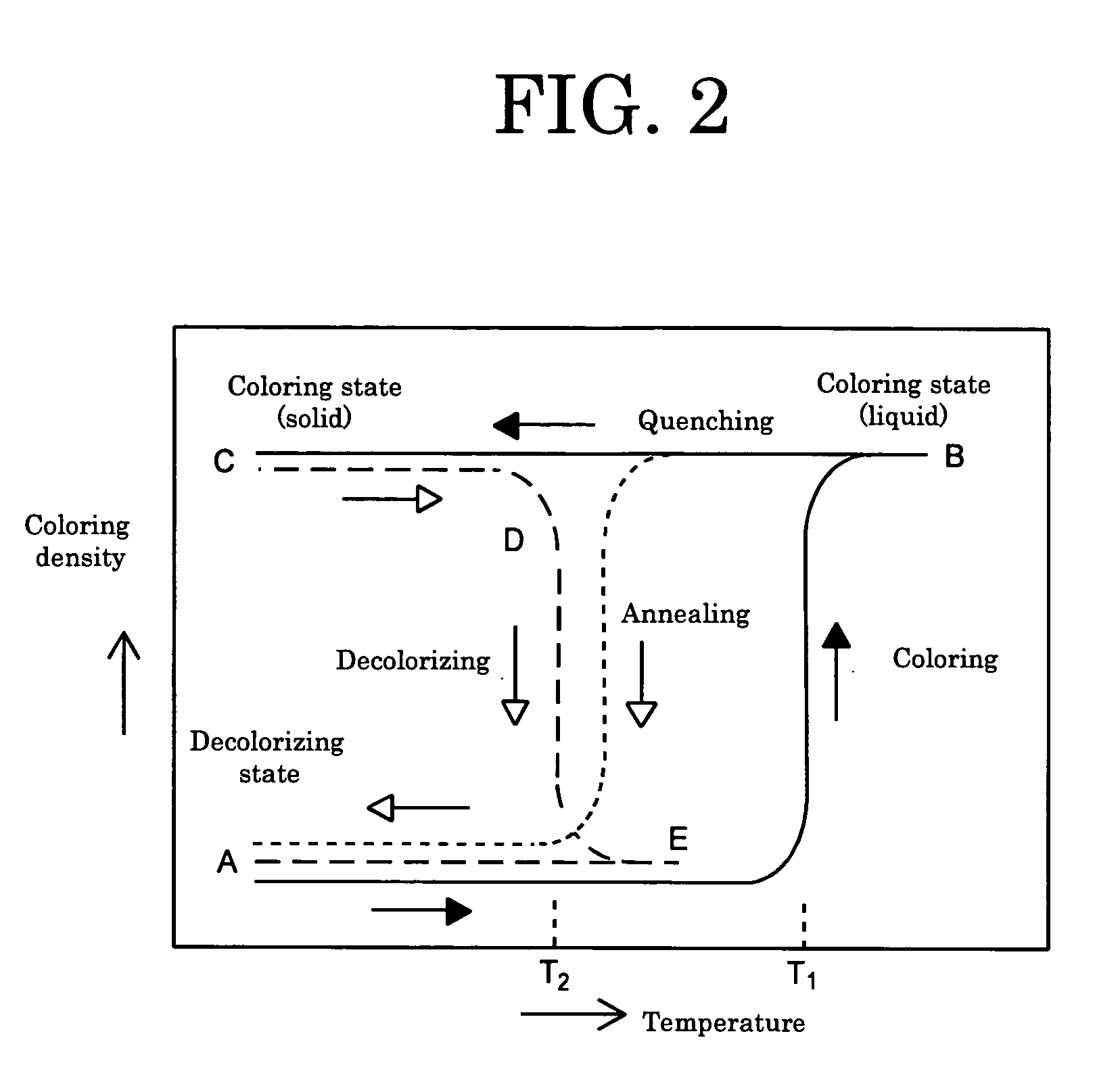
Information recording-displaying card, image processing method using same, and image processor
InactiveUS20050170961A1Excellent in embossabilityEasy scrapingDecorative surface effectsSynthetic resin layered productsRecording layerHeating temperature
An information recording-displaying card, includes: core sheet; and over sheet bonded to core sheet, including: a support including an amorphous polyester resin, and a reversible thermosensitive recording layer on the support, including: an electron-donating coloring compound, and an electron-accepting compound. The reversible thermosensitive recording layer is capable of forming coloring state and decolorizing state, with difference in at least one of the following: heating temperature, and cooling rate after heating. The over sheet is embossable in upper portion thereof, functions as image displaying section, and meets the following conditions (A), (B) and (C): (A) (over sheet's upper limit temperature for erasing−30° C.)>(over sheet's temperature of storage elasticity E′ (1.0 E+08) Pa), (B) 10 μm or less of surface waviness WCM, and (C) 1.0 E+02 Pa≦(storage elasticity E′ of reversible thermosensitive over sheet at 180° C.)≦5.0 E+07 Pa.
Owner:RICOH KK
Power generation device and method
InactiveUS20130133325A1Reduce heat lossIncrease speedGas turbine plantsWind motor combinationsEngineeringTurbine
A power generation device includes an enclosed circuit through which a working medium circulates. The working medium is heated at a first location in the enclosed circuit, and cooled at a second location. The differential heating and cooling causes the working medium to circulate within the enclosed circuit. The circulating medium is used to drive a turbine, which in turn may drive an electric generator.
Owner:MIP
Methods of forming a multilayer capping film to minimize differential heating in anneal processes
InactiveUS20080242038A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDifferential heatingElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:INTEL CORP
Single Stage Glass Lamination Apparatus and Process
A glass sheet assembly including a first glass sheet arranged in an opposing parallel configuration with respect to a second glass sheet is provided, with a heat sensitive layer of adhesive laminating film disposed between the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet, the glass sheet assembly having a leading edge and a trailing edge and being of a fixed length and width, the laminating film having a bonding temperature at which melting of the laminating film is initiated. The glass sheet assembly is heated using an array of heating elements so as to cause differential heating along the length of the glass sheet assembly such that the temperature at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly is higher than the temperature at the trailing edge of the glass sheet assembly with uniform heating across the width of the glass sheet assembly. The first and second glass sheets are pressed toward each other to purge air or moisture from the glass sheet assembly until the first and second glass sheets adhere together via the adhesive laminating film, the step of pressing being initiated at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly when the temperature of the laminating film at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly reaches the bonding temperature of the laminating film.
Owner:BOND BROTHERS CONTRACTING PTY LTD
Numerical control differential heating bending forming mould for titanium tube and method
ActiveCN105537342AIncrease temperatureImprove heating efficiencyShaping toolsNumerical controlJet aeroplane
The invention discloses a numerical control differential heating bending forming mould for a titanium tube and a method. The numerical control differential heating bending forming mould for the titanium tube is characterized in that heating holes and thermometer holes are formed in a pressure mould, a bending mould, a mandril and a crease-resistant mould respectively; and thermometer holes are formed in a clamping mould and an insert block; the pressure mould, the mandril, the bending mould and the crease-resistant mould are heated, and the heating temperatures are set according to tube hot bending simulated reasonable temperature distribution. Compared with the prior art, the moulds and the tube can be heated to the set temperatures faster, the heating efficiency of the tube is improved, temperature nonuniformity is avoided, the bending forming quality and forming limit of a titanium alloy tube are further improved and increased, and a machine tool is protected by a heat insulating plate. After the tube is bent within the forming limit, the inner side of the tube does not crease, the surface of the tube has no scratch, a reduction rate of the wall thickness of the outer side of the tube is less than 17%, and a section flattening rate of the tube is less than 5.0%, so that the requirements of an airplane on a small-bending-radius elbow tube made of major-diameter thin-wall pure titanium tube can be met.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Thermal actuator
ActiveUS7043910B2Improve efficiencyReduce heat transferDisposition/mounting of recording headsElectrothermal relaysNon symmetricMEMS thermal actuator
An asymmetric MEMS thermal actuator device includes a base portion, typically a pair of bond pads, and an actuator element connected to the base portion by a flexure portion. The actuator element has a first arm and a second arm alongside the first arm and spaced from the first arm. The second arm is wider than the first arm so that the actuator element deflects about the flexure element due to differential heating in the first and second arms when an electrical current is passed therethrough. A cut-out portion is provided in the second arm adjacent the first arm so as to increase the spacing therefrom over at least a portion of the second arm. Preferably, a heat sink is also provided laterally adjacent the second arm.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD +1
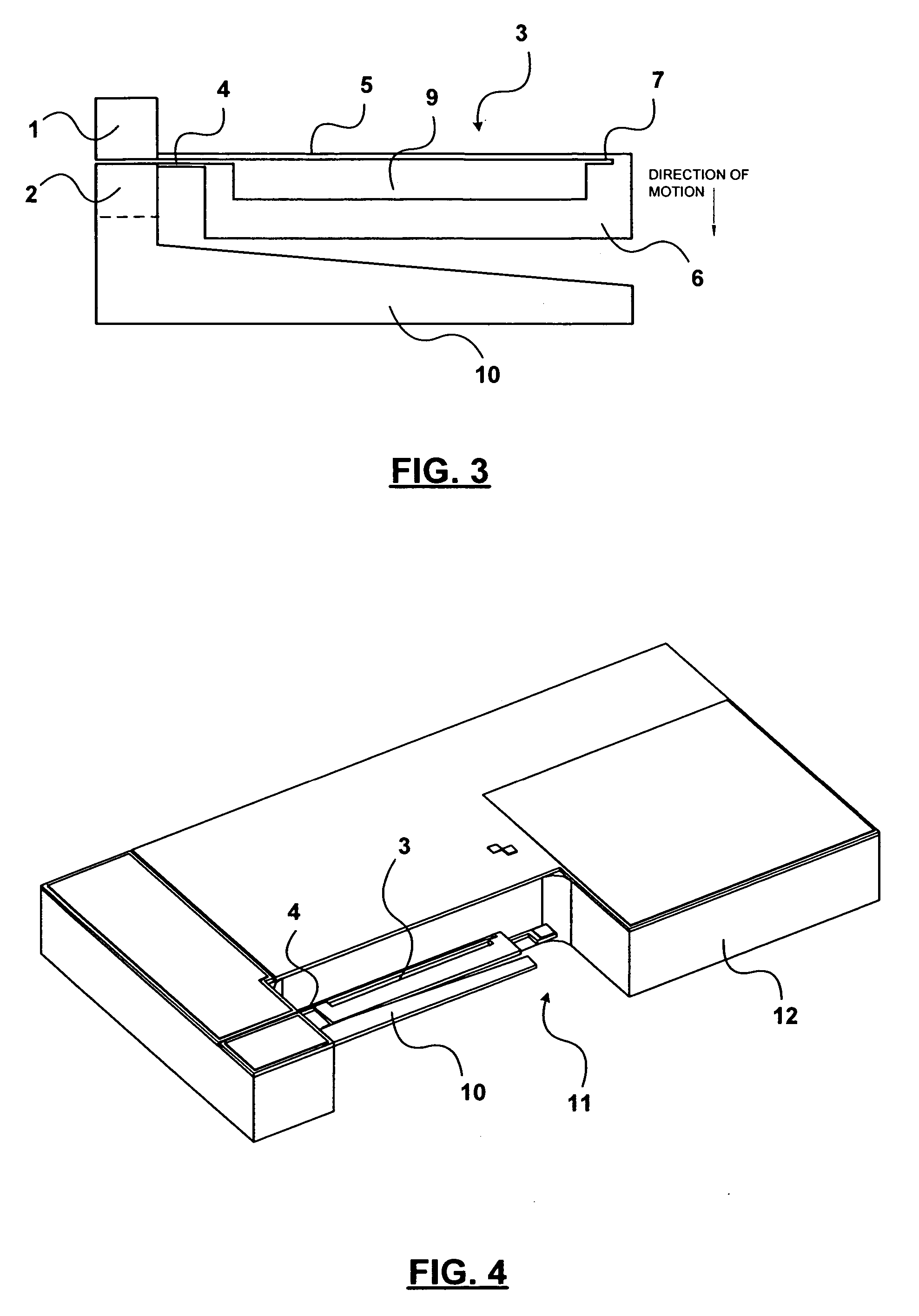
Wearable photoacoustic vascular imaging system
InactiveUS20100160790A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightNon invasiveBlood vessel
A non-invasive wearable imaging apparatus for vascular detection employing photo-acoustic principle is disclosed. Additionally, a wearable micro-display component is also described. The method includes pulsed laser as an energy source at a wavelength range at which both the blood and the adjoining tissue absorb the light and convert the energy into kinetic energy which heats the tissue. The temperature of the tissue rises and falls in sympathy with the frequency of the impinging light. The alternative heating and cooling of the illuminated region causes alternating sympathetic expansion and contraction of the region with corresponding rising and falling of the tissue surface and of the air in contact with the surface, thereby generating sound waves. A sensor enables the differentiation between the venous and surrounding tissues from which imaging of the venous tissue is extracted. In addition to the acoustic sensors, the sympathetic rising and falling of the tissue surface are converted into color characteristic signals representative of the relative displacement of the tissue surface. Additionally, the differential heating of the tissues enables the visual detection of the venous tissues by appropriate filter lenses. These embodiments also present miniaturization of the generation, imaging and display components, enabling the detection of the blood vessels in a wearable form factor.
Owner:IBOKSUNNYVALE EFFIONG ETUKUDO +1
Single stage glass lamination apparatus and process
A glass sheet assembly including a first glass sheet arranged in an opposing parallel configuration with respect to a second glass sheet is provided, with a heat sensitive layer of adhesive laminating film disposed between the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet, the glass sheet assembly having a leading edge and a trailing edge and being of a fixed length and width, the laminating film having a bonding temperature at which melting of the laminating film is initiated. The glass sheet assembly is heated using an array of heating elements so as to cause differential heating along the length of the glass sheet assembly such that the temperature at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly is higher than the temperature at the trailing edge of the glass sheet assembly with uniform heating across the width of the glass sheet assembly. The first and second glass sheets are pressed toward each other to purge air or moisture from the glass sheet assembly until the first and second glass sheets adhere together via the adhesive laminating film, the step of pressing being initiated at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly when the temperature of the laminating film at the leading edge of the glass sheet assembly reaches the bonding temperature of the laminating film.
Owner:BOND BROTHERS CONTRACTING PTY LTD
Method and device for carrying out uniform heating or differential heating on sheet steel in rapid non-deformation non-oxidation mode
InactiveCN102373325ANo deformationNo oxidationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelEngineering
The invention provides a method and a device for carrying out uniform heating or differential heating on sheet steel in a rapid non-deformation non-oxidation mode. The method is characterized in that: the contact heat transfer between each heating template and the sheet steel to be heated is utilized to realize the rapid heating of the sheet steel to be heated; clamping force of the heating templates is utilized to prevent the deformation of the sheet steel; a protection atmosphere which is formed between the heating templates is utilized to avoid the oxidation of heat exchange surfaces of the heating templates and the sheet steel to be heated; and the contact heat exchange coefficient between different positions of the heat exchange surfaces of the heating template and the sheet steel to be heated is changed to realize the controllable differential heating of the sheet steel to be heated.
Owner:刘丽辉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com