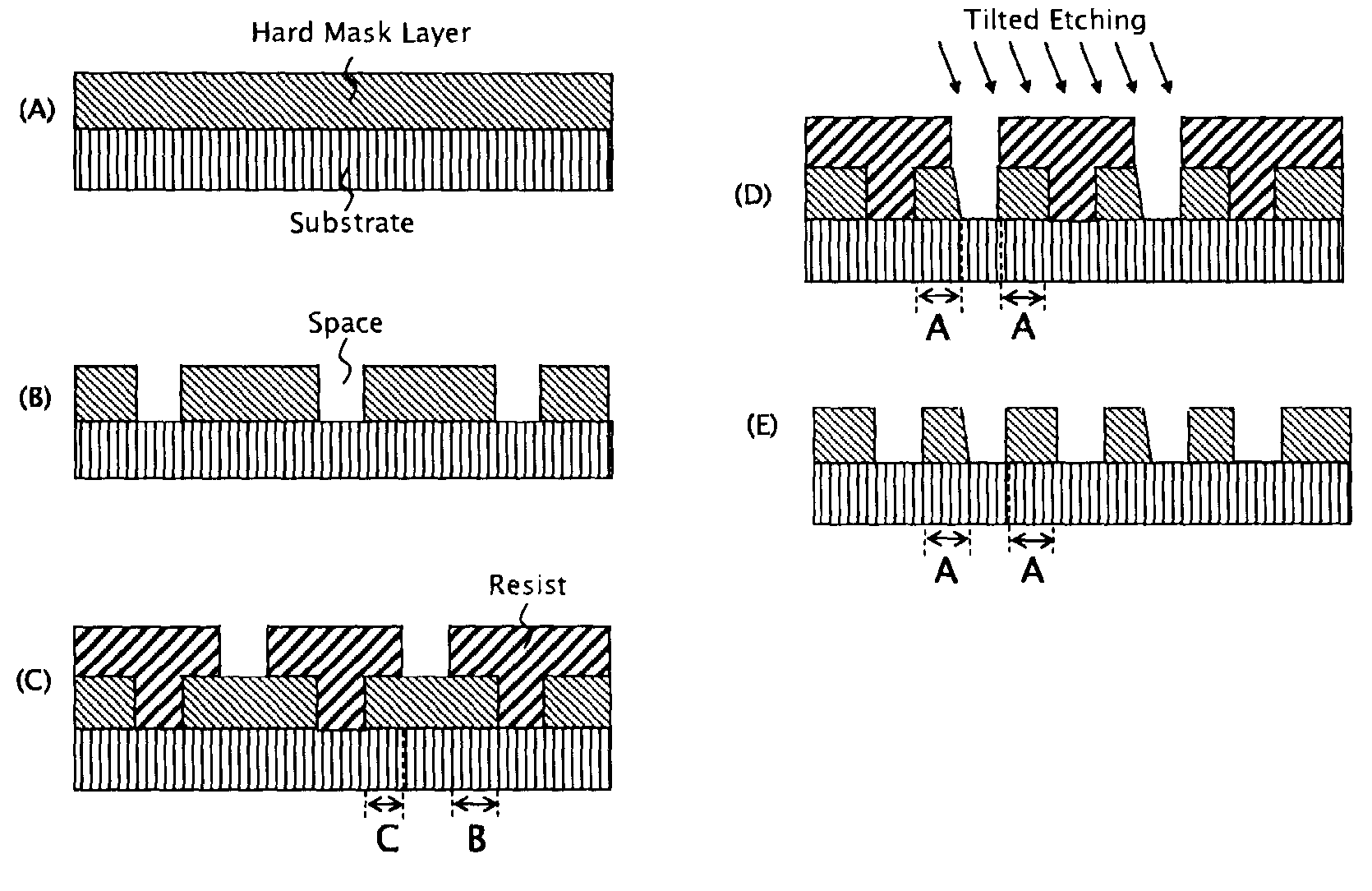
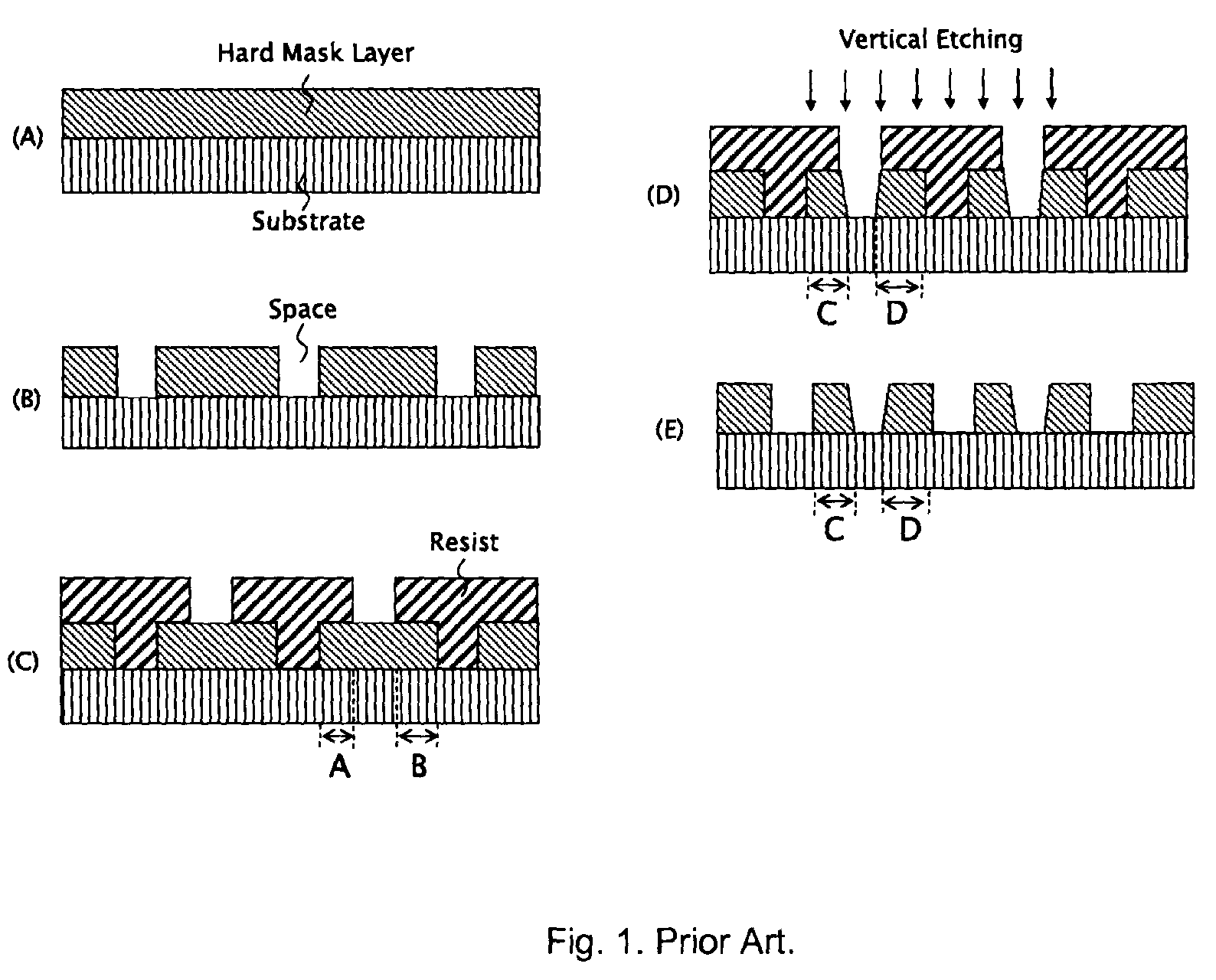
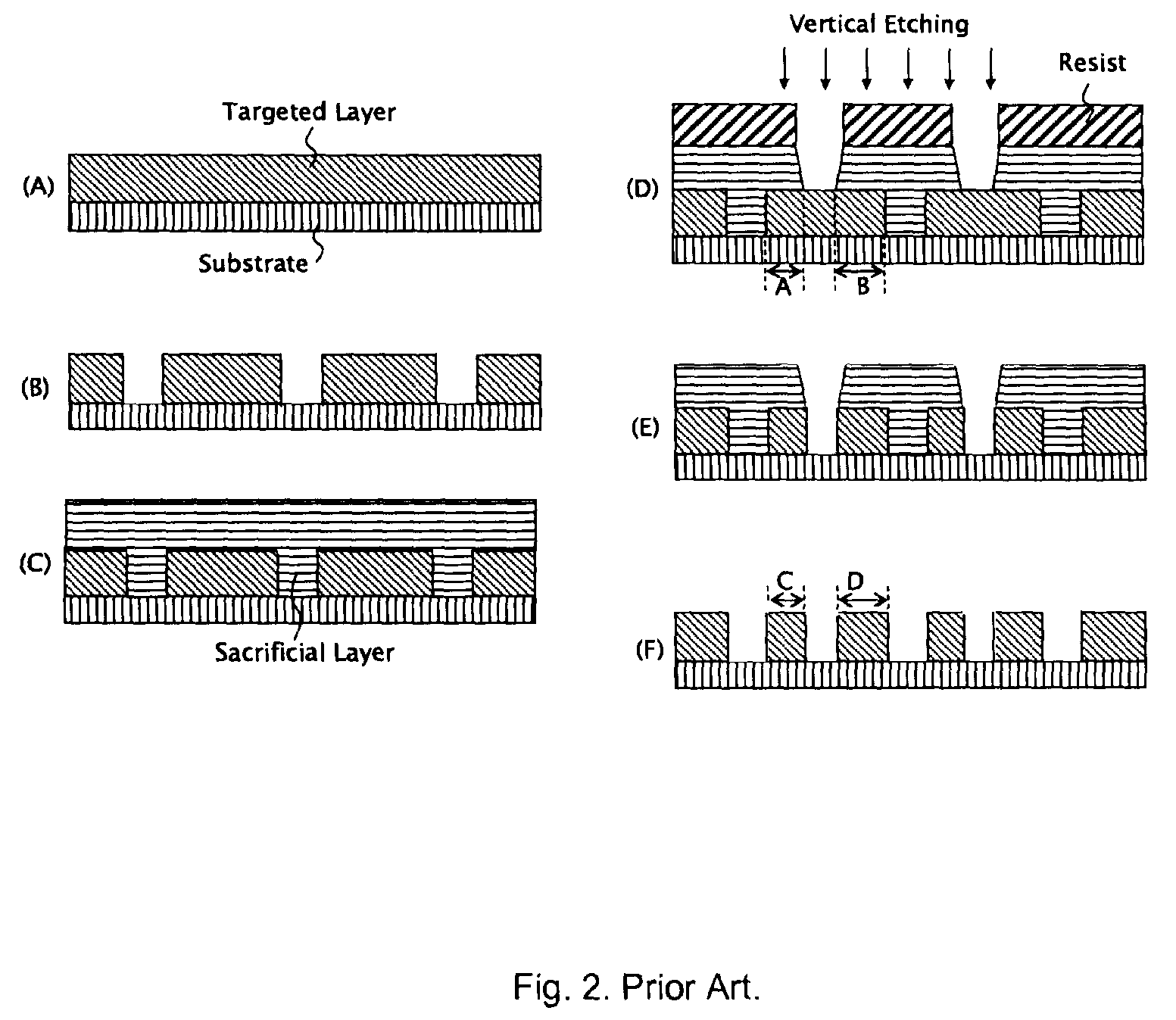
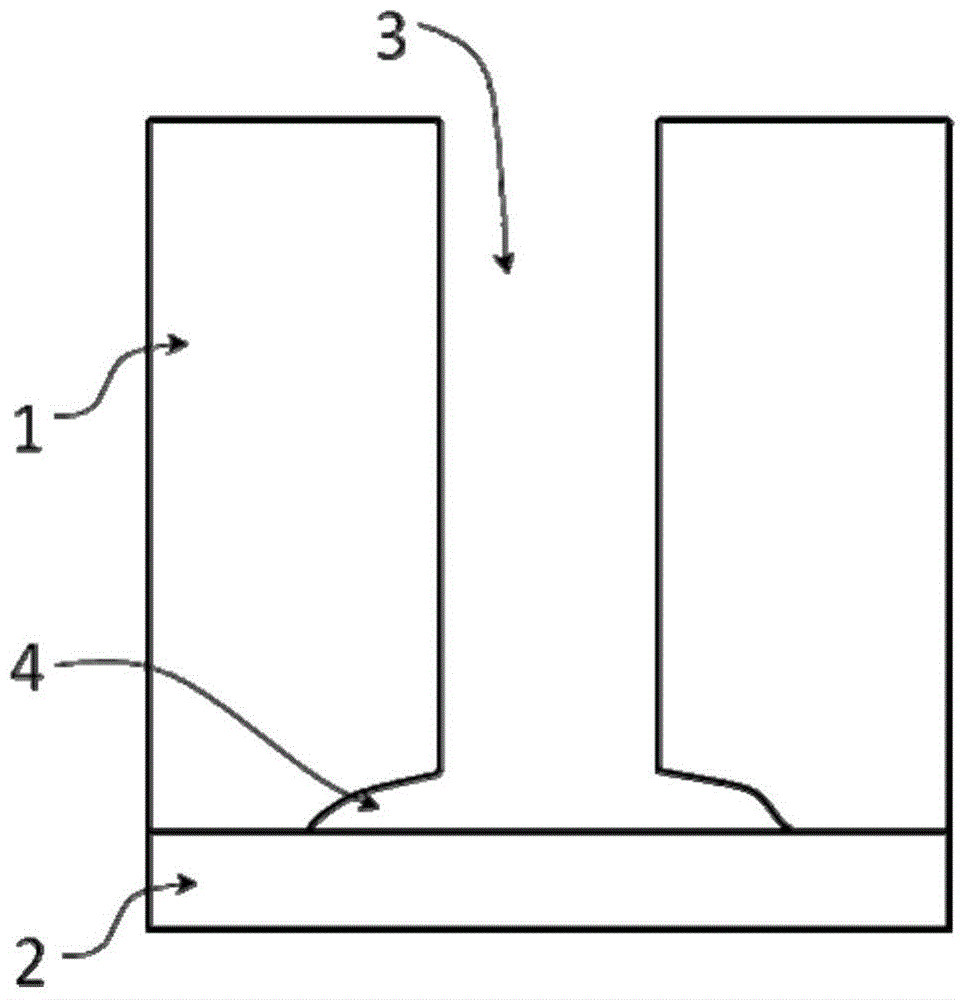
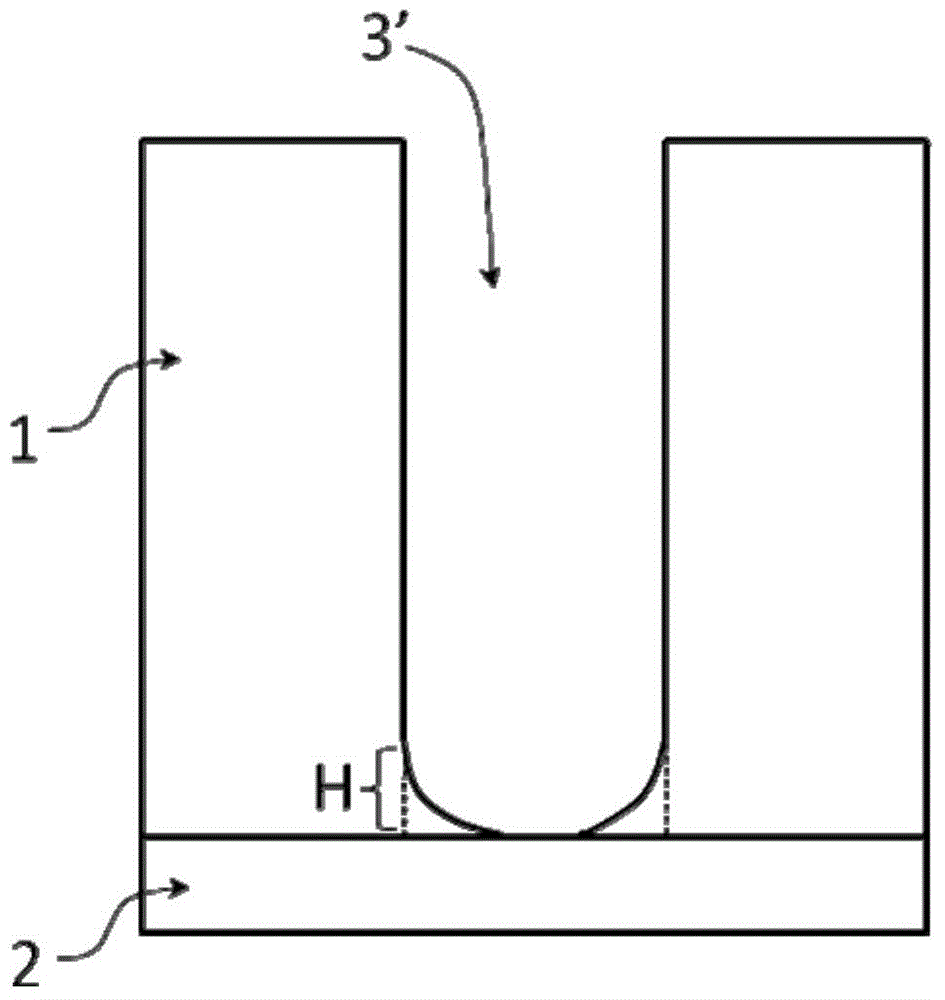
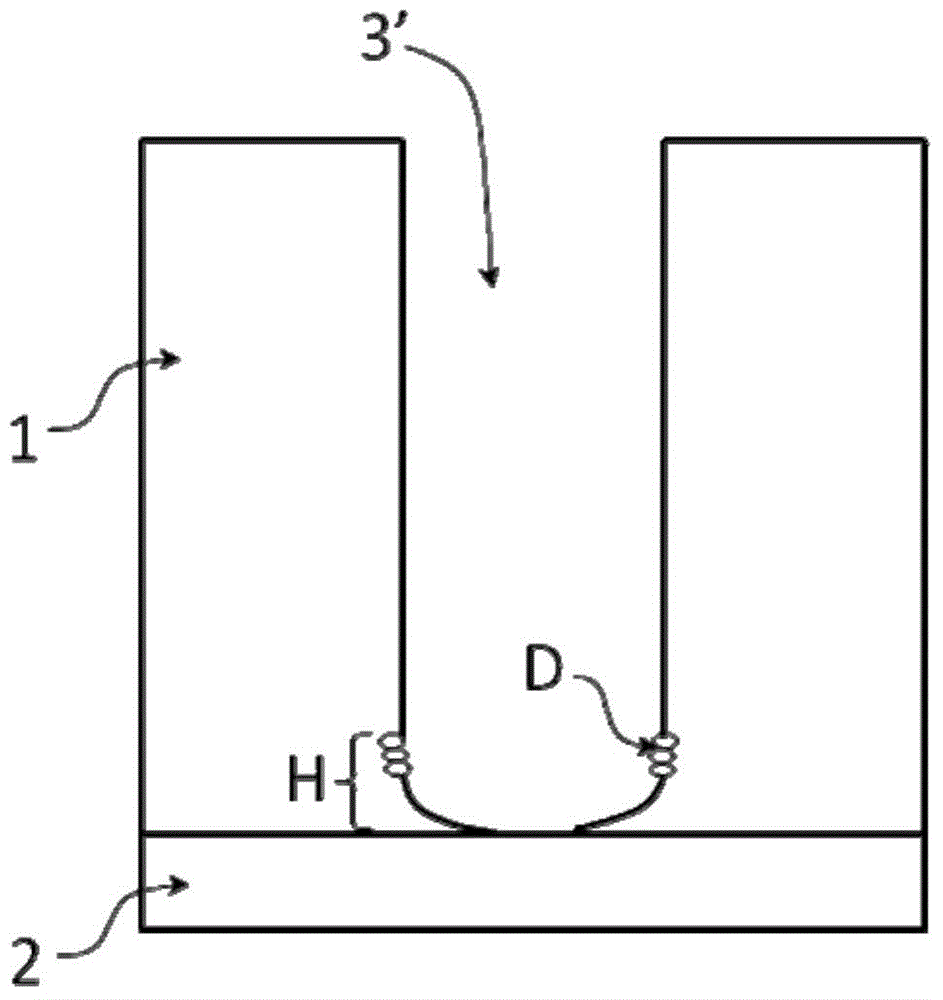
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Anisotropic plasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
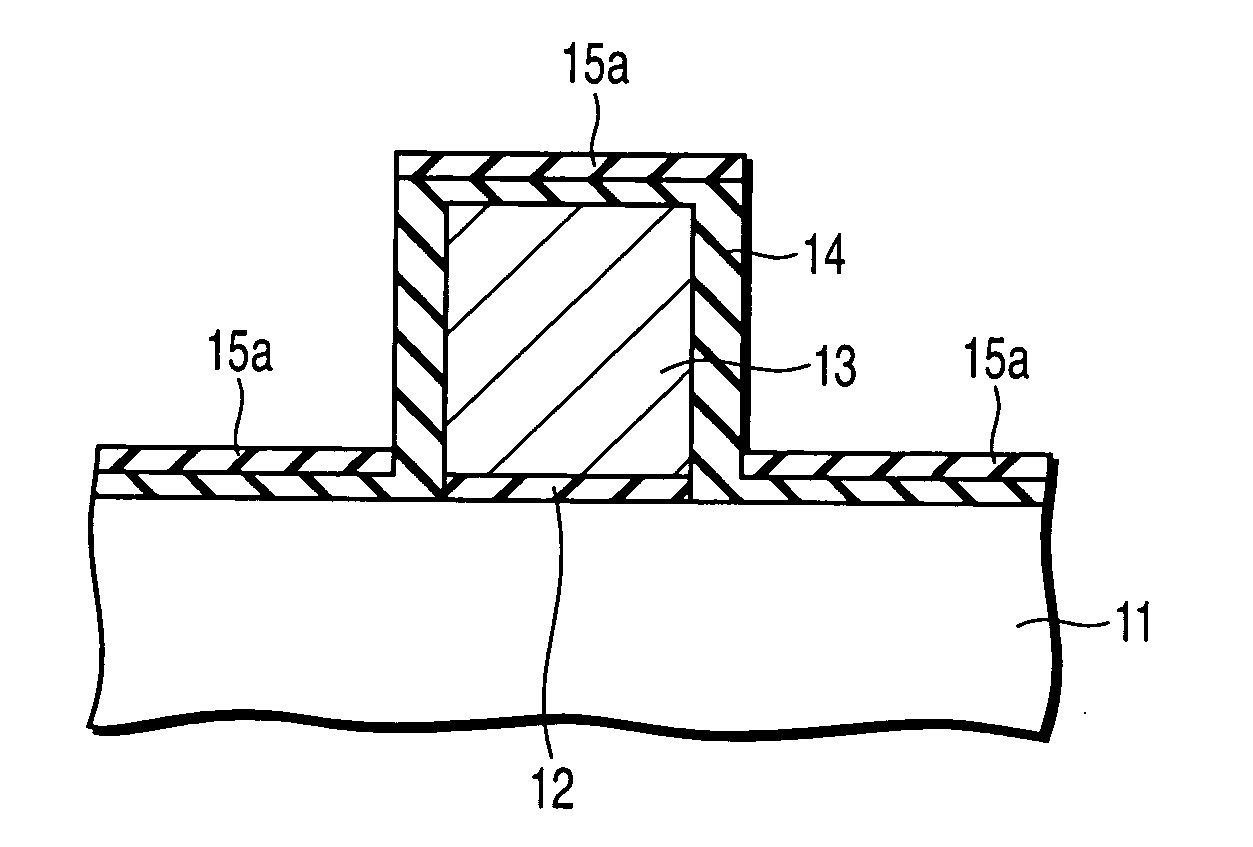
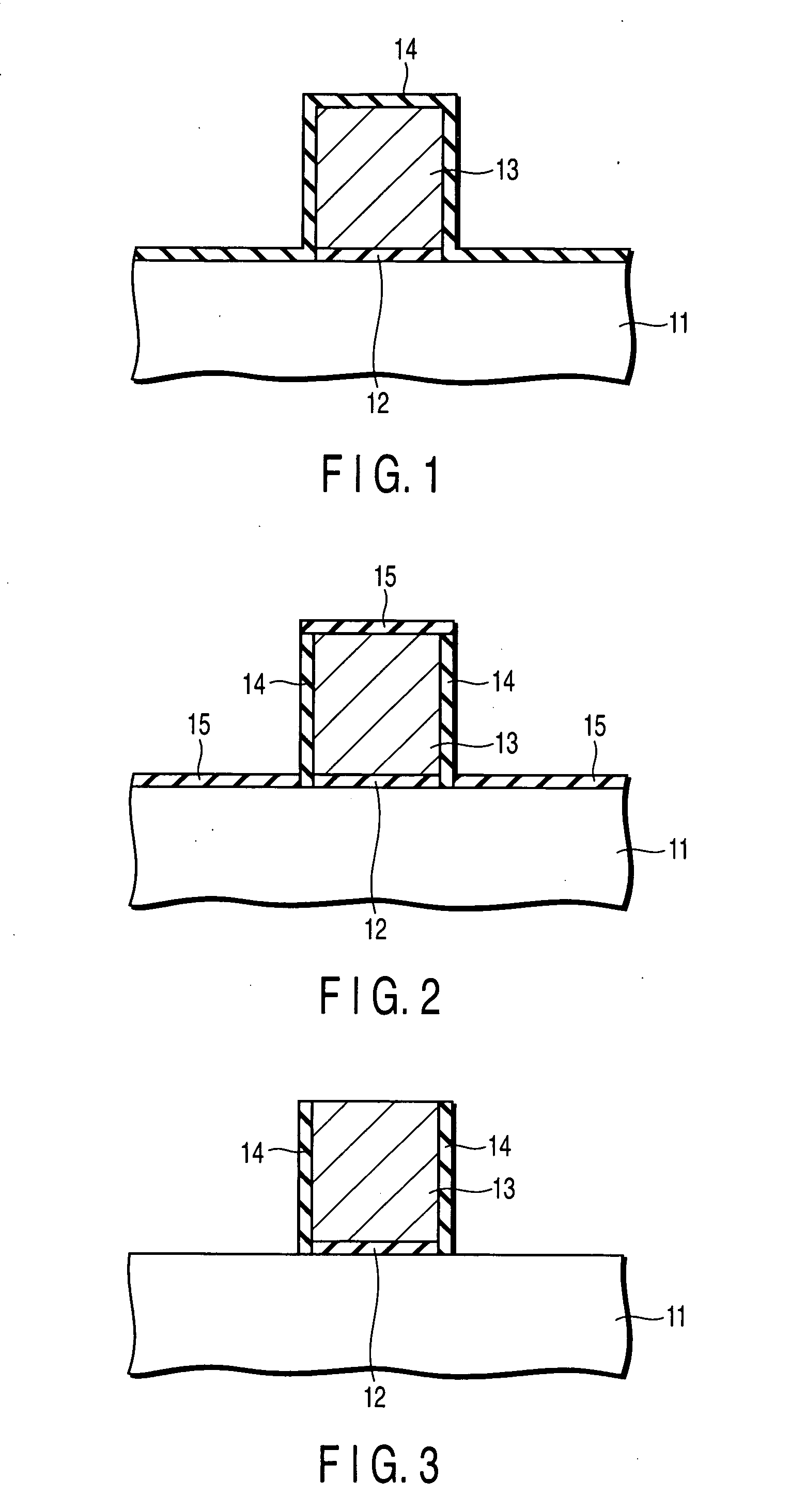
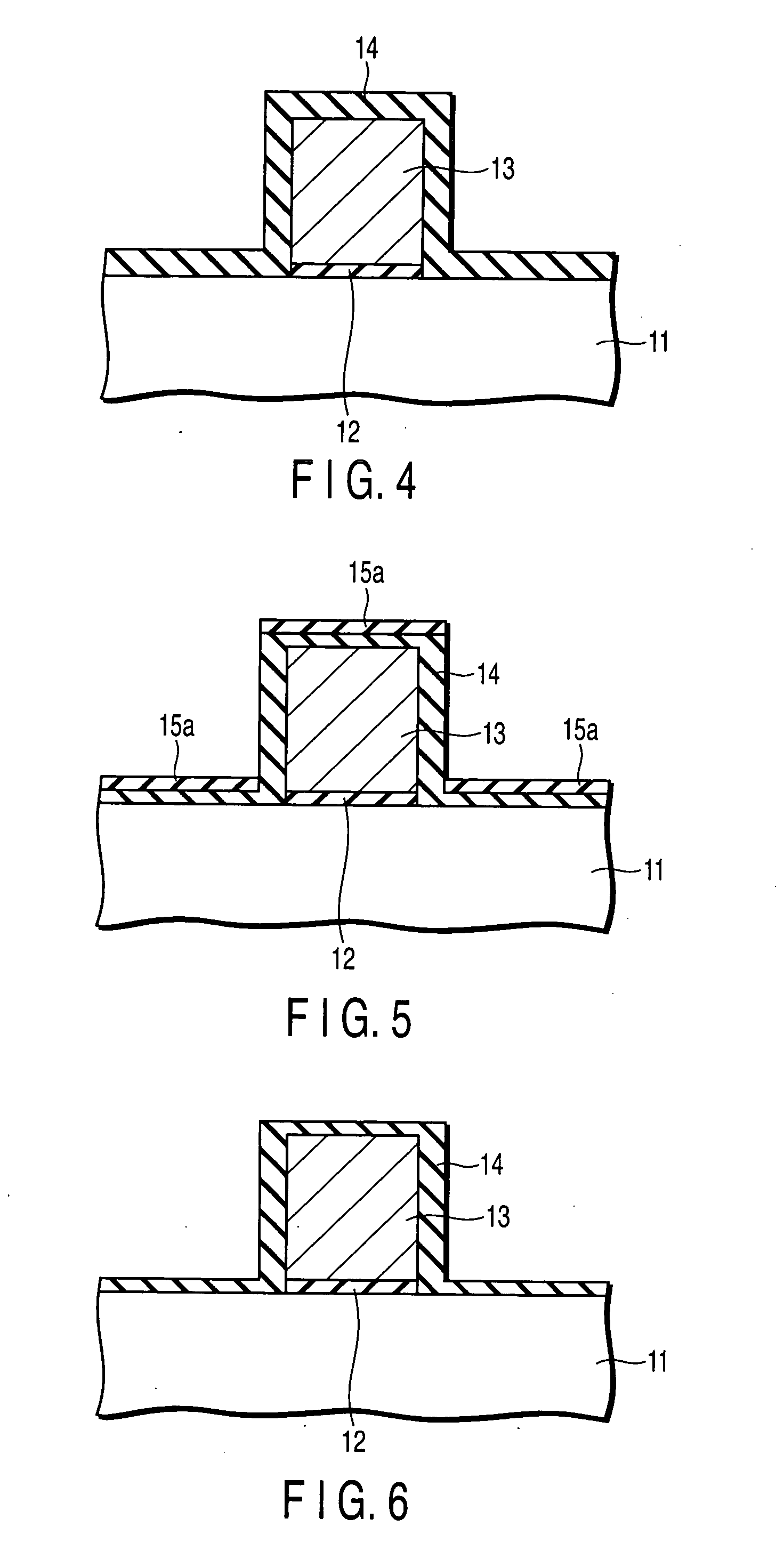
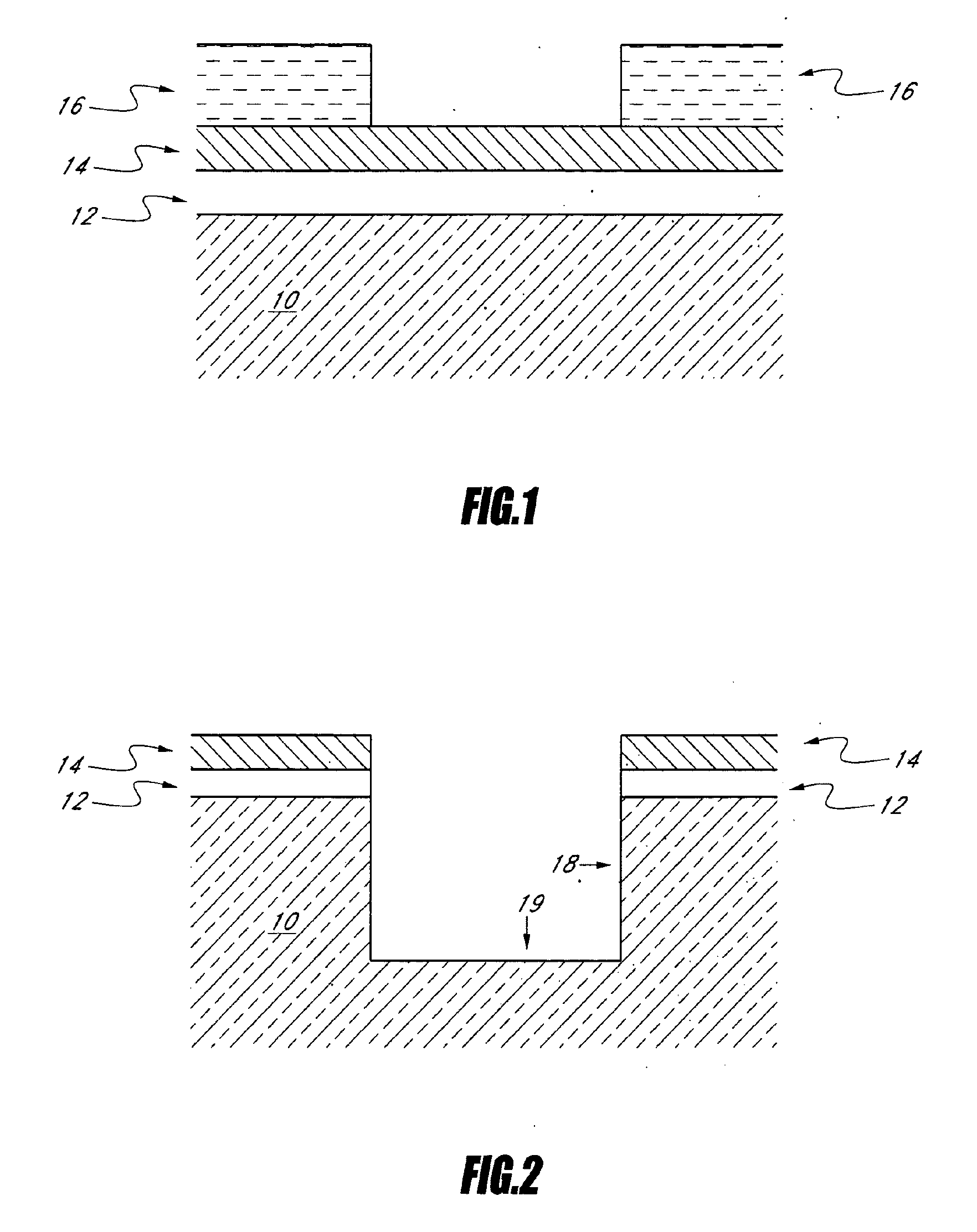
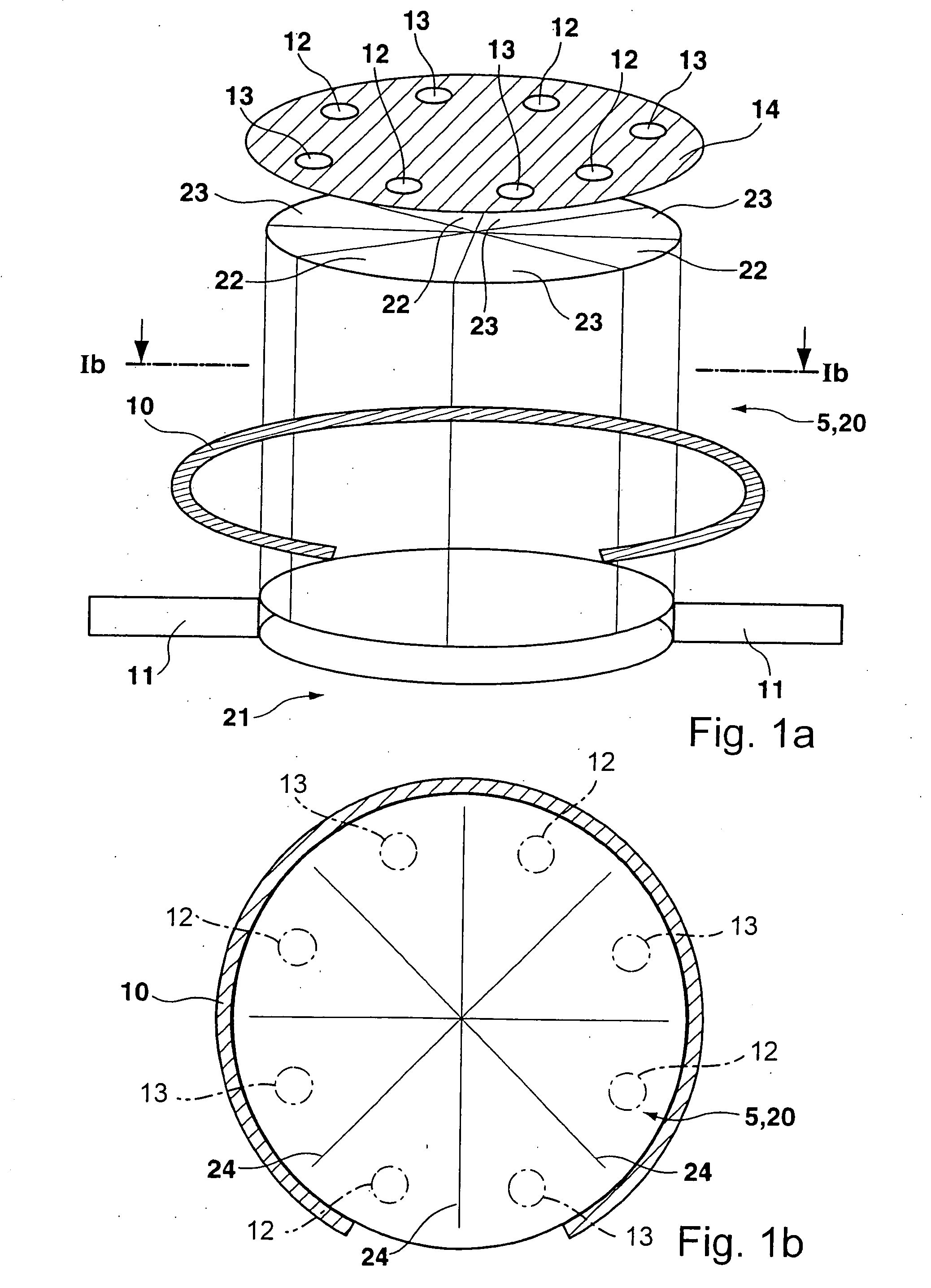
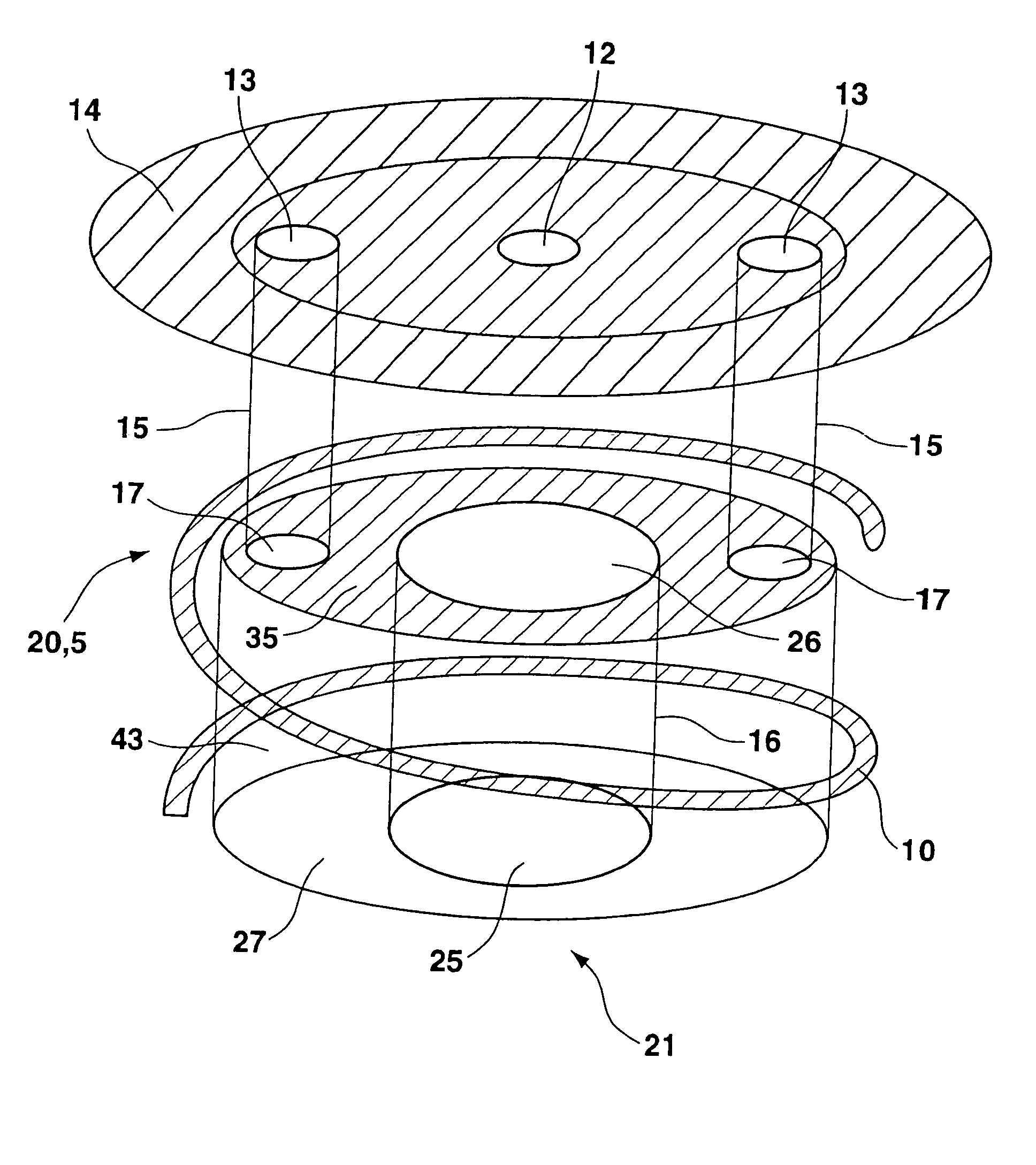
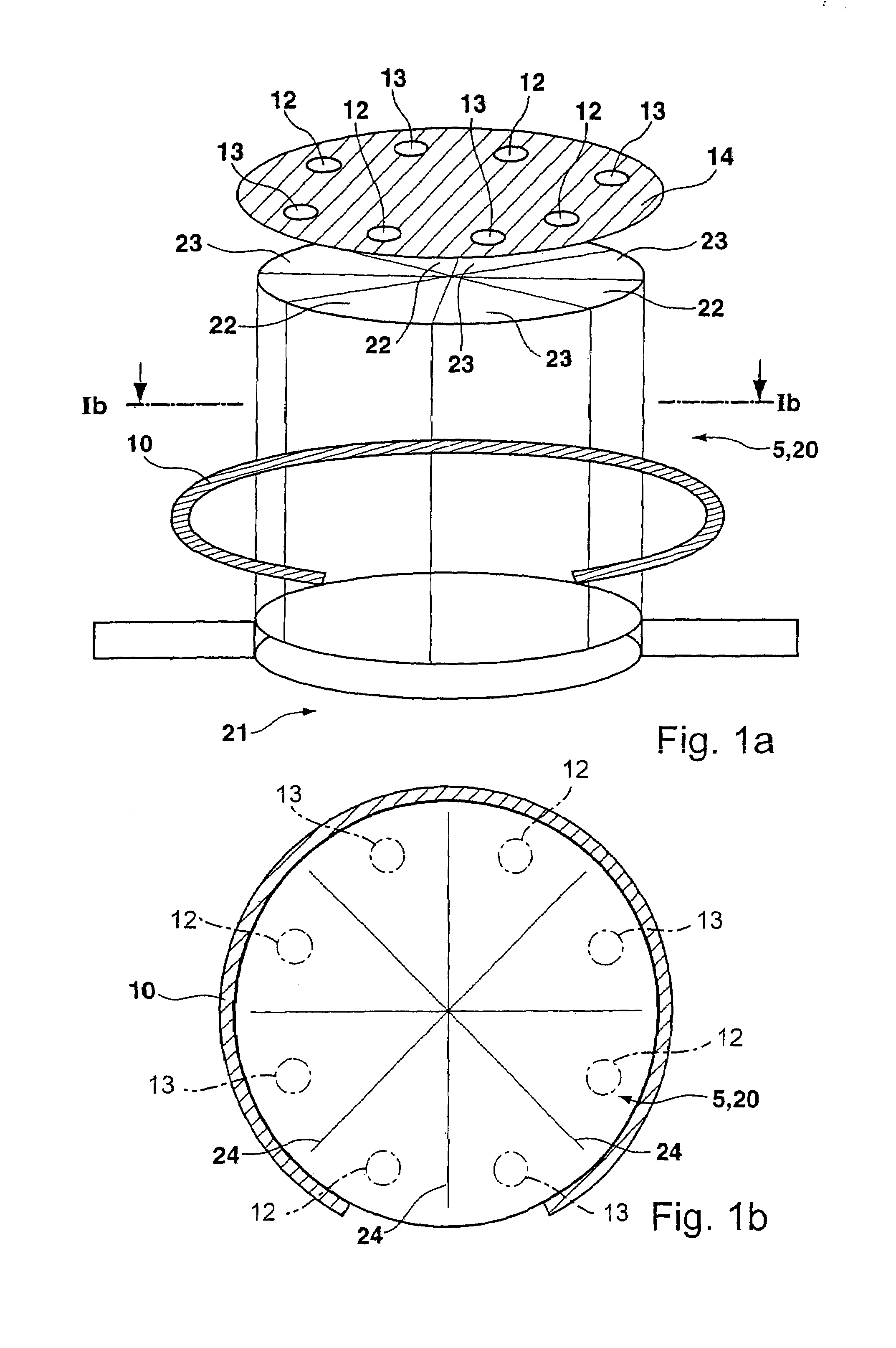
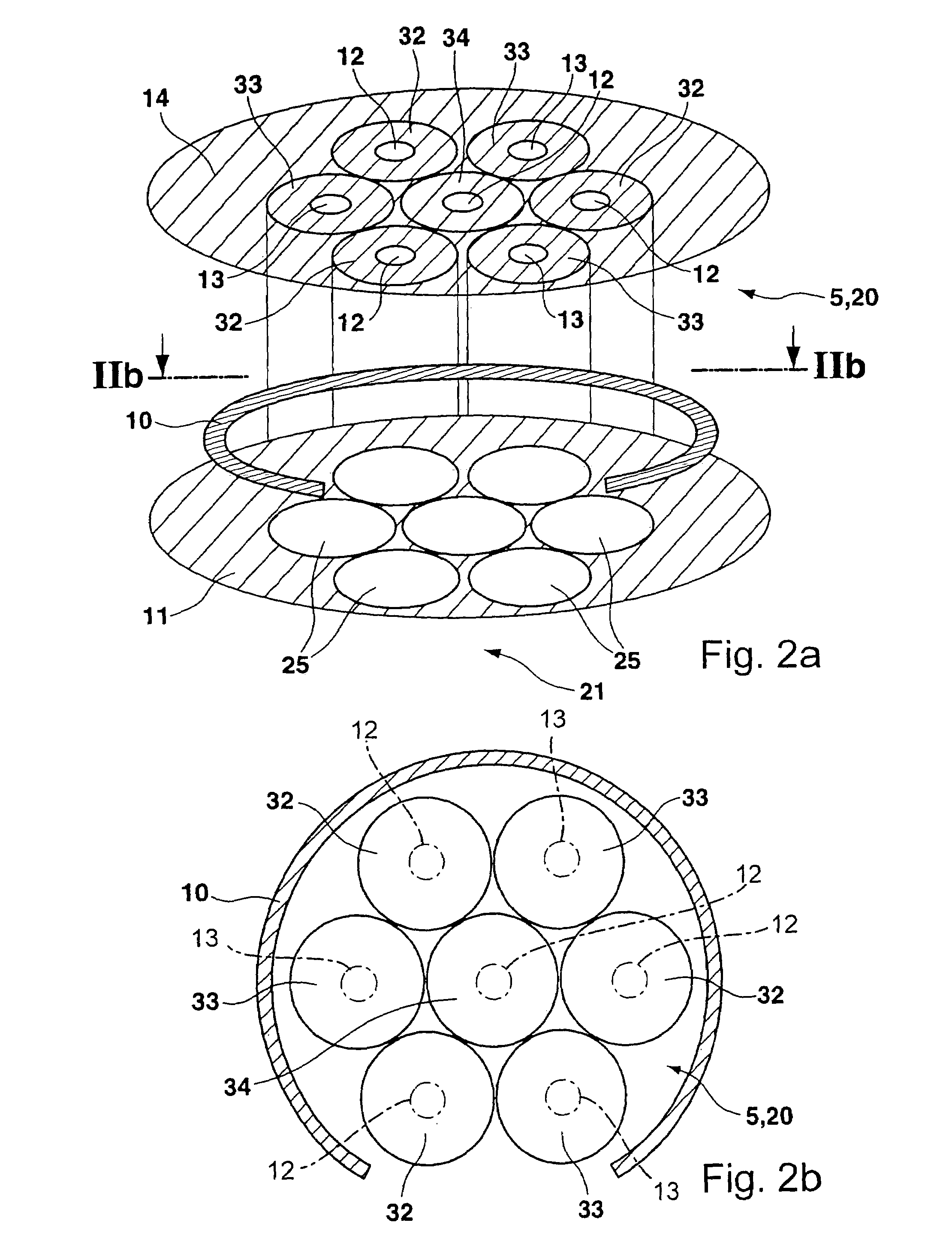
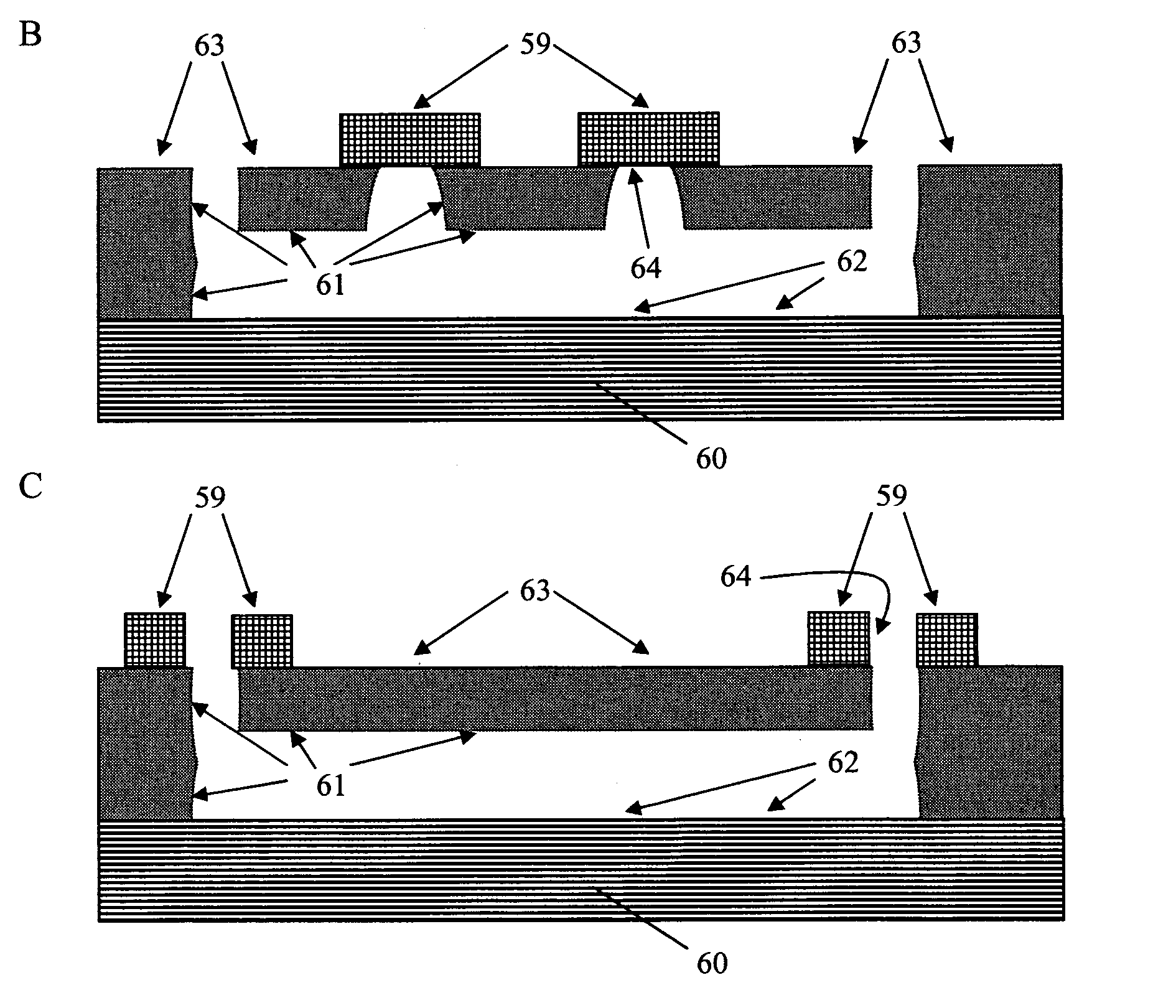
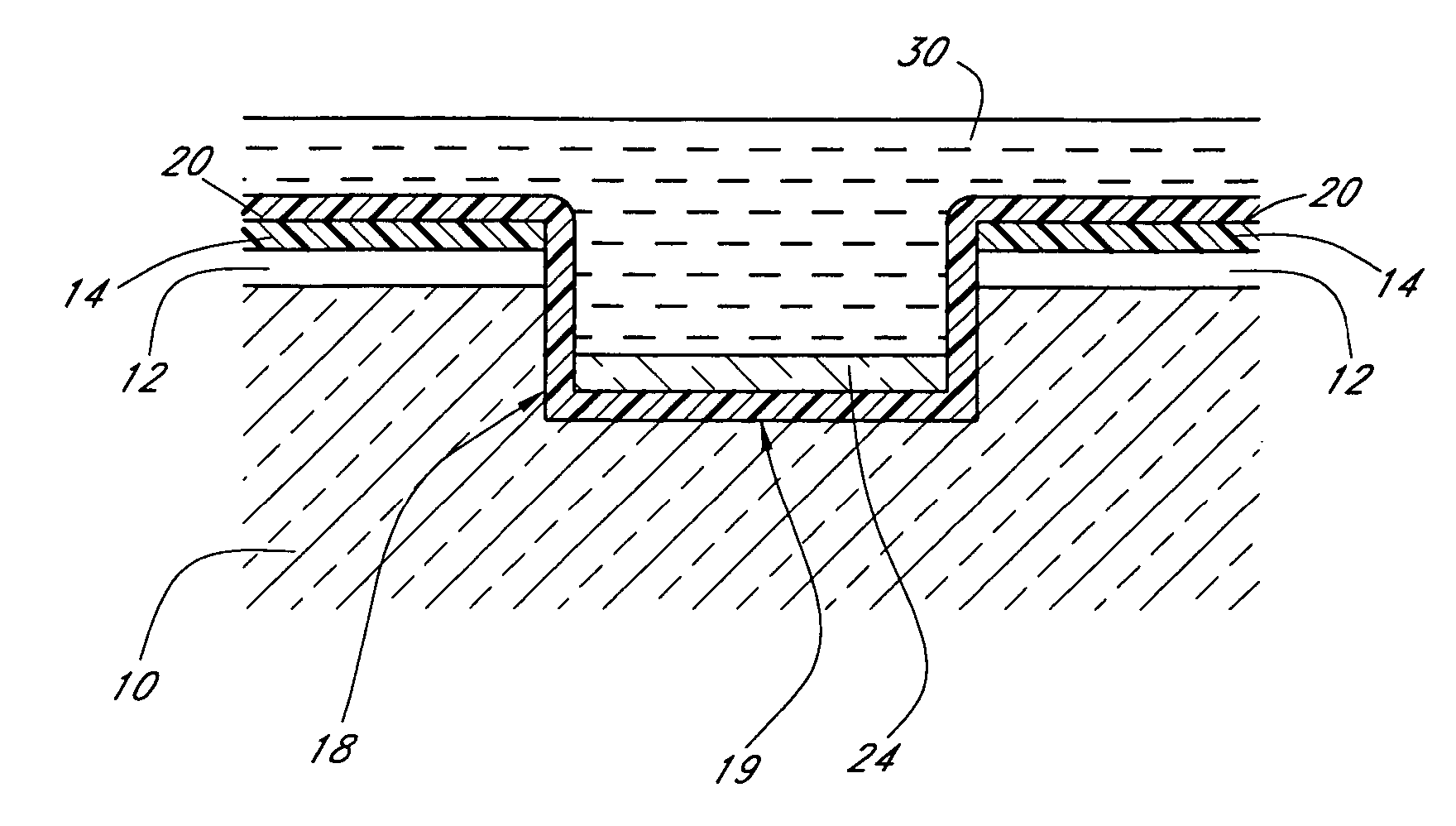
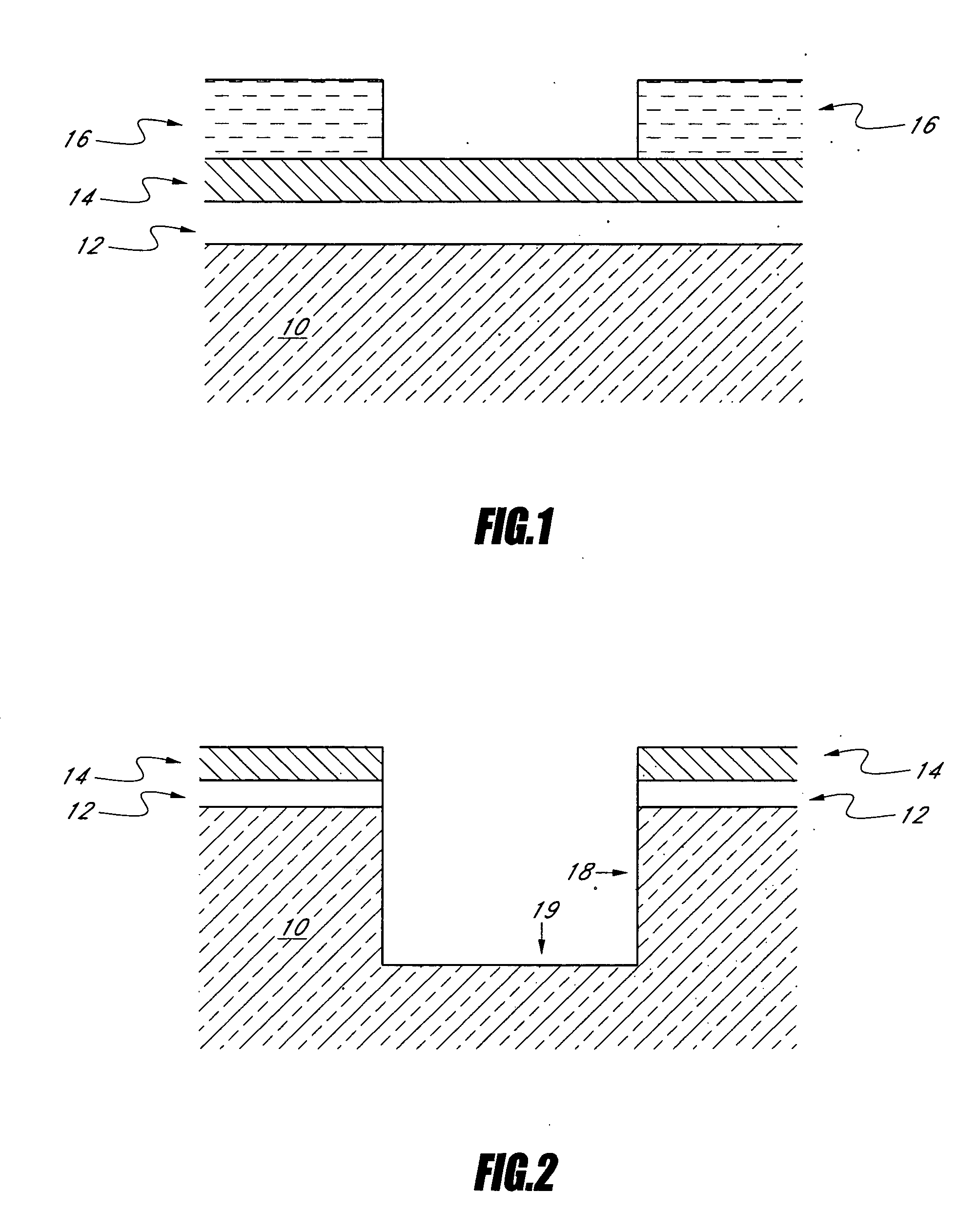
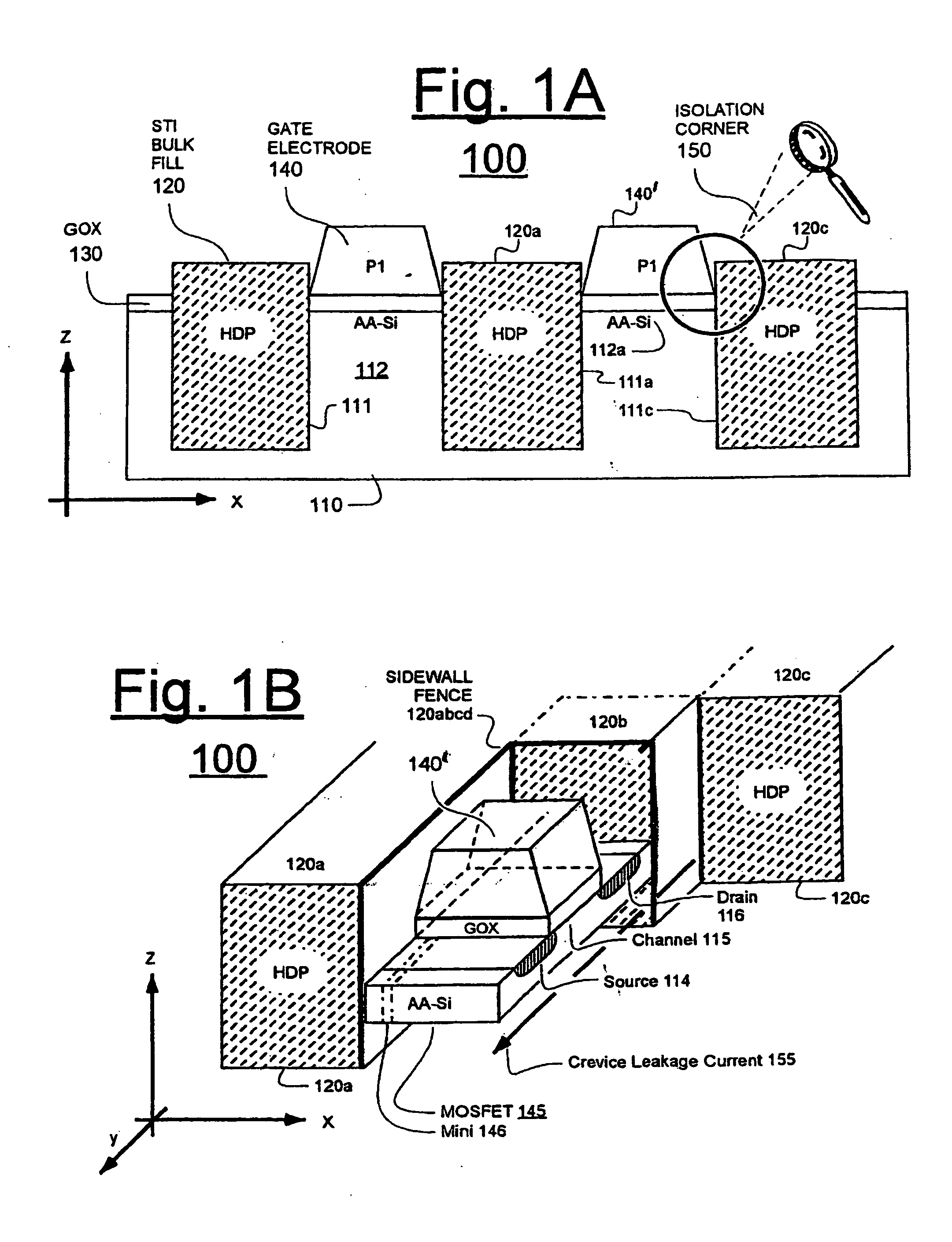
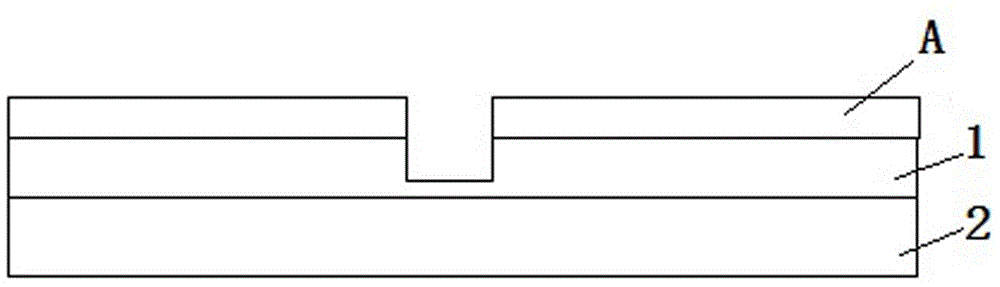
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060057828A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device is disclosed which comprises forming a gate structure on a major surface of a semiconductor substrate with a gate insulating film interposed therebetween, forming a first insulating film to cover top and side surfaces of the gate structure and the major surface of the semiconductor substrate, reforming portions of the first insulating film which cover the top surface of the gate structure and the major surface of the semiconductor substrate by an anisotropic plasma process using a gas not containing fluorine, and removing the reformed portions of the first insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
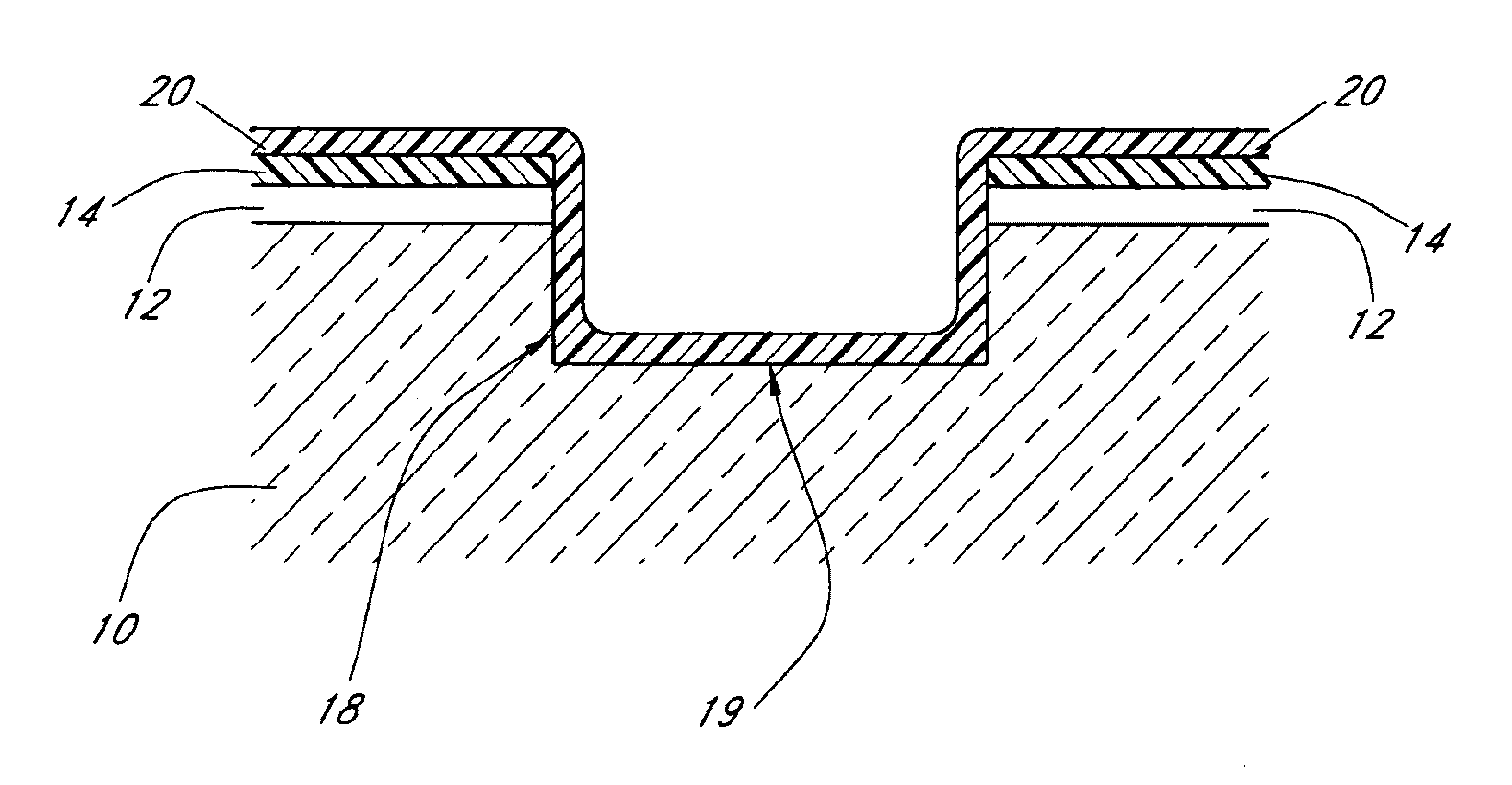
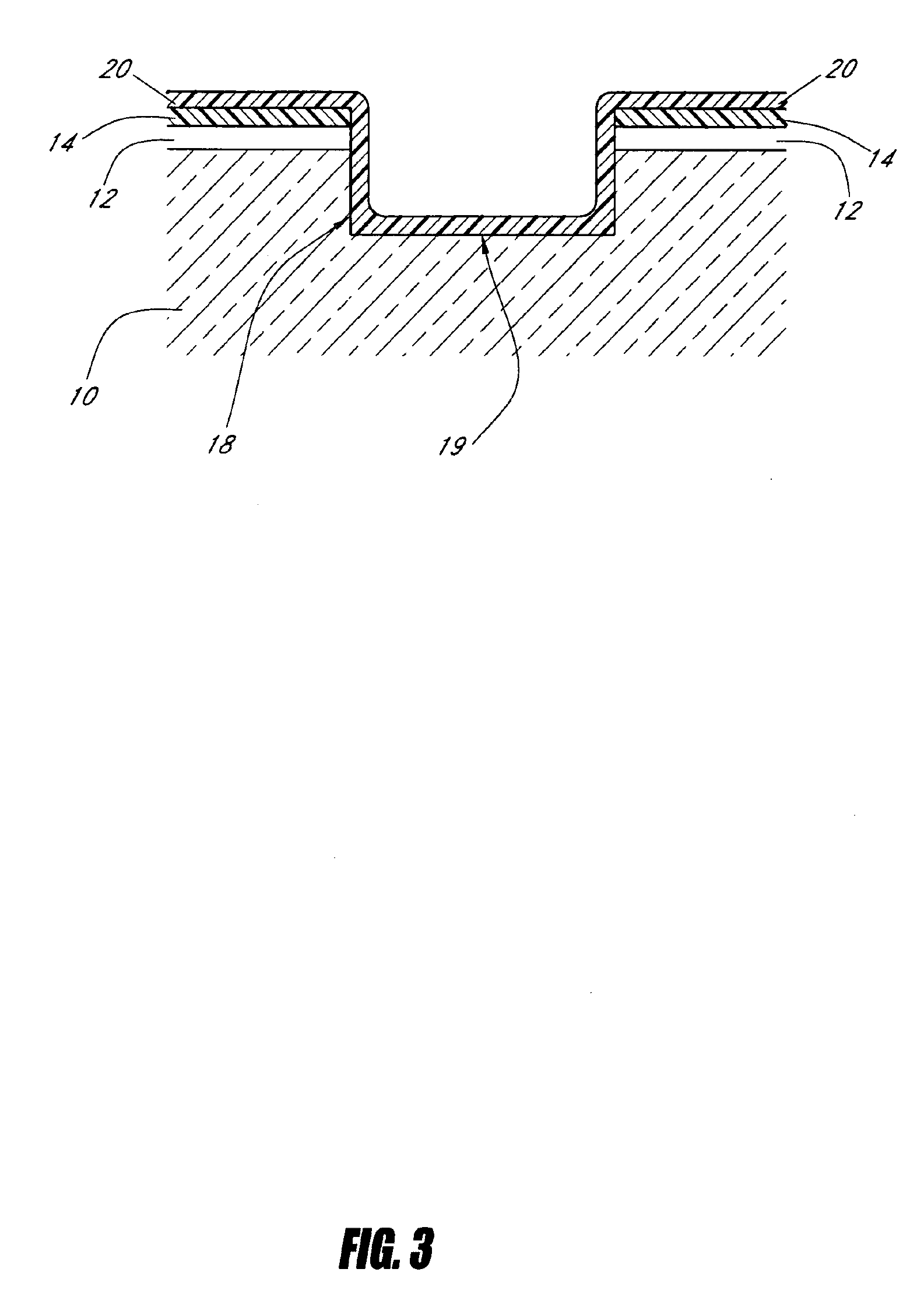
Trench insulation structures and methods
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
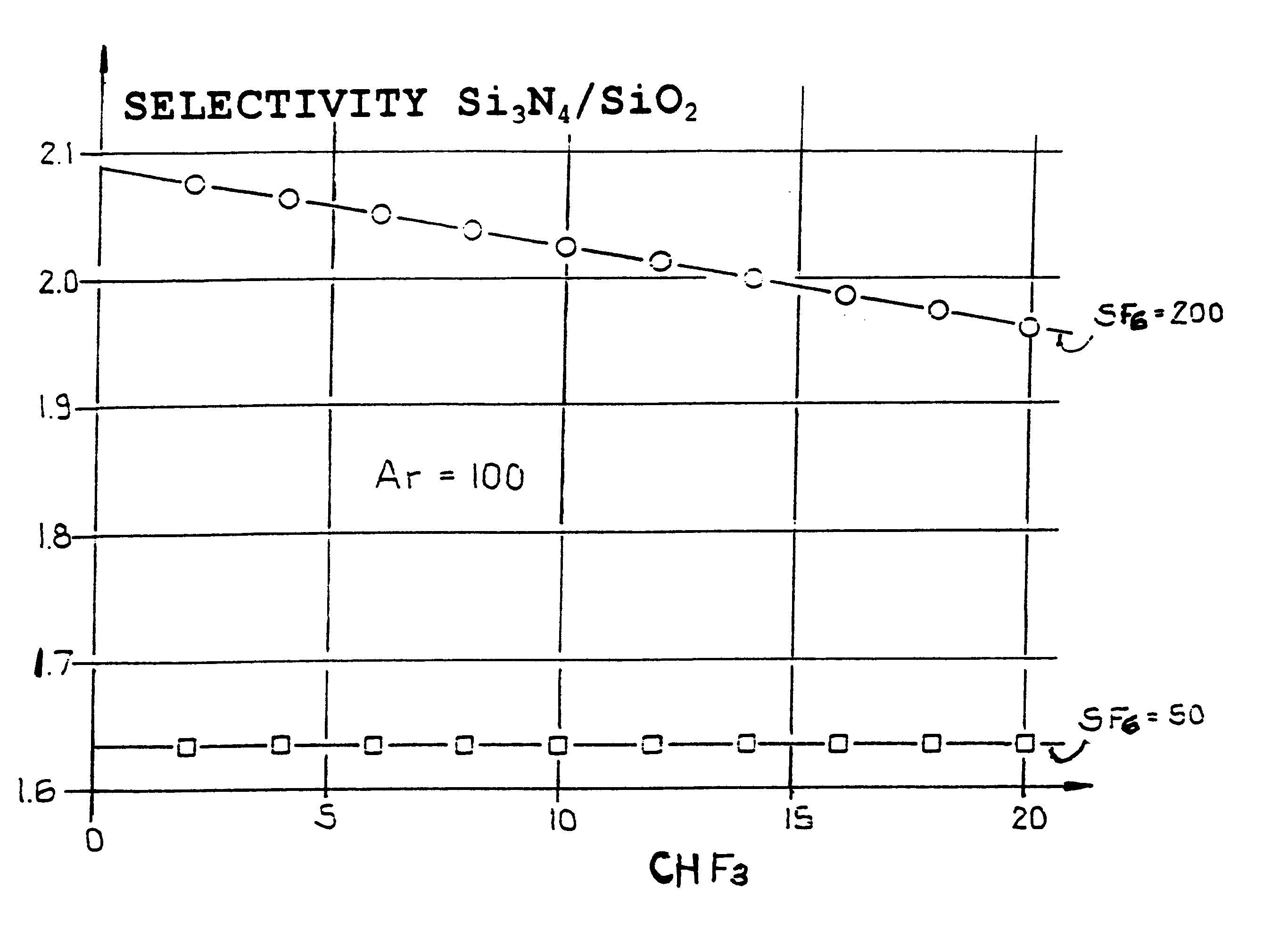
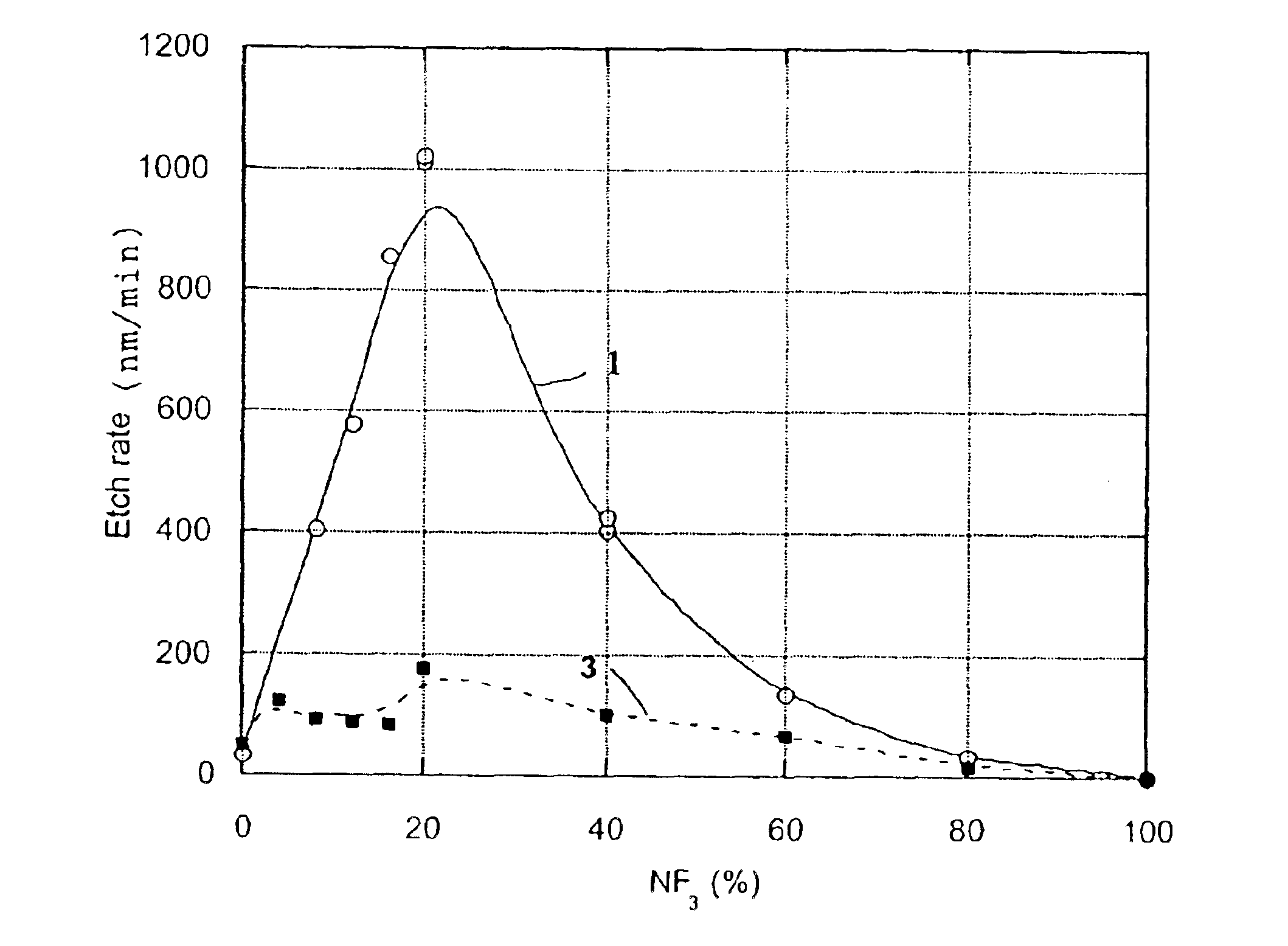
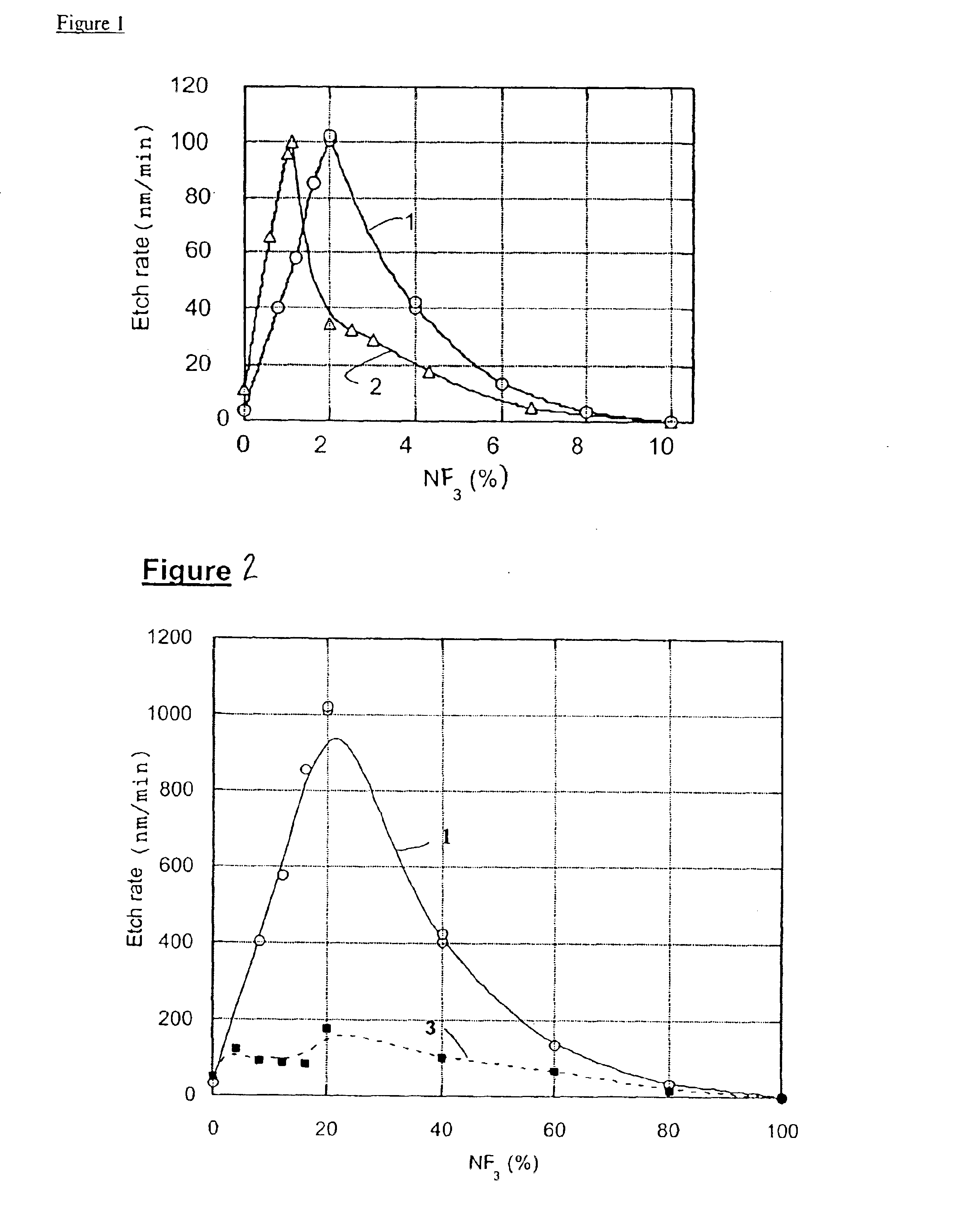
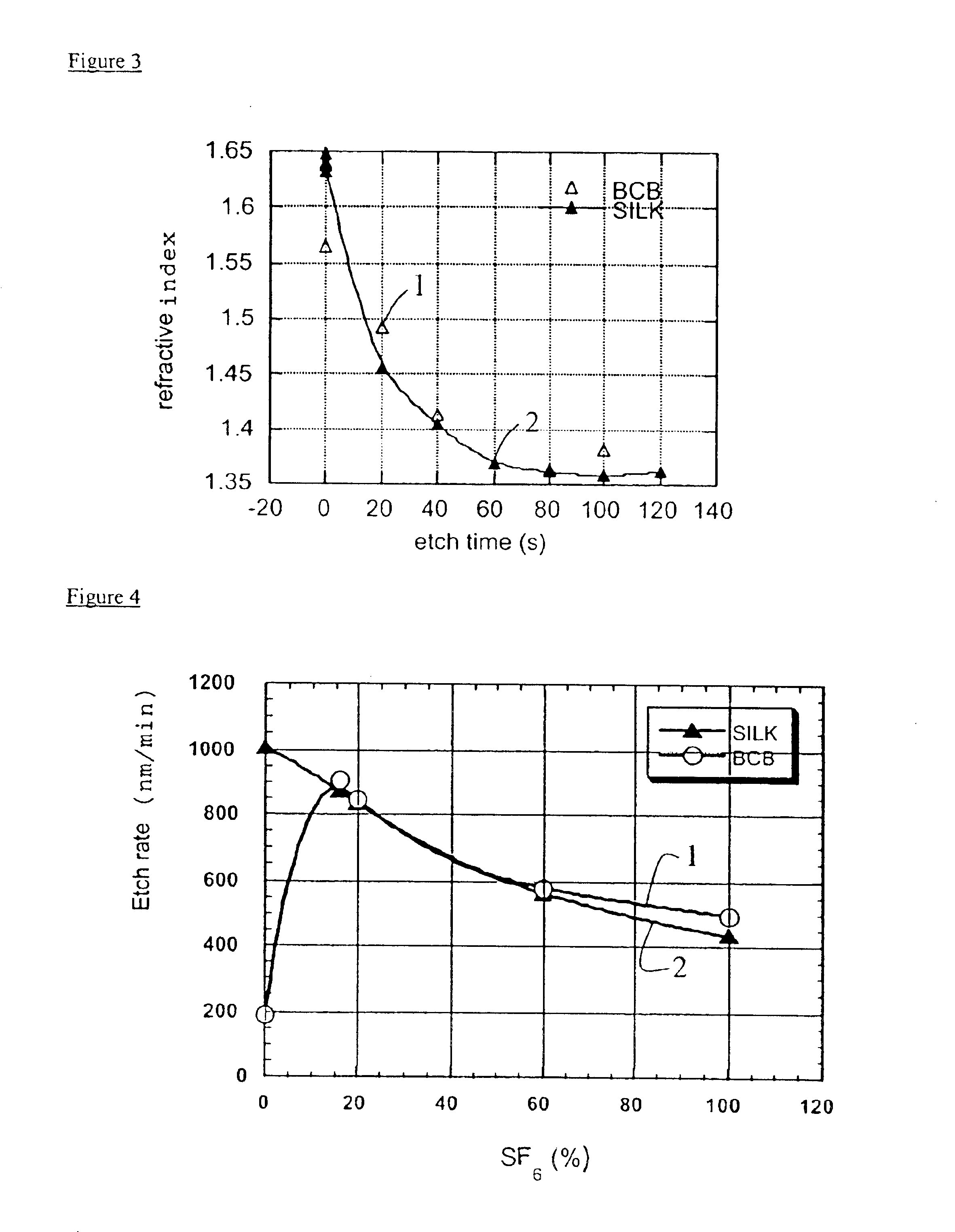
Method for anisotropic plasma-chemical dry etching of silicon nitride layers using a gas mixture containing fluorine
InactiveUS6569773B1Improve uniformityHigh atomic weightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideOxygen
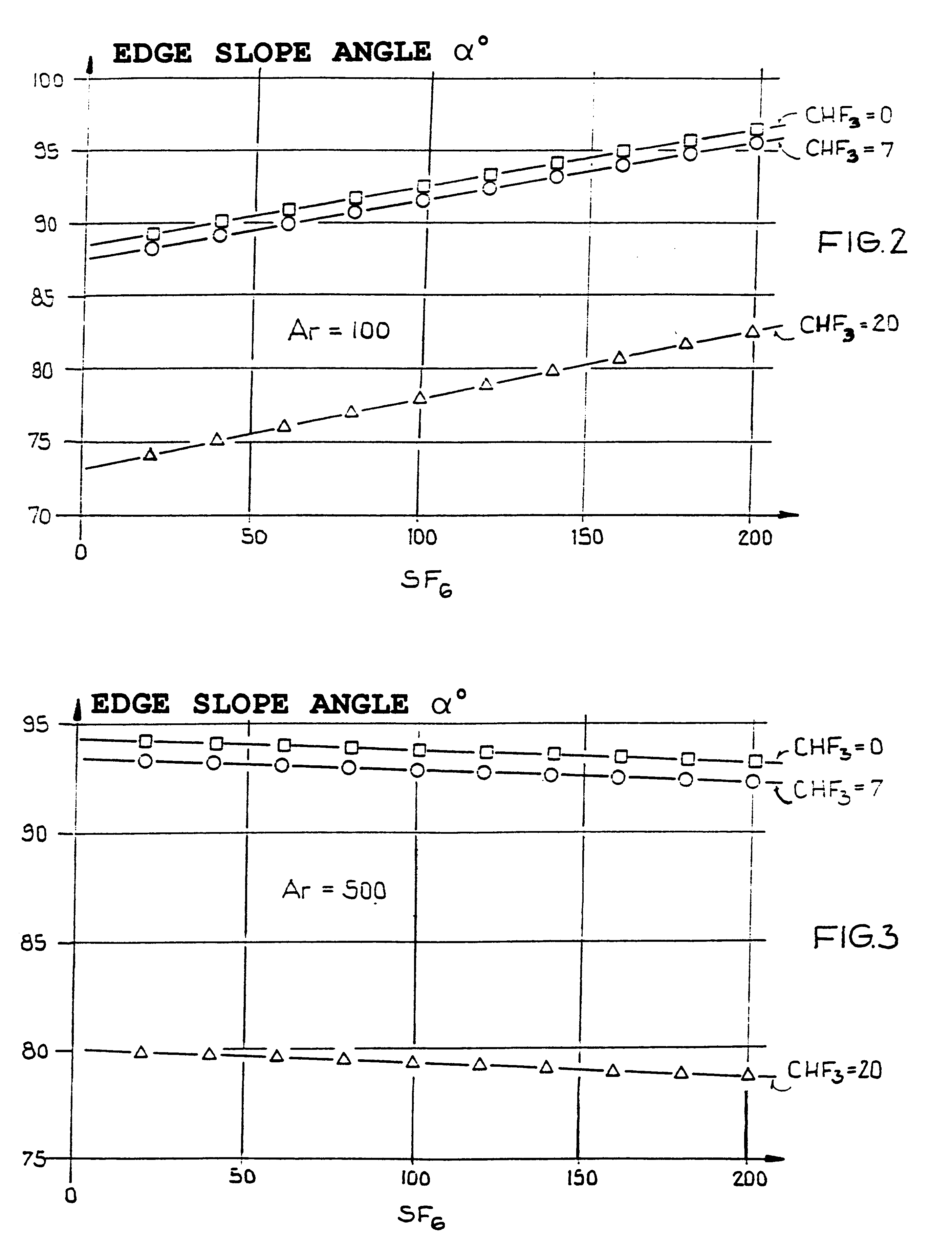
An etching gas mixture containing CHF3, SF6 and a non-oxidizing gas such as Ar is used as an etching gas mixture for the anisotropic plasma-chemical dry-etching of a silicon nitride layer differentially or selectively relative to a silicon oxide layer. The gas mixture does not contain oxygen, chlorine, bromine, iodine or halides in addition to the above mentioned constituents, so that the process can be carried out in reactor systems equipped with oxidizable electrodes. By adjusting the gas flow rates or composition ratios of CHF3, SF6, and argon in the etching gas mixture, it is possible to adjust the resulting etching selectivity of silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, and the particular edge slope angle of the etched edge of the remaining silicon nitride layer. A high etch rate for the silicon nitride is simultaneously achieved.
Owner:ATMEL CORP +1
Damage isolation by shaped beam delivery in laser scribing process
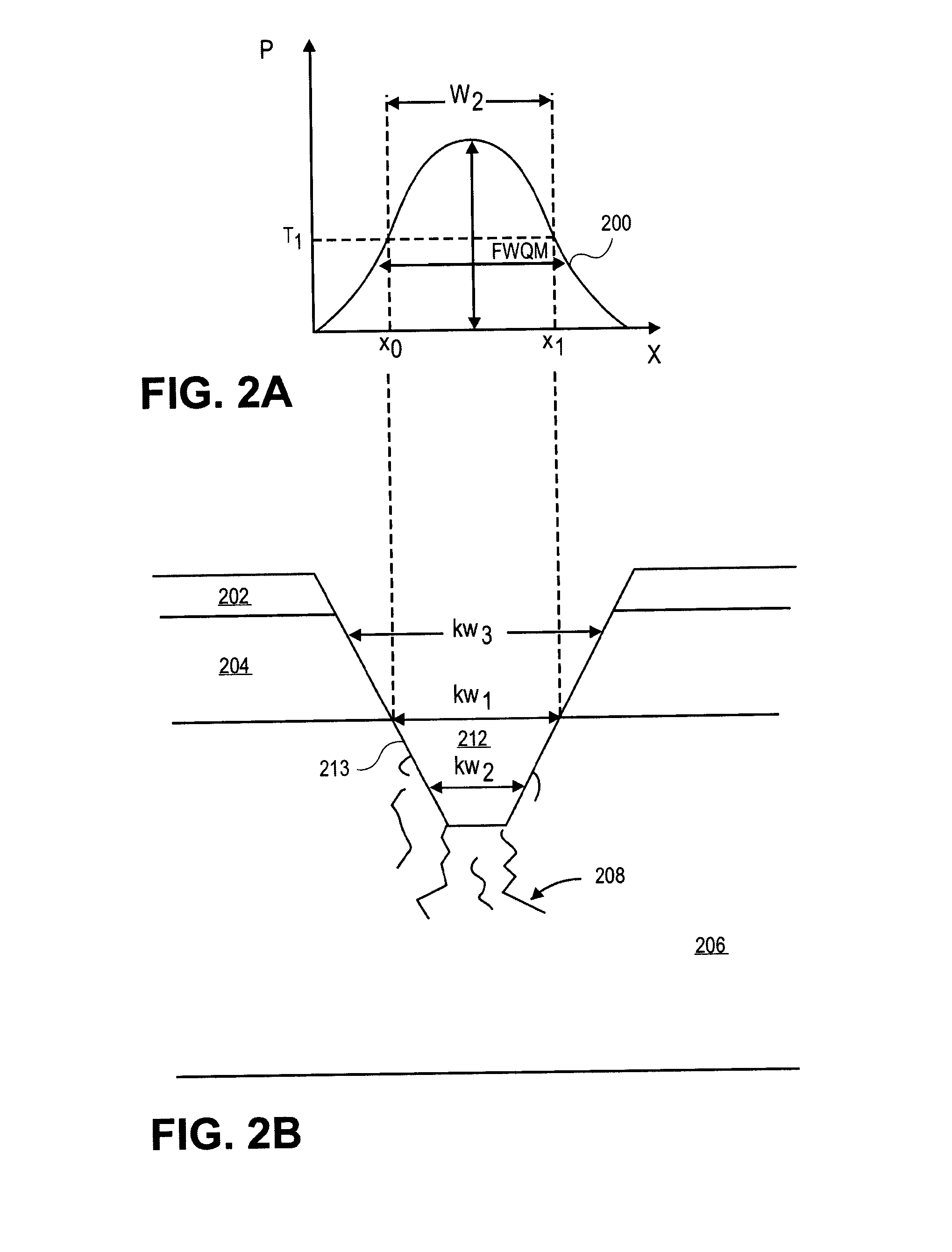
ActiveUS20120322240A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingShaped beamOptoelectronics
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for tunable isotropic recess etching of silicon materials
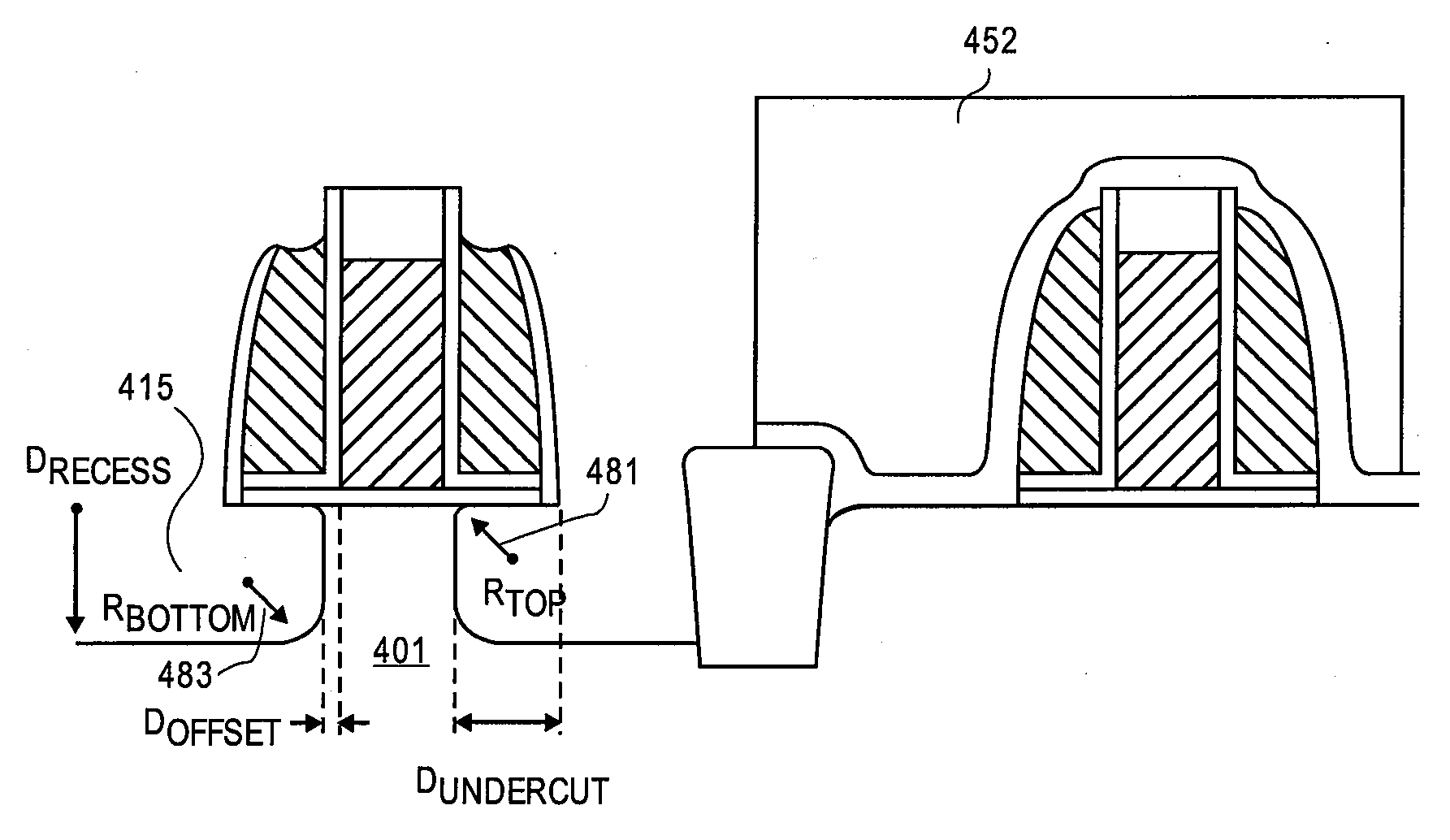
InactiveUS20090032880A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRe entrantAnisotropic plasma
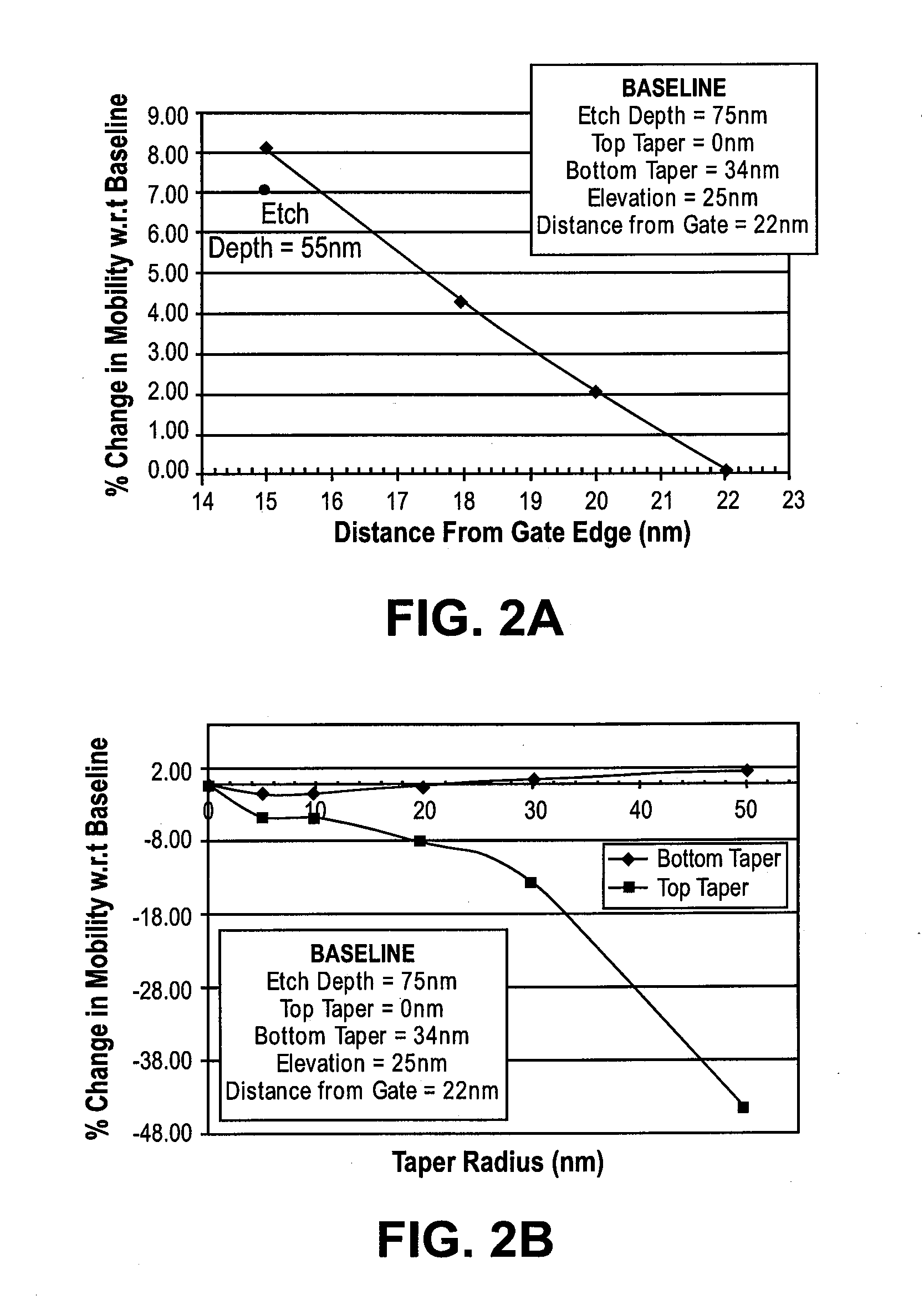
Methods and apparatuses to etch recesses in a silicon substrate having an isotropic character to undercut a transistor in preparation for a source / drain regrowth. In one embodiment, a cap layer of a first thickness is deposited over a transistor gate stack and spacer structure. The cap layer is then selectively etched in a first region of the substrate, such as a p-MOS region, using a first isotropic plasma etch process and a second anisotropic plasma etch process. In another embodiment, an at least partially isotropic plasma recess etch is performed to provide a recess adjacent to the channel region of the transistor. In a particular embodiment, the plasma etch process provides a recess sidewall that is neither positively sloped nor more than 10 nm re-entrant.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
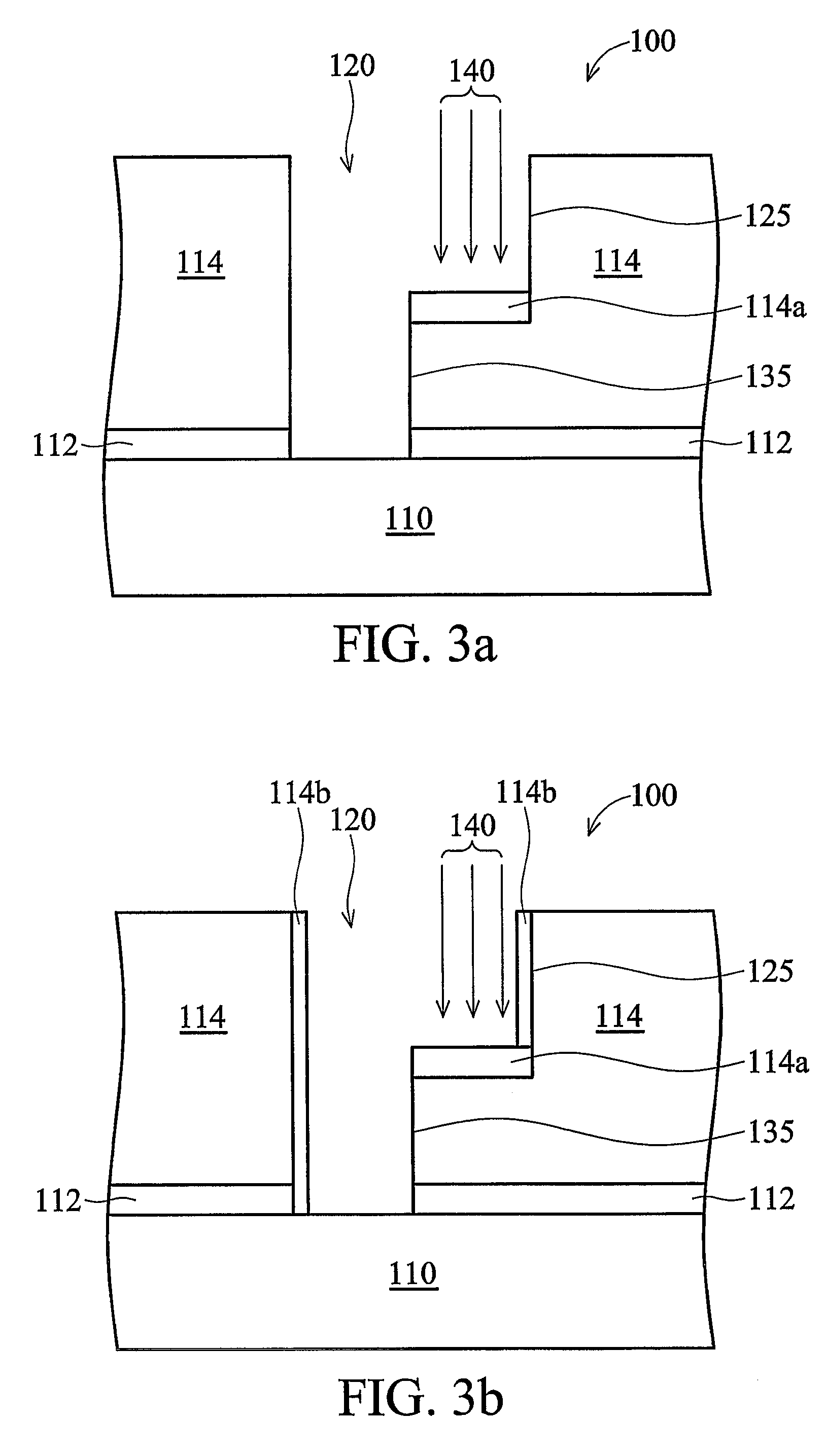
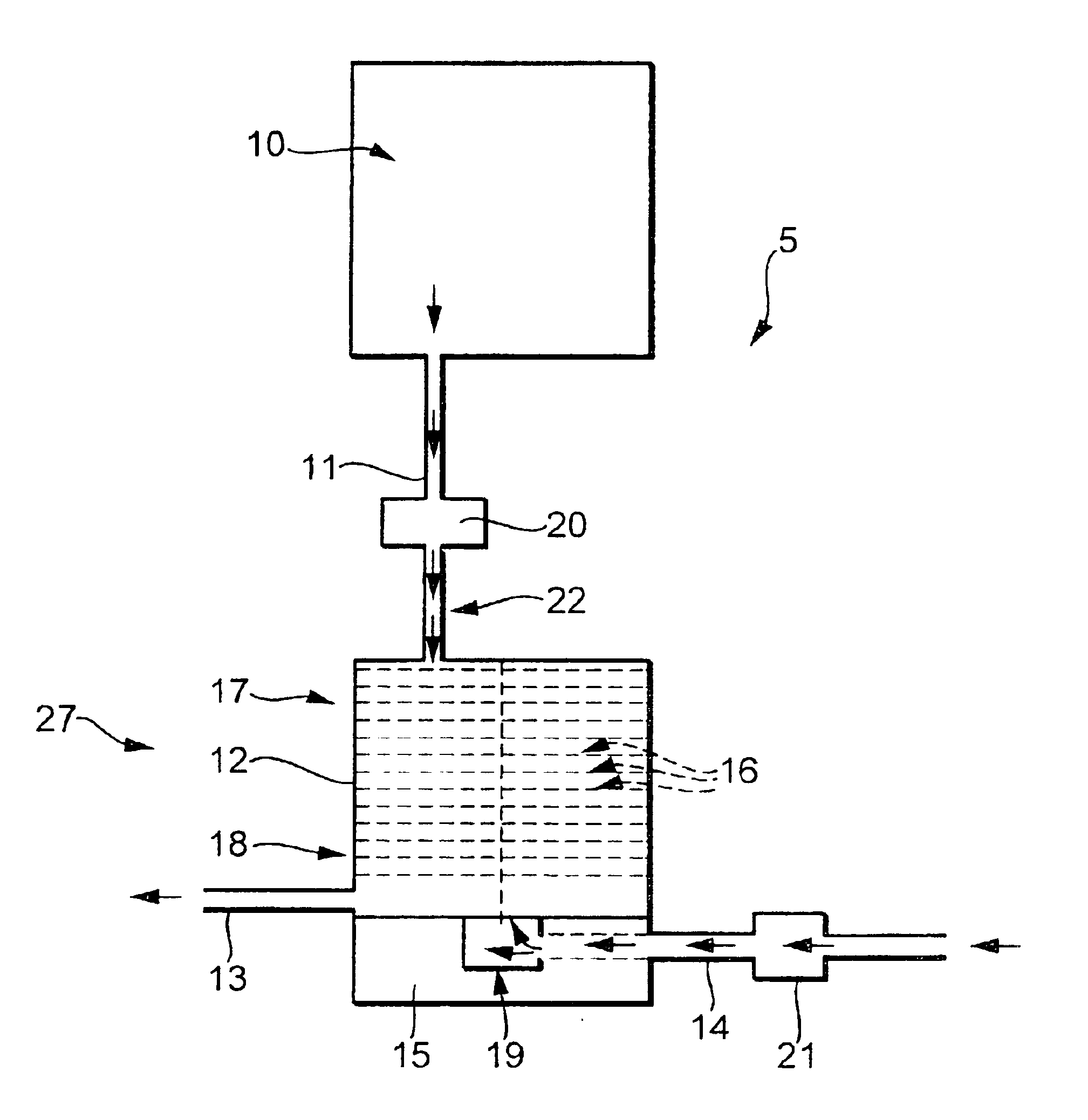
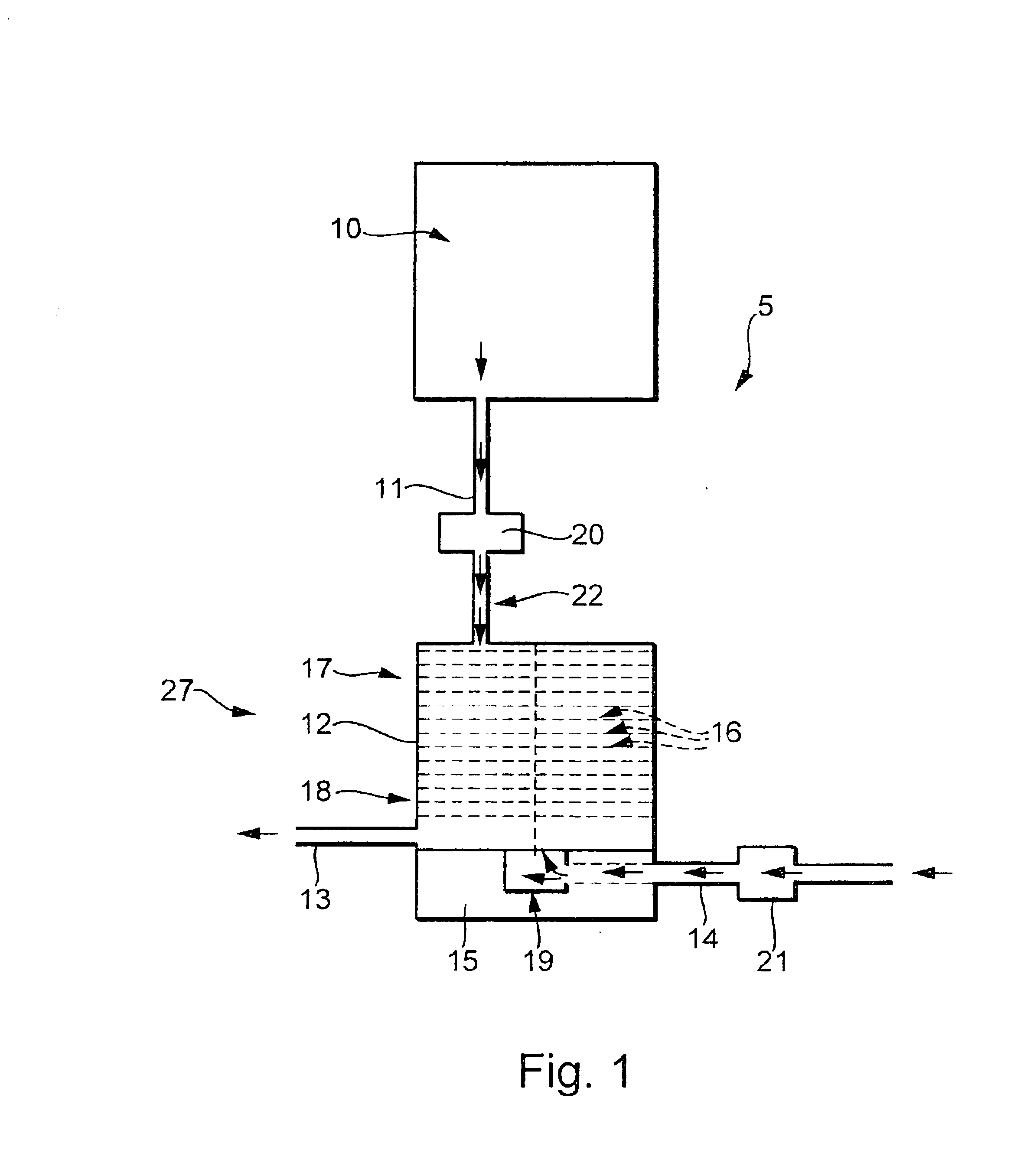
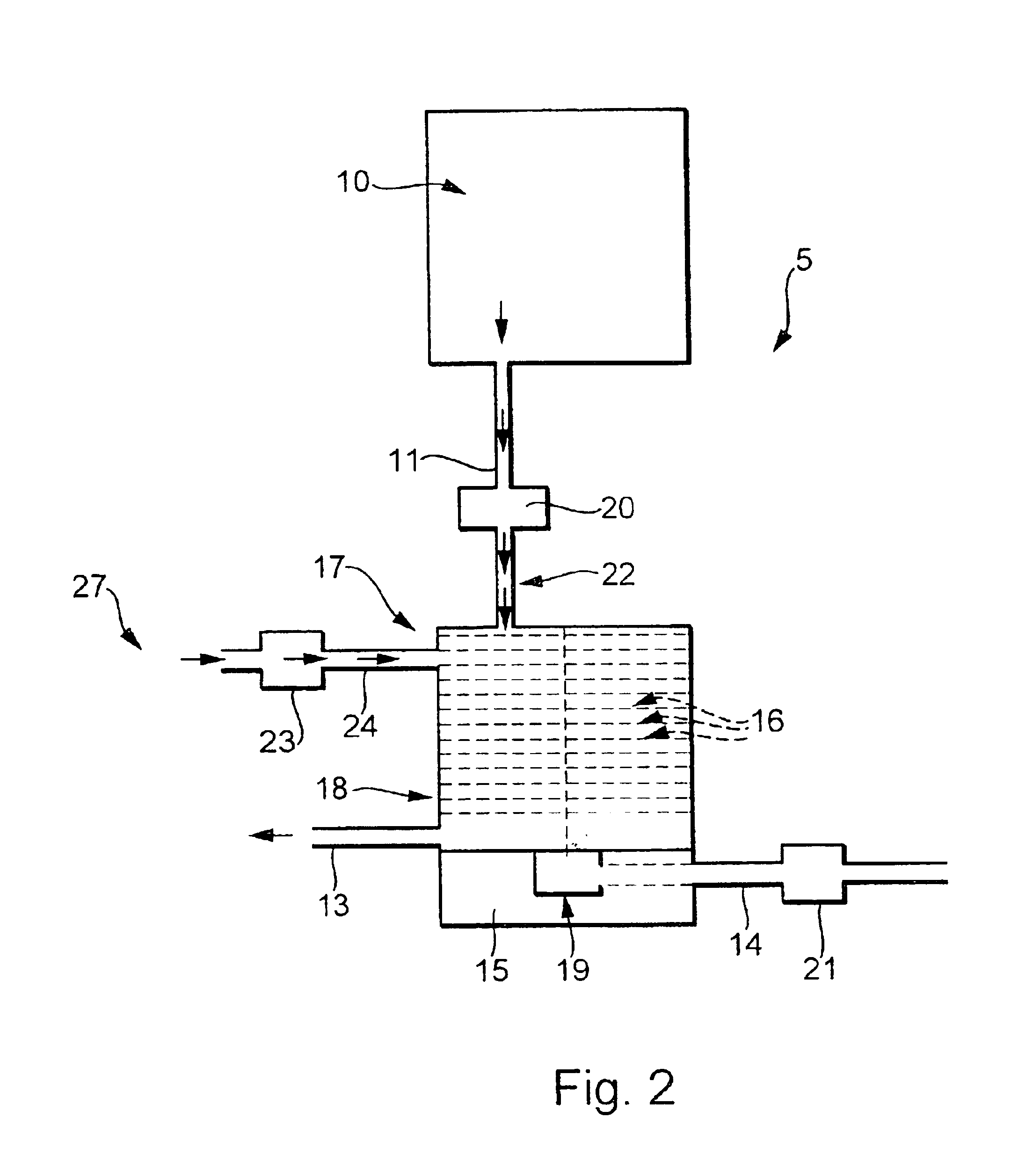
Device and method for anisotropically plasma etching of a substrate, particularly a silicon body
InactiveUS20050126710A1Increase etch rateImprove the level ofDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaSilicon
A method and device for implementing the method for anisotropically plasma etching a substrate (e.g., silicon body). The device has a chamber and plasma source for generating a high-frequency electromagnetic alternating field and a reaction region for generating a plasma having reactive species, within the chamber, that is generated by the action of the alternating field on etching gas and passivation gas introduced at the same time but spatially separated from it. An arrangement defines at least one first zone acted on by the etching gas and at least one second zone acted on by the passivation gas in the reaction region. The device has a mixing region downstream of the reaction region in which the reactive species generated from the etching gas in the first zone and the reactive species generated from the passivation gas in the second zone are blended before they act on the substrate.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Device and method for anisotropic plasma etching of a substrate, a silicon body in particular
InactiveUS7285228B2Increase etch rateImprove the level ofDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaReaction zone
A method and device for implementing the method for anisotropically plasma etching a substrate (e.g., silicon body). The device has a chamber and plasma source for generating a high-frequency electromagnetic alternating field and a reaction region for generating a plasma having reactive species, within the chamber, that is generated by the action of the alternating field on etching gas and passivation gas introduced at the same time but spatially separated from it. An arrangement defines at least one first zone acted on by the etching gas and at least one second zone acted on by the passivation gas in the reaction region. The device has a mixing region downstream of the reaction region in which the reactive species generated from the etching gas in the first zone and the reactive species generated from the passivation gas in the second zone are blended before they act on the substrate.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for fabricating micro-structures with various surface properties in multi-layer body by plasma etching
The technology is based on the anisotropic plasma etching of organic polymer sheets partially protected by a metallic mask. The originality of the process is to pattern the surface properties by the same physical means as the one used for the three dimensional fabrication and simultaneously to this fabrication. Surface properties means, but are not limited to hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, conductivity, reflectability, rugosity and more precisely the chemical and / or physical state of the surface. It is also possible to generate the desired fonctionalities, for instance carboxylic acid, ester, ether, amid or imid, during the etching process. The patterning of the different properties may be achieved by two different techniques that may be used separately or simultaneously.
Owner:DIAGNOSWISS
Apparatus and method for forming heat sinks on silicon on insulator wafers
ActiveUS7119431B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive pasteWafering
An apparatus and method for a heat sink to dissipate the heat sourced by the encapsulated transistors in a SOI wafer. The apparatus includes a transistor formed in the active silicon layer of the wafer. The active surface is formed over an oxide layer and a bulk silicon layer. A heat sink is formed in the bulk silicon layer and configured to sink heat through the bulk silicon layer, to the back surface of the wafer. After the transistor is fabricated, the heat sink is formed by masking, patterning and etching the back surface of the wafer to form plugs in the bulk silicon layer. The plug extends through the thickness of the bulk layer to the oxide layer. Thereafter, the plug is filled with a thermally conductive material, such as a metal or DAG (thermally conductive paste). During operation, heat from the transistor is dissipated through the heat sink. In various embodiments of the invention, the plug hole is formed using either an anisotropic plasma or wet etch.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Dual damascene cleaning method
ActiveUS7329956B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureConductive materials
A semiconductor structure having a pore sealed portion of a dielectric layer is provided. Exposed pores of the dielectric material are sealed using an anisotropic plasma so that pores along the bottom of the opening are sealed, and pores along sidewalls of the opening remain relatively untreated by the plasma. Thereafter, one or more barrier layers may be formed and the opening may be filled with a conductive material. The barrier layers formed over the sealing layer exhibits a more continuous barrier layer. The pores may be partially or completely sealed by plasma bombardment or ion implantation using a gas selected from one of O2, an O2 / N2 mixture, H2O, or combinations thereof.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
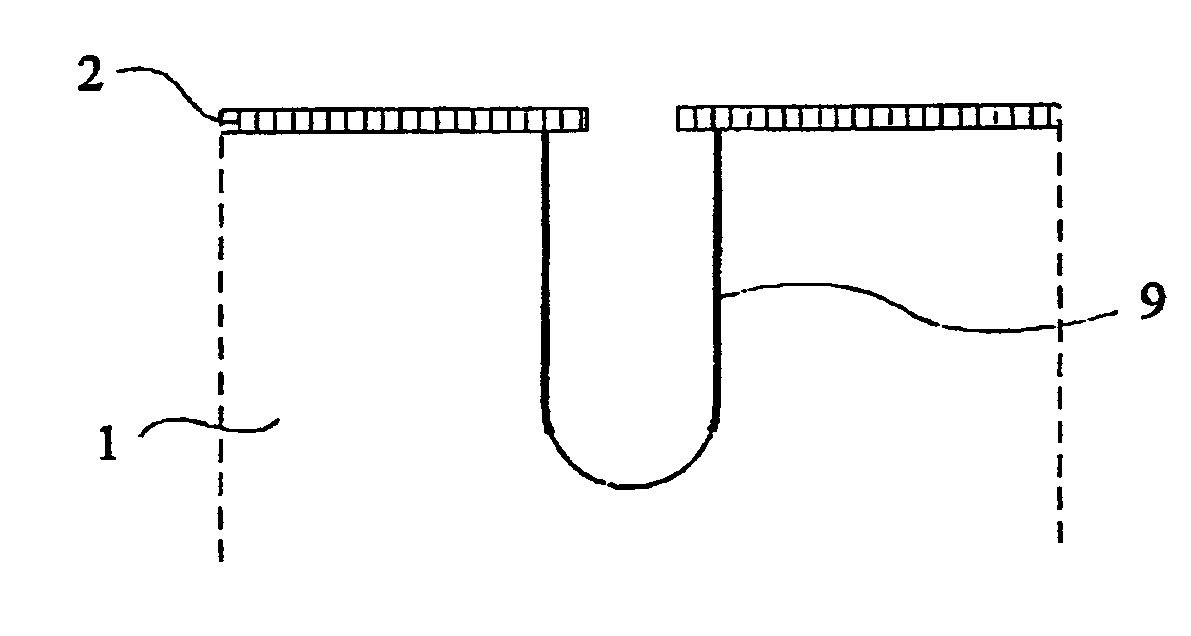
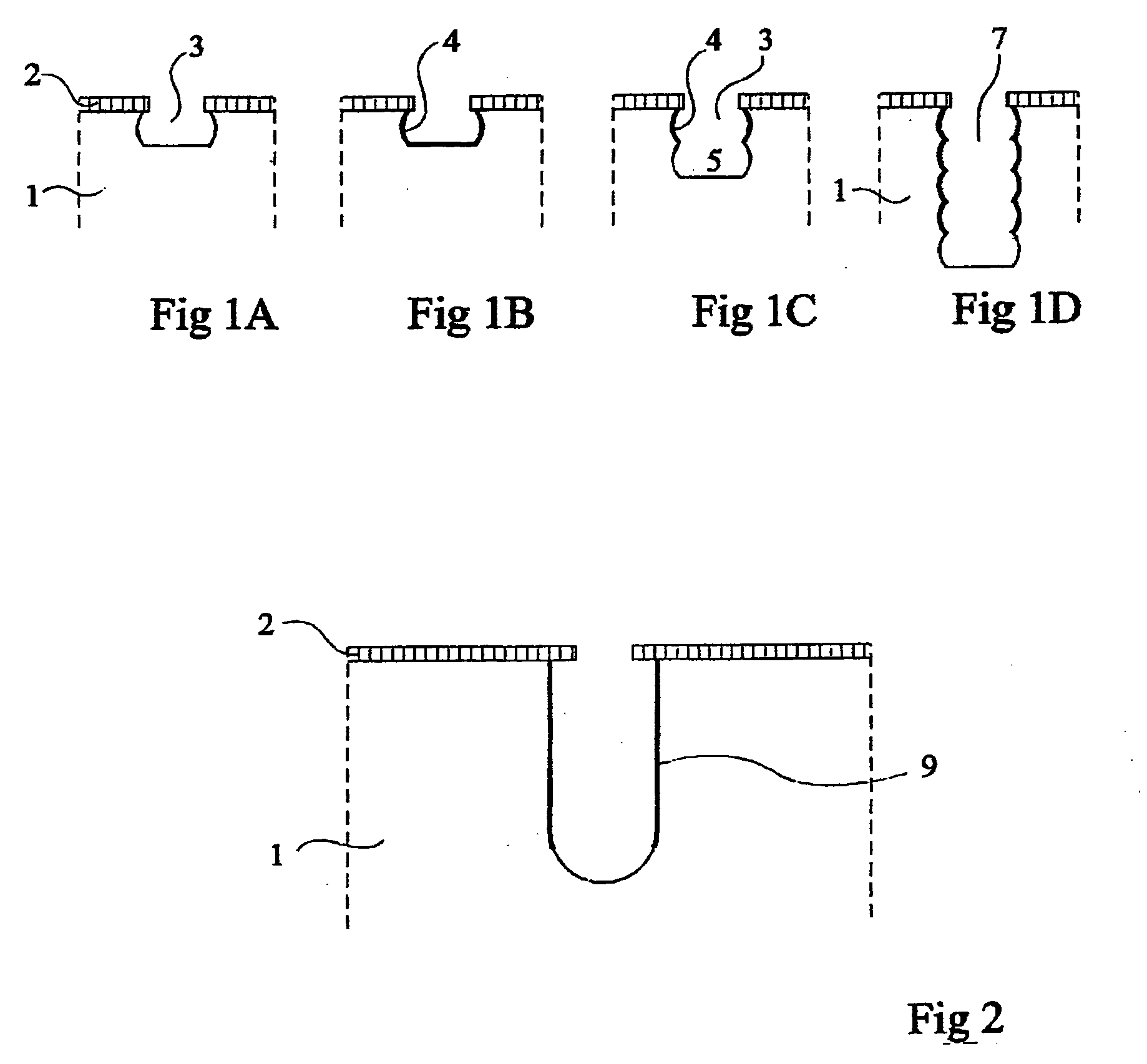
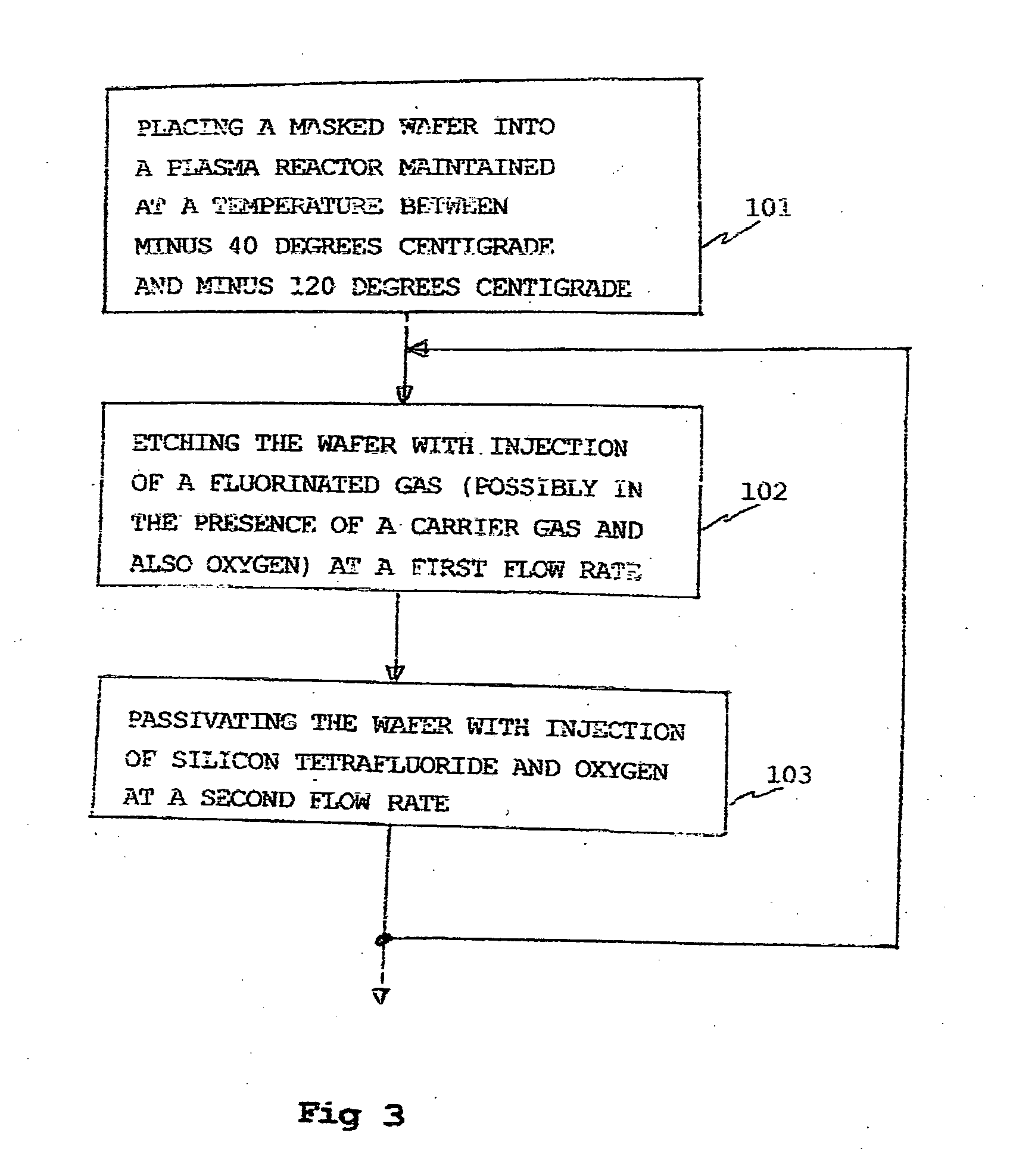
Deep anisotropic silicon etch method
ActiveUS20080293250A1Eliminate disadvantagesDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorinated gasesSilicon tetrafluoride
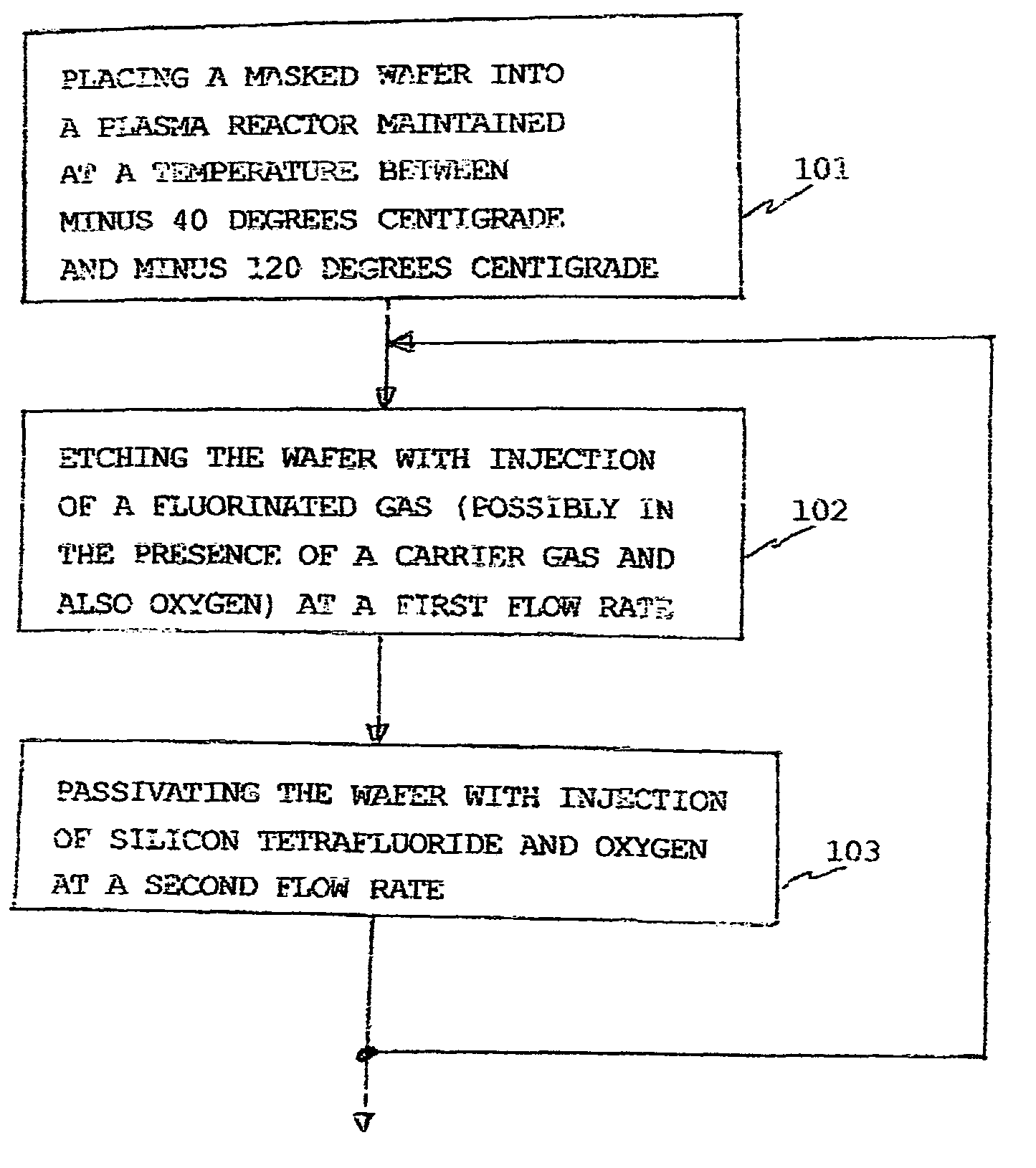
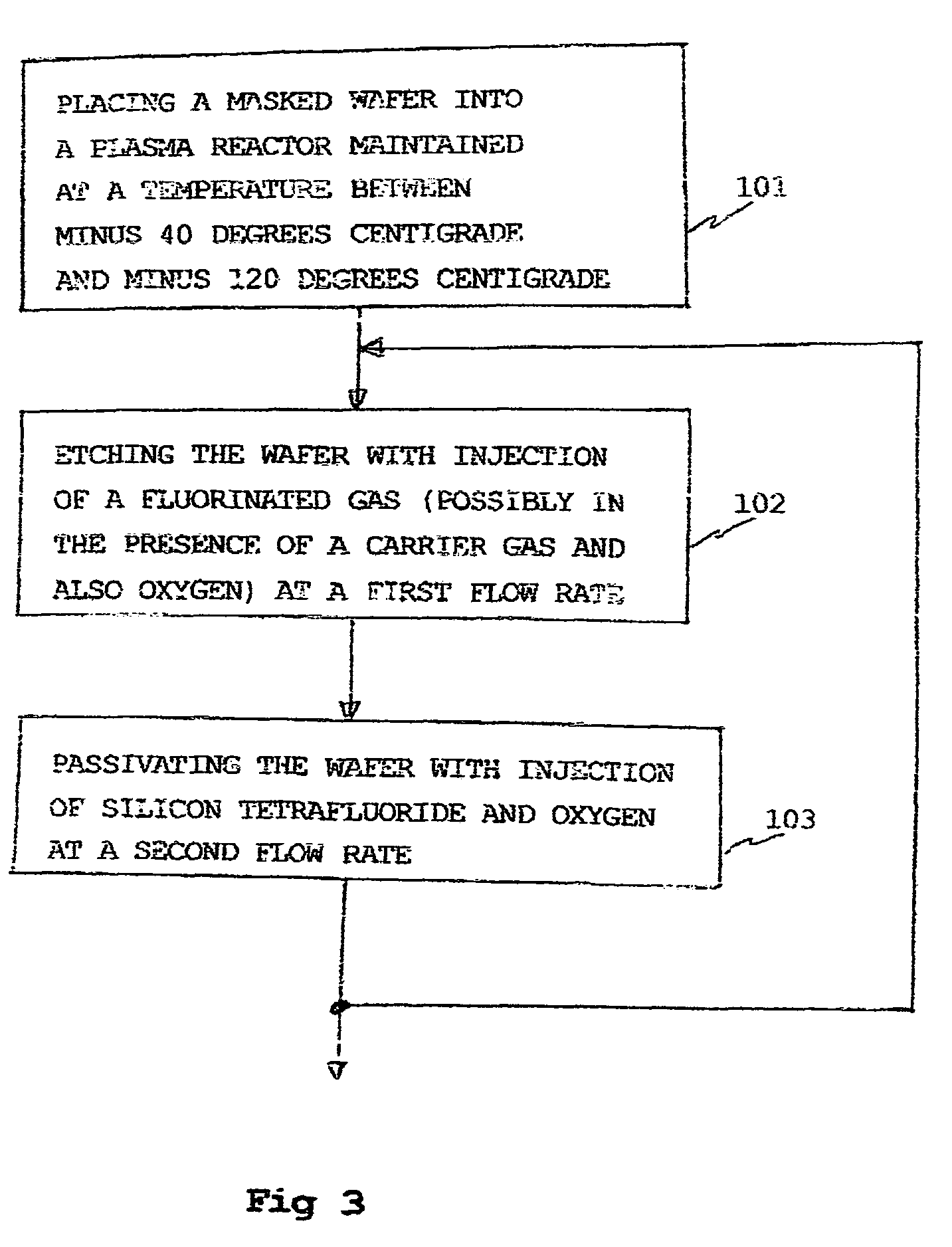
A method of anisotropic plasma etching of a silicon wafer, maintained at a temperature from −40° C. to −120° C., comprising alternated and repeated steps of:etching with injection of a fluorinated gas, into the plasma reactor, andpassivation with injection of silicon tetrafluoride, SiF4, and of oxygen into the plasma reactor, the flow rate of the gases in the plasma reactor being on the order of from 10% to 25% of the gas flow rate during the etch step.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
Anisotropic etching of organic-containing insulating layers
InactiveUS6844266B2Increase etch rateElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistO2 plasma
A method for anisotropic plasma etching of organic-containing insulating layers is disclosed. According to this method at least one opening is created in an organic-containing insulating layer formed on a substrate. These openings are created substantially without depositing etch residues by plasma etching said insulating layer in a reaction chamber containing a gaseous mixture which is composed such that the plasma etching is highly anisotropic. Examples of such gaseous mixtures are a gaseous mixture comprising a fluorine-containing gas and an inert gas, or a gaseous mixture comprising an oxygen-containing gas and an inert gas, or a gaseous mixture comprising HBr and an additive. The plasma etching of the organic-containing insulating layer can be performed using a patterned bilayer as an etch mask, said bilayer comprising a hard mask layer, being formed on said organic-containing insulating layer, and a resist layer being formed on said hard mask layer. A method is disclosed for forming a layer, protecting exposed surfaces of low-k dielectrics. More particularly the method comprises the steps of sealing exposed surfaces of a, preferably porous, low-k dielectric, by forming a protective layer on exposed surfaces during or after the step of patterning openings in the porous dielectric layers. Preferably this protective layer is formed by a N2 / O2 plasma treatment of the exposed surfaces.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
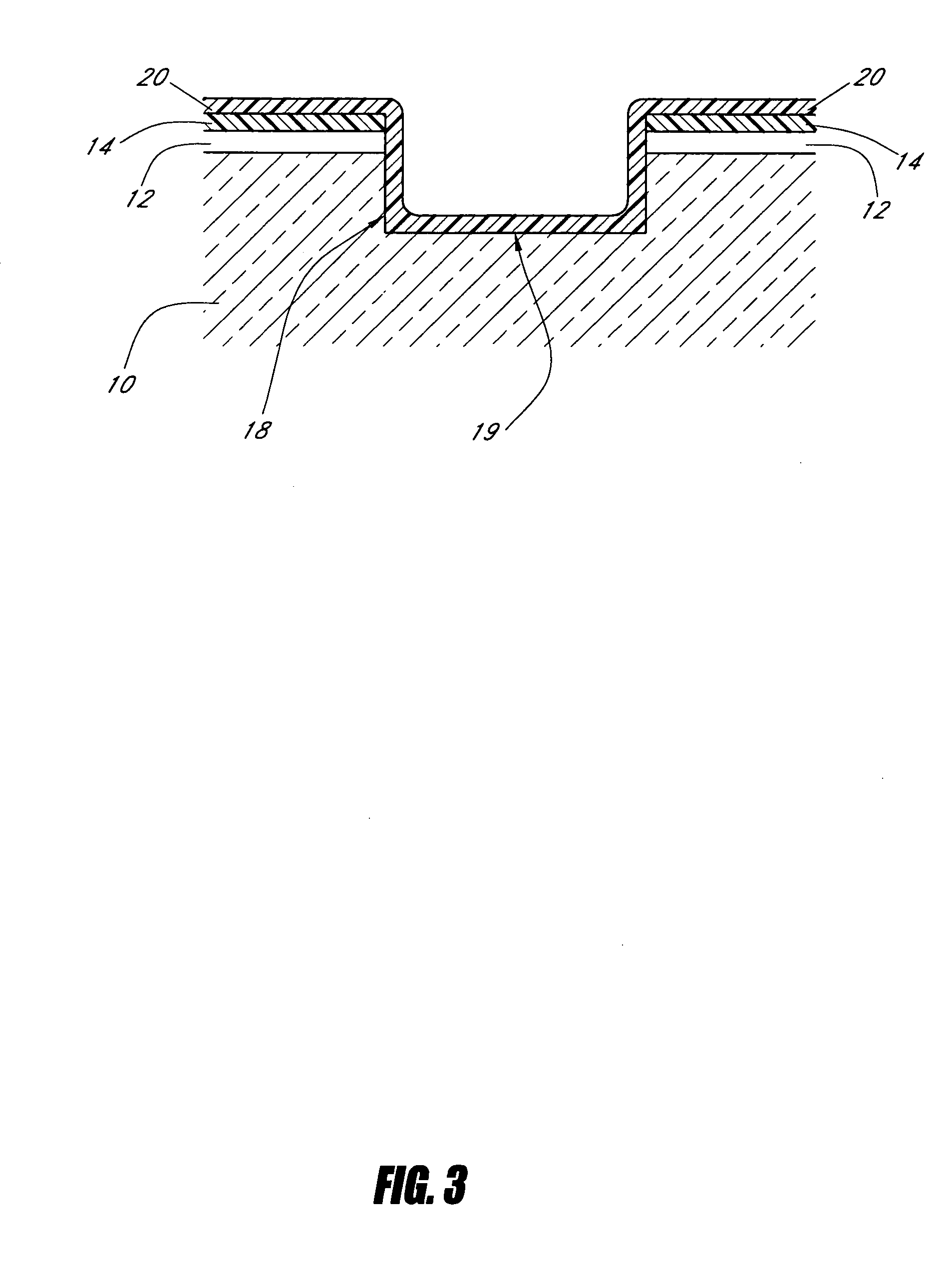
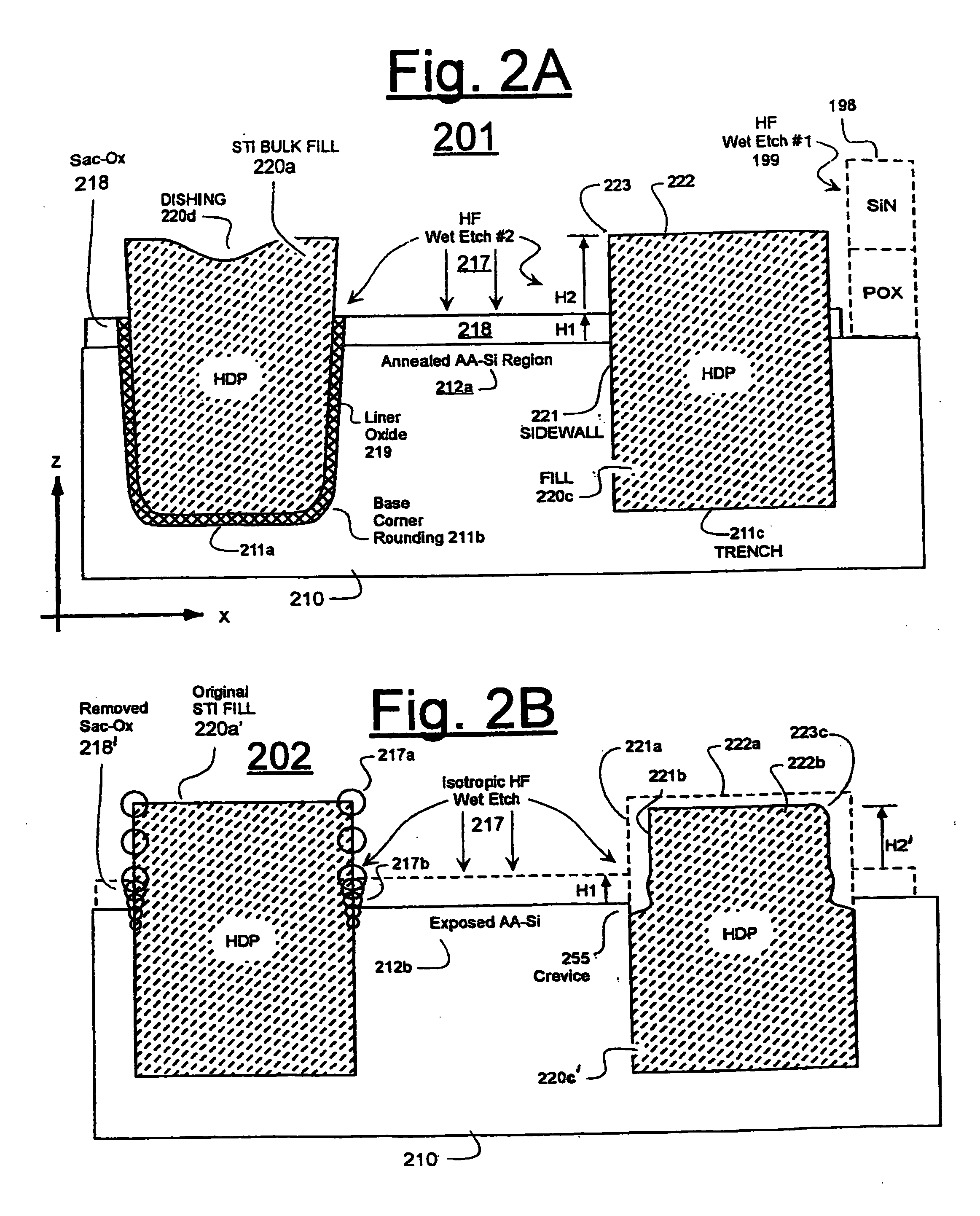
Trench insulation structures and methods
ActiveUS20060125043A1High densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnisotropic plasmaSilicon
A method of depositing dielectric material into sub-micron spaces and resultant structures is provided. After a trench is etched in the surface of a wafer, a liner layer preferably is deposited into the trench. An anisotropic plasma process is then performed on the trench. A silicon layer may be deposited on the base of the trench during the plasma process, or the plasma can treat the liner layer. The trench is then filled with a spin-on precursor. A densification or reaction process is then applied to convert the spin-on material into an insulator, and oxidizing the silicon rich layer on the base of the trench. The resulting trench has a consistent etch rate from top to bottom of the trench.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
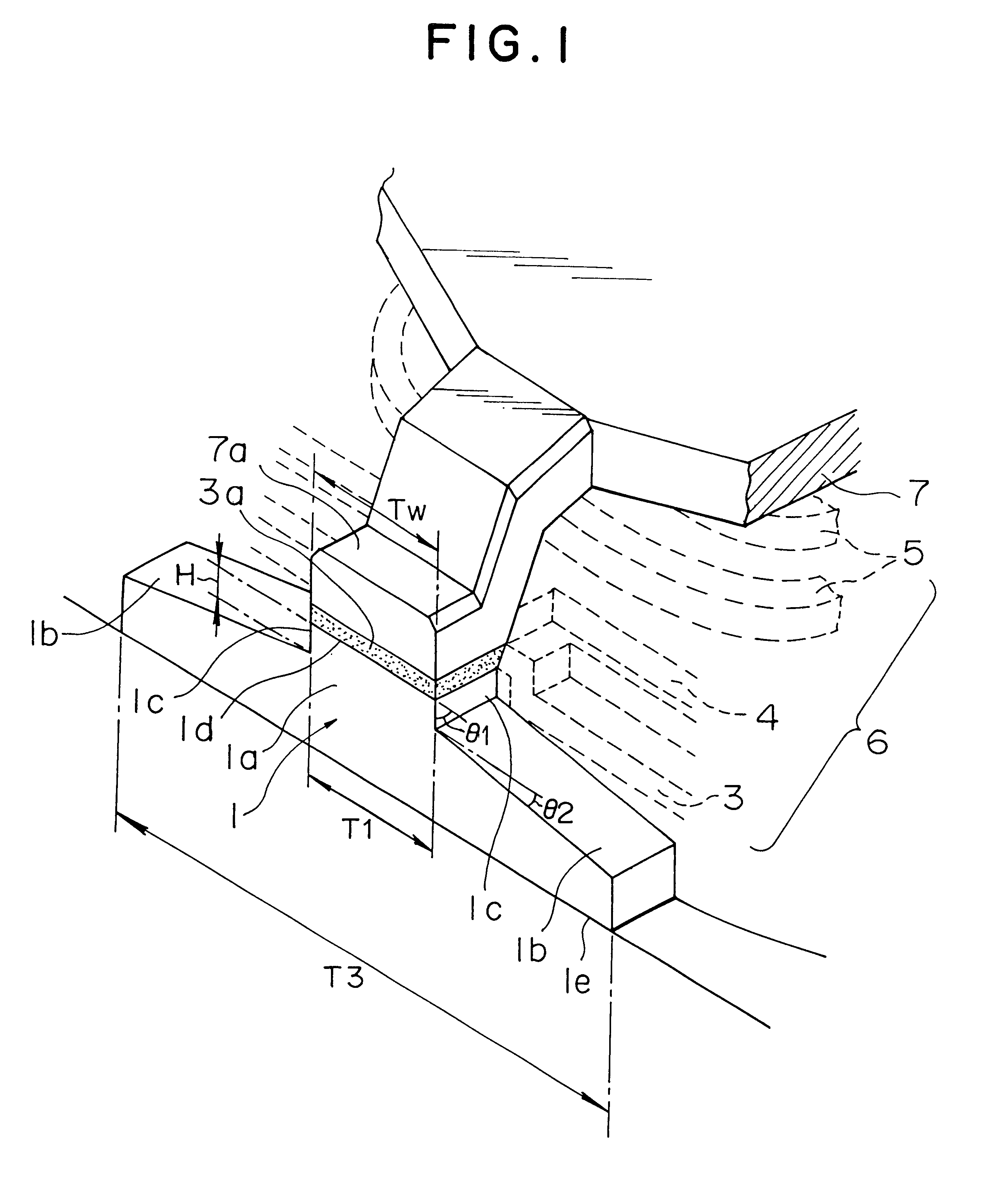
Combination read/write thin film magnetic head and its manufacturing method
A method for manufacturing a combination read / write thin film magnetic head comprising the steps of: forming a nonmagnetic material layer on a lower-core layer and forming an upper-core layer having a width smaller than that of the lower-core layer on the nonmagnetic material layer; leaving the section of said nonmagnetic material layer sandwiched between the lower-core layer and the upper-core layer as a gap layer and removing the nonmagnetic material layer not covered by the upper-core layer, said step for removing said nonmagnetic material being performed by an anisotropic plasma etching process using a CF4 based gas; trimming both ends of the facing surfaces, to be in contact with said gap layer, of the lower-core layer so as to equalize the width of the facing surface with the width of the upper-core layer, and forming a prominence above the lower-core layer facing the upper-core layer through the gap layer; and forming grades on both upper surfaces of the lower-core layer extending from the base ends of the prominence in the direction away from the upper-core layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Post-lithography misalignment correction with shadow effect for multiple patterning
InactiveUS7700444B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEvaporationNext-generation lithography
Misalignment created during a multiple-patterning process is a serious challenge for critical dimension (CD) control and layout design in continuing integrated-circuit device scaling. A number of post-lithography misalignment correction technologies based on the shadow effect are invented for multi-patterning lithographic applications. When applied to transfer patterns from a top layer to an underneath layer, the subtractive shadow effect in anisotropic plasma etching combined with a hard-mask process, will shift the position of features such that the previously produced misalignment can be corrected. Also, additive shadow effect in a sputtering / evaporation process can be used. Misalignment correction methods allow the semiconductor industry to print sub-32 nm (half-pitch) features using the double-patterning technique with currently existing lithographic tools (e.g., 193-nm DUV scanner), therefore postponing the need of expensive next-generation lithography (NGL). The misalignment correction methods can be applied to existing lithography technologies to print features smaller than their physical resolution limits.
Owner:CHEN YIJIAN
Method and device for providing a semiconductor etching end point and for detecting the end point
InactiveUS6974709B2Process economySolve the lack of precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesGas phaseElectrical polarity
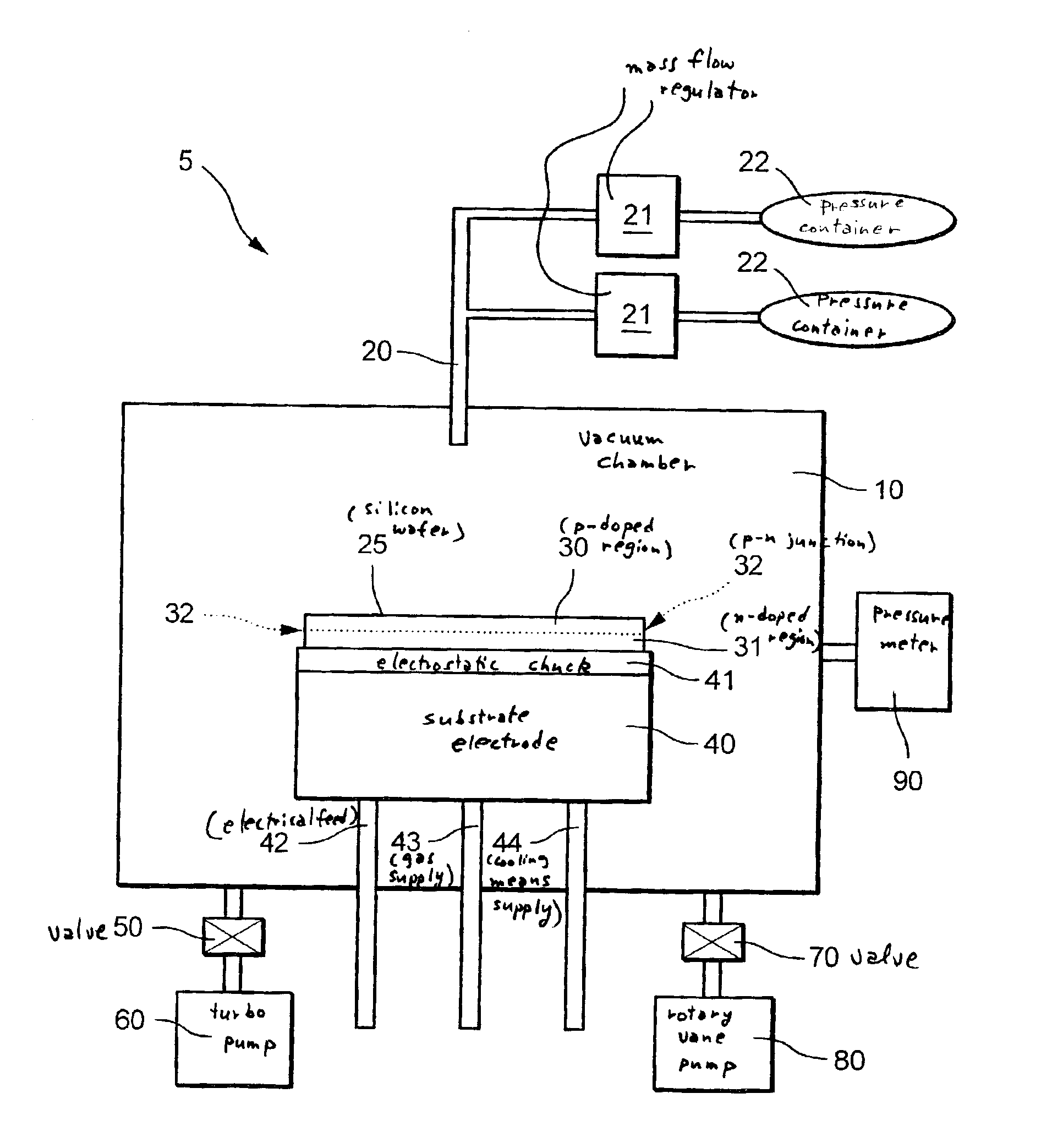
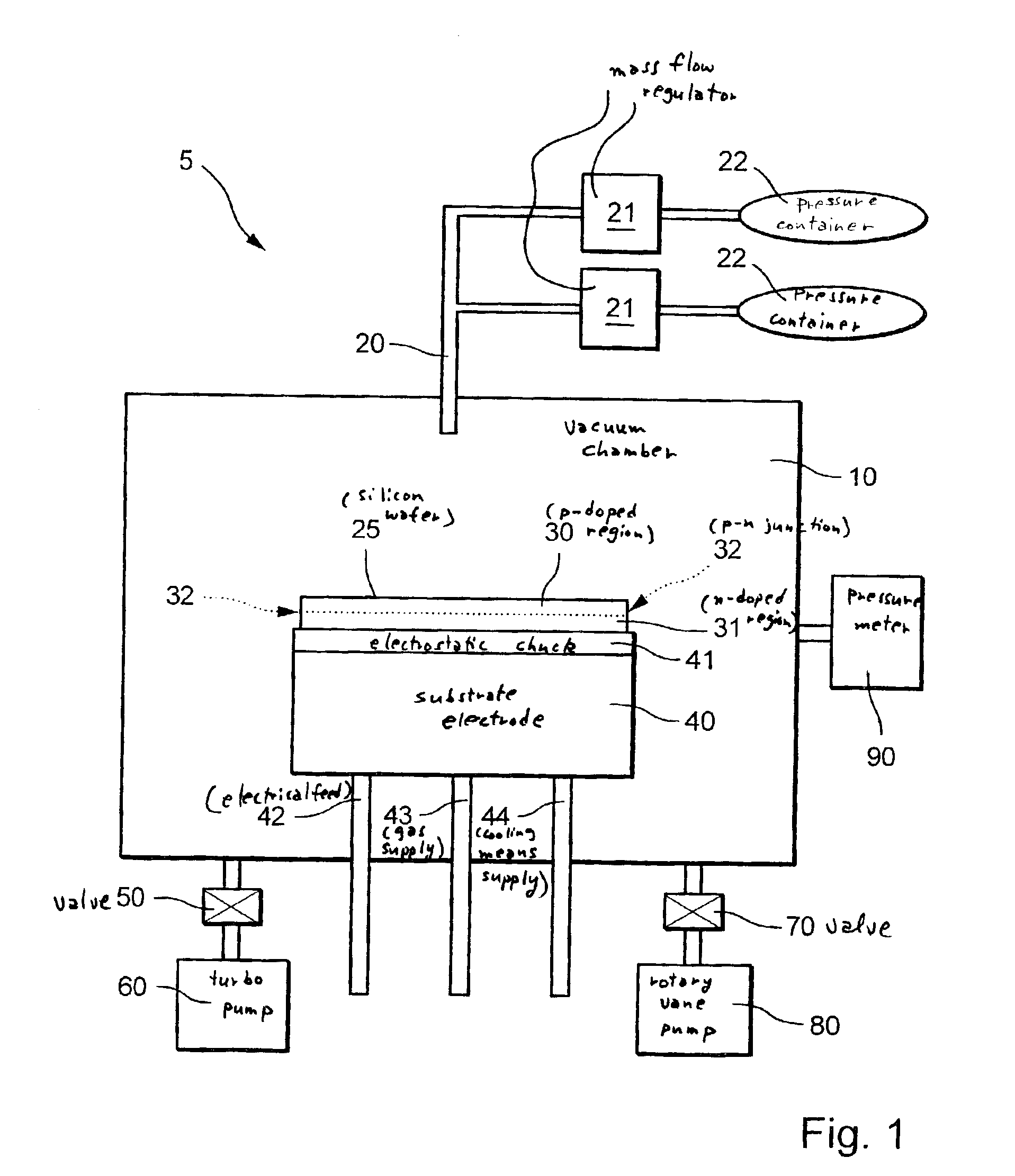
A method is provided for detecting an end point, a material transition or a boundary surface during the etching of a semiconductor element, a zone of the semiconductor element having non-homogeneous load carrier density and / or non-homogeneous load carrier polarity, particularly a p-n junction, which has an electrical voltage applied to it during etching, and an electrical current induced by it in this zone is measured, and reaching of this zone during etching is determined from a change in the electrical current. This method is suitable for the detection of the etching end point in gas phase etching, in particular with the aid of the etching gases ClF3 and / or BrF3, or in the anisotropic plasma etching of silicon substrates. In addition, a method is provided for etching a semiconductor element using a gaseous etching medium, during which the speed of removal of the semiconductor element is set or changed via a setting of the polarity and / or the density of free load carriers in the semiconductor element. In addition, a device for etching a semiconductor element, which device is suitable for carrying out the two methods described above, is provided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for fabrication of polycrystalline silicon thin film transistors
InactiveUS7115449B2Improve mobilityReduce the differenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaActive layer
The present invention provides a method for fabrication of polycrystalline silicon thin film transistors, which forms a silicon spacer on the sidewall of the active layer of a thin film transistor (TFT) by way of anisotropic plasma etching in a single direction. The silicon spacer provides a mechanism for laser recrystallization on the sidewall to prevent the active layer from shrinkage or shelling-off after the laser recrystallization. According to the present invention, large grains can be formed in the channel without additional mask during production. By doing so, the characteristics of the components are enhanced; the uniformity is improved; and, the production cost is lowered. Therefore, this technique will play an important role in the fields of low temperature polycrystalline silicon thin film transistor (LTPS-TFT).
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
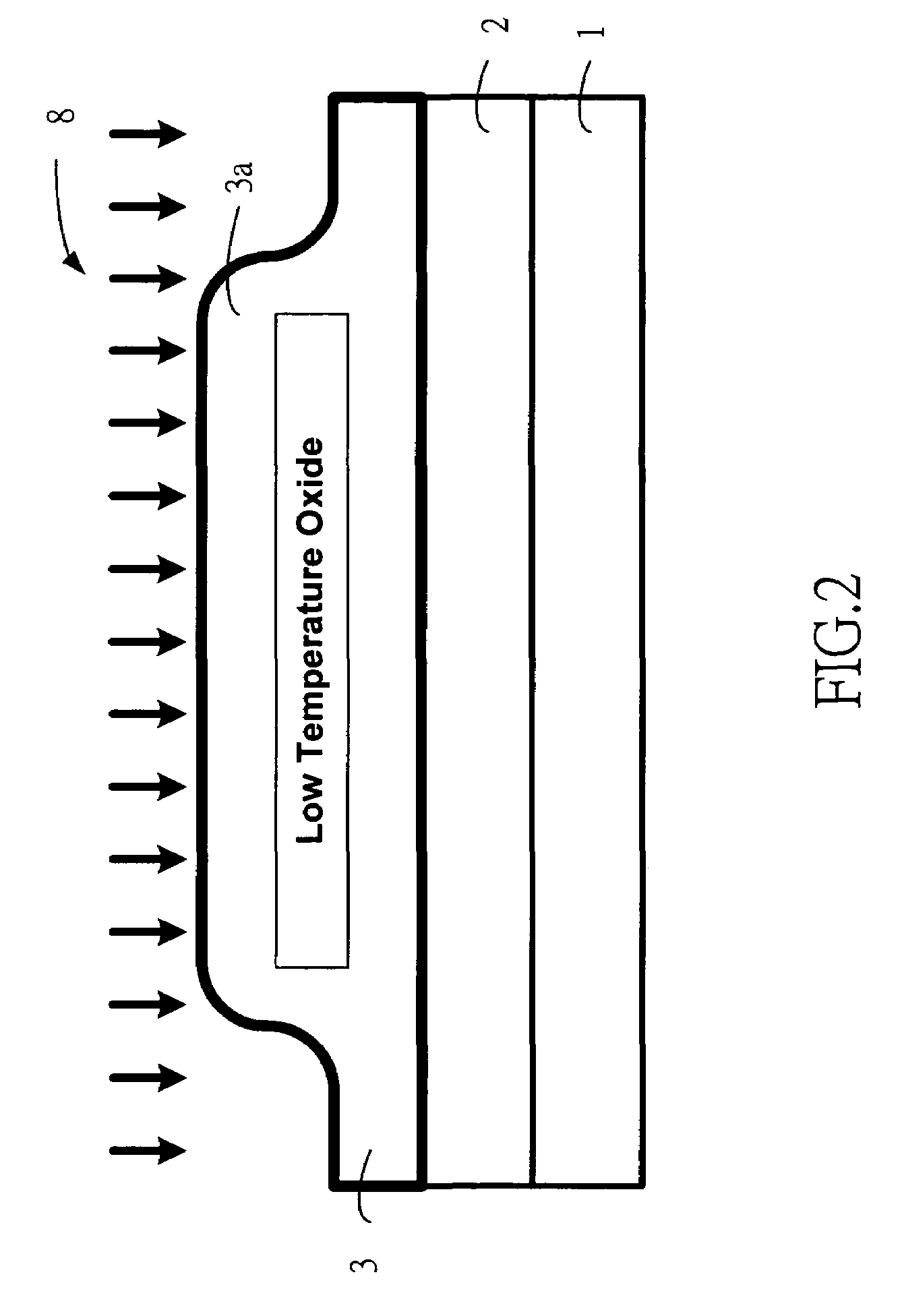
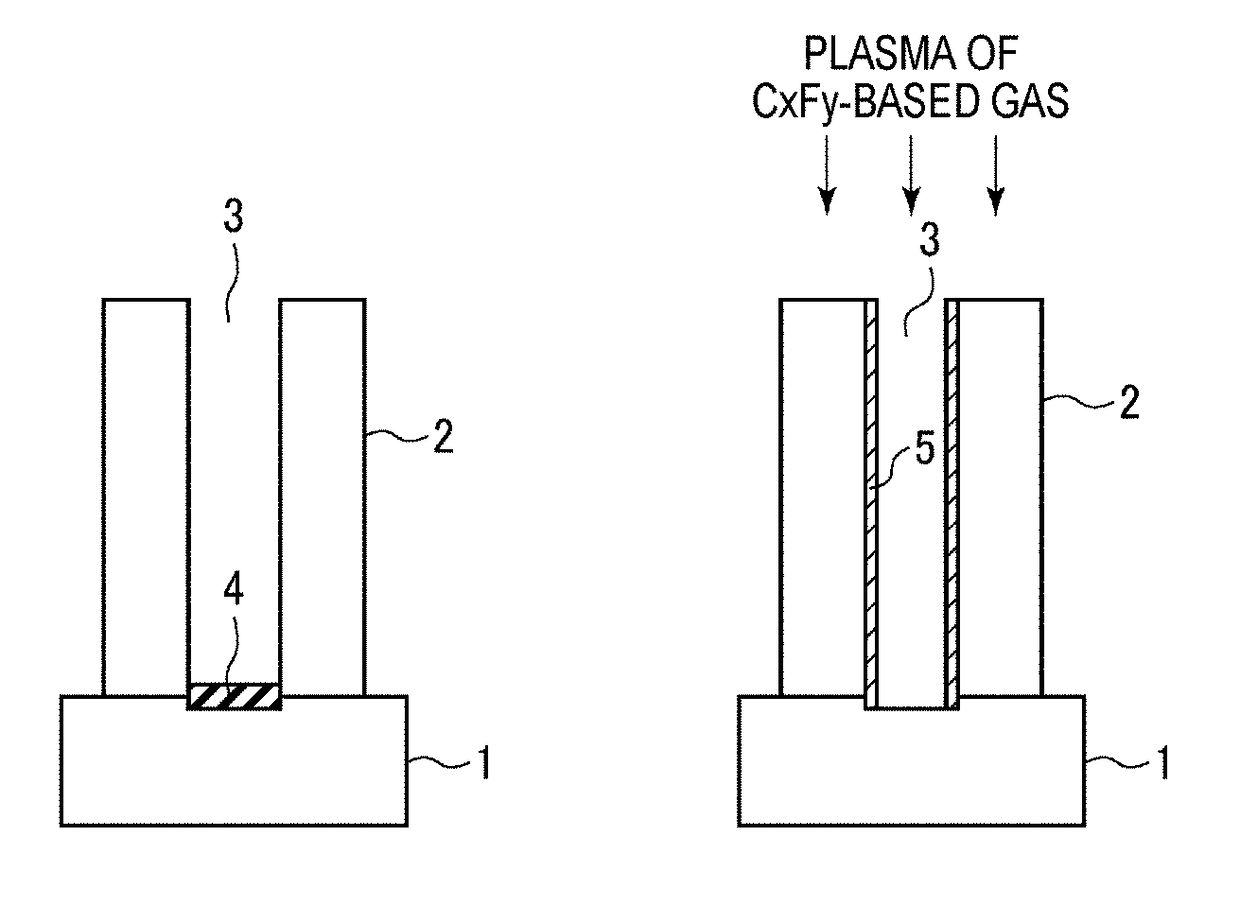
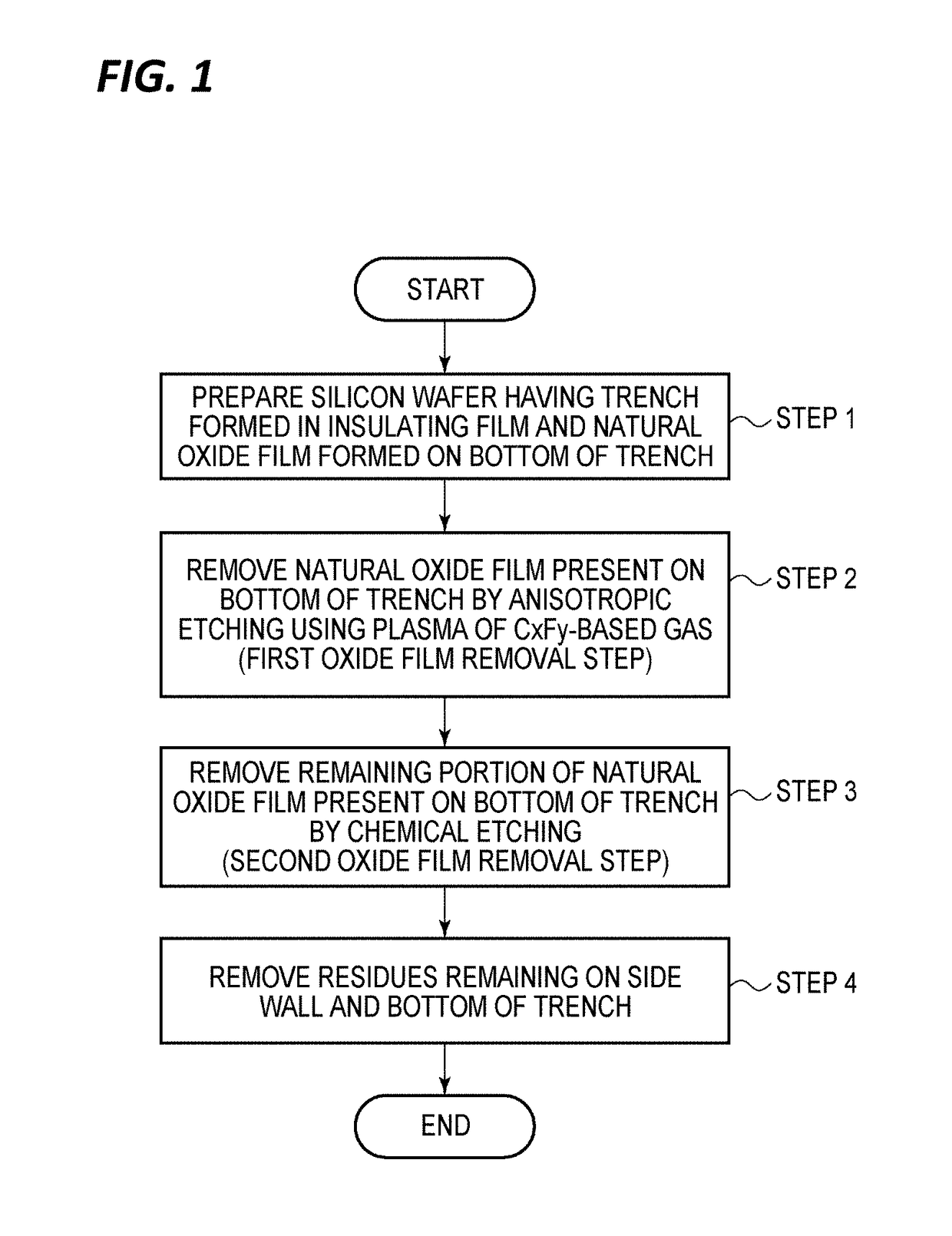
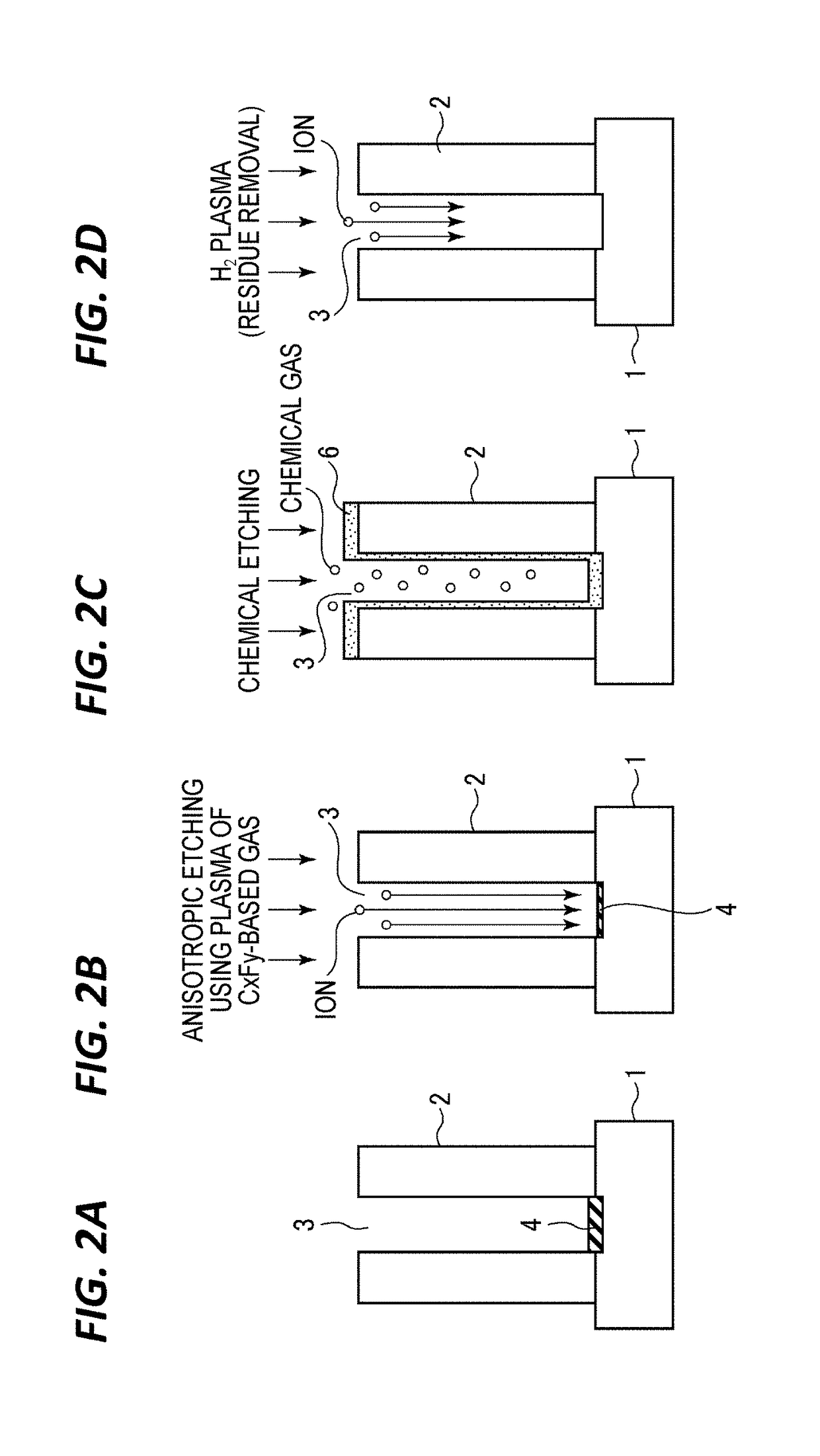
Oxide film removing method, oxide film removing apparatus, contact forming method, and contact forming system
InactiveUS20180261464A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact formationAnisotropic plasma
Disclosed is a method for removing, from a processing target substrate having an insulating film with a predetermined pattern formed thereon, a silicon-containing oxide film formed in a silicon portion of a bottom of the pattern. The method includes: removing the silicon-containing oxide film formed on the bottom of the pattern by ionic anisotropic plasma etching using plasma of a carbon-based gas; removing a remaining portion of the silicon-containing oxide film after the anisotropic plasma etching, by chemical etching; and removing a residue remaining after the chemical etching.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
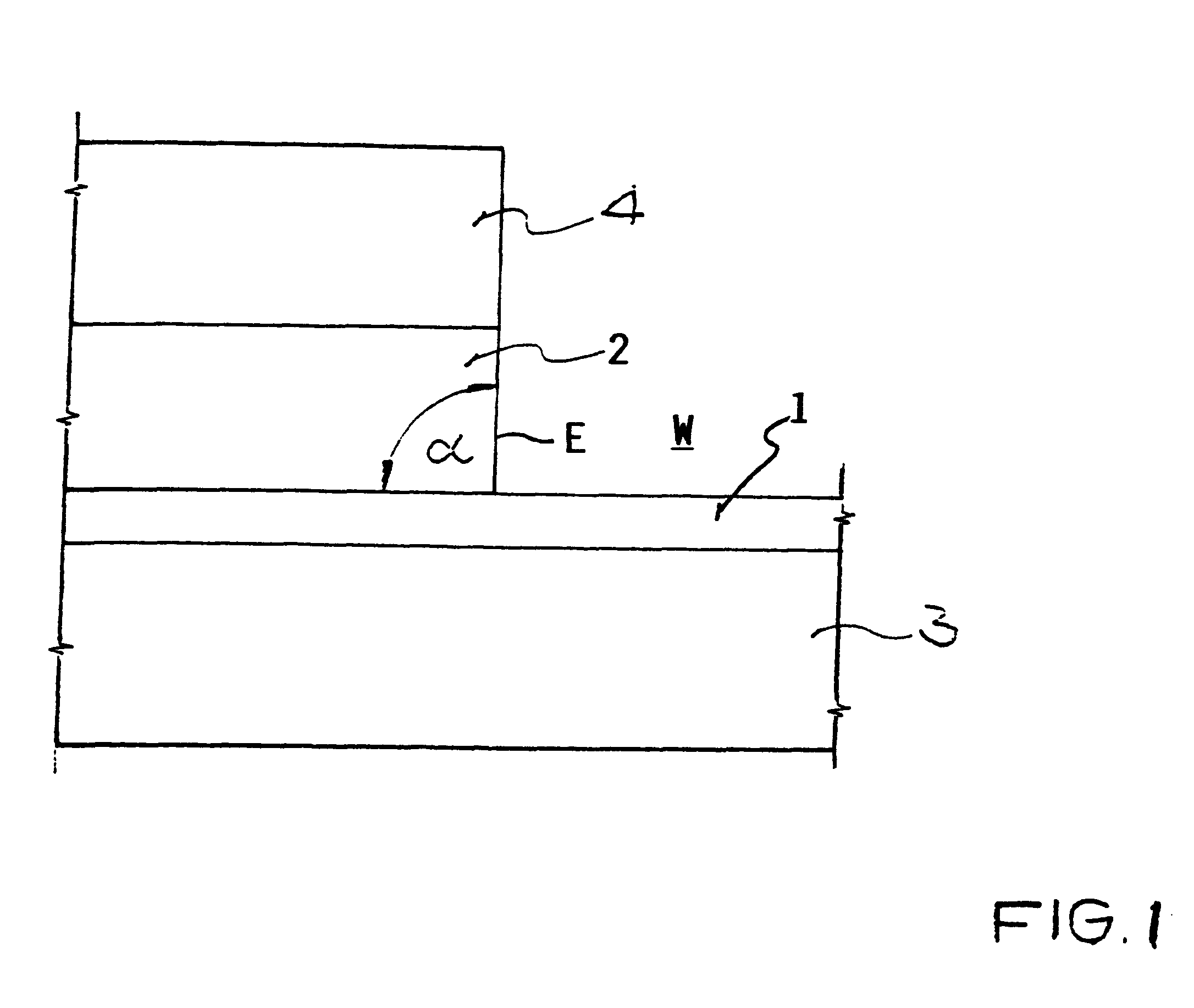
Method for forming a pattern on a substrate and electronic device formed thereby
InactiveUS20100148159A1Overcomes drawbackLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formLight beam
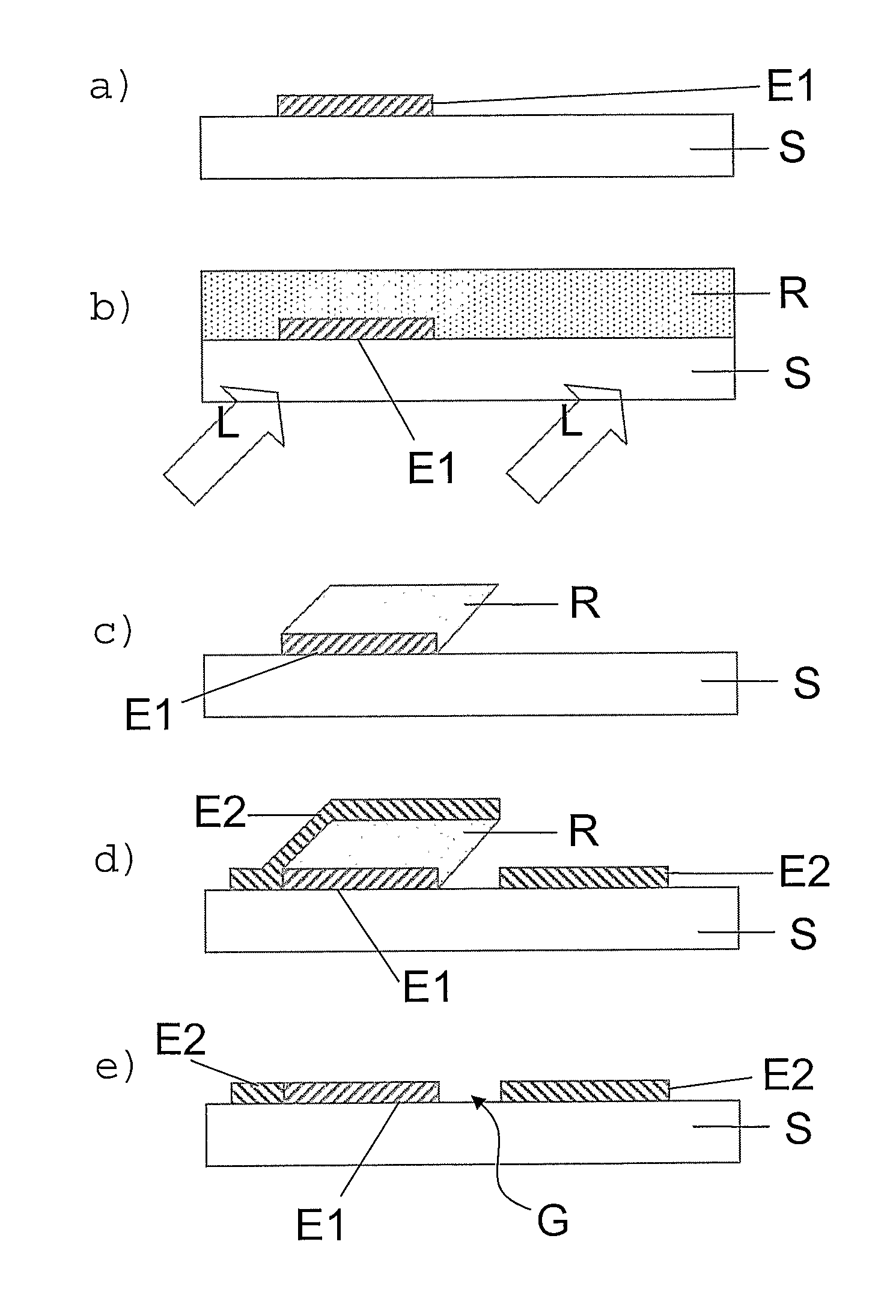
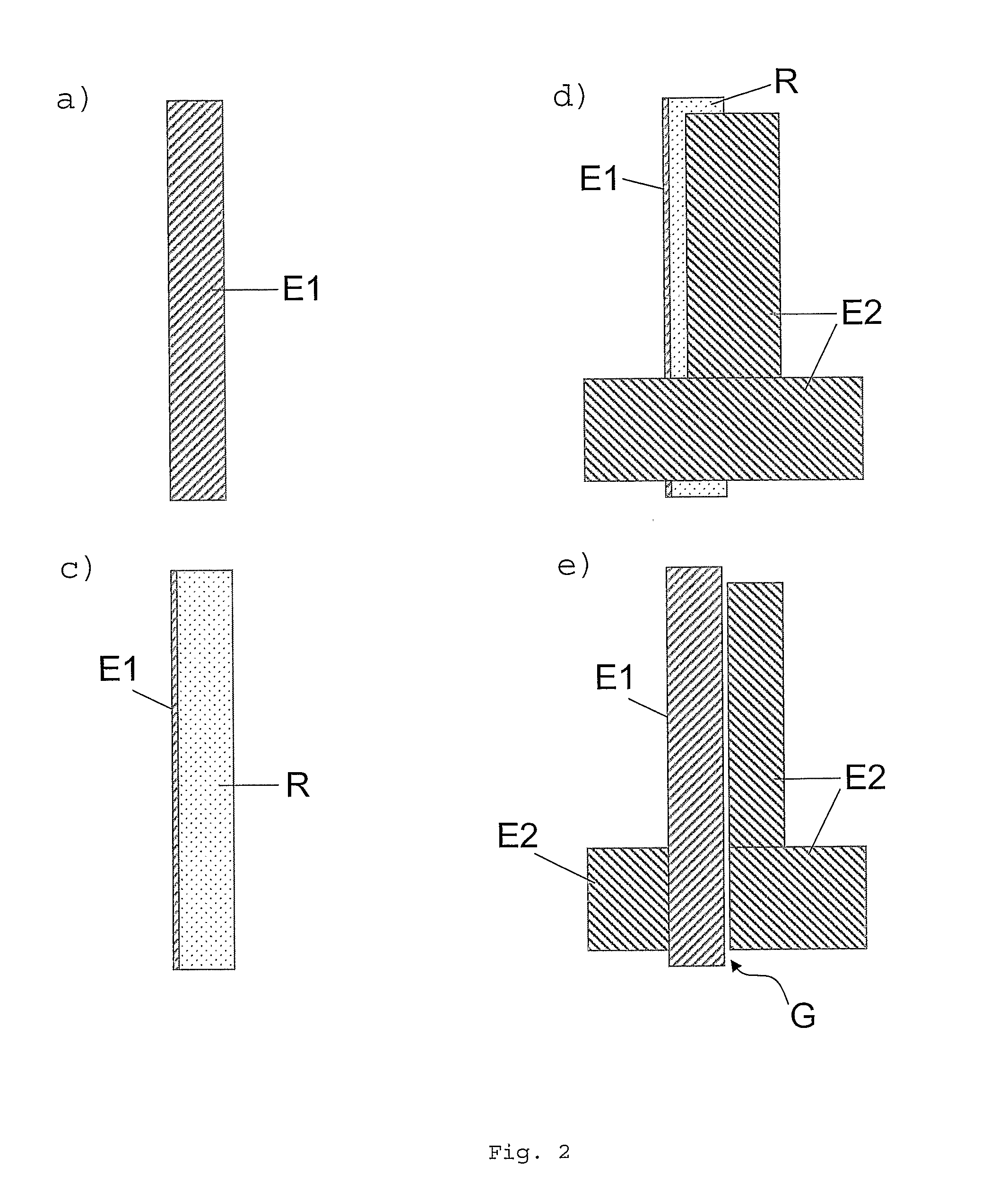
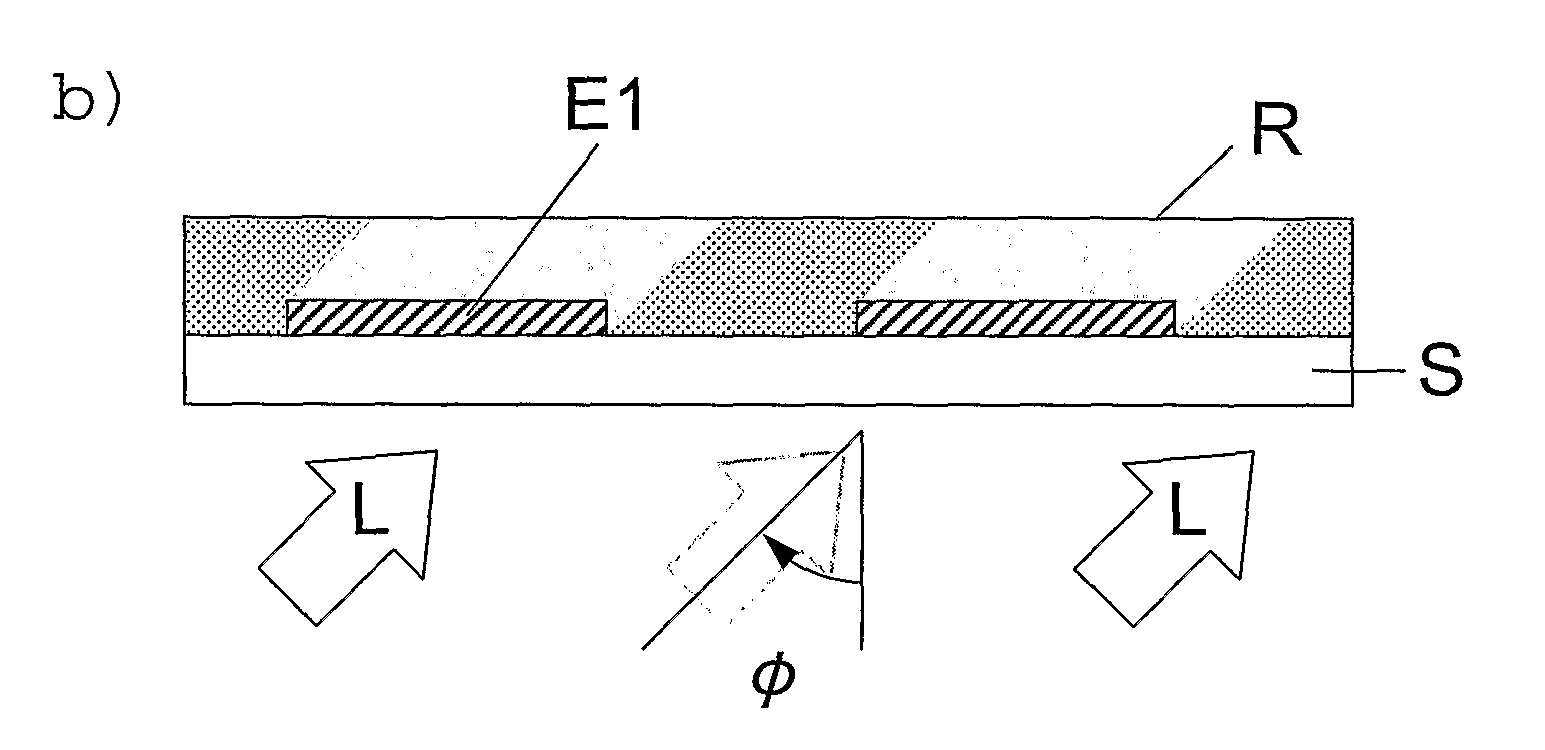
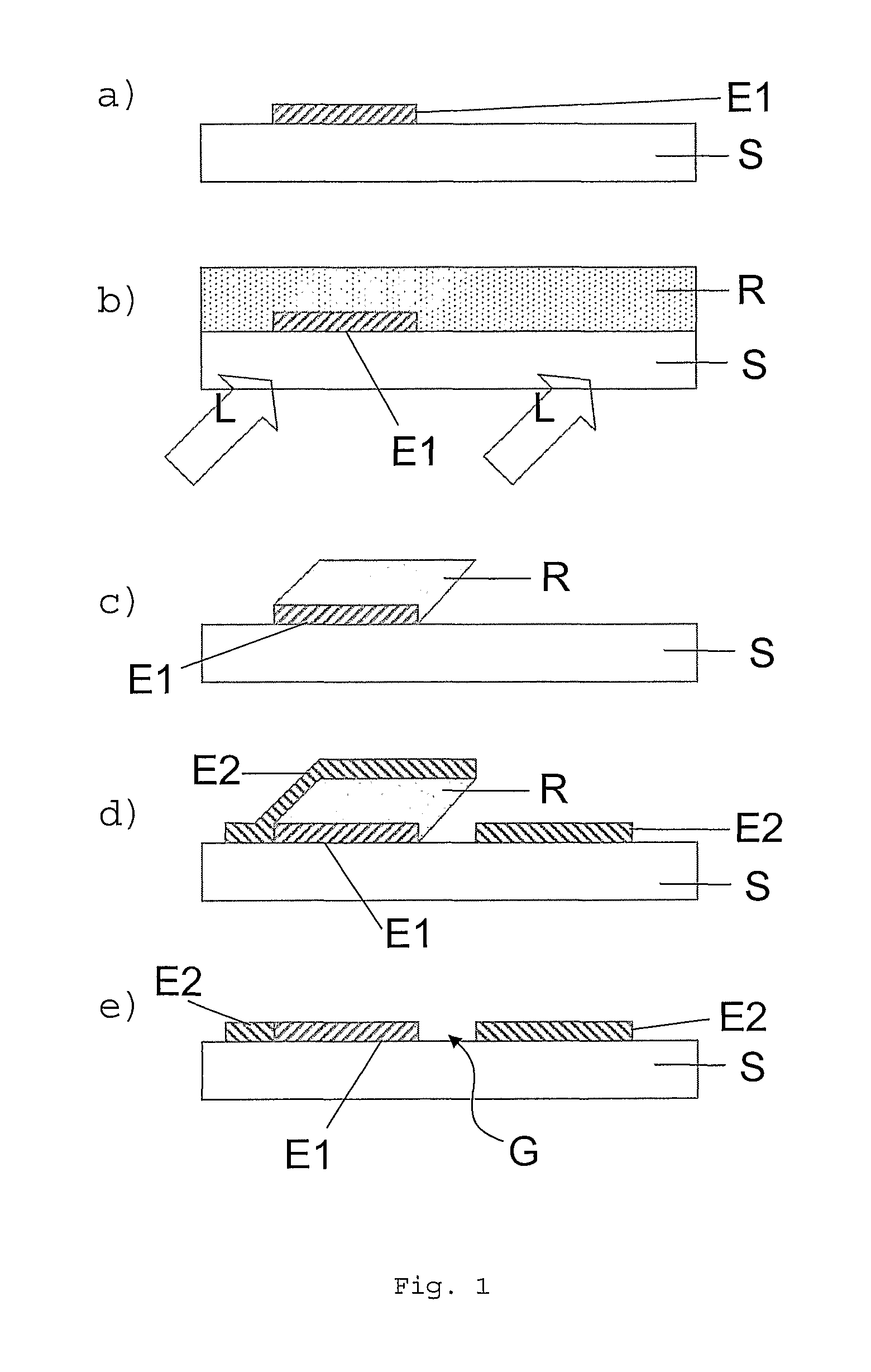
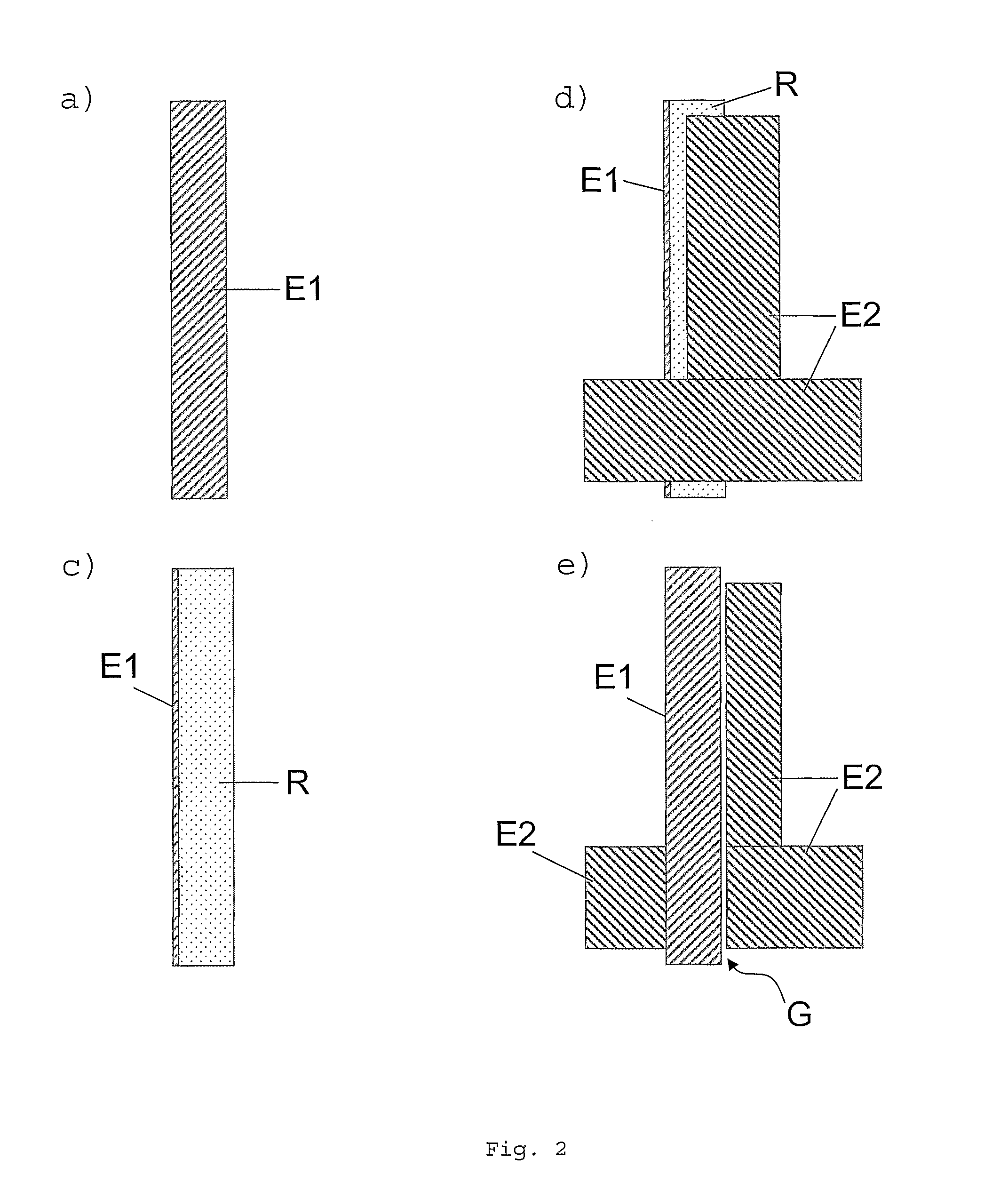
The invention relates to a method for forming a pattern on a substrate (S) with an upper surface and a lower surface which comprises the steps of depositing a first layer (E1) of an opaque material on the upper surface of the substrate (S), depositing a photosensitive layer (R) such that part of the photosensitive layer (R) covers at least part of the first layer (E1), exposing the photosensitive layer (R) to a light beam (L), the light beam (L) impinging on the lower surface of the substrate (S) under an oblique angle (Φ) of incidence, removing the exposed region of the photosensitive layer (R), depositing a second layer (E2) of an opaque material such that part of the second layer (E2) covers a remaining region of the photosensitive layer (R), and removing at least a part of the remaining region of the photosensitive layer (R). According to another aspect of the method of the invention anisotropic plasma etching is applied from above the upper surface of the substrate (S) after removal of the exposed region of the photosensitive layer (R) and thereafter the second layer (E2) is deposited. The method of the invention can be applied for forming a source electrode and a drain electrode of a thin-film field effect transistor. The invention furthermore relates to an electronic device fabricated by such a method.
Owner:BASF AG
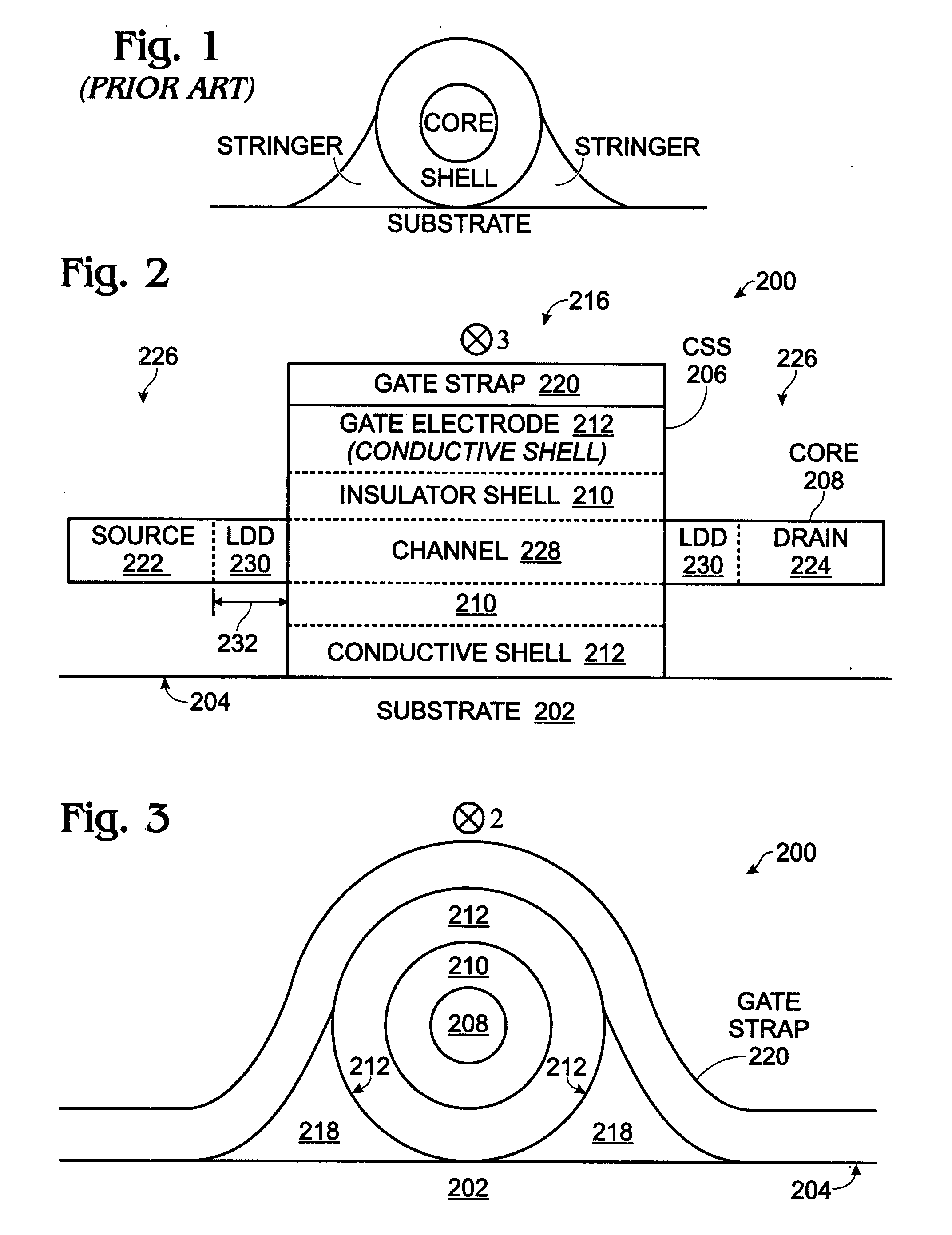
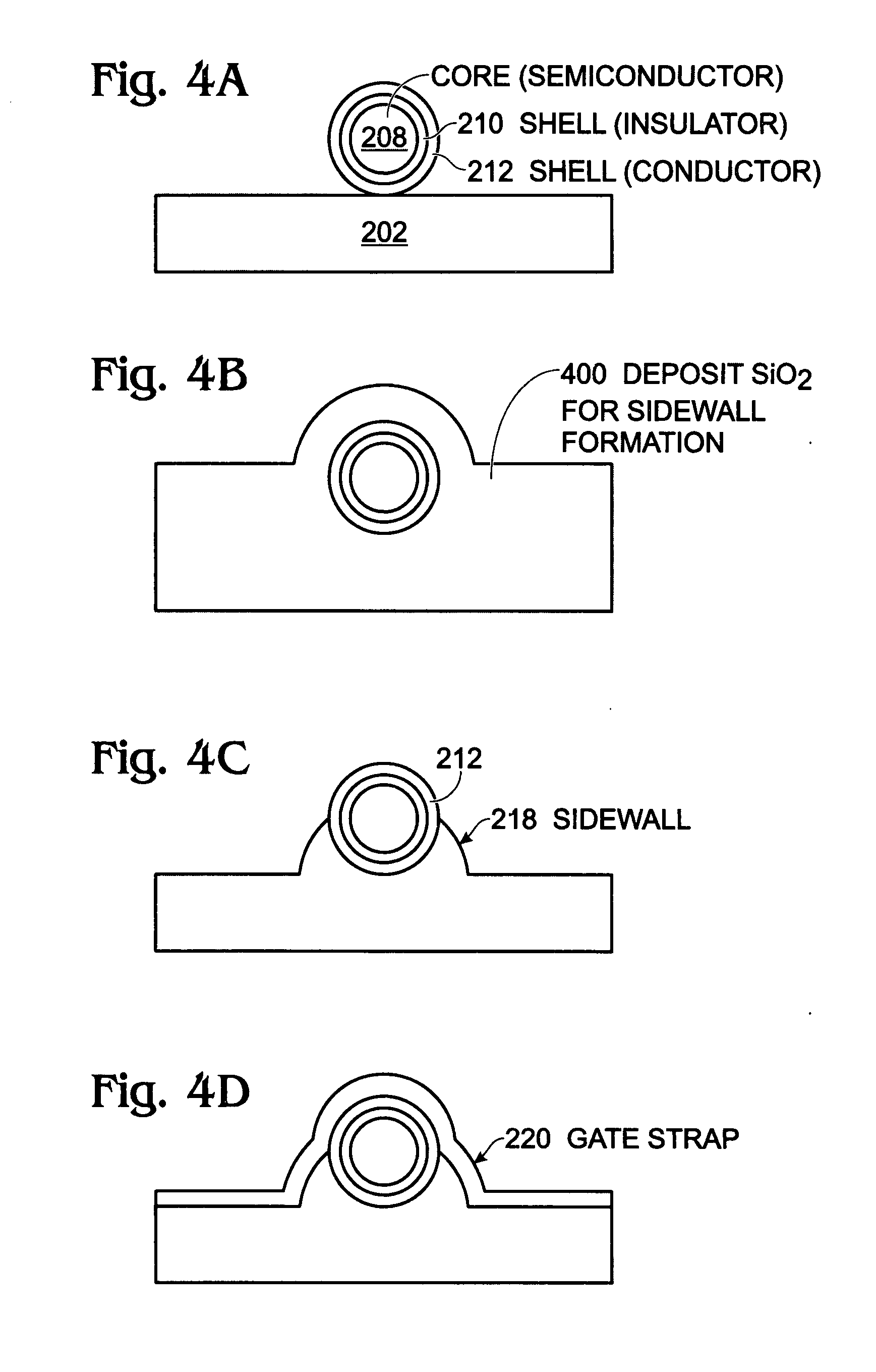
Core-Shell-Shell Nanowire Transistor And Fabrication Method
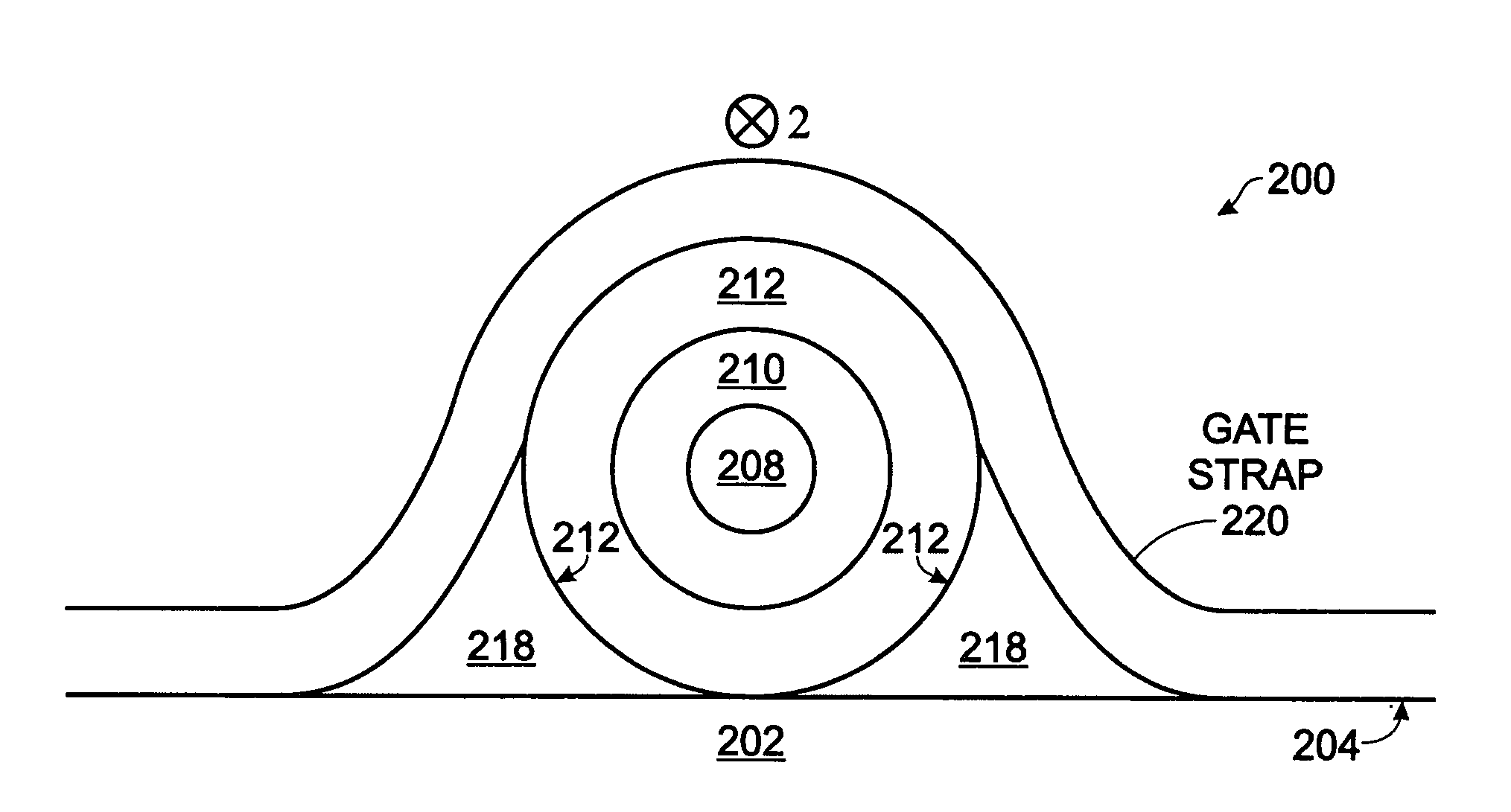
A fabrication method is provided for a core-shell-shell (CSS) nanowire transistor (NWT). The method provides a cylindrical CSS nanostructure with a semiconductor core, an insulator shell, and a conductive shell. The CSS nanostructure has a lower hemicylinder overlying a substrate surface. A first insulating film is conformally deposited overlying the CSS nanostructure and anisotropically plasma etched. Insulating reentrant stringers are formed adjacent the nanostructure lower hemicylinder. A conductive film is conformally deposited and selected regions are anisotropically plasma etched, forming conductive film gate straps overlying a gate electrode in a center section of the CSS nanostructure. An isotropically etching removes the insulating reentrant stringers adjacent the center section of the CSS nanostructure, and an isotropically etching of the conductive shell overlying the S / D regions is performed. A screen oxide layer is deposited over the CSS nanostructure. The source / drain (S / D) regions in end sections of the CS nanostructure flanking are doped.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
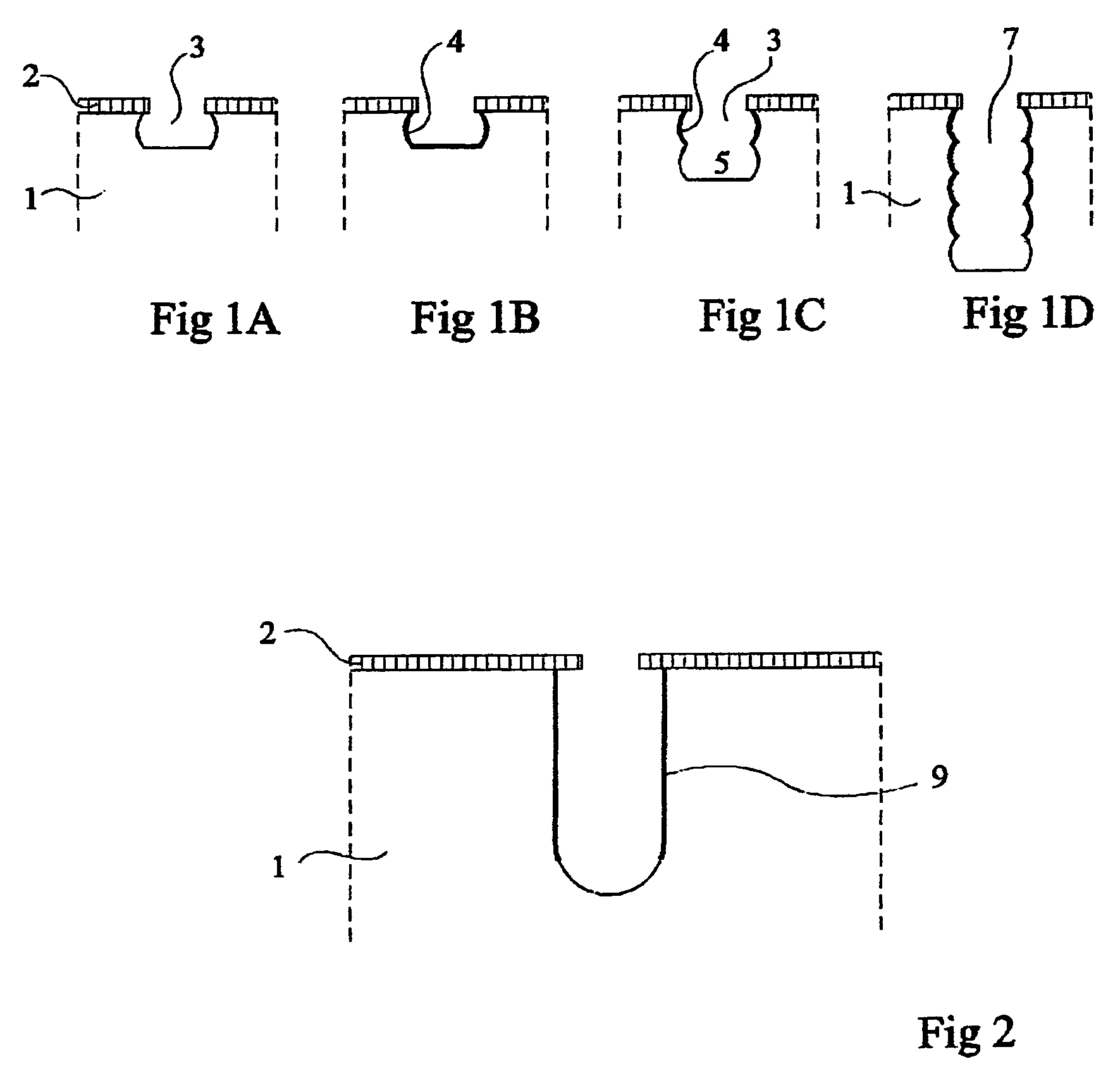
Method for manufacturing separated micromechanical components situated on a silicon substrate and components manufactured therefrom
ActiveUS20110163398A1Reduce depth of cutHigh design freedomSemiconductor electrostatic transducersFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsAnisotropic plasmaLaser light
A method for manufacturing separated micromechanical components situated on a silicon substrate includes the following steps of a) providing separation trenches on the substrate via an anisotropic plasma deep etching method, b) irradiating the area of the silicon substrate which forms the base of the separation trenches using laser light, the silicon substrate being converted from a crystalline state into an at least partially amorphous state by the irradiation in this area, and c) inducing mechanical stresses in the substrate. In one specific embodiment, cavities are etched simultaneously with the etching of the separation trenches. The etching depths can be controlled via the RIE lag effect.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
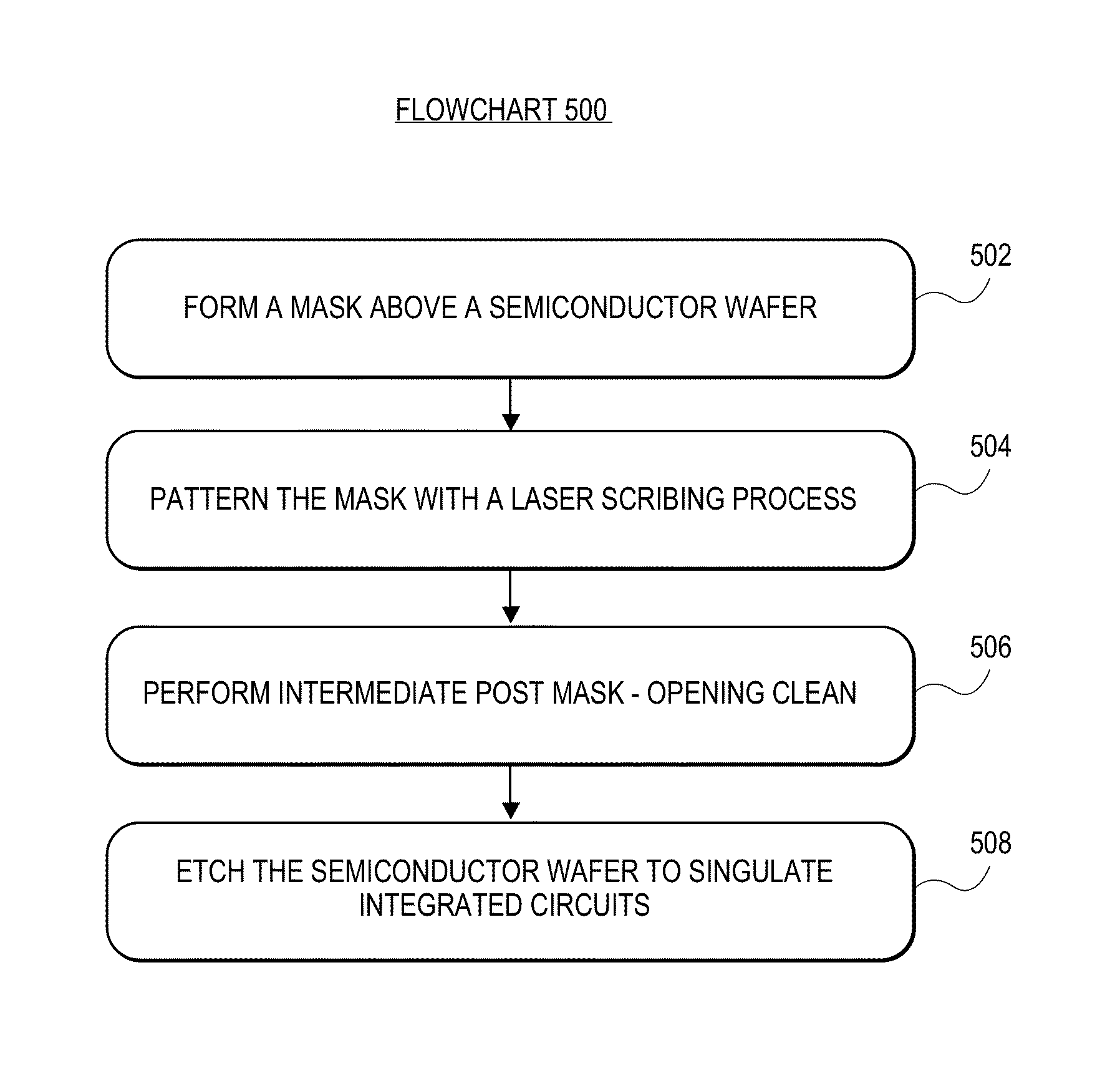
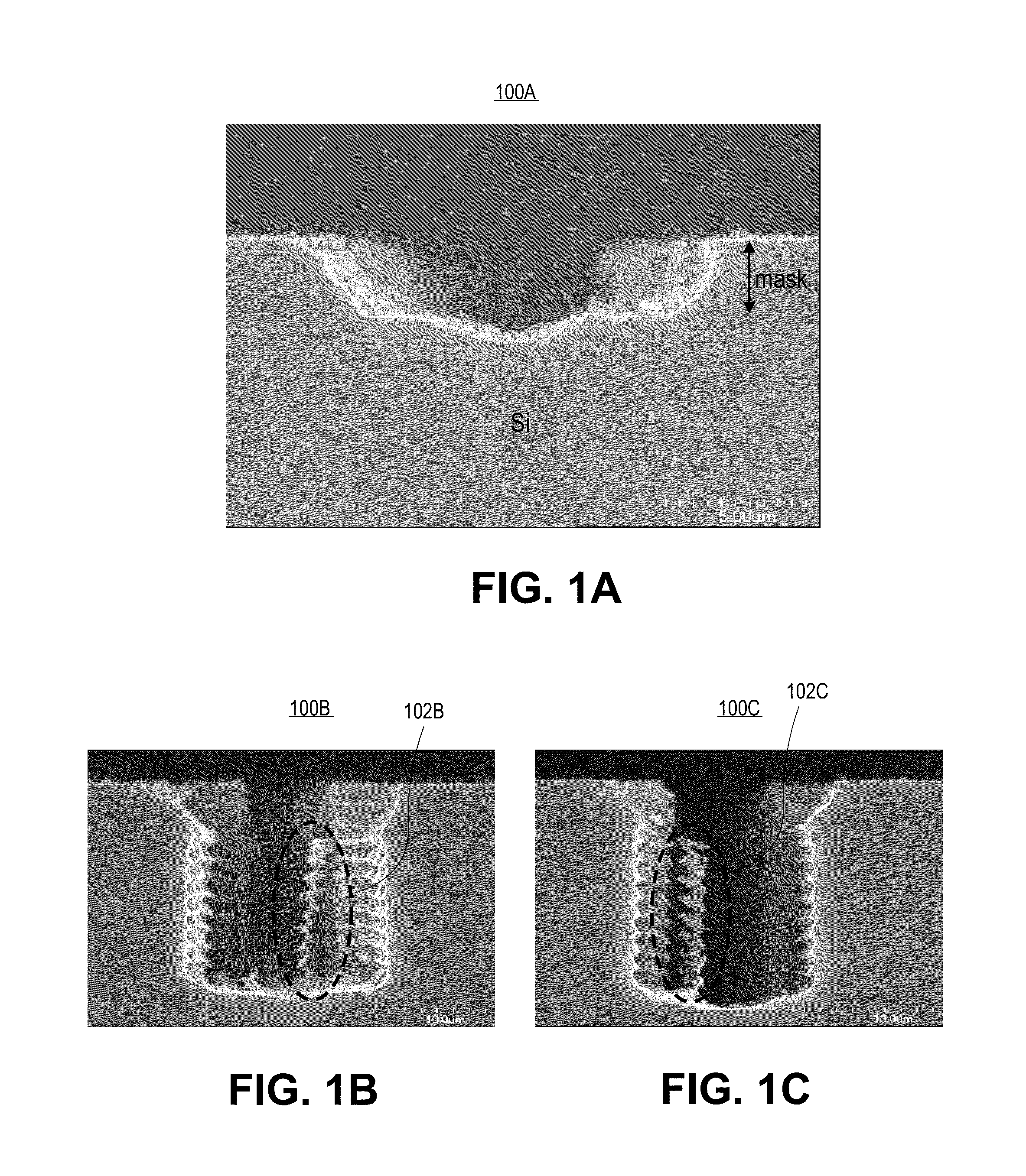
Wafer dicing using hybrid laser scribing and plasma etch approach with intermediate non-reactive post mask-opening clean
Methods of dicing semiconductor wafers, each wafer having a plurality of integrated circuits, are described. In an example, a method of dicing a semiconductor wafer having a plurality of integrated circuits involves forming a mask above the semiconductor wafer, the mask including a layer covering and protecting the integrated circuits. The mask is patterned with a laser scribing process to provide a patterned mask with gaps, exposing regions of the semiconductor wafer between the integrated circuits. Subsequent to patterning the mask, the exposed regions of the semiconductor wafer are cleaned with an anisotropic plasma process non-reactive to the exposed regions of the semiconductor wafer. Subsequent to cleaning the exposed regions of the semiconductor wafer, the semiconductor wafer is plasma etched through the gaps in the patterned mask to singulate the integrated circuits.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Damage isolation by shaped beam delivery in laser scribing process
ActiveUS9029242B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingShaped beamLight beam
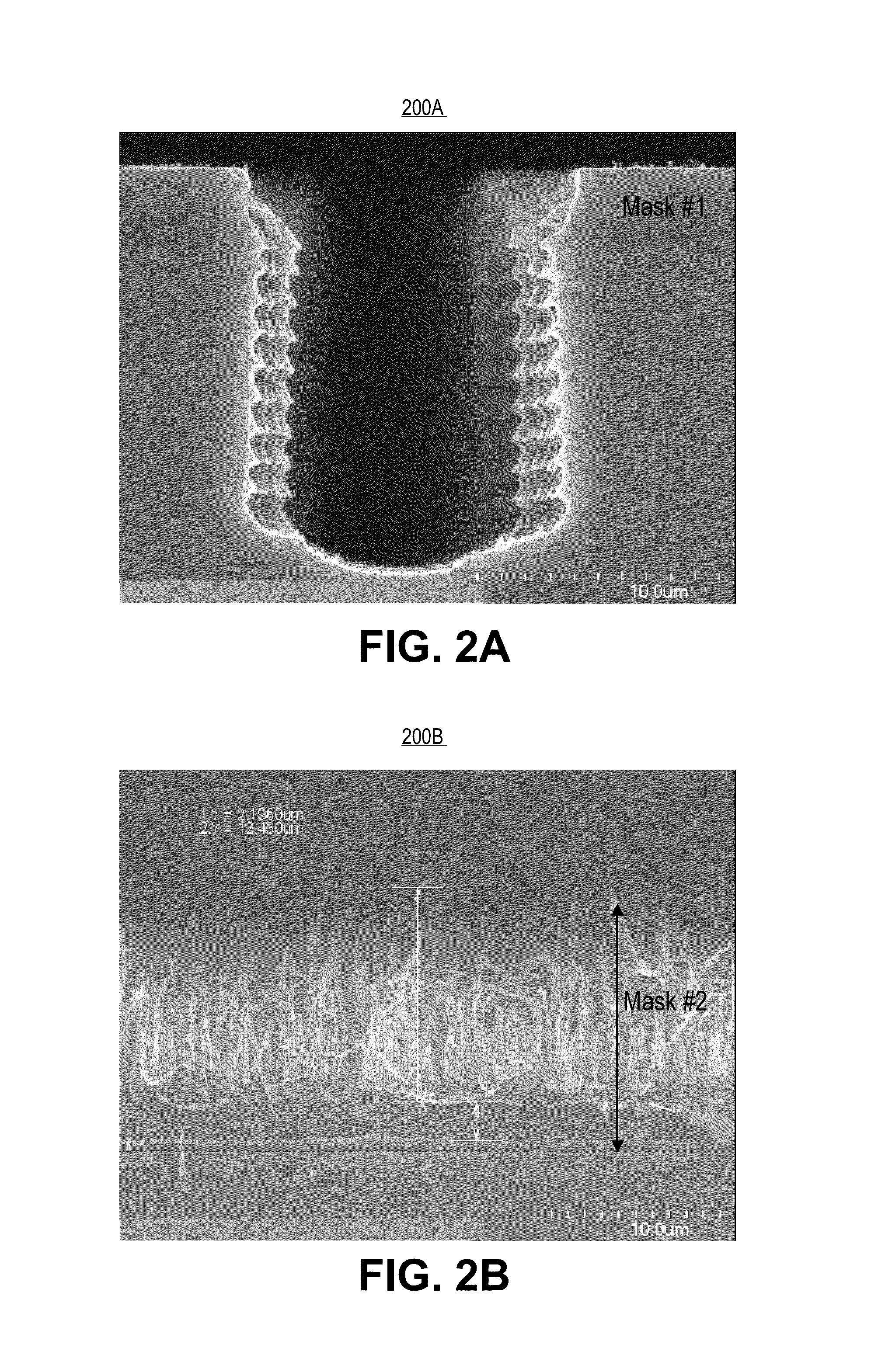
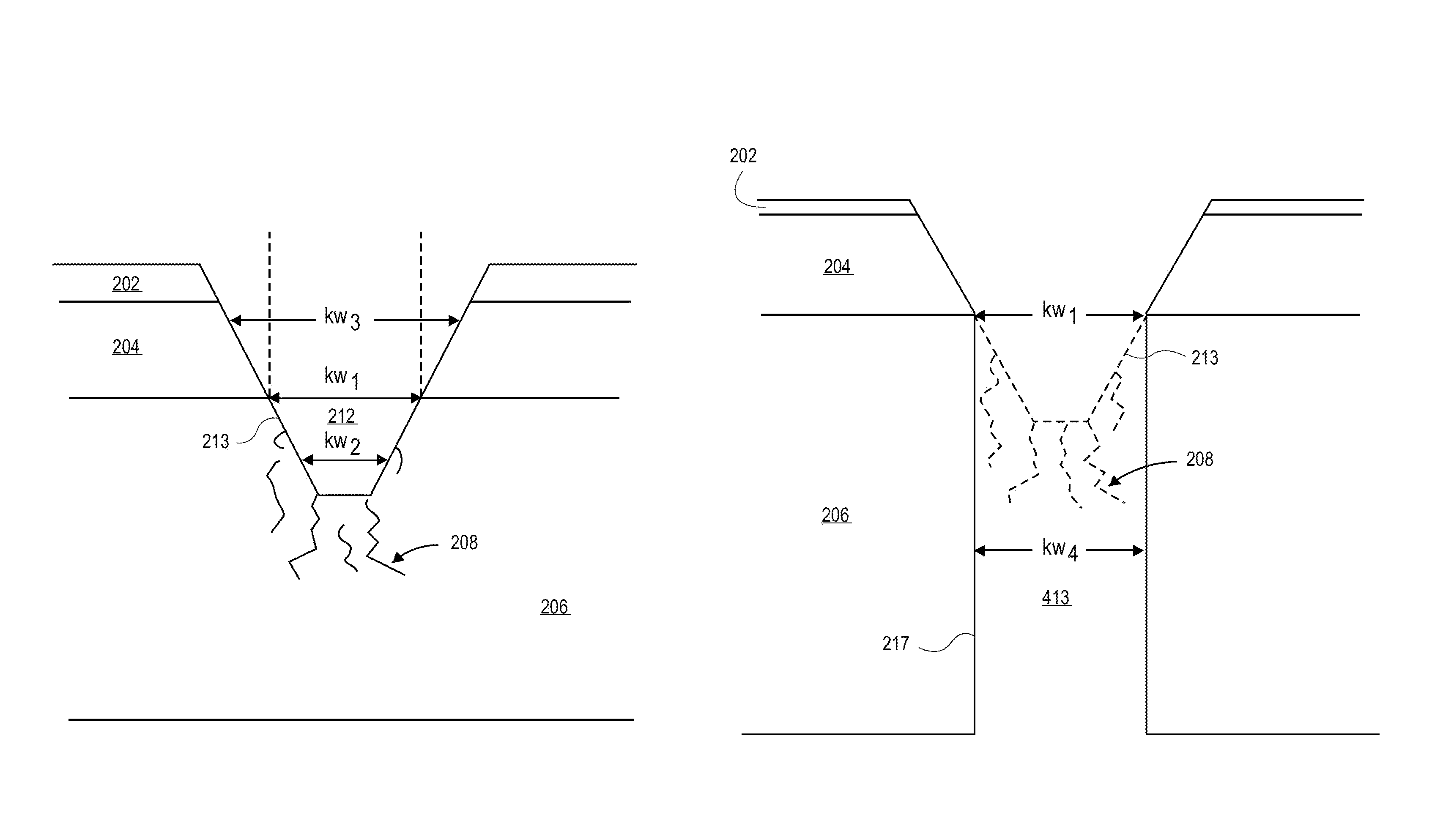
Methods and apparatuses for dicing substrates by both laser scribing and plasma etching. A method includes laser ablating material layers, the ablating by a laser beam with a centrally peaked spatial power profile to form an ablated trench in the substrate below thin film device layers which is positively sloped. In an embodiment, a femtosecond laser forms a positively sloped ablation profile which facilitates vertically-oriented propagation of microcracks in the substrate at the ablated trench bottom. With minimal lateral runout of microcracks, a subsequent anisotropic plasma etch removes the microcracks for a cleanly singulated chip with good reliability.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming a pattern on a substrate and electronic device formed thereby
InactiveUS8343779B2Low costOvercomes drawbackSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice formLight beam
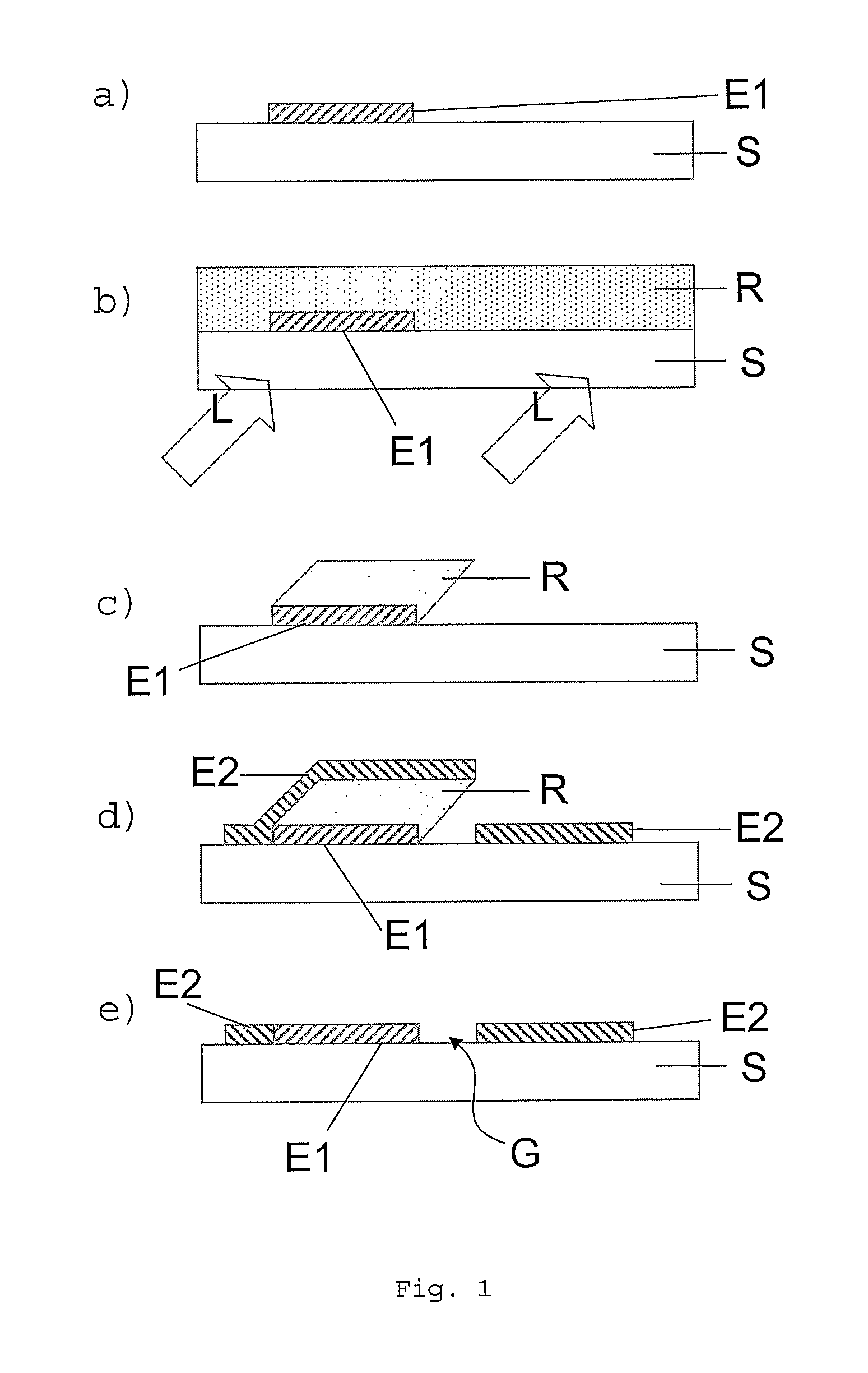
The invention relates to a method for forming a pattern on a substrate (S) with an upper surface and a lower surface which comprises the steps of depositing a first layer (E1) of an opaque material on the upper surface of the substrate (S), depositing a photosensitive layer (R) such that part of the photosensitive layer (R) covers at least part of the first layer (E1), exposing the photosensitive layer (R) to a light beam (L), the light beam (L) impinging on the lower surface of the substrate (S) under an oblique angle (Φ) of incidence, removing the exposed region of the photosensitive layer (R), depositing a second layer (E2) of an opaque material such that part of the second layer (E2) covers a remaining region of the photosensitive layer (R), and removing at least a part of the remaining region of the photosensitive layer (R). According to another aspect of the method of the invention anisotropic plasma etching is applied from above the upper surface of the substrate (S) after removal of the exposed region of the photosensitive layer (R) and thereafter the second layer (E2) is deposited. The method of the invention can be applied for forming a source electrode and a drain electrode of a thin-film field effect transistor. The invention furthermore relates to an electronic device fabricated by such a method.
Owner:BASF AG
Deep anisotropic silicon etch method
ActiveUS8012365B2Eliminate disadvantagesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureFluorinated gasesSilicon tetrafluoride
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
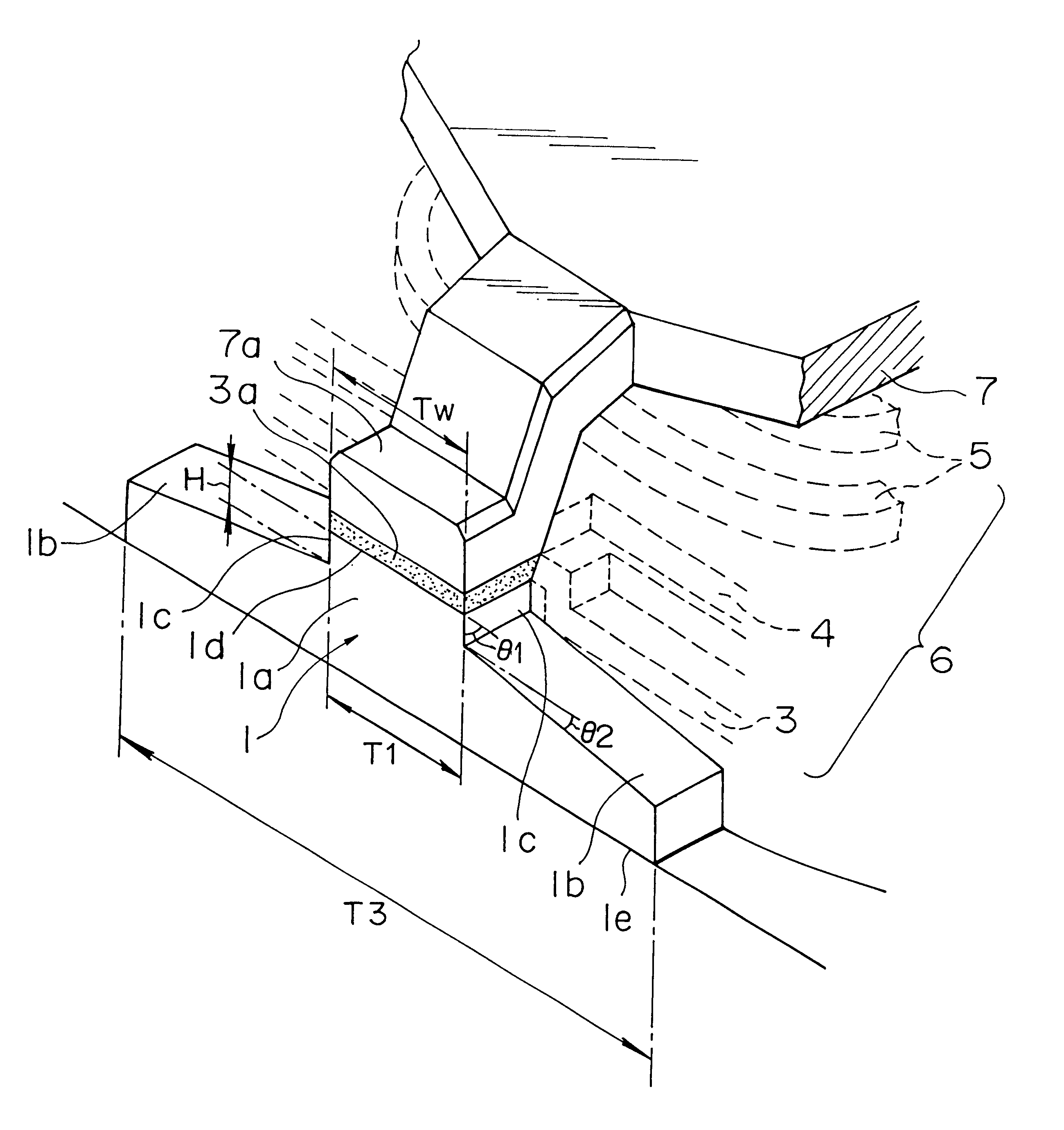
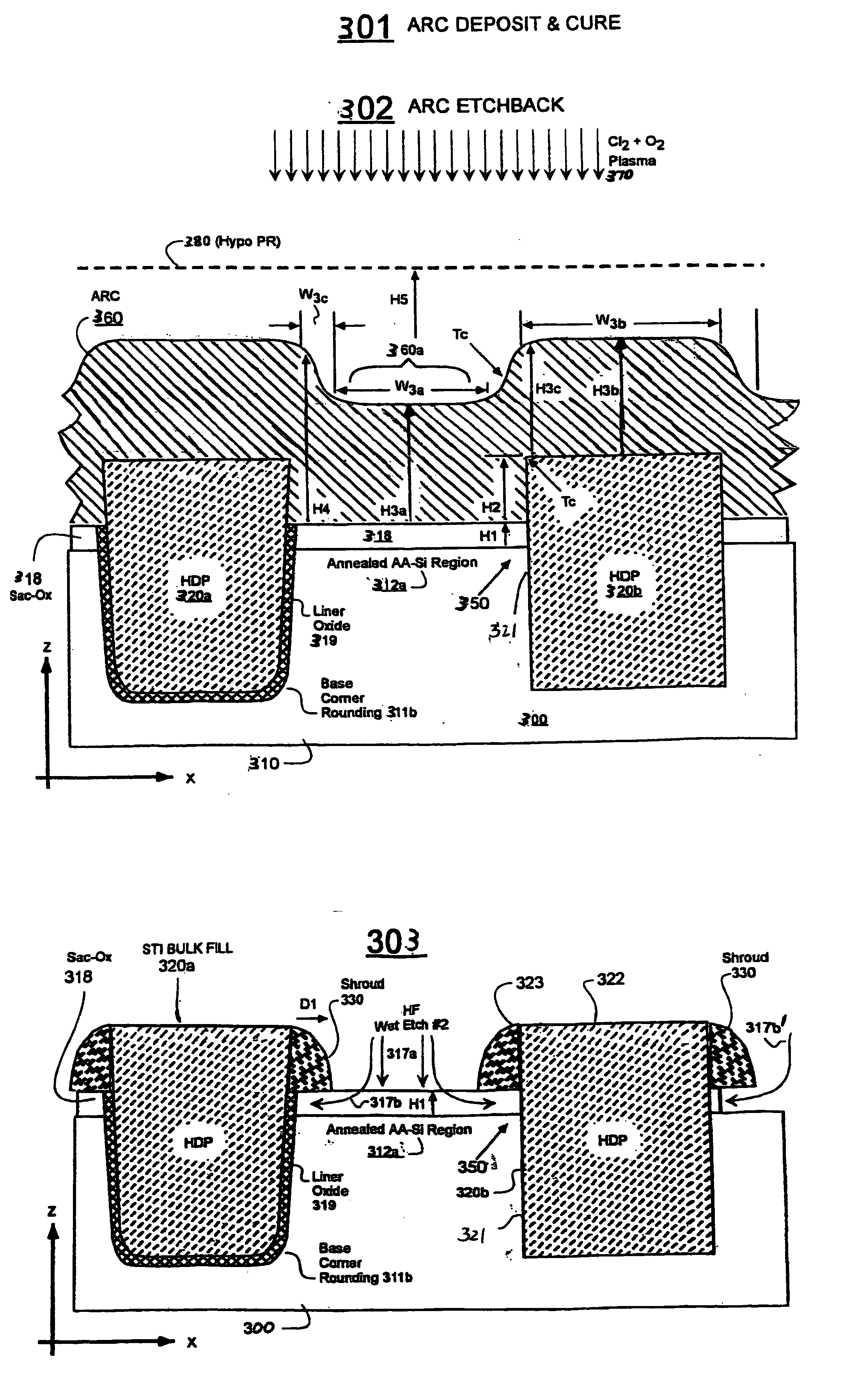
Formation of removable shroud by anisotropic plasma etch
InactiveUS20050287762A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesFilling materialsAnisotropic plasma
Isotropic etching of sacrificial oxide that is adjacent to a trench fill step in an STI wafer can lead to undesired etching away of a sidewall of the trench fill material (e.g., HDP oxide). A sidewall protecting method conformably coats the trench fill step and sacrificial oxide with an etch-resistant carbohydrate. In one embodiment, conforming ARC fluid is spun-on and hardened. A selective, dry plasma etches the hardened ARC over the sacrificial oxide while leaving intact part of the ARC that adheres to the trench fill sidewall. The remnant sidewall material defines a protective shroud which delays the subsequent isotropic etchant (e.g., wet HF solution) from immediately reaching the sidewall of the trench fill material. The delay length of the shroud can be controlled by tuning the etchback recipe. In one embodiment, the percent oxygen in an O2 plus Cl2 plasma and / or bias power during the plasma etch is used as a tuning parameter.
Owner:CHANG LIAO HLDG
Dry etching preparation method of T-shaped hole of integrated circuit
InactiveCN105742178AReduce purchasesSimple preparation stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingAnisotropic plasmaInterconnection
Owner:YANGZHOU GUOYU ELECTRONICS
Method of avoiding or eliminating deposits in the exhaust area of a vacuum system
InactiveUS6874511B2Effectively prevents polymerizationActively removesFouling preventionElectric discharge tubesReactive gasEngineering
Method of avoiding or eliminating deposits in the exhaust area of a vacuum system in which a gas containing depositable constituents in the exhaust area is at least intermittently pumped out of a vacuum chamber that is connected to a vacuum pump via a gas line. A reactive gas that removes deposits from the gas in the vacuum pump and / or units provided downstream therefrom, and / or reduces or eliminates existing deposits in this area is at least intermittently added to the gas directly upstream from or within the vacuum pump. The proposed method is particularly suitable for anisotropic plasma etching of silicon using alternating etching steps and polymerization steps, the vacuum chamber being supplied with a sulfur-containing etching gas during the etching steps and a polymerizing agent-containing gas during the polymerization steps.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method of restraining notch appearing at bottom of hole during etching process, and hole forming method
ActiveCN105374737ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnisotropic plasmaAtmospheric pressure
The invention provides a method of restraining a notch appearing at the bottom of a hole during an etching process, and a hole structure forming method. The hole structure forming method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) a substrate is provided, wherein the substrate comprises an to-be-etched material layer and an insulated layer attached to the lower surface of the to-be-etched material layer; (2) the to-be-etched material layer is subjected to anisotropic plasma etching, and a hole is formed initially; and (3) in a relatively-low working air pressure environment, anisotropic plasma etching is continued to deepen the hole. At least when the process of deepening the hole is over, the insulated layer can be exposed through the hole.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Damage isolation by shaped beam delivery in laser scribing process
ActiveUS20150217401A1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesShaped beamFemto second laser
Methods and apparatuses for dicing substrates by both laser scribing and plasma etching. A method includes laser ablating material layers, the ablating by a laser beam with a centrally peaked spatial power profile to form an ablated trench in the substrate below thin film device layers which is positively sloped. In an embodiment, a femtosecond laser forms a positively sloped ablation profile which facilitates vertically-oriented propagation of microcracks in the substrate at the ablated trench bottom. With minimal lateral runout of microcracks, a subsequent anisotropic plasma etch removes the microcracks for a cleanly singulated chip with good reliability.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com