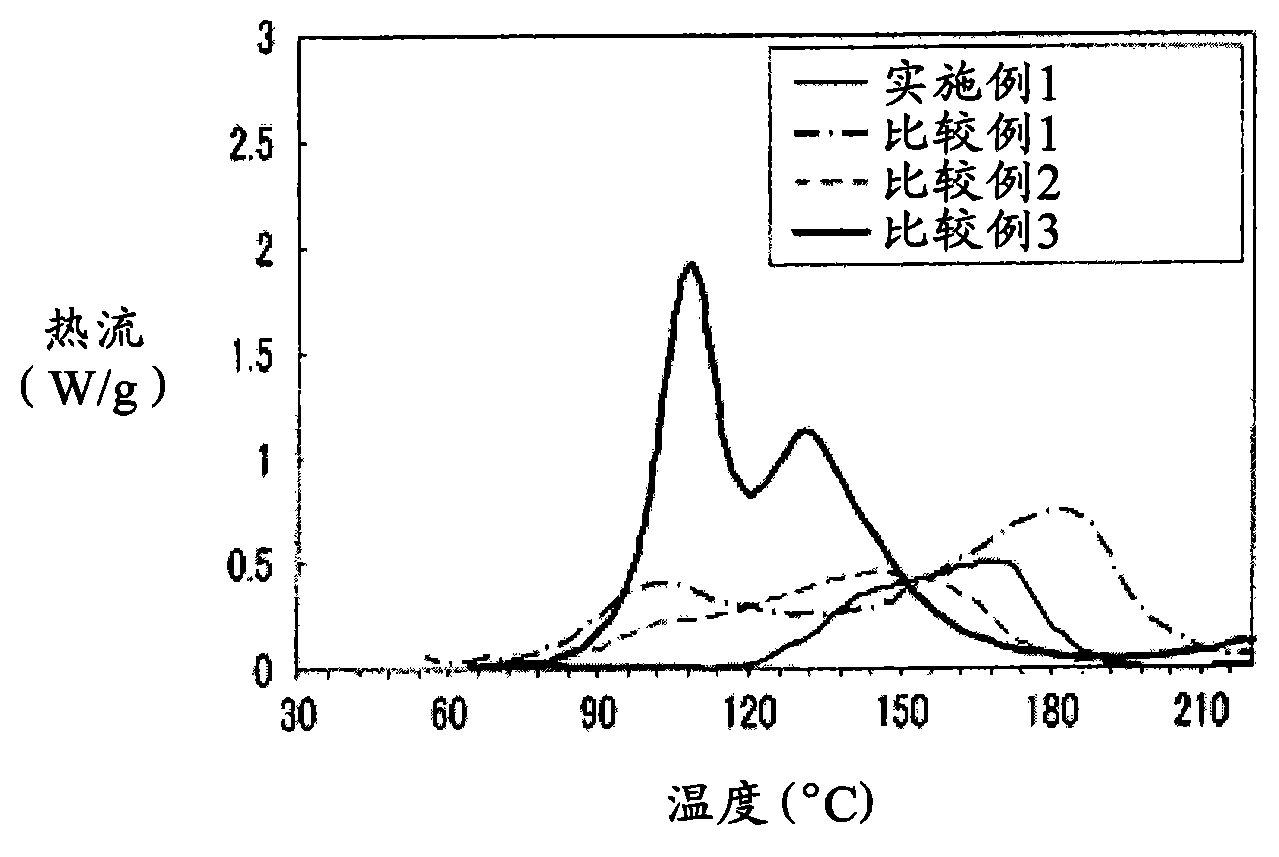
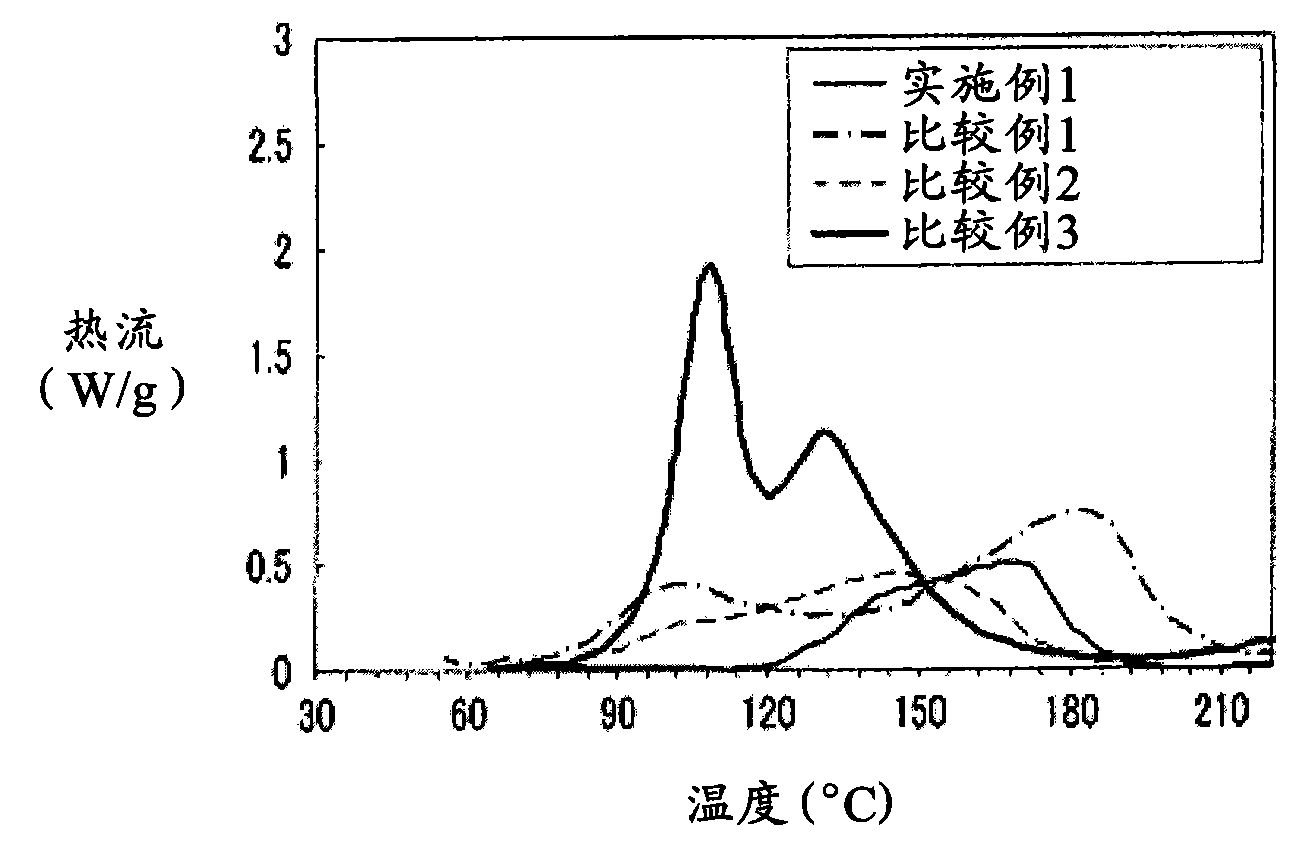
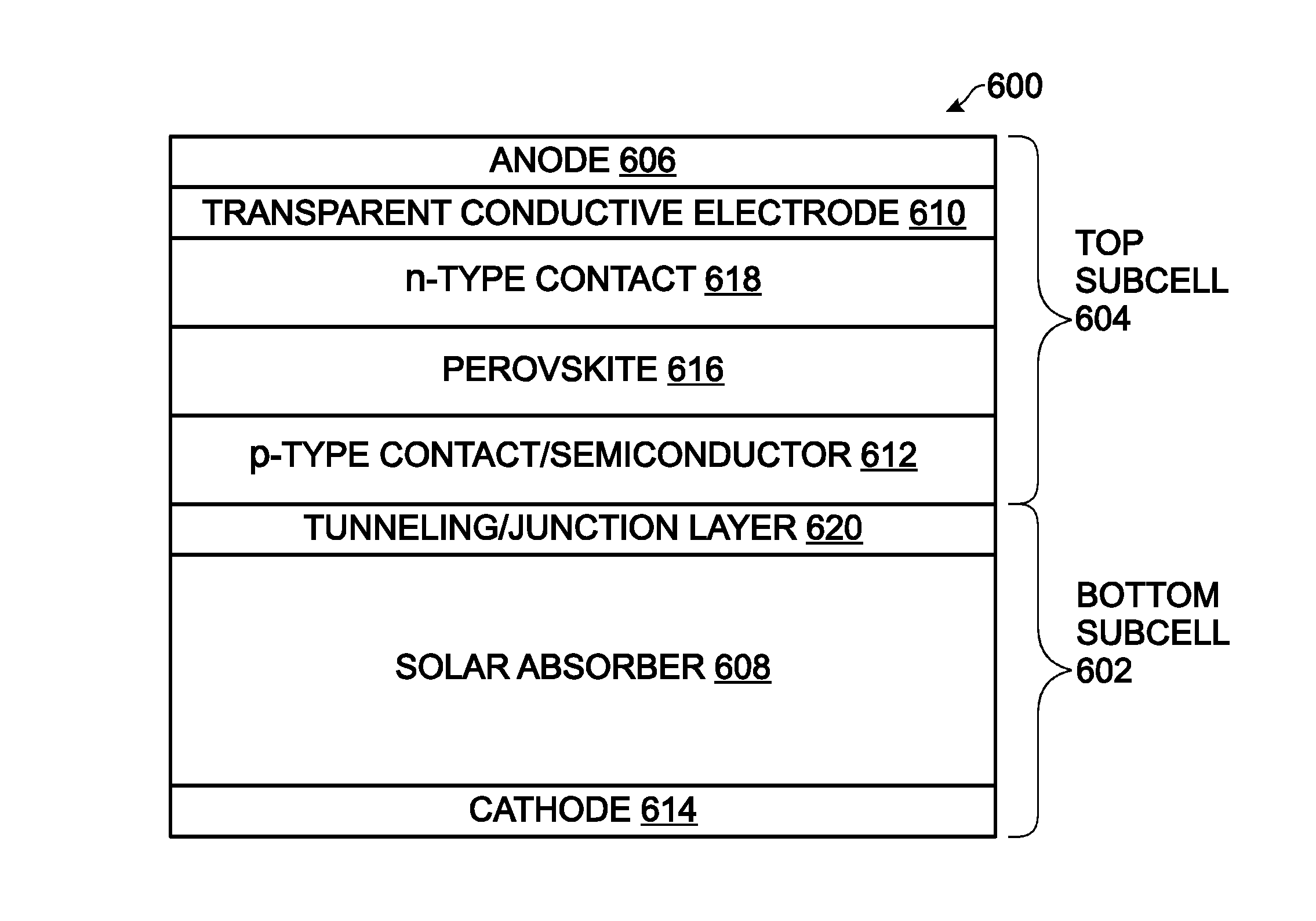
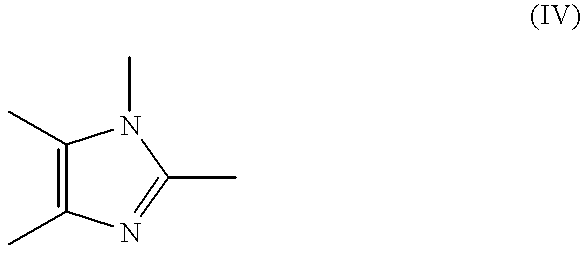Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
356 results about "Ammonium Cation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
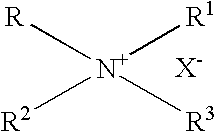
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH + 4.It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (NH 3).Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (NR + 4), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R).
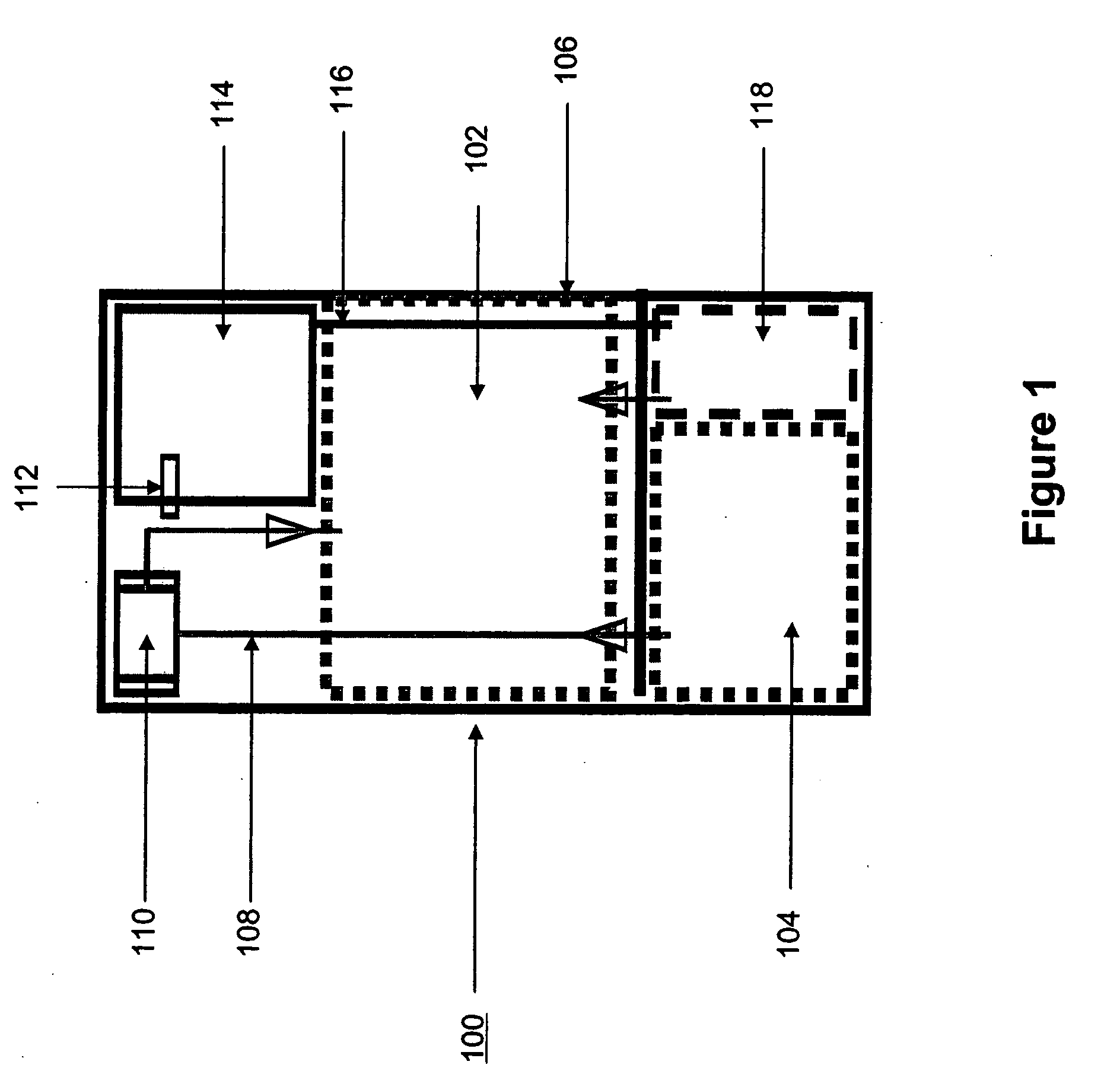
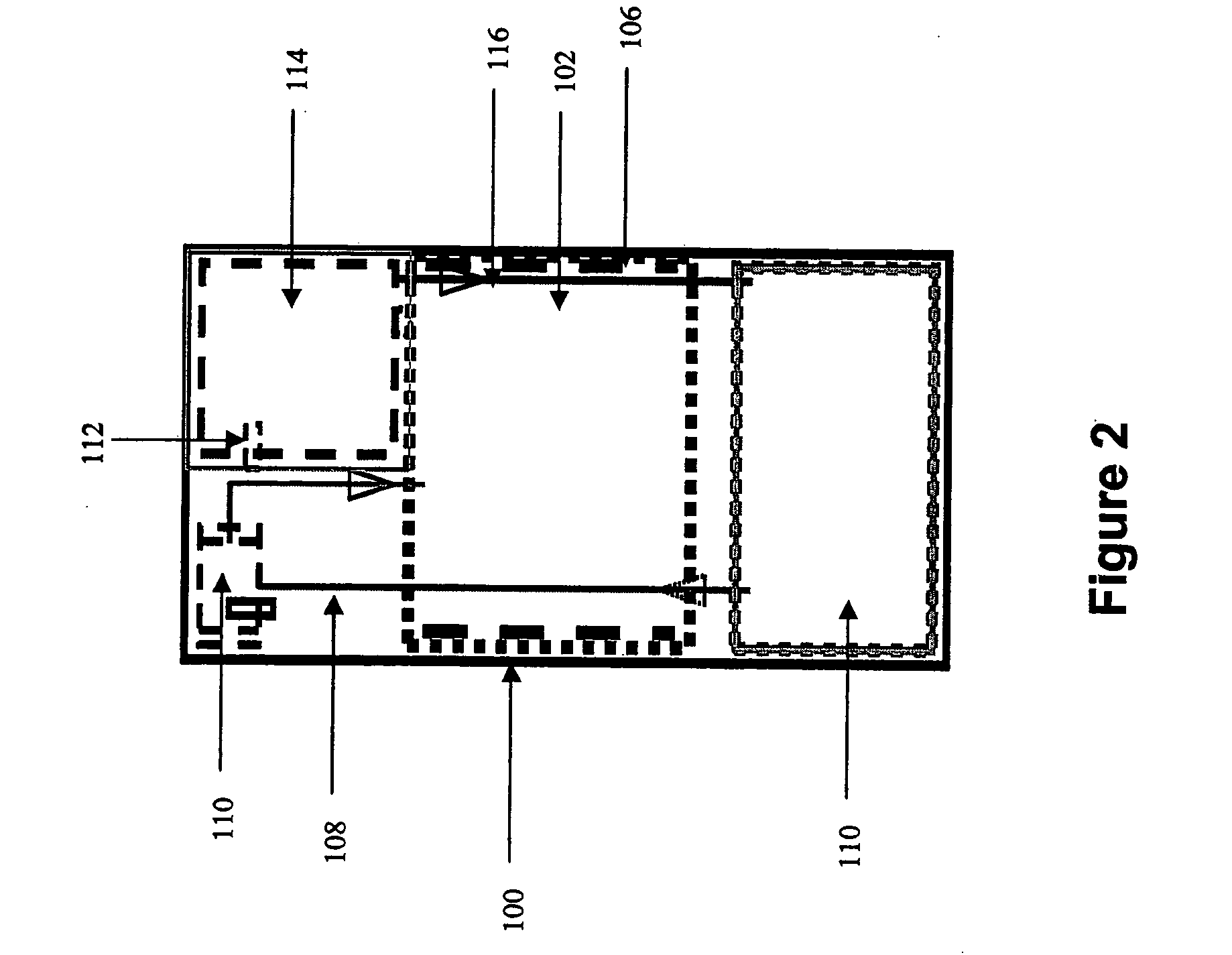
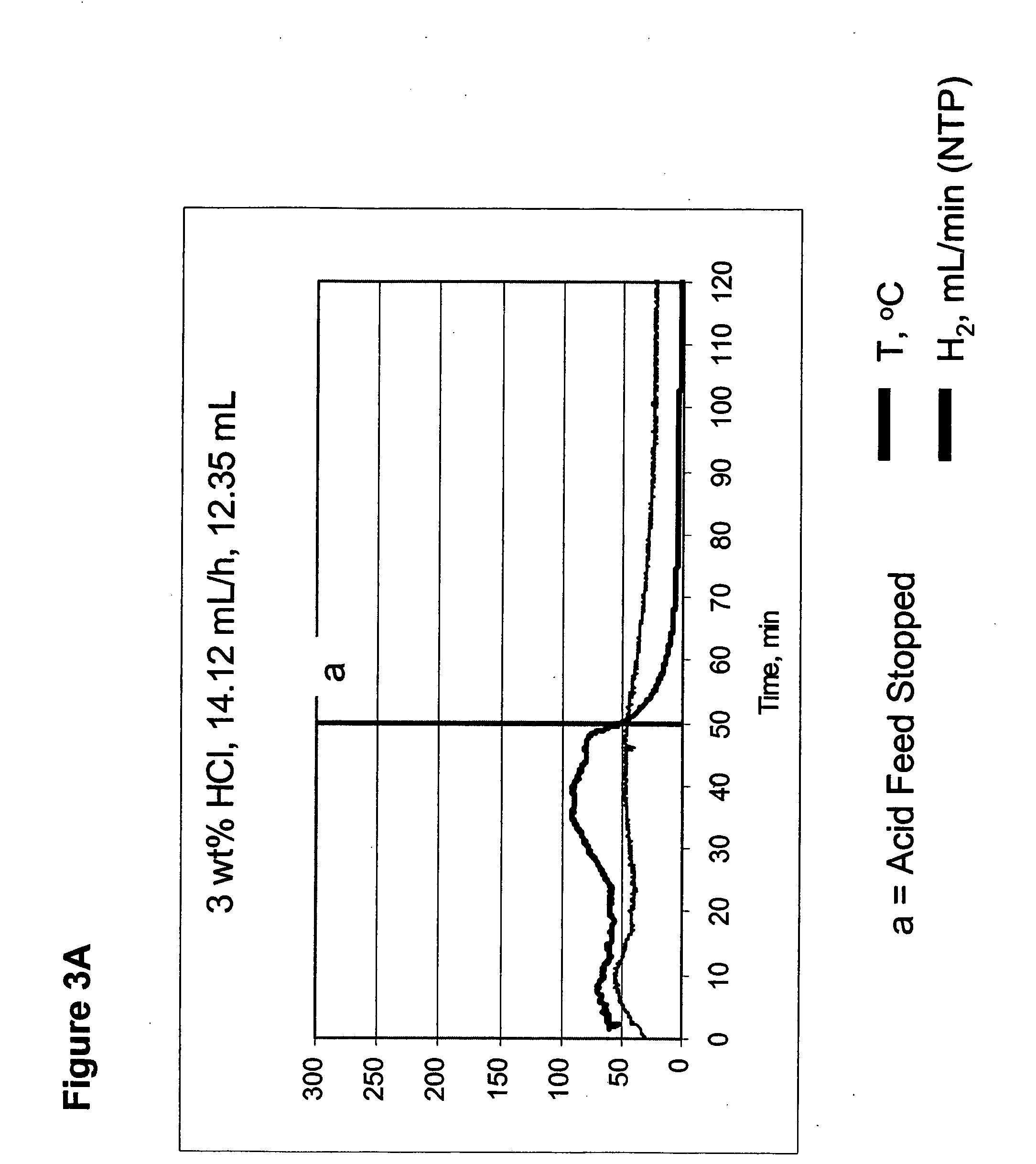
Systems and methods for hydrogen generation from solid hydrides
InactiveUS20050238573A1Regulate rateReactant parameters controlHydrogen productionO-Phosphoric AcidAlkaline earth metal
A system is disclosed for hydrogen generation based on hydrolysis of solid chemical hydrides with the capability of controlled startup and stop characteristics wherein regulation of acid concentration, acid feed rate, or a combination of both control the rate of hydrogen generation. The system comprises a first chamber for storing a solid chemical hydride and a second chamber for storing an acidic reagent. The solid chemical hydride is a solid metal borohydride having the general formula MBH4, where M is selected from the group consisting of alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal cations, aluminum cation, zinc cation, and ammonium cation. The acidic reagent may comprise inorganic acids such as the mineral acids hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid, and organic acids such as acetic acid, formic acid, maleic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL
Method of producing an aromatics alkylation catalyst
This invention provides a method of producing an aromatics alkylation catalyst comprising the steps of: (a) synthesizing a layered oxide material MCM-56 in the presence of alkali and / or alkaline earth metal cations; (b) prior to any calcination of the MCM-56, subjecting the MCM-56 produced in step (a) to ammonium ion exchange so as to at least partially replace the alkaline or alkaline earth metal cations associated with the MCM-56 with ammonium ions; then (c) heating the ammonium-exchanged MCM-56 to decompose the ammonium cations and convert the MCM-56 into the hydrogen form; and (d) after step (b), forming the MCM-56 into catalyst particles. The resultant catalyst exhibits enhanced activity in the alkylation of benzene with ethylene and propylene.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Low-Odor Catalyst for Isocyanate-Derived Foams and Elastomers
InactiveUS20070282026A1Other chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElastomerPolyisocyanurate
Provided herein are catalysts useful in providing foam products which are produced using an organic poly isocyanate as a starting material. A catalyst according to the present invention includes the tris-(hydroxyethyl)methyl ammonium cation, and optionally potassium cation, in combination with a variety of possible counter anions present to maintain charge balance and for compatibility. A catalyst according to the invention is preferably used in conjunction with one or more conventional tertiary amine catalysts in a foam producing process. The foams may be polyurethane foams, polyisocyanurate foams, flexible foams, or elastomeric foams.
Owner:HUNTSMAN PETROCHEMICAL LLC
Borohydride fuel compositions and methods
Solid self-stabilized borohydride fuel compositions, fuel cartridges, related methods of preparation and hydrogen generation are provided. The fuel compositions comprise mixtures of at least one borohydride salt with a cation selected from the group consisting of alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal cations, aluminum cation, zinc cation, and ammonium cation, preferably sodium borohydride, and at least one hydroxide salt with a cation selected from the group consisting of alkali metal cations, alkaline earth metal cations, aluminum cation, zinc cation, and ammonium cation, preferably sodium hydroxide.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL
Layered structure
InactiveUS20110006294A1Increase brightnessElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCharge separationPolymer chemistry
Disclosed is a layered structure including a first electrode and a second electrode, a light-emitting layer or a charge separation layer between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a layer containing a conjugated polymer compound between the light-emitting layer or the charge separation layer and the first electrode, wherein the conjugated polymer compound contains a repeating unit selected from the group consisting of a repeating unit represented by formula (1):wherein Ar1 represents a divalent aromatic group, R1 represents a substituent group having a group represented by formula (2), Ar1 may have a substituent group other than R1, and n1 represents an integer of 1 or more;-(R2)c1-(Q1)n2-Y1(M1)a1(Z1)b1 (2)wherein R2 represents a divalent aromatic group which may have a substituent group, Q1 represents a divalent organic group which may have a substituent group, Y1 represents a carbocation, an ammonium cation, a phosphonyl cation or a sulfonyl cation, M1 represents F−, Cl−, Br−, I−, OH−, RaSO3−, RaCOO−, ClO−, ClO2−, ClO3−, ClO4−, SCN−, CN−, NO3−, SO42−, HSO4−, PO43−, HPO42−, H2PO4−, BF4− or PF6−, Z1 represents a metal ion or an ammonium ion which may have a substituent group, c1 represents 0 or 1, n2 represents an integer of 0 or more, provided that n2 is 0 when c1 is 0, a1 represents an integer of 1 or more, b1 represents an integer of 0 or more, a1 and b1 are selected so that the charge of the substituent group represented by formula (2) is 0, Ra represents an alkyl group having 1 to 30 carbon atoms, which may have a substituent group, or an aryl group having 6 to 50 carbon atoms, which may have a substituent group.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Alternative phthalocyanine dyes suitable for use in offset inks
A phthalocyanine phthalocyanine salt suitable for formulation in a solvent-based or oil-based ink vehicle is disclosed. The phthalocyanine comprises one or more sulfonate groups and a counterion of at least one sulfonate group is an ammonium cation comprising at least 15 carbon atoms. Ammonium salts of sulfonated gallium naphthalocyanines exemplify such phthalocyanine salts.
Owner:BASF SE
Resin composition
ActiveUS20090030158A1Well-balanced suitable curing capabilityEasy to operateOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoniumIonic liquid
Resin compositions which contain a compound having at least two epoxy and / or thiirane groups in the molecule (ingredient (1)) and a specific ionic liquid (ingredient (2)), as combined, are practicable resin compositions which comprise constitutive elements of readily available materials and have well-balanced suitable curing capability and storage stability. Preferably, the ionic liquid (ingredient (2)) comprises a combination of an ammonium cation or phosphonium cation and a carboxylate anion.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Process for converting a hydroxycarboxylic acid, or salts thereof, to an unsaturated carboxylic acid and/or its esters
ActiveUS20090076297A1Preparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationAmmonium CationIon-exchange resin
A process for converting a salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid to an unsaturated carboxylic acid, or esters thereof. The process involves converting an ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid in aqueous solution to a corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acid and ammonium cation in aqueous solution; and separating the ammonium cation from the aqueous solution, leaving the hydroxycarboxylic acid in aqueous solution. The converting and separating steps may be accomplished by employing a hydrophobic acid or an acid ion exchange resin, each of which must have an acid dissociation constant, i.e., pKa, at least 0.5 less that that of the salt of the hydroxycarboxylic acid. Where a hydrophobic acid is used, it must be immiscible in water, and its salt must also be immiscible in water, and the resulting multi-phase solution comprises an aqueous phase comprising the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acid, as well as a non-aqueous phase comprising a neutralized acid. Alternatively, where the ion exchange resin is used, the aqueous solution of the ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid is contacted with the resin, thereby converting the salt to a hydroxycarboxylic acid and capturing the ammonium cations on the resin. In either case, the aqueous solution is treated, such as by heating, to separate and recover the hydroxycarboxylic acid. The non-aqueous phase or resin is treated to separate and recover ammonia useful for preparing additional ammonium salt of a hydroxycarboxylic acid.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Flame retardant electrolyte for rechargeable lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveCN101847750AImprove thermal stabilityImprove flame retardant performanceFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesPhosphoric acidPhysical chemistry
Flame retardant electrolyte solutions for rechargeable lithium batteries and lithium batteries including the electrolyte solutions are provided. The flame retardant electrolyte solution includes a lithium salt, a linear carbonate-based solvent, at least one ammonium cation, a phosphoric acid-based solvent, and an additive including oxalatoborate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Light-emitting diode device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109935708AImprove luminous efficiencyAvoid deprotonation of the methylammonium cationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the field of quantum dots, and specifically relates to a light-emitting diode device and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting diode comprises an anode, a compositelight-emitting layer, an electron transport layer and a cathode which are arranged in a stacked manner, wherein the composite light-emitting layer includes a perovskite quantum dot material and a non-perovskite quantum dot material, and the electron transport layer includes an electron transport material grafted with a defective passivating agent. The light-emitting diode not only can promote thecarrier transport performance, but also can effectively avoid methyl ammonium cation deprotonation between a defective group and the perovskite quantum dot material in the composite light-emitting layer, thereby optimizing the application effect of the perovskite quantum dot material in the light-emitting diode device, promoting the synergistic effect of the perovskite quantum dot material and the non-perovskite quantum dot material to produce excited-state complex electroluminescence, and improving the light-emitting efficiency of the light-emitting diode and the stability of the device.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Process for manufacture of imidazoles
Imidazoles may be manufactured by reacting a glyoxal, ammonia, an aldehyde, and optionally a primary amine, in the presence of a Bronsted acid whose pKa is approximately equal to the pKa of the ammonium cation of the primary amine, or if the primary amine is not present, to the pKa of the ammonium (NH4+) cation. The reaction may be used to make in relatively high yields a wide variety of imidazoles using relatively inexpensive starting materials. The imidazoles are useful as chemical intermediates.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Hybrid Perovskite with Adjustable Bandgap
InactiveUS20160133672A1Ensure chemical stabilityAdjustable bandgapSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIodideTandem solar cell
A method is provided for preparing a thin film of perovskite material having an adjustable bandgap. The method forms a thin film of material having the formula BX2, where anionic part X is a halide, and where the cation B is lead (Pb), tin (Sn), or germanium (Ge). A solution is formed of materials with the formulas A1X and A2X, where cation A1 is formamidinium, and where cation A2 is an organic cation having a larger size larger than a methylammonium cation. The method deposits the solution over the BX2 thin film, and forms a perovskite material having the formula A11-YA2yBX3. For example, the A2 cation may be an ammonium cation such as ethylammonium, guanidinium, dimethylammonium, acetamidinium, or substituted derivatives of the above-mentioned ammonium cations. In one aspect, the perovskite material A1BX3 may be formamidinium iodide (FAI), and A2BX3 may be ethylammonium iodide (EtAI). Tandem solar cells are also provided.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Ionic liquids
InactiveUS20070129568A1Sufficient solubilityReduce volatilityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTransportation and packagingPhosphoniumChemical reaction
Low melting point organic liquid compounds with high boiling points are prepared by a preferred process having the J+xQy(R—COO−)x-y where x is 1 to 8, preferably 1-3, y is 0 to x−1, where R—COO− is an anion selected from the group consisting of 2-ethyl hexanoate, pivalate, neodecanoate, and mixtures thereof, Q is another anion or mixture of other anions, and J+x is a cation selected from cations of Groups IA, IIA, IB, IIB, IIIB, IVB, VB, VIB, VIIB, VIII and lanthanide metals, cations selected from cations of B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te and Po metalloids, an ammonium cation derived from ammonia or an organic amine, an organic phosphonium cation, and mixtures thereof the organic liquid compounds being substantially free of volatile organic compounds. These compounds, as liquids, are useful as low volatile organic solvents, e.g., solvents in which a variety of chemical reactions may be carried out.
Owner:NGIMAT CO
Polishing liquid
ActiveUS20080203354A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaColloid
The invention provides a polishing liquid for polishing a barrier layer of a semiconductor integrated circuit, the polishing liquid comprising: a diquaternary ammonium cation; a corrosion inhibiting agent; and a colloidal silica, wherein the pH of the polishing liquid is in the range of 2.5 to 5.0. According to the invention, a polishing liquid capable of achieving a superior barrier layer polishing rate, as well as suppressing the occurrence of scratching due to the agglomeration of solid abrasive grains can be provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorophosphate surfactants
This invention is directed to a composition capable of imparting surface effects to a liquid by contacting the liquid with a partially fluorinated phosphate with an ammonium cation (NH2R1R2)+ wherein R1 and R2 are independently linear or branched organic groups containing at least one carboxylate moiety and one amino moiety, and optionally be substituted, interrupted, or both with oxygen, sulfur, or nitrogen-containing moieties, or with cyclic alkyl or aryl moieties containing up to 10 carbon atoms.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Method for preparing polyisocyanic acid ester
InactiveCN101165048AOrganic chemistry methodsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolymer sciencePhosphonium
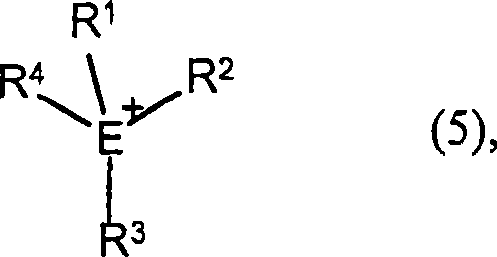
The invention relates to a method for making oligomeric isocyanates by reacting diisocyanates in the presence of a catalyst, wherein the catalyst comprises a saline compound prepared from an anion selected from 1,2,3- or 1,2,4-triazole, a substituted species of 1,2,3- or 1,2,4-triazole and carbocyclically and / or heterocyclically annellated species of 1,2,3- or 1,2,4-triazole and the cation selected from an alkali metal, alkaline-earth metal and / or monovalent ammonium cation and / or phosphonium cation of formula (5), wherein the E, R1, R2, R3, R4 are as defined in the descriotion. The invention also relates to a products obtained by the said method and polymer prepared by the products. The catalyst system for polyisocyanates has high reality and prompts to generate thiourea dione accounting for large proportion of polyisocyanates.
Owner:BAYER AG
Flame retardant electrolyte solution for rechargeable lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveUS20110123869A1Reducing and eliminating decompositionHigh characteristicsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsCell electrodesPhosphoric acidPhysical chemistry
Disclosed are a flame retardant electrolyte solution for a rechargeable lithium battery including a lithium salt, a linear carbonate-based solvent, an ionic liquid including ammonium cations, and a phosphoric acid-based solvent, and a rechargeable lithium battery including the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Polymer film with improved antifouling property and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104383816AInhibition of easy agglomeration propertiesGood dispersionSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisNanoparti clesAmmonium Cation
The invention discloses a polymer film with antifouling property. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles or titanium dioxide nanoparticles with amphoteric ionized surfaces are evenly dispersed in the polymer film, wherein the surfaces of the nanoparticles are coated with carboxyl anion-ammonium cation zwitter-ion pairs; the content of the silicon dioxide nanoparticles or the titanium dioxide nanoparticles in the polymer film is 0.3-10wt%; the surface contact angle of the polymer film is reduced to below 50%; the secondary water flux recovery rate in an antifouling separation test reaches over 95%; and the antifouling property is obviously improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Composition and method for road-film removal
InactiveUS20020128169A1Improved metal protectionCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsOrganic acidHydrotrope
A concentrate and a ready-to-use or diluted formulation for an aqueous vehicle cleaner can remove a wide range of different types of traffic film using either low pressure application, hand pressure application, water jet spray apparatus, clean-in-place systems or other manual or mechanical washing systems. The compositions may comprise, for example, one or more solutions that each or collectively contain or comprises: a) at least one anionic surfactant; b) at least one poly[oxyalkylene] ammonium cationic surfactant; and c) an alkaline agent. Optional additional ingredients may comprise at least one polycarboxylic acid chelating agent (preferably an aminocarboxylic acid chelating agent), at least one non-ionic or amphoteric surfactant, at least one hydrotrope, inorganic and / or organic acids and at least one silicate. The alkaline agent may provide a pH (when the finished product is diluted to 0.5 to 5% by weight in water) will be between about 9 to 13. The concentrate may be provided as a one-part or two part solution. Certain formulations have been found to be shelf stable as one-part concentrate or ready-to-use solutions, even with significantly different properties amongst the components. The compositions of the invention are also used in cleaning processes for surfaces, especially vehicle surfaces in car wash systems. The compositions are used in such processes where there are single or multiple liquid application steps.
Owner:ZEP IP HLDG LLC
A synthetic method of an SSZ-13 molecular sieve
ActiveCN105645426AEasy to removeReduce usageCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesQuaternary ammonium cationHydroxyl ion
A synthetic method of an SSZ-13 zeolite molecular sieve is disclosed. The method includes preparing SSZ-13 crystals under crystallization conditions from raw materials comprising an oxide of at least one quadrivalent element or a quadrivalent element mixture, an oxide of at least one trivalent element and a trivalent element mixture, at least one alkali metal compound, N,N,N-trimethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraazatricyclo[3.3.1.1]decane-2-ammonium hydroxide or a mixture of the N,N,N-trimethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraazatricyclo[3.3.1.1]decane-2-ammonium hydroxide and the SSZ-13 molecular sieve crystal seeds, hydroxyl ions and water. The method is a method of synthesizing the SSZ-13 molecular sieve by adopting a novel and cheap template. The method avoids adoption of traditional expensive N,N,N-trimethyladamantan-1-ammonium cations or benzyl trimethyl quaternary ammonium cations as templates to synthesize the SSZ-13 molecular sieve, thus significantly reducing the cost of synthesizing the SSZ-13 zeolite molecular sieve.
Owner:CHINA CATALYST HLDG CO LTD
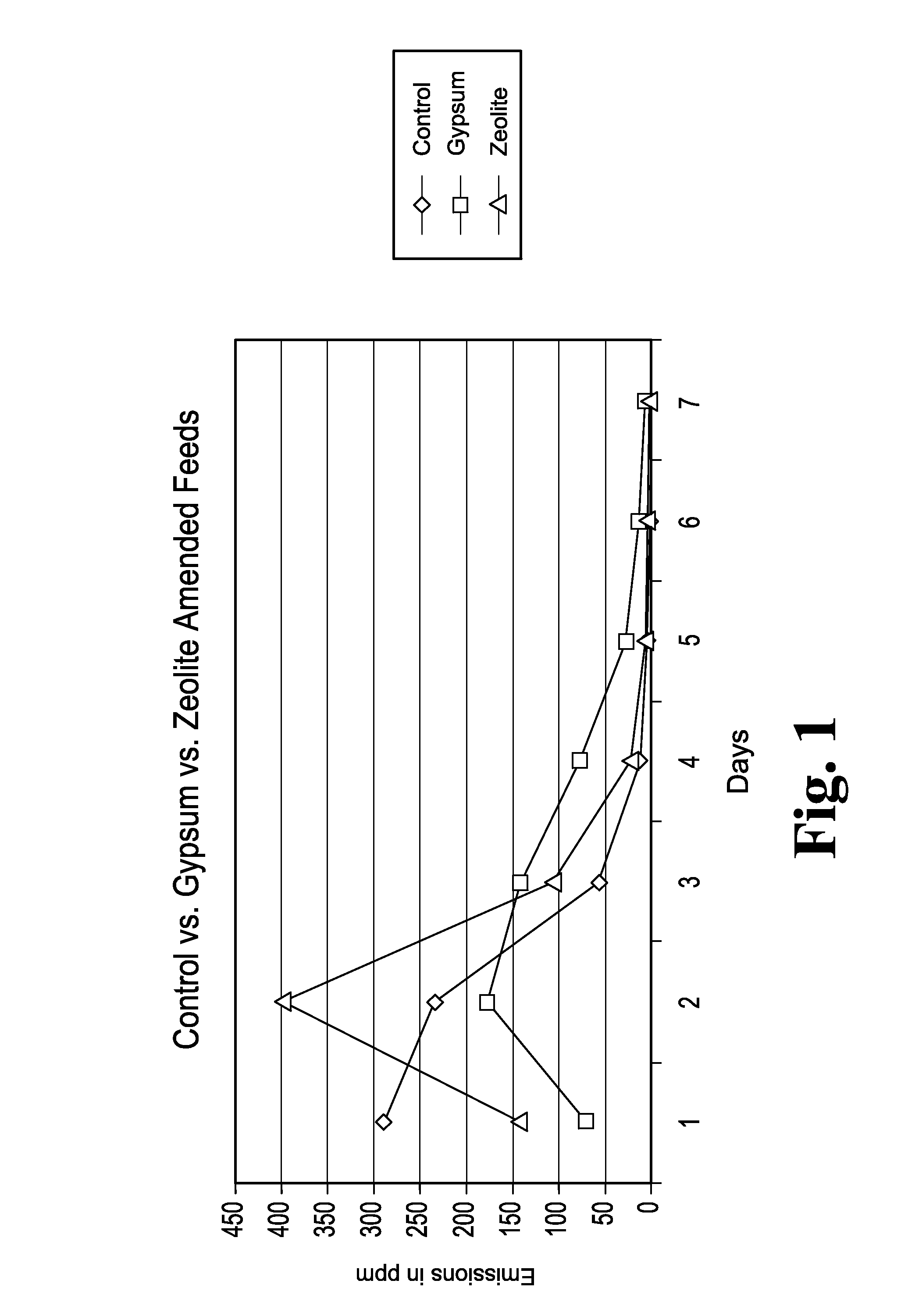
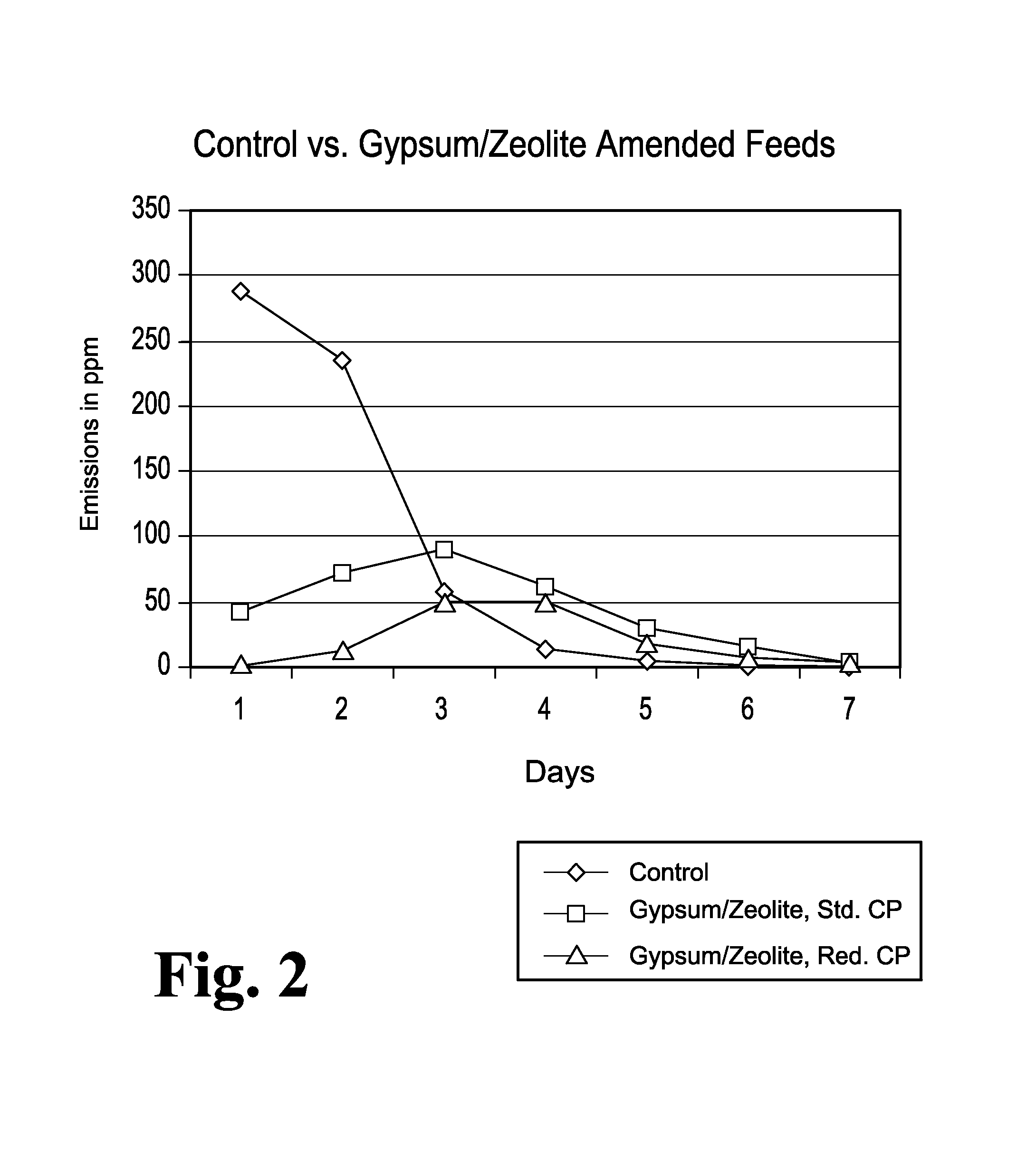
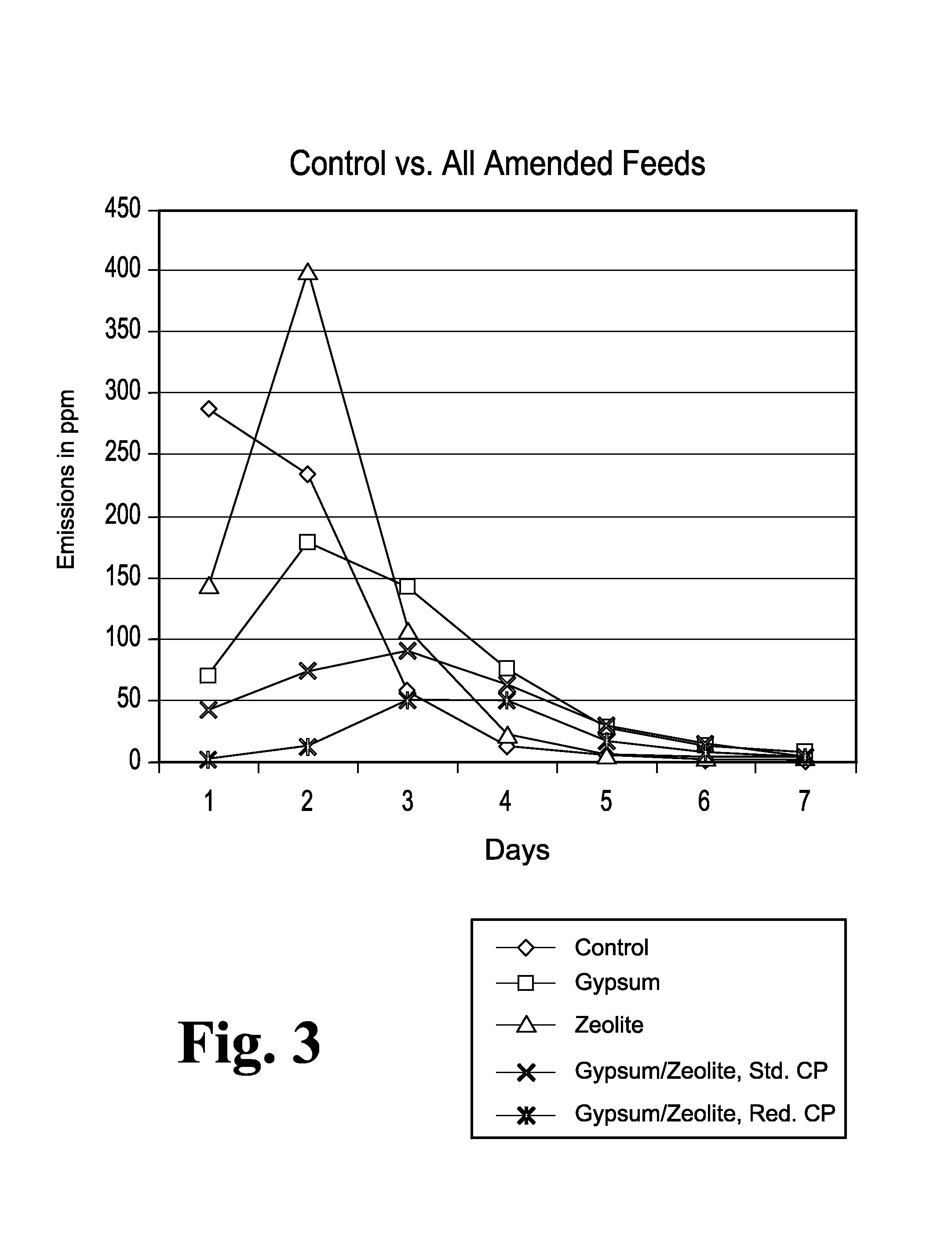
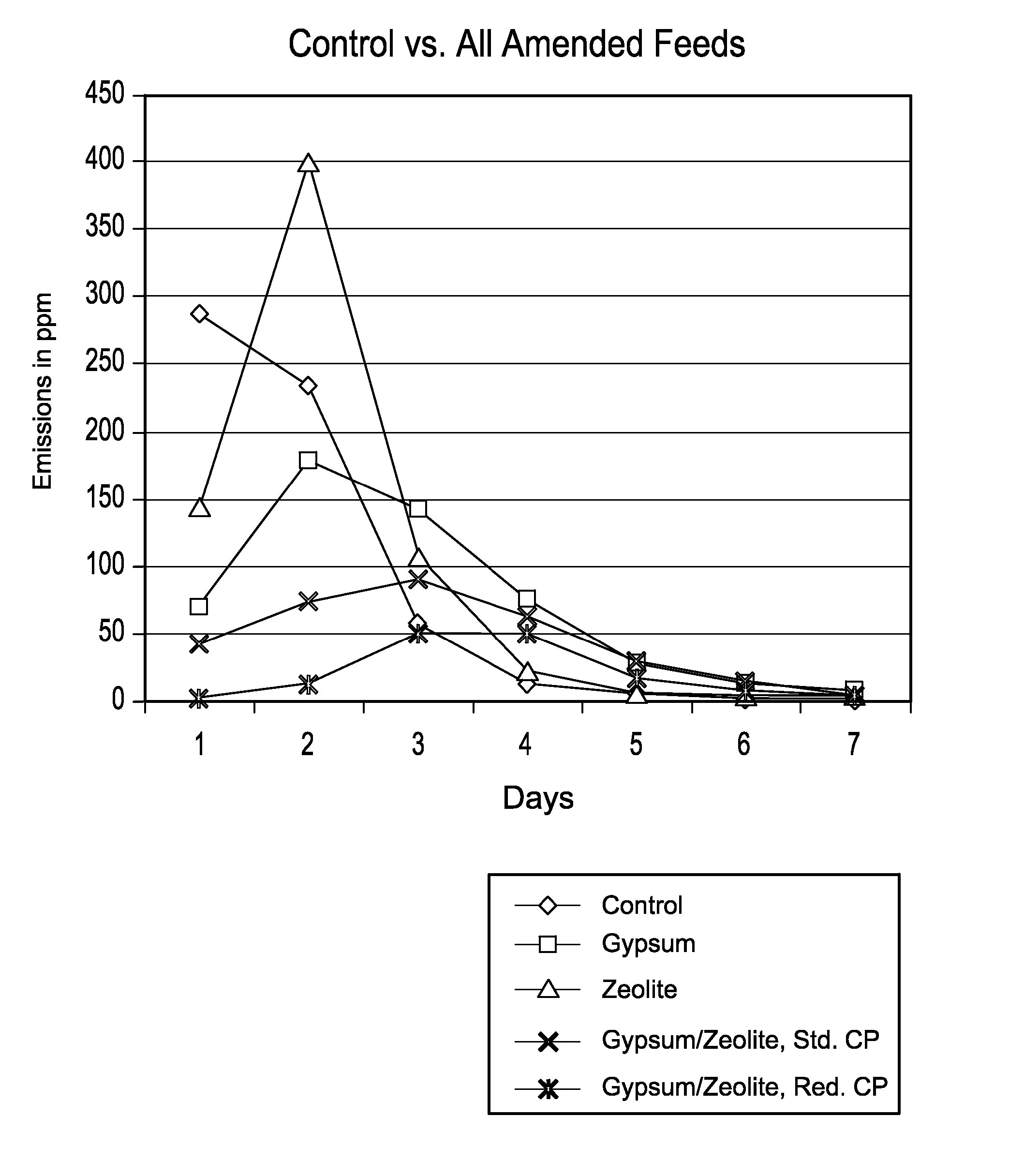
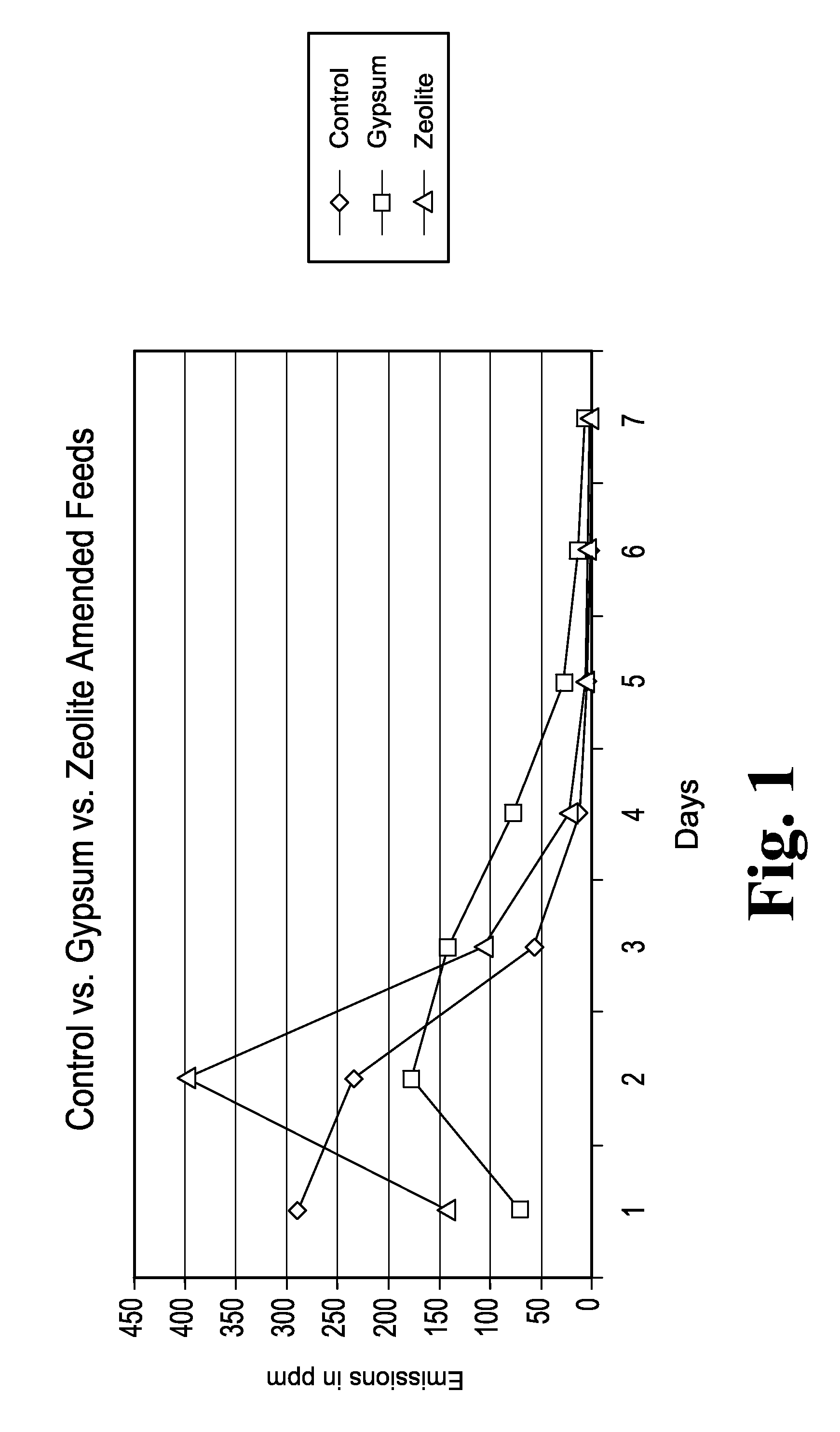
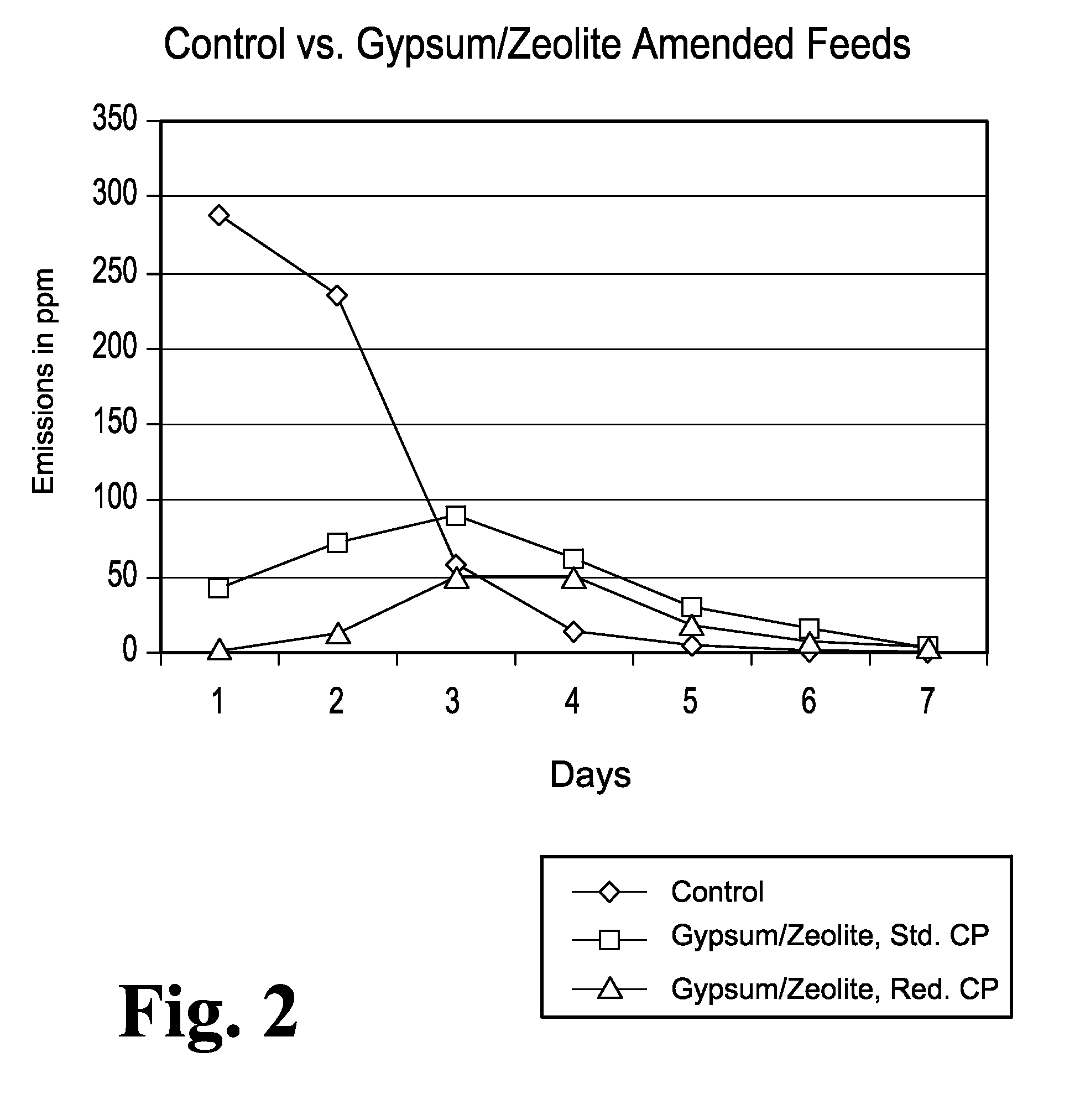
Animal feed and methods for reducing ammonia and phosphorus levels in manure
InactiveUS20080044548A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced pHCalcareous fertilisersProductsCation-exchange capacityFeces
An animal feed is provided that employs a substantially indigestible cation exchanger capable of binding ammonium cations and an acidogenic substance to acidify an animal's manure and thereby create ammonium cations that can be bound by the cation exchanger. The animal feed reduces ammonia emissions from manure produced by animals fed the animal feed compared to the emissions obtained from manure when an acidogenic substance is fed alone and compared to the emissions obtained from manure when a cation exchange capacity material is fed alone. Other aspects provide a method of lowering ammonia emissions from manure is provided. One embodiment provides a method for reducing soluble phosphorus levels in manure and a method for reducing total phosphorus levels in manure. In a further aspects present a method that yields manure that may be used alone or in concert with other materials to act as a fertilizer having advantageous ecological properties. Another aspect provides a method for reducing insect populations associated with manure. One embodiment is a composition for amending animal feed to produce animal waste that is lower in volatile ammonia and higher in nitrogen.
Owner:ROSE ACRE FARMS
Animal feed and methods for reducing ammonia and phosphorus levels in manure
InactiveUS20070218168A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced pHCalcareous fertilisersExcrement fertilisersCation-exchange capacityFeces
An animal feed is provided that employs a substantially indigestible cation exchanger capable of binding ammonium cations and an acidogenic substance to acidify an animal's manure and thereby create ammonium cations that can be bound by the cation exchanger. The animal feed reduces ammonia emissions from manure produced by animals fed the animal feed compared to the emissions obtained from manure when an acidogenic substance is fed alone and compared to the emissions obtained from manure when a cation exchange capacity material is fed alone. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method of lowering ammonia emissions from manure is provided. The present invention also provides a method for reducing soluble phosphorus levels in manure and a method for reducing total phosphorus levels in manure. In a further aspect of the present invention, a method is provided that yields manure that may be used alone or in concert with other materials to act as a fertilizer having advantageous ecological properties. Another aspect of the present invention provides a method for reducing insect populations associated with manure.
Owner:HALE EDWARD CARROLL III
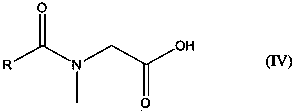
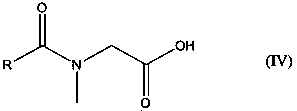
Additive compositions with a friction modifier and a metal dialkyl dithio phosphate salt
A lubricating composition comprising a major amount of base oil and a minor amount of an additive package, wherein the additive package comprises: (A) a friction modifier component selected from: (a) one or more a reaction products of an alcohol with a compound of the formula IV: (see formula IV); and (b) one or more compounds of the Formulae II-III: (see formula II) (see formula III) wherein wherein R is a linear or branched, saturated, unsaturated, or partially saturated hydrocarbyl having about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms; R2 and R3 are independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C18 hydrocarbyl groups, and C1-C18 hydrocarbyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms; and X is an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, or ammonium cation and n is the valence of cation X; and (B) at least one metal dialkyl dithio phosphate salt.
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Preparation method for tetra-alkyl ammonium hydroxide
InactiveCN105112934APrevent precipitationPromote precipitationCellsElectrolytic organic productionComing outElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemical synthesis and relates to a preparation method for tetra-alkyl ammonium hydroxide. A three-film four-chamber electrodialysis device is adopted, and tetra-alkyl ammonium salt serves as raw material to prepare the tetra-alkyl ammonium hydroxide. Firstly, a tetra-alkyl ammonium salt aqueous solution, pure water, anolyte and an acid solution are added to a salt chamber, a cathode chamber, an anode chamber and an acid chamber respectively, power is turned on, tetra-alkyl ammonium cations penetrate a first cation film to enter the anode chamber, anions penetrate an anion film to enter the acid chamber; the anolyte is electrolyzed to generate O2 and cations H+, and the H+ combine with the anions coming out of the salt chamber to generate anolyte after the H+ enter the acid chamber; and water molecules is electrolyzed at a negative plate to form H2 and anions OH-, and the anions OH- combine with the tetra-alkyl ammonium cations to form a tetra-alkyl ammonium hydroxide solution. The preparation method is simple in process, convenient to operate, scientific in principle, low in cost, environmentally friendly, and capable of being applied to large-scale industrial production easily.
Owner:QINGDAO RUNXING PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIAL
Catalytic System for CO2/Epoxide Copolymerization
ActiveUS20100324260A1High activityReduces nucleophilic attackAluminium compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEpoxyCobalt
The present invention related to a method of manufacturing a polycarbonate including the process of copolymerizing epoxide compound and CO2 using cobalt(III) or chromium(III), where the ligands contains at least 3 ammonium cations, central metal has formal −1 charge, and conjugated anions of the two cationic ammonium groups are acid-base homoconjugation, as catalyst.According to the present invention, the initial induction time can be reduced when the said polycarbonate is manufactured and it is possible to improve the activity of the catalyst and the molecular weight of the obtained polymer.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Mixed fluoroalkyl-alkyl surfactants
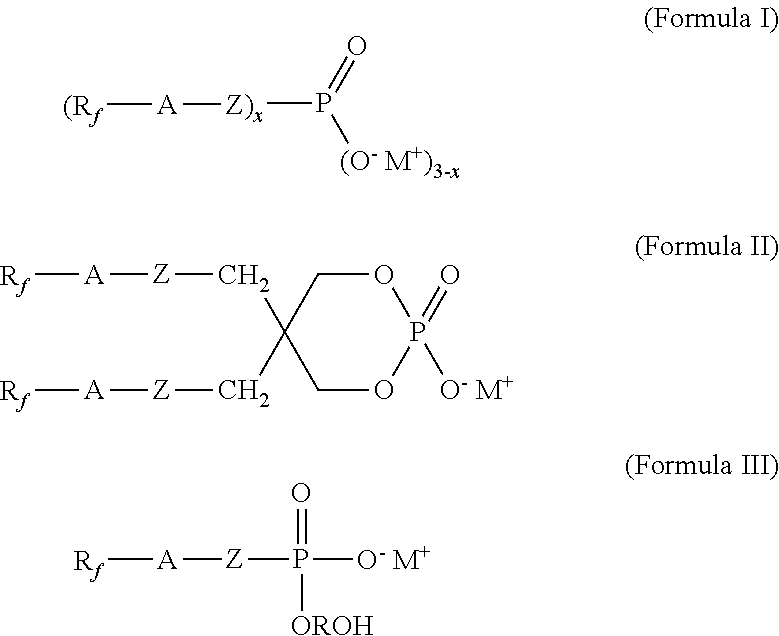
A compound of Formula 1Rf-A-OP(O)(O−M+)(O—RH) Formula 1whereinRf is a C2 to C6 linear or branched perfluoroalkyl optionally interrupted by one, two or three ether oxygen atoms;A is (CH2CF2)m(CH2)n—, (CH2)oSO2N(CH3)(CH2)p—, O(CF2)q(CH2)r—, or OCHFCF2OE-;m is 1 to 4; n, o, p, and r are each independently 2 to 20; q is 2;E is a C2 to C20 linear or branched alkyl group optionally interrupted by oxygen, sulfur, or nitrogen atoms; a cyclic alkyl group, or a C6 to C10 aryl group;M is a Group I metal or an ammonium cation (NHxR2y)+ wherein R2 is a C1 to C4 alkyl, x is 1 to 4, y is 0 to 3 and x+y is 4; andRH is a C1 to C20 linear, branched, or cyclic alkyl, or a C6 to C10 aryl, and its use as a surfactant is disclosed.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Synthetic Lubricating Oil
InactiveUS20090270286A1Improve wear resistanceStable flowabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryImidePyridinium
The object of the present invention is to provide a synthetic lubrication oil which shows low viscosity, is excellent in viscosity properties at high temperature and shows stable lubricating properties in a wide range of temperature. The synthetic lubricating oil is one comprising an ionic liquid containing an organic cation selected from the group consisting of an imidazolium cation, a pyridinium cation, a quaternary ammonium cation and a quaternary phosphonium cation and a bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide anion, and one comprising an ionic liquid composition which comprises an ionic liquid (A) containing a 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium cation and an ionic liquid (B1) containing a 1-methyl-3-propylimidazolium cation and / or an ionic liquid (B2) containing a 1-methyl-3-isopropylimidazolium cation.
Owner:THE NIPPON SYNTHETIC CHEM IND CO LTD
Cyclic quaternary ammonium salt, nonaqueous solvent, nonaqueous electrolyte, and power storage device
InactiveUS20130288112A1Resistance to oxidationLow viscosityHybrid capacitor electrolytesOrganic chemistryDischarge efficiencySolvent
To provide an ionic liquid which has at least one of properties such as high ionic conductivity, a small reduction in ionic conductivity at a low temperature, a low melting point, and a low viscosity. To provide a power storage device having higher initial charge and discharge efficiency than a power storage device containing a conventional ionic liquid. A cyclic quaternary ammonium salt is liquid at room temperature and contains a quaternary spiro ammonium cation having an asymmetrical structure including two aliphatic rings and one or more substituents bonded to one or both of the two aliphatic rings and an anion corresponding to the quaternary spiro ammonium cation. The power storage device includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a nonaqueous electrolyte containing the cyclic quaternary ammonium salt as a nonaqueous solvent.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Additive compositions with plural friction modifiers
A lubricating oil comprising a major amount of base oil and a minor amount of an additive package, wherein the additive package comprises: (A) a friction modifier component selected from: (a) one or more a reaction products of an alcohol with a compound of the formula IV: (see formula IV) and (b) one or more compounds of the Formulae II-III: (see formula II); and (see formula III) wherein R is a linear or branched, saturated, unsaturated, or partially saturated hydrocarbyl having about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms, R2 and R3 are independently selected from hydrogen C1-C18 hydrocarbyl groups, and C1-C18 hydrocarbyl groups containing one or more heteroatoms; X is an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal or ammonium cation and n is the valence of cation X, and reaction products of amines, amino alcohols, alkali or alkaline earth metal hydroxides, alkali or alkaline earth metal oxides and mixtures thereof with compounds of the Formula IV: (see formula IV) wherein R is as defined above; and (B) at least one friction modifier that is different from the one or more compounds (A).
Owner:AFTON CHEMICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com