Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61results about How to "With identification function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
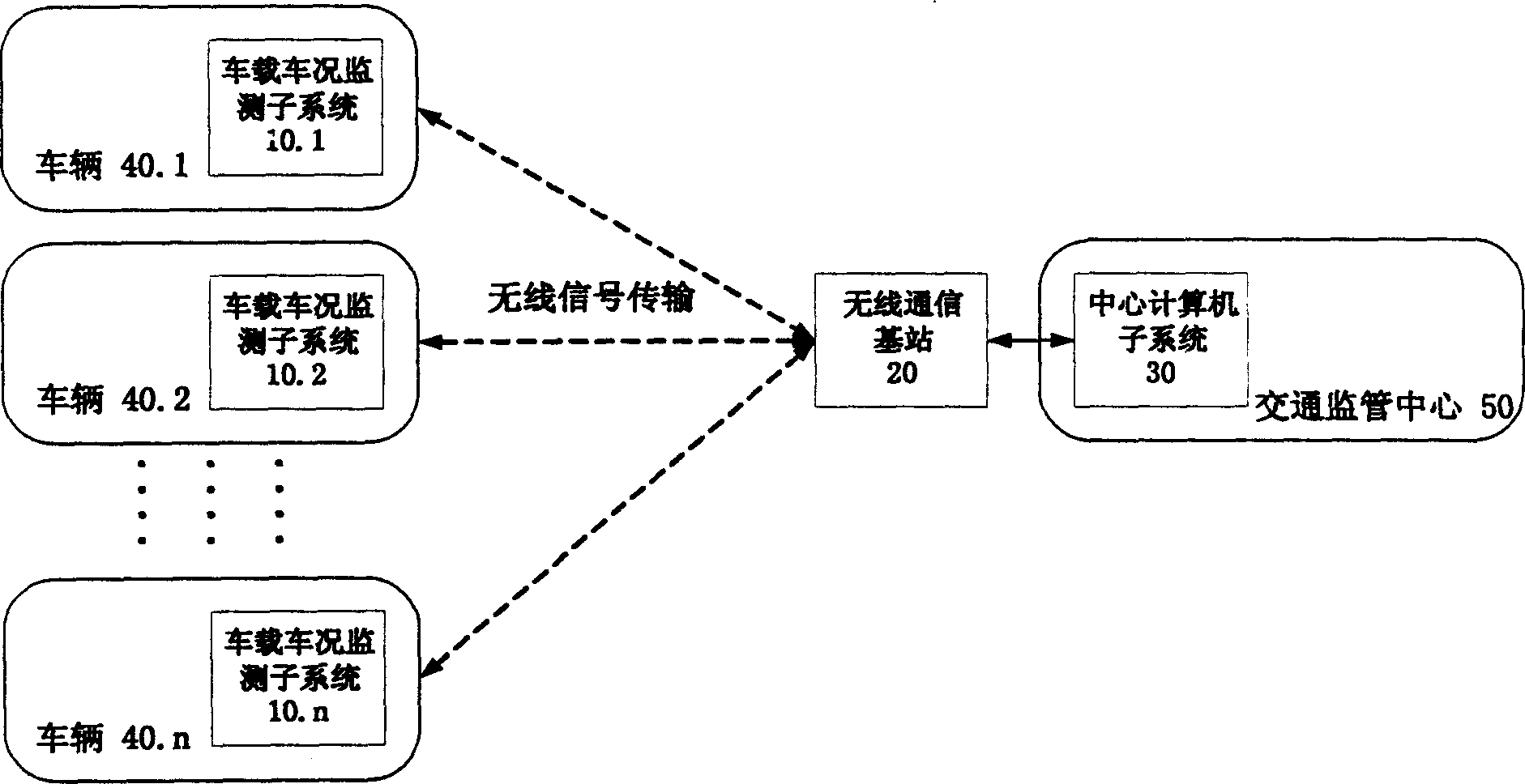
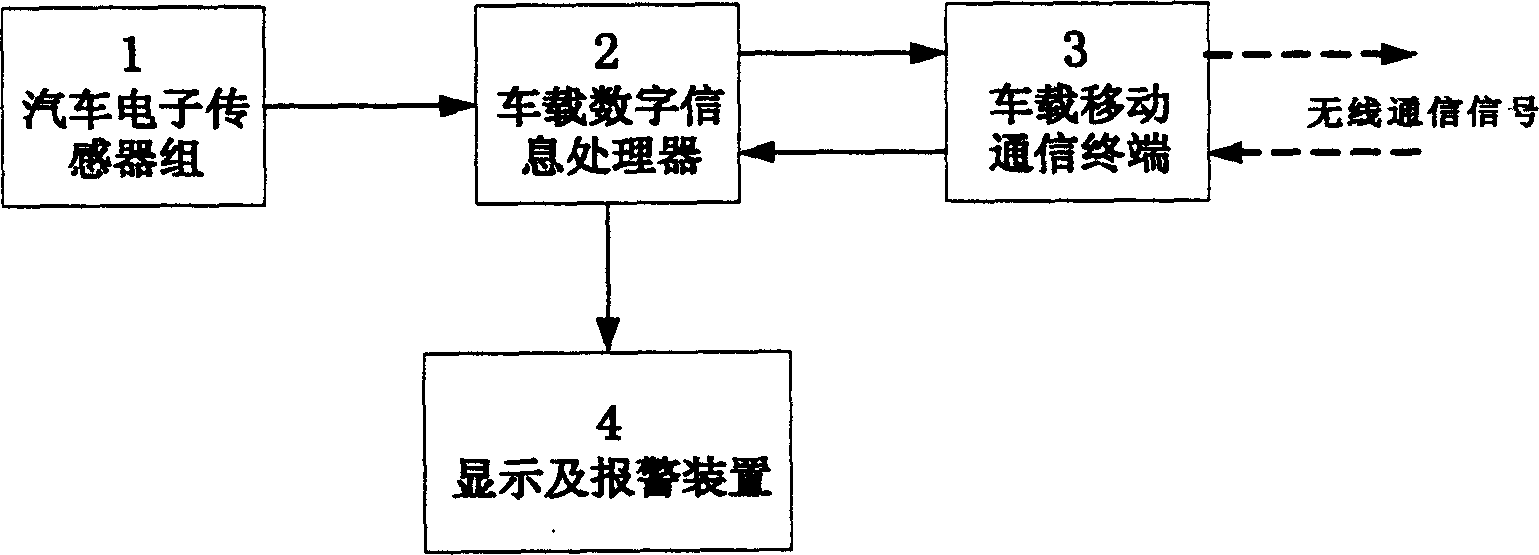
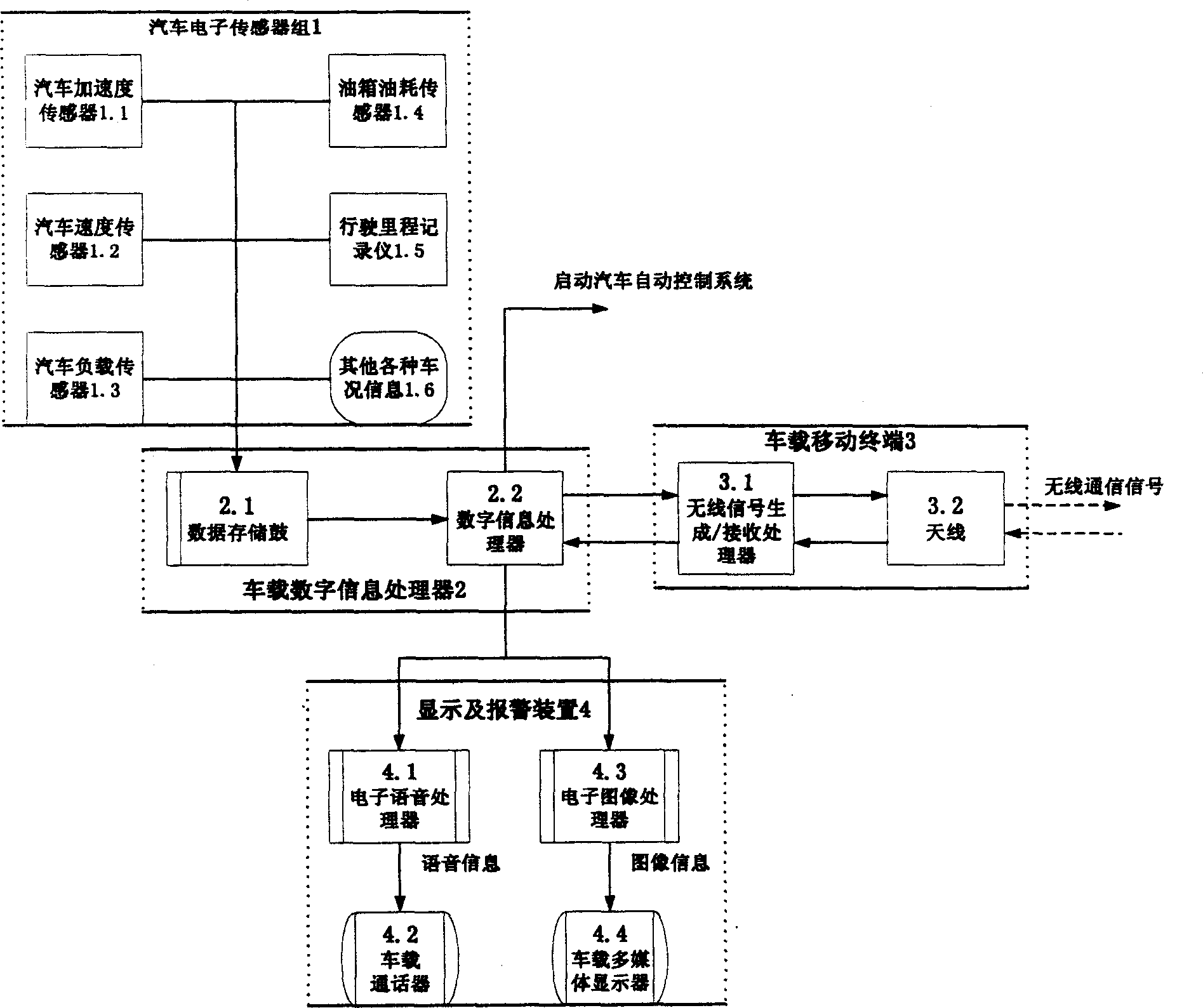
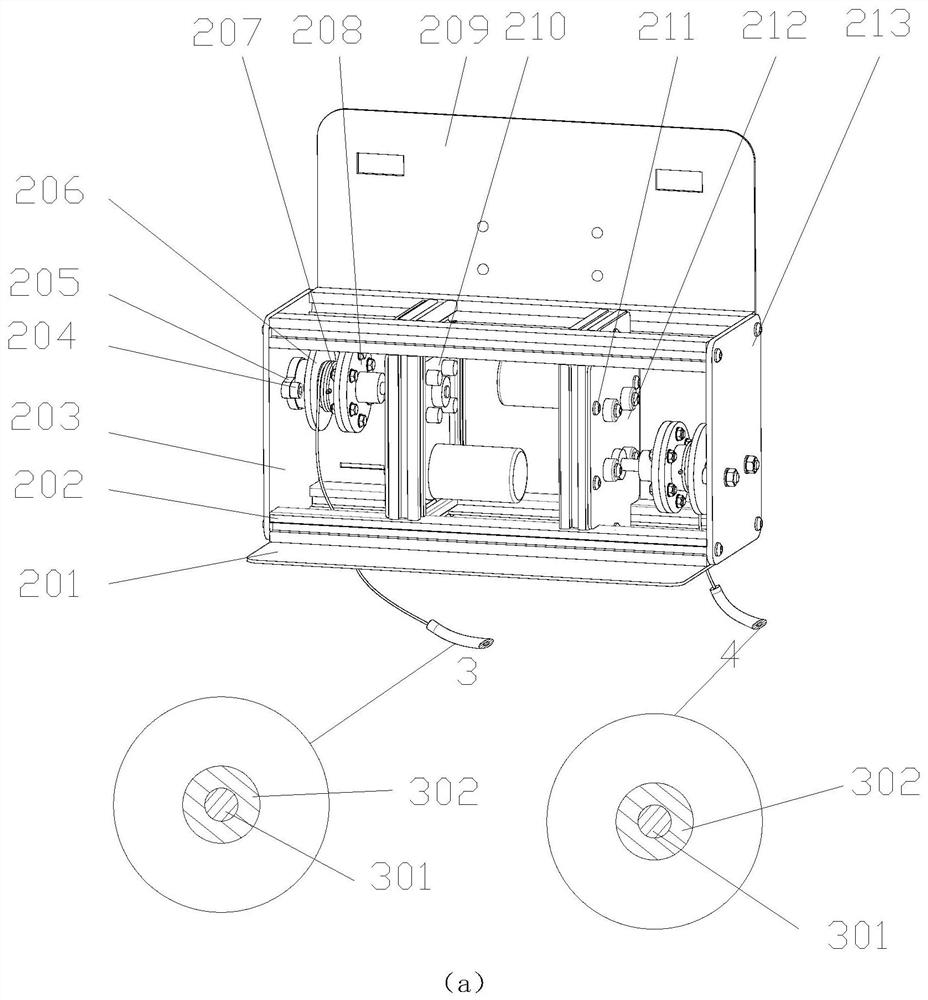
Intelligent vehicle condition monitor system based on mobile communication
InactiveCN1588415ANetworkingFully automatedSpecial data processing applicationsData informationEngineering
The invention discloses an intelligent car state supervising system based on mobile communication. The system includes car borne state supervising subsystem and the center computer subsystem in the traffic monitor. The car borne state supervising subsystem exchanges data information with the center computer subsystem through the base station of the wireless communication network, and forms a traffic monitoring and managing network. The car borne state monitoring subsystem includes a vehicle electron sensor group, car borne digital information processor, car borne mobile communication terminal and displaying and alarming device. The center computer subsystem includes a car identification incriminator, digital information processing computer, storing and recording device, peccancy and deficiency judger and alarm and order information generator. The invention can provide state information to the cit traffic managing department of any car automatically, thus it is convenient to the monitor and management of car state, upgrades the supervising efficiency of traffic state.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser night vision integral high-speed camera with cloud deck and monitoring method thereof
ActiveCN102955328AAchieve synchronous zoomPrevent deviationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsStereo cameraLight spot
The invention relates to monitoring equipment and discloses a laser night vision integral high-speed camera with a cloud deck which is characterized in that a stepping motor electrically connected with a drive control panel is mounted on the cloud deck. An optical zoom lens is horizontally driven by the stepping motor through a screw rod. An interface electrically connected with the integral camera is arranged on the drive control panel. A storage is disposed on the drive control panel. A semiconductor laser generator is mounted in a shell of a semiconductor laser unit and mounted on radiating fins outside the shell of the semiconductor laser unit by means of thermal conduction. The invention further discloses a monitoring method of the laser night vision integral high-speed camera. The monitoring method includes the steps of firstly, building a database list; secondly, zooming synchronously; and thirdly pulse operation. Lighting angle of laser projection can automatically follow viewing angle of the camera, pulse operation is combined with direct radiation, and accordingly normal operation can be guaranteed while size power ration is smaller. In addition, the laser night vision integral high-speed camera with the cloud deck can shoot plate number and externally adjust light spots.
Owner:深圳市安星数字系统有限公司
Low-power Bluetooth intelligent asset management apparatus with identity recognition function
InactiveCN107145915AConvenient statistics and managementImprove efficiencyCo-operative working arrangementsNear-field for read/write/interrrogation/identification systemsIdentity recognitionComputer module
The invention discloses a low-power Bluetooth intelligent asset management apparatus with an identity recognition function. The apparatus comprises electronic tags, an APP loading body and a server, wherein the electronic tags actively send out signals used for the APP loading body to receive, and the single APP loading body receives the signals sent by the electronic tags at the same time; an APP loaded on the APP loading body performs asset check through identity authentication, system updating, data downloading, tag configuration, tag locating and asset management; and during asset management, tag broadcasts are scanned through a Bluetooth module of the APP loading body, then identification and classification processing is performed through a fast addressing algorithm, and the asset management and statistics are finished. The deficiencies of low asset management efficiency, poor timeliness and high error rate caused by existing electronic tag collision and environment interference are overcome; and the apparatus has the characteristics of real-time asset management, high efficiency, no errors, localizability, rechargeability, reusability and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU LIULANG TECH CO LTD
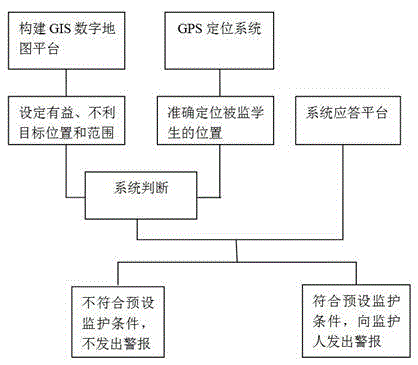
Primary and secondary school student condition monitoring method based on GPS and GIS
The invention discloses a primary and secondary school student condition monitoring method based on a GPS and a GIS. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, constructing a GIS digital map platform, setting favorable target positions and influence ranges, unfavorable target positions and influence ranges, and alarm conditions on the platform; and then utilizing a mobile phone GPS to obtain position information of students in real time, carrying out analysis and judgment according to the time locus of positions and the alarm conditions, making a decision about whether to send out an alarm, if yes, automatically sending out alarm information to parents or teachers by means of messages. According to the invention, the primary and secondary school student condition monitoring method overcomes the defect of existing various monitoring systems that monitoring is carried out by people, automatic monitoring is realized without the need of personnel monitoring, so that the method is suitable for the automatic condition, and much more and more humanized functions are improved on the basis; in addition, the method is flexible and humanized, the design mode is adapted to the rebellious character of teenagers in the growth stage, the physical and mental health of the teenagers is facilitated, and the method is certain to become an essential safety assistant of wide primary and secondary school students.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
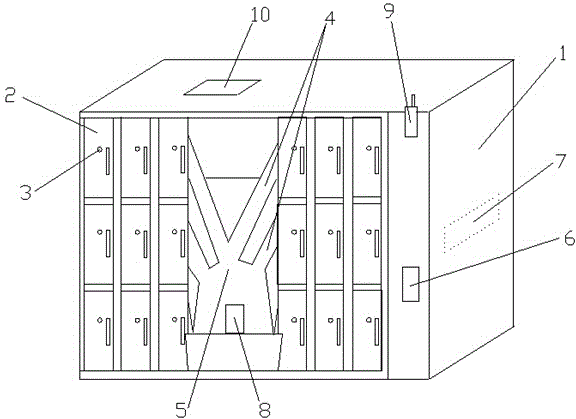
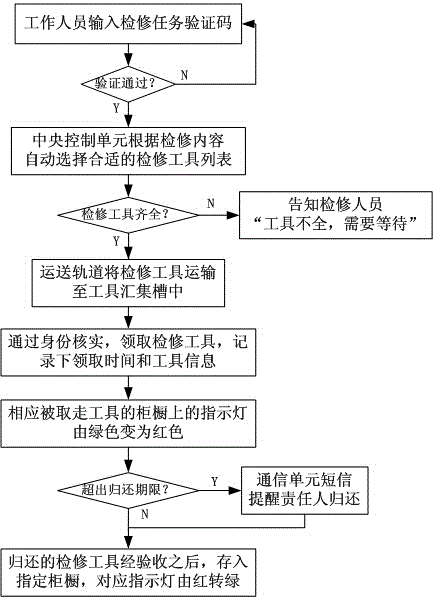
Intelligent storage cabinet for electric power overhaul tools
InactiveCN104669224AWith identification functionIncrease the level of automationWork tools storageCommunication unitQuality of work
The invention discloses an intelligent storage cabinet for electric power overhaul tools. The intelligent storage cabinet comprises a cabinet body, compartments and indicator lamps. The compartments are used for storing appointed overhaul tools and connected with a tool collection cavity through transport rails; the cabinet body is provided with a verification code recognition unit used for verifying overhaul task verification codes provided by staffs; a central control unit reads overhaul task contents from the verification code recognition unit, automatically selects proper tools according to requirements and controls the tools in the corresponding compartments to be transported to the tool collection cavity by the transport rails; the tool collection cavity is provided with a tool receiving confirmation unit which is used for confirming identities of tool receiving personnel and recording receiving time and tool information; the cabinet body is further provided with a communication unit and a tool inspection and acceptance unit. The intelligent storage cabinet for the electric power overhaul tools has the advantages that the overhaul tools can be automatically selected according to the overhaul tasks while the tools can be quickly and reliably checked to timely remind and verify tool recovery conditions, and consequently intelligent management with tool selection, tracking and returning integrated is realized, and operation efficiency and operation quality are improved.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY ZHENGZHOU POWER SUPPLY
Smell detection system based on odor evaporation characteristic spectrum and system thereof
InactiveCN101871898AEfficient detectionWith identification functionInvestigating phase/state changeLiquid stateGas composition
The invention belongs to the odor detection technology, relates to the technical field of odor sample processing and smell and discloses a smell detection system based on an odor evaporation characteristic spectrum and a system thereof. The artificial smell technology has been widely applied in the field of detection of various types of odor, and the smell detection capability can be greatly improved through improving the volume of odor information obtained by a single sensor. The invention describes evaporation characteristics of a liquid sample based on the principles that the components of the liquid sample has different evaporation characteristics, and odor generated in evaporation at different time has different gas components and contents thereof during evaporation of the liquid sample of a finite volume, and a specific type of gas sensor responds to odor generated in evaporation at different time to obtain sensor signals changing along with the time, i.e. the odor evaporation characteristic spectrum. Therefore, the invention increases odor information obtained by the gas sensor, improves the accuracy of odor analysis and has great market application value in food analysis, security testing, medical treatment, public health and other aspects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
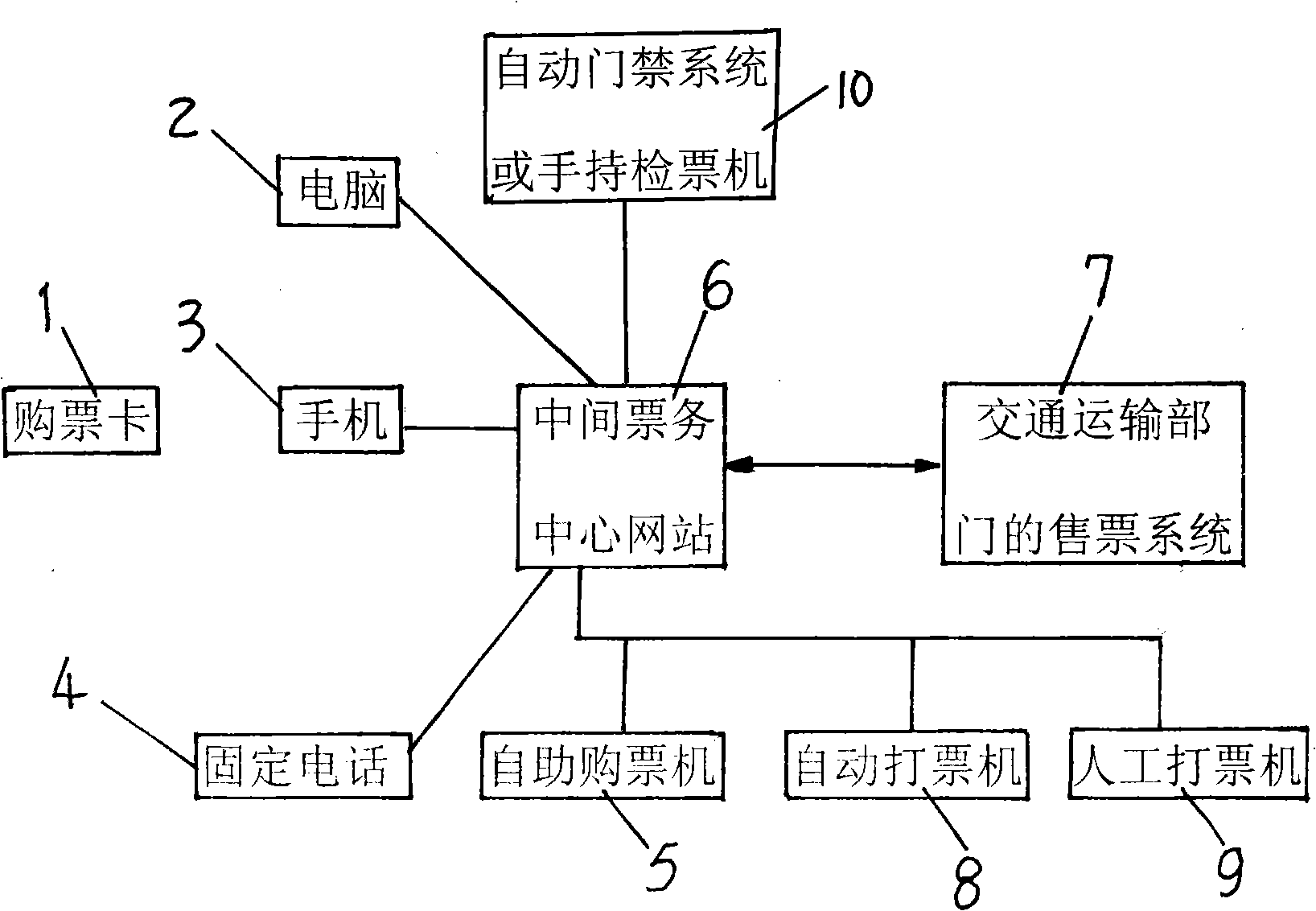
Self-help remote ticket-buying, fetching system possessing personal identification and its method
InactiveCN101290686ARealize the ticket purchase functionPractical practicalityReservationsCommerceBank accountIdentity recognition
The invention discloses a system with identity recognition for self-service remote purchasing and fetching a ticket and a method using the same. The system comprises a ticket purchasing card which has account recording function, identity-recognizing function and the function for settling, transferring, remitting and allocating money with an appointed bank account, a computer used for networking a website of an intermediate ticket center, a mobile phone and a fixed-line telephone which are networked with the website of the intermediate ticket center through dialing numbers, the website of the intermediate ticket center which is networked with a ticket-sale system of a transportation department through an protocol, a self-service ticket purchasing machine, a self-service ticket printing machine and a hand ticket printing machine which are networked with the website of the intermediate ticket center. The method comprises the following steps that: a user logs on the website of the intermediate ticket center for purchasing a ticket and paying fee for the ticket according to the number and the code of the ticket purchasing card with the computer, the mobile phone, the fixed-line telephone and other terminal devices, and directly realizes the transition and determination of the proprietary right of the ticket via network, thereby saving problems of booking the ticket at a ticket point, queuing for purchasing the ticket and wasting time, saving mass social time and improving the operational efficiency for society.
Owner:杨子江
Fingerprint mailbox with code identification function
InactiveCN104665538AWith identification functionWith fingerprint recognition functionCharacter and pattern recognitionKitchen equipmentElectromagnetic lockSecret code
The invention relates to a fingerprint mailbox with a code identification function. The fingerprint mailbox comprises one or more box units, a fingerprint identification device, a code identification device, electromagnetic locks, a central controller, a special mailbox lock and a lock controller. The fingerprint identification device, the code identification device, the electromagnetic locks, the central controller and the lock controller are electrically connected; the fingerprint identification device, the code identification device, the central controller, the lock controller and the special mailbox lock are mounted inside the same box body; the electromagnetic locks are mounted inside the one or more box units; the code identification device comprises a keypad and a display screen. The fingerprint mailbox with the code identification function is simple in structure and stable in functionality, obtains a fingerprint identification and code identification function, improves the security and operability and accordingly is applicable to residential communities, enterprises and public institutions.
Owner:BEIHAI FEIJIUTIAN ELECTRONICS TECH
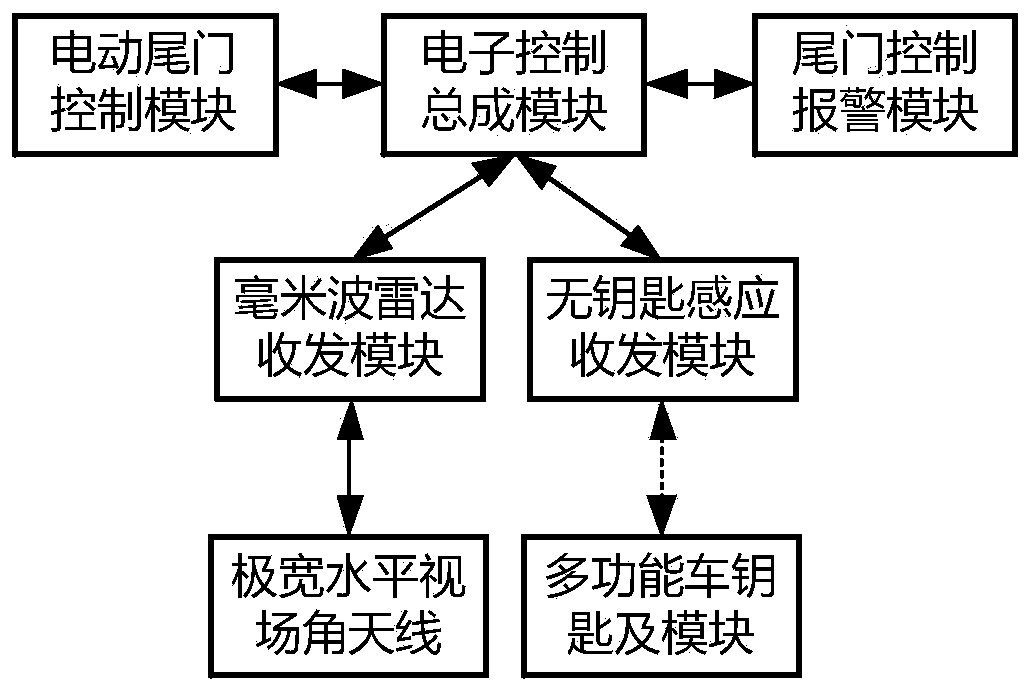
Electric tail gate system based on vehicle radar and control method
PendingCN111409591ASolve wasteImplement proximity detectionAnti-theft devicesPower-operated mechanismIn vehicleControl engineering
The invention provides an electric tailgate system based on a vehicle radar and a control method. The electric tailgate system comprises an electric tailgate control module, an electronic control assembly module, a tailgate control alarm module, a millimeter wave radar receiving and transmitting module, an extremely wide horizontal field angle antenna, a keyless induction receiving and transmitting module, a multifunctional vehicle key and a multifunctional vehicle key module. , one-kick control of the electric tail door of the vehicle can be realized by only depending on one set of existing vehicle millimeter-wave radar transceiving module and keyless induction transceiving module, so that the loading cost is reduced, and the original detection function of the vehicle-mounted radar is still considered. , a user can control the automatic opening of the vehicle door with feet when the user is inconvenient to pull the vehicle door with hands, the problem of resource waste caused by highpower consumption of the existing capacitive sensing system in the working process is avoided, and the problems of low sensitivity, potential safety hazard due to the fact that the user is too close to the vehicle door and the like in the traditional opening method are solved.
Owner:成都多普勒科技有限公司
Silk woven medical suture with color discrimination and anti-bacterial functions and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105497974AImprove antibacterial propertiesLess hairySuture equipmentsYarnEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a silk woven medical suture with color discrimination and anti-bacterial functions and a preparing method thereof. One-ply silk threads are used as a raw material and are dyed through a natural dyestuff post-mordant method; waxing and rewinding are simultaneously conducted on the dyed silk threads with food-grade beeswax, and center threads and shell threads are arranged by the ratio of center threads: shell threads=0.083-0.25 and woven on an automatic weaving machine to obtain silk woven threads; high-temperature fast heat setting is carried out on the silk woven threads, Co60 irradiation sterilization is carried out, and the silk woven medical suture with the diameter range of 0.04-0.5 mm is obtained, wherein the tensile strength is 1.5-50 N, the appearance color is black, the silk woven medical suture does not fade when washed with water, the rate of inhibiting staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli is 99% or more, and the bacterium inhibiting duration time is 7 days or longer. The physical properties and antibacterial performance of the silk woven medical suture meets related standards, and the silk woven medical suture is easy to recognize in the operation process and has excellent antibacterial performance.
Owner:HUBEI SAILUO BIOLOGICAL MATERIAL CO LTD
Ampoule bottle treatment device and use method
ActiveCN105060215AAvoid harmTimely warningOpening closed containersBottle/container closureEngineeringBottle
The invention discloses an ampoule bottle treatment device and a use method. Angle rotary tables are arranged on the base and provided with ampoule bottle clamping jaws. The ampoule bottle treatment device can prevent an ampoule bottle from bursting or hurting the hands of an operator; ampoules bottles of various specifications can be identified, horizontally placed or obliquely pulled or obliquely placed; an ampoule bottle opening inductor is arranged so that the shape of an ampoule bottle opening can be identified, and a warning can be given to the operator in time under the condition that the bottle opening bursts and liquid medicine flows outside; and the structure is simple and the device is quite practical.
Owner:李坚毅
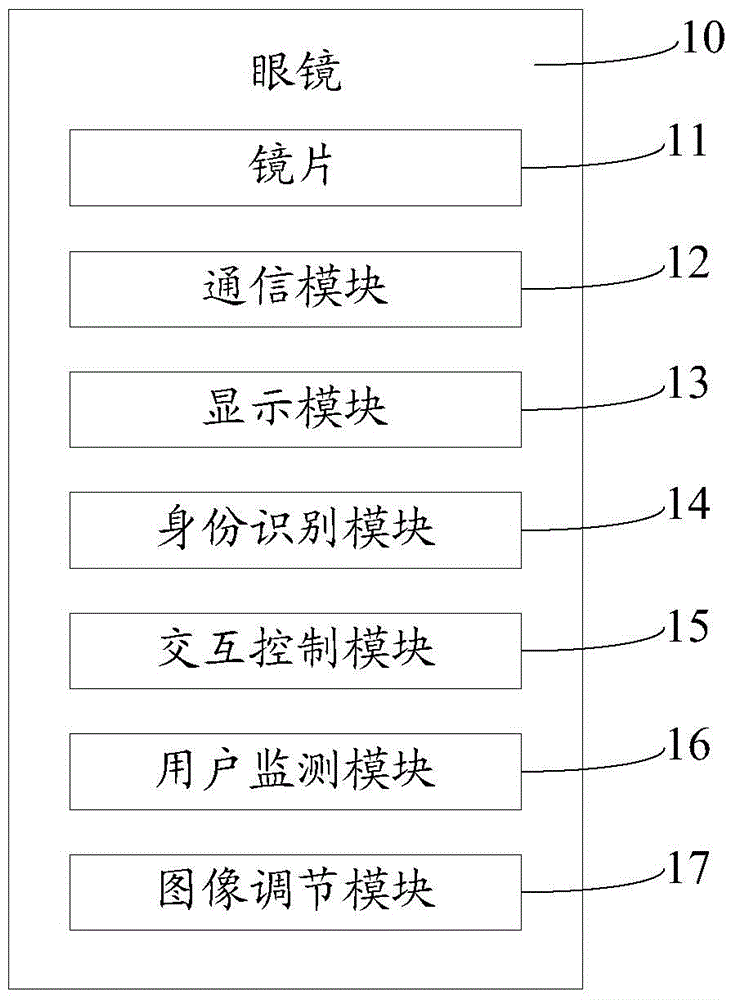
Glasses, display terminal as well as image display processing system and method
InactiveCN105760123AWith security functionWith identification functionNon-optical adjunctsUser identity/authority verificationComputer graphics (images)Eyewear
The invention discloses glasses. The glasses comprise lenses, a communication module and a display module, wherein the communication module is used for establishing communication connection with a display terminal, receiving a first image signal sent by the display terminal and sending the first image signal to the display module; the display module is used for displaying a first image corresponding to the first image signal onto the lenses, so that human eyes can see a target image synthesized by the first image and a second image, which corresponds to a second image signal and is displayed by the display terminal, through the lenses. A valid user of the glasses can see the target image synthesized by the first image and a second image, which is displayed by the display terminal, through the lenses, while other people can only acquire the second image from the display terminal, that is, other people cannot acquire effective information consistent with the information acquired by the valid user of the glasses, and the information confidentiality of the valid user of the glasses is guaranteed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
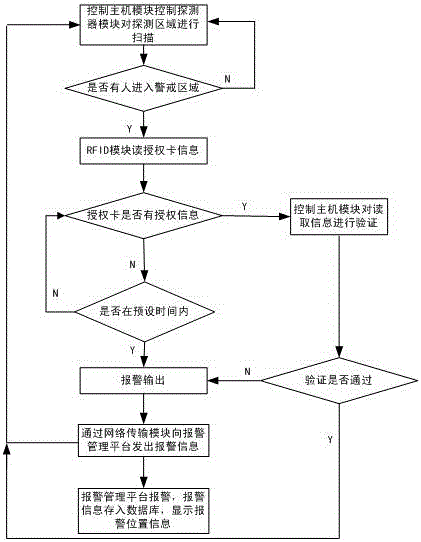
Network alarm system with identity recognition function and method
InactiveCN105894697AWith identification functionRealization of identity recognition functionIndividual entry/exit registersSensing by electromagnetic radiationComputer hardwareIdentity recognition
The invention provides a network alarm system with an identity recognition function. The network alarm system includes a detector module, an RFID module, a control host module, a network transmission module, a sound-light alarm module and an alarm management platform; when the infrared detector and microwave detector of the detector module simultaneously scan intrusion signals, the infrared detector and the microwave detector transmit the intrusion signals to the control host module through an infrared signal processing module and a microwave signal processing module respectively; the RFID module reads the authorization card information of an intruder; when the RFID module does not read authorization information, the RFID module sends a message indicating that the RFID module has not read authorization information to the control host module; the control host module sends alarm signals to the alarm management platform through the network transmission module; and the sound-light alarm gives out a sound-light alarm. The network alarm system integrates functions such as data acquisition, identity recognition, network transmission, warning and positioning, and can be adopted as an intelligent alarm system.
Owner:INFORMATION RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Connection piece in modular wall panel
ActiveCN106374308ATo achieve the purpose of general coordinationEasy to installCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsCouplings bases/casesEngineeringHome appliance
The invention discloses a connection piece in a modular wall panel, and belongs to the field of household appliance. The wall panel comprises a base and a plug-in module, wherein the plug-in module is arranged in the base and can be disassembled and replaced, the connection piece is fixed in the base and is connected with the base to form a whole, the connection piece comprises a connection shell and a control circuit board, and the control circuit board is arranged on the connection shell and is electrically coupled to the plug-in module inserted into the base. The connection piece has the advantages that the connection piece can provide a universal part for the wall panel, and the universality of the wall panel is improved.
Owner:PUTIAN INTELLIGENT LIGHTING INST
Full-automatic medical mask distributing and storing box
PendingCN111341426AEnsure hygieneEasy to control body temperatureThermometers using material expansion/contactionCoin-freed apparatus detailsIdentity recognitionControl system
The invention discloses a full-automatic medical mask distributing and storing box which comprises a first machine body, a mask storage mechanism, a mask carrying mechanism, an identity recognition mechanism and a control system, solves the problems that masks are not placed in containing containers and distribution is not standard, and is suitable for being placed at multiple distribution pointsof social public places. Hand disinfection facilities and functions are achieved, and sanitation of a patient is effectively guaranteed; an identity recognition function is achieved, the identity of apatient, a hospital worker or a management layer of a user can be recognized, the mask can be reasonably allocated to the most needed crowd for use, and resource conflicts with medical treatment areavoided; the body temperature testing function is achieved, and user body temperature conditions can be mastered conveniently; the control system has a cloud platform and a big data collection function, is incorporated into a hospital medical management network, strengthens understanding of health conditions of medical workers on that day or heating sorting management of a first defense line of patients before outpatient treatment, facilitates rapid collection of information, facilitates first-time outpatient guidance, and facilitates hospital medical work deployment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Smart shoe based on near field communication
InactiveCN104997228ASimple structureEasy to useNear-field transmissionFootwearMultiple applicationsEngineering
The present invention relates to a smart shoe based on near field communication (NFC). The smart shoe comprises a smart shoe body, an NFC module, a power supply module and a charging module, wherein the NFC module, the power supply module and the charging module are disposed inside the smart shoe body, the NFC module is connected with the power supply module, and the charging module is connected with the power supply module. The smart shoe is simple in structure and convenient to use; through arrangement of the NFC module, the smart shoe thus has an identity recognition function; and using the identity recognition function as the core, multiple application can be further enlarged, the passing ability and the convenience are greatly raised, hands of a user are liberated, and convenience is brought to the user.
Owner:SHANGHAI MINHANG HIGH SCHOOL
Intelligent connecting rod clamping mechanism
PendingCN110228080AWith identification functionRealize moving up and downGripping headsEngineeringProtection layer
The invention discloses an intelligent connecting rod clamping mechanism. The intelligent connecting rod clamping mechanism comprises a control end, a first connecting rod, a connecting shaft, a second connecting rod, a clamping arm, an adjusting block, a clamping claw, a driving device, a driving rod A, a protective spring, a limiting block, a recognition end A, a recognition end B, a driving rodB, a pressure sensor, a protection layer and a limiting frame, wherein the first connecting rod is arranged at the bottom of the control end, the second connecting rod is connected to the lower end of the first connecting rod, the clamping arm is arranged at the bottom end of the second connecting rod, the driving rod A is welded in the clamping arm, the adjusting block is arranged at the right end of the driving rod A, and the clamping claw is arranged at the bottom of the adjusting block. According to the intelligent connecting rod clamping mechanism, the connecting rods are arranged so that up-down movement can be achieved through the driving device, the clamping claw has an recognition function, and can automatically stretch and contract according to the position so as to clamp an object, the clamping claw intelligently identifies whether the clamped object is correct or not by clamping the object, and the clamping arm is provided with the limiting frame and can perform limitationprotection on the clamping claw. The intelligent connecting rod clamping mechanism is simple in whole, simple in structure, accurate and intelligent and low in power consumption.
Owner:重庆市盈科物联网信息技术有限公司
Intelligent interactive system of sightseeing bicycle and stage lighting
PendingCN109195292AWith identification functionExpand coverageElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementStage lightingIdentity recognition
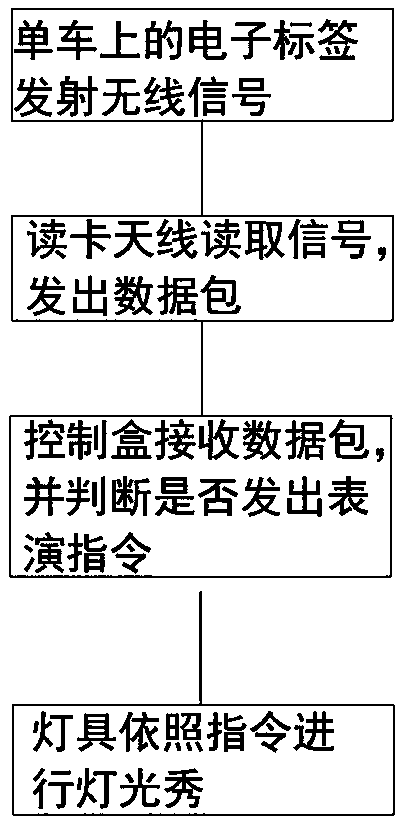
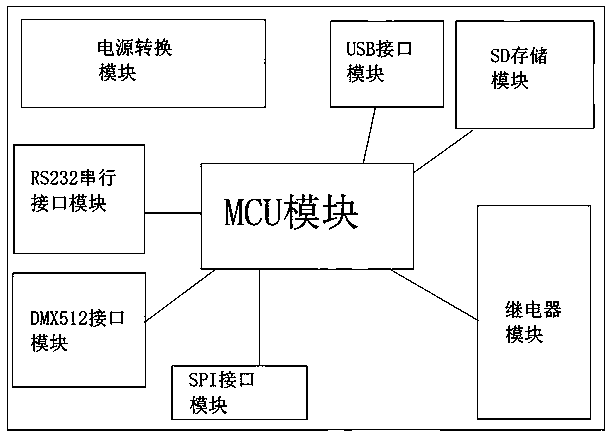
The invention relates to an intelligent interactive system for sightseeing bicycle and stage lighting, it belongs to the interactive performance mode of the combination of innovative scenic spots andstage landscape lamps and lanterns, When a tourist rides a sightseeing bicycle near a scenic spot in a scenic spot, the card reader antenna detects the signal from the electronic tag on the sightseeing bicycle, the card reading antenna transmits the tag information including the card number and the RSSI field strength value to the control box through the RS232 serial interface module. The card number is unique identification information, according to the preset authentication, when the card number on the sightseeing bicycle is identical to a card number in the MCU rica number library and the RSSI value is greater than S (standard), the MCU controls the lighting scene program to run automatically, and the lighting fixture performs according to the control instruction transmitted from the interface module; and when the card number on the sightseeing bicycle is identical to a card number in the MCU rica number library, the MCU controls the lighting scene program to run automatically. Whenthe sightseeing bicycle leaves the attraction and the RSSI value transmitted by the card reader antenna is less than S (standard), the MCU stops the lighting show and the system returns to the initial state.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DASEN LIGHTING ELECTRONICS
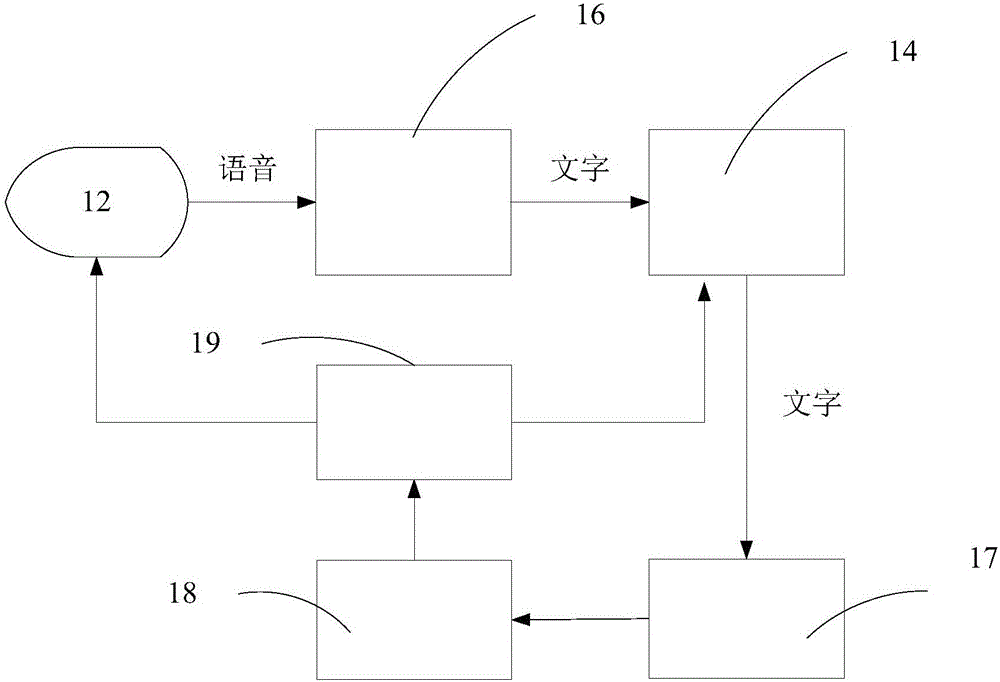
Voice memo device
InactiveCN106205618AWith identification functionWith reminder functionAcoustic time signalsSpeech recognitionBroadcastingSpeech sound
The invention provides a voice memo device which comprises a main body; a voice acquiring unit arranged at one end of the main body; a voice recognizing unit for converting the voice acquired by the voice acquiring unit into fields; a display unit arranged on the surface of the main body to display the fields so that a user can confirm whether the voice conversion is right or not according to the displayed fields; a key word extracting unit for extracting key words of time from the right fields; a storing unit for keeping the right fields in order; a processing unit for acquiring the right fields containing the key words of time that are kept in the storing unit and for sending the words to the display unit and a voice reminding unit ahead of the time; and the reminding unit for converting the right fields containing the key words of time into broadcasting voice.
Owner:王媛媛
Small-sized two-axis sun sensor based on linear array APS image sensor
InactiveCN104142136AHigh precisionReduce volumeAngle measurementNavigation by astronomical meansMicrocontrollerBright spot
The invention relates to a small-sized two-axis sun sensor based on a linear array APS image sensor. The small-sized two-axis sun sensor comprises a photoelectric element, an image acquisition and preprocessing unit and an image processing and error compensation unit, wherein the photoelectric element comprises a mask plate and the APS image sensor; the image acquisition and preprocessing unit comprises a video amplifier, an A / D converter and an FPGA; the image processing and error compensation unit comprises a singlechip microcomputer and an ROM; the mask plate has an'N'-shaped five-light-seam glass plate structure; two sun axis angles can be output by the linear array image sensor, and the linear array image sensor has a function of identifying sun bright spots; the FPGA is used for acquiring and preprocessing images; the singlechip microcomputer is used for carrying out image processing and error compensation; image data processing is completed when an image is acquired, so that the image storage space is greatly saved; the FPGA and the singlechip microcomputer work in parallel in a flow process, so that the product replacement rate reaches up to more than 30 Hz; furthermore, the sun sensor is high in accuracy, small in size, light in weight, high in replacement rate and convenient to connect, and has an integral structure.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
A lake-based eutrophication nutrition footprint index evaluation method
The invention discloses a lake division eutrophication nutrition footprint index evaluation method which mainly comprises the following steps: a phase space track line establishment step: utilizing lake division data to carry out filtering processing according to a time sequence, and establishing a filtering phase space track line of a consequence index and a reason index; A confinement nutrient identification step of identifying a confinement nutrient using the filtered phase-space trajectory; and a filtering track line segmentation step: carrying out time period division on the filtering phase space track line according to the inflection point of the track line, and establishing a multi-time period curve of an algae density and nutrient concentration response relation and a non-linear multi-time period nutrition index (TFI) relation. The method is mainly applied to lake eutrophication evaluation with algae control requirements and lakes with historical data of more than 10 years.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
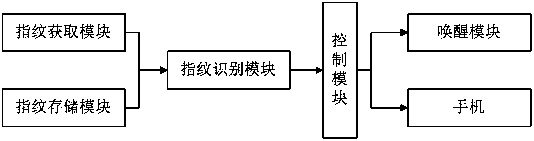
Wireless earphone and control method thereof
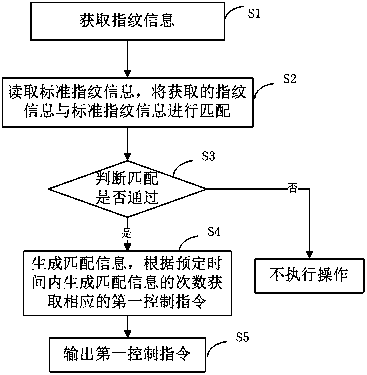
InactiveCN110830864AImprove operation success rateReduce stepsDigital data authenticationEarpiece/earphone mechanical/electrical switchesComputer hardwareIdentity recognition
The invention relates to a wireless earphone and a control method thereof, and the wireless earphone comprises a fingerprint obtaining module which is used for obtaining fingerprint information and transmitting the fingerprint information to a fingerprint recognition module; a fingerprint storage module which is used for storing standard fingerprint information; the fingerprint recognition modulewhich is used for reading the standard fingerprint information, matching the obtained fingerprint information with the standard fingerprint information and generating matching information when the matching is passed, wherein the fingerprint recognition module is used for sending the matching information to a control module; and the control module which is used for acquiring a corresponding first control instruction according to the frequency of the matching information received within the preset time and outputting the first control instruction to the controlled end. According to the wirelessearphone, the earphone or equipment communicating with the earphone is controlled in a fingerprint recognition mode, during fingerprint recognition, the earphone does not need to be touched, only fingers need to be placed near the earphone for recognition, the recognition accuracy is high, and the operation success rate is greatly increased. Moreover, the wireless earphone has an identity recognition function, and the operation of other people on the earphone can be avoided by recognizing the identity through the fingerprint.
Owner:GEER TECH CO LTD
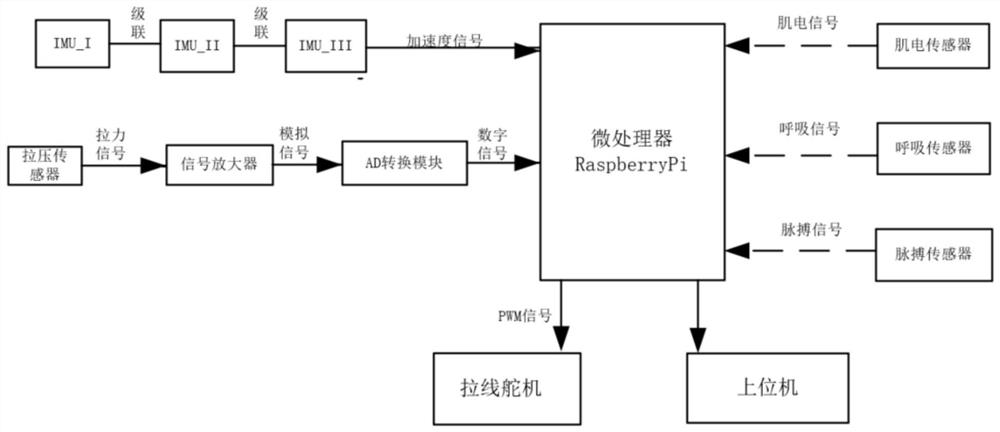
Flexible exoskeleton system and method capable of monitoring multivariate physiological energy consumption of wearer
ActiveCN113288084AAvoid taking its load directlyImprove securityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesPwm signalsExoskeleton
The present invention provides a flexible exoskeleton system and method capable of monitoring the multivariate physiological energy consumption of the wearer, the whole structure is fixed to the wearer through a soft shell, a wire spool is driven to rotate through a high-power steering engine, Bowden wires wound around the wire spool are driven to be wound and unwound, and power assisting and unloading of hip joints and ankle joints are achieved; the flexible exoskeleton control module collects motion information through an IMU, performs motion intention recognition, generates a PWM signal according to a recognition result, drives a stay wire steering engine to rotate, collects a Bowden cable tail end tension through a tension and compression sensor, feeds back a tension result to generate a PWM signal, and drives the stay wire steering engine to rotate; the multi-element physiological energy consumption analysis module collects physiological signals, carries out filtering, feature extraction and weighted fusion on the signals and carries out energy consumption calculation in the upper computer, an energy consumption calculation result is transmitted to the microprocessor through a TCP protocol, the energy consumption result is fed back to generate a PWM signal, and the stay wire steering engine is driven to rotate; and meanwhile, real-time display is carried out based on a labview energy consumption monitoring display interface.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Luminous dust-proof net with making function for construction site
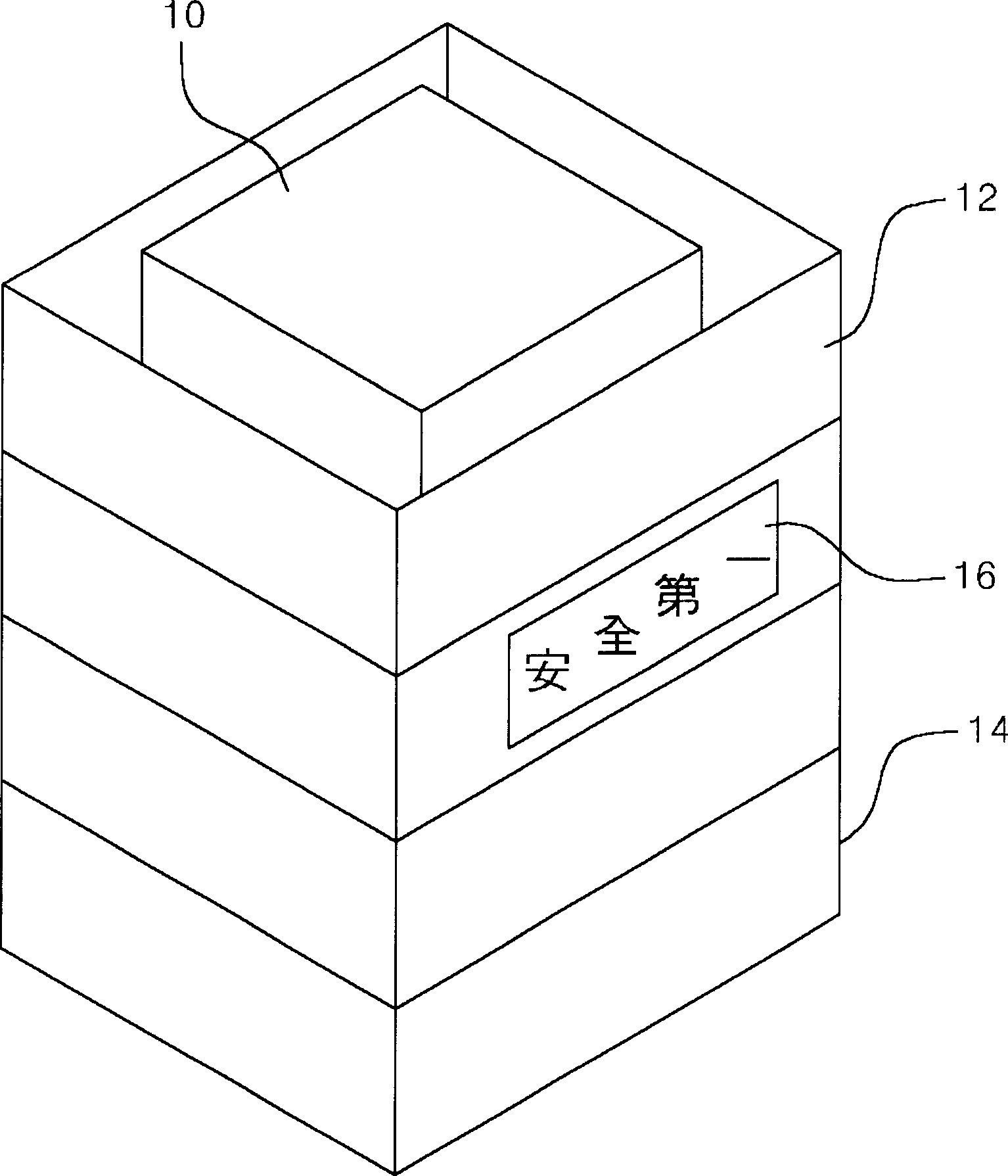
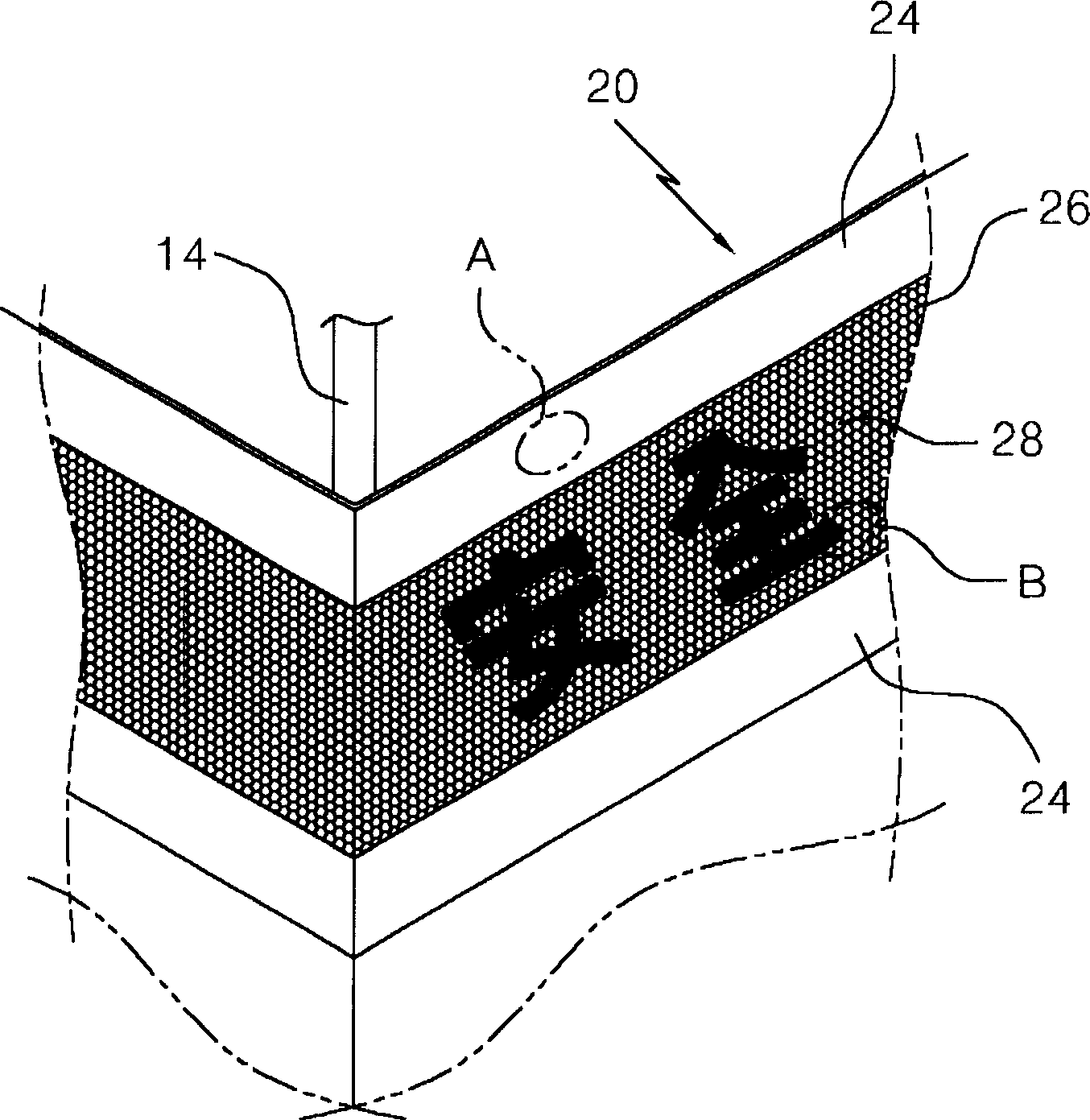
InactiveCN1743625AEasy to set upWith identification functionFlame-proof filament manufactureMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentYarnArchitectural engineering
A luminous dust control net for a construction site having the function of a banner is provided to prevent the scatter and drop of dust in a construction site, to improve the solidify of a dust control net and to function as a safety indication net at night and as a banner without attaching an additional signboard. The luminous dust control net for a construction site having the function of a banner contains: a primary area formed by weaving primary yarn of synthetic resins in the appointed pattern; a secondary area located in the primary area and formed by weaving secondary yarn together with the primary yarn to the outer side of the primary yarn; and a third area located in the secondary area and formed by weaving third yarn together with the primary yarn and the secondary yarn to the outer side of the secondary area.
Owner:DAKOS LUMINET
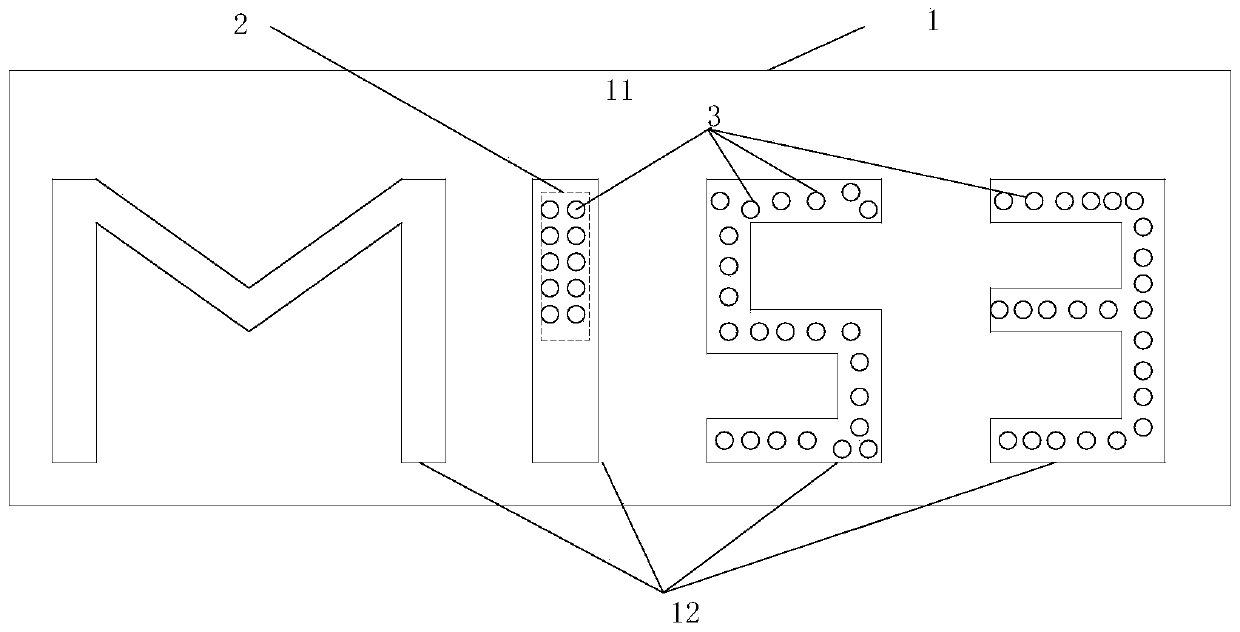
Marker
InactiveCN111539419AWith identification functionRealize anti-counterfeiting functionCharacter recognitionGraphicsAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention discloses a marker, which comprises a marker carrier and a graph arranged on the marker carrier, and the graph can be used for identity recognition; the graph can comprise one or more three-dimensional structure areas, and each three-dimensional structure area can comprise a plurality of concave-convex bodies arranged in a random depth form, wherein the anti-counterfeiting information of the marker at least comprises attributes of the concave-convex body; and attributes of the concavo-convex bodies can include depth information. According to the scheme of the embodiment, the marker with the identity recognition function can achieve the anti-counterfeiting function.
Owner:李峰
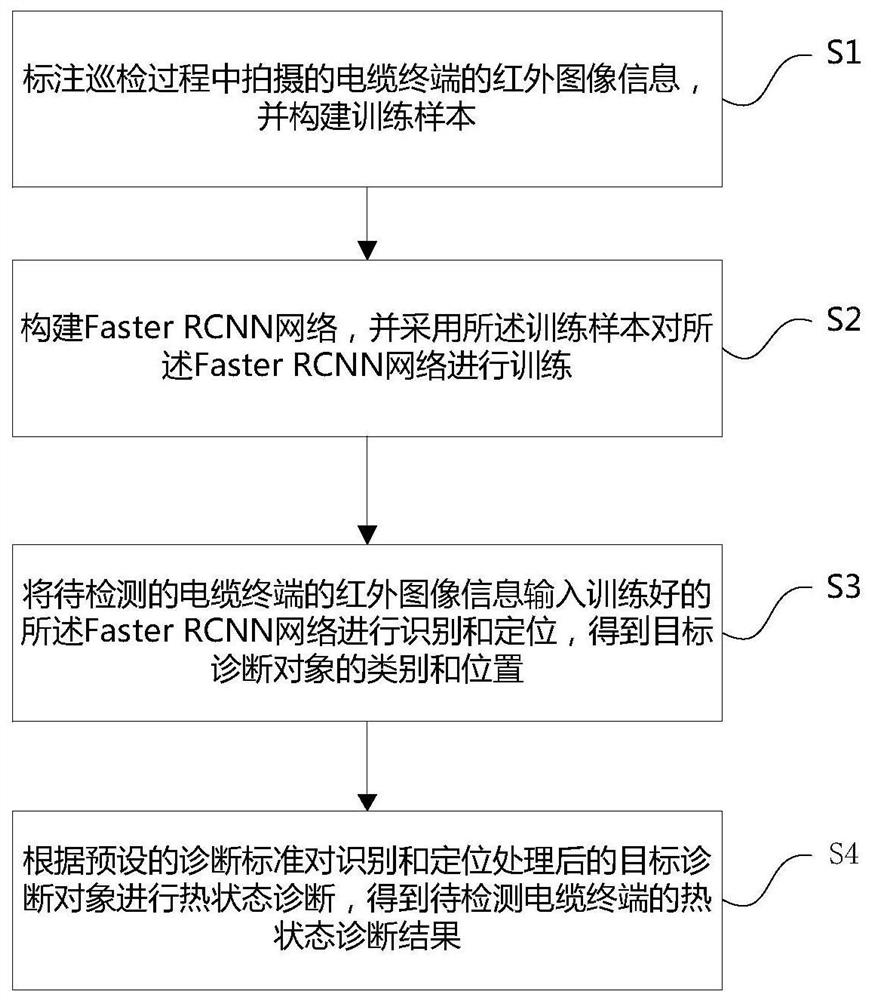
Cable terminal thermal state intelligent diagnosis method and system
PendingCN112465797AReduce dependenceImprove diagnostic efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnosis standardsArtificial intelligence
The invention relates to a cable terminal thermal state intelligent diagnosis method and system, and the method comprises the steps: marking the infrared image information, photographed in an inspection process, of a cable terminal, and constructing a training sample; constructing a Faster RCNN network, and training the Faster RCNN network by adopting the training sample; inputting infrared imageinformation of a to-be-detected cable terminal into the trained Faster RCNN network for recognition and positioning, and obtaining the type and position of a target diagnosis object; and performing thermal state diagnosis on the identified and positioned target diagnosis object according to a preset diagnosis standard. By constructing the Faster RCNN network and utilizing the trained Faster RCNN network to automatically identify and position the infrared image information of the to-be-detected cable terminal, thermal diagnosis is completed, the part of manual operation in current infrared diagnosis can be effectively replaced, the dependence on manual processing and analysis is reduced, the diagnosis efficiency is greatly improved, and the diagnosis accuracy is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD WUHAN POWER SUPPLY CO +1
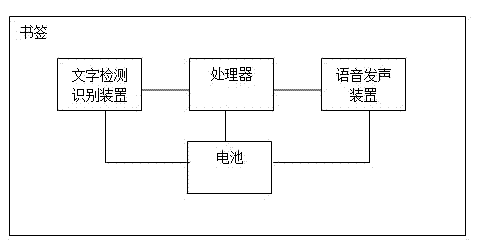
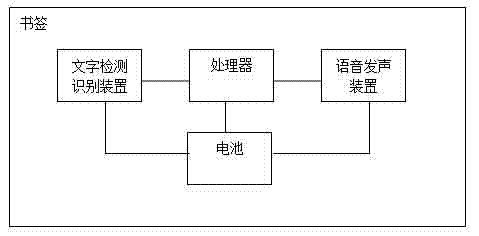
Book mark
InactiveCN102376174AWith detection functioWith identification functionBook markersElectrical appliancesVIT signalsDigital signal processing
The invention discloses a book mark. A character detection and identification device, a processor, a voice sound producing device and a battery are arranged in a book mark body, wherein the character detection and identification device is connected with the processor, a detected character signal is transmitted to the processor, the processor is connected with the voice sound producing device, the processed character signal produces sound through the voice sound producing device and the battery supplies power to all devices. The battery is a button battery. The processor is a singlechip or DSP (Digital Signal Processing) chip. The book mark disclosed by the invention has a character detection and identification function, is placed on a character needing being identified during the use, can produce sound and lets children for identifying words or reading books.
Owner:WUJIANG CHENGDA ELECTRONICS TECH
Wireless remote control coreless invisible lock
InactiveCN101358497ASignificant progressProminentlyElectric permutation locksFire controlRemote control
The invention discloses a wireless remote-control hidden lock which belongs to the field of lock and is structured by including a lock body, a lock holder, a remote controller, a telephone control system and a power part. The lock body is closely fixed on the bottom plate of the lock body and is externally provided with the shell of the lock body; a communicating mode of FSK or ASK or Bluetooth technology of single-directional or bi-directional RF is adopted by the remote-controller. The invention transmits a signal to the lock body by the remote controller; the lock body after receiving the signal returns the signal to the remote controller to communicate information that whether a lock bolt is opened or not until the lock bolt is opened; while when lock bolt is failed to be opened, the remote controller can automatically switch to a spare system to move the carriage of the lock body or the carriage of the lock holder to drive the lock bolt to open the lock; if the lock can not be opened still, manual operation can be selected to open the lock until the lock is opened. The wireless remote-control hidden lock is provided with a plurality of sets of independent unlocking modes, can adopt remote unlocking, telephone unlocking, fire control unlocking, manual unlocking and has the advantages of high automatization degree, good anti-theft performance, humanized design and high practicability; besides, the wireless remote-control hidden lock is a necessary assistant for broad families as well as enterprises and institutions.
Owner:李庚信
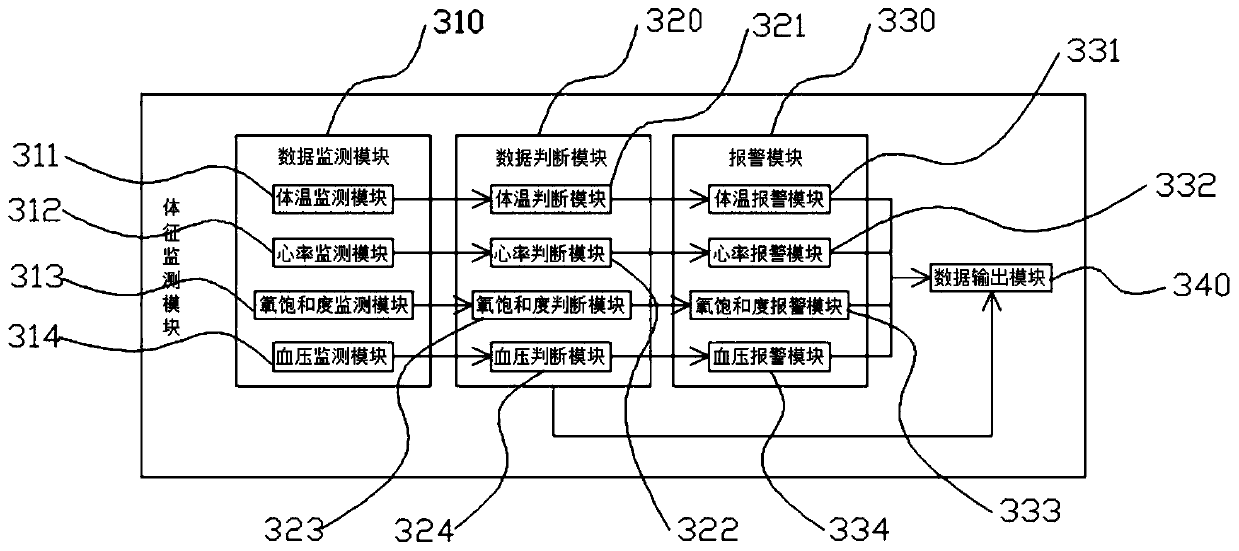
Smart wristband and patient management method based on smart wristband
PendingCN111180090AImprove management efficiencyEasy to useSurgeryAlarmsPatient managementIdentity recognition
The invention discloses a smart wristband, which comprises an identity recognition module, a health propaganda and education module, a physical sign monitoring module and a cost processing module. Theidentity recognition module comprises an information registration module, a two-dimensional code generation module and a two-dimensional code display module. The physical sign monitoring module comprises a data monitoring module, a data judgment module, an alarm module and a data output module; the data monitoring module comprises a body temperature monitoring module, a heart rate monitoring module, an oxygen saturation monitoring module and a blood pressure monitoring module; the data judgment module comprises a body temperature judgment module, a heart rate judgment module, an oxygen saturation judgment module and a blood pressure judgment module; and the alarm module comprises a body temperature alarm module, a heart rate alarm module, an oxygen saturation alarm module and a blood pressure alarm module. The invention further provides a patient management method based on the smart wristband. The smart wristband integrates multiple functions, so that the management efficiency of a patient is improved; and the system is integrated in the smart wristband, and convenient use is achieved.
Owner:ZIGONG NO 4 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Container cover body with identifying function and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103303564AWith identification functionRecord carriers used with machinesLocking devicesEngineeringProtection layer
The invention discloses a container cover body with an identifying function and a manufacturing method therefore. The container cover body comprises a label and a cover body, wherein the label is formed by jointing a protection layer and a wireless radio-frequency identifying label; in the wireless radio-frequency identifying label, a wireless radio-frequency identifying system is arranged on a substrate, is provided with a bonding layer and is jointed with a protection layer; the label is provided with a main body part in which a wireless radio-frequency identifying system and an antenna are arranged; the antenna is provided with extending antennae; the main body part is provided with a plurality of extending parts where the extending antennae are arranged; the cover body is provided with a top wall surface, a circumferential surface and a positioning circumference; a plurality of perforation holes are formed between the positioning circumference and the circumferential surface; abutting parts are formed between adjacent perforation holes; the label is pre-combined with a male die of a cover body forming die; during forming of the cover body, the label is combined with the inner side of the cover body; the extending part of the label extends to the positioning circumference; and when the cover body is opened by screwing, the abutting parts of the cover body are required to be torn, and a part of the extending antennae are broken to obtain the container which can be used for blocking or transmitting a wireless radio-frequency identifying signal, and has anti-counterfeiting and anti-theft functions and the like.
Owner:黄胜昌 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com