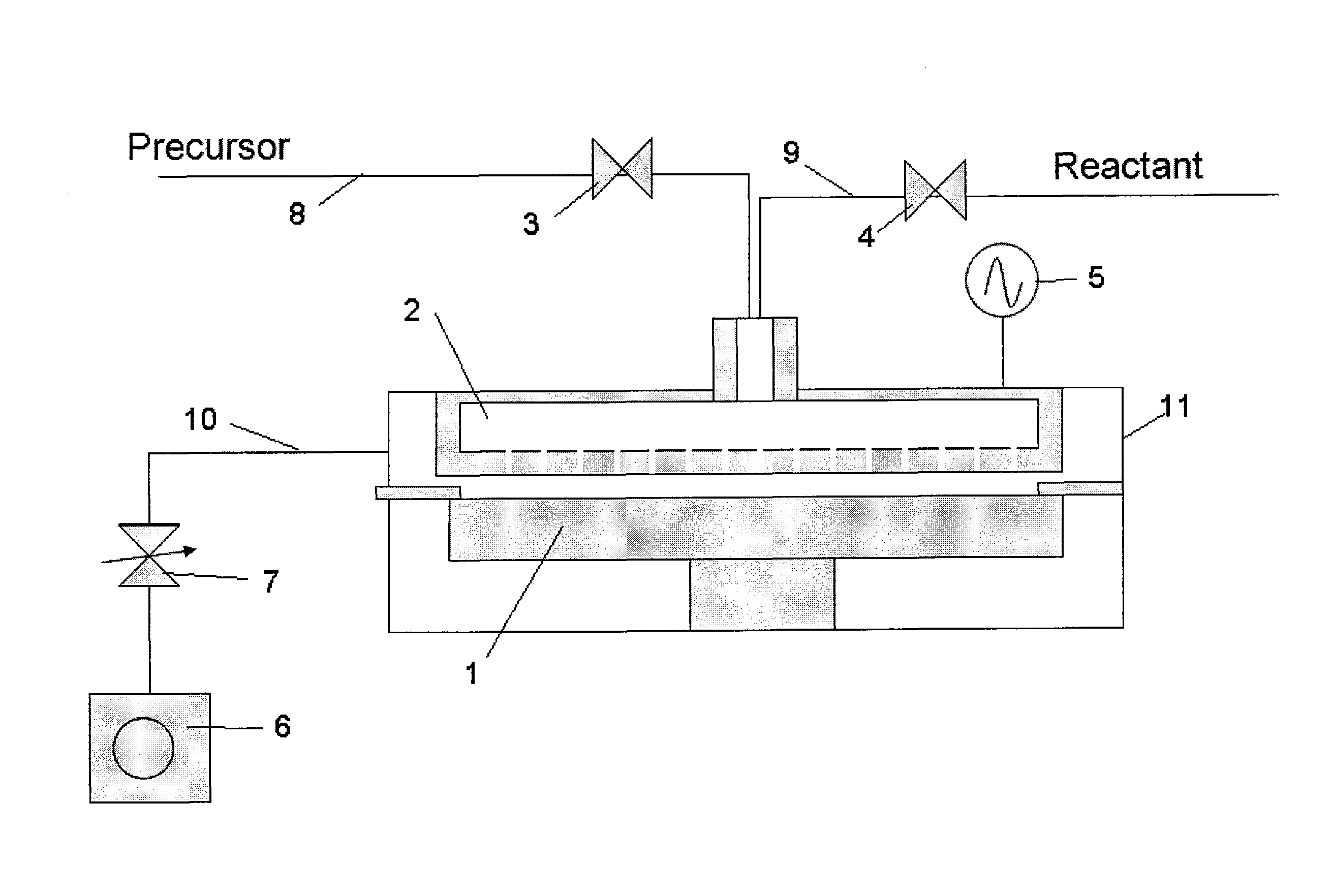
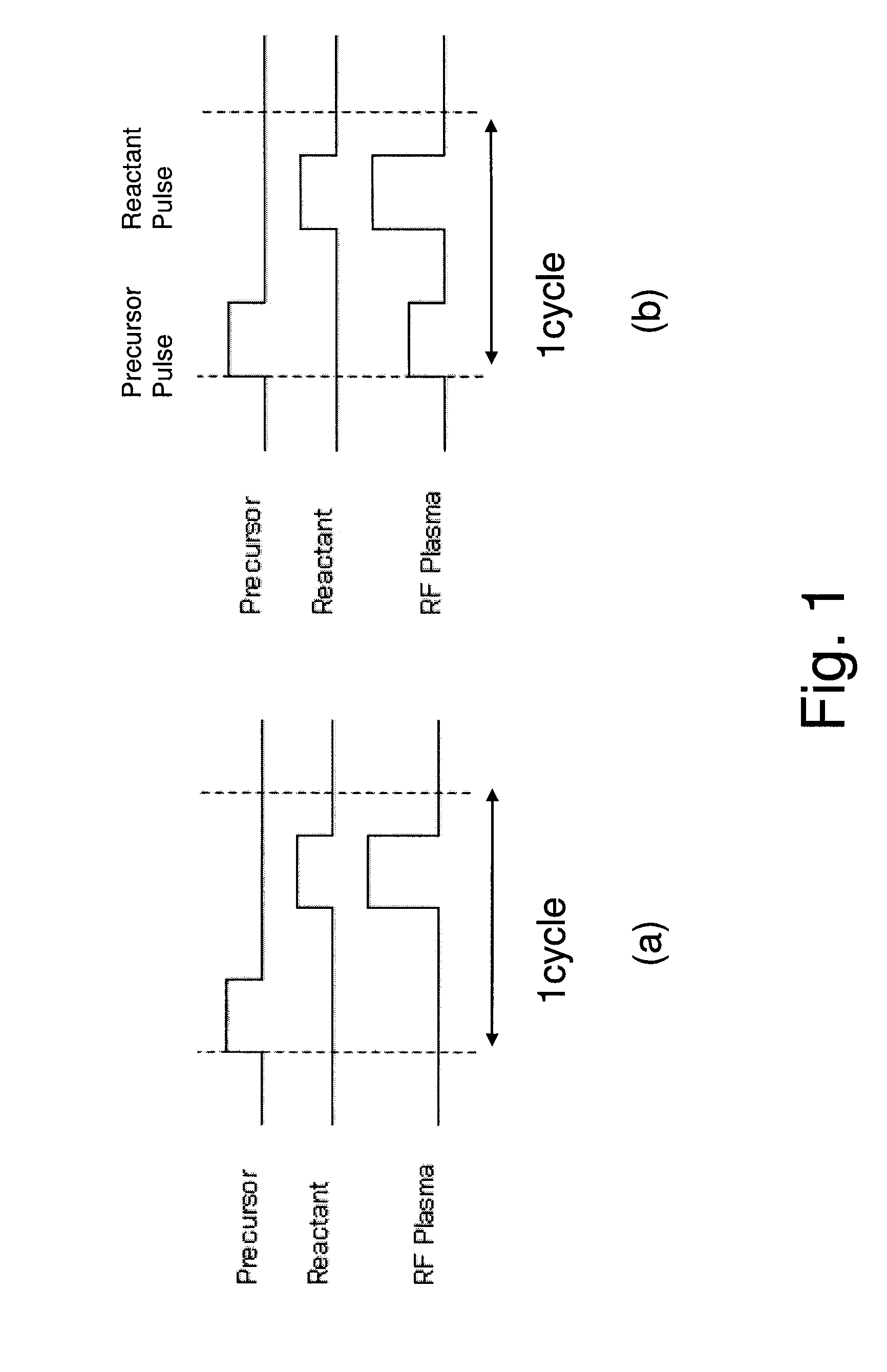
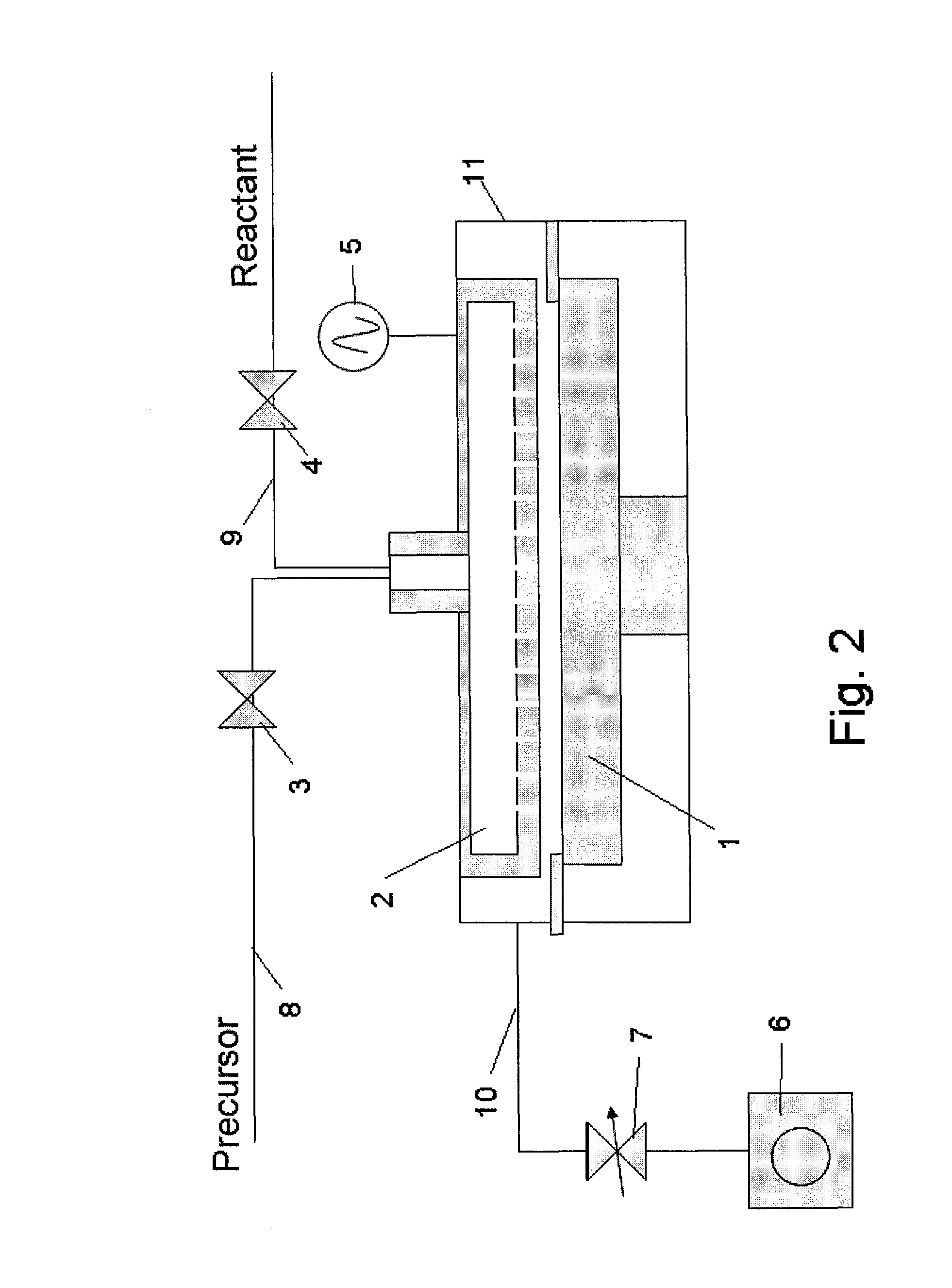
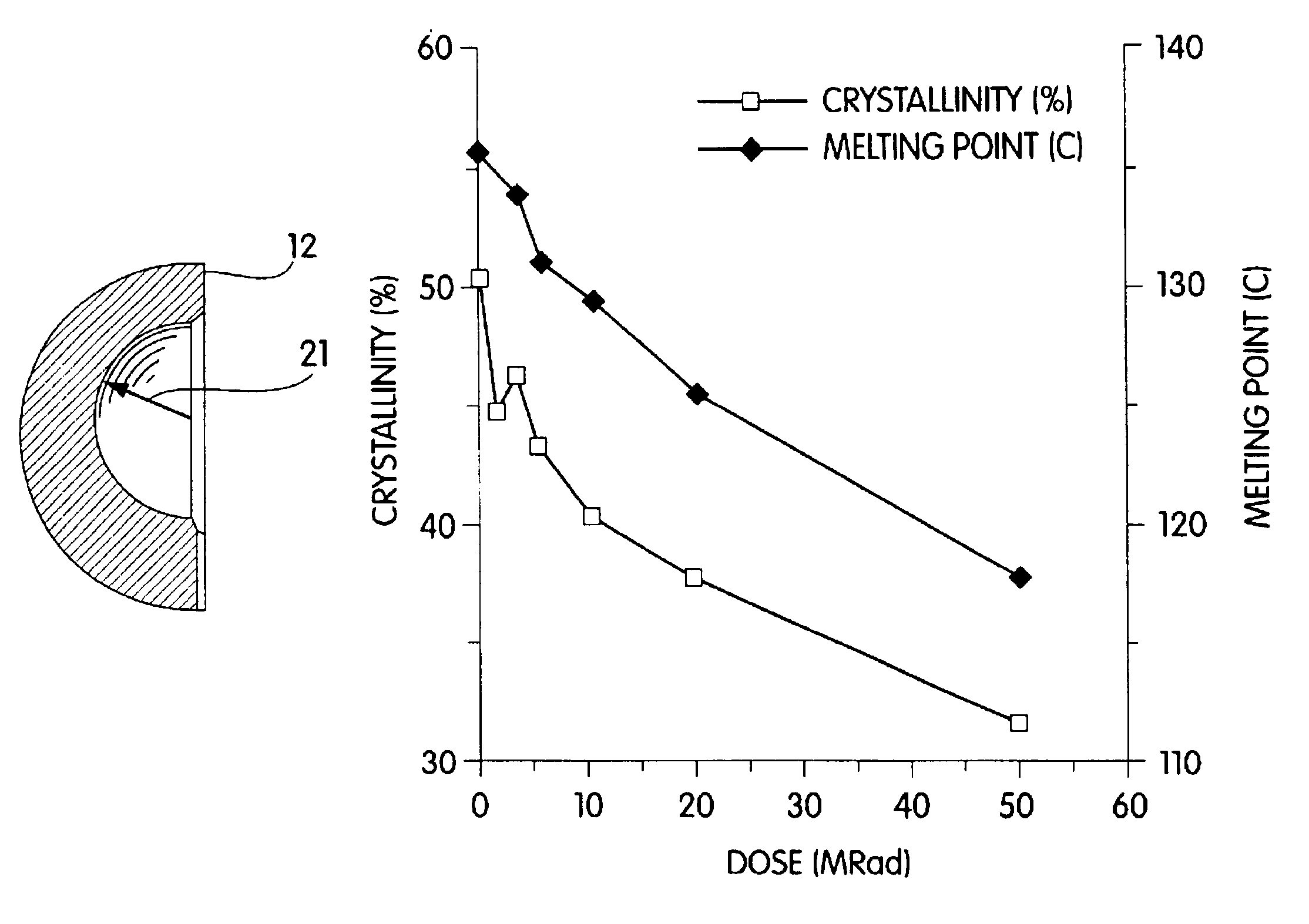
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
114results about How to "Reduce Particle Generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
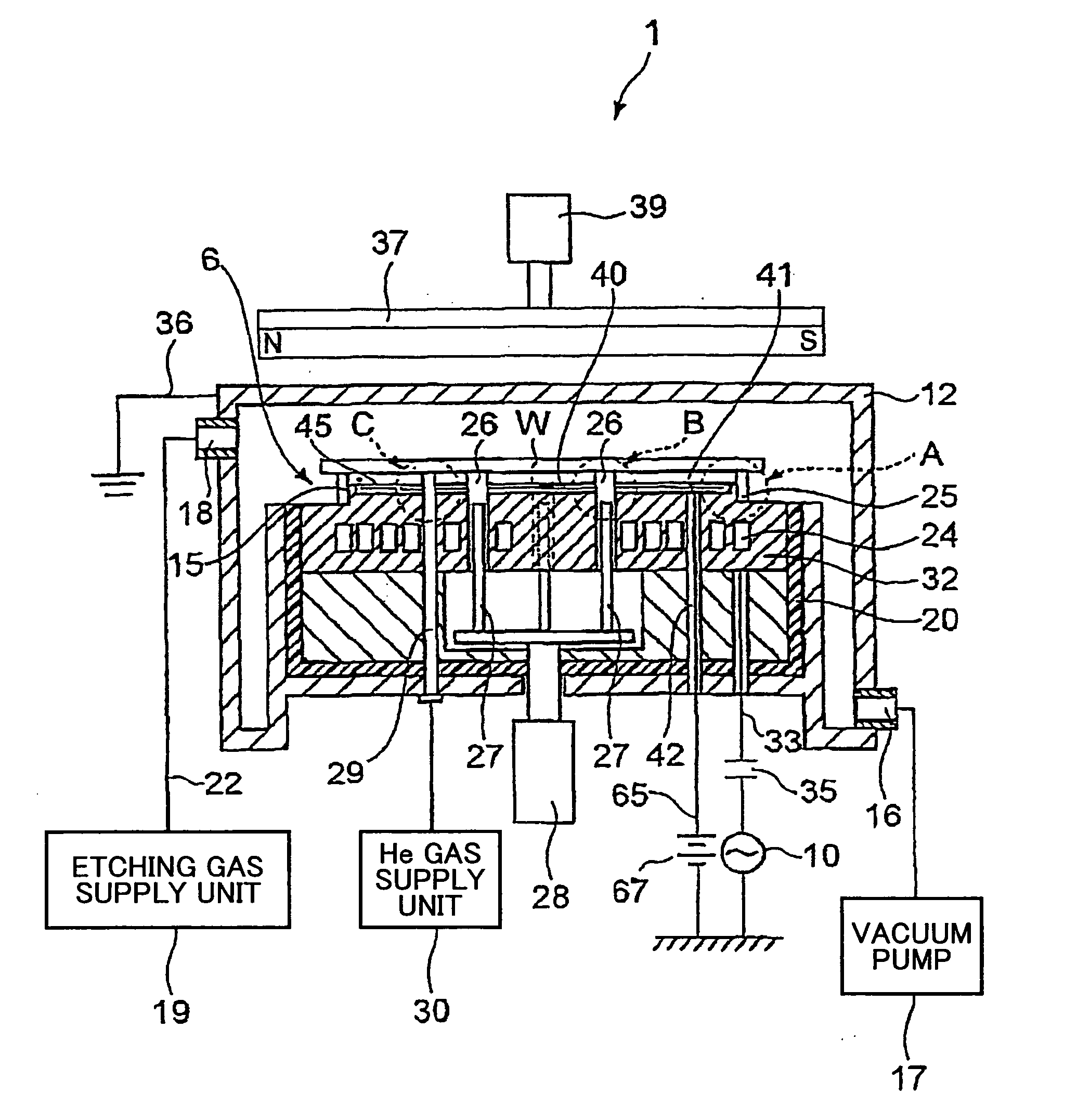
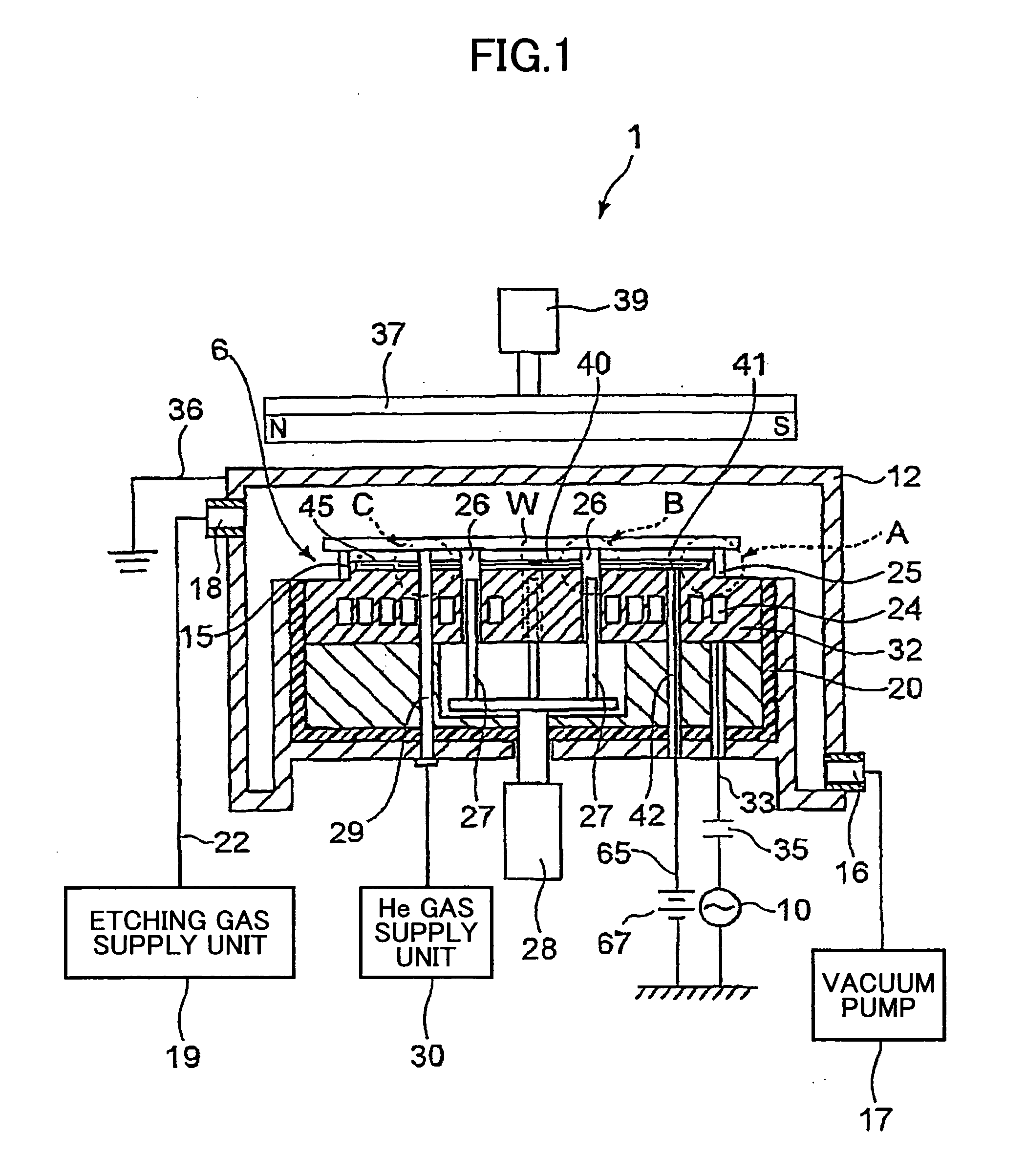
Method of Forming Insulation Film by Modified PEALD
ActiveUS20100124621A1Increase coverageImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringPhysical chemistry
Owner:ASM JAPAN
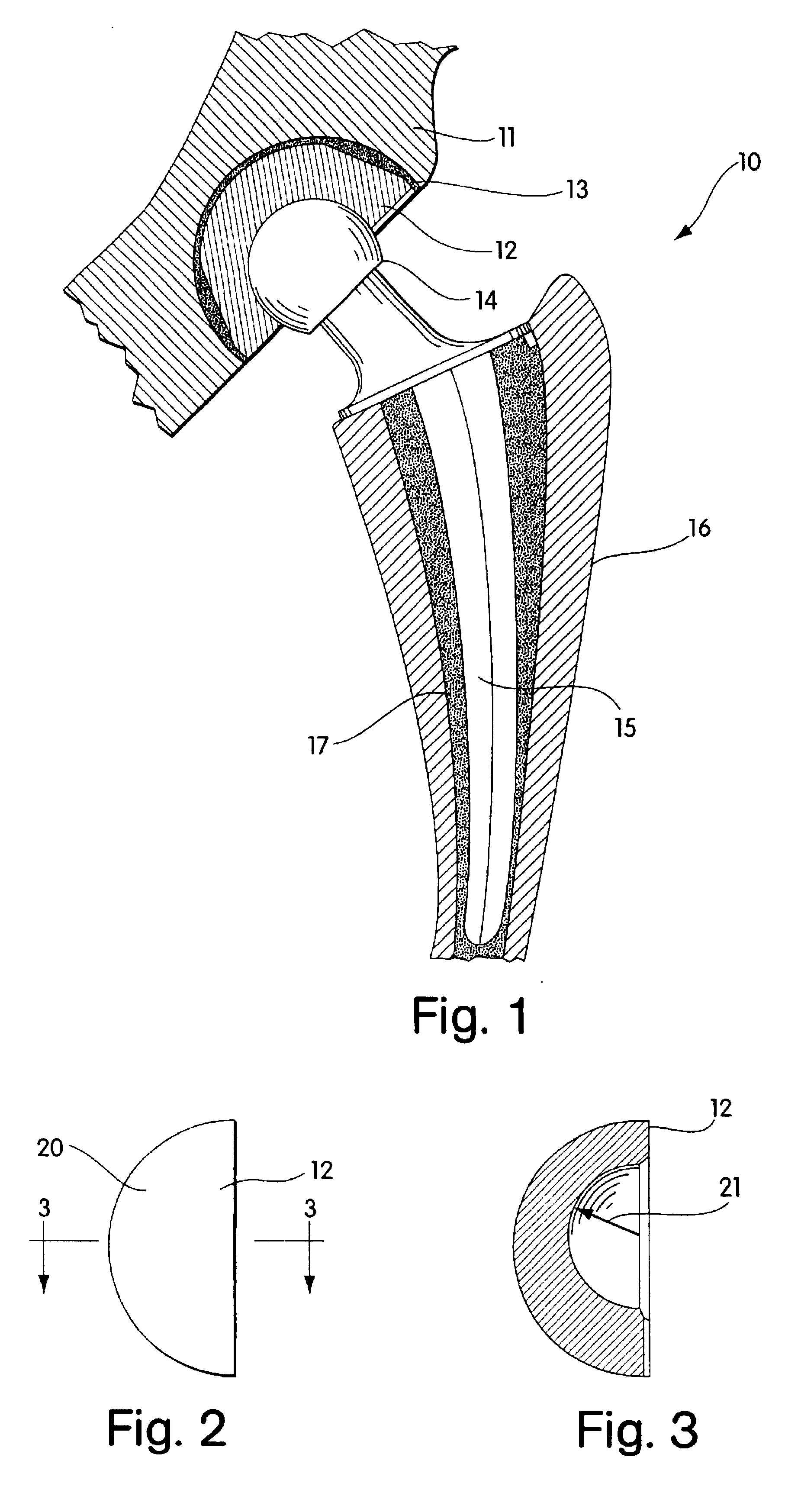
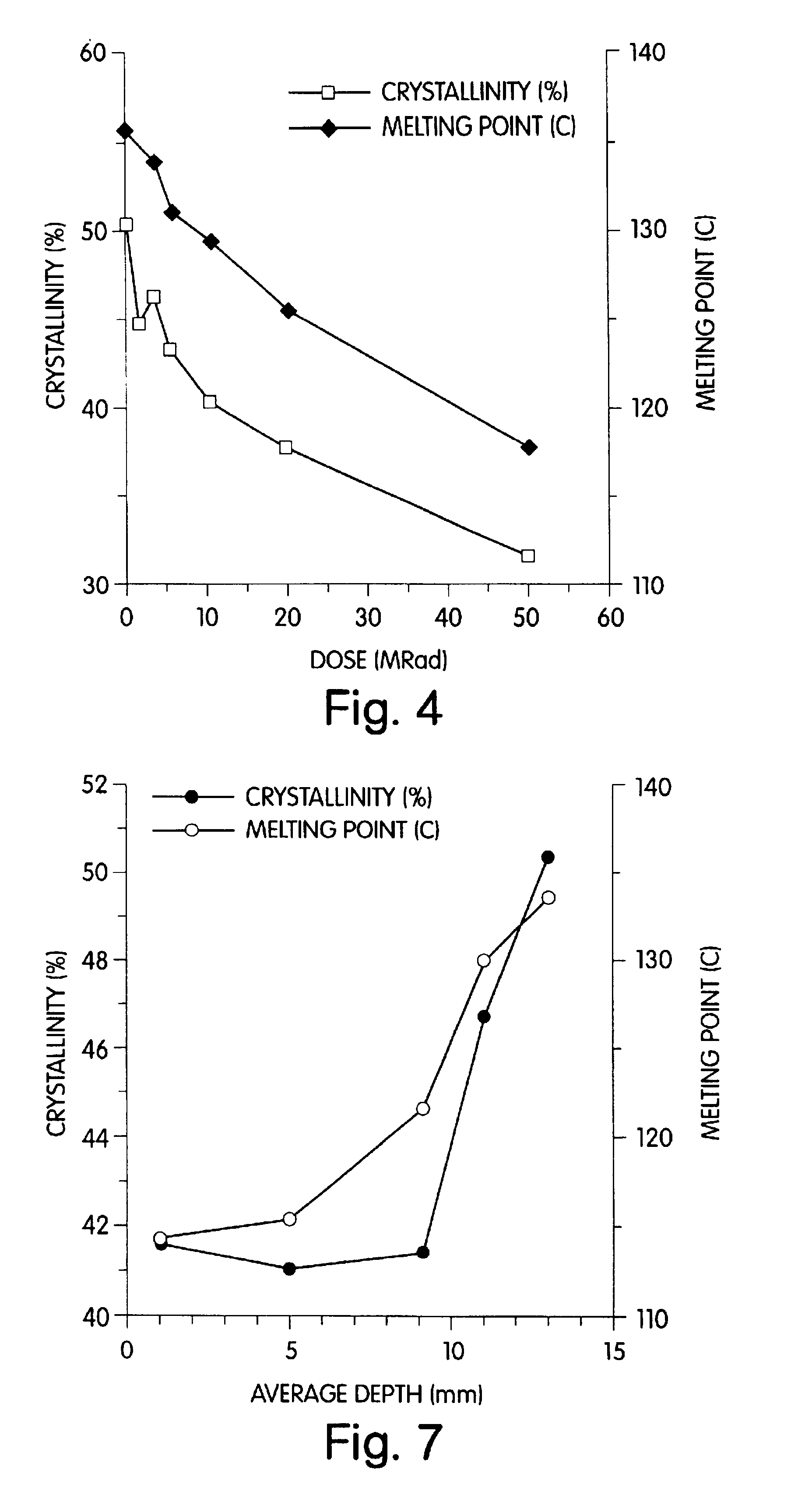
Radiation and melt treated ultra high molecular weight polyethylene prosthetic device and method
InactiveUS6641617B1Reduce productionReduce osteolysis and inflammatory reactionBone implantJoint implantsOxidation resistantPeriprosthetic
A medical prosthesis for use within the body which is formed of radiation treated ultra high molecular weight polyethylene having substantially no detectable free radicals, is described. Preferred prostheses exhibit reduced production of particles from the prosthesis during wear of the prosthesis, and are substantially oxidation resistant. Methods of manufacture of such devices and material used therein are also provided.
Owner:CENTPULSE ORTHOPEDICS +1
Silicon focus ring and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6815352B1Reduce Particle GenerationAvoid roughnessPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesCzochralski methodSingle crystal
There is disclosed a silicon focus ring consisting of silicon single crystal used as a silicon focus ring in a plasma apparatus, wherein concentration of interstitial oxygen contained in the silicon focus ring is not less than 5x10<17 >atoms / cm<3 >and not more than 1.5x10<18 >atoms / cm<3>, and a producing method for a silicon focus ring used for a plasma apparatus, wherein a single crystal silicon wherein concentration of interstitial oxygen contained in the silicon focus ring is not less than 5x10<17 >atoms / cm<3 >and not more than 1.5x10<18 >atoms / cm<3 >is grown by a Czochralski method, the single crystal silicon is processed in a circle, and a silicon focus ring is produced. There can be provided a silicon focus ring, which can prevent disadvantage due to impurities such as heavy metal.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
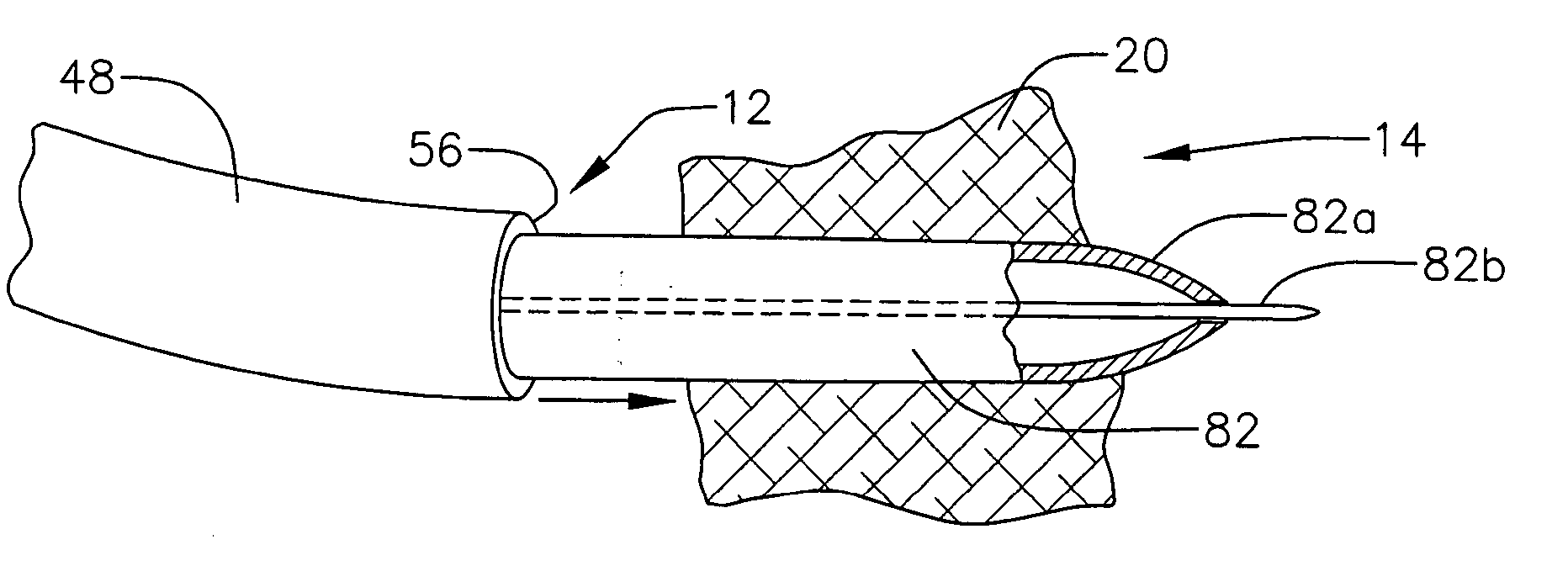
Transseptal needle
InactiveUS20050149097A1Minimise particle productionReduce Particle GenerationGuide needlesSurgeryCatheterBiomedical engineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
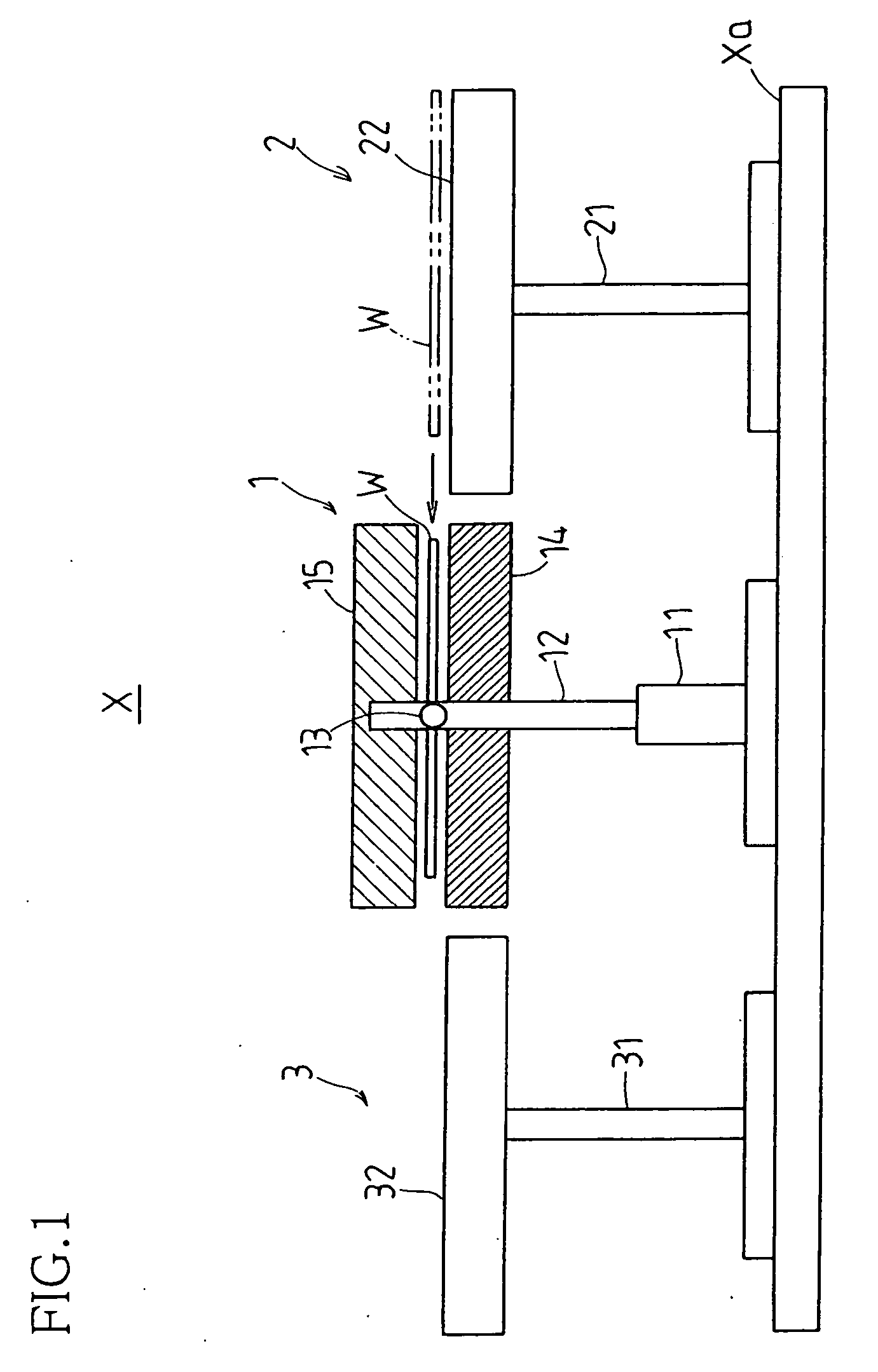
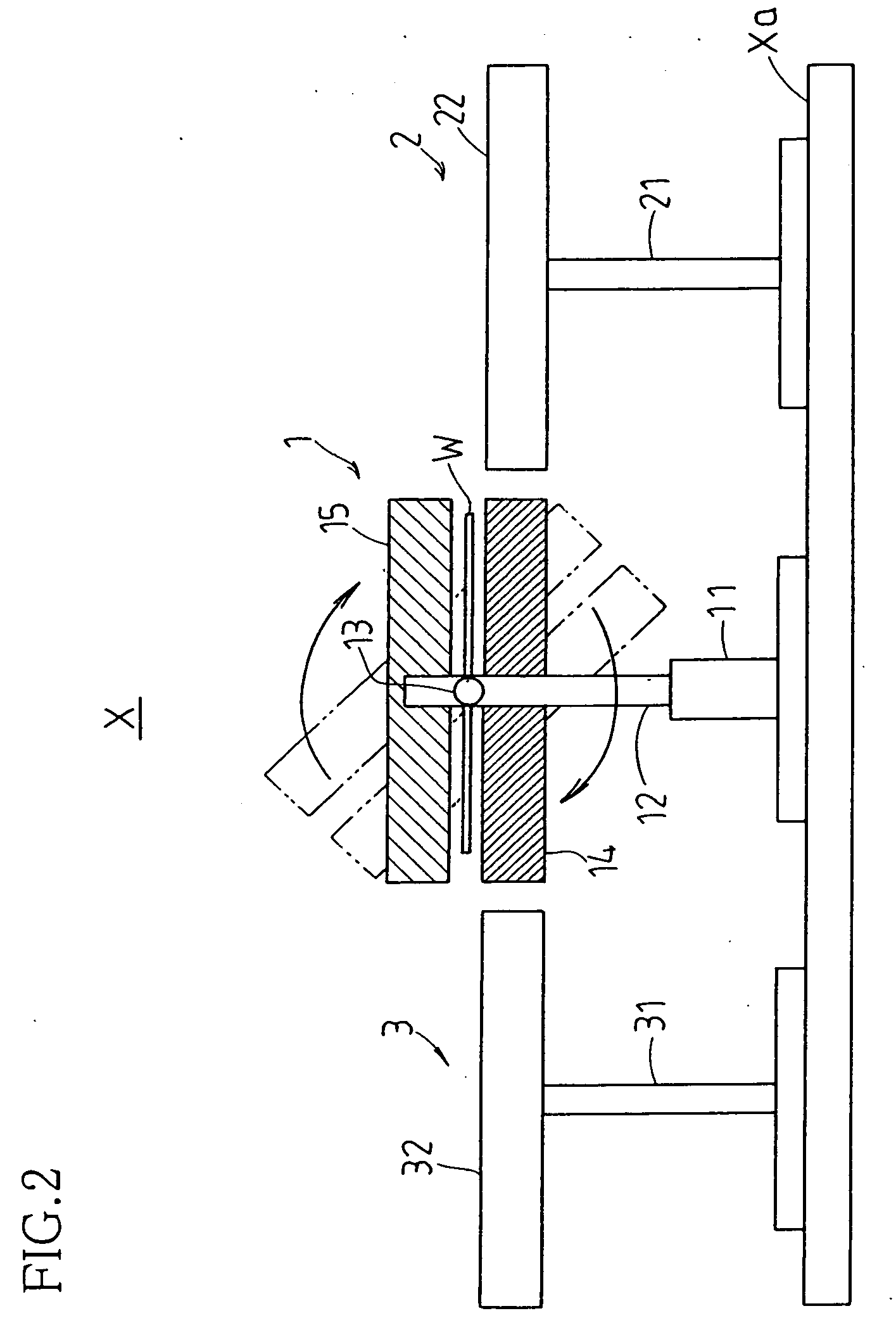
Workpiece transport apparatus
InactiveUS20040197184A1Reduce Particle GenerationEliminate mechanical partForging hammersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransport engineering
While periphery or peripheries of workpiece(s) W lifted in floating fashion by simultaneous suction and expulsion of gas(es) between pair(s) of first and second, or upper and lower, transport stages 14, 15 is / are retained by plurality of elevator pins 16, respective transport stage(s) is / are inverted vertically and workpiece(s) is / are transferred from upper first transport stage(s) to lower second transport stage(s) such that workpiece(s) W is / are lifted in floating fashion thereabove by simultaneous suction and expulsion of gas(es) in accompaniment to lowering of respective elevator pin(s) at said first transport stage(s).
Owner:SHARP KK
Process for producing high-purity ruthenium
InactiveUS6036741AReduce Particle GenerationVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesAlkaline earth metalHydrogen atmosphere
A process comprises forming ruthenium tetroxide by blowing ozone-containing gas into crude ruthenium powder while hypochlorous acid is being added to the powder, allowing a hydrochloric acid solution to absorb the ruthenium tetroxide, evaporating the solution to dryness, and roasting the RuOCl3 crystals thus obtained in a hydrogen atmosphere. Thus a high-purity ruthenium material for thin film deposition, typically sputtering targey, is obtained which contains less than 1 ppm each of alkali metal elements, less than 1 ppm each of alkaline earth metal elements, less than 1 ppm each of transition metal elements, less than 10 ppb each of radioactive elements, a total of less than 500 ppm of carbon and gaseous ingredient elements, the material having a purity of ruthenium of at least 99.995% excluding the gaseous ingredient elements.
Owner:JAPAN ENERGY CORP
Formation of TSV Backside Interconnects by Modifying Carrier Wafers
ActiveUS20100330798A1Reliable alignmentReduce Particle GenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor
An integrated circuit structure includes a semiconductor wafer, which includes a first notch extending from an edge of the semiconductor wafer into the semiconductor wafer. A carrier wafer is mounted onto the semiconductor wafer. The carrier wafer has a second notch overlapping at least a portion of the first notch. A side of the carrier wafer facing the semiconductor wafer forms a sharp angle with an edge of the carrier wafer. The carrier wafer has a resistivity lower than about 1×108 Ohm-cm.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Components for vacuum deposition apparatus and vacuum deposition apparatus therewith, and target apparatus
InactiveUS6855236B2Hardness be lowSuppress peelingCellsMolten spray coatingHardnessVacuum deposition
A component for a vacuum deposition apparatus comprises a component body and a spray deposit formed on a surface of a component body. A spray deposit has surface roughness in which a mean spacing S of tops of local peak of profile is in the range from 50 to 150 μm, and distances to a bottom of profile valley line Rv and to a top of profile peak line are in the ranges from 20 to 70 μm, respectively. Furthermore, a spray deposit has a low hardness coat selected from an Al base spray deposit of Hv 30 (Vickers hardness) or less, a Cu base spray deposit of Hv 100 or less, a Ni base spray deposit of Hv 200 or less, a Ti base spray deposit of Hv 300 or less, a Mo base spray deposit of Hv 300 or less and a W base spray deposit of Hv 500 or less. Such component for a vacuum deposition apparatus may suppress, with stability and effectiveness, peeling of deposition material adhering on a component during deposition. In addition, the number of apparatus cleaning and of exchange of components may be largely reduced. A target comprises a similar spray deposit. A vacuum deposition apparatus is one in which above component for a vacuum deposition apparatus is applied in a holder of a sample to be deposited, a deposition material source holder, a preventive component and so on.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Iron silicide sputtering target and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20060057014A1Reduce the amount requiredGeneration of particleNitrogen compoundsMetal silicidesSputteringIngot
Provided is an iron silicide sputtering target in which the oxygen as the gas component in the target is 1000 ppm or less, and a manufacturing method of such iron silicide sputtering target including the steps of melting / casting high purity iron and silicon under high vacuum to prepare an alloy ingot, subjecting the ingot to gas atomization with inert gas to prepare fine powder, and thereafter sintering the fine powder. With this iron suicide sputtering target, the amount of impurities will be reduced, the thickness of the βFeSi2 film during deposition can be made thick, the generation of particles will be reduced, a uniform and homogenous film composition can be yielded, and the sputtering characteristics will be favorable. The foregoing manufacturing method is able to stably produce this target.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Nonmagnetic Material Particle-Dispersed Ferromagnetic Material Sputtering Target
ActiveUS20110247930A1Stable electrical dischargeLow costCellsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetic fluxHigh density
A nonmagnetic material particle-dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target comprising a mixture of an alloy containing 5 mol % or more and 20 mol % or less of Cr, 5 mol % or more and 30 mol % or less of Pt, and Co as the remainder thereof, and nonmagnetic material particles, wherein the structure of the target includes a phase (A) in which the nonmagnetic material particles are uniformly micro-dispersed in the alloy, and a spherical alloy phase (B) dispersed in the phase (A) in which the ratio of its volume in the target is 4% or more and 40% or less. Obtained is a nonmagnetic material particle-dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target capable of improving the leakage magnetic flux to obtain a stable electrical discharge with a magnetron sputtering device, and which has high density and generates few particles during sputtering.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Film of yttria-alumina complex oxide, a method of producing the same, a sprayed film, a corrosion resistant member, and a member effective for reducing particle generation
InactiveUS7138192B2Improve abilitiesReduce Particle GenerationMolten spray coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrillCorrosion resistant
The invention provides a film of an yttria-alumina complex oxide having a high peel strength with respect to a substrate. A mixed powder of powdery materials of yttria and alumina is sprayed on a substrate to form a sprayed film made of an yttria-alumina complex oxide. Preferably, the powdery material of yttria has a 50 percent mean particle diameter of not smaller than 0.1 μm and not larger than 100 μm, and the powdery material of alumina has a 50 percent mean particle diameter of not smaller than 0.1 μm and not larger than 100 μm. Preferably, the yttria-alumina complex oxide contains at least a garnet phase, and may further contain a perovskite phase.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electrostatic chuck and producing method thereof
InactiveUS20070217117A1Suppresses excessive leak currentReduce Particle GenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic holding devicesCeramicElectrostatic adsorption
An electrostatic chuck using the Johnson-Rahbek force, comprising: a dielectric material layer including a ceramics layer and a resin layer formed on the ceramics layer; and an electrode for generating an electrostatic adsorption power.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Bond method and structure using selective application of spin on glass
ActiveUS20060281227A1High device yieldHigh throughput and yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSpacer device
A method for bonding substrate structures. The method includes providing a transparent substrate structure, the transparent substrate structure comprising a face region and an incident light region, providing a spacer structure, the spacer structure comprising a selected thickness of material, the spacer structure having a spacer face region and a spacer device region, and providing a device substrate structure, the device substrate having a device face region and a device backside region. The method further includes applying a first glue material to the spacer face region and bonding the spacer face region to the face region of the transparent substrate structure. The method also includes applying a second glue material to the spacer device region and bonding the spacer device region to the device face region.
Owner:MIRADIA INC
Substrate holding mechanism using electrostaic chuck and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060175772A1Avoid layeringExtended service lifeSleeve/socket jointsLamination ancillary operationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A substrate holding apparatus includes a stage configured to support a substrate to be processed, the stage including a surface, and a continuous convex portion surrounding a predetermined region of the surface which convex portion includes a periphery surface and an upper surface that is positioned higher than the surface of the stage; an electrostatic attraction sheet configured to attract a substrate with electrostatic force, the electrostatic attraction sheet being arranged on the surface of the stage within the region surrounded by the convex portion; a first protection member configured to protect the electrostatic attraction sheet, the first protection member being arranged on the electrostatic attraction sheet and including a side surface and a portion that is arranged to face opposite the upper surface of the convex portion; an adhesive layer that is arranged at least between the electrostatic attraction sheet and the first protection member and is configured to bond the electrostatic attraction sheet and the first protection member; and a second protection member that covers at least the outer peripheral surface of the convex portion and the side surface of the first protection member to conceal at least the adhesive layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of manufacturing high purity zirconium and hafnium
InactiveUS6861030B2Guaranteed uptimeGuaranteed performanceCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpuritySemiconductor
The present invention relates to high-purity zirconium or hafnium with minimal impurities, particularly where the content of alkali metal elements such as Na, K; radioactive elements such as U, Th; transitional metals or heavy metals or high melting point metal elements such as Fe, Ni, Co, Cr, Cu, Mo, Ta, V; and gas components such as C, O, etc. is extremely reduced, as well as to an inexpensive manufacturing method of such high-purity zirconium or hafnium, thereby reducing the impurities hindering the guarantee of the operational performance of semiconductors. The present invention further relates to an inexpensive and safe manufacturing method of high-purity zirconium or hafnium powder from hydrogenated high-purity zirconium or hafnium powder.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
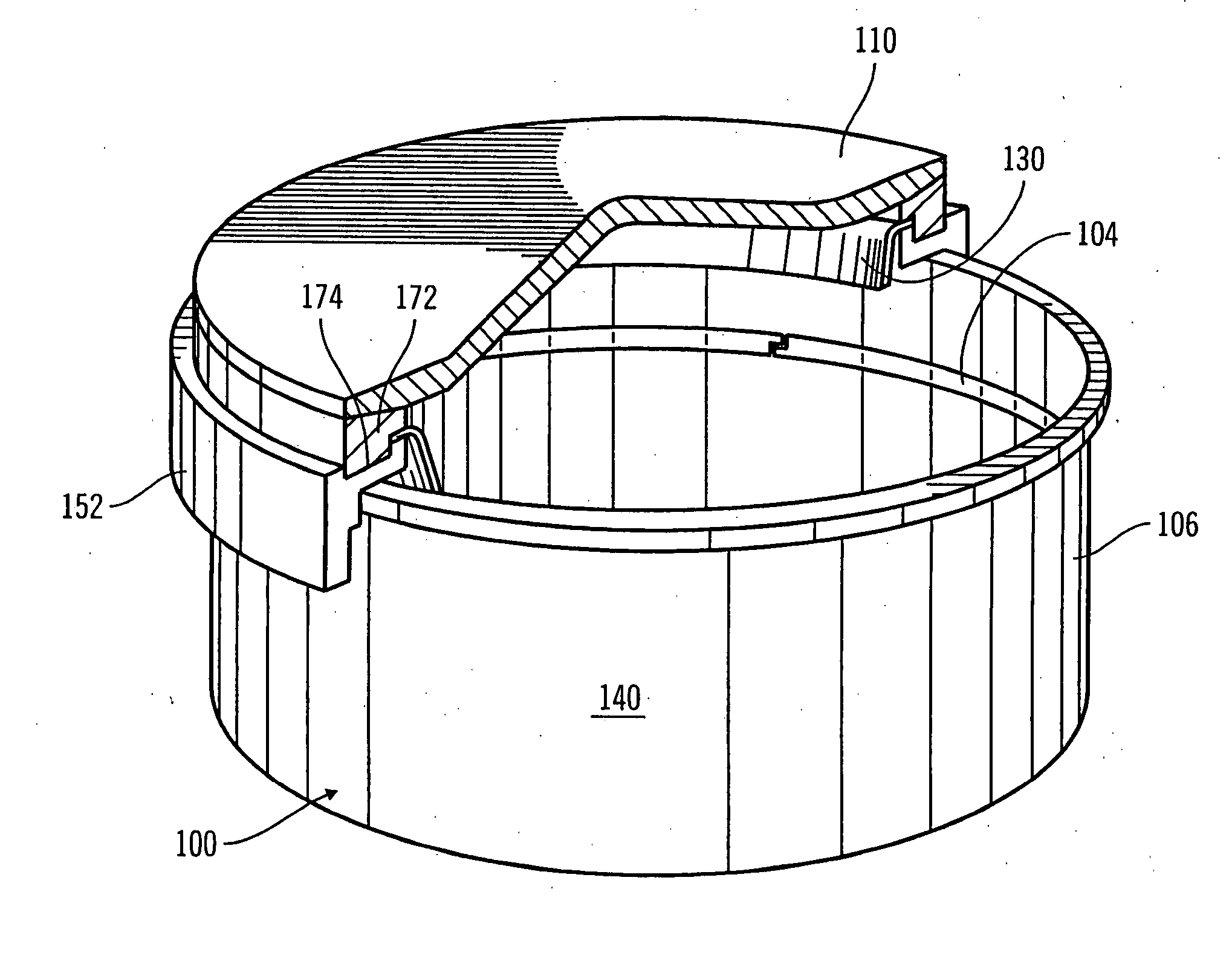
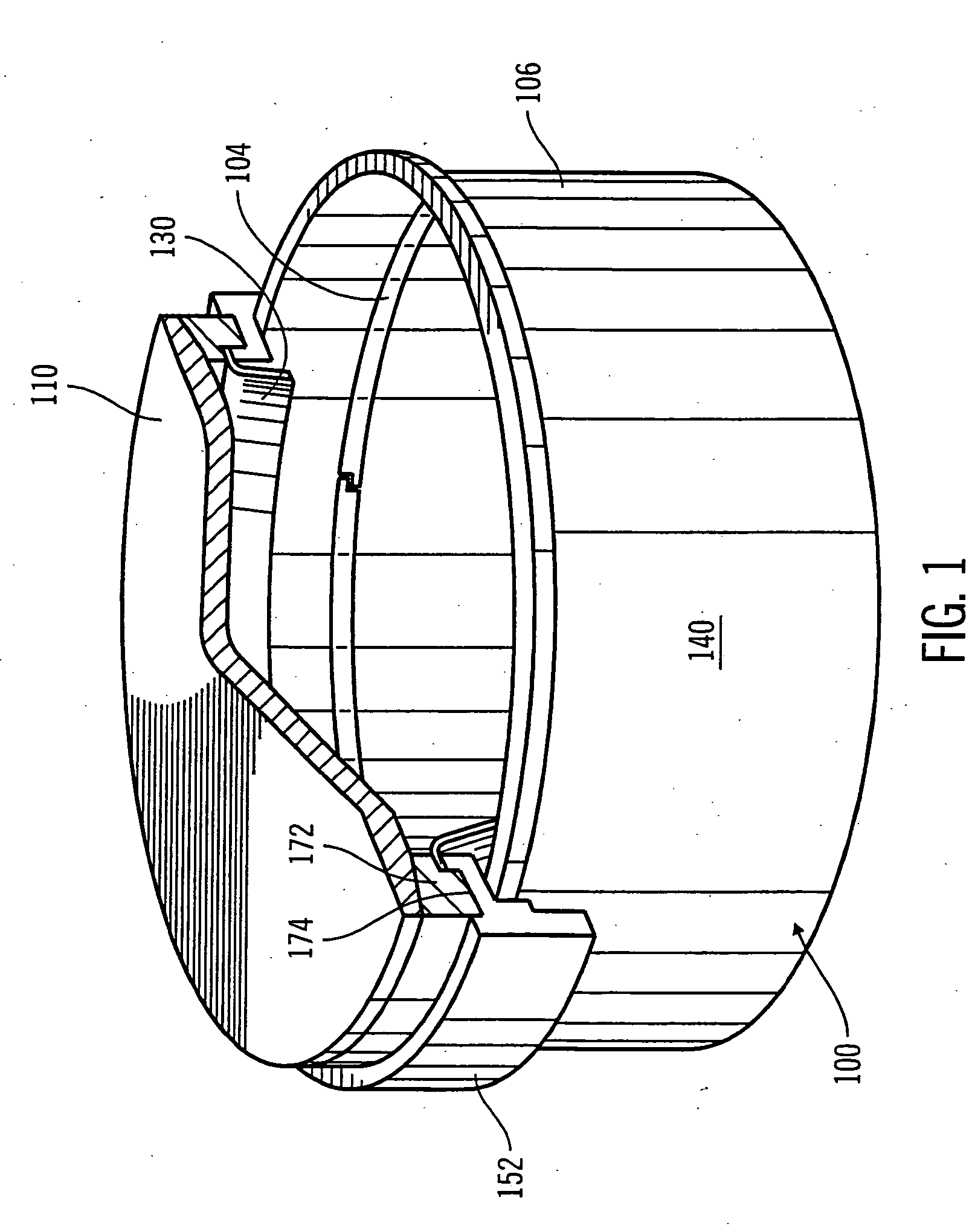
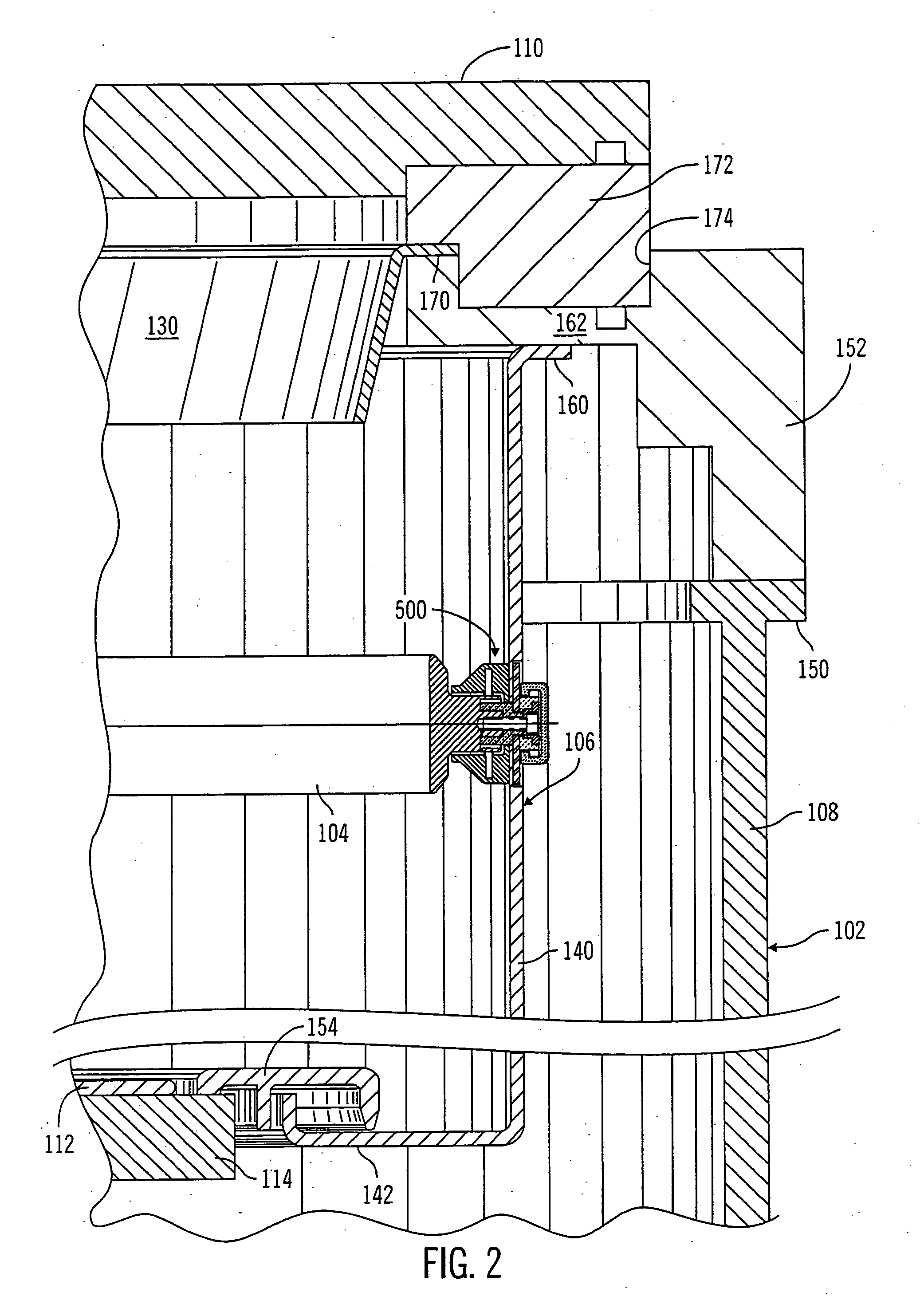
Wafer container
ActiveUS20100282638A1Large thicknessReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOther accessoriesEngineeringMagnet
A wafer container includes a container body, the internal of which is disposed with a plurality of slots for supporting a plurality of wafers and an opening is formed on one sidewall of which, and a door, which is joined with opening of the container body for protecting the plurality of wafers in the container body, the characteristic in that: a magnetic member is formed at the inner edge of the opening of the container body and a magnet is disposed at the inner surface of the door corresponding to the magnetic member, the magnet being disposed in a magnetic yoke with recessed cross section, with the design of which the magnet on the door attracts the magnetic member at the opening of the container body for the door and the container body to be lock-fastened to each other.
Owner:CHIU MING CHIEN +3
Self-retaining seal for undercut groove
Seal ring or other construction for providing a fluid seal intermediate a pair of opposing surfaces. The seal includes a body formed of a resilient material which is configured as having a series of projections which extend radially outwardly from lateral surfaces thereof such that the seal is self-retaining in a dovetail or other undercut groove.
Owner:PARKER HANNIFIN CORP
Treatment of iron oxide agglomerates before introduction into furnace
InactiveUS6214087B1Degrade furnaceReduce Particle GenerationBlast furnace componentsRotary drum furnacesViscous liquidAlcohol
A method for producing solid metal product is disclosed including the steps of providing carbon and metal bearing compounds in compacts, coating the compacts with treatment materials, encapsulating the compacts with carbonaceous containing materials to form a residual layer, and treating the residual layer before introduction of the compacts into a furnace. The compacts contain carbon containing metal bearing compounds, and are coated with mixtures of carbonaceous materials dispersed within a binder material such as a viscous liquid, molasses, alcohol, or fuel oil. The coated compacts are treated to form a hardened outer residual layer. The outer residual layer provides for a sacrificial outer coating on the compacts that reacts with any oxidizing gaseous components within the furnace, while the carbon containing metal bearing compounds within the compacts are heated and metallized inside the compounds. The outer residual layer provides for improved production of higher purity of metal and carbon nuggets with decreased furnace processing times. Therefore, an increase in purity of the metal product is produced at a lower cost, with minimization of the interaction of the molten metal and slag from nuggets with the furnace hearth surface.
Owner:MIDREX TECH INC
Method and apparatus for recovering load/unload zone real estate on data storage media in data storage devices to increase a data storage capacity thereof
InactiveUS6937419B2Increasing efficiency and storage capacityReduce disk damageTrack finding/aligningFluid-dynamic spacing of headsNO storageHard disc drive
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Iron silicide powder and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20060002838A1Easy to crushHigh densityNitrogen compoundsMetal silicidesIron powderHydrogen
Provided is iron suicide powder in which the content of oxygen as the gas component is 1500 ppm or less, and a method of manufacturing such iron silicide powder including the steps of reducing iron oxide with hydrogen to prepare iron powder, heating the iron powder and Si powder in a non-oxidizing atmosphere to prepare synthetic powder containing FeSi as its primary component, and adding and mixing Si powder once again thereto and heating this in a non-oxidizing atmosphere to prepare iron suicide powder containing FeSi2 as its primary component. The content of oxygen as the gas component contained in the iron silicide powder will decrease, and the iron silicide powder can be easily pulverized as a result thereof. Thus, the mixture of impurities when the pulverization is unsatisfactory will be reduced, the specific surface area of the iron silicide powder will increase, and the density can be enhanced upon sintering the iron silicide powder.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Sputtering target containing zinc sulfide as major component, optical recording medium on which phase change optical disk protective film containing zinc sulfide as major component is formed by using the target, and method for manufacturing the sputtering target
ActiveUS7279211B2Reduce the impact of heatIncrease speedPigmenting treatmentCellsTectorial membraneRefractive index
Provided is a sputtering target and an optical recording medium having formed thereon a phase change optical disc protective film having zinc sulfide as its principal component employing such a target, as well as the manufacturing method thereof, characterized in that the sputtering target has zinc sulfide as its principal component, and is capable of adjusting the refractive index of a film containing conductive oxide in the range of 2.0 to 2.6. This sputtering target, and an optical recording medium having formed thereon a phase change optical disc protective film having zinc sulfide as its principal component employing such a target, is capable of reducing particles (dust emission) and nodules that arise during sputtering, has minimal variation in quality and is capable of improving mass productiveness, and in which the crystal grain is fine and has a high density of 90% or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Wafer boat for reducing wafer warpage
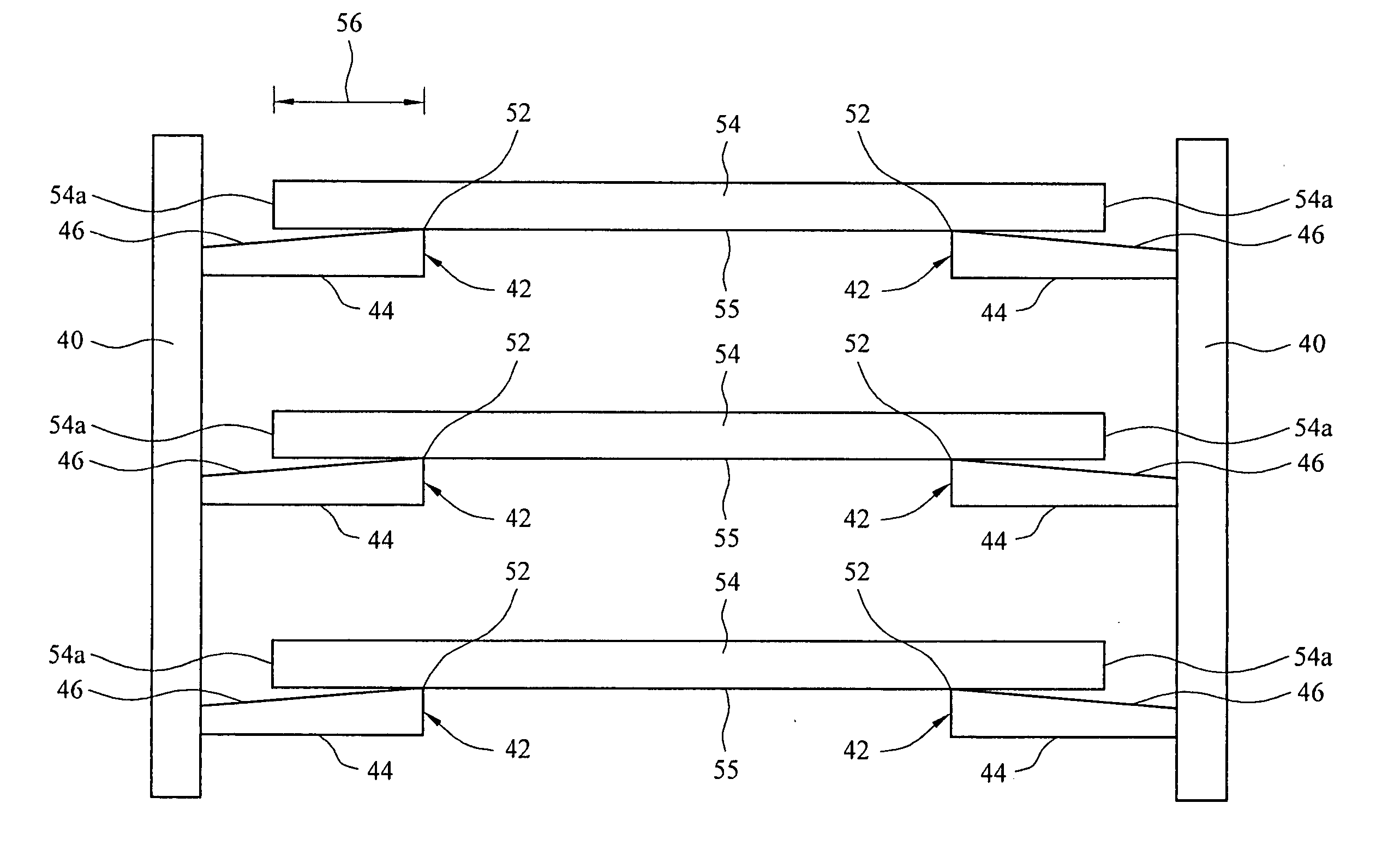
InactiveUS20060027171A1Minimize contact surfaceReduce Particle GenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAcute angleMechanical engineering
A wafer boat which is suitable for supporting wafers in a process furnace is disclosed. The wafer boat includes a base plate, multiple support rods carried by the base plate and multiple wafer support pins carried by each of the support rods. Each of the wafer support pins has an upper surface disposed at an acute angle with respect to a longitudinal axis of each of the support rods. This causes contact of the wafer support pins with the wafer at the wafer's center of gravity and minimizes the contact surface area between the wafer support pins and each wafer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
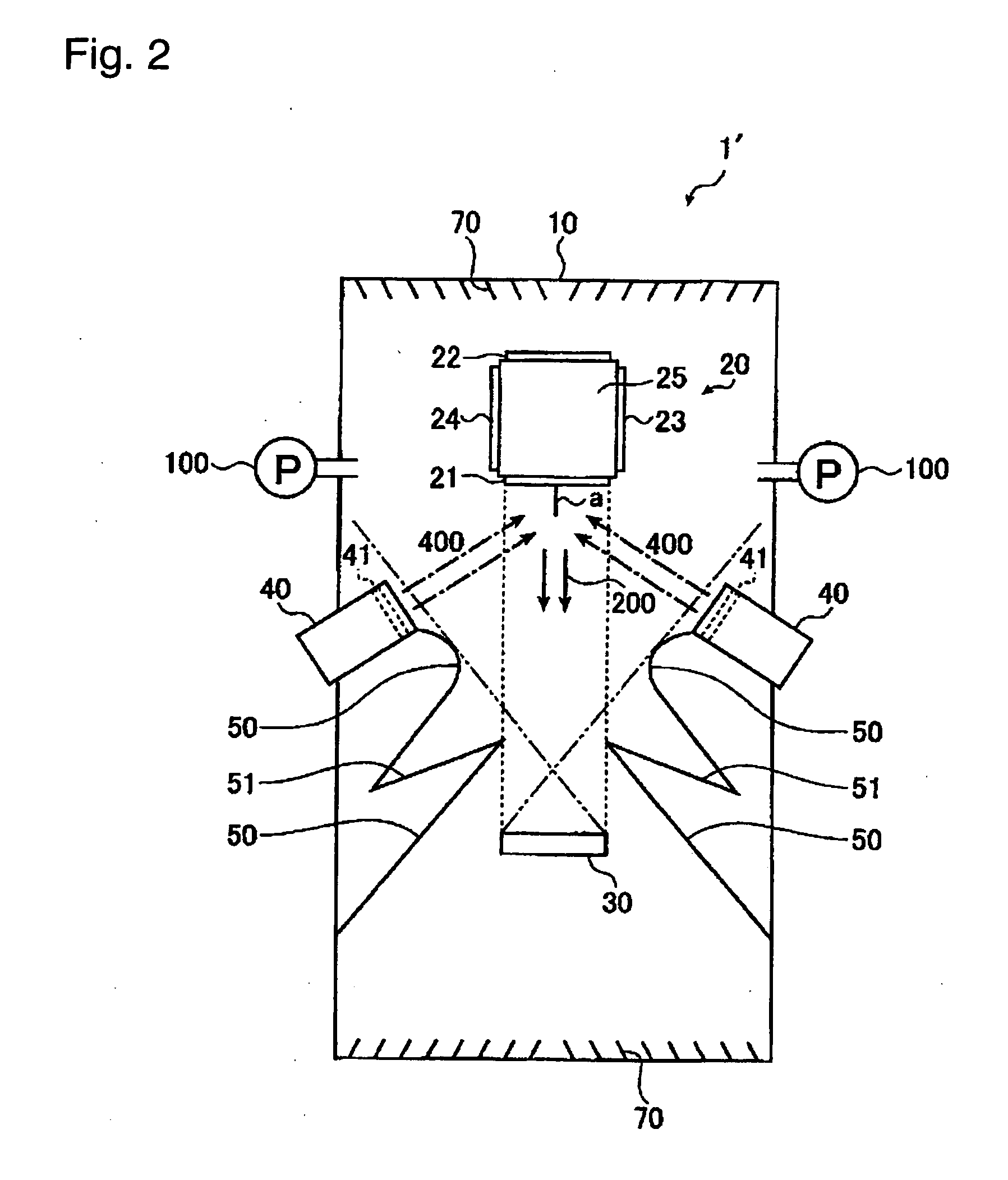
Ion beam sputtering apparatus and film deposition method for a multilayer for a reflective-type mask blank for EUV lithography
InactiveUS20070087578A1Reduce the likelihood of occurrenceReduce the possibilityNanoinformaticsVacuum evaporation coatingLithographic artistIon beam
A film deposition method for a multilayer for a EUV mask blank by which a defect caused by the mixing of a particle in the layer during film formation can be prevented and an ion beam sputtering apparatus suitable for the method are presented. A film deposition method for forming a multilayer for a reflective-type mask blank for EUV lithography on a film deposition substrate by using an ion beam sputtering method, the film deposition method being characterized in that a sputtering target and a film deposition substrate are disposed at opposed positions with a predetermined space, and ion beams are injected to the sputtering target from an ion source which is disposed at a position out of the region where particles move linearly from the film deposition substrate toward the sputtering target.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Coil and coil support for generating a plasma
InactiveUS20070062452A1Reduce Particle GenerationElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingParticulatesEngineering
A coil has an integral fastener portion to facilitate fastening the coil to a shield wall to reduce generation of particulates.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Film of yttria-alumina complex oxide, a method of producing the same, a sprayed film, a corrosion resistant member, and a member effective for reducing particle generation
ActiveUS20040067392A1Reduce fallsReduce dispersionMolten spray coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingParticle generationCorrosion resistant
The invention provides a film of an yttria-alumina complex oxide having a high peel strength with respect to a substrate. A mixed powder of powdery materials of yttria and alumina is sprayed on a substrate to form a sprayed film made of an yttria-alumina complex oxide. Preferably, the powdery material of yttria has a 50 percent mean particle diameter of not smaller than 0.1 .mu.m and not larger than 100 .mu.m, and the powdery material of alumina has a 50 percent mean particle diameter of not smaller than 0.1 .mu.m and not larger than 100 .mu.m. Preferably, the yttria-alumina complex oxide contains at least a garnet phase, and may further contain a perovskite phase.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Approach for controlling operation of oil injectors
ActiveUS20140100765A1Provides a cooling effectReduce Particle GenerationAnalogue computers for vehiclesLiquid coolingPistonPetroleum engineering
Various embodiments of systems and methods related to controlling oil injection for piston cooling in an engine are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes during an engine cold start event, enabling oil injection onto a piston of an engine, disabling oil injection after the engine cold start event, and re-enabling oil injection after the engine cold start event based on a first operating parameter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for providing wafer centering on a track lithography tool
InactiveUS20090110532A1Improved wafer handling reliabilityReduce exposureMechanical apparatusJointsEngineeringSupport surface
An apparatus for centering a substrate in a track lithography tool includes a processing chamber having an opening large enough to admit the substrate. The processing chamber includes a substrate support member. The substrate is characterized by a diameter and comprises a mounting surface, a process surface, and an edge. The apparatus also includes a clamped robot blade including a substrate support surface adapted to support the mounting surface of the substrate, two edge contact regions, and a base contact region. The clamped robot blade also includes a clamping system adapted to move at least one of the two edge contact regions or the base contact region from an unclamped position to a clamped position, thereby making contact between the edge of the substrate and the two edge contact regions and the base contact region in the clamped position. The apparatus further includes a robot arm coupled to the clamped robot blade.
Owner:SOKUDO CO LTD
Apparatus and method for fabricating semiconductor devices and substrates
InactiveUS20080214012A1Reduce Particle GenerationImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSubstation equipmentSusceptorDevice material
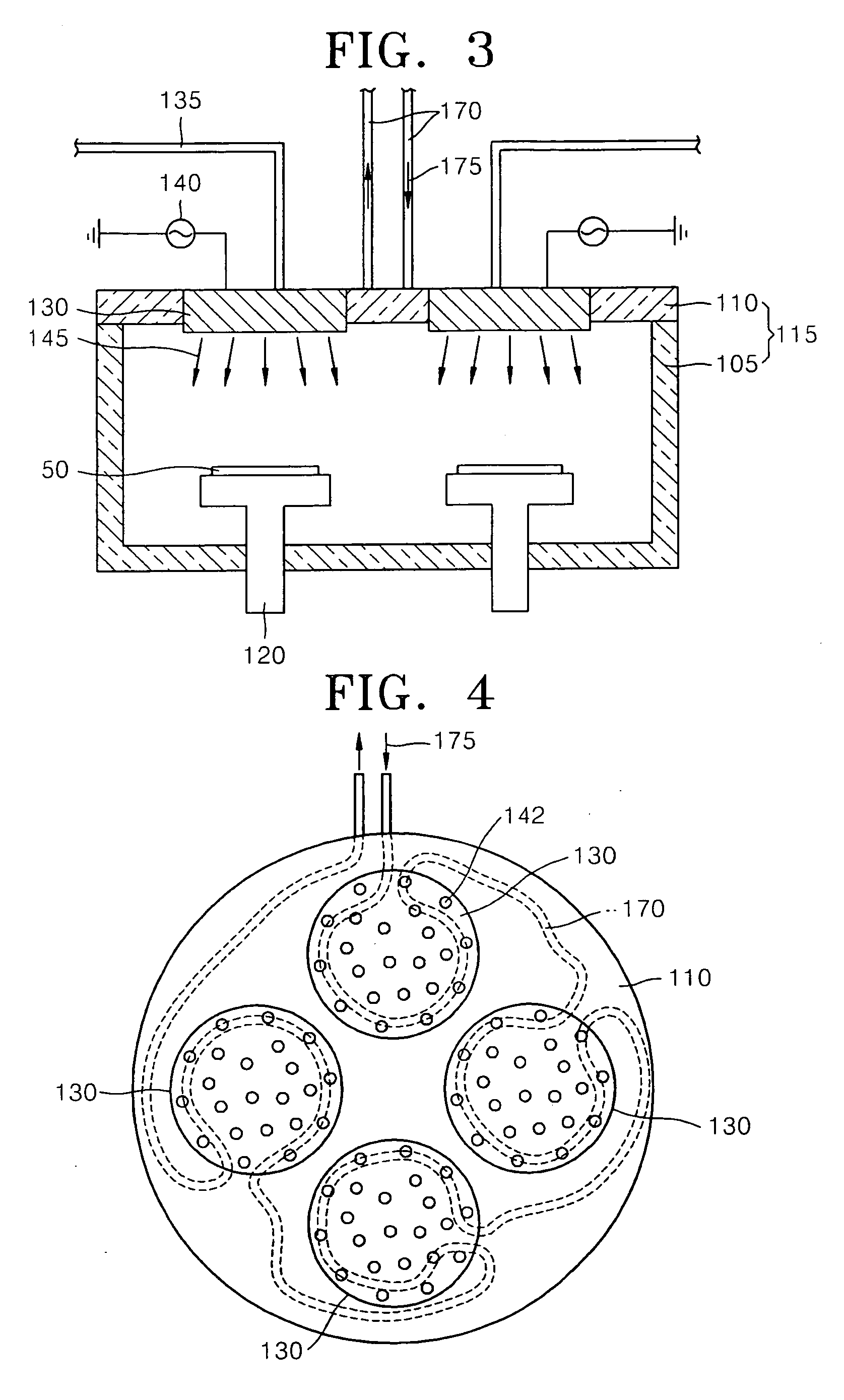
An apparatus and method for fabricating semiconductor devices may increase reliability of the semiconductor devices by decreasing generation of particles and enhancing operation efficiency by decreasing the number of cleanings. The apparatus may include a chamber having a cover plate, susceptors for securely placing semiconductor substrates within the chamber, shower heads located on the cover plate to supply reaction gases into the chamber, and a curtain gas line connected to the cover plate to supply heated curtain gases between the shower heads.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Raw material gas supply system and film forming apparatus
InactiveUS20100236480A1Improve thermal conductivityGood reproducibilityValve arrangementsServomotor componentsTemperature controlMetallic materials
A raw material gas supply system (6) supplies a raw material gas to a gas use system (2) kept in a reduced pressure atmosphere. The system includes: a raw material tank (40) for storing a liquid raw material or a solid raw material; a raw material conduit (46) connected at one end to the raw material tank and connected at the other end to the gas use system; a carrier gas supply mechanism (54), connected to the raw material tank, for supplying a carrier gas into the raw material tank while controlling the flow rate of the gas; on-off valves (48, 50) interposed in the raw material conduit; a heater (64) for heating the raw material conduit and the on-off valves; and a temperature control device (92) for controlling the heater, wherein the raw material conduit and the on-off valves are each formed of a metal material having good thermal conductivity.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Sputtering Target, Thin Film for Optical Information Recording Medium and Process for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080299415A1Reducing the affect of heating the substrateIncrease speedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringProduction rate
A sputtering target is provided that has a relative density of 80% or more and contains a compound having as its principal component zinc oxide satisfying AXBYO(KaX+KbY) / 2(ZnO)m, 1<m, X≦m, 0<Y≦0.9, X+Y=2, where A and B are respectively different positive elements of trivalence or more, and the valencies thereof are respectively Ka and Kb. A ZnO based sputtering target is obtained which does not contain ZnS and SiO2, and, upon forming a film via sputtering, is capable of reducing the affect of heating the substrate, of performing high speed deposition, of adjusting the film thickness to be thin, of reducing the generation of particles (dust) and nodules during sputtering, of improving the productivity with small variation in quality, and which has fine crystal grains and a high density of 80% or more, particularly 90% or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com