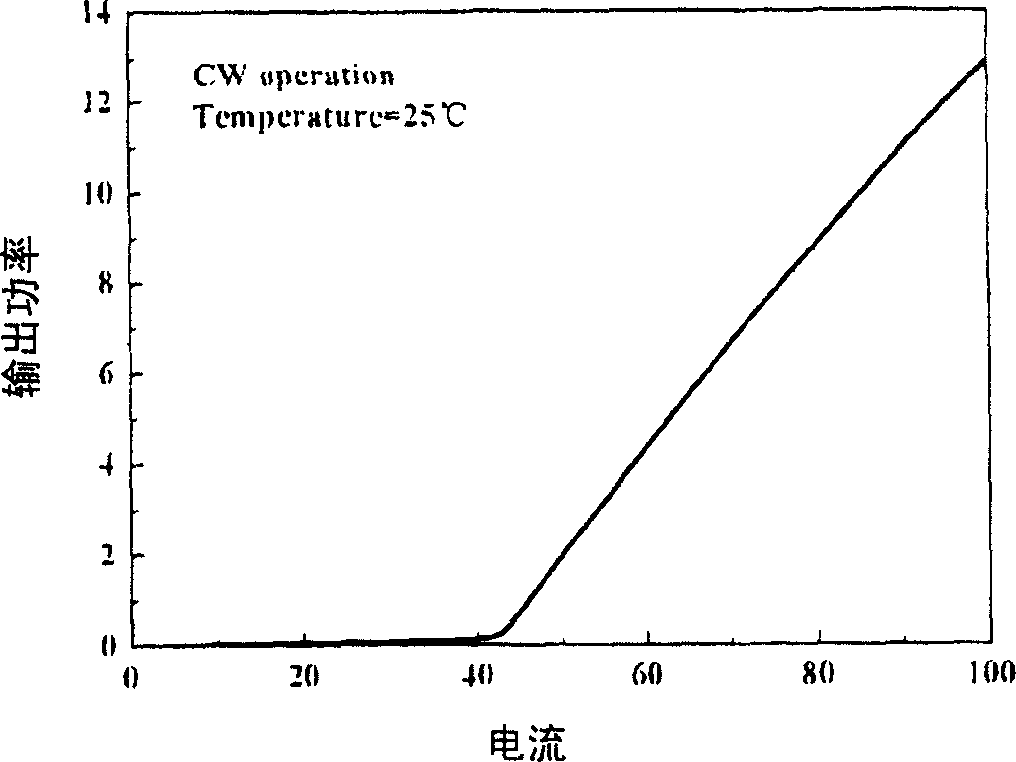
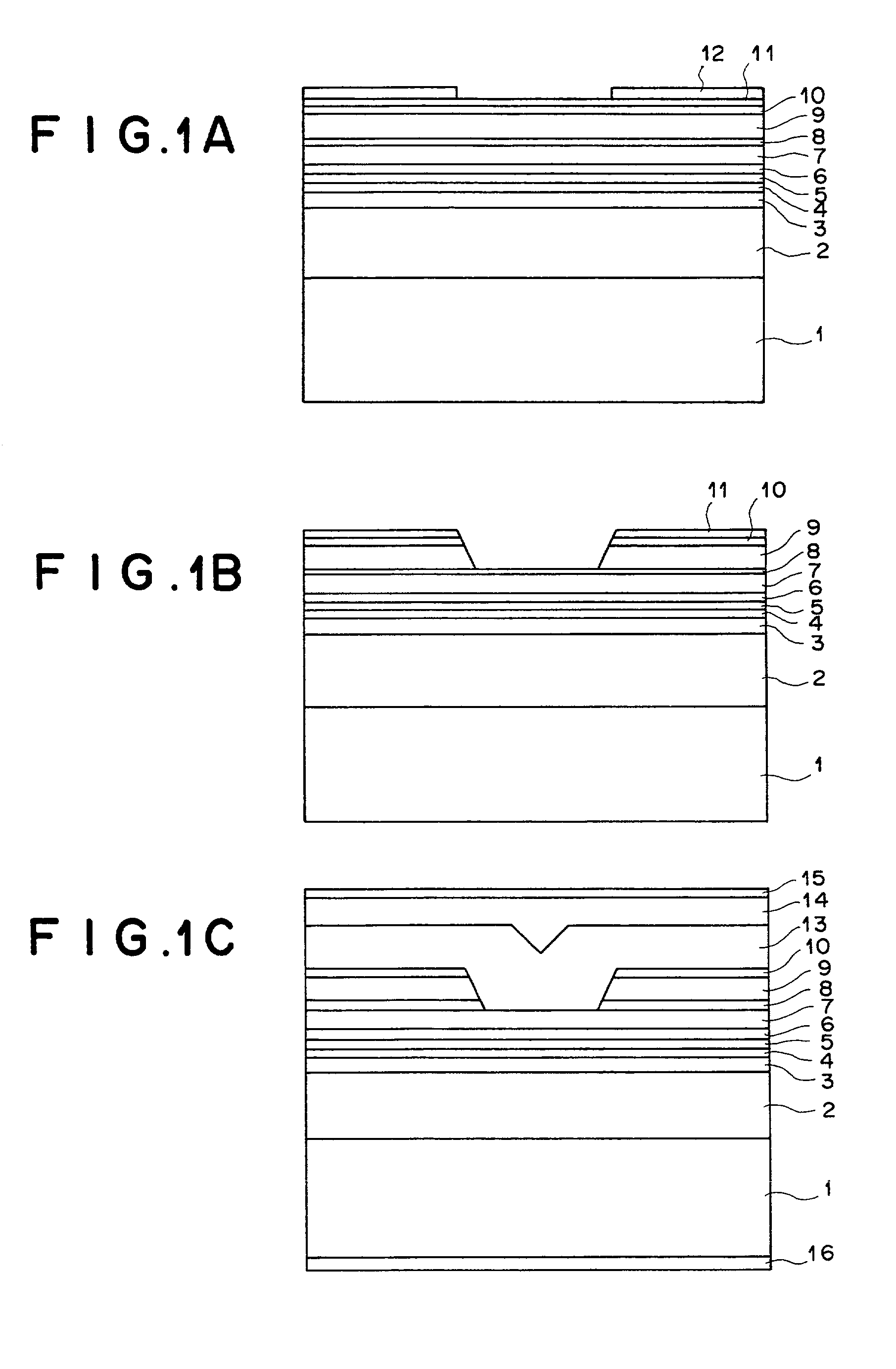
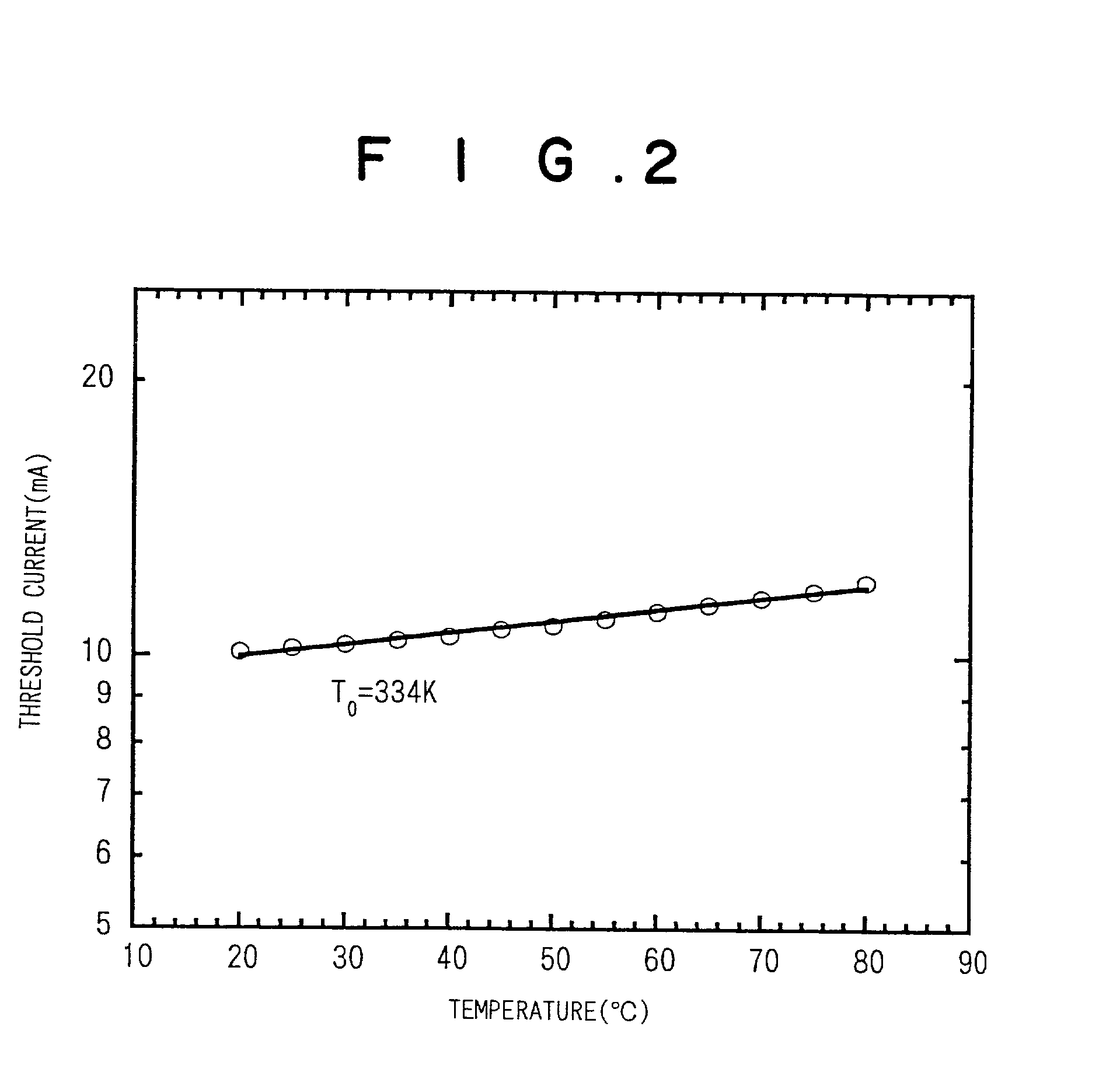
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171results about How to "Increase the bandgap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
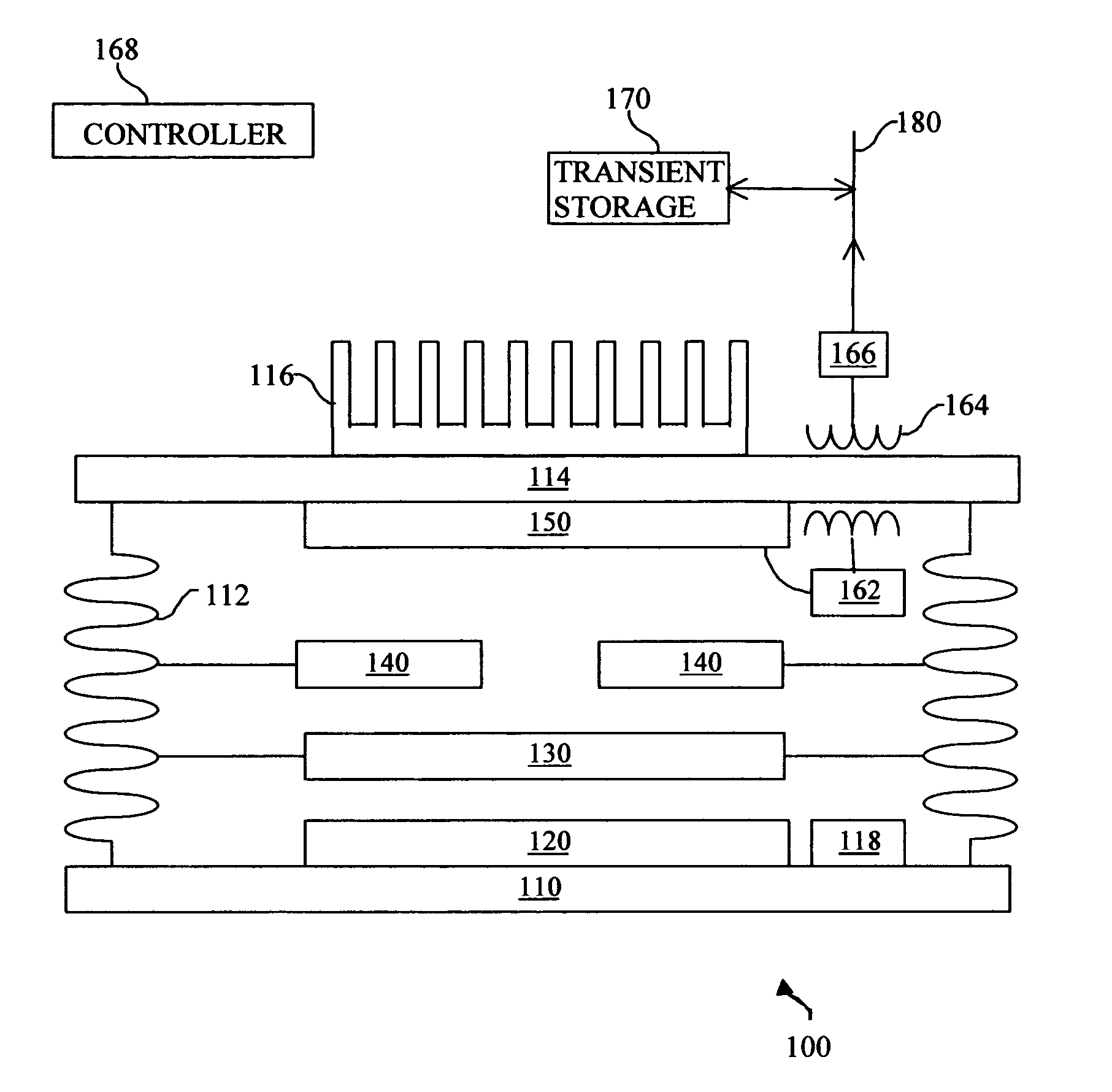
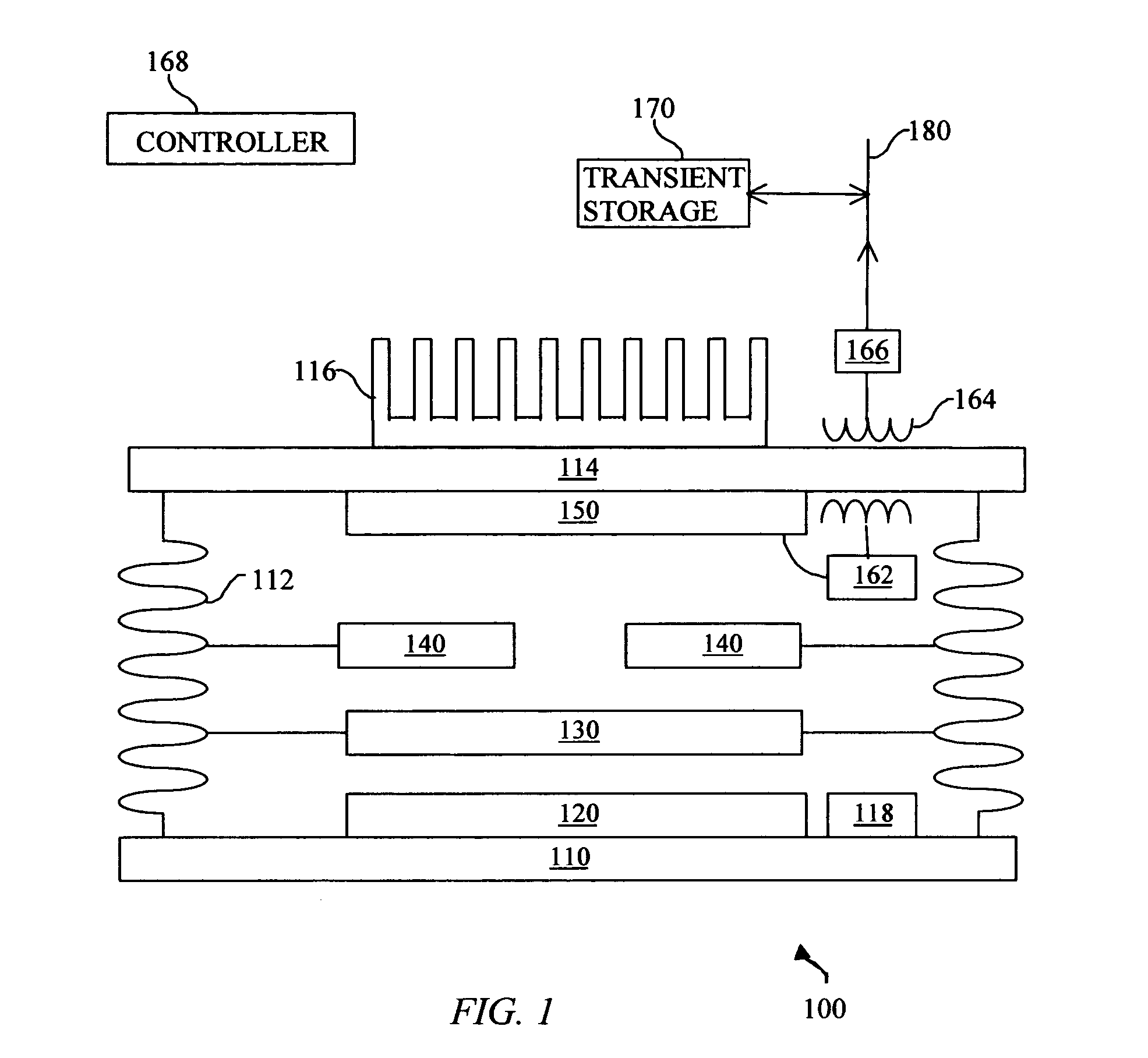
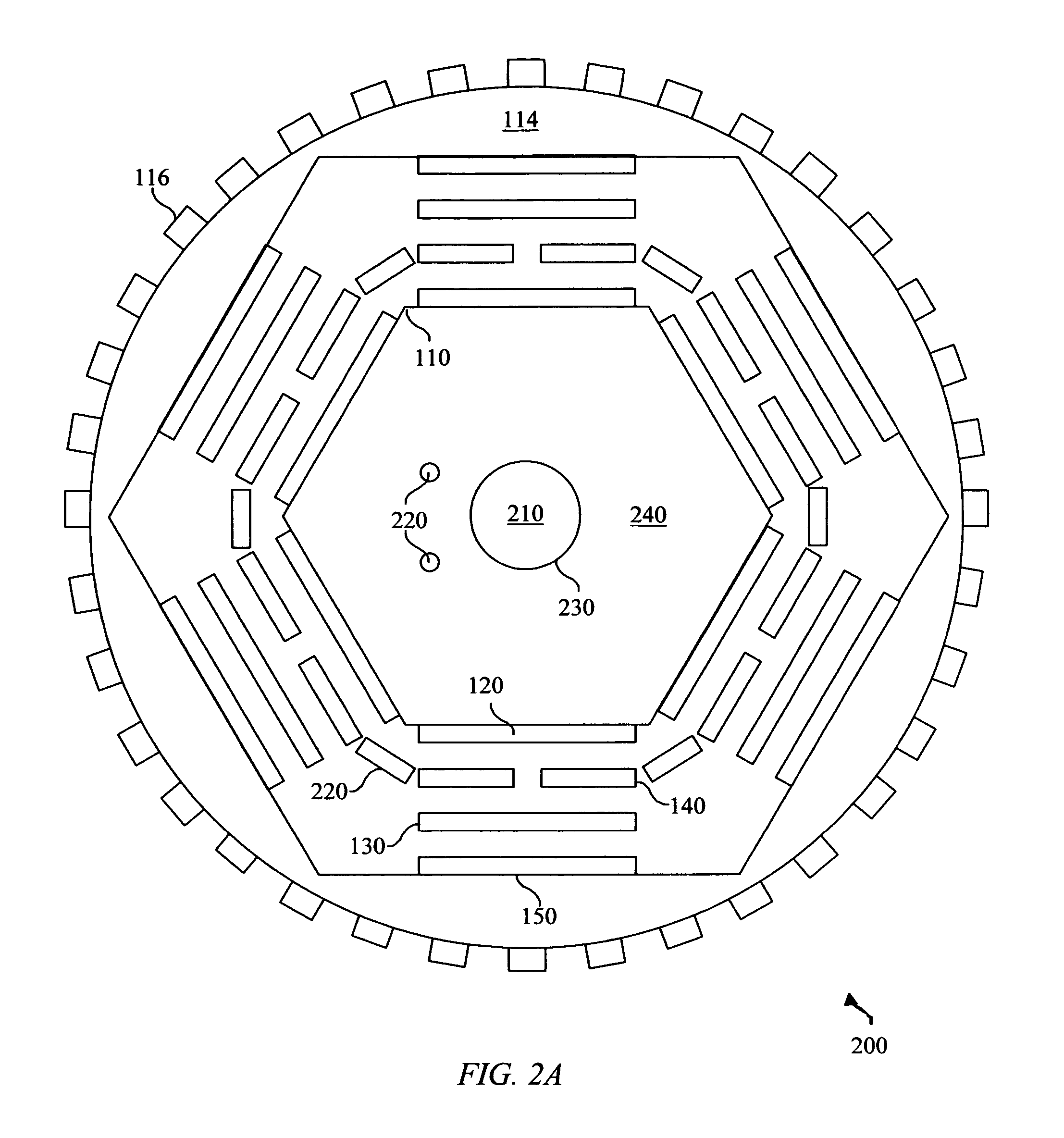
System and method for enhanced thermophotovoltaic generation
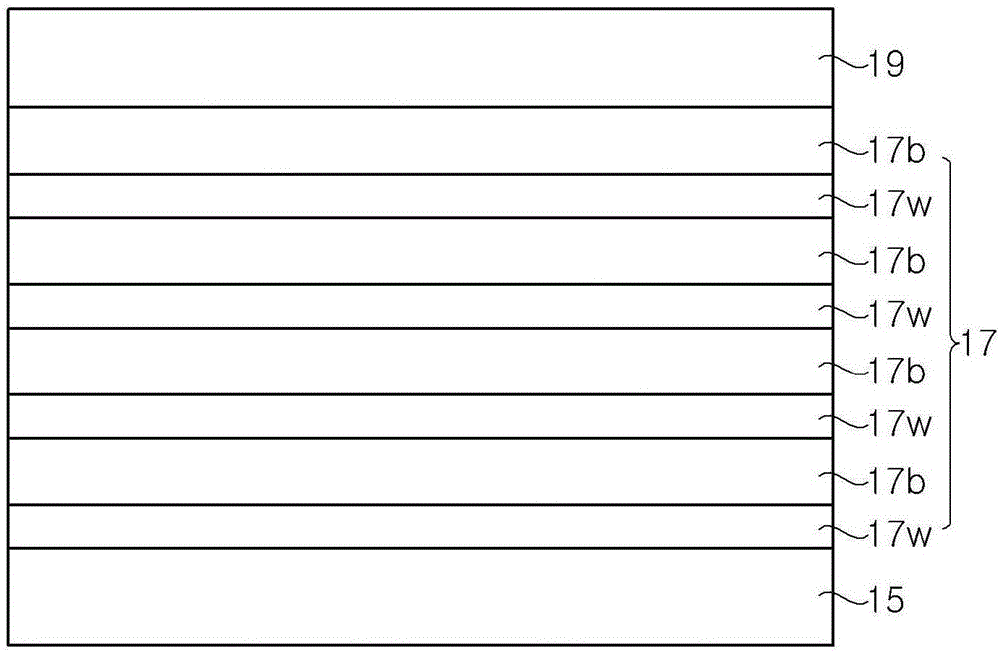
InactiveUS20050109386A1Reduce fossil fueled NOx emissionIncreasing burner efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPV power plantsThermophotovoltaicDistributed generation
A system and method for lower cost, high efficiency, thermophotovoltaic distributed generation includes: an emitter, a photovoltaic cell, and transient electrical energy storage.
Owner:PRACTICAL TECH
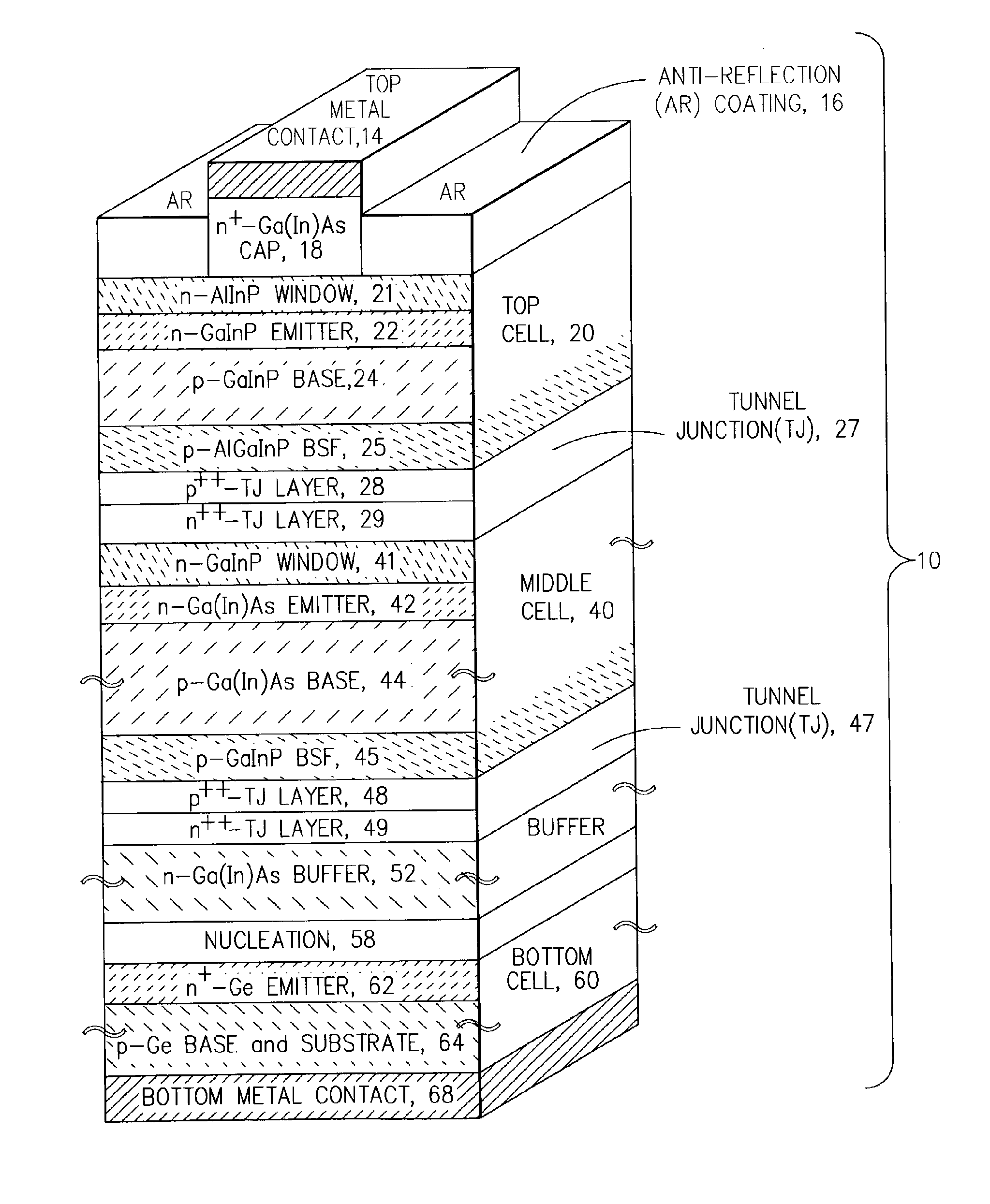
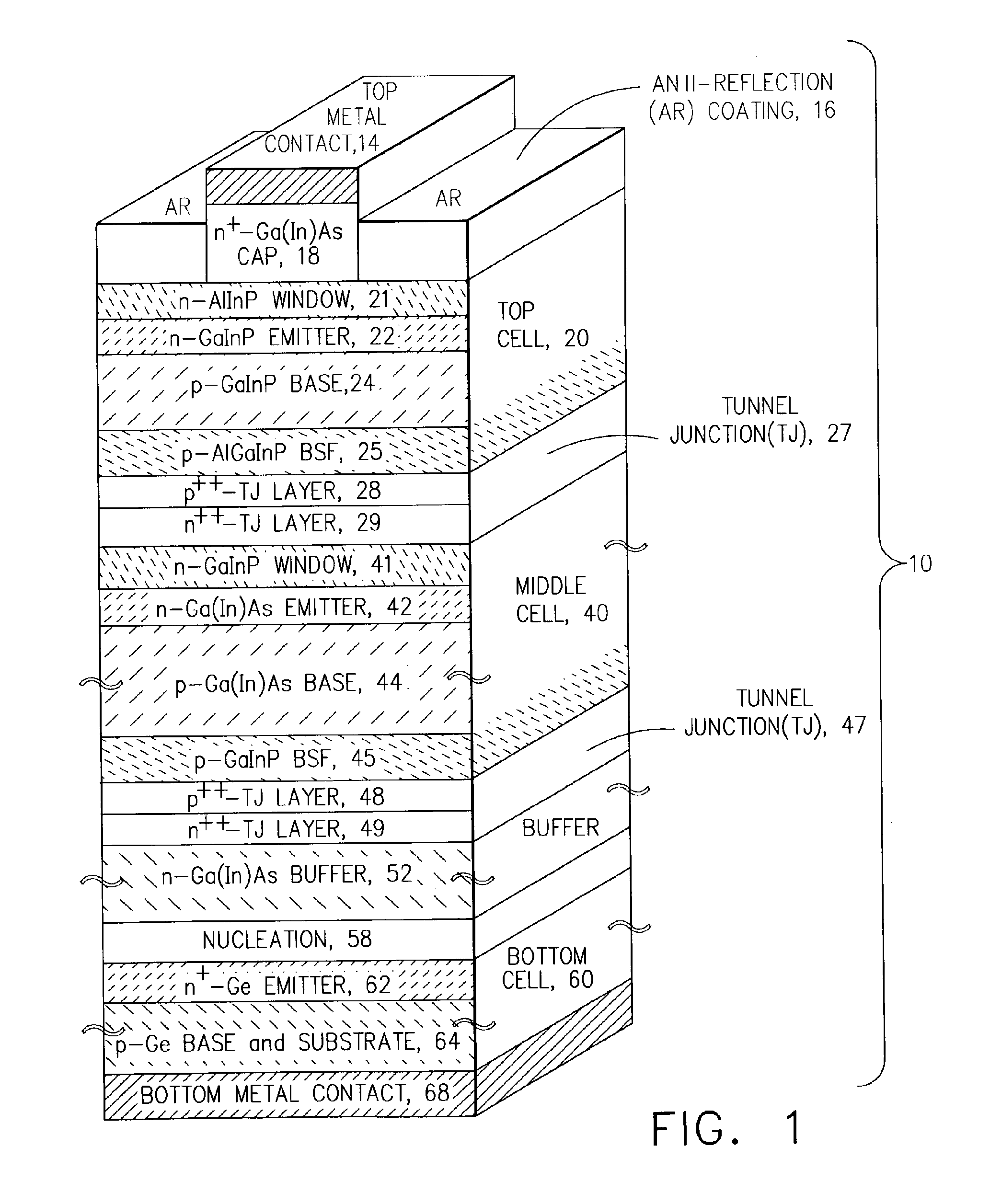
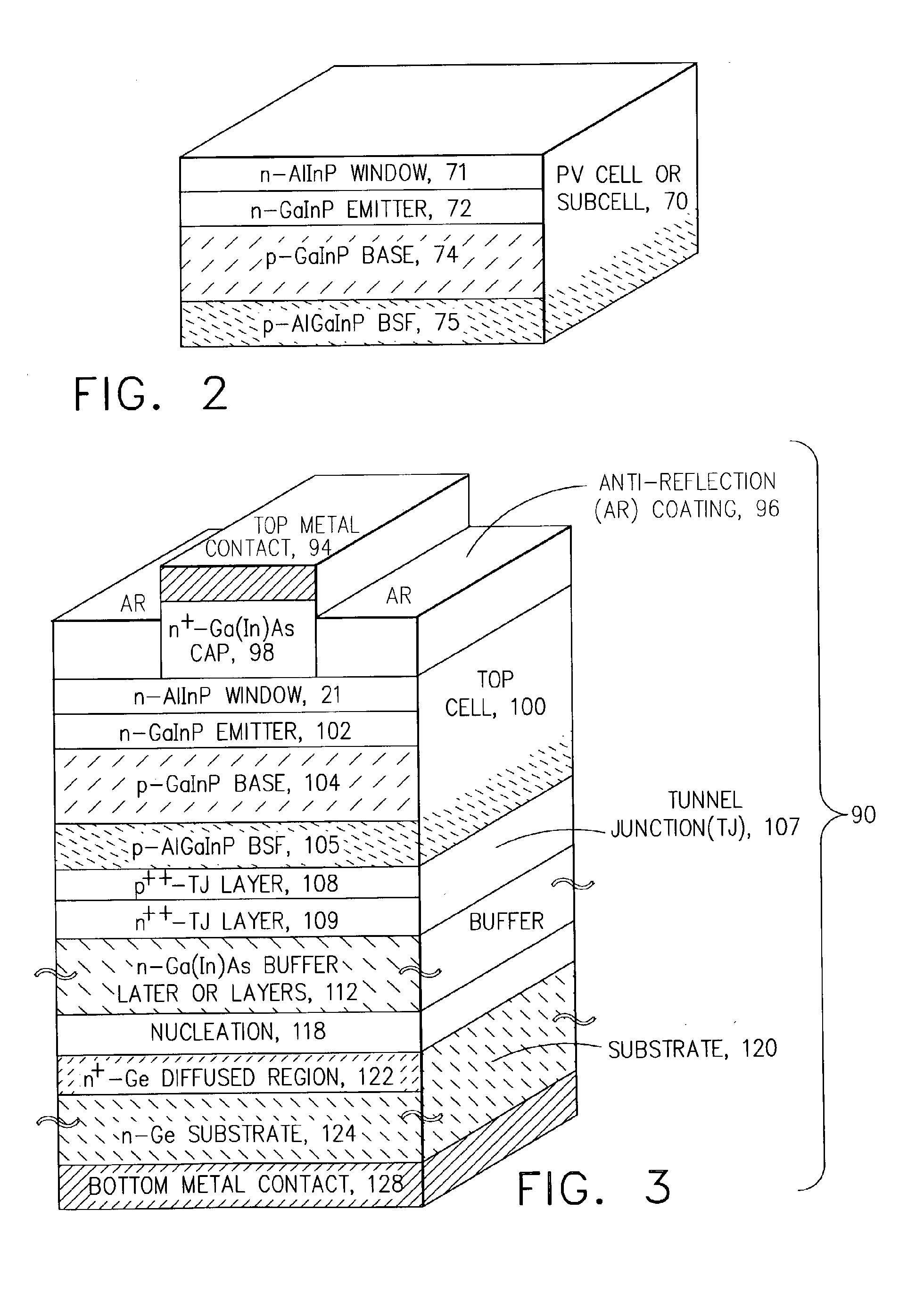
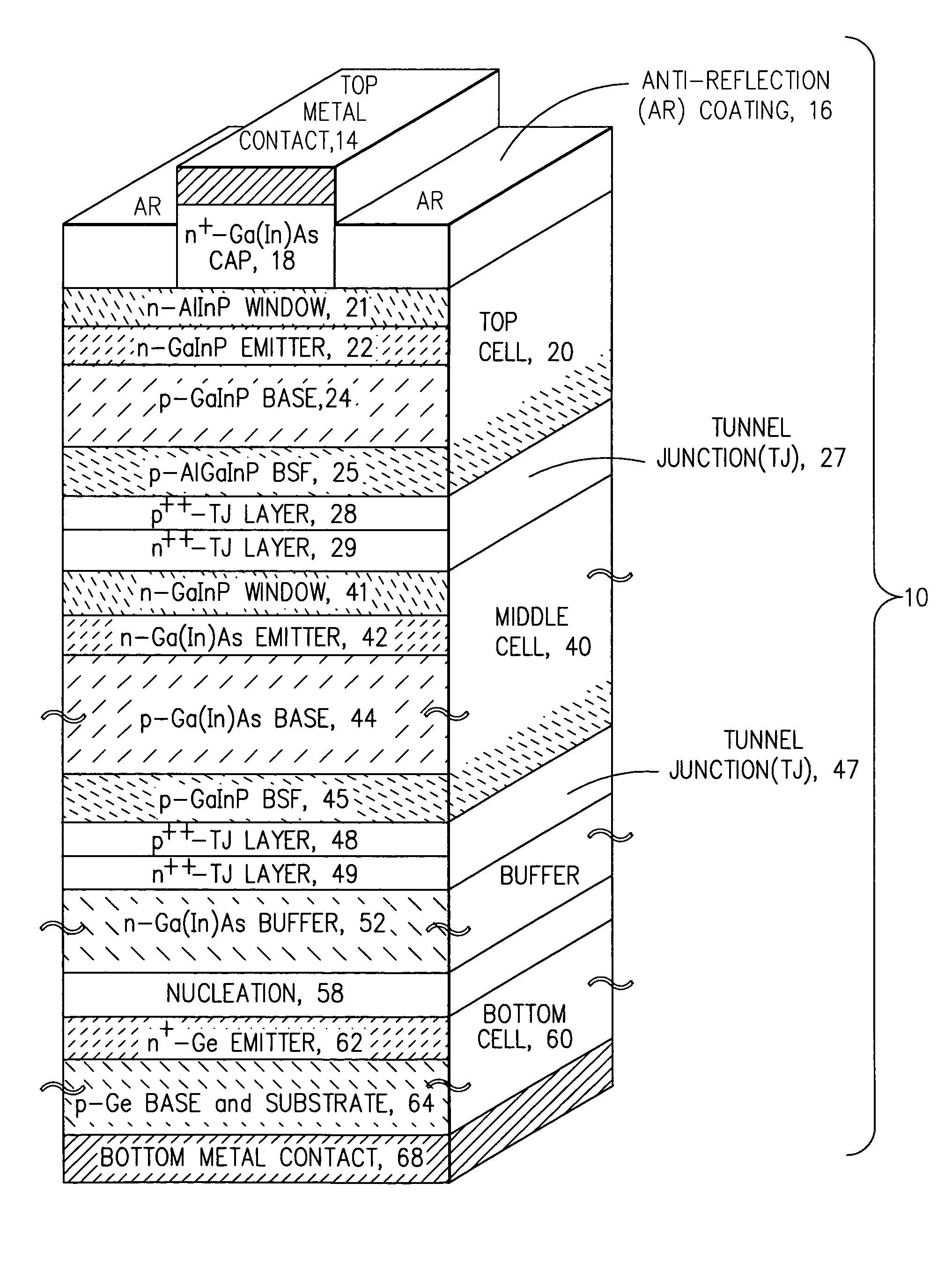
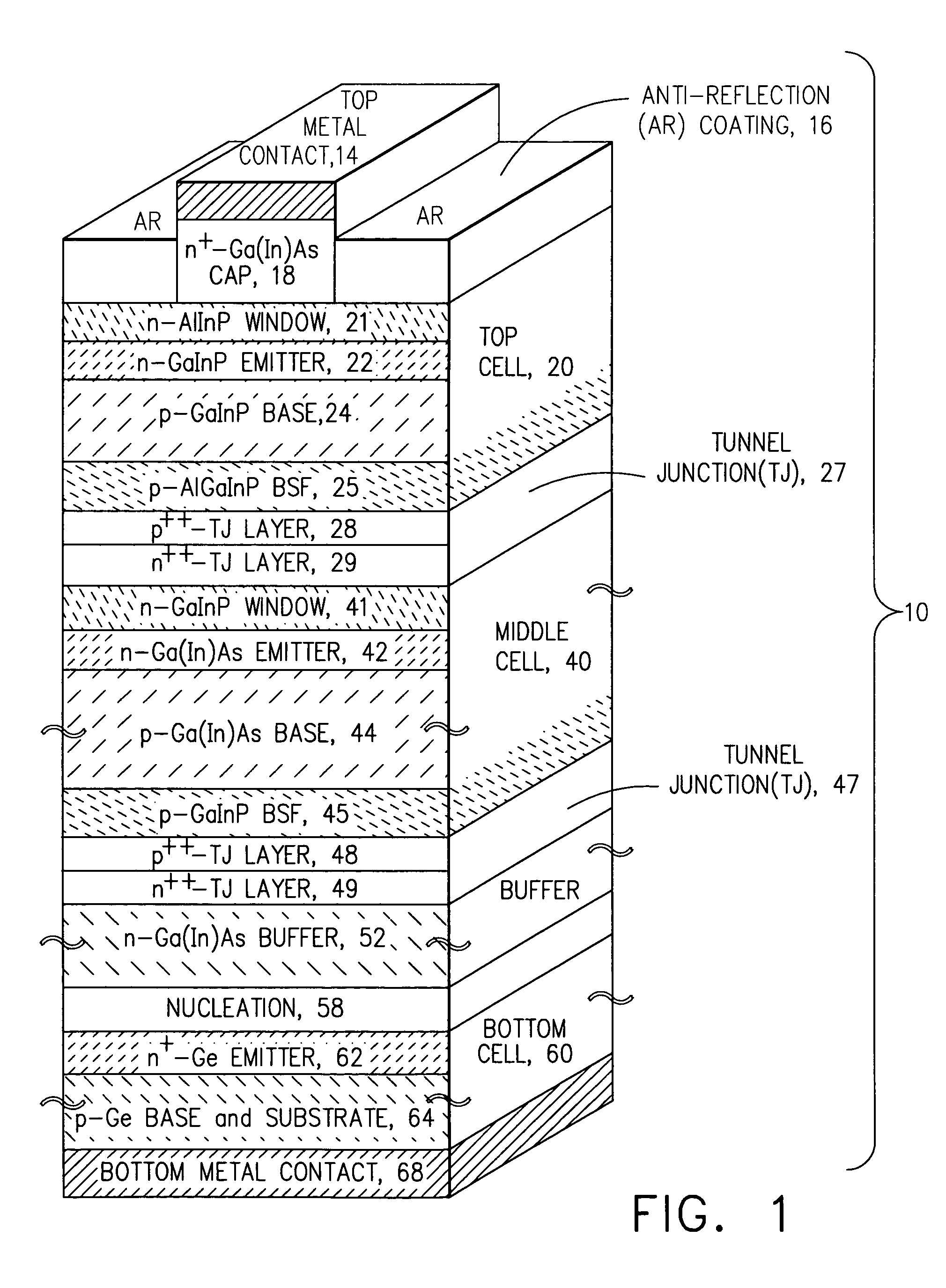
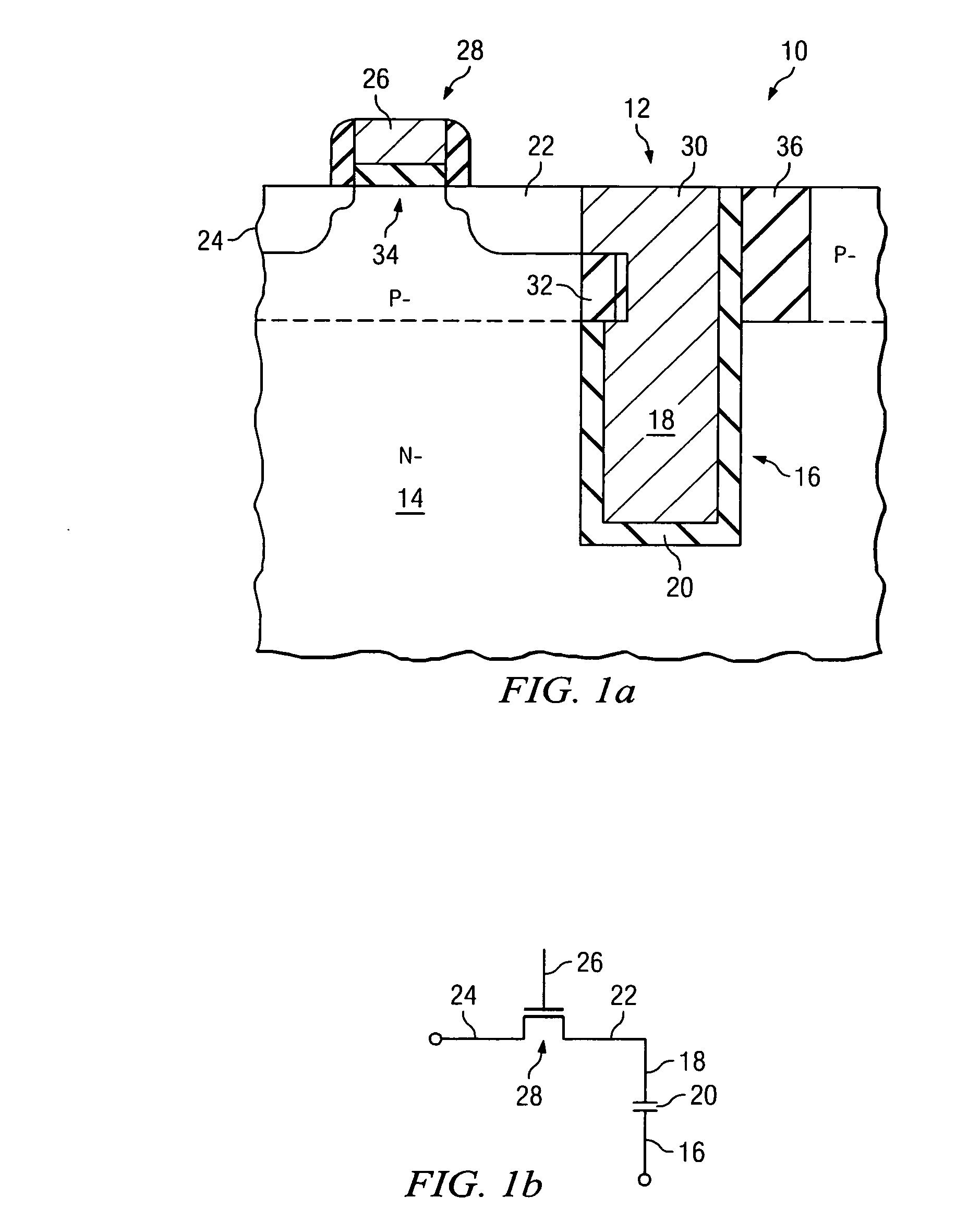
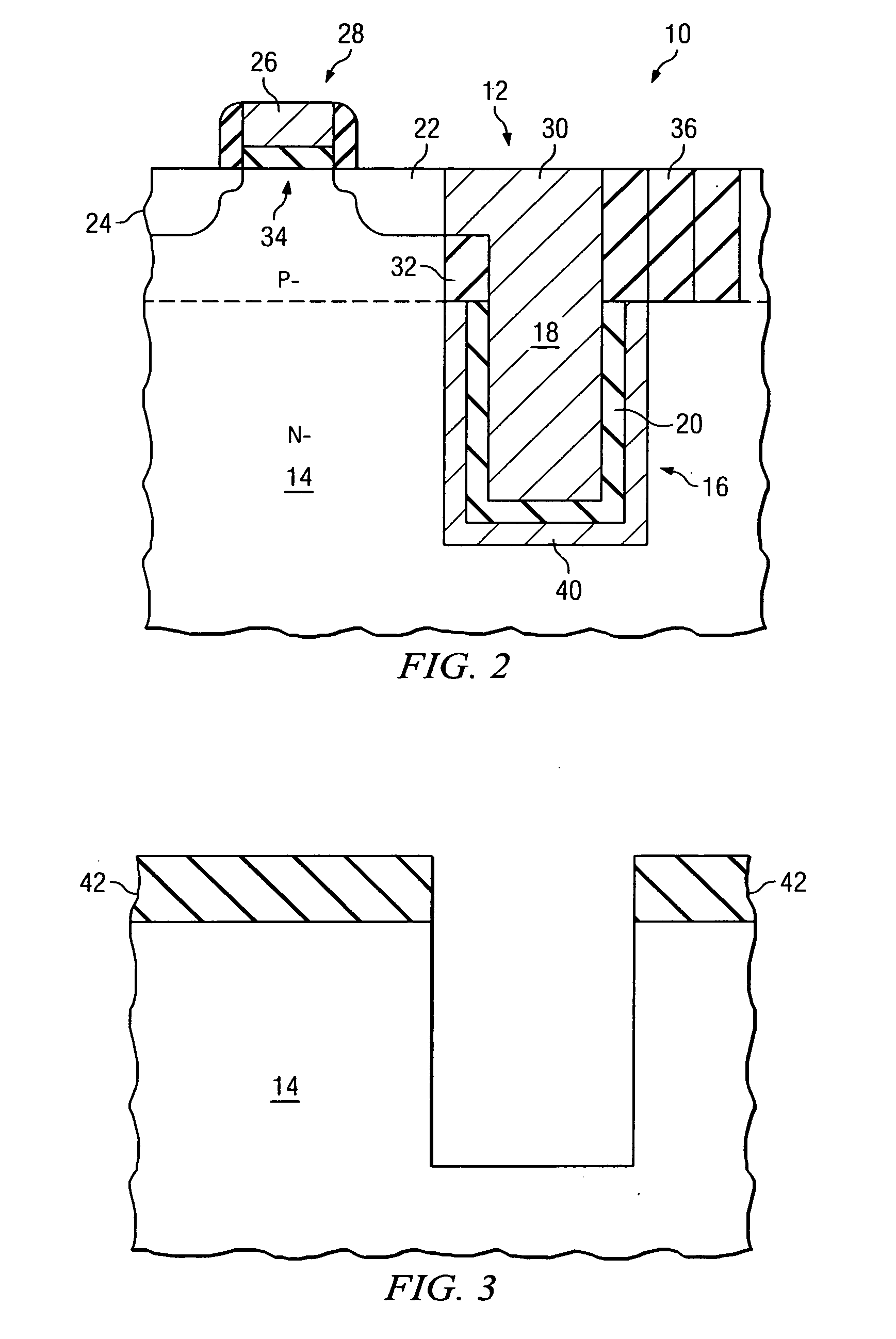
Multijunction photovoltaic cell grown on high-miscut-angle substrate
InactiveUS20110011983A1Shorter cutoff wavelengthIncrease the bandgapCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsMultijunction photovoltaic cellOptics
The present invention provides a photovoltaic cell comprising a GaInP subcell comprising a disordered group-III sublattice, a Ga(In)As subcell disposed below the GaInP subcell, and a Ge substrate disposed below the Ga(In)As subcell comprising a surface misoriented from a (100) plane by an angle from about 8 degrees to about 40 degrees toward a nearest (111) plane.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Alkyl substituted-S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene monomer, preparation method and polymer thereof
ActiveCN101712674AImprove solubilityLow priceOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSolubilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses an alkyl substituted-S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene monomer, a preparation method and a polymer thereof. The presence of the strong electron-withdrawing group -SO2- in the alkyl substituted-S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene is favorable for improving the electron affinity of molecules, and the introduction of the alkyl greatly improves the dissolubility of the monomer in an organic solvent. The alkyl substituted-S,S-dioxo-dibenzothiophene monomer can form a homopolymer or a copolymer through the polymerization reaction of Suzuki, Stille and Yamamoto. The series of polymers have good dissolubility in the organic solvent, are suitable for processing solution, and have broad application prospects in the fields of organic flat displays, photovoltaic cells and organic field-effect tubes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multijunction photovoltaic cell grown on high-miscut-angle substrate
ActiveUS7812249B2Short cutoff wavelengthIncrease the bandgapFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationMultijunction photovoltaic cellOptics
The present invention provides a photovoltaic cell comprising a GaInP subcell comprising a disordered group-III sublattice, a Ga(In)As subcell disposed below the GaInP subcell, and a Ge substrate disposed below the Ga(In)As subcell comprising a surface misoriented from a (100) plane by an angle from about 8 degrees to about 40 degrees toward a nearest (111) plane.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
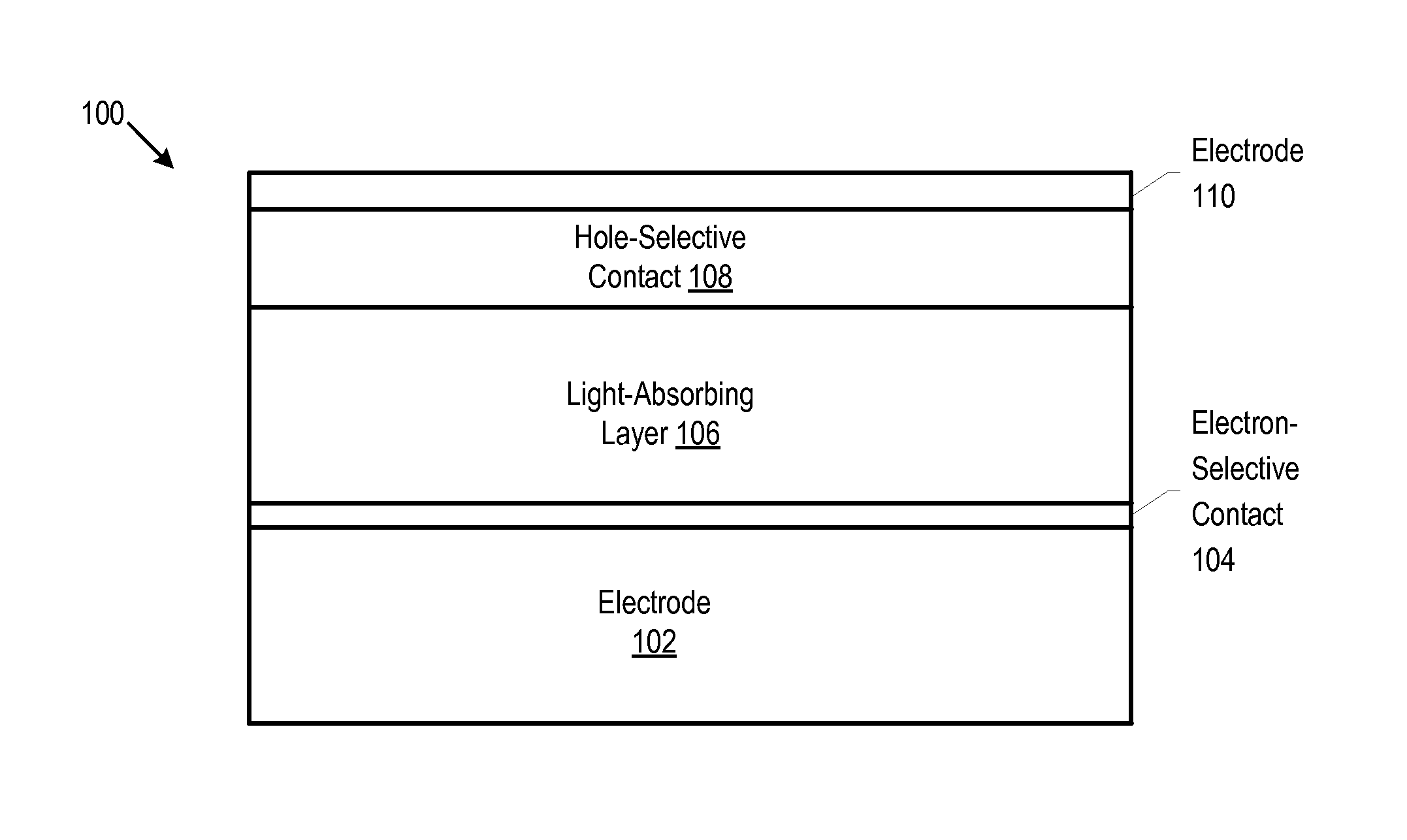
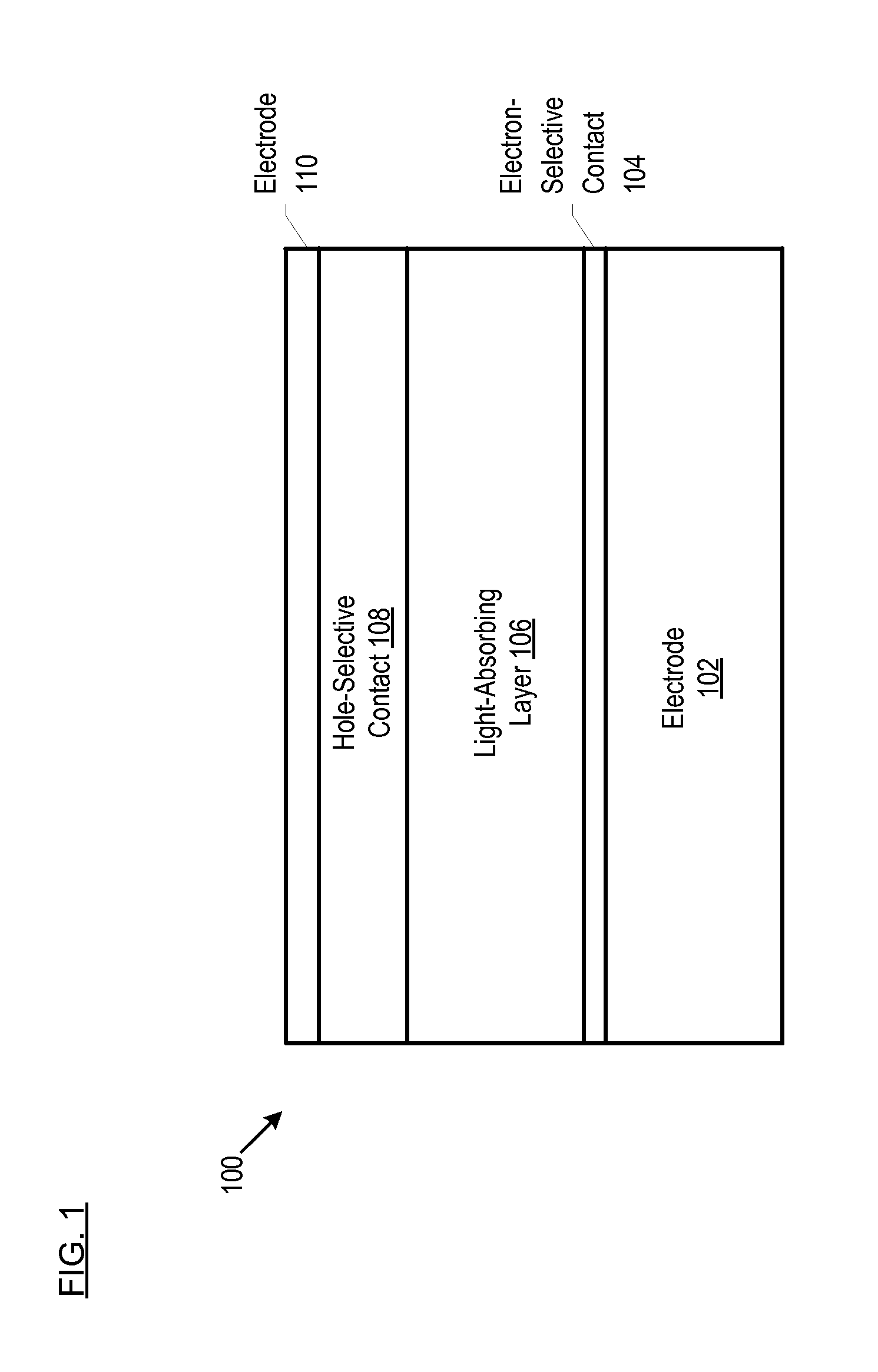
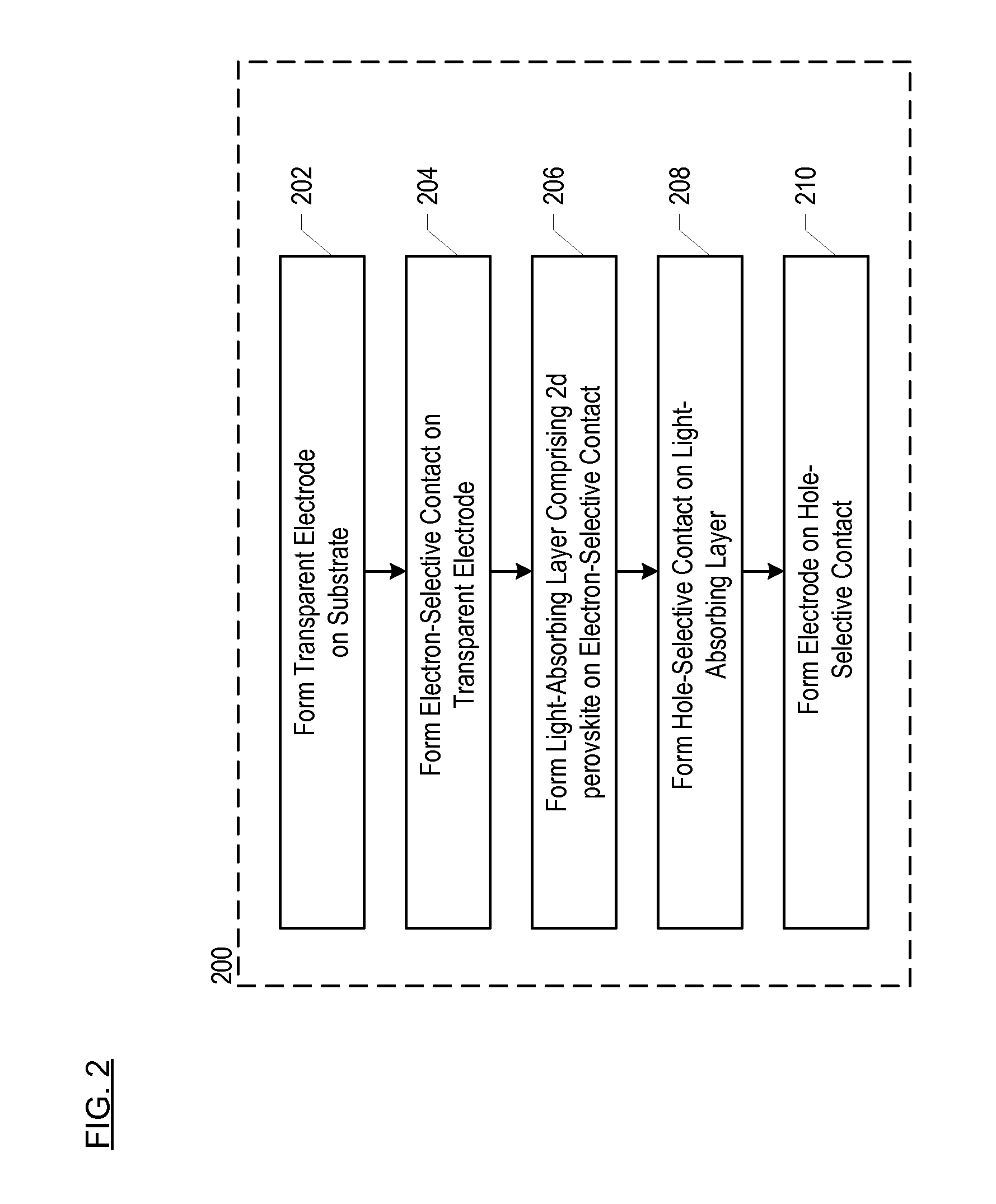
Solar Cells Comprising 2d-Perovskites
ActiveUS20150357591A1Improve efficiencyReduce dimensionalityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSolar cellPerovskite
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
DRAM with high K dielectric storage capacitor and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060205143A1Minimizing contributionIncrease the bandgapSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenDielectric layer
A memory cell is fabricated by forming a first capacitor electrode including silicon. A metal layer is formed in physical contact with the first capacitor electrode. The metal layer is formed from a material having a high affinity for oxygen and a melting point above about 1000° C. A layer of high K dielectric material is formed in physical contact with the metal layer. The high K dielectric material has a dielectric constant greater than about 5. A conductive layer is formed over the high K dielectric material layer. An interface between the high K dielectric layer and the metal layer / silicon body is modified by performing an annealing step. A transistor is also formed to be electrically coupled to one of the conductive layer or the first capacitor electrode.
Owner:GOVINDARAJAN SHRINIVAS
Semiconductor device having source/channel or drain/channel boundary regions
InactiveUS6838698B1Lower resistancePrevent leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesLow voltageDevice material
A semiconductor device and a method for forming the same are disclosed. The semiconductor device comprising an insulated gate field effect transistor provided with a region having added thereto an element at least one selected from the group consisting of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, said region having established at either or both of the vicinity of the boundary between the drain and the semiconductor layer under the gate electrode and the vicinity of the boundary between the source and the semiconductor layer under the gate electrode for example by ion implantation using a mask. It is free from the problems of reverse leakage between the source and the drain, and of throw leakage which occurs even at a voltage below the threshold ascribed to the low voltage resistance between the source and the drain.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
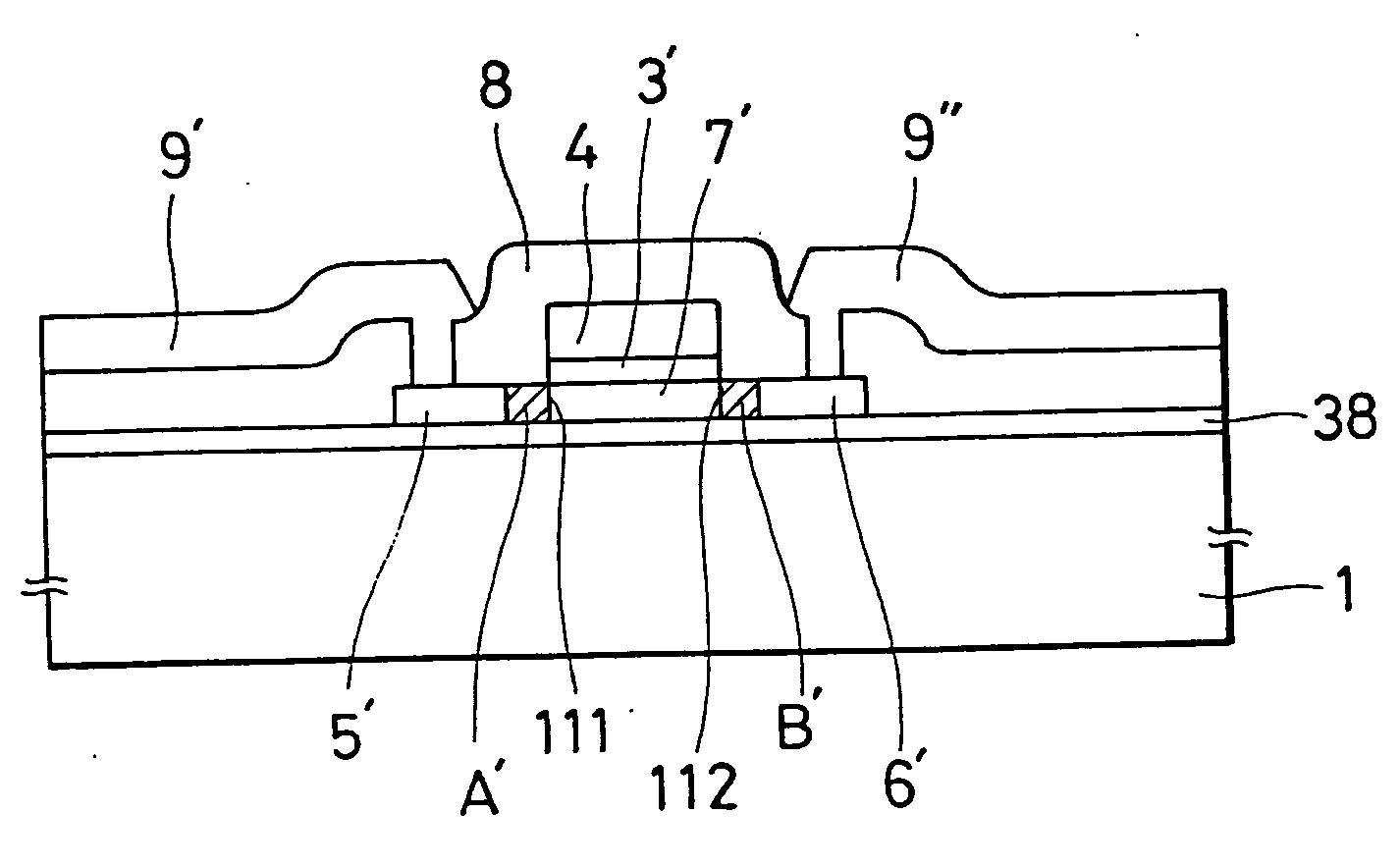
Transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector and preparation method
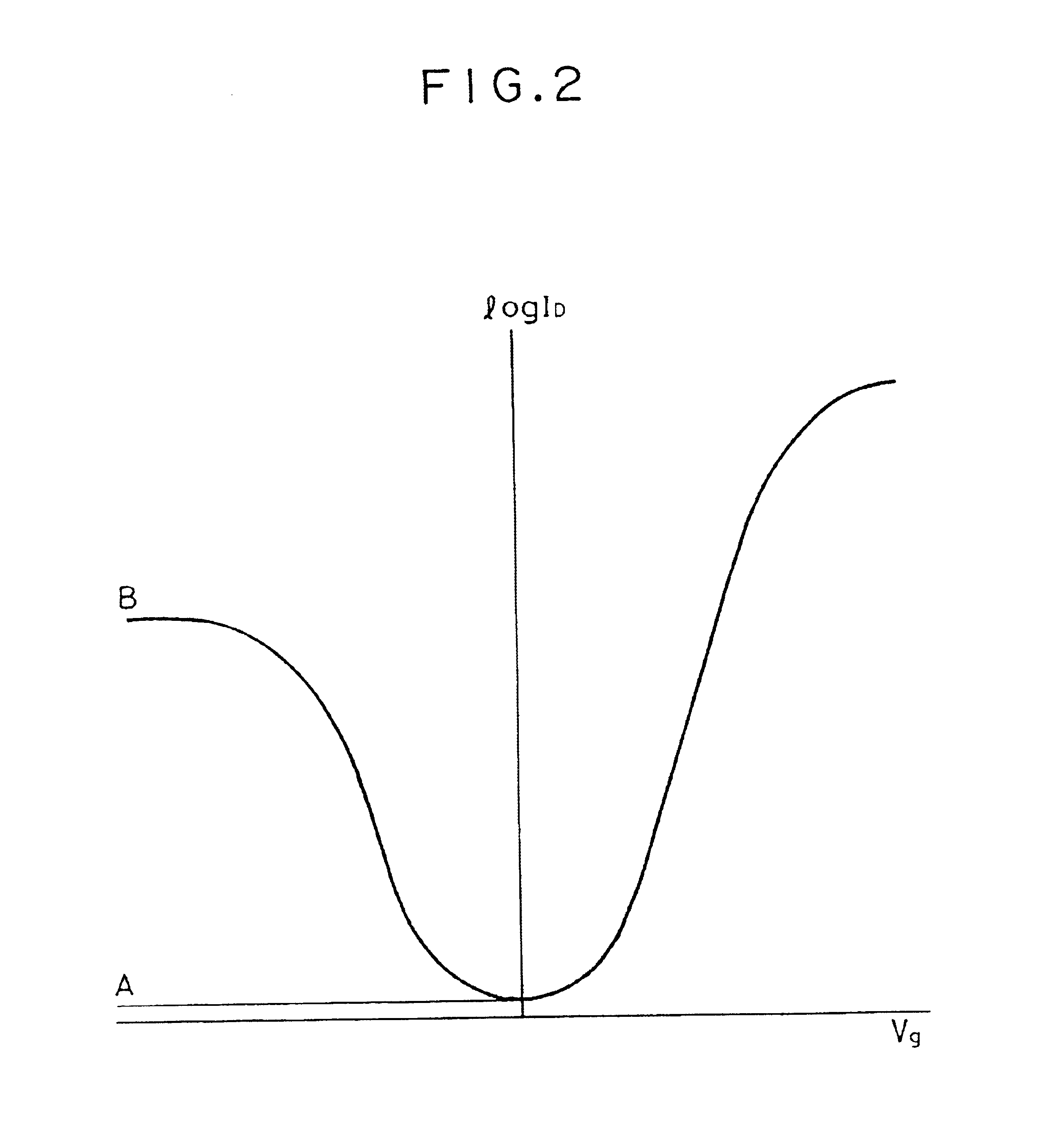
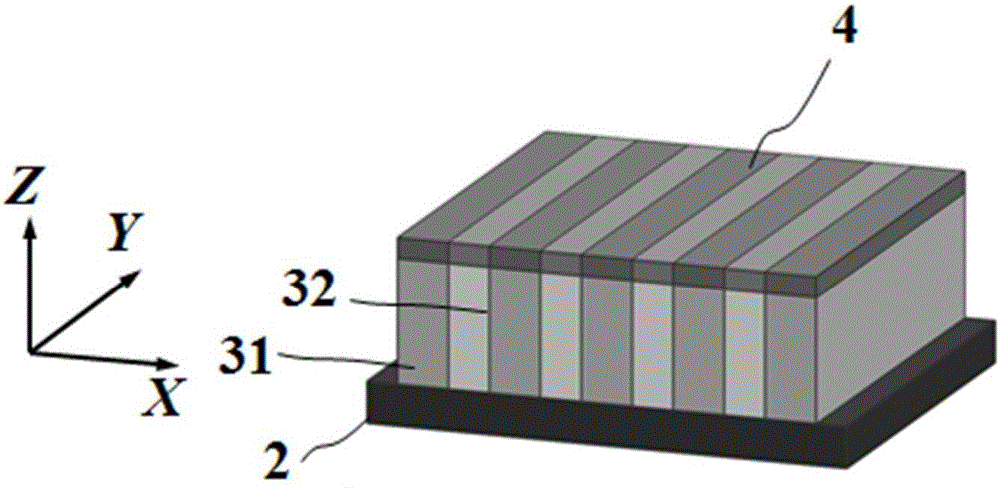
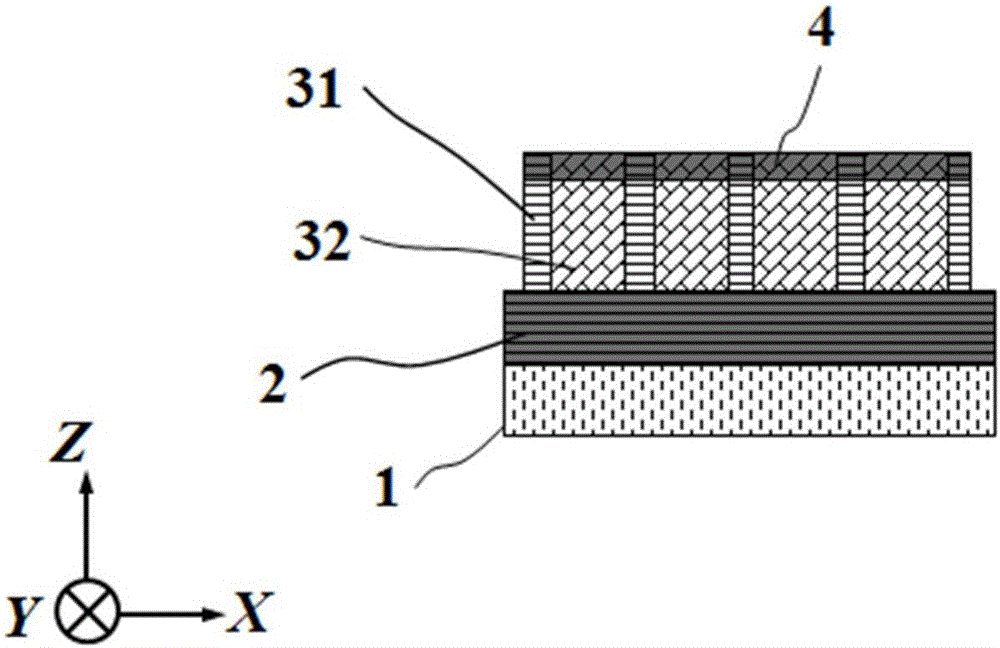
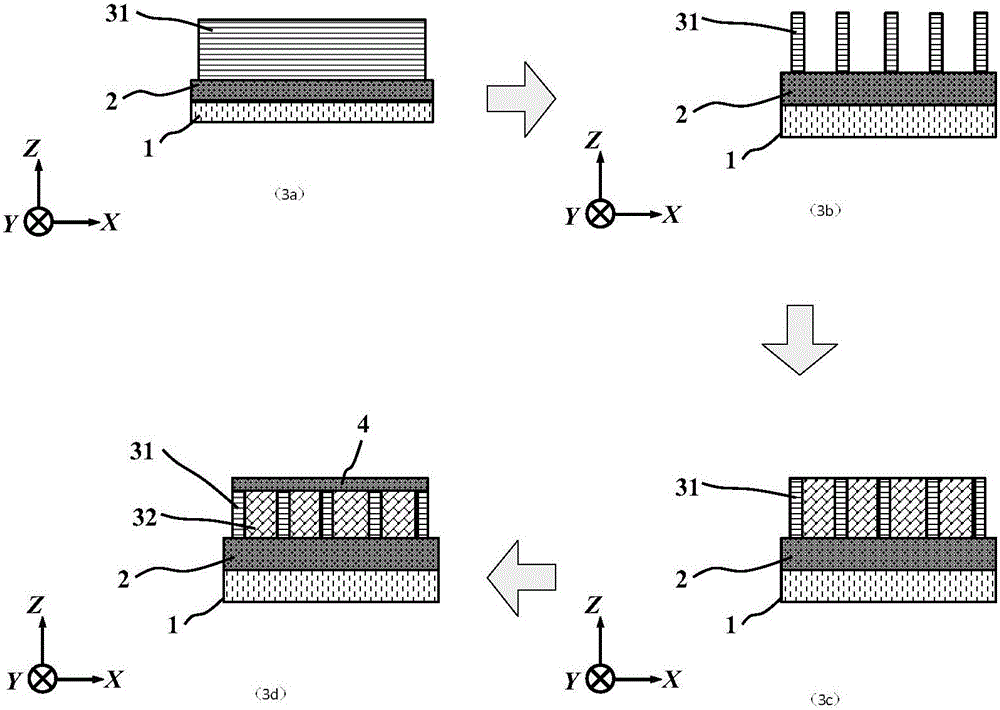
ActiveCN105006500AImprove the effect of bandgap adjustmentEffective adjustment of absorption wavelength rangeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSpectral responseSingle crystal
The invention discloses a transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector and mainly solves problems of high material toxicity and high cost of a conventional infrared photoelectric detector. The transverse IV-clan element quantum well photoelectric detector comprises a substrate (1), a bottom electrode (2), an absorption region (3), and a top electrode (4). A quantum well (31) uses a GeSn strain monocrystalline material with a Sn component more than or equal to 0 but less than 0.3. A barrier layer (32) uses a monocrystalline material with a Sn component more than or equal to 0 but less than 0.3 and a Ge component more than or equal to 0 but less than 1. The quantum well (31) and the barrier layer (32) are stacked transversely to form the absorption region arranged between the bottom electrode and the top electrode. According to the invention, SiGeSn monocrystalline material changes in size in an epitaxial process so as to generate transverse tensile strain in the GeSn quantum well material, thereby changing a GeSn material band gap and enlarging the spectral response range of the detector. The SiGeSn monocrystalline material can be used for producing large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
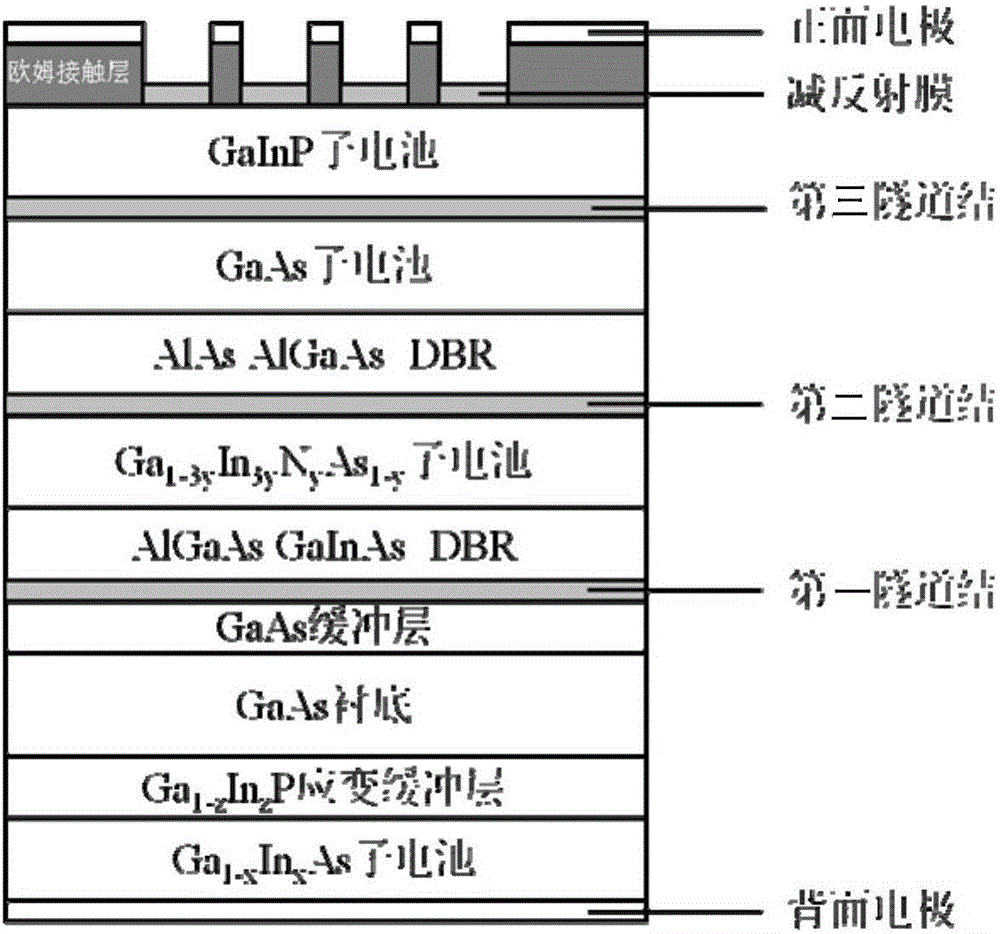
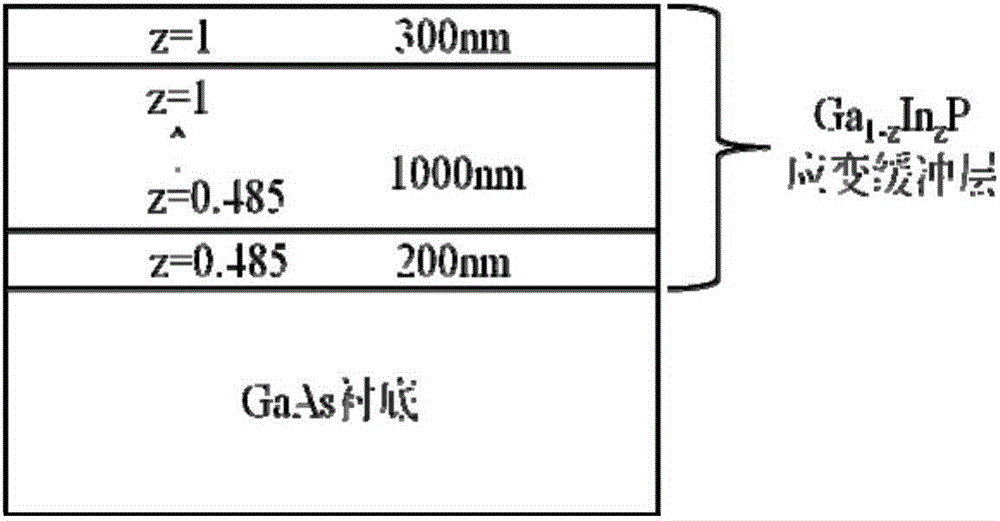
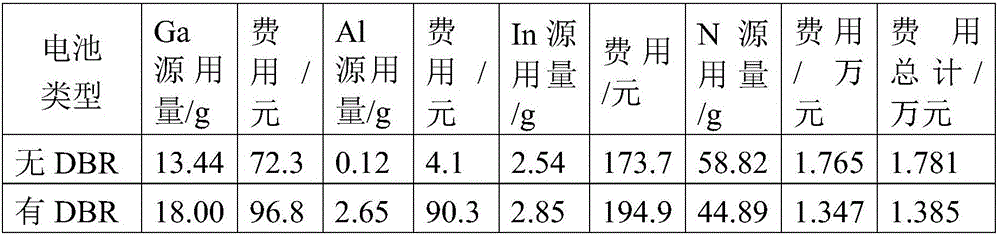
Double-side growth four-junction solar cell with reflecting layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105826420AImprove photoelectric conversion performanceLow costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOhmic contactFill factor
The invention discloses a double-side growth four-junction solar cell with a reflecting layer and a preparation method thereof, and the solar cell comprises a GaAs substrate; the GaAs substrate is an n-type GaAs single-crystal slice that is polished in two sides; a GaAs buffer layer, a first tunnel junction, a AlGaAs / GaInAs DBR reflecting layer, a GaInNAs sub-cell, a second tunnel junction, a AlAs / AlGaAs DBR reflecting layer, a GaAs sub-cell, a third tunnel junction, a GaInP sub-cell, an ohmic contact layer, an antireflection coating, and a front electrode grow on the upper surface of the GaAs substrate from top to bottom; a Ga1-zInzP strain buffer layer, a Ga1-xInxAs sub-cell and a back electrode are provided on the lower surface of the GaAs substrate in order. According to the invention, photon absorption efficiency can be raised; at the same time, the advantages of the four-junction solar cell can play their roles; the integral open-circuit voltage and a fill factor of the GaAs multi-junction cell can be raised; and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the cell can be improved finally.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN DEHUA CHIP TECH CO LTD
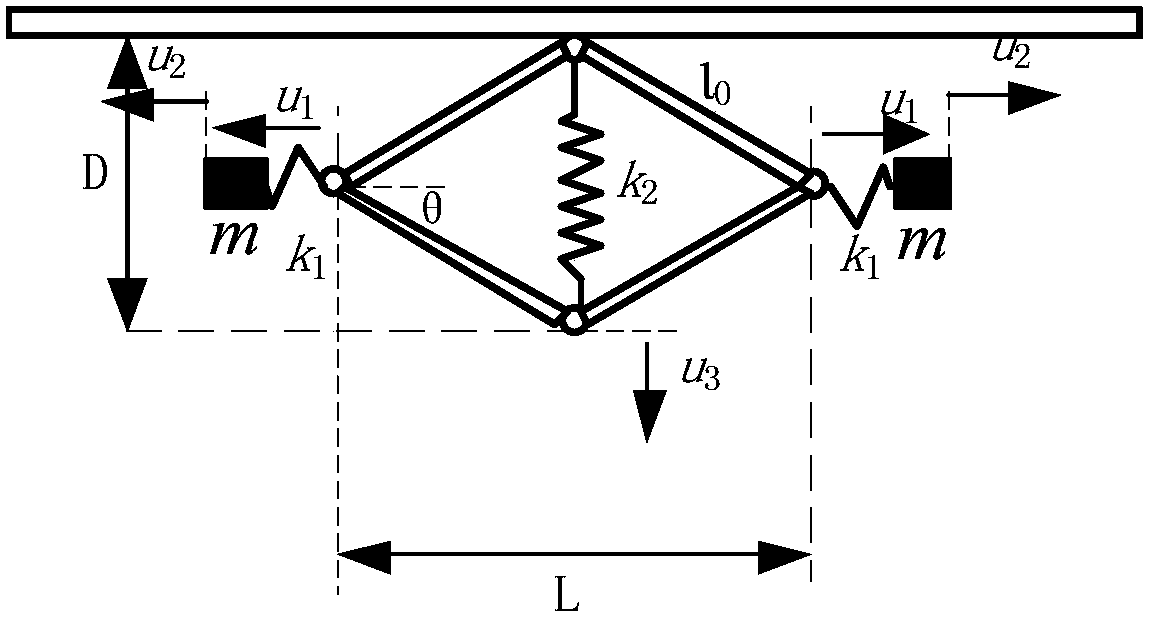
Low-frequency, broad-band and local-area resonance structure with super damping characteristics
ActiveCN107701635ABroaden the low frequency bandgapAccelerate the attenuation of vibrationProtective buildings/sheltersShock absorbersVibration attenuationResonance
The invention provides a low-frequency, broad-band and local-area resonance structure with super damping characteristics. The structure comprises a rhombic frame; a first end of the rhombic frame is connected with a basal body beam through a rubber block; rubber bars are arranged on short diagonal lines in the rhombic frame; and one ends of the rubber bars are connected with the first end of the rhombic frame, and the other ends are connected with a second end of the rhombic frame. Mass blocks are arranged at two ends of the rhombic frame, and the structure is periodically added on a beam unit, so that the low-frequency band gap is widened, and the vibration attenuation is enhanced. The structure is better in geometric nonlinearity, can generate additional damping and mass, and effectivelyimproves low-frequency vibration characteristics of a system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Semiconductor laser device
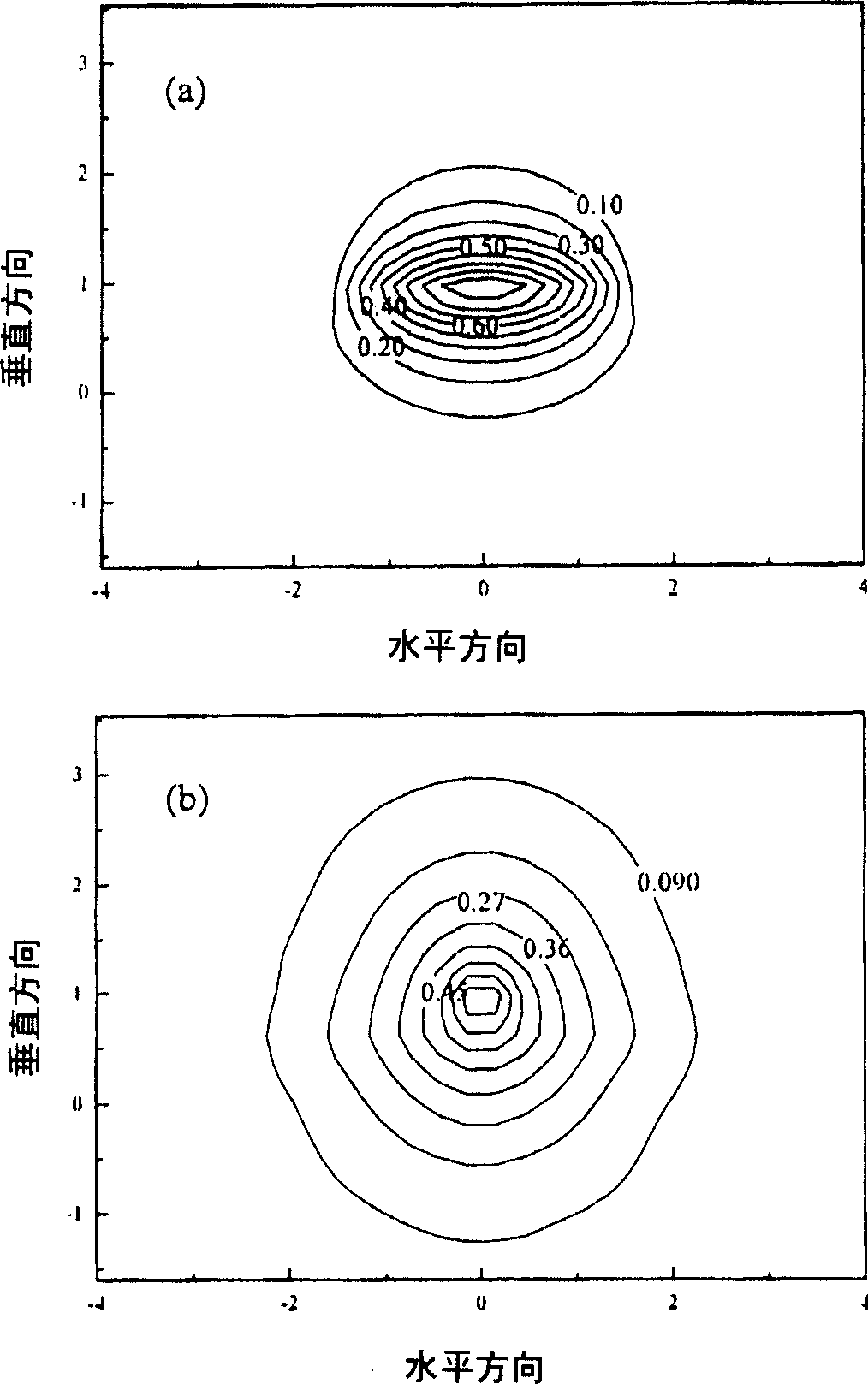
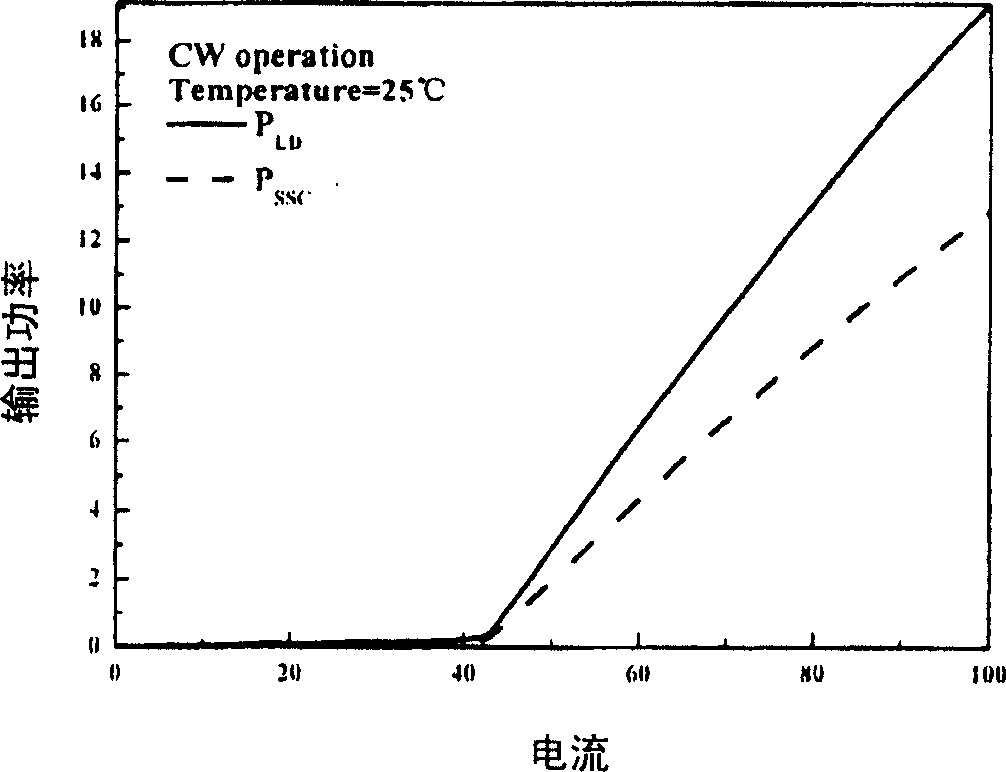
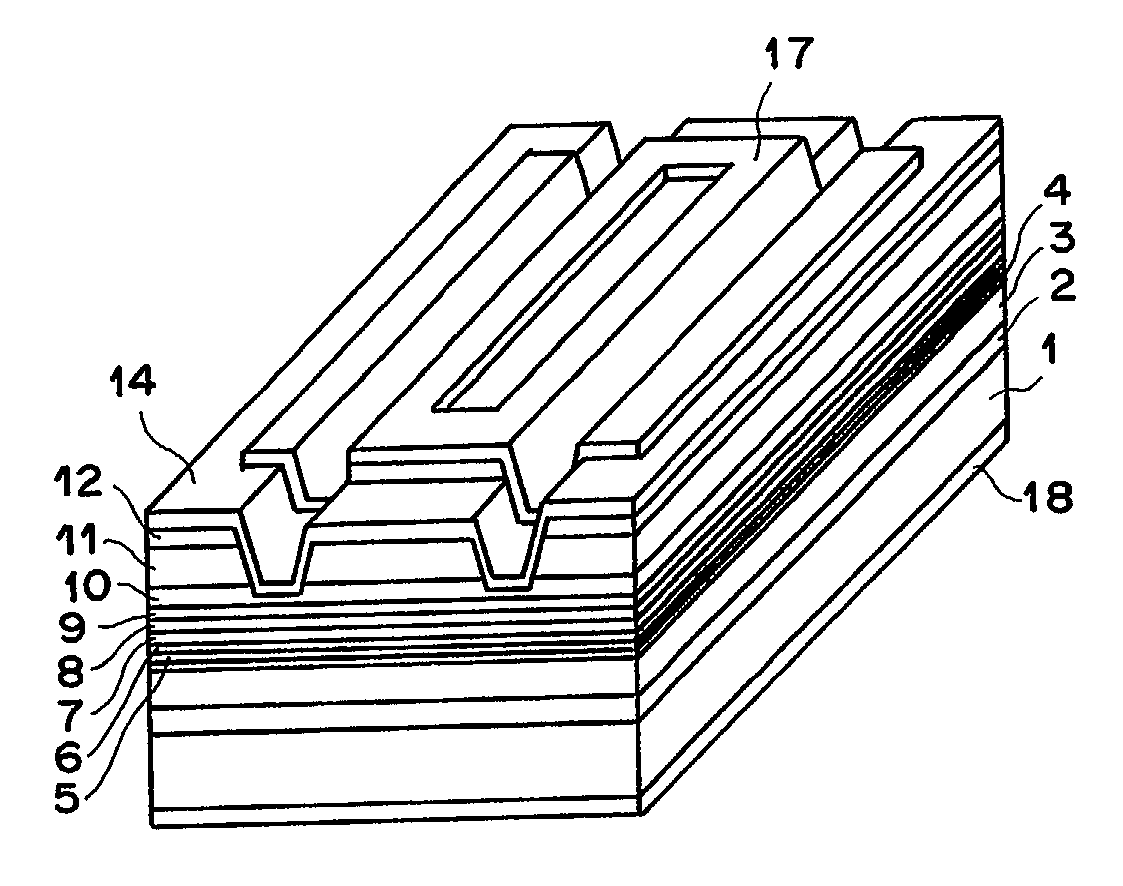
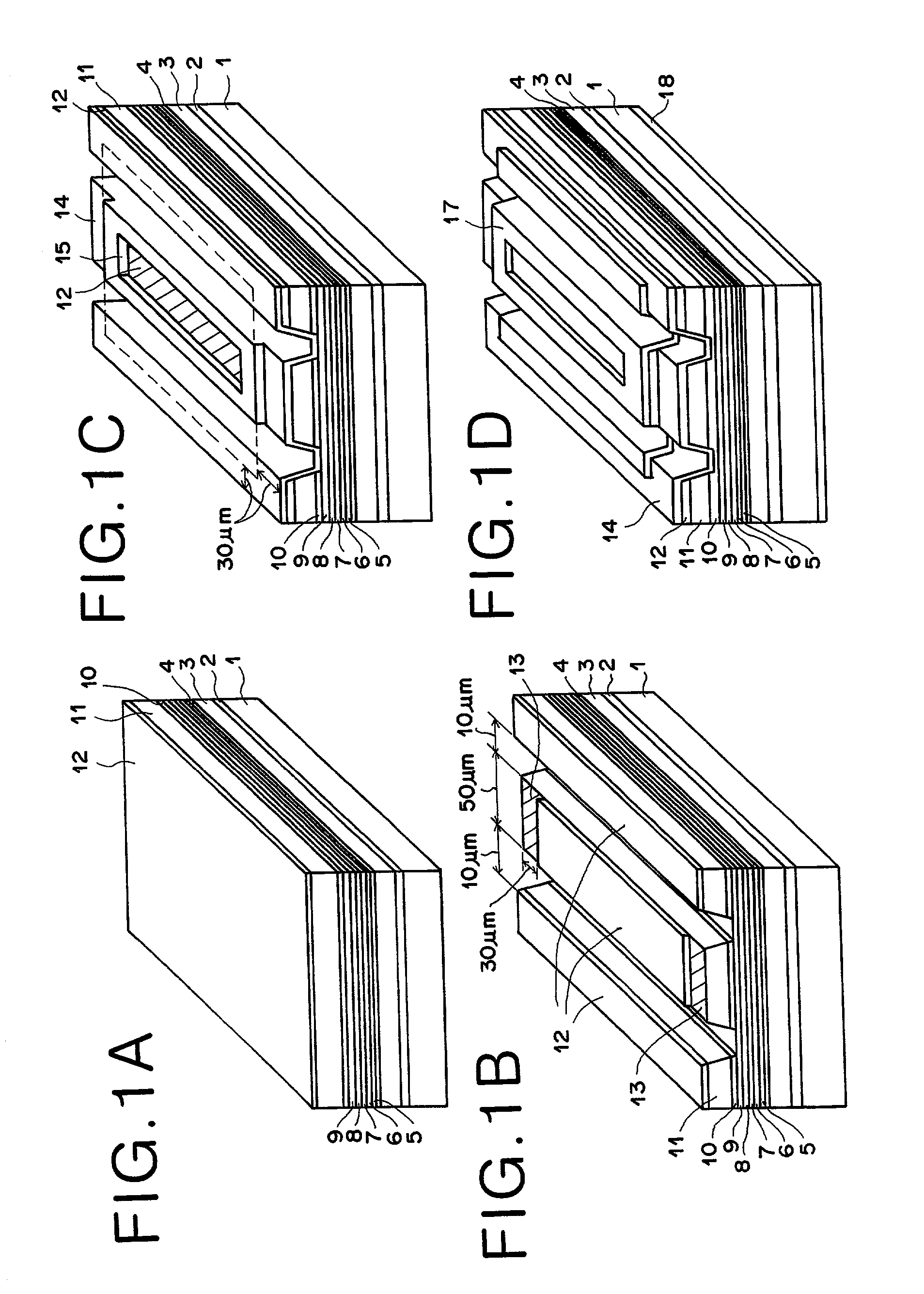
InactiveUS6744797B2High reliability regarding durabilityIncrease the bandgapLaser optical resonator constructionLaser active region structureTensile strainQuantum well
A semiconductor laser device improves reliability during high-power oscillation. An n-type GaAs buffer layer, an n-type In0.48Ga0.52P lower cladding layer, an n-type or i-type Inx1Ga1-x1As1-y1Py1 optical waveguide layer, an i-type GaAs1-y2Py2 tensile-strain barrier layer, an Inx3Ga1-3As1-y3Py3 compressive-strain quantum-well active layer, an i-type GaAs1-y2Py2 tensile-strain barrier layer, a p-type or i-type Inx1Ga1-x1As1-y1Py1 upper optical waveguide layer, a p-type In0.48Ga0.52P first upper cladding layer, a GaAs etching stop layer, a p-type In0.48Ga0.52P second upper cladding layer, and a p-type GaAs contact layer are grown on a plane of an n-type GaAs substrate. Two ridge trenches are formed on the resultant structure, and current non-injection regions are formed by removing the p-type GaAs contact layer in portions extending inwardly by 30 mum from cleavage positions of edge facets of the resonator on a top face of a ridge portion between the ridge trenches.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
DRAM with high K dielectric storage capacitor and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060151822A1Minimizing contributionLow dielectric constantTransistorSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryEngineering
A dynamic random access memory cell that includes a transistor formed in a semiconductor body. A capacitor is coupled to the transistor and includes a first capacitor plate formed from silicon. A metal layer is adjacent to and electrically coupled to the first capacitor plate. A capacitor dielectric layer is adjacent to the metal layer. The capacitor dielectric layer comprises material having a dielectric constant greater than about 5. A second capacitor plate is adjacent to the capacitor dielectric. The capacitor can be either a trench capacitor or a stacked capacitor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Deep-ultraviolet photoelectric detector of amorphous gallium oxide-based thin film transistor
InactiveCN109742180AIncrease the bandgapStrong breakdown resistanceSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a deep-ultraviolet photoelectric detector of an amorphous gallium oxide-based thin film transistor. The deep-ultraviolet photoelectric detector comprises the thin film transistor, wherein the transistor comprises a substrate, a gate electrode, a gate dielectric layer, a channel layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode, the channel layer is an amorphous gallium oxide-based thin film, the thin film transistor is of a bottom gate structure, the gate electrode is arranged on the substrate, the gate dielectric layer covers the gate electrode, the channel covers an upper part of the gate dielectric layer, the source and the drain are respectively arranged at two ends of the channel layer, or the thin film transistor is of a top gate structure, the channel layer covers the substrate, the gate dielectric layer covers an upper part of the channel layer, the source electrode and the drain electrode are respectively arranged at two ends of the gate dielectric layer,and the gate electrode is arranged on the gate dielectric layer. The deep-ultraviolet photoelectric detector provided by the invention has the advantages of relatively high response and low power consumption under irradiation of deep ultraviolet light (320 nanometers), and moreover, the fabrication method is simple, large-area integration can be achieved, and the deep-ultraviolet photoelectric detector is compatible with a flexible substrate.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
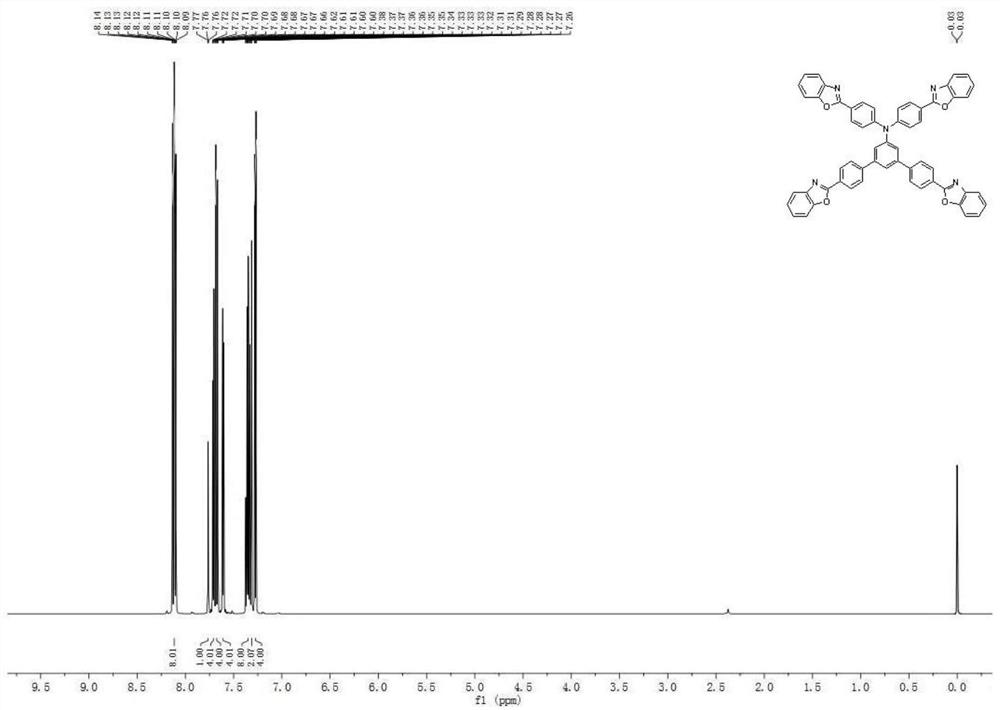
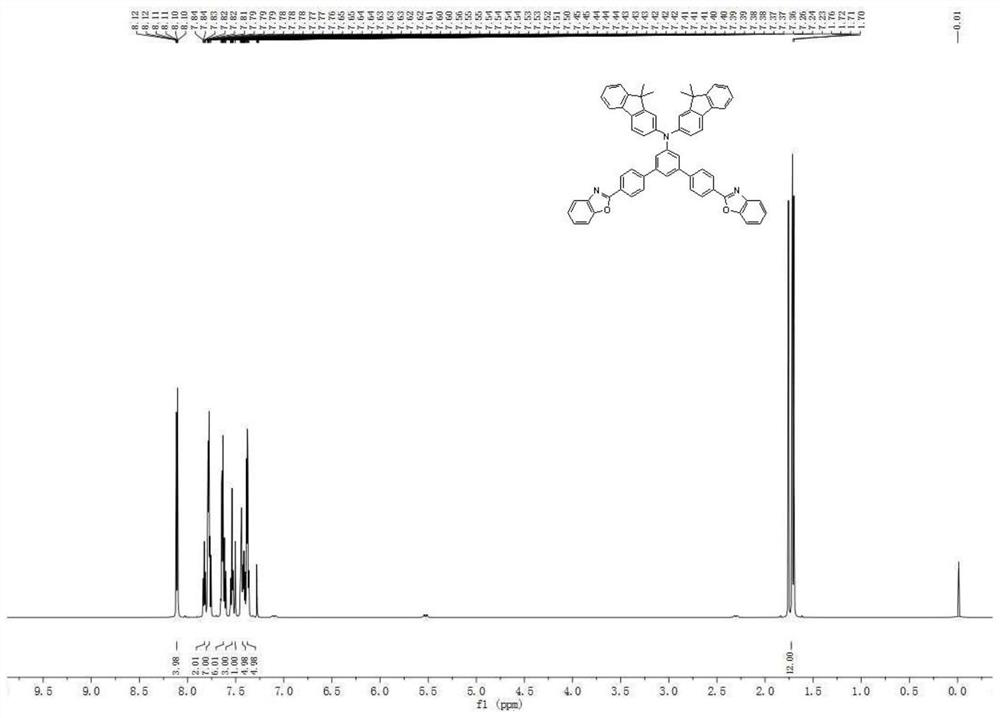
Triarylamine compound and organic light-emitting device thereof
ActiveCN111943902AIncrease the bandgapHigh refractive indexOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesBenzoxazoleOrganic light emitting device
The invention provides a triarylamine compound and an organic light-emitting device thereof, and belongs to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. The triarylamine compound is a compound formed by bonding triarylamine, benzoxazole and / or benzothiazole and / or benzimidazole and / or benzotriazole on a benzene ring serving as a mother nucleus, has a high refractive index, can reduce total reflection of light in a device, greatly improves the light extraction efficiency of the device, and has a wide application prospect. The triarylamine compound has strong rigidity, good thermal stability and good film-forming property, can effectively isolate water and oxygen outside the device and effectively prolong the service life of the device, and is a covering layer material with excellent performance. The triarylamine compound provided by the invention is used as a covering layer to be applied to an organic light-emitting device, and the organic light-emitting device has good light-emitting efficiency and long service life.
Owner:CHANGCHUN HYPERIONS TECH CO LTD
Method for forming semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by once epitaxy
InactiveCN1756008AReduce pollutionLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersTime extensionSemiconductor package
Disclosed a method for one time extension forming the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: (1), on the N type indium phosphide substrate, extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a 2.4 ª–m indium phosphide space layer, a lower light-limited layer of active region, a compression strain quanta active region, a upper light-limited layer, a P type indium phosphide envelope, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; (2), utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of laser and mode spot switch; (3) utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape; (4), growing the SiO2 insulating layer and opening a electrode window; (5) decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡600ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
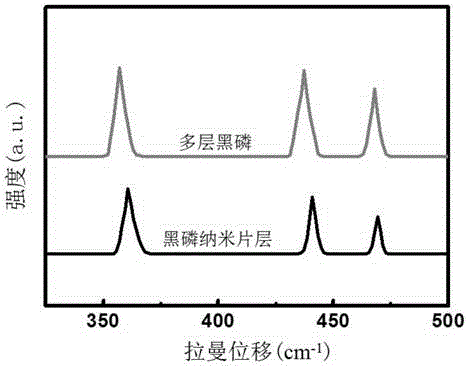
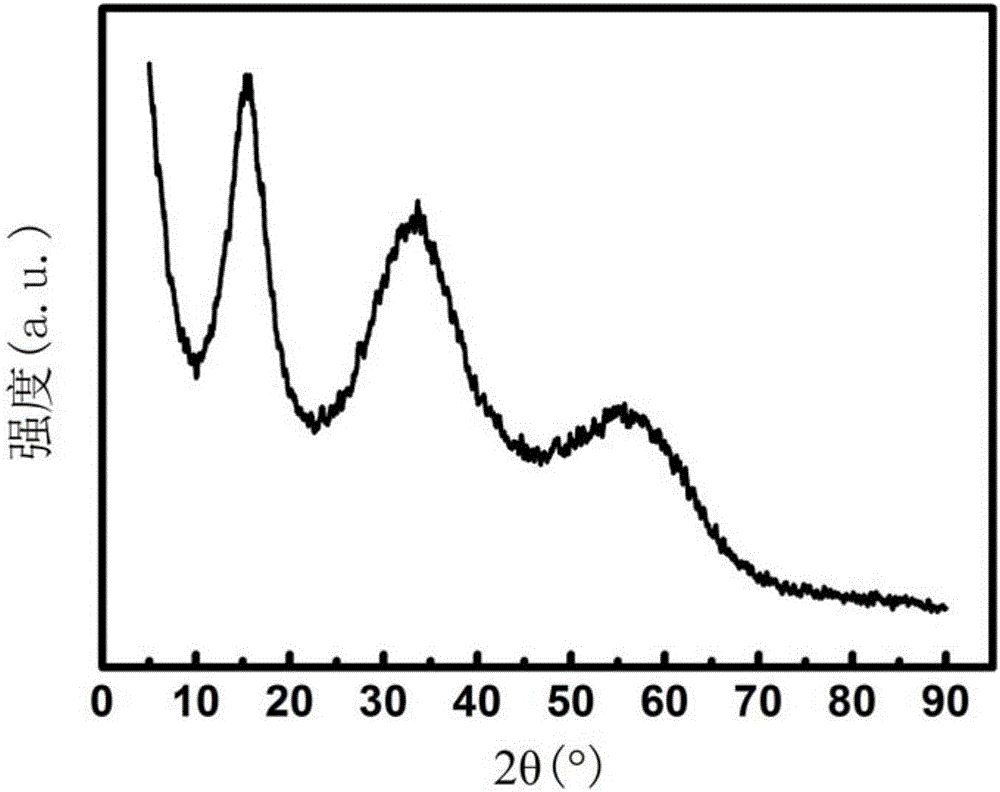
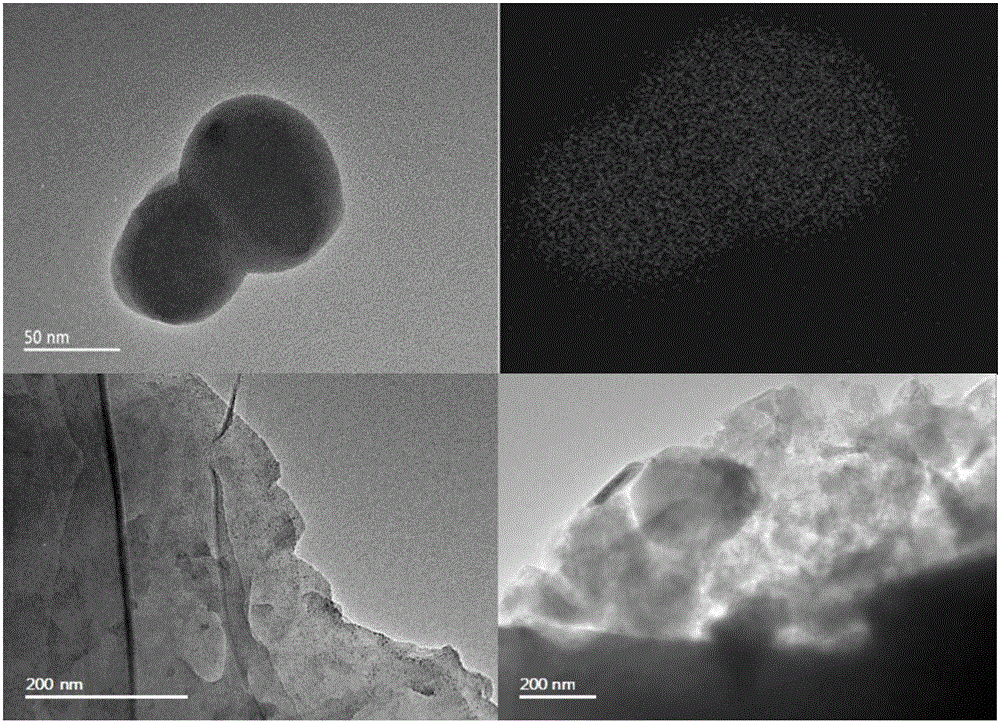
Preparation method of black phosphorus nano lamina for photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater
ActiveCN106586987ASimple preparation processImprove production efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsSurface oxidationCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a black phosphorus nano lamina for photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) preparing multilayer black phosphorus, namely grinding red phosphorus without a surface oxidation layer in a mortar, and then performing mechanical ball milling to obtain the multilayer black phosphorus; and (2) preparing the black phosphorus nano lamina, namely adding the multilayer black phosphorus and a surfactant into water together, performing primary ultrasonic treatment and primary centrifugation, then collecting supernatant, adding the supernatant into water, stirring the materials uniformly, then performing secondary ultrasonic treatment, performing secondary centrifugation to obtain a solid deposit, and drying the solid deposit to obtain the black phosphorus nano lamina. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method provided by the invention is simple in preparation process, high in preparation efficiency, and suitable for large-scale production, and the prepared black phosphorus nano lamina has a higher specific surface area and band gap and photocatalytic activity, and can be used for performing photocatalytic efficient degradation on coloring agents including methylene blue in the dye wastewater.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Laser diode and semiconductor light-emitting device producing visible-wavelength radiation
InactiveUS6983004B2Enhance layeringIncrease the bandgapOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRadiationLaser diode
A laser diode includes a substrate having a lattice constant of GaAs or between GaAs and GaP, a first cladding layer of AlGaInP formed on the substrate, an active layer of GaInAsP formed on the first cladding layer, an etching stopper layer of GaInP formed on the active layer, a pair of current-blocking regions of AlGaInP formed on the etching stopper layer so as to define a strip region therebetween, an optical waveguide layer of AlGaInP formed on the pair of current-blocking regions so as to cover the etching stopper layer in the stripe region, and a second cladding layer of AlGaInP formed on the optical waveguide layer, wherein the current-blocking regions having an Al content substantially identical with an Al content of the second cladding layer.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for making semiconductor laser and spot-size converter by double waveguide technology
InactiveCN1756009AReduce the number of growthLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor packageIntrinsics
Disclosed a method for utilizing the dual-waveguide technology to manufacture the semiconductor laser and mode spot switch comprises following steps: on the N type indium phosphide substrate, sequentially extending growing the N type indium phosphide breaker, a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a active region, and a thinner indium phosphide intrinsic layer, wherein, the indium phosphide intrinsic layer can prevent the oxidation of active region; removing the highest indium phosphide intrinsic layer, partly covering the laser with SiO2, and utilizing the wet corrosion process to etch the upper carinate shape of mode spot switch; utilizing the auto-alignment process to etch the lower carinate shape which comprises a lower waveguide layer, a space layer, a second growth P type indium phosphide coating layer, and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; utilizing the SiO2 to partly cover the mode spot switch and etching the upper and lower carnate shapes again while the upper carinate shape comprises a active region, a P type indium phosphide coating layer and a high doping P type indium gallium arsenide ohmic electrode contract layer; and decreasing the substrate of extended plate to 100 ª–m, and manufacturing P / N electrodes to be scribed into the tube core of 250í‡500ª–m.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20020146051A1High reliability regarding durabilityIncrease the bandgapLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionTensile strainQuantum well
A semiconductor laser device is disclosed that improves reliability during high-power oscillation. On a plane of an n-type GaAs substrate, grown are an n-type GaAs buffer layer, an n-type In0.48Ga0.52P lower cladding layer, an n-type or i-type Inx1Ga1-x1As1-y1Py1 optical waveguide layer, an i-type GaAs1-y2Py2 tensile-strain barrier layer, an Inx3Ga1-x3As1-y3Py3 compressive-strain quantum-well active layer, an i-type GaAs1-y2Py2 tensile-strain barrier layer, a p-type or i-type Inx1Ga1-x1As1-y1Py1 upper optical waveguide layer, a p-type In0.48Ga0.52P first upper cladding layer, a GaAs etching stop layer, a p-type In0.48Ga0.52P second upper cladding layer and a p-type GaAs contact layer. Two ridge trenches are formed on the resultant structure, and current non-injection regions are formed by removing the p-type GaAs contact layer in portions extending inwardly by 30 mum from cleavage positions of edge facets of the resonator on a top face of a ridge portion between the ridge trenches.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
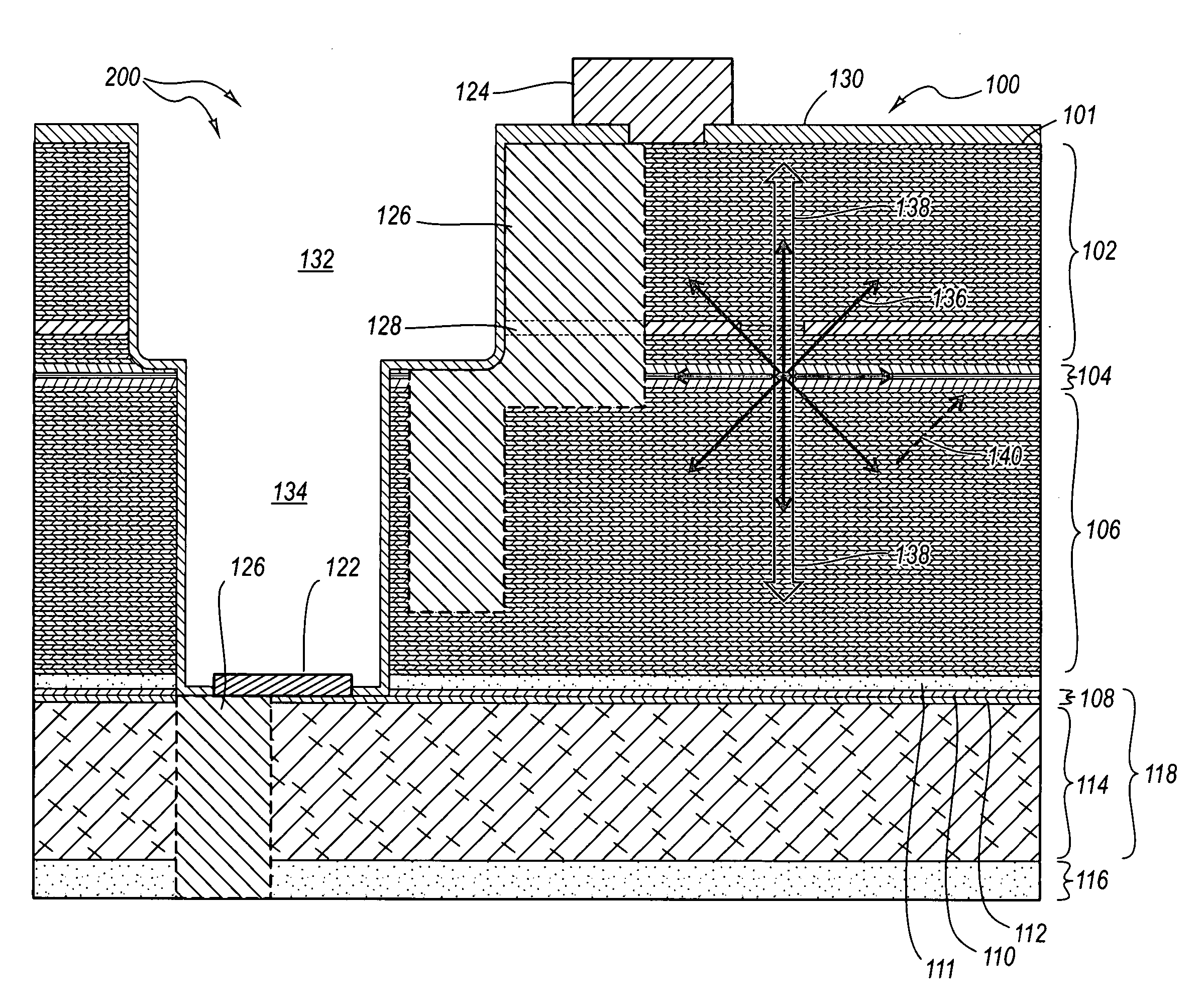
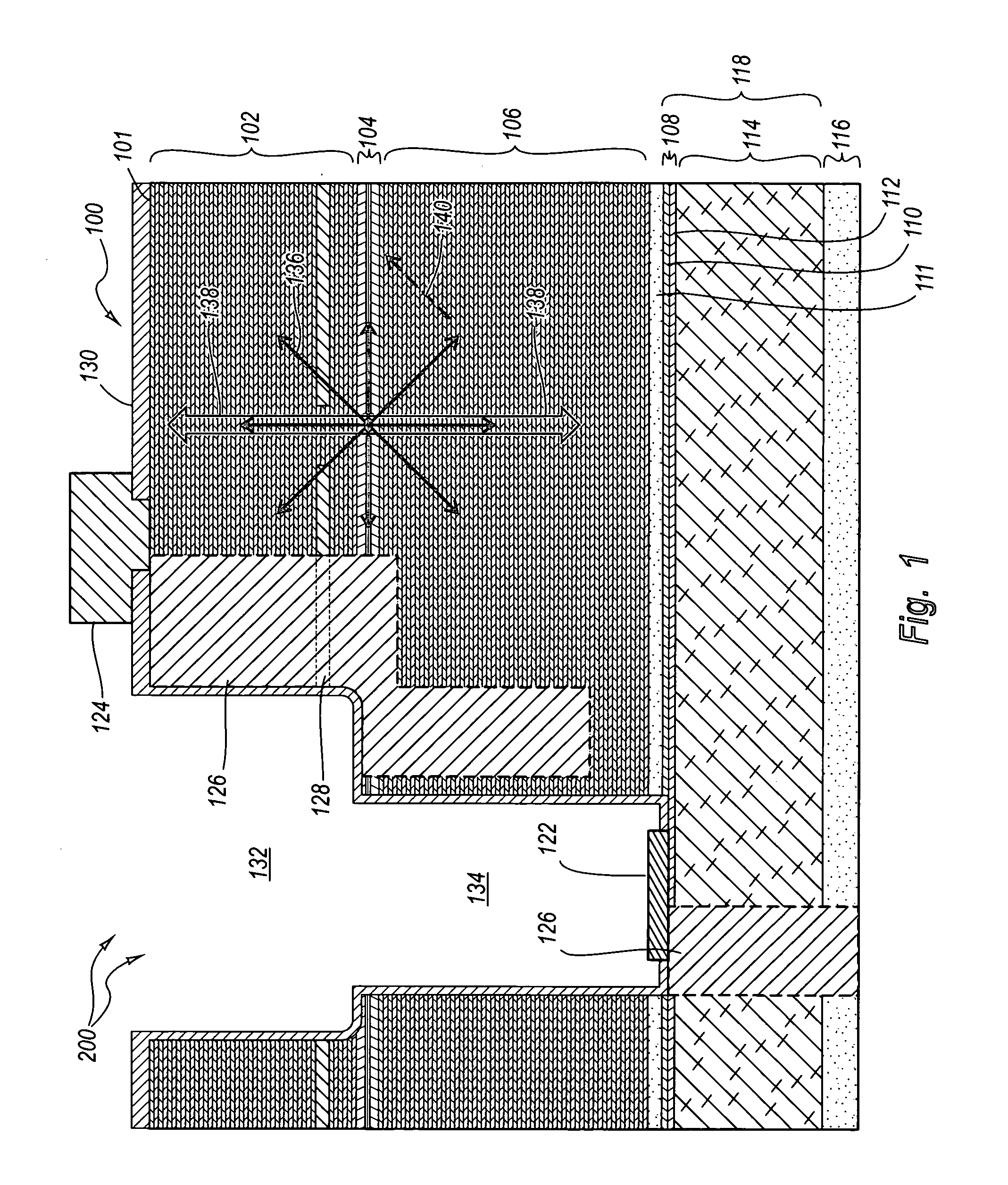
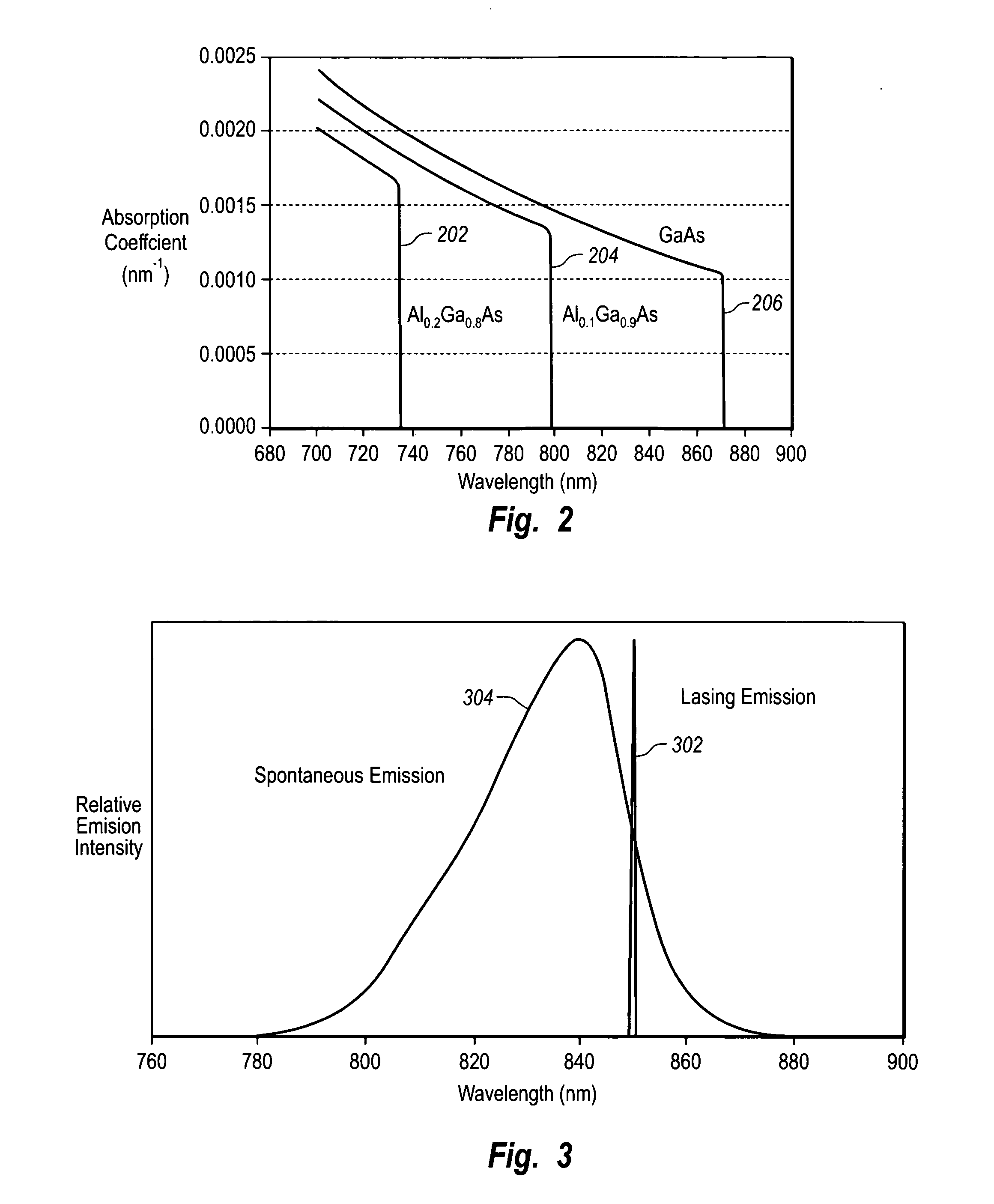
Photodiode bandgaps for reducing spontaneous emissions in photodiodes
ActiveUS20050286585A1Degradation in responsivityIncrease the bandgapLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhotoluminescencePhotodiode
An optical structure that reduces the effects of spontaneous emissions from the active region of a laser. An optical structure includes optimizations to reduce the effects of spontaneous emissions. The optical structure includes a VCSEL with top and bottom DBR mirrors and an active region connected to the mirrors. The optical structure further includes a photodiode connected to the VCSEL. One or more optimizations may be included in the optical structure including optically absorbing materials, varying the geometry of the structure to change reflective angles, using optical apertures, changing the reflectivity of one or more mirrors, changing the photodiode to be more impervious to spontaneous emissions, and using ion implants to reduce photoluminescence efficiency.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Semiconductor device and method for forming the same
InactiveUS20050104065A1Lower resistancePrevent leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLow voltage
A semiconductor device and a method for forming the same are disclosed. The semiconductor device comprising an insulated gate field effect transistor provided with a region having added thereto an element at least one selected from the group consisting of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, said region having established at either or both of the vicinity of the boundary between the drain and the semiconductor layer under the gate electrode and the vicinity of the boundary between the source and the semiconductor layer under the gate electrode for example by ion implantation using a mask. It is free from the problems of reverse leakage between the source and the drain, and of throw leakage which occurs even at a voltage below the threshold ascribed to the low voltage resistance between the source and the drain.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
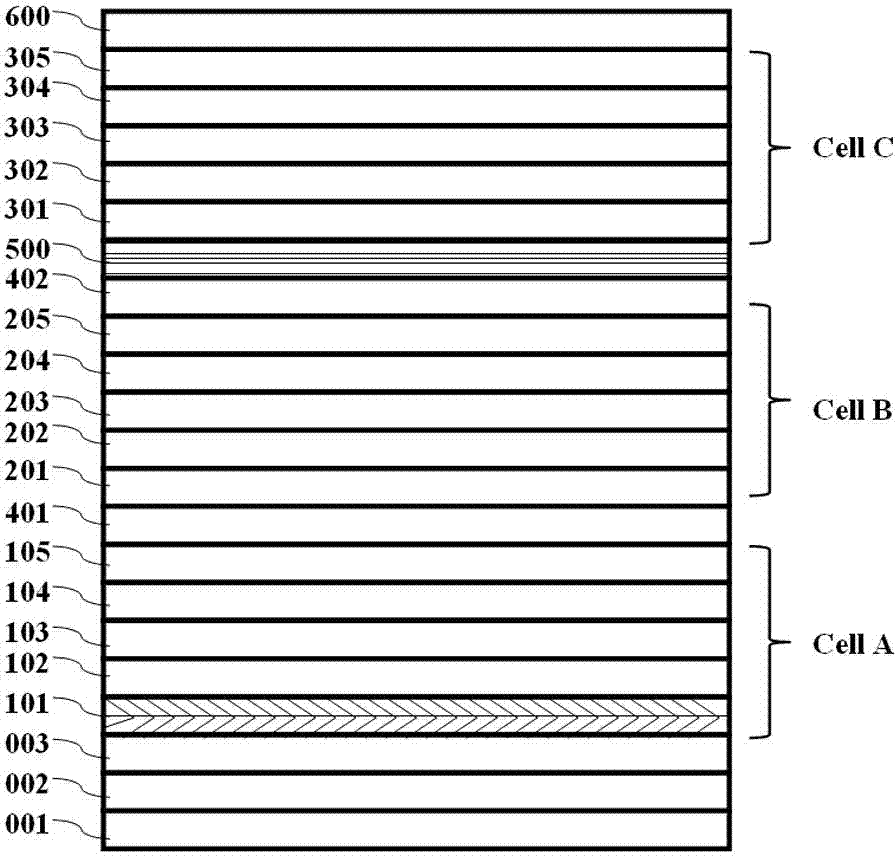
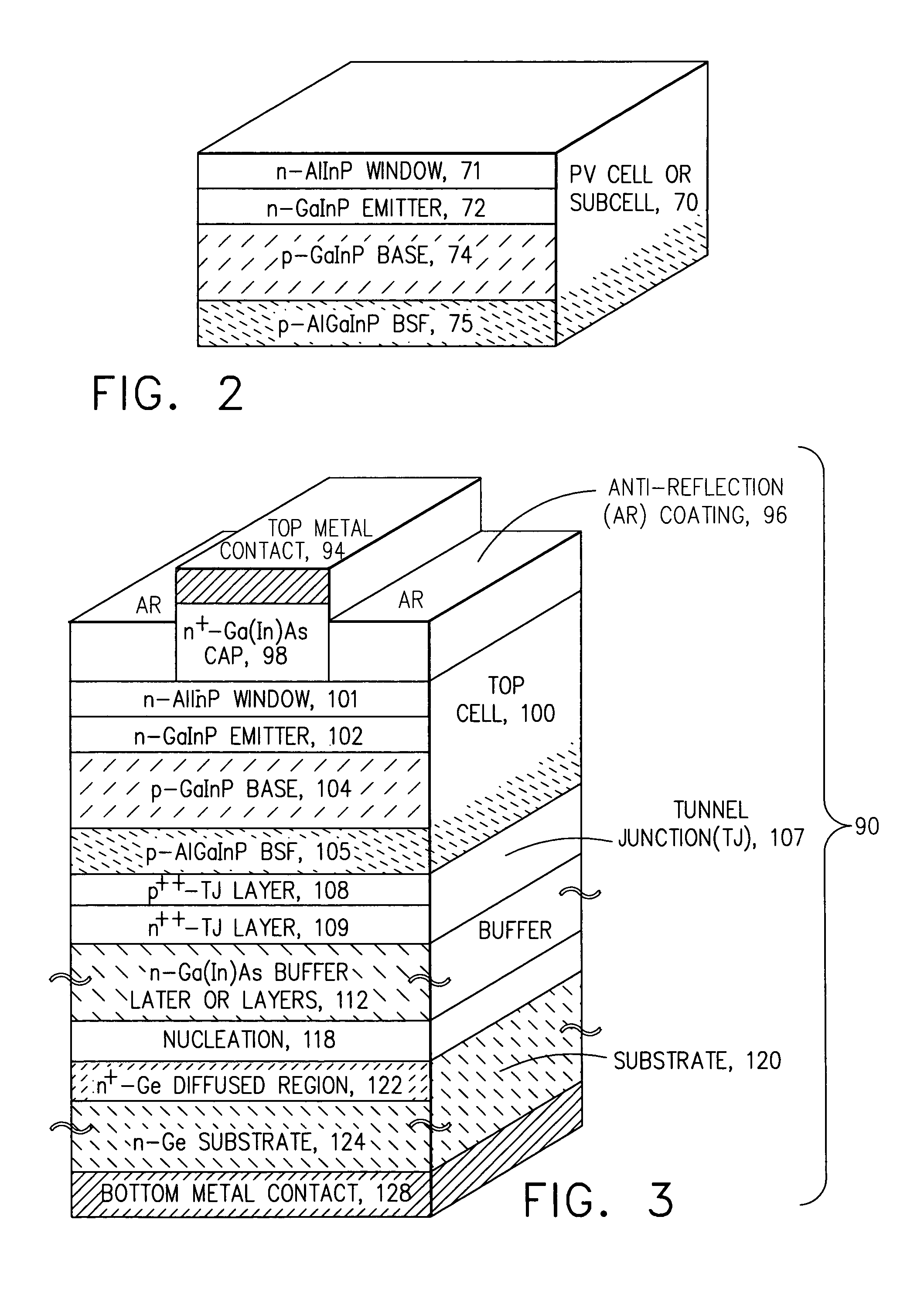
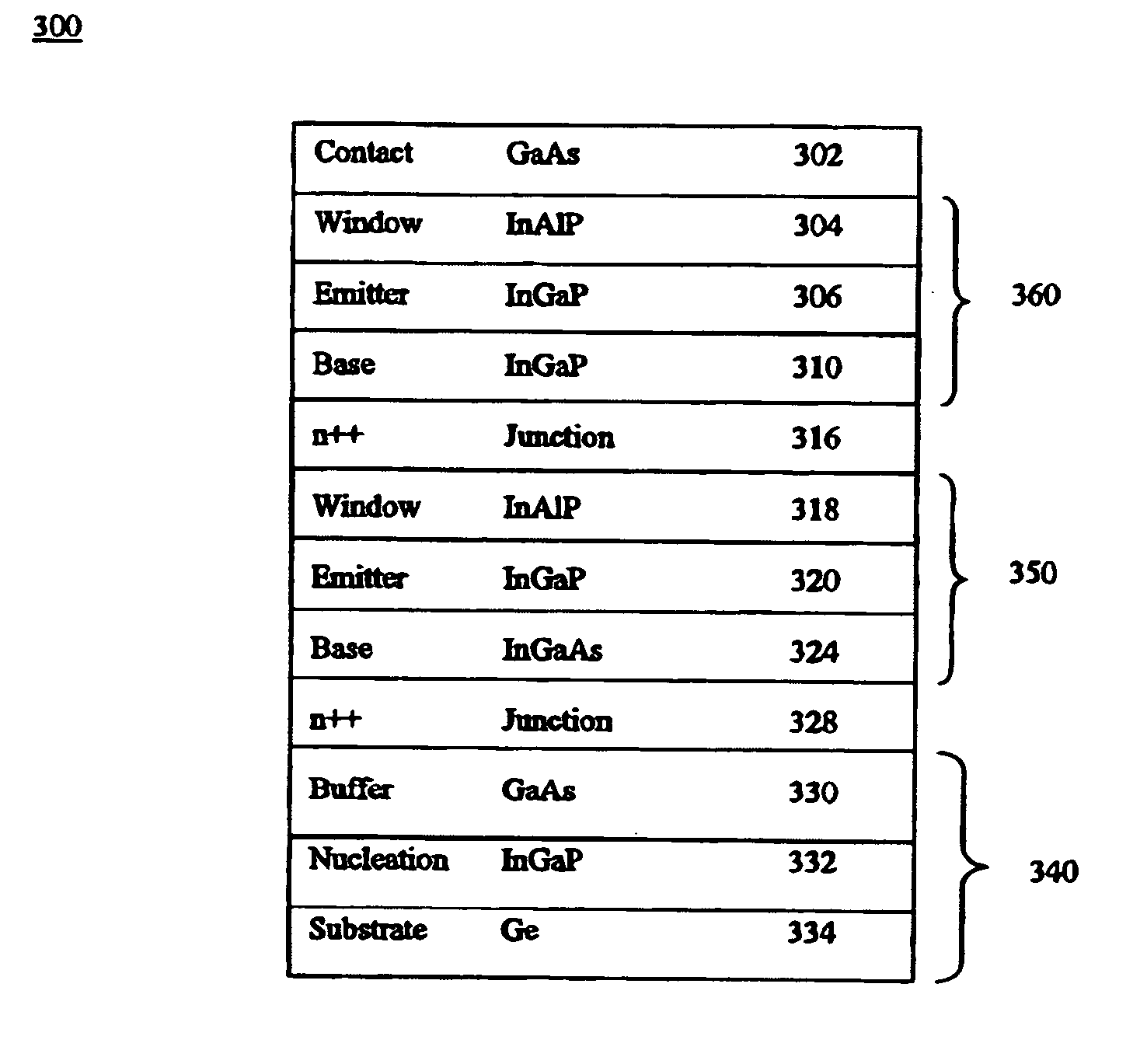
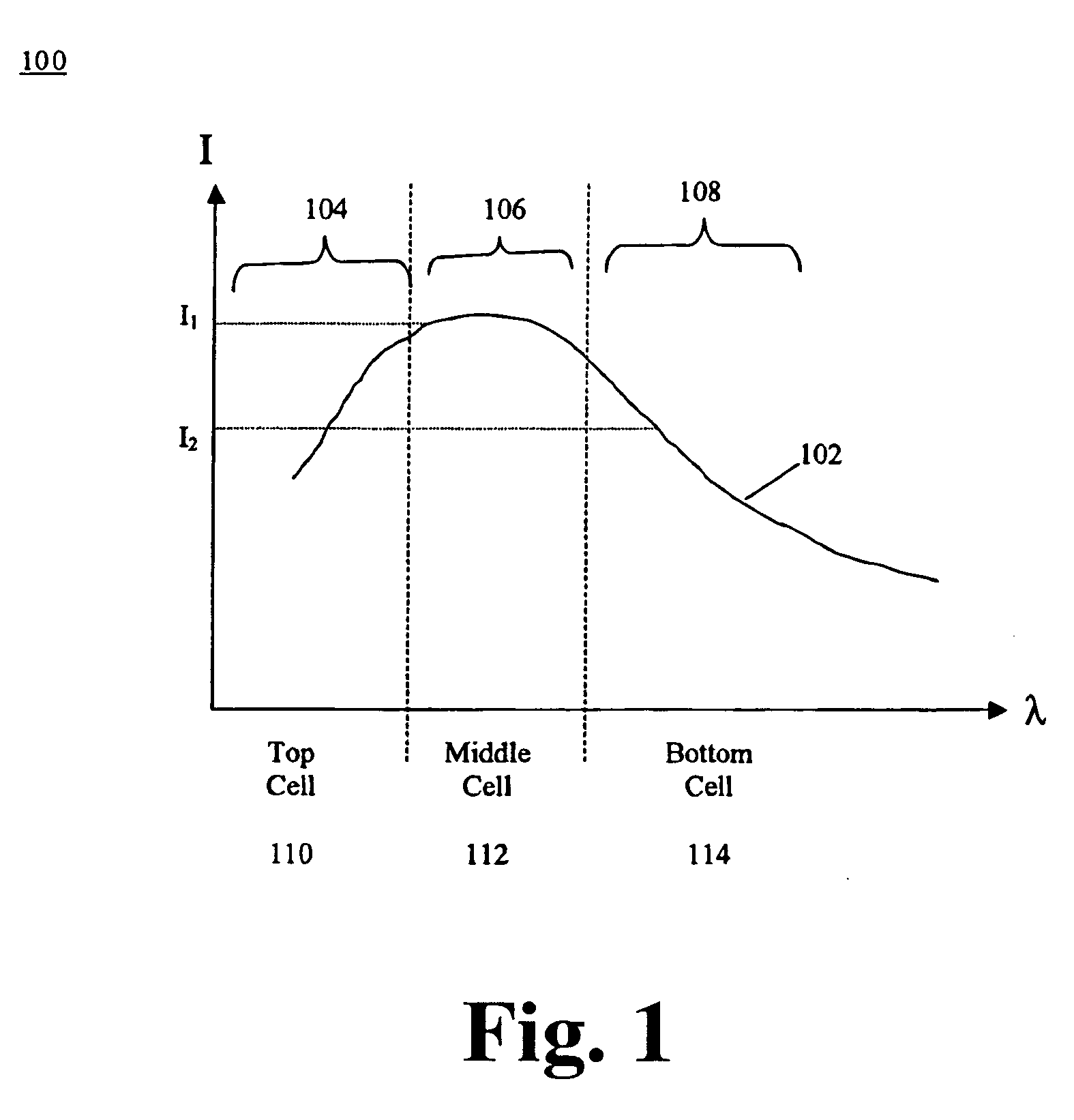
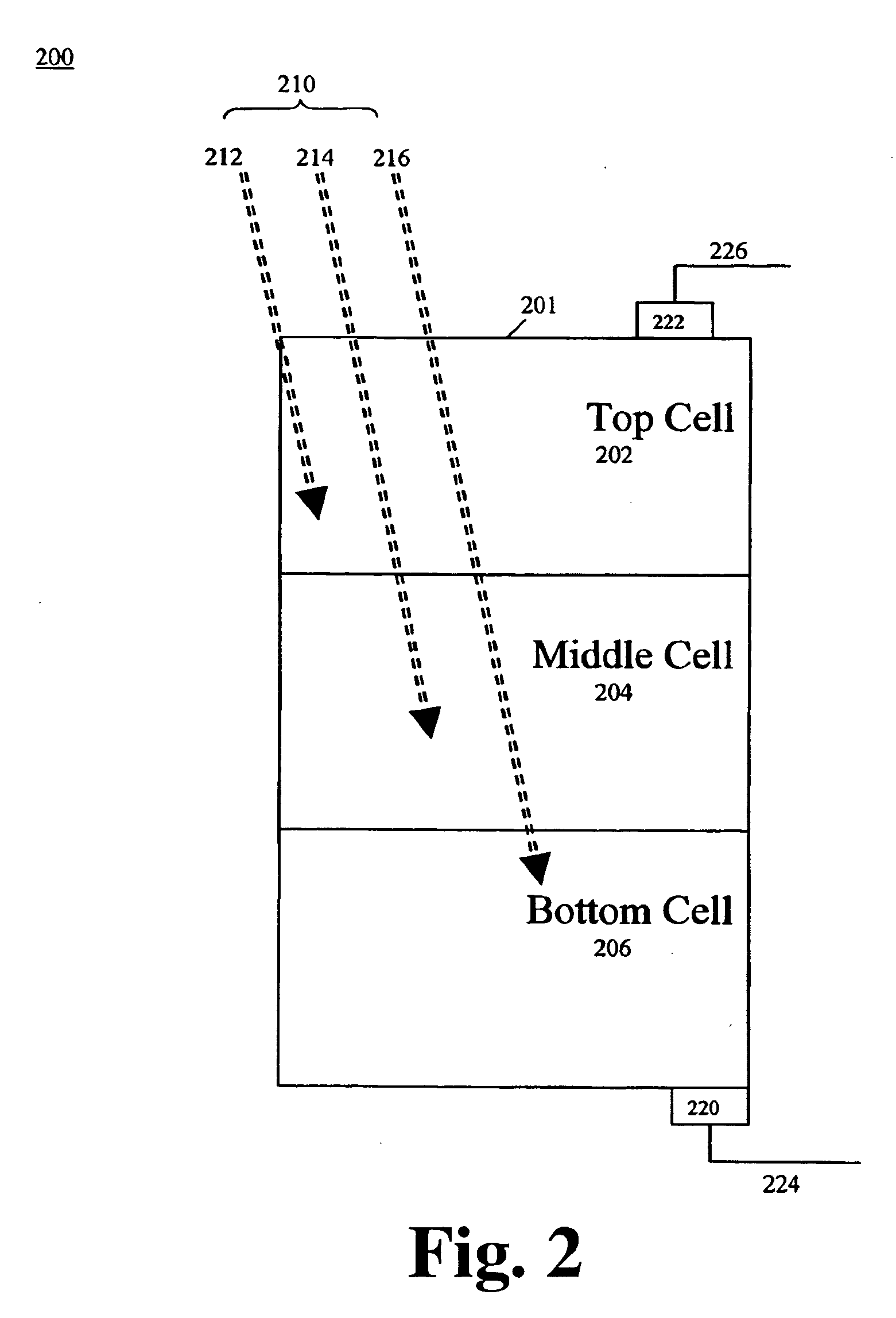
Method and apparatus of multiplejunction solar cell structure with high band gap heterojunction middle cell
ActiveUS20050199281A1Increase the bandgapFinal product manufacturePV power plantsHeterojunctionSolar cell
A method and a multijunction solar device having a high band gap heterojunction middle solar cell are disclosed. In one embodiment, a triple-junction solar device includes bottom, middle, and top cells. The bottom cell has a germanium (Ge) substrate and a buffer layer, wherein the buffer layer is disposed over the Ge substrate. The middle cell contains a heterojunction structure, which further includes an emitter layer and a base layer that are disposed over the bottom cell. The top cell contains an emitter layer and a base layer disposed over the middle cell.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
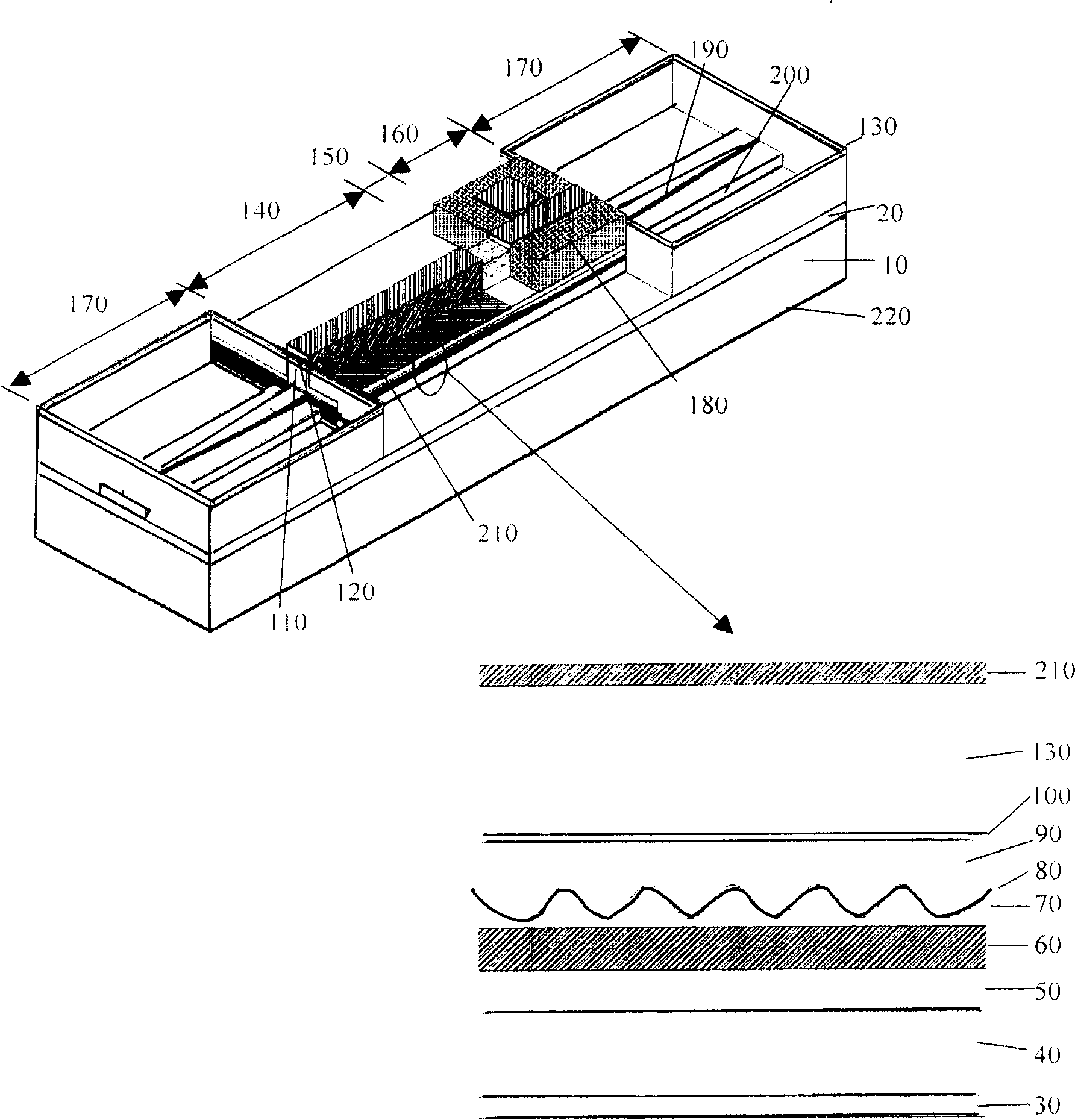
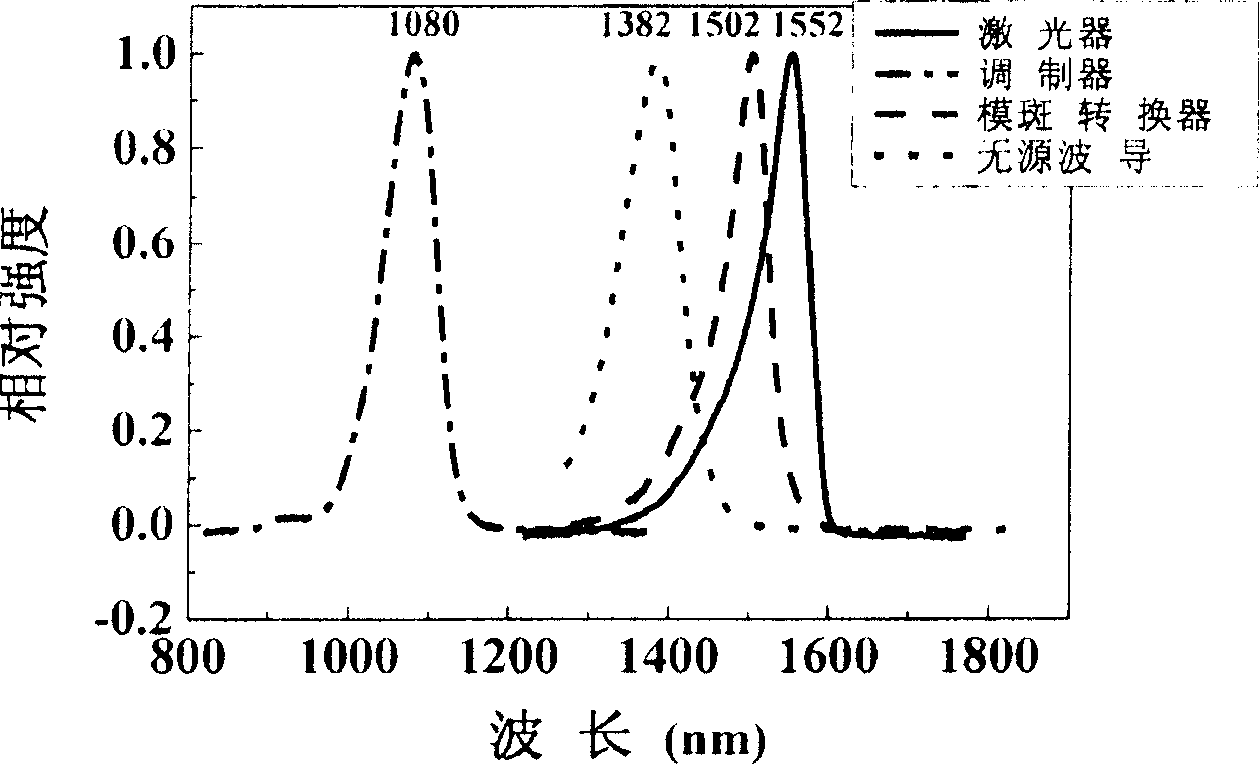
Integration method for electric absorption modulation laser and modular spot converter
InactiveCN1909309AReduce the number of growthHas an effectLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhosphate ionSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to an integration method of electric adsorption modulation laser and mode speckle converter, which comprises: growing n-type indium phosphate buffer layer on the substrate; corroding the upper 1.1Q layer on the chip, to grow buffer layer; growing silica dioxide protective layer on the whole chip, and corroding the silica dioxide protective layer at two ends of mode speckle converter; pouring low-energy phosphate ion; growing the silica dioxide protective layer again; heating, keeping warm, anneal on the chip; corroding silica dioxide protective layer; using relative light etching plate to mask the laser and modulator, to form the upper ridge and lower ridge on the converter; growing p-type indium phosphate and indium gallium arsenic phosphate etching stop layer; etching ridge pilot structure; depositing medlin at two sides of laser and modulator; opening the electrode windows of laser and modulator; etching the electrode images on the laser and modulator to splash the P electrode and remove the P electrode; extending the substrate, and splashing n electrode; slicing the sample to form tubular chip.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gallium-nitride based light emitting diode light emitting layer structure
InactiveUS20060054897A1Improve lighting efficiencyPromote growthNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesInter layerEffect light
A number of light-emitting layer structures for the GaN-based LEDs that can increase the lighting efficiency of the GaN-based LEDs on one hand and facilitate the growth of epitaxial layer with better quality on the other hand are provided. The light-emitting layer structure provided is located between the n-type GaN contact layer and the p-type GaN contact layer. Sequentially stacked on top of the n-type GaN contact layer in the following order, the light-emitting layer contains a lower barrier layer, at least one intermediate layer, and an upper barrier layer. That is, the light-emitting layer contains at least one intermediate layer interposed between the upper and lower barrier layers. When there are multiple intermediate layers inside the light-emitting layer, there is an intermediate barrier layer interposed between every two immediately adjacent intermediate layers.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
UV light emitting diode
ActiveCN105322064AReduce the driving voltageThe overall thickness is thinSemiconductor devicesPolymer light emitting diodesVoltage
A UV light emitting diode having improved internal quantum efficiency is provided. The UV light emitting diode includes: an n-type contact layer including an AlGaN layer or an AlInGaN layer; a p-type contact layer including a AlGaN layer or an AlInGaN layer; and an active layer of a multi-quantum well structure. The active area of the multi-quantum well structure includes barrier layers and well layers which are alternately stacked. The well layers include electrons and holes present according to probability distributions thereof. The barrier layers are formed of AlInGaN or AlGaN and have an Al content of 10% to 30%. At least one of the barrier layers has a smaller thickness than of the well layers and at least one of the barrier layers has a thickness and a band gap preventing electrons and holes injected into and confined in a well layer adjacent to the barrier layer from spreading into another adjacent well layer. So driving voltage of the UV light emitting diode is reduced, and the internal quantum efficiency is improved.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Nano silicon window layer with gradient band gap characteristic and preparation method thereof
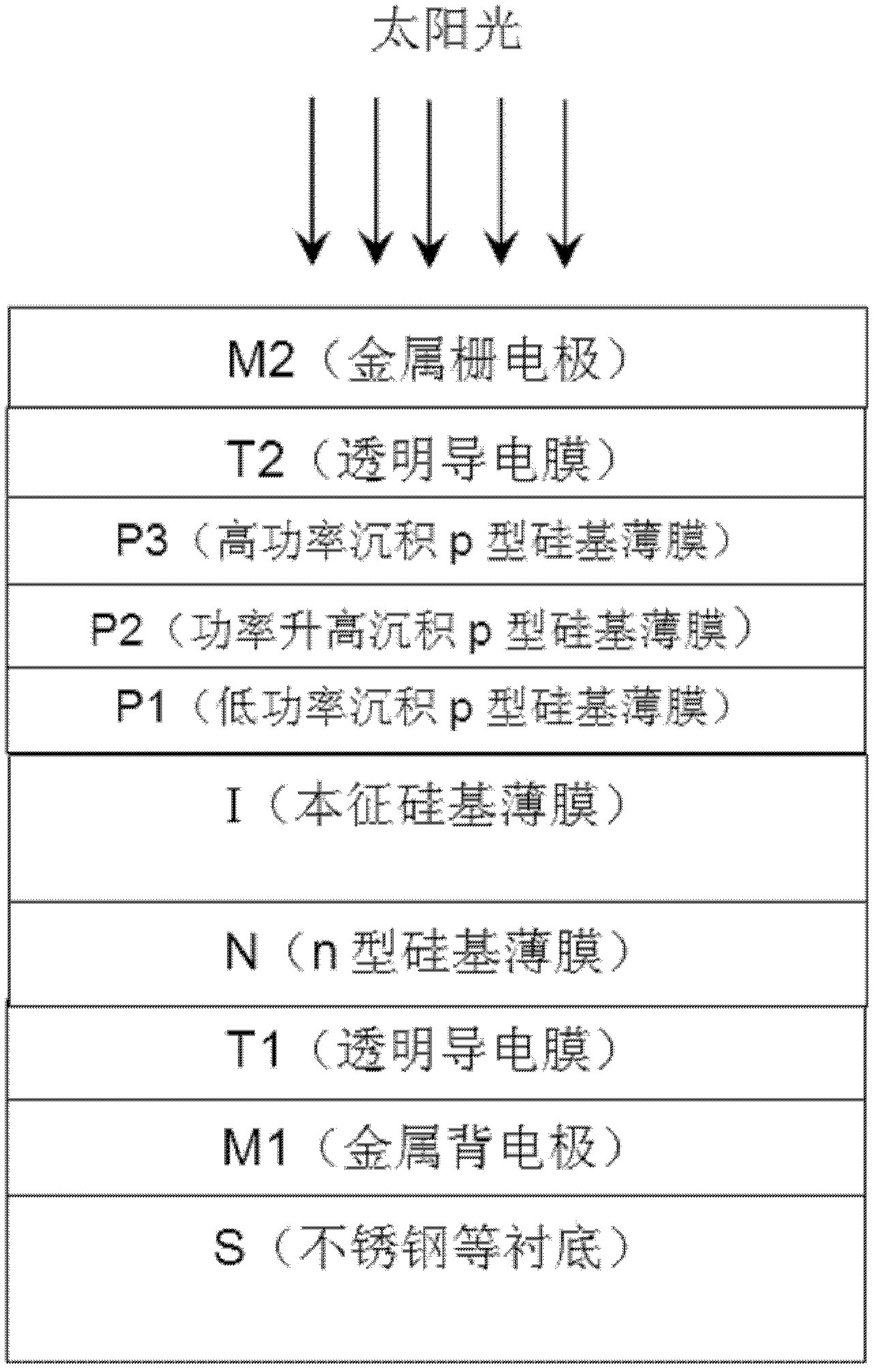
InactiveCN102569481ALittle bombardmentReduce compoundingFinal product manufactureNanoopticsSpectral responseP type silicon
The invention relates to a nano silicon window layer with the gradient band gap characteristic, which is formed by depositing on the surface of a sample to be processed, wherein the surface of the sample to be processed is sequentially stacked with a metal back electrode M, a transparent conductive back electrode T1, an n-type Si-based thin film N and an intrinsic Si-based thin film I. The nano silicon window layer is formed by sequentially stacking a silicon thin film P1, a silicon thin film P2 and a silicon thin film P3. A preparation method of the nano silicon window layer comprises the following steps: depositing the p-type silicon thin film P1 with small thickness under a low glow power; then gradually raising the power and depositing the thin film P2; and finally, and completing the window layer P3 under a high power. The nano silicon window layer has the advantages that when the nano silicon window layer is applied to the window layer of an n-i-p-type silicon-based thin film solar cell, high electric conductance and wide band gap can be acquired, the bombardment of a solar cell i / p interface can be effectively reduced, the band gap matching between an intrinsic layer and the window layer can be implemented and the filling factor, the open-circuit voltage and the spectral response of the solar cell are obviously improved, so that the silicon-based thin film solar cell with high photoelectric conversion efficiency is obtained.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Flip-chip solar cell and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102832274AAvoid damageInhibited DiffusionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionEngineering
The invention discloses a flip-chip solar cell and a manufacture method thereof. In a flip growing procedure of the flip-chip solar cell, a heterojunction window layer is imported in a top cell structure so as to prevent the window layer from being damaged by over etching which probably occurs in a manufacturing process, so that a serious consequence that the performance of the cell is influenced after a single-material window layer is damaged is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS
Semiconductor laser device having inGaAs compressive-strain active layer, GaAsP tensile-strain barrier layers, and InGaP optical waveguide layers
InactiveUS20020122447A1Reduce layeringQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsPhysicsTotal thickness
In a semiconductor-laser device: a compressive-strain quantum-well active layer is made of Inx3Ga1. x3As1-y3Py3 (0<x3<=0.4 and 0<=y3<=0.1); tensile-strain barrier layers made of Inx2Ga1-2AS1-y2P1-y2 (0<=x2<0.49y2 and 0<y2<=0.4)are formed above and under the compressive-strain quantum-well active layer; and optical waveguide layers being made of either p-type or i-type In0.49Ga0.51P are formed above the upper tensile-strain barrier layer and under the lower tensile-strain barrier layer. Preferably, the absolute value of a sum of a first product and a second product is less than or equal to 0.25 nm, where the first product is a product of a strain and a thickness of said compressive-strain active layer, and the second product is a product of a strain of said lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers and a total thickness of the lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
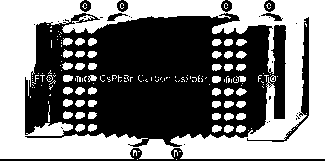
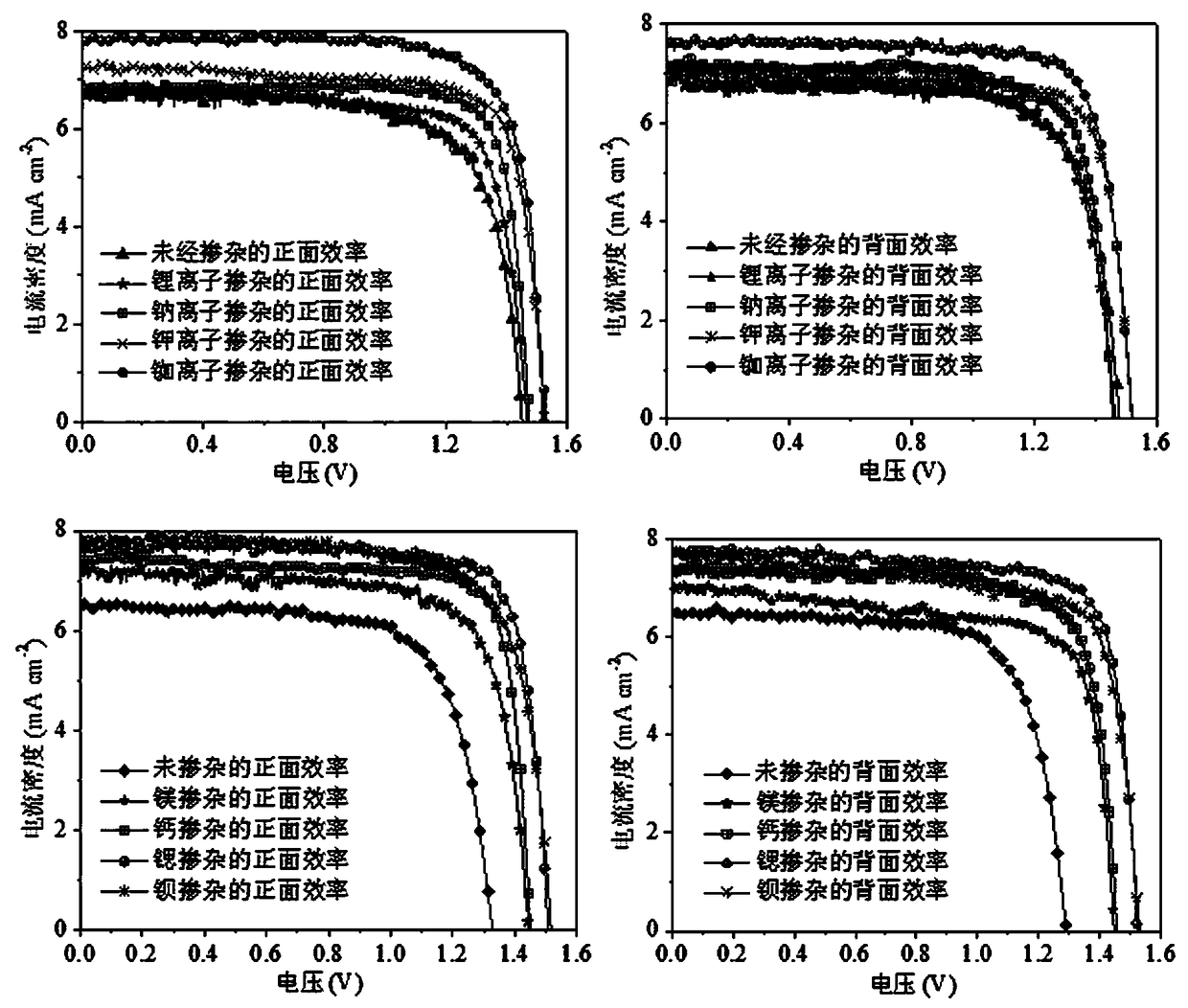
Double-sided inorganic perovskite solar cell doped with alkali metal ions and alkaline earth metal ions and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108963032ATightly boundImprove stabilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesAlkaline earth metalHole transport layer
The invention provides a double-sided inorganic perovskite solar cell doped with alkali metal ions and alkaline earth metal ions and a preparation method and application thereof. An electron transportmaterial is deposited on FTO conductive glass, and then a precursor solution of the perovskite light absorbing material doped with the alkali metal ions and the alkaline earth metal ions is continuously spin-coated so as to form a perovskite light absorbing layer with excellent performance. Finally a carbon electrode is coated in a blading way, and two symmetrical inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite solar cell devices are closely combined by the same carbon electrode through vacuum treatment so as to manufacture the double-sided inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite solar cell. The crystal size of perovskiteis reduced, the band gap is reduced and the photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability of the cell are improved by the kinds and the proportion of the doped alkali metal and alkaline earth metal ions so as to have the advantages of simple preparation method, no hole transport layer, large improvement space of material and technology and the like.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Periodic cavity type vibration isolator with low frequency and broad-band gap and preparation method
ActiveCN105333058AHigh decay rateAdjustable positionRotating vibration suppressionLow frequency bandPhysics
The invention discloses a periodic cavity type vibration isolator with low frequency and a broad-band gap and a preparation method. The vibration isolator comprises two or more than two periodic units. Each periodic unit comprises two thin plate main bodies and a ring cavity scattering body, wherein outer edges of the two thin plate main bodies are connected by virtue of the ring cavity scattering body to form a cavity; and the periodic units are connected through a connecting block scattering body. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting materials to prepare the thin plate main bodies, the ring cavity scattering body and the connecting block scattering body; regulating geometrical parameters of the thin plate main bodies, the ring cavity scattering body and the connecting block scattering body, so that effective band gap frequency of the vibration isolator can cover vibrating frequency of a required vibration isolating environment; checking whether the vibration isolator meets a safety condition or not so as to prepare the periodic cavity type vibration isolator with low frequency and the broad-band gap. The periodic cavity type vibration isolator disclosed by the invention is suitable for isolating low-frequency vibration, can realize vibration isolation within a wide frequency range while keeping corresponding bearing capacity, can form a band gap at a lower-frequency band, and has a boarder band gap, a relatively small dimension, and higher vibration attenuation rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com