Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54results about How to "Further miniaturization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
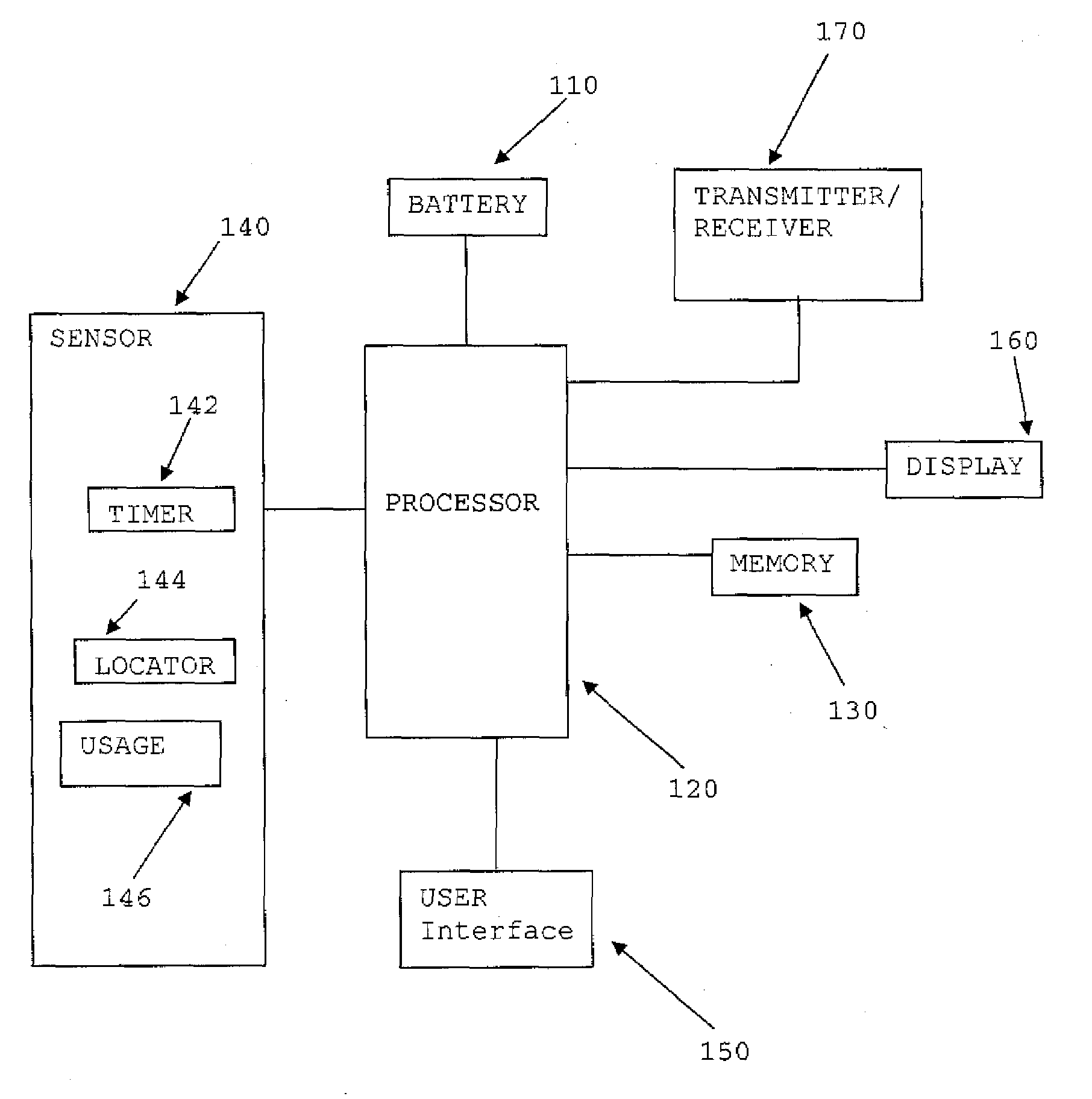
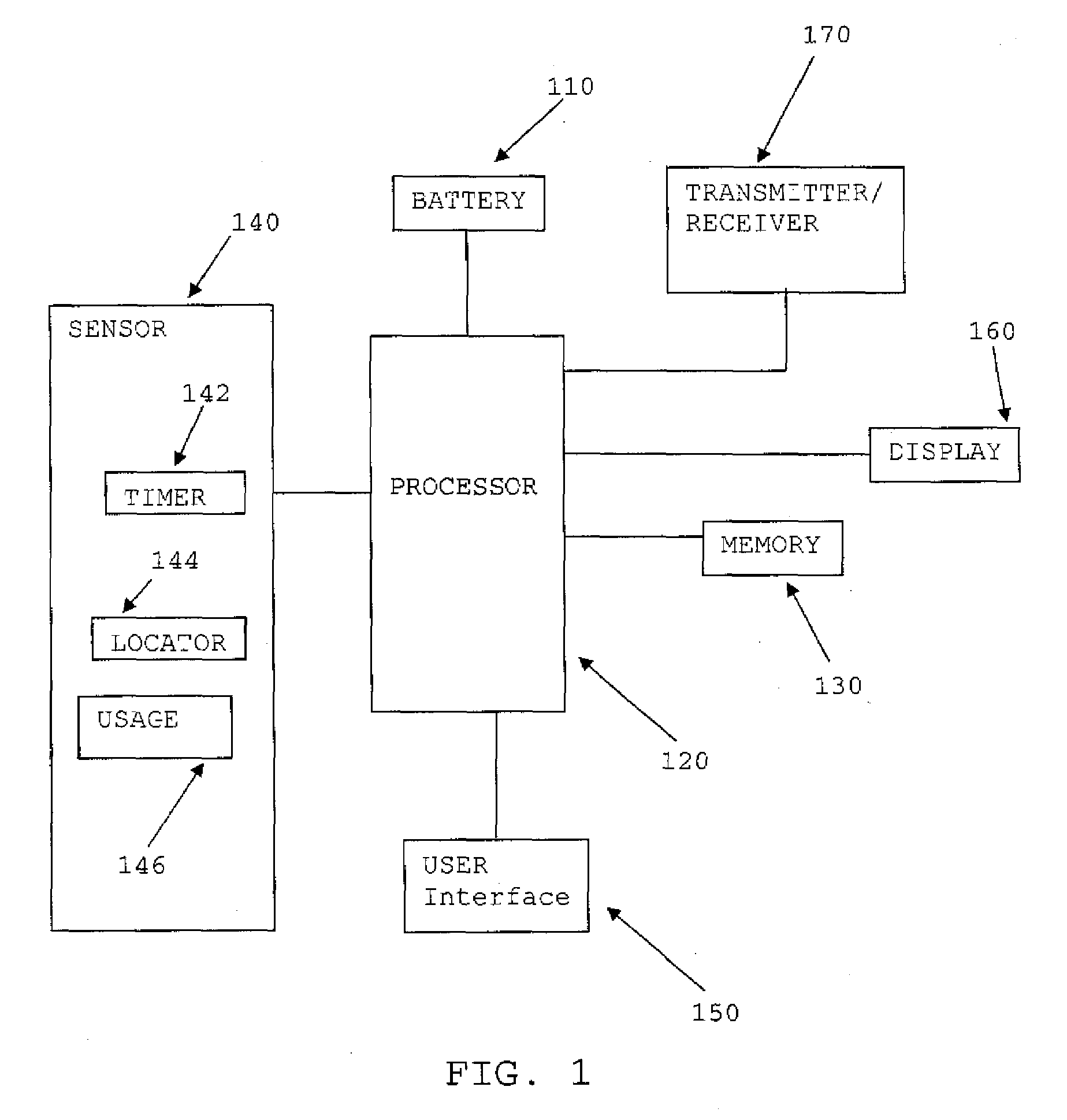
System and method for dynamically configuring a mobile device
InactiveUS20080168267A1Improved power management and configuration of systemImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementPower modeMobile device
A mobile device includes a sensor configured to detect a usage profile of the mobile device, and a processor configured to reconfigure the mobile device in response to the usage profile. The usage profile may be based on at least one of time, dates, location and user of the mobile device. The processor may be further configured to at least one of switch a power mode, reconfigure a user interface and / or a function of a button of the mobile device in response to at least one of the usage profile and a user profile of a user of the mobile device. The sensor may include at least one of a timer, a location detector, a usage detector and a user detector.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
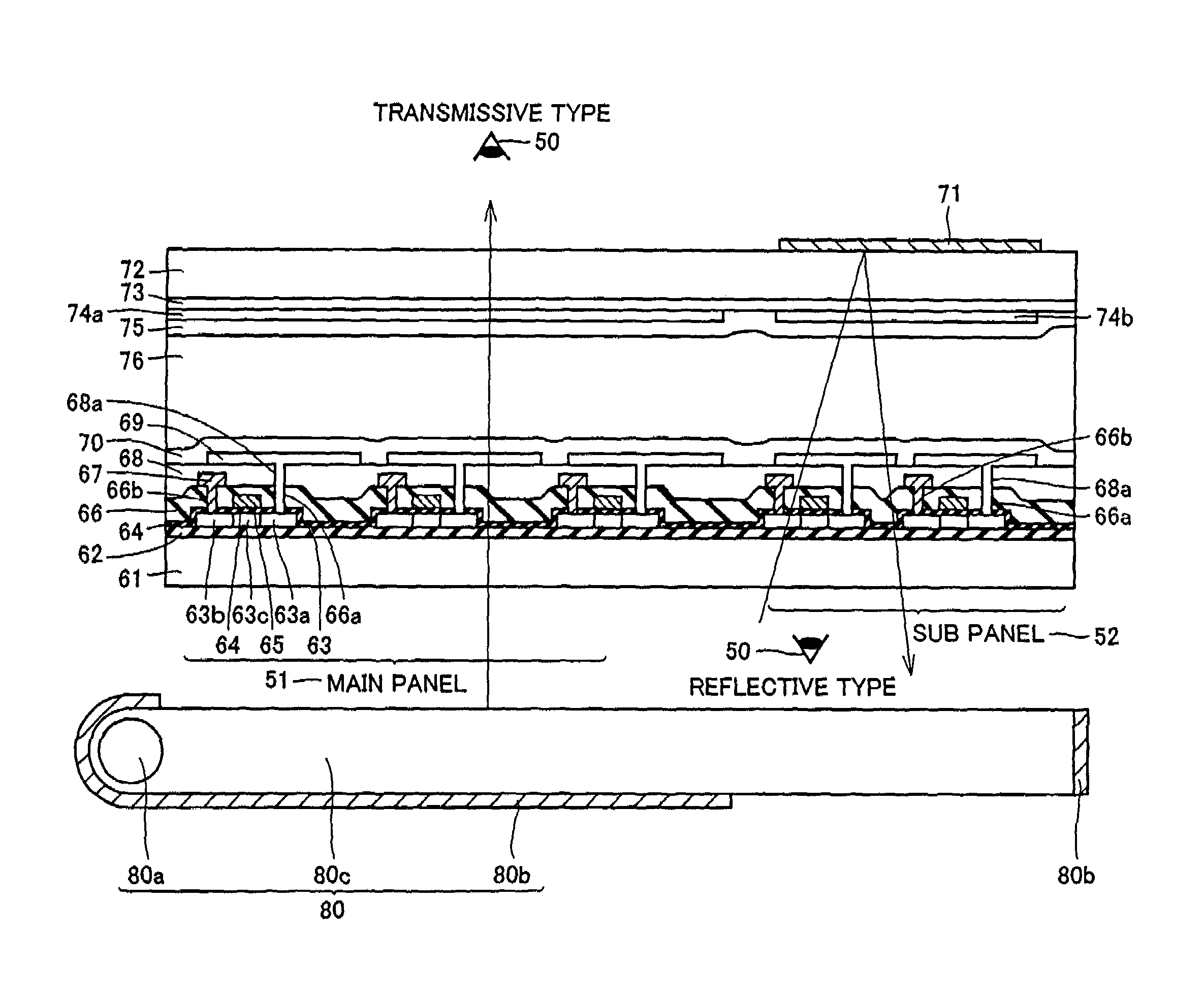
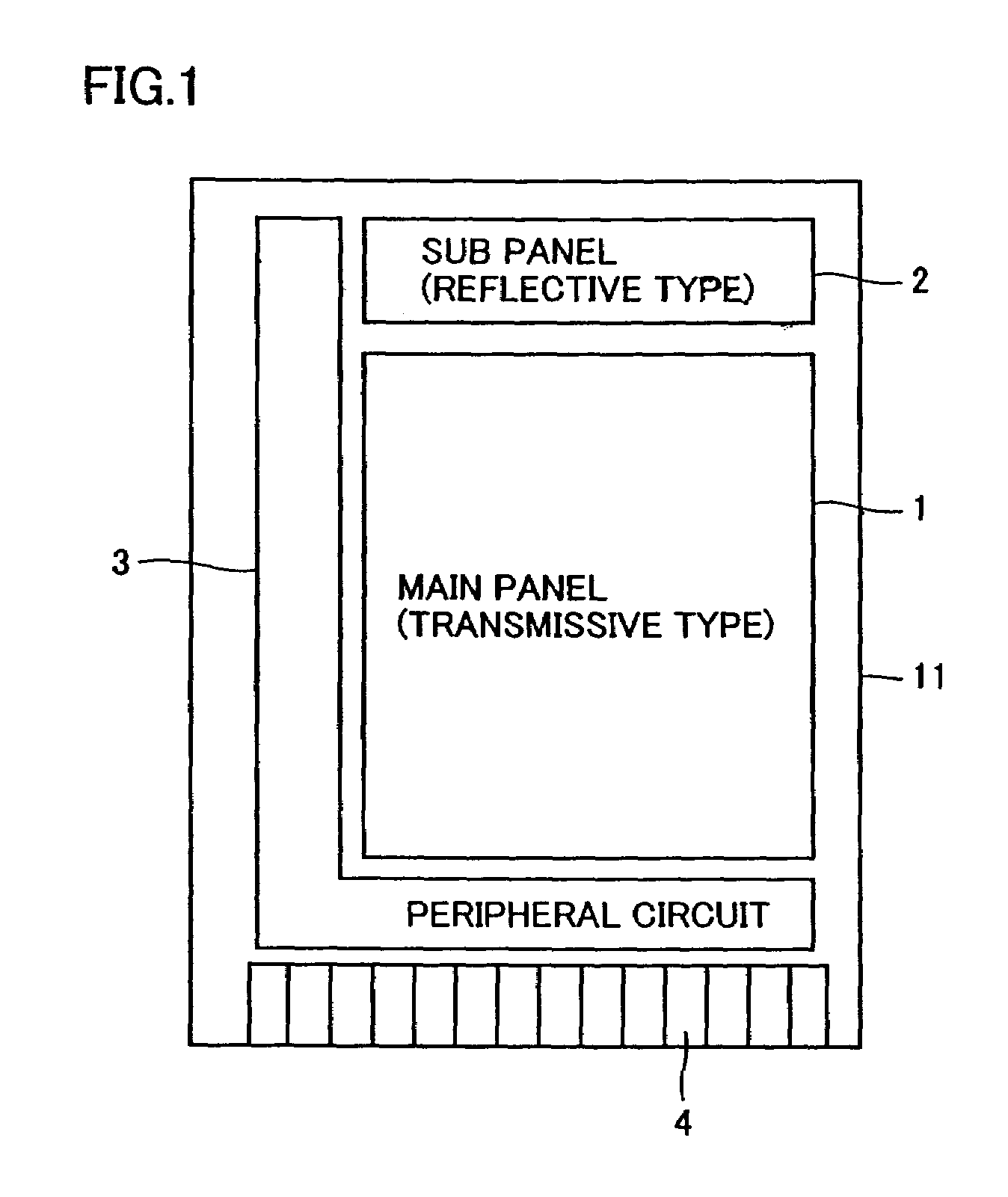
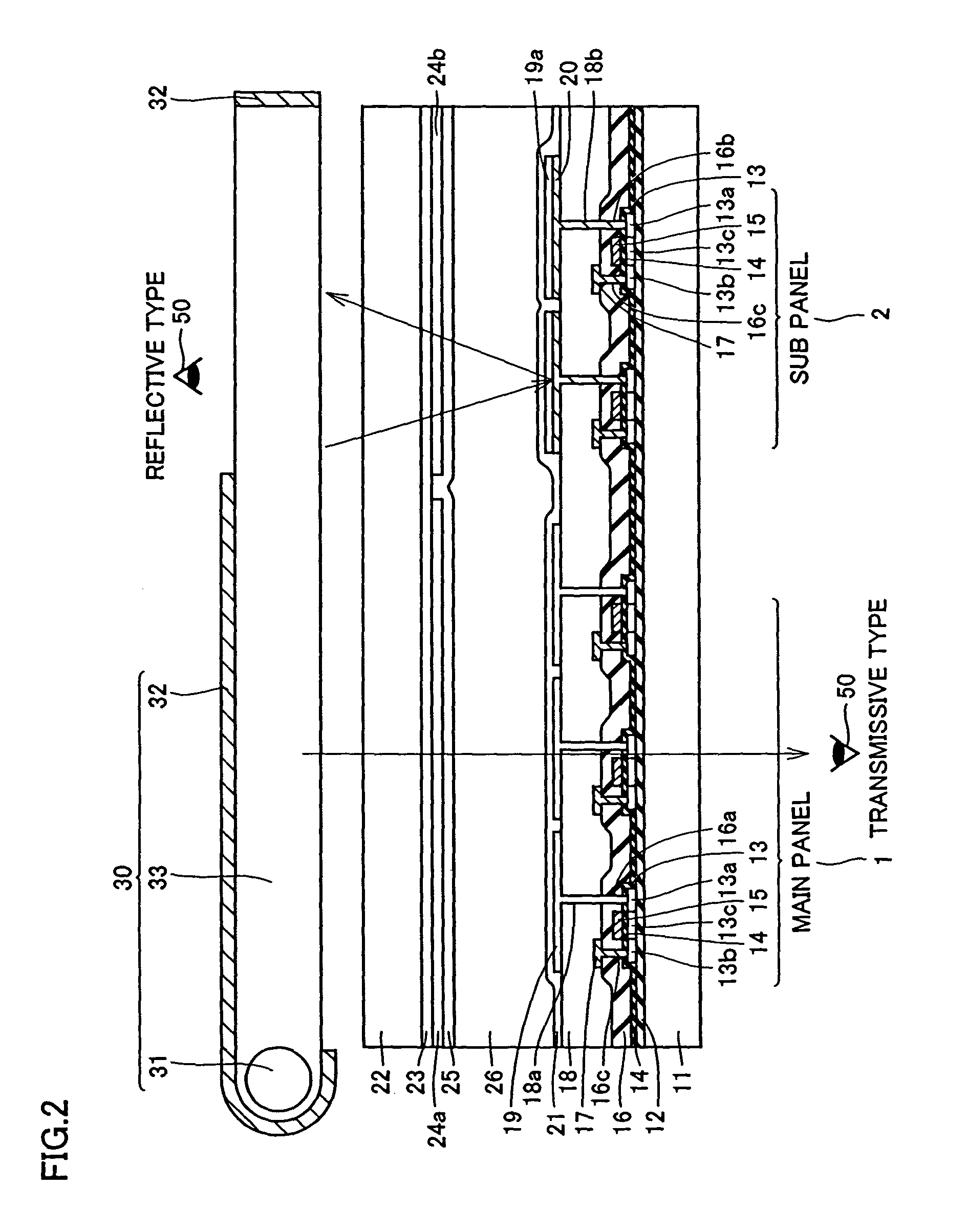
Display including a plurality of display panels
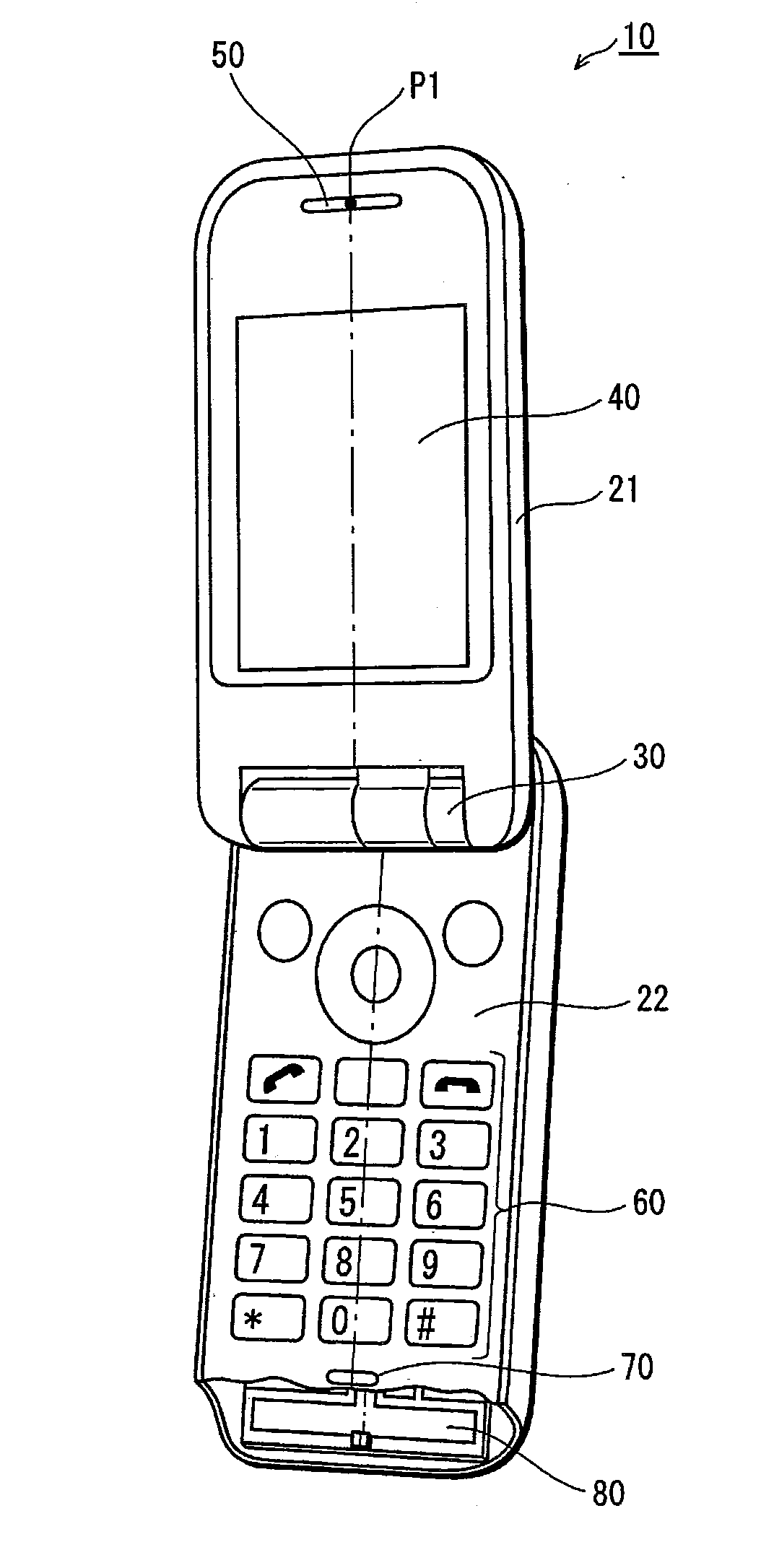
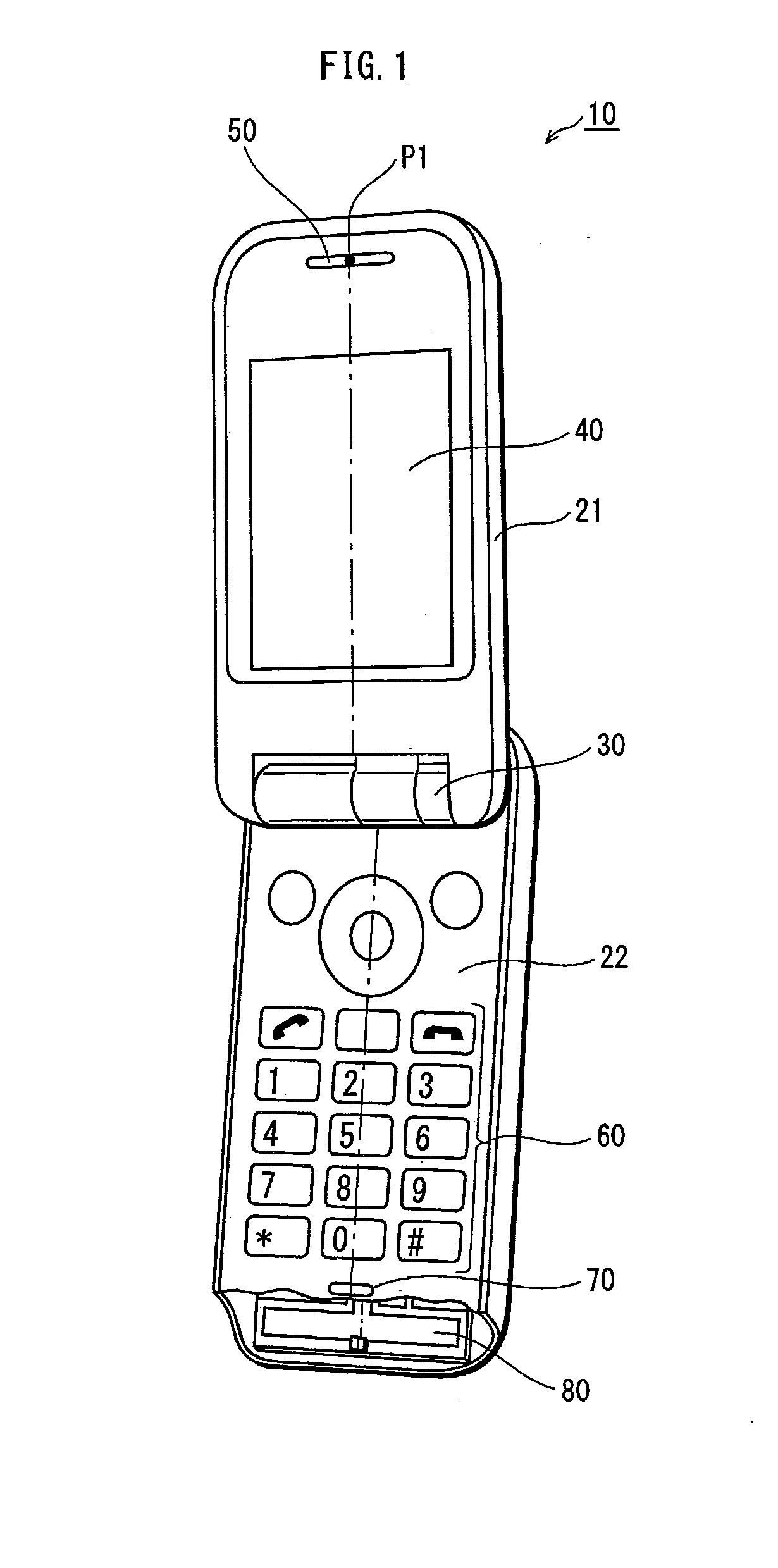
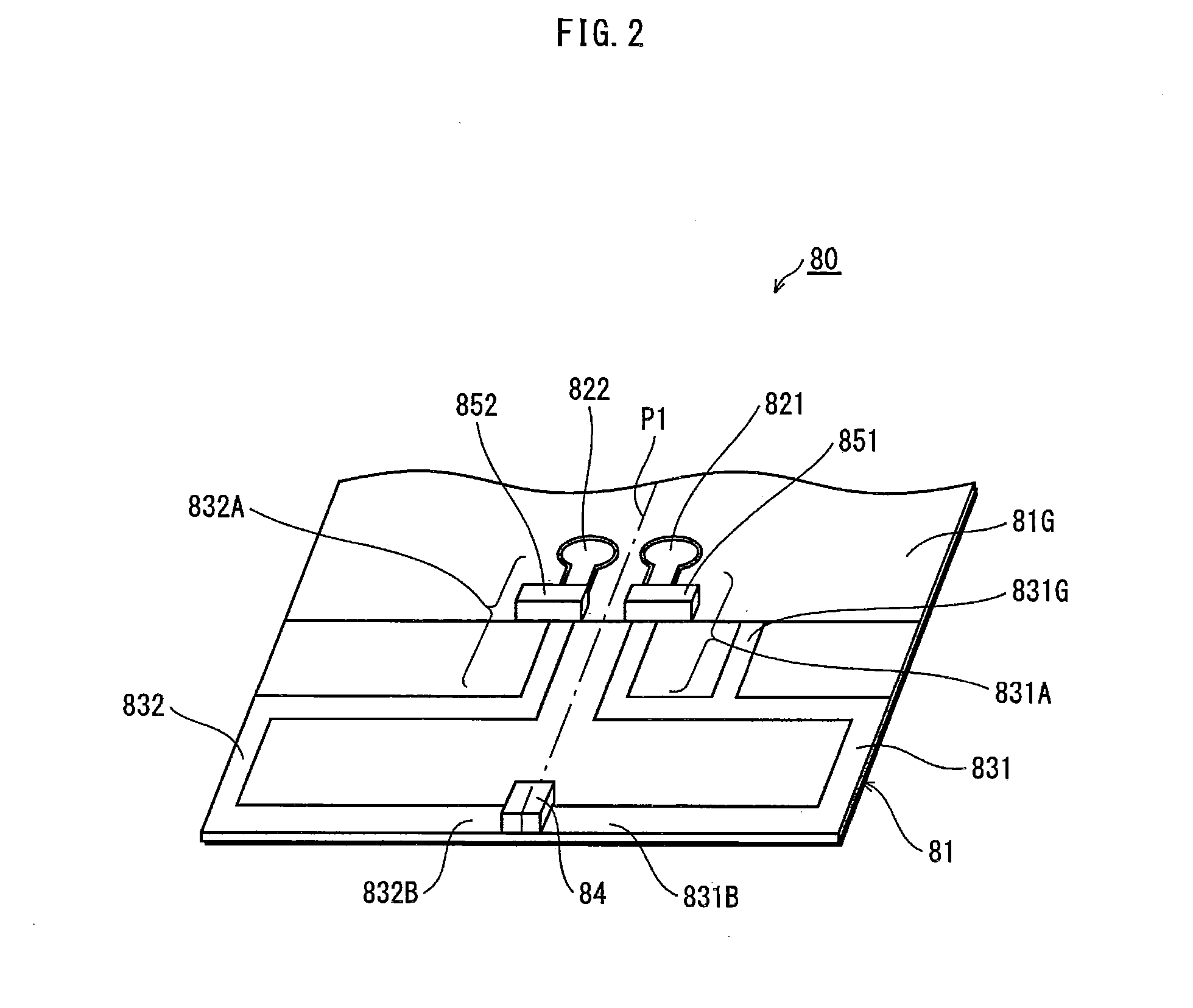
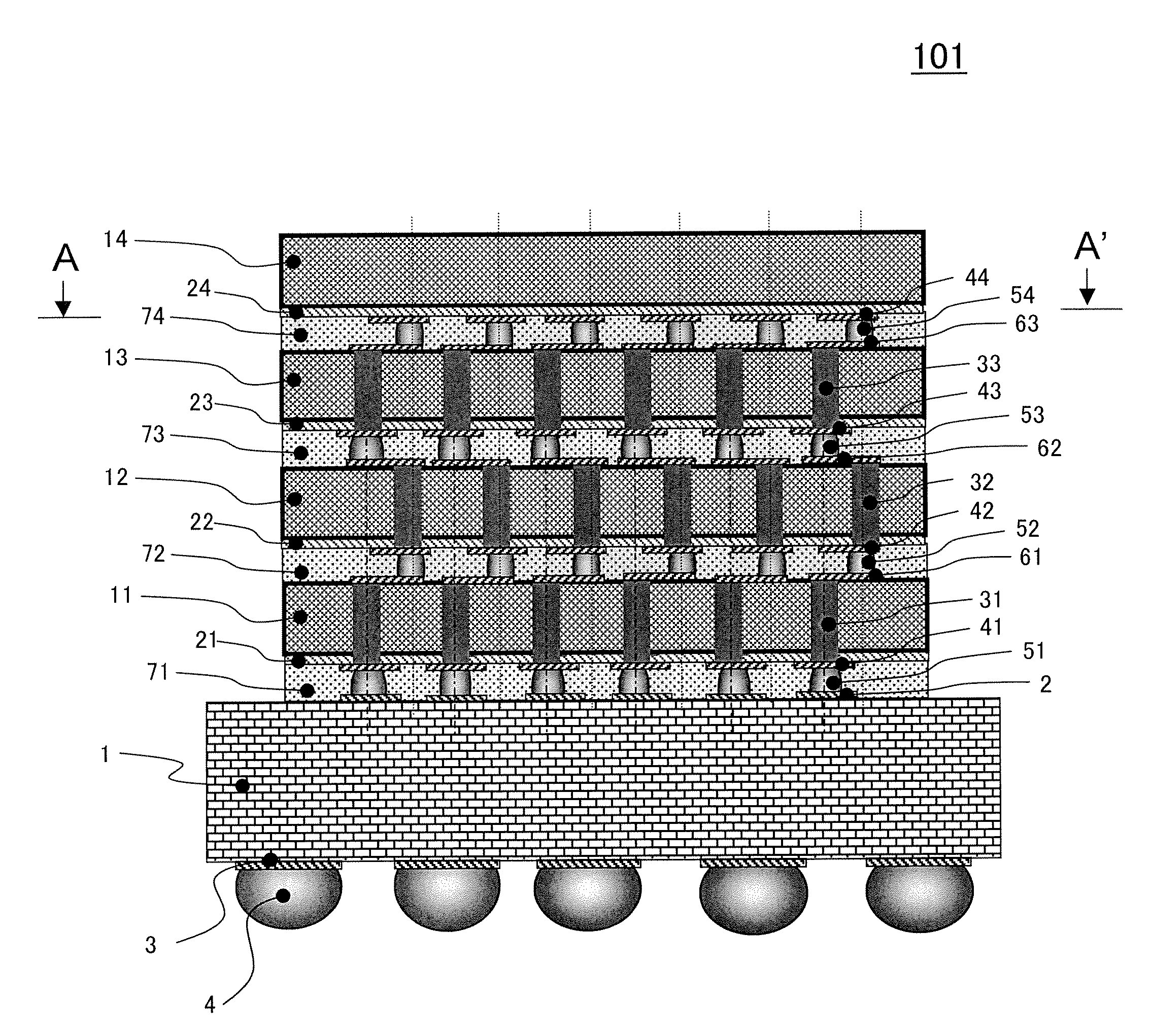
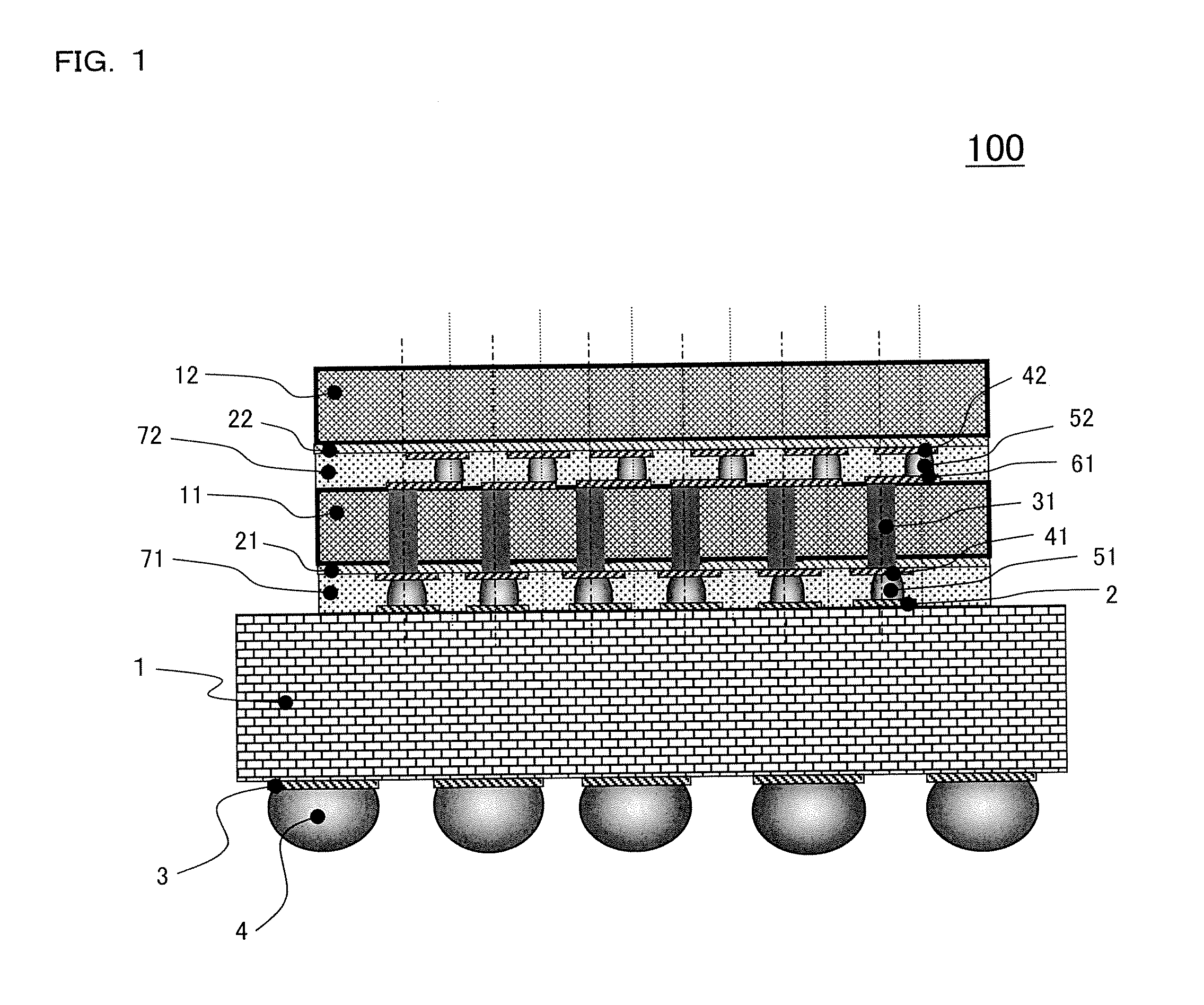
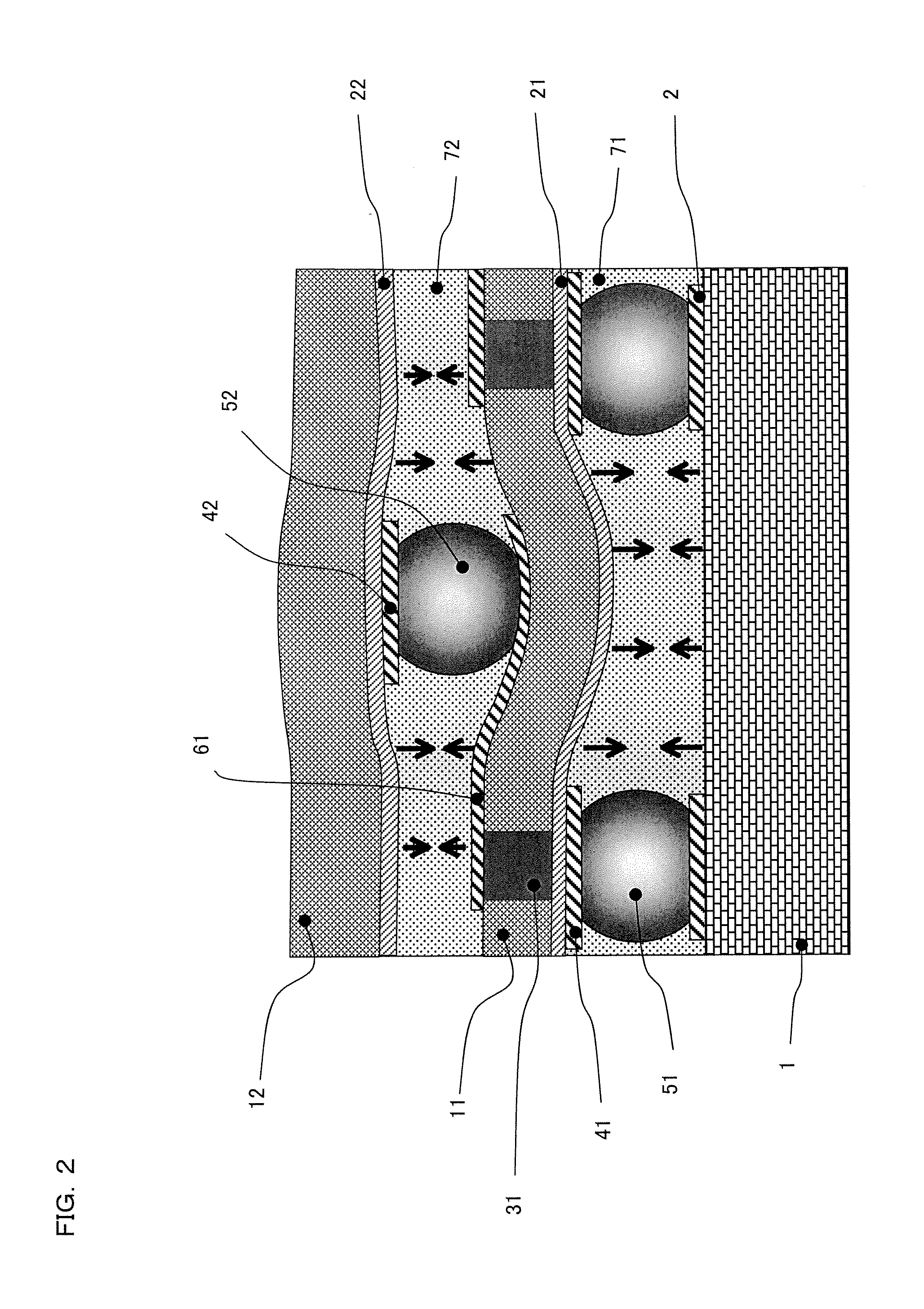
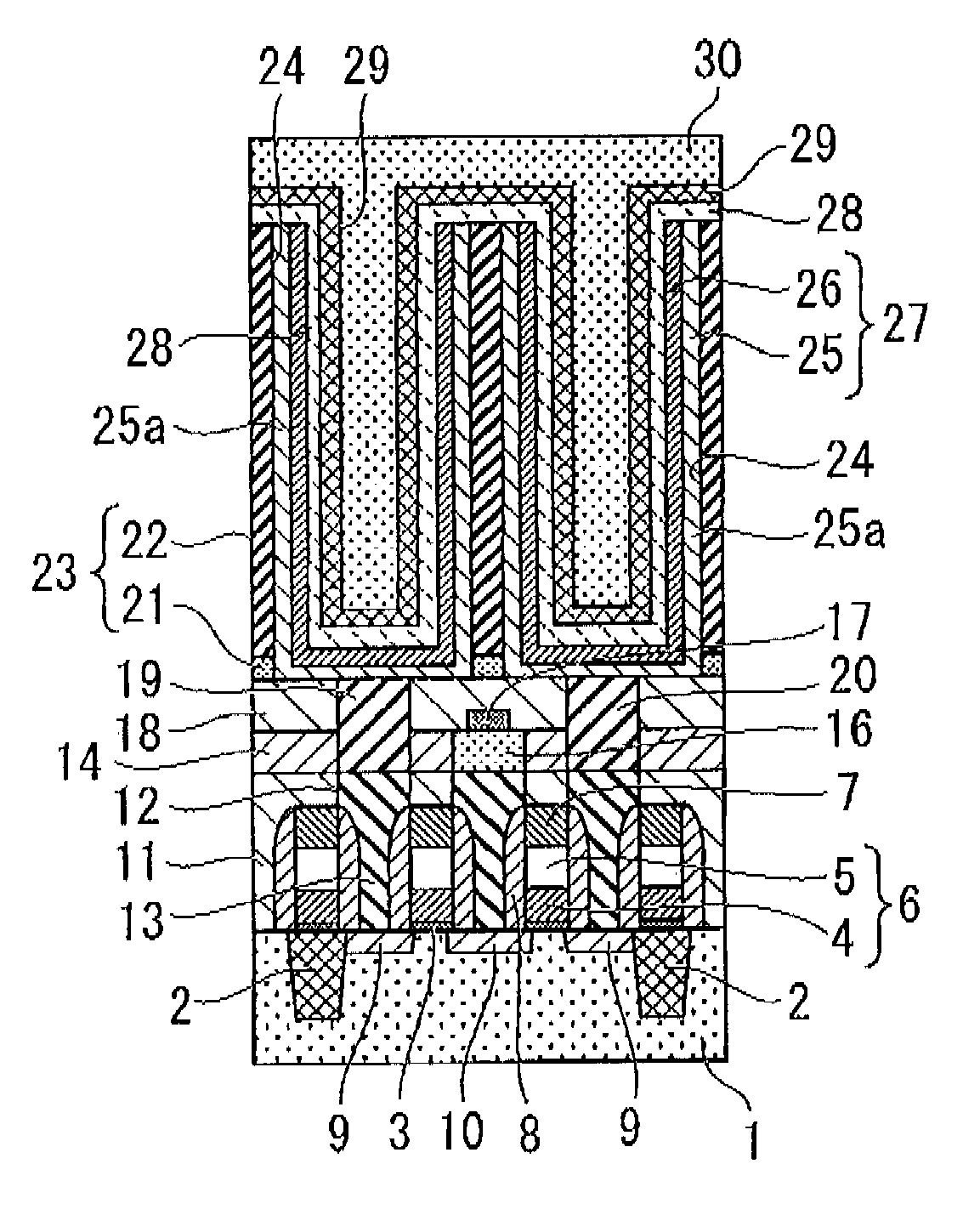
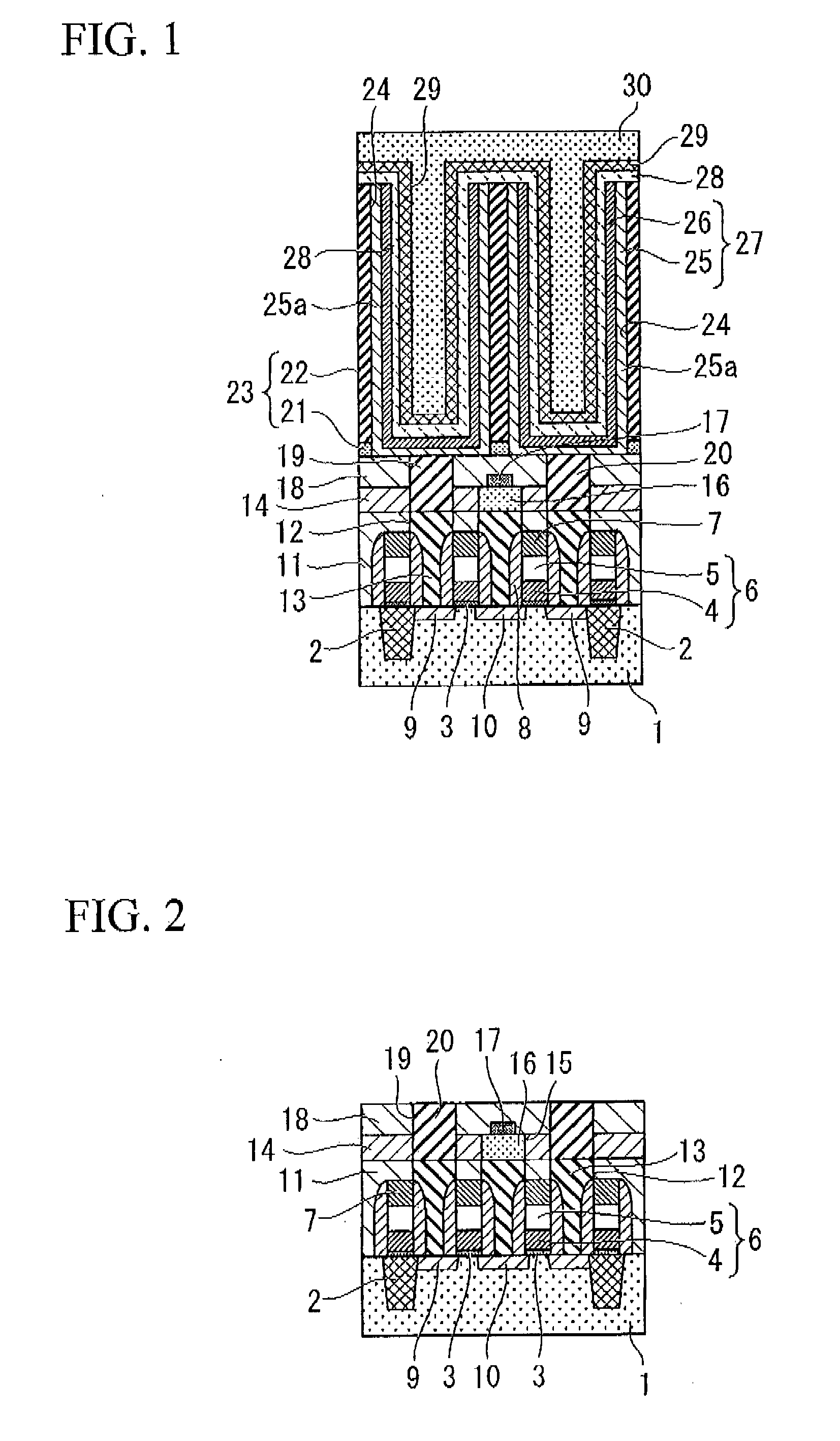
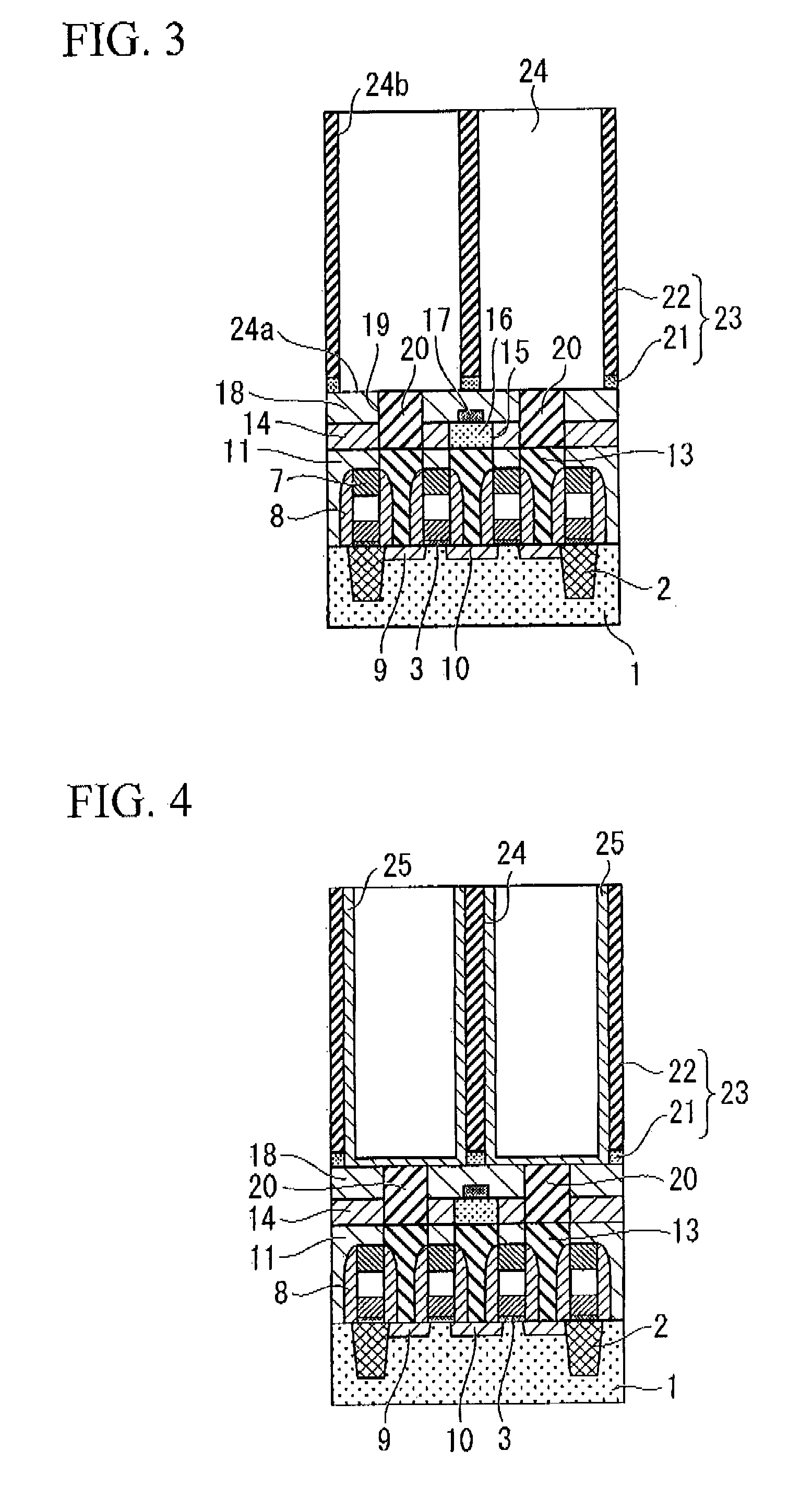
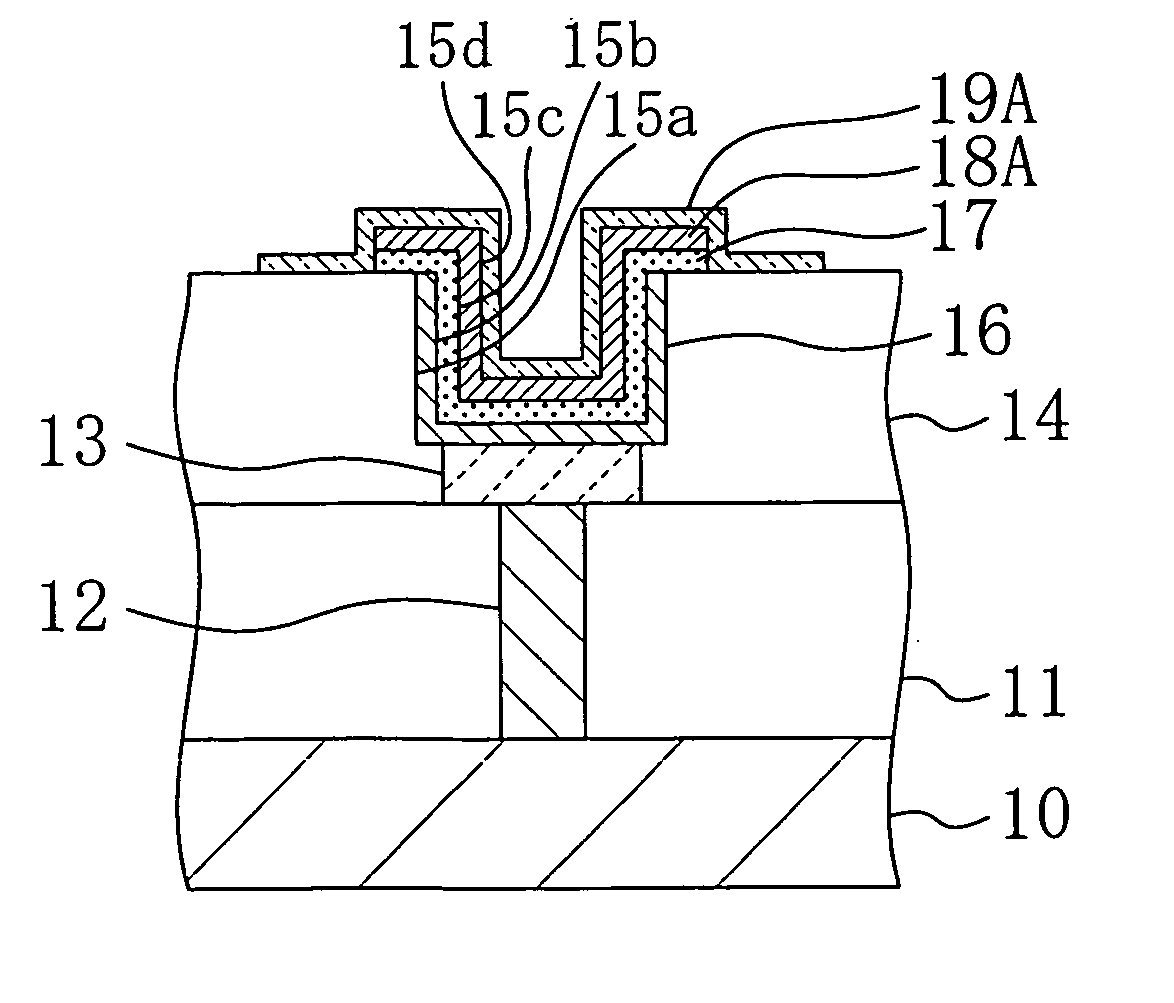
ActiveUS7389476B2Further miniaturizationReduce component countStatic indicating devicesDevices with multiple display unitsMiniaturizationDisplay device
A display allowing further miniaturization when including a plurality of display panels is obtained. This display comprises a first display panel formed on a substrate and a second display panel formed on the same substrate on a region different from that formed with the first display panel. Thus, the display can be further miniaturized as compared with that having a first display panel and a second display panel formed on different substrates.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090218671A1Avoid crackingReduce distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
In a semiconductor device of the present invention, semiconductor chips are stacked in multi-layers. Each of the semiconductor chip includes: through vias extending through a top main surface thereof to a bottom surface opposite to the top main surface; a circuit element surface formed on the top main surface; pads arranged on the circuit element surface; bumps formed on the pads; and via pads, formed on the bottom surface thereof, to which the bumps of its upper semiconductor chip are joined, and positions at which the bumps of each of the semiconductor chips are respectively arranged are different from those at which the bumps of its upper semiconductor chip are arranged.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Composite antenna and portable telephone
ActiveUS20120064954A1MiniaturizationFurther miniaturizationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringAntenna element
A complex antenna has a first antenna element and a second antenna element each connected at one end to a different feed point and connected to each other at the other end through a parallel resonant circuit. Each antenna element has the same resonant frequency as the parallel resonant circuit. A mobile phone has an antenna switch with a first port connected to the first antenna element, a second port connected to the second antenna element, and a third port that can be connected to one of the first port and the second port and switched therebetween. A signal processing unit causes the antenna switch to connect the third port to the first port or to the second port and detects a signal captured by one of the antenna elements from the output of the third port.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Key input device for portable terminal
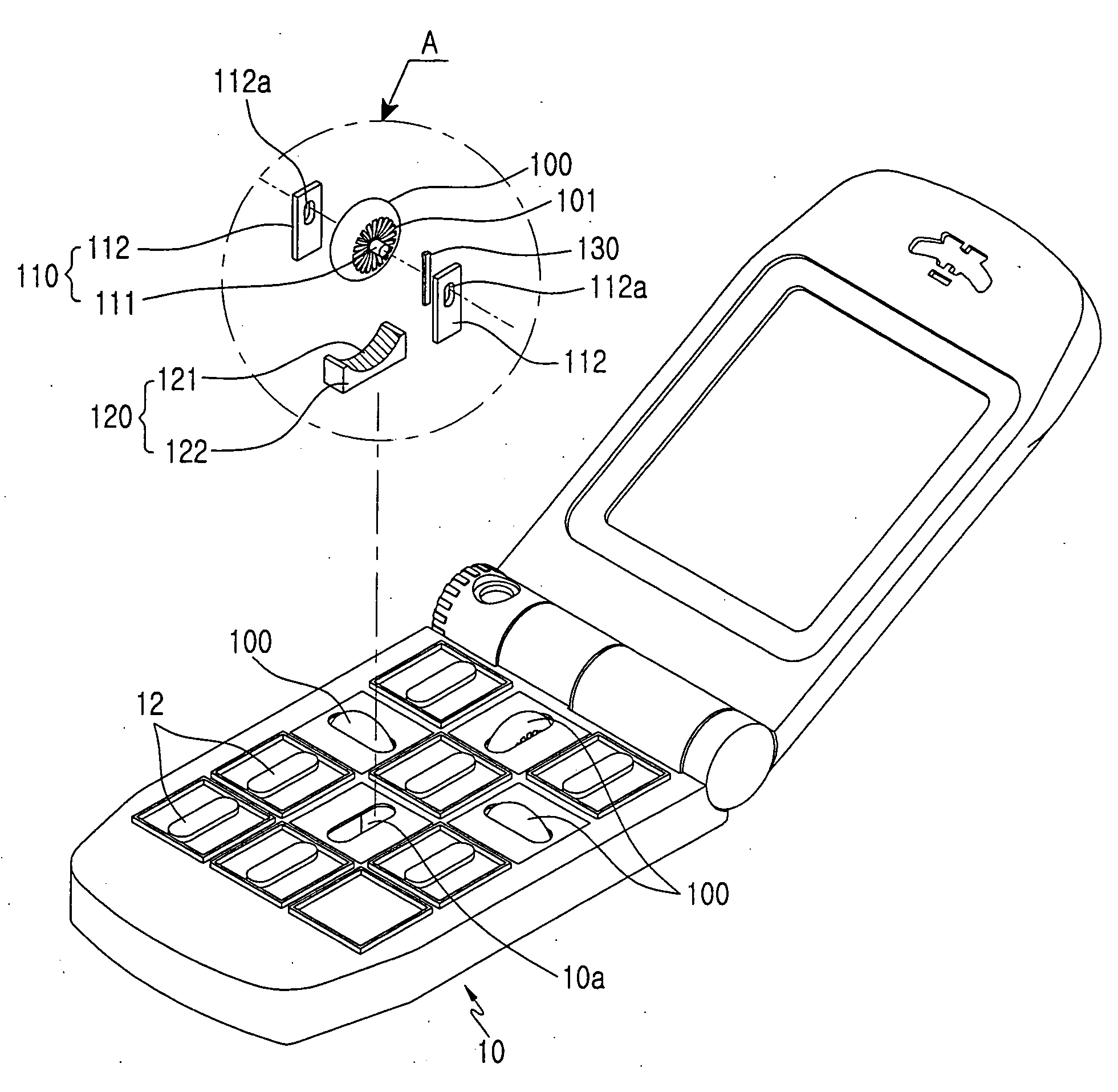
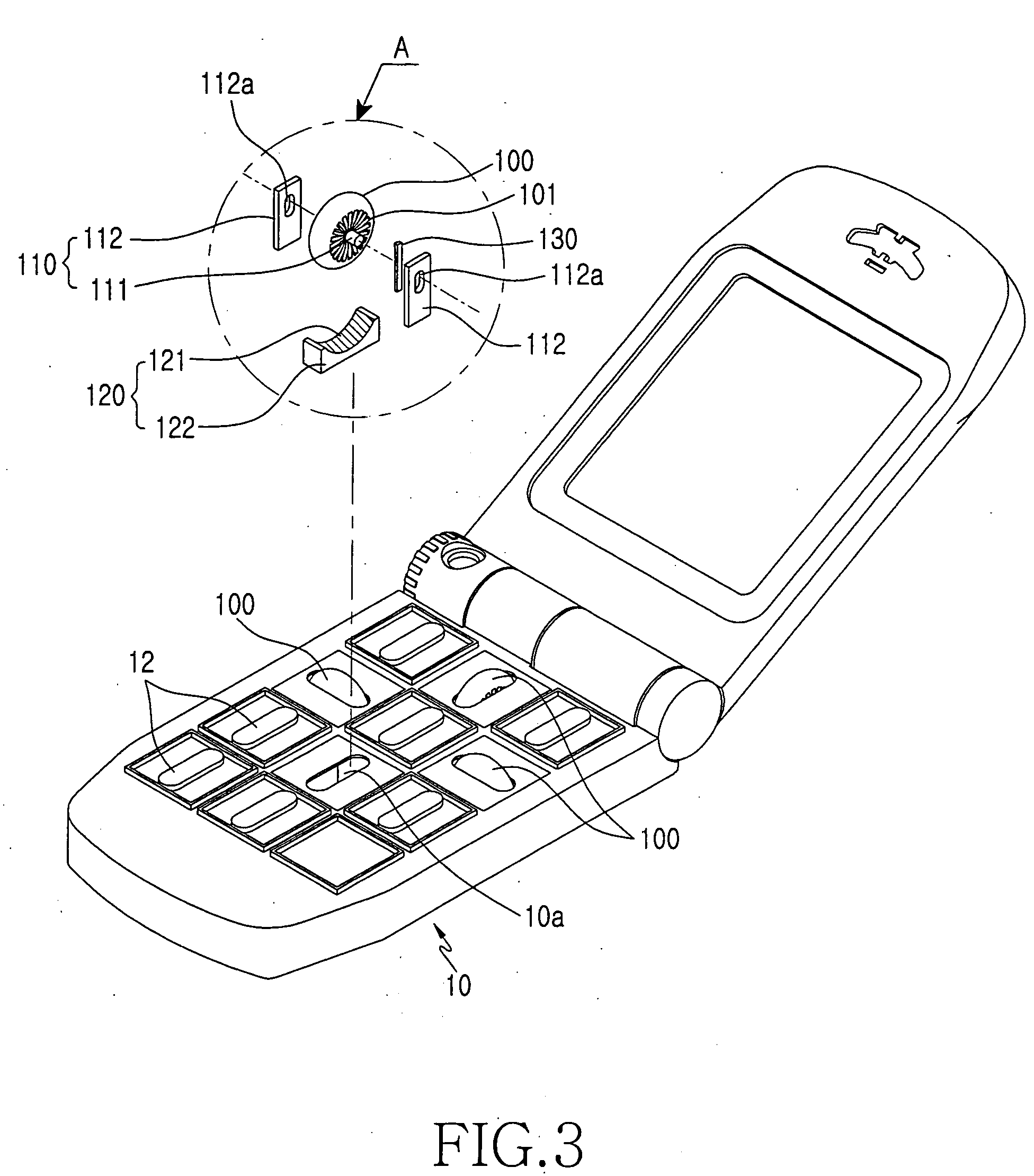
InactiveUS20070123320A1Move quicklyReduced space required for installationTelephone set constructionsInput/output processes for data processingKey pressingBiological activation
A key input device for a portable terminal includes wheel keys capable of rotating in multiple directions and performing a switch function. The key input device including a plurality of keys having at least one wheel keys provided in a main body and rotating in multiple directions, at least one rotating units allowing the wheel keys to rotate in respective directions, and at least one switching units provided under the wheel keys to sense the rotation directions of the wheel keys and to sense a pressure generated by the activation of the rotated wheel keys.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus
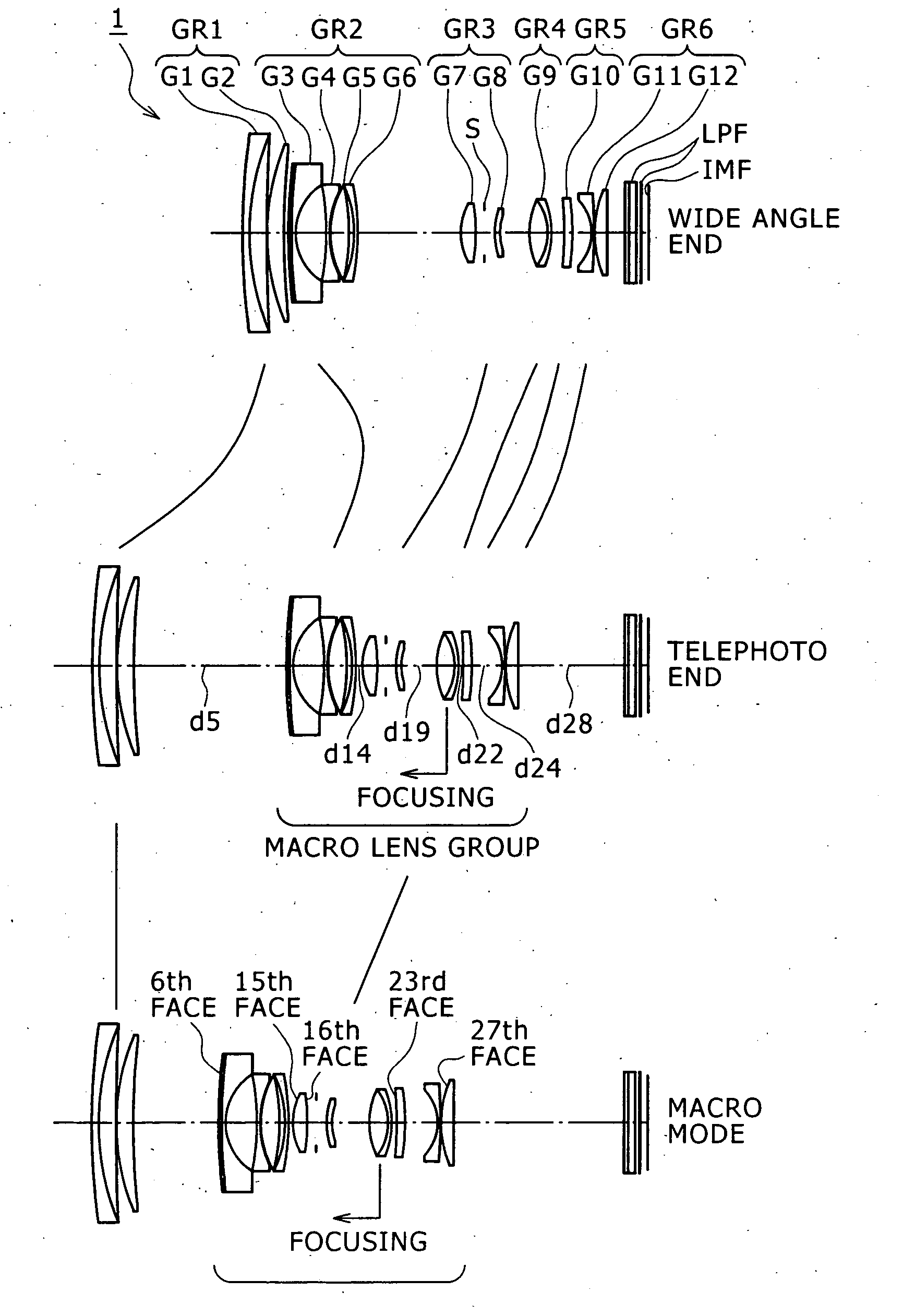
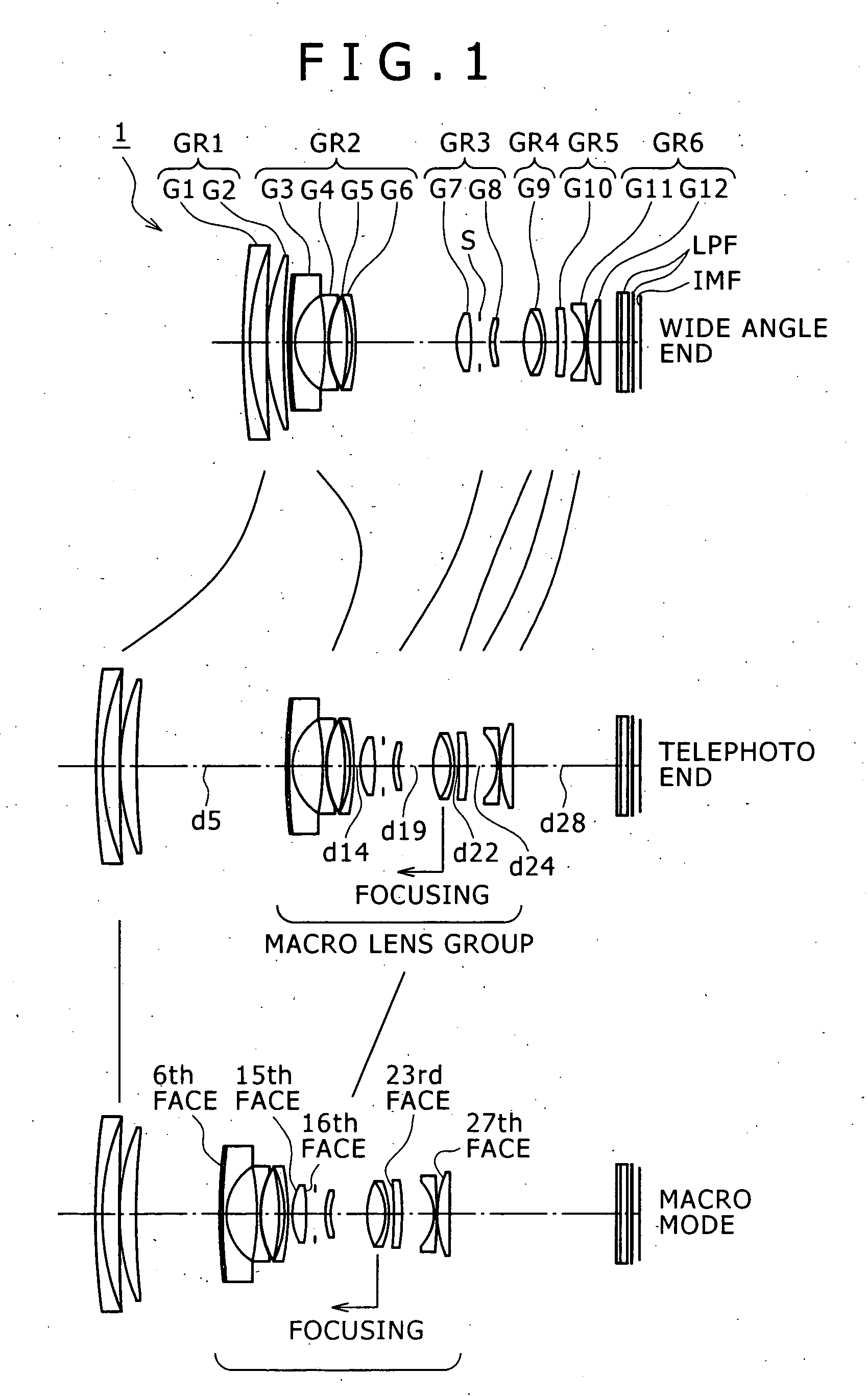
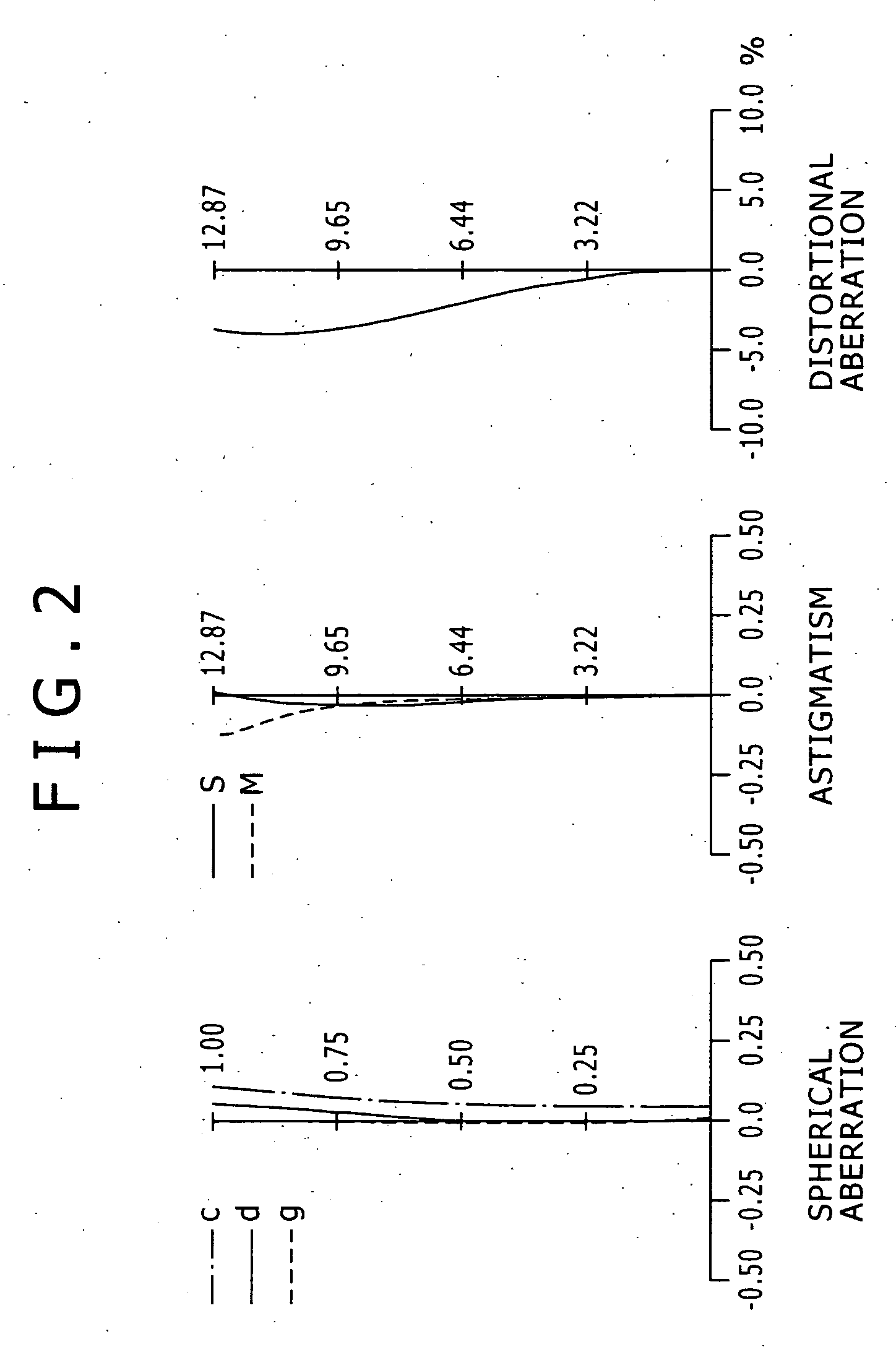
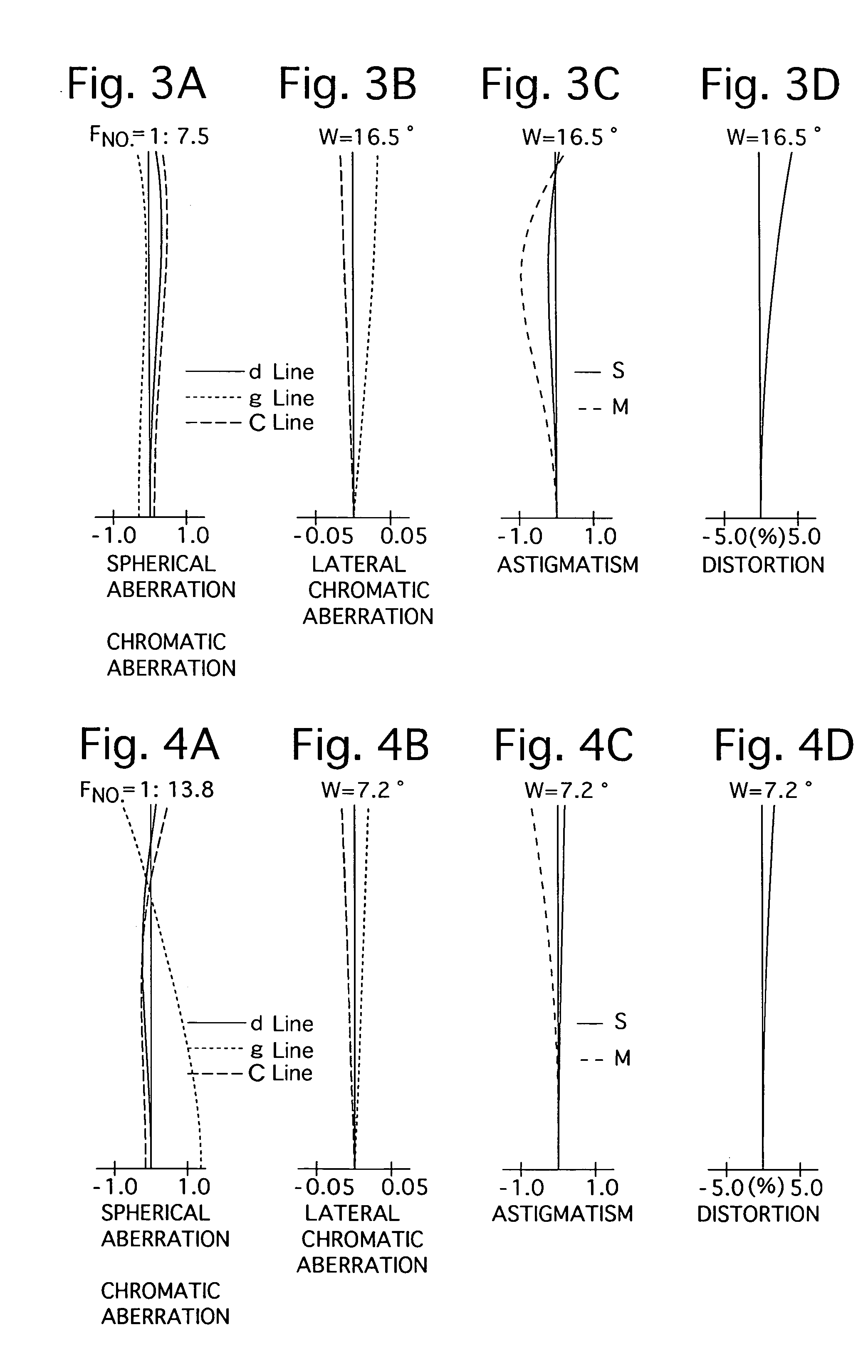
InactiveUS20060268428A1Improve picture qualityHigh image pickup magnificationCamera body detailsLensShortest distanceShort distance
A zoom lens is disclosed which has a macro mode wherein the magnifying power is higher than 0.5. The zoom lens includes a first positive lens group, a second negative lens group movable upon power variation, and a plurality of movable lens groups cooperable with the second group to form a macro lens group, disposed in order from an object side. The movable lens groups include a single focusing group, and an additional negative lens group disposed further on the image side. The zoom lens has a macro mode in which it can be focused at a shorter distance than an ordinary region by moving the macro lens group integrally from a telephoto end position toward the object side while the first lens group is fixed at the telephotograph end.
Owner:SONY CORP
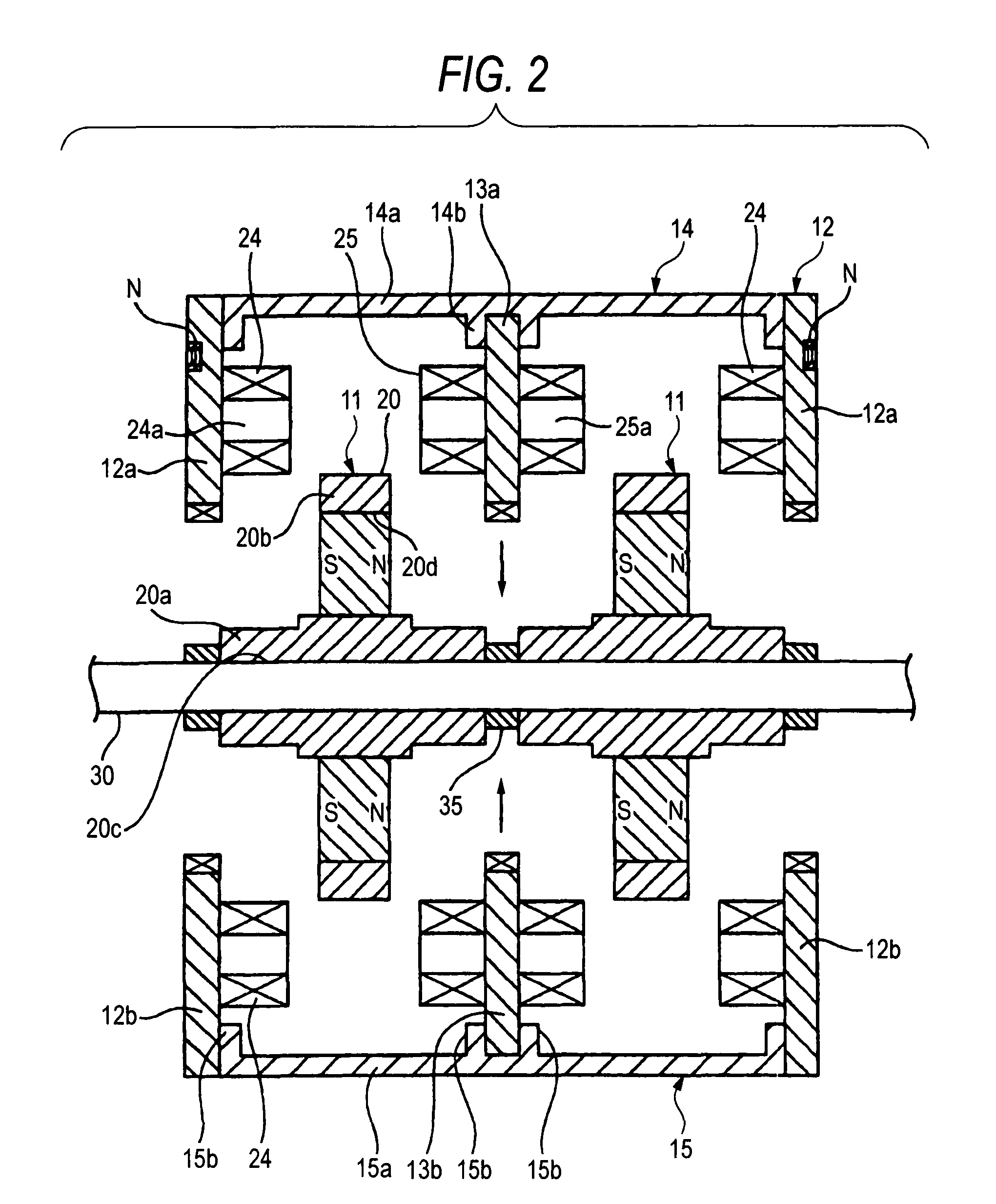
Axial gap type motor
InactiveUS7821169B2Increase productionFurther miniaturizationMagnetic circuit stationary partsSuperconductor devicesEngineeringMagnetic flux
A series coupling synchronous axial gap type motor where rotors and stators are alternately stacked with required air gaps in the axial direction of a rotary shaft as a main shaft, is provided. The rotors are fixed to the rotary shaft, and the stators are disposed such that they cannot be interlocked with the rotary shaft. A plurality of rotary field bodies are attached to each of the rotor around the axis, and a plurality of armature coils are made to face the rotary field bodies with an air gap therefrom and are attached to each of the stators around the axis such that their magnetic-flux directions are directed toward the axial direction. The armature coils have an empty core, or a core member composed of a magnetic body attached thereto.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Electronic apparatus with hidden antenna
ActiveUS8009110B2Reduce manufacturing costEliminate needAntenna supports/mountingsSlot antennasElectricityEngineering
An electronic apparatus with a hidden antenna comprises a metal frame and a substrate. The metal frame comprises a plurality of side walls and a notch is passed through at least one side wall. A feeding terminal is configured at a bottom side of the notch. A first shorting terminal and a second shorting terminal are configured at two lateral sides of the notch. A metal surface of the substrate is electrically connected to the first shorting terminal, the second shorting terminal and the side walls, and the notch is faced to the substrate. The metal frame receives or transmits an electromagnetic signal, and delivers the electromagnetic signal over the feeding terminal, and a length of the bottom side of the notch is one half of a wavelength of the electromagnetic signal.
Owner:HTC CORP
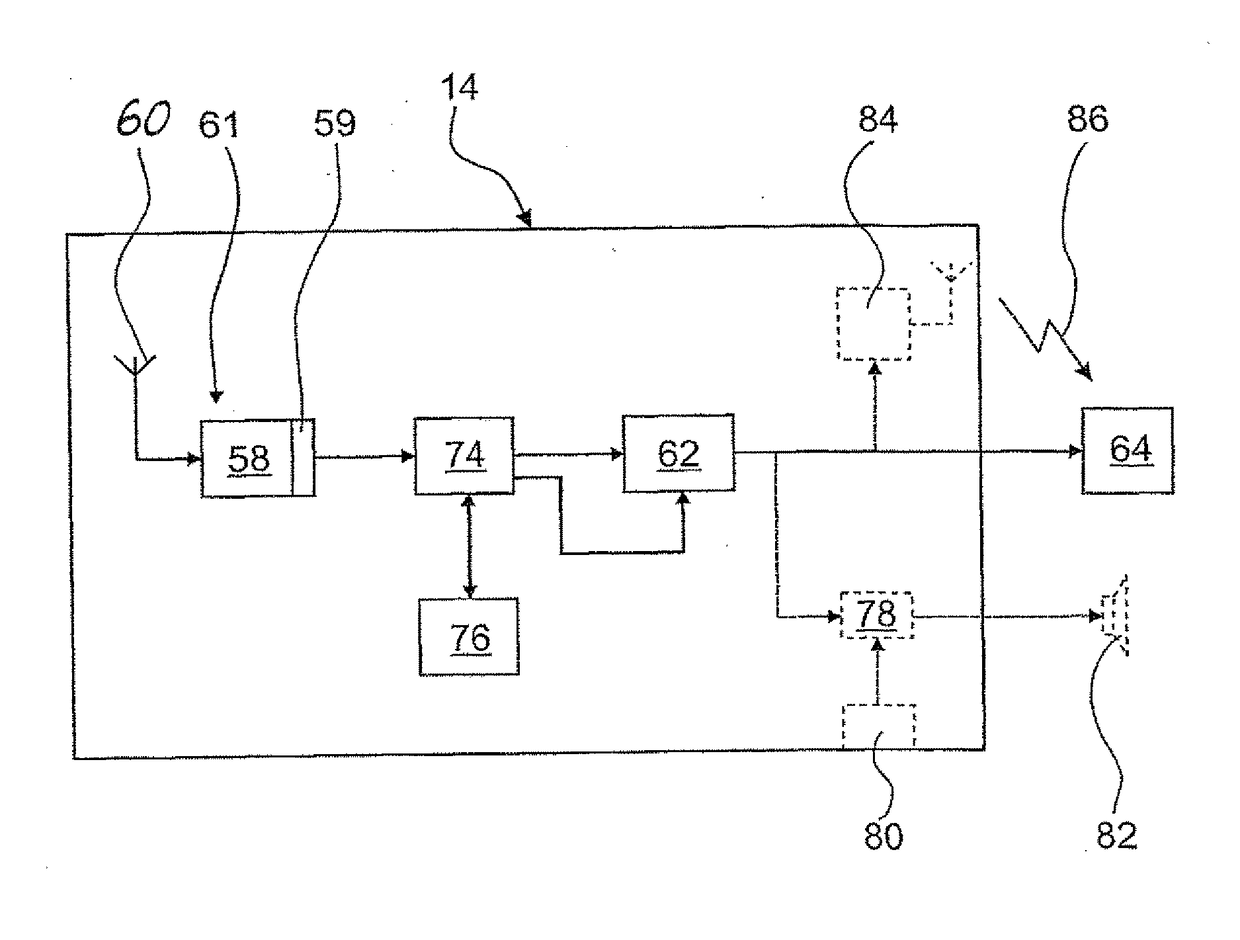
Hearing assistance system and method
InactiveUS20170127197A1Easy to controlLimited controlInput/output for user-computer interactionMicrophones signal combinationWireless transmissionHand held
A hearing assistance system having a hand-held audio signal wireless transmission unit for transmitting an audio signal to at least one receiver unit, and a hearing stimulating device. The transmission unit has at least one microphone for generating an audio signal, a motion sensor unit for sensing the acceleration acting on the transmission unit in three orthogonal axes and sensing the orientation of the transmission unit in space, a memory unit for storing a plurality of motion patterns of the transmission unit corresponding to gestures of a person holding the transmission unit in a hand, a control unit for identifying a motion pattern of the transmission unit from the stored motion patterns by analyzing the time dependence of an output signal of the motion sensor unit and comparing it to the stored motion patterns, and the control unit controlling operation of the transmission unit according to the identified motion pattern.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Image forming apparatus and fixing device
ActiveUS20070053712A1Improve maintainabilityOut dimension is reducedElectrographic process apparatusElectricityImage formation
A fixing unit mounting section is formed to a main body frame. A fixing unit is mounted to the fixing unit mounting section by inserting the fixing unit into the main body along a predetermined inserting direction. An electric power supply section configured to supply electric power to the fixing unit is arranged at a near side of the fixing unit mounting section in the inserting direction. A connecting section configured to establish electric connection to the electric power supply section is formed at the near side of the fixing unit in the inserting direction.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Substrate for mounting device and method for producing the same, semiconductor module and method for producing the same, and portable apparatus provided with the same
InactiveUS20110027945A1Reduce in quantityFirmly connectedPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceElectricity
A substrate for mounting a device comprises: an insulating resin layer; a plurality of projected electrodes that are connected electrically to a wiring layer provided on one major surface of the insulating resin layer, and that project toward the insulating resin layer from the wiring layer; and a counter electrode provided at a position corresponding to each of the plurality of projected electrodes on the other major surface of the insulating resin layer. Among the projected electrodes, a projected length of part of the projected electrodes is smaller than that of the other projected electrodes; and the projected electrode and the counter electrode corresponding thereto are capacitively-coupled, and the projected electrode and the counter electrode are connected electrically.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Hinge device for portable terminal using the same
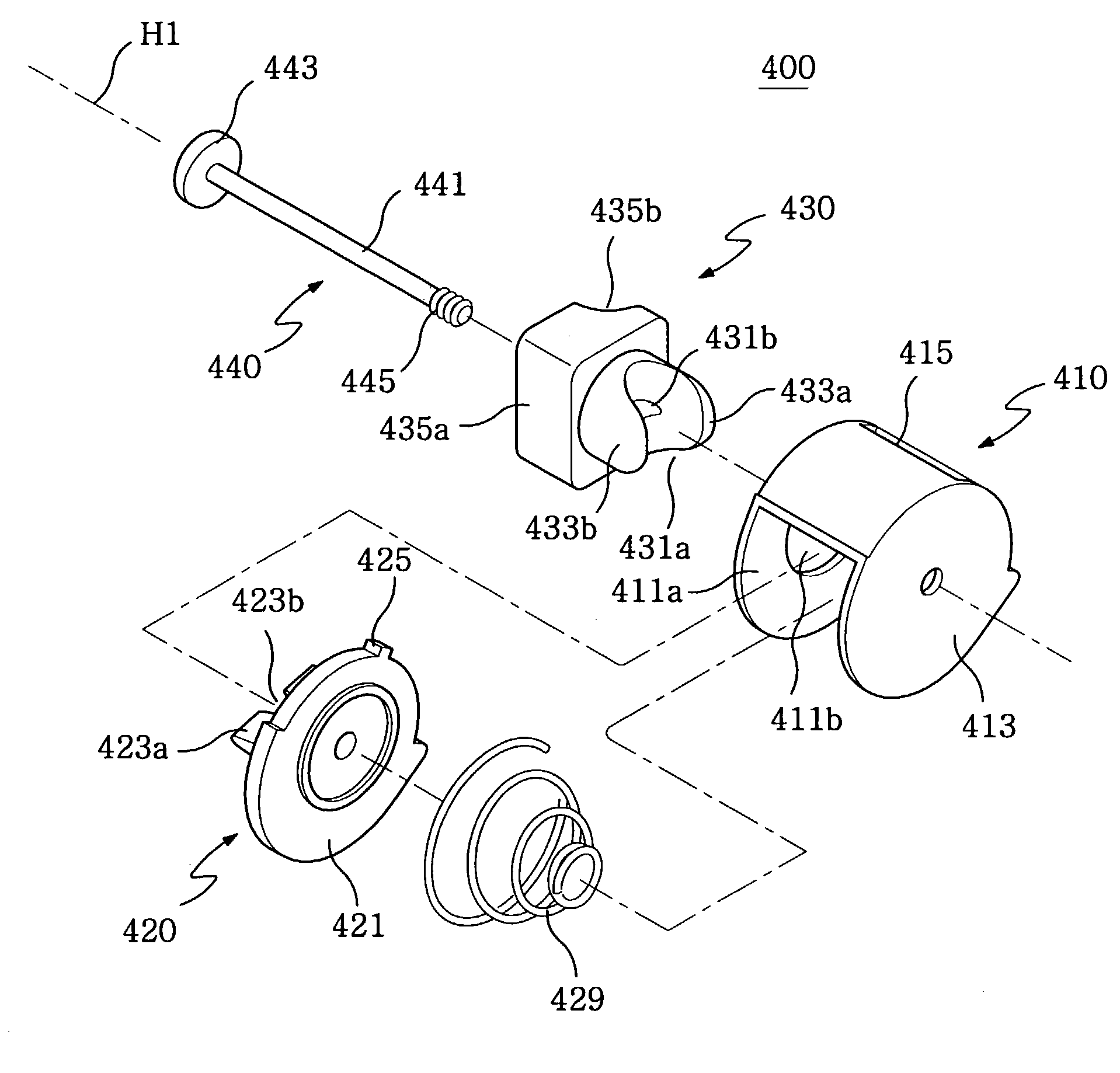
InactiveUS7242975B2Miniaturization of portableFurther miniaturizationInterconnection arrangementsHingesThumb oppositionMiniaturization
A hinge device of a portable terminal couples a body and a folder of the portable terminal and enables rotation of the folder with respect to the body. The hinge device includes a cylindrical hinge housing having an open end, a closed end, and a suspending block that projects from a peripheral surface of the cylindrical hinge housing and extends longitudinally between the open end and the closed end; a hinge shaft having a disk and an angular block projecting from the disk, disposed along a hinge axis, the disk being housed in the cylindrical hinge housing and the angular block protruding through the open end of the cylindrical hinge housing; a hinge cam, disposed outside the cylindrical hinge housing, having a concave block disposed along the hinge axis in opposition to the angular block of the hinge shaft, to engage in a sliding motion in conjunction with the angular block; and a conical compression coil spring, disposed between the closed end of the cylindrical hinge housing and the disk of the hinge shaft, to press the hinge shaft against the hinge cam. The conical compression coil spring is compressible into a plane, so that the space required for installing and assembling the hinge device in the portable terminal can be reduced. When the hinge housing is combined with the folder of a foldable terminal, the hinge cam is combined with the body of the foldable terminal. Combining the hinge housing with the folder and the hinge cam with the body obviates the need for an axis of a conventional hinge cam, which combines the hinge device with the body, thus enabling the miniaturization of the hinge device and a portable terminal using the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
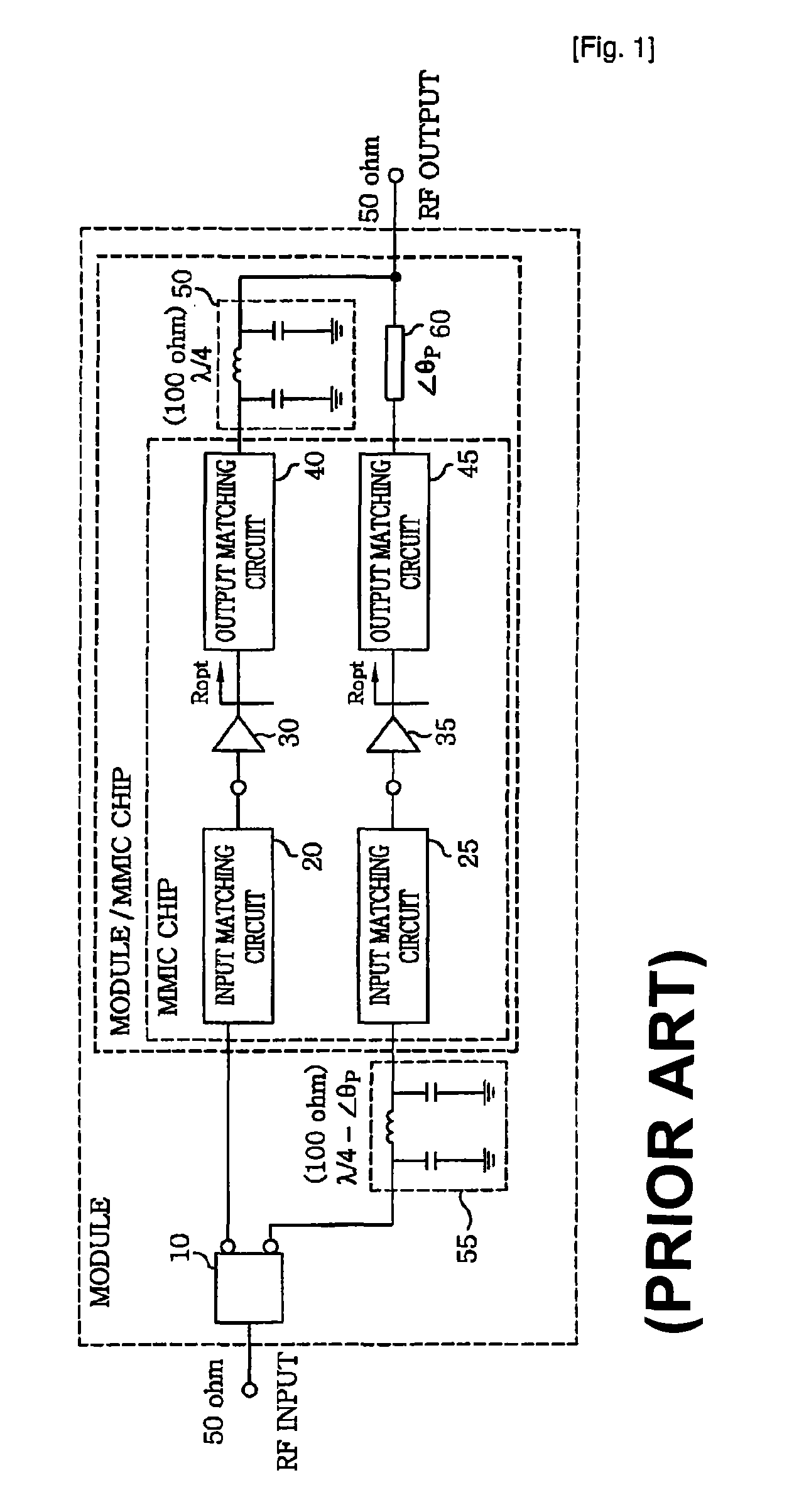
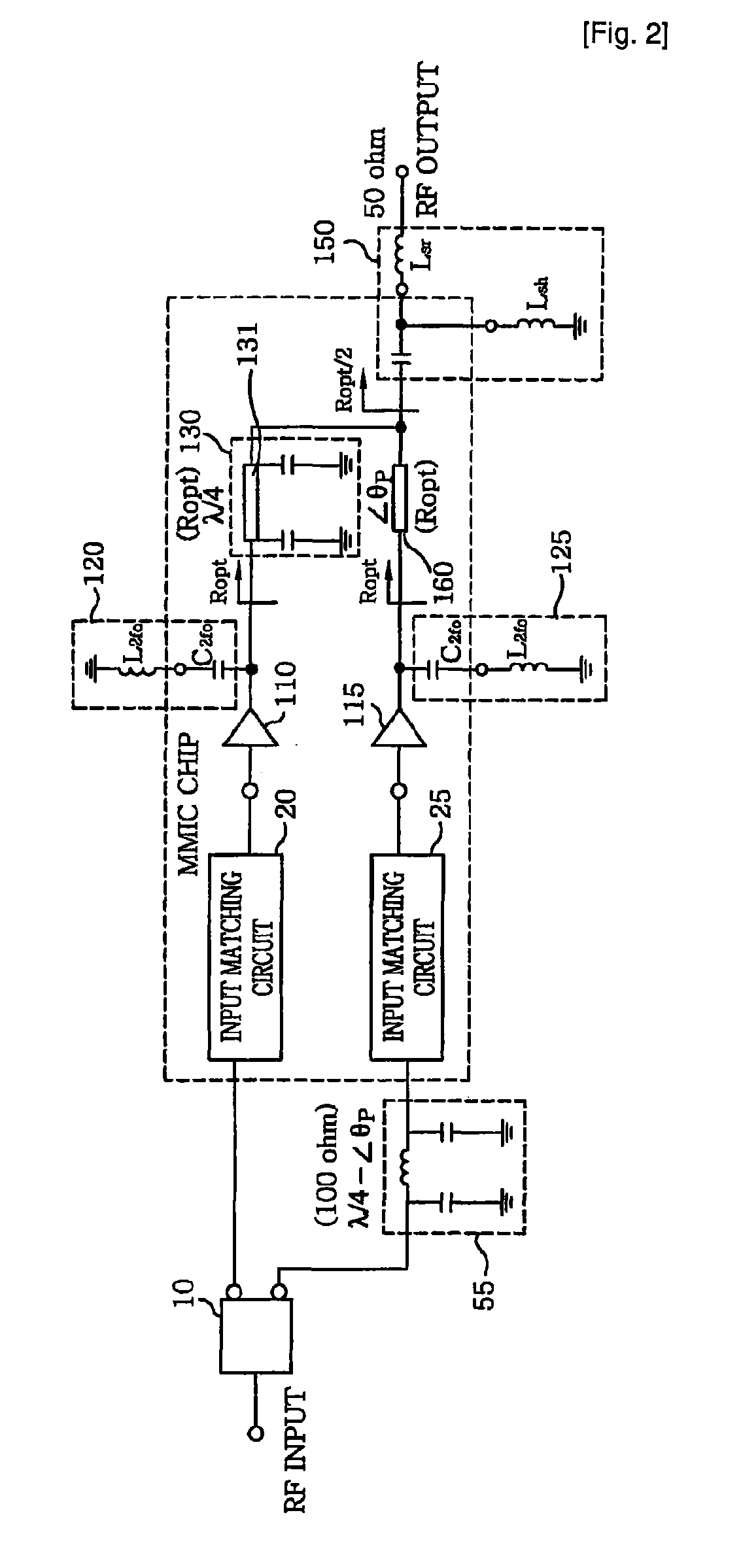
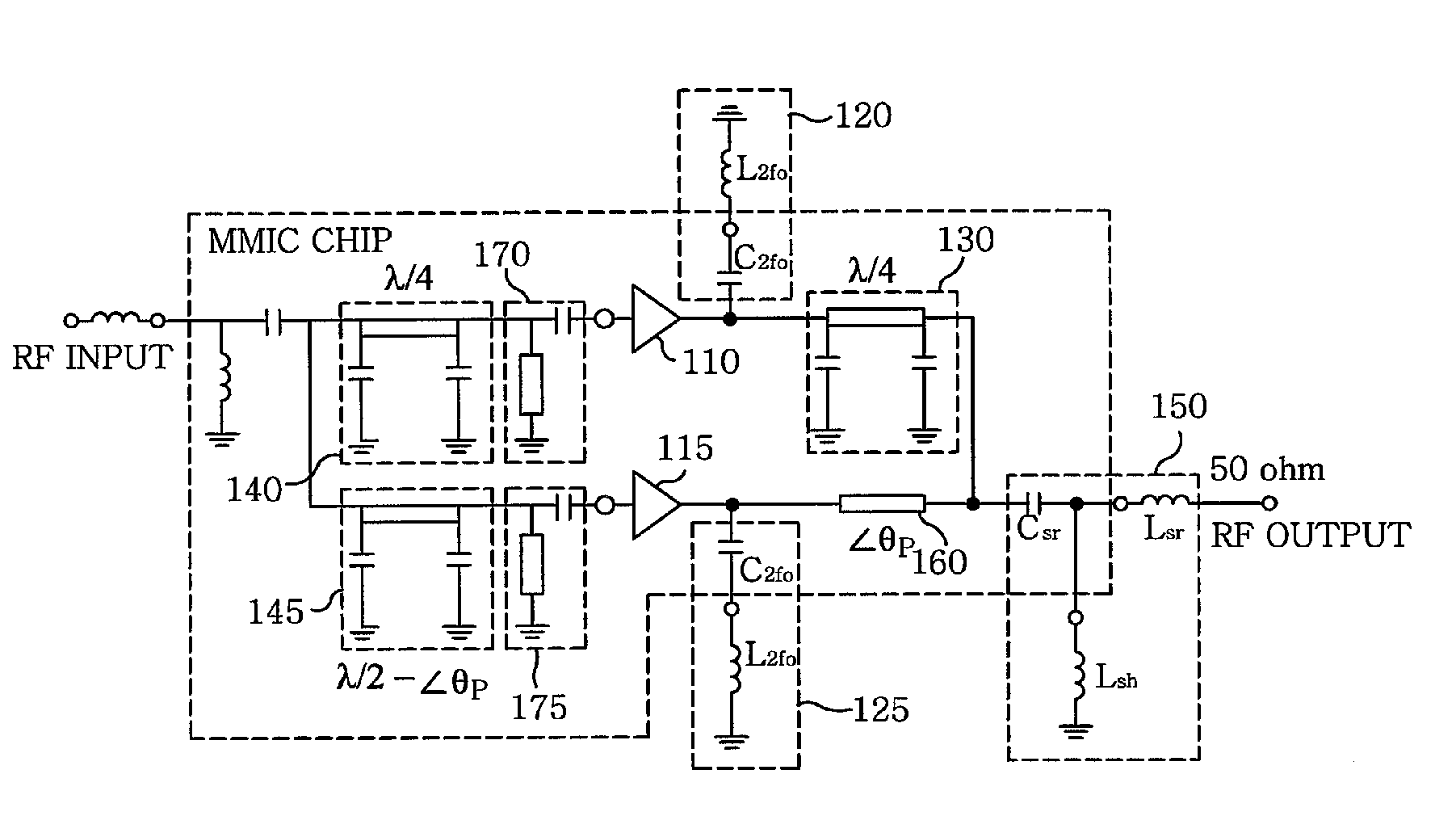
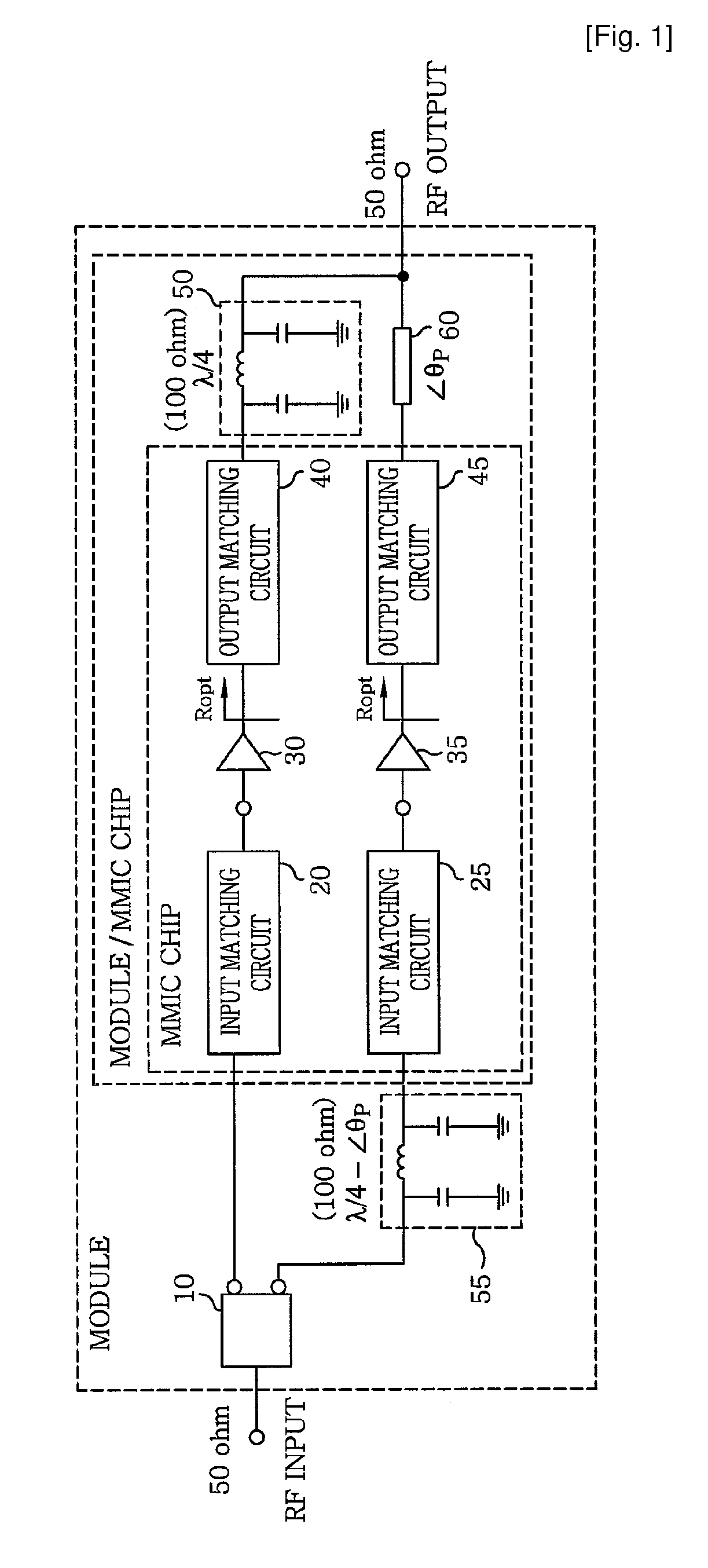
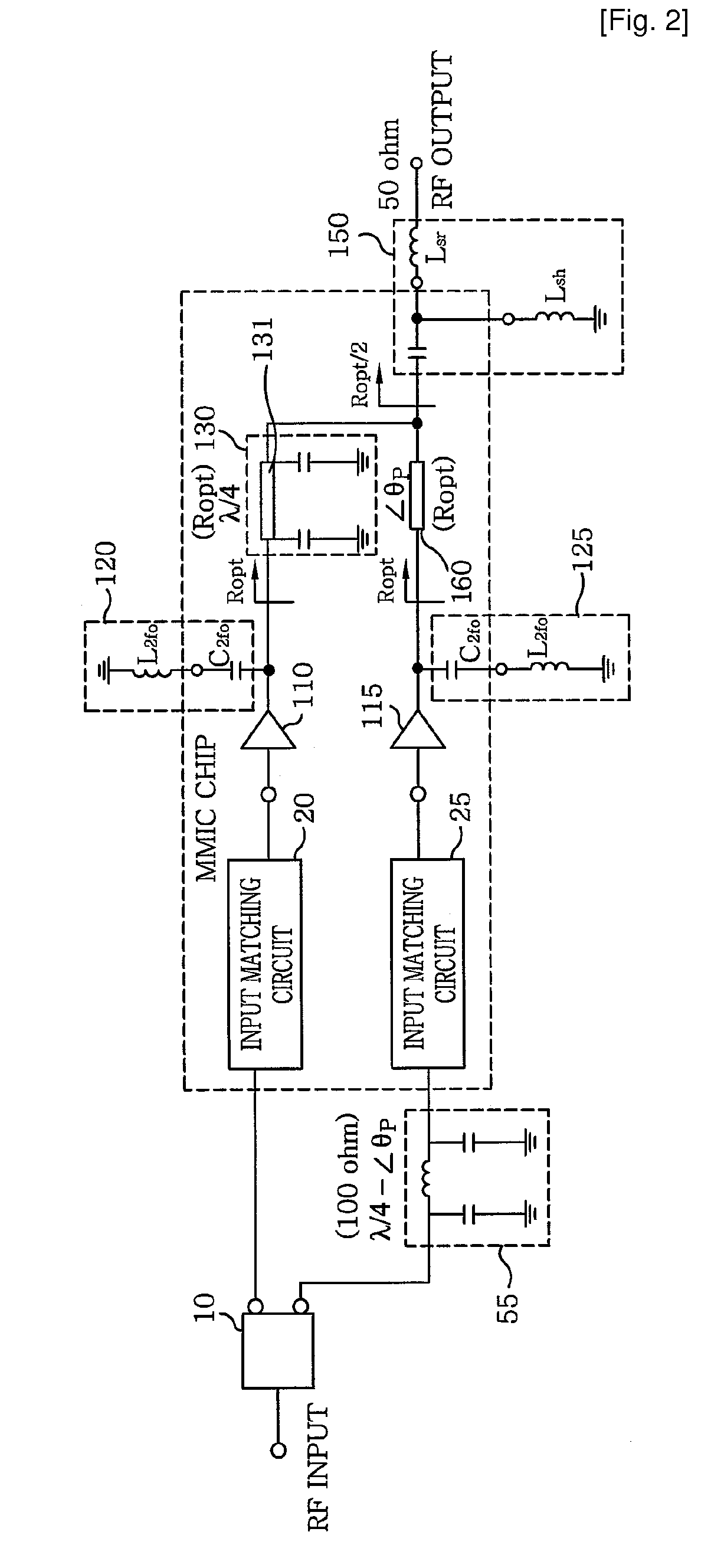
Doherty power amplifier
ActiveUS7973600B2Good effectFurther integrationAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
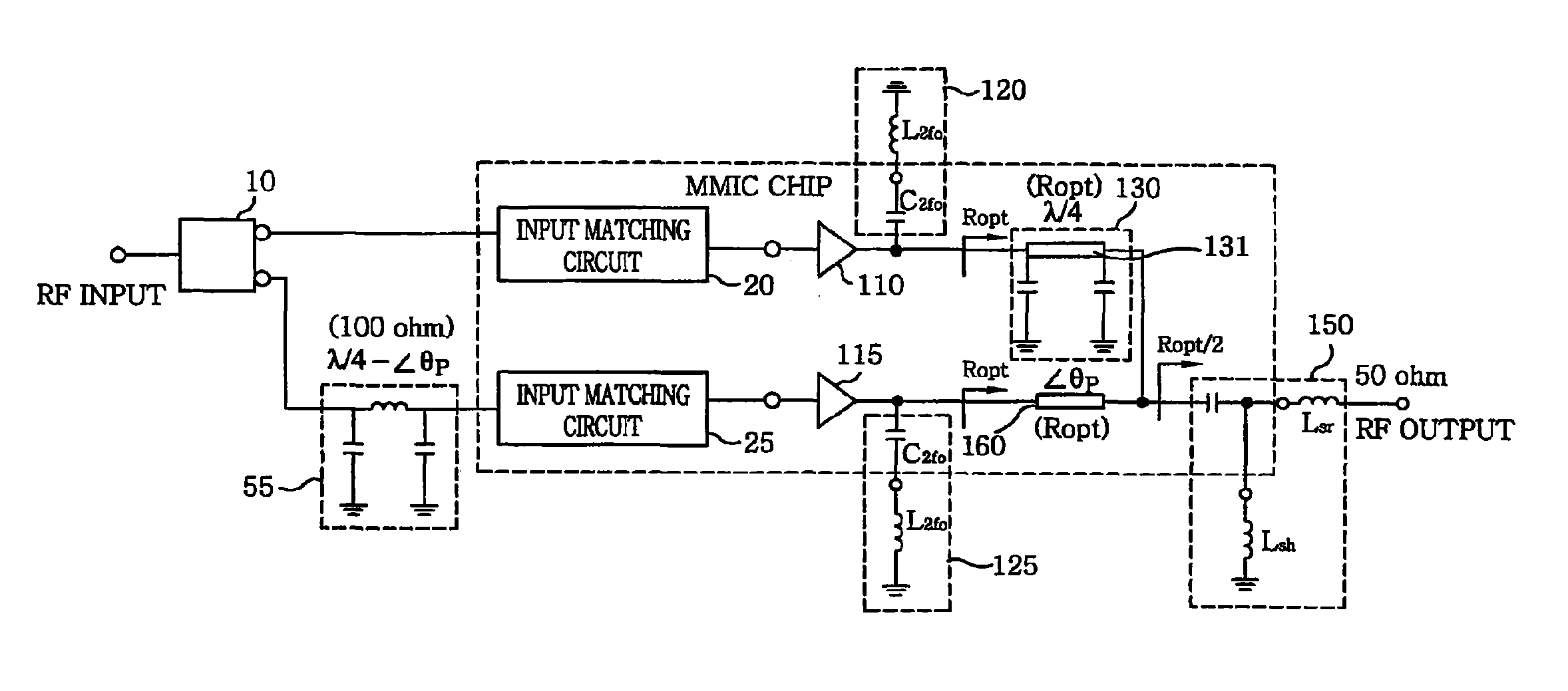
The present invention relates to a power amplifier; and, more particularly, to a Doherty power amplifier. The power amplifier includes at least one carrier amplifier; at least one peaking amplifier arranged in parallel with the carrier amplifier in such a manner that the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier collectively operate as a Doherty amplifier; a plurality of input matching circuits, at least one of which is respectively connected to an input ends of the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier; at least one impedance control circuit, each of which is connected to an output end of each carrier amplifier for controlling a load line impedance of the said each carrier amplifier; at least one output matching circuit directly or indirectly connected to output ends of the impedance control circuit and the peaking amplifier; and at least one first delay circuit for matching delays between the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier. The present invention provides an improved Doherty power amplifier capable of achieving a further miniaturization and integration while maintaining an advantage in terms of efficiency and linearity of a Doherty power amplifier by employing an improved output and input matching method, and capable of operating more similar to the ideal operation of a Doherty power amplifier by applying an improved input power division method thereto.
Owner:WIPAM
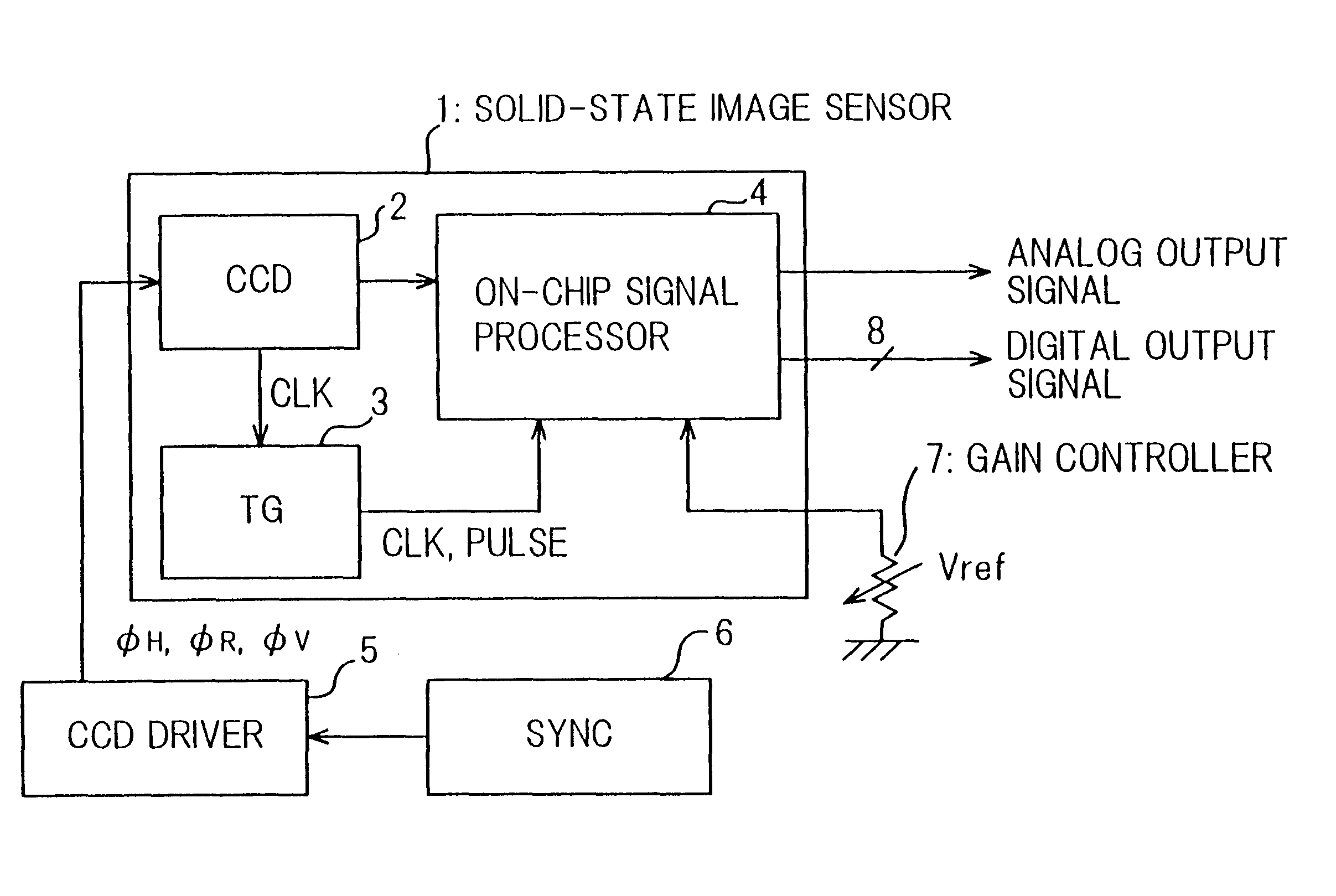
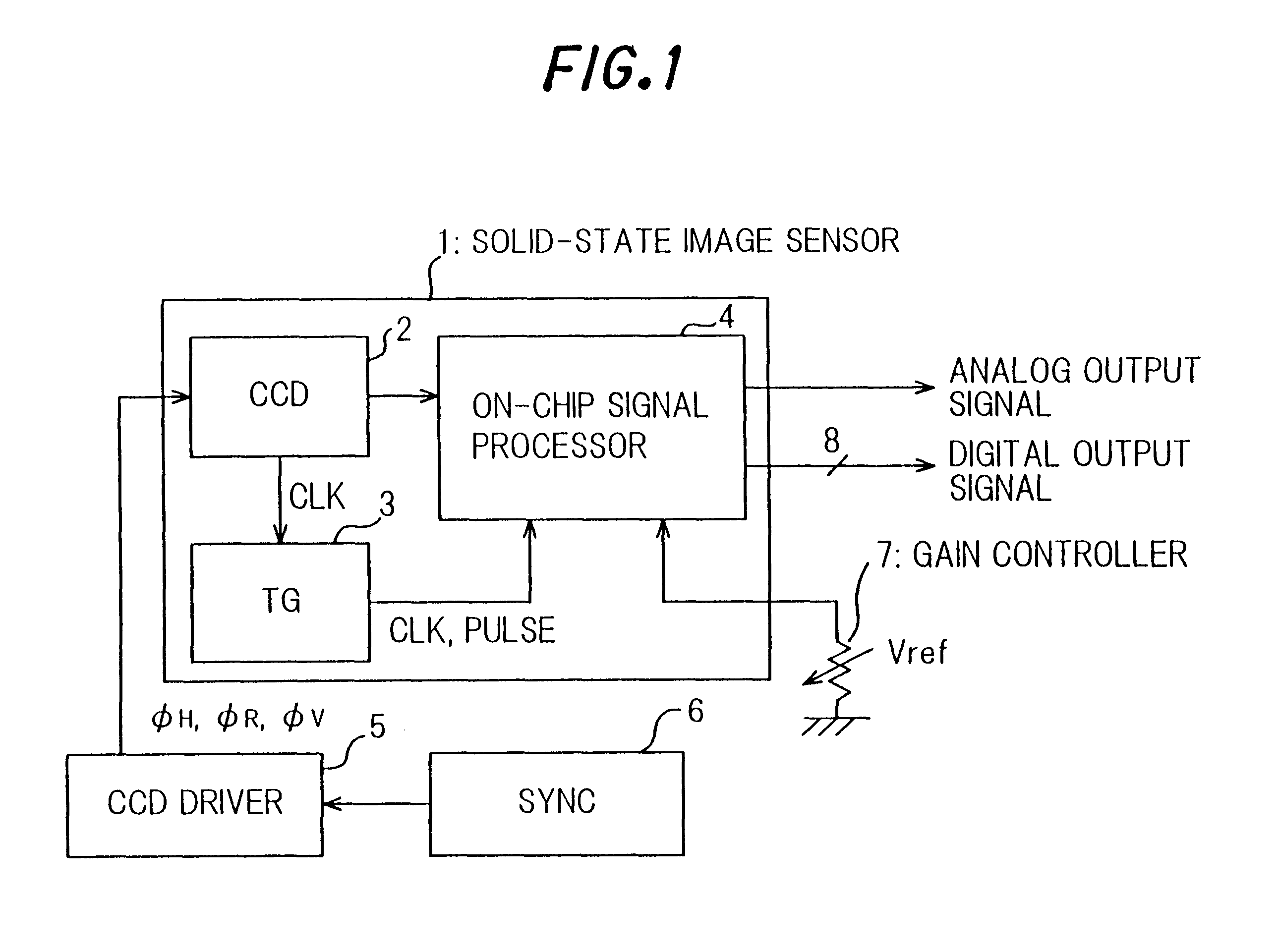
Solid-state camera including a charge coupled device
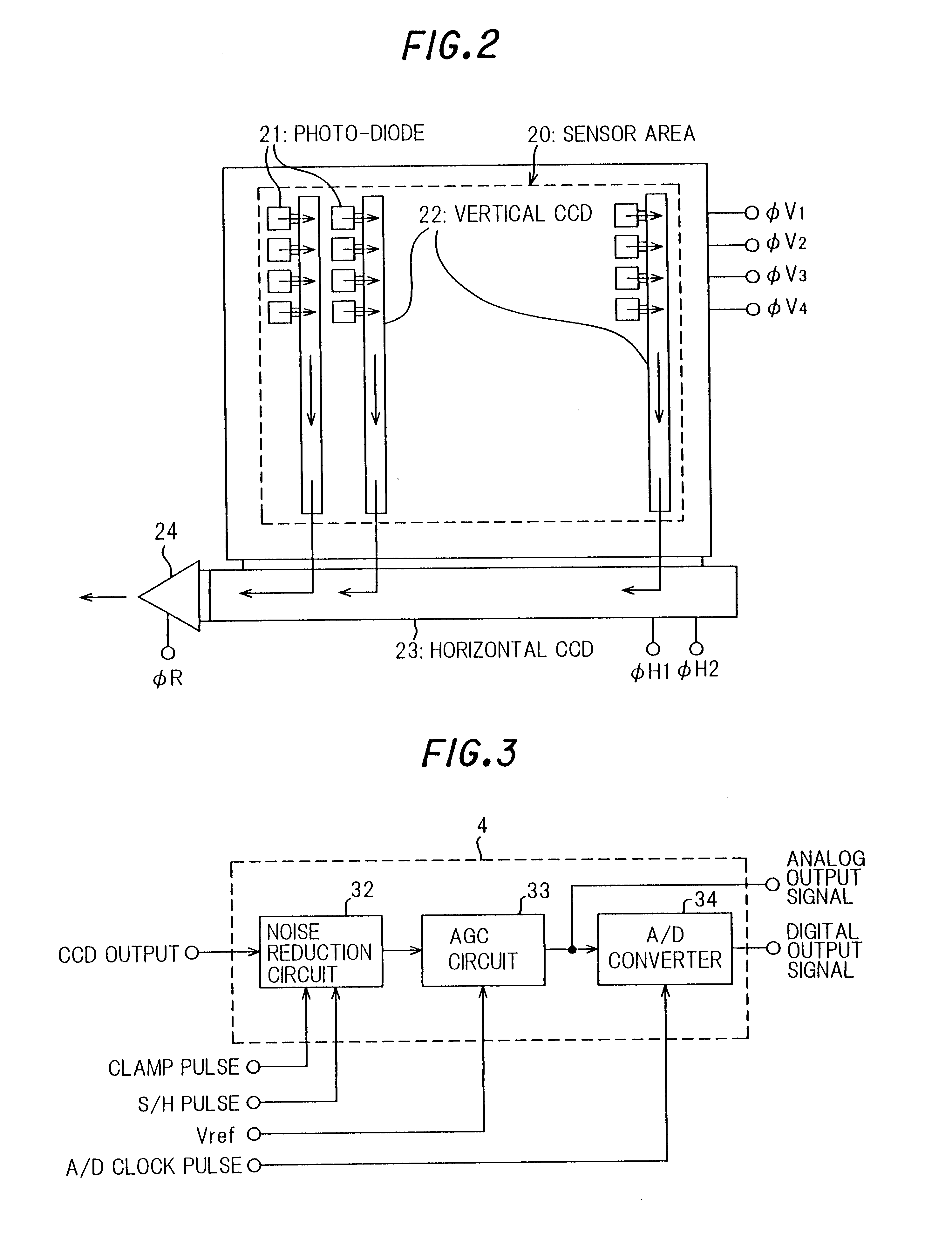
InactiveUS6940553B1Simple and miniaturized and economical configurationImprove performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor chipEngineering
To provide a solid-state image sensor, wherein no field adjustment of timing pulse phases used in the signal processor or of signal balances is needed, and noise performance is more improved, with a simple, miniaturized and economical configuration, a solid-state image sensor (1) of the invention comprises: a CCD (2) configured on a semiconductor chip for generating a CCD signal according to an optical image focused on a sensor area thereof; an on-chip signal processor (4) configured on the semiconductor chip by way of the same fabrication process with the CCD including a noise reduction circuit for eliminating noises from the CCD signal, an AGC circuit for amplifying output of of the noise reduction circuit; and a timing pulse generator (3) configured on the semiconductor chip by way of the same fabrication process with the CCD (2) for generating timing pulses used the on-chip signal processor. The on-chip signal processor (4) of the solid-state image sensor (1) may further comprise an A / D converter for converting output of the AGC circuit into a digital signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Tail lamp structure for vehicles
ActiveUS7341364B2Reduce depthFurther miniaturizationVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20110115085A1Avoid crackingReduce distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor chip
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
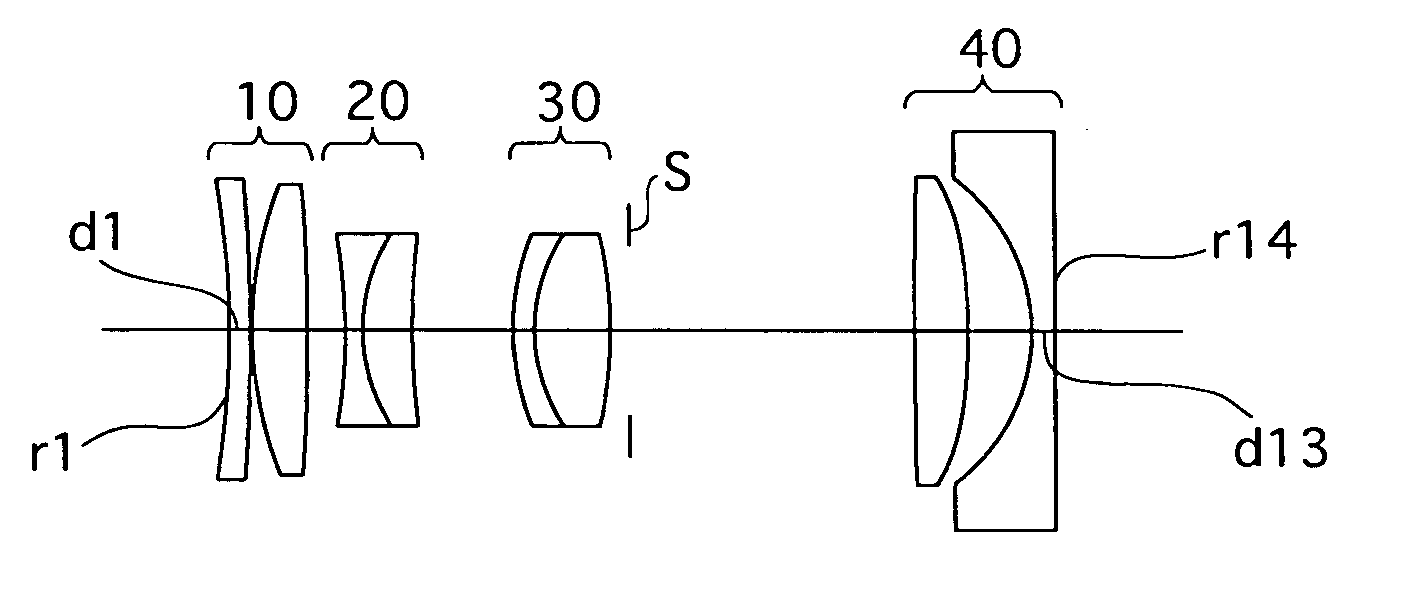
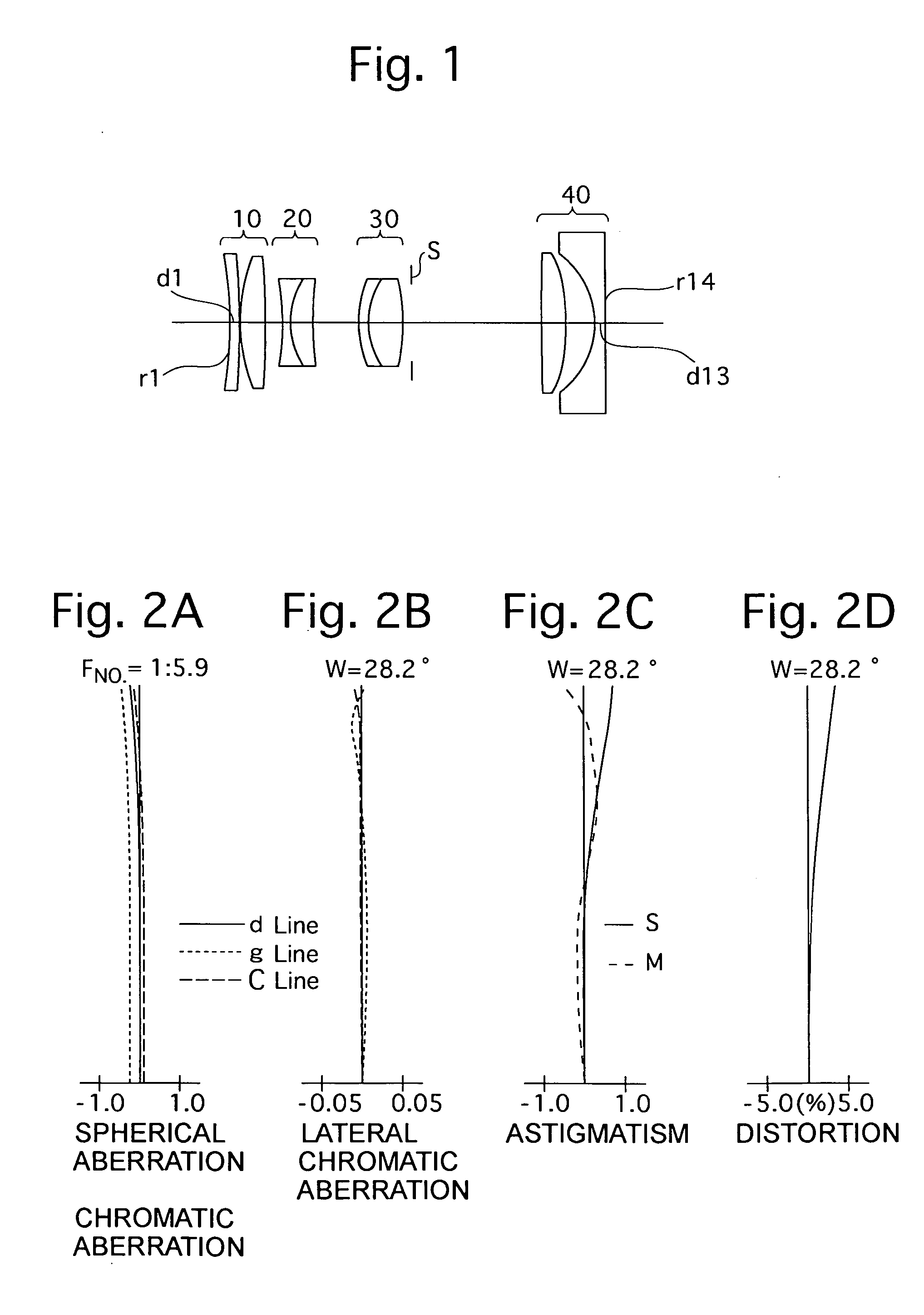
Zoom lens
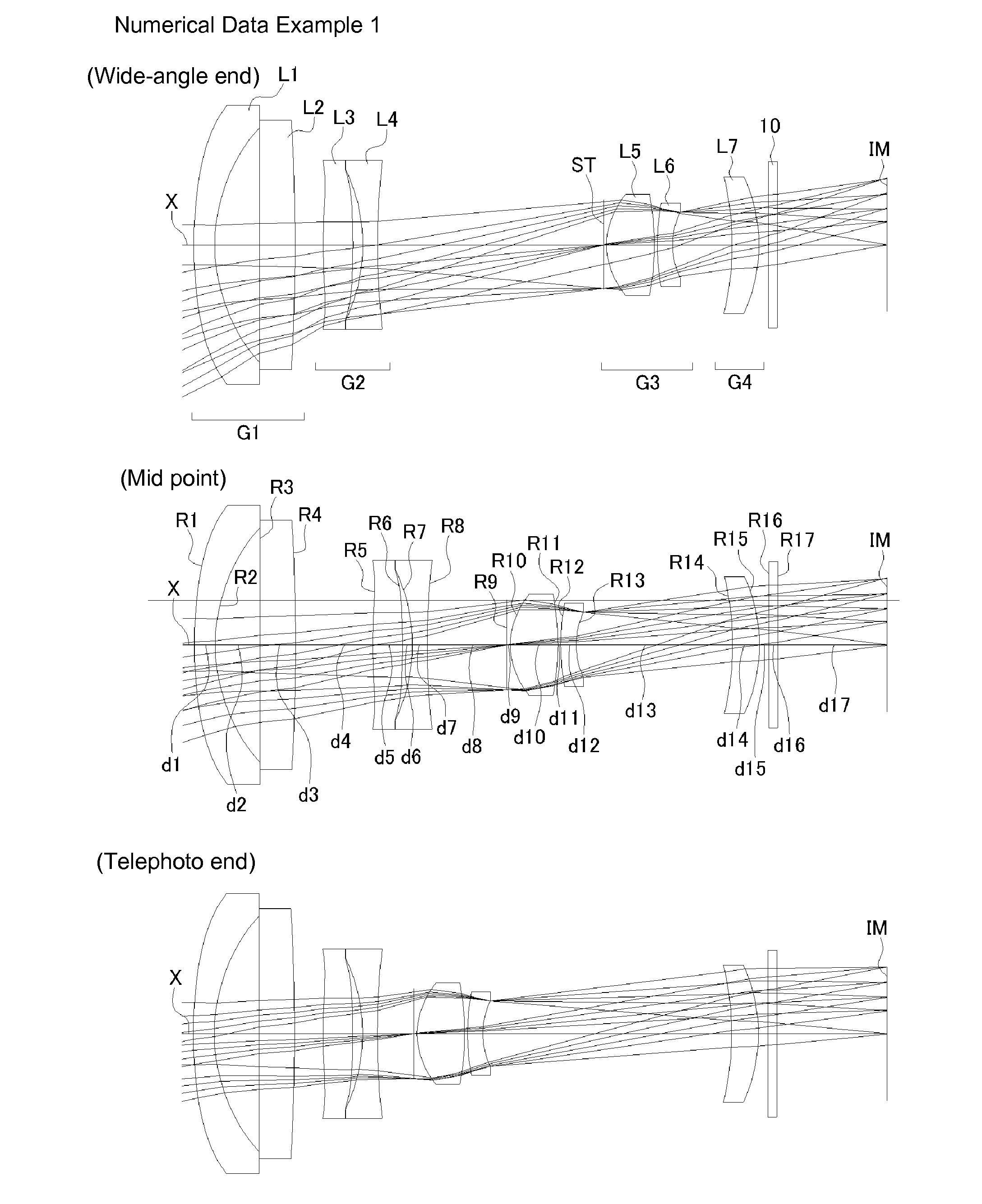
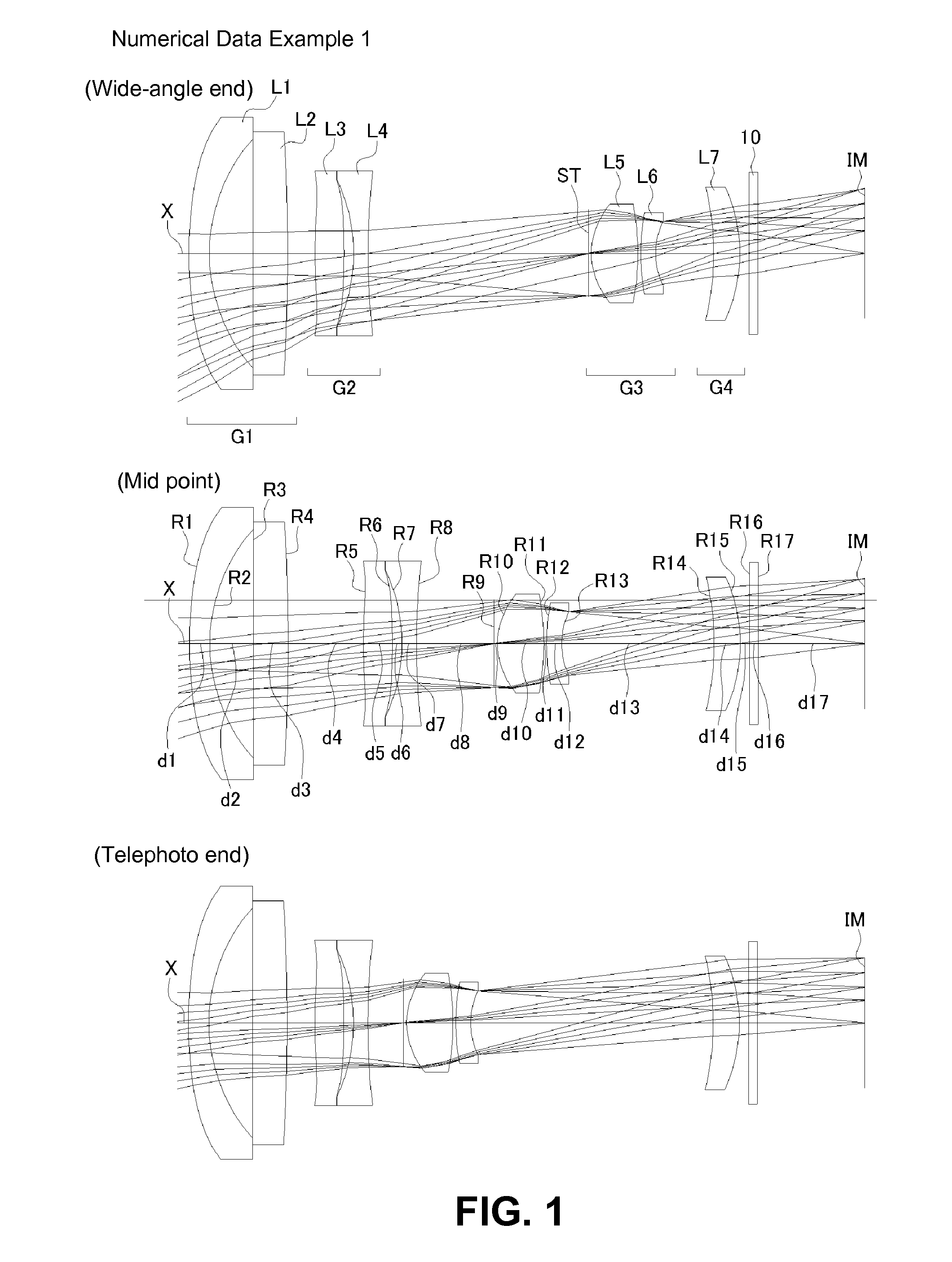
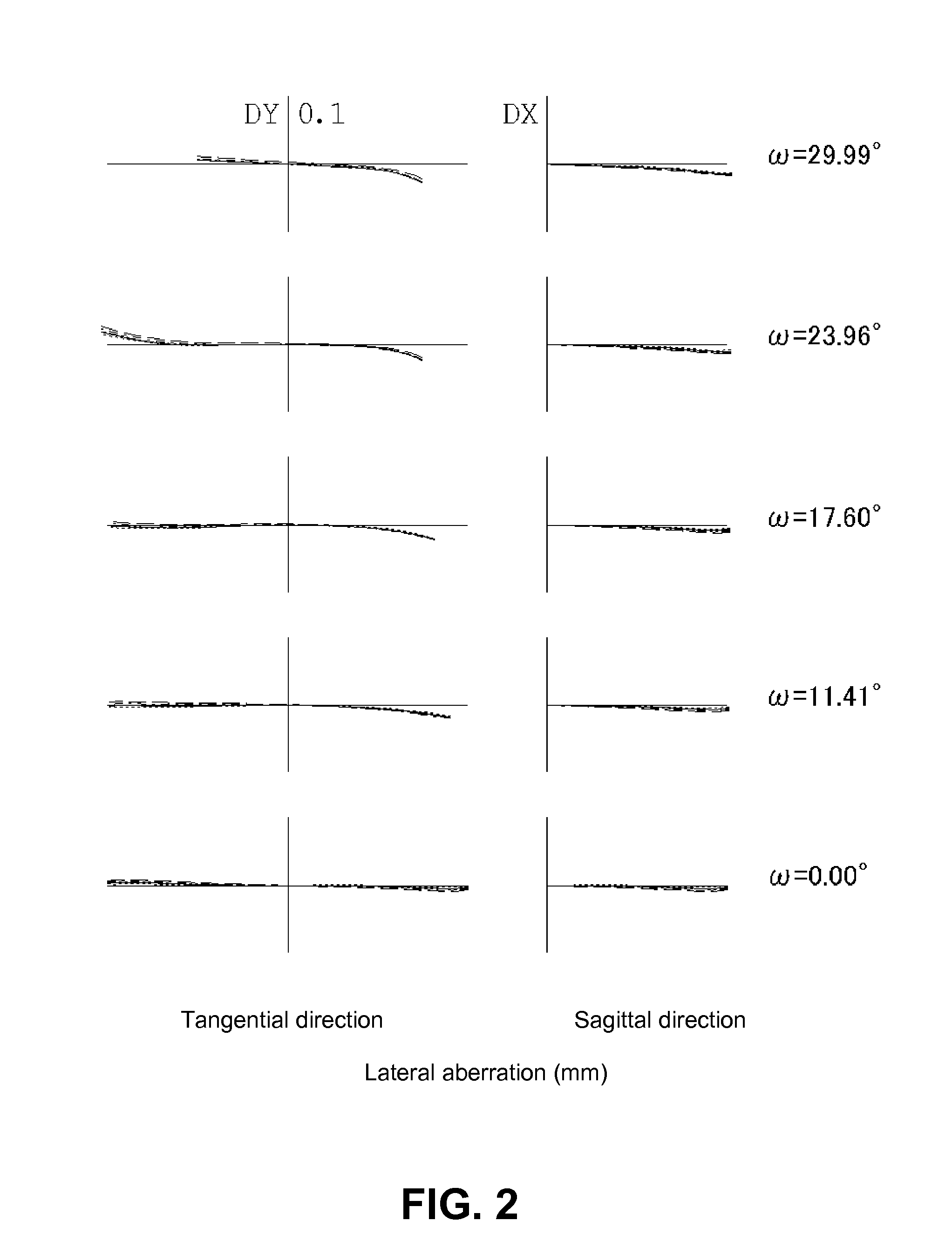
ActiveUS20130021677A1Improve image qualityImprove performanceOptical elementsCamera lensMagnification
A zoom lens includes a first lens group that has a lens having negative refractive power and a light path changing member; a second lens group that includes a lens having positive refractive power and a lens having negative refractive power, and has negative refractive power as a whole; a third lens group that includes a stop, a front group lens having positive refractive power, and a rear group lens having negative refractive power, and has positive refractive power as a whole; and a fourth lens group having positive or negative refractive power. Upon changing magnification from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end, the first lens group and the fourth lens group are fixed. The second lens group moves to the object side after the second lens group moves to an image side, and the third lens group linearly moves to the object side.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Manufacturing method for wiring substrates
ActiveUS20050170631A1High positioning accuracyImprove recognition accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsLocation detectionElectrical conductor
A manufacturing method for wiring substrates for photographing a positioning mark formed with a high precision using reflected light and executing a relative positioning operation between a wiring substrate workpiece and an exposure mask based thereon. The method steps include successively laminating a conductor layer and dielectric layer on a plate-like core and forming a positioning mark by irradiating the main surface of dielectric layer with laser light. By irradiating the positioning mark with position detecting light from the side of the main surface of the dielectric layer and detecting reflected light, relative positioning between the wiring substrate workpiece and the exposure mask is based on the detection result.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080179652A1Lower resistanceImprove production yieldTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
The semiconductor memory device includes: an interlayer insulating film that is formed on a semiconductor substrate; an insulating film that is formed on the interlayer insulating film and has a cylinder hole; and a capacitor that has an impurity-containing silicon film, a lower metal electrode, a capacitive insulating film and an upper electrode, which are formed so as to cover a bottom and a side of the cylinder hole, wherein the cylinder hole extends through the insulating film so as to expose an end side of the contact plug, the end side facing opposite from the source electrode; and the impurity-containing silicon film has a silicide layer near an interface between the impurity-containing silicon film and the lower metal electrode, the silicide layer being produced by a reaction of impurity-containing silicon included in the impurity-containing silicon film with metal included in the lower metal electrode.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
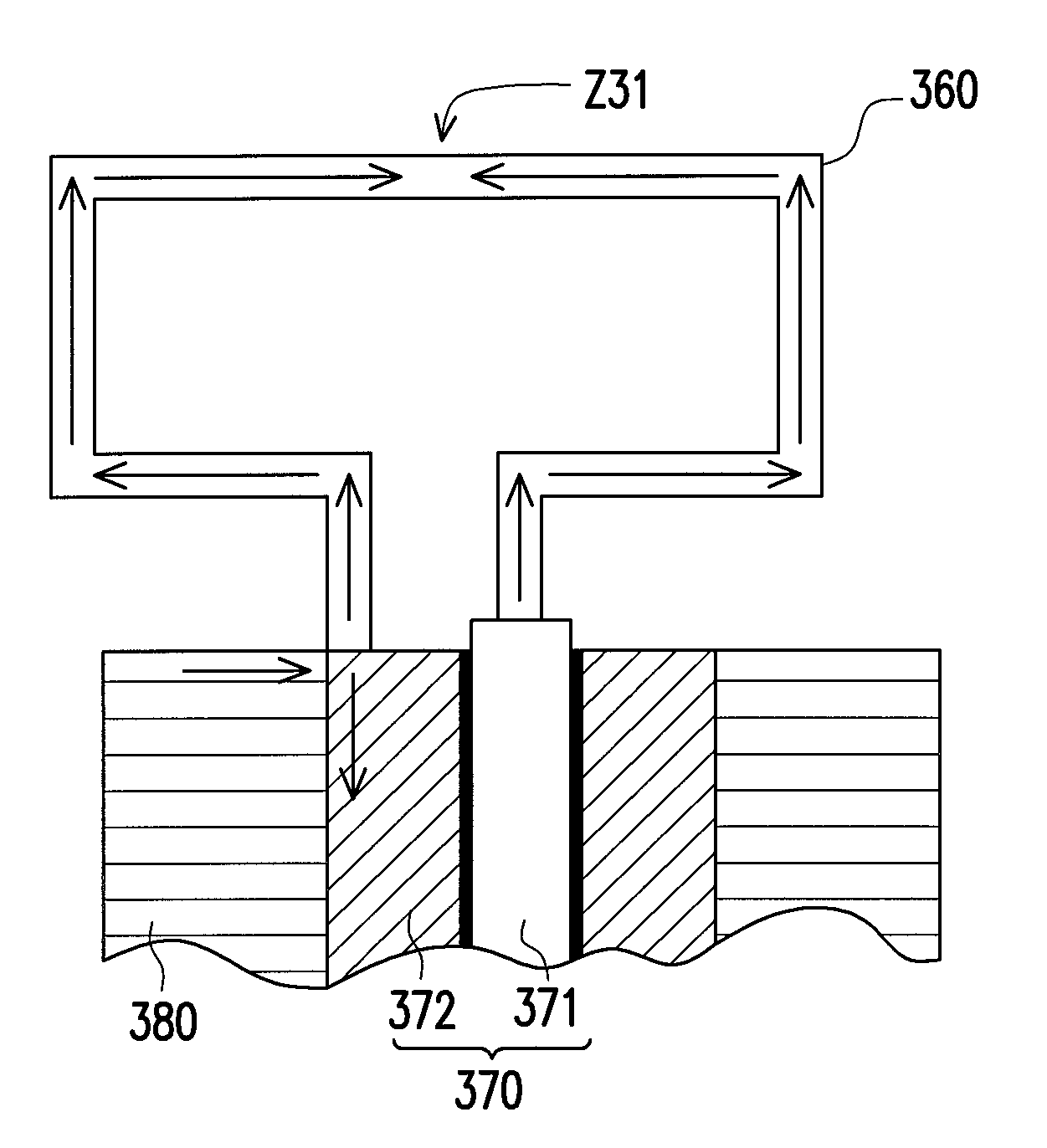
Optical fiber lateral scanner for a miniature optical fiber probe
InactiveUS20060285791A1Easy to assembleFurther miniaturizationCoupling light guidesElectrical conductorMiniaturization
The present invention relates to an optical fiber magnetic scanning arrangement for a miniature optical fiber probe and can be applied for optical beam delivery in various optical imaging techniques. The arrangement is of the type where an optical fiber is rigidly fixed to a current conductor and serving as a flexible cantilever with a capability for the distal part of the optical fiber of being deflected in a direction substantially orthogonal to its own axis. New designs of the magnetic system are less critical to the shape and dimensional tolerances of scanner elements and assembly. These designs provide a potential for a less difficult assembly process and for further miniaturization. According to one aspect of the invention the permanent magnet system includes at least a first permanent magnet with a magnetization direction that is substantially aligned with the own axis of the optical fiber. The current conductor loop is placed adjacent to the one of the end faces of the first permanent magnet. According to another aspect of the invention the permanent magnet system includes at least a first permanent magnet piece with a magnetization direction that is substantially orthogonal to the own axis of the optical fiber. The permanent magnet piece extends in a direction substantially aligned with the own axis of the optical fiber and has an inner surface, the current conductor loop being adjacent to at least a part of the inner surface of the first permanent magnet piece. According to another aspect of the invention the permanent magnet system includes a permanent magnet of a hollow cylinder type with a substantially radial magnetization direction. The permanent magnet cylinder extends in a direction substantially aligned with the own axis of the optical fiber. The current conductor loop is placed inside the permanent magnet cylinder. A miniature optical fiber probe, which incorporates the optical fiber lateral scanner of the invention, will inherit all its benefits.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060292816A1High incidenceImprove compatibilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialCapacitor
A semiconductor device comprises: an insulating film formed over a semiconductor substrate and having a first recess; a plurality of capacitor elements each of which is composed of a capacitor lower electrode formed on wall and bottom portions of the first recess and having a second recess, a capacitor insulating film of a dielectric film formed on wall and bottom portions of the second recess and having a third recess, and a capacitor upper electrode formed on wall and bottom portions of the third recess; and a conductive layer (referred hereinafter to as a low-resistance conductive layer) which is formed to cover at least portions of the respective capacitor upper electrodes constituting the plurality of capacitor elements and to extend across the plurality of capacitor elements and which has a lower resistance than the capacitor upper electrode.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Doherty power amplifier
ActiveUS20090273398A1Good effectEfficiency advantageAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
The present invention relates to a power amplifier; and, more particularly, to a Doherty power amplifier. The power amplifier includes at least one carrier amplifier; at least one peaking amplifier arranged in parallel with the carrier amplifier in such a manner that the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier collectively operate as a Doherty amplifier; a plurality of input matching circuits, at least one of which is respectively connected to an input ends of the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier; at least one impedance control circuit, each of which is connected to an output end of each carrier amplifier for controlling a load line impedance of the said each carrier amplifier; at least one output matching circuit directly or indirectly connected to output ends of the impedance control circuit and the peaking amplifier; and at least one first delay circuit for matching delays between the carrier amplifier and the peaking amplifier. The present invention provides an improved Doherty power amplifier capable of achieving a further miniaturization and integration while maintaining an advantage in terms of efficiency and linearity of a Doherty power amplifier by employing an improved output and input matching method, and capable of operating more similar to the ideal operation of a Doherty power amplifier by applying an improved input power division method thereto.
Owner:WIPAM
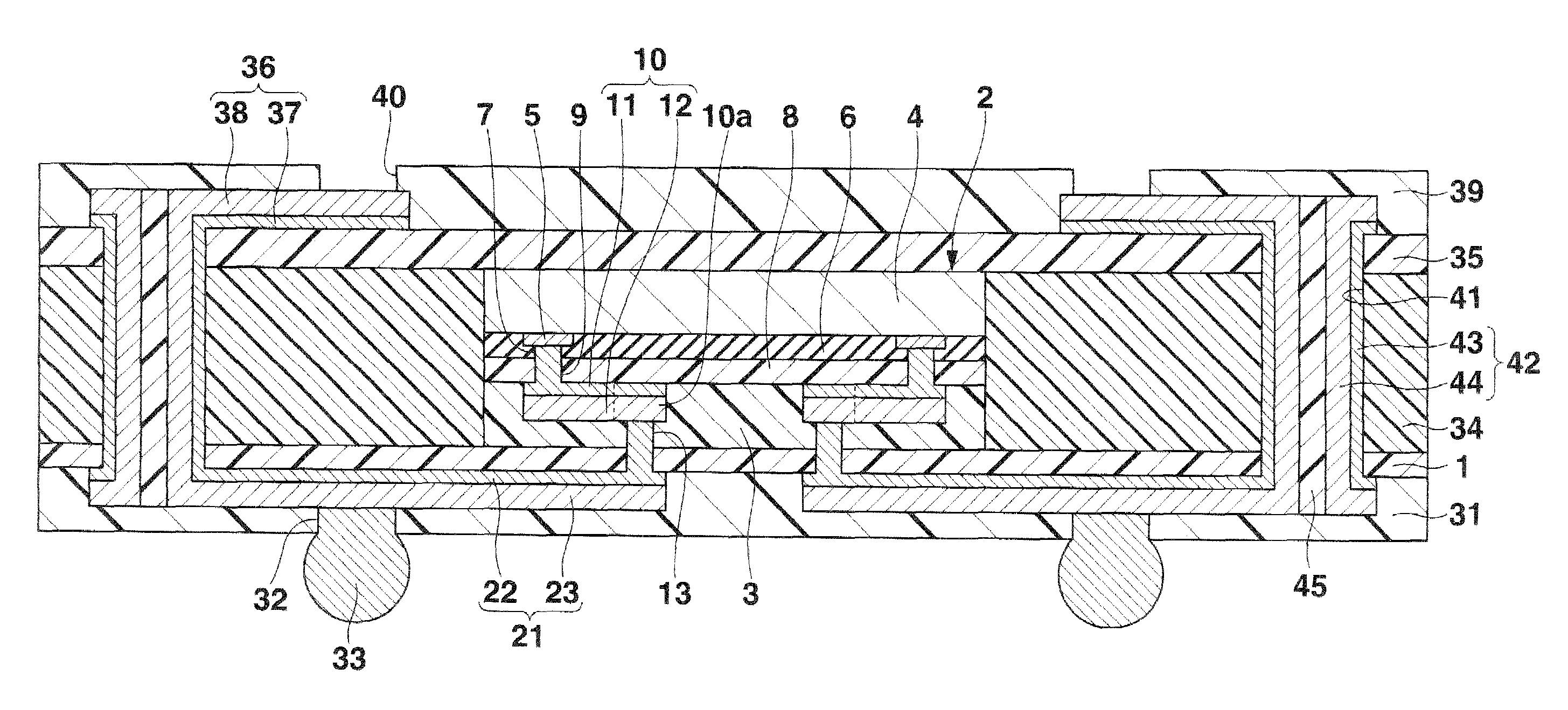
Semiconductor device having wiring line and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090194866A1Further miniaturizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLaser beams
An insulating film covering the upper surface of an external connection electrode of a semiconductor construct is formed. A mask metal layer in which there is formed an opening having a planar size smaller than that of the external connection electrode is formed on the insulating film. The mask metal layer is used as a mask to apply a laser beam to the insulating film, such that a connection opening reaching the external connection electrode is formed in the insulating film. A wiring line is formed on the insulating film in such a manner as to be connected to the external connection electrode via the connection opening.
Owner:TERAMIKROS INC
Tilt focus method and mechanism for an optical drive
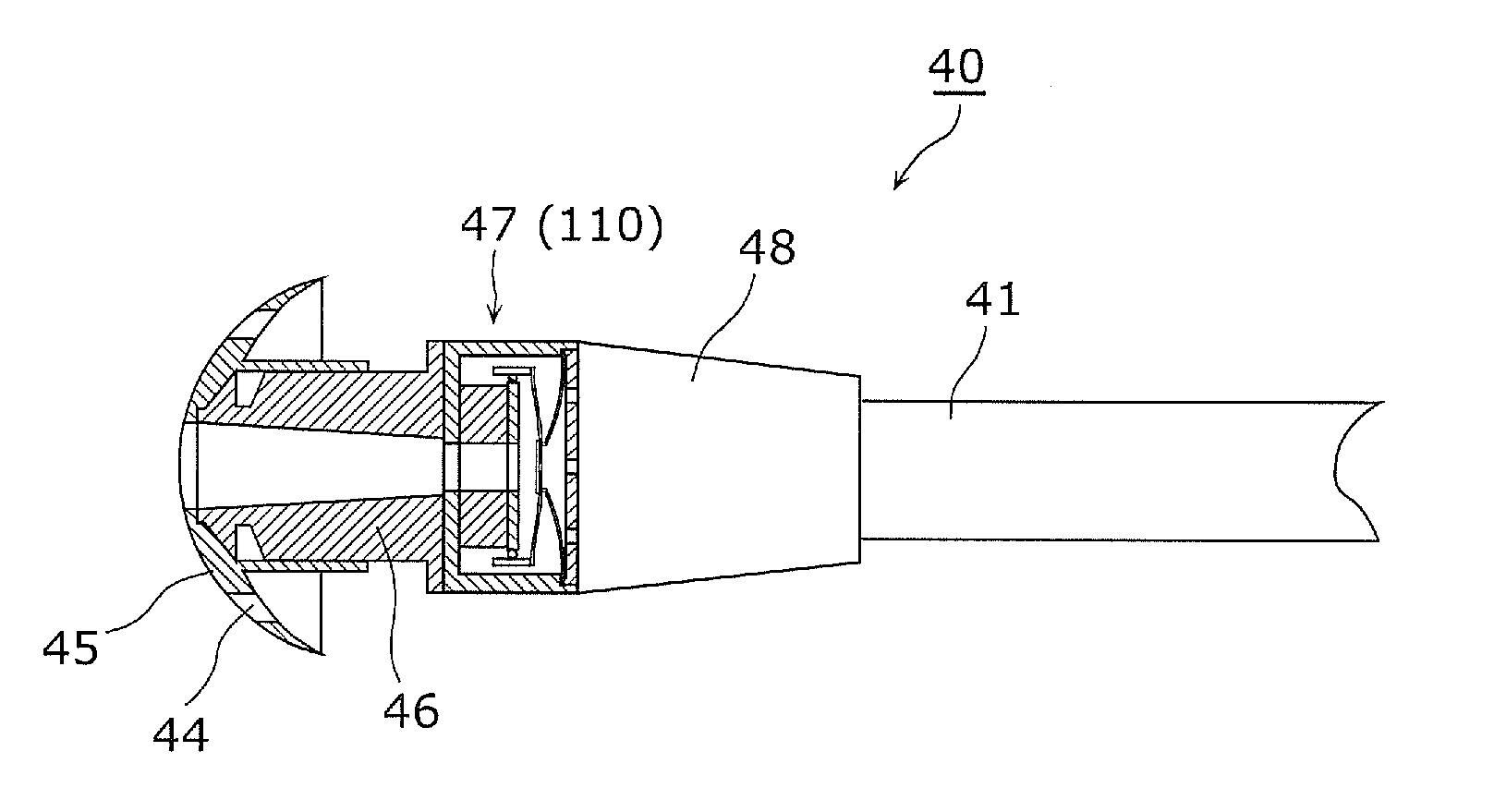
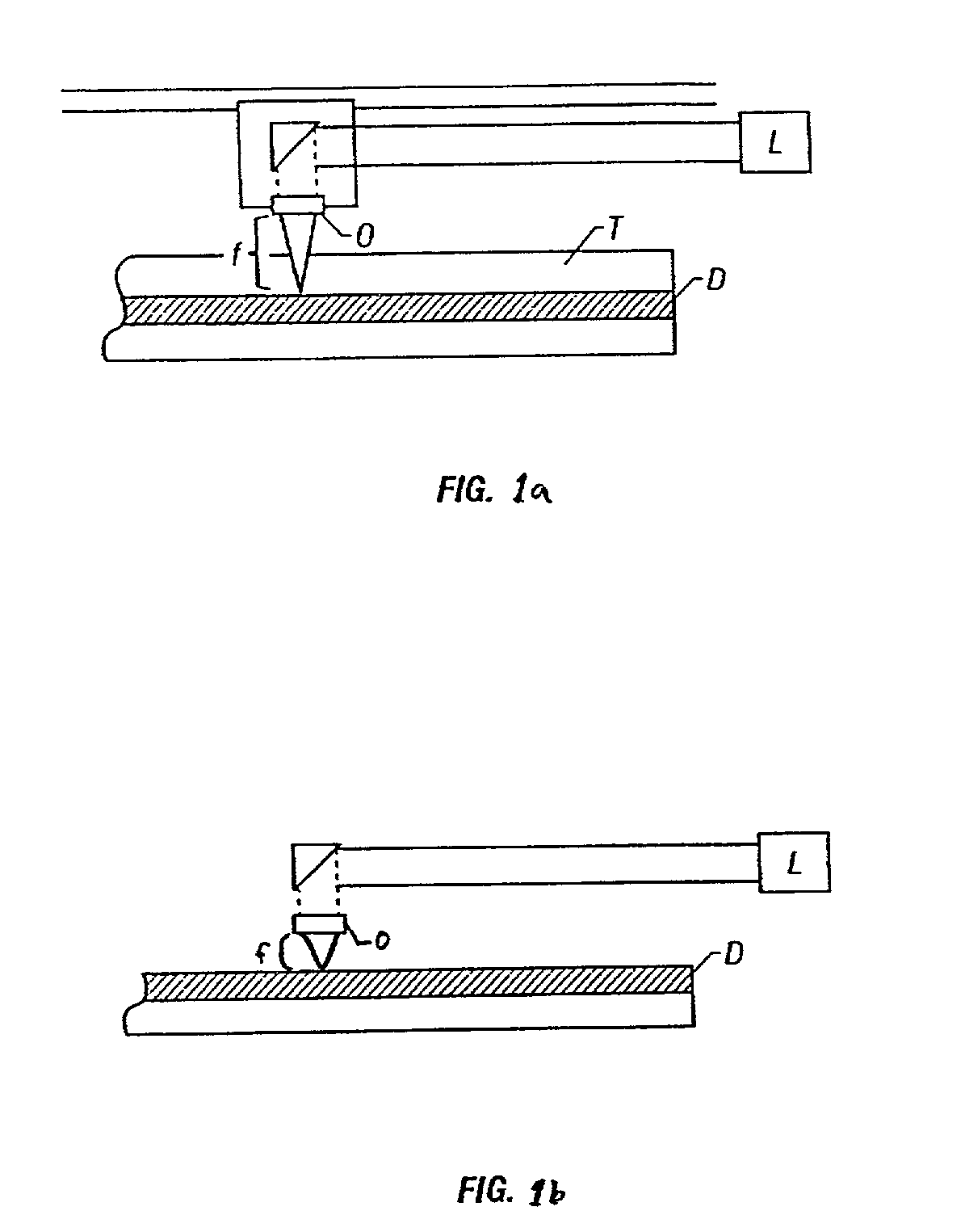
InactiveUS6901598B1Short focal lengthSolve the real problemDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageInformation layerLight beam
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for dynamically positioning the objective lens in an optical disk drive to maintain focus despite loss of perpendicularity between the light beam and the information layer of the optical disk. Loss of perpendicularity may occur as a result of any number of factors, including irregularities in the manufacture of the disk, manufacturing tolerances and assembly of the disk drive components, bearing defect frequencies, shock and vibration. Failure to maintain perpendicularity may interference with the ability of the optical pick up unit of the drive to accurately read and write. The tilt focus mechanism of the present invention utilizes a rotary actuator that positions the objective lens in three dimensions relative to the surface of the optical disk. In one embodiment, a first voice coil motor positions the actuator generally in two dimensions parallel to the surface of the disk and a second voice coil motor positions the objective lens generally along an arcuate path orthogonal to the surface of the disk.
Owner:DPHI ACQUISITIONS
Iron-core coil assembly
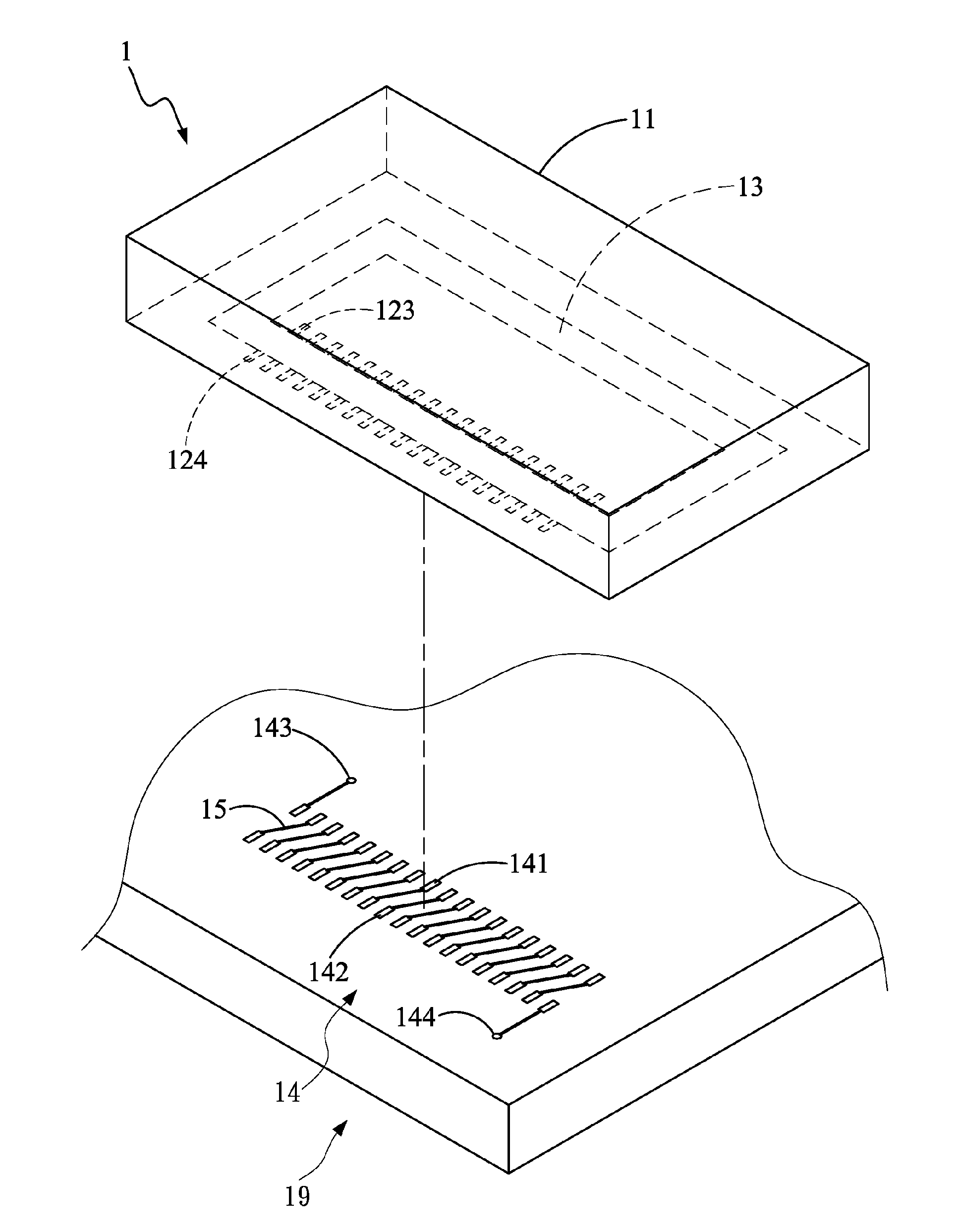
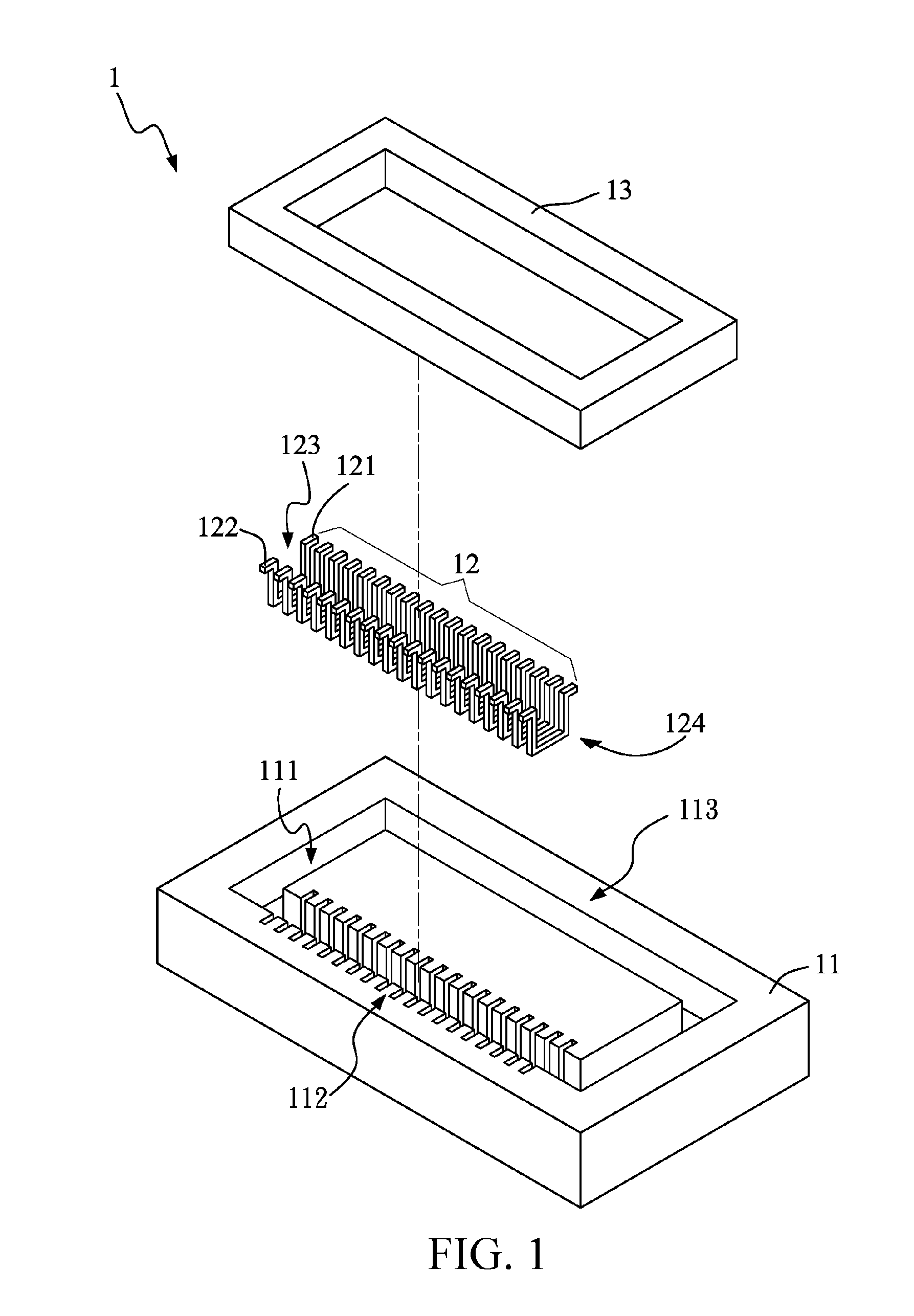
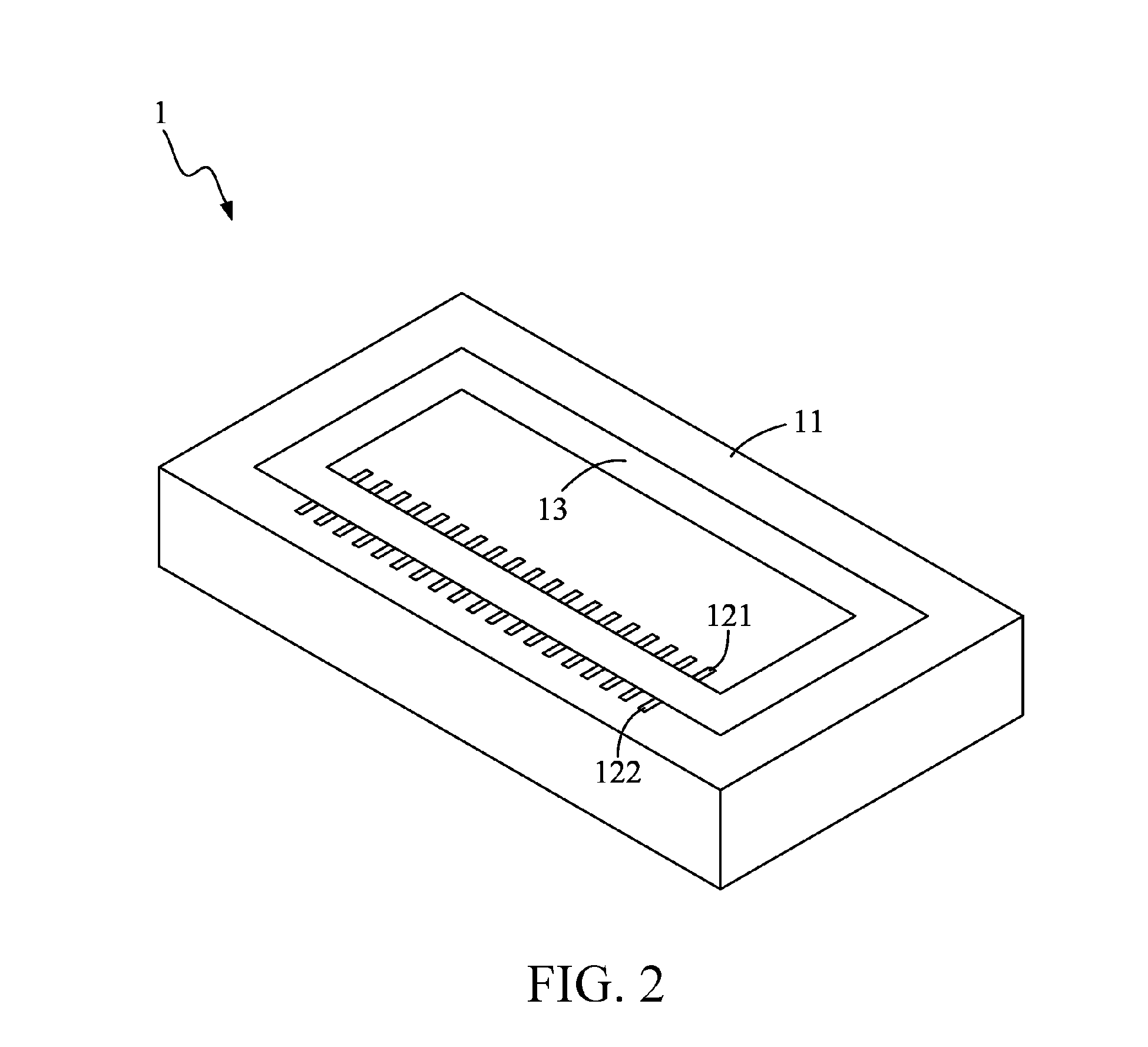
InactiveUS20120025941A1Further miniaturizationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductance with magnetic coreEngineeringConductor Coil
An iron-core coil assembly is provided, which includes a substrate, a plurality of U-shaped wires, a first pin, a second pin, and an iron-core device. The substrate has a groove divided into a winding area and a non-winding area. The plurality of U-shaped wires is disposed in the winding area at a space from each other, and each U-shaped wire has an opening and a recess. The first pin and the second pin are respectively arranged at two ends of the opening, and the recess is located in the groove. The iron-core device is disposed in the groove, and passes through the recess of each U-shaped wire.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTION TECH
Speaker, hearing aid, inner-ear headphone, portable information processing device, and av device
ActiveUS20120087525A1Low frequency reproductionFurther miniaturizationLoudspeaker diaphragm shapeDeaf-aid setsInformation processingEngineering
A speaker including: a chassis internally including a magnet; a plate attached to a top face of the magnet; a voice coil disposed in a magnetic air gap formed in an outer perimeter of the plate so as to be vibratable in a vertical direction; a diaphragm having a periphery that is connected to an upper end of the voice coil; and a suspension connecting the diaphragm and the chassis. The suspension includes a first fixing part fixed to the diaphragm and a second fixing part fixed to the chassis. The second fixing part is positioned above the first fixing part, and at least one of the first fixing part and the second fixing part is disposed in an inner region which is a region located inward of the periphery of the diaphragm as seen from above.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
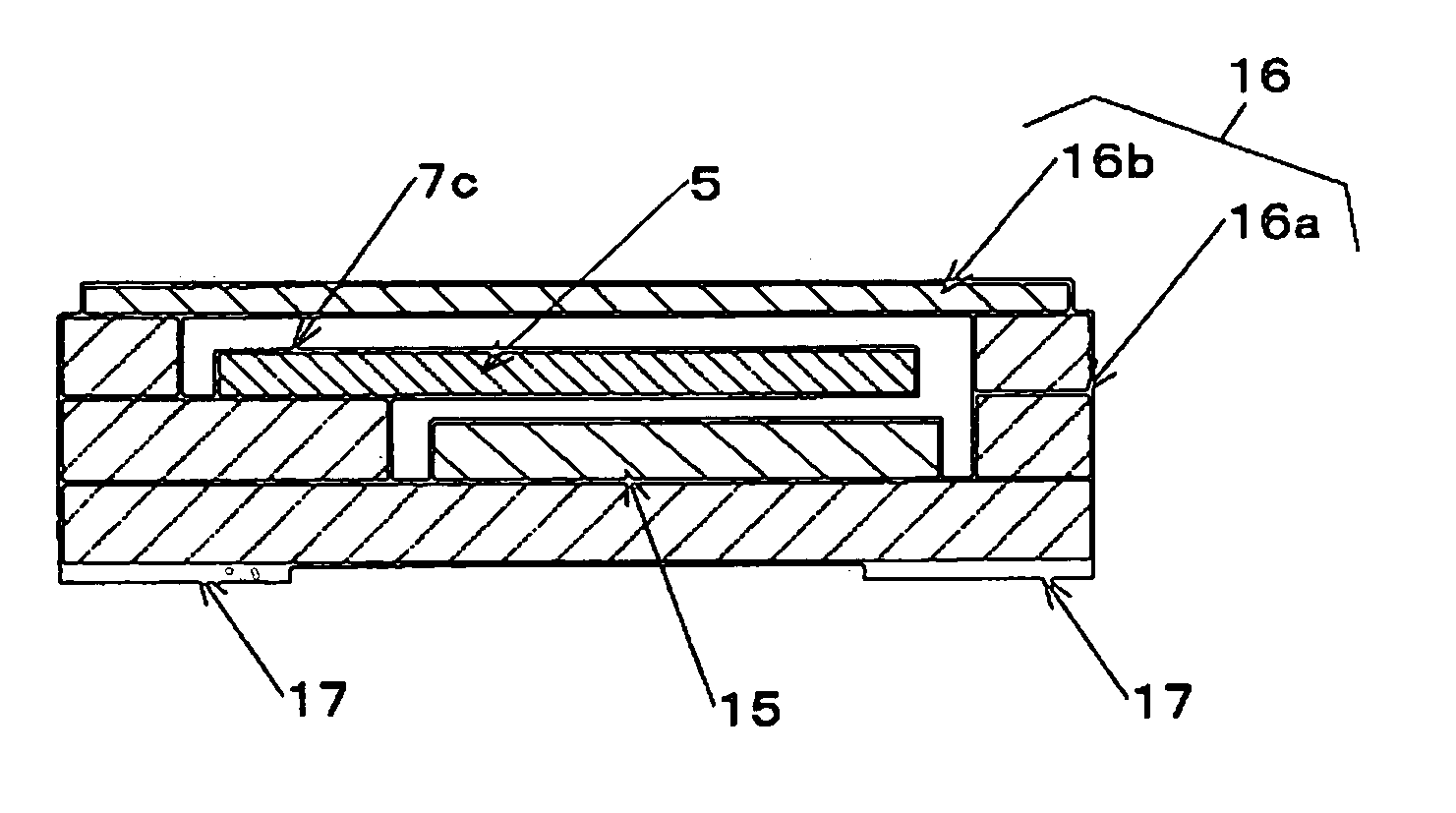
Tuning fork type crystal oscillator with angular velocity detection capability
InactiveUS7446461B2Facilitate downsizingReduce in quantityImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTuning forkAngular velocity
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
Zoom lens system
InactiveUS20050088755A1High zoom ratioFurther miniaturizationDiffraction gratingsOptical axisOptoelectronics
A zoom lens system includes a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group and a fourth lens group. Zooming is performed by moving each lens group in the optical axis direction. The zoom lens system satisfies the following conditions: 0.35<log(fT23 / fW23) / log(ft / fw)<0.55 (1); 0.4<(LDW−LDT) / (ft / fw)<0.7 (2); wherein [0001]f23W: the combined focal length of the second and the third lens groups at the short focal length extremity; [0002]f23T: the combined focal length of the second and the third lens groups at the long focal length extremity; [0003]ft: the focal length of the entire zoom lens system at the long focal length extremity; [0004]fw: the focal length of the entire zoom lens system at the short focal length extremity; [0005]LDw: the distance from the most object-side surface of the first lens group to the most image-side surface of the fourth lens group at the short focal length extremity; and [0006]LDT: the distance from the most object-side surface of the first lens group to the most image-side surface of the fourth lens group at the long focal length extremity.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Tilt focus mechanism for an optical drive
InactiveUS7337452B2Short focal lengthSolve the real problemTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic positioningRotary actuator
An apparatus for dynamically positioning a rotary actuator that positions an objective lens in three dimensions relative to the surface of an optical disk. A first voice coil motor positions the actuator generally in two dimensions parallel to the surface of the disk and a second voice coil motor positions the objective lens generally along an arcuate path orthogonal to the surface of the disk.
Owner:DPHI ACQUISITIONS +1
Fringing field focus motor and mechanism for optical disk drive
InactiveUS6970401B2High bandwidthIncreased bandwidth of trackingCredit registering devices actuationRecord information storageMagnetEngineering
A system for controlling a distance between an optical head and the surface of a rotating optical disk comprising: an actuator arm having a first and second surface, the first surface facing the optical disk, the second surface facing away from the optical disk; an electromagnetic coil having an inner void, said coil adjacent to the second surface of the arm; and at least one permanent magnet producing a magnetic field that passes through the coil such that when an electric current is applied to the coil, a force is created at two or more segments of the coil.
Owner:DPHI ACQUISITIONS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com