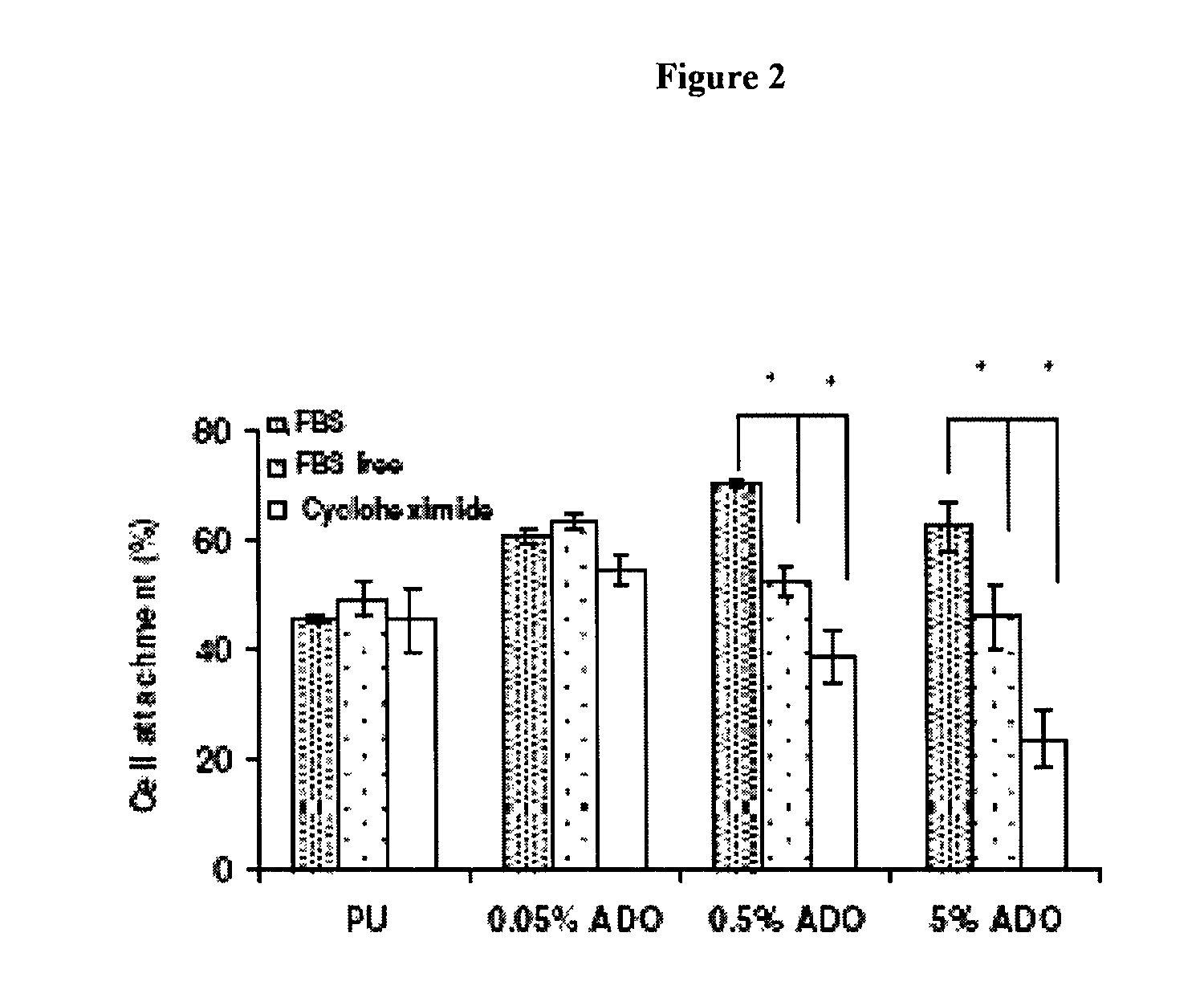
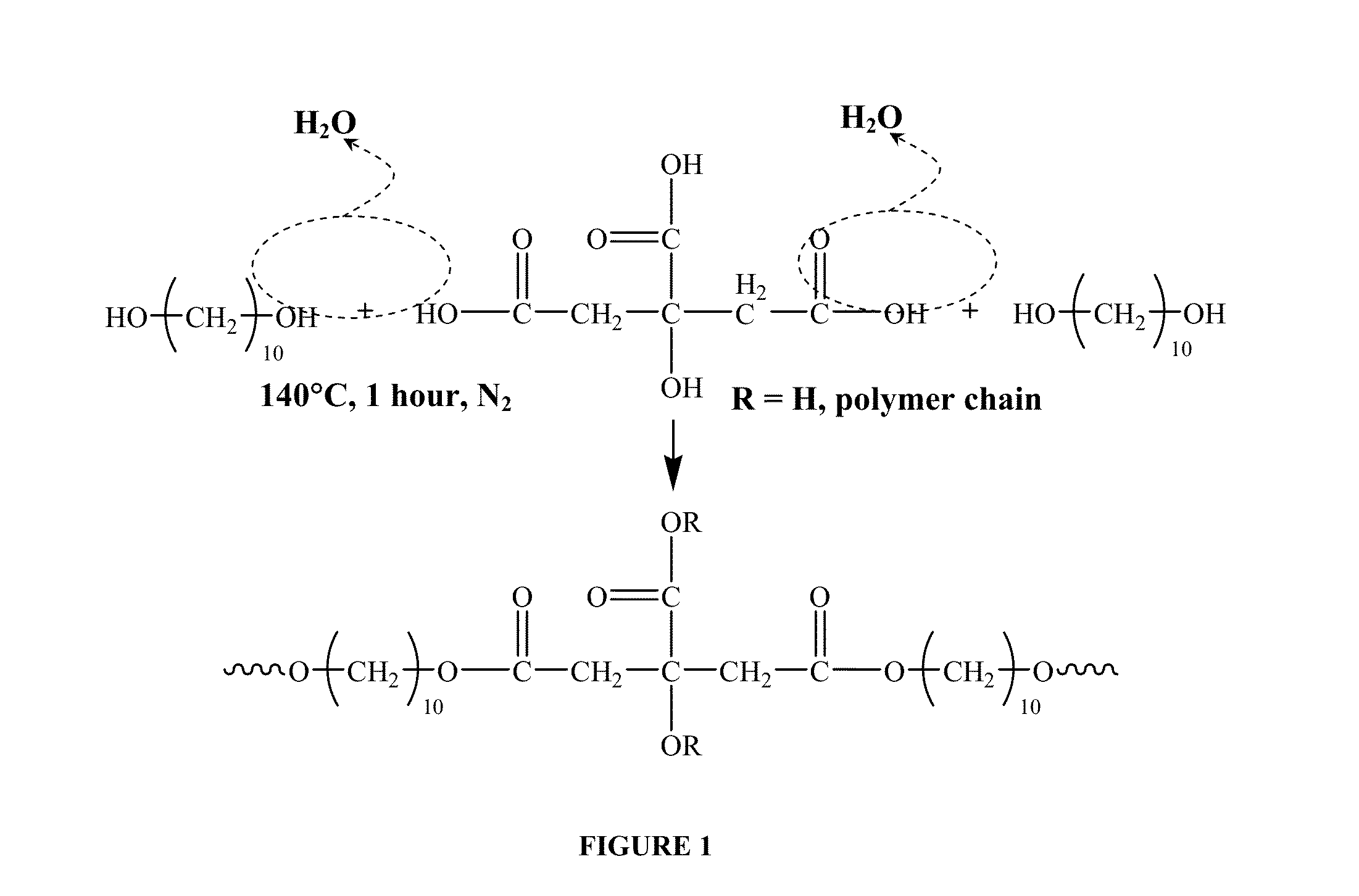
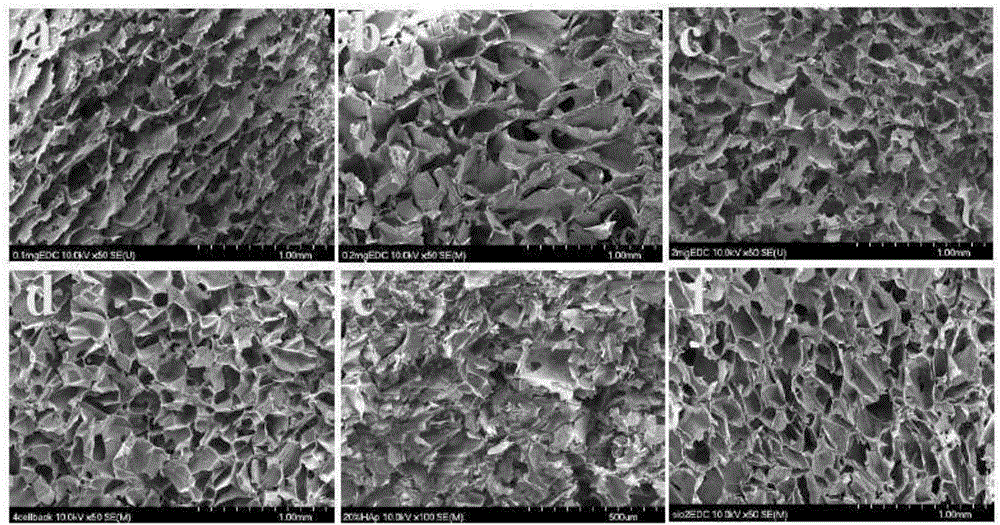
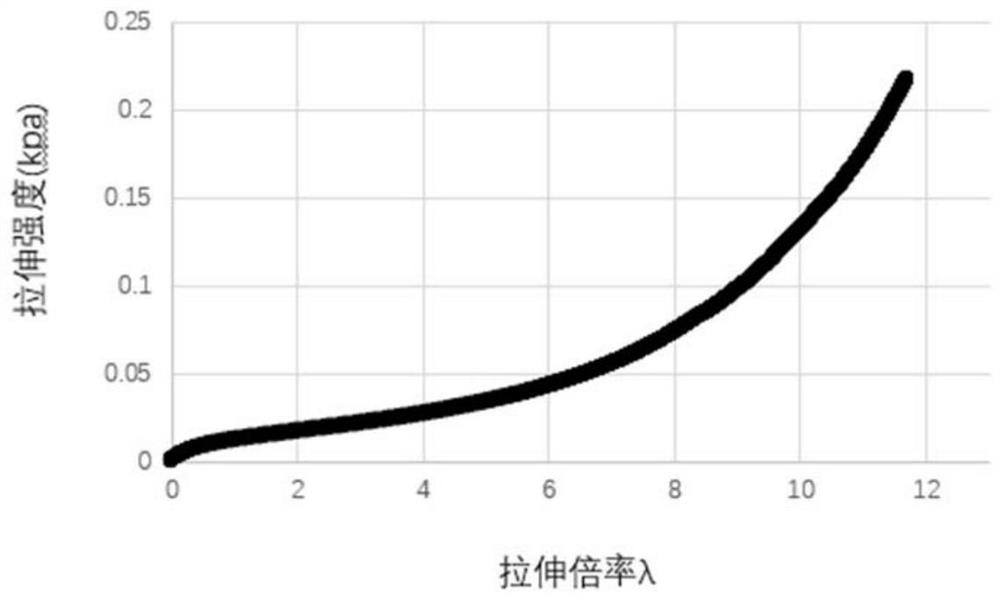
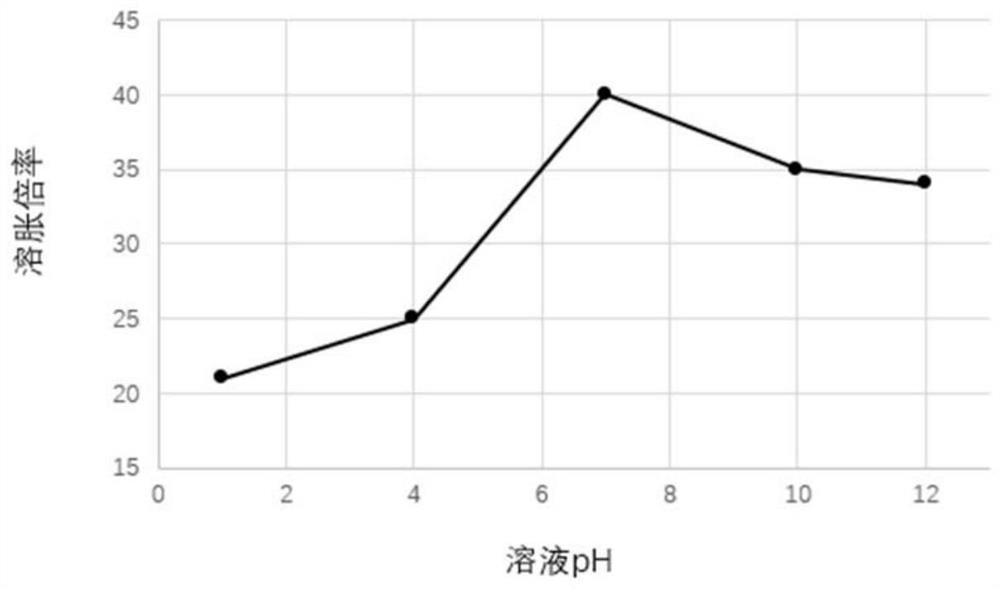
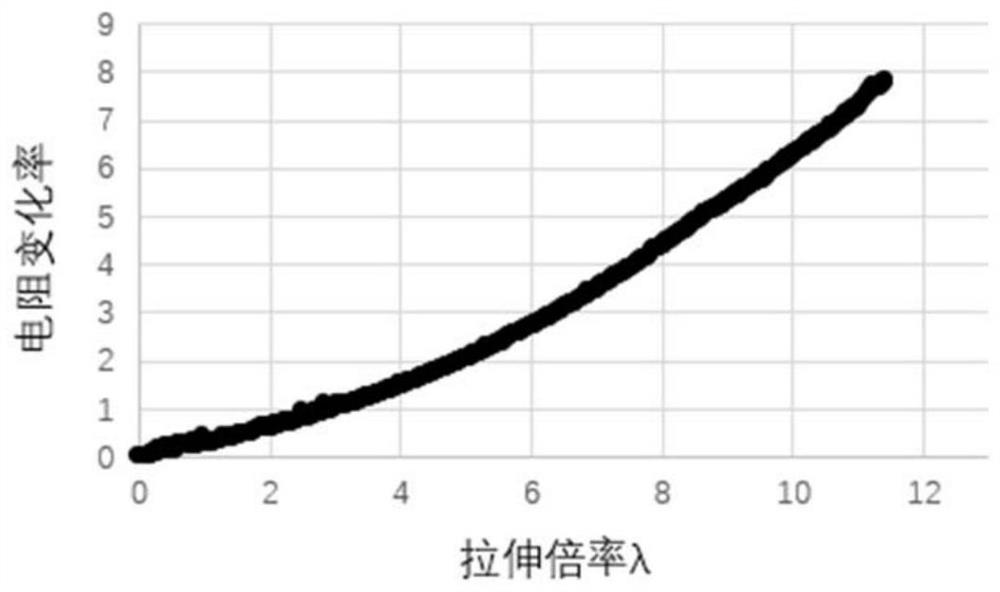
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Soft tissue engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
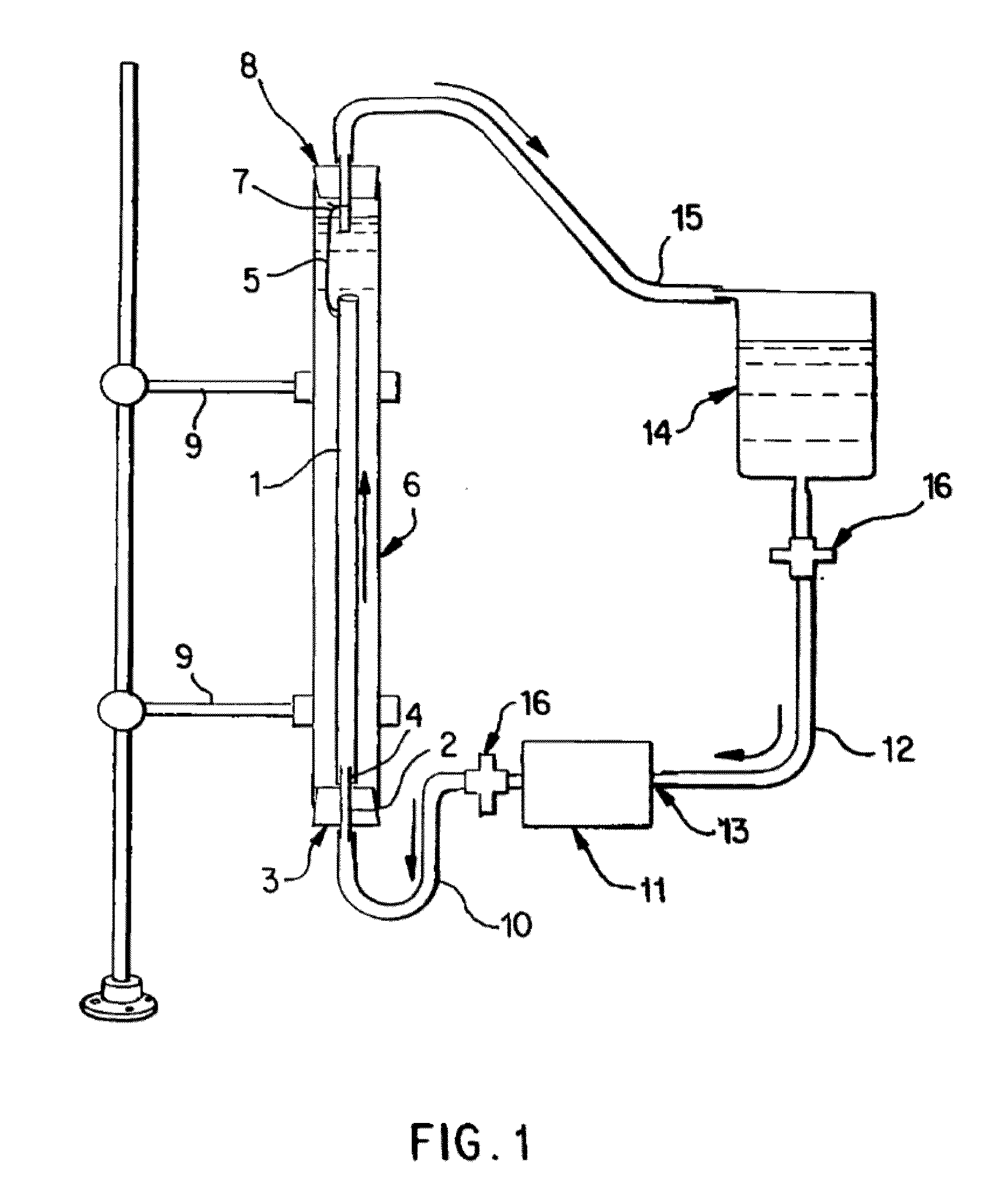
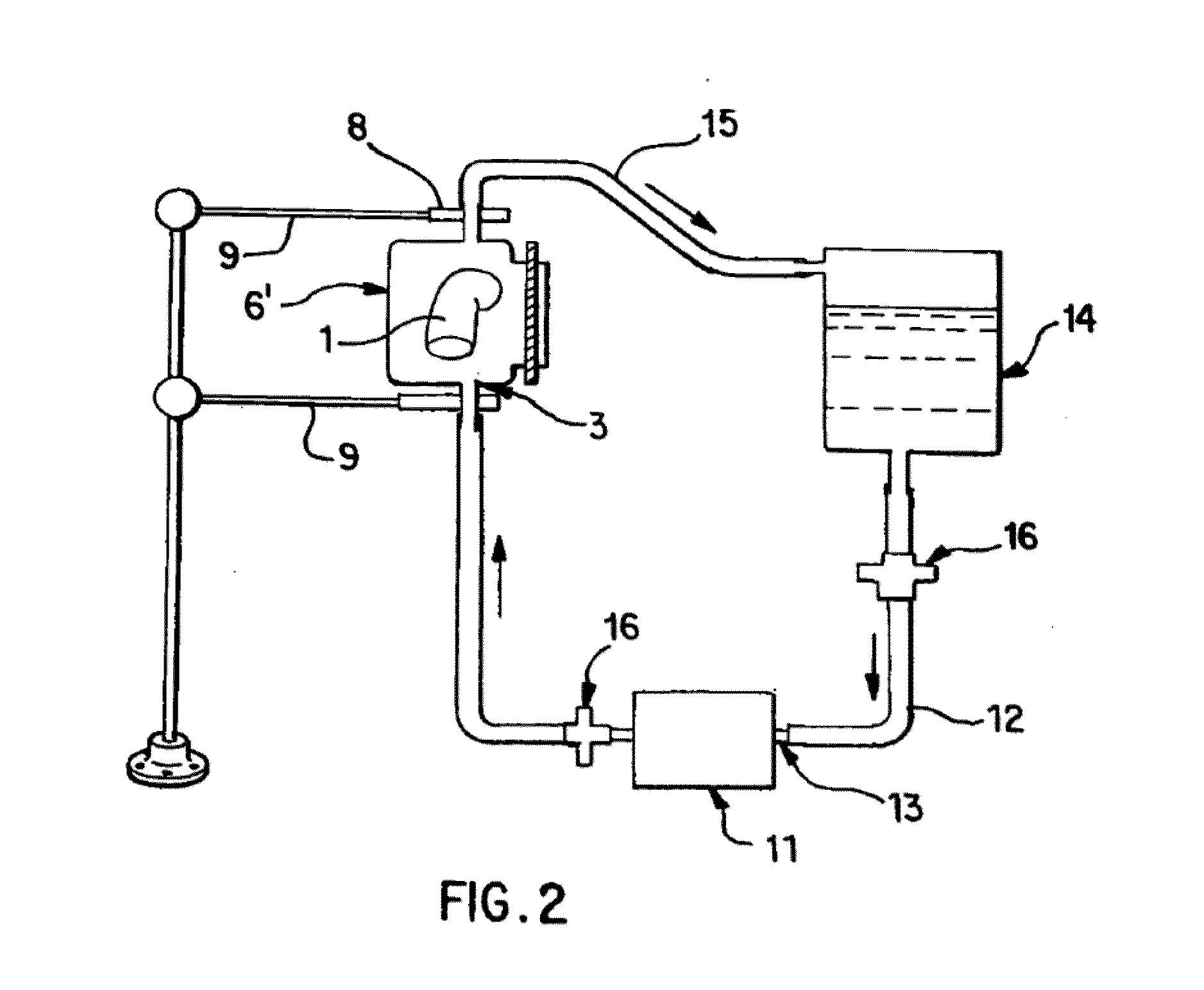
Bioactive, resorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering
InactiveUS20050118236A1High porosityImprove manufacturabilityBiocideSynthetic resin layered productsPorosityFiber
Flexible, bioactive glass meshes and scaffolds made therefrom are provided. The meshes comprise interwoven bioactive glass fibers that can be coated with resorbable polymers. Meshes can also be woven from glass fibers and resorbable polymers. Scaffolds can be constructed by a plurality of meshes, which can have varying porosities to create porosity gradients in the scaffold. Methods of making scaffolds are provided which can comprise pulling bioactive glass fibers, winding the fibers, forming the fibers into bundles, coating the fibers with a resorbable polymer, and creating a biaxial weave with the bundles. Soft tissue engineering methods are also provided for creating scaffolds for incubating cells such as fibroblasts and chondroblasts. Meshes and scaffolds are suitable for tissue engineering, such as bone tissue engineering and cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:GENTIS
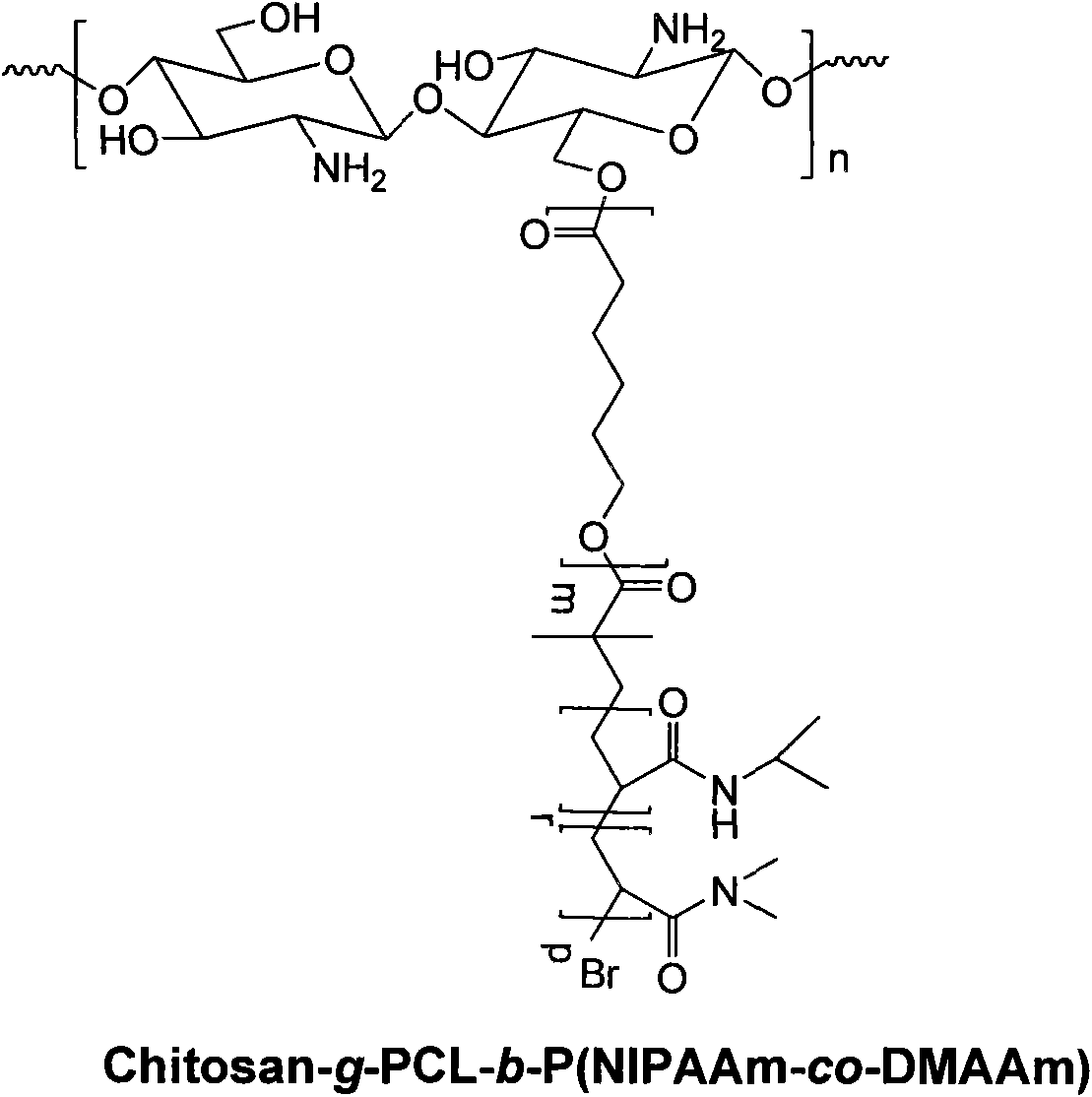
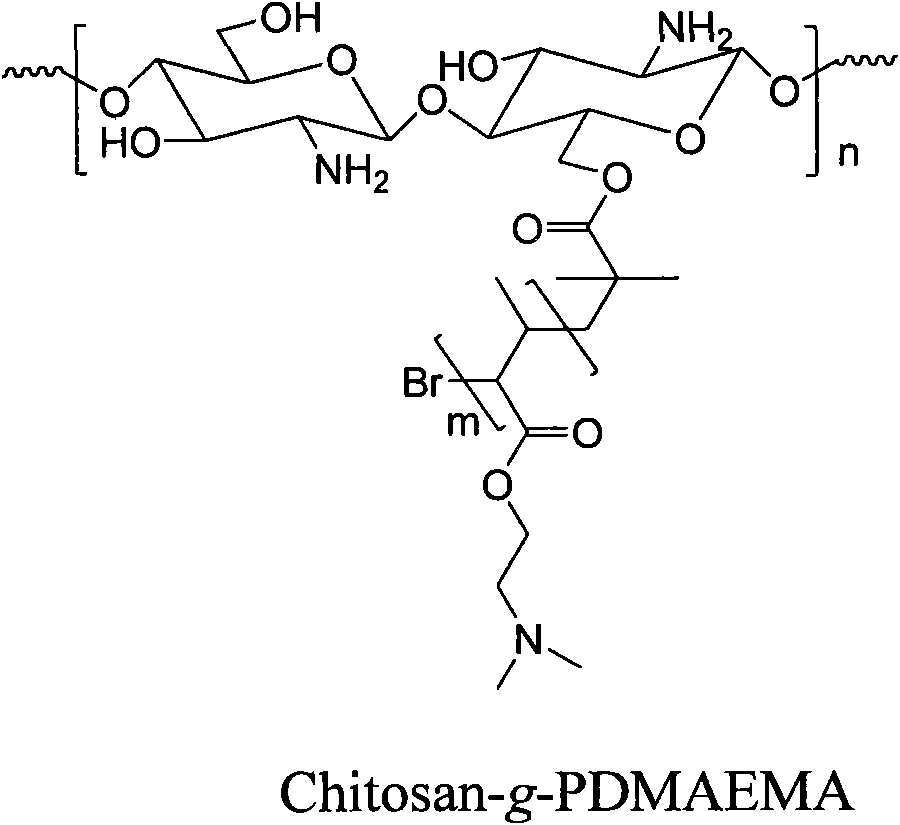
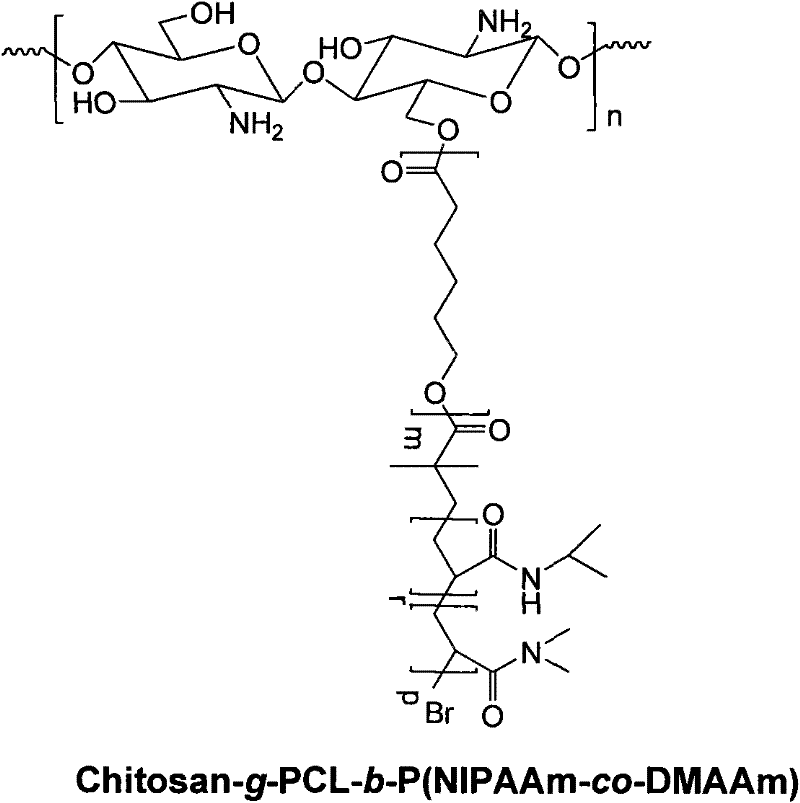
Method for preparing temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as main chain
InactiveCN101580556AWide variety of sourcesSensitive to temperaturePolyesterBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of polymer material and biomedical engineering and in particular relates to a method for preparing temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain. The method comprises the following steps: with the protection of inert gases such as nitrogen and argon, hydroxide group or aminogroup in chitosan main chain are adopted to trigger ring opening polymerization of cyclic ester monomer; then the obtained terminal hydroxide group or aminogroup of aliphatic polyester are converted to bromine group; the bromine group is taken as macroinitiator to polymerize atomic transfer radical of N-isopropyl acrylamide, hydrophilic allyl monomer, thus obtaining the needed product. The temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain is provided with biological degradability, biocompatibility, biological activity and temperature sensibility, can be automatically assembled into stable nano micelle in water, thus enjoying wide application in fields such as drug controlled release carrier, soft tissue engineering support material, immunoassay, memory element switch, biosensor and the like. The synthetic method of the invention is simple and feasible, the raw materials can all be applied to industrialized production, thus enjoying very good value in popularization and application.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Process for devitalizing soft-tissue engineered medical implants, and devitalized soft-tissue medical implants produced
InactiveUS8563232B2Alleviate the conditionReduce processing timeCell dissociation methodsDead animal preservationLong term durabilityVascular grafting
The invention provides methodologies and apparatus for producing devitalized soft-tissue implants where the implant retains metabolically non-viable and / or reproductively non-viable cells, and preferably retains large molecular weight cytoplasmic proteins, such implants produced both in small quantities and in commercializable quantities. Such soft-tissue implants include vascular graft substitutes. A devitalized graft is produced by subjecting the tissue sample to an induced pressure mediated flow of an extracting solution, optionally followed by inducing a pressure mediated flow of a salt solution, then washing the tissue to produce the devitalized graft. The devitalized grafts produced are uniform and non-immunogenic. The inventive method allows for the production of multiple devitalized soft tissue implants, where processing time is significantly less than prior art processes and the number of implants produced per day is increased over prior art processes. In clinical use, the devitalized grafts produced exhibit significantly improved in long-term durability and function, and enhanced recellularization post-implantation.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Methods and means for soft tissue engineering
ActiveUS20110151005A1Tailoring is fastShort incubation timePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingAdipogenesis
Cellfree adipose tissue extracts, implants including the same and methods for the preparation thereof. The extracts and implants are capable of inducing adipogenesis and angiogenesis and are, thus, useful in applications including soft tissue repair and engineering and angiogenesis induction, e.g., in wound healing, treatment of burn injuries and ischemic conditions.
Owner:LINIO BIOTECH OY
Fibrous scaffold for use in soft tissue engineering
The present invention relates to a fibrous scaffold for use as a substrate in soft tissue applications, in particular for preparing annulus fibrosus (AF) tissue. In aspects, the present invention also relates to an engineered biological material comprising AF tissue; constructs comprising one or more engineered biological materials; methods for producing the biological materials and constructs; and methods of using the biological materials and constructs.
Owner:SINAI HEALTH SYST
Process for Devitalizing Soft-Tissue Engineered Medical Implants, and Devitalized Soft-Tissue Medical Implants Produced
InactiveUS20140154663A1Alleviate the conditionShorten the timeCell dissociation methodsDead animal preservationLong term durabilityVascular grafting
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Fibrous scaffold for use in soft tissue engineering
The present invention relates to a fibrous scaffold for use as a substrate in soft tissue applications, in particular for preparing annulus fibrosus (AF) tissue. In aspects, the present invention also relates to an engineered biological material comprising AF tissue; constructs comprising one or more engineered biological materials; methods for producing the biological materials and constructs; and methods of using the biological materials and constructs.
Owner:SINAI HEALTH SYST
Wound healing dressing containing carrageenan, and preparation method and application of wound healing dressing
ActiveCN103386145AGuaranteed nutrient supplyPromote proliferationAbsorbent padsProsthesisCarrageenanComposite film
The invention discloses a wound healing dressing containing carrageenan, and a preparation method and application of the wound healing dressing. The wound healing dressing is a porous composite stent with a three-dimensional porous interlayer structure, or a composite thin film, wherein the porous composite stent is obtained by blending collagen or gelatin with carrageenan in a mass ratio of (5: 95) to (95: 5) and then freeze-drying the mixture, and the composite thin film is obtained by directly drying the mixture after blending. The wound healing dressing disclosed by the invention is capable of guaranteeing nutrition supply required by tissues for normal healing, and can be degraded and disappear after the tissues are healed; simultaneously, the degradation product has the effects of promoting cell proliferation and matrix expression, and truly achieving the effect of wound healing. Besides, the porous composite stent and the composite thin film both are capable of providing a stent for other soft tissue engineering while promoting wound healing. The wound healing dressing disclosed by the invention is wide in use; specifically, the wound healing dressing can be used for healing large skin wounds caused by burn or anabrosis, and also can be used as tissue engineering stent materials such as cartilage, cornea and fat; or, the wound healing dressing can be used for other fields such as clinical medicine.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ANZE REGENERATIVE MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
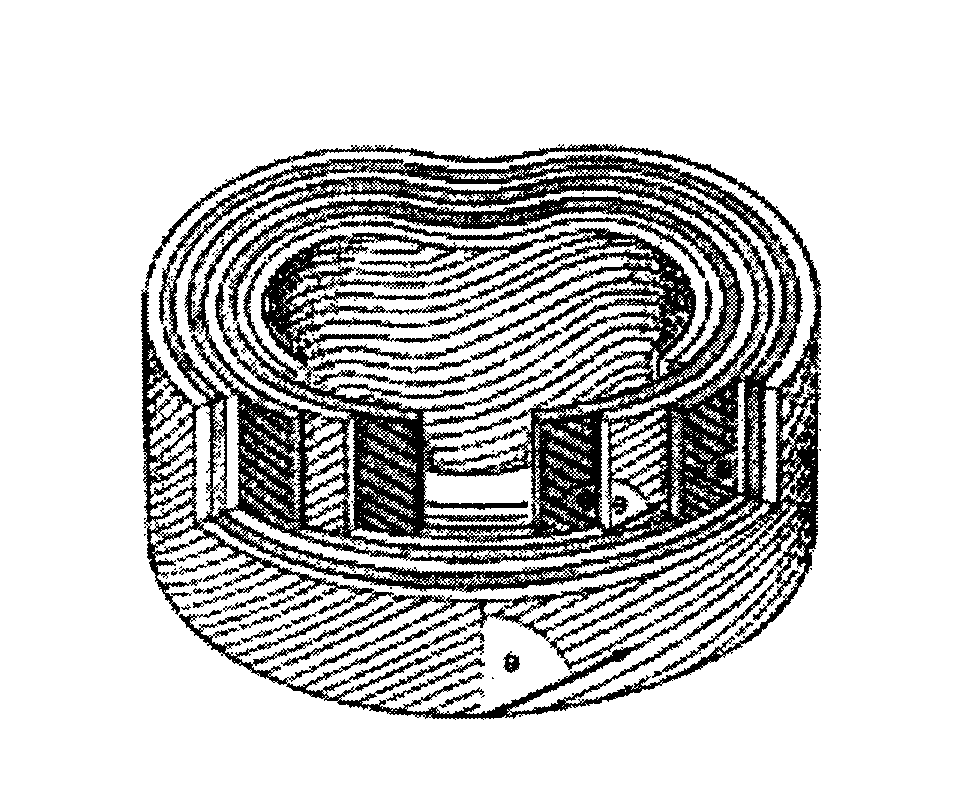
Hybrid hollow microcapsule, scaffold for soft tissue including same, and methods of preparing same
InactiveUS20160346218A1High yieldImprove mechanical propertiesBone implantPretreated surfacesInorganic particleSoft tissue engineering
Disclosed is a method of preparing a hollow microcapsule using freezing of macroporous materials including a crosslinked inorganic particle network capable of elastically recovering from a highly compressed deformation state, and use of the same as a scaffold for soft tissue engineering and as a drug delivery system.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
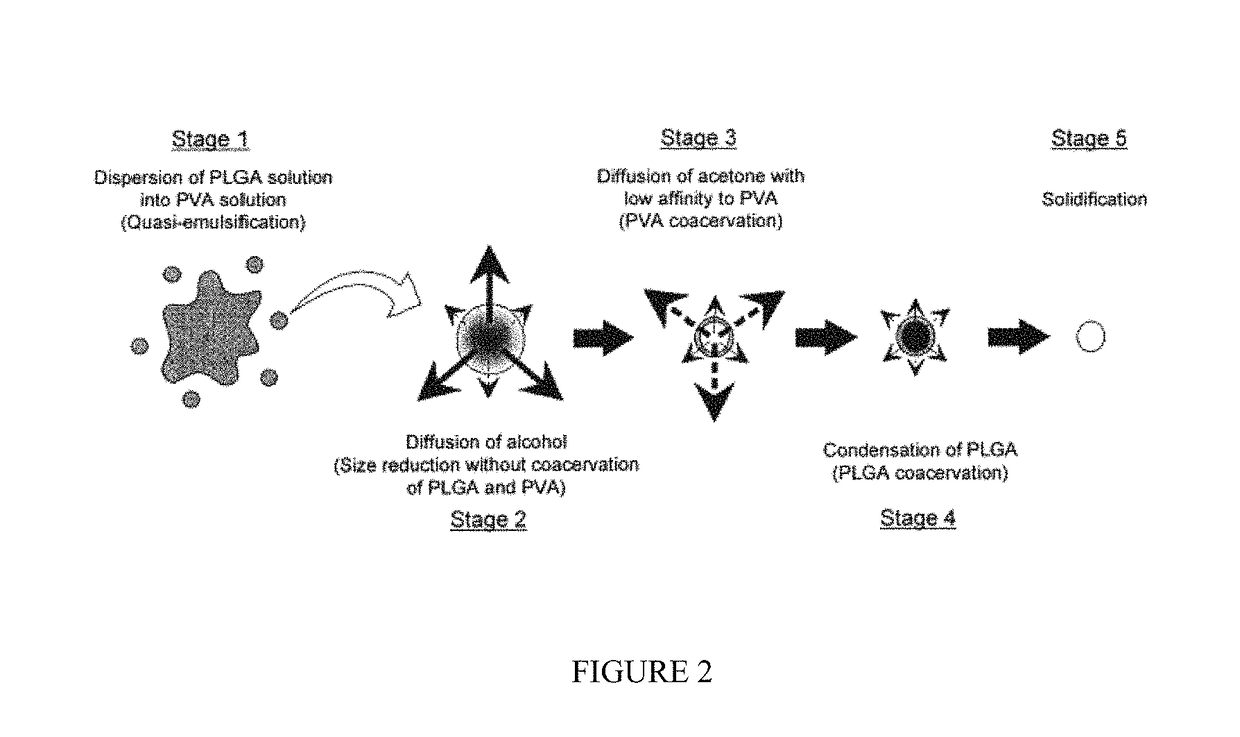
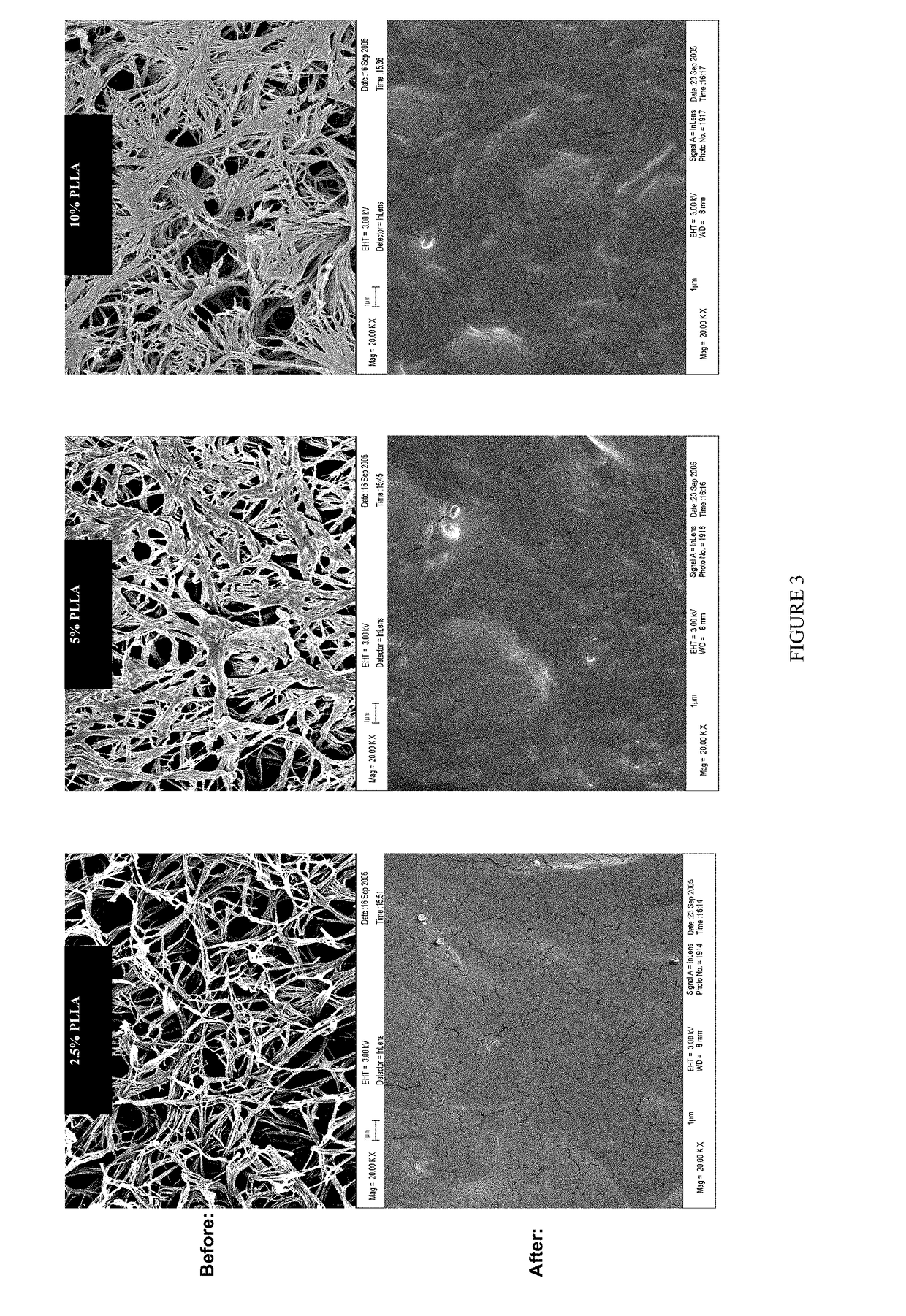
Biodegradable nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties for soft tissue engineering
ActiveUS20140135407A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGluconic acidMechanical property
The present invention is directed to a novel poly(diol citrates)-based nanocomposite materials created using completely biodegradable and biocompatible polymers that may be used in tissue engineering. More specifically, the specification describes methods and compositions for making and using nanocomposites comprised of citric acid copolymers and polymers including but not limited to poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA).
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Test device and method for sliding friction force of biological soft tissue material
ActiveCN107228722AEasy to operateHigh precisionUsing mechanical meansApparatus for force/torque/work measurementSoft tissue engineeringBiological materials
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of material performance testing, discloses a test device and method for a sliding friction force of a biological soft tissue material. According to the method, on the basis of the law of conservation of energy, testing of a sliding friction force between soft tissue materials is carried out; and the method is especially suitable for biological soft tissue materials that can not be tested easily currently and include the muscle, skin, cartilage and blood vessel. The testing technique based on a simple principle is easy to operate; the testing precision is high; and the sliding friction characteristic between the biological materials can be reflected effectively. The test device and method have the potential application value in biomaterial testing and soft tissue engineering fields.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional chitosan hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102604149AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisToxicantSoft tissue engineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing three-dimensional chitosan hydrogel by using a high temperature crosslinking method and the obtained chitosan hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) dispersing chitosan powder into a deionized water; (b) adjusting the pH of chitosan dispersion obtained in the step (a) to be subacid; (c) carrying out high temperature crosslinking on the solution obtained in the step (b) at the high temperature of 80-125 DEG C; and (d) after the crosslinking reaction is completed, soaking and cleaning an obtained product by using a posttreatment liquid so as to remove a residual acid liquid. The high temperature crosslinking method is simple in the preparation process; the reaction time is short; raw materials are unnecessary for special treatment; highly-toxic chemical substances such as crosslinking agents are not introduced to a preparation course; no any chemical toxicant remains in a final product; and the three-dimensional chitosan hydrogel is even in pore structure, good in connectivity and easy to form, and is very suitably used as a support material of soft tissue engineering such as skin and cartilage.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI BIO LAB CO LTD
Methods and means for soft tissue engineering
ActiveUS9056084B2Tailoring is fastShort incubation timePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCell freeAdipogenesis
Owner:LINIO BIOTECH OY
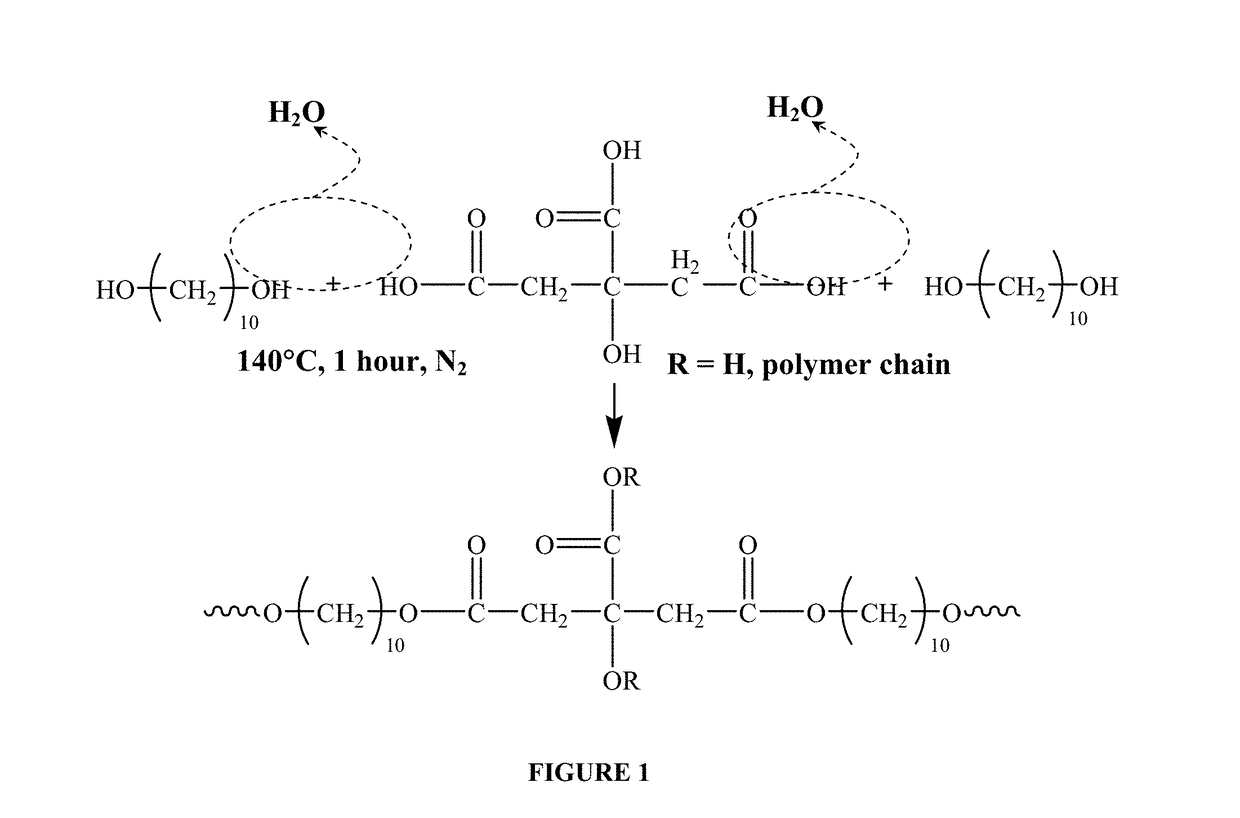
Biodegradable polyester elastomer and preparation method thereof
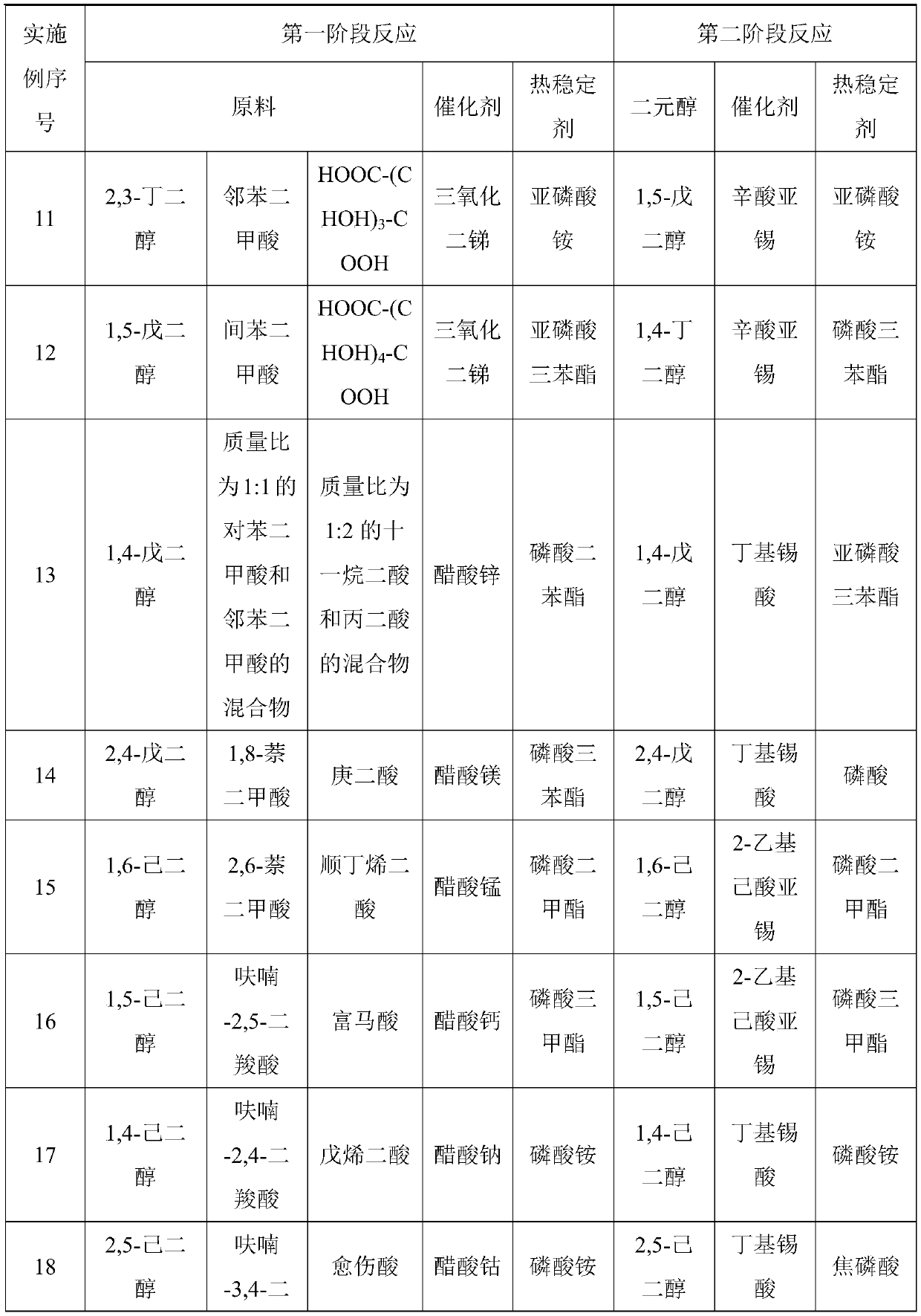
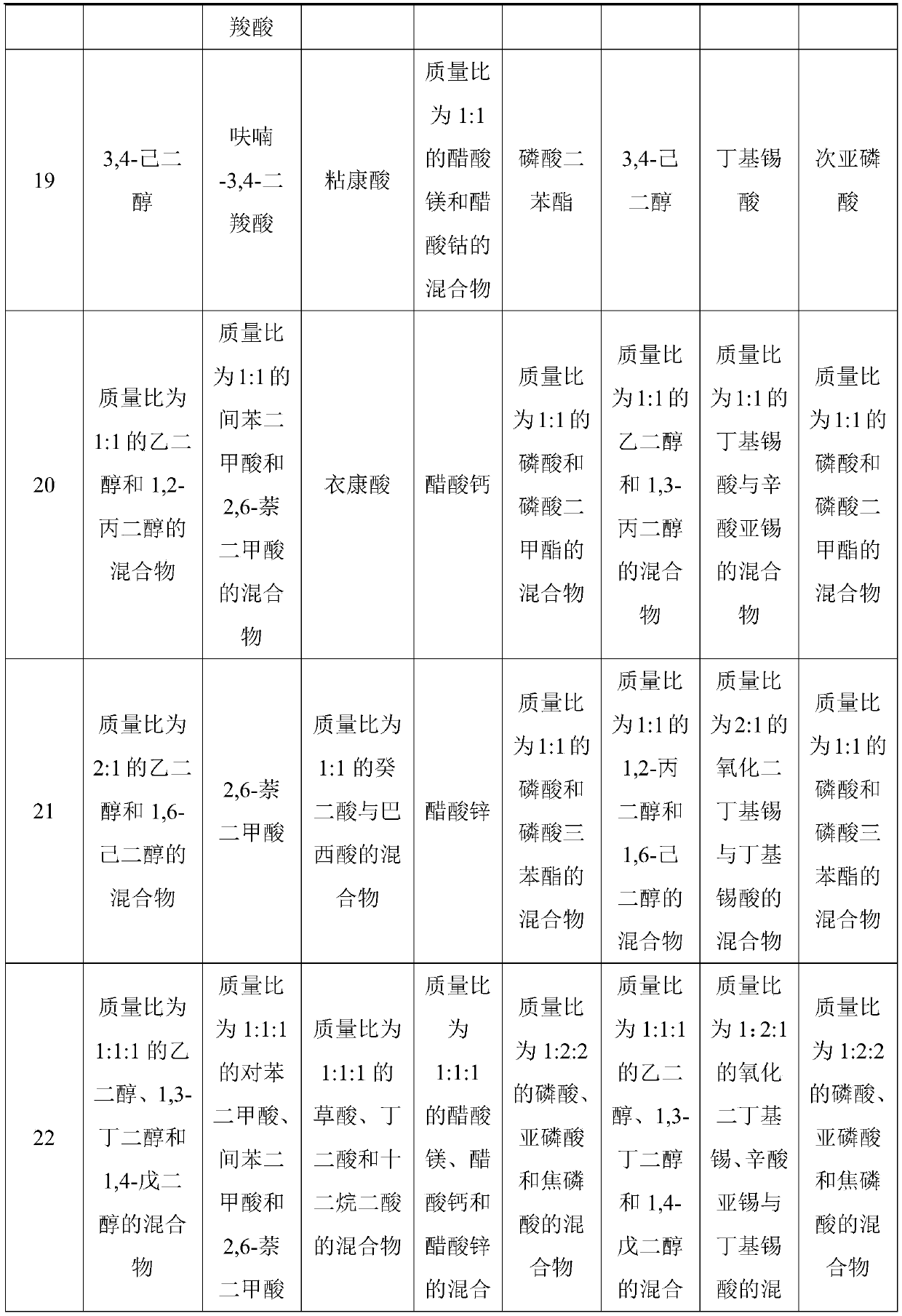
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biodegradable polyester elastomer. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking A1, B1 and B2 as raw materials, and carrying out first-stage reaction under the action of a first catalyst under a high-temperature condition; taking the first-stage product, a rigid monomer, A2 and citric acid as raw materials, carrying out a second-stagereaction under a low-temperature condition and under the action of a second catalyst, and finally carrying out a condensation polymerization reaction to obtain the biodegradable polyester elastomer.The first-stage reaction and the second-stage reaction are esterification or transesterification; the tensile strength of the finally prepared elastomer is 12.8-34.5 MPa, the elongation at break is 380-700%, and the mass loss after the elastomer is cultured for 30 days in a 37 DEG C lipase solution is 6-14%. The problems that IHDCA or IHDXC is degraded seriously and polyester network type elastomers are difficult to degrade are solved, and the method can be applied to toughening modification of brittle biodegradable polyester such as PHA and PLA and in-vivo soft tissue engineering.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation and application of linear biodegradable polyester elastomer with controllable elasticity and shape memory effect
InactiveCN105504248AMeet biomechanical needsHigh viscoelasticitySuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElastomerTissue repair
The invention discloses preparation and application of a linear biodegradable polyester elastomer with a controllable elasticity and shape memory effect. The linear biodegradable polyester elastomer with the controllable elasticity and shape memory effect is formed by conducting copolymerization on a caprolactone monomer containing a lateral cyclic ether structural unit and caprolactone, wherein the molar ratio of the caprolactone monomer containing the lateral cyclic ether structural unit to the caprolactone is 5:95-25:75, and the structural formula can be found in description. The viscoelasticity of the linear biodegradable polyester elastomer with the controllable elasticity and shape memory effect is remarkably improved, the elongation at break can reach 1600% and above, the elastomer can be dissolved in a conventional organic solvent, a three-dimensional porous support can be constructed conveniently through a construction technology of the porous support such as, electrostatic spinning, three-dimensional printing and phase separation, tissue engineering blood vessel scaffold materials, myocardial patches, nervous tissue engineering scaffold materials and the like are prepared, and the preparation and application of the linear biodegradable polyester elastomer can be widely applied to the fields of soft tissue engineering scaffolds, tissue repair and regenerative medicine.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing dual-sensitivity graft copolymer with chitosan as main chain
InactiveCN101580568AWide variety of sourcesSensitive to temperatureBiocompatibility TestingNitrogen gas
The invention belongs to the field of polymer material and biomedical engineering and particularly relates to a method for preparing dual-sensitivity amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain. The method comprises the following steps: with the protection of inert gases such as nitrogen and argon, hydroxide group or aminogroup in chitosan main chain are adopted to carry out esterification reaction with bromine-containing compound; the hydroxide group or aminogroup are converted into the bromine group; then the bromine group is taken as macroinitiator to polymerize atomic transfer radical of methacrylic acid-N and N-dimethylamino-ethyl methylacrylate monomer to form polymer featuring dual sensitivity of temperature and pH value, thus finally obtaining the dual-sensitivity graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain. The dual-sensitivity graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain is provided with biological degradability, biocompatibility, biological activity and pH value sensibility, can be automatically assembled into stable nano micelle in water, thus enjoying wide application in fields such as drug controlled release carrier, soft tissue engineering support material, immunoassay, memory element switch, biosensor and the like. The synthetic method of the invention is simple and feasible, the raw materials can all be applied to industrialized production, thus enjoying very good value in popularization and application.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Skin wound repairing agar/collagen dressing and its prepn and application
InactiveCN1887359ANutrient supply is not affectedMaintain normal healing mechanismsAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze-dryingSoft tissue engineering
The present invention provides one kind of skin wound repairing agar / collagen dressing and its preparation process and application. Agar and collagen or gelatin are mixed, and the mixture is freeze dried to obtain porous compound rack or compound film for promoting the repair of skin wound, and the rack may be also used in other soft tissue engineering. The porous compound rack and compound film of present invention has simple operation, low cost and wide use, and may be used in repairing burnt and ulcer skin as well as for cartilage, cornea, fat and soft tissue engineering.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Process for preparing porous support frame of soft tissue engineering with water-soluble high-molecular material as mould
A porous support for cartrilage tissue engineering is prepared from the high-molecular material of polyethanediol, polyamide, or polyacrylic acid type as mould material, polyhydroxy alkanoate as polymer for the porous support chloroform as solvent and water-soluble crystal as pore-forming agent through smelting the said mould material, pouring it into a container in which there is a soft silica gel male mould, obtaining a high-molecular femal mould, filling the mixture of polymer solution and pore-forming agent particles in the said femal mould, closing compacting, baking to remove solvent, dissolving the mould and pore-forming particles, and drying.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
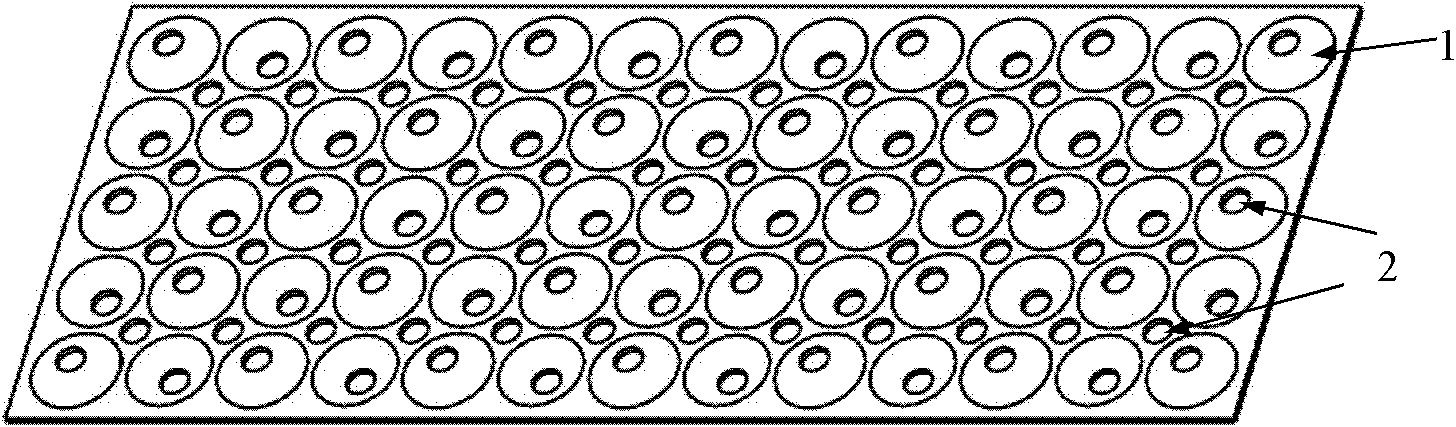
Soft tissue engineering scaffold and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN101879097ASimple structureEasy to curlLigamentsMusclesBiocompatibility TestingSoft tissue engineering
The invention discloses a soft tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation process thereof. Millimeter-grade pellets and films are combined together to form a cell scaffold by a curling process or superimposing process. The pellets and the films can be made from different biological materials so as to fully play different roles of both the pellets and the films, wherein the films are made from an elastic biological material and used for accommodating the pellets; the elastic biological material is provided with a millimeter-grade pit structure of which the size and the shape correspond to those of the pellets; and the pellets are made from a material which has high biocompatibility. In order to increase the conduction, pores are formed on the pellets, contact points between the films and the pellets and areas among pits. The pellets and the films can be independently compounded with cells to form a cell scaffold compounded body respectively, then the pellets are placed into the pitsformed on the films one by one, and finally the films are curled or superimposed layer by layer. A large number of pellets are clamped among the films, and the compounded body can be directly implanted into a body and can also be used for culture in vitro.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing elastic wood based on ultraviolet light initiated graft polymerization
ActiveCN111978490APrevent crushingGuaranteed natural mechanical propertiesOpen tank impregnationFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a method for preparing elastic wood based on ultraviolet light initiated graft polymerization. The method comprises the following steps: by using balsa wood as a raw material,carrying out mild delignification treatment by using an acidic sodium chlorite solution to obtain a complete wood fiber skeleton; treating the obtained product with a sodium hydroxide alkaline solution; preparing a mixed solution of an acrylamide monomer and a cross-linking agent, and regulating the mixing ratio of the acrylamide monomer and the cross-linking agent; fully mixing the obtained product with an acrylamide monomer through an impregnation method; and putting the obtained product into a mold, and initiating a grafting cross-linking reaction through ultraviolet light with the wavelength of 320-380 nm to obtain polyacrylamide / wood fiber skeleton composite gel, namely the elastic wood. According to the method, the elastic wood can be prepared under the condition that a chemical initiator is not used, and due to the fact that the elastic wood has high biocompatibility, excellent mechanical performance and excellent light transmission performance, the elastic wood has potential application value in the fields of artificial skin, biosensors, soft tissue engineering materials, wearable flexible electronic base materials, stimulus response soft robots and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method of chitosan hydrogel stent for tissue engineering
InactiveCN102921046AThe preparation process is simple and controllableMild reaction conditionsProsthesisPolyethylene glycolBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a chitosan hydrogel stent for tissue engineering. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing a crosslinking agent and preparing gel and specifically comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing the crosslinking agent, placing 1,6-diisocyanatohexane and polyethylene glycol in a container according to a mol ratio of (1-2.5):1, reacting for 1-7 days at a temperature of 20-40 DEG C to obtain the crosslinking agent; 2, preparing a chitosan hydrogel stent for tissue engineering, (A) preparing a chitosan water solution with a concentration of 0.1-10 percent in weight ratio; and (B), adding the crosslinking agent in the chitosan water solution to obtain the chitosan hydrogel stent for tissue engineering, wherein the volume proportion of the crosslinking agent to the chitosan water solution is 1000:(1-50). Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has the advantages of simple and controllable process, mild reaction conditions, no need of catalyst, high speed and better property of chitosan hydrogel, and good biocompatibility because infinitesimal chemical crosslinking agent is introduced during crosslinking, and is a better tissue engineering stent material, and is especially suitable for a soft tissue engineering material.
Owner:川北医学院第二临床医学院
Method for preparing temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as main chain
InactiveCN101580556BWide variety of sourcesSensitive to temperaturePolyesterBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of polymer material and biomedical engineering and in particular relates to a method for preparing temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan asthe main chain. The method comprises the following steps: with the protection of inert gases such as nitrogen and argon, hydroxide group or aminogroup in chitosan main chain are adopted to trigger ring opening polymerization of cyclic ester monomer; then the obtained terminal hydroxide group or aminogroup of aliphatic polyester are converted to bromine group; the bromine group is taken as macroinitiator to polymerize atomic transfer radical of N-isopropyl acrylamide, hydrophilic allyl monomer, thus obtaining the needed product. The temperature-sensitive amphipathic graft copolymer with chitosan as the main chain is provided with biological degradability, biocompatibility, biological activity and temperature sensibility, can be automatically assembled into stable nano micelle in water, thus enjoying wide application in fields such as drug controlled release carrier, soft tissue engineering support material, immunoassay, memory element switch, biosensor and the like. The synthetic method of the invention is simple and feasible, the raw materials can all be applied to industrialized production, thus enjoying very good value in popularization and application.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Biodegradable nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties for soft tissue engineering
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Process for preparing porous support frame of soft tissue engineering with water-soluble high-molecular material as mould
A porous support for cartrilage tissue engineering is prepared from the high-molecular material of polyethanediol, polyamide, or polyacrylic acid type as mould material, polyhydroxy alkanoate as polymer for the porous support chloroform as solvent and water-soluble crystal as pore-forming agent through smelting the said mould material, pouring it into a container in which there is a soft silica gel male mould, obtaining a high-molecular femal mould, filling the mixture of polymer solution and pore-forming agent particles in the said femal mould, closing compacting, baking to remove solvent, dissolving the mould and pore-forming particles, and drying.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of high strength hydrogel with simulated insect cuticle structure
The invention belongs to the field of biomass materials, and relates to a preparation method of a high strength hydrogel with a simulated insect cuticle structure. The preparation method comprises following steps: (1) subjecting chitin to a partial deacetylation treatment; (2) diluting the product obtained in the step (1) by an acetic acid solution, and then grinding the product; (3) diluting theproduct obtained in the step (2) by distilled water, carrying out an ultrasonic treatment, filtering the solution in vacuum, and carrying out film forming; (4) fully impregnating the product obtainedin the step (3) in a gelatin solution; and (5) impregnating the product obtained in the step (4) into a quinone crosslinking reaction solution, and making the product carry out quinone crosslinking reactions at a room temperature to obtain partially de-acetylated chitin nano fiber / gelatin composite gel. The operation of the method is simple and rapid; and moreover, the prepared composite hydrogelhas excellent mechanical properties and has a great application value in fields such as artificial skin, biosensors, soft tissue engineering materials, and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Hybrid hollow microcapsule, scaffold for soft tissue including same, and methods of preparing same
The invention relates to a hybrid hollow microcapsule, a scaffold for a soft tissue including the same, and methods of preparing the same. Disclosed is a method of preparing a hollow microcapsule using freezing of macroporous materials including a crosslinked inorganic particle network capable of elastically recovering from a highly compressed deformation state, and use of the same as a scaffold for soft tissue engineering and as a drug delivery system.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
High-strength self-recoverable multifunctional conductive hydrogel with temperature/pH dual response as well as preparation method and application of high-strength self-recoverable multifunctional conductive hydrogel
ActiveCN114316144AExcellent temperature sensitive performanceNIPA improvedControlled releasePharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to high-strength self-restorable conductive hydrogel with temperature / pH dual response as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The hydrogel is prepared by dissolving a comonomer A, a comonomer B, a biomacromolecule C, a chemical cross-linking agent D and a physical cross-linking agent E in water and then polymerizing. The hydrogel prepared by the invention not only has temperature sensitive characteristics and pH sensitive characteristics, but also has relatively high strength and tensile rate, can be circularly stretched, and can be self-recovered and even self-enhanced. Besides, the hydrogel disclosed by the invention also has electrical conductivity, and the electrical conductivity of the hydrogel can be changed along with the change of the temperature, the stretching ratio and the environmental pH value, so that the electrical conductivity of the hydrogel has multiple sensitivities, and in addition, the hydrogel also has universal adhesion. Based on the attributes, the hydrogel is expected to be applied to a plurality of biomedical fields such as biosensors, wearable electronic skin, soft tissue engineering, drug controlled release and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Partioning of adult mesenchymal stem cells
PendingUS20210395685A1Strengthen bonesImproved soft tissue engineeringSkeletal disorderUnknown materialsAdipogenesisSoft tissue engineering
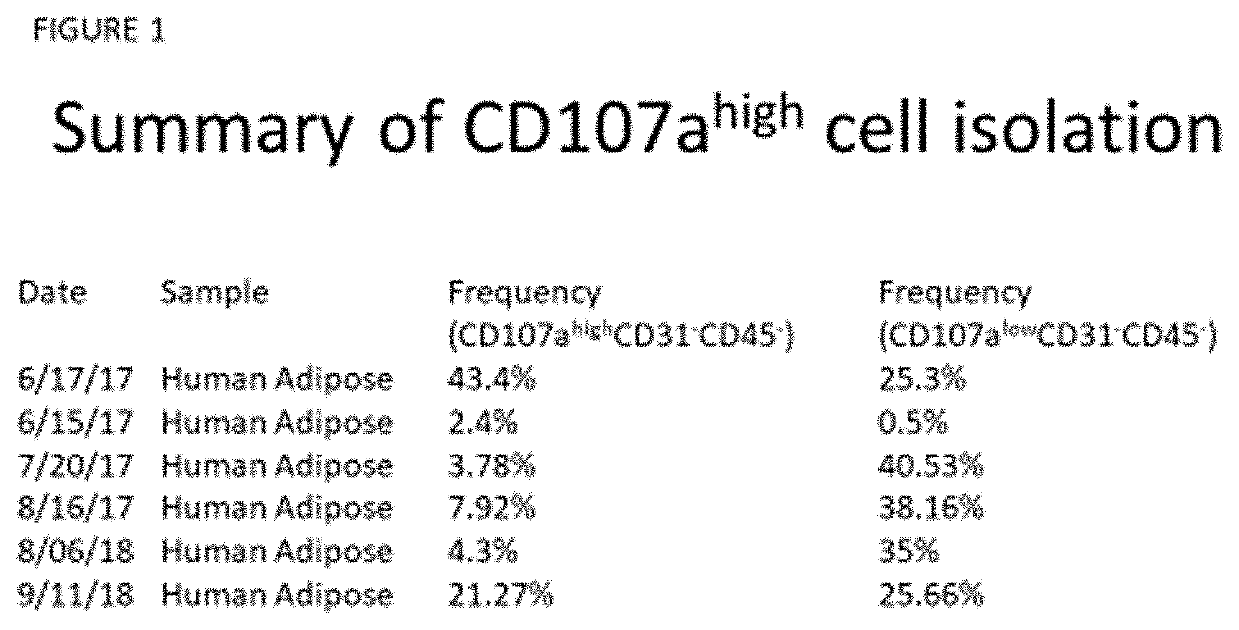
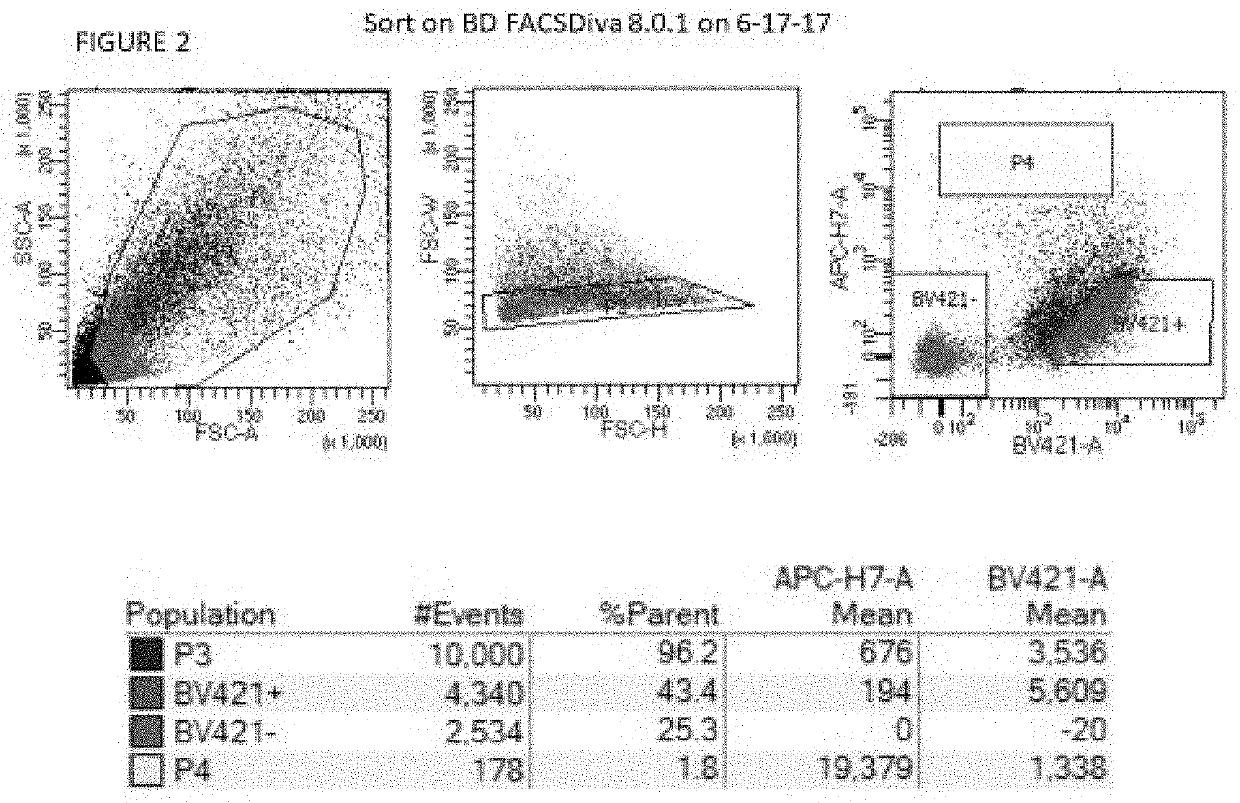
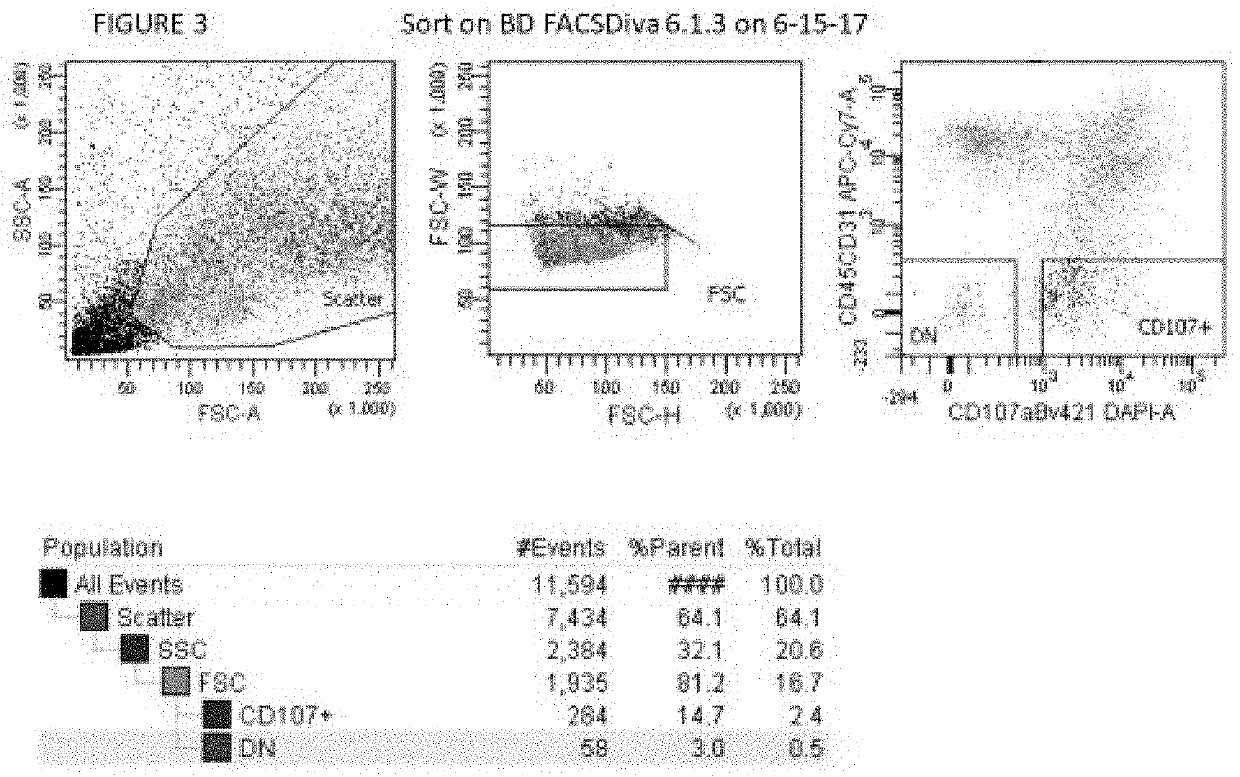
The present invention has developed methods and compositions utilizing the cell surface CD107a (LAMP-1) as a marker that divides bone-forming and fat-forming progenitor / stem cells within human adipose tissue. The present invention is able to partition stromal progenitors for improved bone and soft tissue engineering and therapies.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
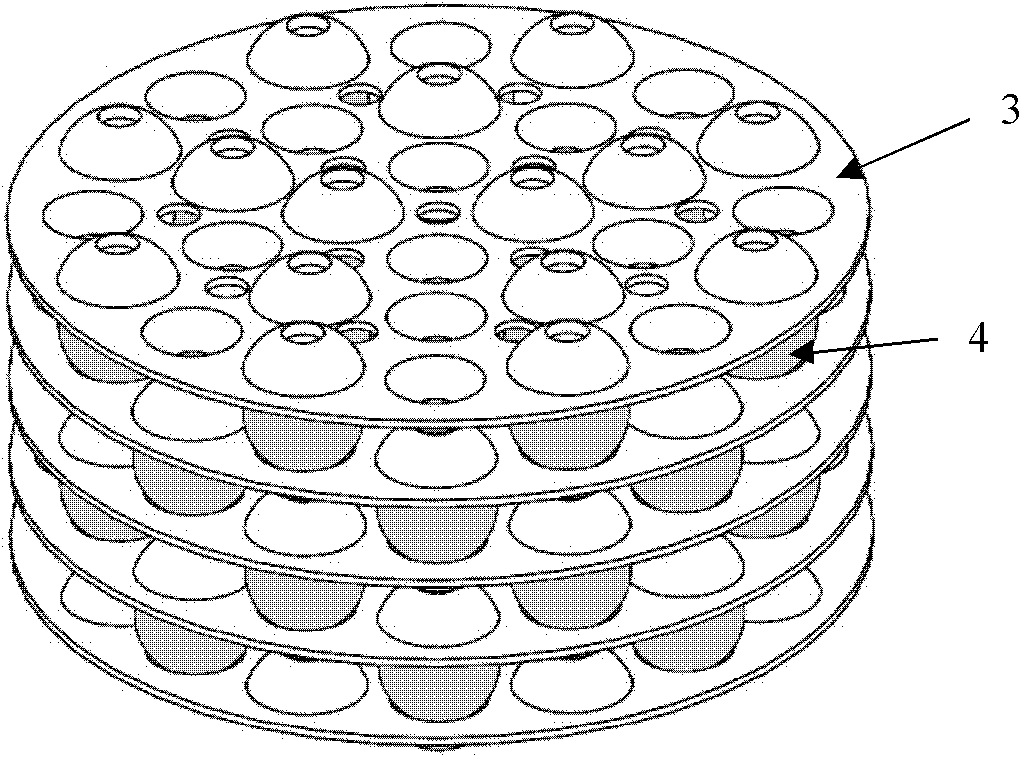
Particle suitable for the manufacture of an implantable soft tissue engineering material
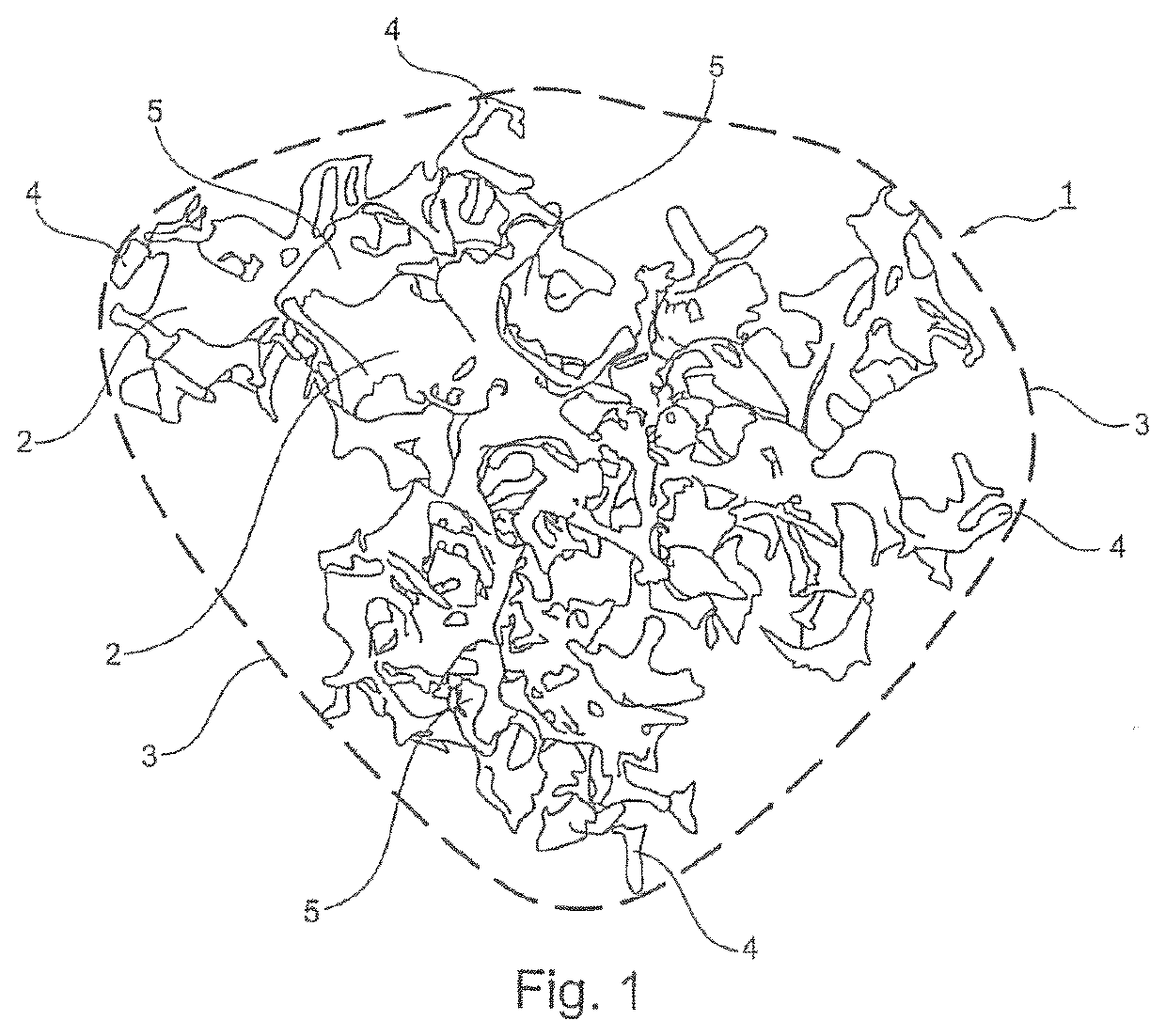
ActiveUS20200384152A1Increase in sizeIncrease volumePowder deliveryMammary implantsEngineeringSoft tissue engineering
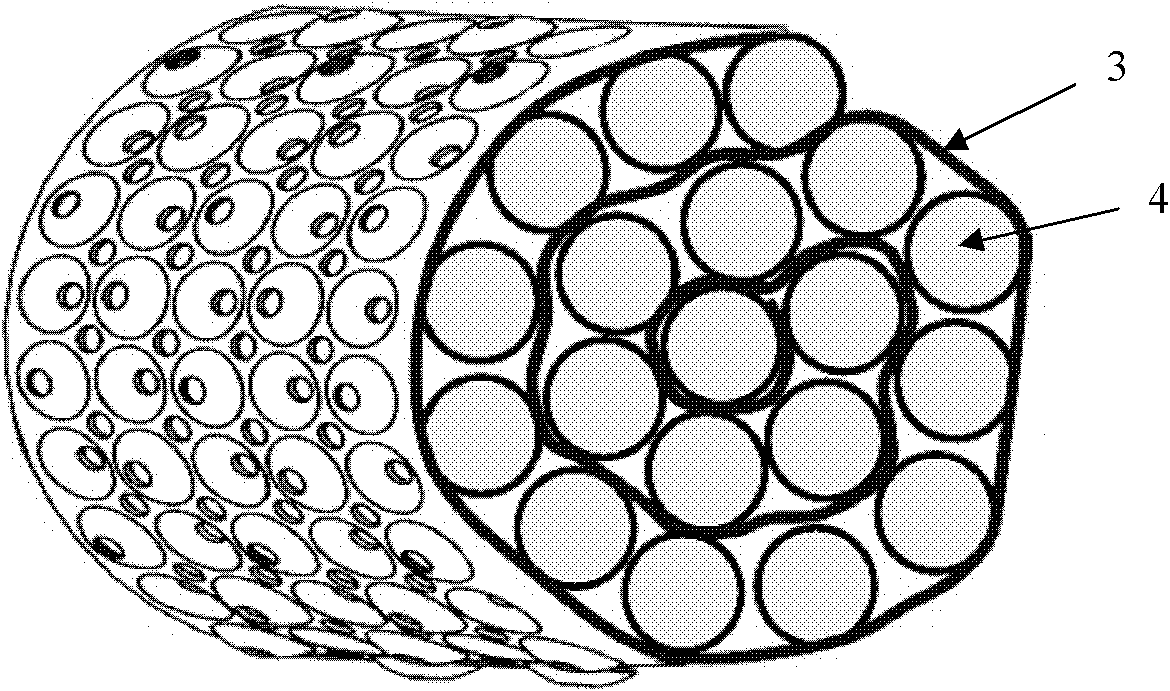
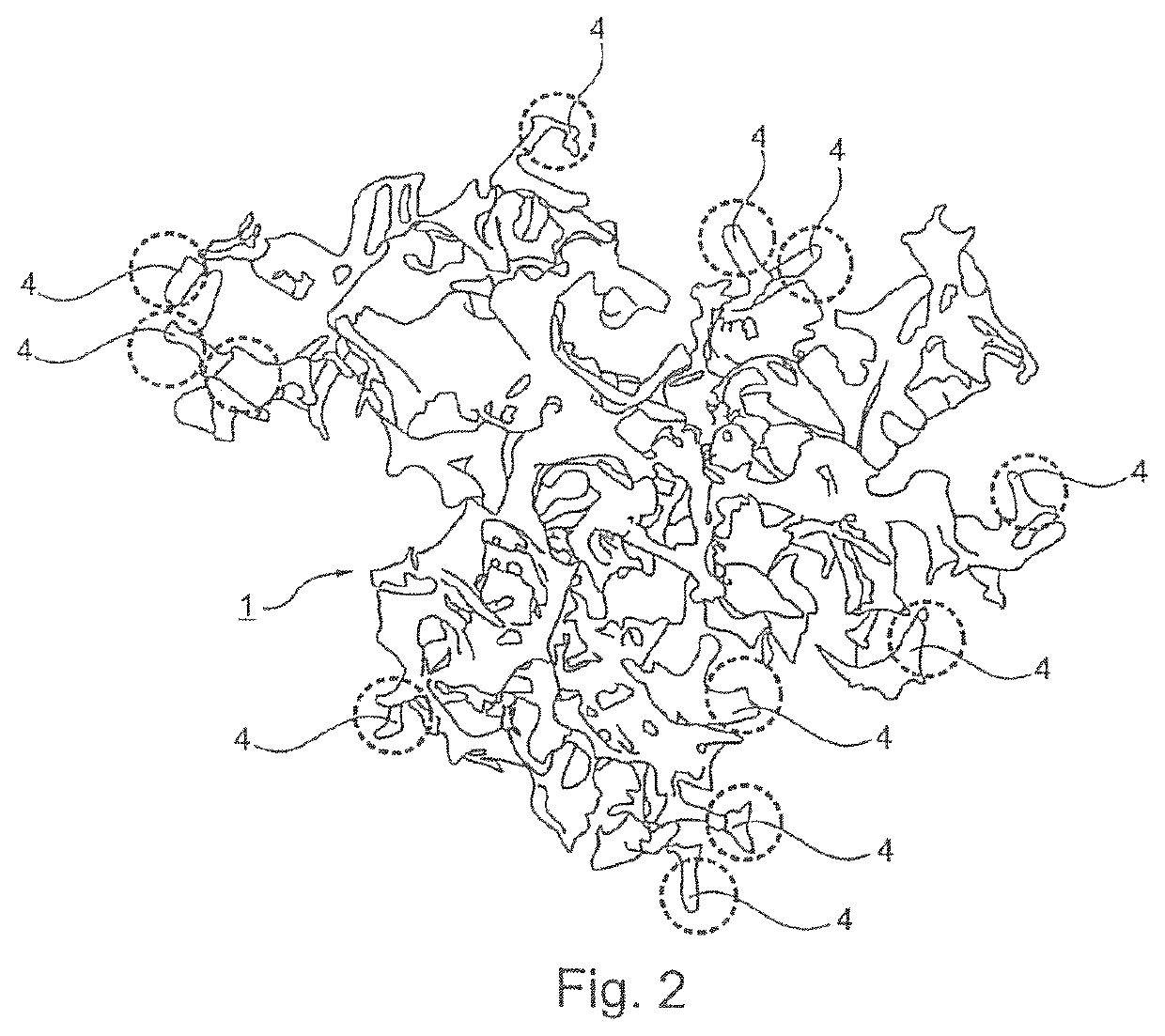
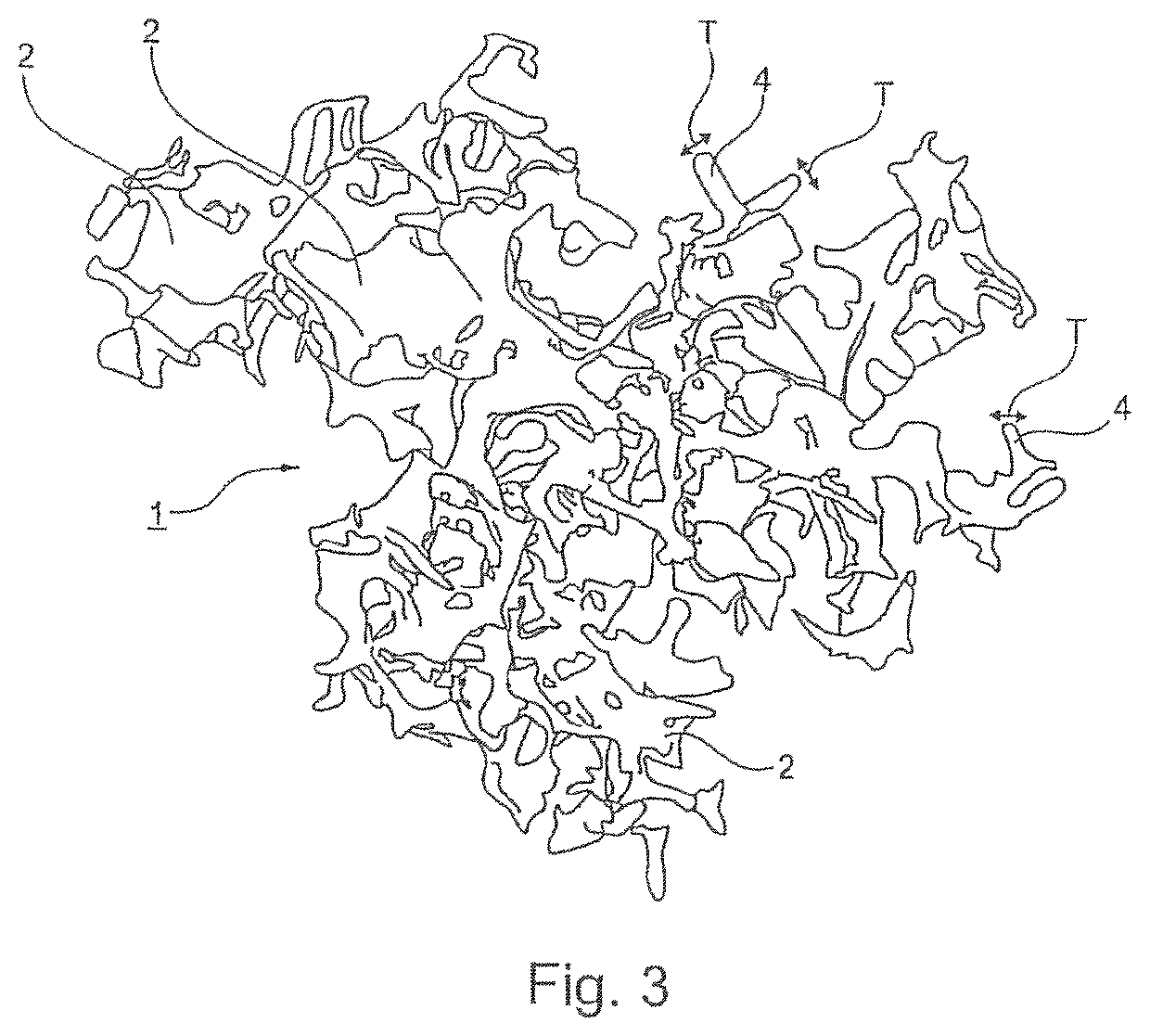
The particle (1) is suitable for the manufacture of an implantable soft tissue engineering material and comprises: a three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) where (i) the three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) is made from a biocompatible material having a Young's modulus of 1 kPa to 1 GPa; (ii) the three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) has an irregular shape which is encompassed in a virtual three-dimensional envelope (3) having a volume VE; (iii) the three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) has a mean sheet thickness T; iv) the three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) has a volume VS; (v) the particle (1) has a Young's modulus of 100 Pa to 15 kPa; and (vi) the particle (1) further comprises a number of protrusions where the three-dimensionally warped and branched sheet (2) reaches the envelope (3); (vii) the particle (1) has a number of interconnected channel-type conduits (5) defined by the branching of the sheet (2) and / or by voids in the sheet (2); and (viii) where the conduits (5) have (a) a mean diameter DC; and (b) an anisotropicity index of 1.01 to 5.00.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
A kind of nontoxic and harmless high mechanical strength high elasticity hemicellulose foam composite material and its preparation method
The invention discloses a non-toxic, harmless, high-mechanical-strength, high-elasticity hemicellulose foam composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding hemicellulose and cross-linking agent into deionized water, heating and stirring until dissolved to obtain a mixed solution; (2) dissolving PVA in water, heating and stirring to dissolve to obtain a PVA solution; (3) adding The mixed solution is mixed and stirred with the PVA solution to obtain a cross-linked product, which is cooled and molded, washed and dried to obtain the non-toxic, harmless, high-mechanical-strength, and highly elastic hemicellulose foam composite material. The foam composite material is easy to process, non-toxic and harmless, has high mechanical strength and high elasticity, and has great application potential in the aspects of anti-shock and compression materials, elastic response materials, soft tissue engineering materials and biomedical materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com