Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Self burning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
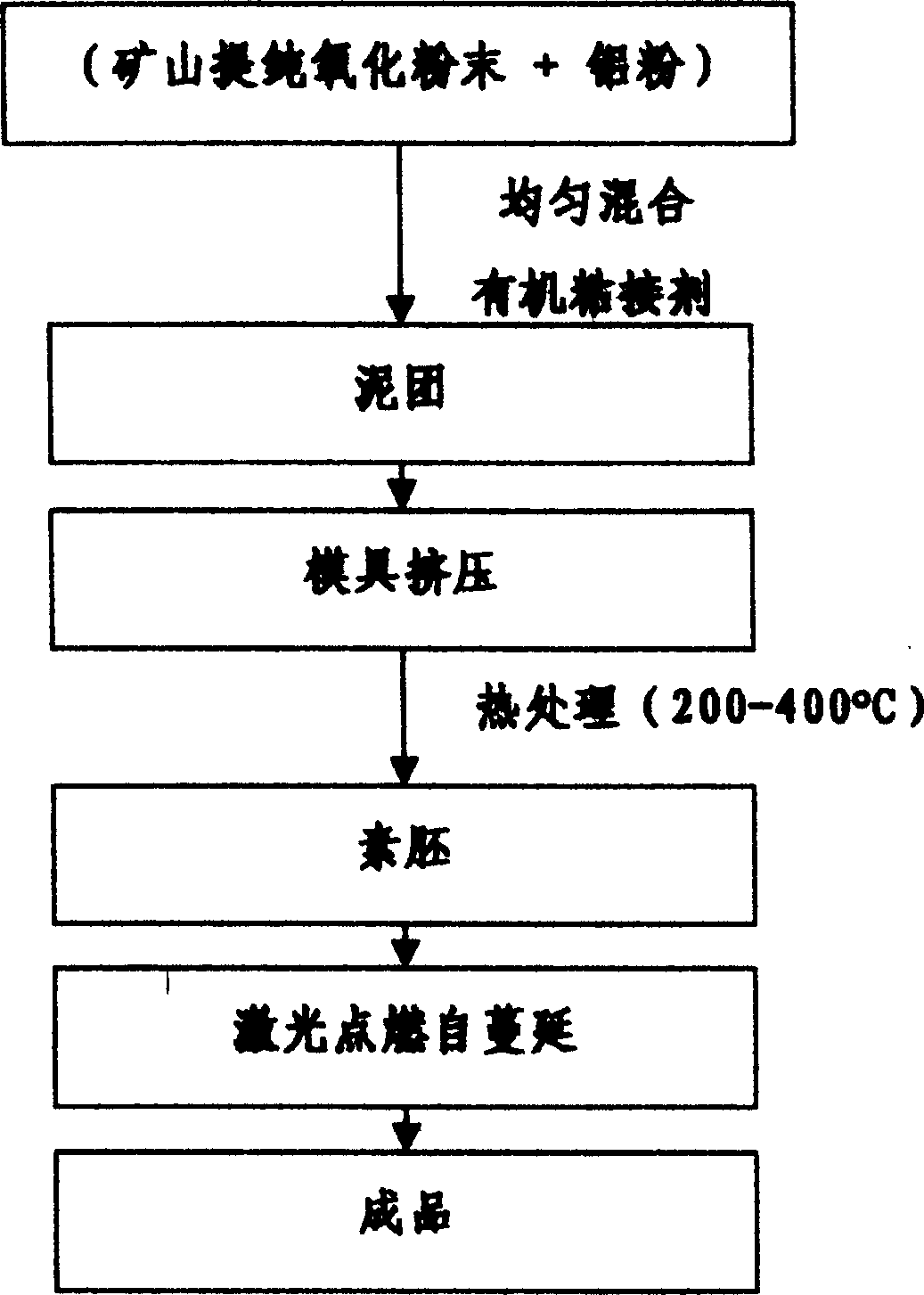
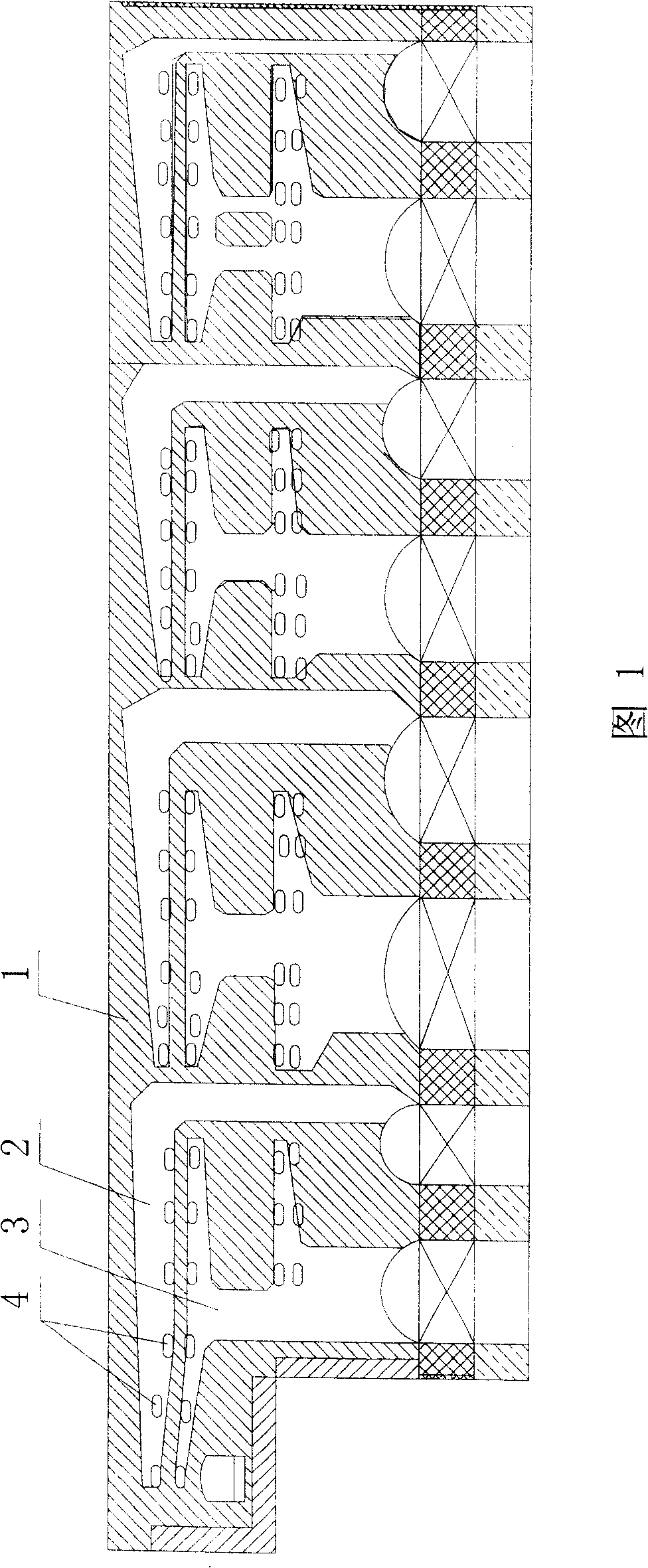
Laser cutting method and laser cutter
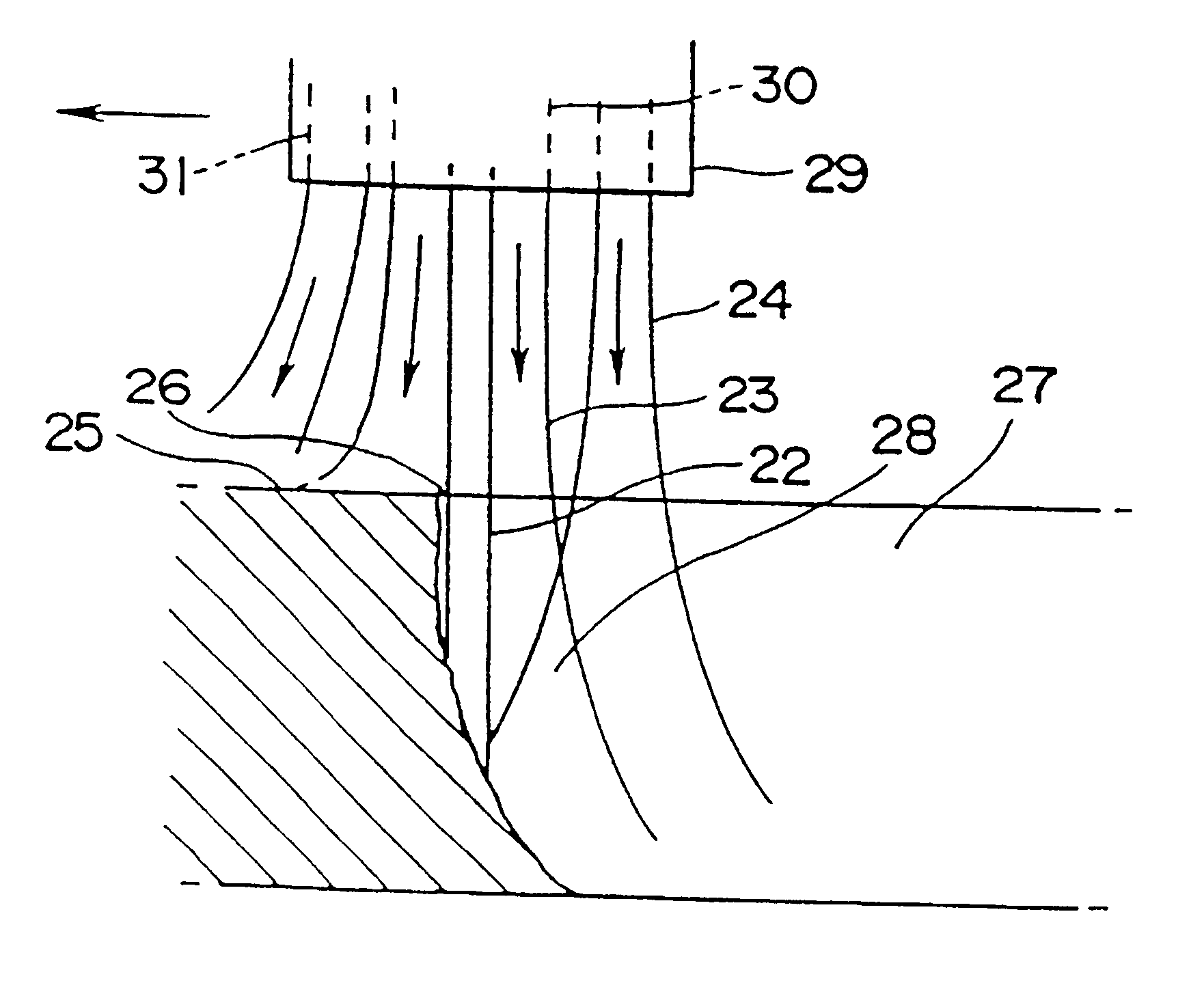
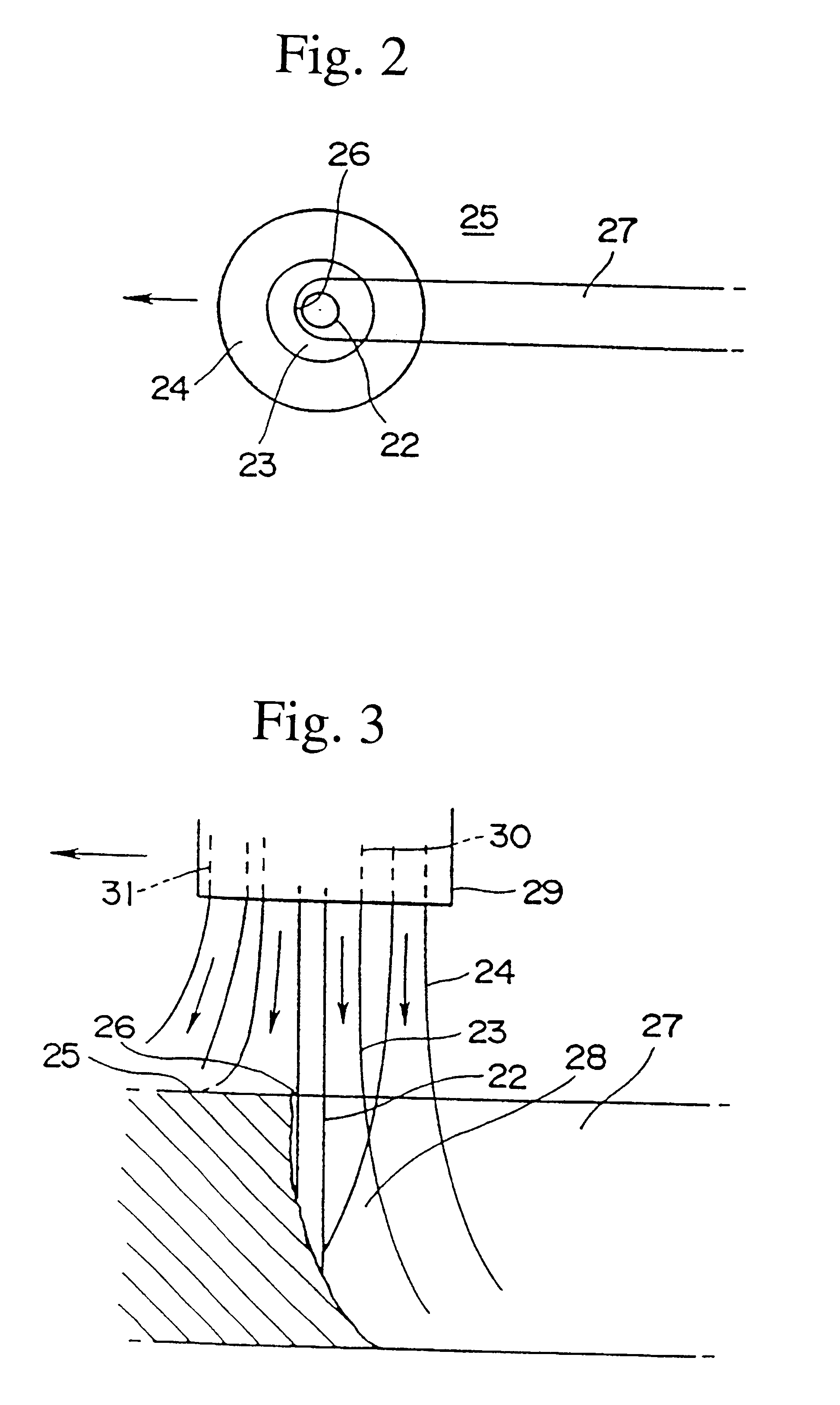
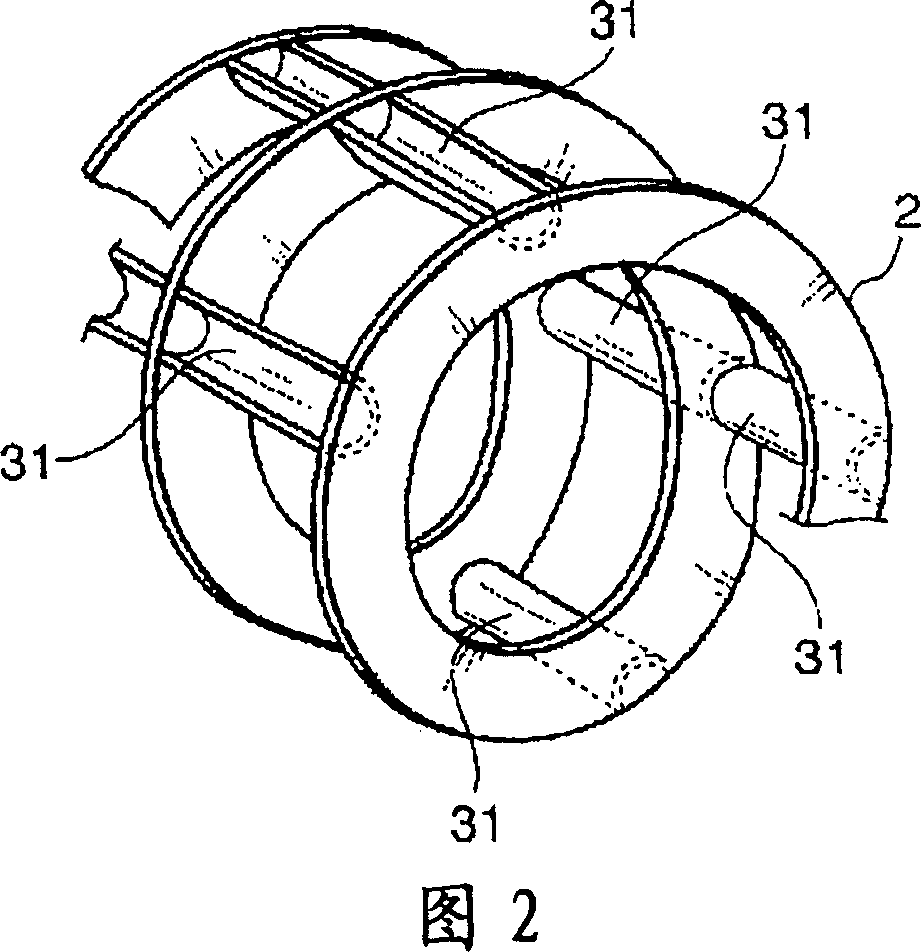
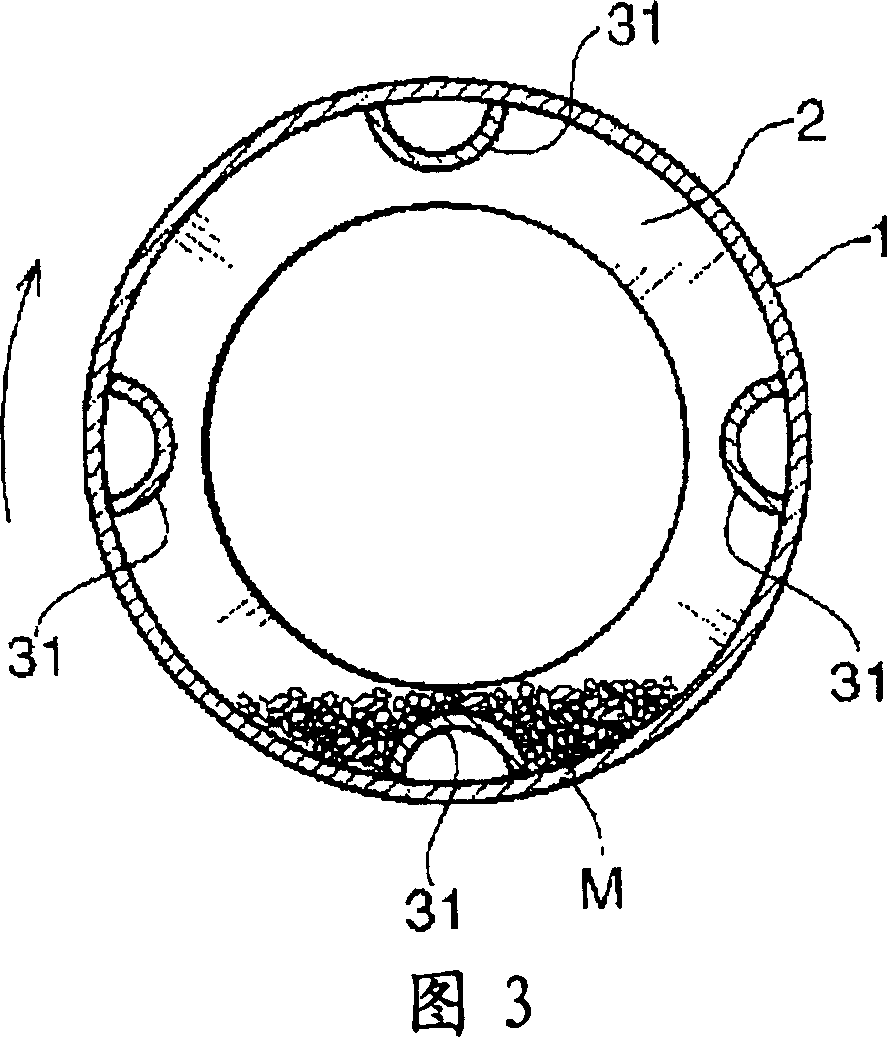
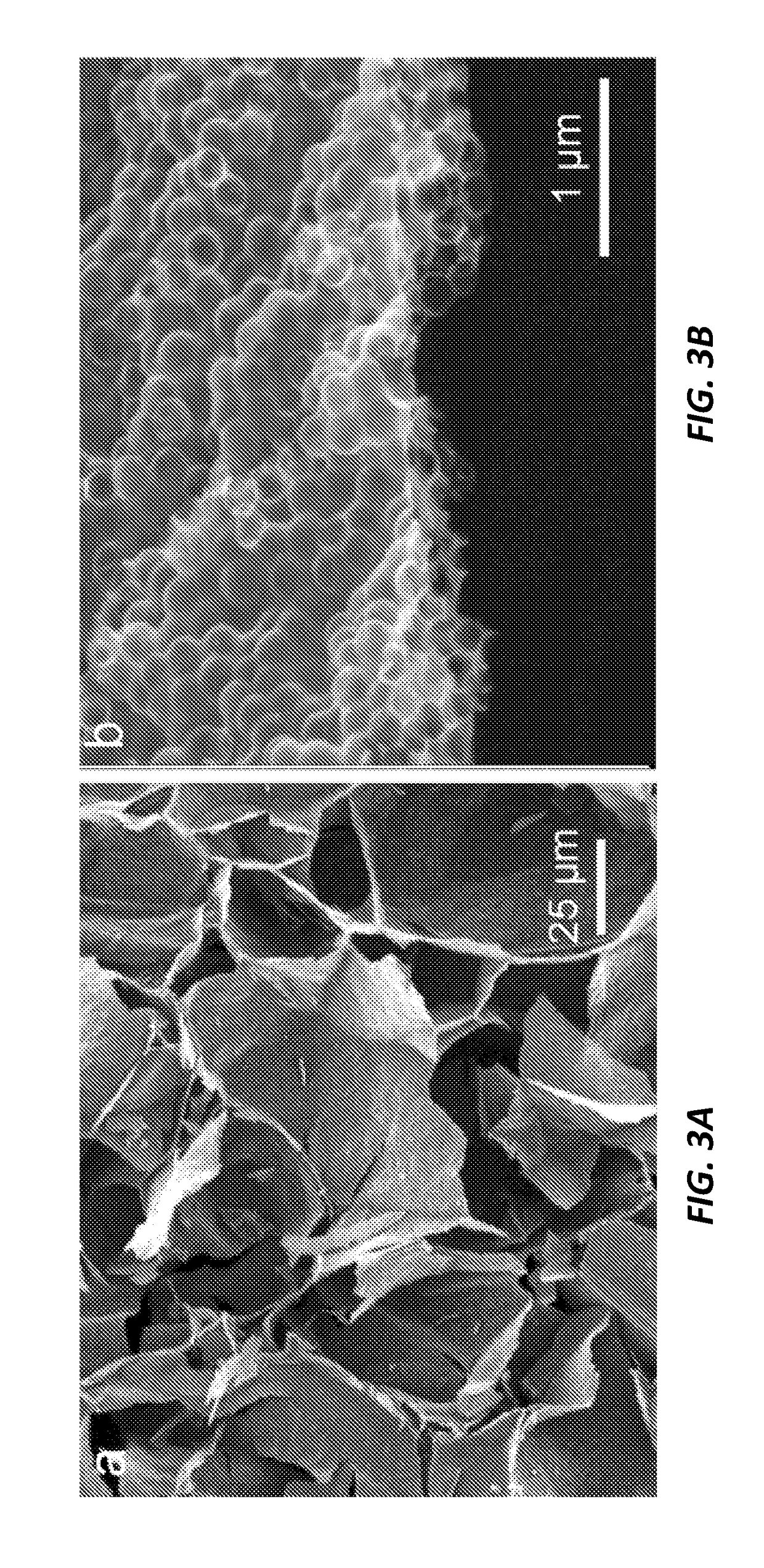
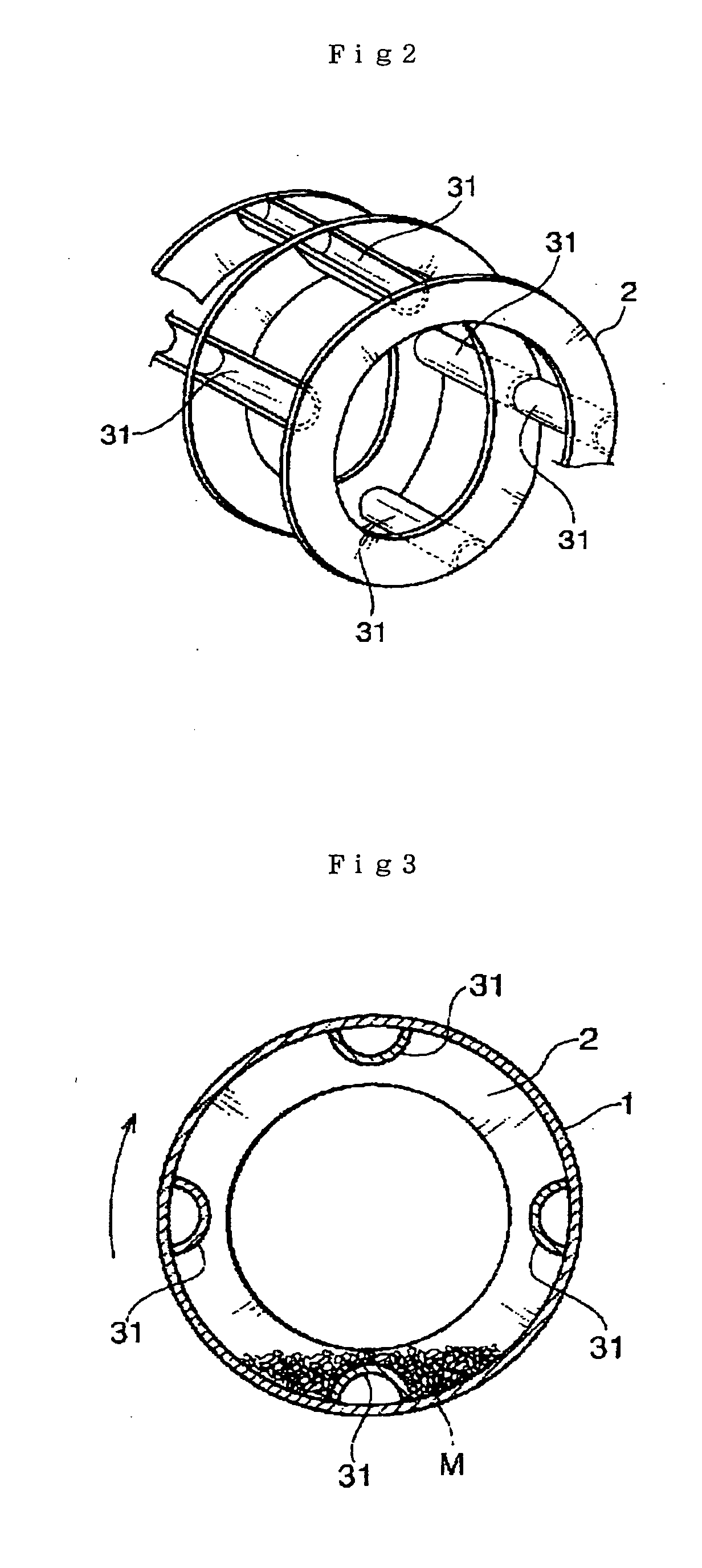
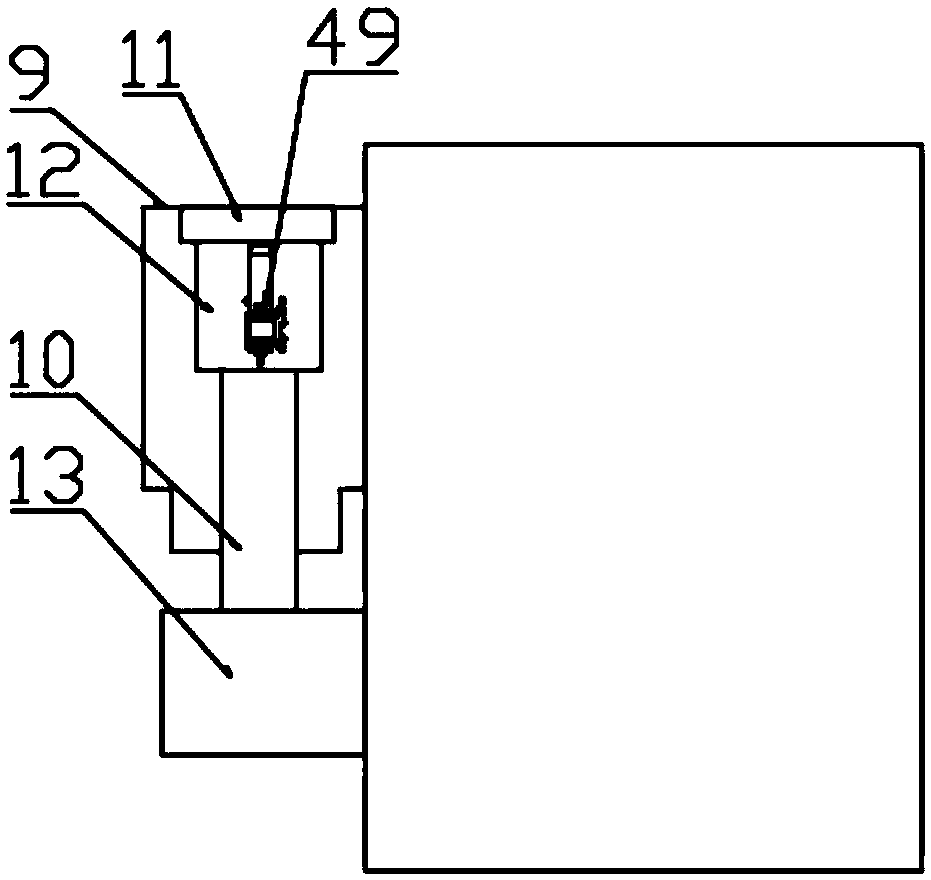
A development of a laser cutting method and a laser cutter in which the adverse effects such as self burning to the cutting surface can be prevented, when the material is cut at a high speed, has been desired. In order to achieve the object, the present invention provides a laser cutting method and a laser cutter in which a cutting laser beam 22 is applied to a material 25 to be cut at a cutting point 26, while ejecting gases 23 and 24 to the cutting point 26 or its surrounding area from a plurality of nozzle openings 30 and 31 arranged in a ring or in a line, wherein the oxygen concentrations of the gases 23 and 24 ejecting from at least one of the nozzle opening 30 and 31 are changed to adjust the oxygen concentration distribution in an area within several millimeters of the cutting point 26; thereby the cutting quality can be improved.
Owner:NISSAN TANAKA
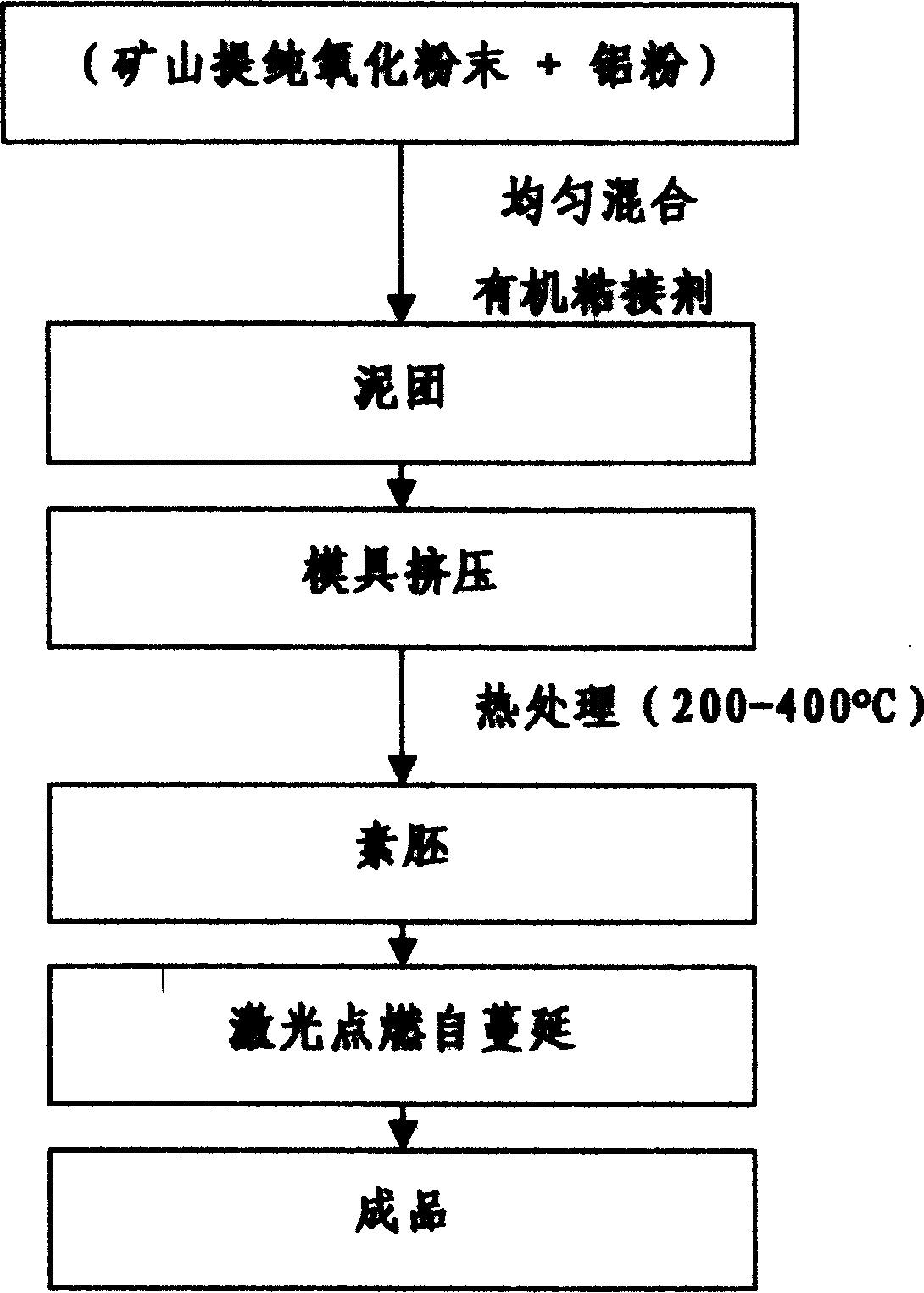
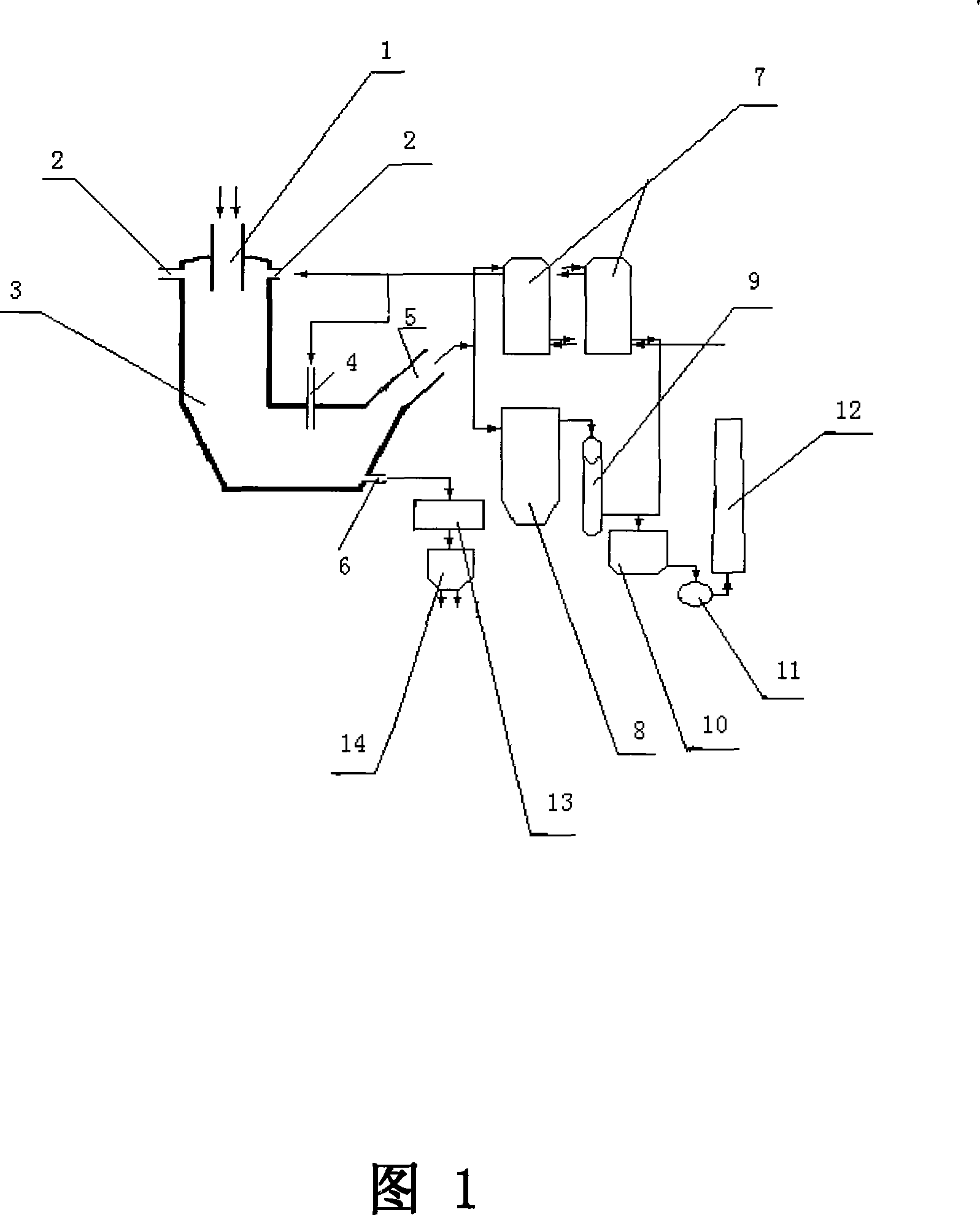
Continuous carbonizing treatment method by internal heating self-combusting mode
The present invention provides a processing method which can process biomass resources to a carbide having a uniformity and including a large amount of high-carbon charcoal, can hold down an initial cost while capable of executing a large amount of process (for example, 100 ton per day), has a low running cost while can suppress a fuel consumption to a significantly low level, and can continuously carbonize a object having a high water content, having an unstable shape and having a high viscosity such as a sewage sludge even being a simple structure. The carbonization processing method has the steps of (i) continuously supplying a processing object M which is not preliminarily treated, or a processing object M which is formed at a predetermined magnitude by a preliminary treatment such as a fragmentation, a water content reduction or the like, from an upstream side of a cylindrical rotary kiln in which a spiral carrier wall is provided in an inner peripheral surface in an entire length and an agitating wall cutting across the carrier wall is formed in the carrier wall in a middle portion from the upstream side at a predetermined unit amount while rotating the rotary kiln, (ii) blowing a flame in an inner portion of the rotary kiln from a downstream side in a carrying direction of the rotary kiln in the state (i), and stopping the blowing of the flame if the processing object M is ignited within the rotary kiln, (iii) supplying an air necessary for burning a combustible gas generated from the processing object M to an inner portion of the rotary kiln from a downstream side, and self burning the combustible gas without supplying any fuel, (iv) sucking a gas generated in the inner portion of the rotary kiln from the upstream side of the rotary kiln so as to detoxify and discharge, and (v) discharging the carbide of the processing object M from an outlet in the downstream side of the rotary kiln so as to cool by executing the operations in the (i) to (iv).
Owner:MAYEKAWA MFG CO LTD
Oil reservoir fire-flooding thermal-ignition method
InactiveCN1995697AAutoignition point reachedRealize the purpose of burning oil layer to drive oilFluid removalThermal energyWater vapor
The invention relates to a thermal igniting method in fire-flooding oil recovery reservoir for ignition in fire-flooding oil recovery reservoir in oilfield and oil well. An active prying gas-steam generator system is used to burn diesel oil to generate mixed air with nitrogen air, carbon dioxide and water steam so on and a mass of heat energy by high-temperature high-pressure burning technology. When the burning temperature in gas-steam generator achieves 1800DEG C, temperature is fallen to 300-400DEG C by mixing water and the pressure is less than 25MPa. The mixed air injects into reservoir by wellhead equipment of oil well and injection tube. The mixed air with the temperature of 300-400DEG C and the cubage of 3-10*104Nm3 is injected to preheat the reservoir and air is injected in the well continuously. In reservoir, the crude oil and the air generate oxygenation to discharge heat. The self-burning point is achieved and burning happens so that the purpose of flooding by combustion. The method solves following problems that the heater is destroyed easily because of over high heating temperature in prior technology and the successful ignition by chemical method is low. The invention can be widely applied in ignition in fire-flooding oil recovery reservoir in oilfield and oil well.
Owner:LIAOHE GASOLINEEUM EXPLORATION BUREAU
Gas water heater with CH4, CO and fire monitoring device and alarm function
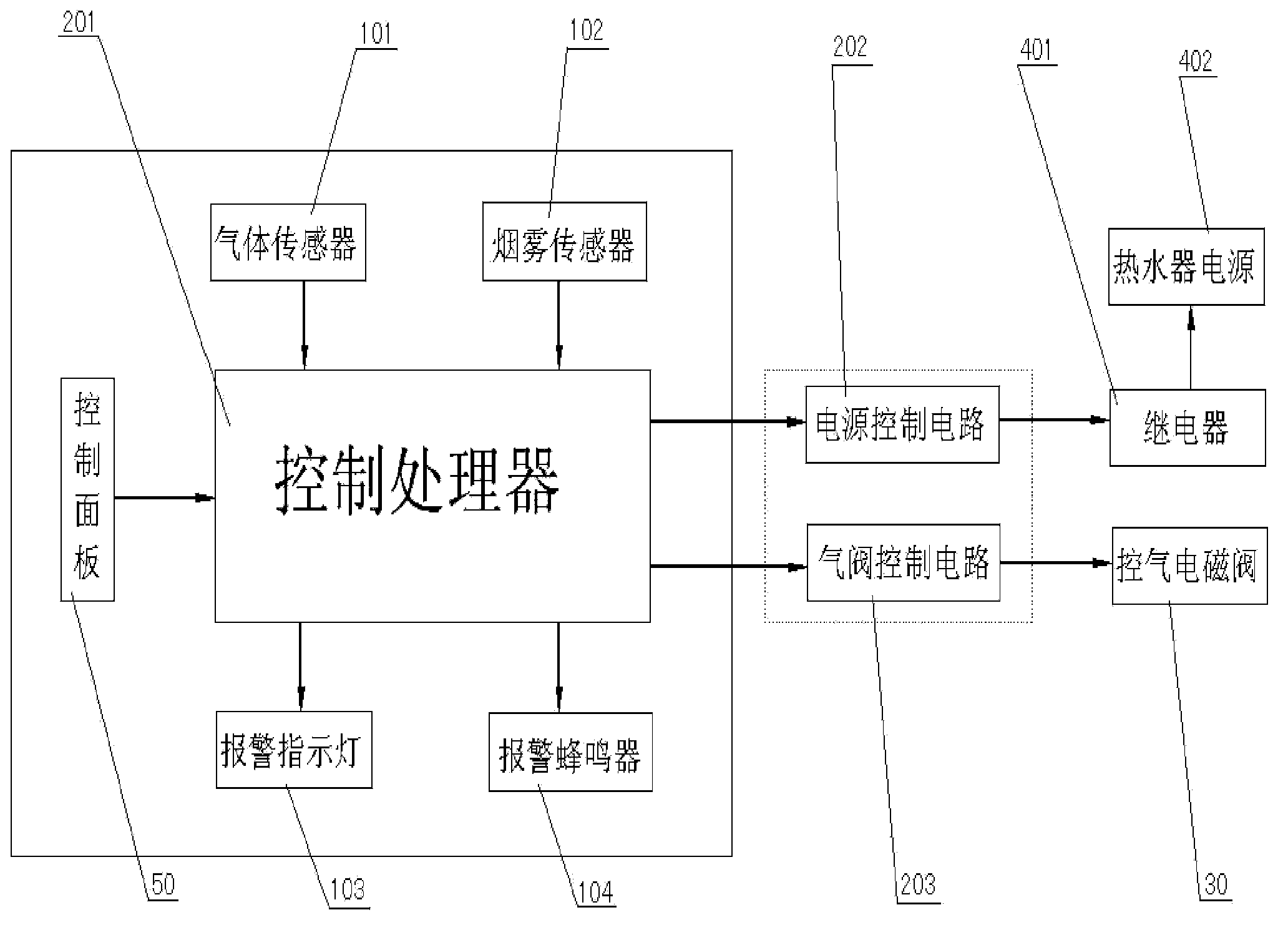
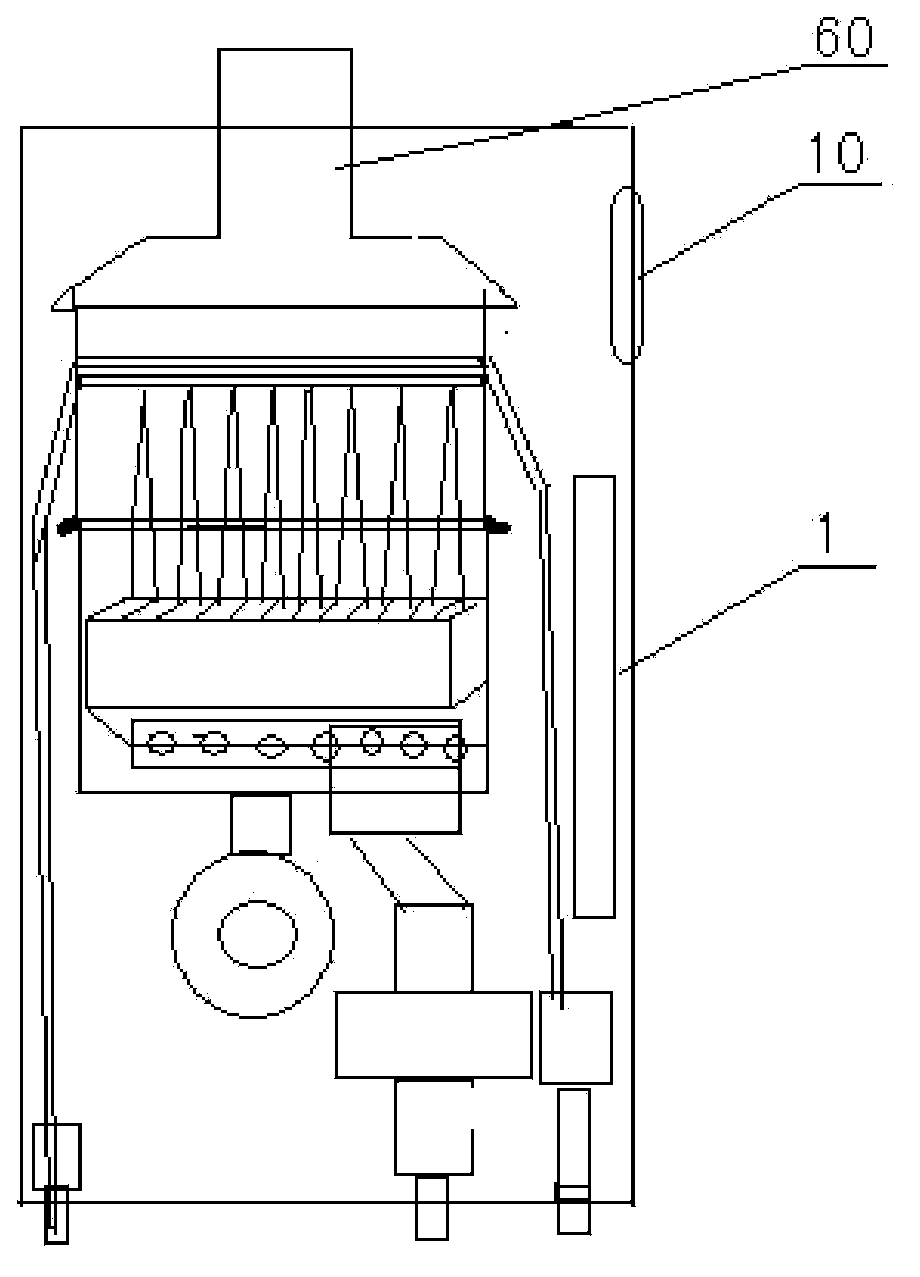
The invention discloses a gas water heater with a CH4, CO and fire monitoring device and an alarm function. The gas water heater comprises a control processor and an information detection device in communication with the control processor. The information detection device at least comprises a gas sensor and a smoke sensor, the gas sensor is used for detecting gas concentration information, and the smoke sensor is used for detecting fire information; the control processor is respectively connected with a gas valve and a relay and used for controlling the gas valve to be off when concentration of gas detected by the gas sensor is out of limits and controlling the gas valve and the relay to be off when receiving fire information detected by the smoke sensor. The gas water heater is capable of not only effectively dealing with conditions of gas leakage, insufficient combustion and overhigh CO concentration and alarming but also timely alarming dangerous conditions of environmental fires and self burning through.
Owner:QINGDAO ECONOMIC & TECHN DEV ZONE HAIER WATER HEATER +1
Mould proof insect prevention antistaling technology of wet wood material
An antimildew and worm-killing process for wet wood includes such steps as sawing, putting the wood in a sealed space, burning sulfur for smoke fumigation, proportionally mixing potassium permanganate with form-aldehyde, loading in a container, self-burning for smoke fumigation, and periodically and alternatively repeating said steps.
Owner:李可锌
Self-burning simple harmless life refuse high temperature combustion furnace
A kind of self-combustion simplified harmless living garbage hyperthermia burning boiler and it is consisted of a firebox, a secondary air intake combustion area, a hyperthermia coddled combustion area, and a heat-sink area. The combustion happens besides in the firebox also the fume is burning drastically in the secondary combustion area and the hyperthermia coddled combustion area. The secondary air intake combustion area is the multi-strip narrow slits and on the wall of multi-strip narrow slits layout two rows or multi-row holes. The hyperthermia coddled combustion area ensures that the fuel gas contacts with the oxygen completely and the hyperthermia with the need of complete combustion and the time of reaction so it can ensure the combustion processing completely. The hyperthermia radiation return bore bakes the living garage by the heat-flash so it has a low requirement for the moisture content of the garage in the firebox. There isn't any combustible component no longer in the ashes. The complete combustion means the complete analytical so it implements the clear burning. In order to ensure the hyperthermia condition of combustion the whole combustion area is enclosed by the heat insulating material.
Owner:王延德 +1
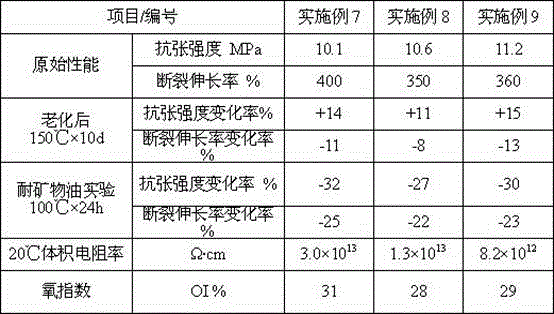
Low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant anti-aging cable material for cables
ActiveCN103571116AGood compatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsChemical reactionPlasticizer
The invention relates to a low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant anti-aging cable material for cables. The cable material is characterized in that the cable material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-50 parts of EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer), 50-80 parts of EVM (ethylene vinyl acetate rubber), 2.5-5 parts of a vulcanizing agent, 1.5-6 parts of a vulcanizing additive, 2-8 parts of an anti-aging agent, 10-30 parts of a plasticizer, 0.5-1.5 parts of a coupling agent, 15-30 parts of a reinforcing agent, 20-40 parts of a filling agent, and 50-70 parts of a flame retardant. According to the invention, because raw materials which do not produce dense smoke in the process of self burning, and do not produce dense smoke during chemical reactions thereof, and can absorb smoke are selected, the smoke density of cables in the process of burning is effectively reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN MINGXING CABLE
Nano-desulfurizing agent for gas, its preparation and use
InactiveCN1895743ASimple preparation processMild reaction conditionsDispersed particle separationCombustible gas purificationSelf burningZinc
A nano-class desulfurizing agent in the form of powder is prepared from zinc oxide (20-50 Wt%) and iron oxide (50-80 Wt%) through preparing sol, preparing gel, self-burning and calcining.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
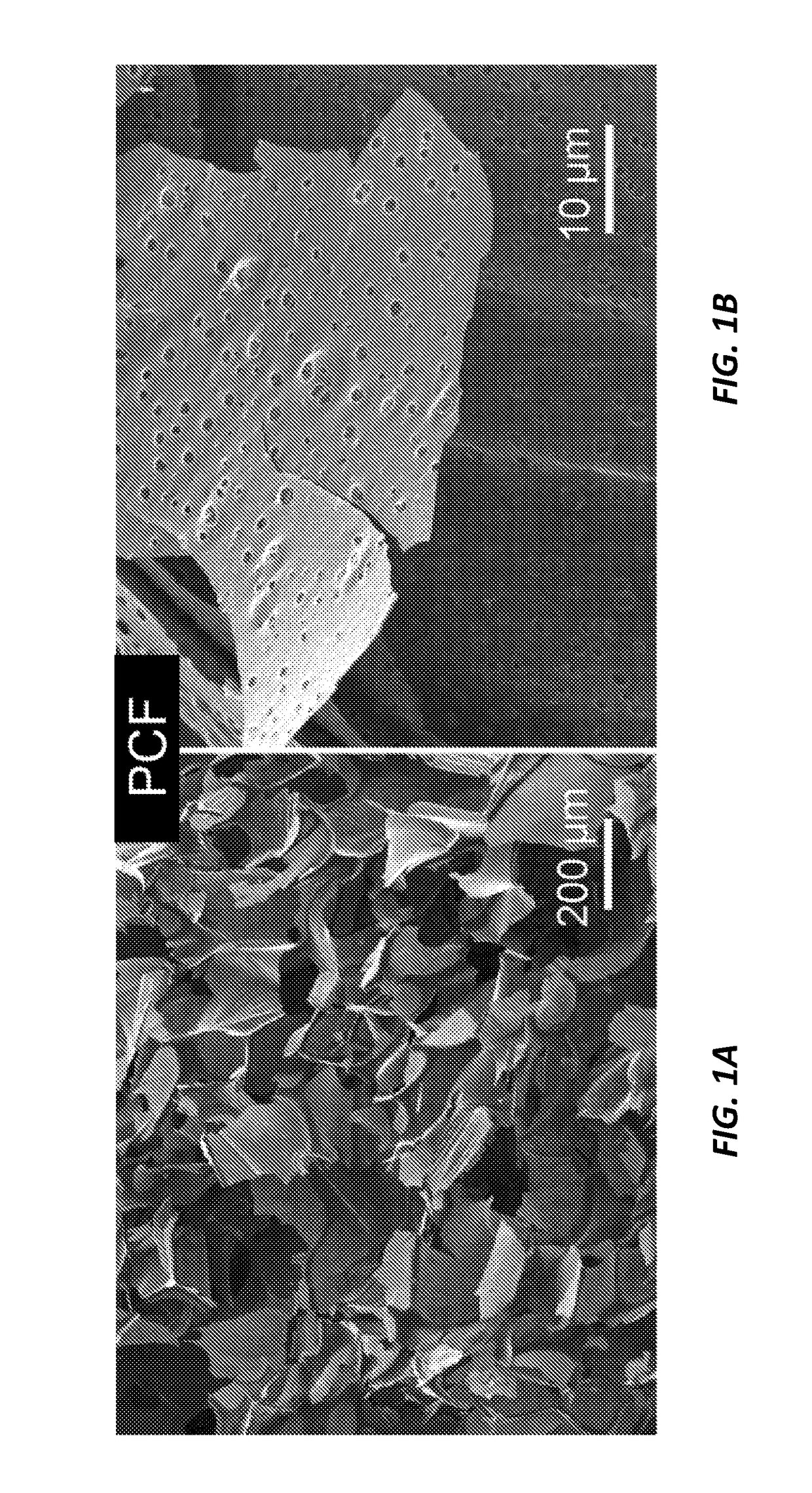
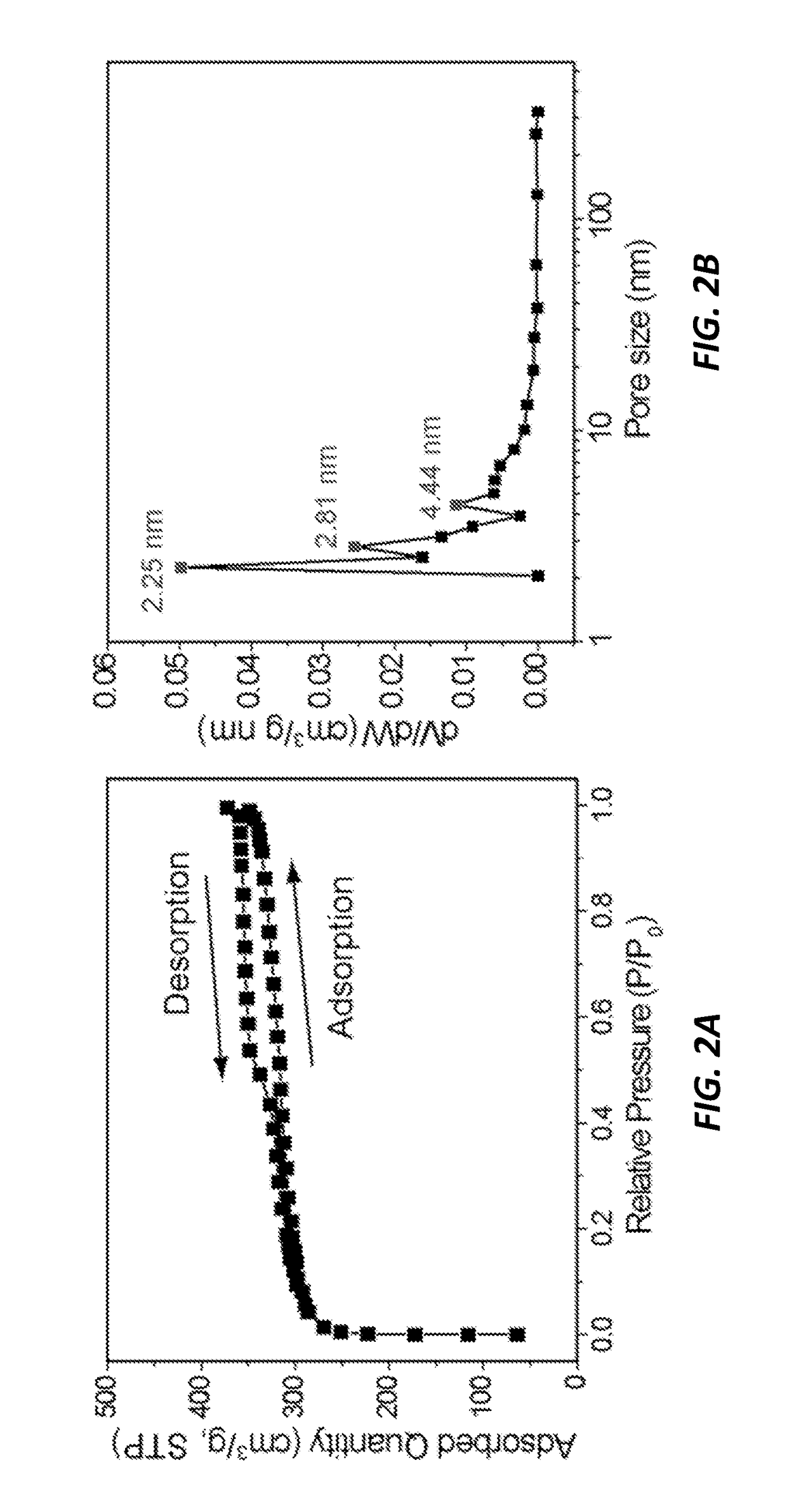
Three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbon foams for supercapacitors
ActiveUS20190077664A1Hybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon preparation/purificationNitrogen atmosphereSupercapacitor
A method of fabricating porous carbon foam includes mixing equal masses of SiO2 particle dispersion with a chitosan solution, dropwise adding a glutaraldehyde aqueous solution into the mixture and solidifying it in air forming a room temperature hydrogel, lyophilizing the hydrogel to form a sponge-like SiO2-embedded aerogel, carbonizing in a furnace the aerogel to form a SiO2-embedded carbon foam, soaking the embedded carbon foam in NaOH to dissolve the SiO2 particles to form a carbon foam having carbon sheets with sub-micron cavities, immersing the carbon sheets in de-ionized water to remove any NaOH residuals followed by drying, placing the carbon foam in KOH solution followed by drying, annealing in nitrogen atmosphere the dried carbon foam to synthesize a carbon foam with a multi-dimensional porous system, immersing the synthesized carbon foam in de-ionized water to prevent self-burning in air, and rinsing the carbon foam in HCl and water, then oven drying.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
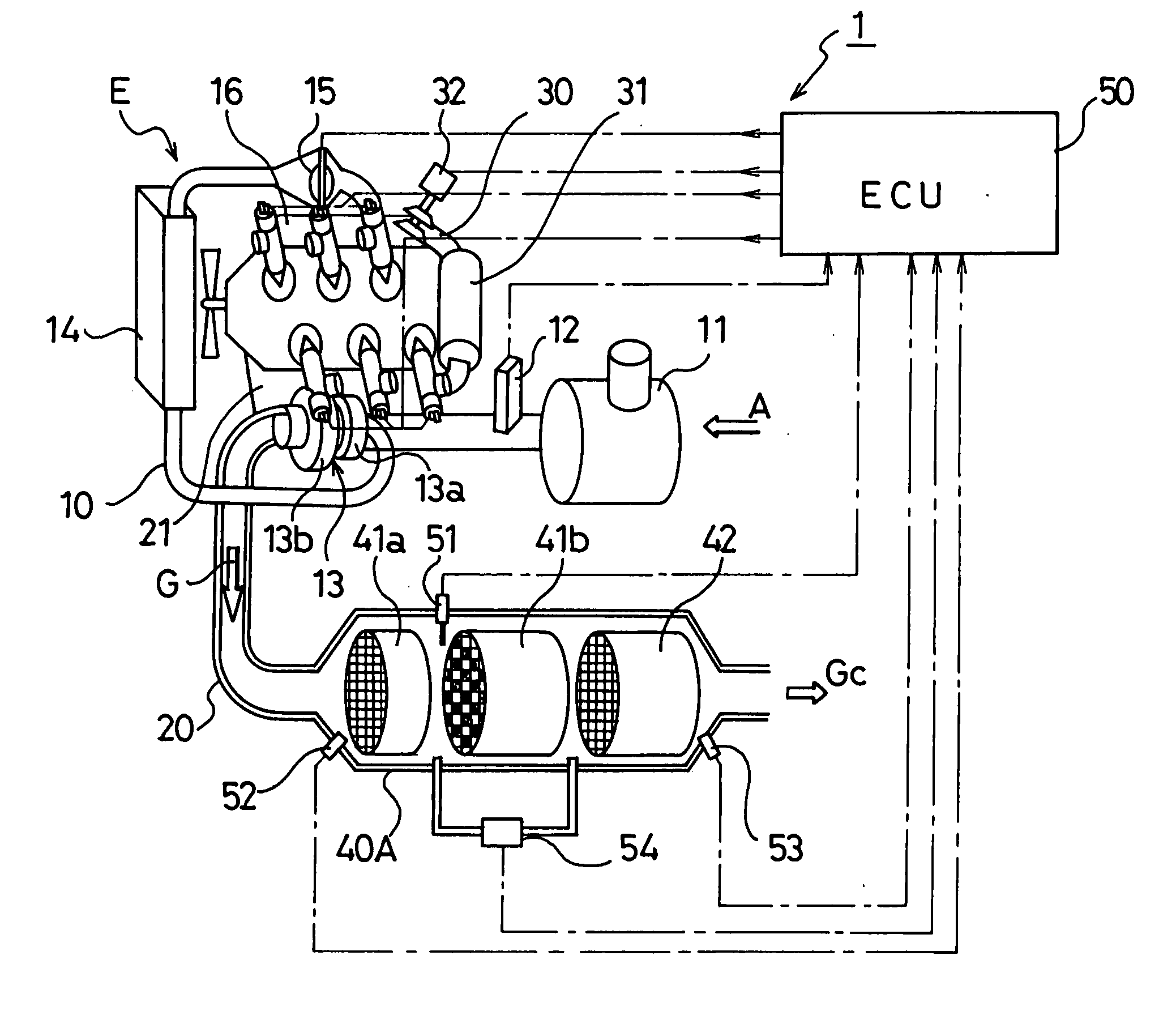
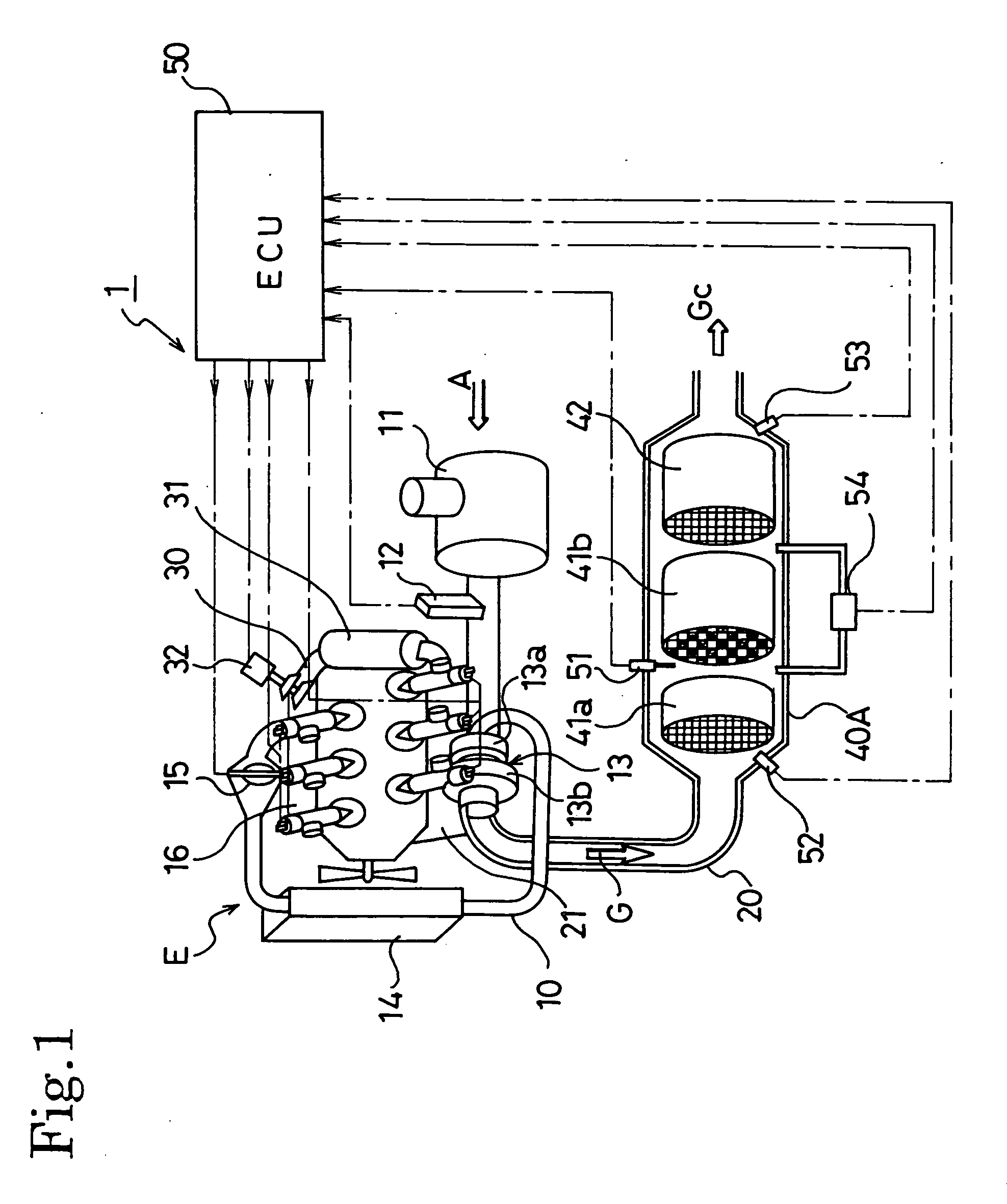
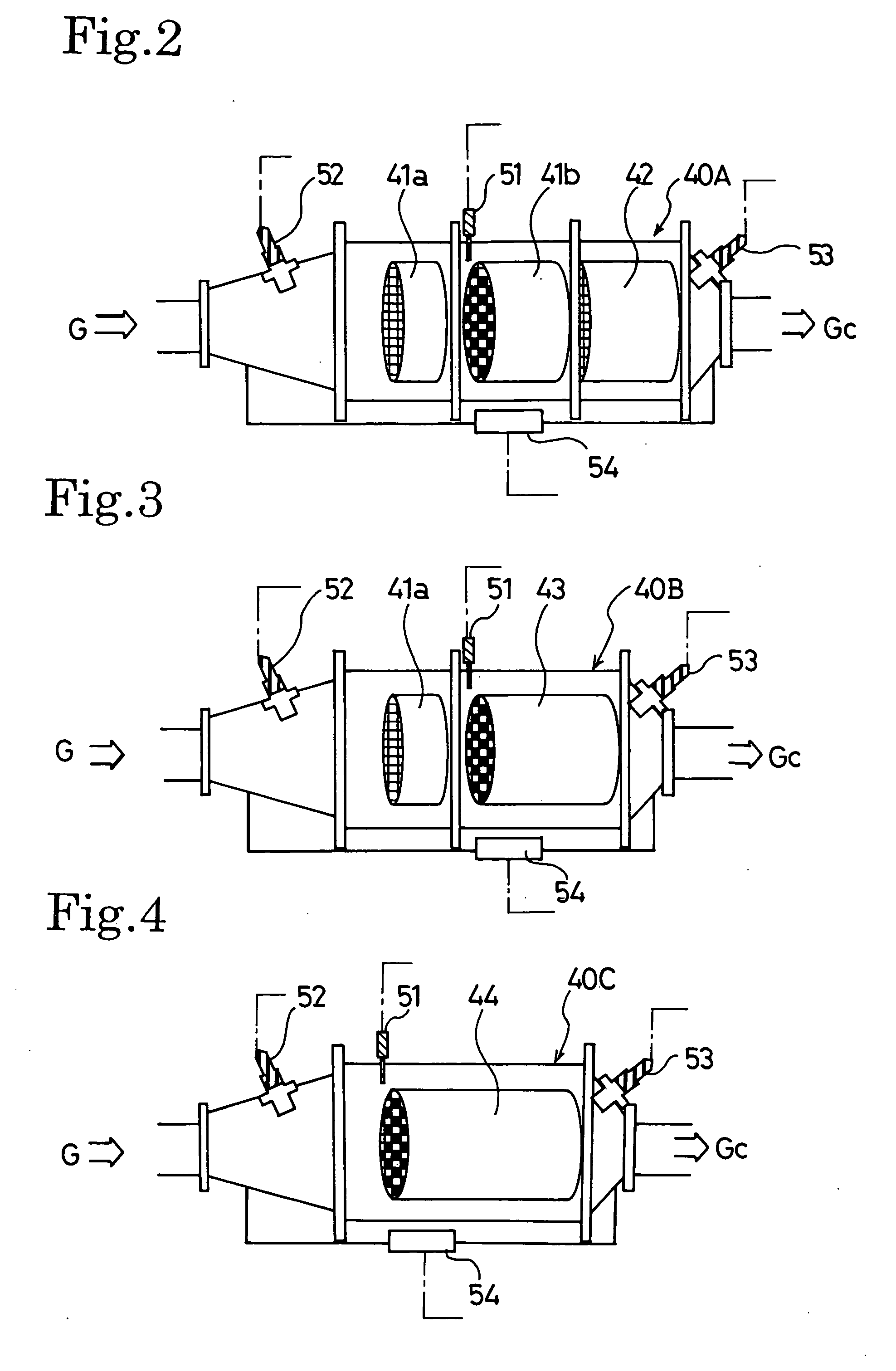
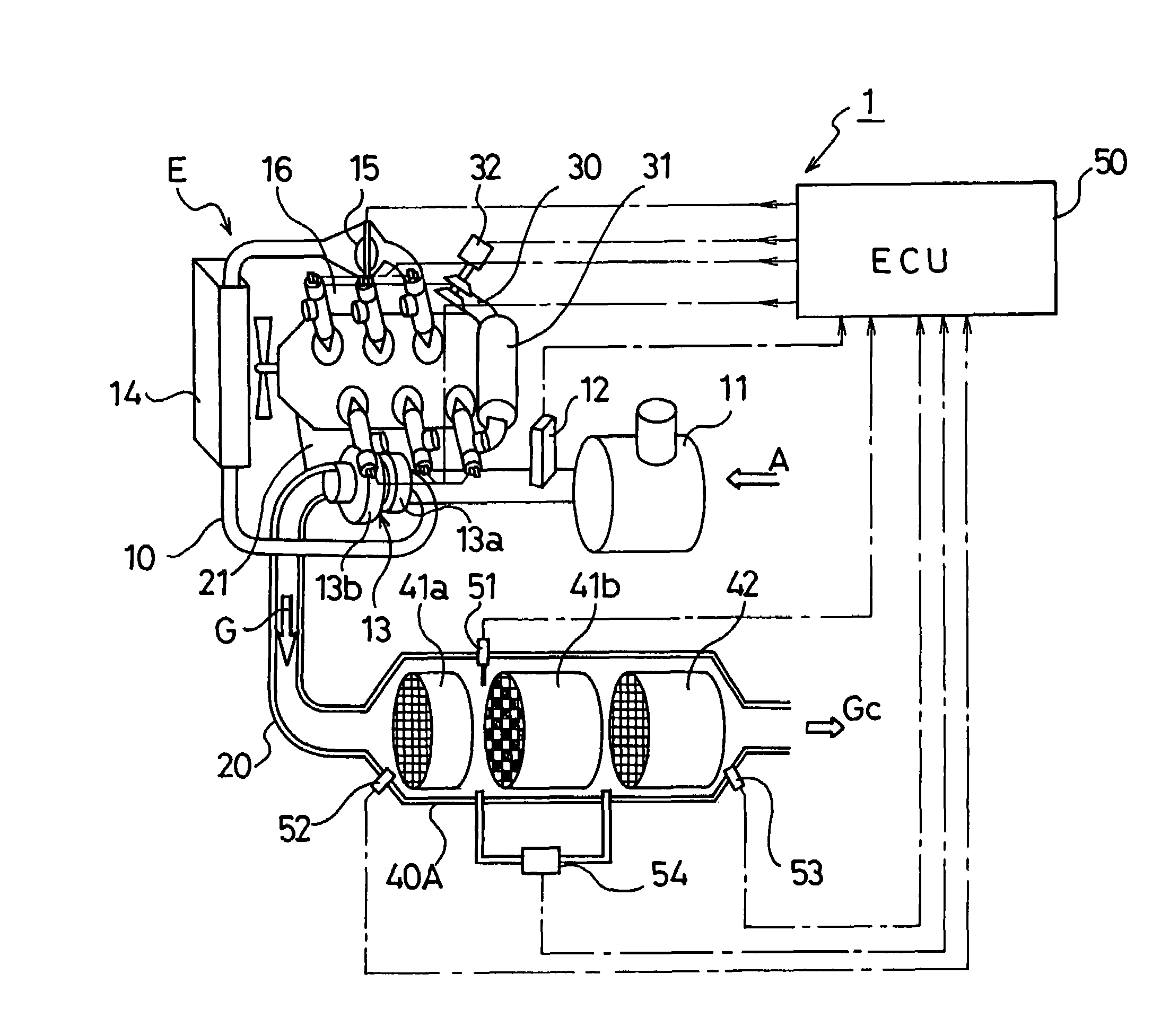
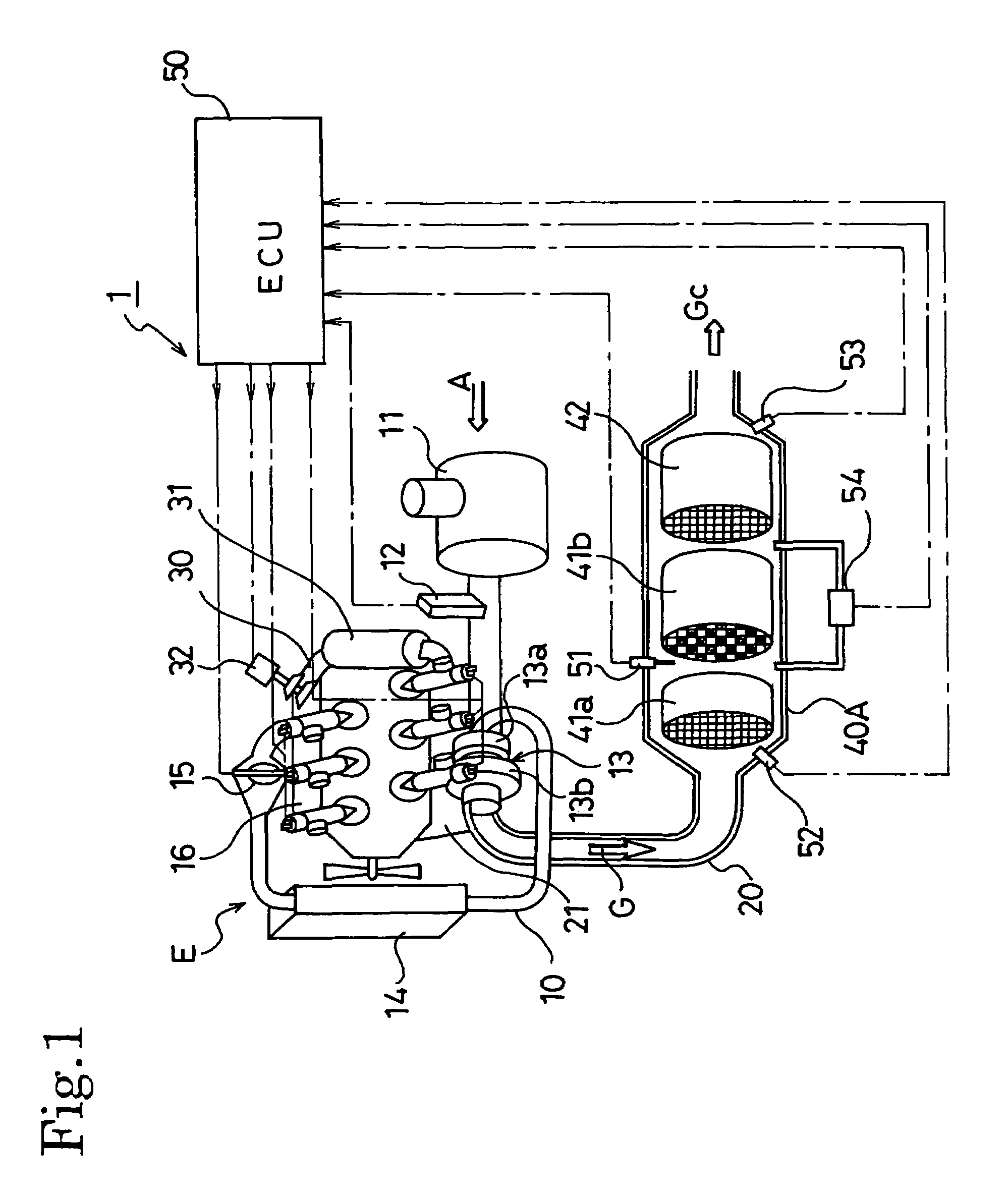
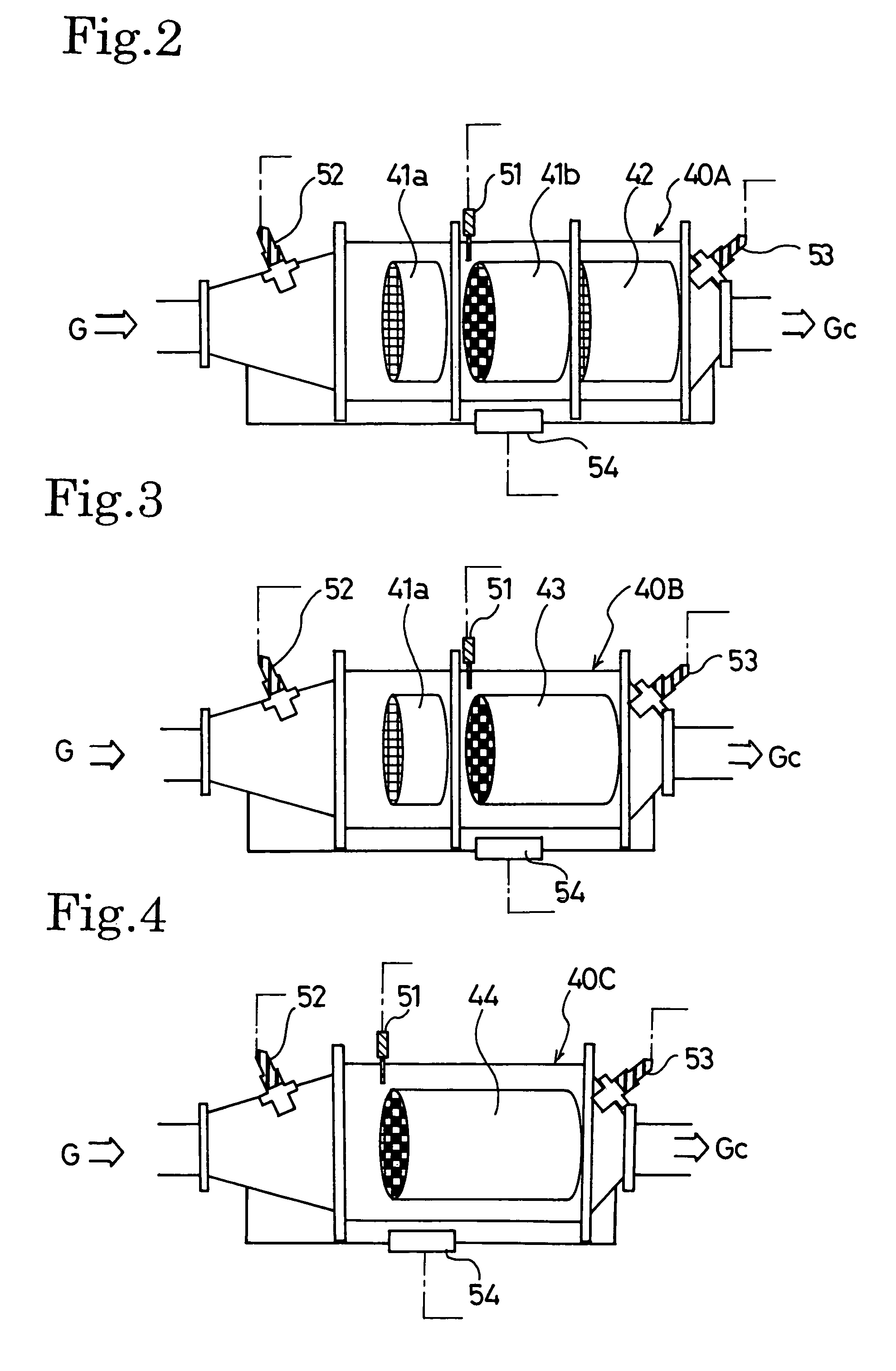
Exhaust gas cleaning method and exhaust gas cleaning system
ActiveUS20070022742A1Richness is reducedAvoid accumulationElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelDifferential pressureExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas cleaning method capable of maintaining an optimum NOx purification ratio in the continuously regenerative range of DPF in an exhaust gas cleaning system (1) having an NOx purification function and a PM purification function combined with each other and the exhaust gas cleaning system (1). In the exhaust gas cleaning system (1), NOx purification by an NOx occlusion / reduction type catalyst (42) and PM purification by a continuous regeneration type DPF (41) are preformed for exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine. When the temperature (Tent) of the exhaust gas flowing in the DPF (41b) exceeds the self-burning temperature (Tent0) of PM and the differential pressure increasing rate (dP) of a differential pressure across the DPF (41b) exceeds a specified determination value (dP0), at least either of a control to reduce the frequency of enriching the exhaust gas and a control to reduce the degree of richness is performed in a catalyst regenerative control for regenerating the NOx occlusion / reduction type catalyst (42).
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
Conductive honey comb ceramic catalyst carrier and its preparation method
InactiveCN1651143AProperly conductiveAppropriate heat conductionCatalyst carriersAl powderSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesis
An electrically conductive cellular ceramic as the carrier of catalyst used for car is prepared from purified titanium oxide or Ti powder, graphite powder and pure Al powder through proportionally mixing, adding organic adhesive, stirring, die pressing, heat treating, igniting and self burning for high temp synthesis.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Exhaust gas cleaning method and exhaust gas cleaning system
ActiveUS7451593B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the air-fuel ratioElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelDifferential pressureExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas cleaning method capable of maintaining an optimum NOx purification ratio in the continuously regenerative range of DPF in an exhaust gas cleaning system (1) having an NOx purification function and a PM purification function combined with each other and the exhaust gas cleaning system (1). In the exhaust gas cleaning system (1), NOx purification by an NOx occlusion / reduction type catalyst (42) and PM purification by a continuous regeneration type DPF (41) are preformed for exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine. When the temperature (Tent) of the exhaust gas flowing in the DPF (41b) exceeds the self-burning temperature (Tent0) of PM and the differential pressure increasing rate (dP) of a differential pressure across the DPF (41b) exceeds a specified determination value (dP0), at least either of a control to reduce the frequency of enriching the exhaust gas and a control to reduce the degree of richness is performed in a catalyst regenerative control for regenerating the NOx occlusion / reduction type catalyst (42).
Owner:ISUZU MOTORS LTD
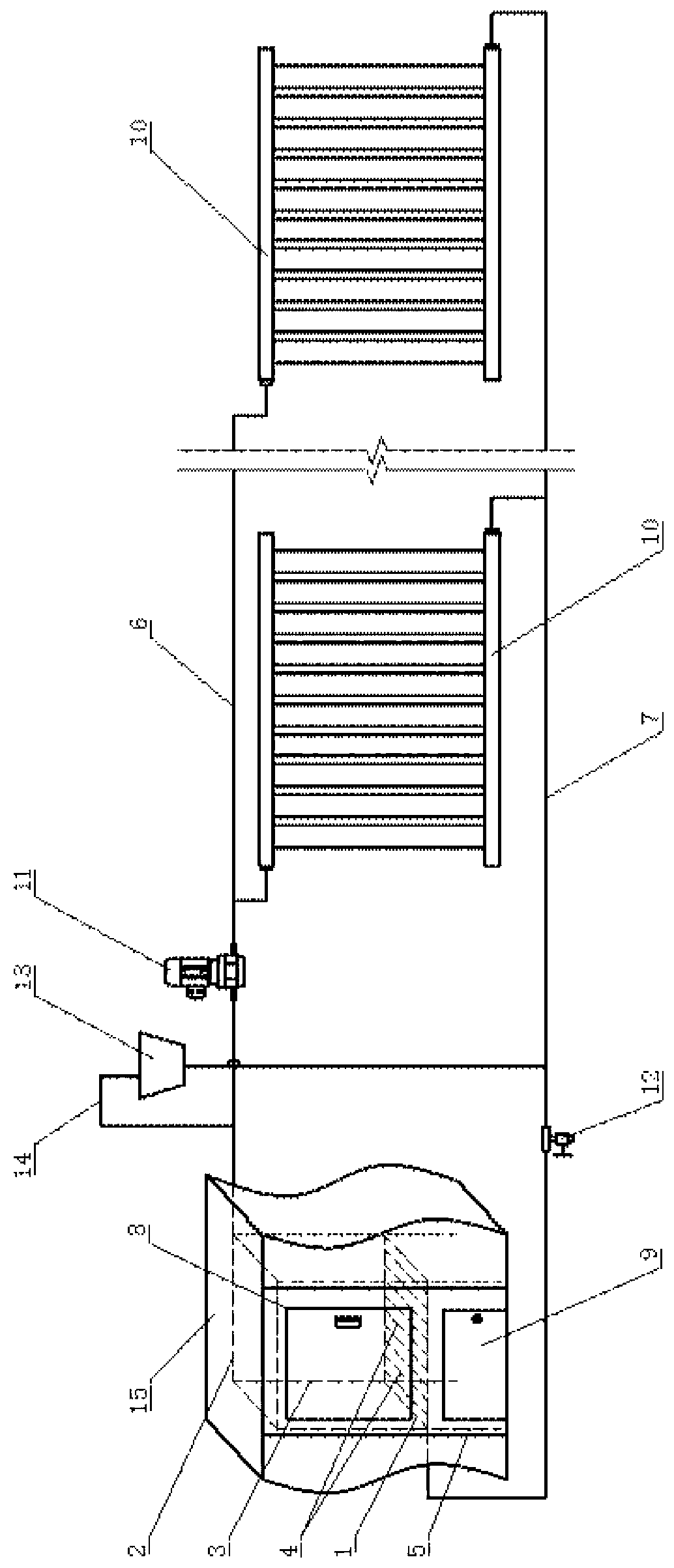
Consumer waste self-burning device
InactiveCN101196302AAchieving molten self-immolationNo need for oxygenCombustion technology mitigationIncinerator apparatusOxygenHigh heat
The invention discloses a self-burning device for domestic garbage, which enables the inflammable vapor generated by pyrolyzing garbage to be directly utilized in the burning device. The device is characterized in that the structure comprises: a furnace body, a feeding pipe, an upper thermal air opening, a lower thermal air opening, a high temperature gas outlet, a cinder notch, a heat transfer, a waste heat boiler, a quench tower, a dust catcher, a draught fan, a chimney, a water quench machine and a separator. Heat for the invention can be supplied by burning without needing ant assistant fuel; besides, high temperature air is used for helping the burning, thereby saving oxygen; volatile matters generated from gasification are burned completely in the burning furnace, which has high heat efficiency.
Owner:辽宁省烟草公司鞍山市公司
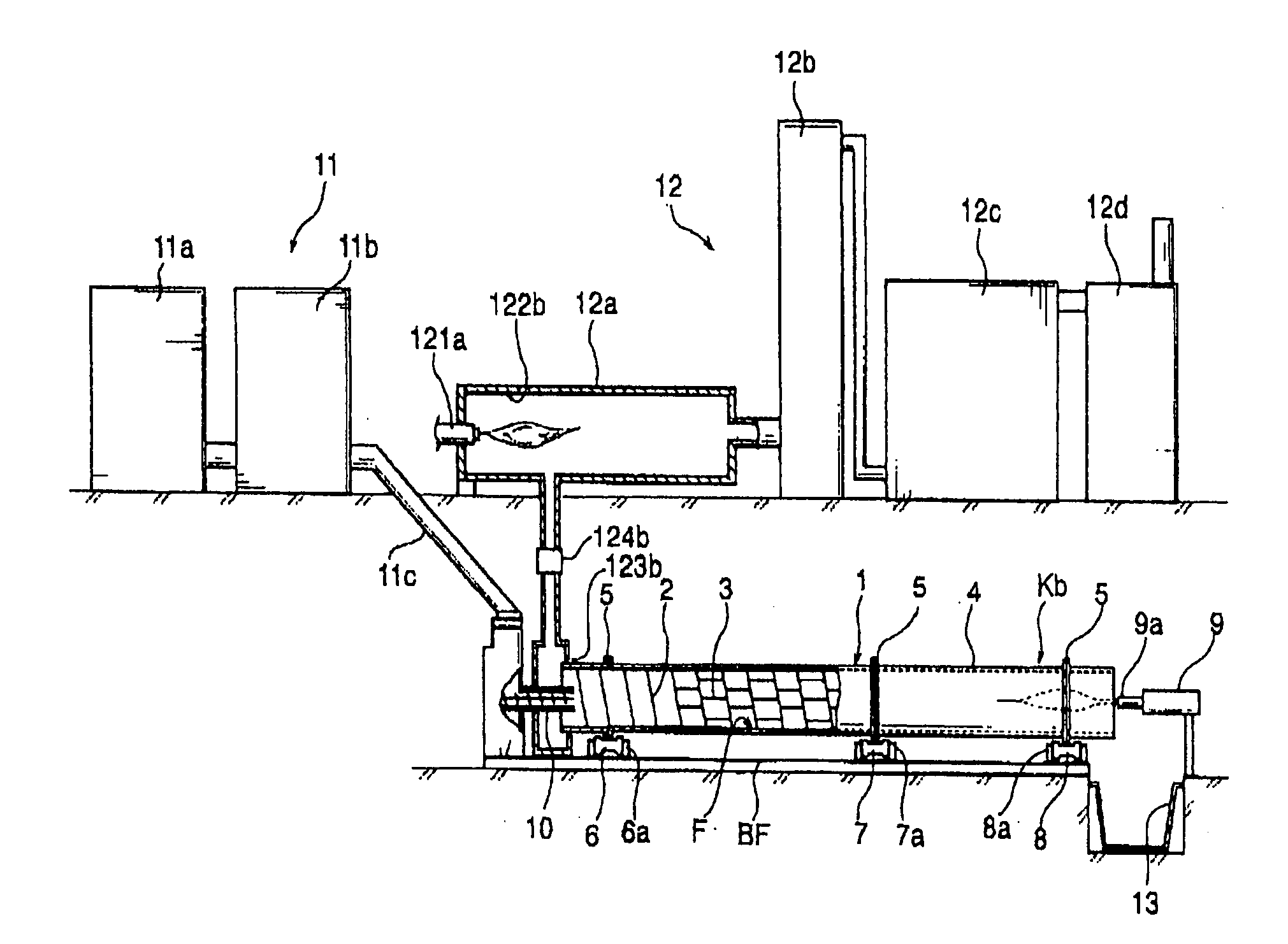
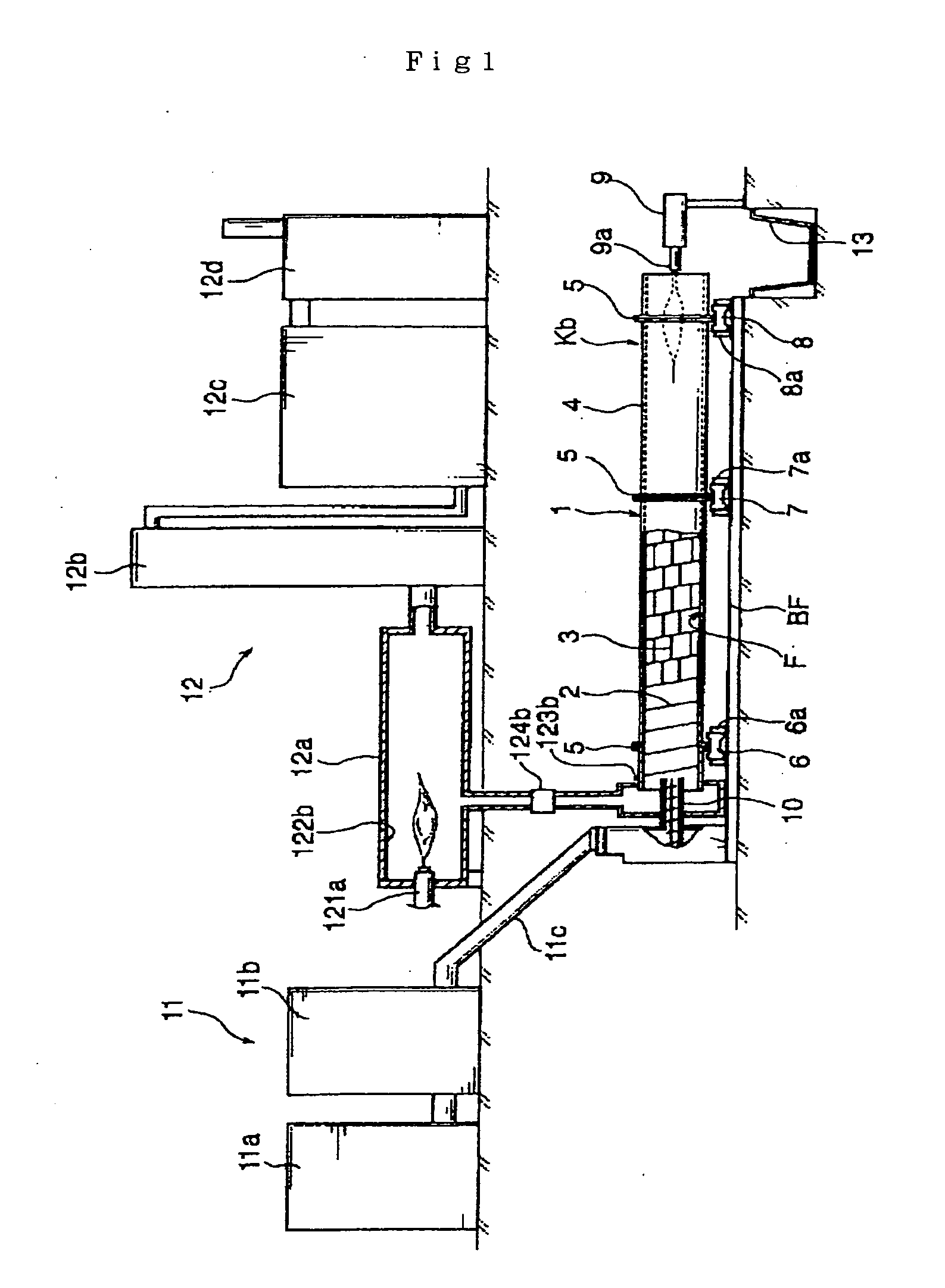
Continuous Carbonization Processing by Internal Heat Type Self-Substained Combustion System
InactiveUS20070281268A1Low running costLower initial costDirect heating destructive distillationRotary drum furnacesSludgeHigh carbon
The present invention provides a processing method which can process biomass resources to a carbide having a uniformity and including a large amount of high-carbon charcoal, can hold down an initial cost while capable of executing a large amount of process (for example, 100 ton per day), has a low running cost while can suppress a fuel consumption to a significantly low level, and can continuously carbonize a object having a high water content, having an unstable shape and having a high viscosity such as a sewage sludge even being a simple structure. The carbonization processing method has the steps of (i) continuously supplying a processing object M which is not preliminarily treated, or a processing object M which is formed at a predetermined magnitude by a preliminary treatment such as a fragmentation, a water content reduction or the like, from an upstream side of a cylindrical rotary kiln in which a spiral carrier wall is provided in an inner peripheral surface in an entire length and an agitating wall cutting across the carrier wall is formed in the carrier wall in a middle portion from the upstream side at a predetermined unit amount while rotating the rotary kiln, (ii) blowing a flame in an inner portion of the rotary kiln from a downstream side in a carrying direction of the rotary kiln in the state (i), and stopping the blowing of the flame if the processing object M is ignited within the rotary kiln, (iii) supplying an air necessary for burning a combustible gas generated from the processing object M to an inner portion of the rotary kiln from a downstream side, and self burning the combustible gas without supplying any fuel, (iv) sucking a gas generated in the inner portion of the rotary kiln from the upstream side of the rotary kiln so as to detoxify and discharge, and (v) discharging the carbide of the processing object M from an outlet in the downstream side of the rotary kiln so as to cool by executing the operations in the (i) to (iv).
Owner:MAEKAWA SEISAKUJO
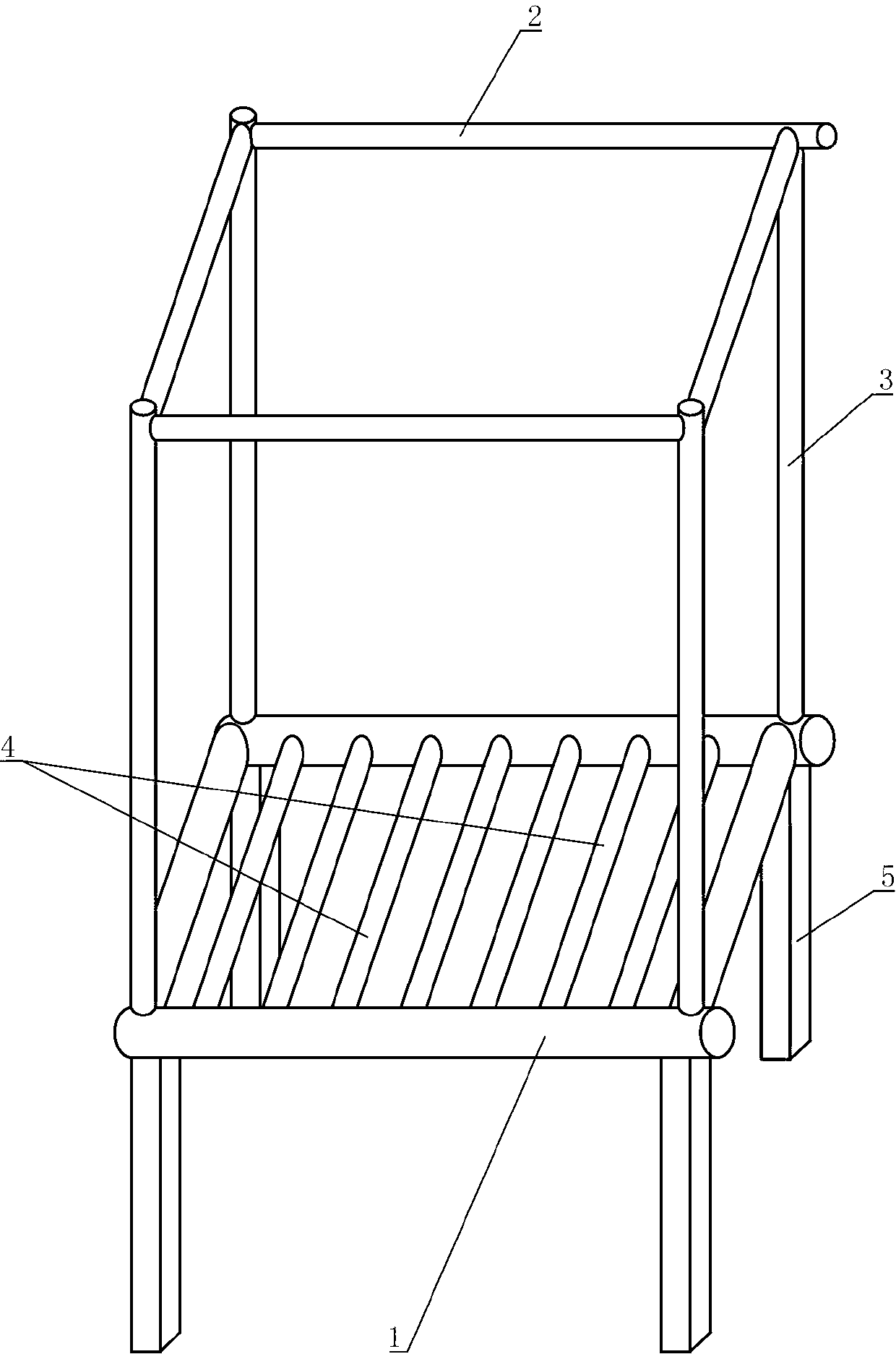
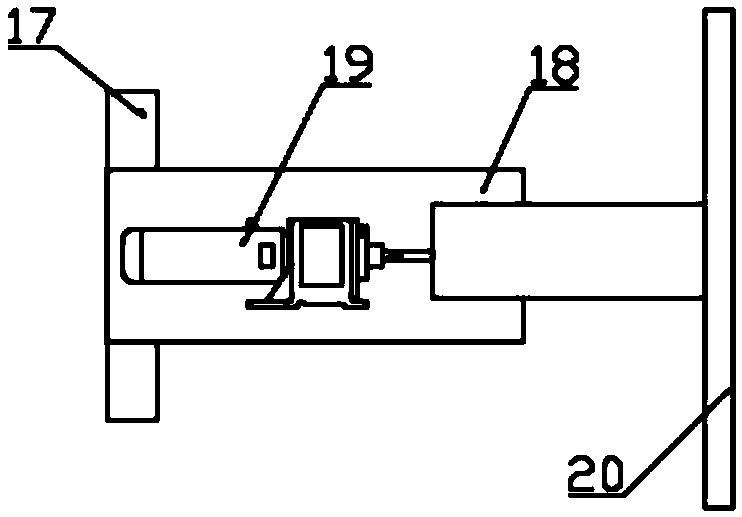
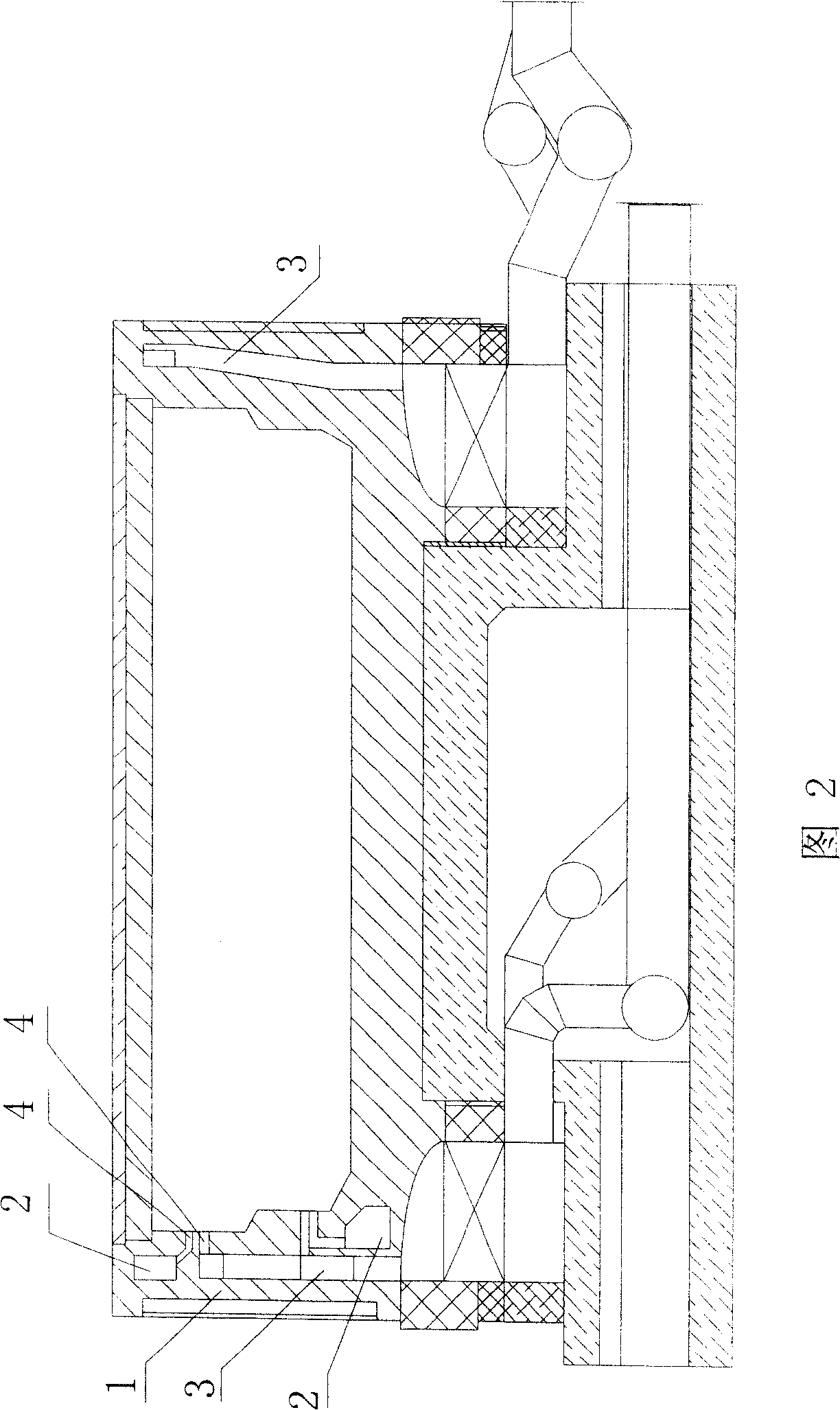
Earthen bed self-burning boiler and heating system thereof
InactiveCN103017211ASimple structureEasy to transformLighting and heating apparatusStove/ranges for heating waterEngineeringHearth
The invention relates to heating equipment and system, in particular to an earthen bed self-burning boiler, which can efficiently heat indoors only by using straws, is low in cost, does not need to change the structure of an earthen bed, and does not need coal, as well as a heating system using the earthen bed self-burning boiler. The earthen bed self-burning boiler comprises water inlet pipes (1) and water outlet pipes (2), wherein communicating pipes (3) are arranged between the water inlet pipes (1) and the water outlet pipes (2); a plurality of heating pipes (4) communicated with the water inlet pipes (1) or the water outlet pipes (2) are formed in the water inlet pipes (1) or the water outlet pipes (2); the heating pipes (4) are arranged in the same horizontal plane; and a gap is formed between adjacent heating pipes (4). The heating system of the earthen bed self-burning boiler comprises an earthen bed main body (15), a hot water pipe (6) and a water return pipe (7) and further comprises the earthen bed self-burning boiler, wherein the earthen bed self-burning boiler is arranged in a fuel hole of the earthen bed main body (15); and the fuel hole is divided into a burning chamber and an ash discharging chamber through the plane of the heating pipes (4).
Owner:钟殿玺
Construction method for burner, air channels, gas flues inside furnace wall of heating furnace in heat storage type
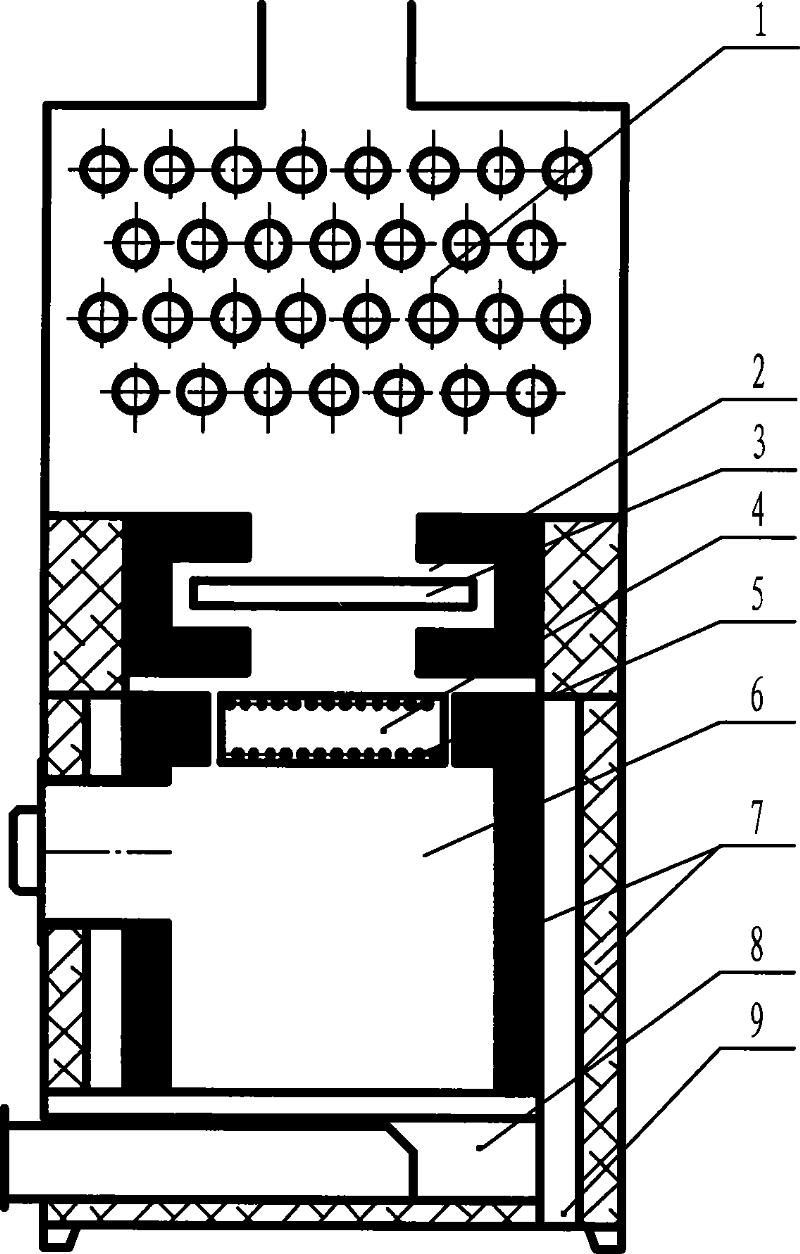
InactiveCN1959204AGuaranteed cleanlinessSimple processCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelHeating furnaceSelf burning
A method for constructing nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel on wall of thermal storage heating furnace includes plotting out template drawing of nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel according to their sizes on said wall then preparing cavity template by PVC material as per said template drawing, transporting their cavity templates into their positions on two sides of said wall and fixing them there, pouring fireproof material then self burning said cavity templates prepared by PVC material for forming nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel.
Owner:CHINA FIRST METALLURGICAL GROUP
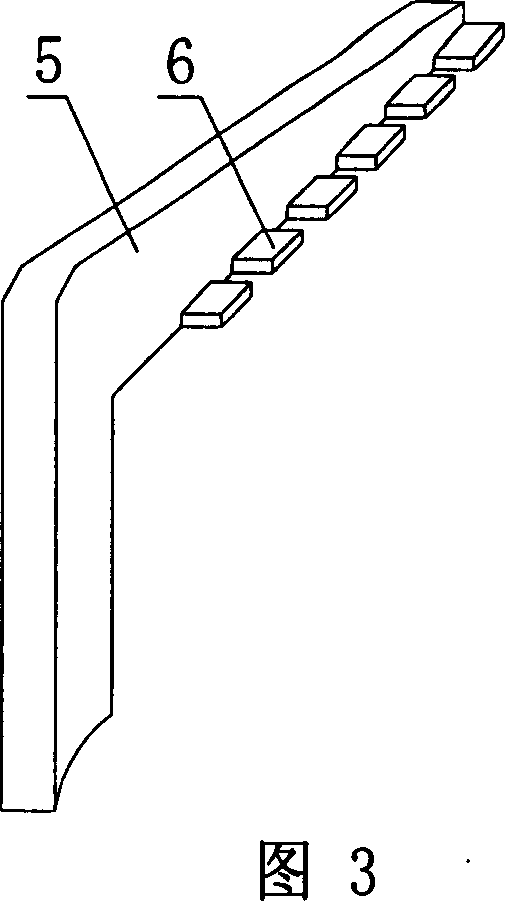
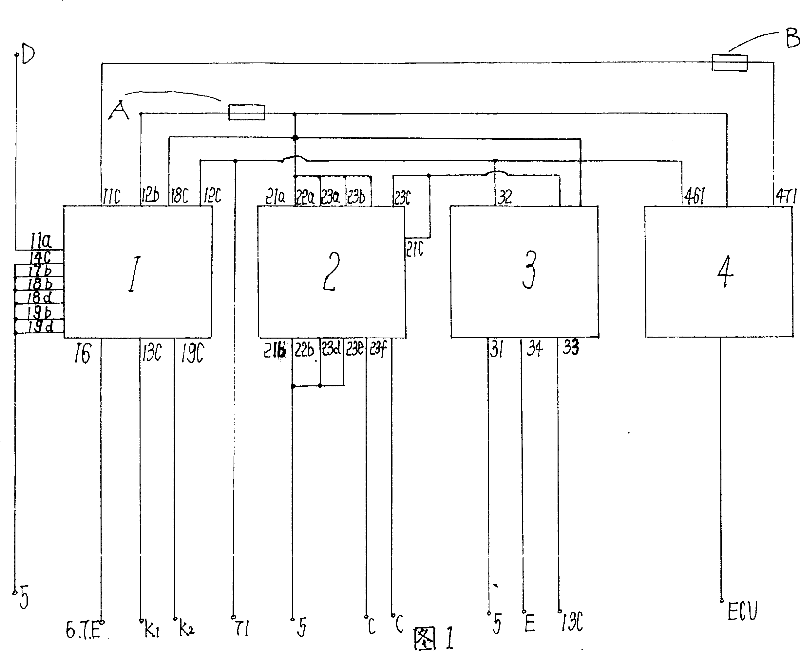
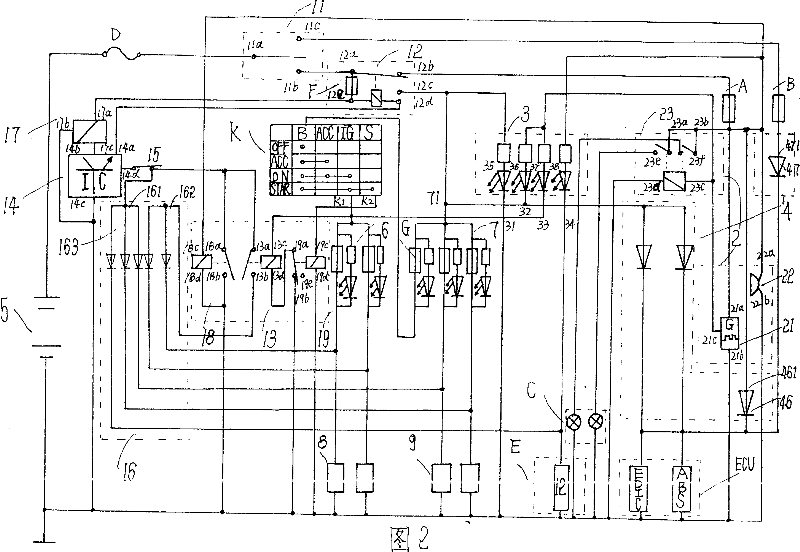
Protecting device for self-burning of vehicle
InactiveCN101041339APrevent spontaneous combustionWon't hurtElectric/fluid circuitSelf burningAlarm device
The invention relates to a protective device for automobile self-ignition, comprising failure protection control device, failure alarming device, failure indicating device and power supply guaranteeing device. The invention is provided with high sensitivity, stability, reliability, no damage for circuits in automobile after short circuit happens, quickly cutting power supply of automobile off after the temperature of engine chamber arises rapidly and low producing cost. The indicator light allocated in the invention is favor of finding failure point accurately by maintenance worker and removing rapidly. If the output end 11C of two-position switch is closed it also has anti-theft performance. The structure in invention makes the whole automobile obtain inspection and protection. Any electric leakage problem bringing ignition possibly and the problem of over-high temperature in engine chamber can make the whole automobile break off so that self-ignition generated by electric leakage and over-high temperature in engine chamber is avoided effectively.
Owner:丁靖
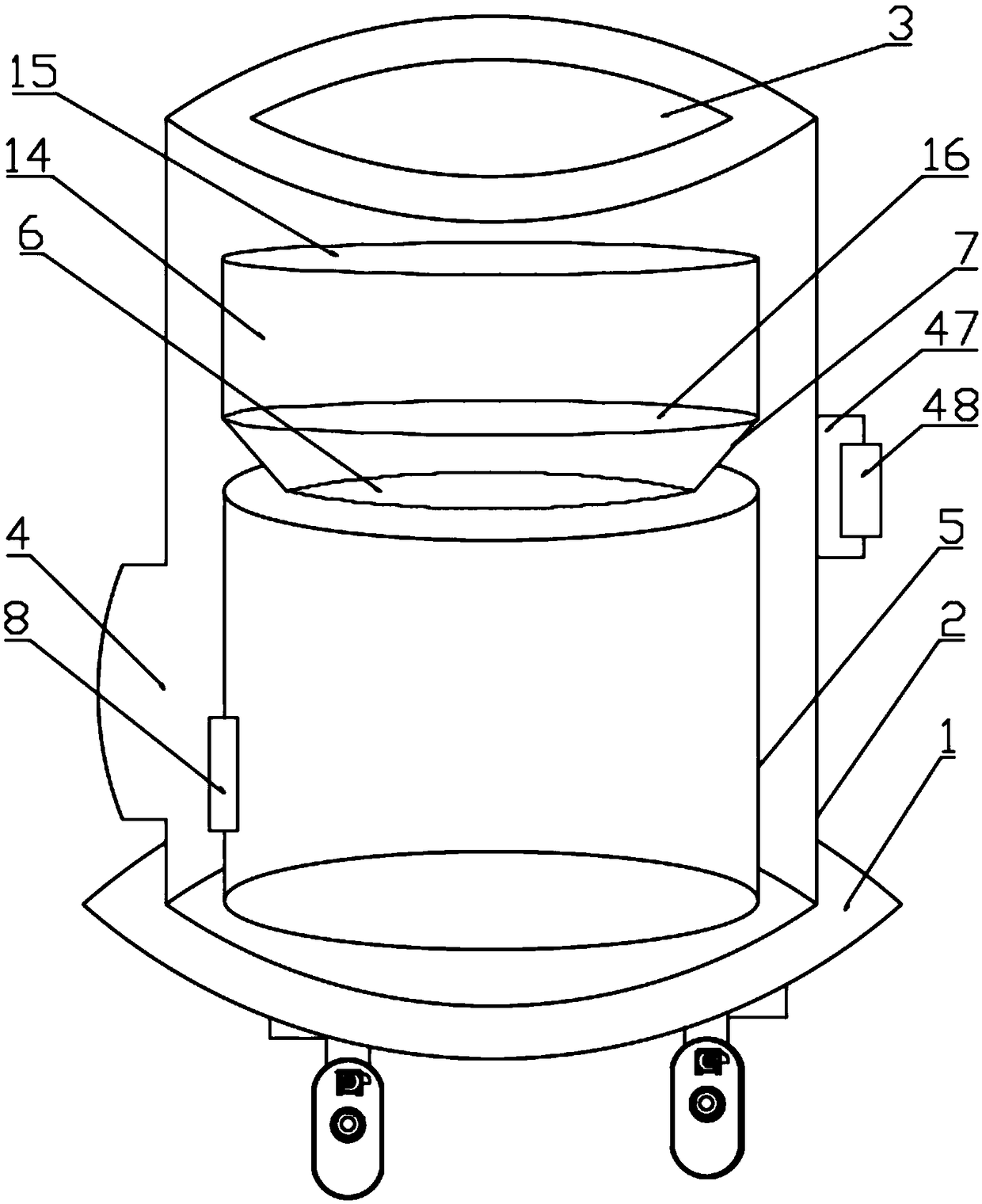
Movable environmentally-friendly self-burning garbage can
InactiveCN108726042AMobile Compression Combustion ProcessingReduce pollutionRefuse receptaclesCompression deviceSelf burning
The invention discloses a movable environmentally-friendly self-burning garbage can. The movable environmentally-friendly self-burning garbage can comprises a garbage can bottom plate, a movable device is arranged on the lower portion of the garbage can bottom plate, and a self-burning barrel device is arranged on the upper portion of the garbage can bottom plate. The self-burning barrel device iscomposed of a self-burning barrel fixedly installed on the upper portion of the garbage can bottom plate, a garbage inlet formed in the middle portion of the top of the self-burning barrel, a self-burning device installed at the lower one third position of the interior of the self-burning barrel, a compression device installed on the middle portion in the self-burning barrel, a first spacing device installed on the lower portion of the compression device, a second spacing device installed on the upper portion of the compression device, a garbage outlet formed in the side surface of the lowerportion of the self-burning barrel, and a garbage outlet door device installed on the garbage outlet jointly. The movable environmentally-friendly self-burning garbage can has the beneficial effects of simple structure and high practicability.
Owner:河南金土商贸有限公司
Fireproof rubber production process
The present invention provides a fireproof rubber production process, wherein a flame retardant rubber is used as a raw material during a raw material production process and mastication, mixing, calendering, extrusion, molding and vulcanization are performed to produce the fireproof rubber, and in the case of encountering flame, firing can be effectively delayed, the fireproof rubber can not melt and be burned out for a long time in the flame or near the flame, and if the fireproof rubber contacts the flame for a long time so as to cause the firing, the self-burning flame can be rapidly extinguished after the fireproof rubber leaves the external flame so as to substantially enrich the selectivity of industrial manufacturing.
Owner:ANHUI MEIXIANG IND
Preparation method of expanding flame-retardant plastic
The invention relates to a preparation method of expanding flame-retardant plastic. The expanding flame-retardant plastic comprises the following components: polypropylene, ricinoleic acid, carbon black, expanded graphite and red phosphorus, wherein the mass ratios of the components of the expanding flame-retardant plastic are as the follows in parts by mass: 40%-50% of the polypropylene, 10%-15%of the ricinoleic acid, 10%-15% of the carbon black, 20-30% of the expanded graphite and 10%-15% of the red phosphorus. According to the invention, self-burning is avoided, and combustion is further prevented, namely, the other substance oxygen of the combustion condition is considered. The expanding flame-retardant plastic disclosed by the invention is expanded quickly when encounters fire, flamepoints are wrapped in the expanded flame-retardant plastic, and surrounding air is isolated out, so that existence of the surrounding air is avoided, and occurrence of a fire disaster is prevented from physical significance.
Owner:陆伯川
A self-promoting burning type electronic paste and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106782750BImprove performance and stabilityFlexible adjustment of square resistanceNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureCombustionDecomposition
The invention discloses self-promoted combustion type electronic paste and a preparation method thereof. The self-promoted combustion type electronic paste comprises a solid phase and an organic binding phase, wherein the solid phase comprises metal powder, a metal oxide, glass powder and a thermal decomposition oxidization agent, and the organic binding phase comprises resin, a solvent and an additive. The preparation method comprises the steps of (a) preparing the glass powder; (b) preparing the organic binding phase; and (c) preparing the paste. By material combination and a corresponding preparation method, the prepared paste has the following advantages that: 1, the thermal decomposition oxidization agent is added into the paste, the resin in the paste can be oxidized by the oxidization agent during the paste sintering process, the carbon content in a sintered film is reduced, and the performance stability of the paste after formation is improved; 2, K2O generated after decomposition of the thermal decomposition oxidization agent in the paste melts into the glass powder, and the glass property such as thermal expansion and dielectricity can be adjusted so that the demands of different substrates are satisfied; and 3, MnO2 is generated after the decomposition of the thermal decomposition oxidization agent in the paste, and the square resistance of the paste can be flexibly adjusted according to special demands.
Owner:DONGGUAN COREHELM ELECTRONICS MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
A low-smoke, halogen-free, flame-retardant and aging-resistant cable material for cables
ActiveCN103571116BLow smoke densityImprove aging resistancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsChemical reactionVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant anti-aging cable material for cables. The cable material is characterized in that the cable material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-50 parts of EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer), 50-80 parts of EVM (ethylene vinyl acetate rubber), 2.5-5 parts of a vulcanizing agent, 1.5-6 parts of a vulcanizing additive, 2-8 parts of an anti-aging agent, 10-30 parts of a plasticizer, 0.5-1.5 parts of a coupling agent, 15-30 parts of a reinforcing agent, 20-40 parts of a filling agent, and 50-70 parts of a flame retardant. According to the invention, because raw materials which do not produce dense smoke in the process of self burning, and do not produce dense smoke during chemical reactions thereof, and can absorb smoke are selected, the smoke density of cables in the process of burning is effectively reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN MINGXING CABLE
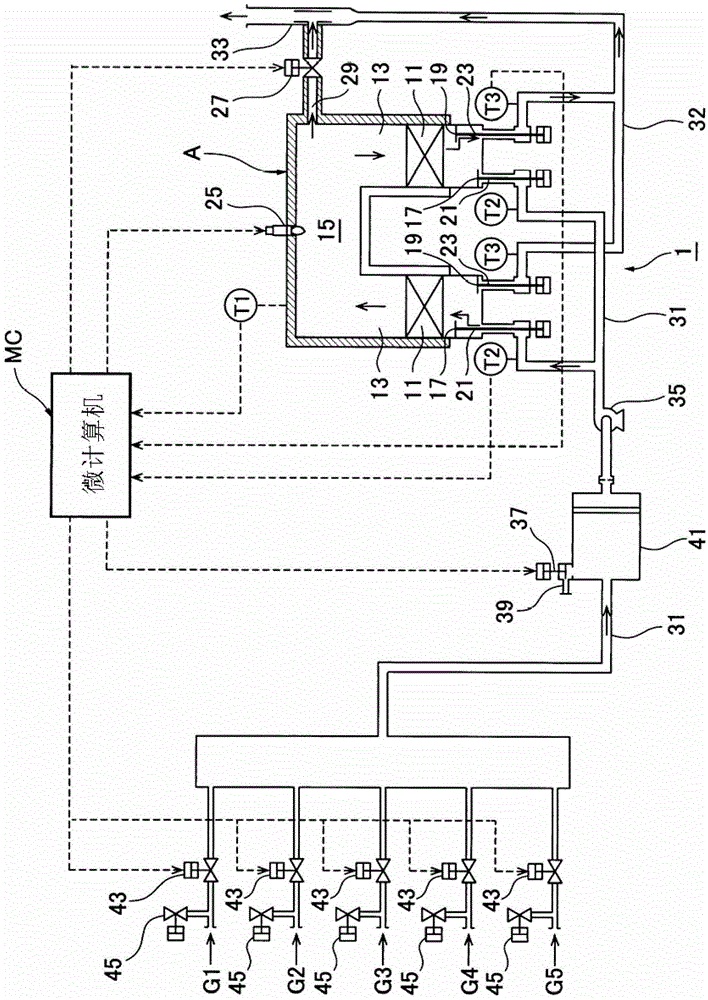
Exhaust gas purification device and temperature control method thereof
ActiveCN102782409BIncrease exhaust temperatureReduce the temperatureEnergy industryIncinerator apparatusMicrocomputerTemperature control
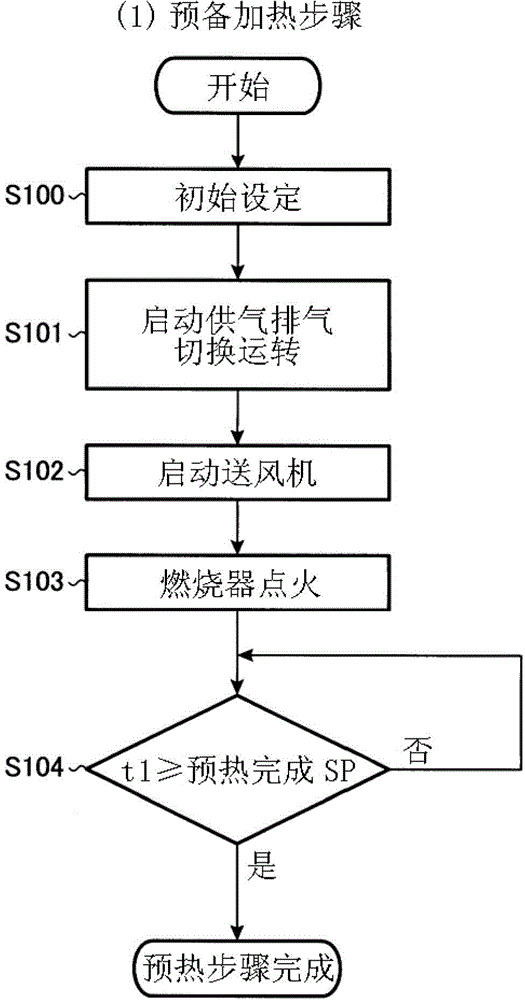
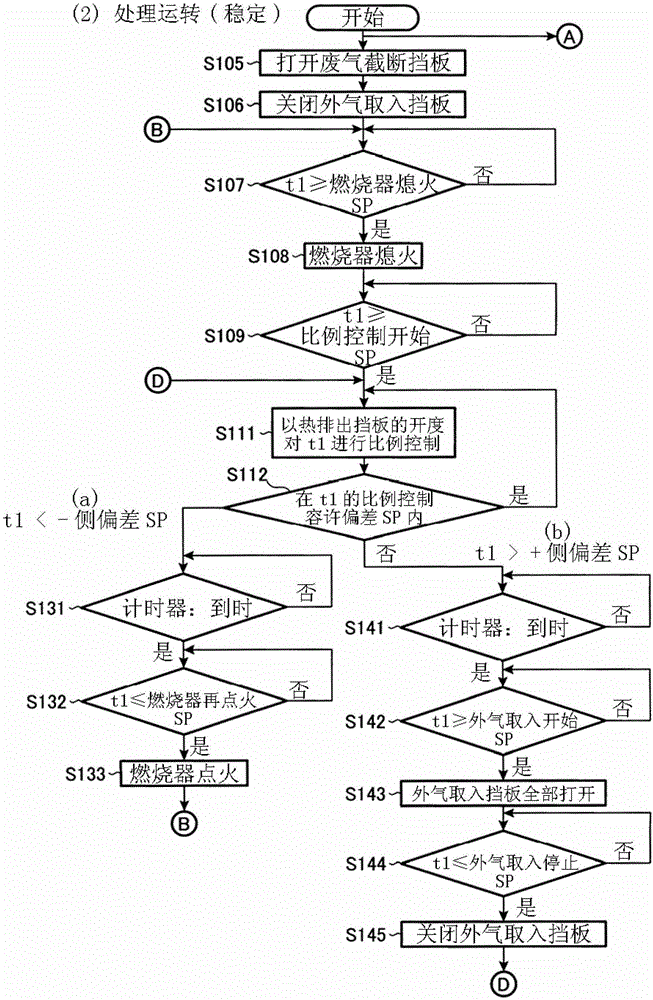
The present invention is an exhaust gas purification device (1, 501) for purifying exhaust gas containing a combustible toxic component. This exhaust gas purification device comprises a plurality of heat storage chambers (13) which are each provided with a heat storage element (11) therein and provided with a pair of an air supply port and an air evacuation port (21, 23), a combustion chamber (15) which is formed to communicate with the upper parts of the plurality of heat storage chambers, air evacuation and air supply valves (17, 19) which are mounted to the air supply port and the air evacuation port of each of the heat storage chambers in order to perform switching between the supply of air to and the evacuation of air from the heat storage chamber, a heating burner (25) which is provided in the combustion chamber, a heat discharge damper (27) which discharges surplus heat from the combustion chamber, and a microcomputer (MC) which ignites / extinguishes the heating burner on the basis of a combustion chamber temperature (t1) and controls the temperature such that the combustion chamber temperature becomes a set value (SP) by adjusting the degree of opening of the heat discharge damper. This microcomputer determines whether early combustion, in which the temperature of exhaust gas rises to a self-burning temperature or higher when the exhaust gas passes the heat storage element, and the exhaust gas burns before arriving at the combustion chamber, is performed or not, when determining that the early combustion is performed, executes an early combustion countermeasure operation for forcibly opening the heat discharge damper and extinguishing the heating burner, and thereafter when determining that the early combustion is not performed, cancels the early combustion countermeasure operation.
Owner:SINTOKOGIO LTD
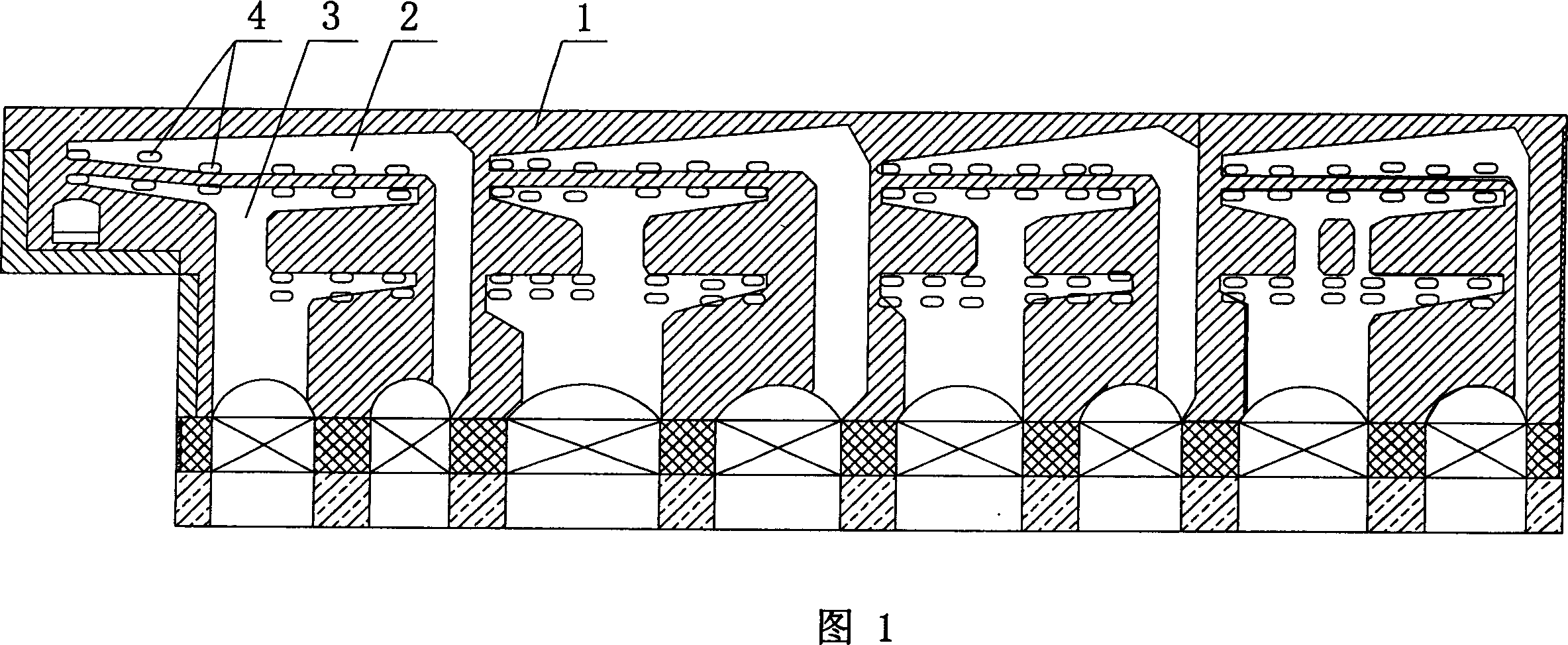
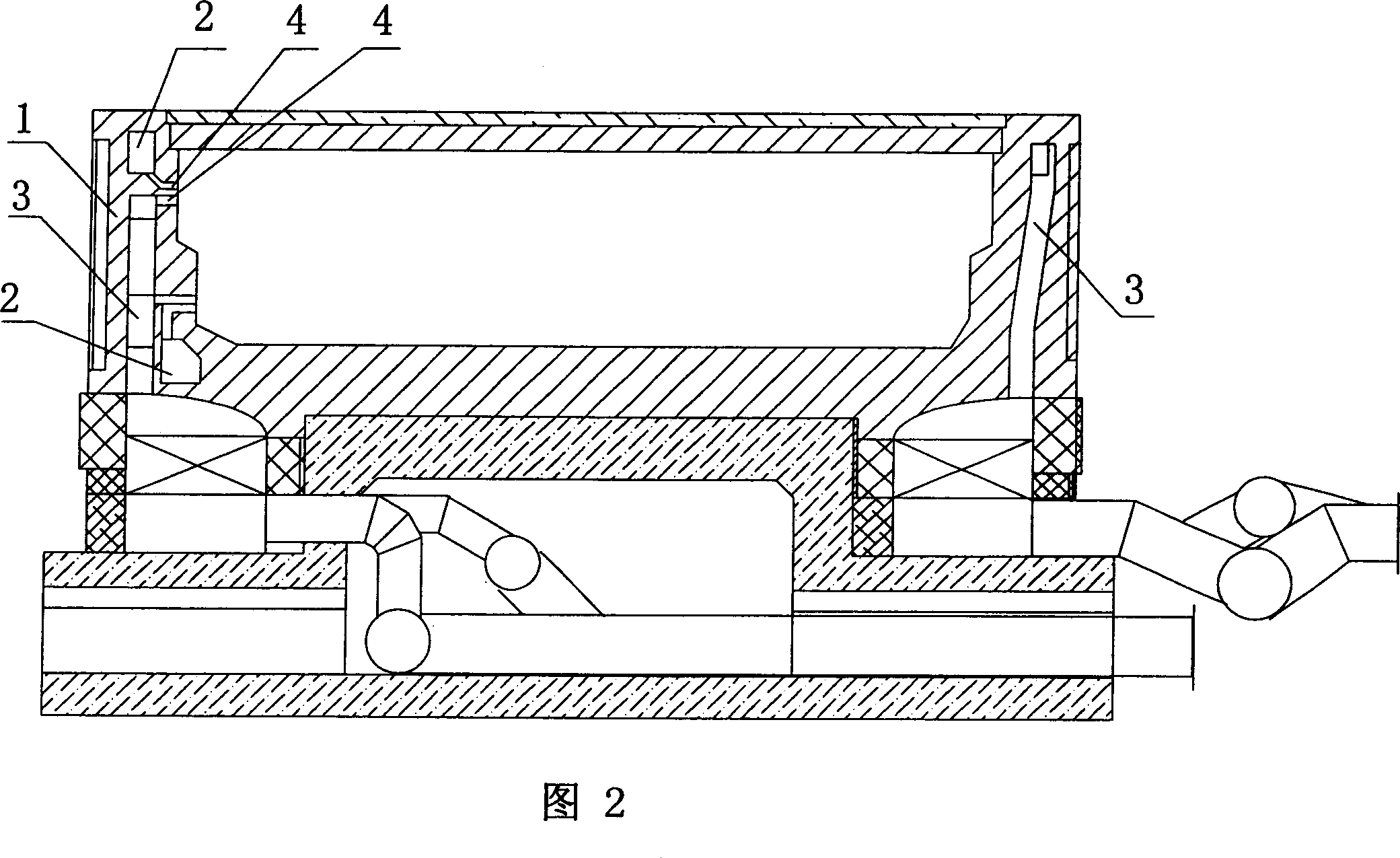
Self-ignition machined rod carbonization and carbonized kiln
InactiveCN101029236BQuality improvementUniform qualityBiofuelsSpecial form destructive distillationCarbonizationEngineering
A self-burning machine-made rod carbonization is carried out by preparing raw material, mixed proportioning, drying, forming, loading, entering it into kiln, carbonizing, cooling, inspecting and packing. Kiln opening(3) and matched kiln gate(8) are arranged in front of special carbonizing kiln body, rail(2) is placed at kiln bottom, positioning ridge(7) is set in internal end of rail, smoke-discharging hole(5) in placed at internal wall of kiln wall(1), which is connected with chimney(6), kiln top is arched ceiling(4) and kiln wall(1) is sandwiched wall with thermal-insulating layer between double layers. It is efficient and cheap, has better quality and homogeneity. It can be used to fire machine-made carbon with refuse as raw material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
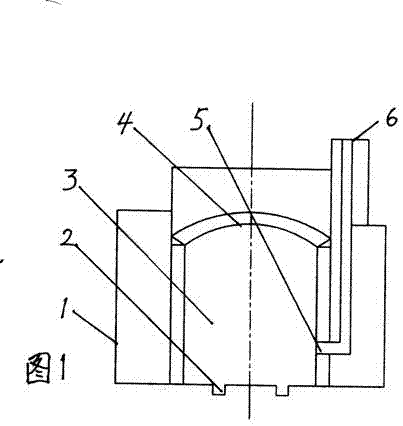
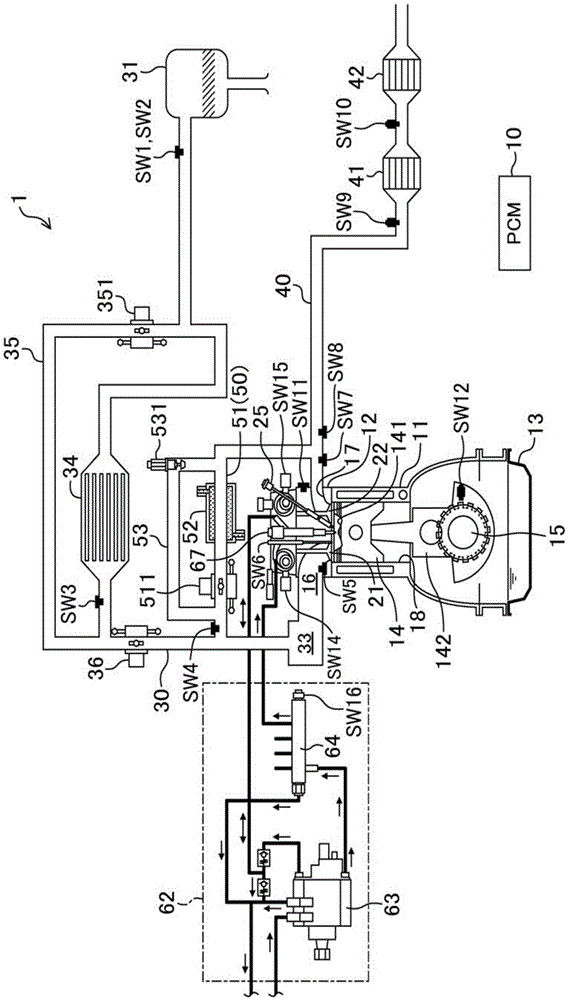
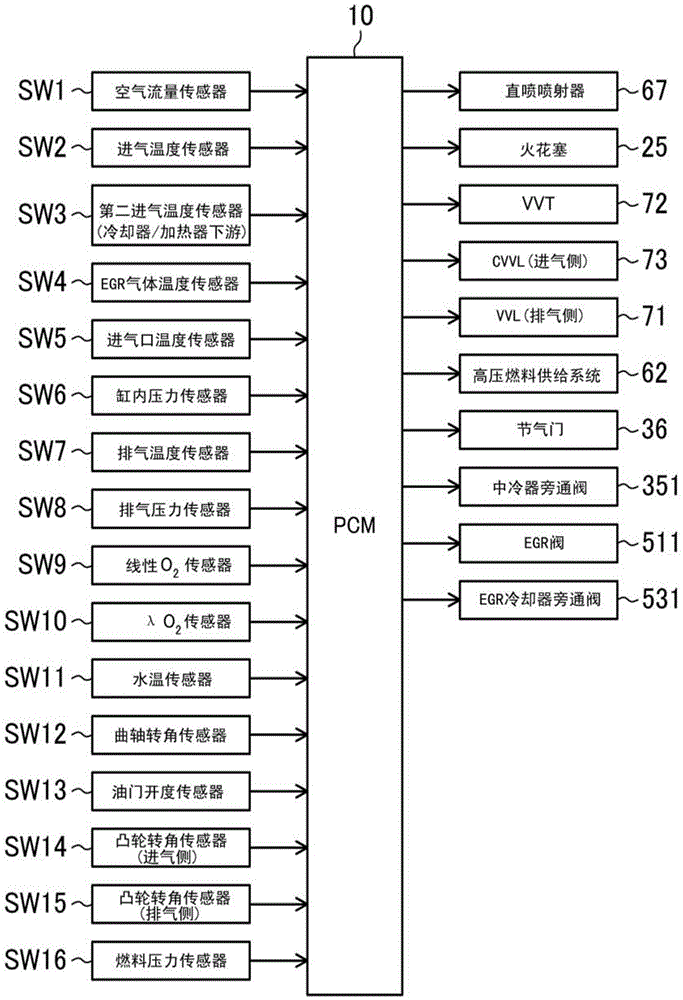
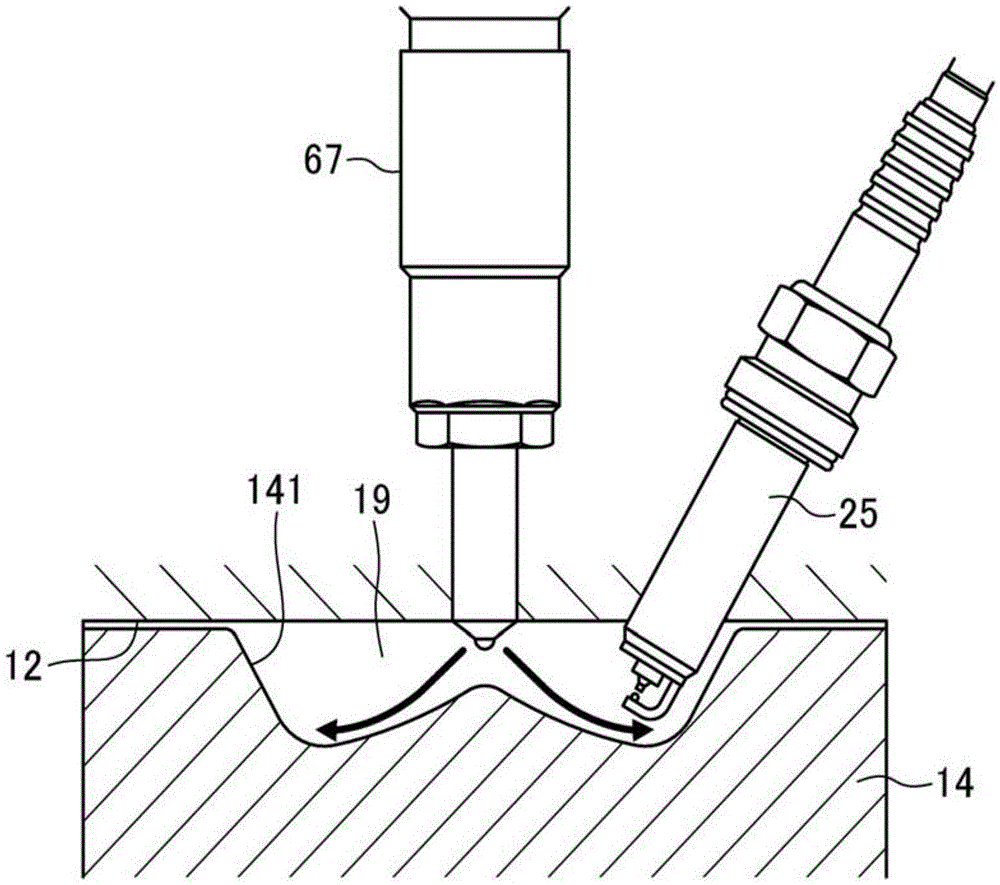
spark ignition direct injection engine
ActiveCN103670872BAvoid increased combustion noiseAvoid premature fireElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion noiseSelf burning
A spark ignition direct injection engine avoids increased combustion noise when switching from spark ignition combustion to compression ignition combustion. Immediately after the controller (PCM (10)) switches from the spark ignition mode to the compression ignition mode, the fuel pressure is set to a high fuel pressure of 30 MPa or more through the fuel pressure setting mechanism, and the fuel injection valve (injector (68) ) so that fuel injection is performed at least during the period from the late stage of the compression stroke to the early stage of the expansion stroke, thereby causing the engine main body (engine (1)) .
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Conductive honey comb ceramic catalyst carrier and its preparation method
InactiveCN1268430CProperly conductiveAppropriate heat conductionCatalyst carriersAl powderSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesis
An electrically conductive cellular ceramic as the carrier of catalyst used for car is prepared from purified titanium oxide or Ti powder, graphite powder and pure Al powder through proportionally mixing, adding organic adhesive, stirring, die pressing, heat treating, igniting and self burning for high temp synthesis.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
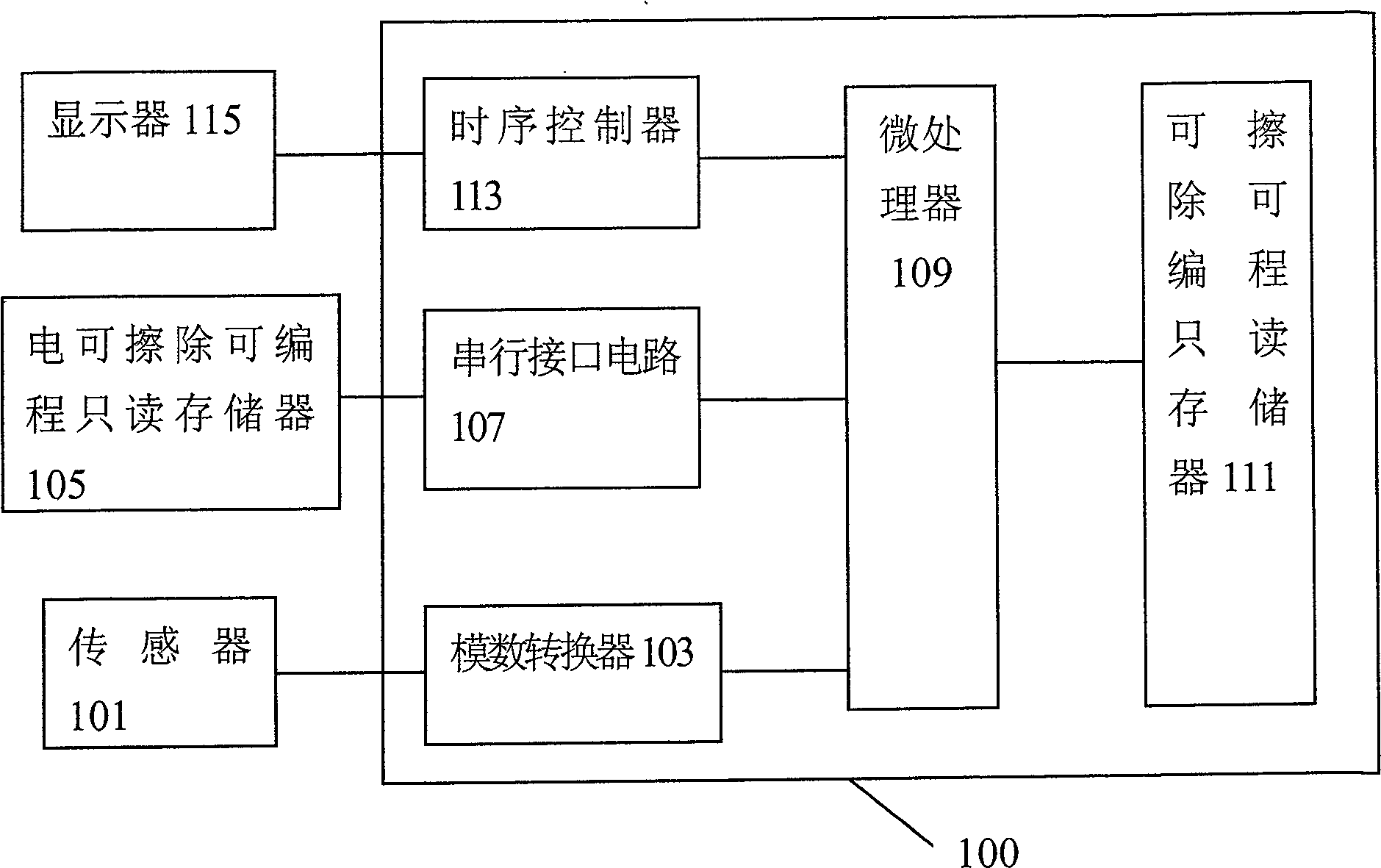
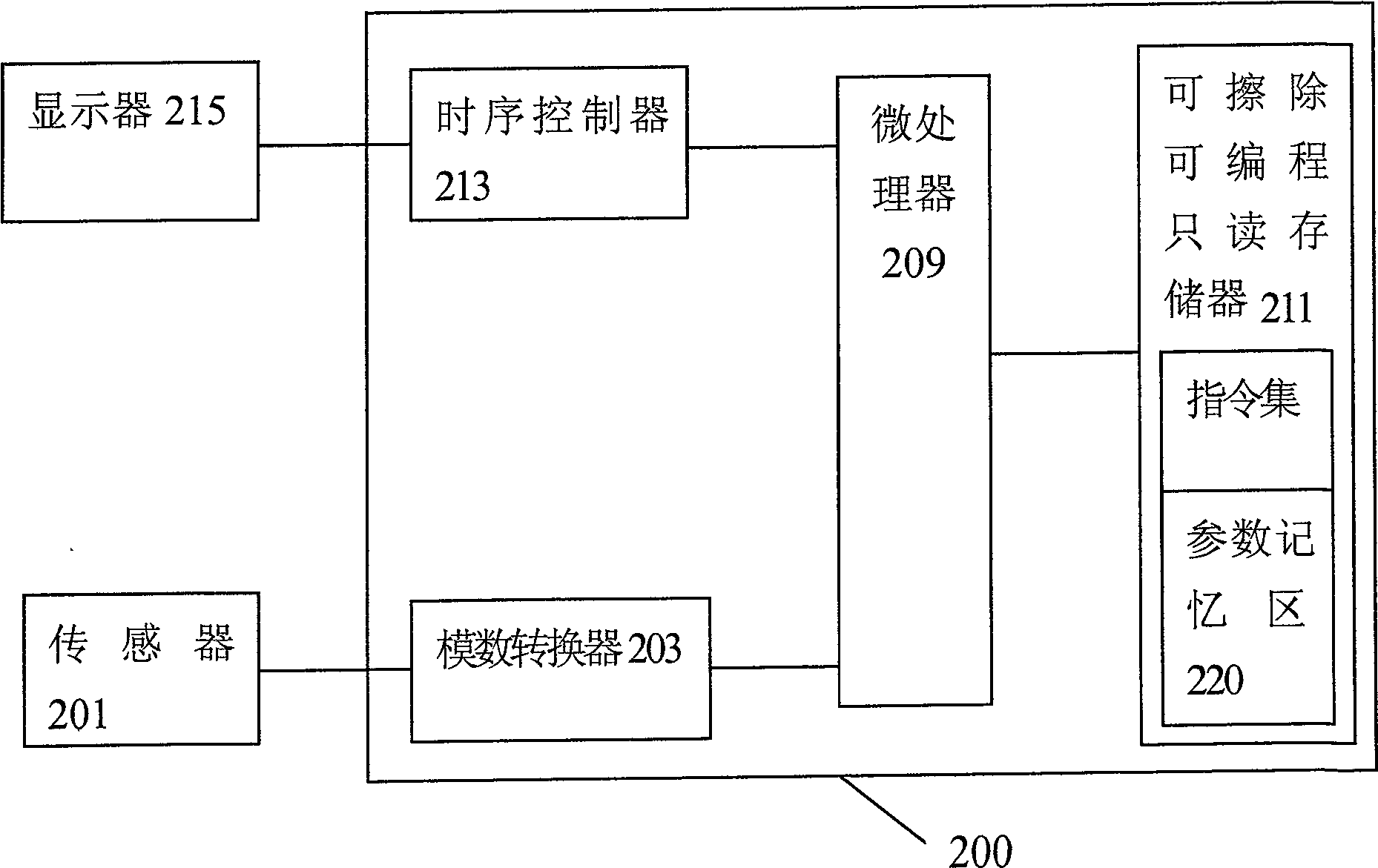
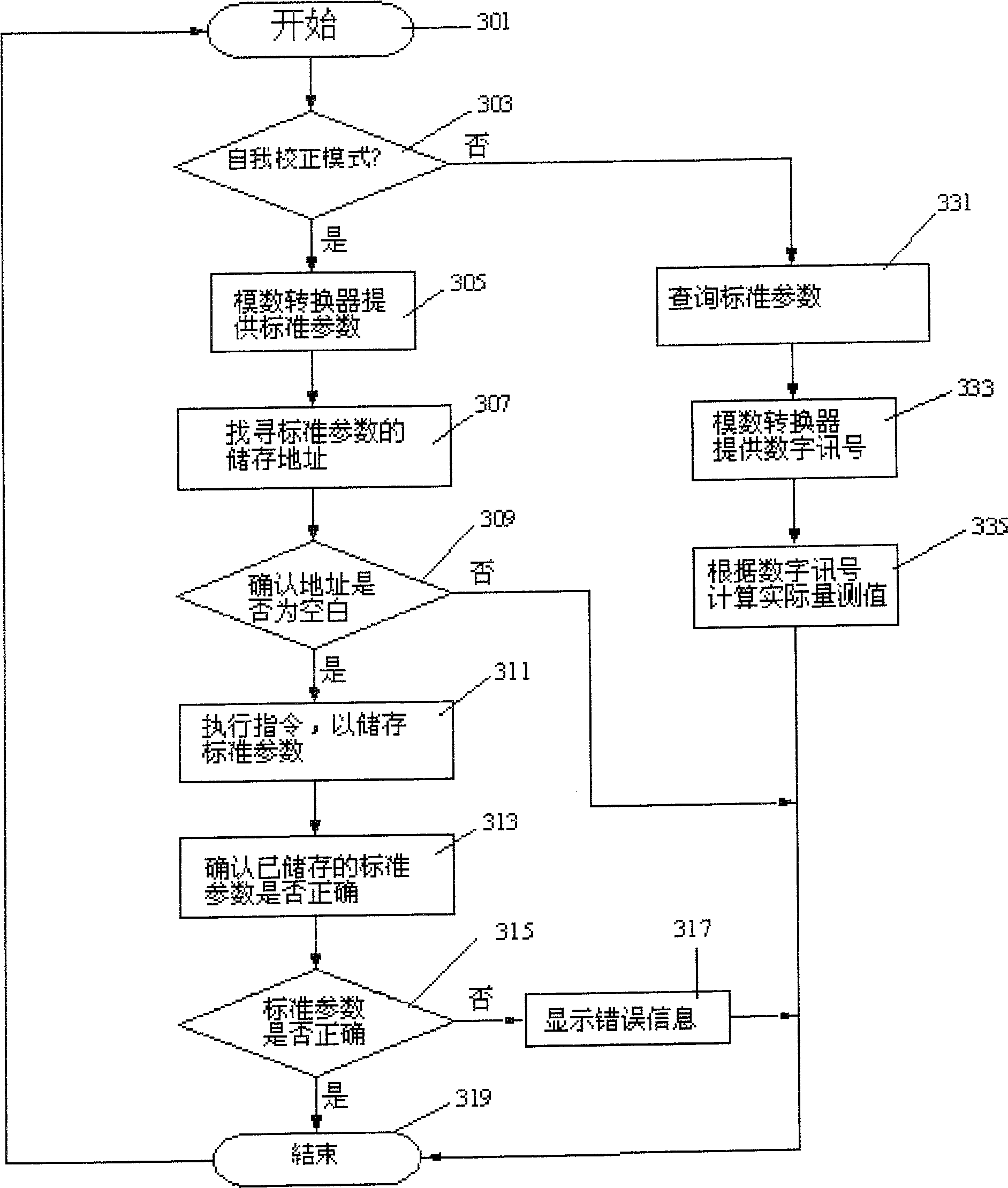
Integrated circuit with self-correcting function, measuring apparatus therefor and parameter self-recording method
InactiveCN100533067CLow costLess componentsConverting sensor outputSpecial purpose recording/indication apparatusMeasurement deviceExternal storage
The invention discloses an integrated circuit, a measuring device using the integrated circuit, and a parameter self-programming method of the integrated circuit. The integrated circuit includes a microprocessor and a one-time programmable memory. At least one instruction set storage area and a parameter storage area, the parameter storage area is used to store standard parameters for calibration; the microprocessor calculates the actual value corresponding to the digital signal according to the standard parameters in the one-time programmable memory. measured value. The integrated circuit of the present invention does not need additional external storage components, saves components of the final system product, and reduces the cost of the final electronic measuring device. Since the integrated circuit provided by the present invention has the function of self-programming calibration parameters, it can directly perform self-calibration after the final system product is manufactured, thereby simplifying the calibration procedure and reducing production costs for application manufacturers or integrated circuit manufacturers.
Owner:FUXIANG MICROELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
Construction method for burner, air channels, gas flues inside furnace wall of heating furnace in heat storage type
InactiveCN100434796CGuaranteed cleanlinessSimple processCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelHeating furnaceSelf burning
A method for constructing nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel on wall of thermal storage heating furnace includes plotting out template drawing of nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel according to their sizes on said wall then preparing cavity template by PVC material as per said template drawing, transporting their cavity templates into their positions on two sides of said wall and fixing them there, pouring fireproof material then self burning said cavity templates prepared by PVC material for forming nozzle mouth and air channel as well as gas channel.
Owner:CHINA FIRST METALLURGICAL GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com