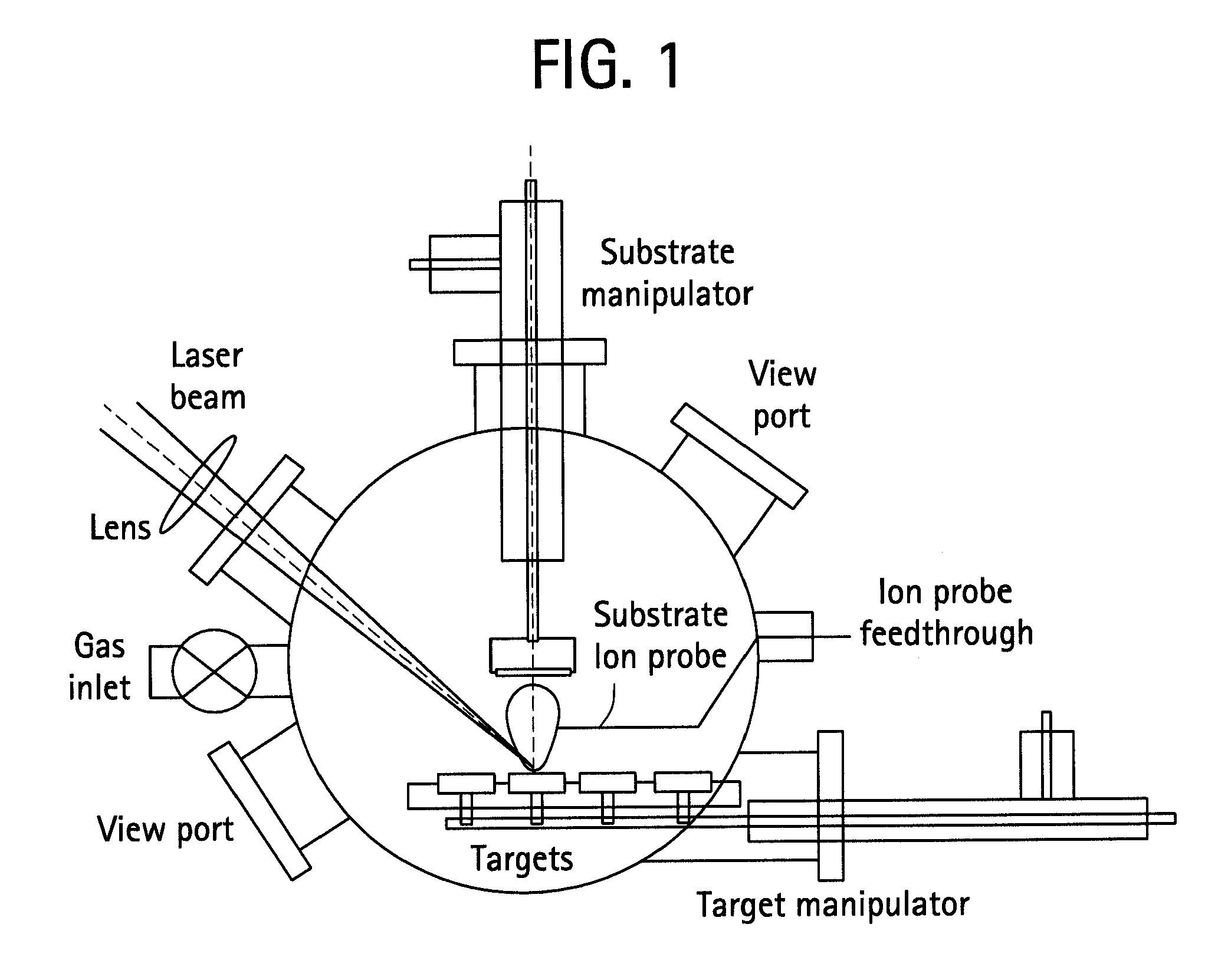
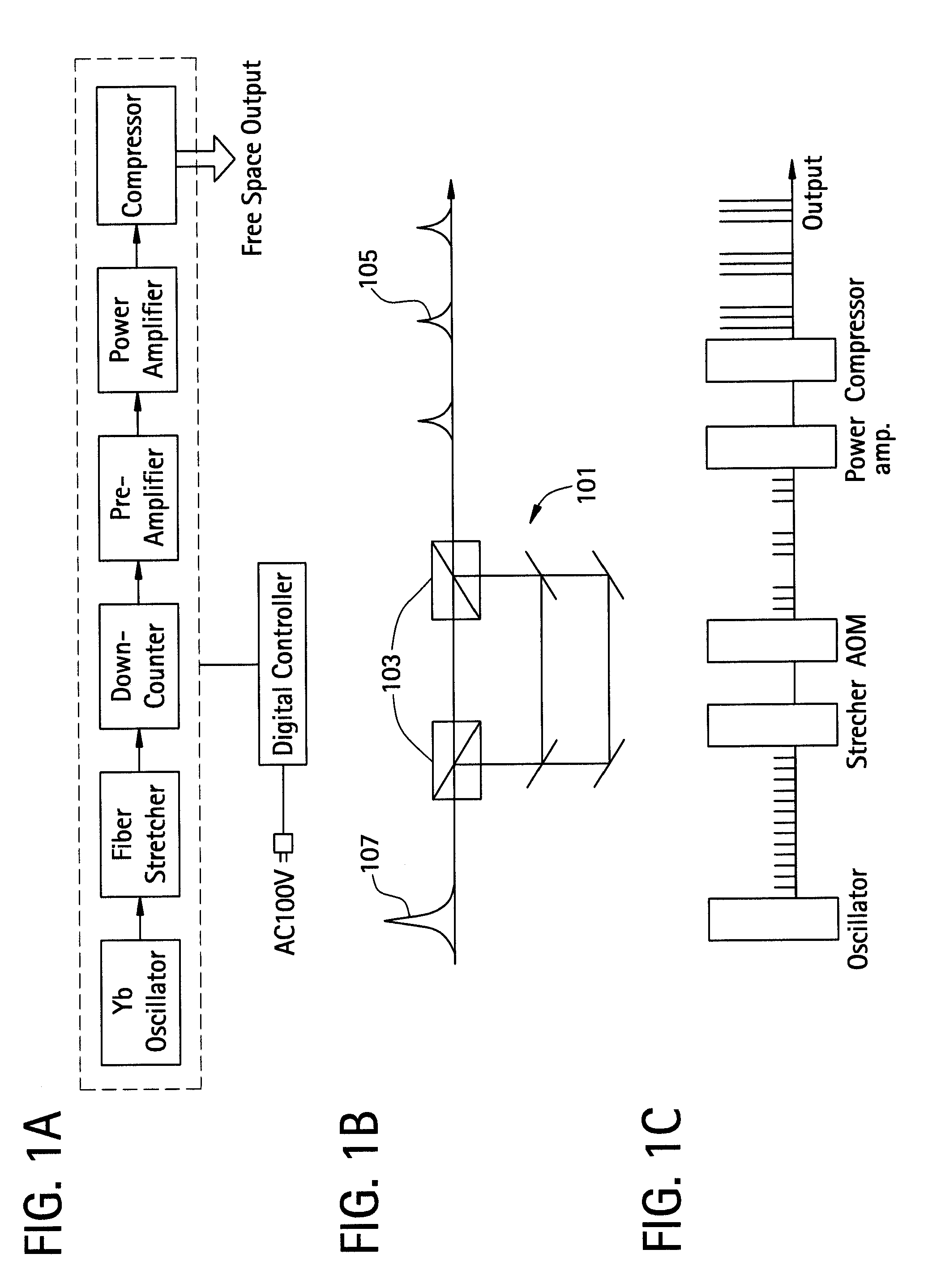
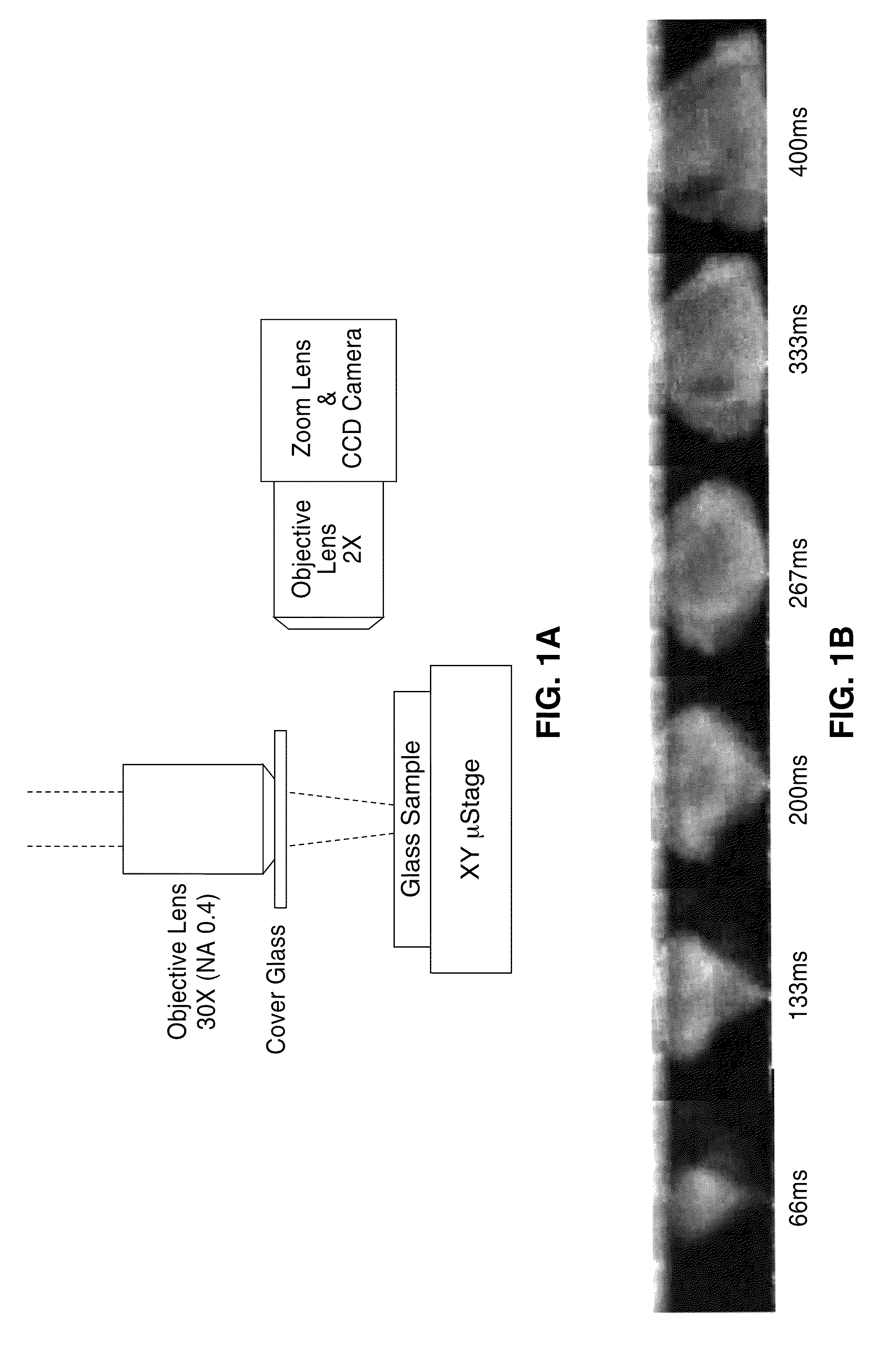
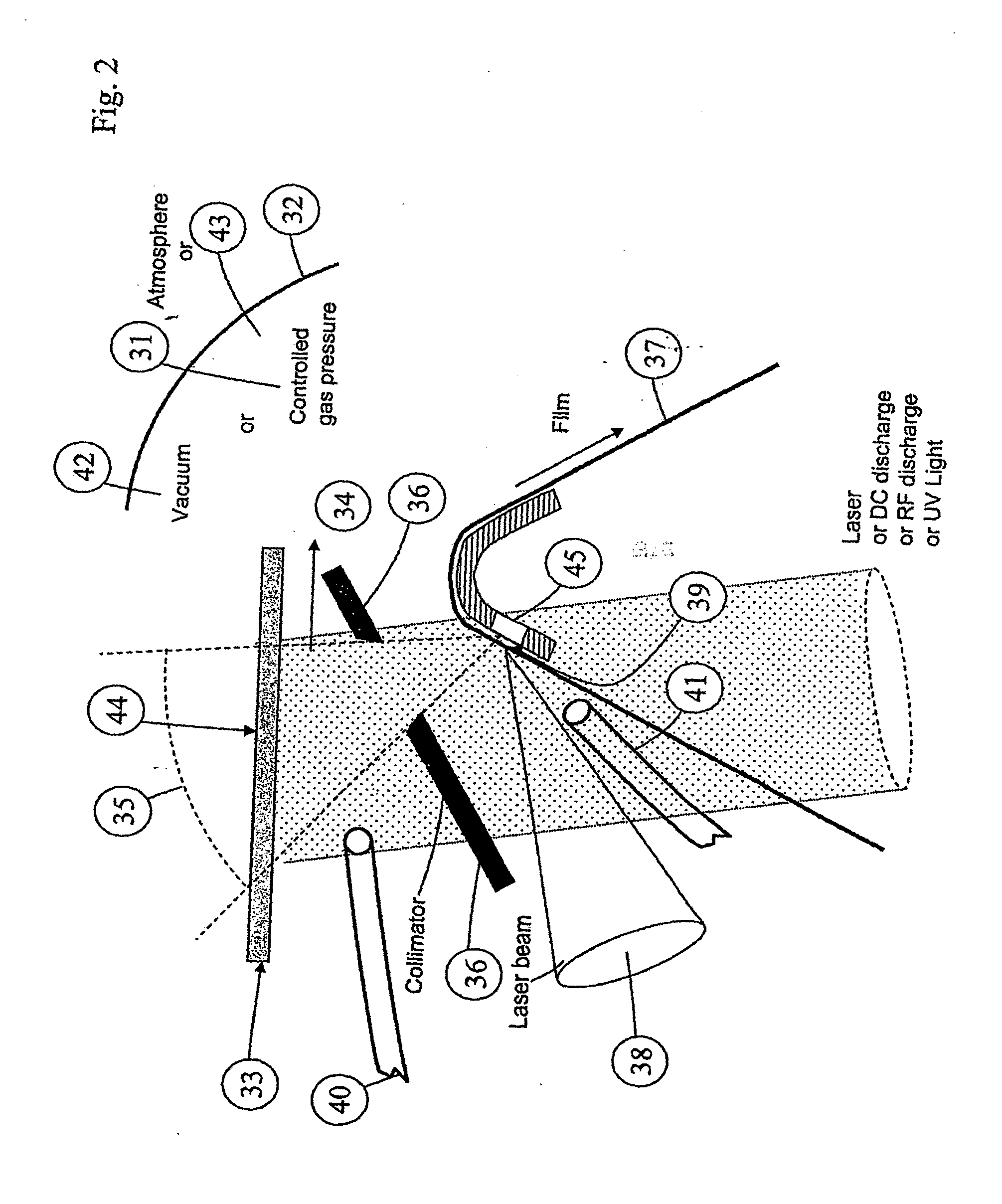
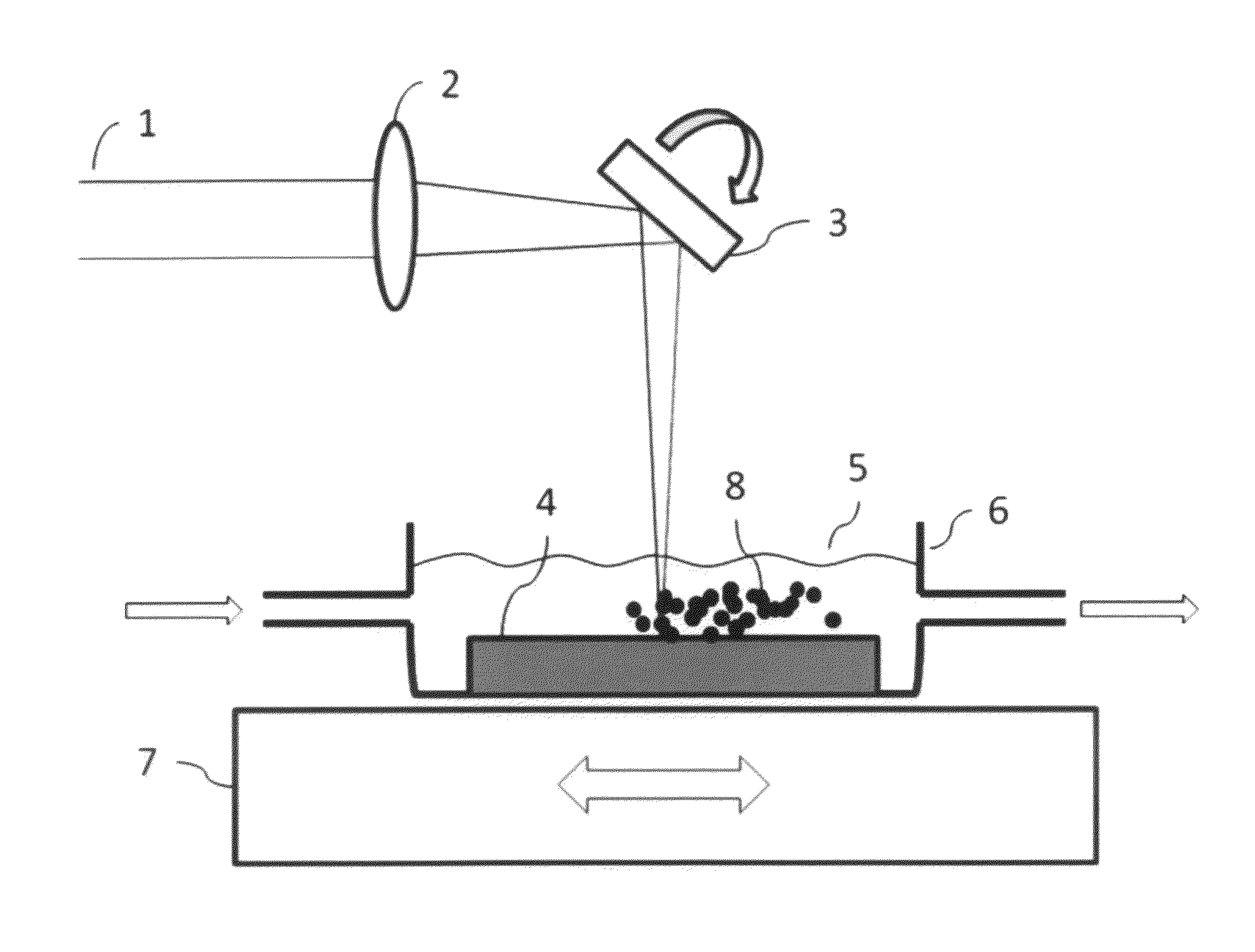
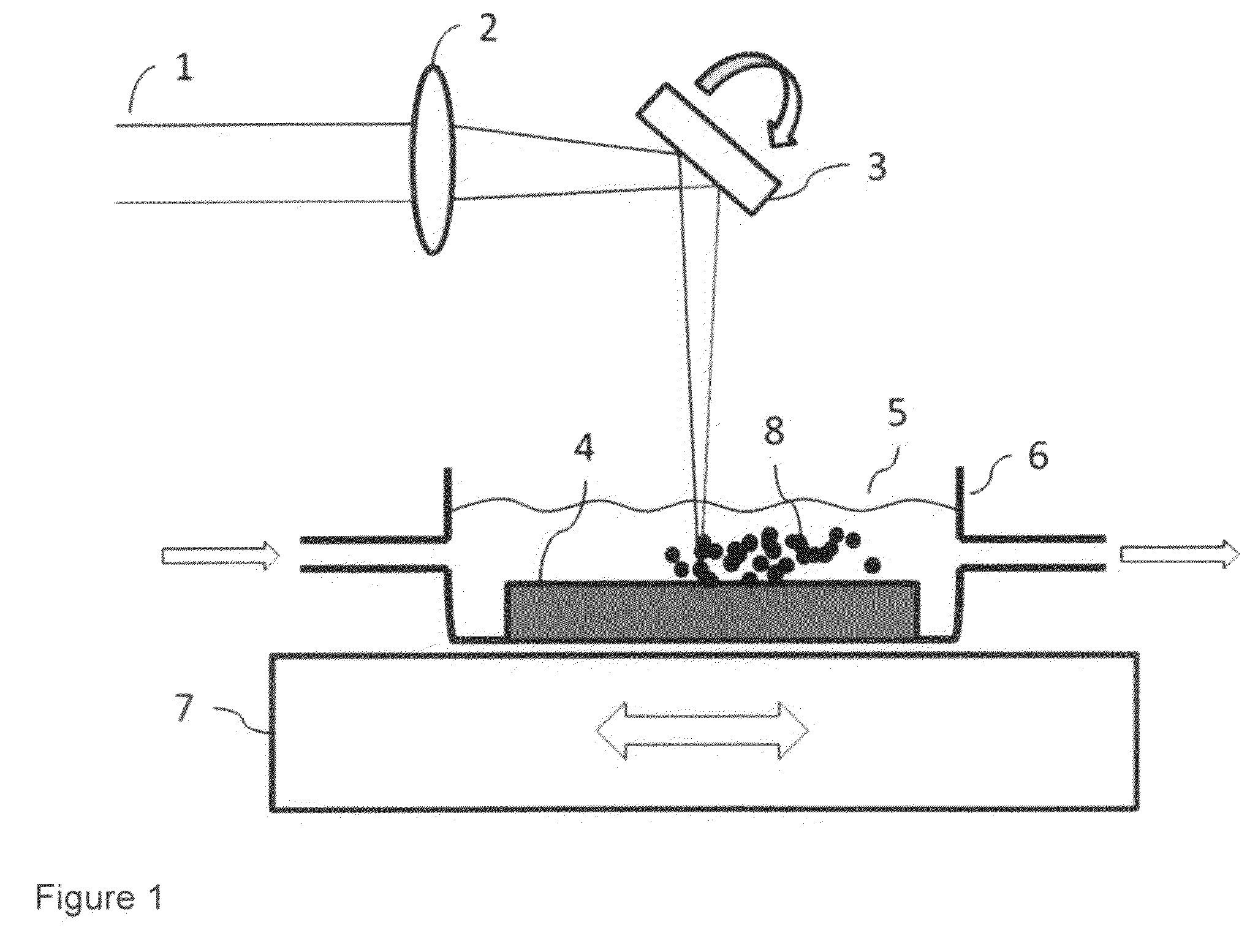
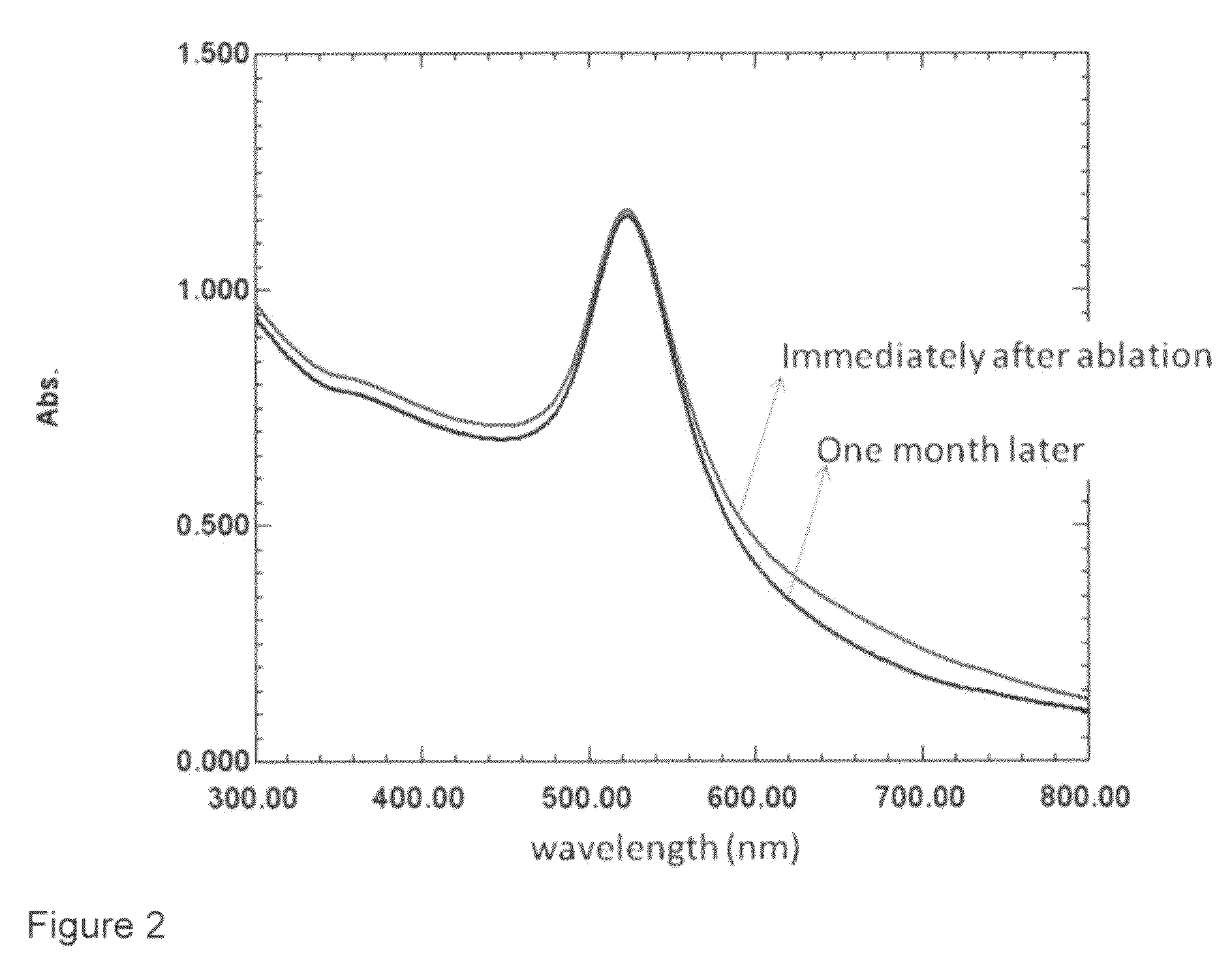
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121 results about "Pulsed laser ablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for preparing coated drug particles and pharmaceutical formulations thereof
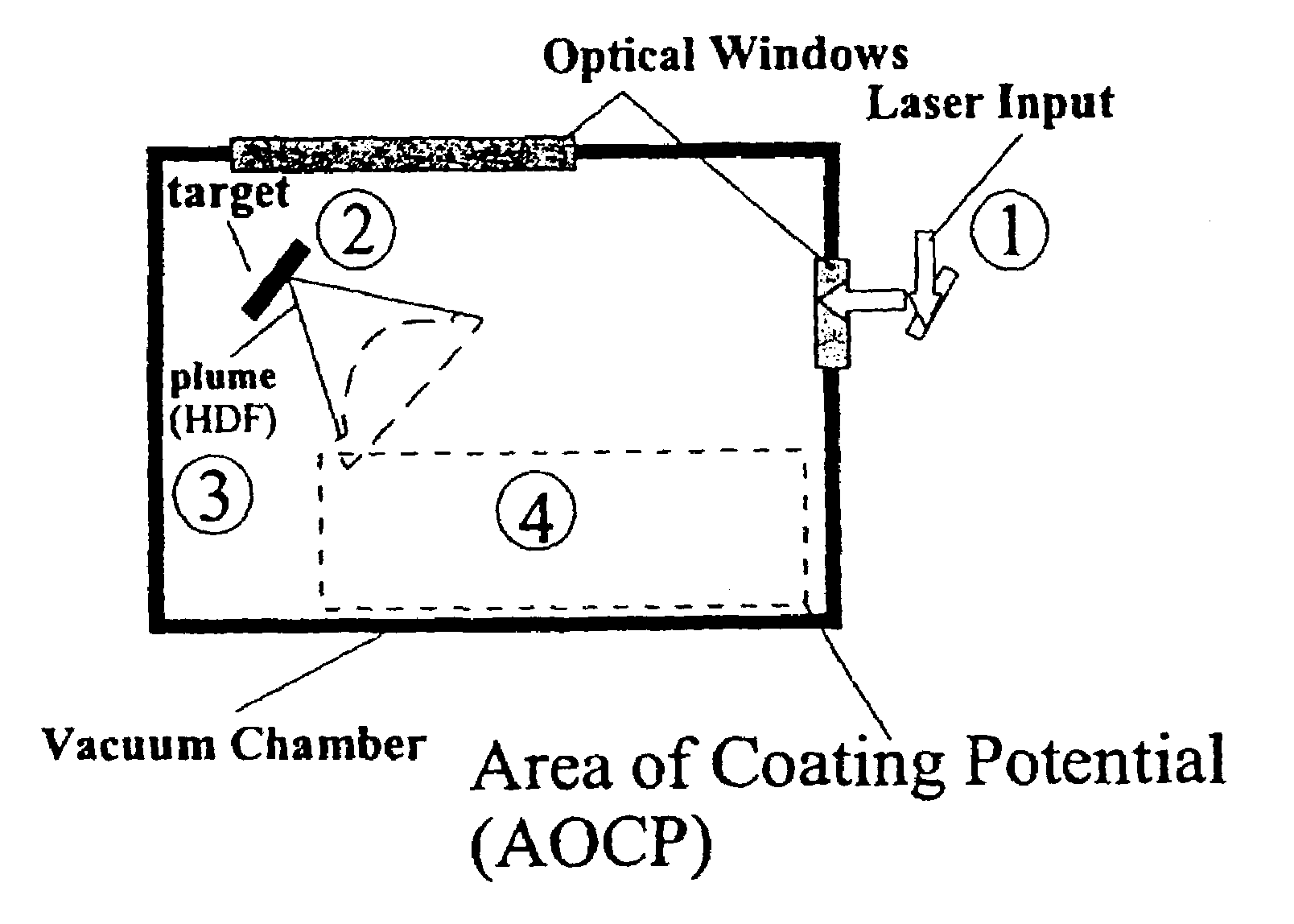
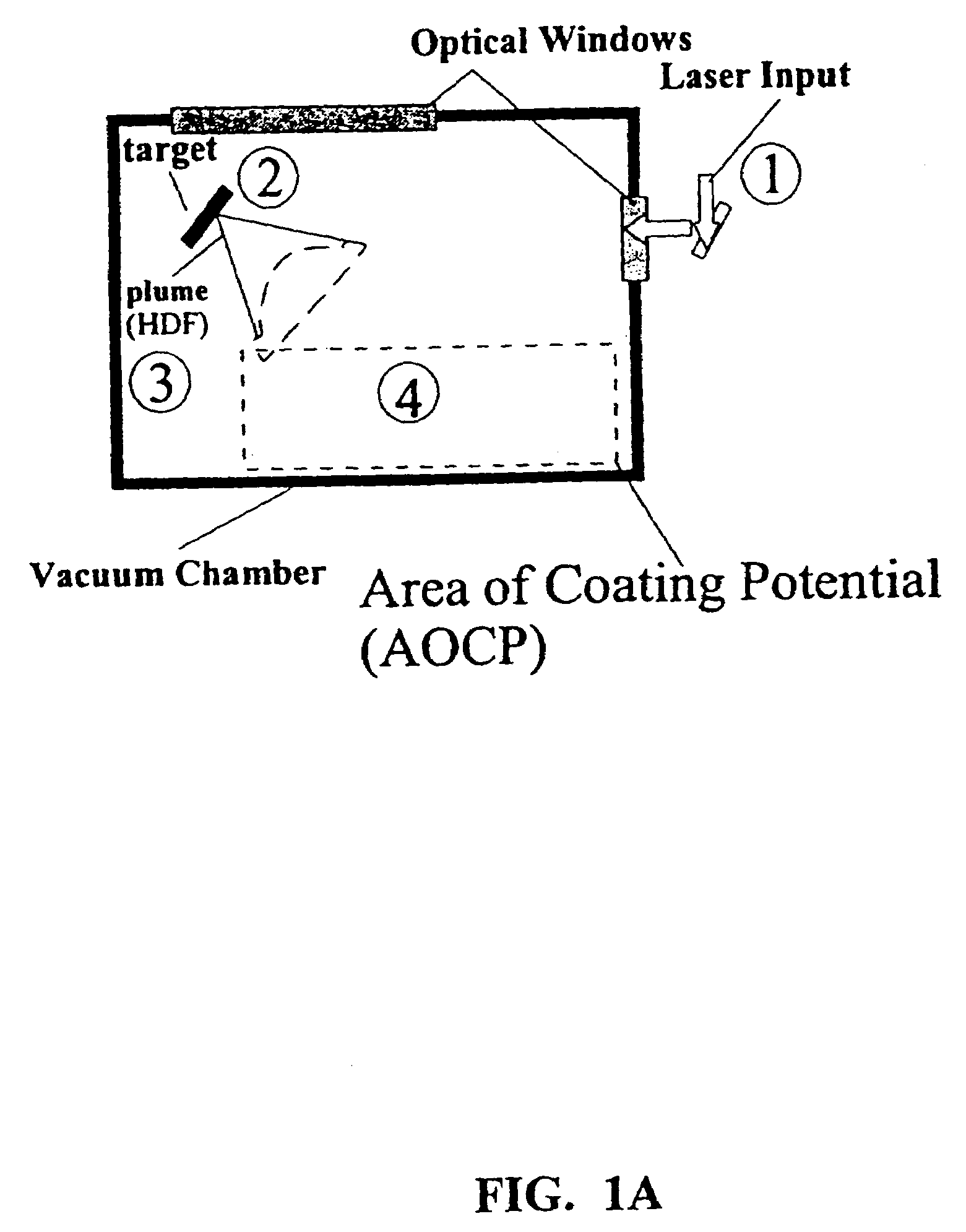
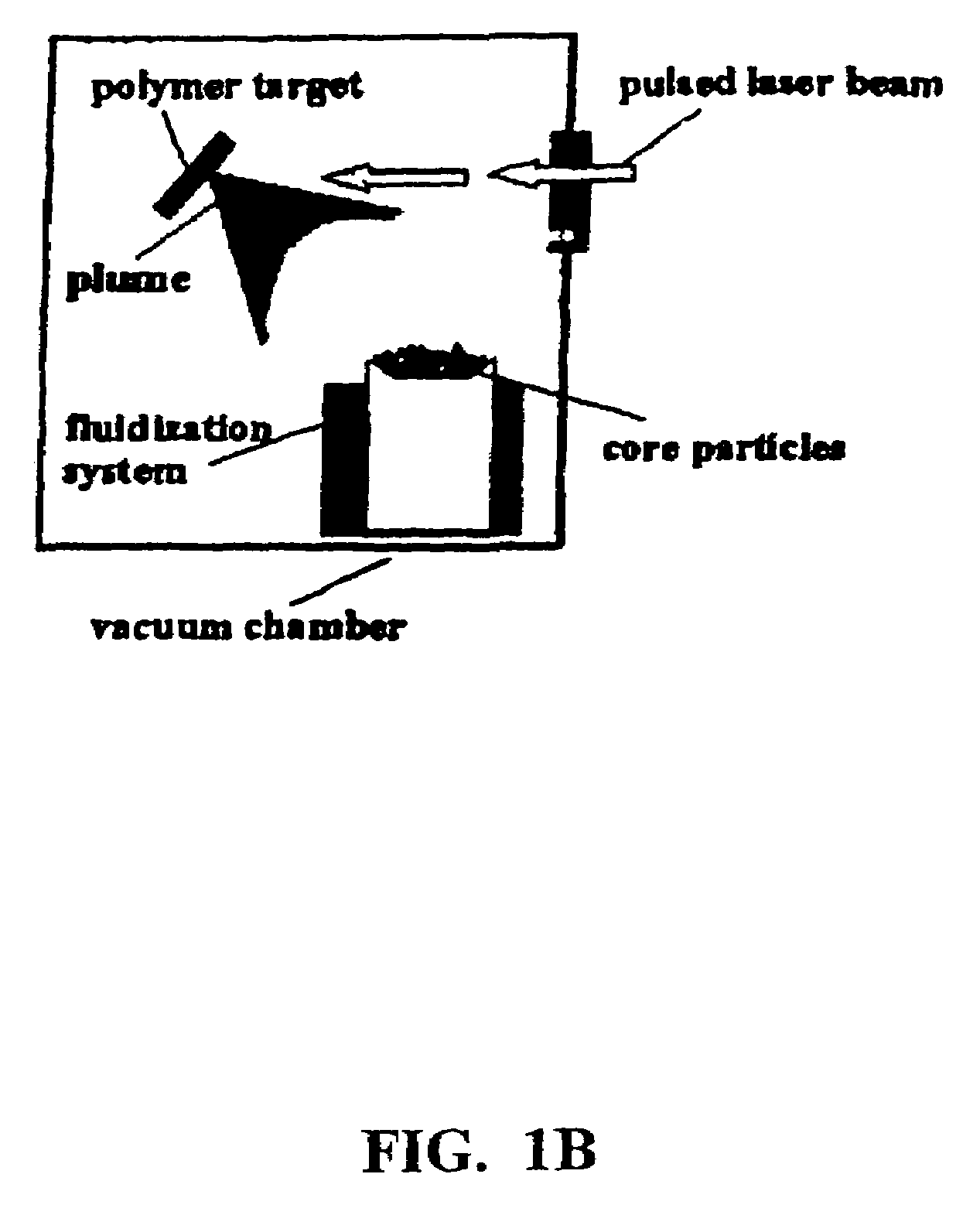
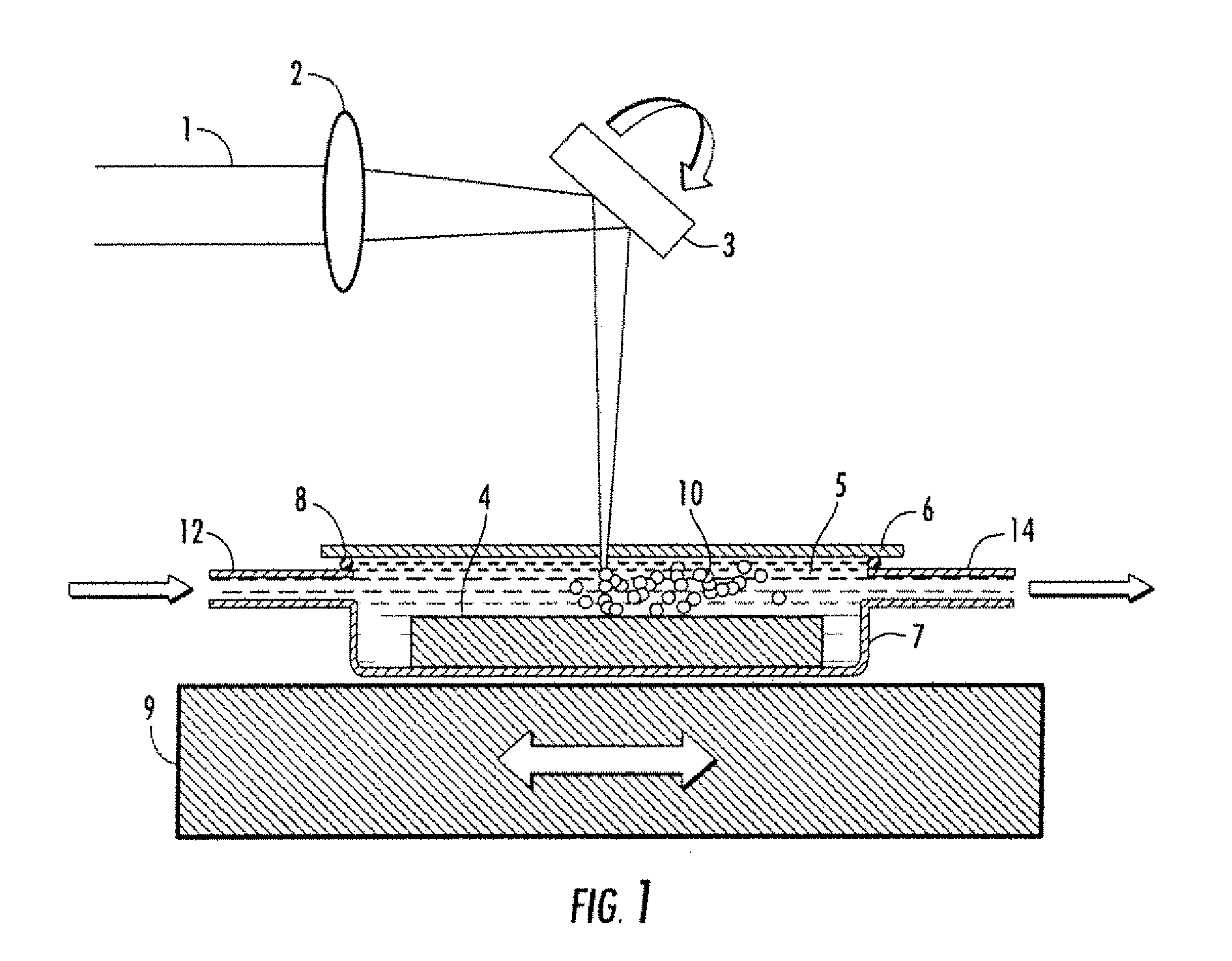
Disclosed are methods using pulsed laser ablation to prepare coated drug particles of uniform size and thickness. The coated drug particles ranged in size from several nanometers to several millimeters in diameter size, and were coated with organic polymer particle having average diameter sizes from about 1 to 50 nm. In illustrative embodiments, coated drug particles or drug delivery particles are disclosed comprising a biodegradable or biocompatible polymer coating having controlled thickness and controlled coating uniformity, that offer superior pharmaceutical properties for controlled delivery and increased bioavailability.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV PF +2
Production of metal and metal-alloy nanoparticles with high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser ablation in liquids
ActiveUS20100196192A1Prevent coagulationFaster throughputMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesUltrashort laserFocal volume
Various embodiments include a method of producing chemically pure and stably dispersed metal and metal-alloy nanoparticle colloids with ultrafast pulsed laser ablation. A method comprises irradiating a metal or metal alloy target submerged in a liquid with ultrashort laser pulses at a high repetition rate, cooling a portion of the liquid that includes an irradiated region, and collecting nanoparticles produced with the laser irradiation and liquid cooling. The method may be implemented with a high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser source, an optical system for focusing and moving the pulsed laser beams, a metal or metal alloy target submerged in a liquid, and a liquid circulating system to cool the laser focal volume and collect the nanoparticle products. By controlling various laser parameters, and with optional liquid flow movement, the method provides stable colloids of dispersed metal and metal-alloy nanoparticles. In various embodiments additional stabilizing chemical agents are not required.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for producing and depositing nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080006524A1Increase influenceIncrease rangeCellsTransportation and packagingPicosecondVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention provides a one-step process for producing and depositing size-selected nanoparticles onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of solid target materials. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and the background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method For Fabricating Thin Films
InactiveUS20090246530A1Small particle sizeEasily realizedLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingSheet filmAlloy
A method of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) capable of continuously tuning formed-film morphology from that of a nanoparticle aggregate to a smooth thin film free of particles and droplets. The materials that can be synthesized using various embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, metals, alloys, metal oxides, and semiconductors. In various embodiments a ‘burst’ mode of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation and deposition is provided. Tuning of the film morphology is achieved by controlling the burst-mode parameters such as the number of pulses and the time-spacing between the pulses within each burst, the burst repetition rate, and the laser fluence. The system includes an ultrashort pulsed laser, an optical system for delivering a focused onto the target surface with an appropriate energy density, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
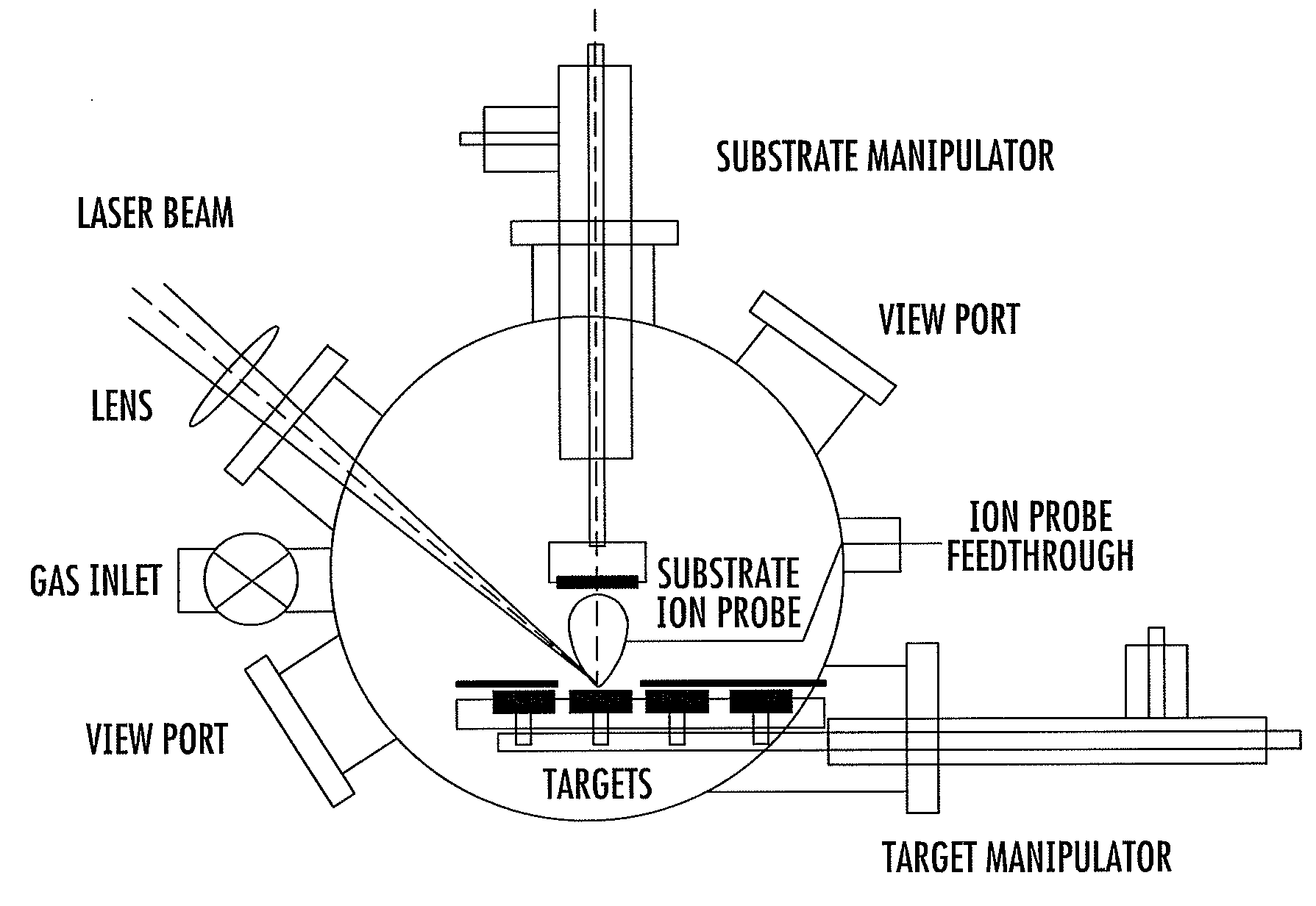
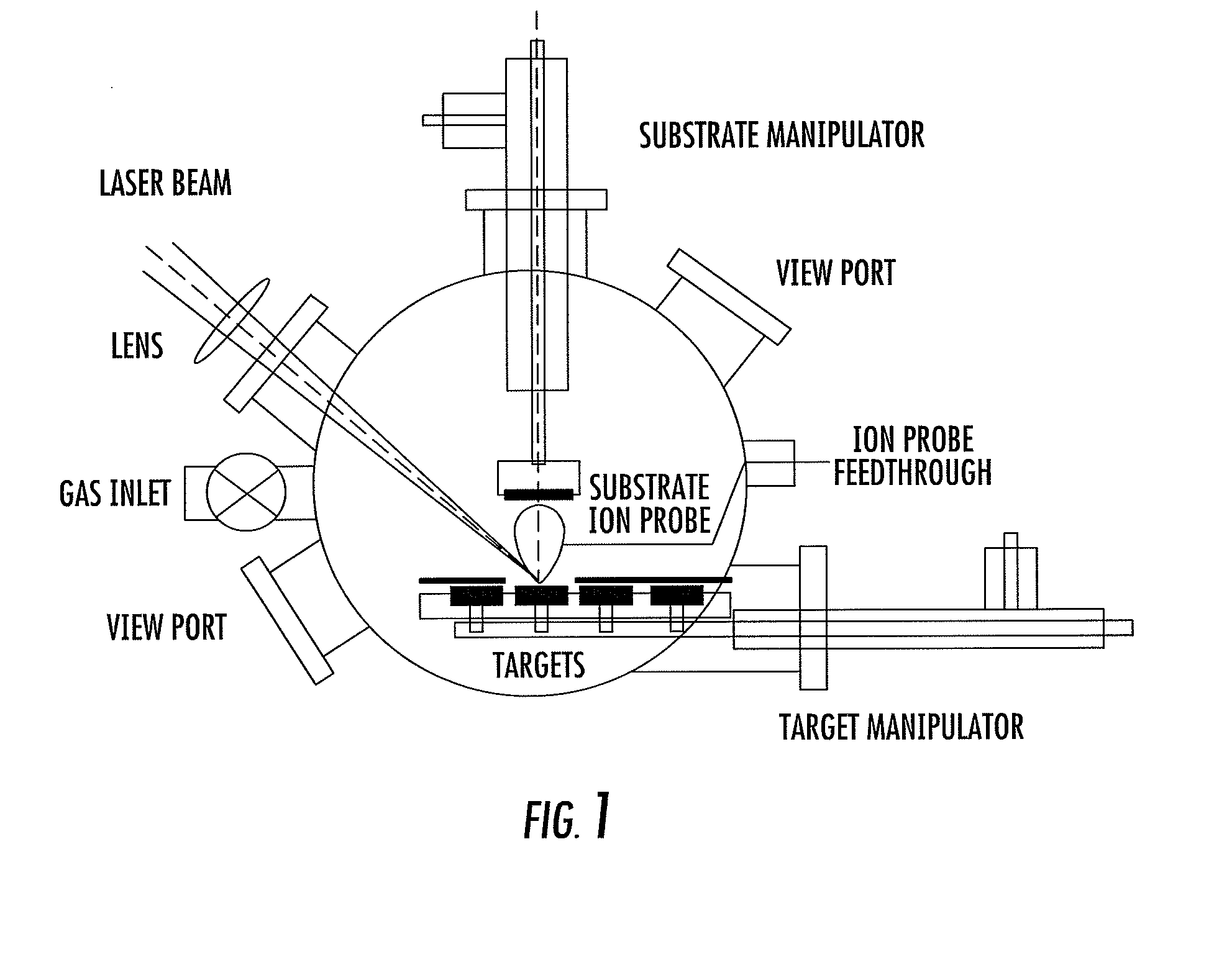
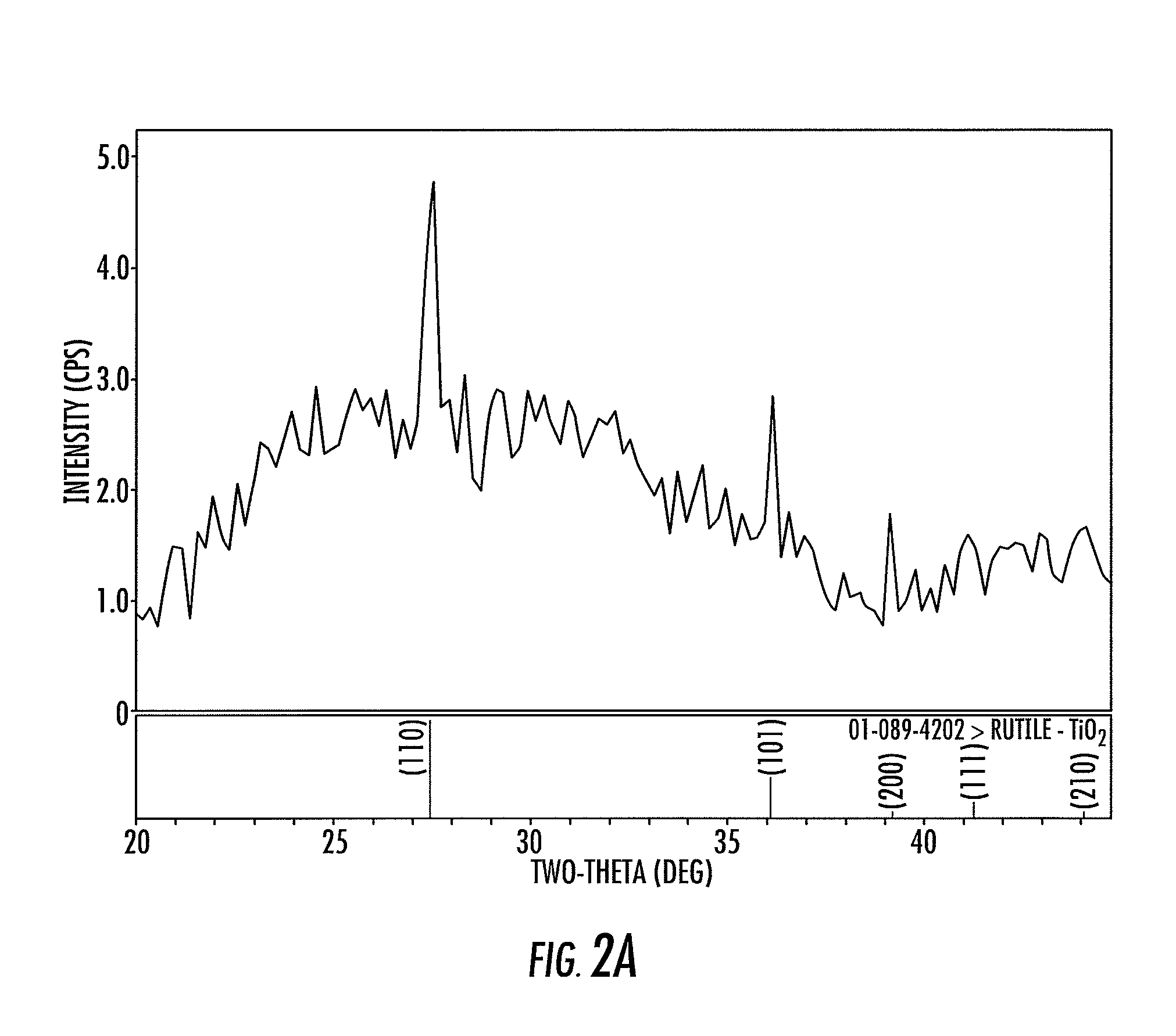
Method for depositing crystalline titania nanoparticles and films
InactiveUS20080187684A1Easily realizedImprove photocatalytic activityPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge heatingVolumetric Mass DensityPicosecond
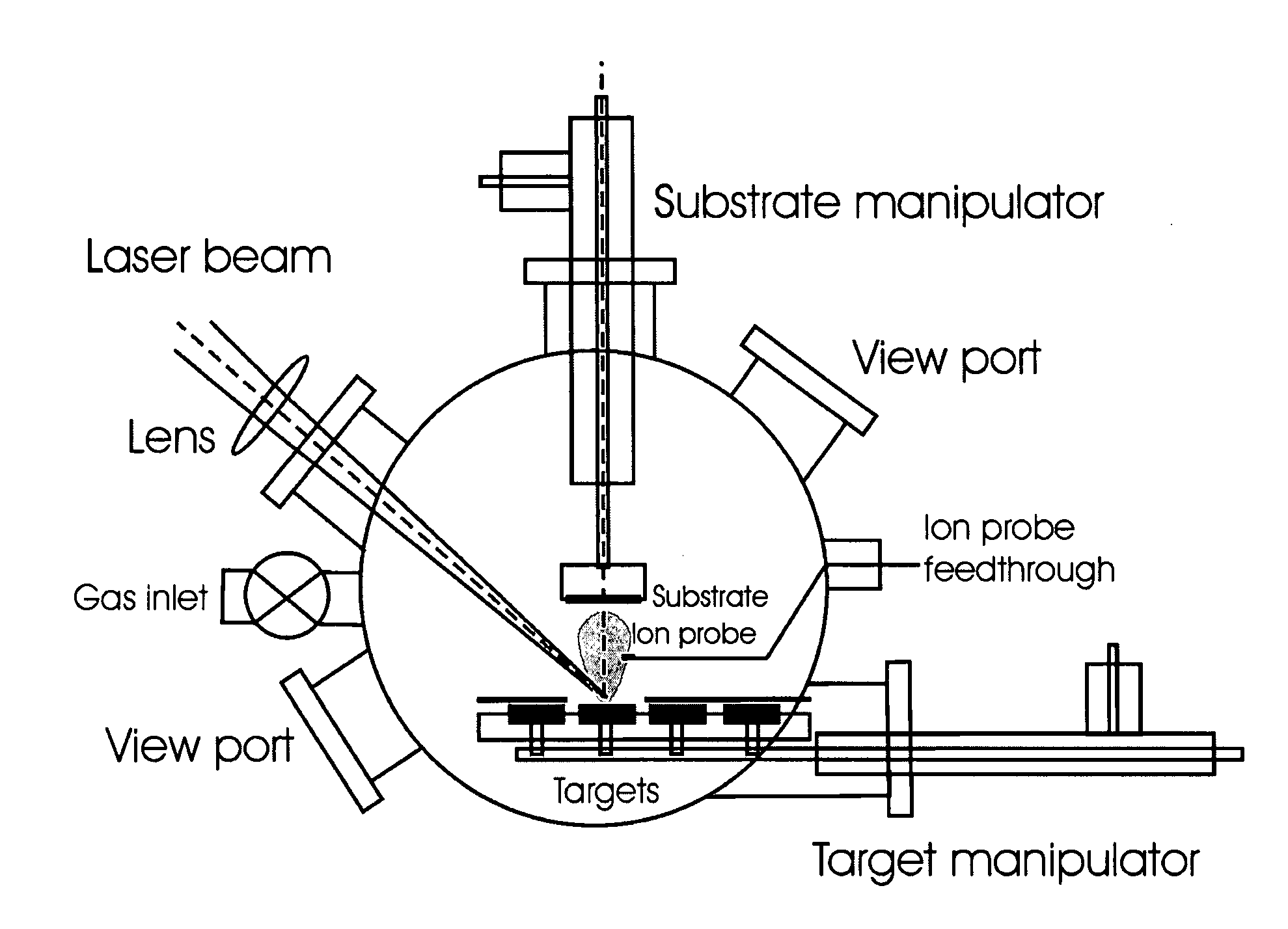
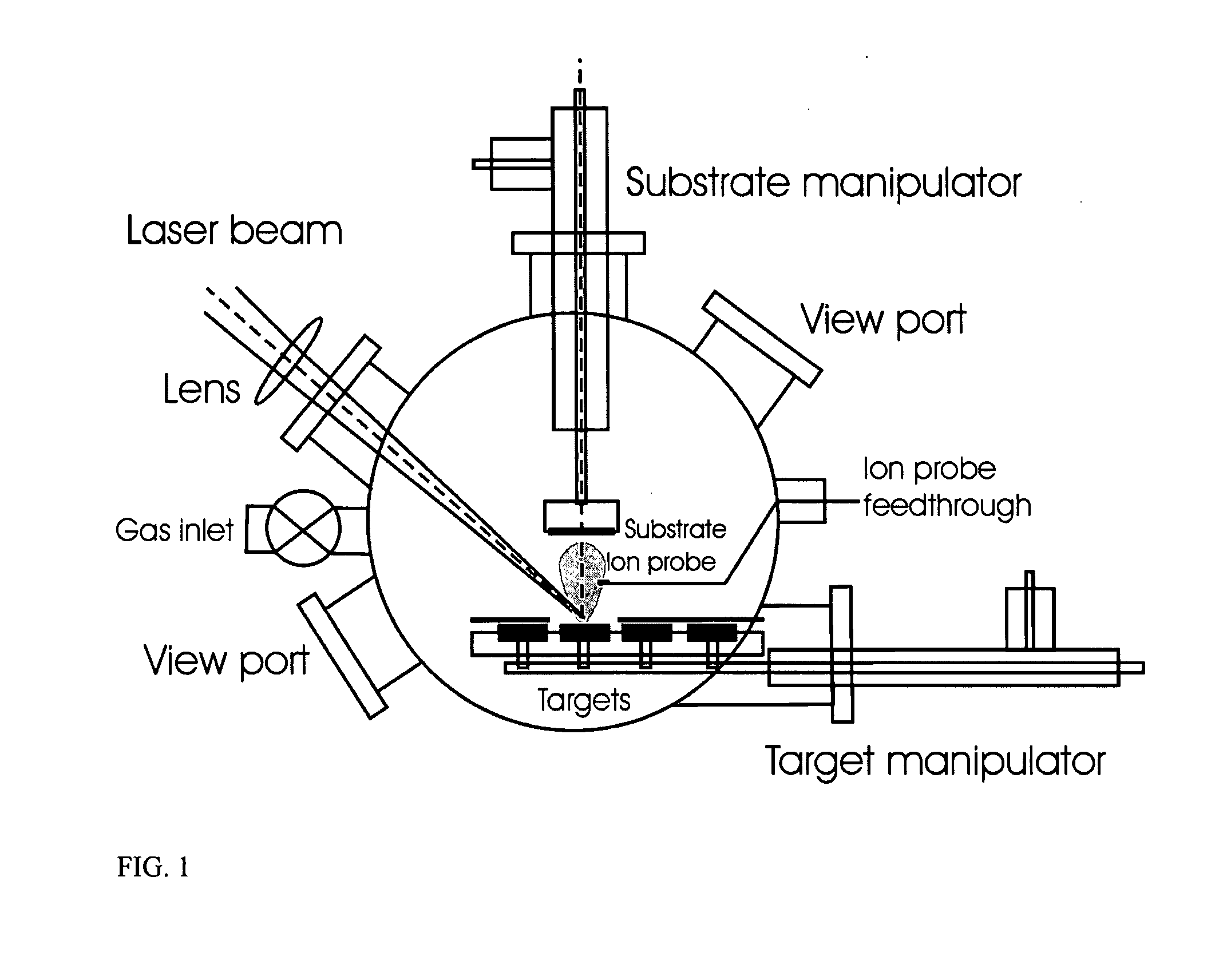
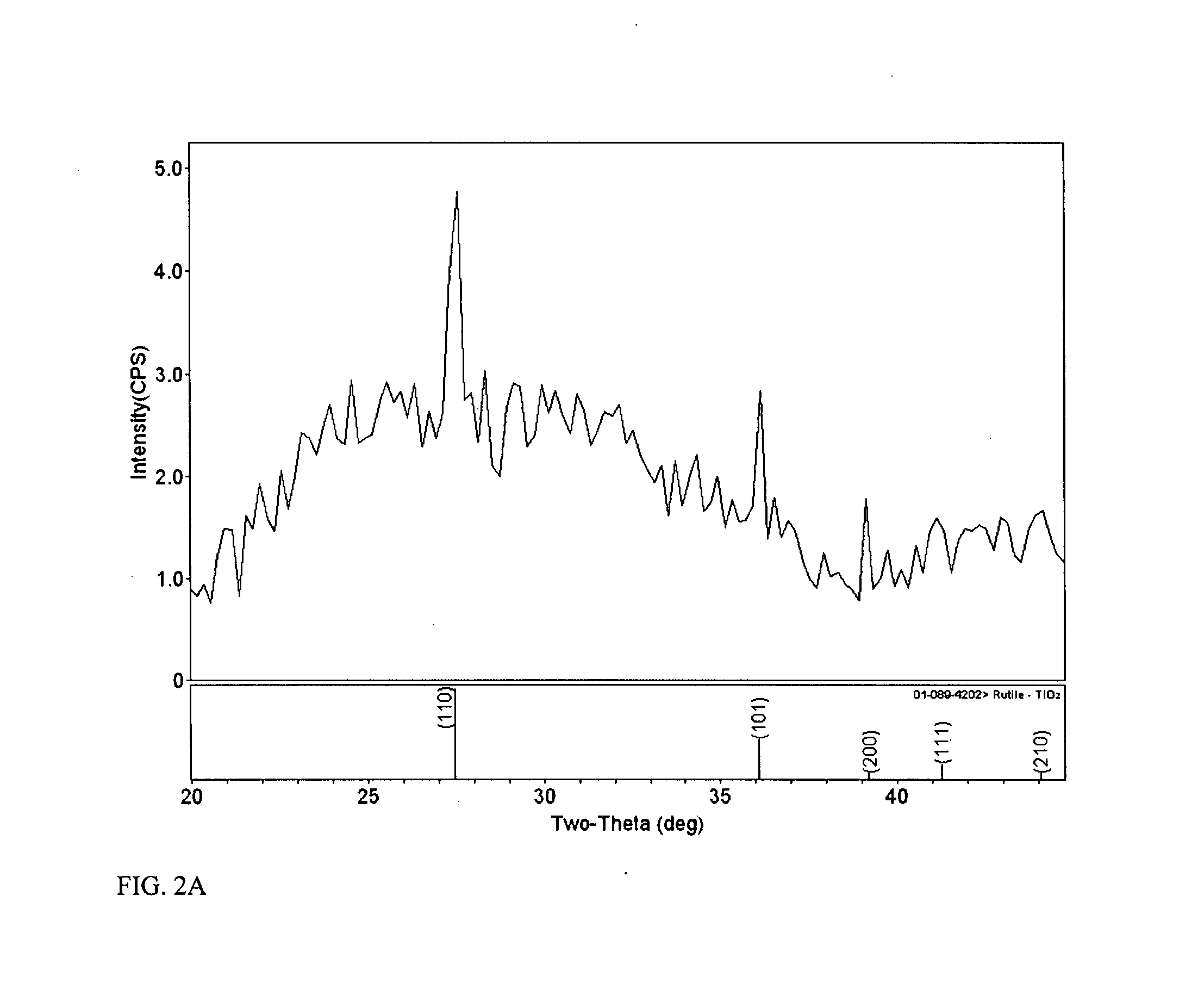
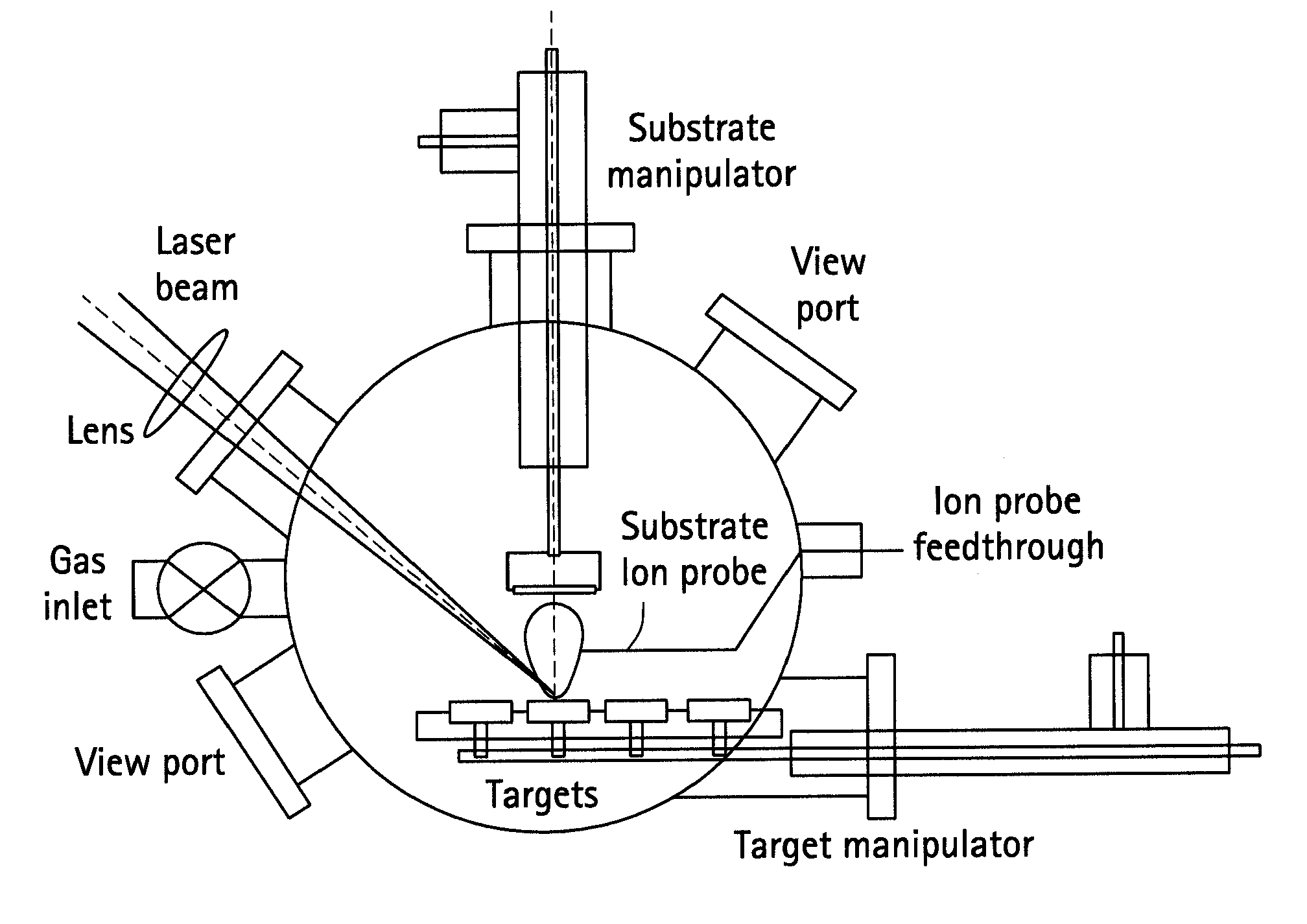
The present invention provides a one-step and room-temperature process for depositing nanoparticles or nanocomposite (nanoparticle-assembled) films of crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2) onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of Titania or metal titanium target. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for fabricating thin films
A method of ultrashort pulsed laser deposition (PLD) capable of continuously tuning formed-film morphology from that of a nanoparticle aggregate to a smooth thin film completely free of particles and droplets. The materials that can be synthesized using various embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, metals, alloys, metal oxides, and semiconductors. A ‘burst’ mode of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation and deposition is provided, where each ‘burst’ contains a train of laser pulses. Tuning of the film morphology is achieved by controlling the burst-mode parameters such as the number of pulses and the time-spacing between the pulses within each burst, the burst repetition rate, and the laser fluence. The system includes an ultrashort pulsed laser, an optical setup for delivering the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density (fluence), and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for producing active glass nanoparticles by laser ablation
InactiveUS20100072645A1Improve efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleOptoelectronics
A method for producing active glass nanoparticles that exhibit upconversion is described. The method employs pulsed-laser ablation of an active glass substrate using, for example, a high repetition rate ultra-short pulse duration laser under normal atmospheric conditions or in a liquid environment.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for producing nanoparticle solutions based on pulsed laser ablation for fabrication of thin film solar cells
InactiveUS20110192450A1Quality improvementProcessing speedTransportation and packagingFinal product manufactureSolar lightPicosecond
A method of producing nanoparticles of solar light absorbing compound materials based on pulsed laser ablation is disclosed. The method uses irradiation of a target material of solar light absorbing compound material with a pulsed laser beam having a pulse duration of from 10 femtoseconds to 500 picoseconds to ablate the target thereby producing nanoparticles of the target. The nanoparticles are collected and a solution of the nanoparticles is applied to a substrate to produce a thin film solar cell. The method preserves the composition and structural crystalline phase of the starting target. The method is a much lower cost fabrication method for thin film solar cells.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for producing active glass nanoparticles by laser ablation
A method for producing active glass nanoparticles that exhibit upconversion is described. The method employs pulsed-laser ablation of an active glass substrate using, for example, a high repetition rate ultra-short pulse duration laser under normal atmospheric conditions or in a liquid environment.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pulse laser plasma electricity hybrid micro-propulsion unit and method
ActiveCN102374146AImprove specific impulseHigh thrust power ratioMachines/enginesUsing plasmaElectric fieldPulsed laser
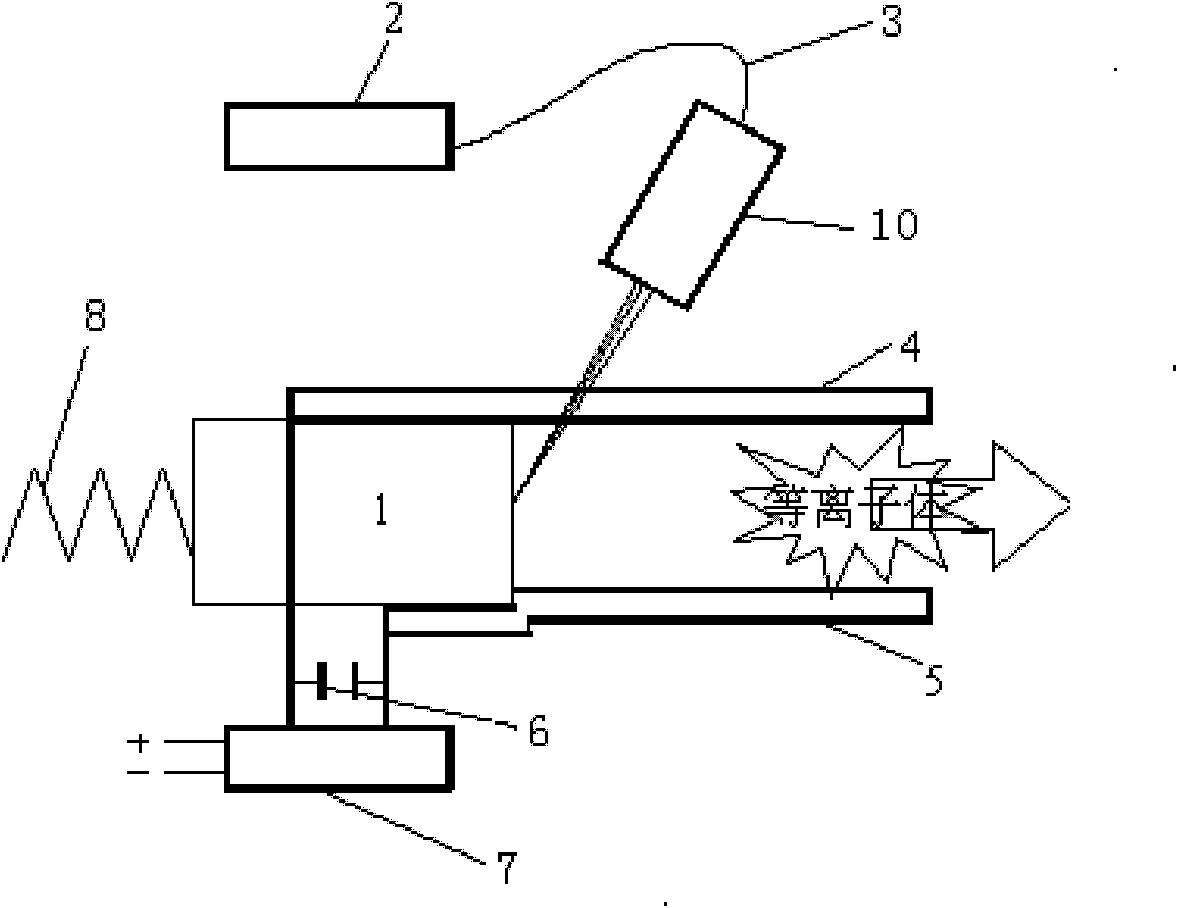
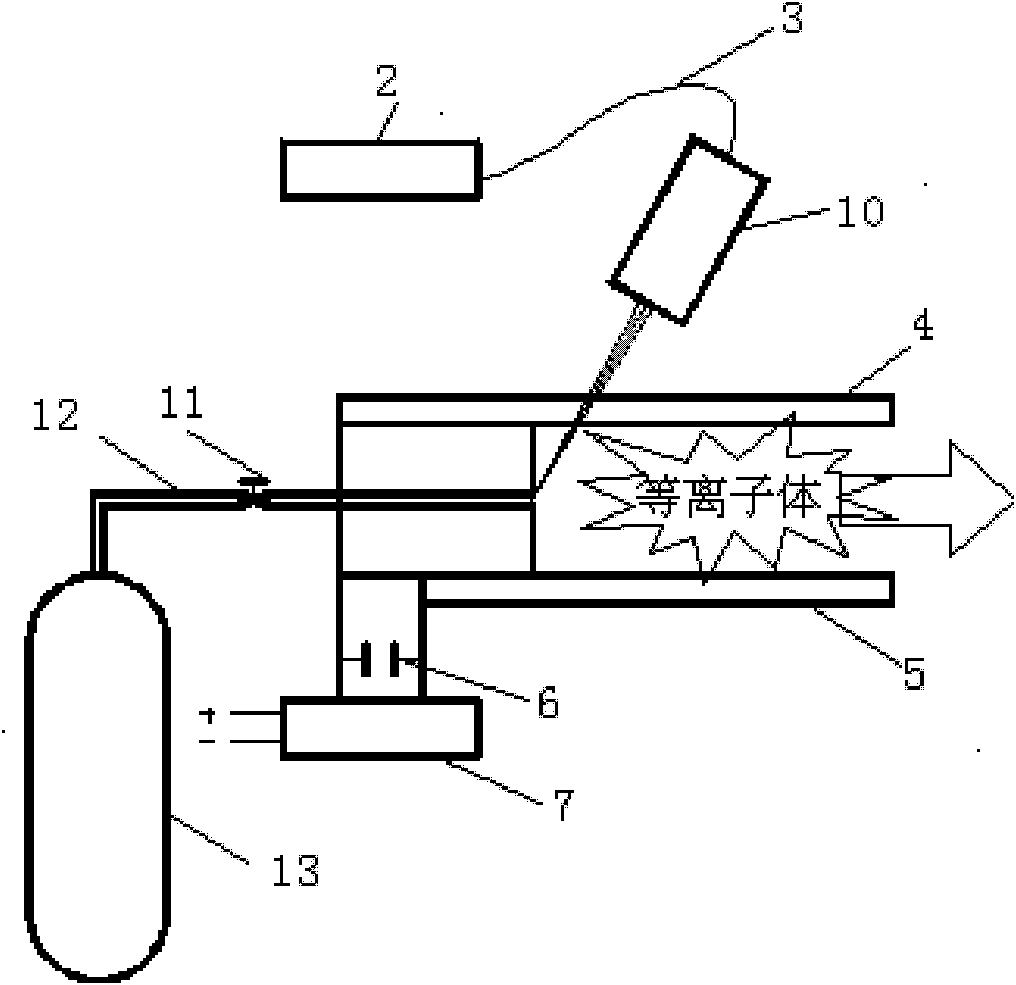
The invention discloses a plasma laser plasma electricity hybrid micro-propulsion unit which comprises a pulse laser ablation device, a propellant supply device and a plasma accelerating device, wherein the pulse laser ablation device irradiates a propellant supplied by the propellant supply device to generate high-speed plasma; and the plasma accelerating device is used for accelerating the high-speed plasma again. The invention also provides a pulse laser plasma electricity hybrid micro-propulsion method which comprises the following steps of: generating high-temperature and high-speed plasma through the high-frequency pulse laser ablation propellant; and accelerating the high-temperature and high-speed plasma through an electric field or magnetic field. According to the invention, a pushing force with high specific impulse and high thrust-to-power ratio can be provided for a mini satellite.
Owner:苏州纳飞卫星动力科技有限公司
Charged particle beam masking for laser ablation micromachining
ActiveUS8168961B2High resolutionHigh processing of sampleElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusTemporal resolutionCharged particle beam
An improved method for substrate micromachining. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide improved methods for the utilization of charged particle beam masking and laser ablation. A combination of the advantages of charged particle beam mask fabrication and ultra short pulse laser ablation are used to significantly reduce substrate processing time and improve lateral resolution and aspect ratio of features machined by laser ablation to preferably smaller than the diffraction limit of the machining laser.
Owner:FEI CO
Charged Particle Beam Masking for Laser Ablation Micromachining
ActiveUS20120200007A1High resolutionHigh processing of sampleElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusTemporal resolutionImage resolution
An improved method for substrate micromachining. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide improved methods for the utilization of charged particle beam masking and laser ablation. A combination of the advantages of charged particle beam mask fabrication and ultra short pulse laser ablation are used to significantly reduce substrate processing time and improve lateral resolution and aspect ratio of features machined by laser ablation to preferably smaller than the diffraction limit of the machining laser.
Owner:FEI CO
Surface-enhanced raman scattering apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20120242987A1Good repeatabilityImprove throughputMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryAnalyteOptical integration
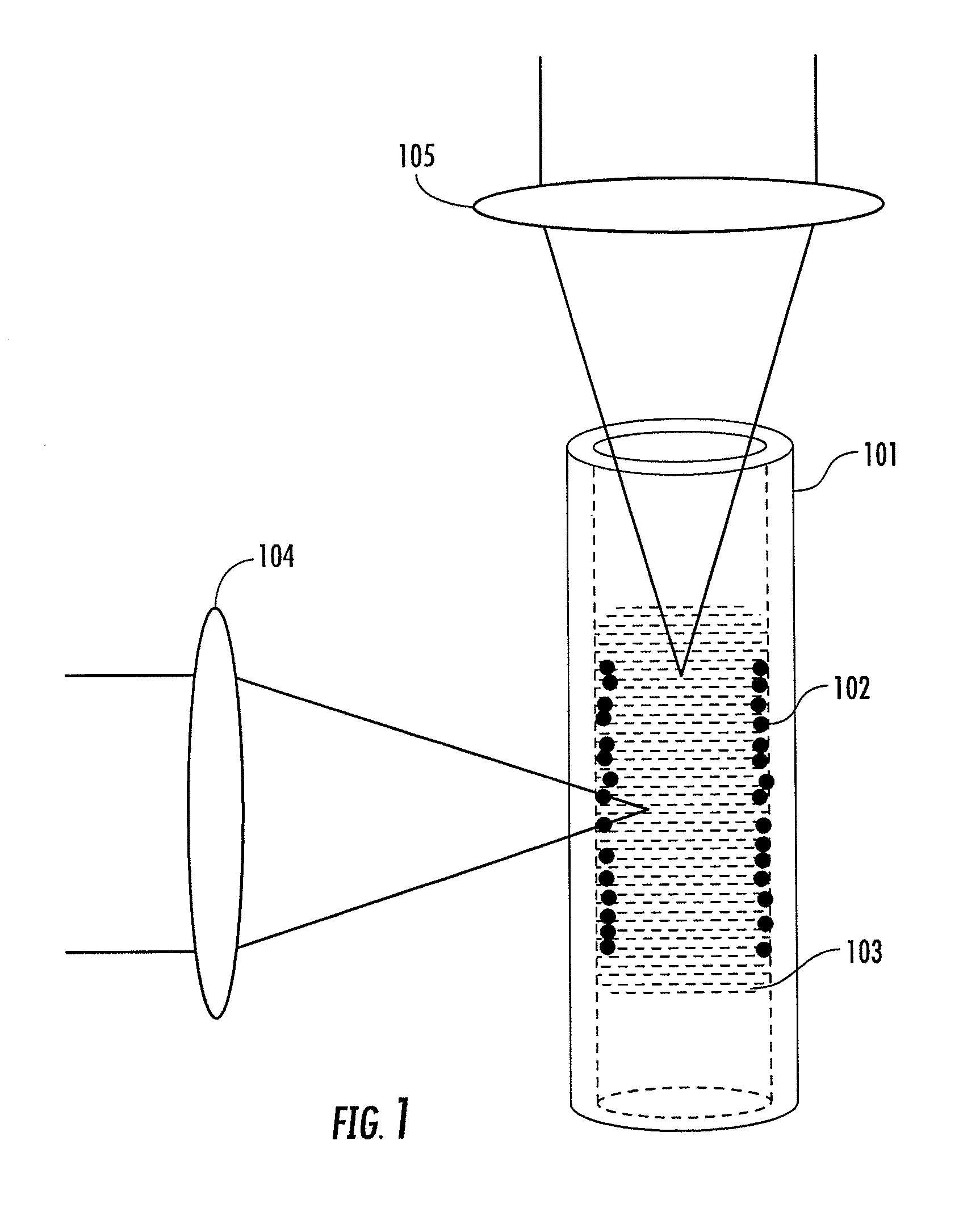
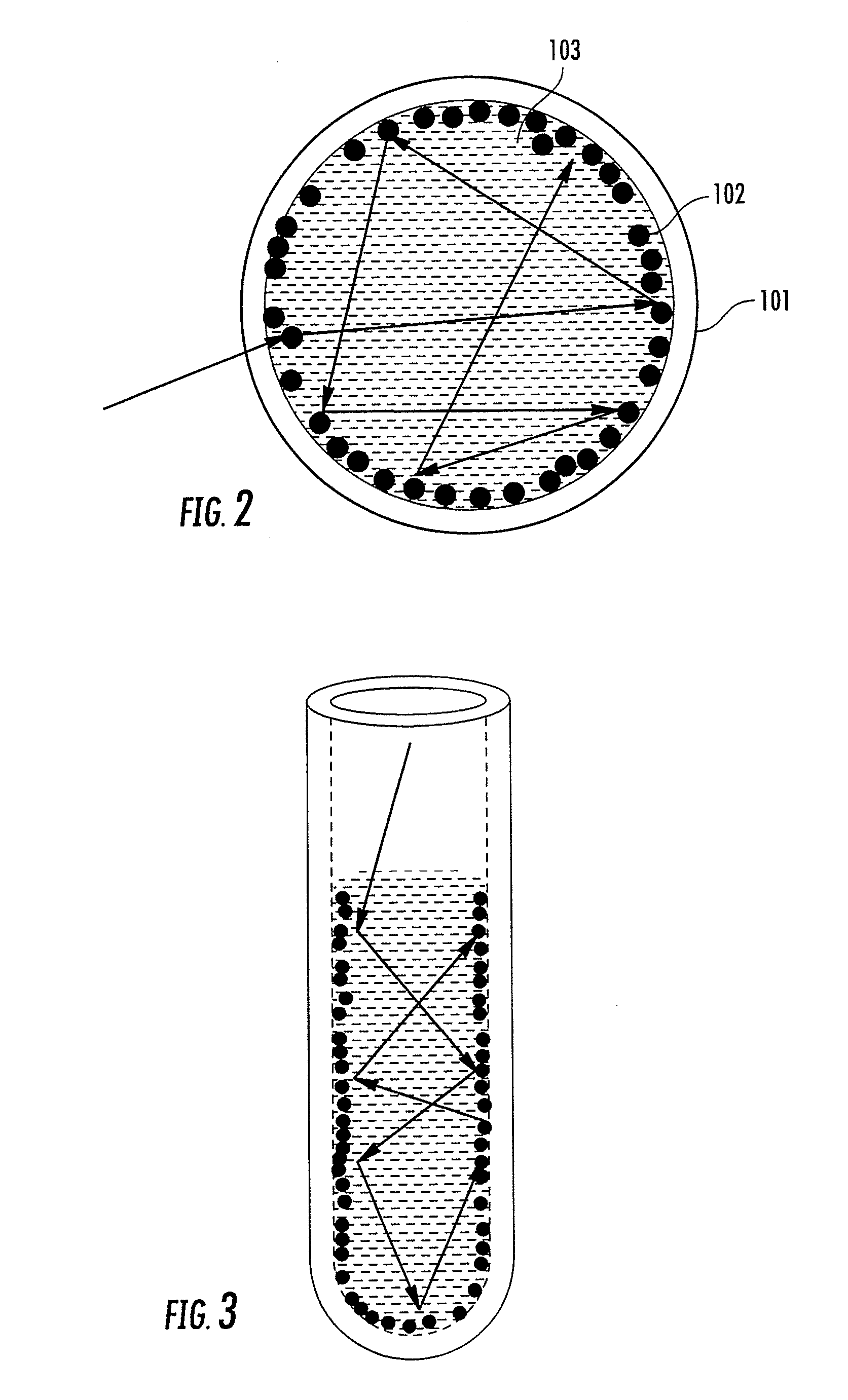
An apparatus for performing surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is disclosed wherein an inner surface of a container is coated with SERS active materials such as nanoparticles of noble metals. Such a container can provide a partially enclosed, optical diffuse cavity whose inner surfaces serve for dual purposes of enhancing Raman scattering of the contained analyte and optical integration, therefore improving the efficiency of optical excitation and signal collection. The container may be configured to isolate the SERS active material from the external environment. The container, which may be a cylindrical tube, may be referred to as a SERS tube. Methods of coating the inner wall of a container with pulsed laser ablation and with nanoparticle colloids, respectively, are disclosed.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and device for detecting trace metal elements in water body by using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted by direct current discharging vaporization
ActiveCN104237178ARealize detectionIncrease concentrationAnalysis by material excitationDirect-current dischargeTrace metal
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting trace metal elements in a water body by using the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy assisted by direct current discharging vaporization. High voltage direct current discharging is utilized to vaporize a liquid sample, the vaporized sample is separated through a separation device, gas is injected to a graphite bearing piece, the graphite bearing piece containing elements to be detected is subjected to pulse laser ablation induction to generate plasma and transmit spectroscopy signals, and finally a spectrograph is utilized to conduct detection analysis to measure the trace metal in the water body. By means of the method and the device, the pulse laser sample ablation efficiency is greatly improved, the detected spectroscopy signals are greatly strengthened, the detection sensitivity is improved, the detection limit of the metal elements is reduced, and the method is feasible for online high-efficiency quick detection of the metal elements in the water body.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for depositing crystalline titania nanoparticles and films
InactiveUS20090311513A1Easily realizedImprove photocatalytic activityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsVolumetric Mass DensityPicosecond
A one-step and room-temperature process for depositing nanoparticles or nanocomposite (nanoparticle-assembled) films of metal oxides such as crystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2) onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of Titania or metal titanium target. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Micro-nanoparticle having special morphology, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101327946AAchieve preparationEasy to operateIndividual molecule manipulationGermanium dioxideTarget surfacePulsed laser ablation deposition
The invention provides a preparation method of a micron-nano particle with a special morphology comprising the following operation steps: arranging a reaction target in the liquid substance, placing a reactor in an ultrasonic dispersing groove which works in a certain oscillation frequency during the whole reaction process, focusing a pulsed laser beam after passing a focusing lens on the surfacewhere the reaction target contacts with the liquid substance so as to generate plasma plumes on the reaction target surface, loading a controllable electric field by an electrode plate around the reaction region to control the reaction while the pulsed laser ablation is conducted, stopping the pulsed laser radiating the target materials after conducting the pulsed laser ablation reaction for 120-180 minutes, drying and separating the takeout reaction products and preparing the micron-nano particle with a special morphology. The micron-nano particle with a special morphology prepared by the above method can be applied in the field such as microelectronics processing, optics, biology, catalytic chemistry or medicine.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Production of organic compound nanoparticles with high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser ablation in liquids
InactiveUS20110196044A1High repetition rateImprove efficiencyBiocidePowder deliveryUltrashort laserOrganic compound
Disclosed is a method of producing a chemically pure and stably dispersed organic nanoparticle colloidal suspension using an ultrafast pulsed laser ablation process. The method comprises irradiating a target of an organic compound material in contact with a poor solvent with ultrashort laser pulses at a high repetition rate and collecting the nanoparticles of the organic compound produced. The method may be implemented with a high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser source, an optical system for focusing and moving the pulsed laser beam, an organic compound target in contact with a poor solvent, and a solvent circulating system to cool the laser focal volume and collect the produced nanoparticle products. By controlling various laser parameters, and with optional poor solvent flow movement, the method provides stable colloids of dispersed organic nanoparticles in the poor solvent in the absence of any stabilizing agents.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for connecting materials difficult to connect through ultrafast lasers
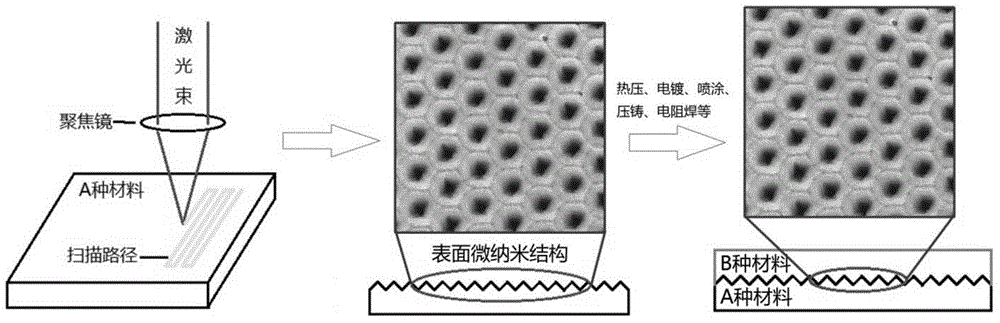
ActiveCN104439956AImprove power densityReduce meltingLaser beam welding apparatusNuclear fusionAdvanced composite materials
The invention discloses a method for connecting materials difficult to connect through ultrafast lasers. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a material A is ablated through ultrashort pulse lasers, removing is achieved through laser ablation, and a nano-micro-meter structure is obtained on the surface of the material A; secondly, impurities on the surface, with the nano-micro-meter structure, of the material A are removed through corrosive liquid; thirdly, in an inert gas or vacuum environment, a material B is deformed and flows to fill the nano-micro-meter structure of the material A, the material A and the material B are combined in a mechanical combination mode, and therefore the material A and the material B are connected, wherein the melting point and the hardness of the material A are higher than the melting point and the hardness of the material B. The method for connecting the materials difficult to connect through the ultrafast lasers is a new method which is flexible, high in efficiency and wide in application range and is used for improving the connecting strength of the materials, and the application of the method includes but is not limited to the development of a nuclear fusion reactor oriented to plasma materials, electric contact materials, heat sink materials, electronic packaging and advanced composite materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Graphene-platinum nano-composite catalyst for lithium air battery, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102423703AGood dispersionComponent concentrations can be adjustedCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationCharge dischargeElectrochemistry
The present invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry, specifically relates to a graphene-platinum (RGO-Pt) nano-composite catalyst for a lithium air battery, and a preparation method thereof. The nano-composite catalyst material is prepared by a liquid phase pulsed laser ablation technology (LP-PLA). With adopting the membrane electrode prepared by the composite catalyst for the lithium air battery anode material, the lithium air battery has good charge-discharge cycle reversibility, the charge-discharge over voltage is significantly decreased, and the reversible specific capacity under the current density of 100 mA / g is more than 4000 mAh / g. The membrane anode material based on the graphene-platinum (RGO-Pt) nano-composite catalyst has characteristics of good chemical stability, high specific capacity, excellent cycle performance and simple preparation method, and is applicable for the lithium air battery.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A method for fabricating thin films
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method for Producing Surfaces and Materials by Laser Ablation
InactiveUS20090166343A1Low costGood repeatabilityNanostructure manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingNanoparticleOptoelectronics
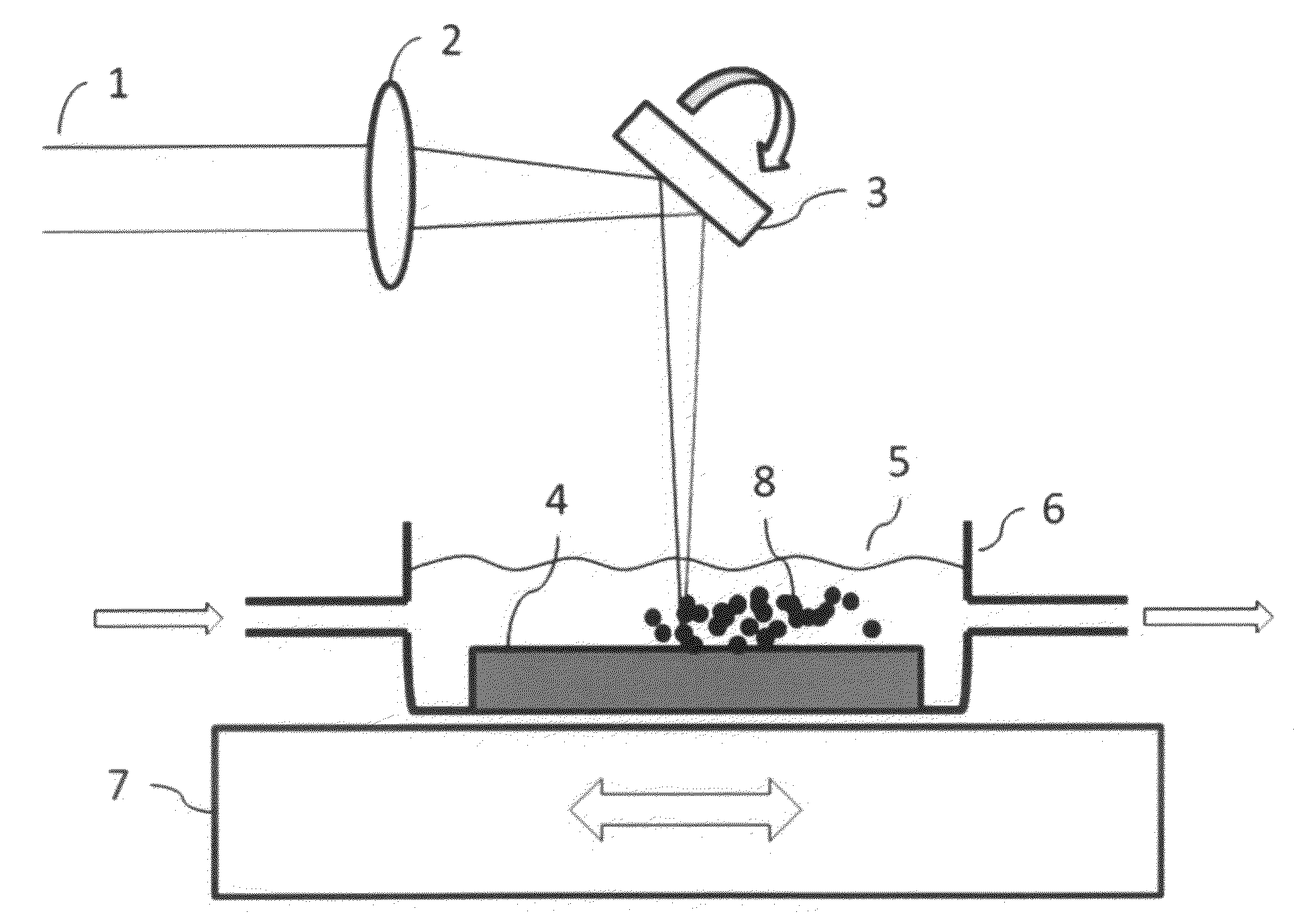
The invention relates to a laser ablation coating method, where the laser ablation is carried out in a space with 10−3 atmospheres at most. A low vacuum level enables an advantageous industrial production of surfaces without remarkably weakening the quality features of the deposited surfaces. The invention also relates to a method for producing nano particles, so that target material is ablated by pulse laser for generating nano particles in a space with 10−3 atmospheres at most.
Owner:PICODEON OY
Method for preparing graphene based nano composite material through in-situ reduction of graphite oxide
ActiveCN103879999AHigh activityImprove responseGrapheneMaterial electrochemical variablesColloidHigh activity
The invention discloses a method for preparing a graphene based nano composite material through in-situ reduction of graphite oxide. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing pulse laser ablation on a rotating metal target material to obtain metastable colloid with high activity and high reactivity, subsequently mixing and oscillating the metastable colloid having high activity with graphite oxide prepared by using a classic Hummers method, and standing at a dark place for more than one weak. The prepared nano composite material, such as SnO2-rGO and ZnO-rGO, is simple to operate, environmental friendly, efficient and high in universality.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of metal and metal-alloy nanoparticles with high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser ablation in liquids
ActiveUS8246714B2Prevent coagulationFaster throughputMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingUltrashort laserFocal volume
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Pulse laser processing-based novel positive rake diamond abrasive tool manufacturing method
ActiveCN105728961AReduce microcracksReduce residual stressGrinding devicesWelding apparatusLaser processingPhase change
The invention relates to a pulse laser processing-based novel positive rake diamond abrasive tool manufacturing method, being characterized in that a diamond grinding wheel with orderly-arranged abrasive particles is eroded by pulse laser, so that a vertex angle of the diamond abrasive particles is changed from being greater than 90 degrees to being smaller than 90 degrees, thus a traditional negative rake grinding method of a diamond abrasive tool is changed, and the abrasive particles taking part in the grinding are changed into a positive rake machining mode during grinding. Compared with traditional grinding (namely negative rake grinding), when the positive rake diamond grinding wheel is used for grinding, three processes of scratching, plowing and cutting are not needed, cutting is directly performed, and the traditional grinding machining mode is changed. When the diamond grinding wheel performs positive rake grinding on a hard and brittle material, normal grinding force is less than tangential grinding force, and the normal grinding force and the tangential grinding force during positive rake grinding are both less than those during negative rake grinding, so that surface / subsurface damages, such as microcracks, residual stress, phase change, dislocation and ripple, of the hard and brittle material subjected to grinding are effectively reduced, and the surface completeness of the material can be greatly improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for fabricating graphene electrode materials through pulsed laser deposition and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for fabricating graphene electrode materials through pulsed laser deposition and an application thereof. Graphene oxide (GO) is fabricated through the Hummers method, the graphene oxide is compressed into a sheet with thickness of 2 mm, pulse laser ablates the graphene oxide target material, and graphene electrode materials are sputtered and deposited on a nickel foam substrate. The process of the method of fabricating graphene electrode materials does not need any adhesion agent, so that effects of adhesion agents on the capacitance of electrode materials are avoided.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Producing nanoparticle solutions based on pulsed laser ablation
InactiveCN102781660AImprove qualityFast processLayered productsFinal product manufactureSolar lightNanoparticle
A method of producing nanoparticles of solar light absorbing compound materials based on pulsed laser ablation is disclosed. The method uses irradiation of a target material of solar light absorbing compound material with a pulsed laser beam having a pulse duration of from 10 femtoseconds to 500 picoseconds to ablate the target thereby producing nanoparticles of the target The nanoparticles are collected and a solution of the nanoparticles is applied to a substrate to produce a thin film solar cell. The method preserves the composition and structural crystalline phase of the starting target. The method is a much lower cost fabrication method for thin film solar cells.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Production of organic compound nanoparticles with high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser ablation in liquids
InactiveUS8992815B2Improve efficiencyHigh repetition rateBiocidePowder deliveryUltrashort laserOrganic compound
Disclosed is a method of producing a chemically pure and stably dispersed organic nanoparticle colloidal suspension using an ultrafast pulsed laser ablation process. The method comprises irradiating a target of an organic compound material in contact with a poor solvent with ultrashort laser pulses at a high repetition rate and collecting the nanoparticles of the organic compound produced. The method may be implemented with a high repetition rate ultrafast pulsed laser source, an optical system for focusing and moving the pulsed laser beam, an organic compound target in contact with a poor solvent, and a solvent circulating system to cool the laser focal volume and collect the produced nanoparticle products. By controlling various laser parameters, and with optional poor solvent flow movement, the method provides stable colloids of dispersed organic nanoparticles in the poor solvent in the absence of any stabilizing agents.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Preparation method of curved conformal microstrip antenna array surface
ActiveCN109755760AAvoid quality risks of electrical performance deteriorationAvoid quality risksIndividually energised antenna arraysSilver pasteMicrostrip antenna array
The invention discloses a preparation method of a curved conformal microstrip antenna array surface and aims to provide a technological method of a microstrip antenna completely conformal to a metal structural part. According to the technical scheme, microstrip patches selected to serve as antenna conformal array units, and a curved antenna array surface is directly printed on the metal structuralpart; sand-blasting roughening processing is performed first, wherein a direct writing pen A is adopted to spread a polyimide precursor solution in a layered mode on a sand-blasting surface of a metal carrier according to the shape and size of a dielectric layer of the microstrip antenna array surface till the requirement of total thickness is met, and after surface drying, temperature is raisedthrough a heating substrate for dehydration, and a conformal dielectric layer of the microstrip antenna array surface is formed through aggregation on the surface of the metal carrier; pulse lasers are adopted to ablate bottom holes of vertical interconnected holes in the array units of the polyimide dielectric layer, the bottom holes are filled with conductive silver paste to serve as the vertical interconnected holes, and sintering is performed to solidify the conductive silver paste; and a conductive silver paste array unit pattern is spread on the conformal dielectric layer and is solidified onto the surface of the dielectric layer after surface drying, so that the curved conformal microstrip antenna array surface is formed.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
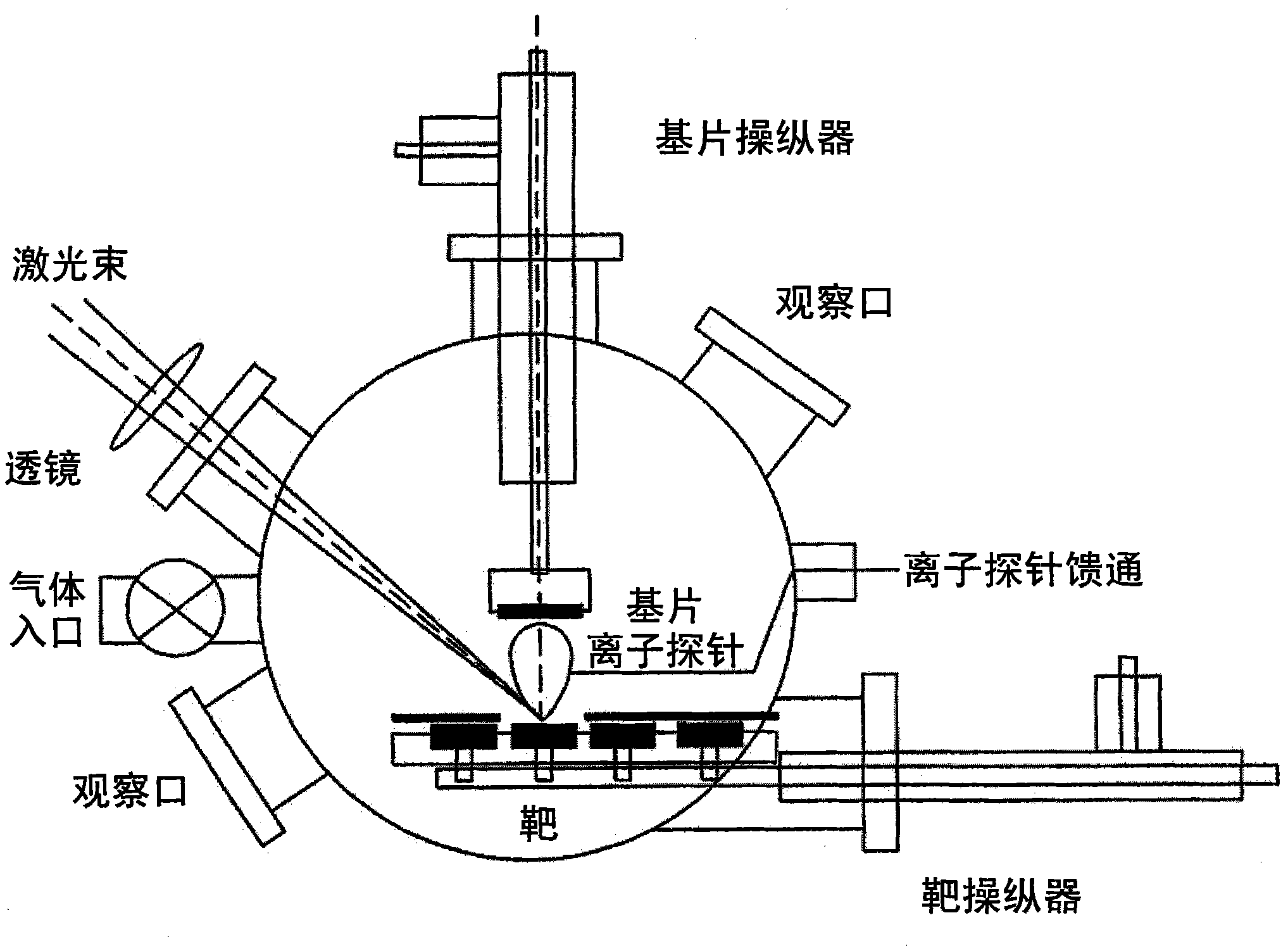
Device of preparing metal nanometer particle colloid by liquid phase medium pulse laser ablation
The present invention relates to a equipment for preparing metal nano particle colloid by utilizing pulse laser ablation in liquid phase. Said equipment includes the following several portions: laser generator, ablation container in which the liquid can be held and metal target. The described metal target is fixed on a pedestal, and said pedestal is passed through the bottom portion of said ablation container and its placed in the base frame interior under the ablation container, the described pedestal and the described ablation container are sealed, in the described base frame interior a motor is set, and the output, shaft of said motor is fixedly connected with pedestal, and the described metal target can be rotated. Besides, said invention also provides the working principle of said equipment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com