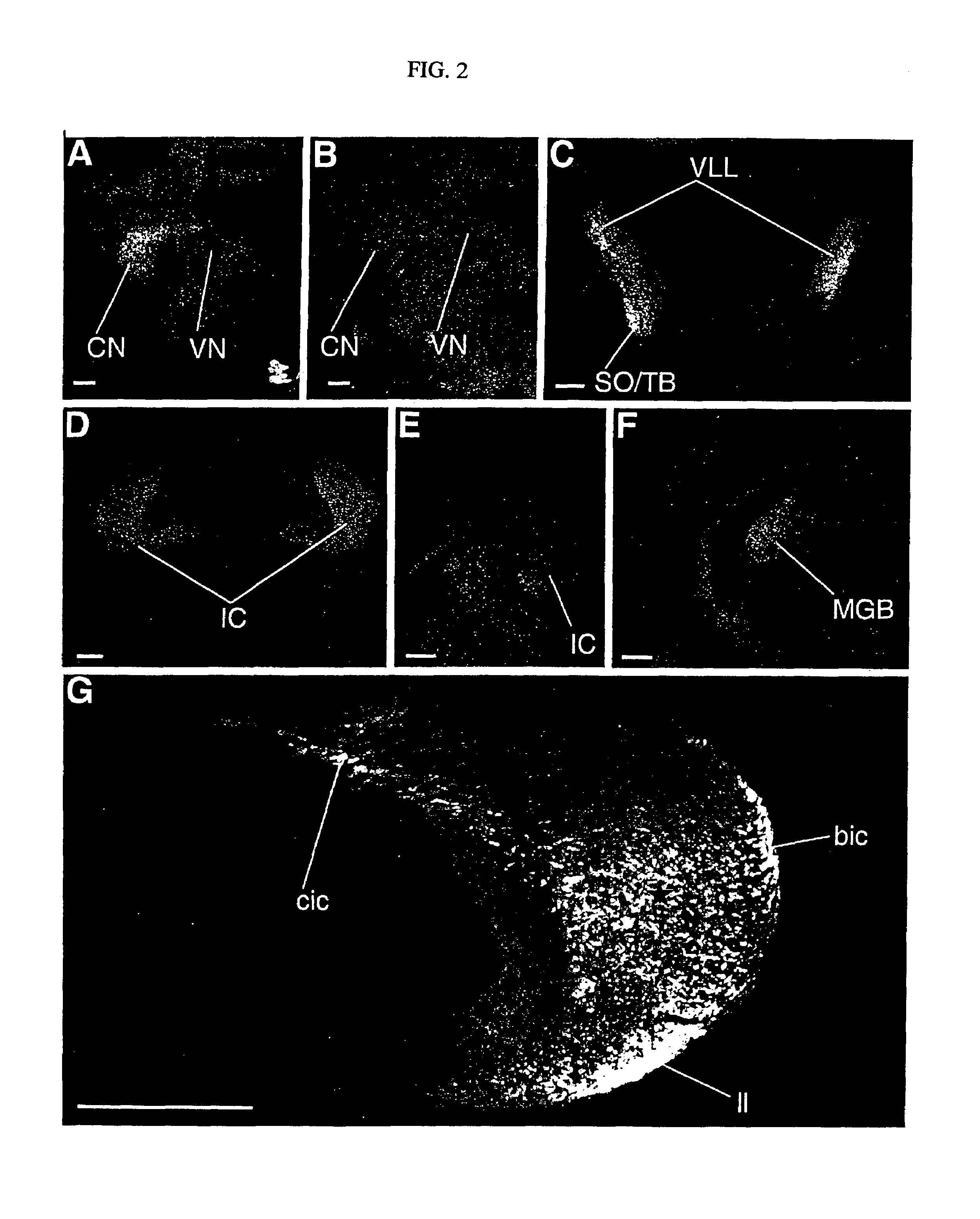
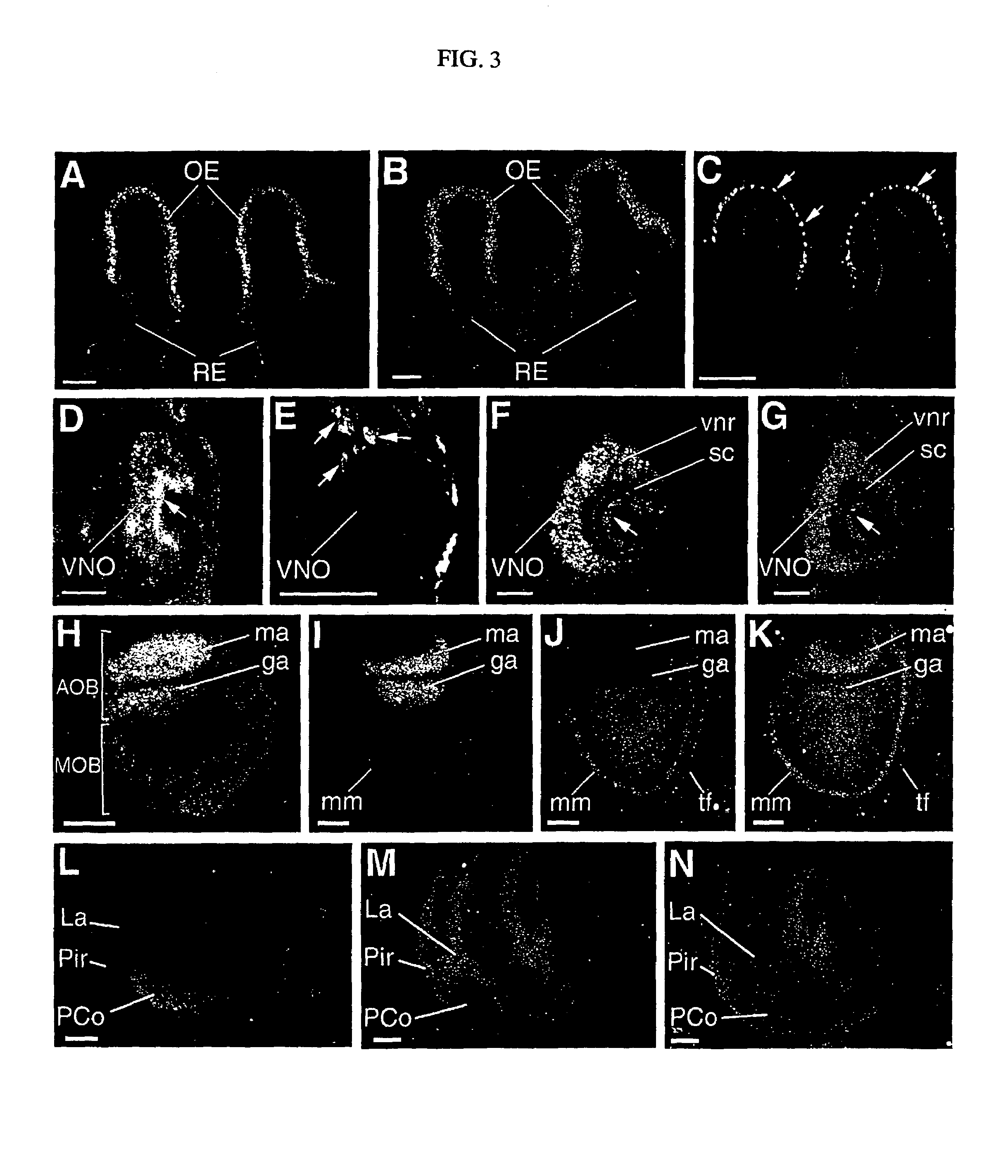
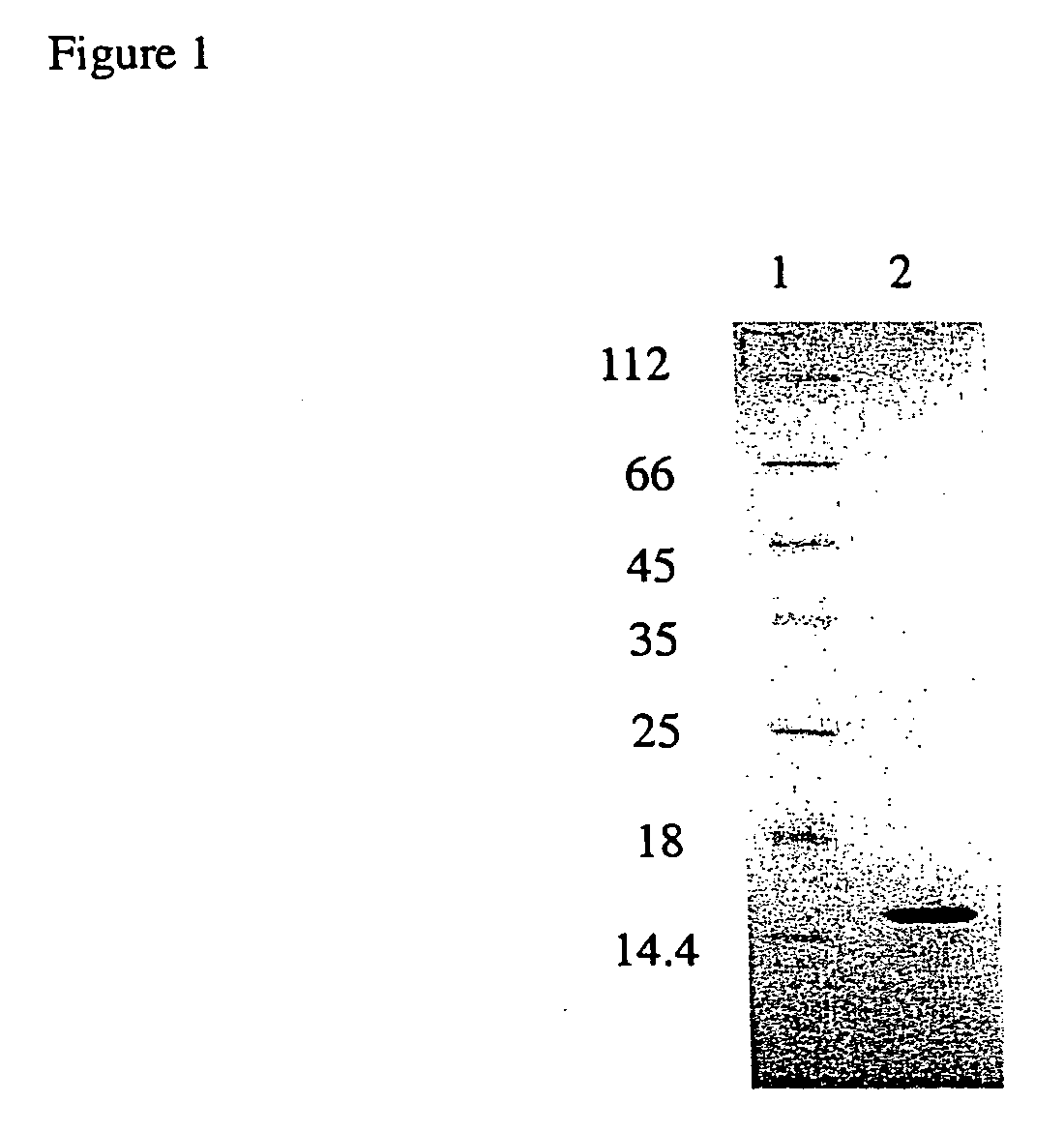
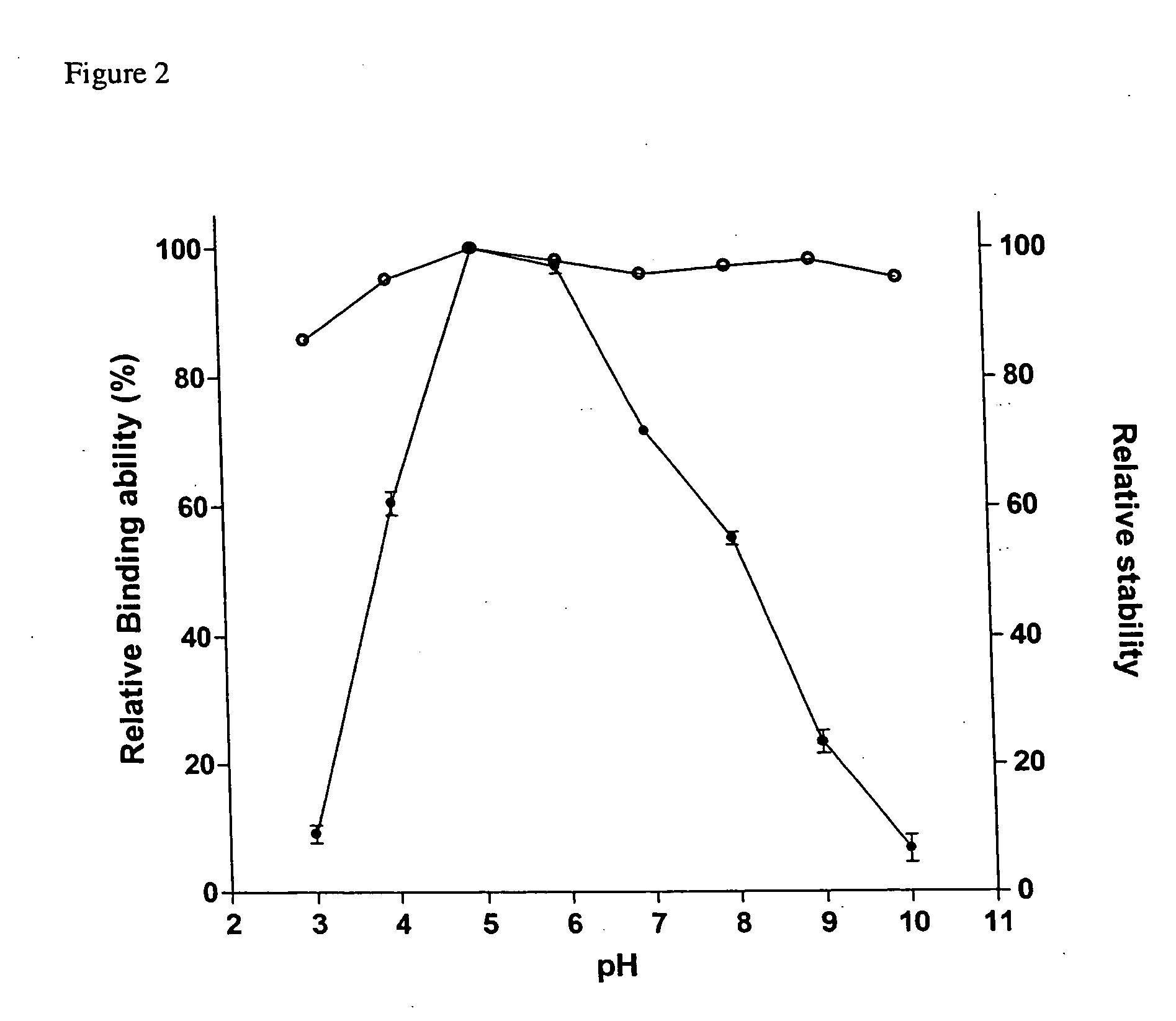
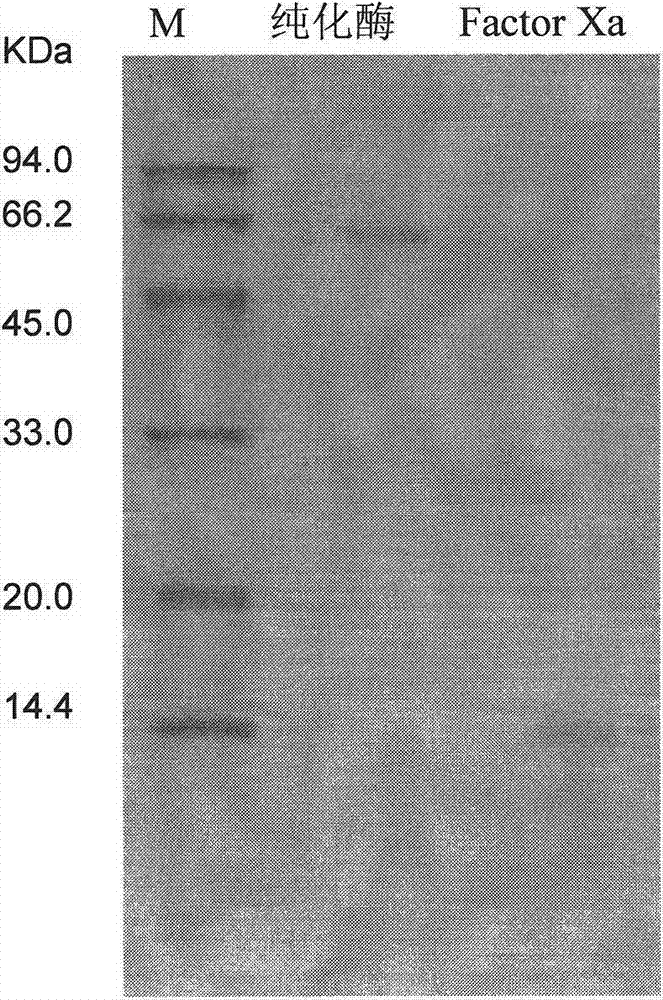
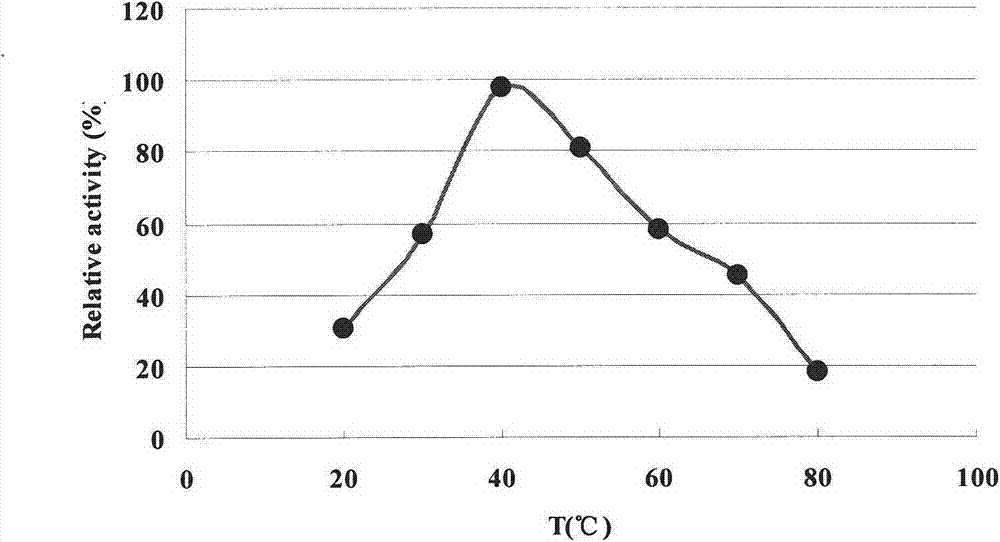
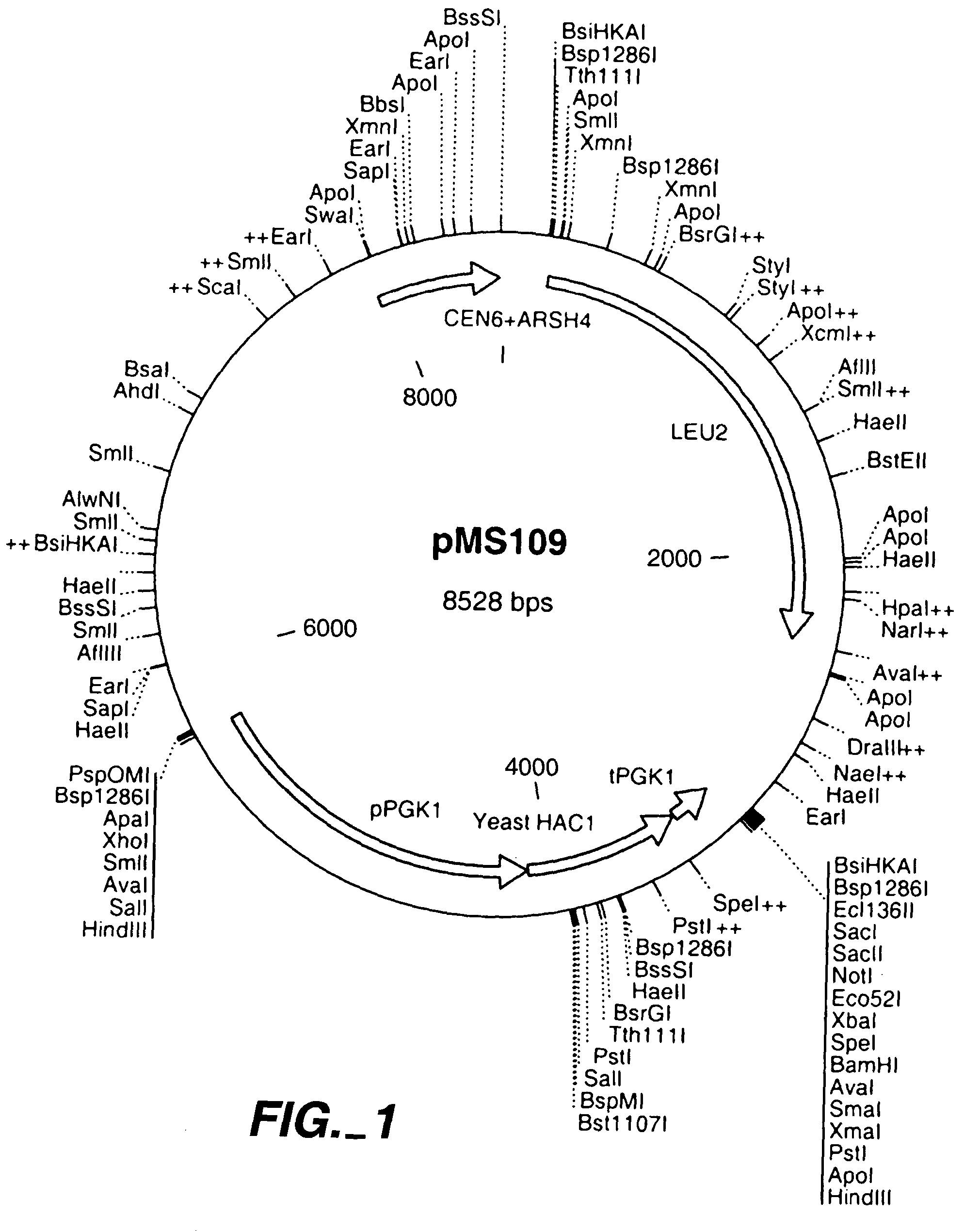
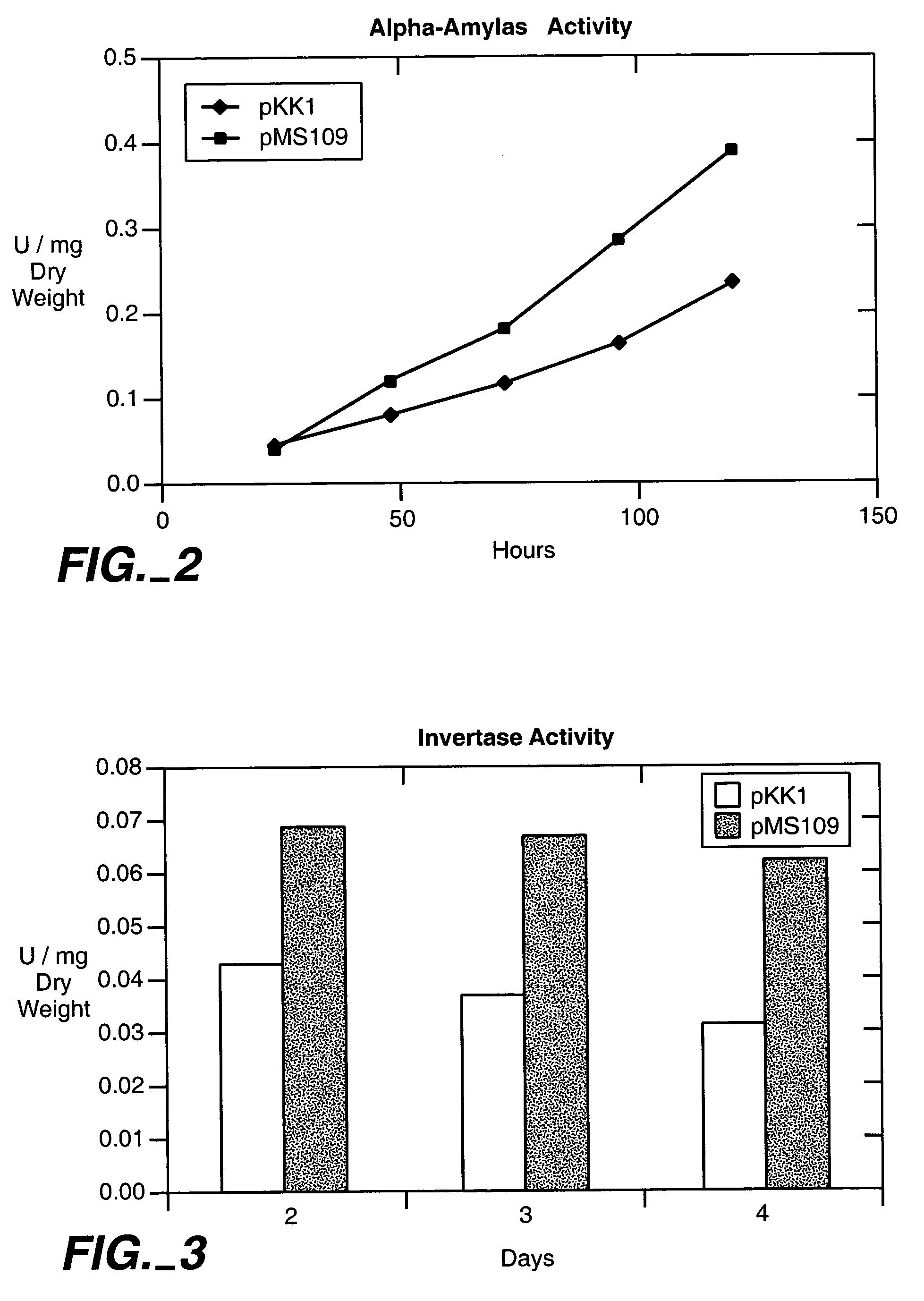
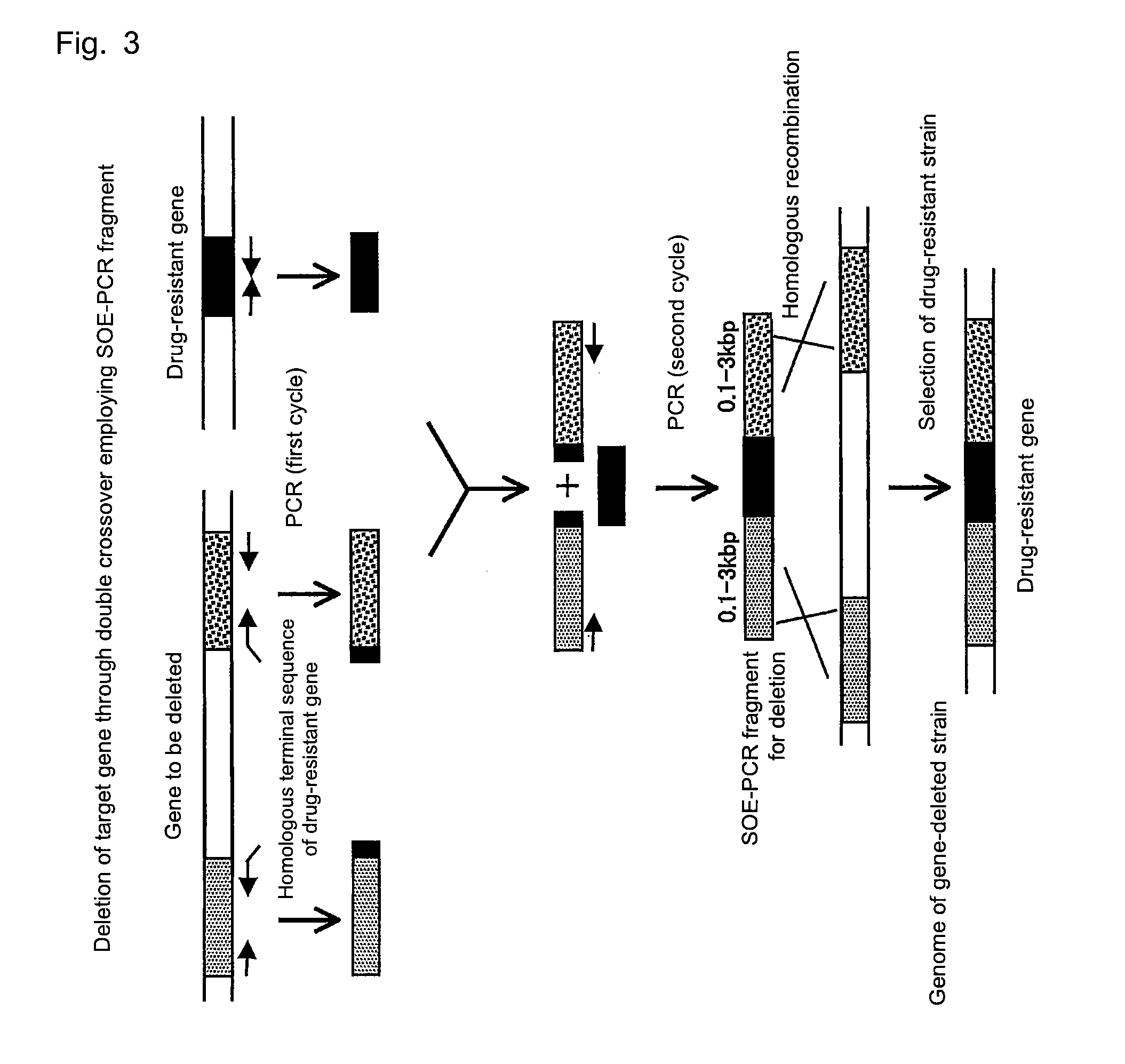
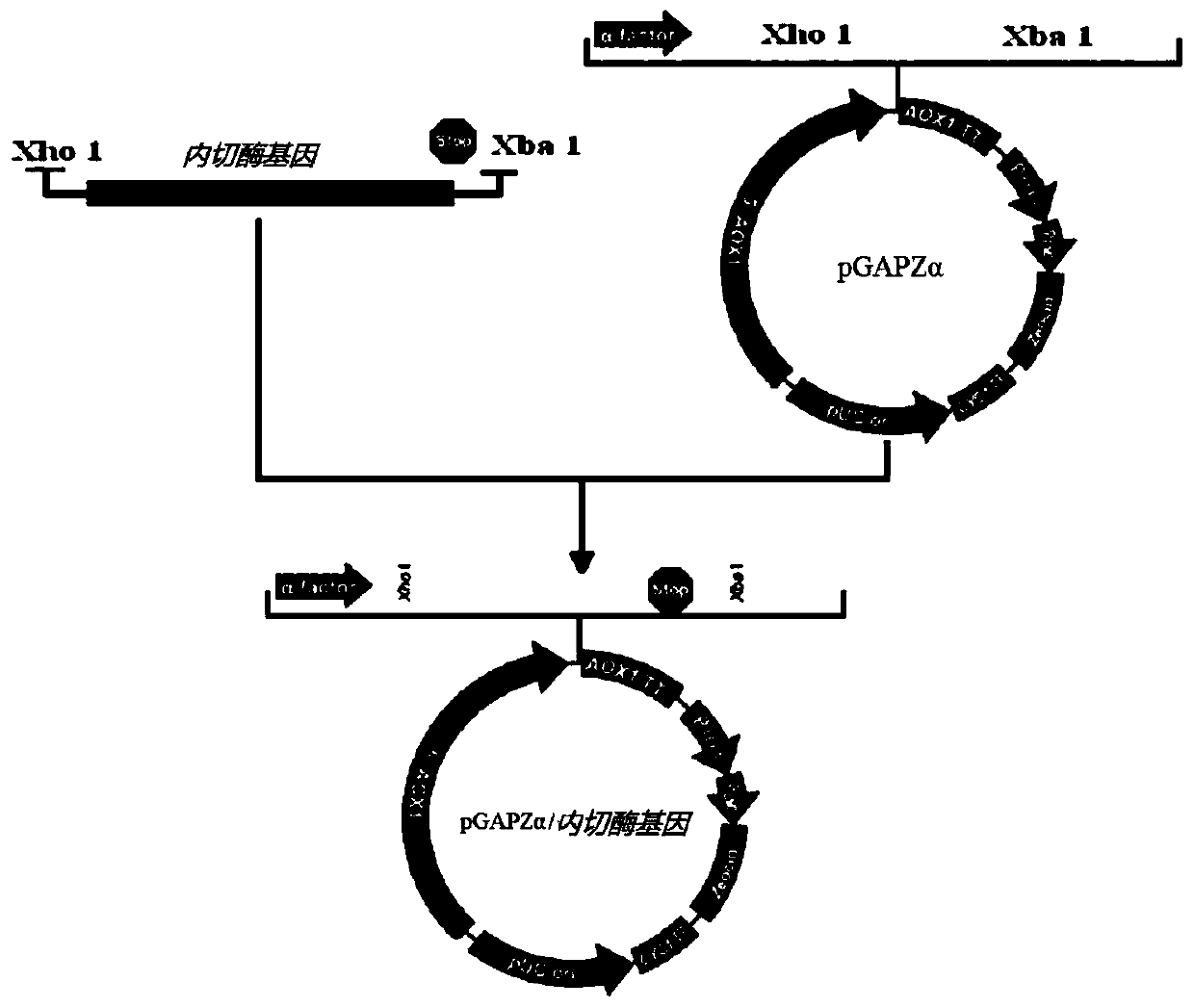
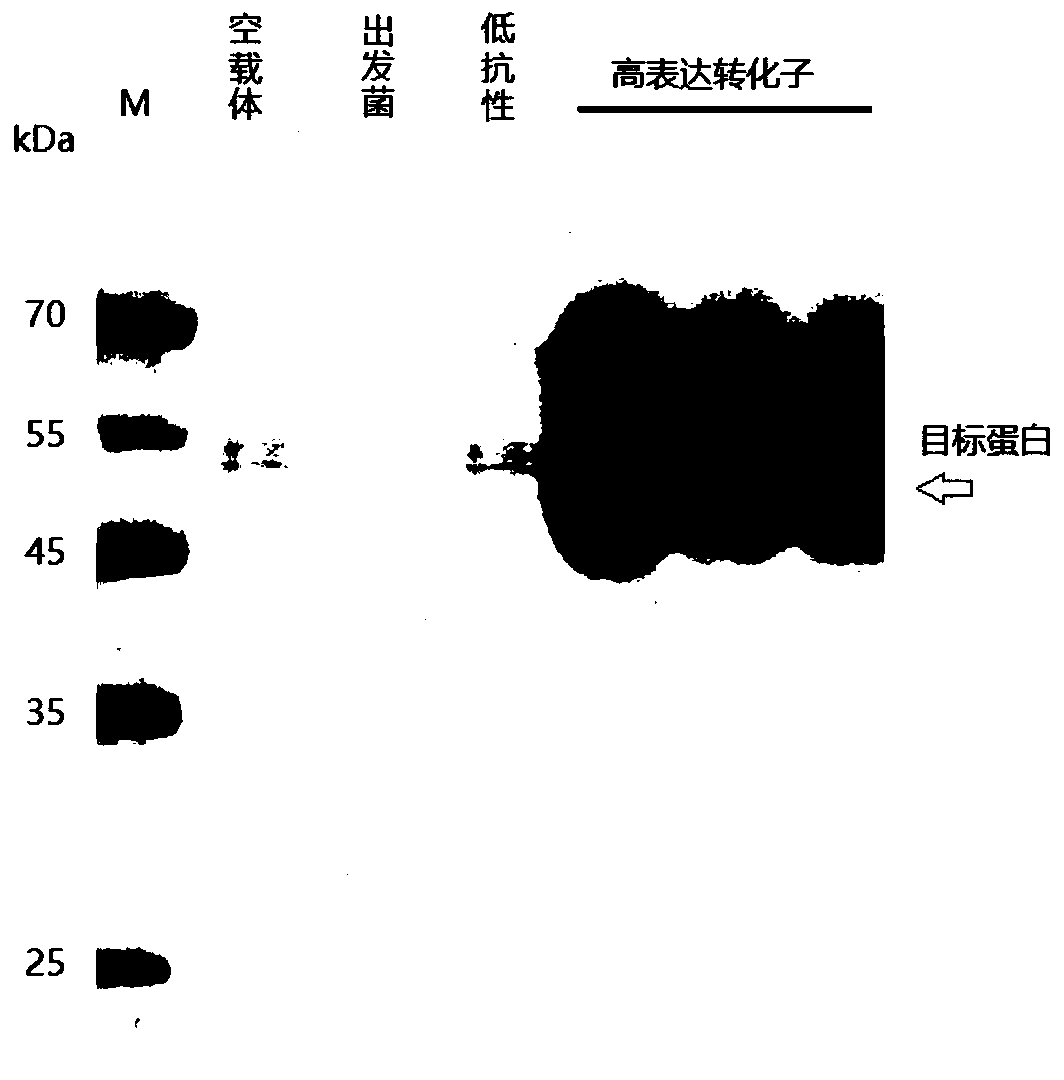
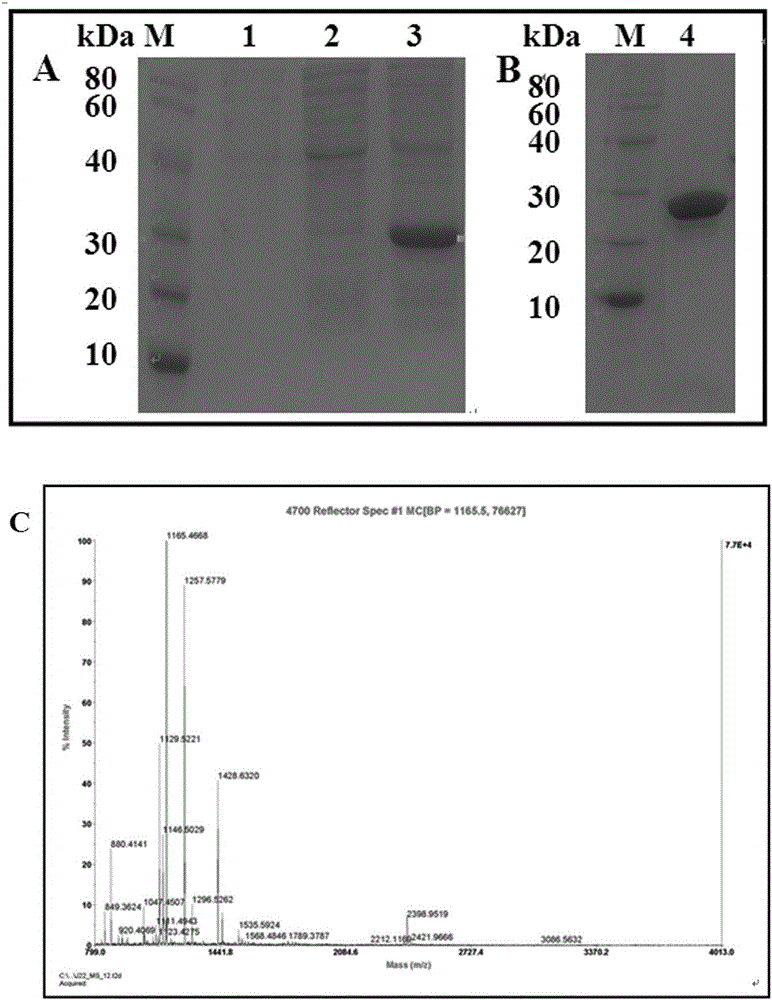
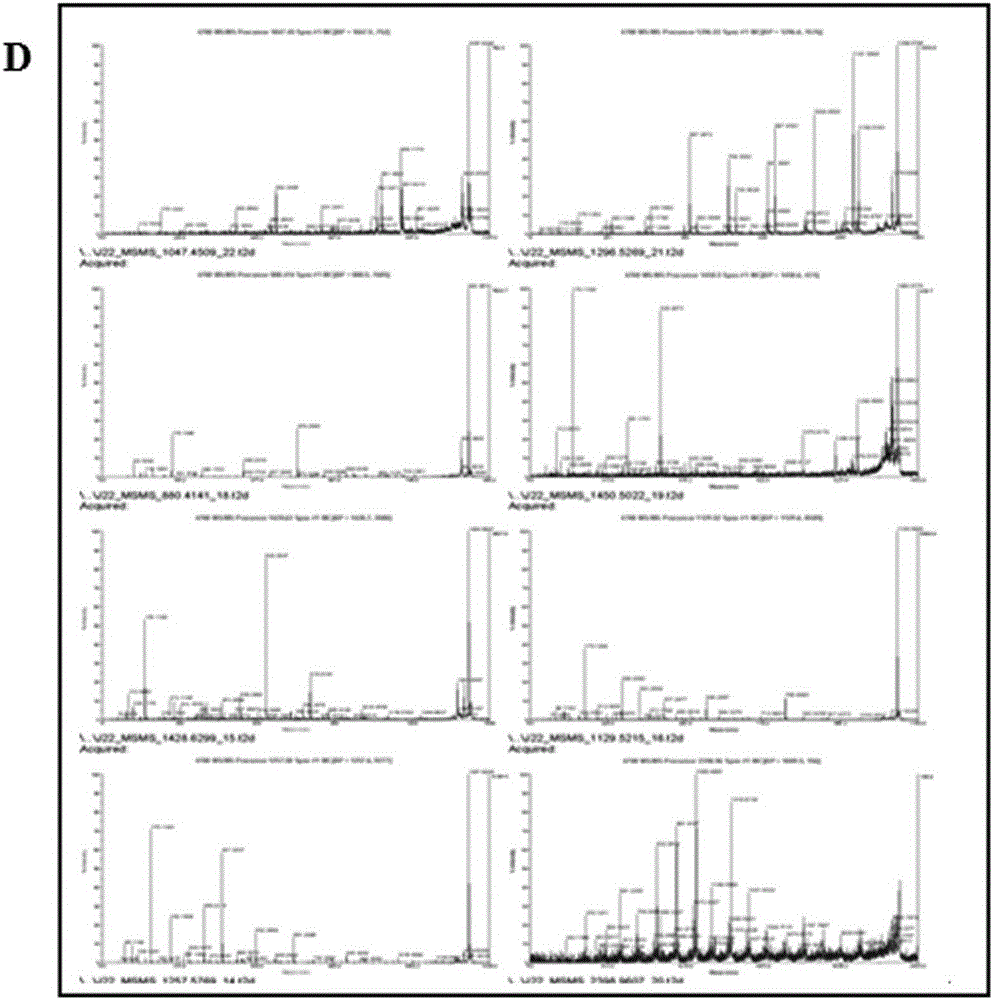
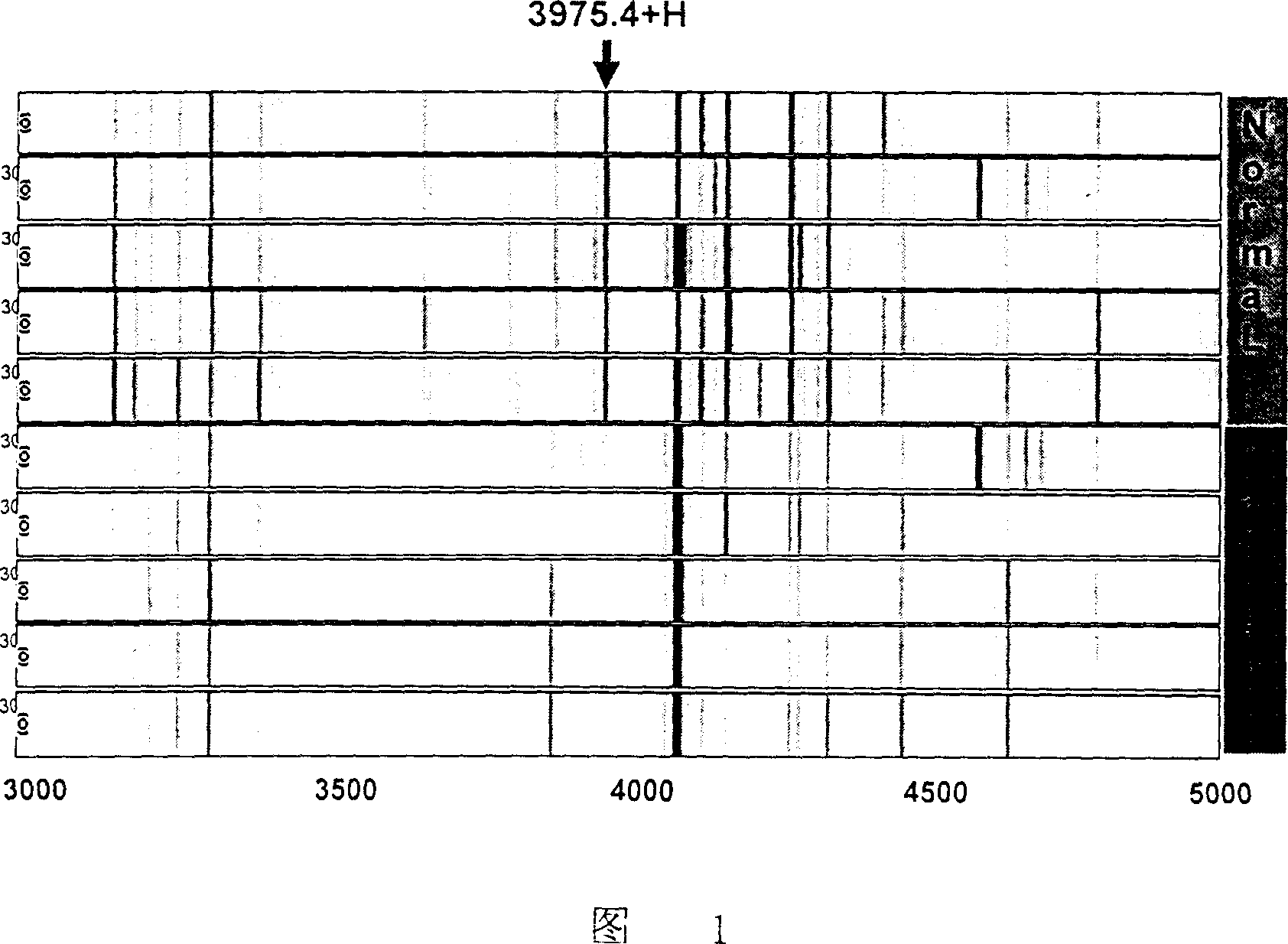
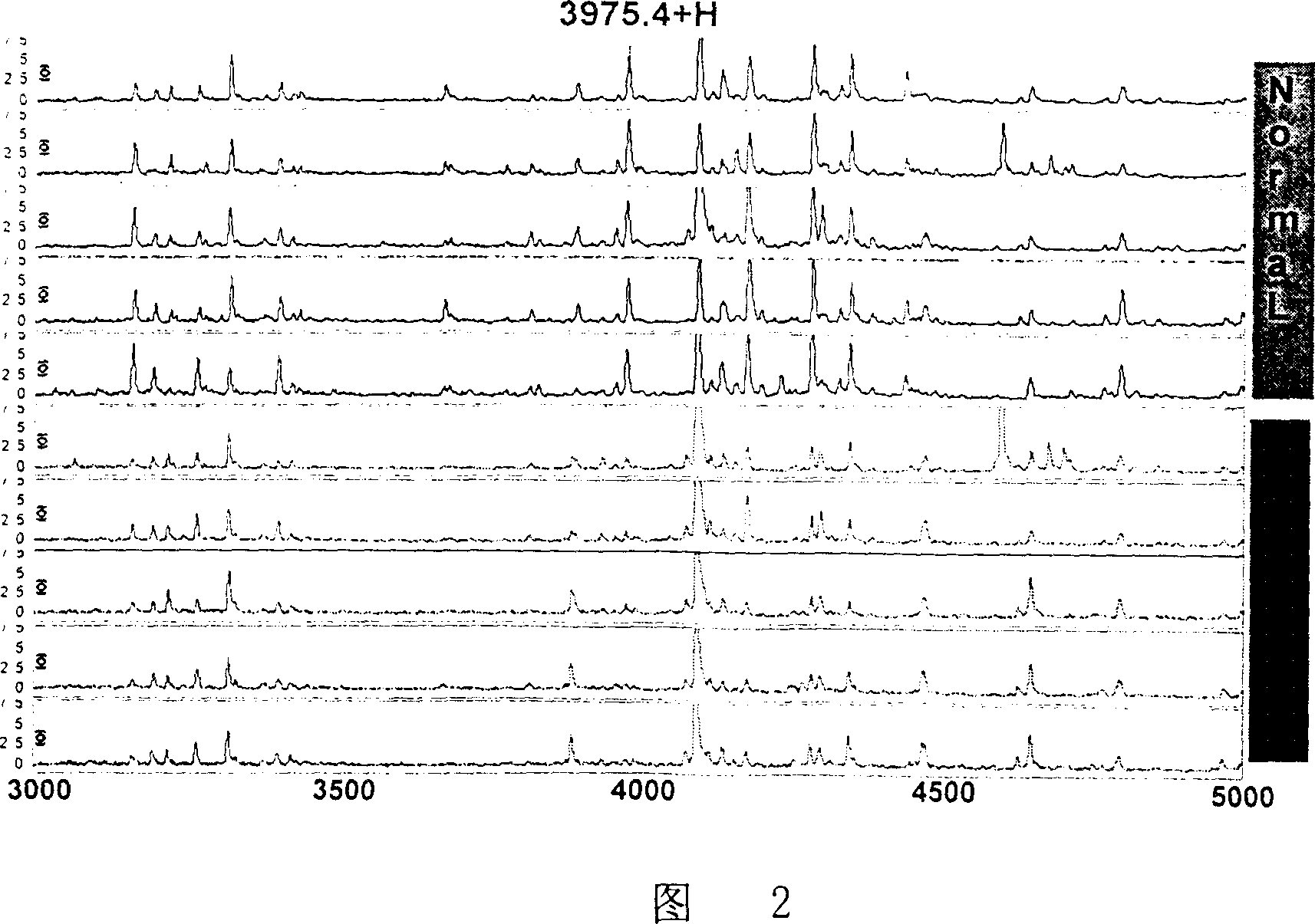
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Protein Sa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
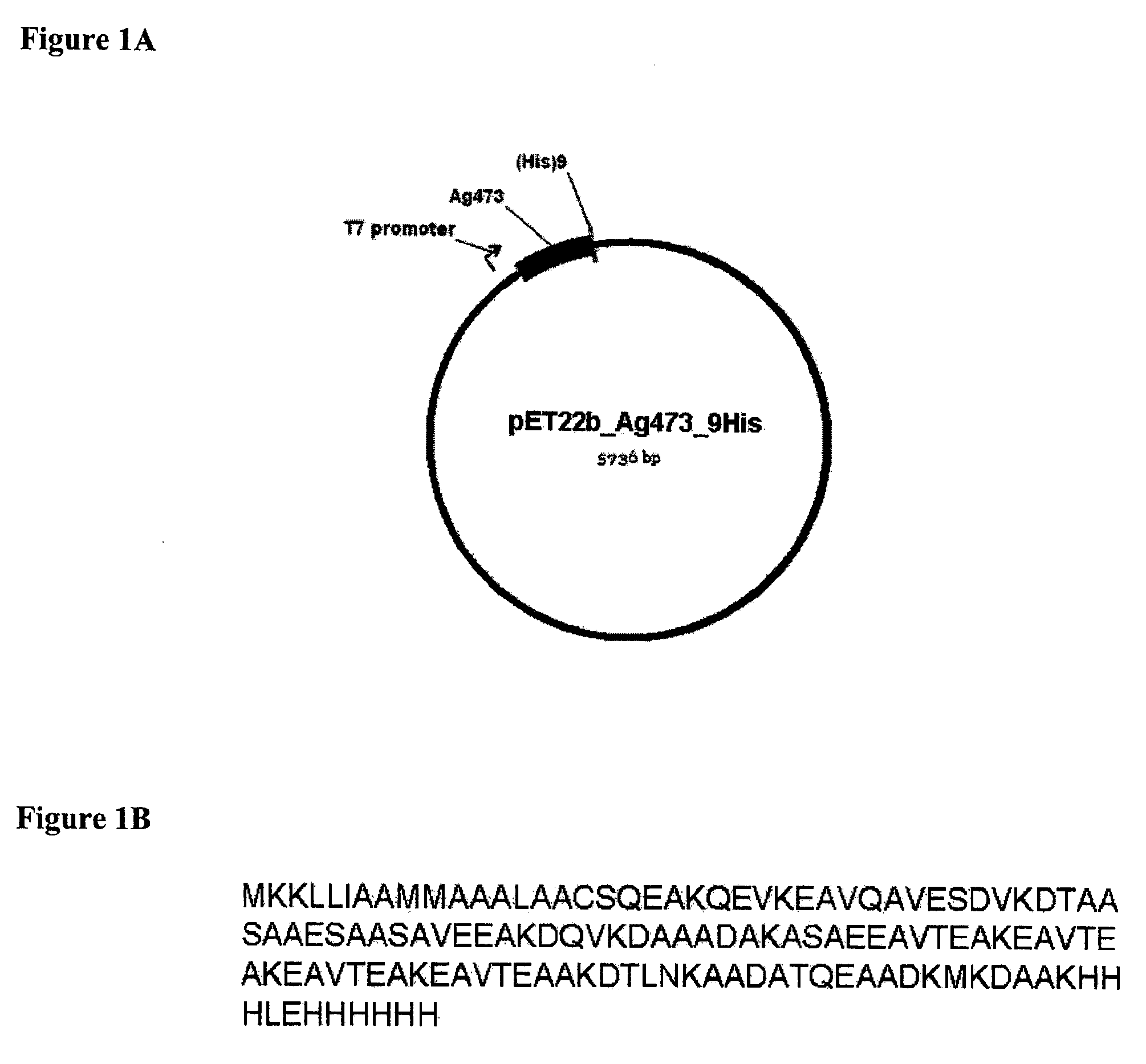
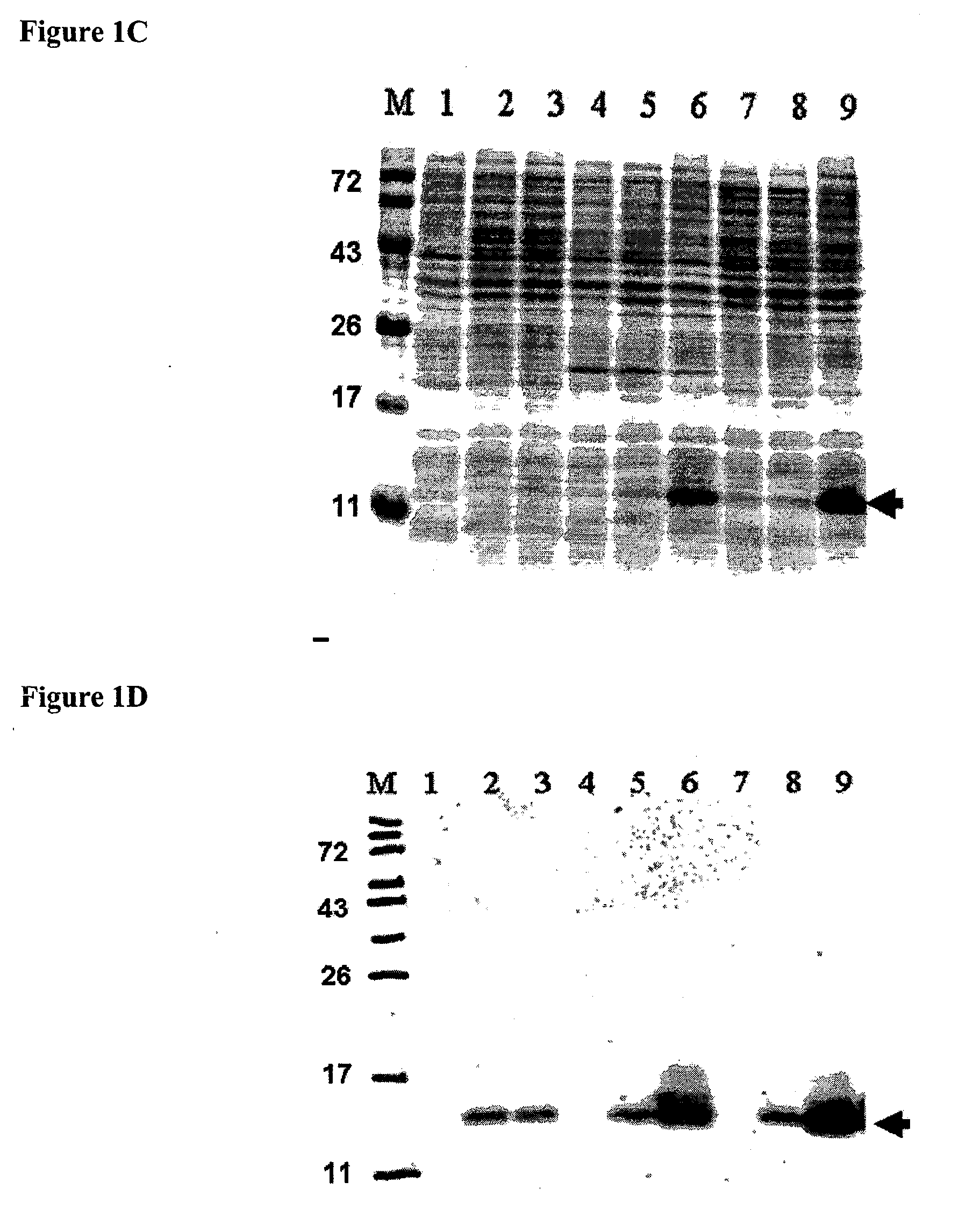
Production of Lipidated Proteins In E. coli
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Novel proteins and methods for producing the proteins
InactiveUS20020051969A1Efficient productionSure easyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsCulture mediums
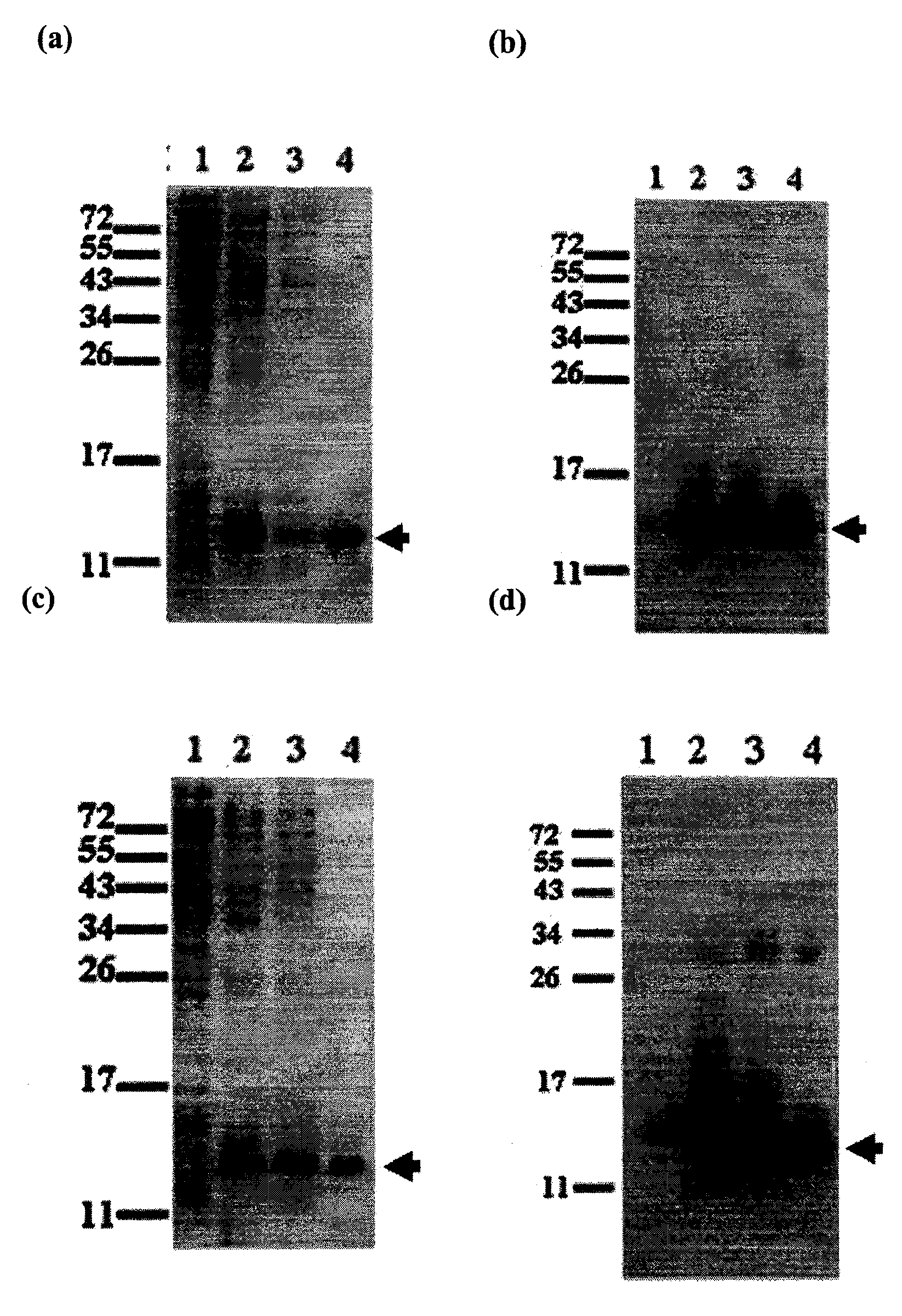
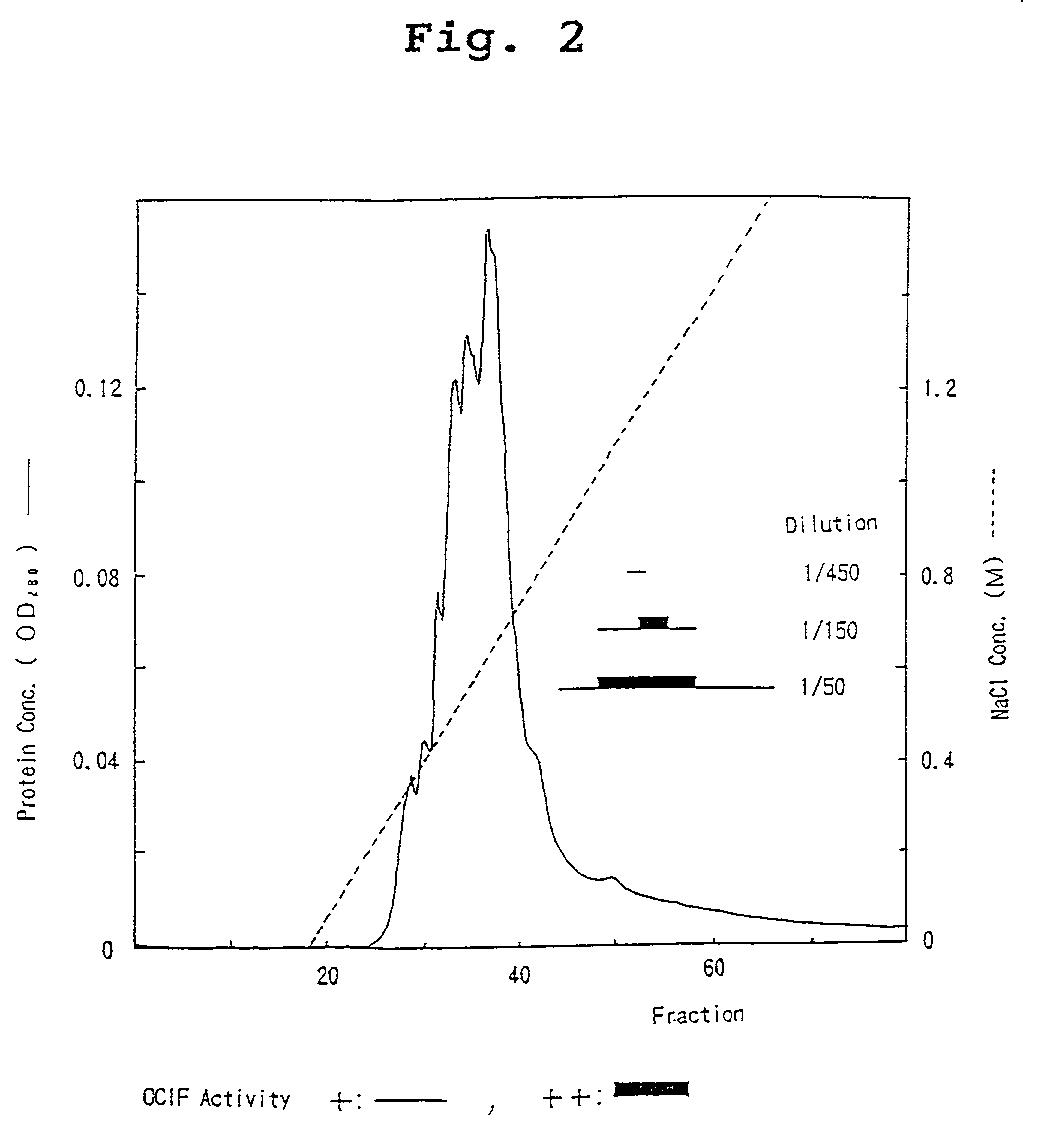
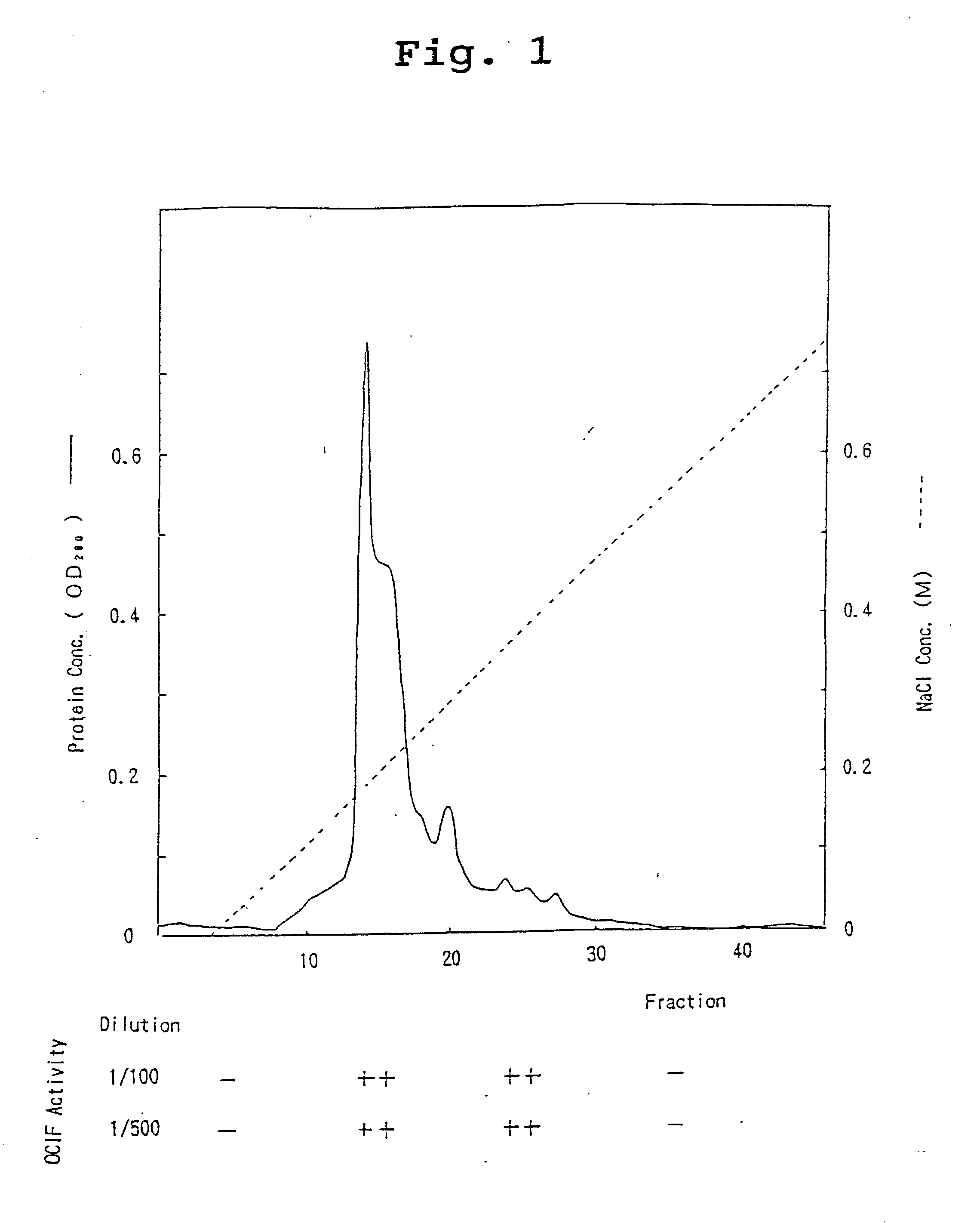
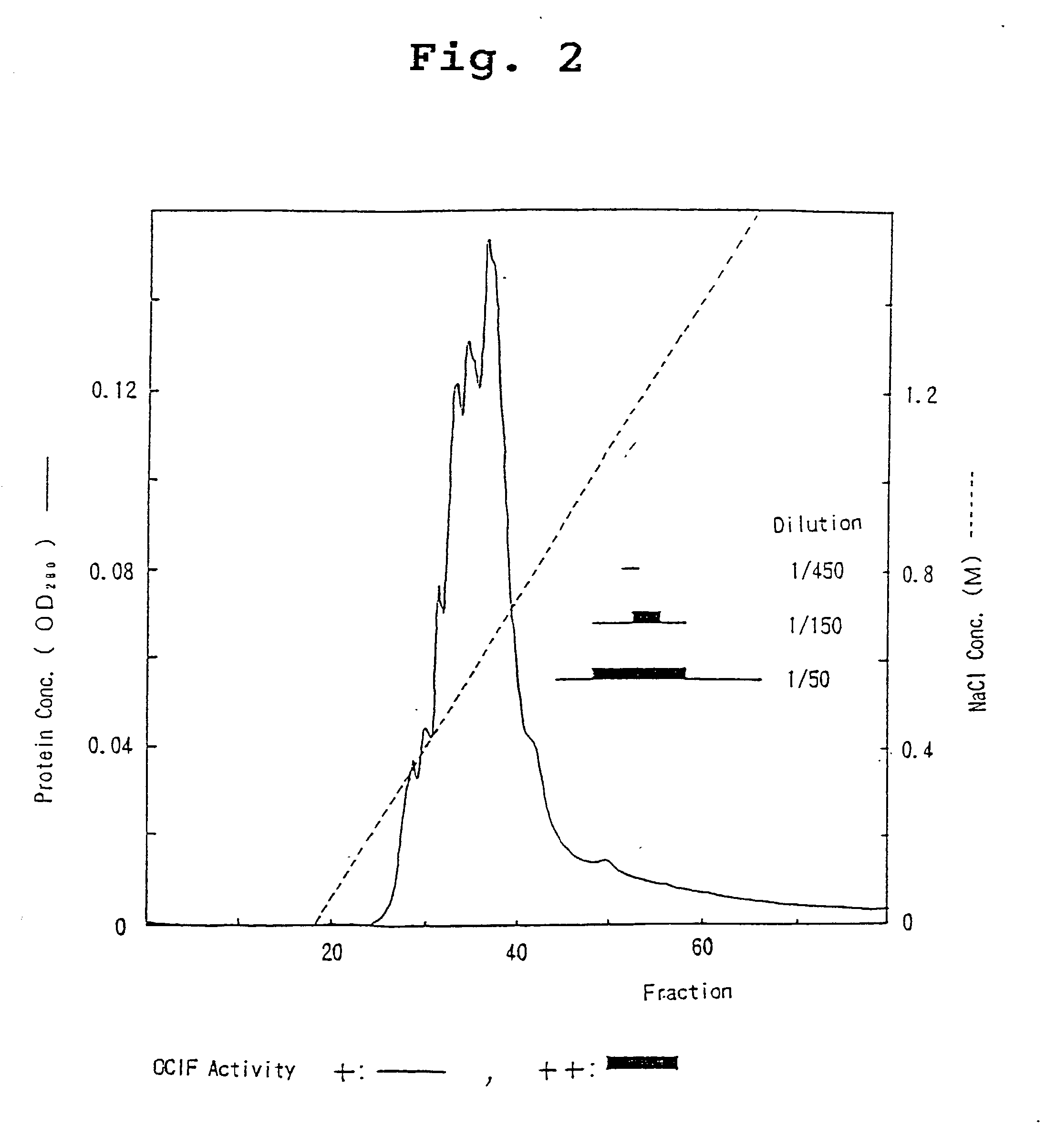
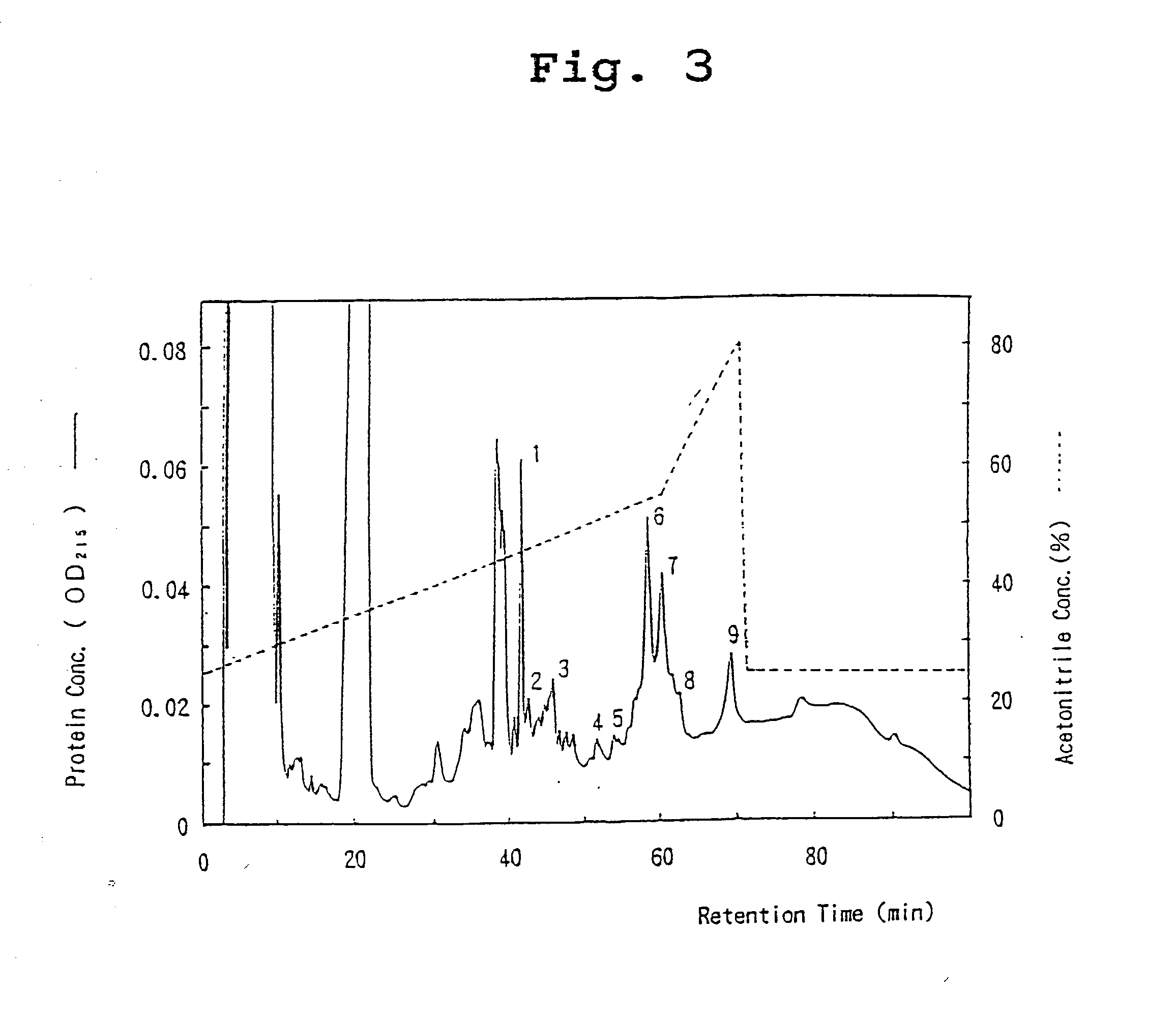
A protein which inhibits osteoclast differentiation and / or maturation and a method of production of the protein. The protein is produced by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and has molecular weight of about 60 kD and about 120 kD under non-reducing conditions and about 60 kD under reducing conditions on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively. The protein can be isolated and purified from culture medium of the said fibroblasts. Furthermore, the protein can be produced by gene engineering. The present invention includes cDNA for producing the protein by gene engineering, antibodies having specific affinity to the protein or a method for determination of the protein concentration using the antibodies.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Protein/Peptide Sequencing By Chemical Degradation in the Gas Phase
ActiveUS20080248585A1The parameters are accurate and reliableHigh performance resultIsotope separationRadio frequency spectrometersGas phaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A fast and sensitive method and device for protein sequencing are disclosed. The method uses a combination of Edman degradation chemistry and mass spectrometry to sequence proteins and polypeptides. A peptide degradation reaction is performed on a polypeptide or protein ion reactant in the gas phase. The reaction yields a first ion product corresponding to a first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant and a polypeptide or protein fragment ion. The mass-to-charge ratio for the first ion product, or the polypeptide or protein fragment ion, or both, is then determined. The first amino acid residue of the polypeptide or protein reactant is then identified from the mass-to-charge ratio so determined.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Screening method for agonists or antagonists of semaphorin 6C by determining the effect of a test compound on the interaction between semaphorin 6C and plexin-A1
The present invention provides screening methods for agonists or antagonists of Sema6C using Plexin-A1, and tools for the screening and the like. It evaluates a case of making a recombinant protein having an extracellular domain of Semaphorin 6C contact a protein having an extracellular domain of Plexin-A1 by comparing it with a case of contacting a recombinant protein and a target substance having an extracellular domain of Semaphorin 6C, or the target substance with a protein having an extracellular domain of Plexin-A1. The evaluation will be carried out by the connectivity of a protein having an extracellular domain of Semaphorin 6C, a growth cone collapse activity of Plexin-A1 expressing cell, or a contractile activity of Plexin-A1 expressing cell.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD +1
Recombinant protein comprising starch binding domain and use thereof
A recombinant protein is prepared comprising a polypeptide of interest and a starch binding domain (SBD). The said SBD is obtainable from glucoamylase of fungi genus Rhizopus. The said recombinant protein comprising the said SBD can be purified by contacting with an affinity matrix such as starch, the SBD binds to the affinity matrix to isolate the recombinant protein. The recombinant protein can be purified by separating the association between the SBD and the affinity matrix by acid, alkaline, salt, or sugar. The polypeptide of interest may be an antibody, an antigen, a therapeutic compound, an enzyme, or a protein and may apply in pathogen destruction, vaccine producing, and oral care product manufacturing. The SBD further provides as a tool to screen or identify polysacchrides.
Owner:SIMPSON BIOTECH CO LTD
Recombinant protein containing a C-terminal fragment of plasmodium MSP-1
The invention relates to a recombinant protein fabricated in a baculovirus system, of which the essential constitutive polypeptide sequence is that of a C-terminal fragment of 19 kilodalton (p19) of the surface protein 1 (protein MSP-1) of the merozoite parasite of the Plasmodium type, particularly Plasmodium falciparum, which is infectious for humans, said C-terminal fragment remaining normally anchored at the surface of the parasite at the end of its penetration phase into human erythrocytes, in the occurrence of an infectious cycle. Said recombinant protein is applicable to the production of vaccines against malaria.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
Recombinant microorganism
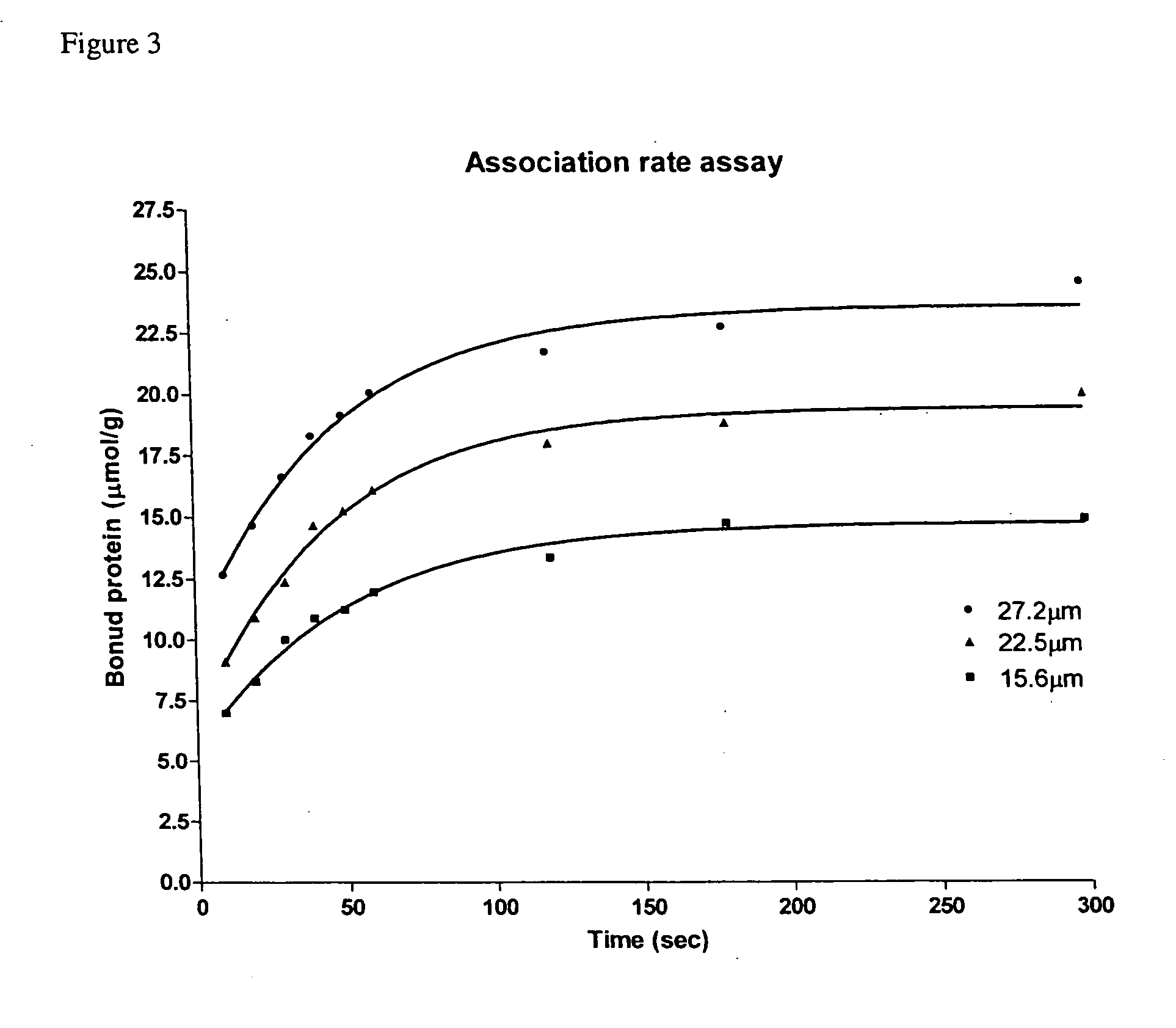
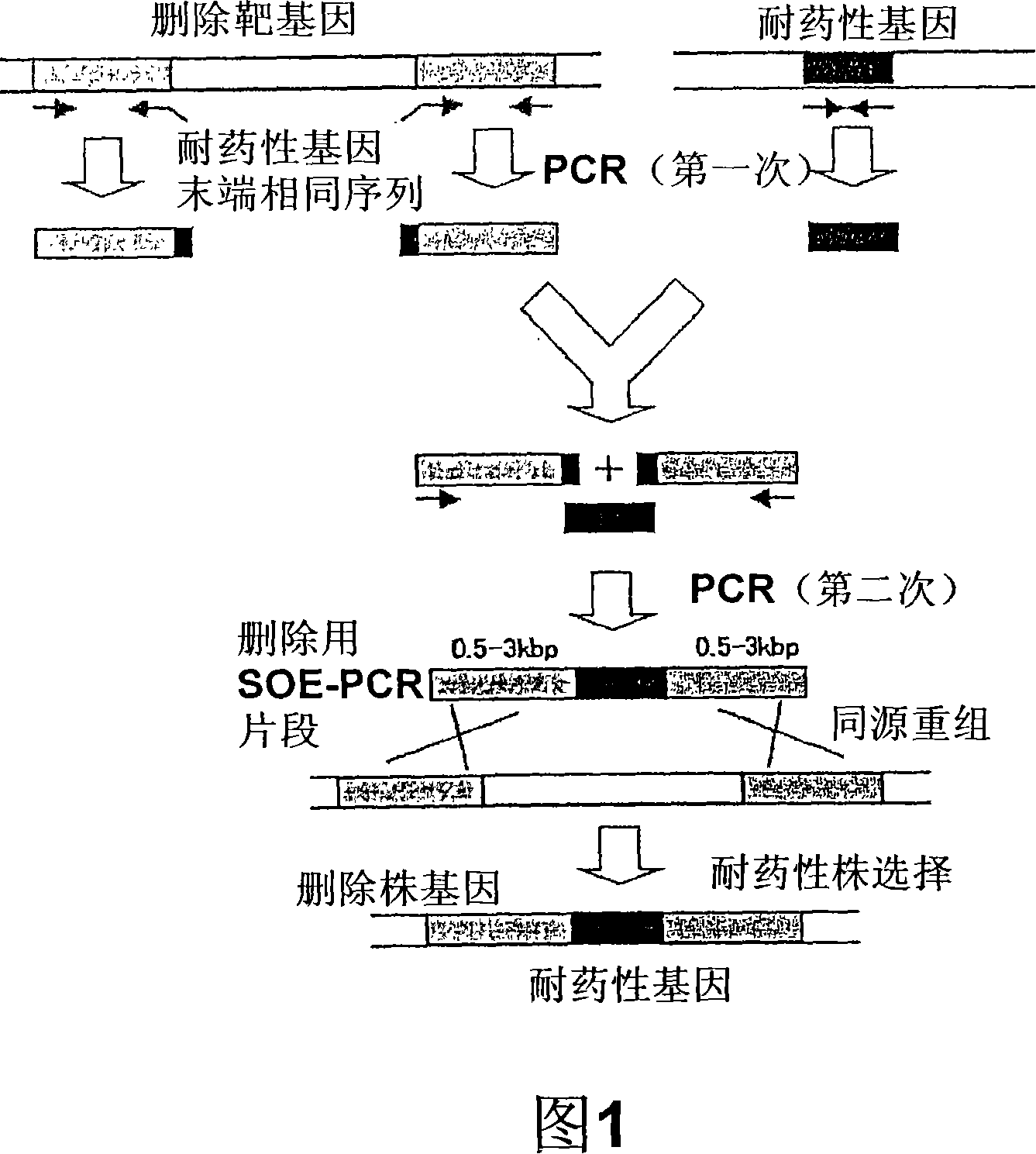
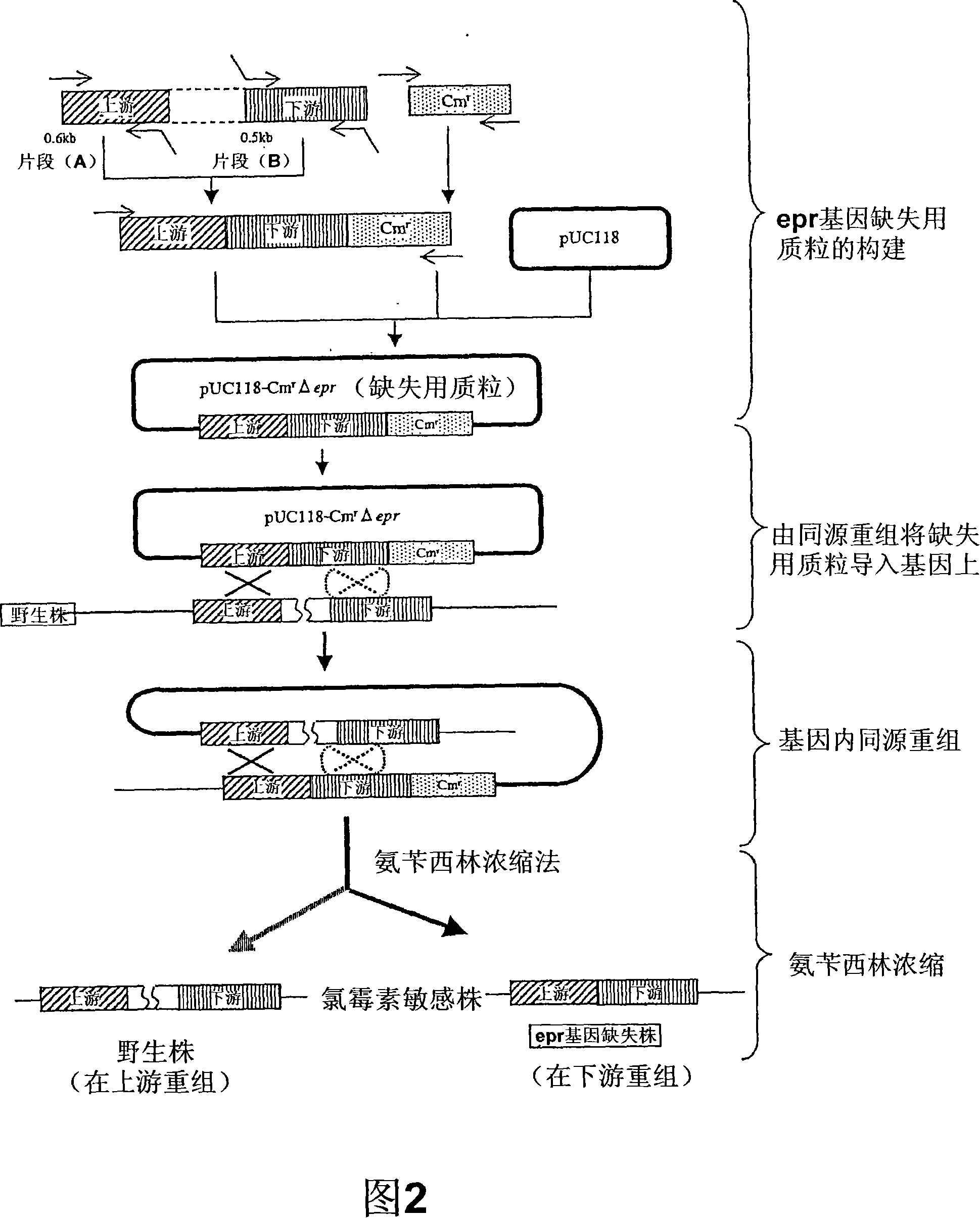
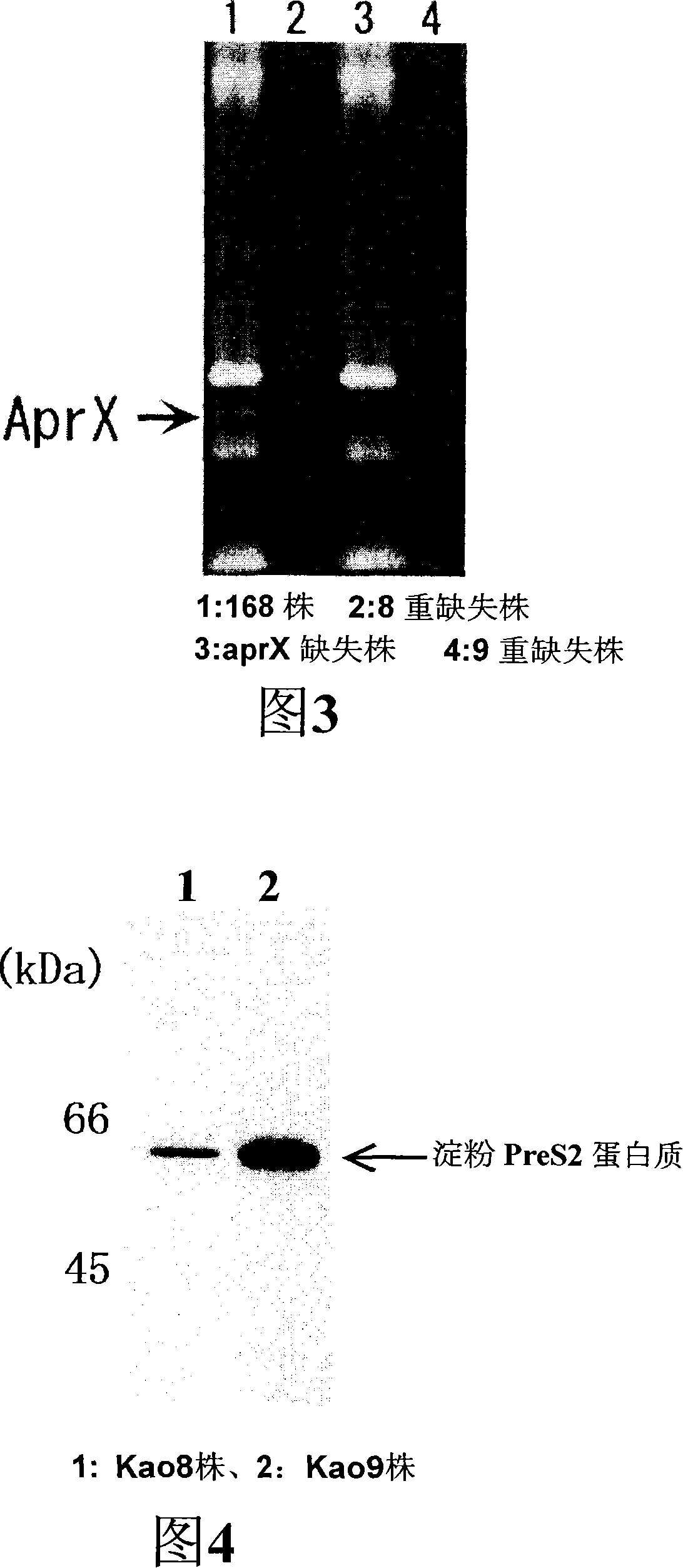
It is intended to provide a host microorganism capable of increasing productivity of a protein or a polypeptide; a recombinant microorganism obtained by introducing a gene encoding a protein or a polypeptide into the host microorganism; and a process for producing a protein or a polypeptide using the recombinant microorganism. The recombinant microorganism is prepared by using a microorganism, in which aprX gene of Bacillus subtilis or a gene corresponding to the gene has been deleted or inactivated, as a host and introducing a gene encoding a heterologous protein or polypeptide into the host. The recombinant microorganism is used in the process for producing a protein or a polypeptide.
Owner:KAO CORP
Novel proteins and methods for producing the proteins
InactiveUS20030153048A1Efficient productionSure easyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsCulture mediums
A protein which inhibits osteoclast differentiation and / or maturation and a method of production of the protein. The protein is produced by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and has molecular weight of about 60 kD and about 120 kD under non-reducing conditions and about 60 kD under reducing conditions on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively. The protein can be isolated and purified from culture medium of the said fibroblasts. Furthermore, the protein can be produced by gene engineering. The present invention includes cDNA for producing the protein by gene engineering, antibodies having specific affinity to the protein or a method for determination of the protein concentration using the antibodies.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
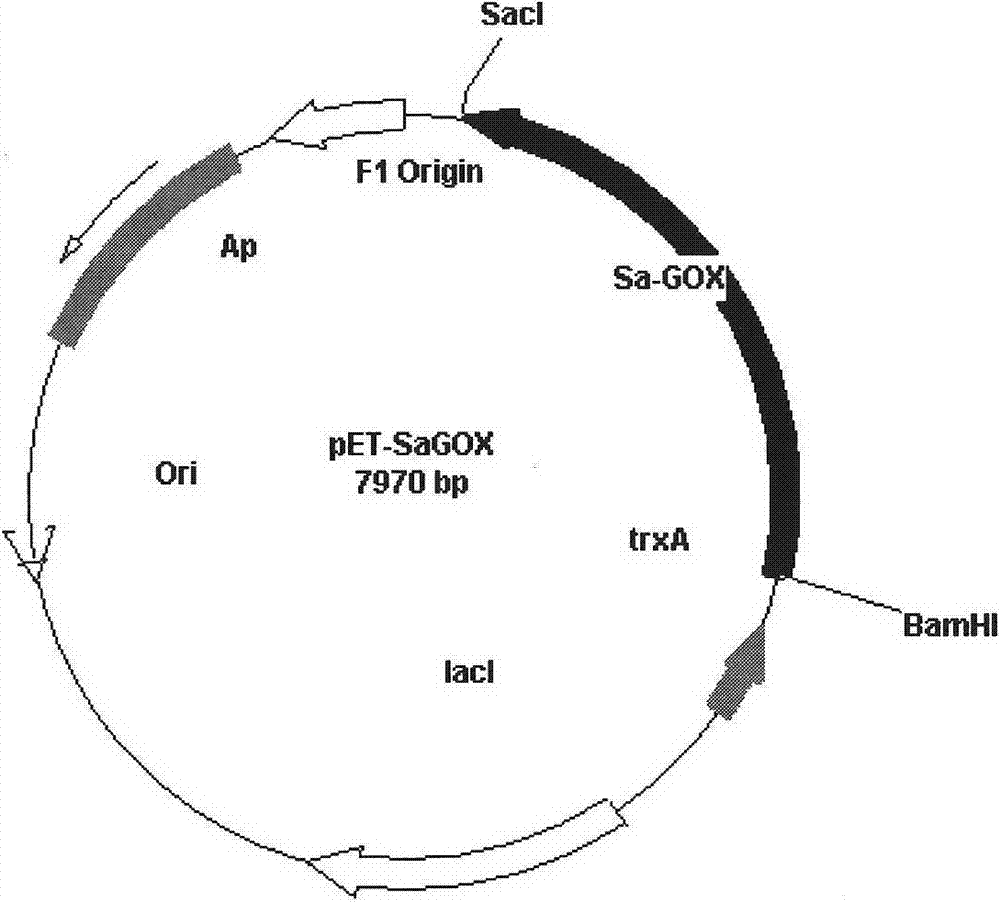
L-glutamate oxidase gene from Afghanistan streptomyces and application thereof
InactiveCN104726472AReduce extraction costsActiveMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliStreptomyces
The invention relates to an L-glutamate oxidase gene from Afghanistan streptomyces and an application thereof and in particular relates to a recombinant bacterium which is obtained by screening Afghanistan streptomyces capable of generating L-glutamate oxidase from soil, cloning and coding the L-glutamate oxidase gene from the bacterium by a homological cloning method and artificially synthesizing the gene and recombining the gene in an escherichia coli and has the activity of L-glutamate oxidase. The nucleotide sequence of the L-glutamate oxidase gene is SEQ ID No 1, the full length of the L-glutamate oxidase gene is 2073bp, and a coding protein sequence of the L-glutamate oxidase gene is SEQ ID No 2. L-glutamate oxidase coded by the gene can be used for specifically catalyzing L-glutamic acid, can serve as an enzyme for detecting the content of L-glutamic acid and is applied to the fields of the food industry and clinical biochemical detection.
Owner:上海瑞丰农业科技有限公司
Increased production of secreted proteins by recombinant eukaryotic cells
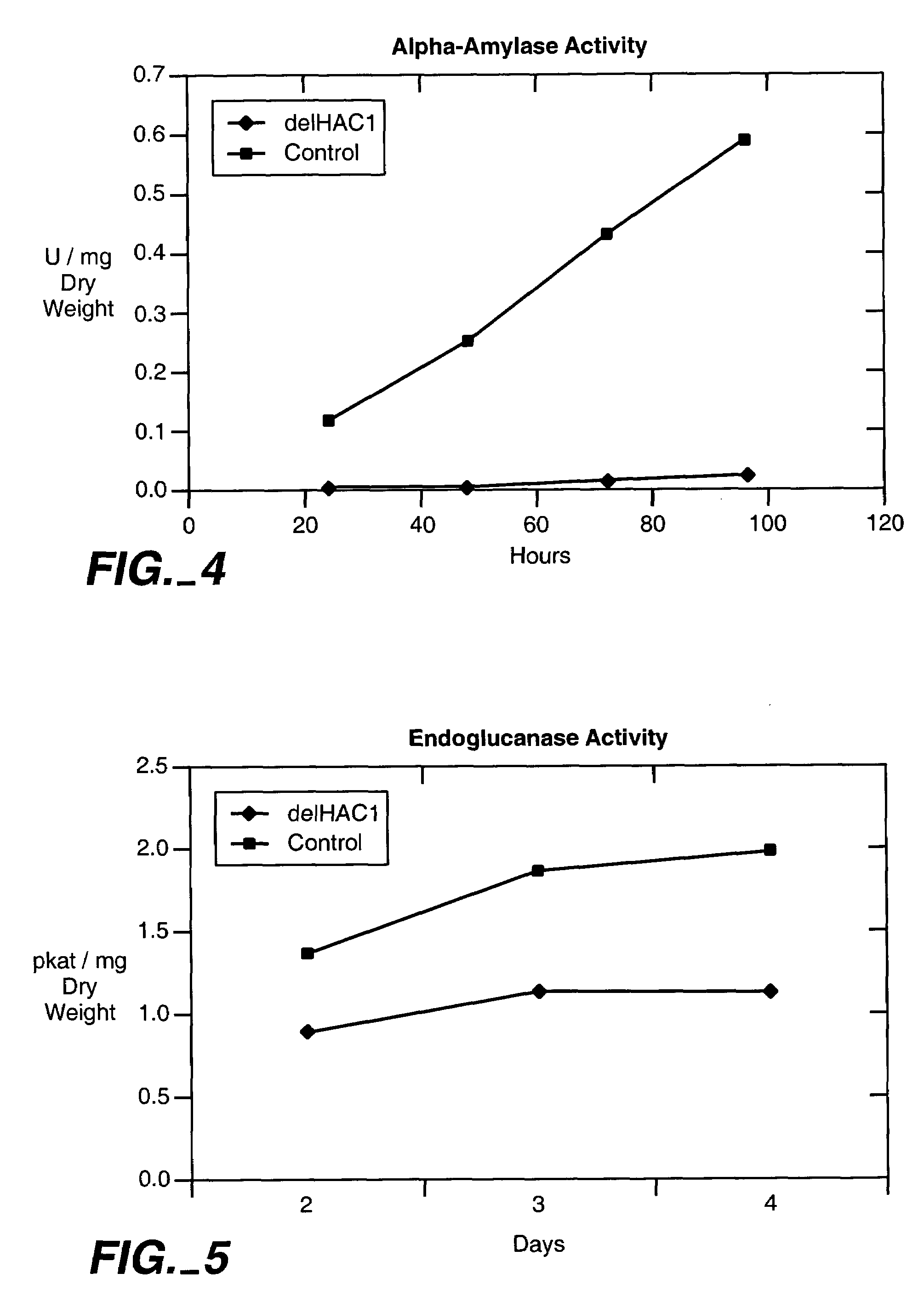
Described herein are methods for increasing the amount of protein secreted by a cell. In one case, a cell is provided which contains a heterologous nucleic acid encoding a protein having unfolded protein response modulating activity and a heterologous nucleic acid encoding a protein of interest to be secreted. In one case, the protein having unfolded protein response modulating activity is selected from the proteins selected from the group consisting of HAC1, PTC2 and IRE1. The protein of interest can be any secreted protein such as a therapeutic or an industrial enzyme. For example the protein can be selected from the group consisting of lipase, cellulase, endo-glucosidase H, protease, carbohydrase, reductase, oxidase, isomerase, transferase, kinase, phosphatase, alpha-amylase, glucoamylase, lignocellulose hemicellulase, pectinase and ligninase.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Malus xiaojinensis Cheng et Jiang MxHA5 protein, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102559631AImprove solubilityIncrease resistance to iron deficiencyFungiBacteriaIonProtein Sa
The invention discloses a malus xiaojinensis Cheng et Jiang MxHA5 protein, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is protein (a) or protein (b), wherein the protein (a) has amino acid sequences shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and the protein (b) has an amino acid residue sequence which is derived from the sequence 1 by substituting and / or losing and / or adding one or more amino acid residues and is related with the P type H<+>-ATPase enzymatic activity in plant. The MxHA5 protein provided by the invention has an important effect of adjusting ion-deficient stressed plant, and the invention further provides good theoretical basis for the research on the ion-deficiency resistance of malus xiaojinensis Cheng et Jiang, and has significance to cultivation of stress-tolerant plant.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
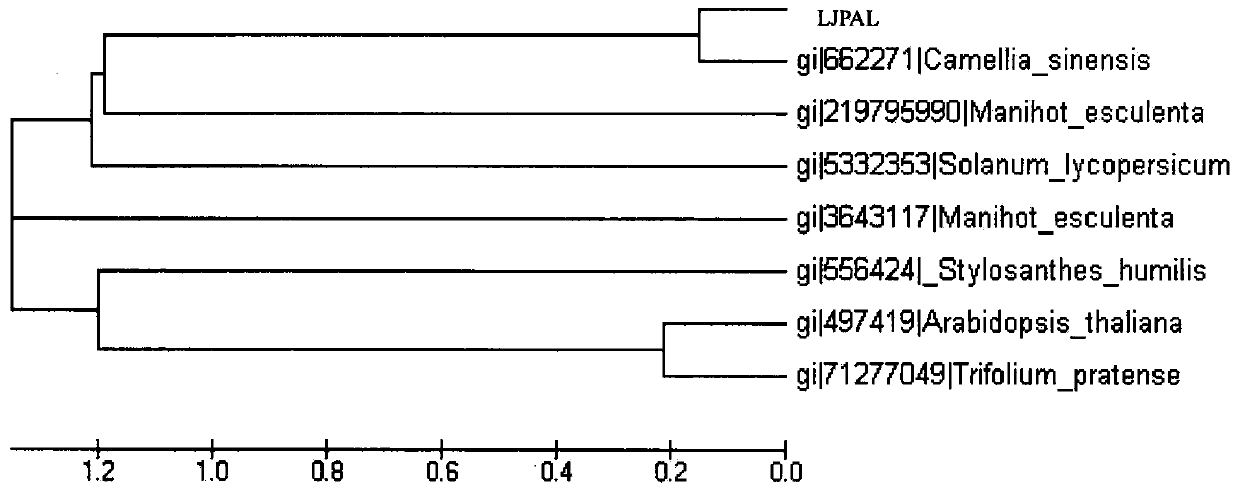
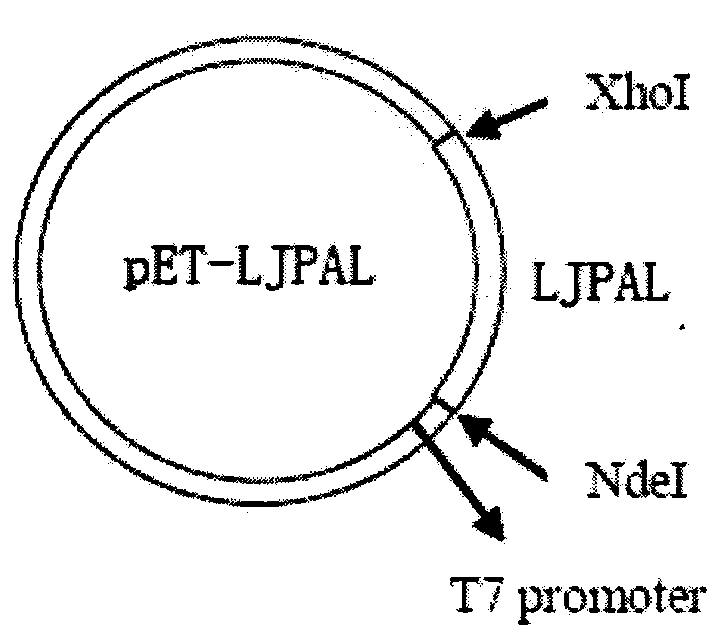
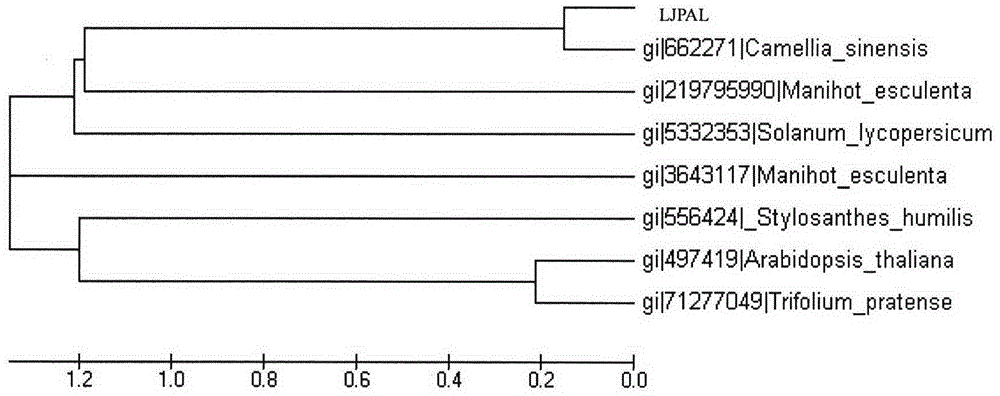
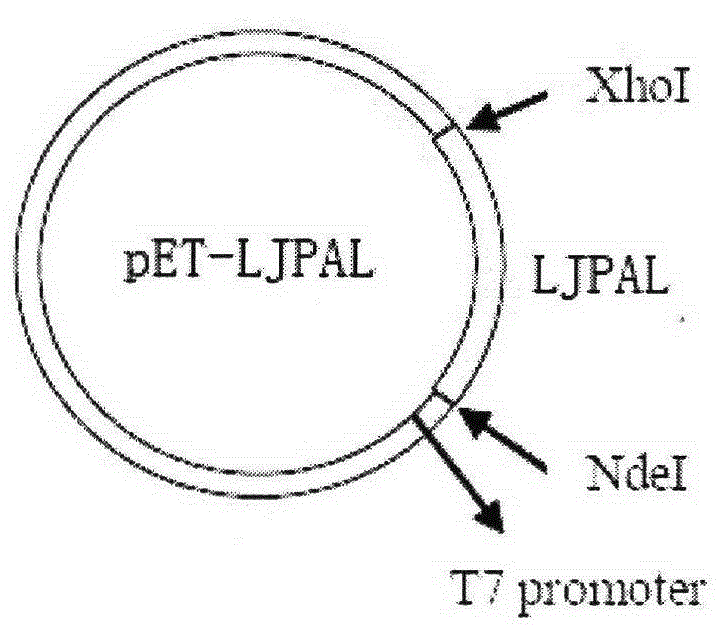
Lonicera japonica thunb phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (LJPAL) gene as well as product coded by same and application of gene
The invention discloses a lonicera japonica thunb phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (LJPAL) gene as well as a protease coded by the same and application of the gene. The LJPAL gene has nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or homologous sequences obtained through addition, substitution, insertion or deletion of one or a plurality of nucleotides or nucleotide sequences derived from alleles of the gene and the gene. A protein coded by the gene has amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or homologous sequences obtained through addition, substitution, insertion or deletion of one or a plurality of amino acids.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Earthnut acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase carboxyltransferase beta subunit gene and encoding protein and cloning method thereof
InactiveCN101550421AFast assemblyHigh oil contentGenetic engineeringFermentationNucleotideProtein Sa
The present invention discloses an earthnut acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase carboxyltransferase beta subunit gene and an encoding protein and a cloning method thereof. The gene sequence is composed of a nucleotide sequence from 92th to 1570th bits of SEQ ID No.1; the protein encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence represented by the SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence table. The nucleotide sequence of the earthnut acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase carboxyltransferase beta subunit (AhCT beta) gene and the encoding protein sequence and the gene cloning method of the invention may be used for improving the earthnut quality and the earthnut cultivation widely, especially a field where the earthnut is used for developing and using oil crops.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
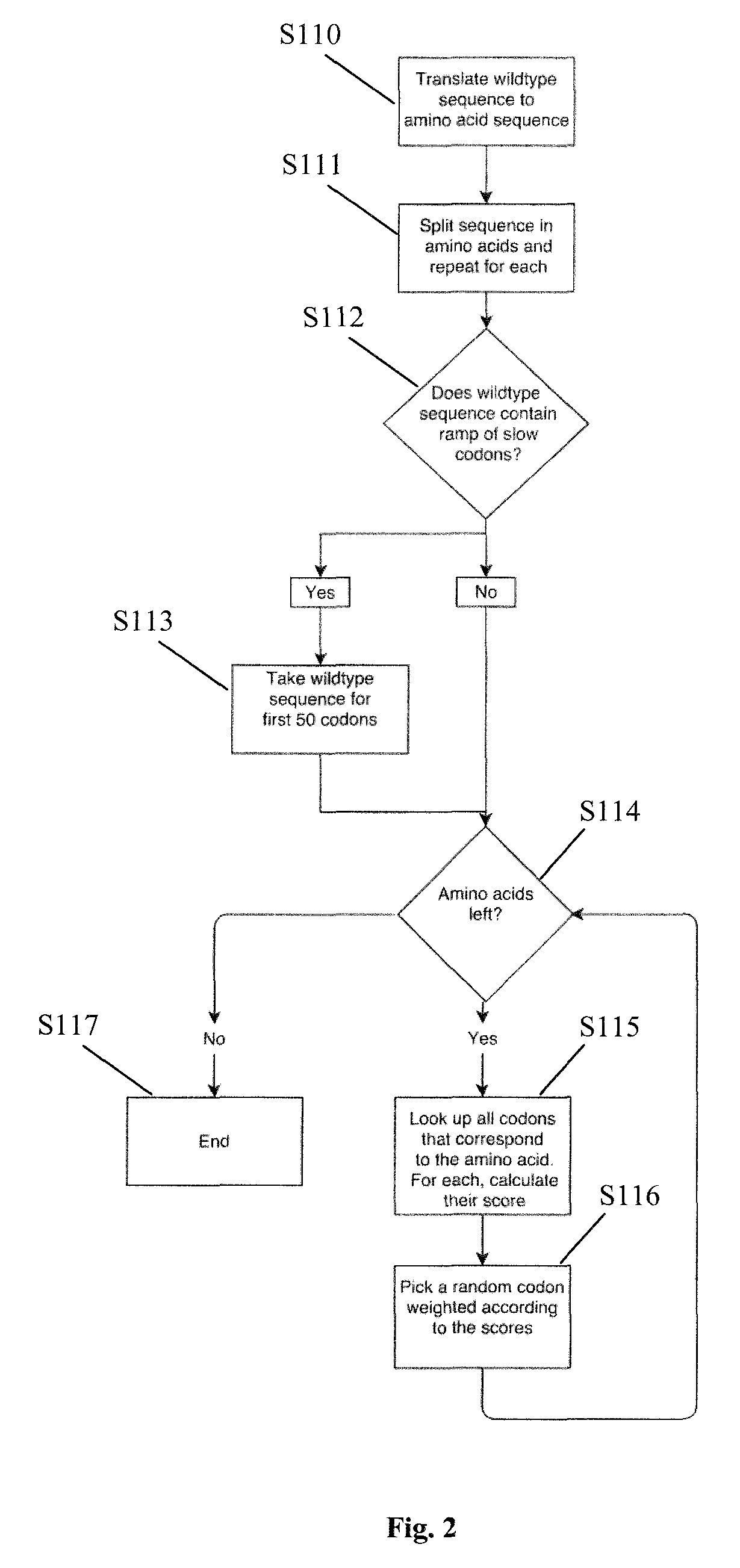
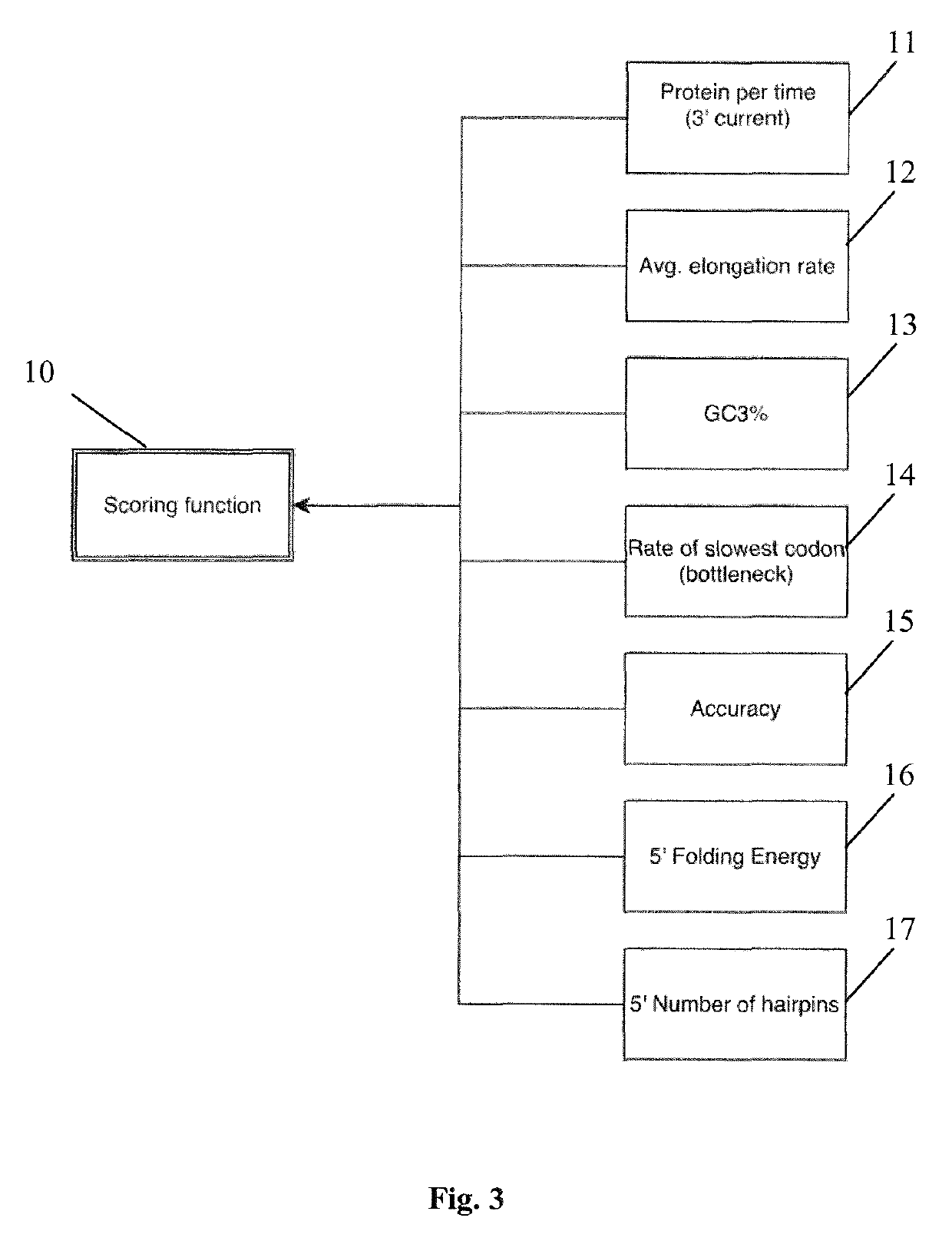
Codon optimization
PendingUS20190325989A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsProtein SaNucleotide sequencing
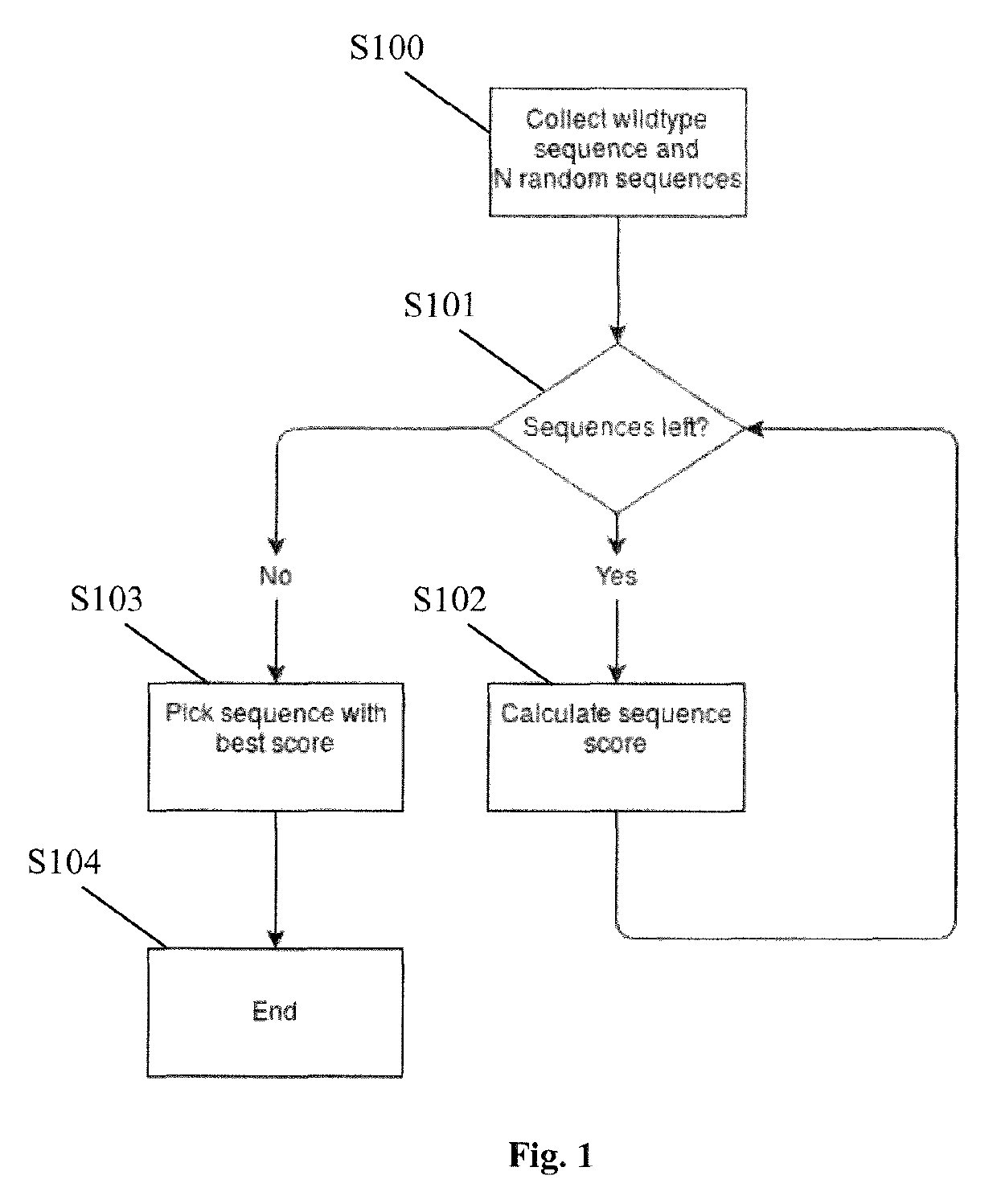
A method for determining an optimized nucleotide sequence encoding a predetermined amino acid sequence, wherein the nucleotide sequence is optimized for expression in a host cell, and wherein the method comprises the steps of: (a) generating a plurality of candidate nucleotide sequences encoding the predetermined amino acid sequence; (b) obtaining a sequence score based on a scoring function based on a plurality of sequence features that influence protein expression in the host cell using a statistical machine learning algorithm, wherein the plurality of sequence features comprises one or more sequence features selected from the group consisting of protein per time, average elongation rate and accuracy for each of the plurality of candidate nucleotide sequences of step (a); and (c) determining the candidate nucleotide sequence with optimized protein expression in the host cell as the optimized nucleotide sequence.
Owner:GOTTFRIED WILHELM LEIBNIZ UNIV HANNOVER
Recombinant microorganism
Owner:KAO CORP
Plant-Based Production of Heterologous Proteins
ActiveUS20120045818A1Low production costImprove energy balanceFermentationGenetic engineeringHeterologousBiotechnology
Described herein are viral amplicon-based protein expression systems and methods useful for producing heterologous proteins, such as enzymes, by agroinfiltration. The methods involve producing an Agrobacterium with a Ti plasmid encoding a heterologous protein, infecting plant cells with the Agrobacterium, allowing expression of the heterologous protein, and recovering the heterologous protein from the plant cells. In one embodiment, the protein produced is an endoglucanase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-expression cellulose endonuclease gene as well as recombinant vector and protein thereof
ActiveCN110592121AImprove biological activityAvoid degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh level expression
The invention relates to a high-vitality cellulose endonuclease artificially synthetic gene shown in a nucleotide sequence in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table or a sequence which has 90% homology or above and coding the same biological functional protein with the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1. The nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table can use pichia pastoris constitutive expression plasma pGAPZaA as a vector and realize high-level recombination expression of target protein in pichia pastoris host bacteria X33. Meanwhile, a screened high-level expression transformant can realize high-level secretion of recombinant protein by use of inorganic salt high-density fermentation, and by simple nickel affinity chromatography purification, a novel recombinant cellulose endonuclease protein pure product with high vitality can be obtained. The recombinant protein has very high capacity for hydrolyzing cellulose substances and producing glucose and has important application value in biological energy source, feed and food industries.
Owner:HUNAN BUTIAN PHARMA
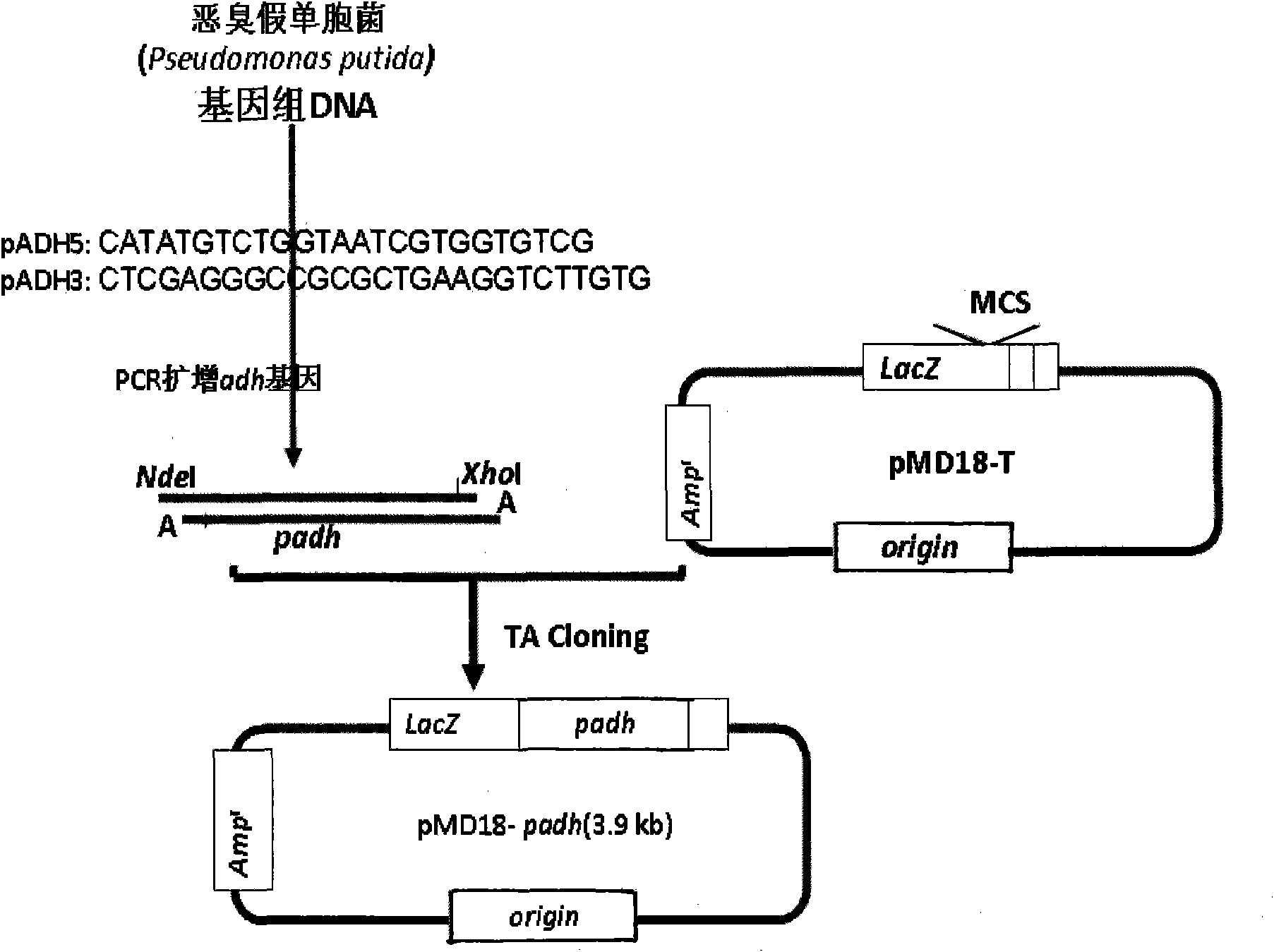
Prokaryotic expression vector of Pseudomonas putida glutathione-independent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a prokaryotic expression vector pET28a-PADH for efficiently expressing Pseudomonas putida glutathione-independent formaldehyde dehydrogenase protein. The vector is a prokaryotic expression vector containing a Pseudomonas putida glutathione-independent formaldehyde dehydrogenase gene (PADH). In the invention, the PADH gene is cloned from Pseudomonas putida, and the expression of the PADH gene in colon bacillus is controlled by using a T7 promoter; 40 percent of expressed recombinant protein exists in a supernate in a soluble mode (accounting for 30 percent of soluble total protein of the colon bacillus), and 60 percent of expressed recombinant protein exists in an inclusion body; the high-purity PADH recombinant protein can be easily obtained from the upper inclusion body through tapping and purification and can be used as an antigen used for preparing a PADH specific antibody. The PADH recombinant protein with activity can be easily purified from the soluble total protein of the colon bacillus by affinity chromatography and is used for the production and the physiological-biochemical characteristic analysis of PADH enzyme preparations.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Beta-1,3 endo-glucanase with immune-enhancing activity andfrom Arca inflata Reeve and coding polynucleotide of beta-1,3 endo-glucanase
The invention relates to endo-glucanase with immune-enhancing activity and nucleotide sequences of genes coding the endo-glucanase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention provides a beta-1,3 endo-glucanase protein sequence and nucleotide sequences of genes of beta-1,3 endo-glucanase. Beta-1,3 endo-glucanase is one of key enzymes in a glucan hydrolytic enzyme system. The beta-1,3 endo-glucanase is from Arca inflata Reeve, 333 amino acids are included, the total length of corresponding coding gene nucleotide is 999 bp, the content of (G+C) is 39.34%, and a novel glucan hydrolytic enzyme resource is achieved. Engineered strains constructed by using the enzyme gene nucleotide can high-efficiently express the beta-1,3 endo-glucanase, a Kd value of the beta-1,3 endo-glucanase is 13.09 muM when laminarin is used as a substrate, produced enzymic preparations can be used for food industry, medicine industry, fodder industry, washing industry and other industries, the problem of recycling of biomass waste being rich in glucan can be solved, and rich glucosyl-oligosaccharides can be obtained to generate considerable economic benefits.
Owner:于荣敏
Modified leukotoxin gene and protein
InactiveUS7304151B2Devoid of toxic activityImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsBacteriaWhite blood cellMANNHEIMIA HAEMOLYTICA
The present invention provides nucleic acid sequences encoding a modified leukotoxin protein, wherein the modification comprises the removal of nucleic acid sequences encoding amino acids within hydrophobic transmembrane domains of full length leukotoxin protein, preferably from Mannheimia haemolytica. The modified leukotoxin proteins are useful in vaccine compositions effective against Mannheimia haemolytica in animals.
Owner:GUELPH UNIV OF
Sperm specific proteins
The present invention relates to sperm specific surface proteins, nucleic acid sequences encoding those proteins and antibodies raised against those proteins. Compositions comprising the sperm specific proteins or inhibitors of said proteins can be used in contraceptive applications.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
UGD gene in kelp, protein thereof and application
ActiveCN107287170AHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideReaction temperature
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, particularly belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and more particularly relates to UGD gene in kelp, protein thereof and application. the UGD gene is from the kelp and is named as SjaUGD gene, and a nucleotide sequence of the SjaUGD gene is a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention further provides GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase which is coded by the SjaUGD gene, an amino acid sequence of GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase is a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:2 while specific activity of the same is 7.99nanokatals.mg-1, and GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase has wider optimum reaction temperature range and higher thermostability. Excellent gene resources and enzyme resources are provided for biological preparation of algin.
Owner:青岛海大蓝科生物科技有限公司
Application of protein AxMan113A as beta-mannase
ActiveCN108220271AImprove acid resistanceImprove heat resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringWAS PROTEINHeat resistance
The invention discloses application of protein AxMan113A as beta-mannase. The protein AxMan113A provided by the invention is protein with an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 2 in a sequence table or protein with an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 4 in the sequence table. Proved by experiments, the protein AxMan113A has the activity of the beta-mannase, so that vegetable gum, such aslocust bean gum and konjac powder, with rich mannan can be hydrolyzed in a high-efficiency manner; meanwhile, the protein AxMan113A has good acid resistance, heat resistance and hydrolysis characteristic, and is obviously different from the existing beta-mannase. The protein AxMan113A and an encoding gene of the protein AxMan113A have important economic value and practical significance in the industries of foods, feed and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Recombinant Microorganism
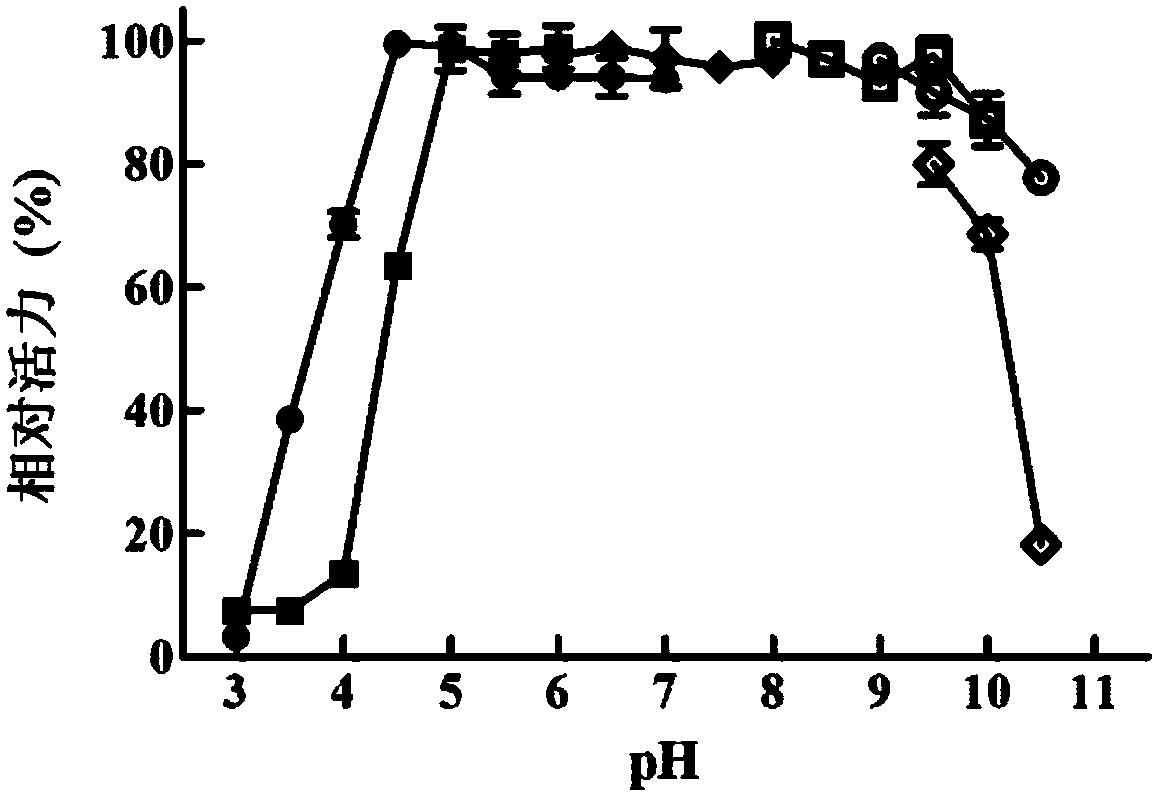
A recombinant microorganism having improved productivity for a protein or a polypeptide, and a method for producing a protein or a polypeptide using the recombinant microorganism, are provided. A recombinant microorganism obtained by transfecting a gene for encoding a desired protein or polypeptide into a microorganism strain which is obtained by genetically constructing to overexpress secY gene of Bacillus subtilis or a gene corresponding to the secY gene, and deleting or inactivating one or more genes selected from sporulation-associated genes and genes corresponding to the sporulation-associated genes from the genome.
Owner:KAO CORP
Dermatophagoides farina allergen Der f9 gene coded protein and application thereof
The invention discloses dermatophagoides farina allergen Der f9 gene recombinant protein and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is shown in SEQ ID No:2. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the recombinant protein. The dermatophagoides farina allergen Der f9 gene recombinant protein and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages that a dermatophagoides farina allergen Der f9 full-length gene sequence is obtained, the recombinant protein is prepared according to the gene sequence, and the coded recombinant protein is high in purity, good in specificity and high in yield. The dermatophagoides farina allergen Der f9 gene recombinant protein can be applied to diagnosing whether a patient suffers from allergic diseases caused by a dermatophagoides farina allergen ninth component.
Owner:崔玉宝
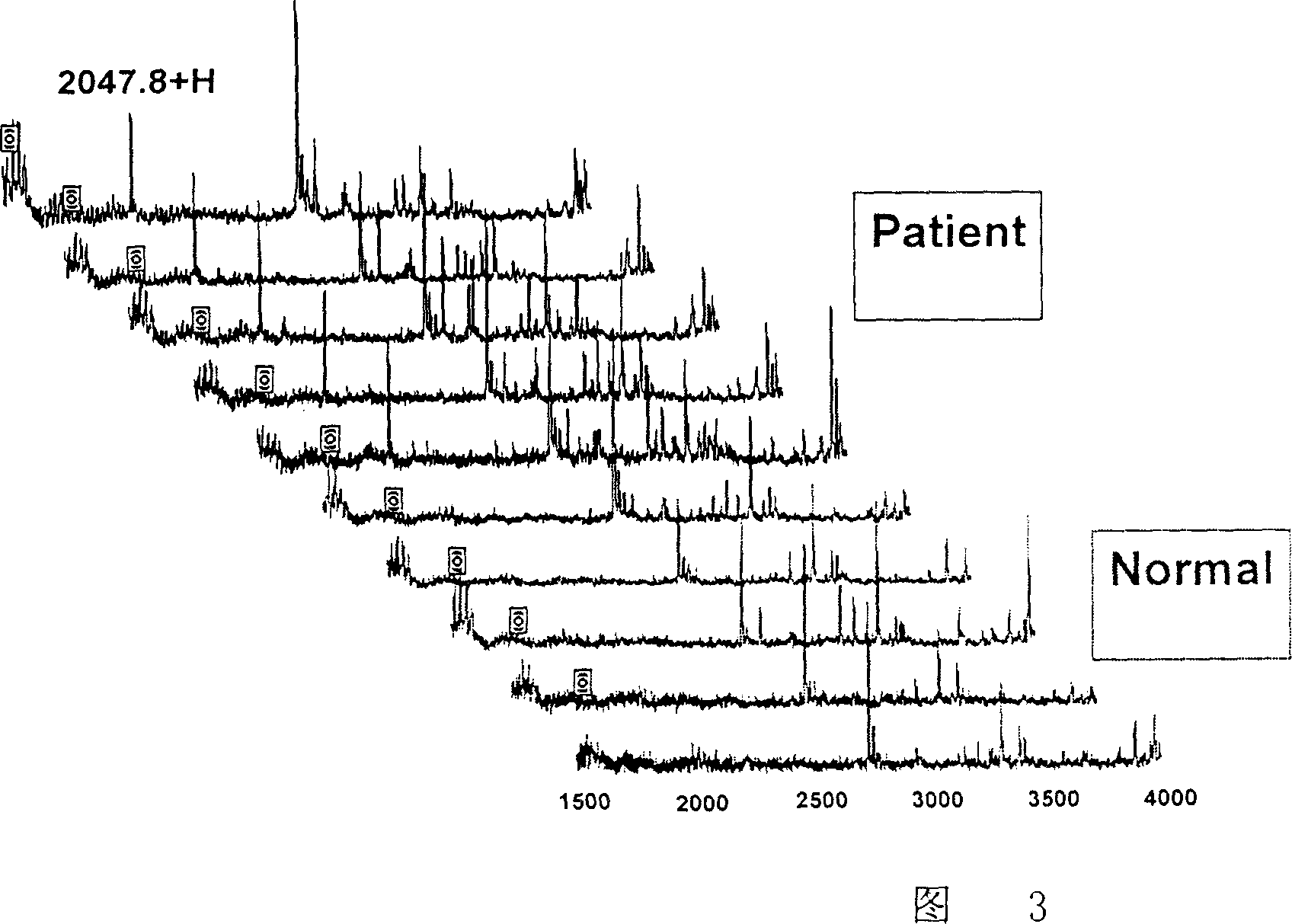
New method for detecting esophageal cancer haemocyanin fingerprint
InactiveCN1310033CHigh sensitivityImprove throughputComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh risk populationsProtein composition
The present invention relates to one method of detecting serum protein fingerprint of esophagus cancer. The serum protein fingerprint is obtained through collecting human serum, combining human serum with weak cationic affinity protein chip, reading serum protein map in mass spectrograph and analyzing the map data with protein fingerprint analyzing software. The serum protein fingerprint of esophagus cancer consists of 12 proteins with different mass-to-charge ratios. The serum protein fingerprint of esophagus cancer the present invention provides may be used in the early detection of esophagus cancer and has sensitivity and specificity over 80 %.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Antibody like protein
A general method and recombinant nucleic acid sequences, by means which the method selects a recombinant protein containing an FHA domain for binding a target molecule from a library proteins with a high-throughput method of creating protein variations within the FHA domain in non-conserved or non-structural sequences of the FHA scaffold, and the library may also be in the form of a phagemid or phage library wherein the ALP nucleic acid sequence is inserted into a vector capable of allowing the vector and expressed ALP protein from being virally packaged, and the recombinant nucleic acid sequences which are randomly mutated at varying non-conserved or non-structural FHA domain sequences.
Owner:IDEA ORCHARD LLC
Lonicera japonica thunb phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (LJPAL) gene as well as product coded by same and application of gene
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
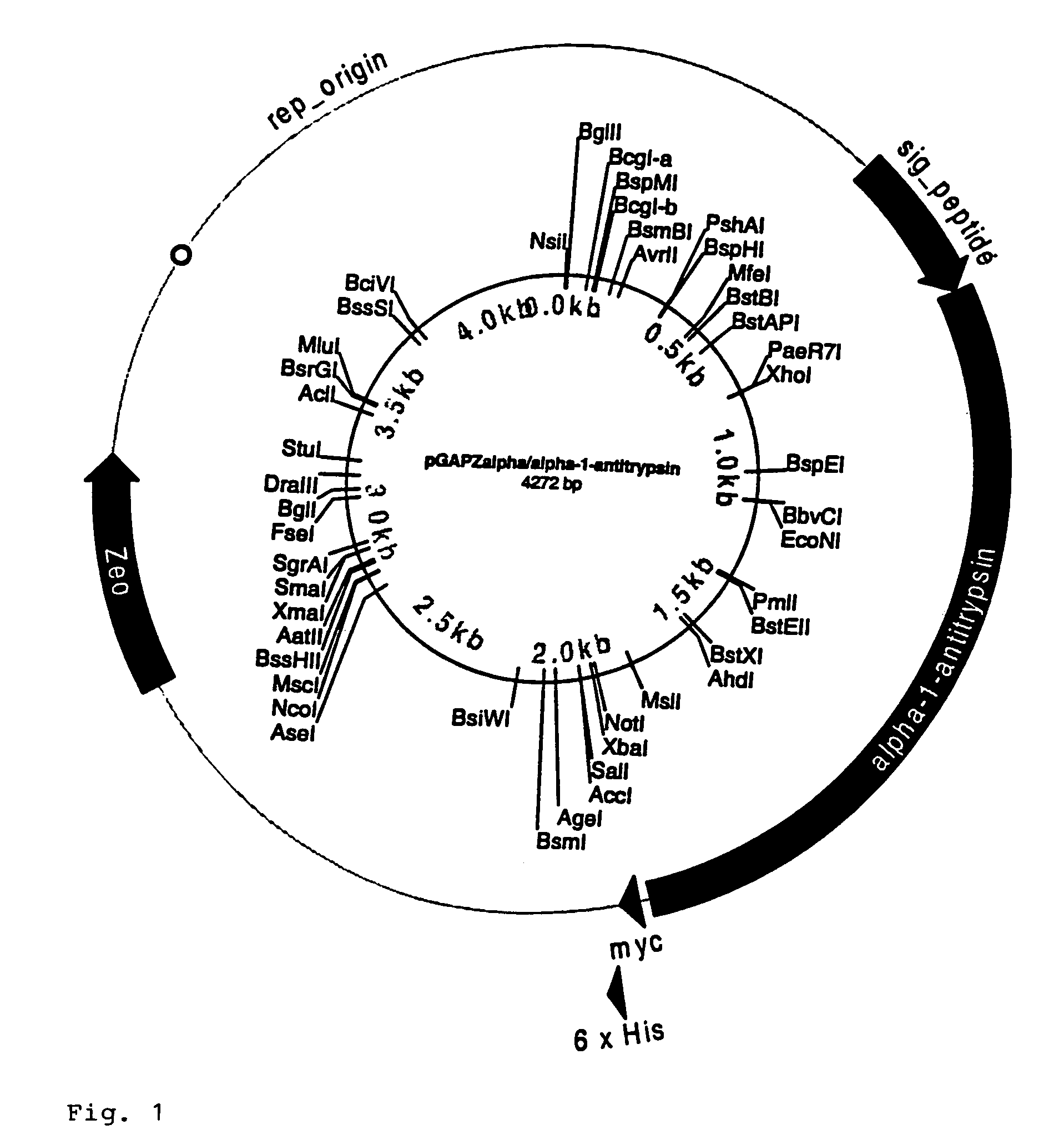
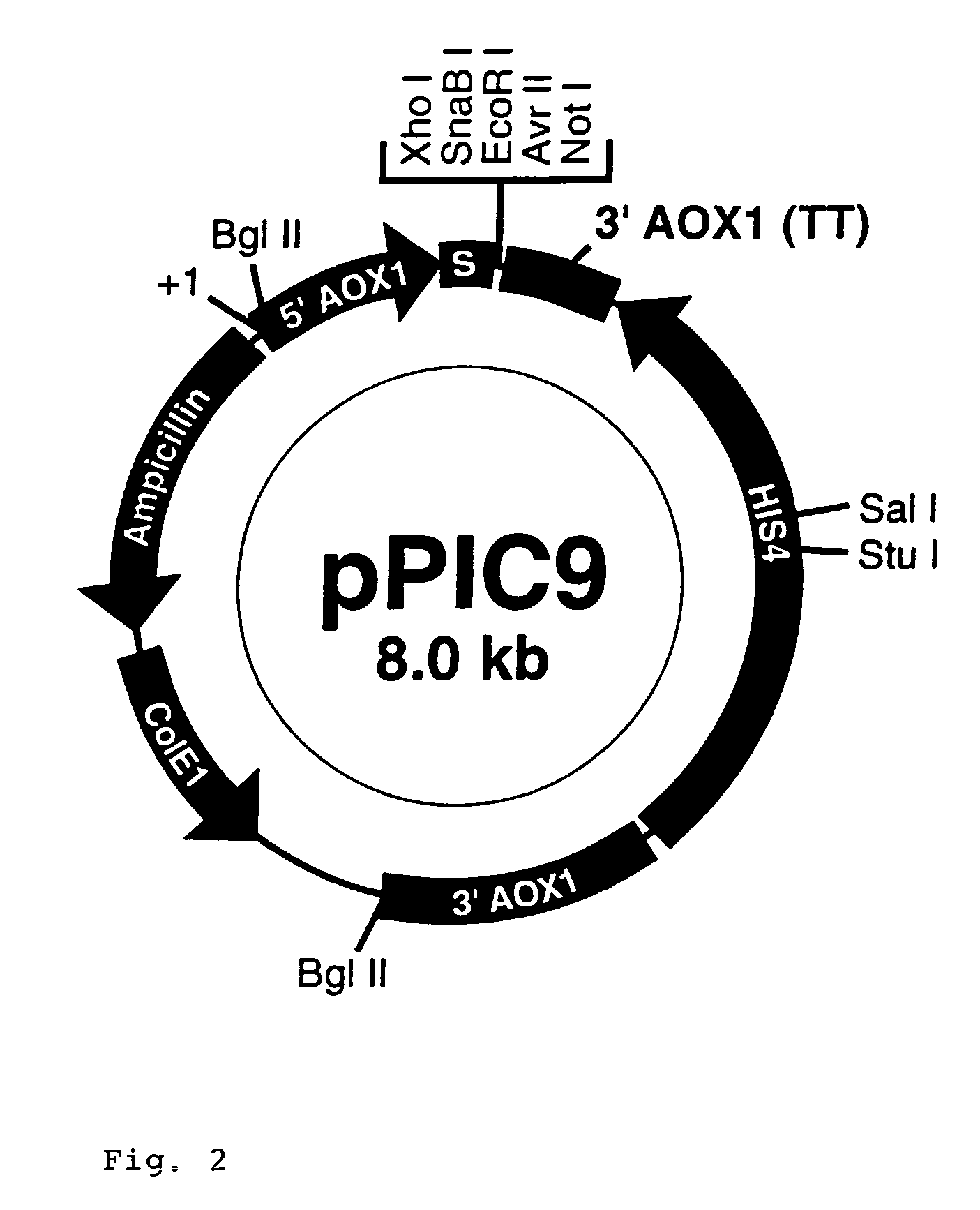
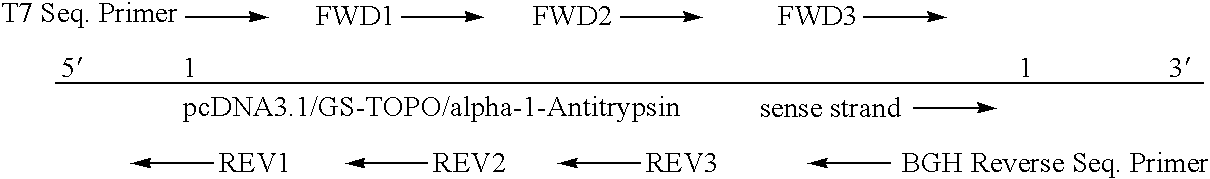
DNA for expression of alpha 1-antitrypsin in methylotropic yeast
InactiveUS7270979B1No loss in AAT productivityStably integratePeptidesRecombinant DNA-technologyDNA constructRecombinant zymomonas
Alpha 1-antitrypsin is prepared by growing in a fermentor methylotropic yeast transformants containing in their genome at least one copy of DNA encoding alpha 1-antitrypsin, in operational linkage with DNA encoding a signal sequence, which is effective for directing secretion of proteins from the host cells, DNA constructs and recombinant yeast strains used for the expression and secretion of alpha 1-antritrypsin are also provided. The fermentation medium requires a pH of 6.5 to 7.5. The fermentation is at a pH between 5 and 6.8.
Owner:PROTEASE PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com