Prokaryotic expression vector of Pseudomonas putida glutathione-independent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and construction method and application thereof
A Pseudomonas putida, prokaryotic expression technology, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, can solve problems that have not been reported yet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: Preparation and detection of Pseudomonas putida genomic DNA:
[0042] The Pseudomonas putida used in the present invention was purchased from China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Center, and the genome DNA of Pseudomonas putida was prepared by using a common bacterial genome extraction method. Centrifuge 2 mL of the overnight culture at 4000 rpm for 2 min at 4°C, discard the supernatant, and collect the cells; add 100 µl of Solution I; 30 µl of 10% SDS, 1 µl of 20 mg / mL proteinase K, mix well, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour; Add 100 μl 5mol / L NaCl, mix well; add 20 μl CTAB / NaCl solution (CTAB 10%, NaCl0.7mol / L), mix well, 65°C, 10 minutes; add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixture ( Phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) and mix well; centrifuge at 12000rpm for 5 minutes; take the supernatant, add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol, 0.1 times the volume of 3mol / LNaOAC, and place it at -20°C for 30 minutes; cent...
Embodiment 2
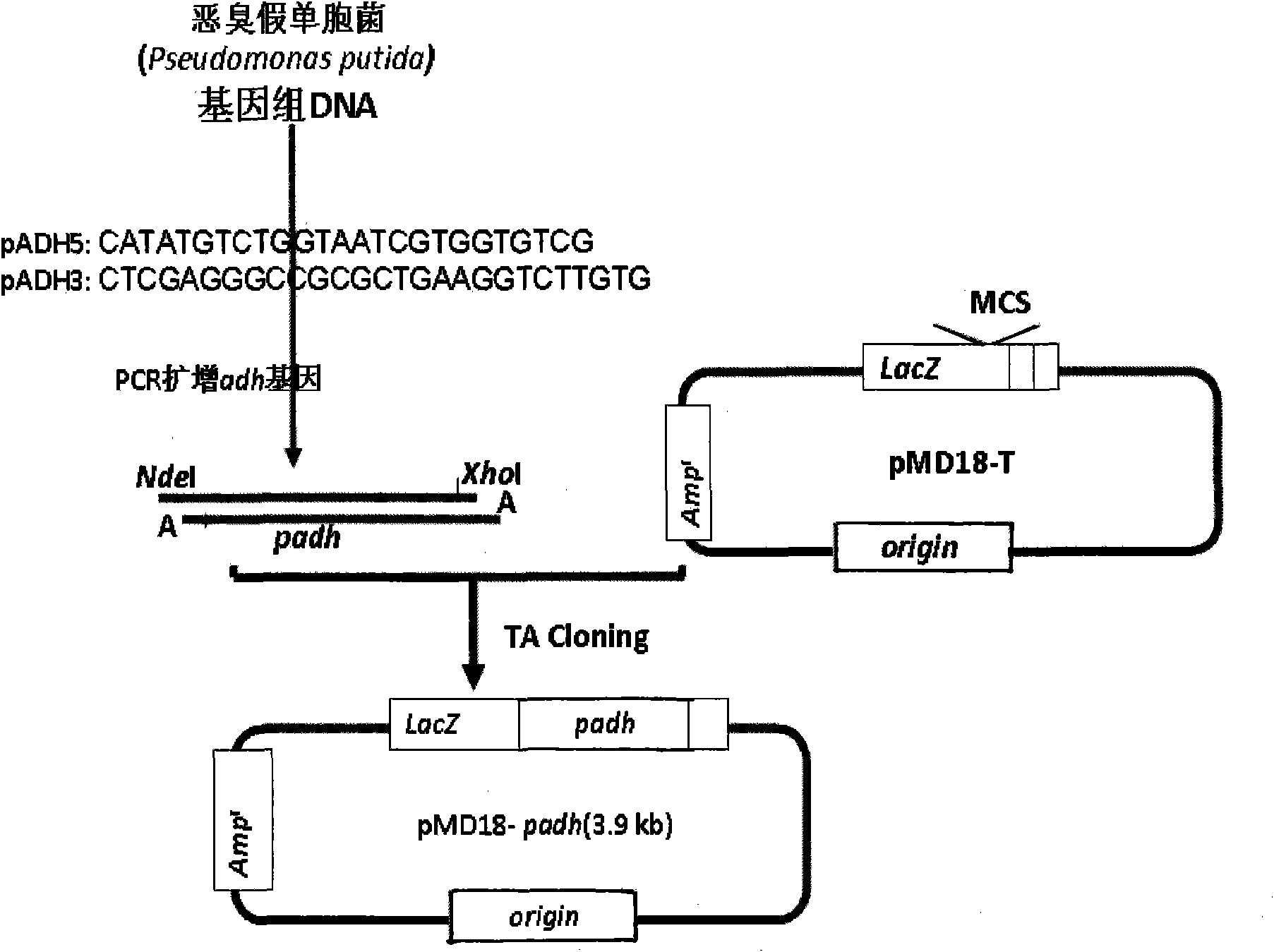
[0043] Embodiment 2: Amplification and TA cloning of PADH gene:
[0044] ADH gene amplification and TA cloning strategies such as figure 2 As shown, firstly search the full-length gene sequence of PADH from GenBank (the GenBank accession number of ADH gene is D21201), and design a pair of primers, the sequence is as follows:
[0045] PADH5: CATATGTCTGGTAATCGTGGTGTCG
[0046] PADH3: CTCGAGGGCCGCGCTGAAGGTCTTGTG
[0047] The 5' end primer has a CATATG characteristic sequence, which forms an Nde I restriction site; the 3' primer end adds a CTCGAG characteristic sequence to the 3' end, thereby forming an Xho I restriction site.
[0048] Add 10ng of Pseudomonas putida genomic DNA as a template in the PCR reaction mixture, add 50ng of specific primers PADH5 and PADH3, 1.8 μl of NTP (10mM), 12.5 μl of 2×GCBuffer I and 0.4 μl of Taq plus ( 2.5U / μl) polymerase (Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.), and double distilled water was added to make the final reaction volume 20 μl. H...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: Construction of prokaryotic expression vector pET28a-PADH:
[0050] The construction strategy of pET28a-PADH is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the purified prokaryotic expression plasmid vectors pET28a (purchased from Novagen) and pMD18-PADH were cut with NdeI (Fermentas) and XhoI (Fermentas), and the cut vectors and inserts were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The vector fragment pET28a (5.3kb) generated after pET28a was cut and the DNA fragment (1.2kb) of the PADH gene generated by cutting pMD18-PADH were recovered from the gel, and then the pET28a vector was ligated with the ligase kit of TaKaRa Fragmentation and DNA fragmentation of the PADH gene to generate the prokaryotic expression vector pET28a-PADH. Use the ligation reaction mixture to transform high-efficiency (108) Escherichia coli competent cells (DH5α, Tiangen Biochemical Technology), and spread the transformed Escherichia coli on a plate added with kanamycin (Km, 50 μg / ml), Cultiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com