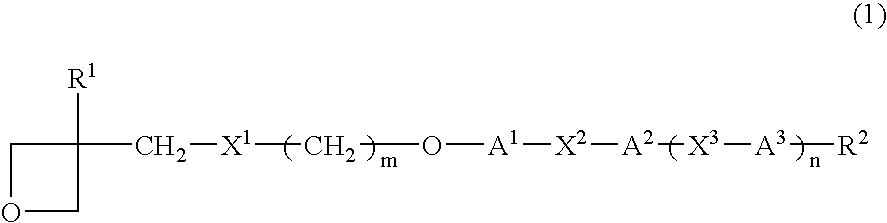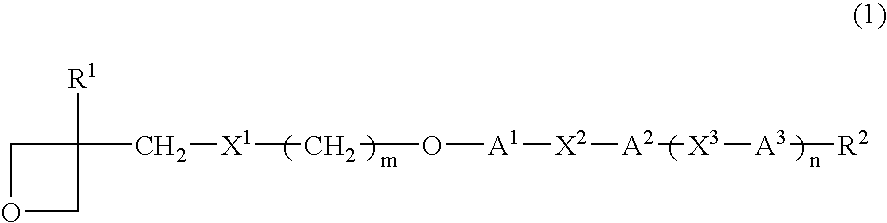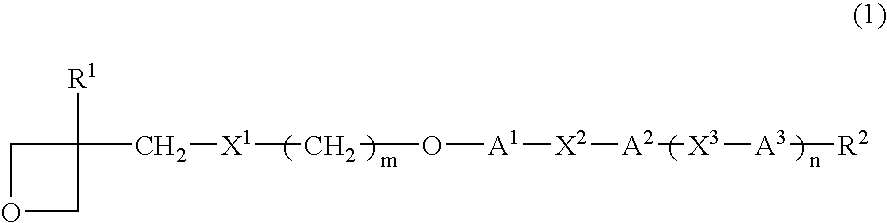Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Oxepane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxepane is a heterocyclic chemical compound with the formula C₆H₁₂O. Oxepane can be polymerized by cationic initiators such as (C₂H₅)₃OSbCl₆ to form a crystalline solid with a melting point around 56–58 °C.
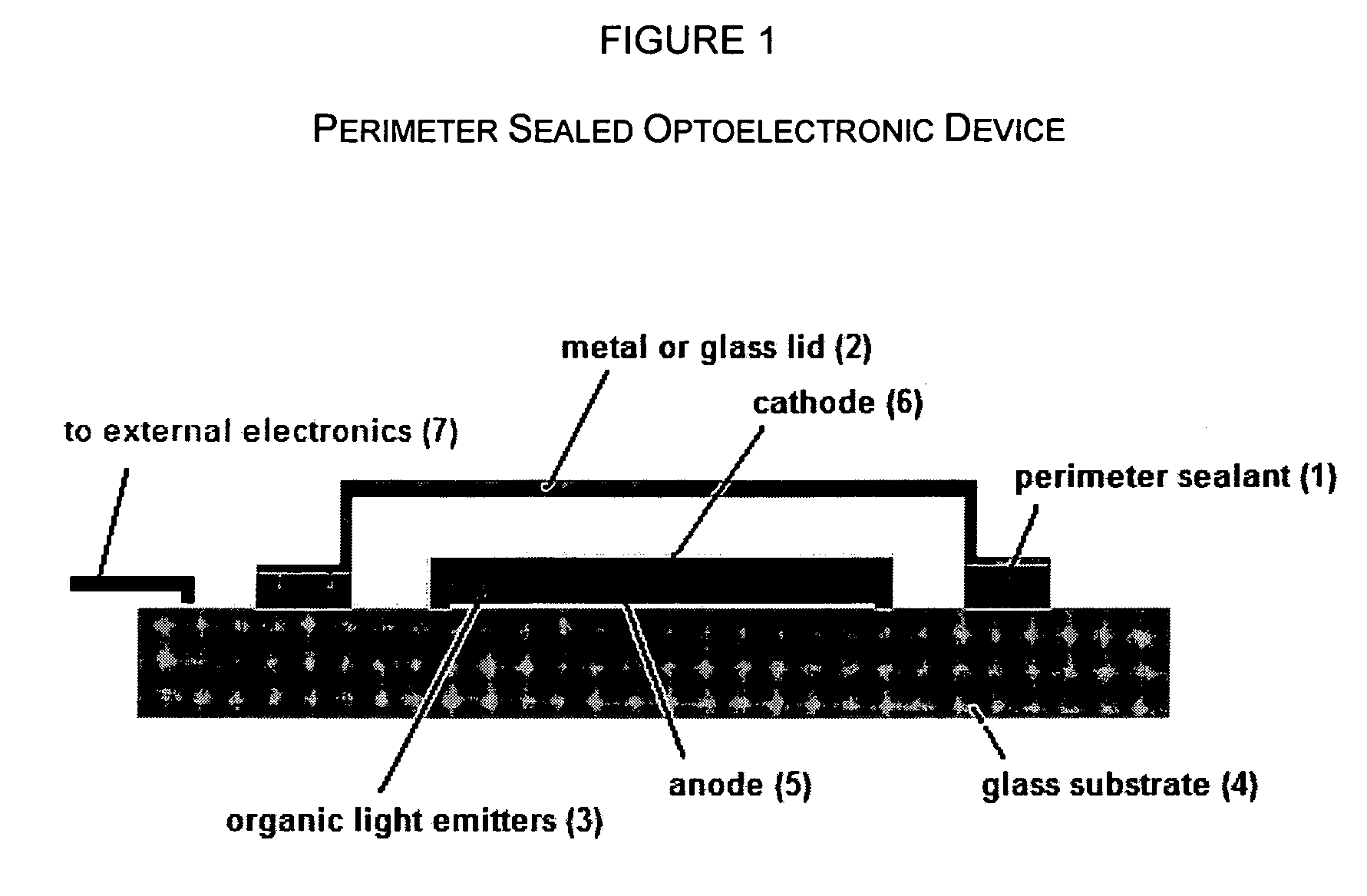
Ink composition, inkjet-recording method and printed material
InactiveUS20060222832A1Measurement apparatus componentsDecorative surface effectsOxepanePolymerization
An ink composition including a cationically polymerizable compound having a styryl or α-methylstyryl group such as 4-methylstyrene and a photocationic polymerization initiator. the ink composition preferably further includes another cationically polymerizable compound having at least one group selected from oxirane and oxetane groups.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
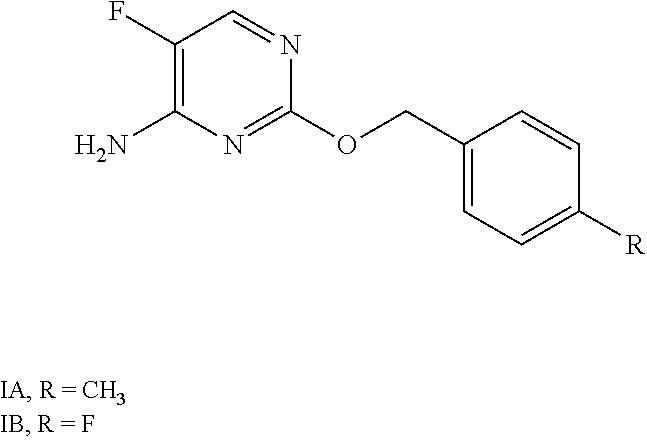
Synergistic fungicidal compositions containing a 5-fluoropyrimidine derivative for fungal control in cereals
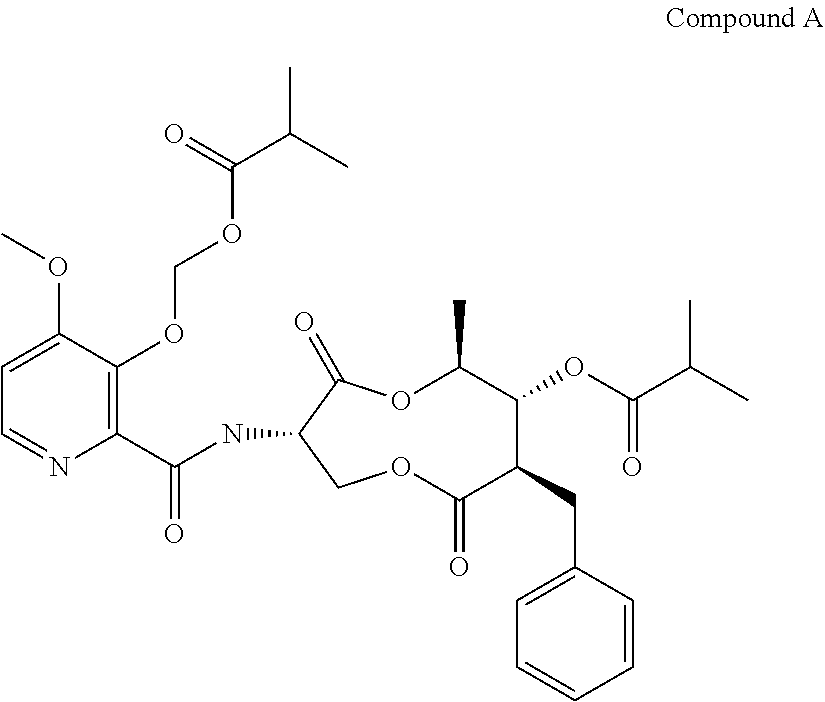
A fungicidal composition containing a fungicidally effective amount of a) a compound of Formula IA and / or IB and (b) at least one fungicide selected from the group consisting of epoxiconazole, prothioconazole, azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, penthiopyrad, isopyrazam, bixafen, boscalid, prochloraz, chlorothalanil, isobutyric acid (3S,6S,7R,8R)-8-benzyl-3-[(3-isobutyryloxymethoxy-4-methoxypyridine-2-carbonyl)-amino]-6-methyl-4,9-dioxo-[1,5]dioxonan-7-yl ester, and (5,8-difluoroquinazolin-4-yl)-{2-[2-fluoro-4-(4-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yloxy)-phenyl]-ethyl}-amine provides synergistic control of selected fungi.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
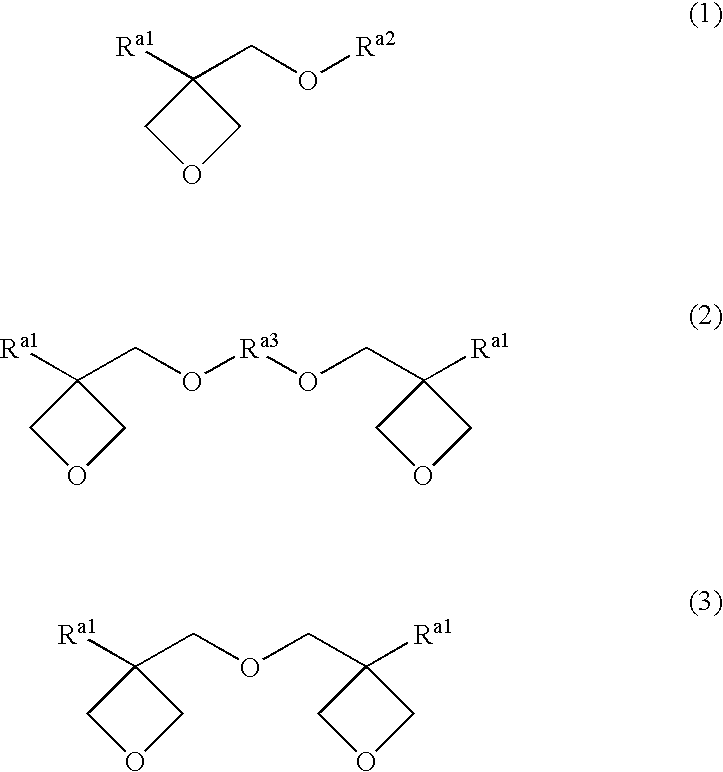
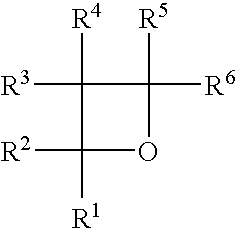
Photopolymerizable oxetane derivative and liquid-crystal composition containing it
InactiveUS20050224757A1High sensitivityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsHydrogenPolymer science
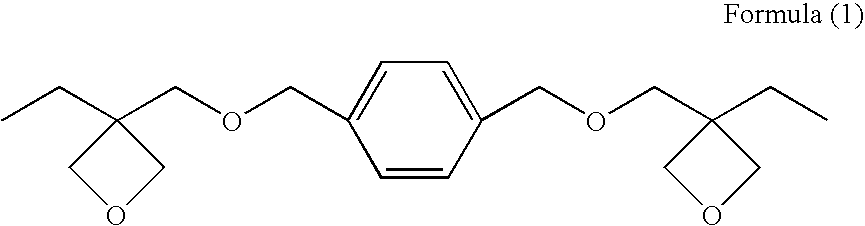
Provided are a liquid-crystal compound and a liquid-crystal composition containing the compound, of which the advantages are that they show nematic hybrid orientation on a rubbed TAC substrate, they are polymerizable in open air and they readily give a polymer having a high degree of polymerization even when exposed to a relatively small total quantity of light. The films formed by photopolymerizing them keep nematic hybrid orientation. The compound is represented by formula (1): wherein R1 is a hydrogen or an alkyl; R2 is a hydrogen, —OCF3, etc.; A1 is a 1,4-phenylene, etc.; A2 and A3 are independently a 1,4-cyclohexylene, a 1,4-phenylene, etc.; X1 is a single bond, —O—, etc.; X2 and X3 are independently a single bond, —COO—, —C≡C—, —CONH—, etc.; m is an integer of from 0 to 20; and n is 1 or 0.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM CORP +1
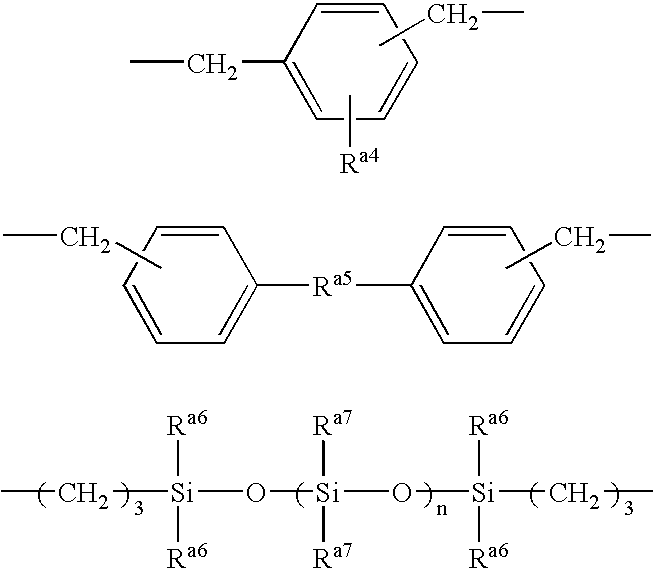
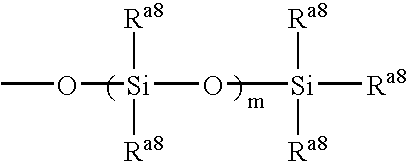
Methods, compositions, and biomimetic catalysts for the synthesis of silica, polysilsequioxanes, polysiloxanes, non-silicon metalloid-oxygen networks, polymetallo-oxanes, and their organic or hydrido conjugates and derivatives
InactiveUS20050090634A1SilicaOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer networkNanostructure
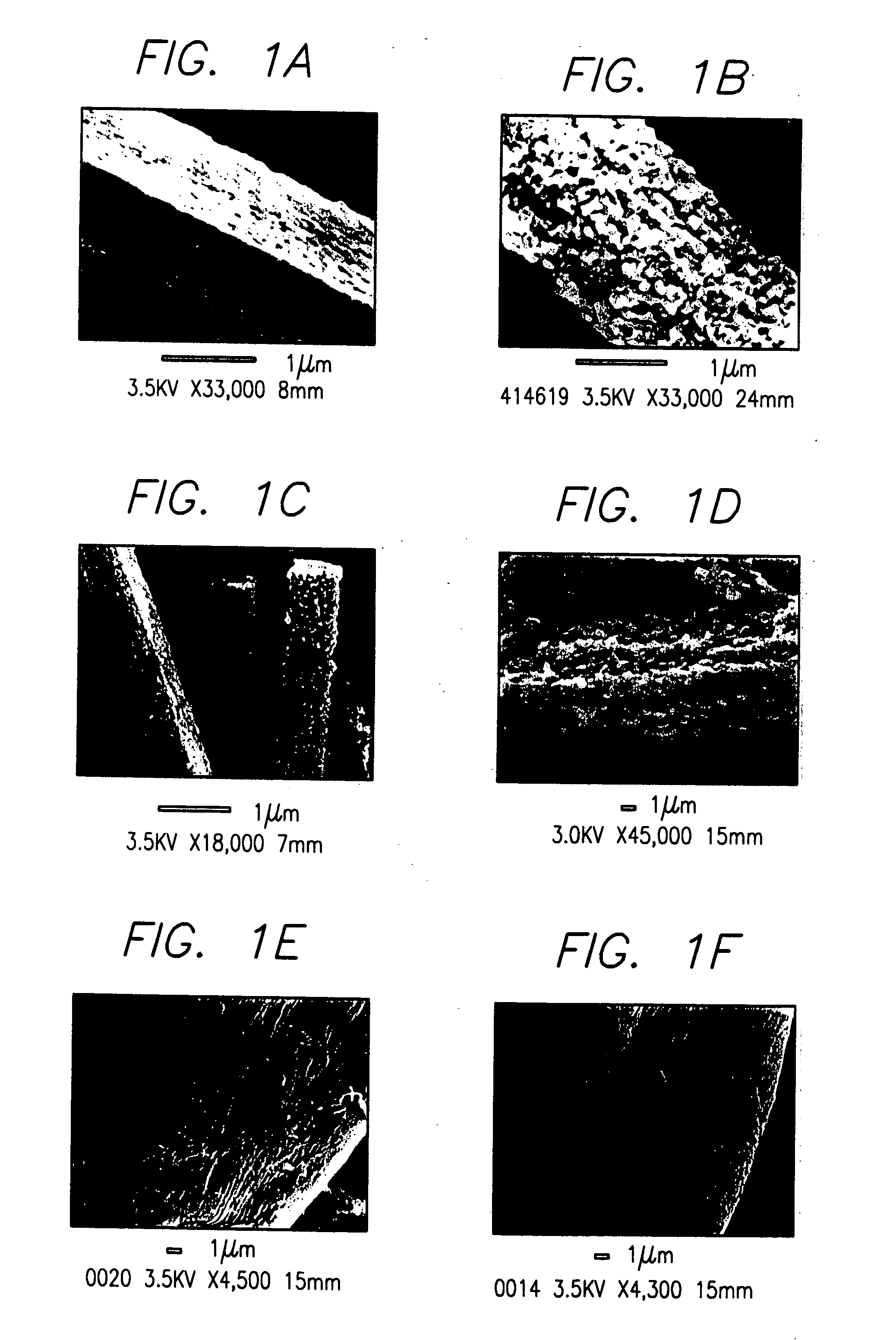
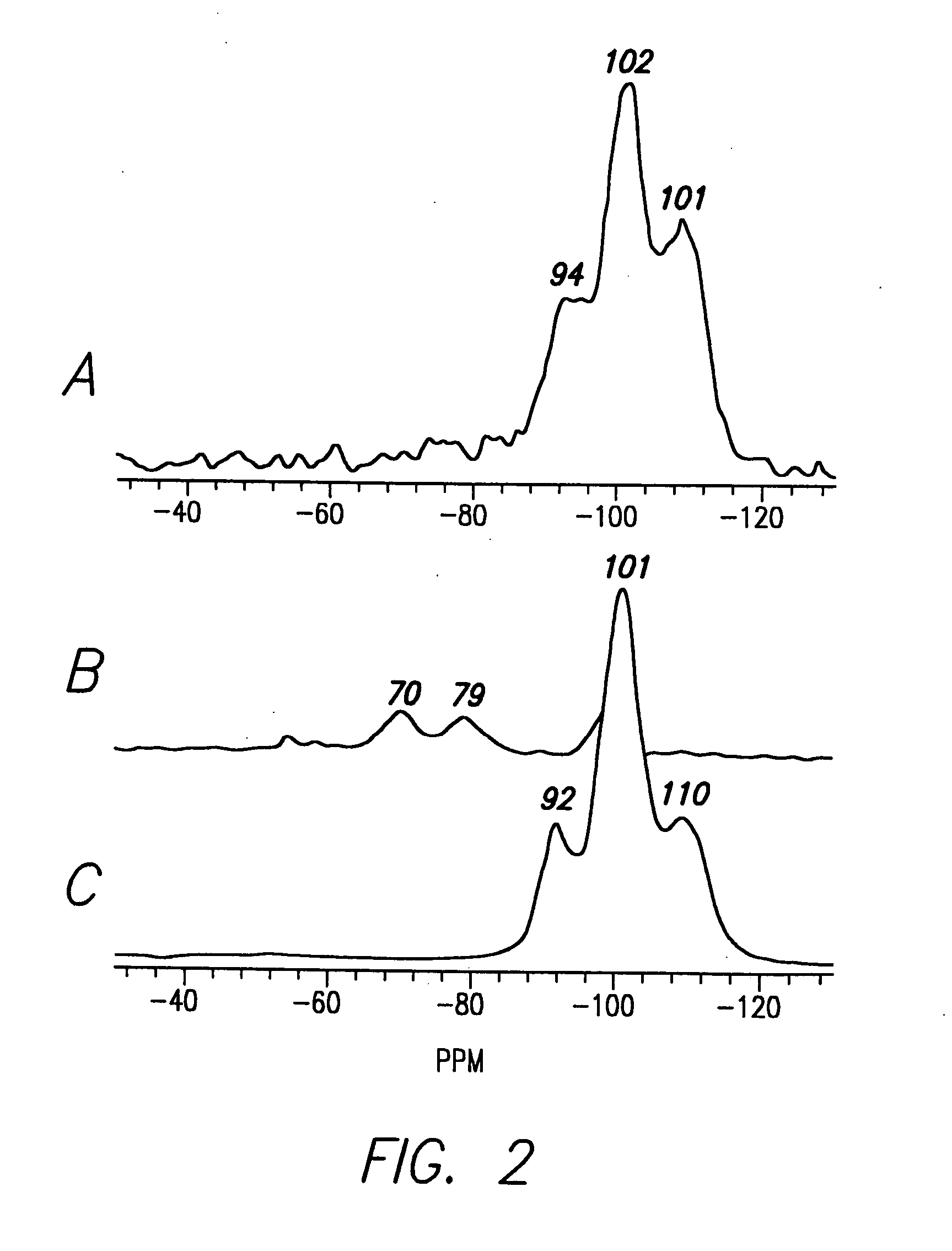
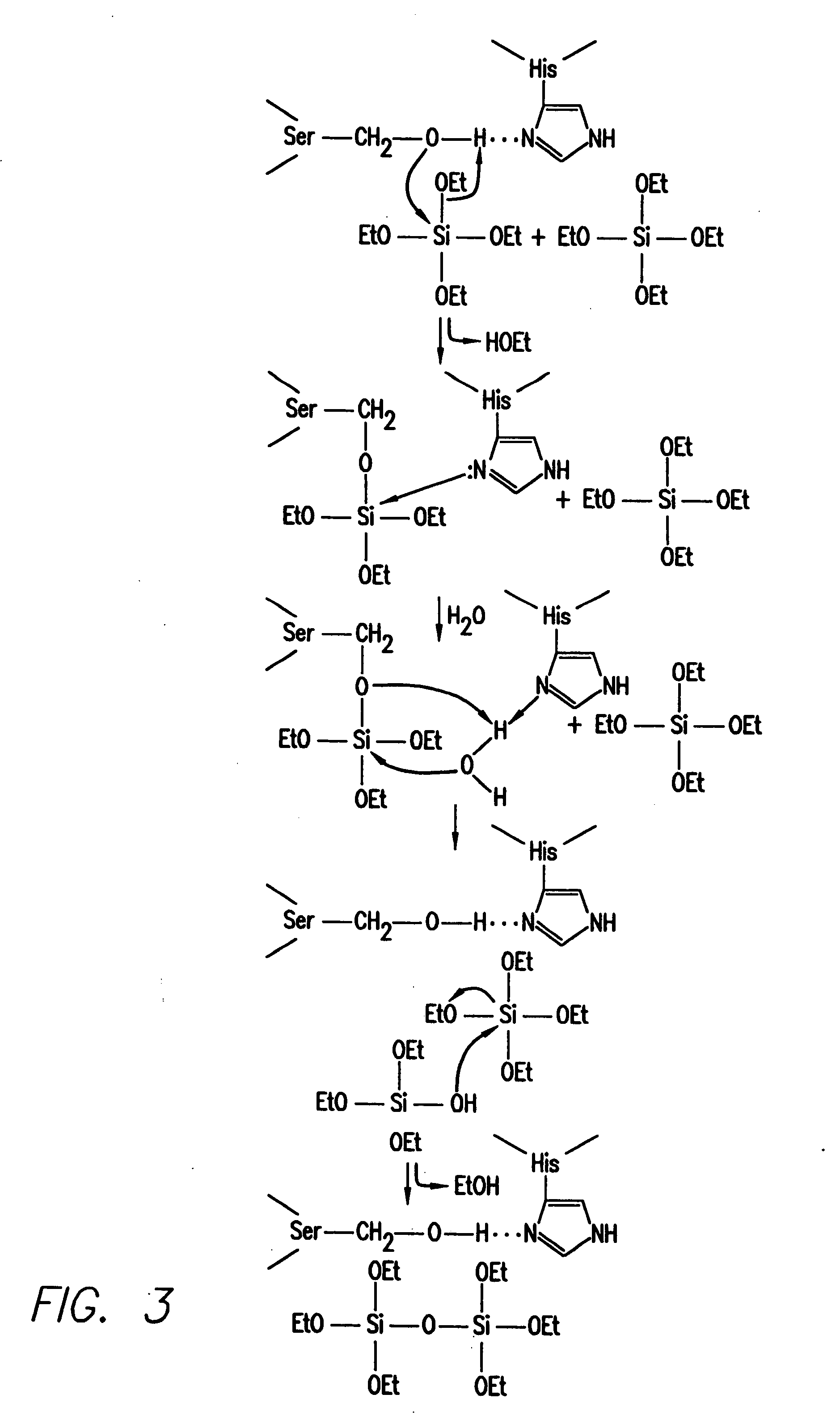
The in vitro polymerization of silica, silicone, non-silicon metalloid-oxane and metallo-oxane polymer networks, by combining a catalyst and a substrate to polymerize the substrate to form silica, polysiloxanes, polymetalloid-oxanes polymetallo-oxanes (metal oxides), polyorganometalloid oxanes, polyorganometallo oxanes, and the polyhydrido derivatives thereof, at about neutral pH. The nanostructure-directing catalysts have a nucleophilic functionality and a hydrogen-bonding acceptor group, and include: silicateins, enzymes that work by a mechanism functionally related to that of the silicateins; self-assembling peptides related to those synthesized and demonstrated capable of acting as biomimetic substitutes for the silicateins; non-peptide-based synthetic polymers containing a nucleophilic group and a hydrogen bonding amine such that the polymer functions by a mechanism of action related to that of the silicateins; materials having such chemical functionality as a nucleophilic group and or a hydrogen bonding amine which, acting in concert with nanoconfinement and or chemical functionality of the surface or matrix to which the functionality is attached, acts catalytically by a mechanism related to that of the silicateins; and small-molecule non-polymeric biomimetic catalysts that operate by the same mechanism as silicateins. The substrate is selected from groups consisting of silicon alkoxides, non-silicon metalloid alkoxides or metal alkoxides, and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; inorganic and organic oxygen-containing chelates of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; and inorganic and organic esters of the hydoxides of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; and inorganic and organic hydolyzable salts, complexes or conjugates of the hydroxides of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic and hydrido derivates of the foregoing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antireflection film and making method
InactiveUS7229686B2Improve the level ofImprove anti-reflection functionSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageRefractive indexTitanium oxide
A high refractive index layer of a cured first coating composition comprising (A) metal oxide fine particles selected from among titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, cerium oxide, iron oxide, tin oxide, and compound oxides thereof and (B) a compound having an acrylic, methacrylic, vinyl or styryl group, and a low refractive index layer of a cured second coating composition comprising (D) voided silica-base inorganic oxide fine particles and (C) a compound having at least two epoxy and / or oxetane groups are successively stacked on a substrate to form an antireflection film.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Tyre and crosslinkable elastomeric composition comprising an oxetane derivative and an amino acid
The present invention relates to a tyre comprising at least one structural element including a crosslinked elastomeric material obtained by crosslinking a crosslinkable elastomeric composition comprising: (a) 100 phr of at least one elastomeric polymer; (b) from about 0.1 phr to about 120 phr of at least one reinforcing filler; (c) from about 0.01 phr to about 20 phr of at least one oxetane derivative; and (d) from about 0.01 phr to about 10 phr of at least one amino acid. Preferably, said structural element is selected from: tread band, tread underlayer, bead filler, sidewalls, and sidewall inserts.
Owner:PIRELLI TYRE SPA
Textiles treated with copolymers of epoxy compounds and amino silanes having enhanced wet-strength
InactiveUS20090117793A1Not loose their strengthImprove wet strengthSynthetic resin layered productsLiquid repellent fibresSilanesEthylene oxide
The present invention provides for textiles treated with a composition comprising the reaction product ofe) an oxirane or oxetane compound comprising at least two oxirane or oxetane groups; andf) an amino silane having the formula:N(H)(R1)R2Si(OR3)3-a-b-c(OR4)a(R5Si(OR6)d(R7)e)bR8c with R1 is chosen from the group consisting of H or a monovalent hydrocarbon radical containing one to 20 carbon atoms;R2 and R5 are independently selected from a group consisting of oxygen or a divalent linear or branched hydrocarbon radical consisting of 1-60 carbons;R4 is a hydrocarbon radical that contains 3 to 200 carbon atoms;R3, R6, R7, and R8 and are each independently selected from the group of monovalent linear or branched hydrocarbon radicals having from 1 to 200 carbon atoms;the subscript b is zero or a positive number and has a value ranging from 0 to 3;the subscripts a, and c are zero or positive and have a value ranging from 0 to 3 subject to the limitation that (a+b+c)≦3; andthe subscripts d and e are zero or positive and have a value ranging from 0 to 3 subject to the limitation that (d+e)≦3, wherein the treated textile has enhanced wet strength.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Textiles treated with copolymers of epoxy compounds and amino silanes having enhanced wet-strength
InactiveUS20110020627A1Not loose their strengthImprove wet strengthEnergy efficient ICTSynthetic resin layered productsSilanesOxygen
The present invention provides for textiles treated with a composition comprising the reaction product of e) an oxirane or oxetane compound comprising at least two oxirane or oxetane groups; and f) an amino silane having the formula: N(H)(R1)R2Si(OR3)3−a−b−c(OR4)a(R5Si(OR6)d(R7)c)b R8c with R1 is chosen from the group consisting of H or a monovalent hydrocarbon radical containing one to 20 carbon atoms; R2 and R5 are independently selected from a group consisting of oxygen or a divalent linear or branched hydrocarbon radical consisting of 1-60 carbons; R4 is a hydrocarbon radical that contains 3 to 200 carbon atoms; R3, R6, R7, and R8 and are each independently selected from the group of monovalent linear or branched hydrocarbon radicals having from 1 to 200 carbon atoms; the subscript b is zero or a positive number and has a value ranging from 0 to 3; the subscripts a, and c are zero or positive and have a value ranging from 0 to 3 subject to the limitation that (a+b+c)≦3; and the subscripts d and e are zero or positive and have a value ranging from 0 to 3 subject to the limitation that (d+e)≦3, wherein the treated textile has enhanced wet strength.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Radiation- or thermally-curable oxetane barrier sealants
InactiveUS20070034515A1Improve barrier propertiesIncrease crosslink densityCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesPhotosensitizerMoisture permeability
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
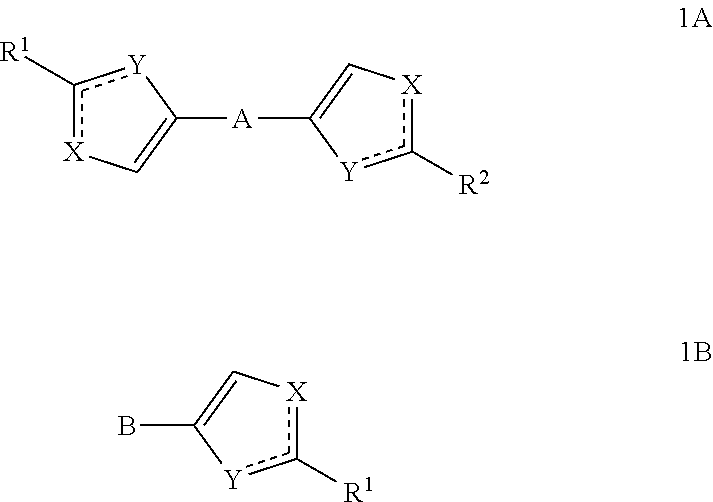
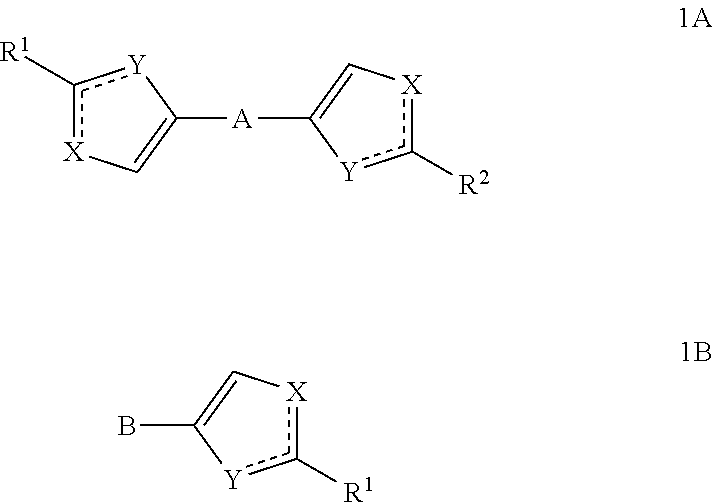
Substituted azoles, antiviral active component, pharmaceutical composition, method for preparation and use thereof
The present invention relates to novel azoles, novel antiviral active components of the general formulas 1A and 1B, pharmaceutical composition, antiviral medicament, method for prophylaxis and treatment of viral diseases, particularly caused by hepatitis C viruses (HCV). In general formulas 1A and 1Bwherein: solid lines with accompanying dotted lines () represent ordinary bond or double bond, provided that one of them is an ordinary bond, the other one is double bond; X and Y accept various meanings, one of them is—nitrogen, the other—oxygen, sulfur or NH group; R1 and R2—optionally the same radicals selected from 2-(R)- and (S)-substituted N-acyl pyrrolidine derivatives; N-methyl-N-[2-(R) and (S)-substituted 2,2-disubstituted acetamides; methyl[2-(R) and (S)-substituted ((methyl)amino)-(1-oxobutan-2-yl)-2-(R)-] and (S)-iso-propyl)-carbamates. A represents aliphatic C2-C8 biradical; dioxane, cyclo- and bicycloaliphatic, alkyloxyalkyl, alkyloxyalkylenoxyalkyl, alkenyloxyalkyl, alkynyloxyalkyl biradicals and their thioanaloges; aryl and thiophene alkynylcycloalkyl, alkynyldioxane, alkynylaryl, alkylthiophene, alkenylthiophene and alkynylthiophene, alkyloxyaryl, alkenyloxyaryl, alkynyloxyaryl, alkylthioaryl, alkenylthioaryl, alkynylthioaryl, cycloalkylthiophene, aryldioxane and thiophenyldioxane biradicals. B represents: aliphatic C2-C8 radical, including 1, 2 or 3 triple C≡C bonds; aryl and thiophene, alkynylcycloalkyl, alkynyldioxane, alkynylaryl, alkylthiophene, alkenylthiophene and alkynylthiophene, cycloalkylbenzene, 4-cycloalkylbiphenyl, bicycloalkylbenzene, 4-bicycloalkylbiphenyl, cycloalkylthiophene, aryldioxane and thiophenyldioxane radicals.
Owner:IVACHTCHENKO ALEXANDRE VASILIEVICH DR +3
Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives
InactiveUS6903225B2Carboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationSolventAcid derivative
This invention provides a process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives, which are of value as intermediates of drugs, from inexpensive starting materials without using any special equipment such as that required for super-low temperature reactions.A process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives which comprisesreacting an acetic acid derivative at a temperature of not less than −30° C. with an enolate prepared by permitting either a base or a metal having a valency of 0 to act on the derivative to produce a hydroxyoxohexanoic acid derivative,reducing this compound with the aid of a strain of microorganism to provide a halomethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative,treating this compound with an acetalizing agent in the presence of an acid catalyst to provide a halomethyl-dioxanylacetic acid derivative,reacted with an acyloxylating agent to provide a acyloxymethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative, andsubjecting this compound to solvolysis in the presence of a base.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
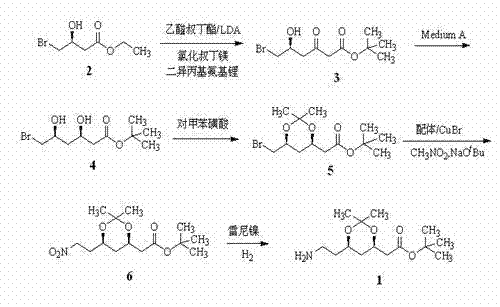
Synthetic method of atorvastatin calcium intermediate
InactiveCN103614430AFew stepsLow costOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesEthyl groupNitromethane
The invention discloses a synthetic method of an atorvastatin calcium intermediate. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: preparing [(4R, 6S)-6- brooethyl-2,2-diemthyl-1,3-dioxane-4-group] tert-butyl acetate (5) by (3S)-4-bromine-3-hydroxyl ethyl butyrate through condensation, asymmetric biological catalytic reduction and hydroxyl protection; and preparing an atorvastatin calcium intermediate [(4R, 6S)-6-(2-aminoethyl)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-group] tert-butyl acetate through catalytic hydrogenation reduction of raney nickel after 5 is condensed with nitromethane under action of cuprous bromide and a nitrogen-containing compound ligand. According to the synthetic method disclosed by the invention, steps are shortened, cost is lowered, and therefore, the synthetic method is more suitable for large-scale preparation.
Owner:SUZHOU HEALTH COLLEGE
Multifunctional composition base 1,3-oxazinan-6-ones with corrosion inhibition and heavy organic compounds inhibition and dispersants and obtaining process
ActiveUS20110269650A1Control foulingAvoid corrosionAmino-carboxyl compound preparationFlushingPropanoic acidKerosene
Base compounds including 1,3-oxazinan-6-one derivatives of N-alkyl or N-alkenyl or N-cycloalkyl or N-aryl propionic acids and paraformaldehyde, and their application as corrosion inhibitors with multifunctional properties serving as inhibitory / dispersant of asphaltene in production processes, transportation, refining and storage of crude oil and derivatives. The corrosion inhibitor with inhibitory / dispersant of asphaltenes properties comprises an active substance base of 1,3-oxaninan-6-ones and hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, toluene, mixed xylenes, o-xylene, m-xylene and p -xylene, diesel, kerosene, jet fuel, alcohols, aliphatic branched and unbranched alcohols containing from 3 to 10 carbon atoms, such as isopropanol, butanol and pentanol, and mixtures of hydrocarbon solvents with aliphatic branched or unbranched liquid fuels. In addition, a process for obtaining 1,3-oxazinan-6-ones derivatives of N-alkyl or N-alkenyl or N-cycloalkyl or N-aryl propionic acids and paraformaldehyde is described.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives
InactiveUS7094594B2Easy to manufactureImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryFermentationSolventSolvolysis
The present invention is to provide a production technology by which an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative, which are of value as pharmaceutical intermediates, can be produced from inexpensive and readily available starting materials without using any extraordinary equipment such as an ultra-low-temperature reactor.The present invention is a production process of an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivativewhich comprises reacting an enolate, prepared by permitting a base or a 0-valent metal to act on an acetic acid ester derivative with (S)-β-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone at a temperature not lower than −30° C. to give a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid derivative,treating the same with an acylating agent in the presence of a base to produce a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid monoacyl derivative,reducing this compound with a microorganism to produce a trihydroxyhexanoic acid monoacyl derivative,treating this compound with an acetal-forming reagent in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an acyloxymethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative, andfinally, subjecting this compound to solvolysis in the presence of a base.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
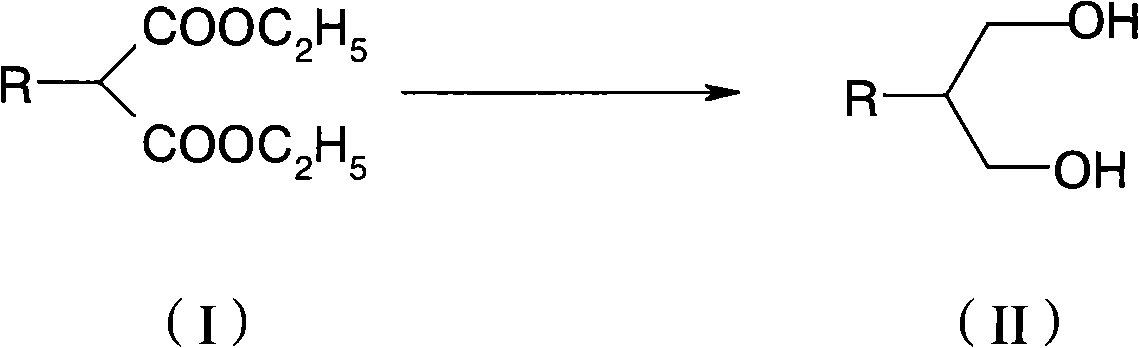
Process for synthesizing liquid crystal compounds containing 1,3-dioxane
InactiveCN101407446AEasy to storeFeeding method is simpleLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic compound preparationLiquid crystalPropanediol
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a liquid crystal compound containing 1, 3-dioxahexane, which comprises procedures of hydrogenating and reducing alkyl or alkyl cyclohexyl diethyl malonate into alkyl or alkyl cyclohexyl propanediol by a reducing agent. With the method for synthesizing the liquid crystal compound containing 1, 3-dioxahexane, a compound composed by potassium borohydride and anhydrous lithium chloride is adopted as the reducing agent which is easy to be preserved; the batch charging method is simple; and the yield coefficient of the reaction is relatively ideal, with low cost and safe operation.
Owner:BEIJING BAYI SPACE LCD MATERIALS TECH
Photosensitive resin composition, photocurable pattern and image display device
ActiveCN106970504AExcellent adhesionGood chemical resistancePhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusHydrogen atomHydrogen
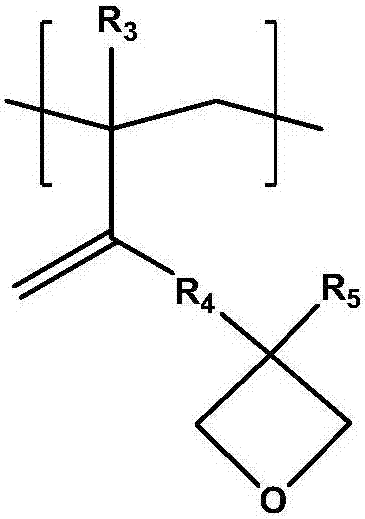
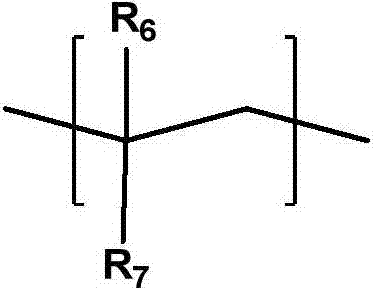
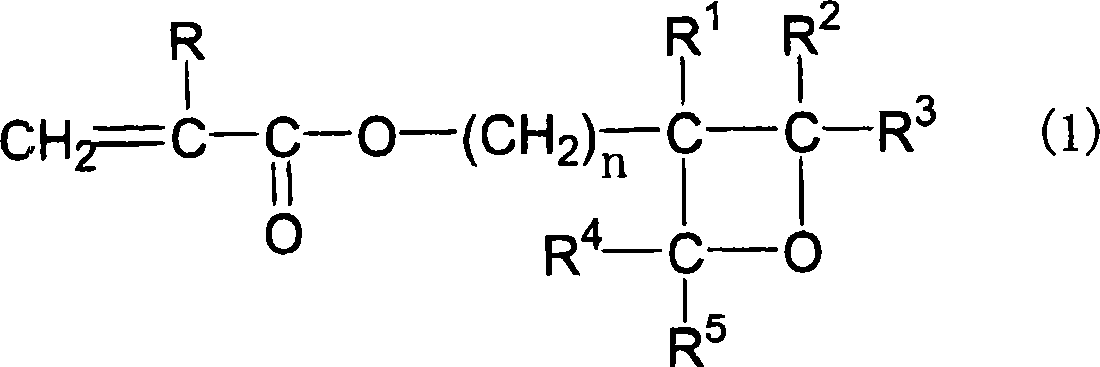
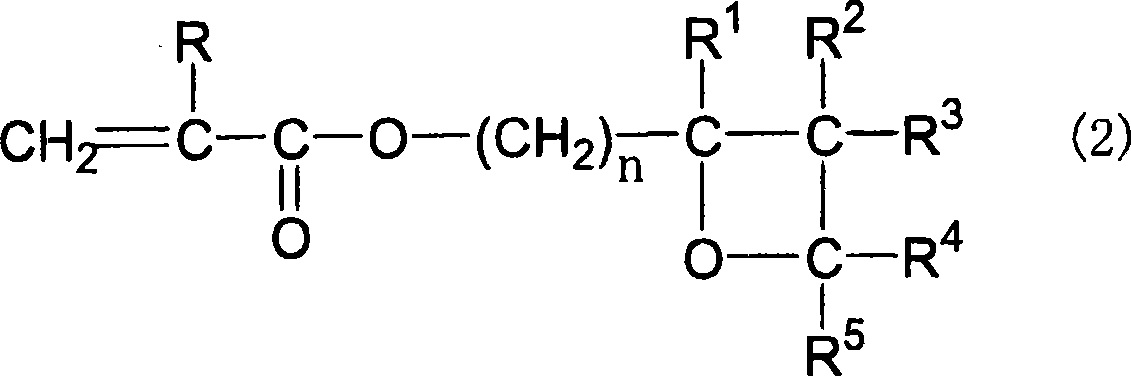
The invention relates to a photosensitive resin composition, photocurable pattern and image display device, more specifically, the abovementioned photosensitive resin composition contains an alkali-soluble resin (A), a photopolymerizable compound (B), a photopolymerization initiator (C), a solvent (D) and an additive (E), the abovementioned alkali-soluble resin (A) contains specific resin, the specific resin contains a repetitive unit containing an oxetane functional group and a repetitive unit represented by the following chemical formula 1, and thus excellent adhesion, chemical resistance and storage stability are achieved due to high solidification density. In the chemical formula 1, R1 is hydrogen atom or methyl, and R2 is an alkyl group with 1 to 6 hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD
Radiation sensitive composition for forming a colored layer, color filter and color liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN101082772APhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusOptical elementsLiquid-crystal displayColor filter array
A radiation sensitive composition comprising a colorant, an alkali-soluble resin, a polyfunctional monomer and a photopolymerization initiator. The alkali-soluble resin is a copolymer of (b1) at least one first unsaturated compound selected from the group consisting of an unsaturated carboxylic acid, an unsaturated carboxylic anhydride and an unsaturated phenolic compound and at least one second unsaturated compound selected from the group consisting of (b2) an unsaturated compound having an oxetane skeleton and (b3) an unsaturated compound having a tetrahydrofuran skeleton. The radiation sensitive composition is used to form a colored layer.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives
InactiveUS20050080277A1Easy to manufactureImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryFermentationAcetic acidAcid derivative
The present invention is to provide a production technology by which an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative, which are of value as pharmaceutical intermediates, can be produced from inexpensive and readily available starting materials without using any extraordinary equipment such as an ultra-low-temperature reactor. The present invention is a production process of an optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivative which comprises reacting an enolate, prepared by permitting a base or a 0-valent metal to act on an acetic acid ester derivative with (S)-β-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone at a temperature not lower than −30° C. to give a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid derivative, treating the same with an acylating agent in the presence of a base to produce a dihydroxyoxohexanoic acid monoacyl derivative, reducing this compound with a microorganism to produce a trihydroxyhexanoic acid monoacyl derivative, treating this compound with an acetal-forming reagent in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an acyloxymethyldioxanylacetic acid derivative, and finally, subjecting this compound to solvolysis in the presence of a base.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Synthetic method of 1, 3-dioxane type organic compounds
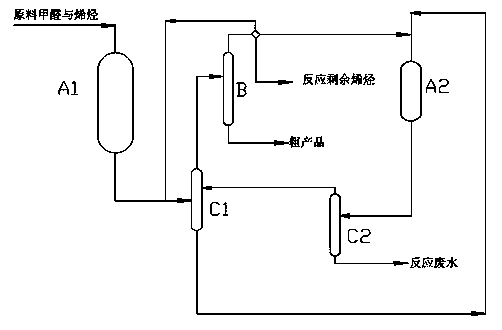
InactiveCN103420973AReduce formaldehyde contentEasy to handleOrganic chemistryPtru catalystSolid acid
The invention relates to a synthetic method of 1, 3-dioxane type organic compounds. The synthetic method comprises: taking industrial formaldehyde and butylene-containing four-carbon hydrocarbons as raw materials, under the effect of a solid acidic resin catalyst, performing a reaction in a secondary fixed catalytic bed and extraction and rectification, reacting formaldehyde with butylenes for a condensation reaction to obtain the 1, 3-dioxane type organic compounds. The effective content of butylenes in the four-carbon hydrocarbons is 15 wt% or more, conjugated diene content is 2000 ppm or less, the butylenes is one or a mixture of 1-butylene, 2-butylene or isobutylene with any proportions, and the formaldehyde is subjected to deionization processing. The method has the advantages of wide raw material source, green and environment-friendly catalyst, high reactant conversion rate, high reaction selectivity, simple operation, easily-separable product and applicability to continuous industrial production.
Owner:武汉椿岭科技有限公司
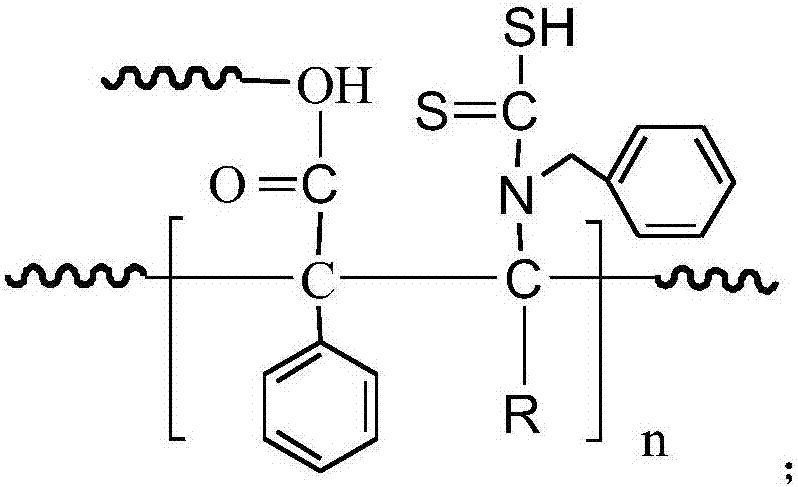
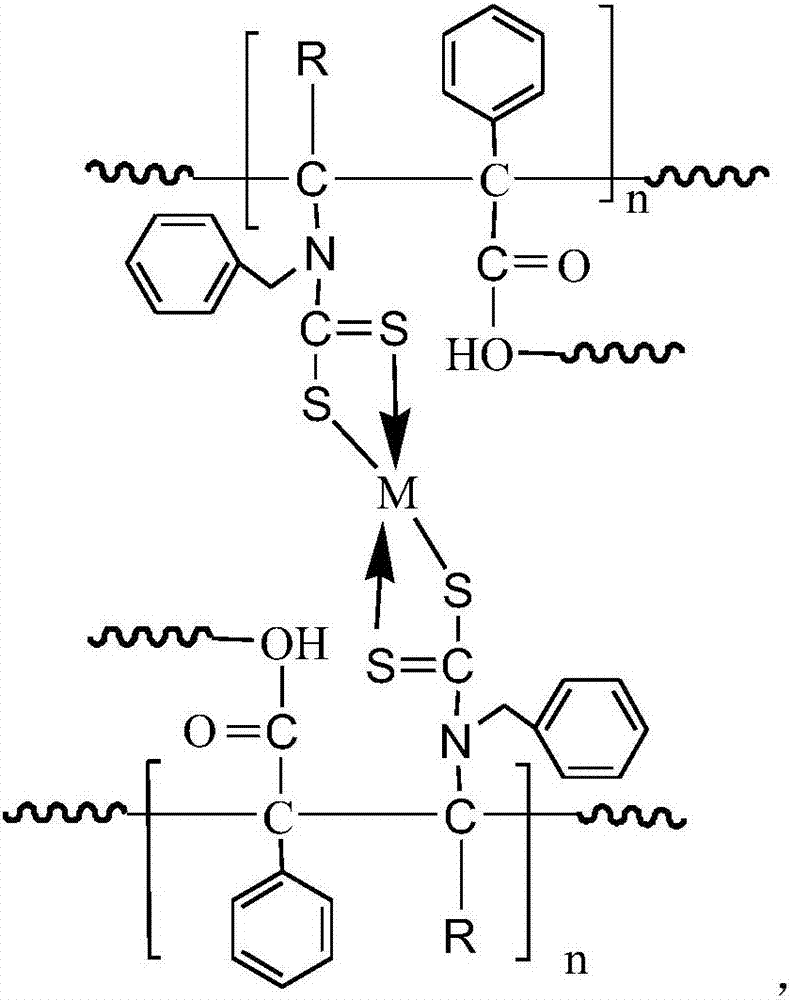
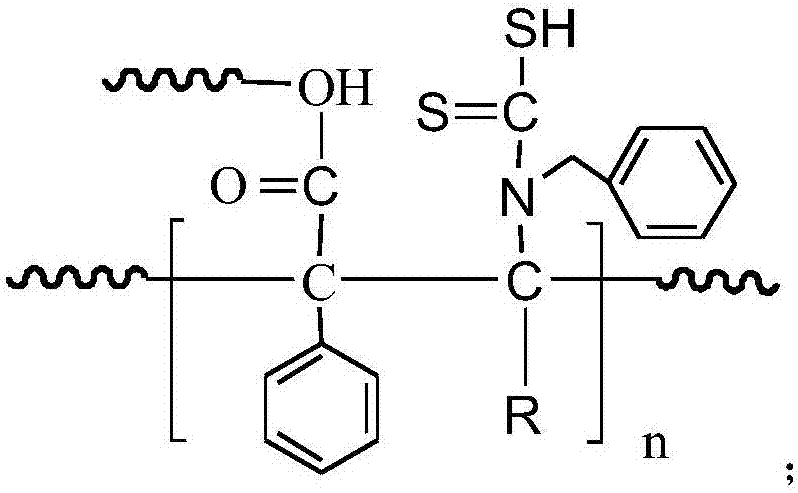
Heavy metal adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107376874AThe synthesis method is simpleImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsResin microsphereHydrogen
The invention relates to a preparation method of a heavy metal adsorbent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing polystyrene microspheres with benzylamine in water to react at 20-40 DEG C, so as to obtain aminated resin microspheres; and uniformly mixing the aminated resin microspheres, water and dioxahexane to obtain a mixed solution, adjusting the pH value of the mixed solution to 10-11, and adding carbon disulfide to react at 20-40 DEG C, so as to obtain the heavy metal adsorbent. The invention further provides the heavy metal adsorbent prepared by virtue of the preparation method. The structural formula of the heavy metal adsorbent is as shown in the description, wherein R represents phenyl, methyl or hydrogen, and n is equal to 1000-4000. According to the heavy metal adsorbent, a sulfur atom in a dithiocarboxyl group serves as a coordination atom and forms a multi-tooth chelating center of heavy metals.
Owner:JIANGSU HELPER FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS
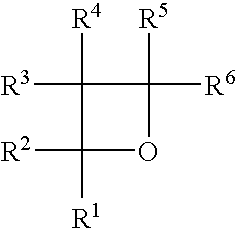
Photopolymerizable oxetane derivative and liquid-crystal composition containing it
InactiveUS7407691B2High sensitivityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsHydrogenPolymer science
Provided are a liquid-crystal compound and a liquid-crystal composition containing the compound, of which the advantages are that they show nematic hybrid orientation on a rubbed TAC substrate, they are polymerizable in open air and they readily give a polymer having a high degree of polymerization even when exposed to a relatively small total quantity of light. The films formed by photopolymerizing them keep nematic hybrid orientation. The compound is represented by formula (1):wherein R1 is a hydrogen or an alkyl; R2 is a hydrogen, —OCF3, etc.; A1 is a 1,4-phenylene, etc.; A2 and A3 are independently a 1,4-cyclohexylene, a 1,4-phenylene, etc.; X1 is a single bond, —O—, etc.; X2 and X3 are independently a single bond, —COO—, —C≡C—, —CONH—, etc.; m is an integer of from 0 to 20; and n is 1 or 0.
Owner:JNC PETROCHEM CORP +1
Cationically curable composition for dental use
A cationically curable composition for dental use containing a cationic polymerization initiator (I) and cationically polymerizable monomers (II), the cationically polymerizable monomers (II) containing an oxetane compound and an epoxy compound or an alkenyl ether compound at a ratio of amounts that satisfy the conditions expressed by the following formula,(a×A):(b×B)=91:9 to 45:55wherein A is a mol number of the oxetane compound, “a” is an average number of the oxetane functional group contained in one molecule of the oxetane compound, B is a mol number of the epoxy compound or the alkenyl ether compound, and “b” is an average number of the epoxy functional group contained in one molecule of the epoxy compound or an average number of the alkenyl ether functional group contained in one molecule of the alkenyl ether compound.The composition is not hindered by oxygen from being polymerized, cures quickly even without using a special polymerizable monomer or a particular polymerization initiator, little forms an unpolymerized layer on the surface even when polymerized and cured in a highly humid environment such as in the oral cavity, and is suited as a filling / restorative material for dental use.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP +1
Wear-resistant paint applied to suitcase and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108250911AImprove wear resistanceGood anti-aging performanceEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyWear resistant
The invention discloses anti-wear paint applied to suitcase and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of paint. The anti-wear paint is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 65 to 85 parts of epoxy resin, 35 to 45 parts of tung oil, 25 to 35 parts of acetic ether, 20 to 25 parts of modified silicon carbide, 15 to 20 parts of modified nano silicon dioxide, 10 to 12 parts of modified nano titanium oxide, 10 to 12 parts of modified quartz powder, 5 to 8 parts of trioxane, 5 to 8 parts of barium sulfate, 3 to 6 parts of polymethyl methacrylate, 3 to6 parts of zinc borate, 1 to 4 parts of sodium phytate, 1 to 4 parts of curing agent, 1 to 4 parts of methyl isothiazolinone, 0.6 to 1.2 parts of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 14 to 16 parts of aid and 25 to 35 parts of water. The anti-wear paint disclosed by the invention has the advantages of excellent wear resistance and ageing resistance.
Owner:HEFEI YUANKE GARMENT DESIGN CO LTD
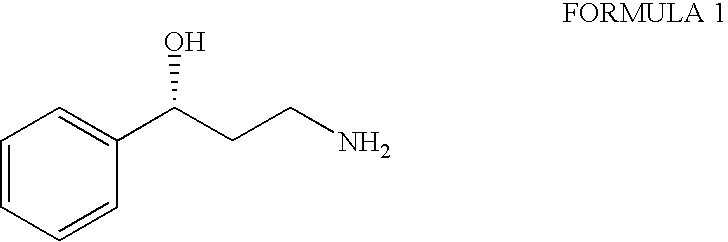
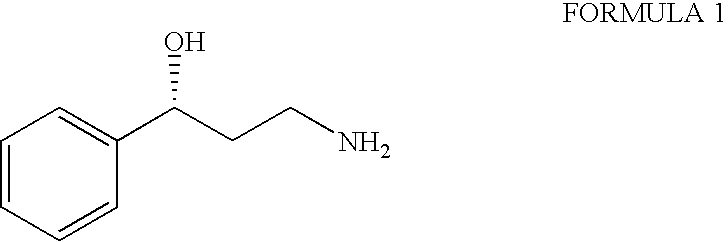
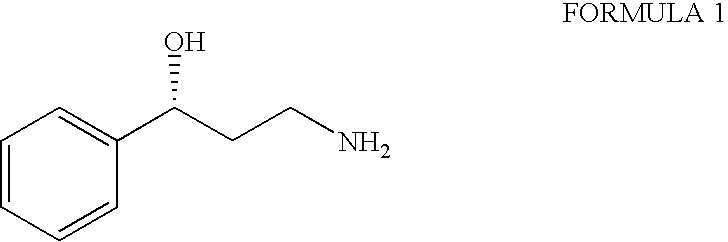
Process for the preparation of enantiomerically pure 3-phenyl-3-hydroxypropylamine
InactiveUS20040110985A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPrimary alcoholMedicinal chemistry
The present invention relates to an improved process for the synthesis of enantiomerically pure 3-phenyl-3-hydroxypropylamine of formula I; more particularly the present invention relates to the said process using styrene; the synthetic strategy features a Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation (SAD) route to the target compound, using styrene, a readily accessible starting material gives the optically pure dihydroxy compound (ee >97%; the selective monotosylation of primary alcohol, nucleophilic displacement by cyano and subsequent reduction to amino group furnishes the desired 3-phenyl-3-hydroxypropylamine in enatiomerically pure form, a key intermediate in the synthesis of variety of oxetine related anti-depressant drugs.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
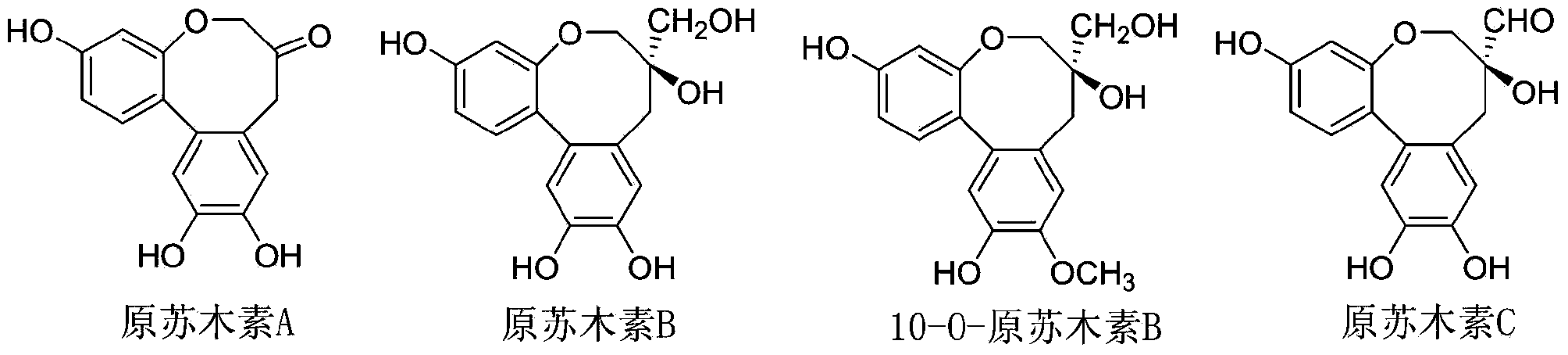
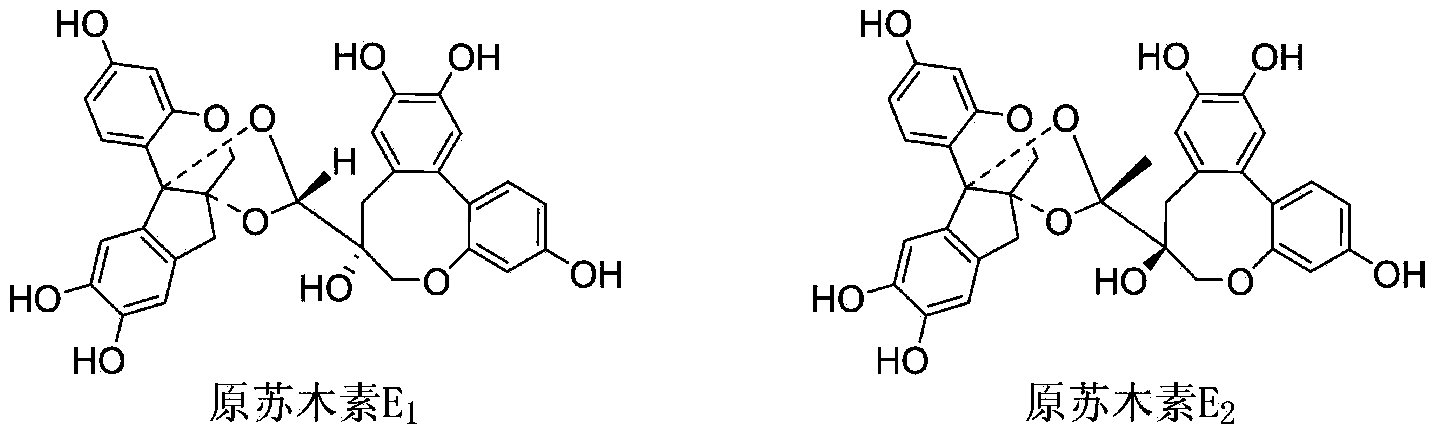
Biochemical total synthetic method for protosappanin A and derivatives thereof
InactiveCN104016959ASimple and fast operationReduce the difficulty of synthesisOrganic chemistryArylChemical reaction
The invention discloses a biochemical total synthetic method for protosappanin A and derivatives thereof. The synthetic method for protosappanin A and derivatives thereof comprises the main steps: taking a dibenzo[d,f]oxepane-3-one compound as a raw material, performing cyan addition on carbonyl, performing reduction, Tiffeneau-Demjanov rearrangement, deprotection and other reactions, so as to synthesize the protosappanin A derivatives with the total yield of 85% or more. Chemical total synthesis of protosappanin A compounds is developed for the first time. The synthetic method is simple to operate, reduced in synthetic difficulty because routine chemical reaction methods are employed, mild in reaction conditions, friendly to environment, simple in post-treatment and high in yield, and has good industrialization production prospect.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Salt of sulfinylbenzimidazole compound, and crystal and amorphous form thereof
InactiveCN101336240AExcellent gastric acid secretion inhibitory effectGood physical propertiesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderBenzimidazoleDimethpyrindene
Salts of 2-[({4-[(2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methoxy]-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl}methyl)sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, and crystals and amorphous forms thereof.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
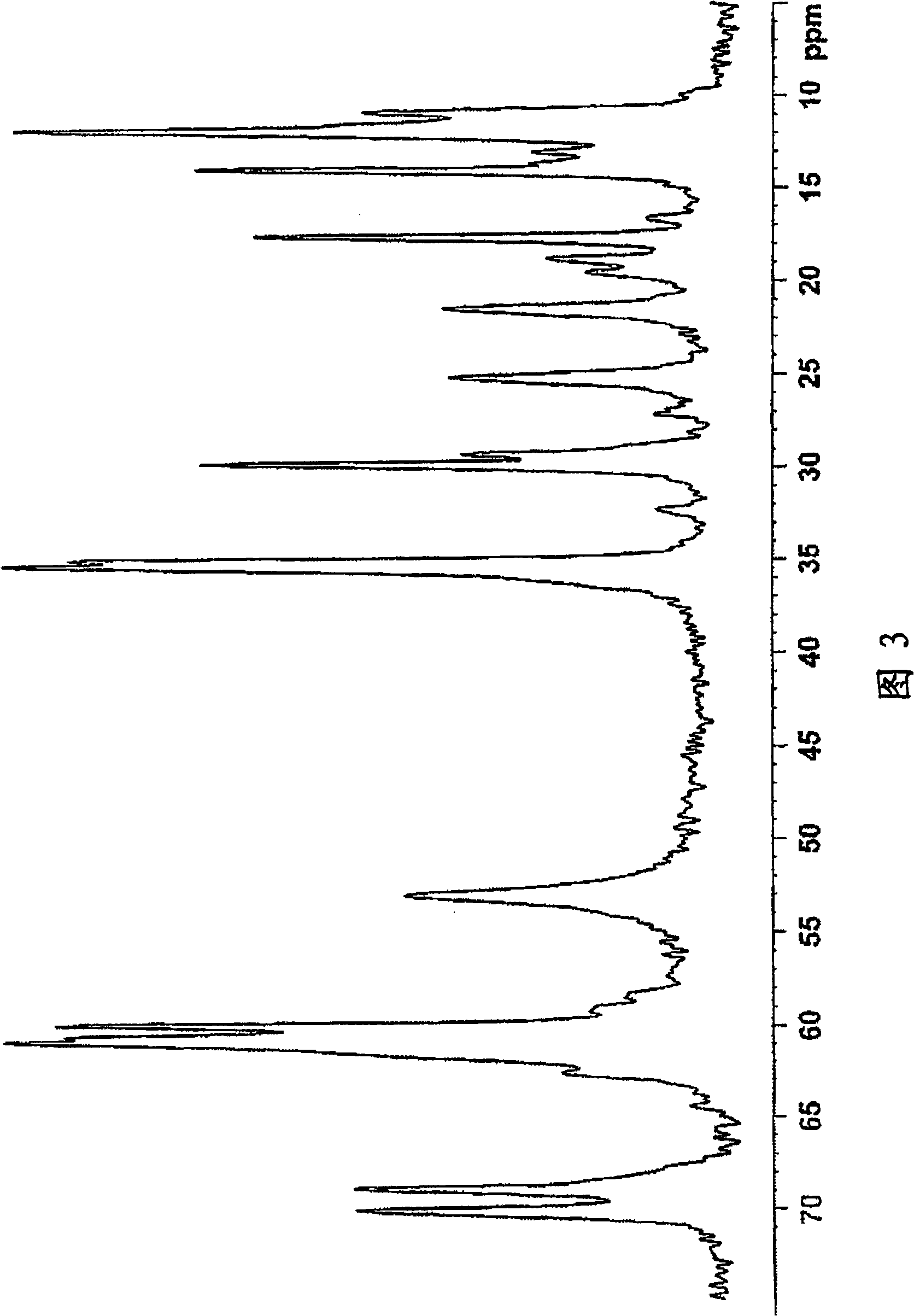
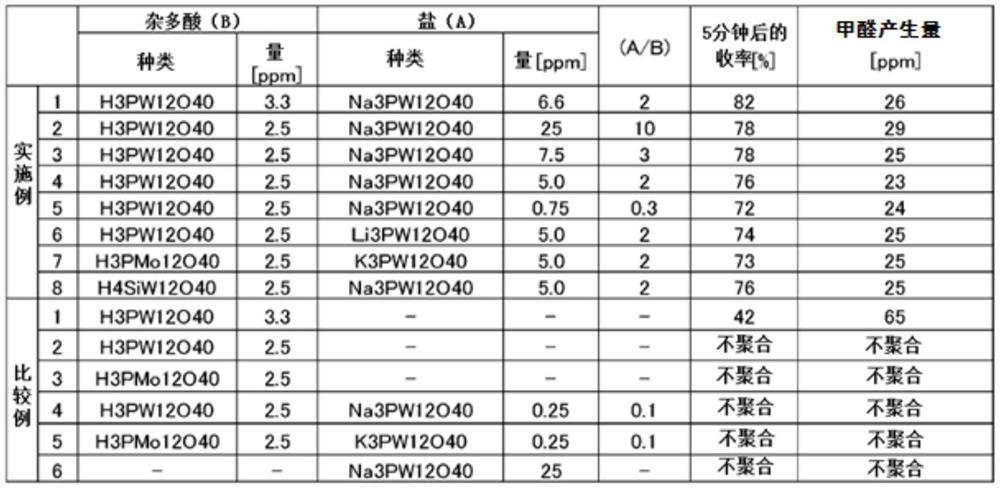
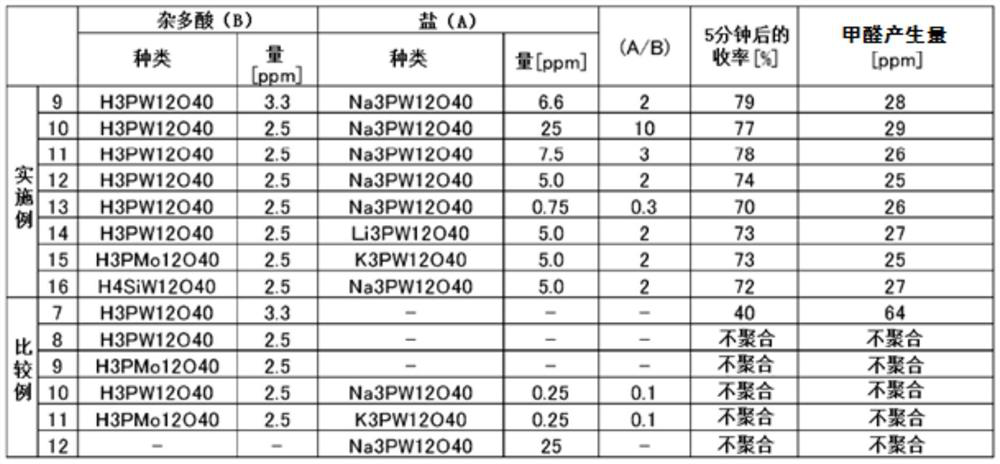
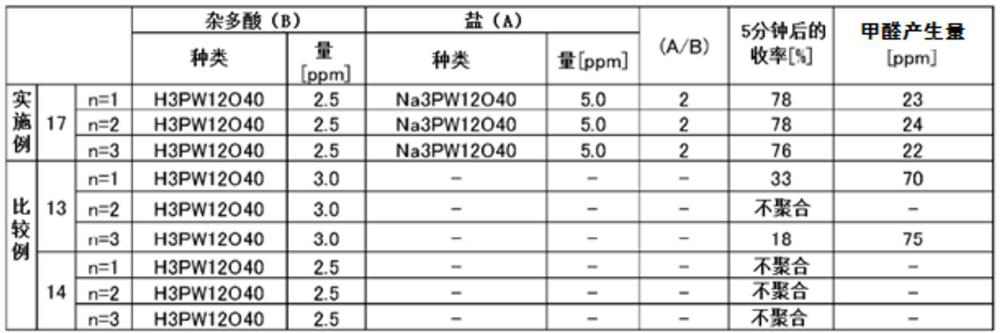
Method for producing polyacetal copolymer
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a polyacetal copolymer, in which any disturbances in mass production less affect the polymerization. The method is for producing a polyacetal copolymer from trioxane as a main monomer (a) and a comonomer (b) copolymerizable therewith, and comprises using a polymerization catalyst (c) obtained by mixing a heteropolyacid (B) represented by general formula (1) with a heteropolyacid salt (A) represented by general formula (2) in a mass ratio of 10>=(A) / (B)>=0.2. H<m>[M<1]<x>*M<2><y>O<z>]*nH<2>O ...(1), M<3><m>[M<1><x>*M<2><y>O<z>]*nH<2>O... (2). [In formulae (1) and (2), M<1> represents one or two central elements selected from between P and Si, M<2> represents one or more coordination elements selected from among W, Mo,and V, M<3> represents an alkali metal, x is an integer of 1-10, y is an integer of 6-40, z is an integer of 10-100, m is an integer of 1 or larger, and n is an integer of 0-50.]
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Catalyst for preparing monohydric alcohol and dihydric alcohol by hydrogenation of dimethyl substituted 1,3-dioxane, and application
InactiveCN103182306AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAlcohol
The invention relates to a catalyst for preparing monohydric alcohol and dihydric alcohol by hydrogenation of dimethyl substituted 1,3-dioxane. The catalyst is characterized by consisting of an active metal, a solid acid and an adhesive Al2O3, wherein the mass percentage of the active metal is 8-20%; the mass percentage of the solid acid is 20% and the balancing being the adhesive Al2O3. High conversion rate and high selectivity of a reaction substrate are realized by using the solid hydrogenation catalyst with double active sites of the solid metal and acid and by using a hydrogenation reaction.
Owner:武汉椿岭科技有限公司
Process for producing hexabromocyclododecane
InactiveUS6420617B1Improve overall utilizationImprove solubilityPreparation by halogen additionFluid phaseCyclododecatriene
This invention relates to the production of an hexabromocyclododecane product, which process comprises brominating cyclododecatriene in the presence of a 1,4-dioxane and water based solvent and from about 0.5 to about 30 wt % bromide ion in the liquid phase of the reaction mass. Optional post-reaction heat treatment in a finishing step increases process yields if needed. The hexabromocyclododecane product is unrecrystallized and contains no more than about 1.5 wt % tetrabromocyclododecene impurities.
Owner:ALBEMARLE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

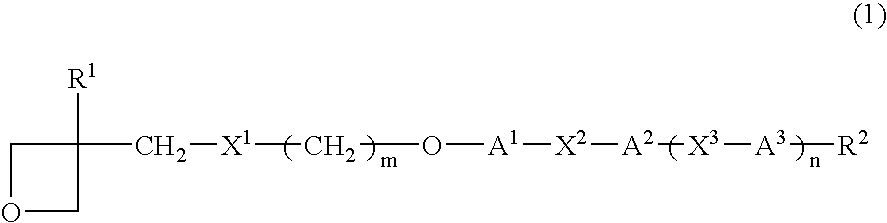
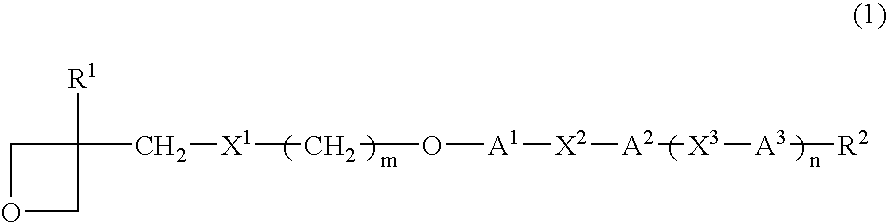
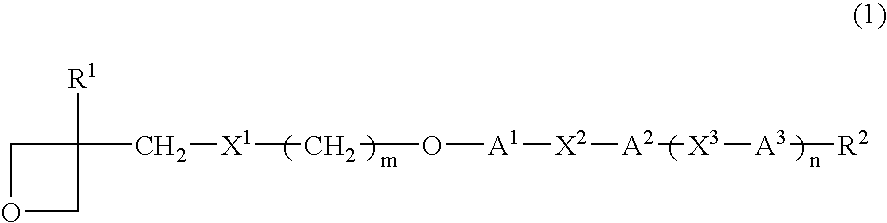
![Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/28c70bb9-80f8-4e62-8b6d-1f2bee180cf4/US06903225-20050607-C00001.png)
![Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/28c70bb9-80f8-4e62-8b6d-1f2bee180cf4/US06903225-20050607-C00002.png)
![Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives Process for producing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl]acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/28c70bb9-80f8-4e62-8b6d-1f2bee180cf4/US06903225-20050607-C00003.png)

![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/89ae92db-da16-4ac3-989c-170d79ca11c3/US07094594-20060822-C00003.png)
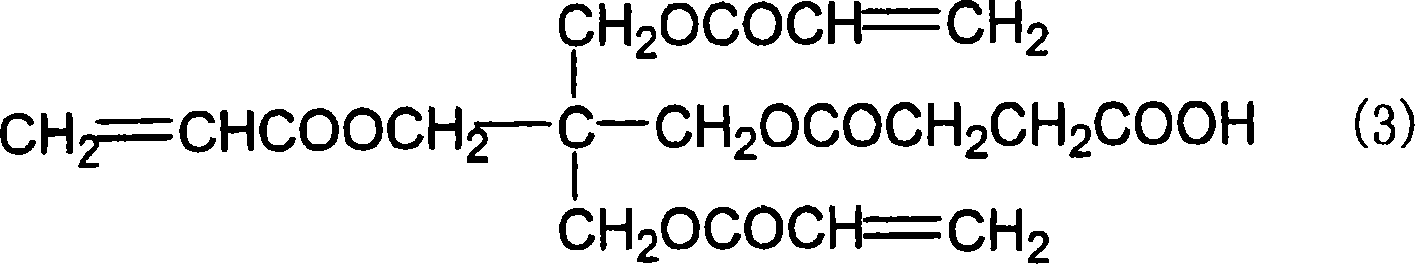
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00001.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00002.png)
![Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives Process for preparing optically active 2-[6-(hydroxy-methyl)-1,3-dioxan-4-yl] acetic acid derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e1d29781-cd6b-412f-a42a-451e24f40515/US20050080277A1-20050414-C00003.png)