Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Molecular recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exchange, replacement, or insertion of sequences especially between, of, or into DNA molecules. Molecular recombination is the consequence of crossing over during meiosis, though involves additional mechanisms including in non-eukaryotes.
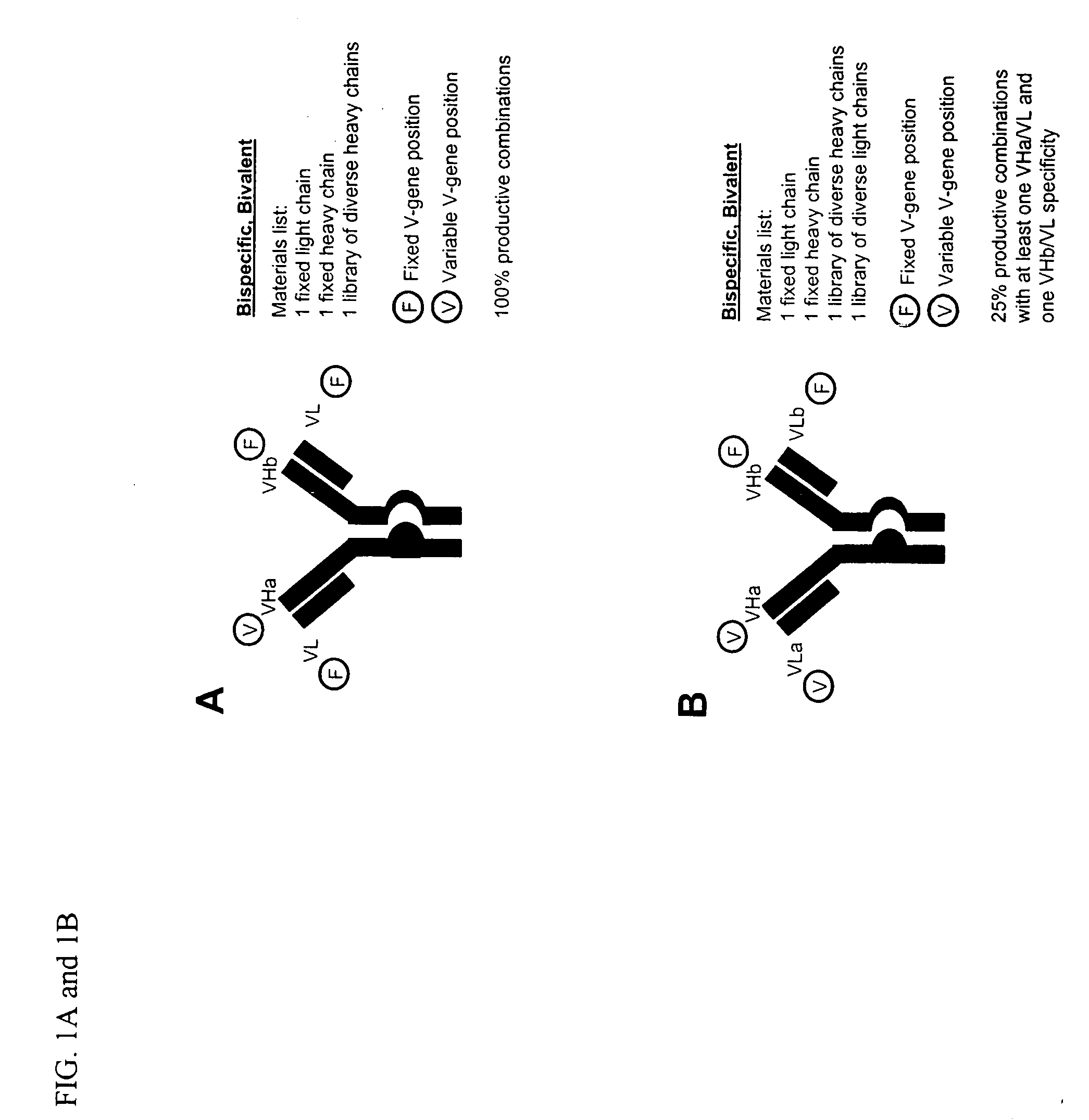
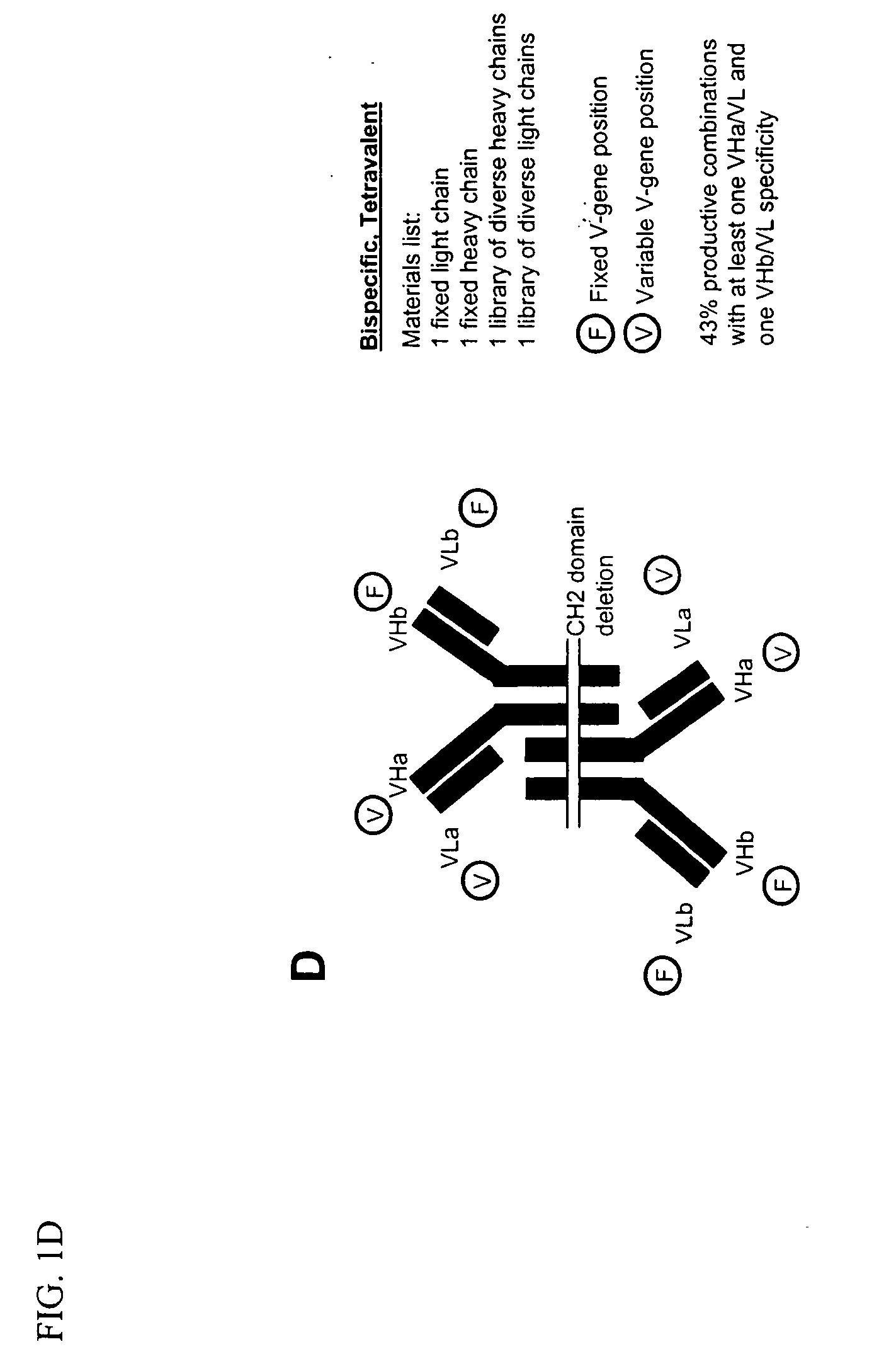
Methods for producing and identifying multispecific antibodies
The present invention relates to a high efficiency method of expressing multispecific antibodies in eukaryotic cells. The invention is further drawn to a method of producing immunoglobulin heavy and light chain libraries, particularly using the trimolecular recombination method, for expression in eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides methods of selecting and screening for multispecific antibodies, and antigen-binding fragments thereof. The invention also provides kits for producing, screening and selecting multispecific antibodies. Finally, the invention provides multispecific antibodies, and antigen-binding fragments thereof, produced by the methods provided herein.
Owner:VACCINEX
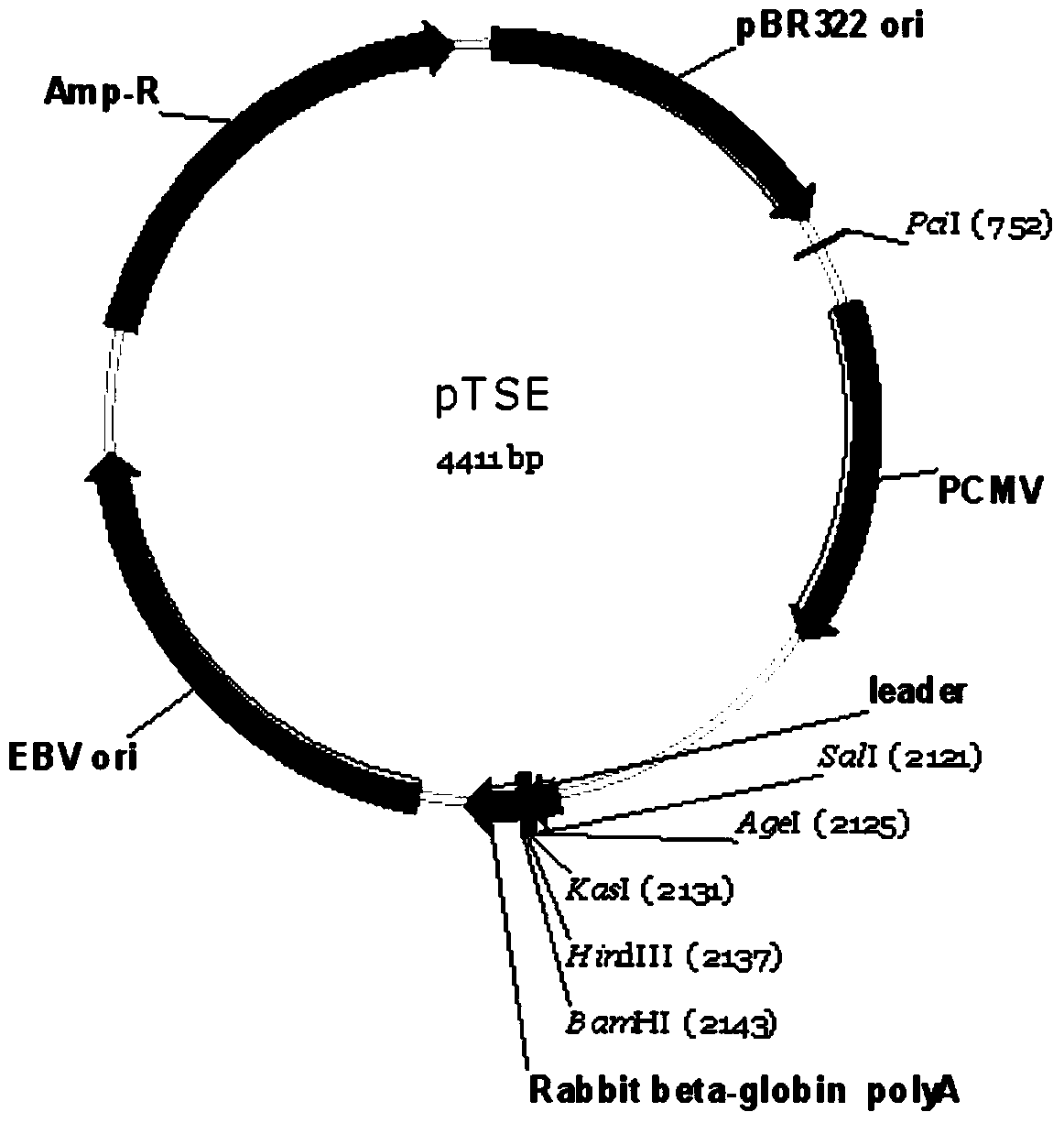
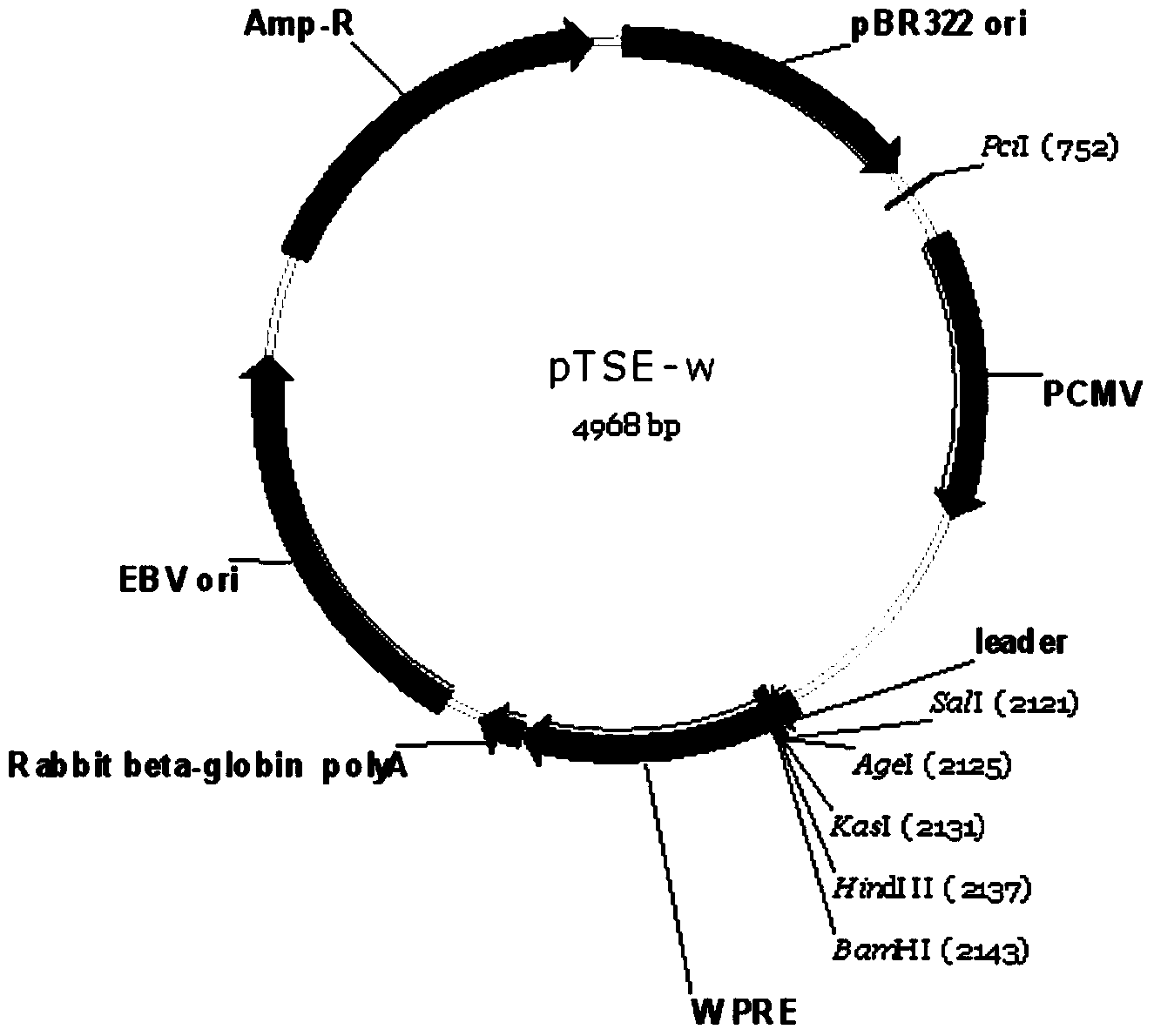
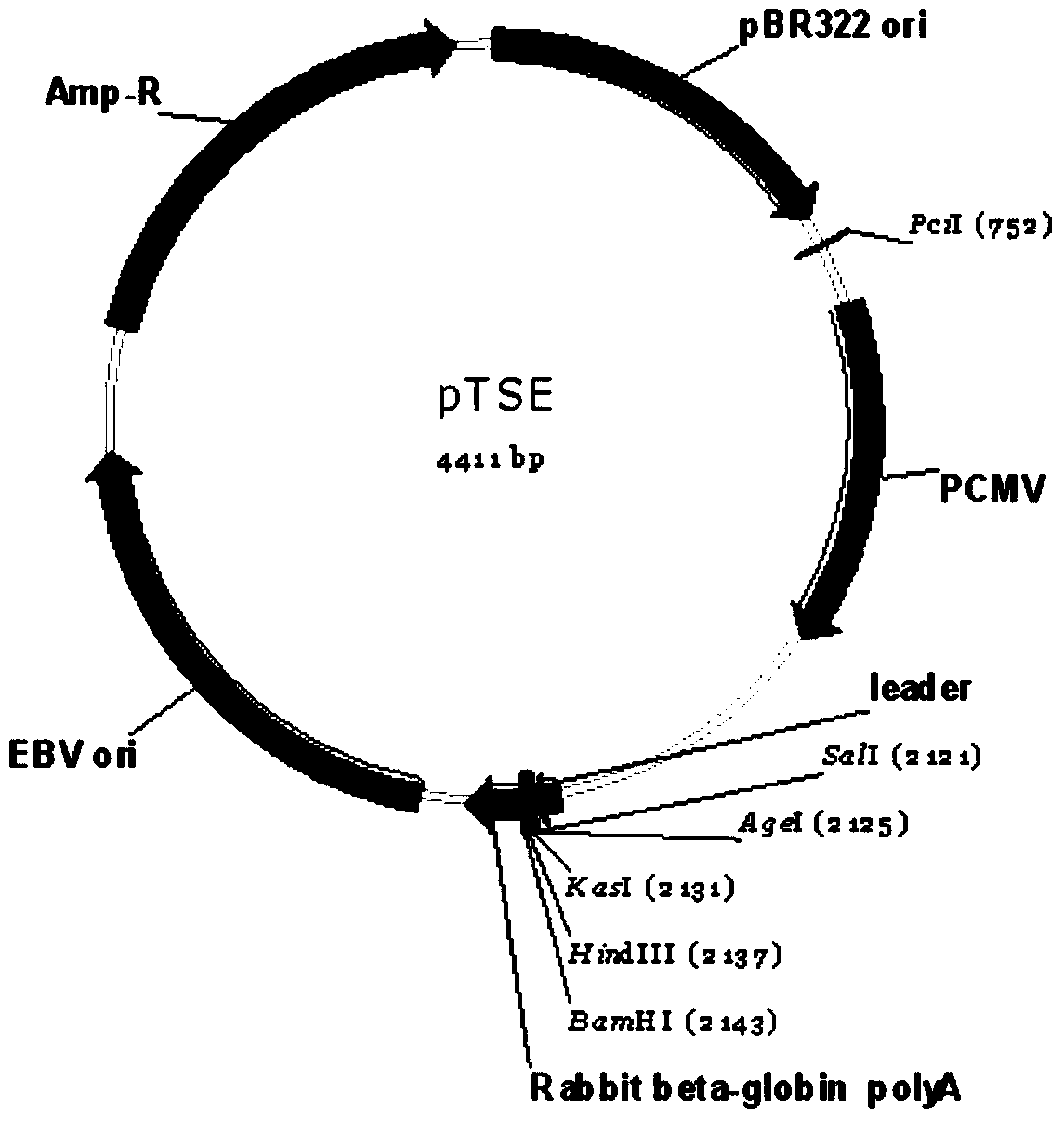
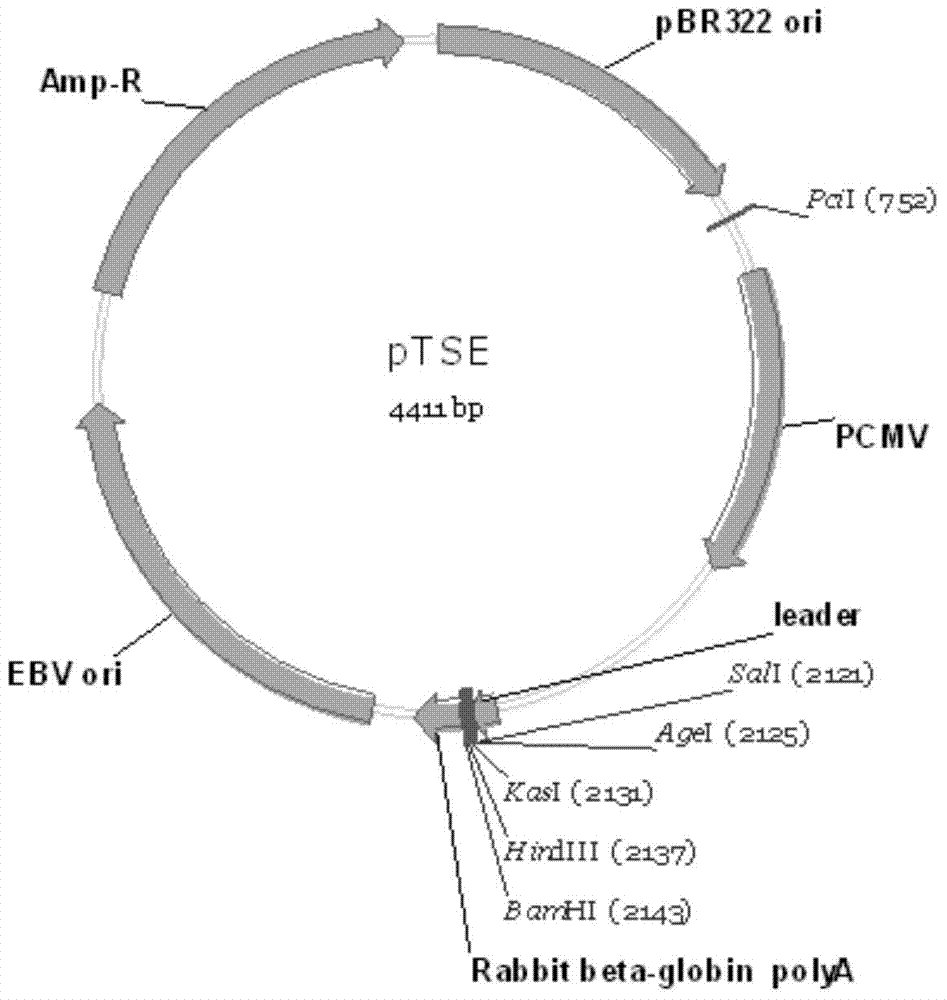
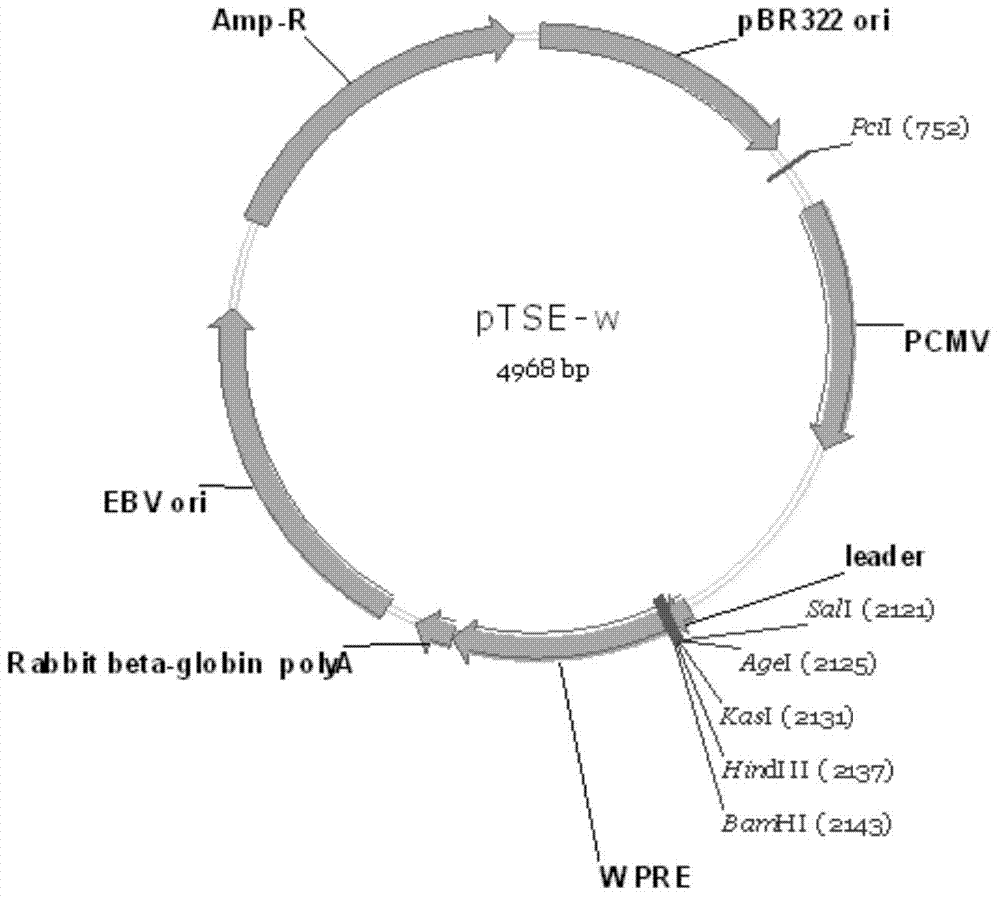
Construction and application of mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector
ActiveCN103525868AReduced transcript levelsShorten the development cycleVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCloning SiteDeletion mutation
The invention relates to a mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector pSNEO. The vector is constructed on the basis of neomycin resistance screening gene NEO by combined strategy of weakening screening gene expression and reinforcing target gene expression. The screening gene weakening comprises the following two sides: introducing deletion mutant into the promoter to implement transcription weakening of the screening gene, and introducing a hairpin structure sequence before the translation initial site of the screening gene to implement the translation weakening of the screening gene. The expression reinforcement of the target gene is implemented by adding a transcription control element WPRE sequence between polyclone site and polyA tail of the target gene expression frame. The pSNEO vector can conveniently and quickly complete the construction of the stable high-expression cell strain of the target gene, and provides a new tool for preparing the high-polymer recombinant protein.
Owner:BIOTECH PHARMA CO LTD
Lentiviral packaging cells and uses therefor
InactiveUS6955919B2Improve securityRule out the possibilitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsPol genesVpr Protein
Owner:GENETIX PHARMA
Beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103881994AHigh transglycosidic activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationAspergillus oryzaeMutant
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity. On the basis of removal of an amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase of aspergillus candidus and aspergillus oryzae of a signal peptide, the beta-galactosidase mutant is obtained through fixed point saturated mutation of a unit point. The transglycosylation activity of the mutant is improved by above 15 percent in comparison of the transglycosylation activity of a wild type mutant. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a DNA molecule for coding the mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing the DNA molecule and a host cell for expressing the DNA molecule. In addition, the invention further provides a method for preparing the beta-galactosidase mutant with high transglycosylation activity by adopting the recombinant expression vector, and application of the mutant, the DNA molecule, the recombinant expression vector and the host cell to the preparation of the beta-galactosidase.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Yeast fermentation small-molecular recombinant fibronectin protein peptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110204608AImprove heat resistanceHigh degree of glycosylationCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsATPaseBinding domain
The invention discloses a yeast fermentation small-molecular recombinant fibronectin protein peptide comprising at least one sodium-potassium ATPase beta subunit binding domain, and the sodium-potassium ATPase beta subunit binding domain has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the yeast fermentation small-molecular recombinant fibronectin protein peptide and an application of the yeast fermentation small-molecular recombinant fibronectin protein peptide. The yeast fermentation small-molecular recombinant fibronectin protein peptidecan be effectively absorbed by skin and has excellent healing and repairing effects on traumatic skin lesions or subcutaneous lesions with intact keratin.
Owner:MELLGEN SHENZHEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombinant receptor binding protein and recombinant receptor protein for detecting new coronavirus neutralizing antibody
ActiveCN112707968AEasy to mass produceMeet the needs of tracking and testingPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSsRNA viruses positive-senseReceptorImmunogenicity
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, and relates to a recombinant receptor binding protein and a recombinant receptor protein for detecting a new coronavirus neutralizing antibody, in particular to the recombinant receptor binding protein, the recombinant receptor protein, a nucleic acid molecule, a recombinant expression vector, a recombinant host cell, a reagent composition, a kit and application. The recombinant receptor binding protein is an RBD trimer protein, the RBD trimer protein has an optimized spatial structure and higher immunogenicity, the recombinant receptor protein is an ACE2 dimer protein, the ACE2 dimer protein has a natural protein conformation capable of simulating ACE2, after the recombinant receptor binding protein and the recombinant receptor protein are combined, the new coronavirus neutralizing antibody can be detected through the principle of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, the sensitivity, specificity and stability are remarkably improved, and the requirement for tracking detection of the new coronavirus neutralizing antibody on the market can be greatly met.
Owner:SUZHOU CUREMED BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Construction and application of vector used for developing high-expression cell strain
ActiveCN103525867AReduce formation rateEasy to getVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsVersus geneBiochemistry
The invention relates to a pSGS vector and application of the vector to development of a high-expression cell strain. The construction of the vector comprises the following steps: based on a neomycin resistance screening gene NEO, through combined strategy of weakening screening gene expression and reinforcing target gene expression, constructing an expression vector pSNEO, and in view of the amplification function of a GS system, through designing a primer, replacing the hairpin structure sequence and the NEO gene of the vector pSNEO with a hairpin structure sequence and a GS gene to obtain a universal vector pSGS for screening a high-expression and stable-transfection cell strain. Through the pSGS vector constructured by the invention, the construction of a stable and high-expression cell strain of the target gene can be finished conveniently and quickly, and a new tool is provided for preparation of macromolecular recombinant protein.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
Beta-glucosaccharase, beta-glucosaccharase mutant and application
ActiveCN104531637AIncrease hydrolysis rateSame enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseAlglucerase
The invention discloses a composition which comprises an enzyme. The enzyme has the activity of glucosaccharase, and provides a degrading function in cellulose degradation. The enzyme is a protein shown in (a) or (b), wherein (a), the amino acid sequence of the is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; (b), one or several amino acid are displaced, removed out or added into the amino acid sequence in the (a), and the protein is derived from the (a) and has the activity of the glucosaccharase. DNA molecules of the enzyme are coded. Carriers are recombined and comprise the DNA molecules and adjusting sequences connected with the DNA molecules and used for conducting expressions. Host cells comprise the DNA molecules or the recombined carriers. Compared with the beta-glucosaccharase (with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1), a beta-glucosaccharase mutant with the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NO:6 and SEQ ID NO:7 has the beneficial effects that the heat stability is improved; and the hydrolysis rate of compound enzyme liquid can be improved in enzyme system compounding.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for processing plant-based chicken fiber food by using soybean protein isolate
ActiveCN112515034AIncrease moisture contentGreat tasteProteins working-up by texturisingVegetable proteins working-upBiotechnologyProtein molecules
The invention discloses a process for processing a plant-based chicken fiber food by using soybean protein isolate. The plant-based chicken fiber food is obtained by performing twin-screw extrusion processing on the soybean protein isolate, wheat protein, low-temperature soybean meal, corn modified starch and soybean oil according to a specific ratio. Through high-temperature, high-pressure and high-strength shearing and molecular recombination, 2, 3 and 4-level structures of protein molecules are opened, then the protein molecules are crosslinked and recombined with starch and other components and fully fused with water, the chicken-like fiber is obtained, the water content is high, the eating taste is good, the plant-based chicken fiber food can replace chicken to be widely applied to various foods, functional foods and the like, and healthier protein is provided for human beings.
Owner:LINYI SHANSONG BIOLOGICAL PRODS
Beta-galactosidase combination mutant with high transglycosylation, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107201352AHigh transglycosidic activityIncrease reaction rateFungiMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringMutagenesis
The invention belongs to the fields of gene engineering and genetic engineering, and discloses a beta-galactosidase combination mutant with high transglycosylation. The beta-galactosidase combination mutant is obtained through site-saturation mutagenesis of two sites on the basis of removing an amino acid sequence of beta-galactosidase of aspergillus candidus and aspergillus oryzae of self-signal peptide, and the transglycosylation reaction rate of the mutant is improved by more than 100 percent compared with a wild type under the condition of keeping oligosaccharide forming amount unchanged. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) molecule for coding the combination mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing the DNA molecule, and a host cell expressing the DNA molecule. In addition, the invention also provides a method for preparing the beta-galactosidase combination mutant with high transglycosylation by adopting the recombinant expression vector, and application of the combination mutant, the DNA molecule, the recombinant expression vector and the host cell in preparing the beta-galactosidase.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of preparing a eukaryotic viral vector
The inventive method of producing a eukaryotic viral vector comprises contacting a eukaryotic cell, which comprises a unique enzyme that nicks or cleaves a DNA molecule, with a recombinant phage vector, or contacting a eukaryotic cell, which does not comprise a unique enzyme that nicks or cleaves a DNA molecule, simultaneously or sequentially, in either order, with (i) a unique enzyme that nicks or cleaves a DNA molecule, and (ii) a recombinant phage vector. The recombinant phage vector comprises the DNA molecule comprising (a) a eukaryotic viral vector genome comprising a coding sequence, (b) a phage packaging site that is not contained within the eukaryotic viral vector genome, and (c) a promoter that is operably linked to the coding sequence.Alternatively, the DNA molecule is not present within the recombinant phage vector. The eukaryotic cell is contacted with the first DNA molecule and a recombinant phage vector. The first DNA molecule comprises a replication deficient eukaryotic viral vector genome comprising at least one adenoviral inverted terminal repeat and a packaging signal. The recombinant phage vector comprises a second DNA molecule and a phage packaging site, wherein the second DNA molecule complements in trans the replication deficient eukaryotic viral vector genome.The DNA molecule(s) enter the eukaryotic cell, and the unique enzyme nicks or cleaves the DNA molecule in the eukaryotic cell in at least one region not contained within the eukaryotic viral vector genome, thereby inducing the production of and ultimately producing a eukaryotic viral vector.
Owner:GEN VEC INC
Soybean meal adhesive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110894422AImprove efficiencyHigh reactivityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesProtein adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
The invention relates to an adhesive, in particular to a soybean meal adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The soybean meal adhesive comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30-33parts of a main agent, 67-70 parts of a dispersion medium, 2-3 parts of a treatment agent, 1-2 parts of a molecular recombination agent, 2-3 parts of a cross-linking agent, 0.4-0.8 part of a reinforcing agent and 1-2 parts of a viscosity regulator. The preparation method of the soybean meal adhesive comprises the following steps: (1) pre-reaction: adding soybean meal powder, water and the treatment agent into dispersion medium water, carrying out ultrasonic treatment for 7-14 minutes, heating to 50-70 DEG C, and stirring for 15-25 minutes; (2) microphase separation: adding the molecular recombination agent into a mixture obtained in the step (1), adjusting the pH value to 9-11, reacting at 70-90 DEG C for 25-35 minutes, cooling to 25-35 DEG C, and discharging; and (3) cross-linking synthesis: adding the reinforcing agent and the cross-linking agent into a mixed material obtained in the step (2), uniformly stirring, carrying out ultrasonic treatment for 15-25 minutes, adding the viscosity regulator, and uniformly stirring. The soybean meal adhesive disclosed by the invention is high in adhesion degree, good in water resistance and relatively good in stability.
Owner:DEHUA TB NEW DECORATION MATERIAL CO LTD +1
Beta-glucosaccharase, beta-glucosaccharase mutant and application
ActiveCN104560917AIncrease hydrolysis rateImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseAlglucerase
The invention discloses a composition, containing an enzyme, wherein the enzyme has the activity of glucosaccharase and provides a degradation function in cellulose degradation, and the enzyme is the following protein (a) or (b): (a) protein with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 1, (b) protein with one or more amino acids substituted, lost or added in the amino acid sequence in (a), having the activity of glucosaccharase and derived from (a). The invention also discloses a DNA molecule for encoding the enzyme, a recombinant vector containing the DNA molecule and a regulation sequence connected with the DNA molecule and used for expressing, and a host cell containing the DNA molecule or the recombinant vector. According to the beta-glucosaccharase mutant having the amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No: 2, 3 and 4 provided by the invention, compared with wild beta-glucosaccharase, the thermostability is improved, and the integral hydrolysis rate of compound enzyme liquid in enzyme system compound can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Beta-galactosidase combined mutant with high transglycosylation activity as well as preparation method and application of beta-galactosidase combined mutant
ActiveCN104263710AHigh transglycosidic activityIncrease reaction rateFungiFermentationReaction rateWild type
The invention belongs to the fields of gene engineering and genetic engineering, and discloses a beta-galactosidase combined mutant with high transglycosylation activity. On the basis of amino acid sequences of beta-galactosidase of aspergillus candidus and aspergillus oryzae, from which signal peptides are removed, a beta-galactosidase combined mutant is obtained through fixed-site saturation mutagenesis of double sites; under the condition of keeping the oligosaccharide production amount invariable, the transglycosylation reaction rate of the mutant is improved by over 100% in comparison with a wild mutant; and meanwhile, the invention also discloses a DNA molecule of encoding the combined mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing the DNA molecule, and a host cell of expressing the DNA molecule. In addition, the invention also provides a method for preparing the beta-galactosidase with high transglycosylation activity by using the recombinant expression vector, and applications of the combined mutant, the DNA molecule, the recombinant expression vector and the host cell in preparation of the beta-galactosidase.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant production systems for aromatic molecules
ActiveUS9637763B2Improve abilitiesAllow flexibilitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsEscherichia coliYeast
Owner:RHO RENEWABLES
DNA molecule, recombinant plasmid and recombinant bacterium for production of D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine
InactiveCN103993010AImprove conversion rateMild conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesN-carbamoylaseHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a DNA molecule, a recombinant plasmid and a recombinant bacterium for production of D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine. The DNA molecule provided by the invention comprises a PL promoter, a D-hydantoinase gene and an N-carbamoylase gene, and expression of the D-hydantoinase gene and the N-carbamoylase gene is initiated by the PL promoter. The invention provides the DNA molecule able to stably and massively express D-hydantoinase and N-carbamoylase, and the recombinant plasmid and the recombinant bacterium based on the DNA molecule. At the same time, the invention also provides a method for converting DL-p-hydroxyphenylhydantoin into D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine by the recombinant bacterium or fermented recombinant bacterium. The method only generates D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine, has no need of splitting and separating an enantiomer, and the conversion rate is high. The whole production process has the advantages of mild conditions, simple operation, and environmental friendliness.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
III-type bacteriocin from L. crispatus, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN107245491AHas antibacterial activityShorten the production cycleBacteriaFood preservationFood preservationBacteriocin
The invention discloses III-type bacteriocin Helveticin-M molecular from L. crispatus. The Helveticin-M molecular possesses antibacterial effect, and is a polypeptide selected from polypeptide (a), polypeptide (b), or polypeptide (c). The polypeptide (a) is obtained via coding of a DNA molecular with a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1; the polypeptide (b) is obtained via coding of a DNA molecular with a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2; and the polypeptide (a) is a derivative of polypeptide (b), is obtained via substitution, deletion, or addition of one or a plurality of amino acids, and possesses antibacterial activity. The invention also discloses a DNA molecular used for coding Helveticin-M molecular. The invention also discloses a preparation method of III-type bacteriocin Helveticin-M molecular, and applications of III-type bacteriocin Helveticin-M molecular, the DNA molecular, recombinant vectors, or host cells in food preservation bacteria inhibition and decomposition inhibition. The III-type bacteriocin Helveticin-M molecular possesses antibacterial activity, and can be used in food fresh keeping; heterologous expression can be realized; and the preparation method possesses guidance meaning in research and study on III-type bacteriocin.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for separating and purifying molecule recombination collagen protein
InactiveCN101157719ALow priceAbundant raw materialsPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesSurgical materialPhosphate
The present invention pertains to the technical field of collagens, in particular to a method for separation, purification and recombination of the collagens. The present invention takes the shark scalps as the raw materials, the soaking, the salt precipitation and the chromatography in the phosphate buffer solutions with the different concentrations are carried out sequentially for extraction and purification of the collagens. The obtained collagens can better maintain the spatial structural features of the collagens which exists naturally, the collagens can be prepared into the biomedical engineering materials with the good anti-leakage capacity and long degradation time after the molecular recombination, which can be used as various medical surgical materials with the higher requirements for reconstruction of veins and arteries and so on. The method of the present invention has rich sources, low price, simple process and no environmental pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES UNIV
In Vitro methods of producing and identifying immunoglobulin molecules in eukaryotic cells
ActiveUS20080167193A1VirusesMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulin heavy chainSpecific immunoglobulins
The present invention relates to a high efficiency method of expressing immunoglobulin molecules in eukaryotic cells. The invention is further drawn to a method of producing immunoglobulin heavy and light chain libraries, particularly using the trimolecular recombination method, for expression in eukaryotic cells. The invention further provides methods of selecting and screening for antigen-specific immunoglobulin molecules, and antigen-specific fragments thereof. The invention also provides kits for producing, screening and selecting antigen-specific immunoglobulin molecules. Finally, the invention provides immunoglobulin molecules, and antigen-specific fragments thereof, produced by the methods provided herein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Molecular-rearrangement whole-nutrient edible oil
InactiveCN1437859AMaintain nutritional balancePromote absorptionEdible oils/fatsMolecular rearrangementMolecular level
The present invention relates to a full nutrient edible oil series. According to their respective composition, fatty acid content and fatty acid content necessary for human body said series is made up by adopting three or more than three kinds of edible oil. It is characterized by that it is a new type full-nutrient edible oil reconstituted on molecular level by adopting molecular recombination techinque, and the composition proportion of S, M, P, omega 6 and omega 3 being in edible oil is reasonable, and its nutrients are easily absorbed by human body, and beneficial for health for human body.
Owner:郑春学
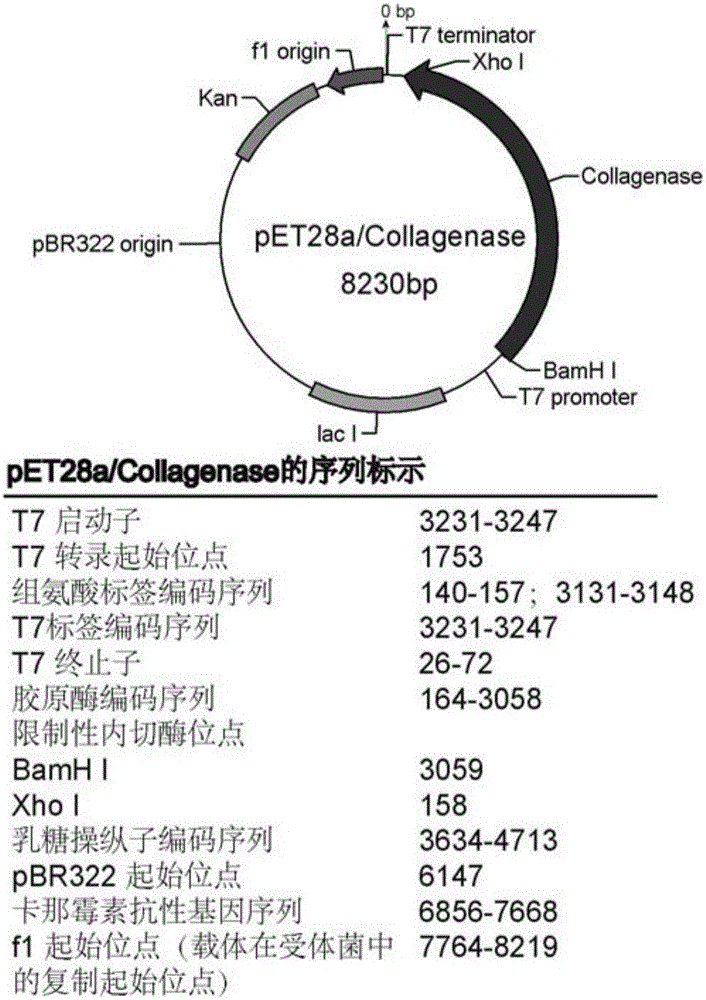
DNA molecule for expressing collagenase in Escherichia coli and method and application of recombinant collagenase
The invention discloses Escherichia coli for expressing a collagenase and a construction method and application thereof. An amino acid sequence (shown in SEQ ID NO:1) and a nucleotide sequence (shown in SEQ ID NO:2) of the collagenase excreted by Bacillus cereus R75E are provided. The invention provides an expression bacterium comprising the collagenase genes in the Escherichia coli. The recombinant Escherichia coli containing the expressed DNA molecule is an Escherichia coli strain obtained by guiding an Escherichia coli recombinant expression vector into host bacteria. The invention provides a method for purifying the recombinant collagenase and an application for degrading type I collagen in fish scales. The recombinant collagenase can efficiently degrade natural type-I collagen fibers, is remarkable in effect, and can be applied to development and utilization of collagen in agricultural and sideline products, processing and utilizing of collagen of aquatic products, and production in medical and food industries.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Mineral coating for ceramic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108485332AGood lookingImprove breathabilityAntifouling/underwater paintsAlkali metal silicate coatingsMetasilicateWater vapor
The invention relates to mineral coating for ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The mineral coating is prepared from the following raw materials according to a weight percent: 20-35% of anti-bacterial base liquid, 20-40% of potassium metasilicate, 1-5% of dispersing agent, 1-4% of diluent, 3-10% of emulsion, 1-7% of talcum powder, 1-5% of ferric oxide, 5-10% of aedelforsite and 10-15% of kaoline. According to the provided mineral coating for the ceramic and the preparation method thereof, through inorganic molecular recombination, a molecular structure of a product is changed from an original crystal structure to a net-like structure, a molecular gap is less than a water molecule, and greater than a water vapor molecule, so water of a wall body is turned into water vapor under a temperature difference effect and is freely discharged from a coating, a pressure to a wall surface caused by evaporation of the water is relieved, and a base surface is kept dry. Through the good air permeability of a coating film, the coating is guaranteed not to crack, and maintains a good appearance effect. Through adding the anti-bacterial base liquid, the sterilizing effect can be achieved, andthe safety of the coating is improved.
Owner:FOSHAN RUNHUIHE CHEM CO LTD
Knockout method for stem cell gene
PendingCN111073908AKnockout fastFunctional analysis is accurateVector-based foreign material introductionIntracellularVector (molecular biology)
The invention discloses a knockout method for a stem cell gene, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology. The method specifically includes the following steps: S1, establishing a gene sequence, querying a code sequence (CDS) of a target gene in a database according to the gene sequence, obtaining a complete CDS of the gene by using a single-stranded CDNA as a template, and performing comparison to obtain a complete target gene exon sequence; S2, designing the target gene according to the S1, designing homologous recombination double exchange homologous arms, and constructing target gene knockout plasmid on the basis of knocking out template plasmid; and S3, recombining the target gene and DNA molecules homologous with a specific fragment of a target gene in cells onto a vector with a marker gene. According to the knockout method for the stem cell gene, the stem cell gene can be quickly knocked out on the basis of not introducing exogenous genes by using the knockout method for the stem cell gene provided by the invention, so that a worker can analyze the target gene function more accurately in the later stage, and the gene knockout efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Novel lentiviral packaging cells
InactiveUS20050170507A1Improve securityRule out the possibilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousPol genes
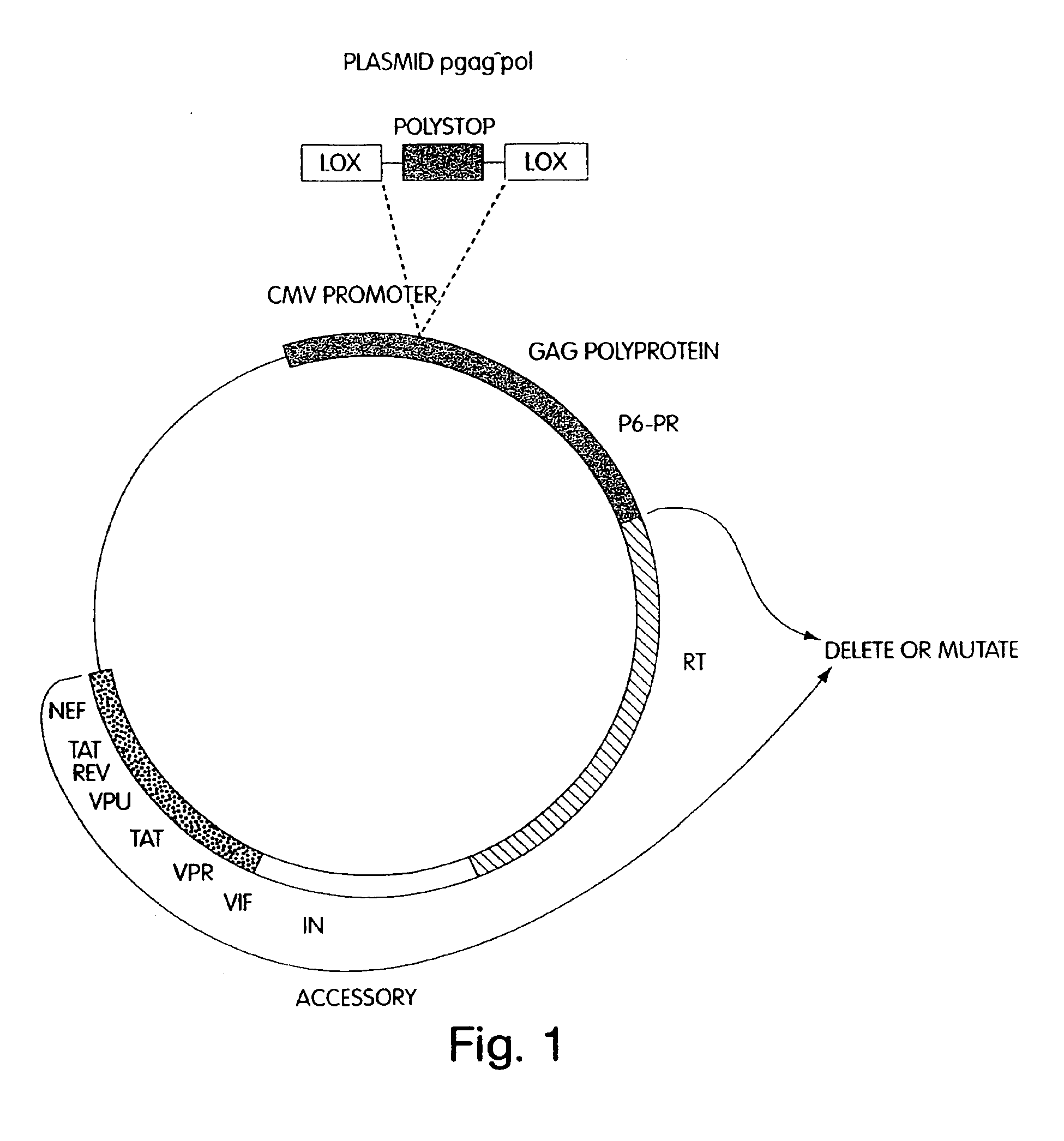
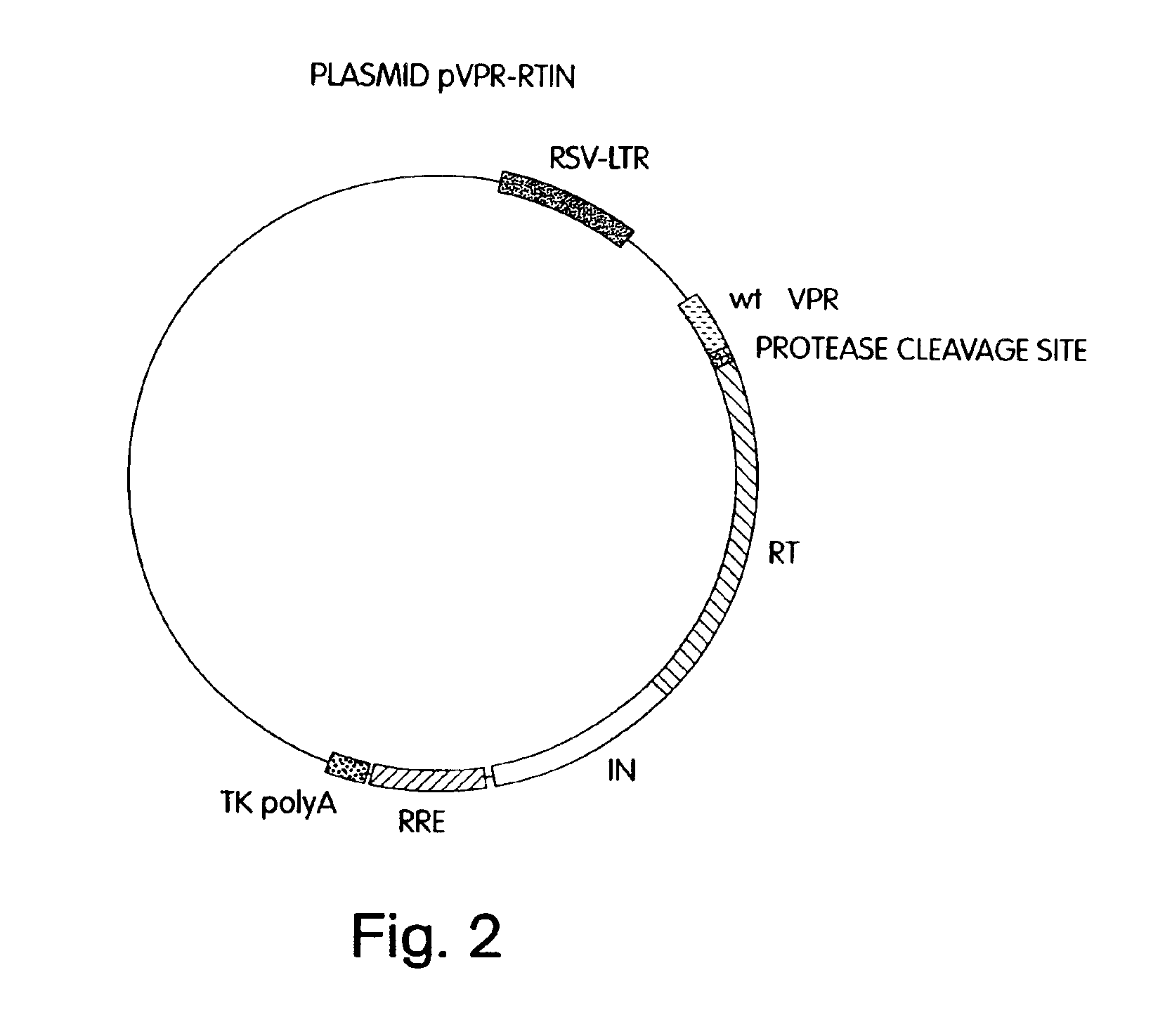
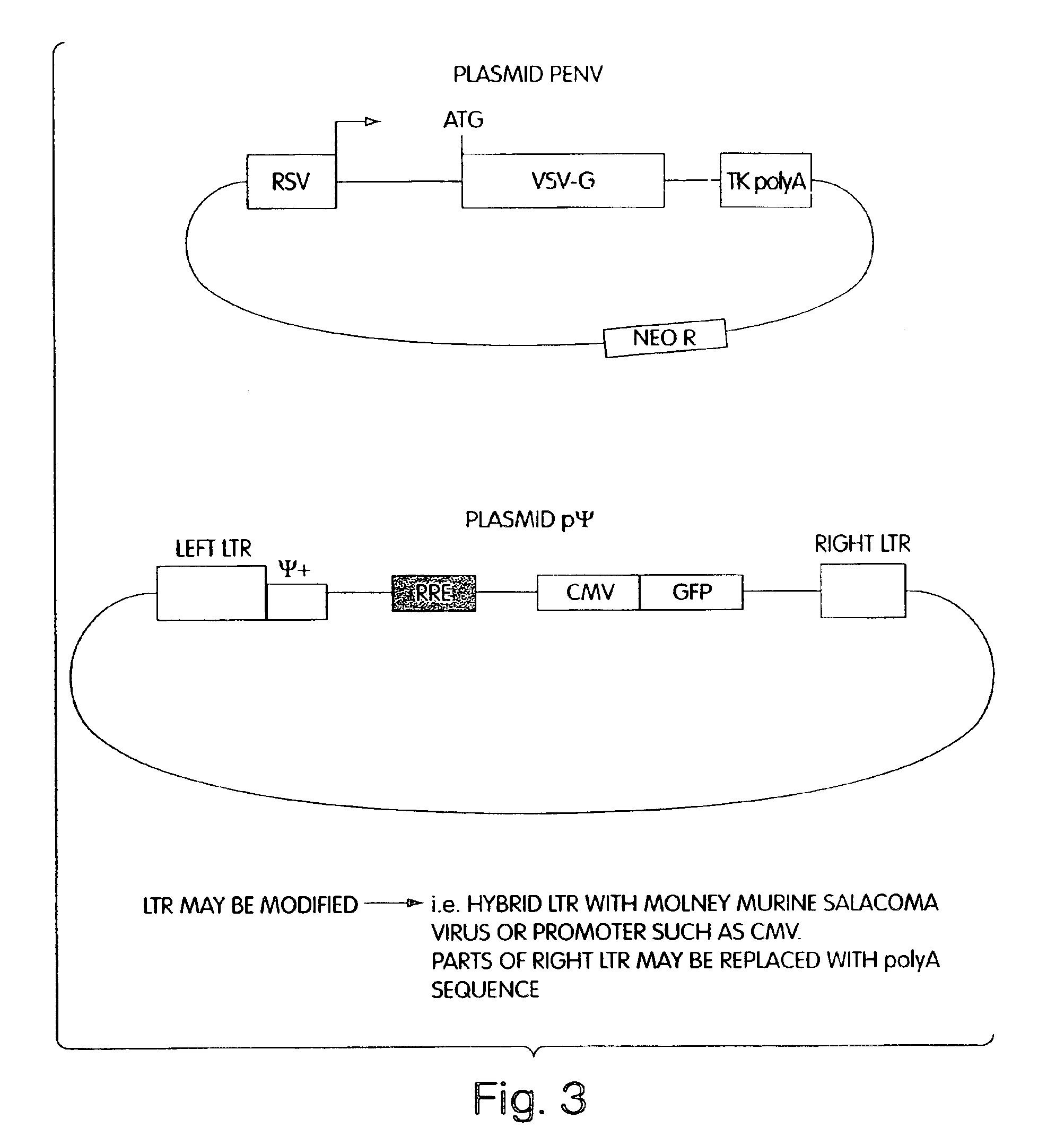
Novel packaging cell lines which produce recombinant retrovirus, free of detectable helper-virus are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of making the cell lines and methods of producing recombinant retroviruses from the cell lines. Retroviruses produced by the cell lines include lentiviruses, such as HIV, capable of transfering heterologous DNA to a wide range of non-dividing cells. The packaging cells contain at least three vectors which collectively encode retroviral gag, pol, and env proteins, wherein the gag and pol genes are separated, in part, onto two or more different vectors. This is made possible by fusing Vpr or Vpx to pol proteins separated from gag so that the proteins are targeted to assembling virions. Among other advantages, the packaging cells provide the benefit of increased safety when used in human gene therapy by virtually eliminating the possibility of molecular recombination leading to production of replication-competant helper virus.
Owner:GENETIX PHARMA
shRNA molecule of knockdown mouse endogenous CYP3A, recombinant expression vector, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102443584AReduced activityReduce expressionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCYP3ANucleotide
The invention discloses a shRNA molecule of knockdown mouse endogenous CYP3A. The nucleotide sequence of the shRNA molecule is as shown in SEQID No.6. The invention also discloses a recombinant expression vector pRIME-CMV-eGFP-miR-shRNA containing the shRNA molecule, a preparation method of the vector and an application of the shRNA molecule in the knockdown mouse endogenous CYP3A. Expression of a mouse endogenous CYP3A gene is effectively blocked in transgenic mouse produced by the invention. By the use of the invention, a transgenic mouse model of the knockdown mouse endogenous CYP3A is established and human CYP is expressed in the mouse model. The invention can be applied in drug research and development to make the drug effect index in mouse to be more close to that in human.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Ketoreductase dna molecule, recombinant vector and bacterial strain and application
ActiveCN107794270BSimple and fast operationHigh expression of enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArabinoseGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to DNA molecules, protein or polypeptide sequences for producing ketoreductase, recombinant vectors, strains and applications. The base sequence of the ketoreductase DNA molecule is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; or it is selected from the gene encoding the following protein (a) or (b): (a) the amino acid shown in SEQ ID NO.2 (b) a polypeptide or protein derived from (a) that has undergone substitution, deletion or addition of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence defined in (a) and has ketoreductase activity. In the present invention, the connection of the mutant gene with the plasmid pBAD is more stable, and under the induction of arabinose, the fermentation enzyme activity is higher, which can reach more than 120U / mL, and has the characteristics of high expression, stable expression system, and simple fermentation control. Suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:安琪酶制剂(宜昌)有限公司
Construction and application of mammal cell high-efficiency expression vector
ActiveCN103525868BShorten the development cycleVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsTranscriptional Regulatory ElementsCloning Site
The present invention relates to a mammalian cell high-efficiency expression vector pSNEO, which is constructed based on the neomycin resistance screening gene NEO by combining the strategy of weakening the expression of the screening gene and enhancing the expression of the target gene. Wherein, the attenuation of the screening gene includes two aspects, the introduction of a deletion mutation in the promoter to achieve the attenuation of the transcription of the screening gene, and then the introduction of a hairpin structure sequence before the translation start site of the screening gene to achieve attenuation of the translation of the screening gene. To enhance the expression of the target gene, a transcriptional regulatory element WPRE sequence is added between the multiple cloning site of the target gene expression frame and the PolyA tailing signal. The pSNEO vector constructed by the invention can conveniently and quickly complete the construction of a stable high-expression cell line of the target gene, and provides a new tool for the preparation of macromolecular recombinant proteins.
Owner:BIOTECH PHARMA CO LTD
A process for processing plant-based chicken fiber food by using soybean protein isolate
ActiveCN112515034BIncrease moisture contentGreat tasteProteins working-up by texturisingVegetable proteins working-upBiotechnologyProtein molecules
The invention discloses a process for processing soybean protein isolate into plant-based chicken fiber food. A specific proportion of soybean protein isolate, wheat protein, low-temperature soybean meal, corn modified starch and soybean oil is processed by twin-screw extrusion to obtain a Plant-based chicken fiber foods. The invention opens the 2nd, 3rd and 4th grade structures of protein molecules through high temperature, high pressure and high strength shearing and molecular recombination, then crosslinks and reorganizes with starch and other components, and fully integrates with water to obtain chicken-like fibers with high water content. It has a good taste and can be widely used in various foods, functional foods, etc. to replace chicken, providing healthier protein to human beings.
Owner:LINYI SHANSONG BIOLOGICAL PRODS
Modified starch catalyzed by compound bio-enzymes and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101942119BSimple processImprove modification efficiencyNon-fibrous pulp additionFibre treatmentReaction rateRates reactions
The invention provides a preparation method and application of modified starch catalyzed by compound bio-enzymes. The modified starch is a non-toxic environment-friendly new material prepared by modifying raw plant starch by starch modifying assistants and compound bio-enzyme catalysts through special processes. The invention adopts the following technical scheme: the compound bio-enzyme catalysts are adopted to improve the reaction rate, shorten the reaction time and simplify the production process; and molecular recombination, namely grafting, is simultaneously carried out when the requiredviscosity is achieved, thus improving the use performance of the starch, reducing the use quantity of the assistants and reducing COD emission. The modified starch is widely applied to such fields asdisposable environment-friendly tableware, wrappers, non-woven fabrics, pulp for paper-making, industrial and agricultural membranes, fabrics warp sizing, especially to fabrics warp sizing, and can replace PVA and other size.
Owner:WUHAN GREEN BOAT ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com