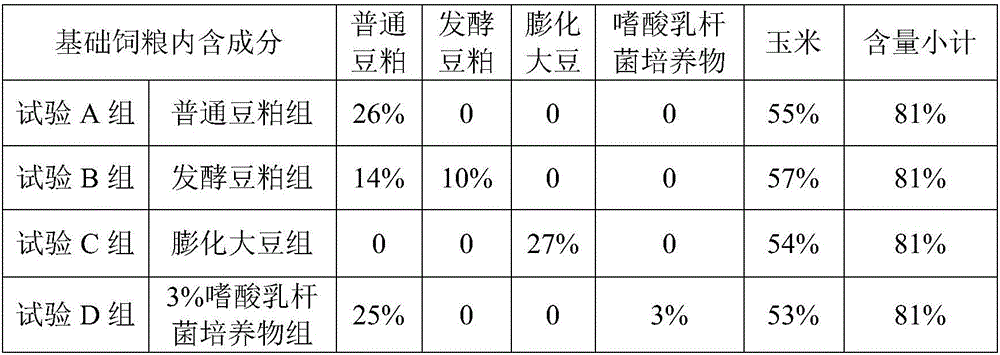
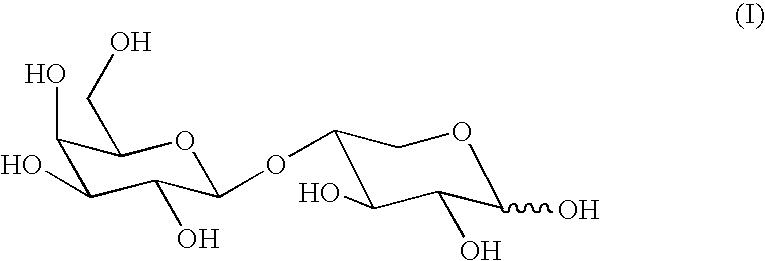
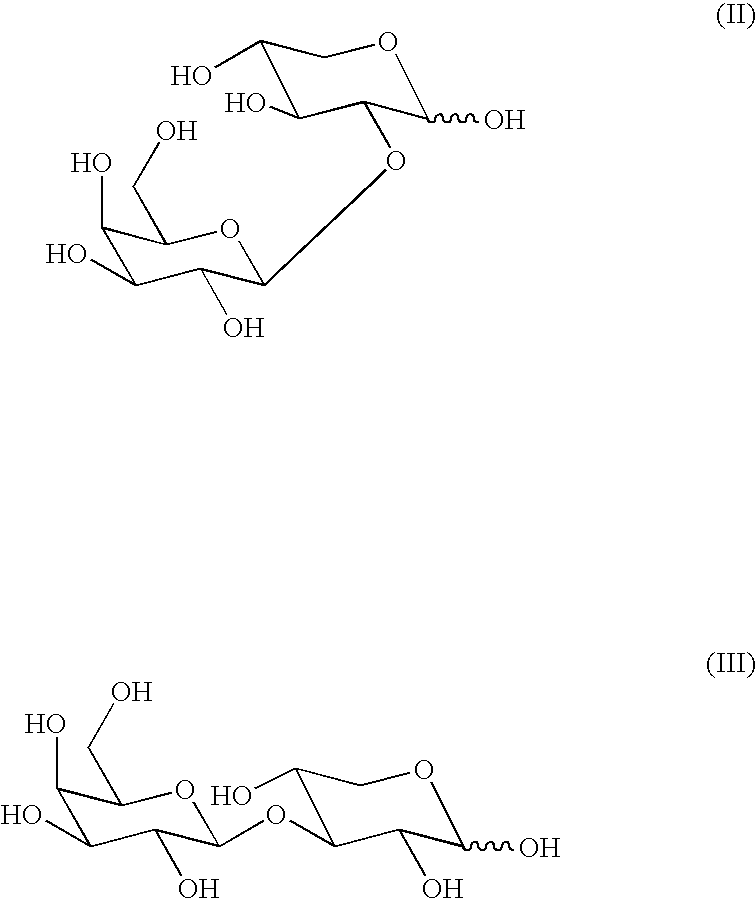
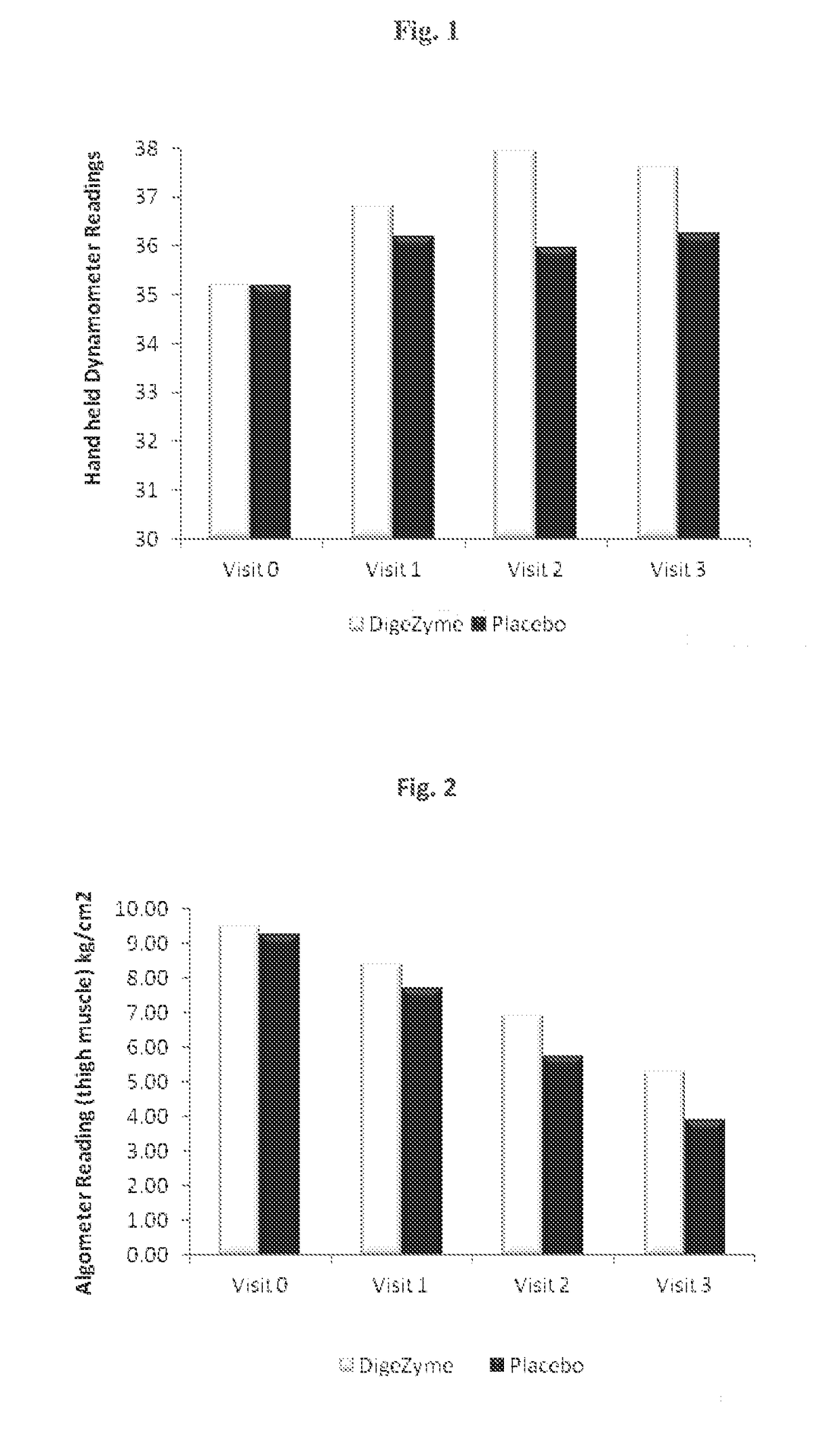
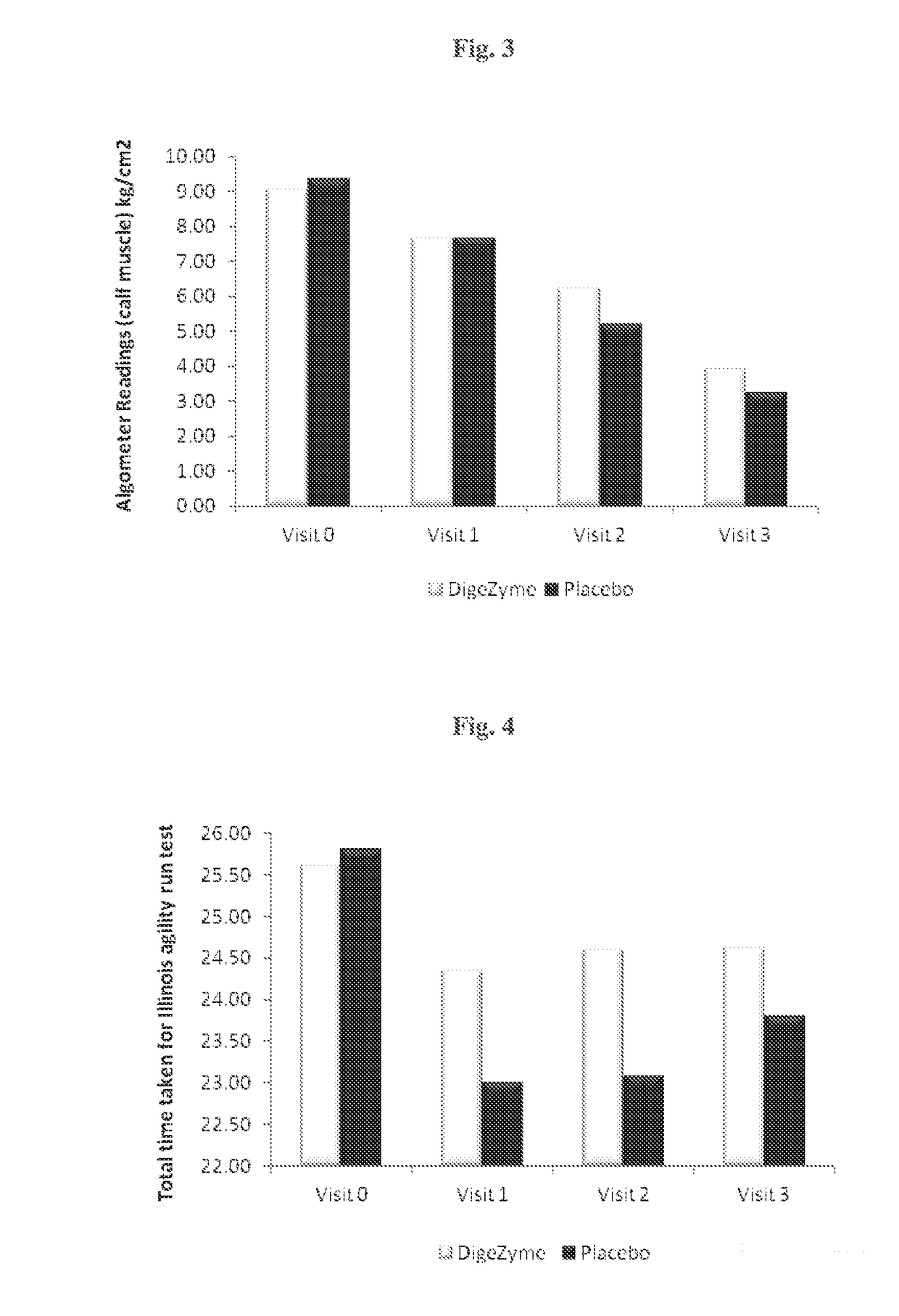
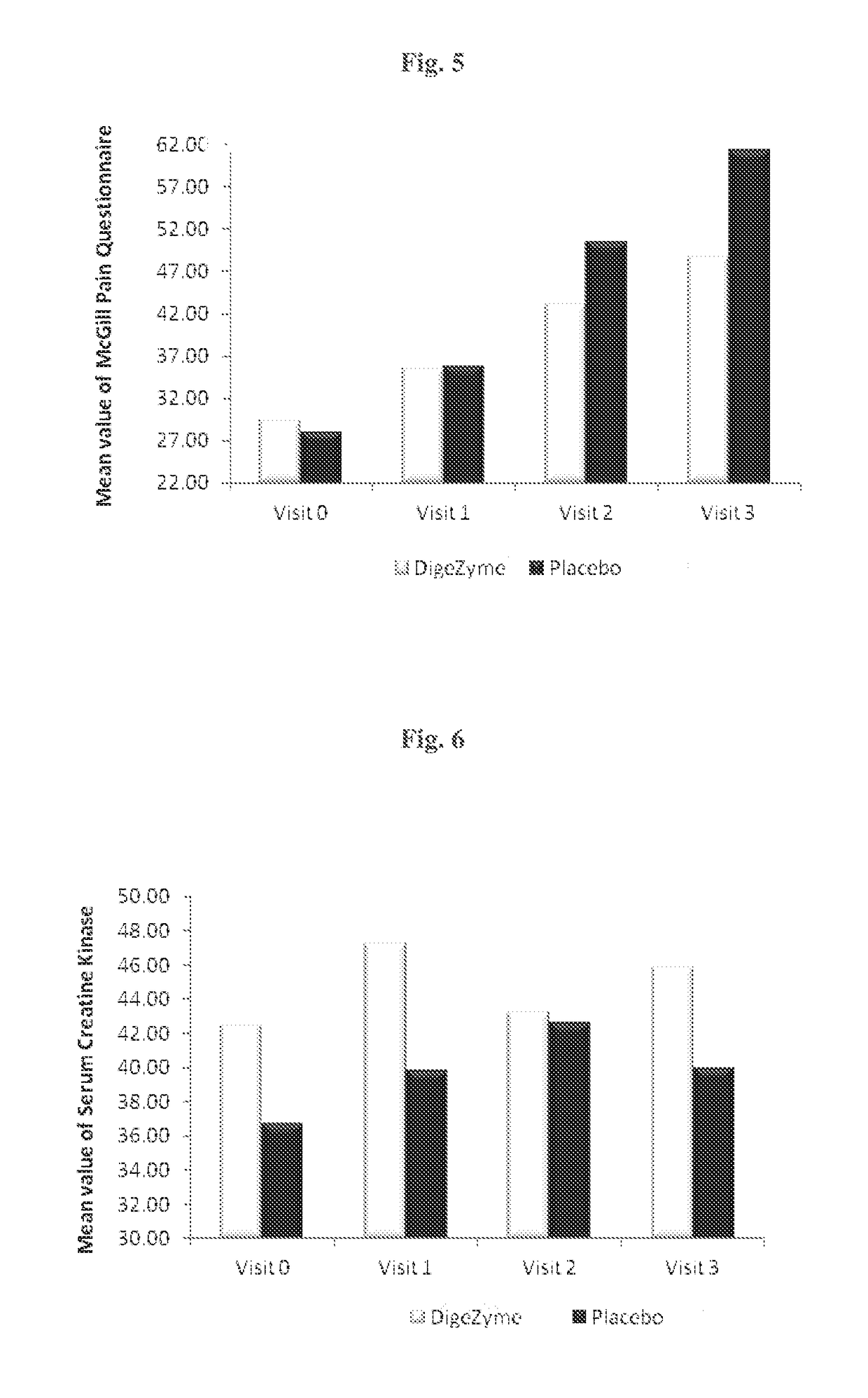
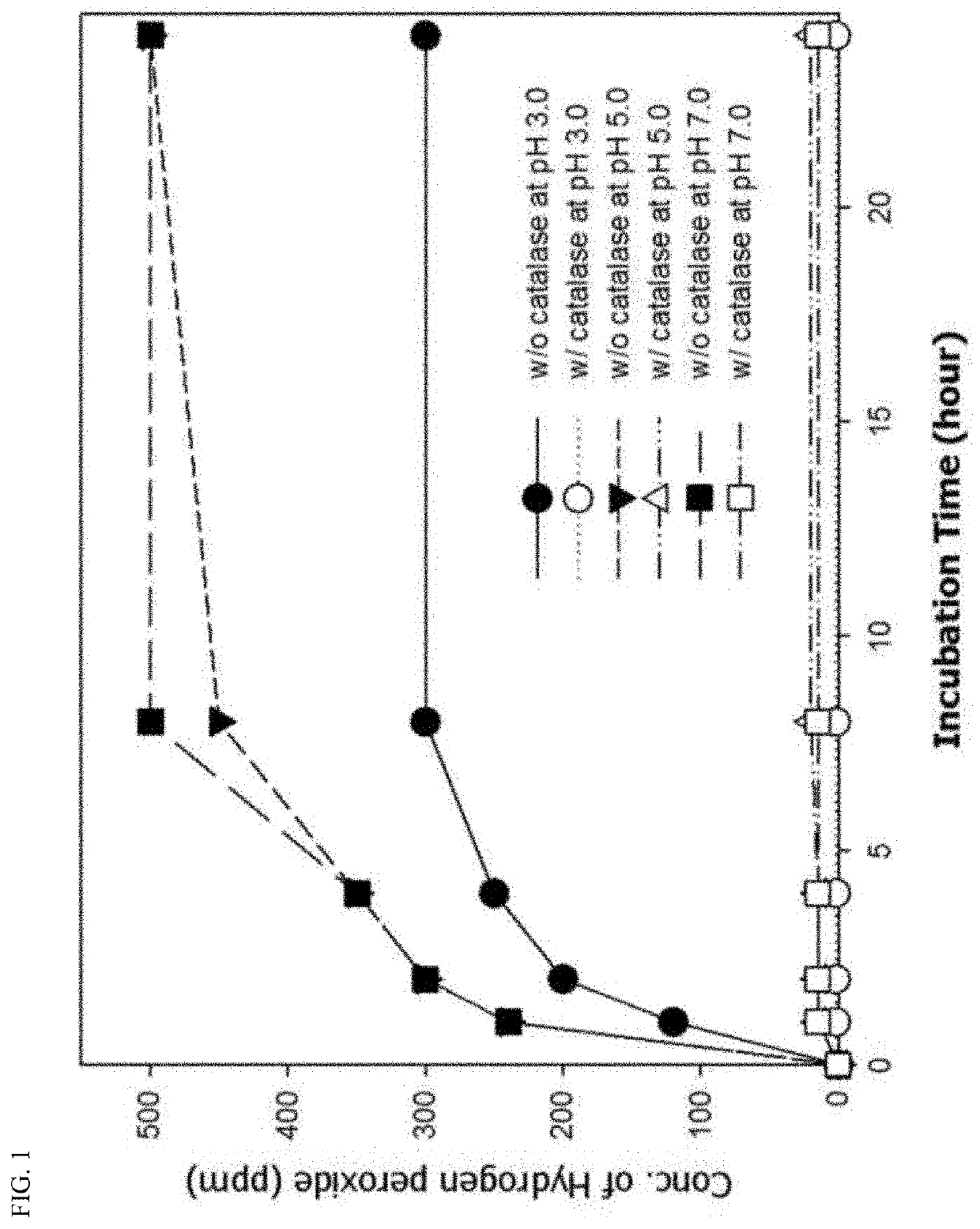
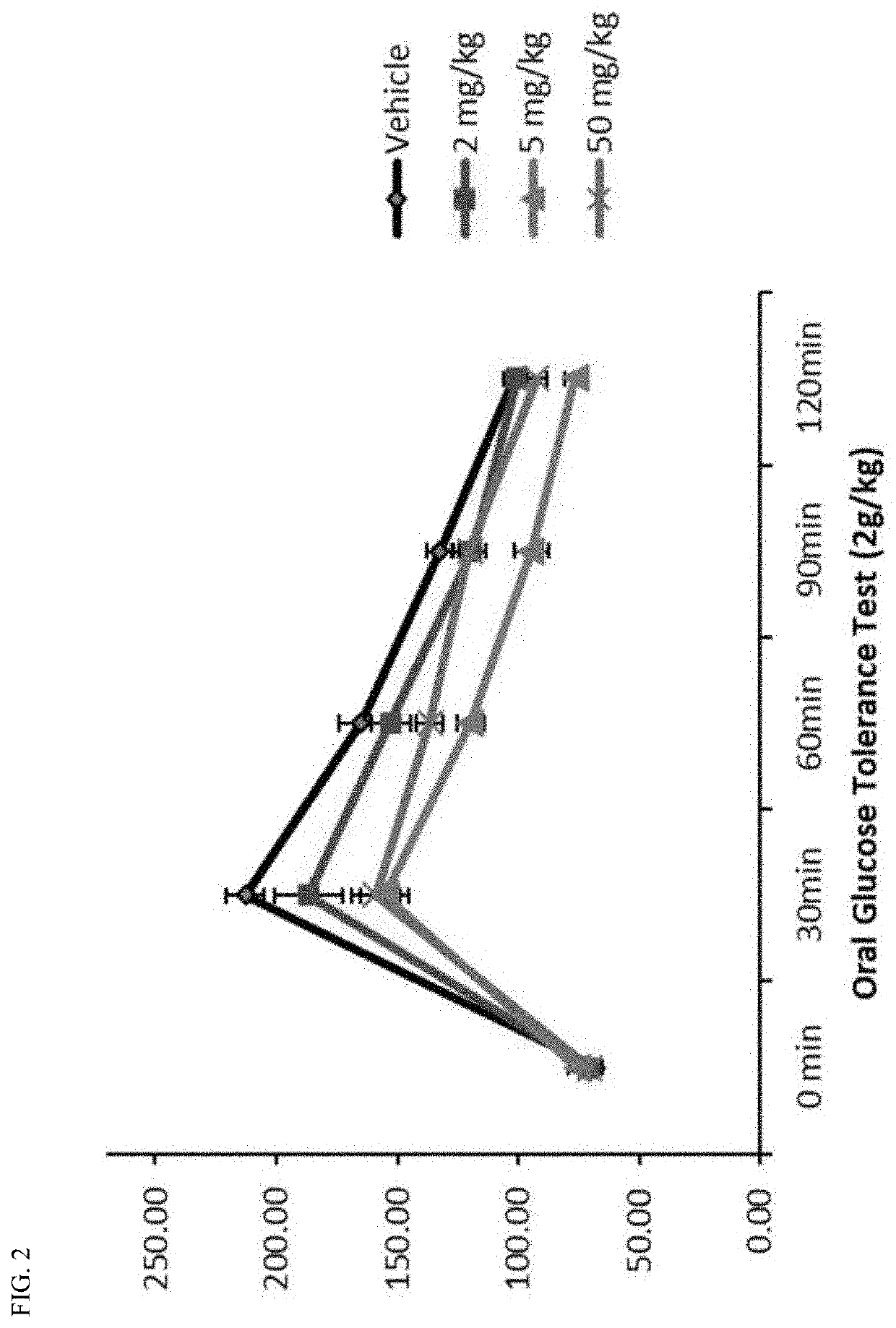
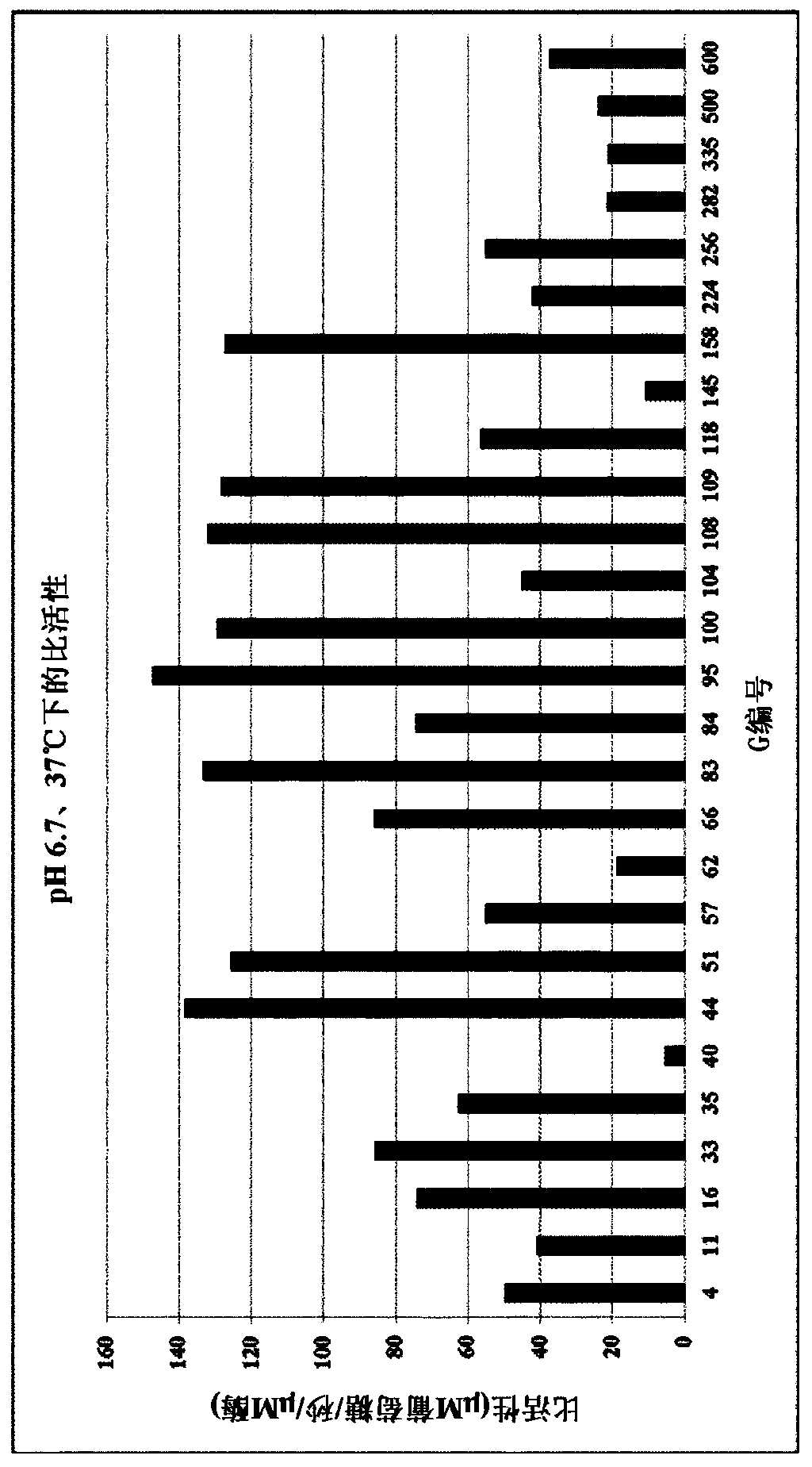
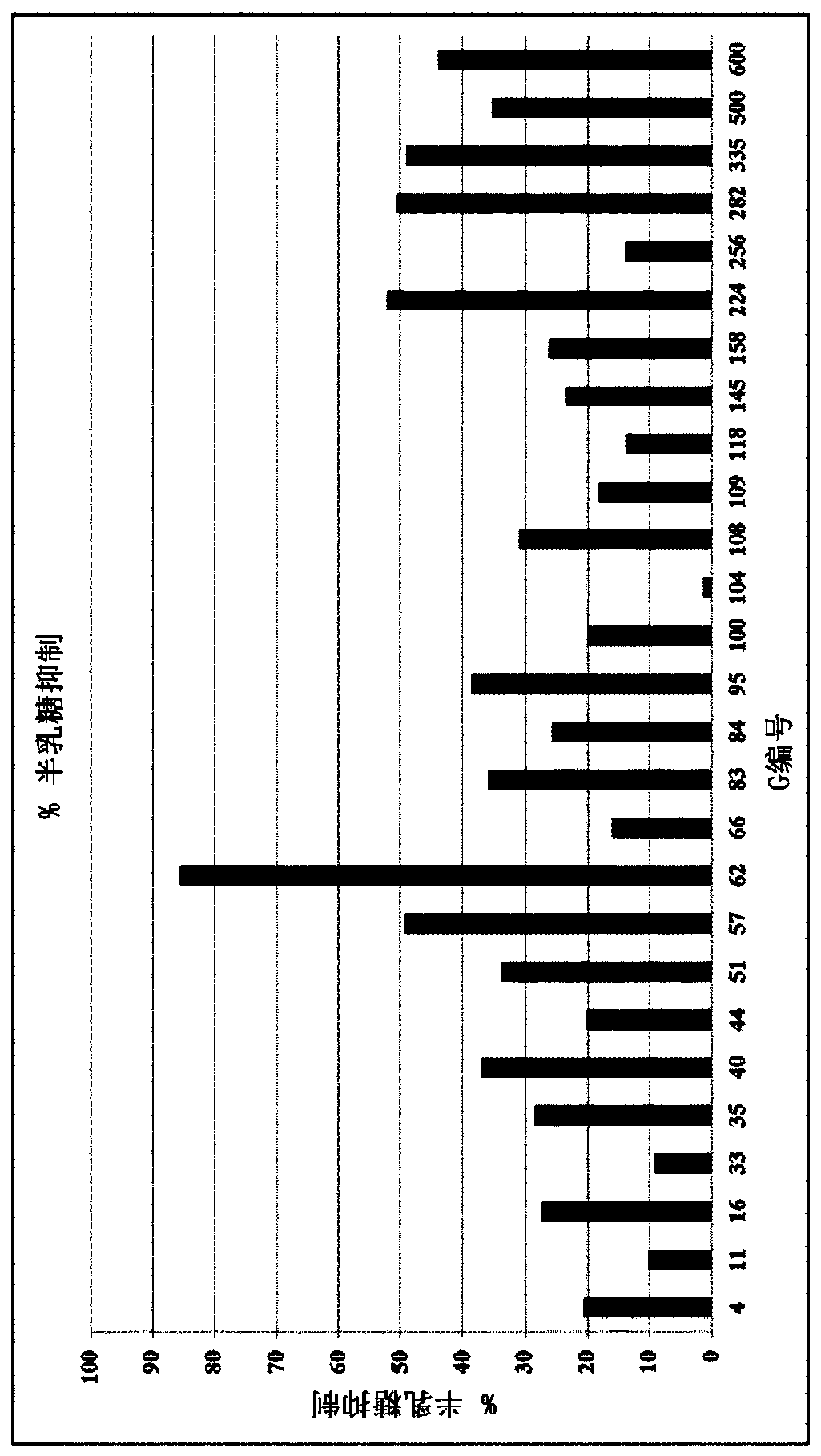
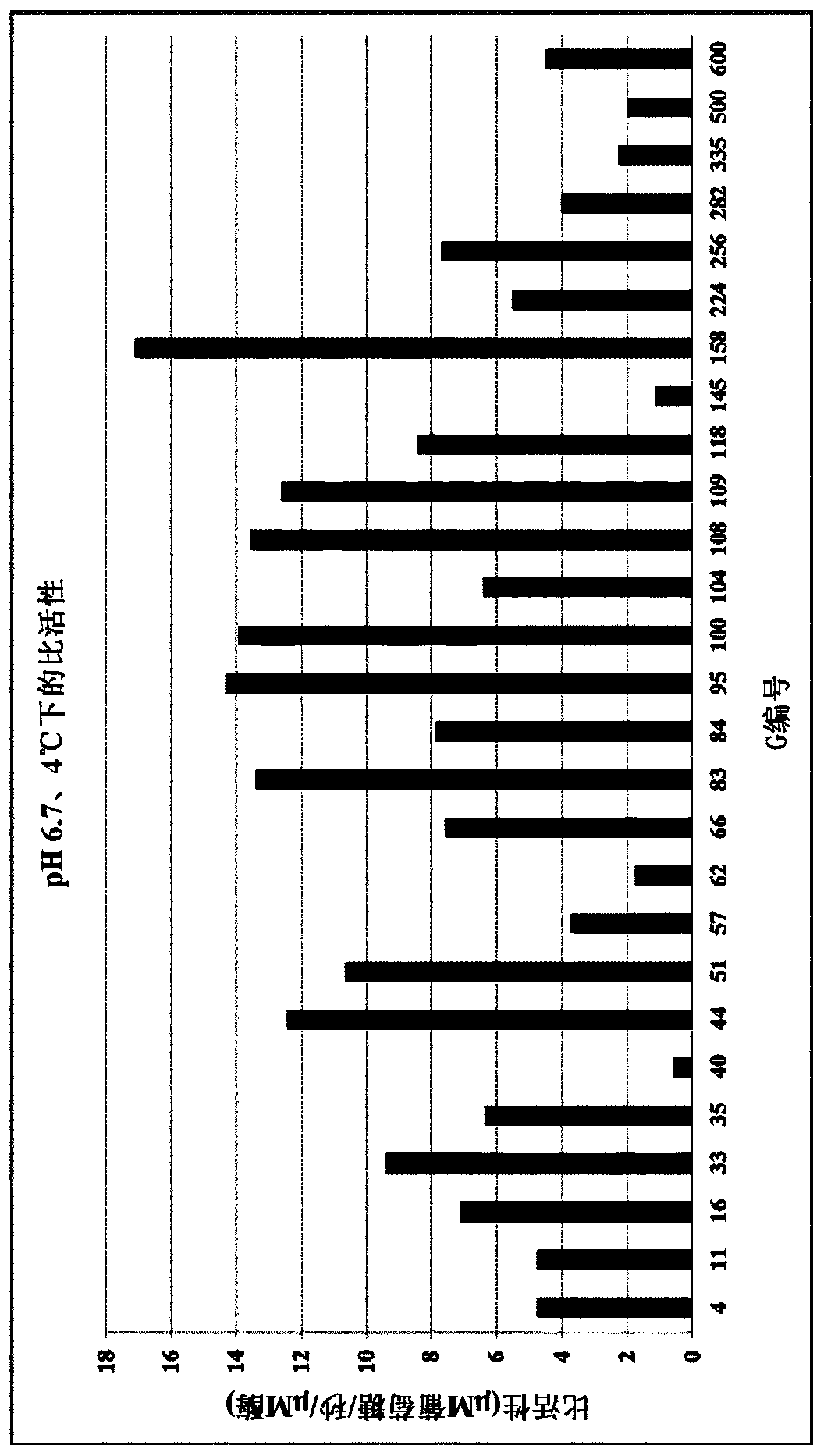
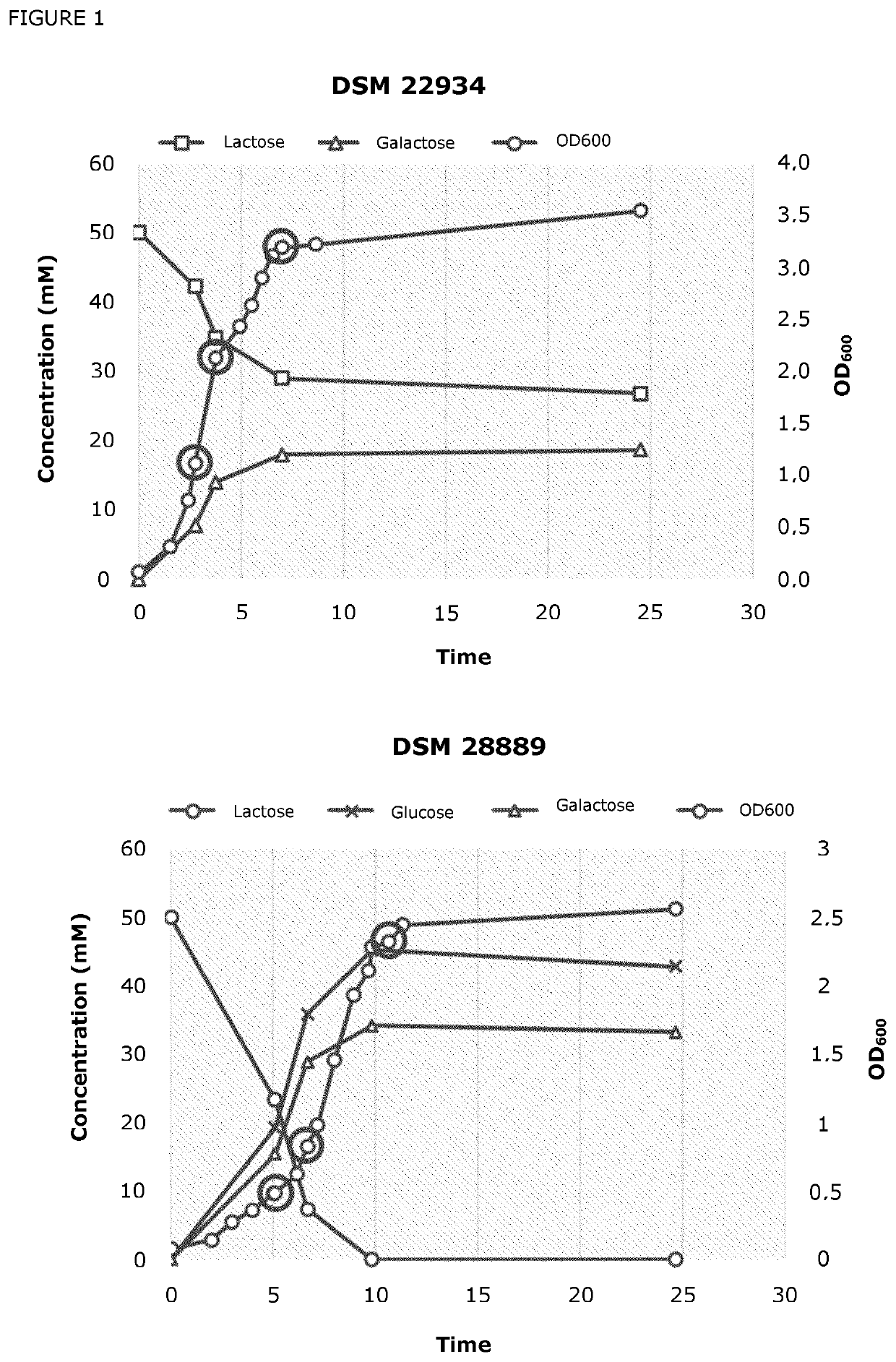
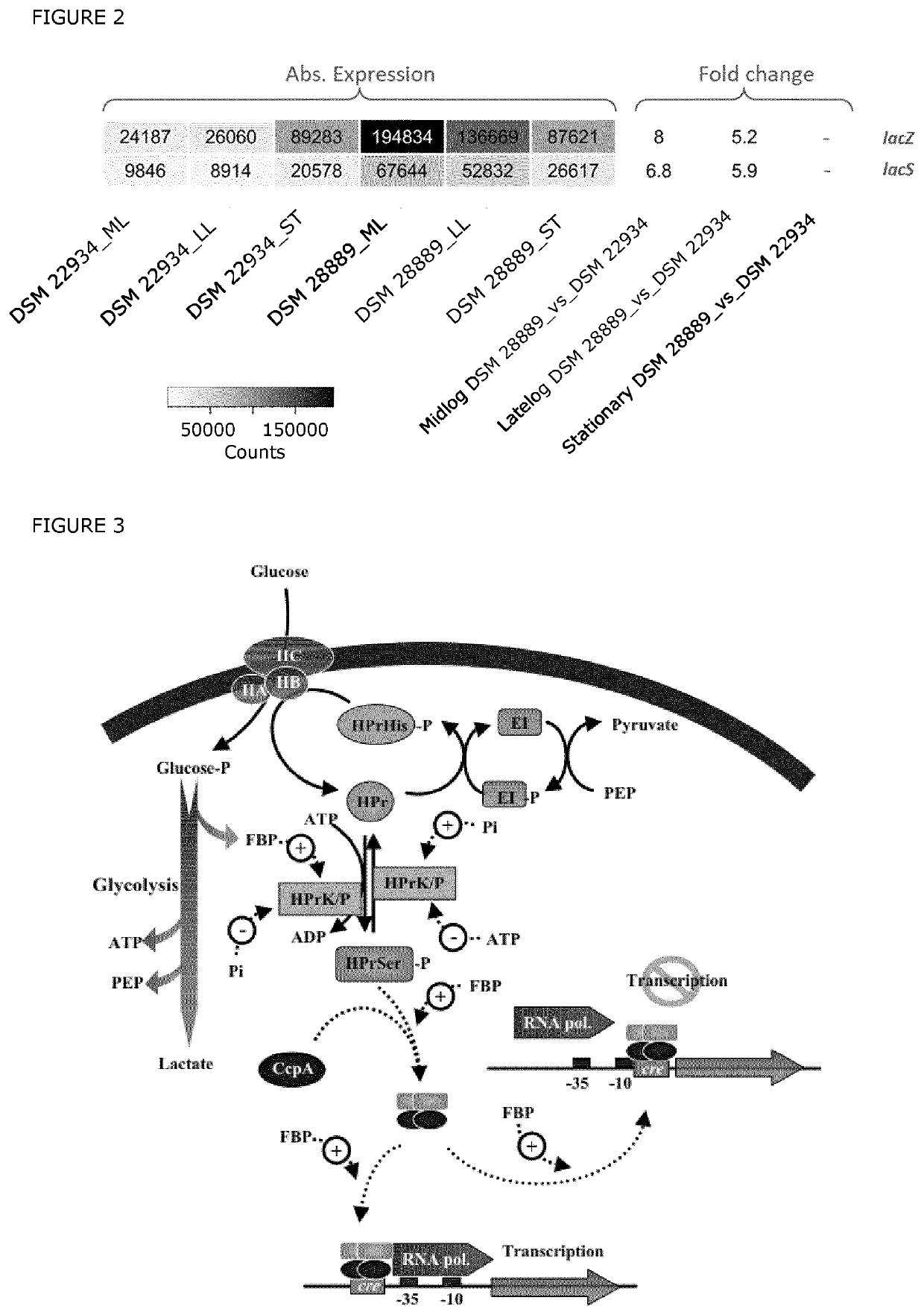
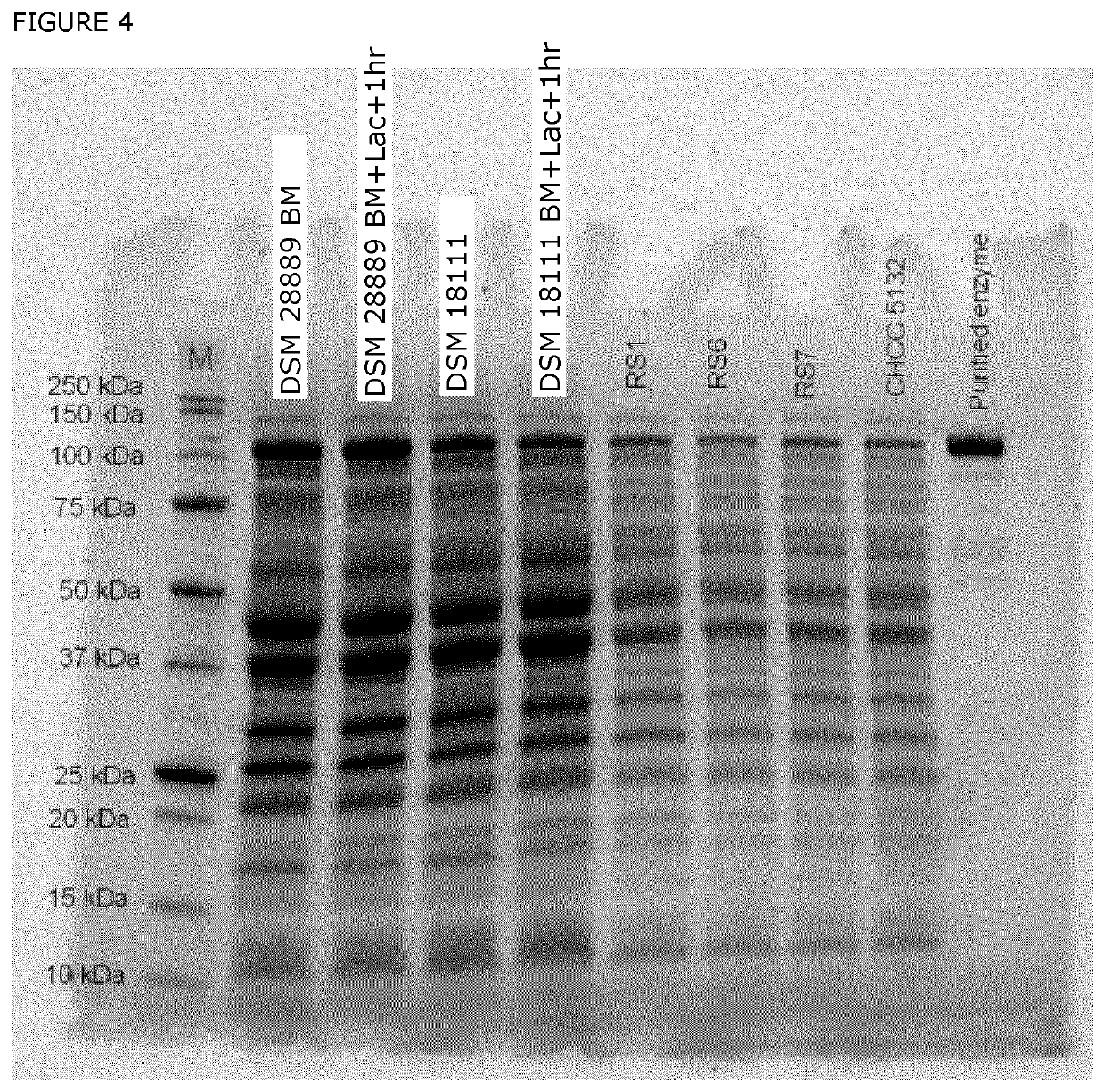
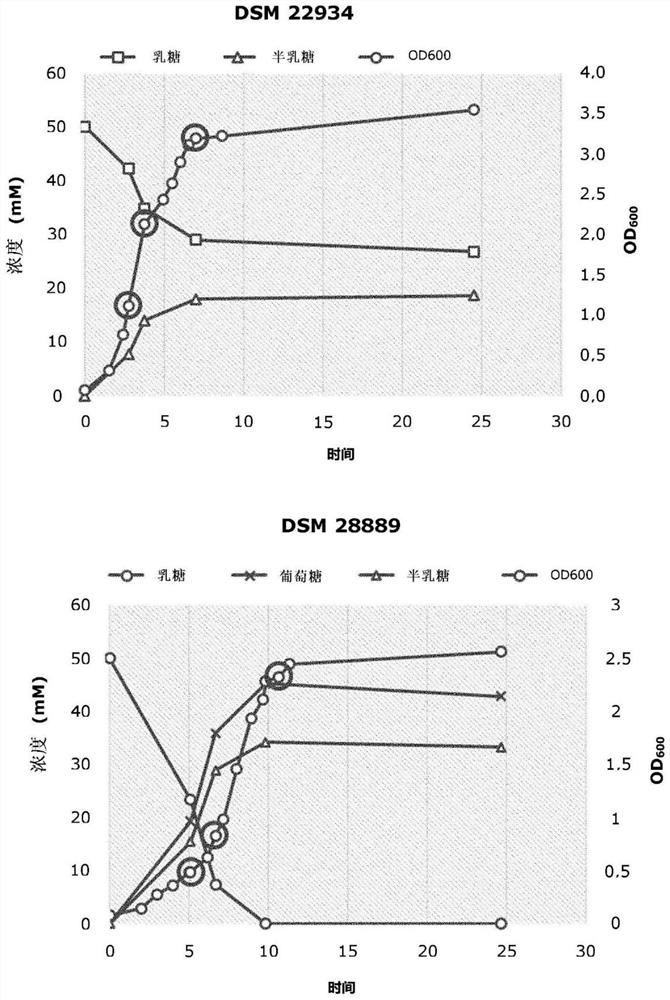
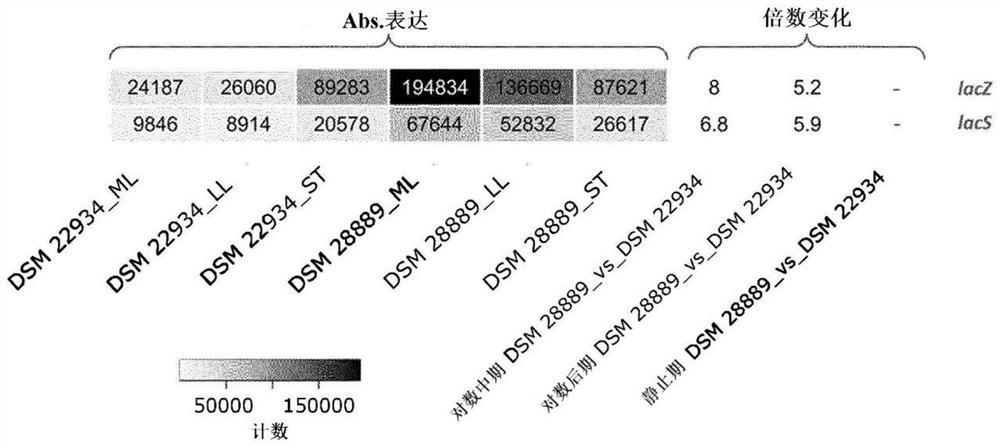
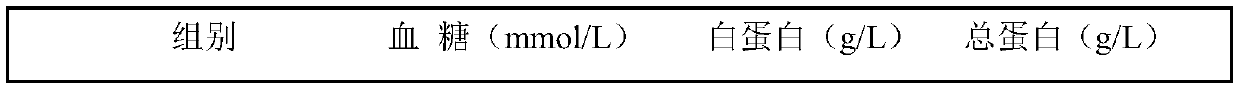Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
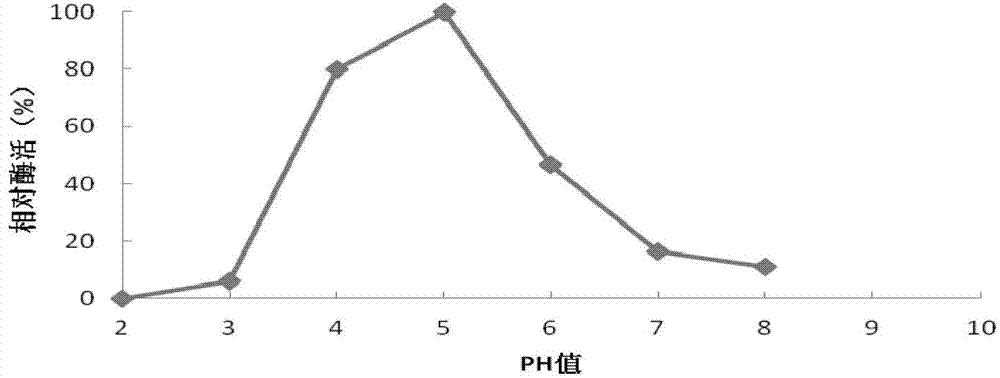
32 results about "Lactase Enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lactase is primarily a digestive enzyme that is produced by specialized cells that line the lumen of the small intestine, Genetics Home Reference explains. These cells absorb nutrients within your digestive tract.
Aspergillus niger capable of highly yielding compound enzyme for feed and application thereof
ActiveCN103740601APromote healthy developmentReduce anti-nutritional factorsFungiHydrolasesNutritionDigestion
The invention discloses aspergillus niger capable of highly yielding a compound enzyme for a feed and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The strain of the aspergillus niger specifically is aspergillus niger DM-18 which is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection with the collection number of CCTCC M2013541. A crude enzyme which is obtained through culture medium optimization and fermentation for 72-96 hours contains a plurality of kinds of enzymes, wherein the activity of protease is 6500U / ml, the activity of mannase is 1500U / ml, the activity of alpha-galactase is 1200U / ml and the activity of pectase is 1000U / ml. The optimum pH value for the activity of each enzyme in the compound enzyme ranges from 2 to 7, and is suitable for the digestion and absorption environment of the gastrointestinal tract of the animal; the compound enzyme for feed can be widely applied to the feeds for beasts and birds, is capable of reducing the antinutritional factors and increasing the digestibility, and has excellent economic benefits; simultaneously, the compound enzyme is also advantageous for protecting the economic environment and promoting healthy development of the animal husbandry.
Owner:HUNAN HONGYING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Lactase mutator, secretory expression method and application thereof
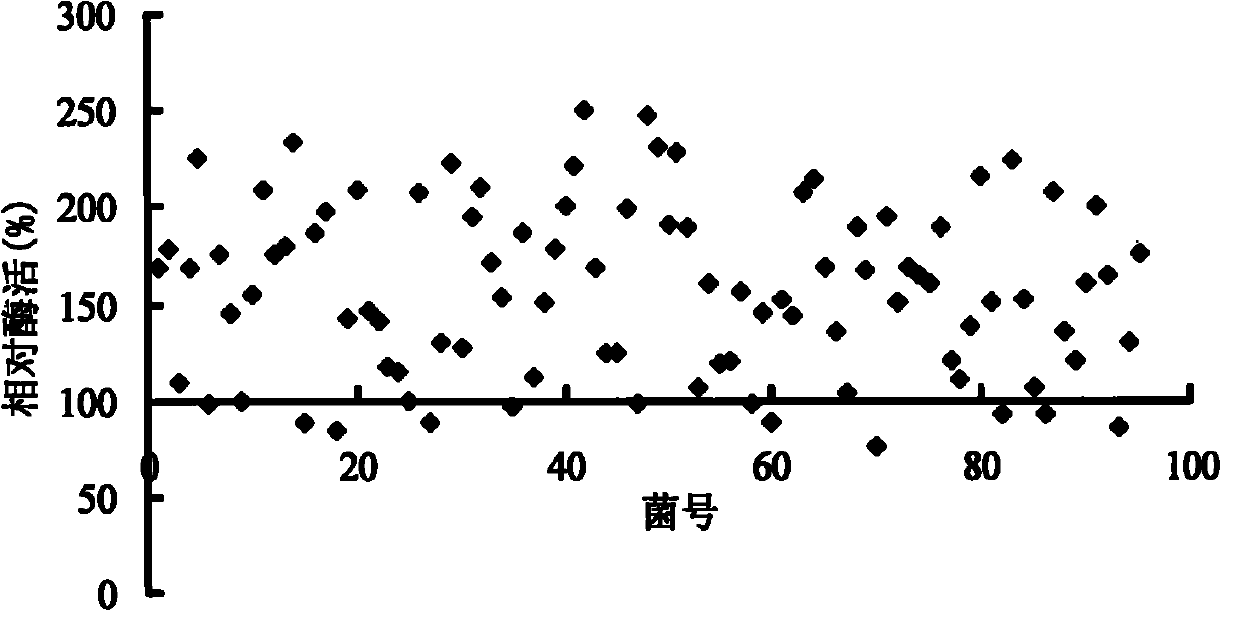
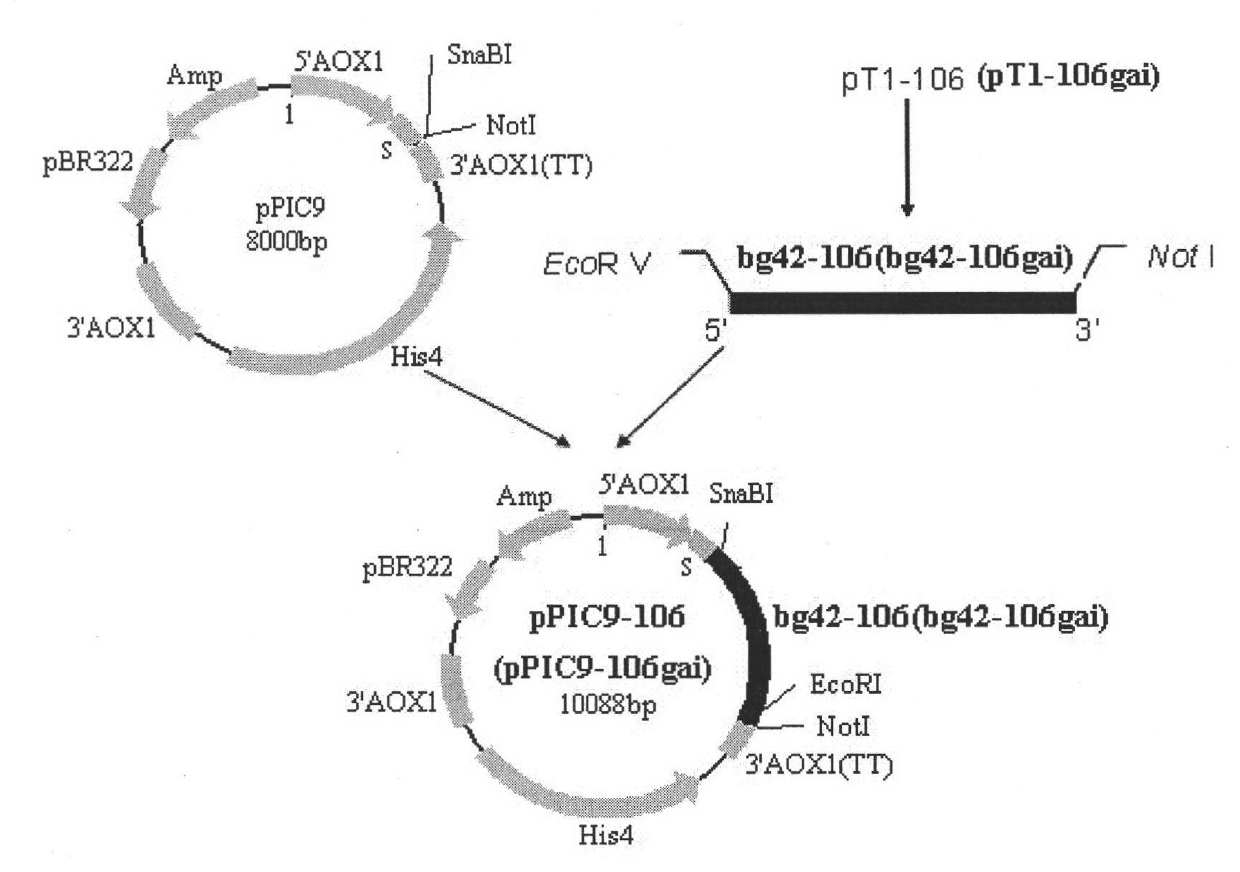
ActiveCN101948854AIncrease relative enzyme activityIncrease secreted expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisLactase
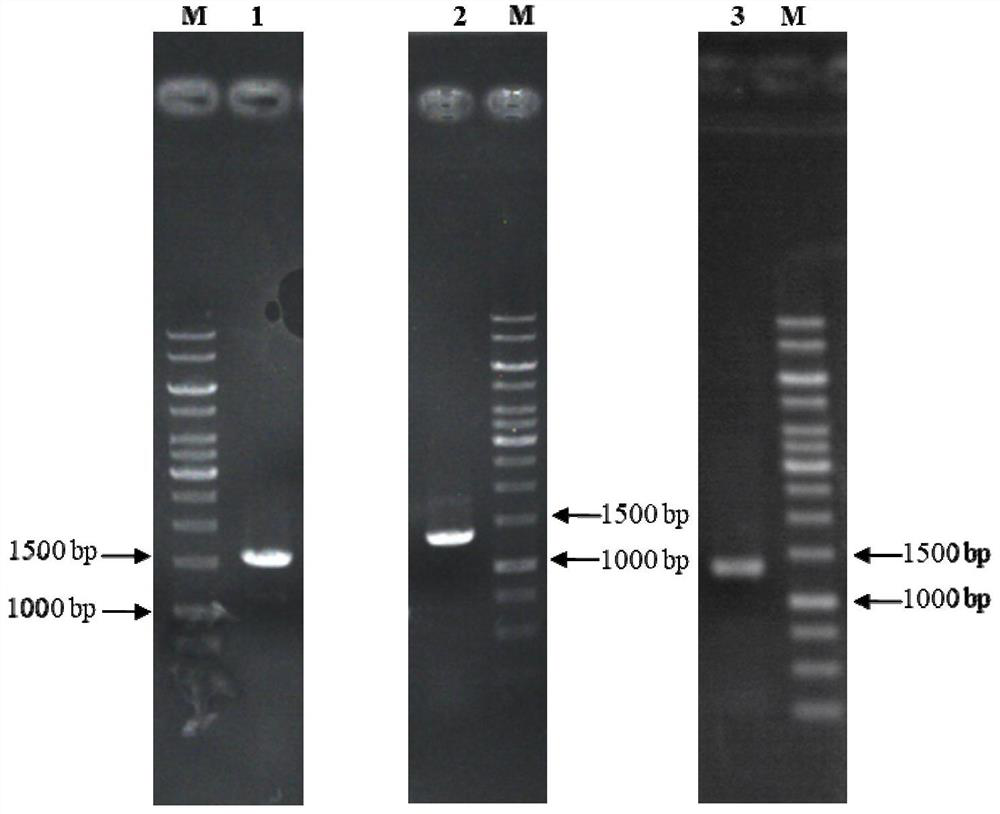
The invention discloses a lactase mutator with optimized codon and high specific activity and a secretory expression method thereof. The lactase gene cloned in bifidobacterium animalis is optimized for codon of the gene and the GC content on condition that the amino acid sequence of the gene is not changed according to the preference of the codon of Pichia pastoris; the optimized lactase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2.After optimizing, 461 basic groups are changed; the percentage of GC% is lowered to 53.79% from 61.11%t; the enzymatic activity of the lactase is obviously increased after the codon is optimized. Moreover, the method shows that: since the lactase gene and protein disulfide isomerase are transformed into the Pichia pastoris cell, the relative activity of the lactase is obviously increased; and the secretory expression content of the lactase gene in the Pichia pastoris is obviously increased.
Owner:北京森根比亚生物工程技术有限公司
Oedaleus decorus asiaticus lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH) as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108611338AReduced survival rateReduced growth rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyLactase-phlorizin hydrolase
The invention discloses oedaleus decorus asiaticus lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH) as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH is cloned from oedaleus decorus asiaticus at first, and a primer is designed for the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH, so as to synthesize a dsRNA for interfering with an oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH gene; and the dsRNA is introduced into the oedaleus decorus asiaticus through an injection method to perform RNA interfering (RNAi) on the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH. A result shows that after the dsRNA is injected into the oedaleus decorus asiaticus, the survival rate, the growth rate, the weight and the overall expressiveness are obviously reduced, which indicates that the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH plays an important role in an insect growth process. A new method is provided for molecular regulation and control of pests, and a theoretical basis is also provided for deeply understanding an insect growth mechanismand preparing a new biological pesticide preparation.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Lactase and recombinant expression engineering bacterium thereof
InactiveCN103031289AIncrease hydrolysis rateFungiMicroorganism based processesLactaseAspergillus oryzae
The invention relates to lactase and a recombinant expression engineering strain thereof. The conservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M2012482. The trichoderma reesei strain disclosed by the invention can efficiently express the lactase of aspergillus oryzae, and the enzyme activity can reach 251U / ml. The optimum acting pH value of the lactase is 5.0 and the optimum acting temperature is 50 DEG C, and the lactase can effectively hydrolyze lactose in the milk by a hydrolysis rate of 70%, so that the lactase has a potential application value for industrial production of low-lactose milk.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Process for preparing a lactose-free milk
ActiveUS20190335779A1Reduce scrap rateMilk preparationOther dairy technologyLactose free milkEnzymatic hydrolysis
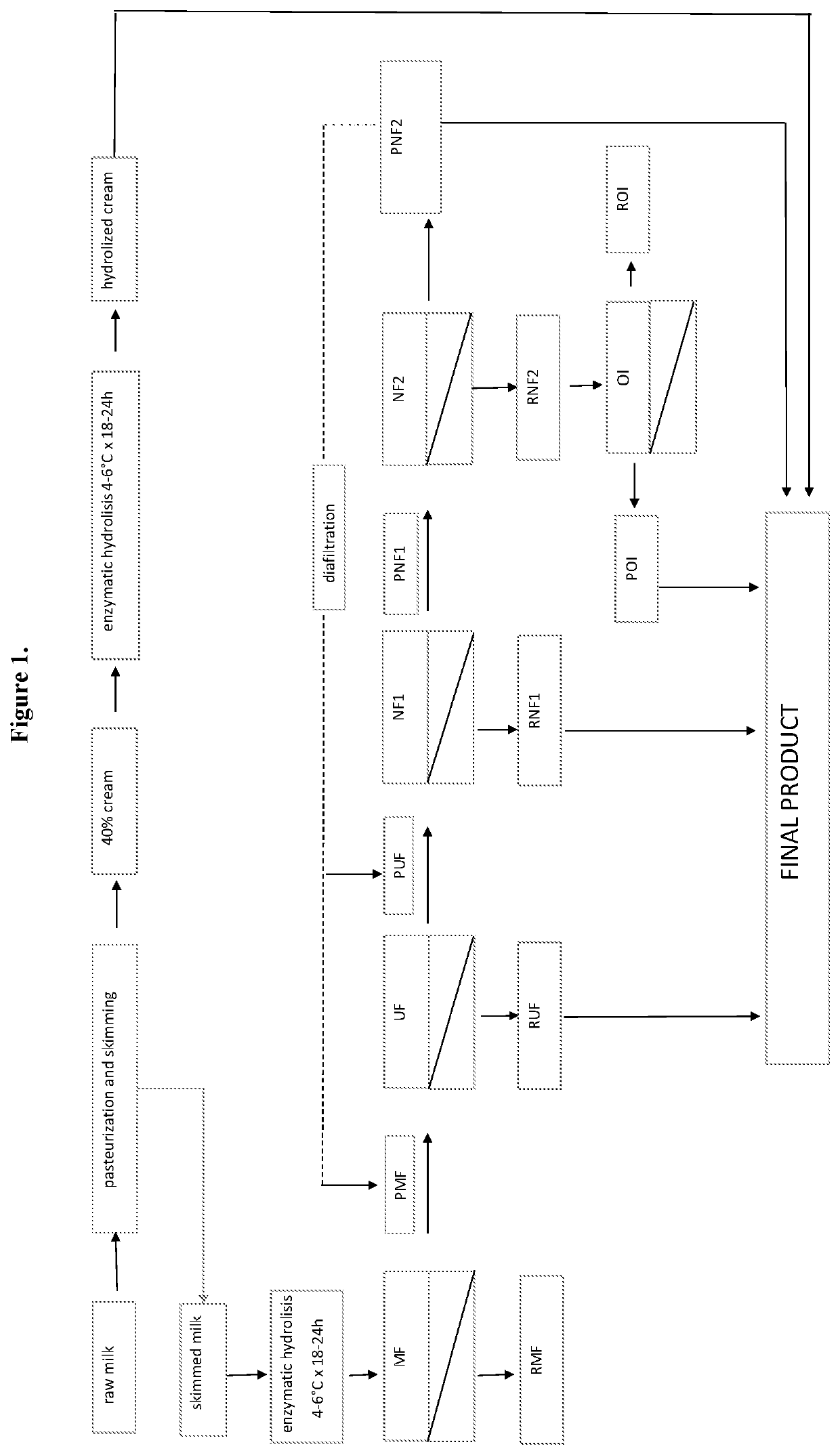
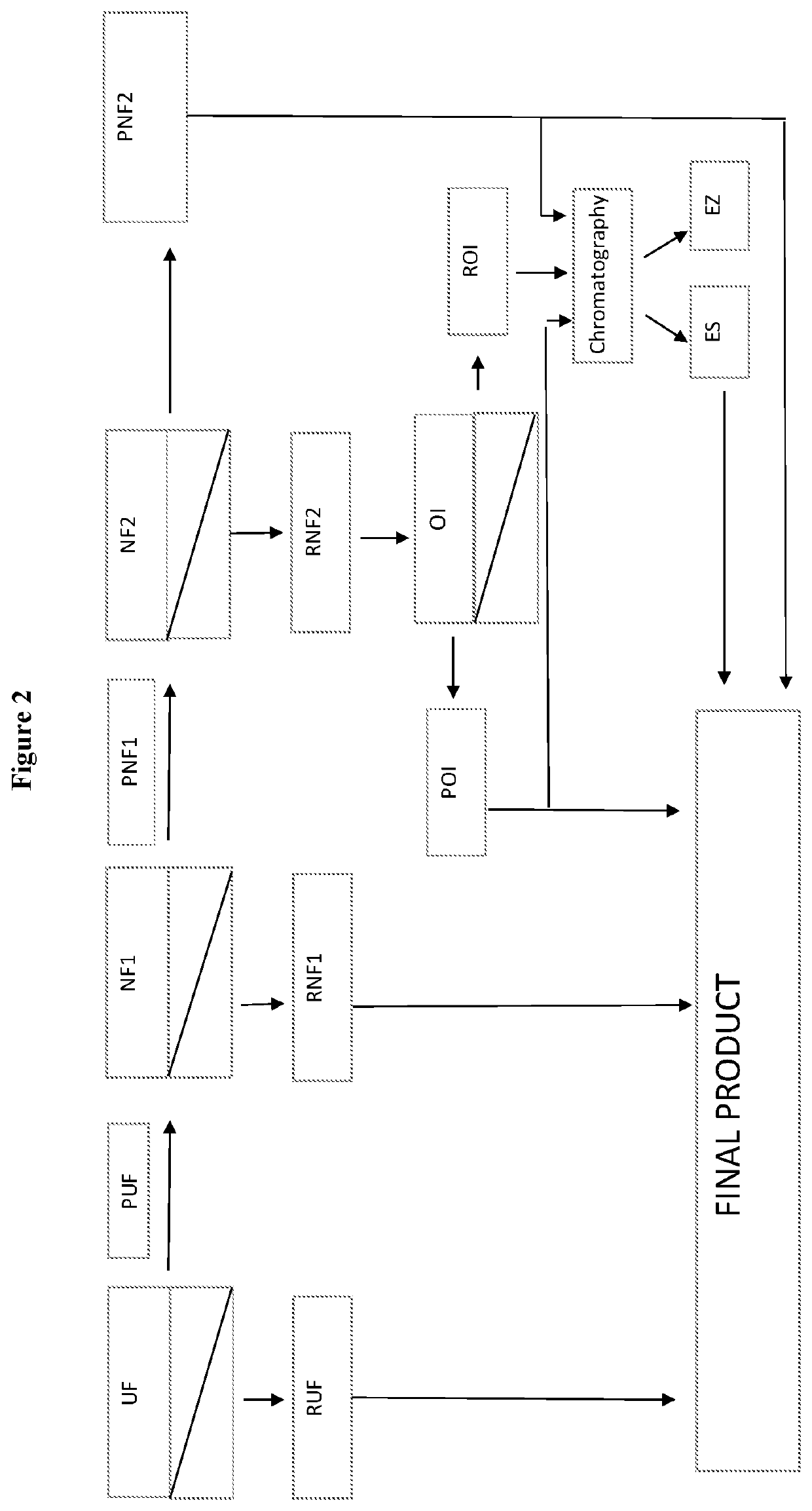
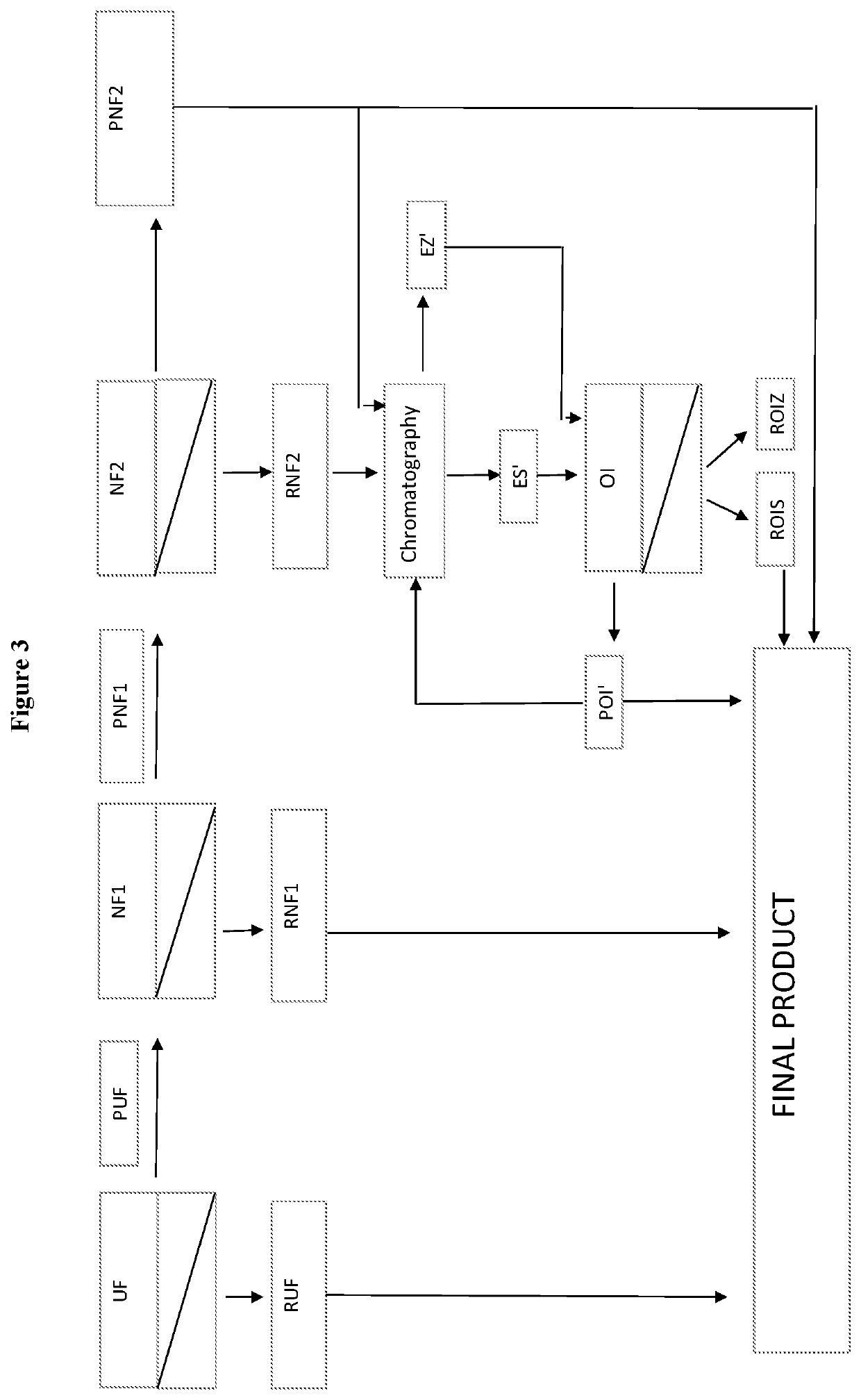
Process for preparing lactose-free skimmed, partially skimmed and whole milk, comprising the following steps: 1) pasteurization and skimming, 2) enzymatic hydrolysis of the skimmed milk by lactase enzyme, 3) microfiltration of the hydrolysed skimmed milk and obtainment of a microfiltration retentate (RMF) and of a microfiltration permeate (PMF), 4) PMF ultrafiltration and obtainment of an ultrafiltration retentate (RUF) and of an ultrafiltration permeate (PUF), 5) first PUF nanofiltration and obtainment of the first nanofiltration retentate (RNF 1) and of a first nanofiltration permeate (PNF 1), 6) second PNF 1 nanofiltration and obtainment of a second nanofiltration retentate (RNF2) and of a second nanofiltration permeate (PNF2), and 7) final step: obtainment of lactose-free milk by mixing one or more of the fractions deriving from one or more of the previous steps, which is characterized in that: (I) the first nanofiltration of step 5) is carried out with membranes having a molecular weight cut-off ranging from 400 to 600 Da and the second nanofiltration is carried out with membranes having a molecular weight cut-off ranging from 150 to 250 Da, and (II) the final step 7) is carried out by mixing a composition comprising at least RUF, RNF1 and PNF2.
Owner:GRANAROLO
Probiotic viable bacterium particle and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a probiotic viable bacterium particle and a preparation method of the probiotic viable bacterium particle. The product of the probiotic viable bacterium particle is prepared from the following ingredients: probiotics, food fiber powder and vegetable juice bonding agents. The preparation method of the product of the probiotic viable bacterium particle comprises the following steps that the probiotics, the food fiber powder and the vegetable juice bonding agents are stirred, mixed and kneaded into cake with the proper humidity, then, the cake is made into particles with the sizes like soybeans, and qualified products are obtained through baking, weighing and packaging. 200 to 300 hundred million strains of probiotic active factors are contained in the product, harmful microbes and pathogenic bacteria can be killed after the viable bacteria enter the human body, in addition, various kinds of enzymes such as amylase, protease, lipase, lactase, cellulose and peptidase can be produced, the metabolism can be promoted through the enzyme effect generated by the enzymes, and the human body immunization function is enhanced, so the effect of preventing and treating various kinds of diseases can be realized.
Owner:陈应交
Formula feed capable of improving intestinal barrier function and digestive enzyme activity of early-weaned piglets, and feeding method of formula feed
InactiveCN106720941AIncrease average daily feed intakeRaise the pile heightFood processingAnimal feeding stuffLactaseEarly weaning
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of pig feed, and in particular discloses formula feed capable of improving the intestinal barrier function and digestive enzyme activity of early-weaned piglets, and a feeding method of the formula feed. The formula feed is prepared from basal diet and a lactobacillus acidophilus culture, wherein the mass of the lactobacillus acidophilus culture accounts for 1-5% of the total mass of the formula feed. After the formula feed provided by the invention is used for feeding the early-weaned piglets, the average daily feed intake of the weaning stress piglets can be remarkably improved, the heights of villi in the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum are remarkably increased, the depths of recesses of the duodenum and the ileum are obviously reduced, and the heights of villi or the depths of recesses of all intestinal tracts of small intestines are significantly improved. The contents of sucrase, lactase and maltase of the jejunum are remarkably improved. The formula feed is easy in obtaining of raw materials, simple in preparation method and convenient to use.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enzymatic method of producing 4-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose, 4-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose obtained using said method, compositions contain same and the use thereof in evaluating intestinal lactase
InactiveUS7537909B2Increase the proportion of 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xyloseMicrobiological testing/measurementUltrafiltrationGramIn vivo
An enzymatic process to obtain 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose useful in compositions or solutions in the in vivo evaluation of intestinal lactose activity in humans, that comprises the steps of preparing a reaction mixture of D-xylose, a β-D-galactopyranoside and a reaction medium that comprises water buffered to a pH between 5.0 and 9.0; adding 10 to 1,000 units of β-D-galactosidase per gram of β-D-galactopyranoside; subjecting the reaction mixture to a reaction or a temperature between a temperature higher than the freezing point of the reaction mixture and 45° C., for 2 to 48 hours; for the reaction by deactivation of the β-D-galactosidase; and to isolate and crystallize the fractions that contain 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose from a crystallization mixture selected between mixtures of acetone / methanol in a ratio between 5 / 1 to 20 / 1 and mixtures of acetone / water in a ratio between 5 / 1 to 20 / 1.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Dual-enhanced acidic lactase Pichia pastoris expression strain, and construction method and fermentation technology thereof
InactiveCN110903992AHigh expressionIncrease industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesSecretion expressionMicrobiology
The invention provides a composition and induction dual-enhanced acidic lactase recombinant Pichia pastoris expression strain constructed by combining a lactase gene-containing integrative plasmid with a free plasmid. The recombinant Pichia pastoris is sued to express lactase at a high density. The lactase gene-containing integrative plasmid is combined with the free plasmid to construct the expression strain to make the lactase expression quantity of the expression strain greatly improved, and the secretion expression quantity of the expression strain can reach 8000 ALU / mL or above through high-density fermentation, so that the expression strain can be industrially applied, and the industrial production quantity of lactase is improved.
Owner:NINGBO XINUOYA MARINE BIOTECH CO LTD
Enzyme composition for sugar metabolic regulation
InactiveUS20210177026A1Regulate the absorption of glucoseOxidoreductasesGlycosyltransferasesAmylaseSucrose
Disclosed is an enzyme composition for regulating sugar metabolism which can regulate the absorption of glucose into the body by converting the carbohydrates in food to a form of sugar that is not absorbed in the stomach and the like before being decomposed in the small intestine into glucose by the activity of various enzymes such as maltase, sucrase, or lactase and the like and absorbed, wherein the enzyme composition includes: one or more enzymes selected from the group consisting of glucoamylase, sucrase and lactase; glucose oxidase; and transglucosidase.
Owner:HWANG JI HWAN +1
Enzyme composition for management of metabolic health
InactiveUS20180339025A1Lower cholesterol levelsGut healthPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderNeutral proteasePhysiology
The present invention discloses compositions containing digestive enzymes for the management and maintenance of metabolic health. Specifically, the invention discloses the use of digestive enzymes comprising α-amylase, lactase, lipase, cellulase and Neutral protease or Acid protease in weight management, reducing cholesterol levels, maintaining healthy gut and improving quality of life.
Owner:MAJEED MUHAMMED +2
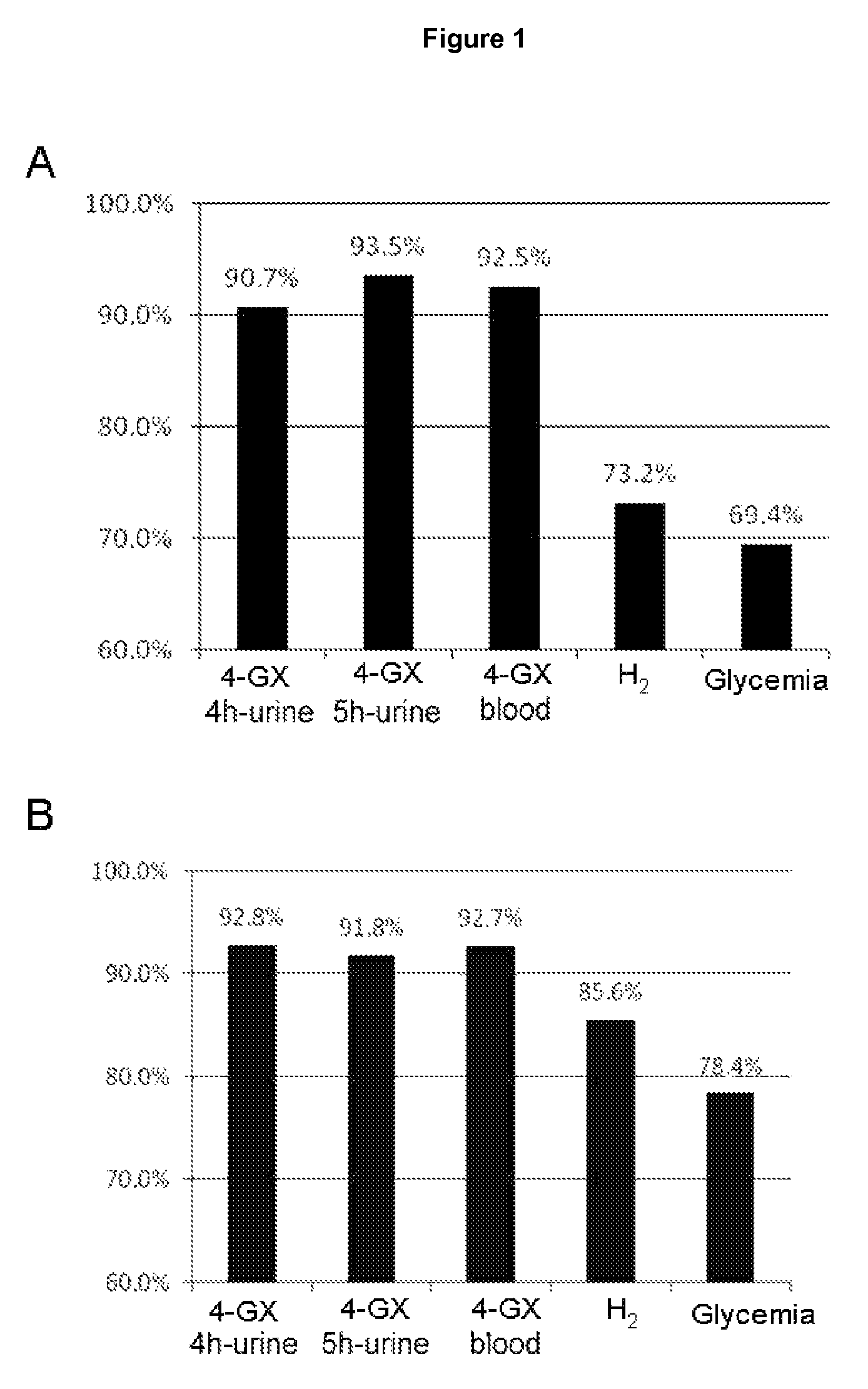
Non-invasive diagnostic method for the evaluation of intestinal lactase deficiency (hypolactasia)
InactiveUS9128100B2Absence of adverseFunction increaseMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiagnostic testDirect evaluation
The test of the invention comprises the measuring the total amount of xylose in urine and / or its concentration in blood following oral administration of 4-O-β-D-galactopyranosyl-D-xylose (4-GX) to the patient. It is a non-invasive test that is based on the direct evaluation of the global enzyme activity in the whole individual, not on measuring the metabolic consequences derived from its deficiency. It does not require specialized equipment, does not cause apparent discomfort in patients with lactase deficiency and is very reliable, thus overcoming the drawbacks of the diagnostic tests currently in use and is a statistically significantly better test in terms of its reliability; consequently it should become the reference or gold standard test for the indication of hypolactasia.
Owner:VENTER PHARMA
Preparation method of high-activity composite enzyme for feed
ActiveCN103689241AIncrease vitalityHigh activityHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffTemperature resistanceHigh activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-activity composite enzyme for feed, belonging to the technical field of preparation of an enzyme preparation for feed. An Aspergillus niger DM-18 strain for a high-yield composite enzyme for feed, which is used as an initial strain, is subjected to liquid submerged mixed fermentation in an optimized culture medium under specific fermentation conditions by an improve fermentation technique to obtain the composite enzyme for feed, which has the advantages of complete enzymatic system, high enzyme activity, high temperature resistance and wide pH value resistance range. The prepared crude enzyme fermentation liquid contains multiple enzyme activities, wherein the proteinase activity is 6500-6700 U / ml, the mannase activity is 1500-1700 U / ml, the alpha-galactase activity is 1200-1300 U / ml, and the pectinase activity is 1000-1200 U / ml. The enzymes still have higher enzyme activity (up to 80% or above) at 30-75 DEG C under the pH value of 2-7; and thus, the composite enzyme is more suitable for the demands of a processing technique in feed industry, and the processed feed has low loss of enzyme activity.
Owner:HUNAN HONGYING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Lactase enzymes with improved properties at acidic ph
PendingUS20210348147A1Low in lactoseSpeed up the processMilk preparationMilk preservationLactase EnzymePeptide
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Composition and method for synbiotics supplement containing probiotics, digestive enzymes, prebiotics, yeast, protein, b vitamins, and flavoring agent
PendingUS20220192246A1Improve the ecosystemEasy to solveLactobacillusStrepto/lacto-coccusDietary supplementYeast Proteins
A composition and method for use of a dietary supplement for promoting gastrointestinal health including effective amounts of probiotics, digestive enzymes, prebiotics, a dried, non-viable yeast, protein, B vitamins, and flavoring agent. The multi-strain of probiotics may be viable and dried bacteria like Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus. The multistrain and multispecies probiotics may show synergistic effects. Digestive enzymes can be protease, lactase, cellulose, and / or pancreatin. The prebiotics may be inulin and other dietary fiber. The yeast may be Brewer's or Baker's yeast. The protein may be whey or soy or rice protein concentrates. The B vitamins may be Pantothenic Acid, Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacinamide, Pyridoxine, Cyanocobalamin, Folic Acid and Biotin. The flavoring agent may be natural vanilla.
Owner:VIVA LIFE SCIENCE INC
Production process of liposome-coated lactase
PendingCN114209817AImprove stabilityEasy accessAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid filmMicrofiltration membrane
The invention belongs to the technical field of lactase, and particularly relates to a production process of liposome-coated lactase, which comprises the following process steps: dissolving a membrane material in an organic solvent, and removing the organic solvent through reduced pressure evaporation to form a lipid membrane; dissolving lactase in a solvent to obtain a lactase solution; adding a lactase solution into the lipid film, dissolving the lipid film, and carrying out ice-bath ultrasonic treatment to obtain a liposome-lactase solution; and filtering by using a microfiltration membrane to obtain the lactase-coated lipidosome. The lactase is wrapped by the lipidosome, the lactase is separated from the external environment, the lactase is protected from being affected by environmental conditions, oxidative deterioration of the lactase is prevented, the activity time of the lactase is prolonged, the stability of the lactase is improved, and the lipidosome can transfer protease into cells through endocytosis or membrane fusion and the like. The problem that the biomacromolecule is difficult to penetrate through a cell membrane can be effectively solved, and the action effect and the utilization rate can be greatly improved.
Owner:山东源科生物科技股份有限公司
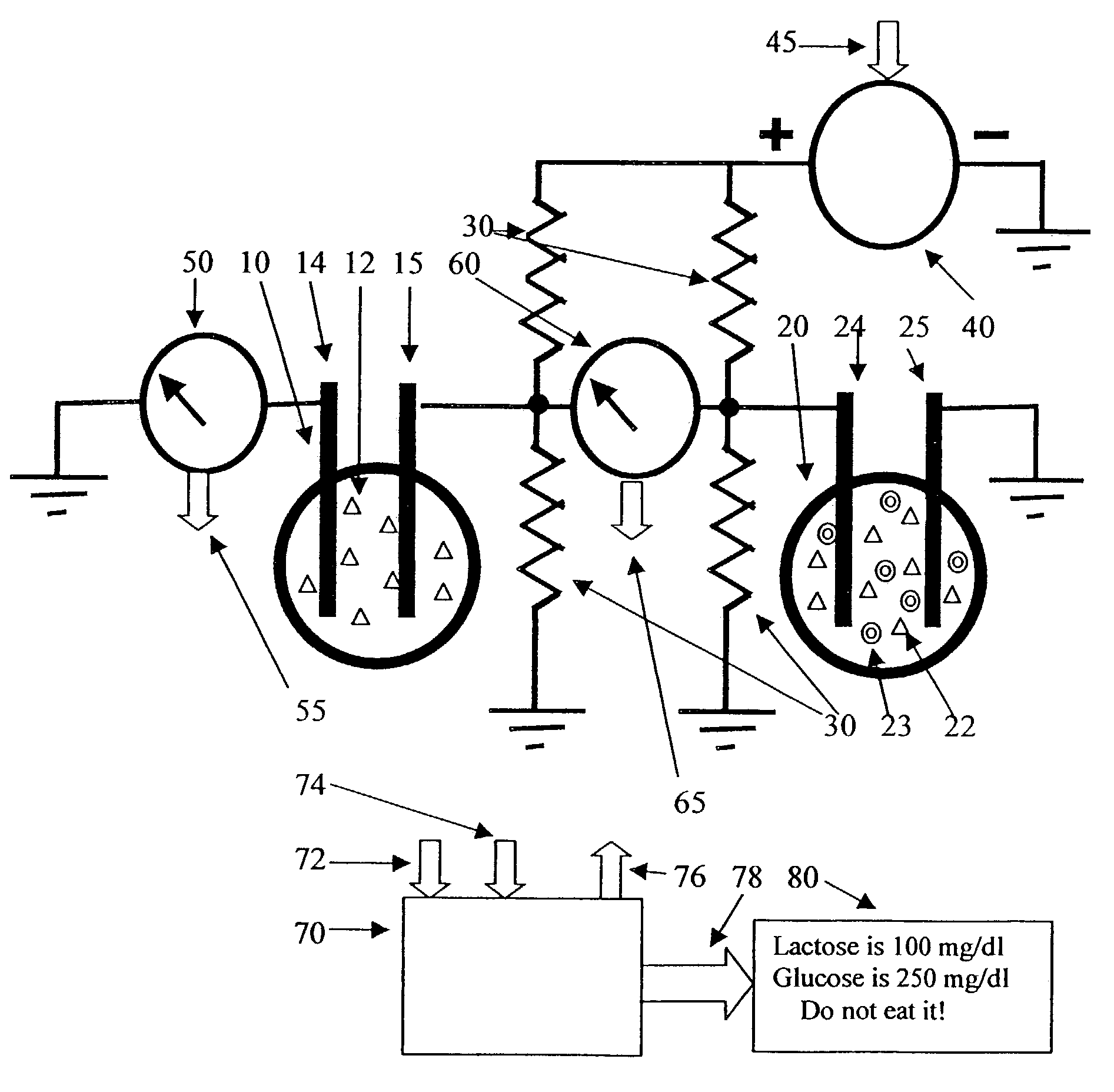
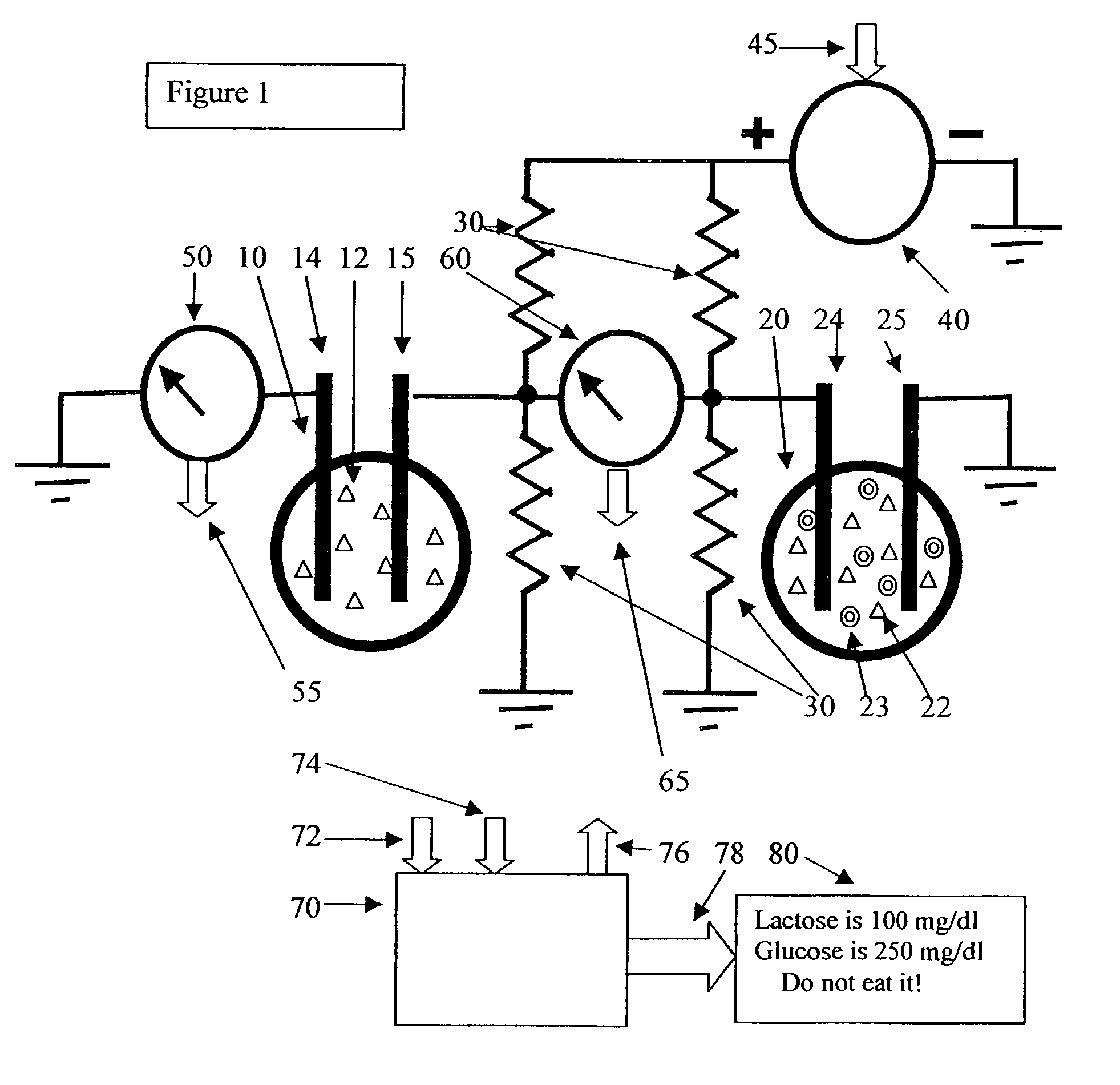
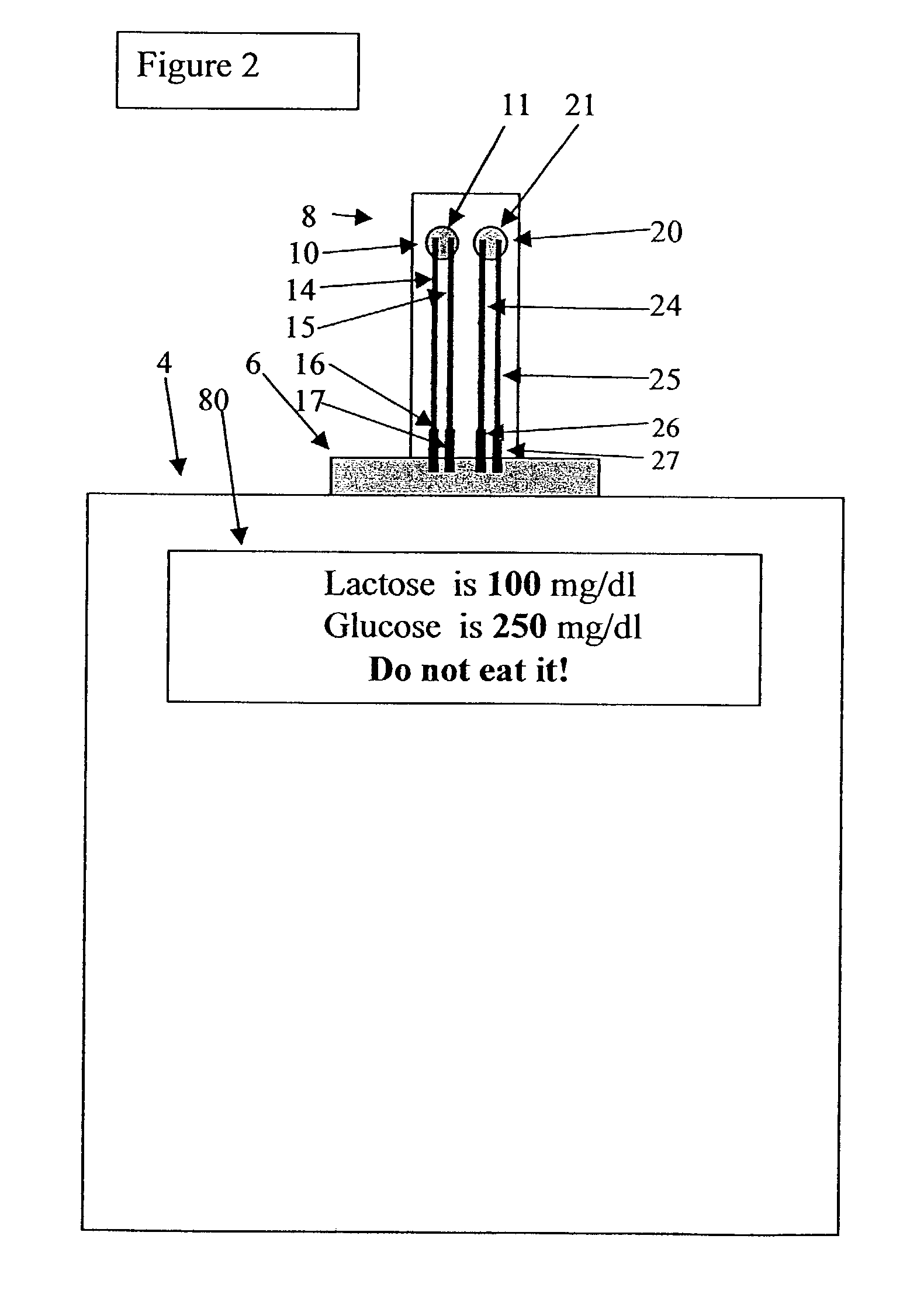
Lactase-added instant milk tea
InactiveCN105685239AReduce usageHigh sweetnessMilk preparationTea substituesInstant teaEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention relates to the technical field of food processing, specifically to lactase-added instant milk tea. By applying a lactase enzyme immobilization technology to the preparation process of the lactase-added instant milk tea, heat resistance and stability of lactase which is originally easy to destroy are raised. By applying lactase enzyme immobilization to a processing technology of instant milk tea, the instant milk tea with the effect of enzymatic hydrolysis of lactose is prepared. Patients with lactose intolerance and patients with lactase deficiency can enjoy the delicious milk tea product anytime and anywhere.
Owner:陈慧
A method for preparing condensed milk with caramel flavor
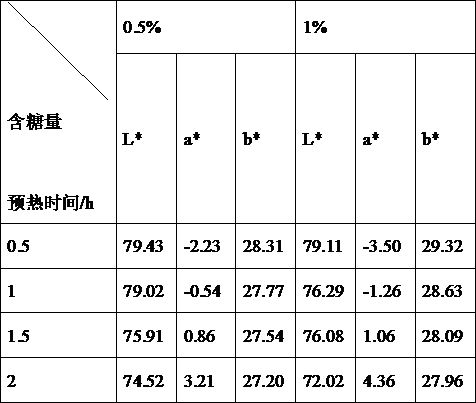
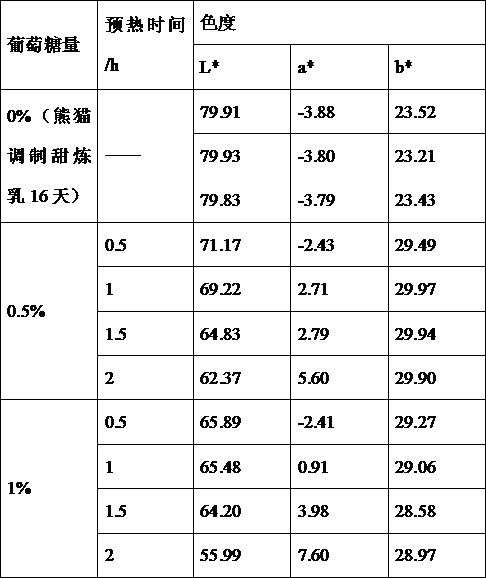
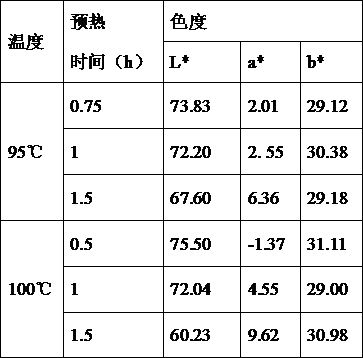
The invention relates to a method for preparing condensed milk with caramel flavor, which at least includes the following steps: (1) Raw milk preparation: fresh milk is filtered, milk is cleaned, sucrose syrup is added, and sucrose and water are dissolved in a ratio of 6.65:10 , and then mix the dissolved milk solution with the sucrose solution; (2) Add sugar: add 0.25‑1.0% glucose or fructose syrup to the solution prepared in step (1); (3) hydrolyze with lactase; (4) Protease hydrolysis; (5) Homogenization; (7) Concentration; (8) Homogenization; (9) Cooling; (10) Crystallization. By adopting the above technical solution, the present invention provides a method for preparing condensed milk with caramel flavor. The lactose produced has caramel flavor, good color and good taste, and can inhibit the absorption of sucrose in the small intestine and lower blood sugar. The content is suitable for people with high blood sugar and diabetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PANDA DAIRY GRP COMPANY +1
Preparation method of high-activity composite enzyme for feed
ActiveCN103689241BIncrease vitalityHigh temperature resistanceHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesProteinase activityLactase Enzyme
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-activity composite enzyme for feed, belonging to the technical field of preparation of an enzyme preparation for feed. An Aspergillus niger DM-18 strain for a high-yield composite enzyme for feed, which is used as an initial strain, is subjected to liquid submerged mixed fermentation in an optimized culture medium under specific fermentation conditions by an improve fermentation technique to obtain the composite enzyme for feed, which has the advantages of complete enzymatic system, high enzyme activity, high temperature resistance and wide pH value resistance range. The prepared crude enzyme fermentation liquid contains multiple enzyme activities, wherein the proteinase activity is 6500-6700 U / ml, the mannase activity is 1500-1700 U / ml, the alpha-galactase activity is 1200-1300 U / ml, and the pectinase activity is 1000-1200 U / ml. The enzymes still have higher enzyme activity (up to 80% or above) at 30-75 DEG C under the pH value of 2-7; and thus, the composite enzyme is more suitable for the demands of a processing technique in feed industry, and the processed feed has low loss of enzyme activity.
Owner:HUNAN HONGYING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
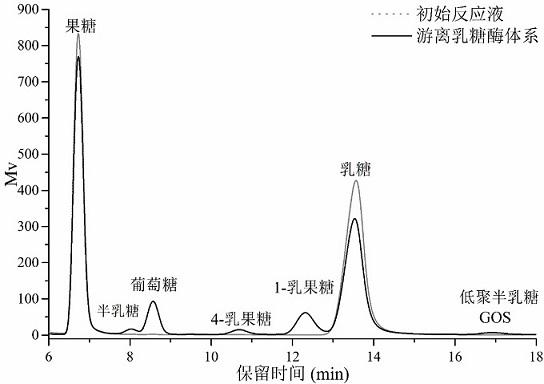
A special enzyme for galacto-oligosaccharide production and its preparation and application
ActiveCN112574977BLower Fermentation Manufacturing CostsQuality improvementBacteriaFood processingActive enzymeSubmerged fermentation
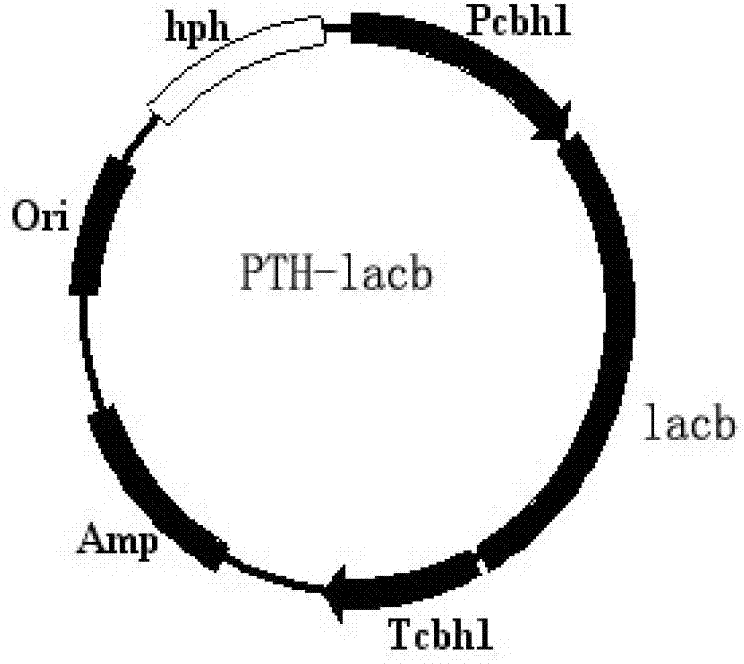
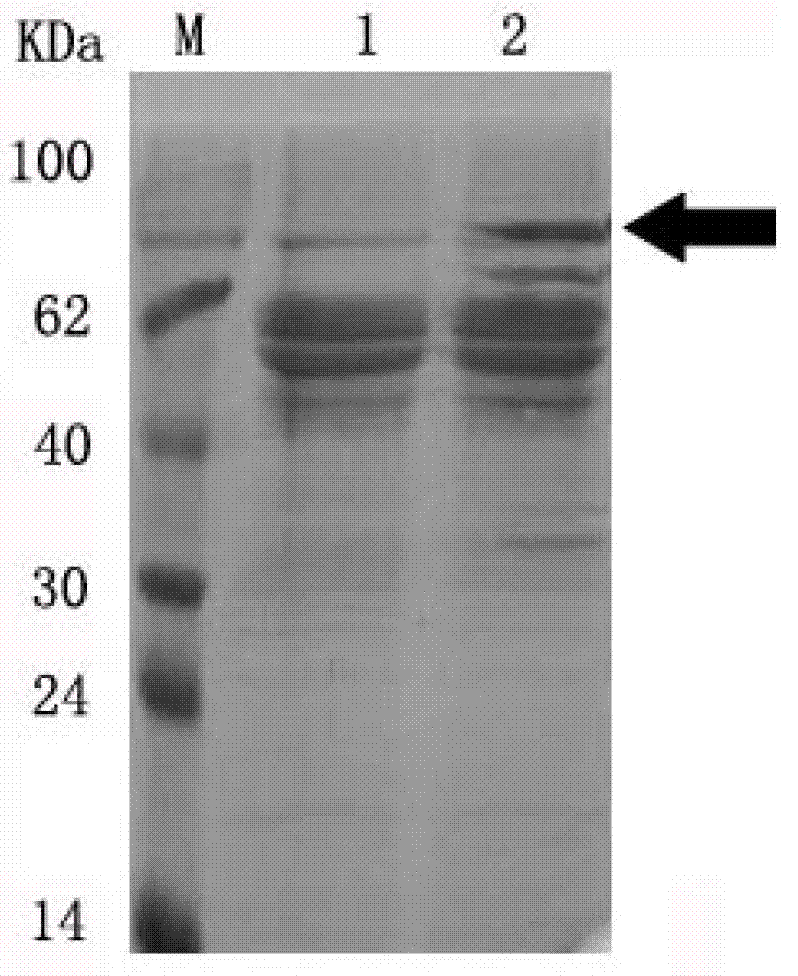
The invention belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering, and particularly relates to a lactase for generating galacto-oligosaccharides and its preparation and application. The present invention carries out molecular evolution on the basis of two sources of lactase (BglD305 derived from Bacillus circulans B2301 and BglD derived from Bacillus circulans ATCC 31382) molecules to obtain high efficiency of synthesizing galacto-oligosaccharides and good expression performance and construct a high-yielding strain of lactase, which can efficiently synthesize lactase and secrete the enzyme protein molecule into the medium during submerged fermentation, and directly prepare a highly active enzyme preparation from the fermentation supernatant. The expression level can reach 2208U / mL, which is helpful to reduce the fermentation manufacturing cost of lactase, simplify the fermentation manufacturing process and improve the quality of the lactase enzyme preparation.
Owner:森大(天津)生物科技有限公司
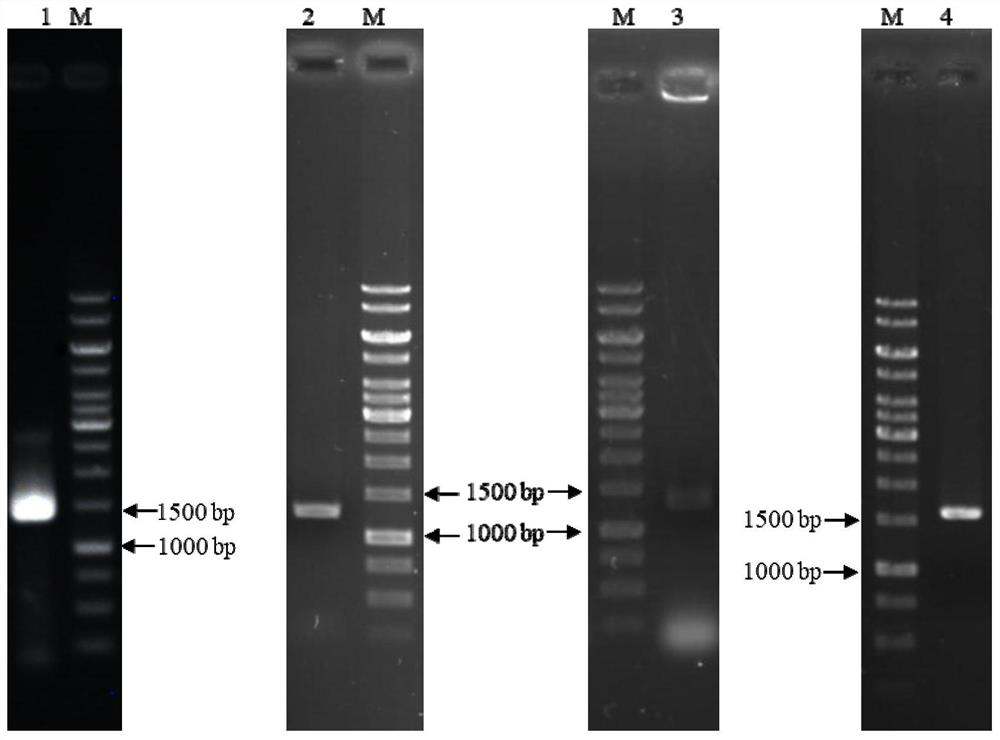
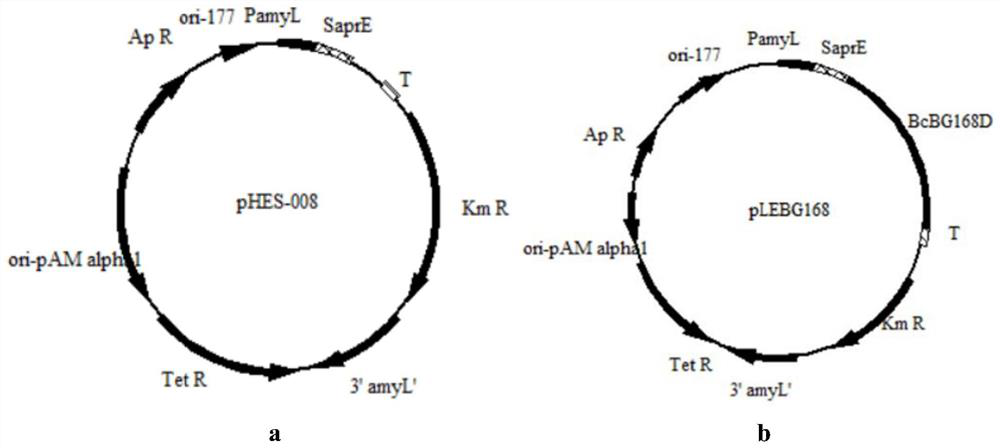
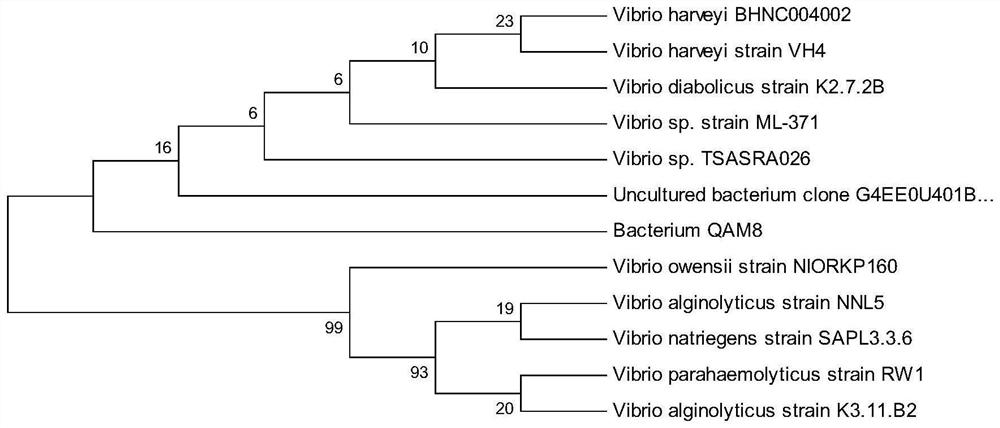
Vibrio harveyi variant capable of producing lactase and application thereof
PendingCN114317341AEase of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention provides a vibrio harveyi variant capable of producing lactase, the strain number is BHNC004002, the strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on October 11, 2021, and the preservation number is CCTCC No: M20211247. The invention also provides an application of the vibrio harveyi variant in expression of lactase. The lactase expressed by the vibrio harveyi variant has wide application ranges of enzyme activity temperature and enzyme activity PH value.
Owner:NINGBO XINUOYA MARINE BIOTECH CO LTD
Immobilized activating enzyme for promoting food nutrition absorption and preparation technology
InactiveCN108179144AHigh activityAdaptableOn/in organic carrierOn/in inorganic carrierLactaseSodium Caseinate
The invention discloses an immobilized activating enzyme for promoting food nutrition absorption. The immobilized activating enzyme is prepared by the following steps: preparing a mixture A from FeSO4.7H2O, FeCl3.6H2O, FeCl2.4H2O and NH3.H2O; washing the mixture A, and treating with a mixed solution prepared from hydroxypropylcyclodextrin, potassium alginate and sodium caseinate, to obtain a mixture C; washing the mixture C, and treating with a mixed solution prepared from chitosan and ammonium persulfate, to obtain a mixture D; washing the mixture D, and treating with a mixed solution prepared from aluminum ammonium sulfate, polyvinyl pyrrolidone, glutaraldehyde and lactase so as to obtain a substance which is the immobilized activating enzyme for promoting food nutrition absorption. In the invention, the prepared immobilized activating enzyme for promoting food nutrition absorption has the characteristics of high activity, strong adaptability, long service life, convenience in separation, reutilization, etc.
Owner:BEIJING HUANERKANG TECH DEV
Production of lactase enzymes using altered regulation strains
PendingUS20220304323A1Negative effectAbsenceMilk preparationTransferasesLactic acid bacteriumHeterologous
The present invention relates to new improved methods for expressing native lactases in their native hosts. Methods for homologous as well as heterologous expression of lactase in lactic acid bacteria with altered expression dynamics are comprised by present invention.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Production of lactase using regulatory altered strains
PendingCN114514317AHas lactase activityMilk preparationTransferasesLactic acid bacteriumHeterologous
The present invention relates to a novel improved method of expressing these natural lactases in a natural host of the natural lactases. The invention comprises a method for homologous and heterologous expression of lactase in lactic acid bacteria with altered expression kinetics.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
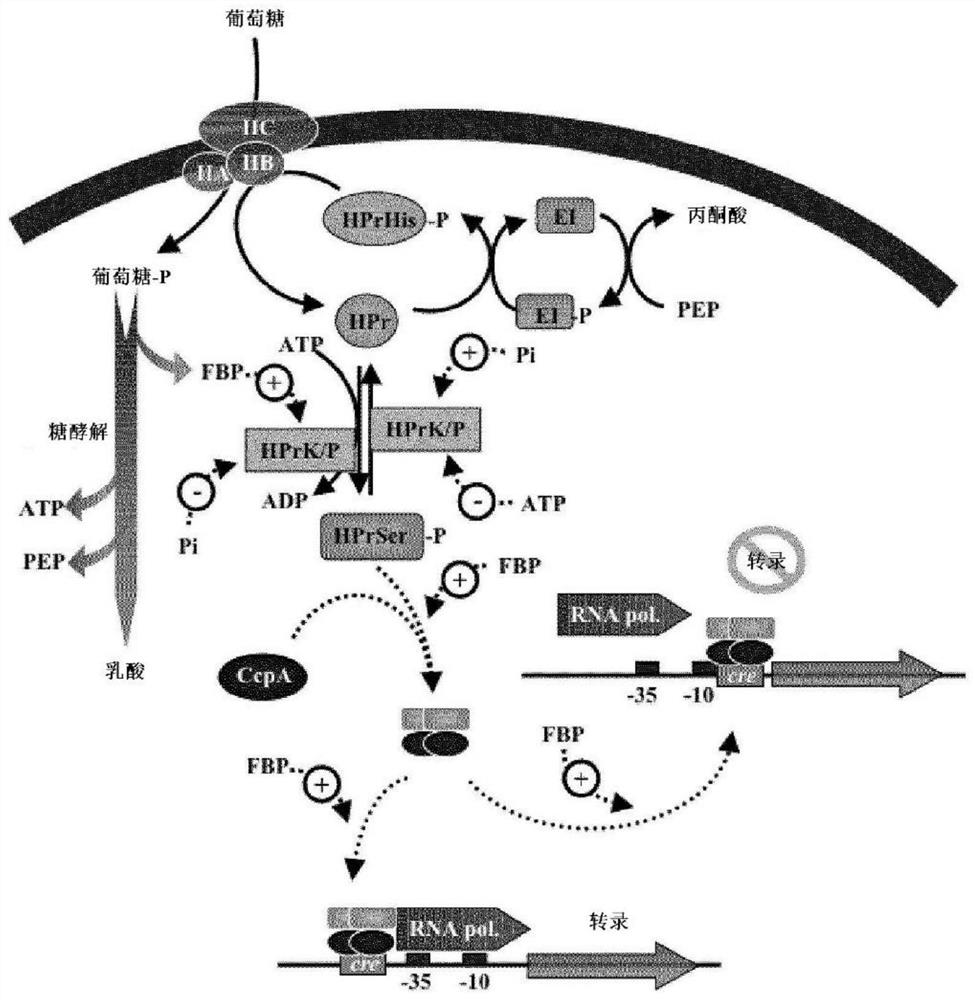
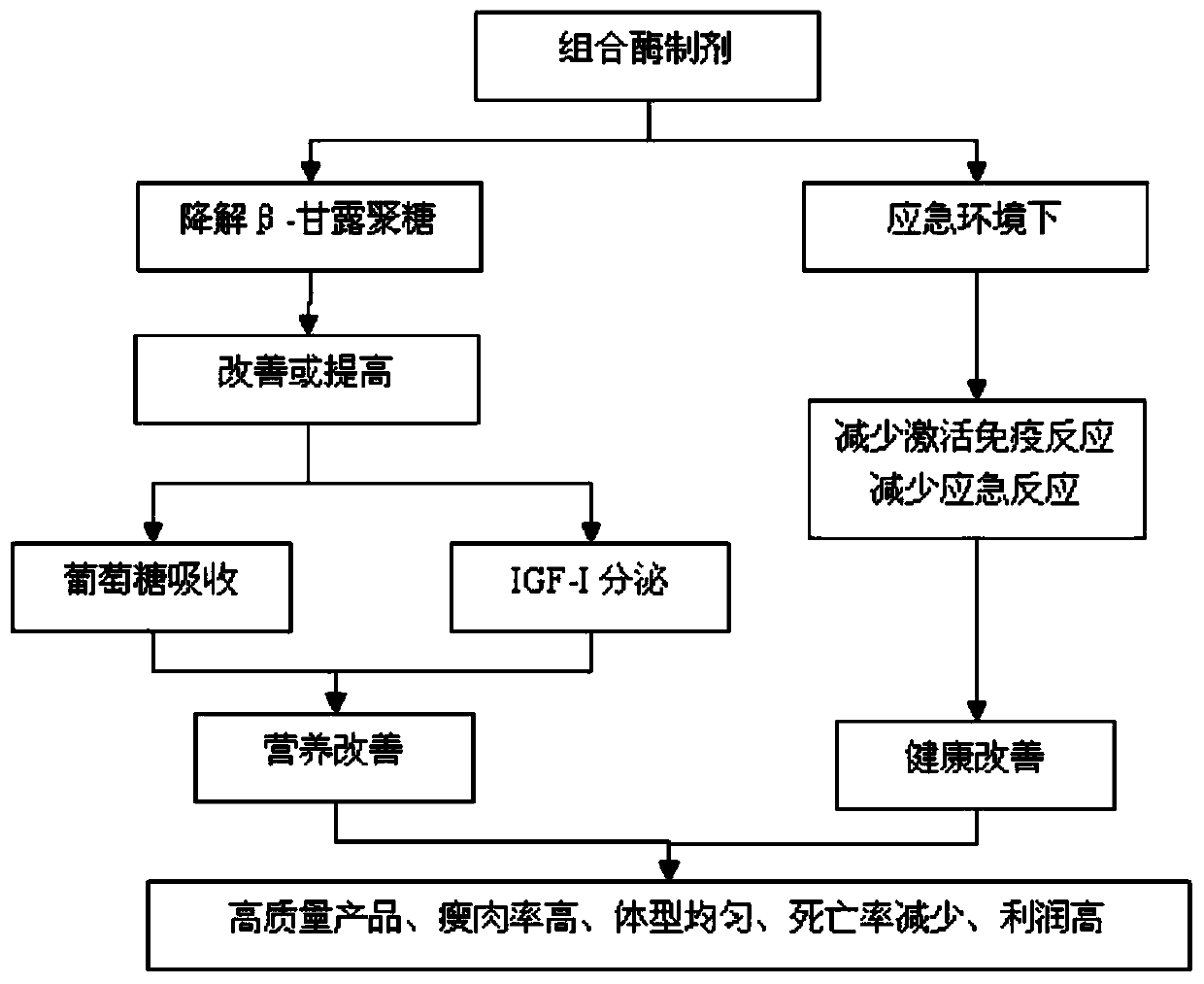
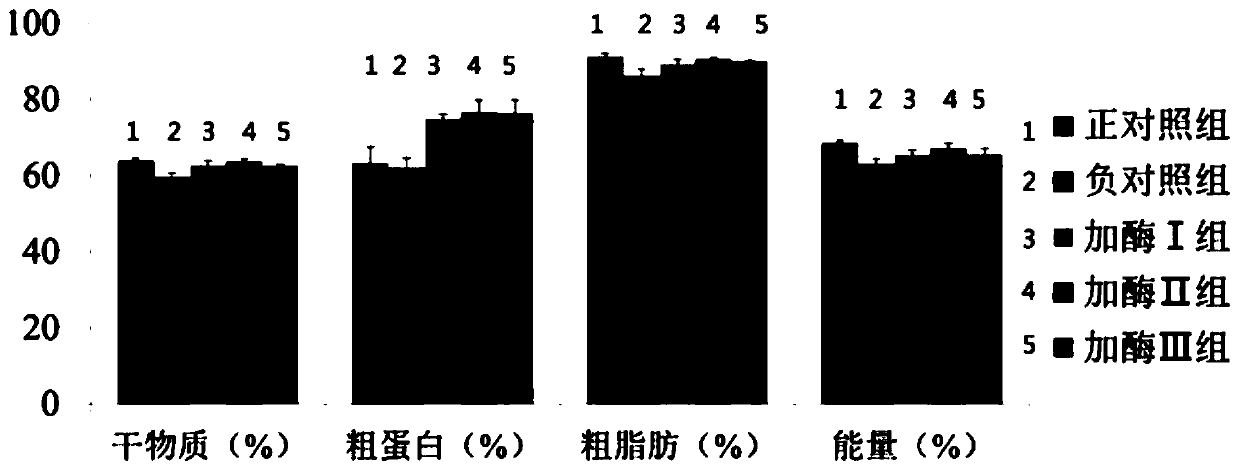
Combination enzyme preparation for solving problem of activating innate immune response by beta-mannan
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed additives, and particularly relates to a combination enzyme preparation for solving the problem of activating an innate immune response by beta-mannan. The combination enzyme preparation for solving the problem of activating the innate immune response by beta-mannan is prepared from, by weight, 5-7 parts of beta-mannan, 2-4 parts of alpha-amylase, 3-5 parts of xylanase, 2-4 parts of cellulase and 1-3 parts of alpha-galactase. The combination enzyme preparation can have the advantages of increasing the utilization rate of feed energy and protein, promoting the growth of livestock and poultry, increasing the utilization rate of feed and increasing economic benefits; the combination enzyme preparation participates in immune regulation, improves immunity, can effectively prevent the invasion of pathogenic bacteria and parasites to the intestinal tract and has the function of replacing antibiotics.
Owner:长沙微威生物科技有限公司
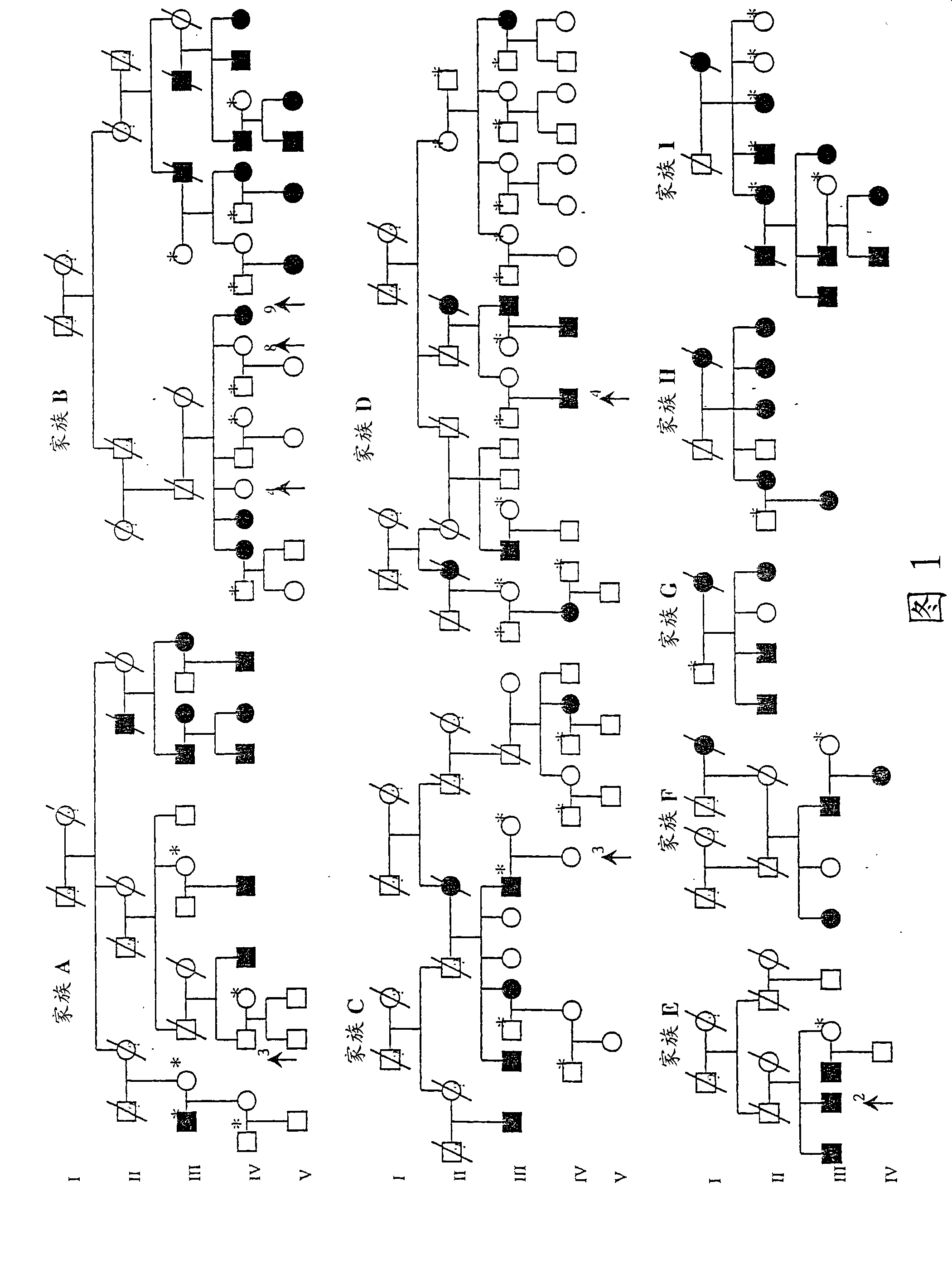
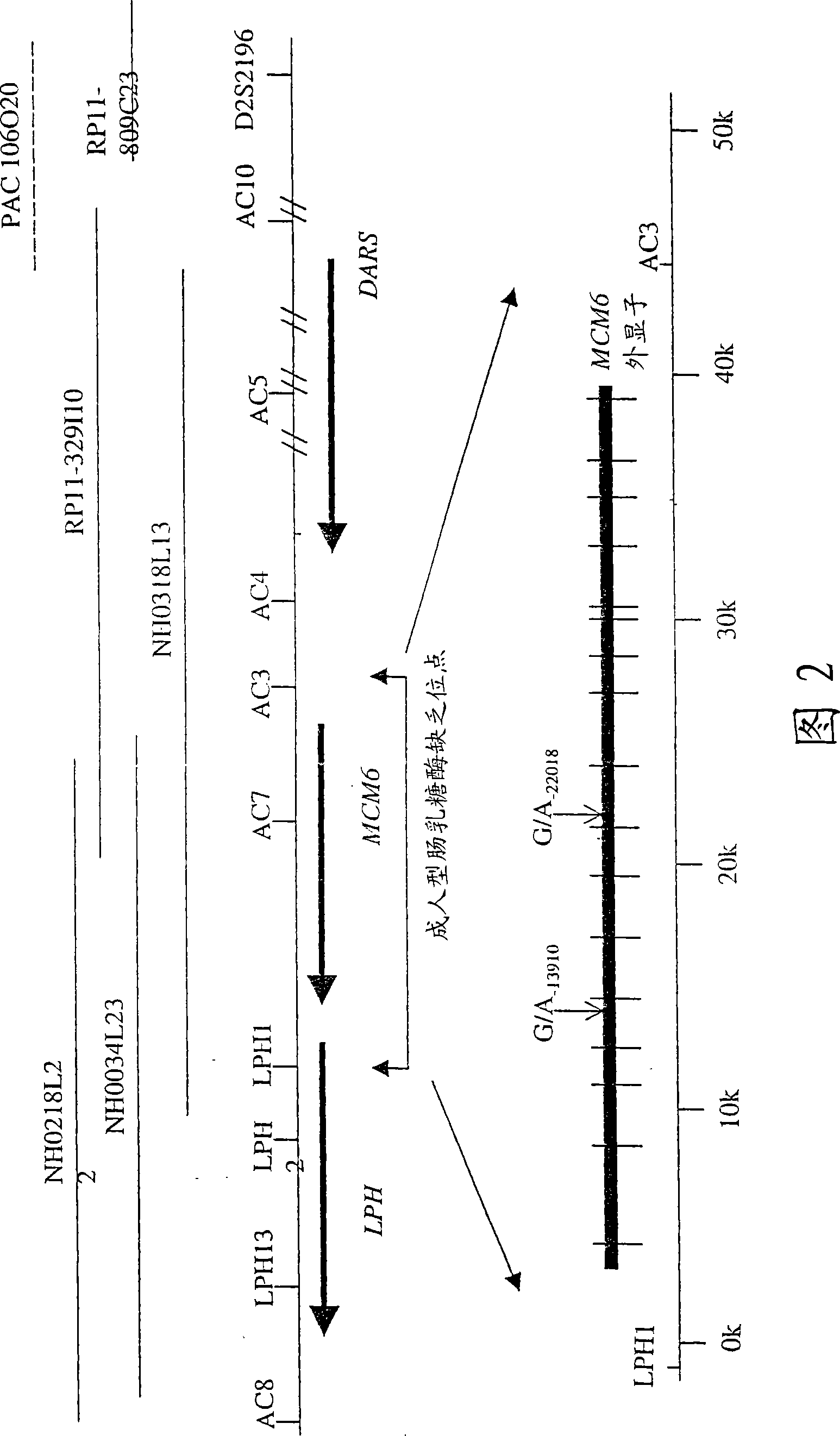
Identification of DNA variant associated with adult type hypolactasia
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule that causes or indicates human-type intestinal lactase deficiency and comprises the 5' portion of the intestinal lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH) gene, the nucleic acid molecule being selected from the group consisting of: (a) having or comprising SEQ The nucleic acid molecule of the nucleic acid sequence of ID NO:1, the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 is also described in Figure 4 and is included in the sequence described in Figure 8; (b) has or comprises the nucleic acid of the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 Molecule, the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 is also described in Figure 5 and is included in the sequence described in Figure 9; (c) a nucleic acid molecule of at least 20 nucleotides, the complementary strand of which is under stringent conditions with (a ) or (b) nucleic acid molecule hybridization, wherein said polynucleotide / nucleic acid molecule has a cytosine residue at a position corresponding to the 5'-13910 position of the LPH gene; and (d) at least 20 nucleosides A nucleic acid molecule of acid, the complementary strand of the nucleic acid molecule hybridizes with the nucleic acid molecule of (a) or (b) under stringent conditions, wherein said polynucleotide / nucleic acid molecule is at the 5'-22018 site corresponding to the LPH gene There is a guanine residue in the position. The present invention also relates to a method for testing the presence or susceptibility of human-type intestinal lactase deficiency based on the analysis of the SNPs contained in the above-mentioned nucleic acid molecules. Furthermore, the present invention relates to diagnostic compositions and kits for detecting the presence or susceptibility to human-type intestinal lactase deficiency.
Owner:NAT PUBLIC HEALTH INST
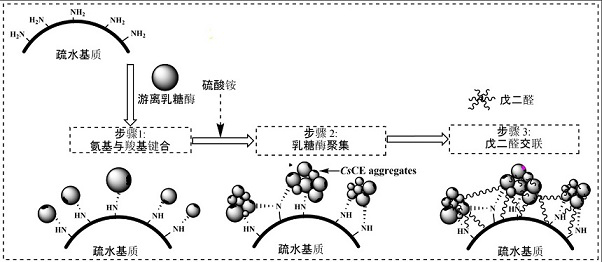
Immobilized lactase with hydrophobic property and method for preparing lactulose by applying immobilized lactase
ActiveCN112481239AWon't happenWill not polluteImmobilised enzymesFermentationGlycosideLactase Enzyme
The invention discloses immobilized lactase with a hydrophobic property and a method for preparing lactulose by using the immobilized lactase. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, immobilizing lactase to endow the lactase with a hydrophobic property; taking the lactulose as a bio-catalyst, and catalyzing lactose under mild conditions to prepare lactulose, wherein the yield of the lactulose can reach 33.6%, the content of the lactulose is 83.9 g / L, and the yield of the lactulose is nearly two times that of lactulose obtained by free lactase. The method is characterized in that through immobilization operation, the immobilized lactase is endowed with a certain hydrophobic property, so that the hydrolysis activity and transglycosylation activity of the lactase are regulated andcontrolled, and the lactase is enabled to be carried out in the transglycosylation direction beneficial to generation of lactulose. The method effectively solves the problem that the hydrolysis activity is too high when lactase is applied to lactulose production, the immobilized lactase with a hydrophobic characteristic is adopted, lactulose can be efficiently prepared without assistance of an organic phase, the practicability is high, and the method is a beneficial substitute for preparing lactulose through a chemical method and a free enzyme method.
Owner:苏州福赛思生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com