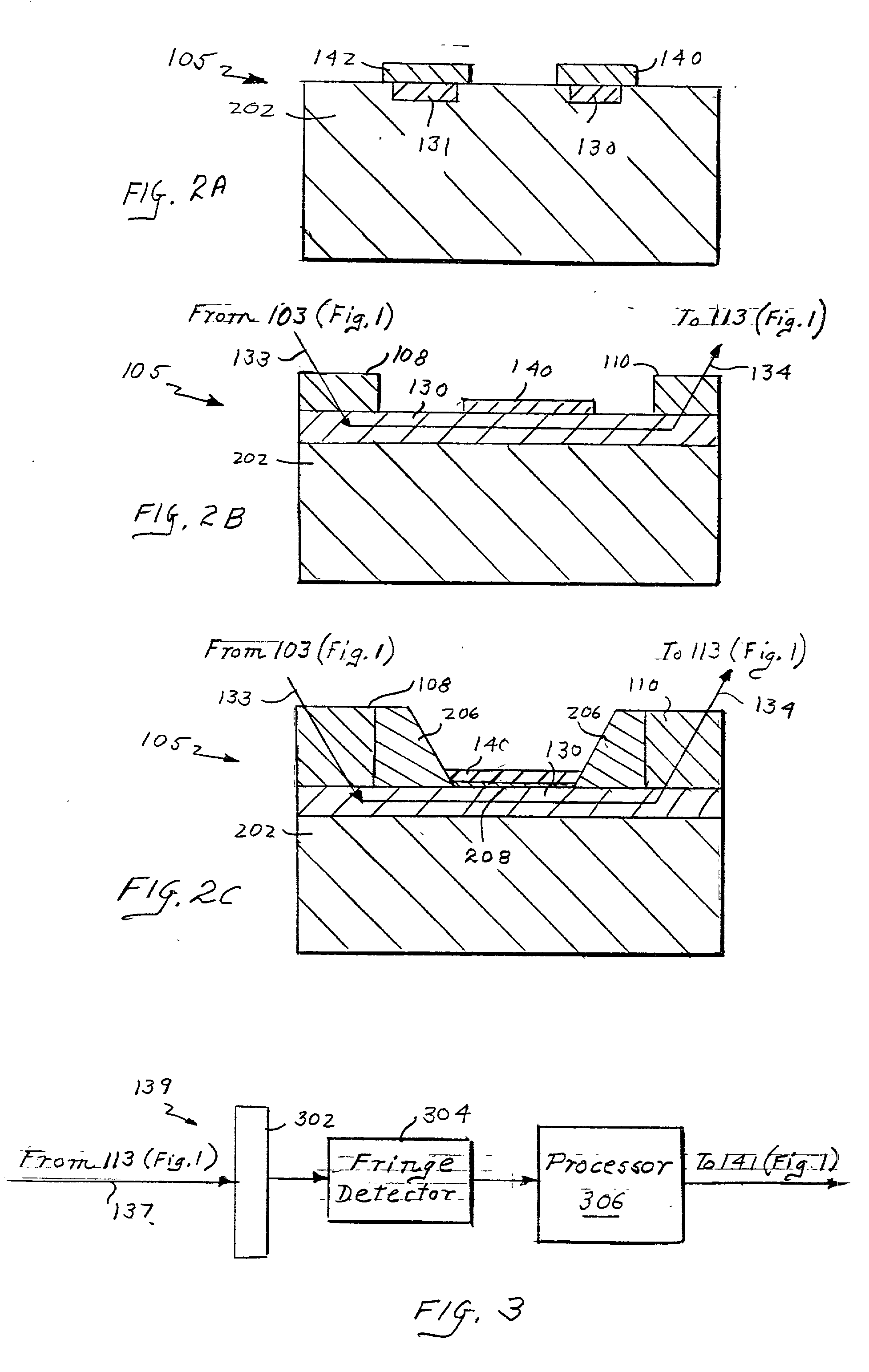
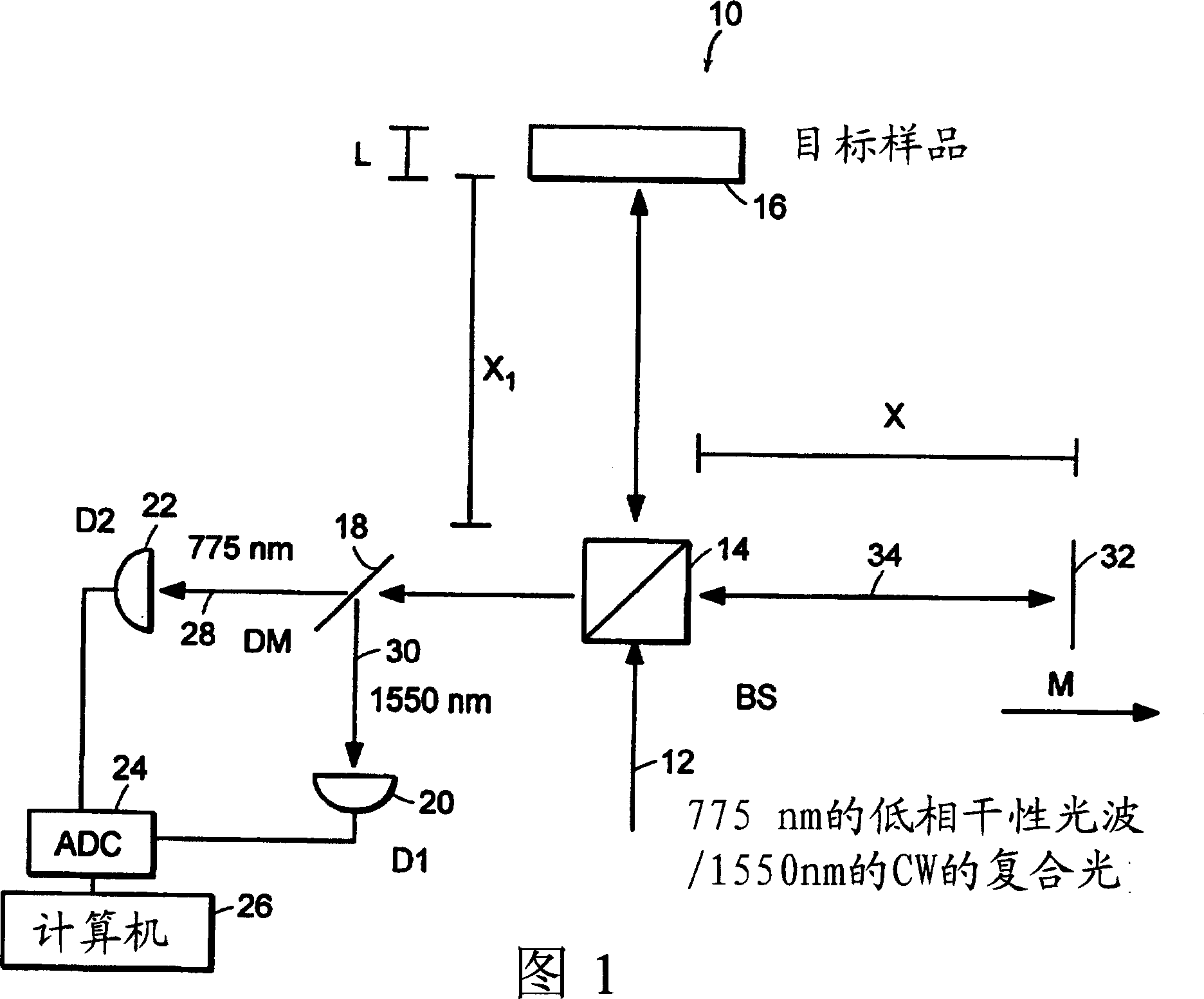
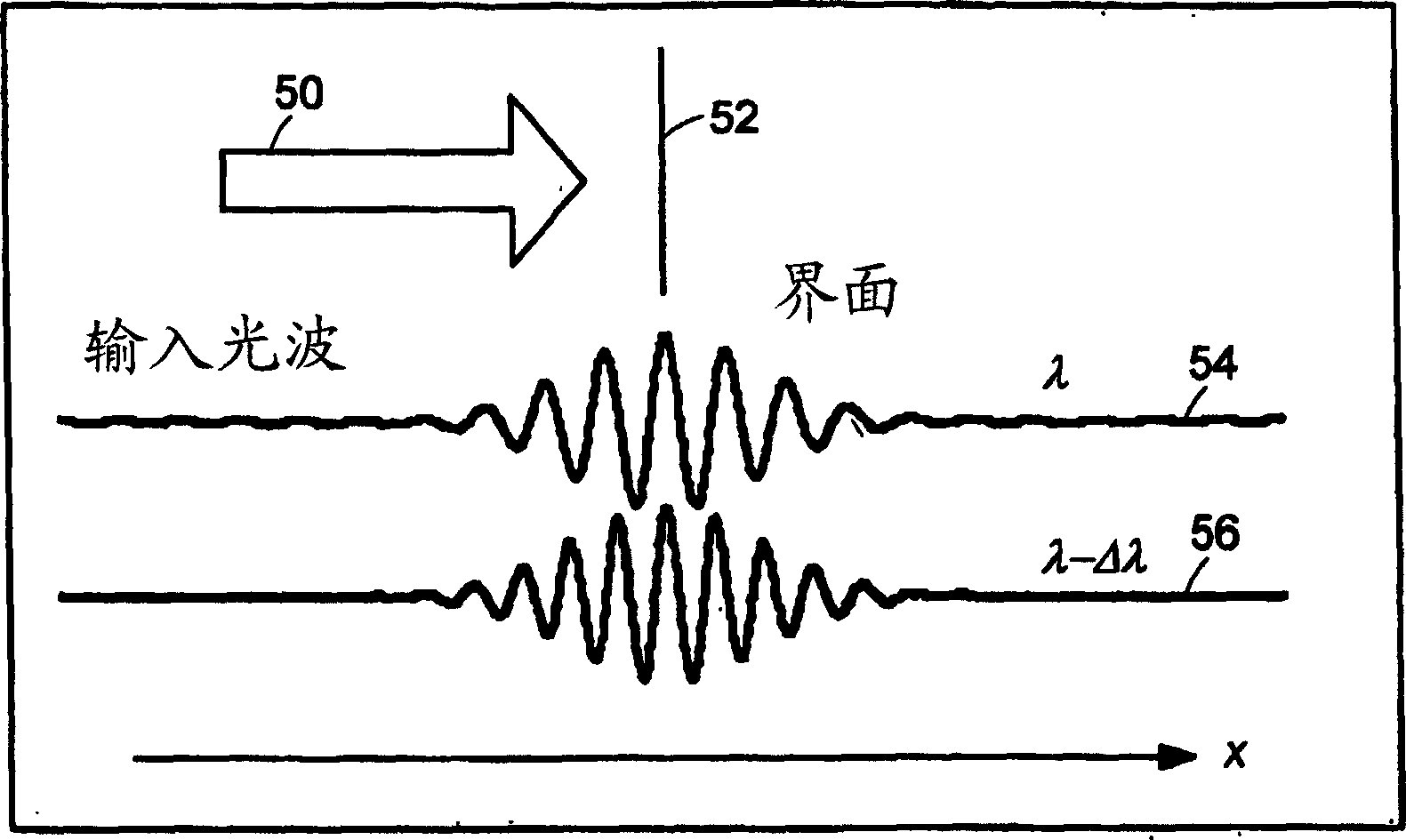
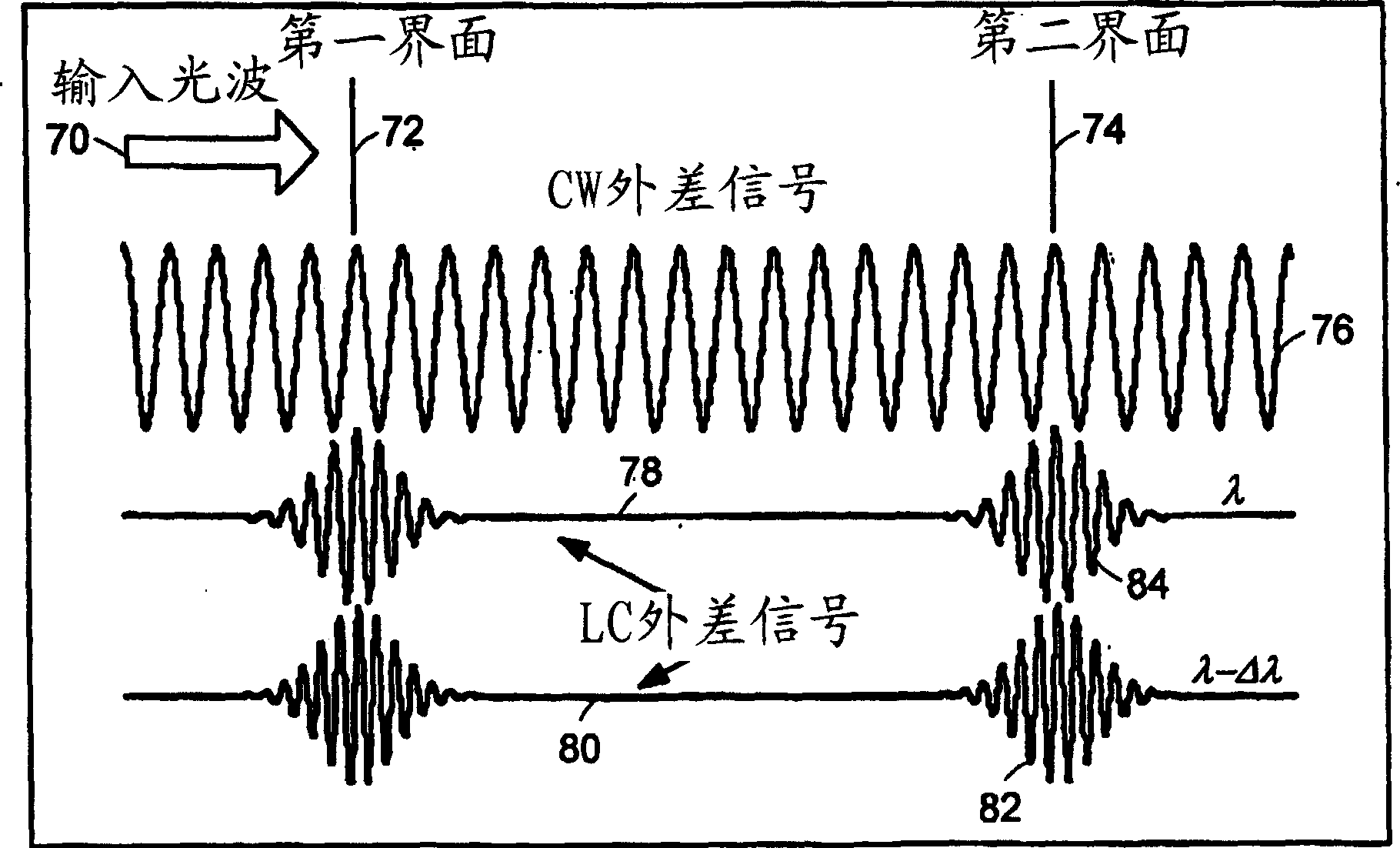
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Interferome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interferome is an online bioinformatics database of interferon-regulated genes (IRGs). These Interferon Regulated Genes are also known as Interferon Stimulated Genes (ISGs). The database contains information on type I (IFN alpha, beta), type II (IFN gamma) and type III (IFN lambda) regulated genes and is regularly updated. It is used by the interferon and cytokine research community both as an analysis tool and an information resource. Interferons were identified as antiviral proteins more than 50 years ago. However, their involvement in immunomodulation, cell proliferation, inflammation and other homeostatic processes has been since identified. These cytokines are used as therapeutics in many diseases such as chronic viral infections, cancer and multiple sclerosis. These interferons regulate the transcription of approximately 2000 genes in an interferon subtype, dose, cell type and stimulus dependent manner. This database of interferon regulated genes is an attempt at integrating information from high-throughput experiments and molecular biology databases to gain a detailed understanding of interferon biology.
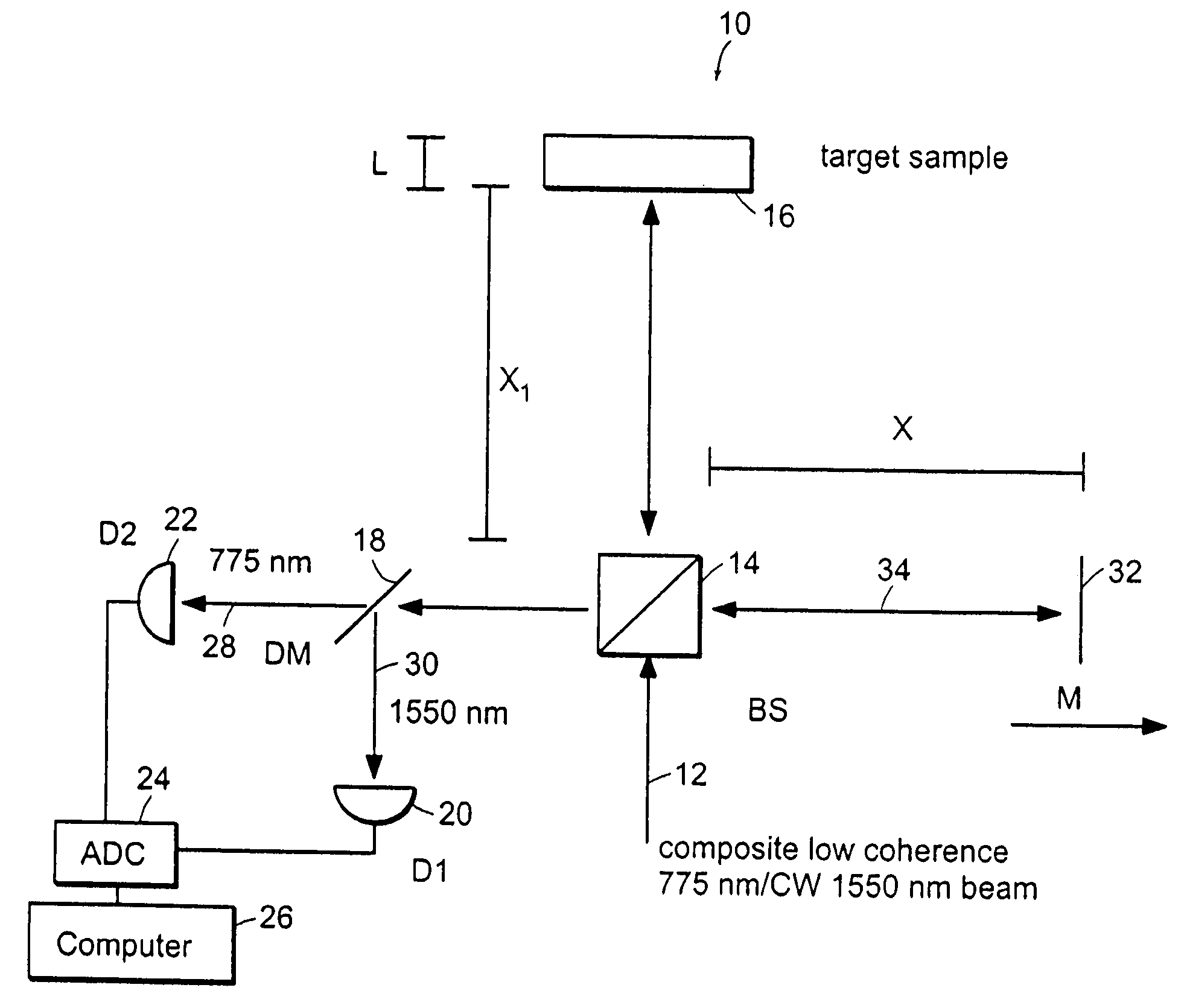
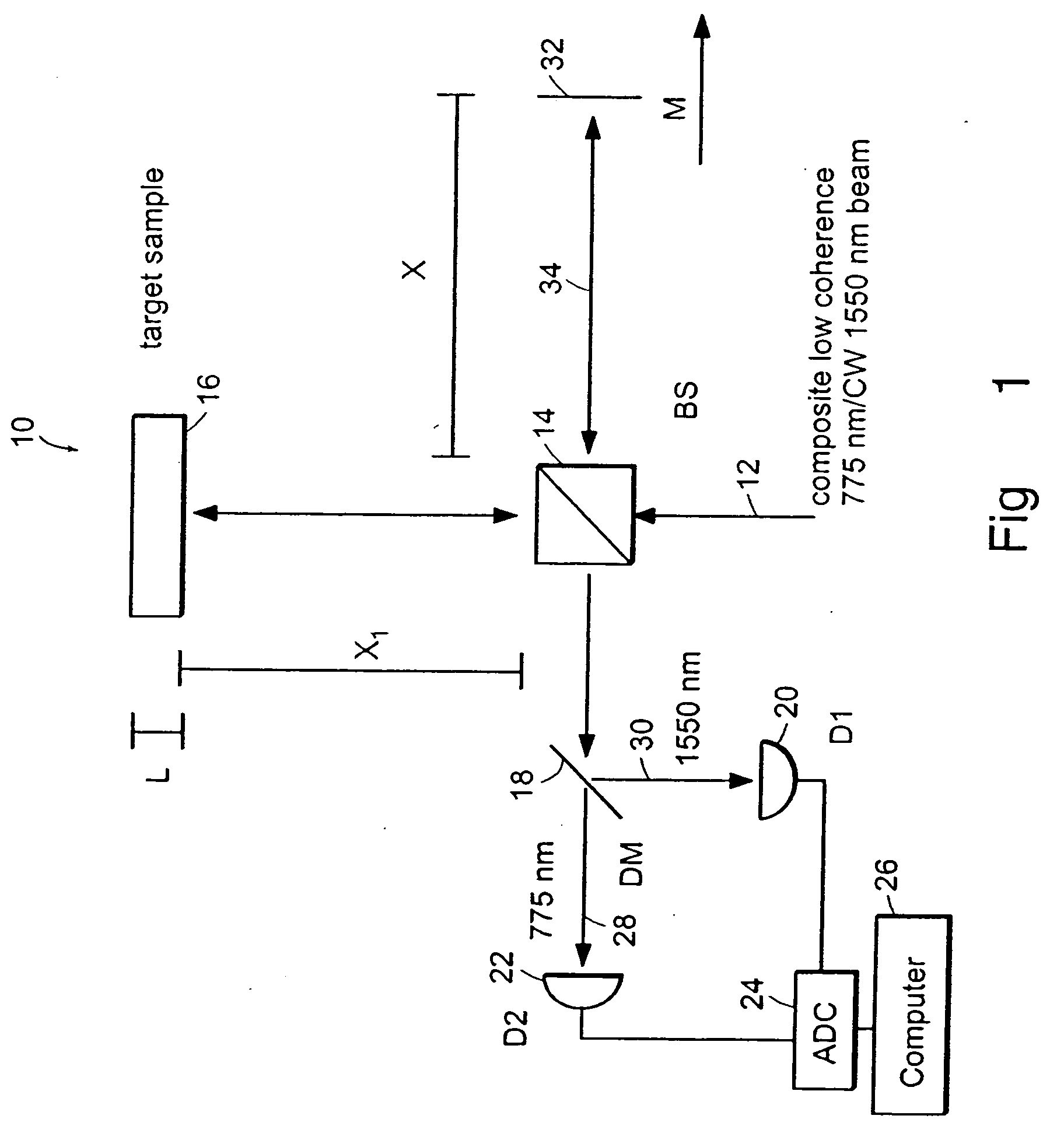
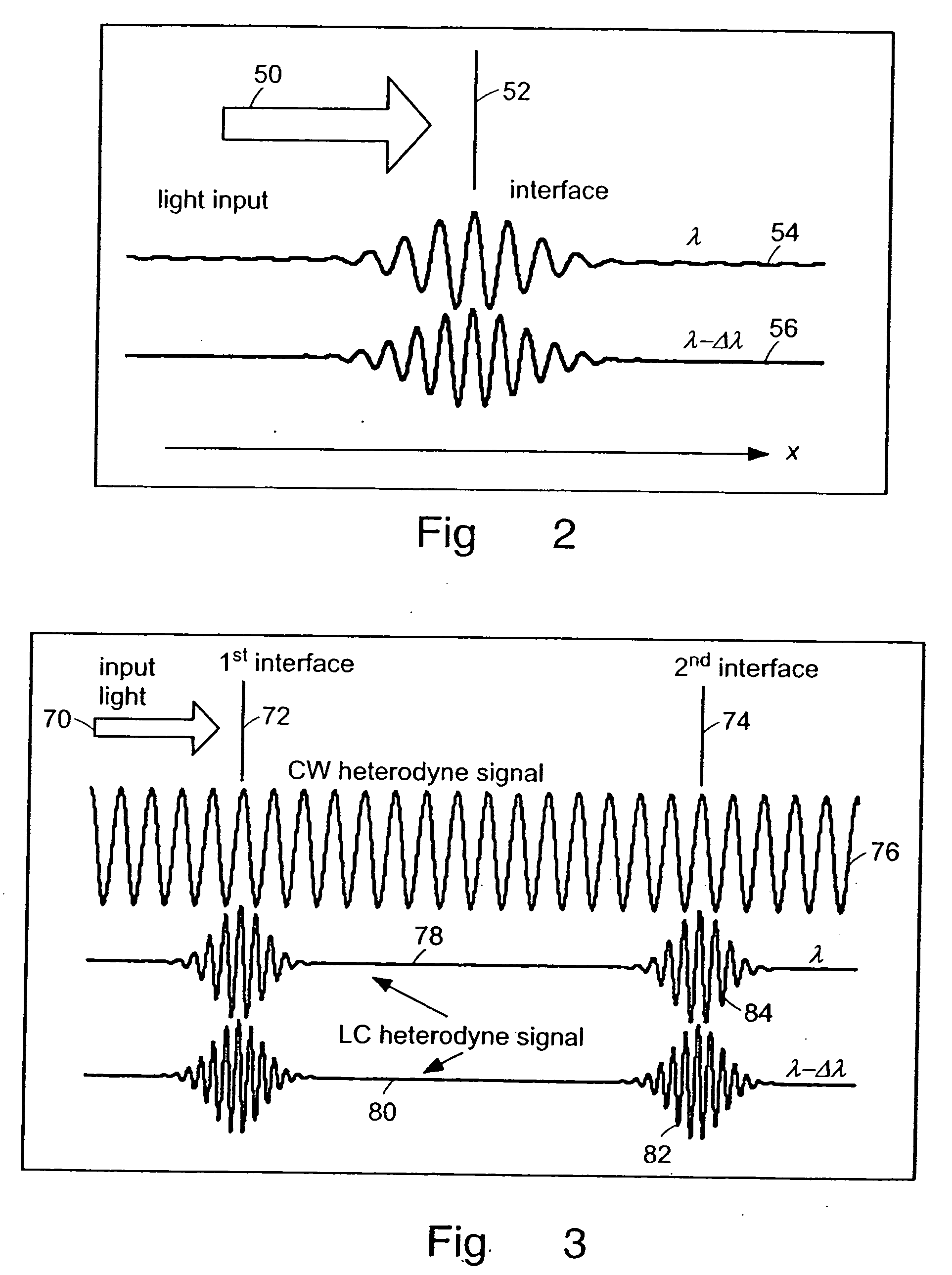
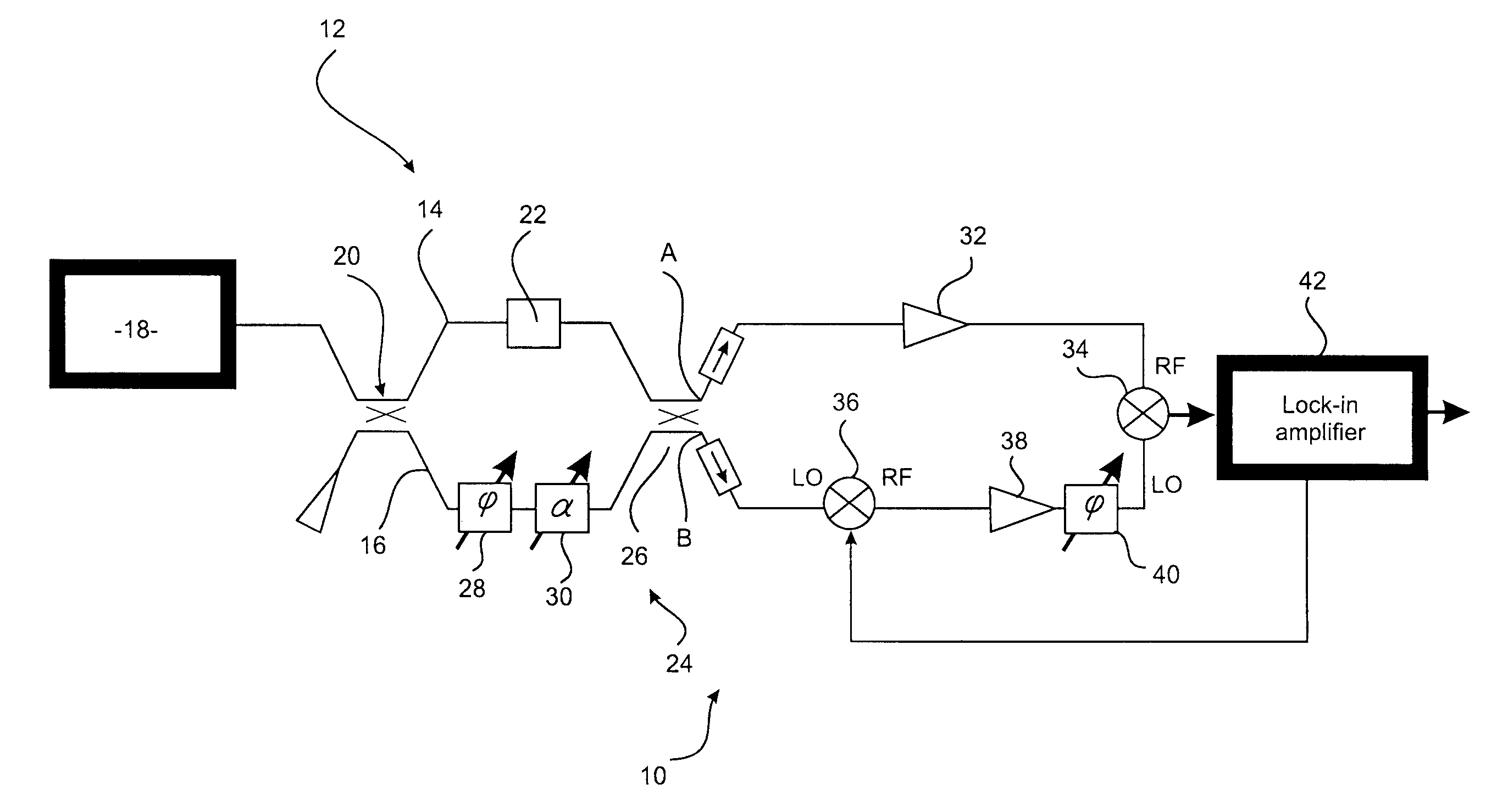
Systems and methods for phase measurements
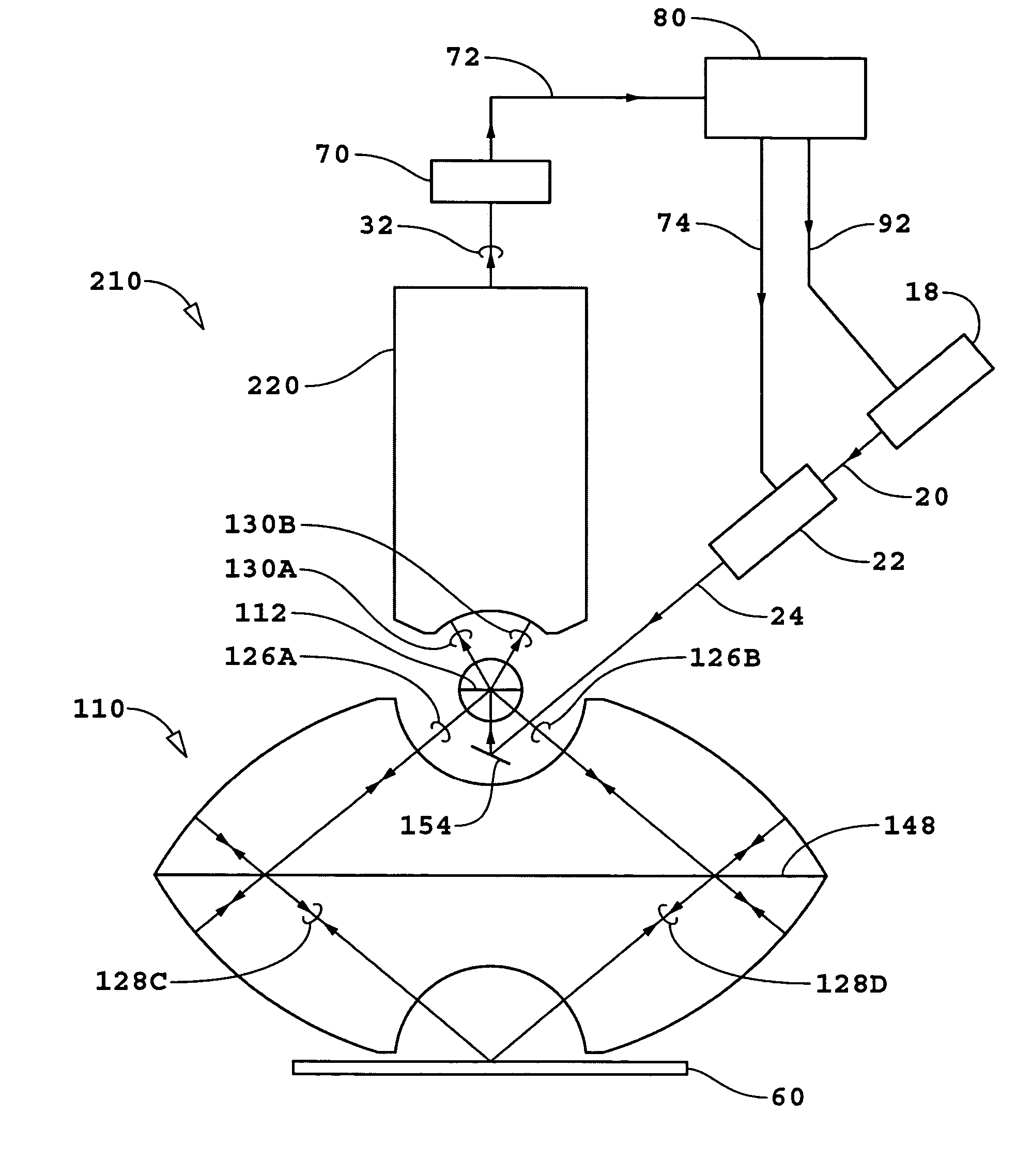
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
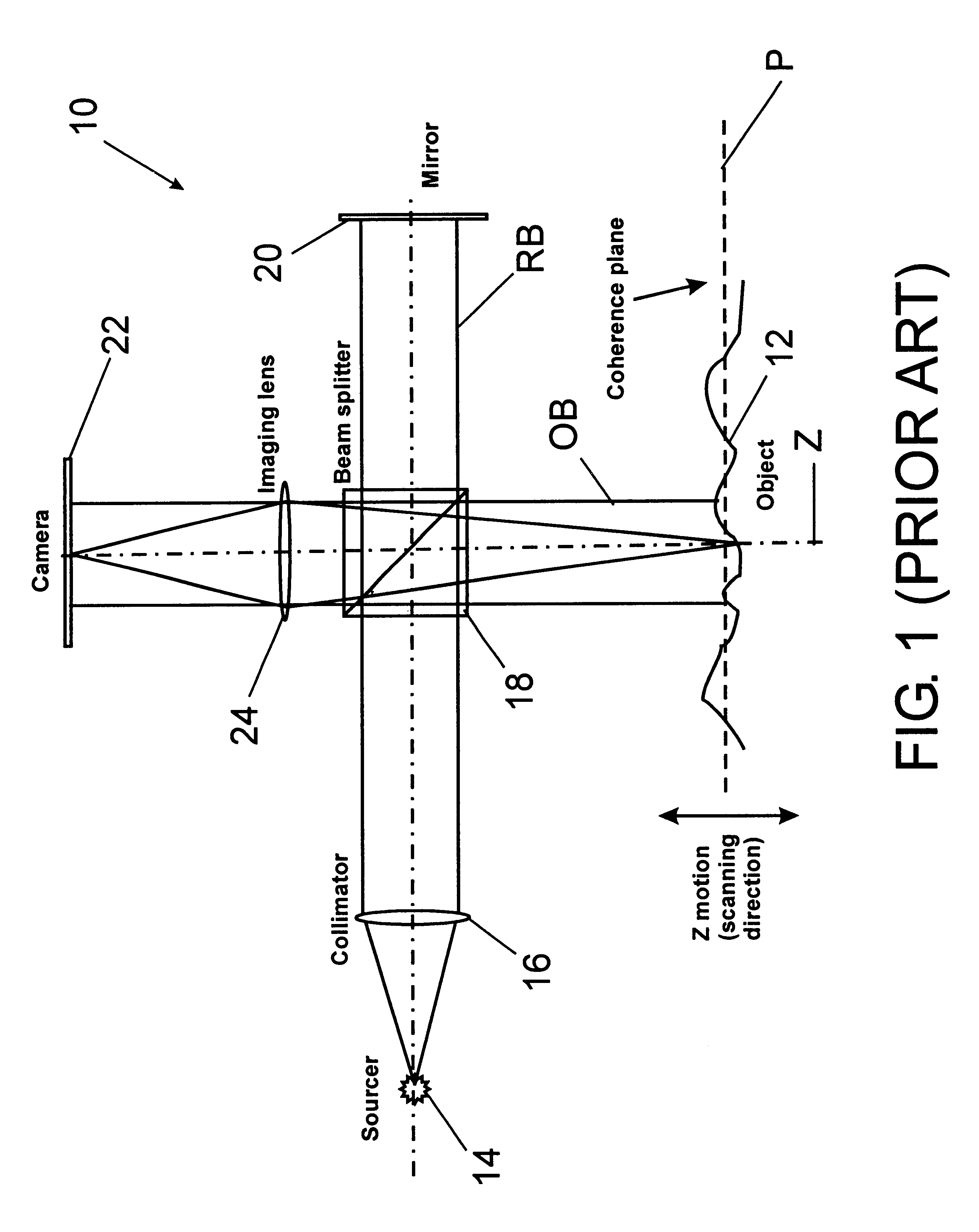
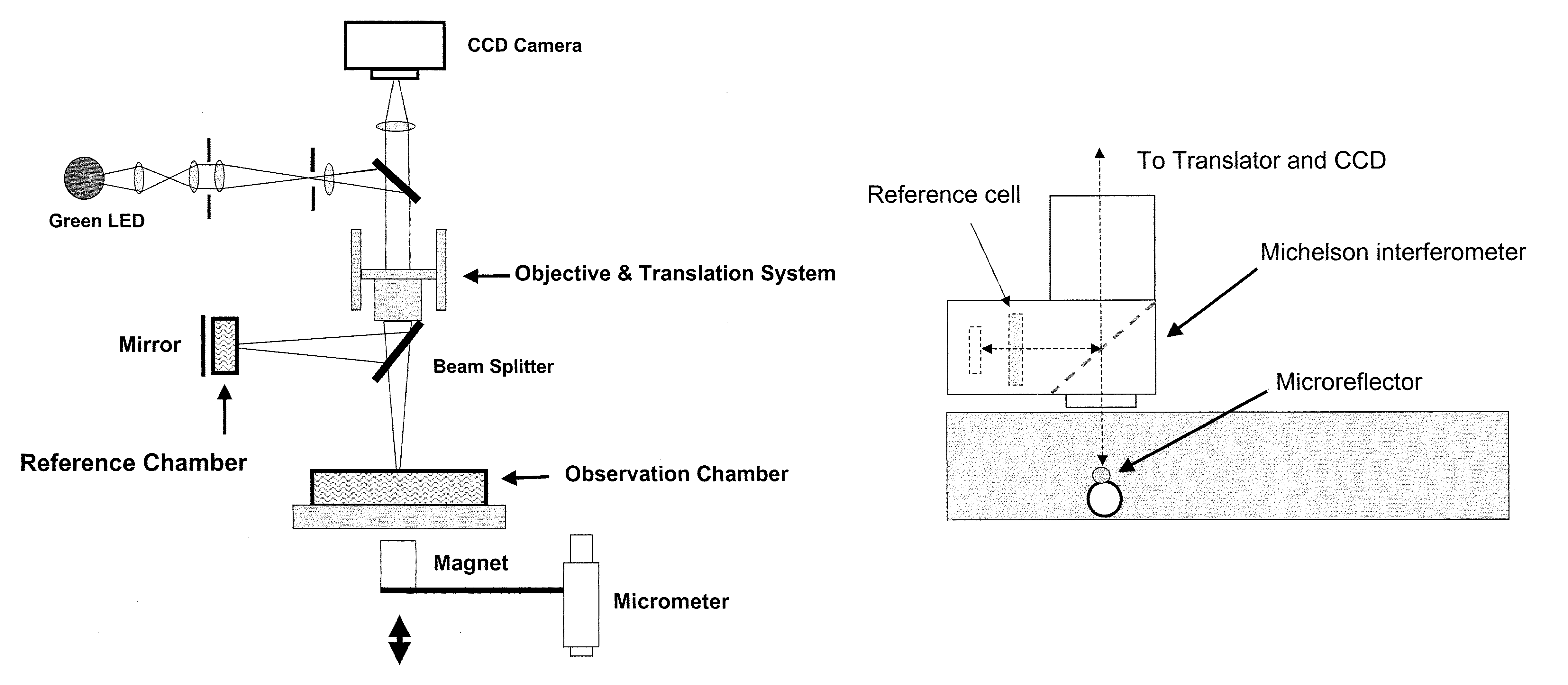
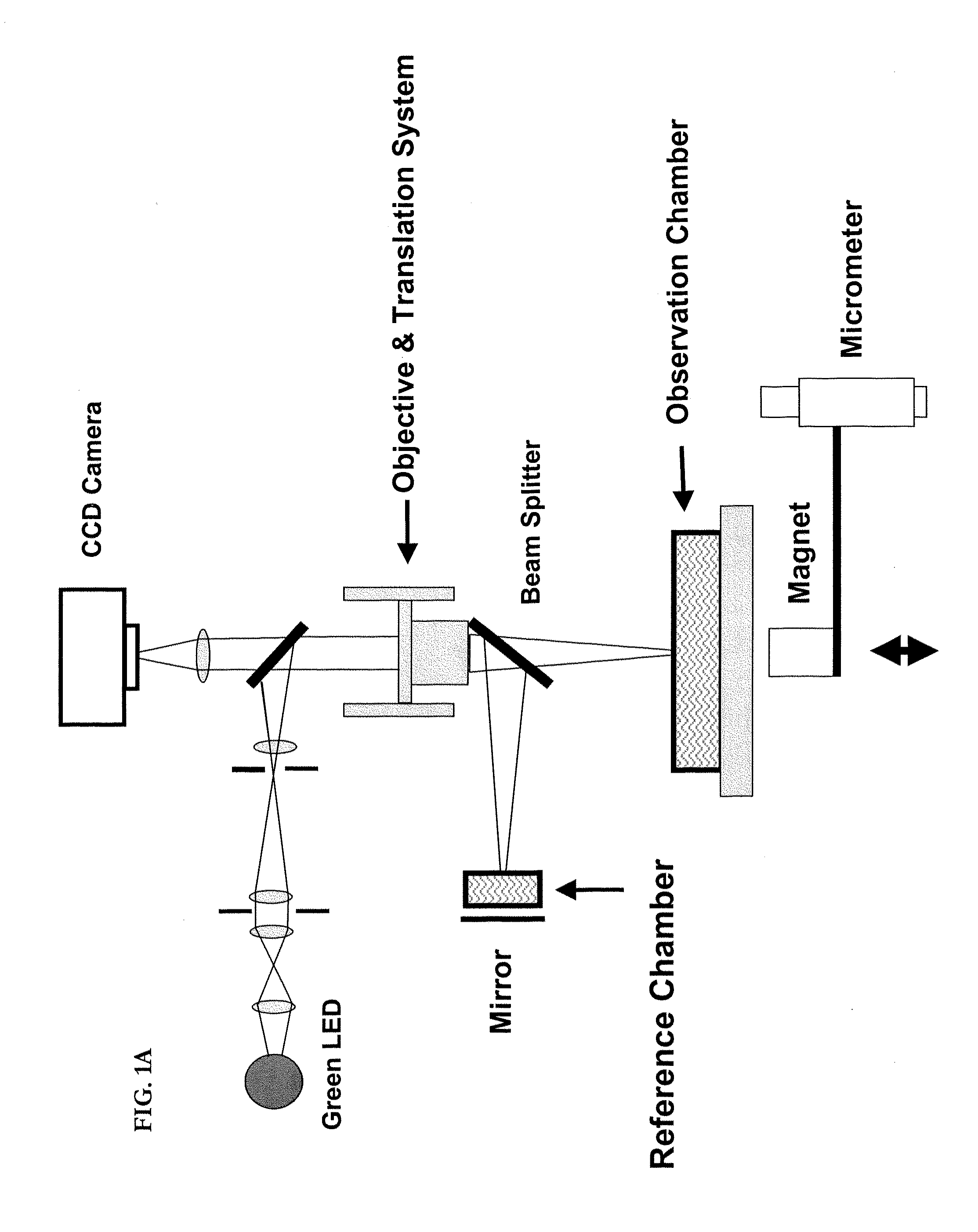
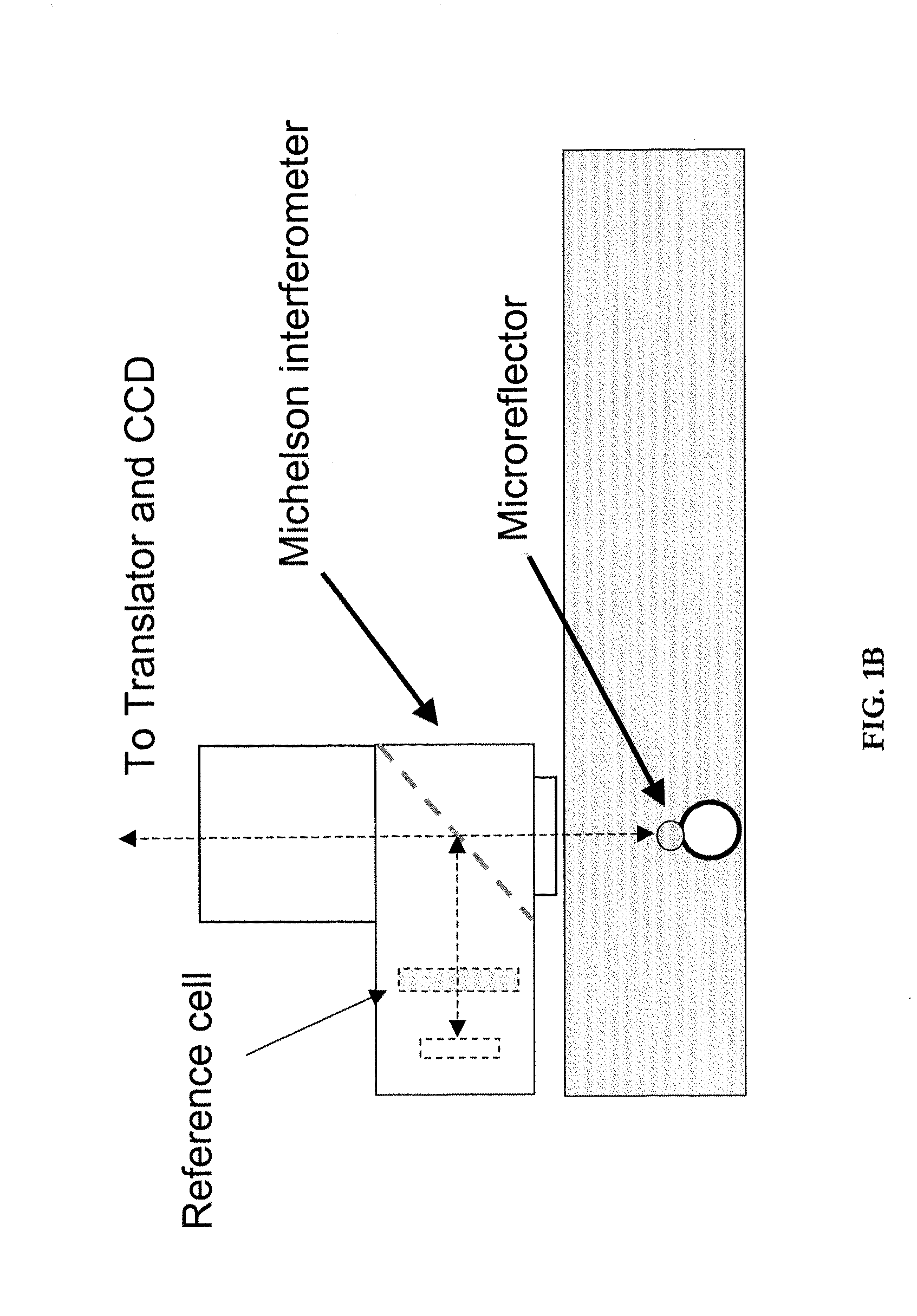
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
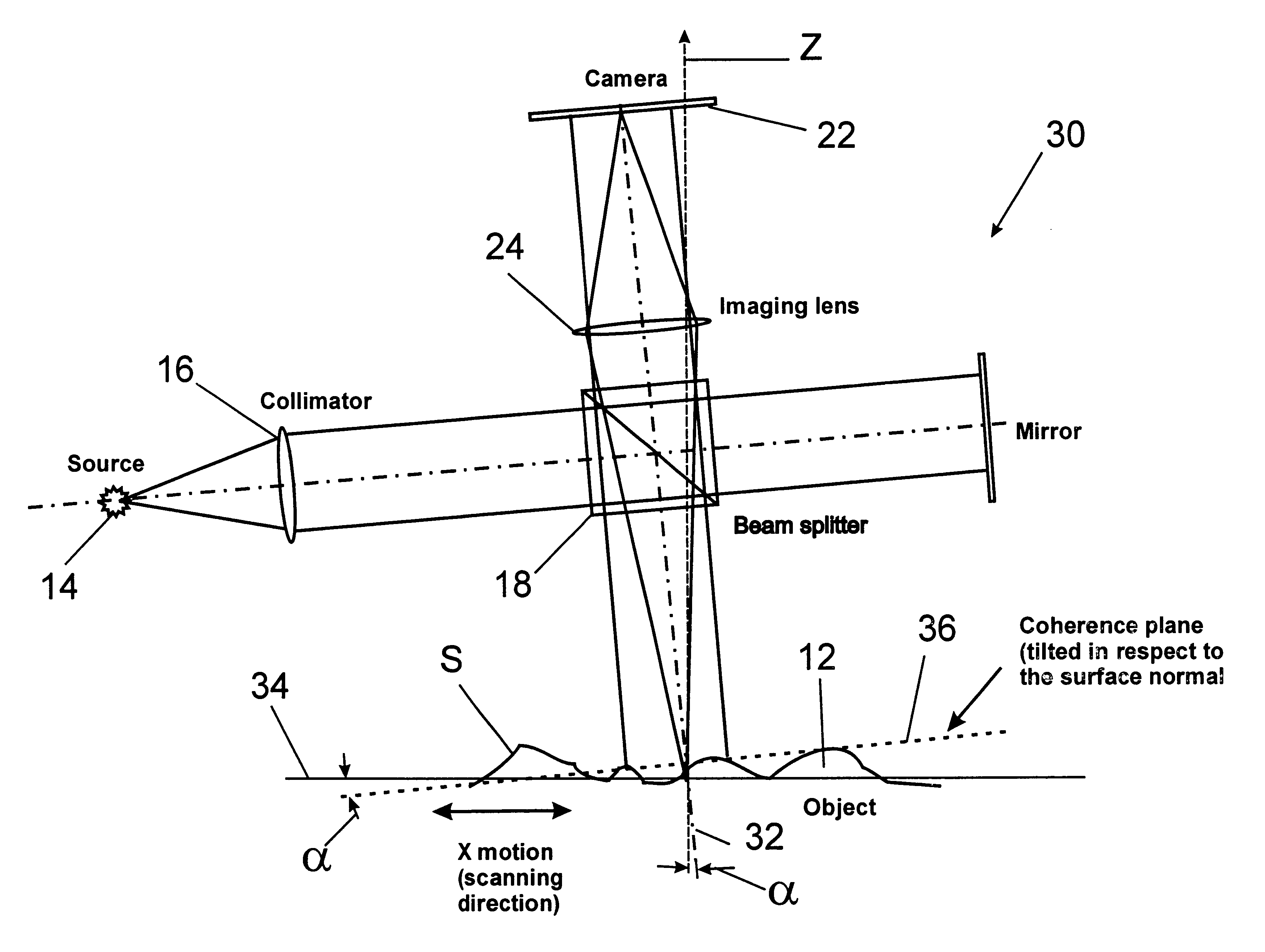
Lateral-scanning interferometer with tilted optical axis
An interferometer scans the sample surface laterally with respect to the optical axis of the interferometric objective. The objective is tilted, so that the sample surface is placed at an angle with respect to the maximum coherence plane of the instrument. By moving the sample stage laterally, at an angle, through a point at a set distance from the objective on the objective's optical axis, rather than vertically along the optical axis, different parts of the object intersect the maximum coherence plane at different times as the surface passes through the coherence plane, the precise time depending on the profile of the surface. When the OPD of a point on the object's surface is greater than the coherence length of the light source, the intensity of light reflected from this point does not produce interference fringes. Therefore, the intensity registered by the detector is approximately constant. However, when the object point enters the zone of coherence, the interference effects modulate the intensity the same way as in a regular VSI procedure. As the object moves along the scanning direction, it also has a relative vertical speed with respect to the objective because of the tilt of the objective's optical axis with respect to the scanning plane; therefore, the lateral scanning motion produces an OPD variation as the vertical scan in a conventional system. As a result, light intensity data are acquired continuously as the test surface is scanned, thus elimination the need for stitching multiple sub-sets of data.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Doubly-differential interferometer and method for evanescent wave surface detection
InactiveUS20020003627A1Easy to disassembleMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhase-affecting property measurementsReference sampleBio molecules
A high speed, highly sensitive optical sensing platform and a method for detecting and / or measuring characteristics of a substance in a measurement sample are disclosed. The platform includes at least one pair of optical paths formed in a waveguide, a light source for injecting optical beams along the optical paths, a light modulator for enabling the excitement of a transverse electric and a transverse magnetic guide modes, and a phase detector for detecting phase differences between the beams propagating along the optical paths. One of the optical paths has a target analyte of unknown concentration with a measurement sample bound to its upper surface, while the second optical path has a reference sample containing a known concentration of the target analyte bound to its upper surface. A guided mode modulator causes an optical beam to propagate through the waveguide sequentially as two polarized modes. The highly sensitive platform is especially useful for directly detecting and / or measuring very small numbers of small molecules, bio-molecules, microorganisms in a liquid or gaseous test sample.
Owner:PERFECT GALAXY INT
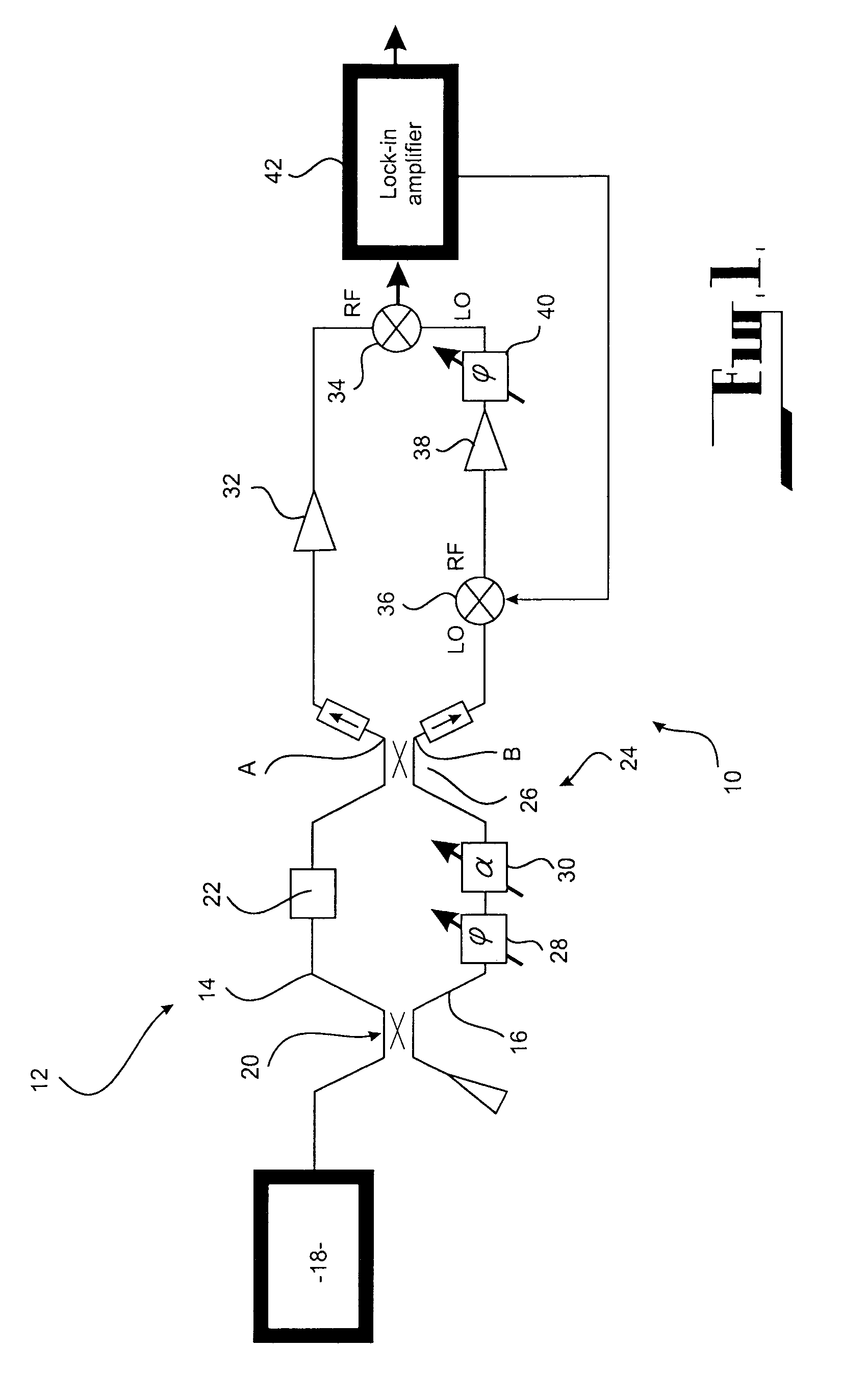
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical cytometry
The present invention provides optical systems and methods for determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, biological state and the like. The methods typically involve using interferometry to observe membrane properties in a cell and then use this information to determine one or more characteristics of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening as well as diagnostic techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
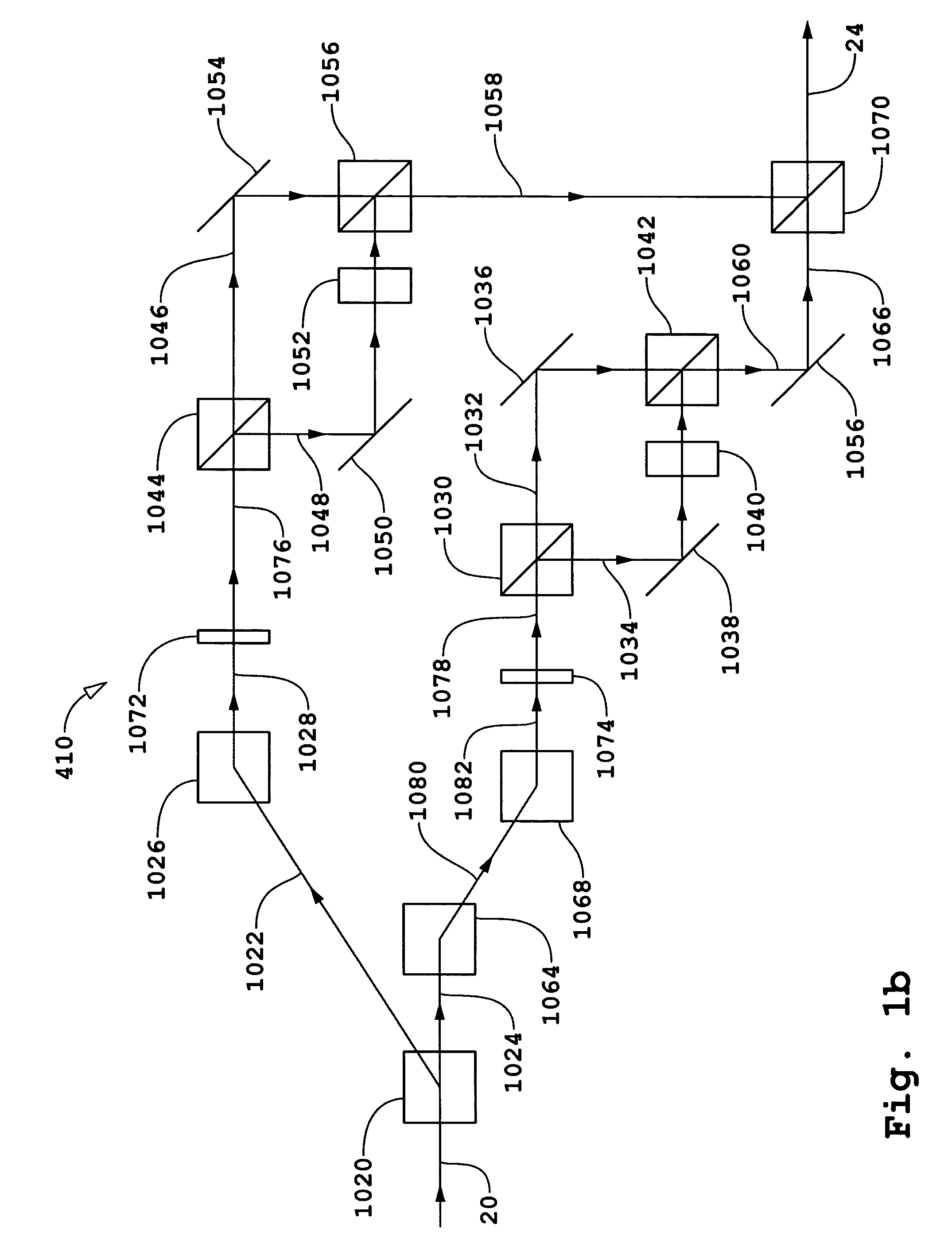
Phase noise compensation in an interferometric system
InactiveUS6900895B2Reliable determinationAccurate measurementNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementResistance/reactance/impedencePhase noisePhase difference
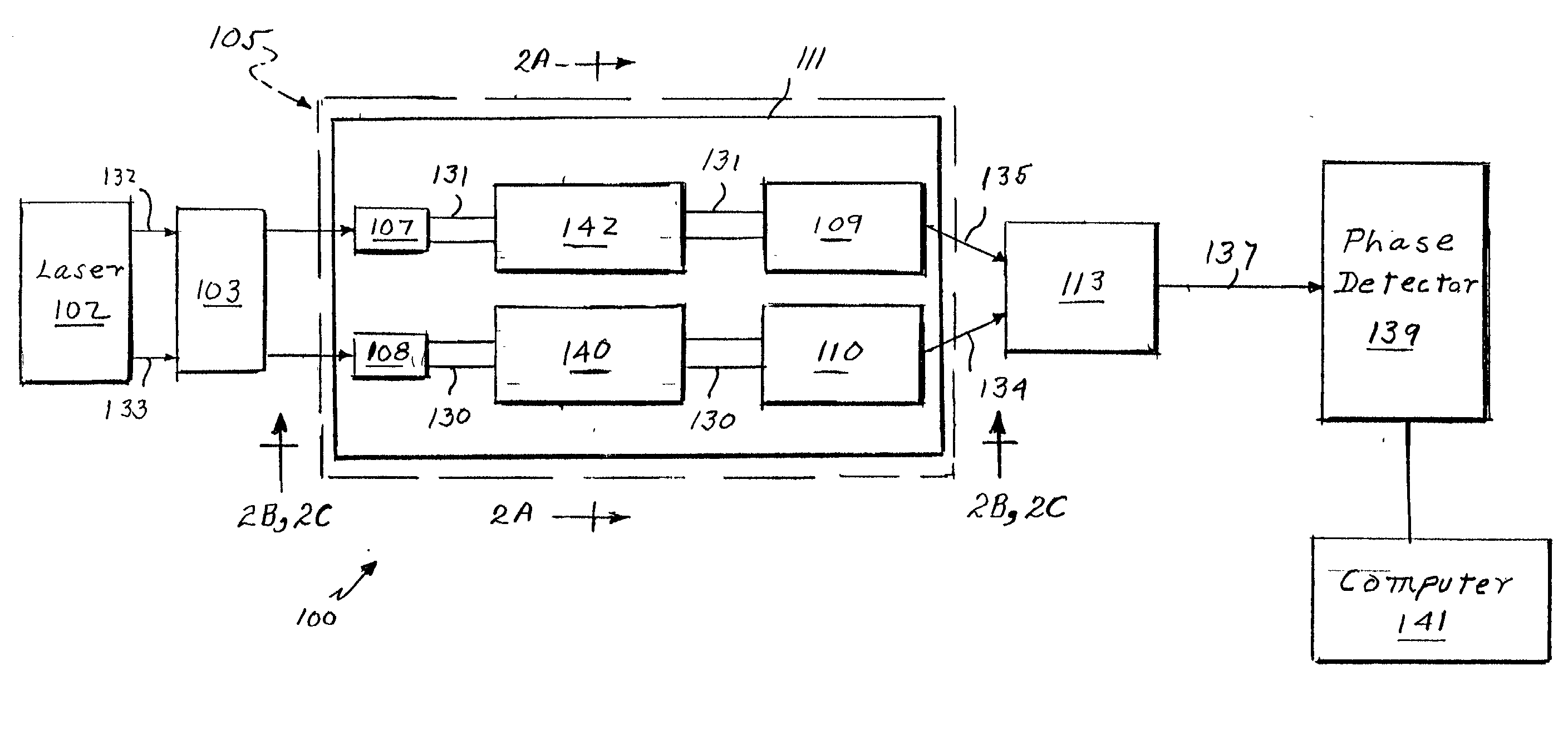
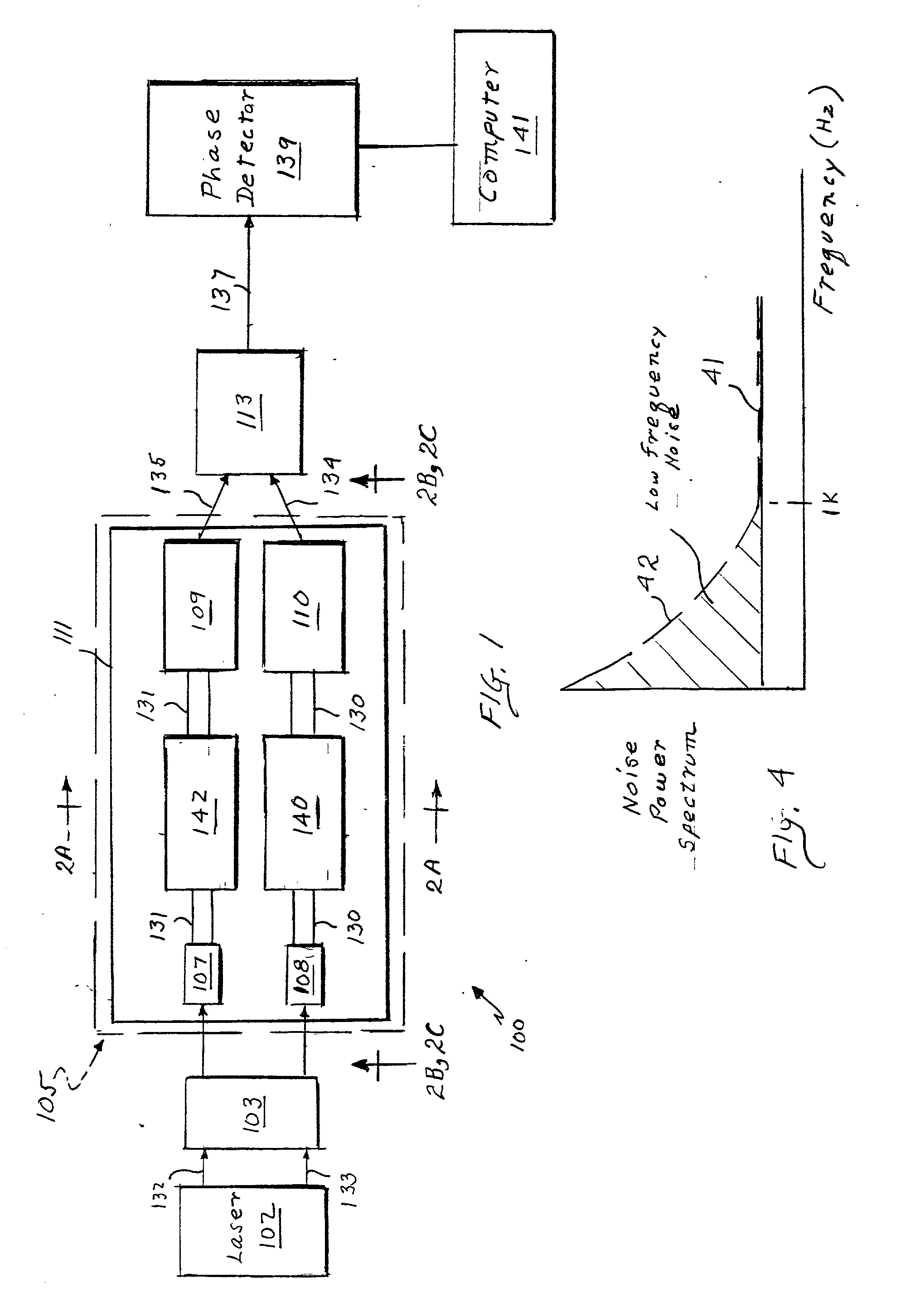
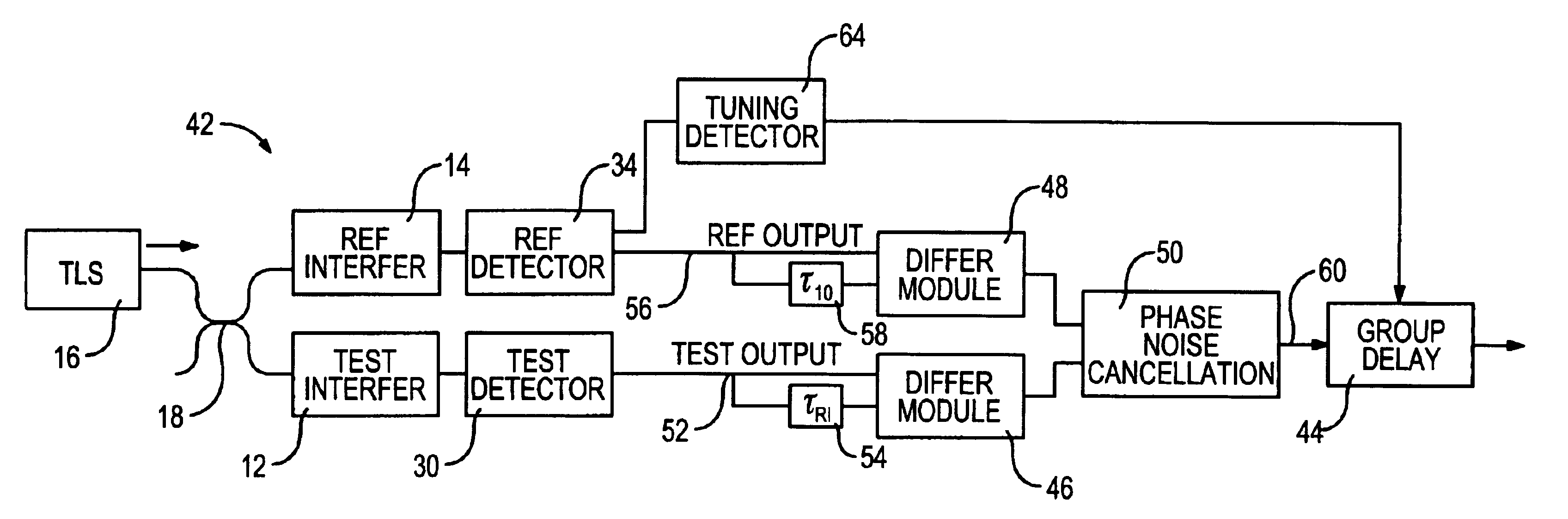
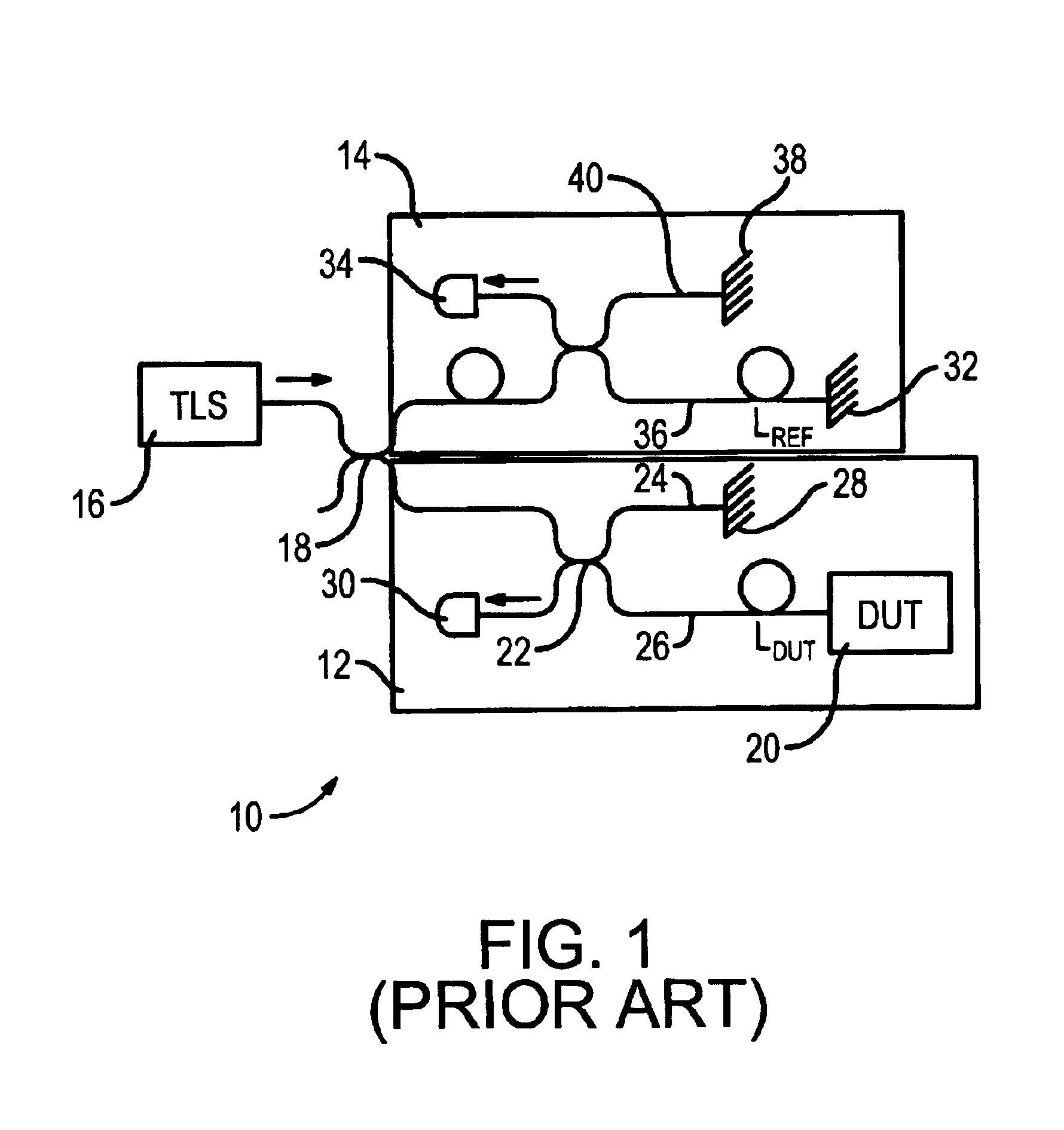
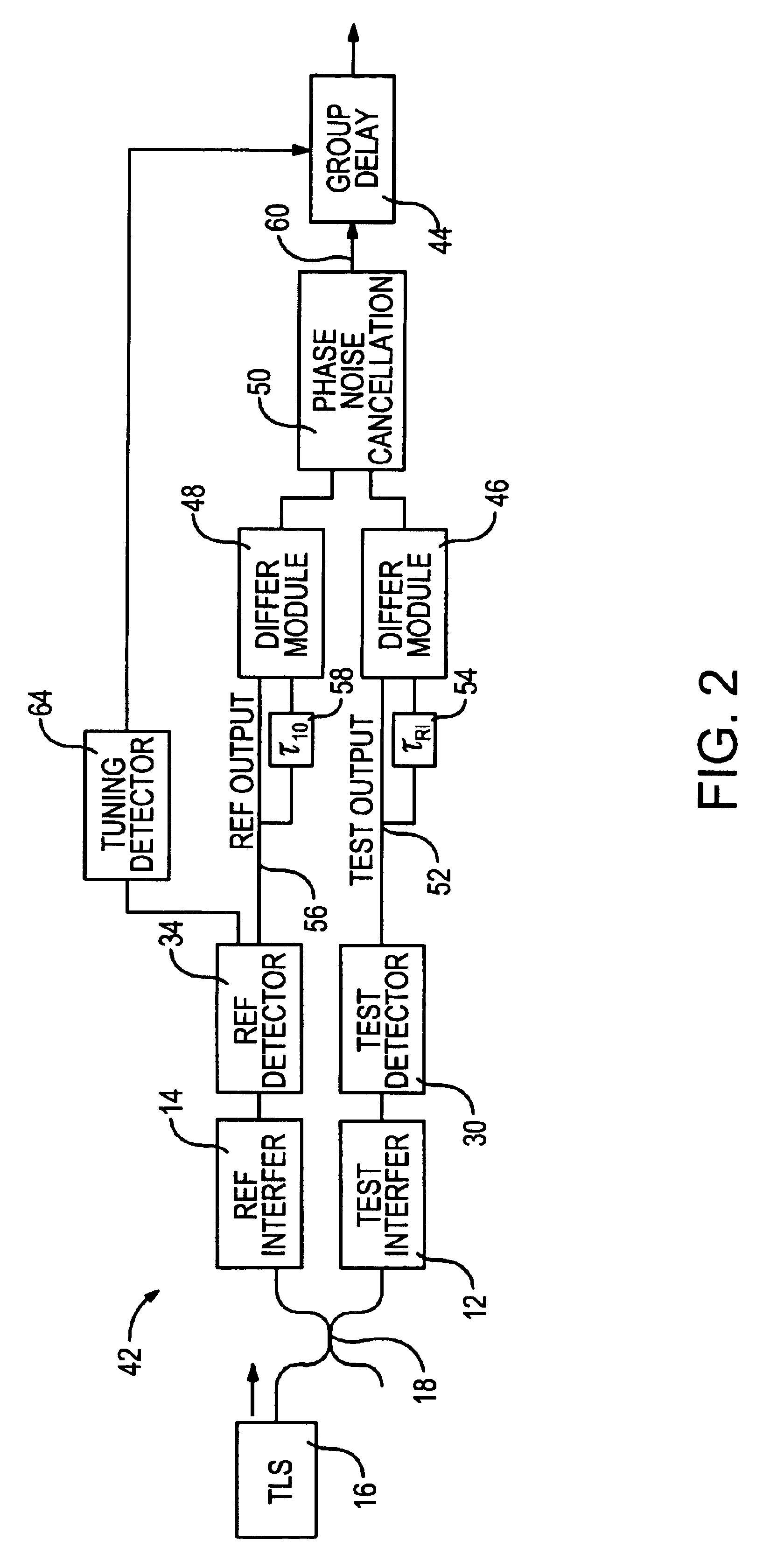
Phase noise is at least partially cancelled for an interferometric system by using a delay / phase cross-correlation approach for two interferometers within the system. The cross-correlation approach may be used in measuring group delay of a device under test and includes determining the differences between the phase of the output of each interferometer at time t and the phase of the same output at the time t minus the delay of the other interferometer. In one embodiment, the first phase difference is the difference between the phase of a test interferometer output at time t and the phase of the test interferometer output at the time t offset by the known delay of a reference interferometer. The second phase difference is calculated using the same technique, but the time offset is a delay representative of the relative delay of two light propagations within the test interferometer. A noise-cancelled time series output that is indicative of group delay can then be generated by determining the difference between the first and second differences.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
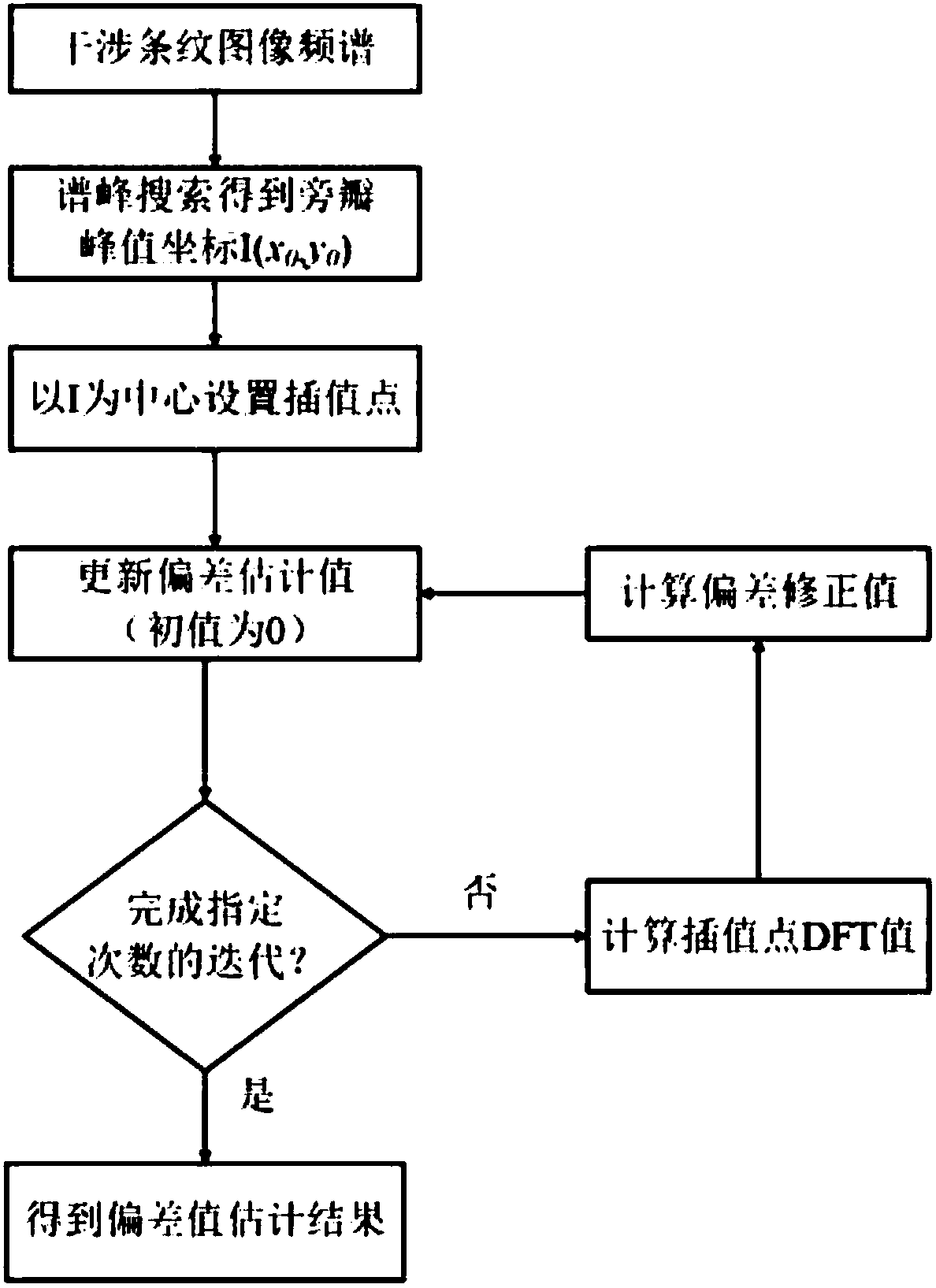
Interferometric method based on spectrum analysis of fringe image
ActiveCN107917676AShort timeImprove developmentUsing optical meansFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
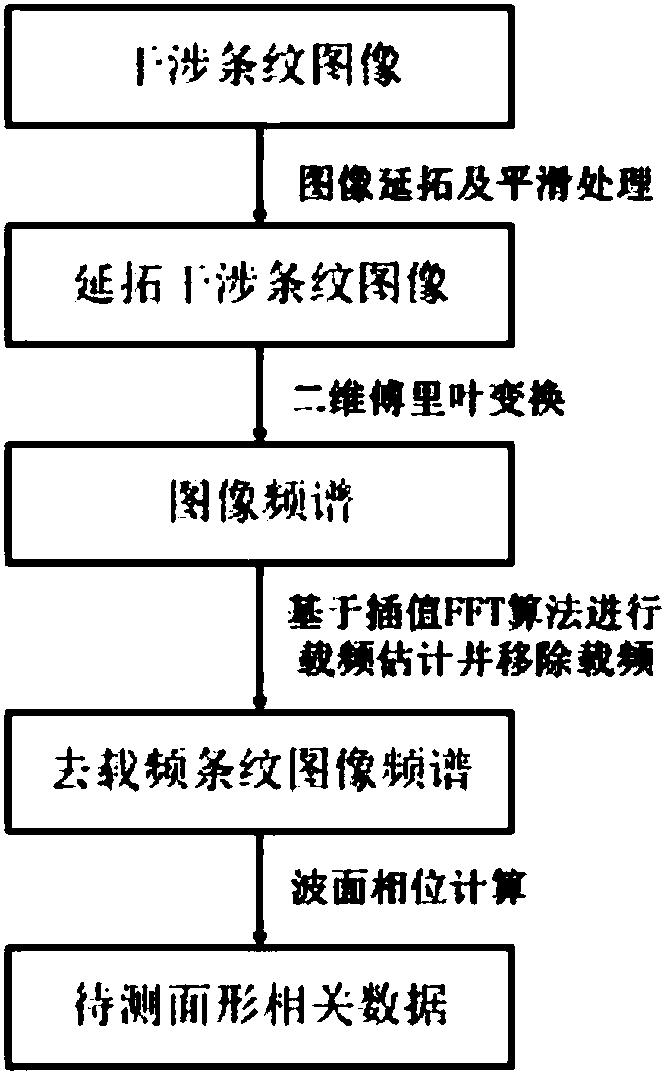
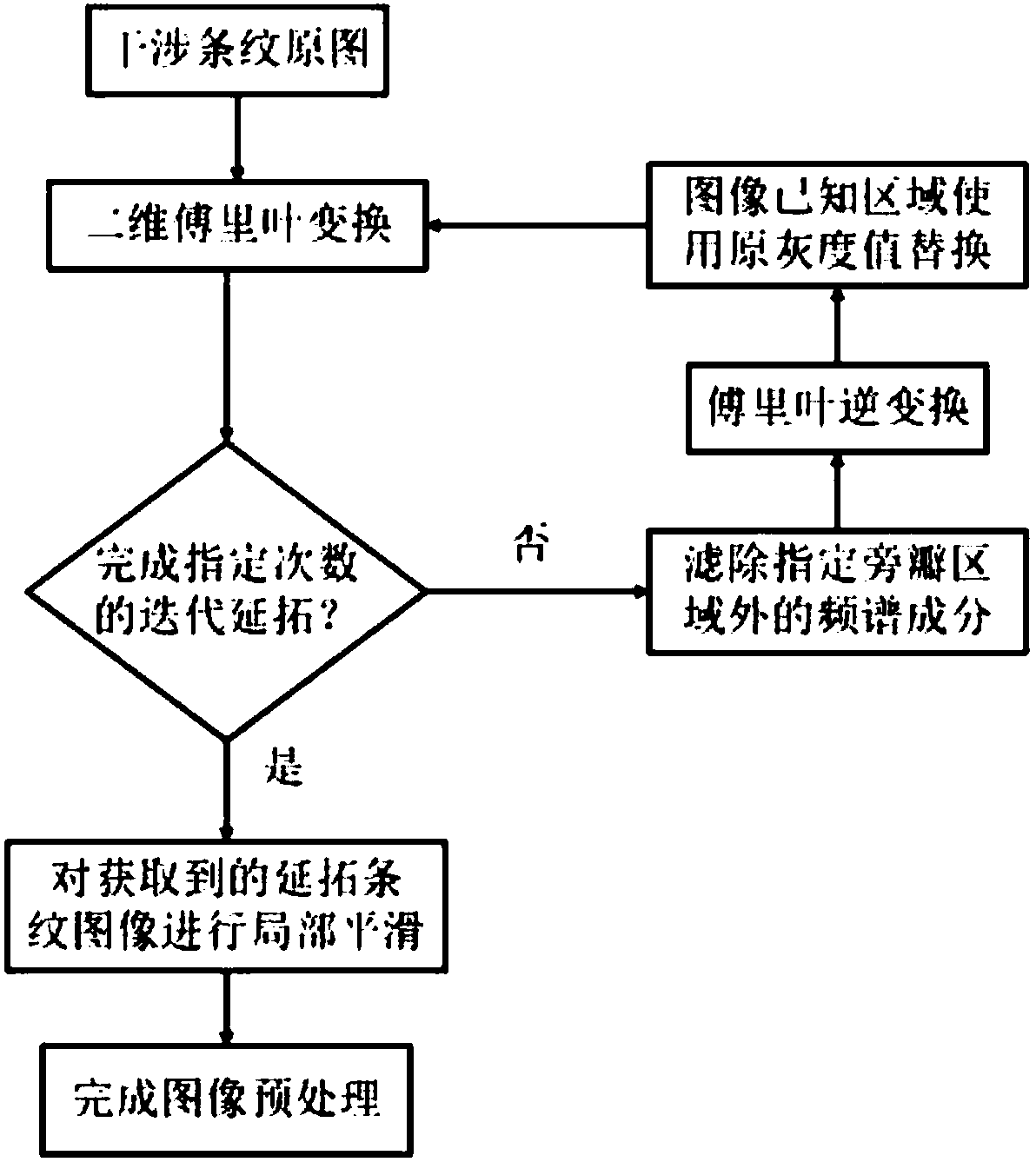
The invention discloses an interferometric method based on spectrum analysis of a fringe image. A single carrier frequency loaded interference fringe image, generated by an interferometer, of a to-be-measured component is obtained; prolongation and edge smoothing are carried out on the fringe image, and FFT (fast Fourier transform) is carried out on the prolonged fringe image to obtain a frequencyspectrum of the image. Aimed at the frequency spectrum, a 2D interpolation FFT algorithm is used to estimate a position of a spectral sidelobe peak value, and the image carrier frequency is removed according to an estimation result. Phase information of a wave surface to be measured is obtained by calculated, and the surface shape of the to-be-measured component is estimated. According to the method of the invention, the fringe image is analyzed and processed on the basis of improved fringe image prolongation and fringe carrier wave estimation methods, and the interferometric precision is higher.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
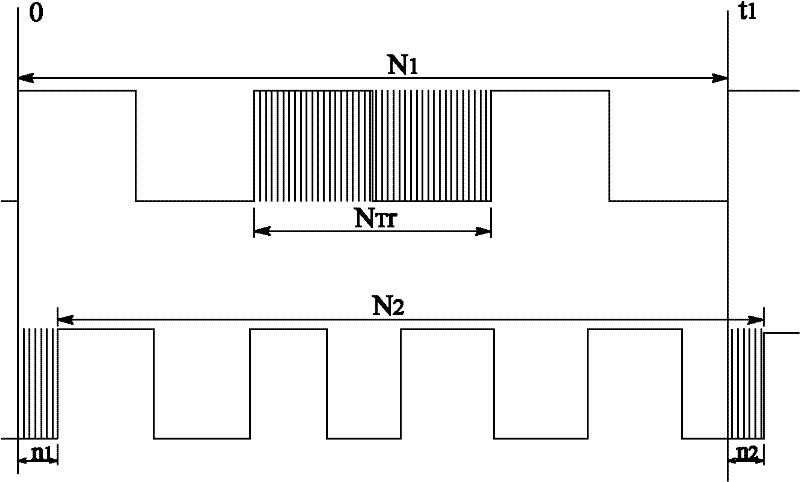
Signal processing method for heterodyne interferometer
InactiveCN102230826AHigh dynamic measurement resolutionOptical measurementsPhase differenceHeterodyne interferometer
The invention discloses a signal processing method for a heterodyne interferometer. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a Span3-series XC3S1500 chip for an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), chopping a reference signal and a measurement signal through a high-frequency small-power Schottky diode respectively to obtain positive half period signals and connecting with a pin of the FPGA; countering two paths of signals respectively at the counting period of 100 mum s and latching every 100 mum s, wherein the phase difference of the entire period is N1-N2; setting a count value of an initial phase difference in a first sampling counting period as n1 and latching by taking a reference signal as a standard, setting a count value of a tail end phase difference as n2, and setting a count value of a non-period phase different as n2-n1; setting a count value of an ith non-period phase difference as ni+1-n1; performing pulse filling counting on one period of the reference signal to obtain a count value NTr of the reference signal in the entire period; setting the phase difference in the sampling period as (N1-N2)+(ni+1-n1) / NTr; and obtaining measured displacement: L=lambda / 2[(N1-N2)+(ni+1-n1) / NTr], wherein lambda is a laser wavelength, (i=1,2,---,n). According to the method, dynamic and real-time measurement of phases can be realized, a high resolution is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for dark field interferometric confocal microscopy
A differential interferometric confocal microscope for measuring an object, the microscope including: a source-side pinhole array; a detector-side pinhole array; and an interferometer that images the array of pinholes of the source-side pinhole array onto a first array of spots located in front of an object plane located near where the object is positioned and onto a second array of spots behind the object plane, wherein the first and second arrays of spots are displaced relative to each other in a direction that is normal to the object plane, the interferometer also (1) imaging the first arrays of spots onto a first image plane that is behind the detector-side pinhole array, (2) imaging the first array of spots onto a plane defined by the detector-side pinhole array, (3) imaging the second array of spots onto a second image plane that is in front of the detector-side pinhole array, and (4) imaging the second array of spots onto the plane defined by the detector-side pinhole array, wherein each spot of the imaged first array of spots in the first image plane is aligned with a corresponding different spot of the imaged second array of spots in the second image plane and a corresponding different pinhole of the detector-side pinhole array, and wherein each spot of the imaged first array of spots in the plane defined by the detector-side array coincides with a corresponding different spot of the imaged second array of spots in the plane defined by the detector-side array and coincides with a corresponding different pinhole of the detector-side pinhole array.
Owner:ZETETIC INST
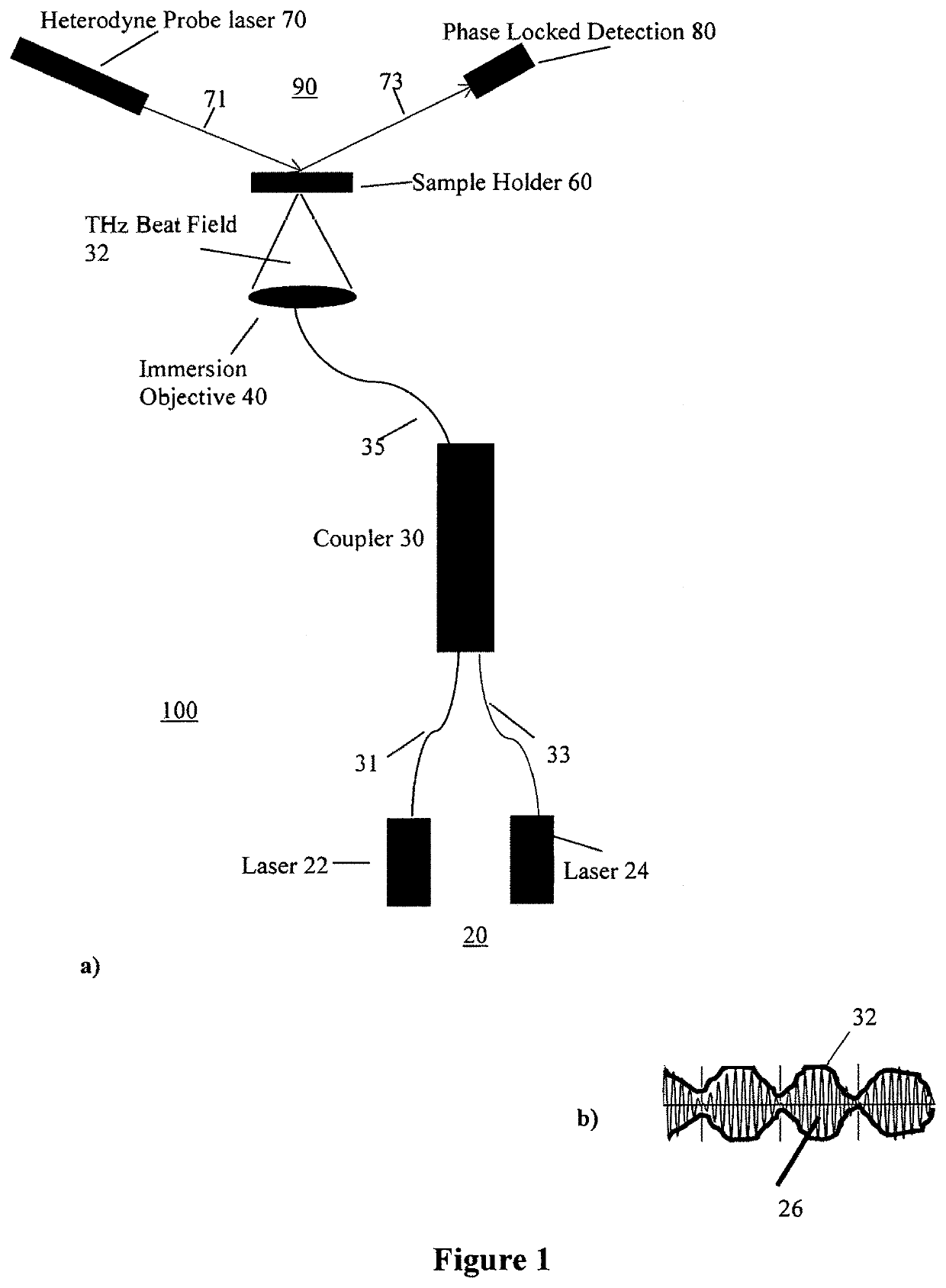
Sensor device and method for label-free detection of double strand nucleotides
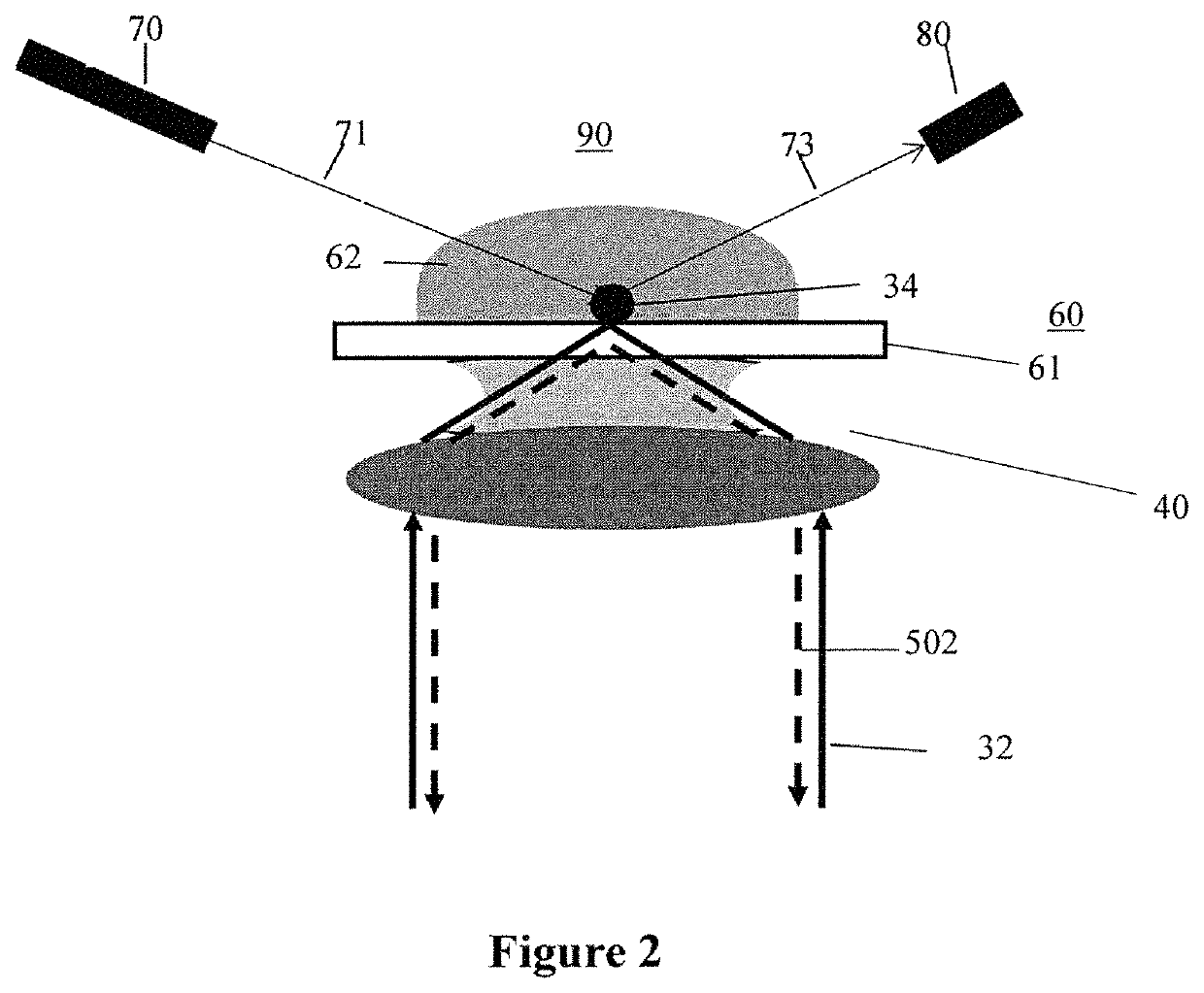
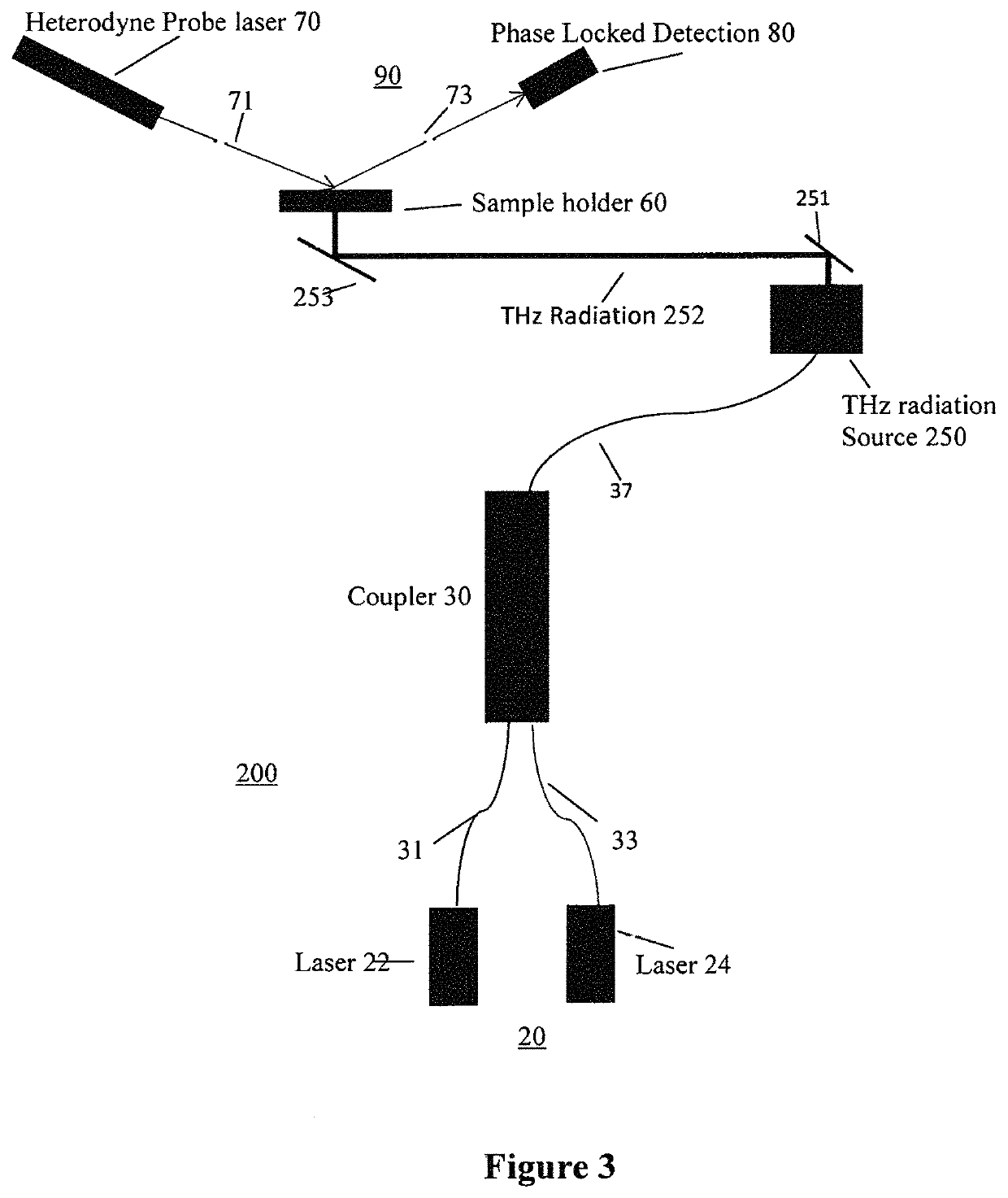
ActiveUS10584372B1Strong specificityIncreased sensitivity & reusabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsHeterodyne interferometerNucleotide
A sensor device which is adapted for detecting target molecules having a target nucleic acid sequence located in nano / micro channels, comprises a THz source for exciting the target molecules and a heterodyne interferometer, having a detection frequency MHz, for probing the excited molecules. The nano-channel array in the sample holder is functionalized with electric field to linearize the target alleles and genes. The linearized molecules are exposed to THz field whereby the different vibrational modes of base pairs are resonantly excited. The excitation of base-breathing mode and base-shifting mode leads to differential induced dipole moments along and perpendicular to the double helix axis. This induced asymmetry in polarizability leads to optical anisotropy. The dipole-dipole interaction between adjacent bases affects polarizability along the helix axis and hence the intrinsic molecular anisotropy is a function of number of base pairs in the strand. The resulting birefringence can be measured using the heterodyne interferometer as a function of changes in the number of base pairs in the strand. Furthermore, a sensing method for detecting birefringence in terms of phase shift of the MHz signal, as a function of target molecule size, is described.
Owner:AIYER ARUN ANANTH
Design method of anisotropic super-hydrophobic surface of common nepenthes-imitating sliding area
ActiveCN111597728AAchieving controllable designAdjustable superhydrophobic effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSuperhydrophobeInterferome
The invention discloses an anisotropic super-hydrophobic surface design method of a common nepenthes-imitated sliding area. A scanning electron microscope and a three-dimensional white light morphology interferometer are used for carrying out micro-morphology observation on the common nepenthes sliding area and obtaining micro-morphology structure characteristic parameters; establishing an anisotropic super-hydrophobic surface bionic model imitating a common nepenthes slippage region according to the extracted micro-topography structure characteristic parameters; based on a Cassie-Baxter model, calculating a numerical relationship between anisotropic super-hydrophobic surface micro-topography structure characteristic parameters of a common nepenthes-imitating sliding region and a super-hydrophobic function; according to the derived numerical relationship, the super-hydrophobic effect of the anisotropic super-hydrophobic surface imitating the common nepenthes slippage region is regulated and controlled by regulating and controlling the characteristic parameters of the micro-morphology structure. According to the design method, controllable design of the super-hydrophobic effect canbe achieved, the super-hydrophobic effect of the designed super-hydrophobic surface can be regulated and controlled, and the design method further has the characteristics of anisotropy of the super-hydrophobic effect and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
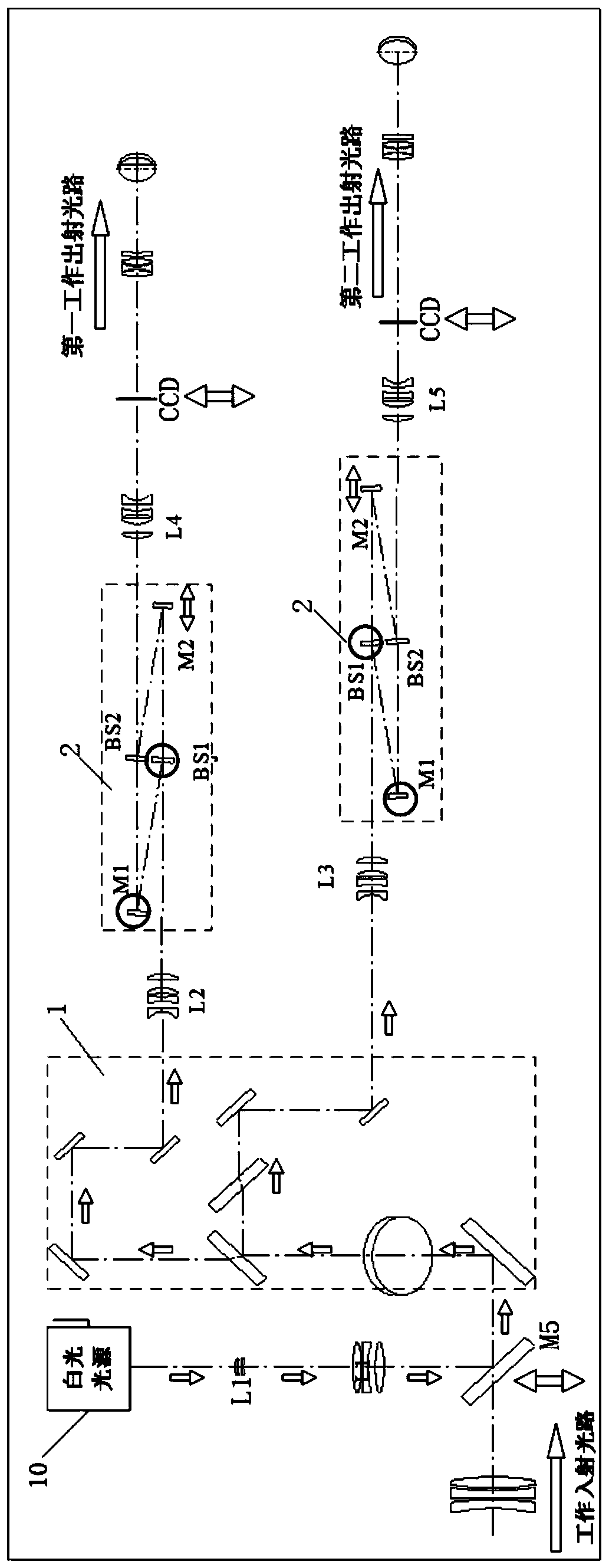
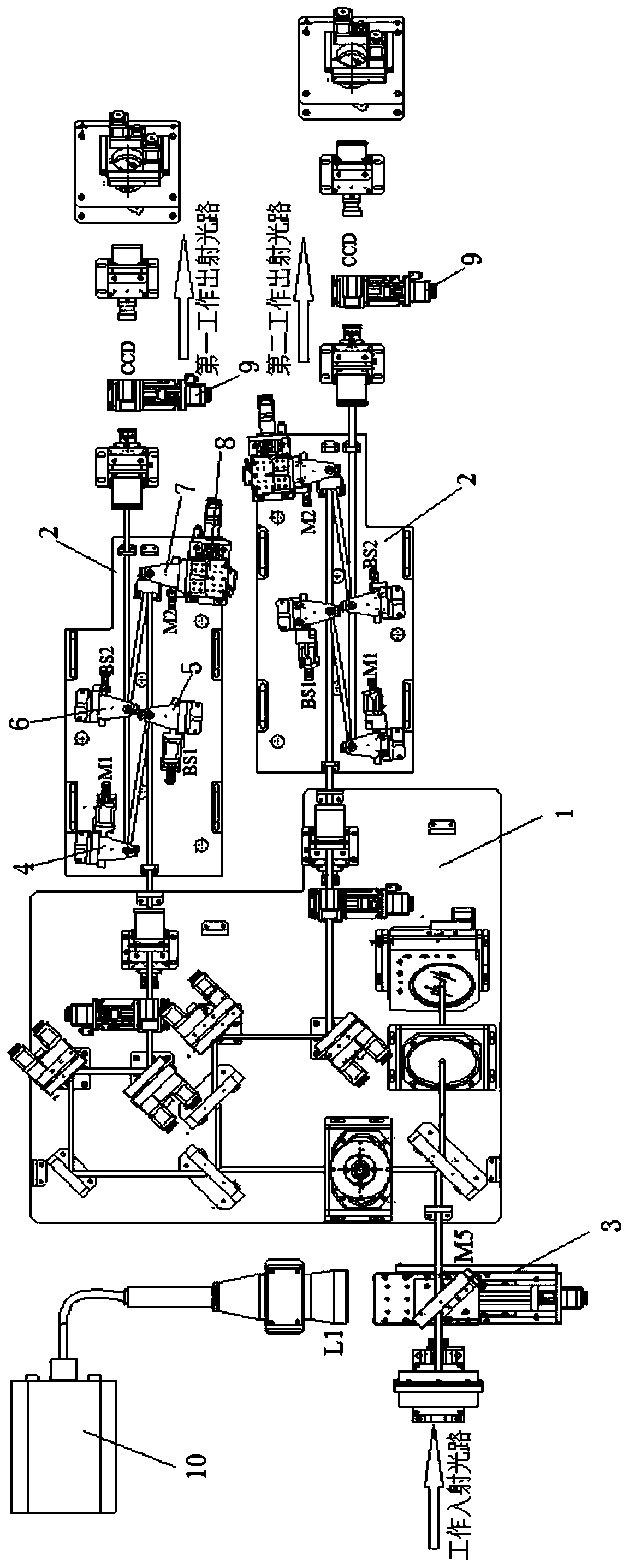
Low coherence interferometric system for phase stepping shearography combined with 3D profilometry
Owner:COCKERILL MAINTENANCE & INGIE +1
Interferometric apparatus for producing an output signal characteristic of phase and/or amplitude noise of a device
ActiveUS7505141B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement deviceAudio power amplifier
An interferometric apparatus (10) for producing an output signal characteristic of phase and / or amplitude noise of a device under test (22), an input signal being provided to the interferometric apparatus (10), comprising a signal generation means (36,38) arranged to produce a third signal having a carrier frequency offset from that of the input signal; a first bridge (12) having first (14) and second (16) arms, the first (14) and second (16) arms having input thereto first and second signals, respectively, produced from one of the input signal or the third signal; the device under test (22) being provided in one of the first (14) or second (16) arms of the first bridge (12); a carrier suppression means (24) connected to the first (14) and second (16) arms of the first bridge (12) to produce a carrier suppressed signal; a first amplifier (32) arranged to amplify the carrier suppressed signal; first mixing means (34) responsive to the third signal and to the carrier suppressed signal to produce a signal characteristic of phase and / or amplitude noise of the device under test (22) at an offset frequency.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
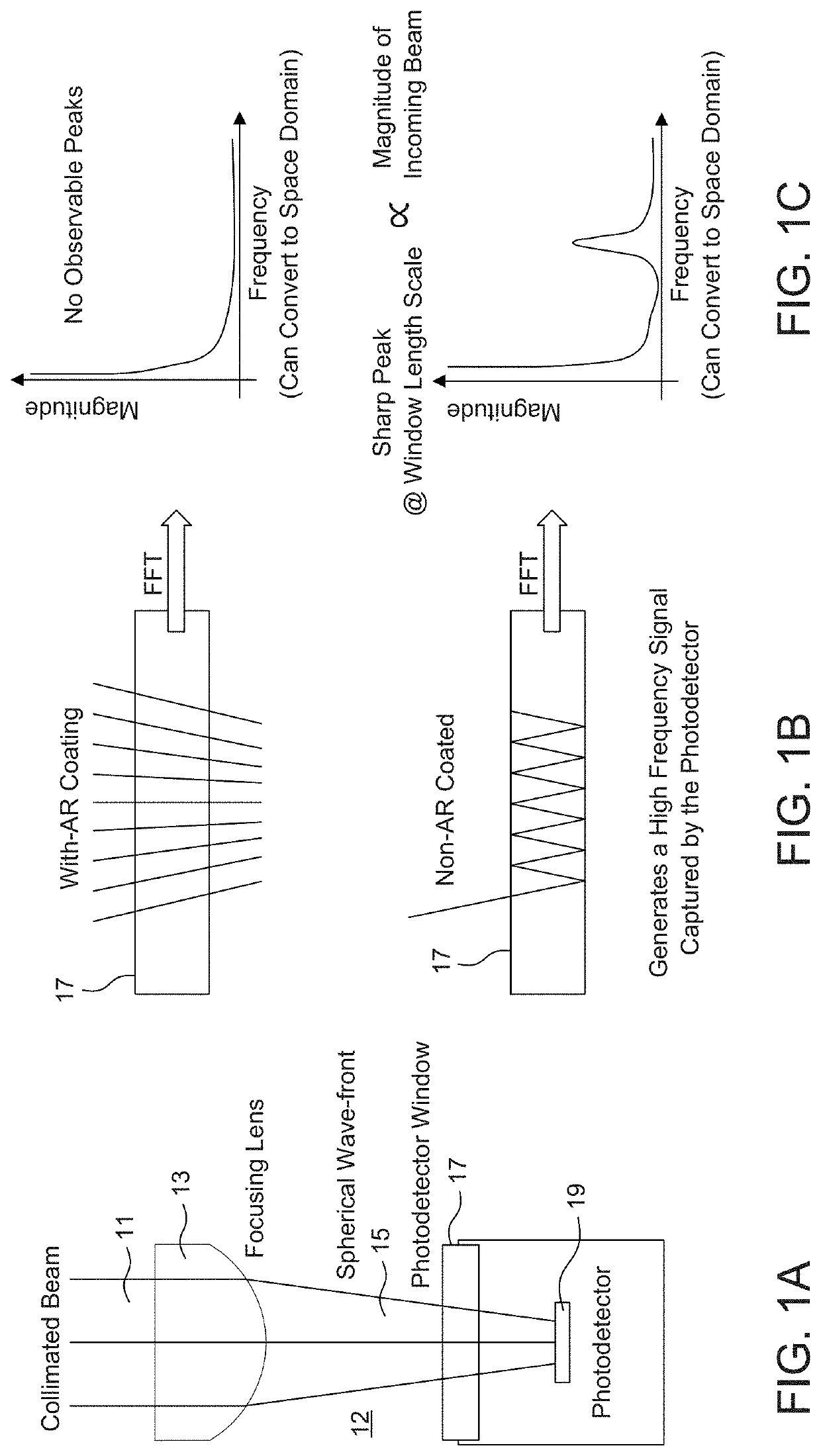
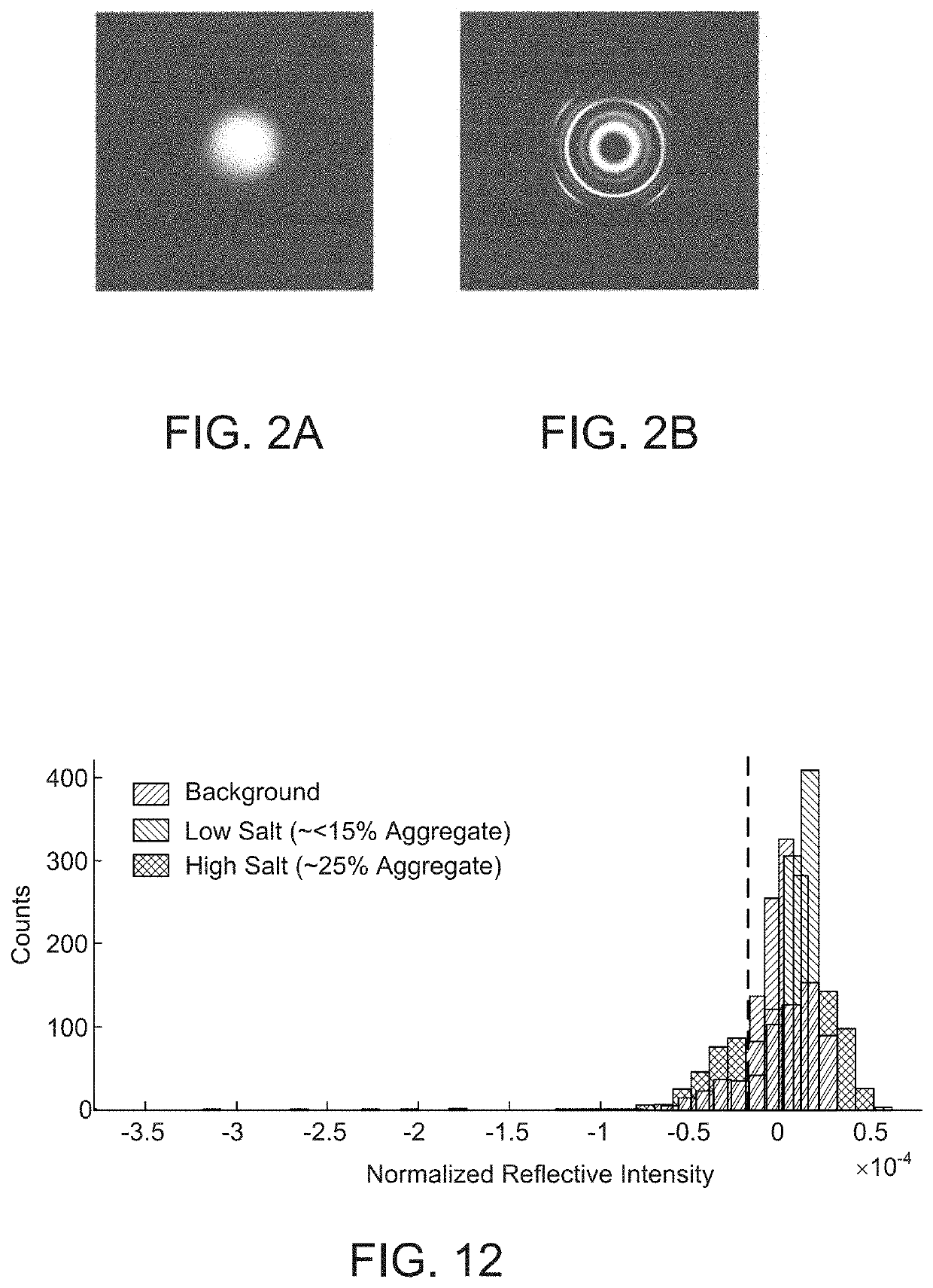
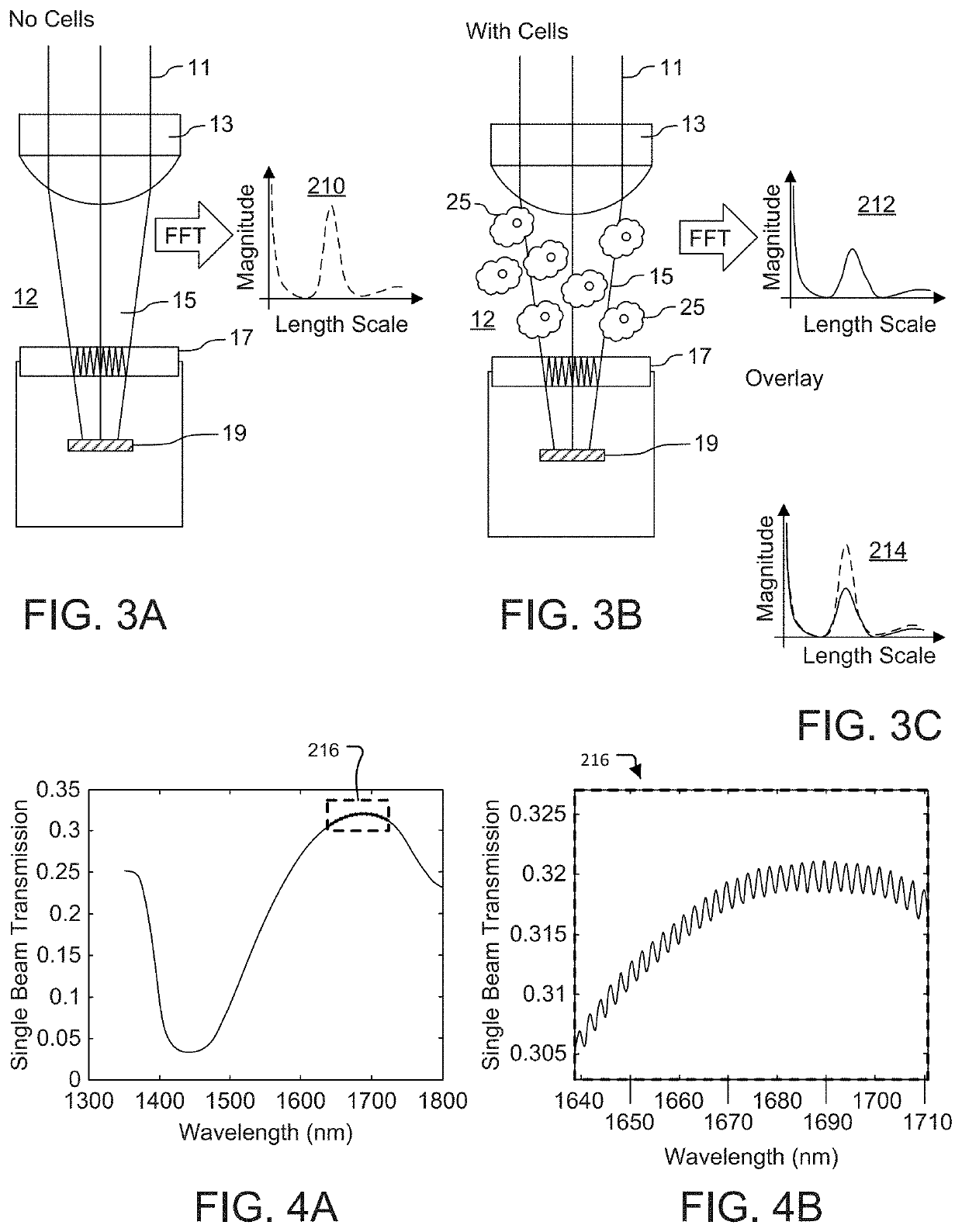
Fabry Perot Interferometry for Measuring Cell Viability
PendingUS20210140881A1Accurate measurementPromote cell growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell AggregationsProtein aggregation
A method for studying cell viability and protein aggregation involves establishing a Fabry Perot etalon signal within an optical spectroscopic feature, e.g., in the near infrared region. Protein aggregation and cell viability can be reflected by changes observed in the magnitude of the Fourier Transform peaks observed in the frequency or space domain associated with the contrast of the etalon. In short, the presence of viable cells and protein aggregates can degrade the etalon contrast of an etalon window. In some cases, the concentration of cells and monomeric protein can be measured as well.
Owner:NIRRIN BIOPROCESS ANALYTICS INC
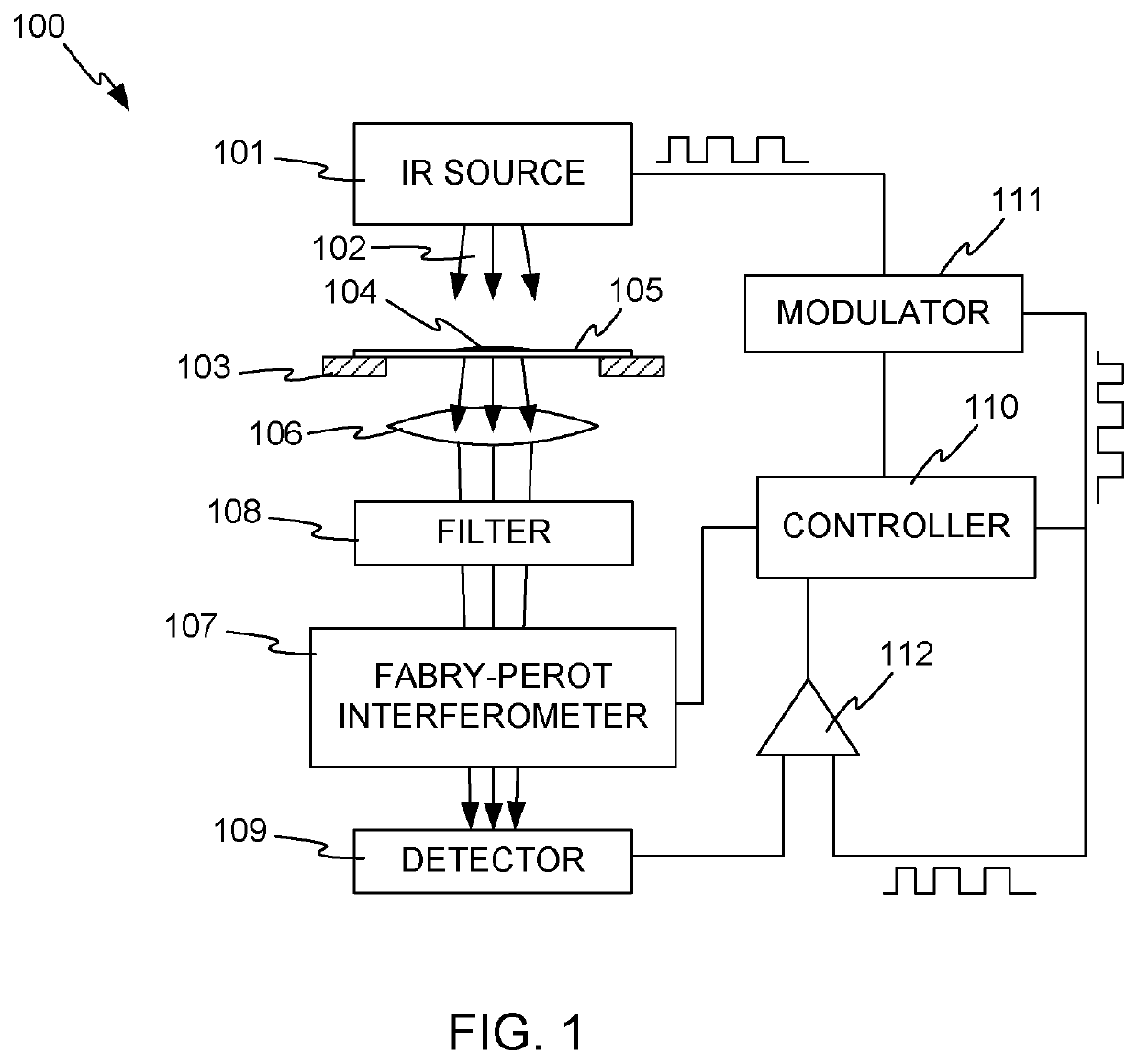
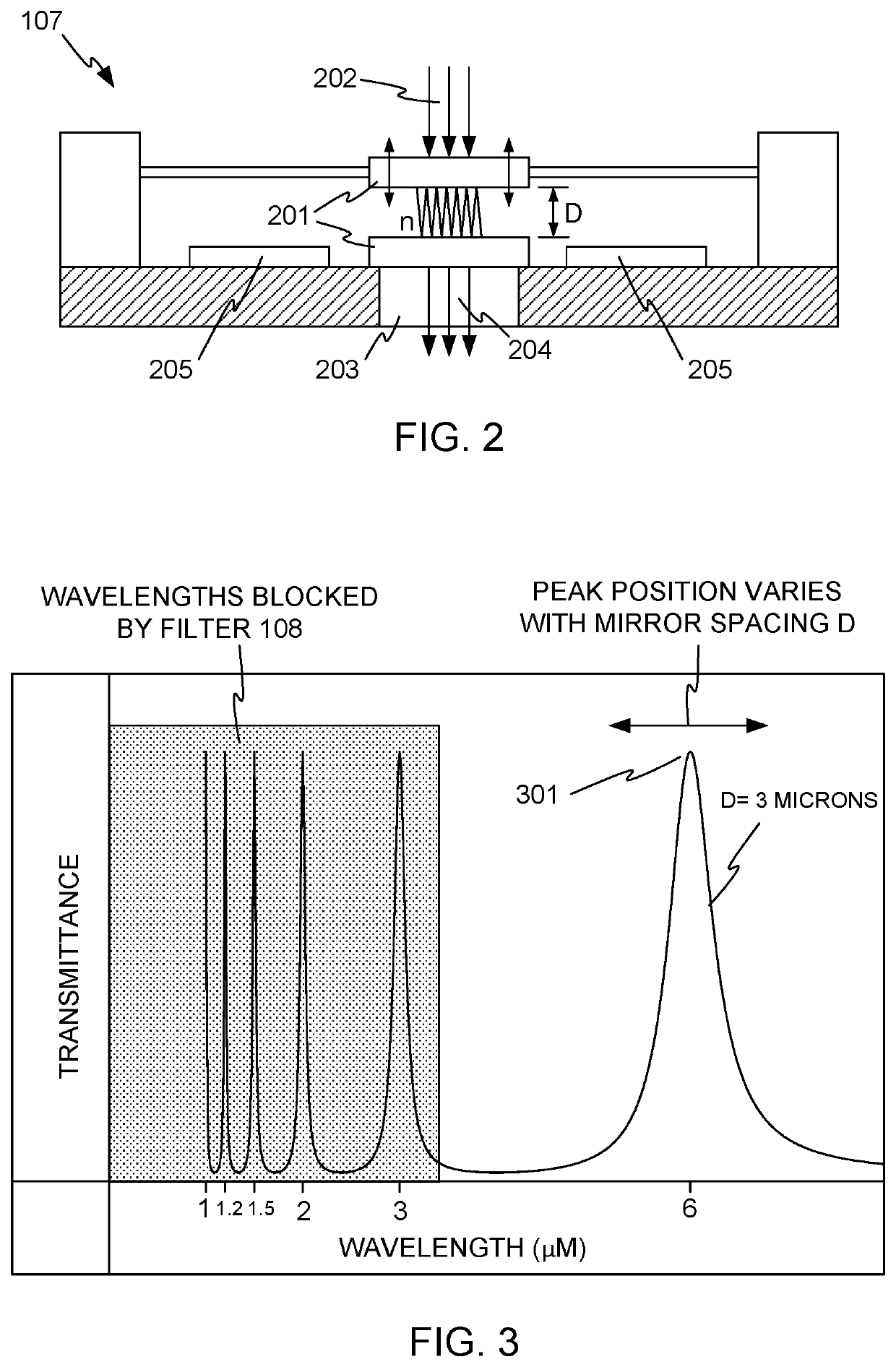
Protein quantitation device
ActiveUS10948403B2Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionResonance wavelengthInterferome
Systems for protein quantitation using a Fabry-Perot interferometer. In one arrangement, a quantitation device includes an infrared source, a sample holder, and a Fabry-Perot interferometer positioned to receive infrared radiation from the source passing through a sample on the sample holder. A band pass optical filter sets the working range of the interferometer, and radiation exiting the interferometer falls on a detector that produces a signal indicating the intensity of the received radiation. A controller causes the interferometer to be tuned to a number of different resonance wavelengths and receives the intensity signals, for determination of an absorbance spectrum.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
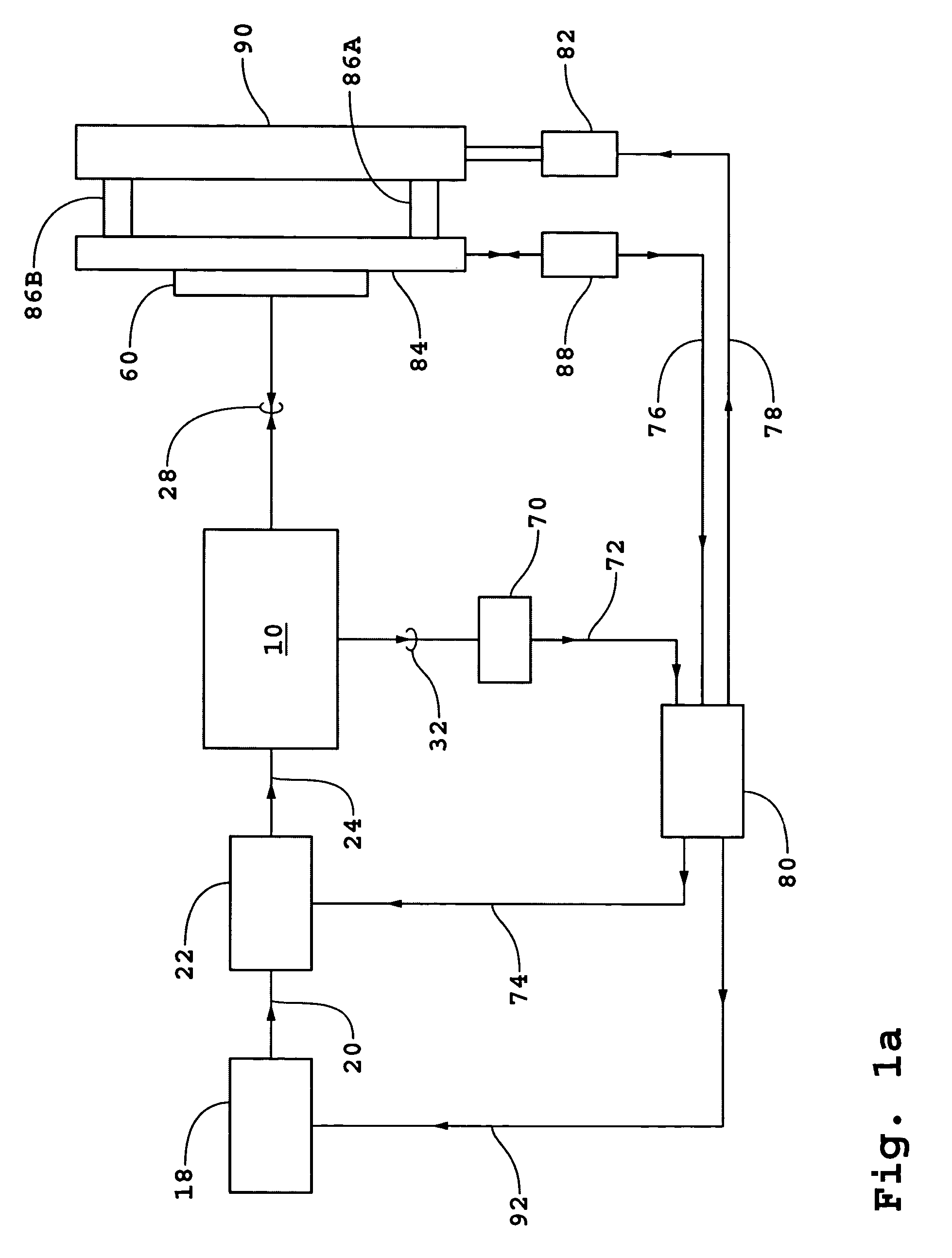
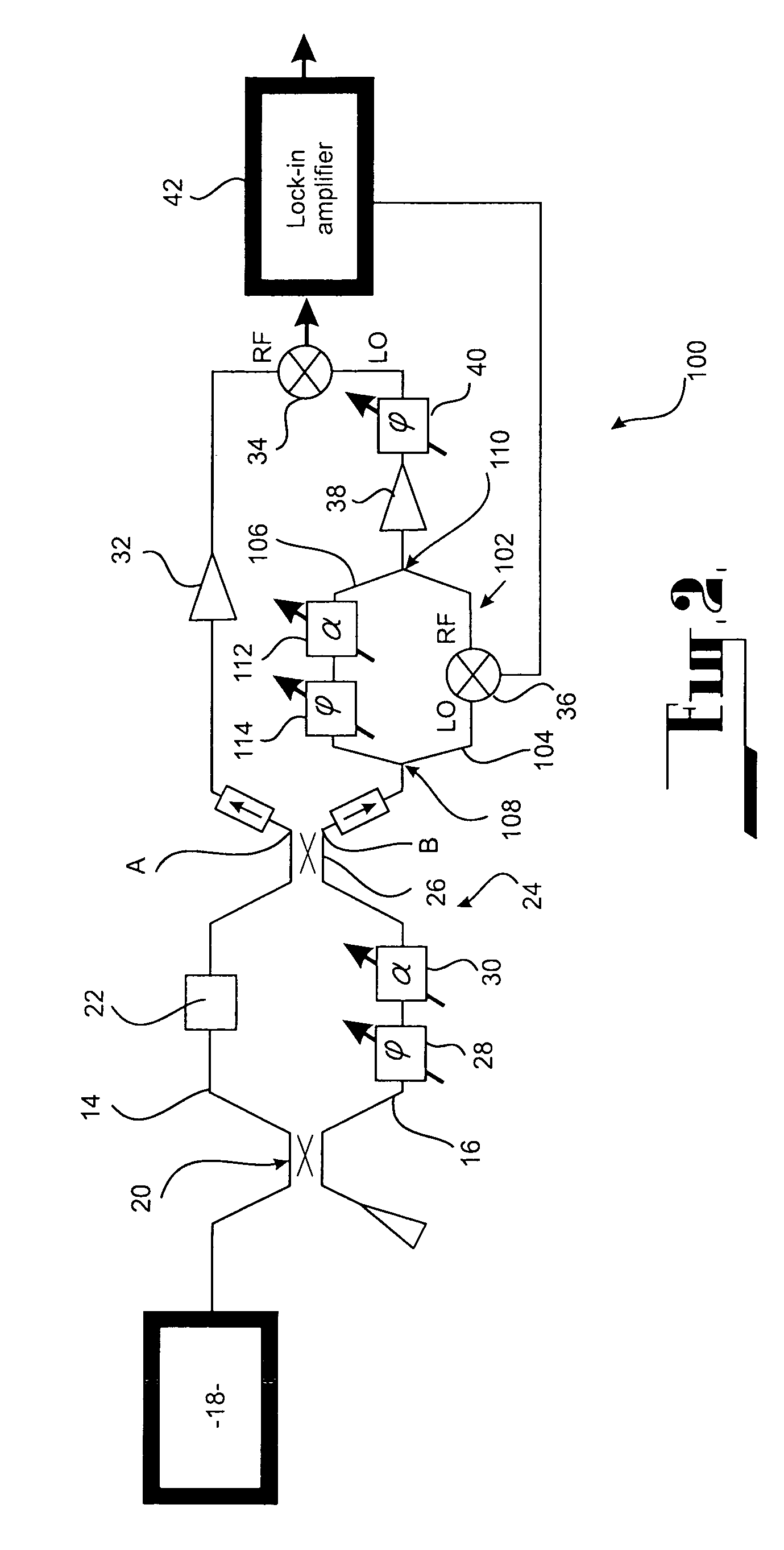
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light.These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imagingorigins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in theirnative state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference withinthe cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bilateral Fizeau interferometer detection device
ActiveCN113203357ARealize splittingEliminate the effects ofUsing optical meansOptical axisFizeau interferometer
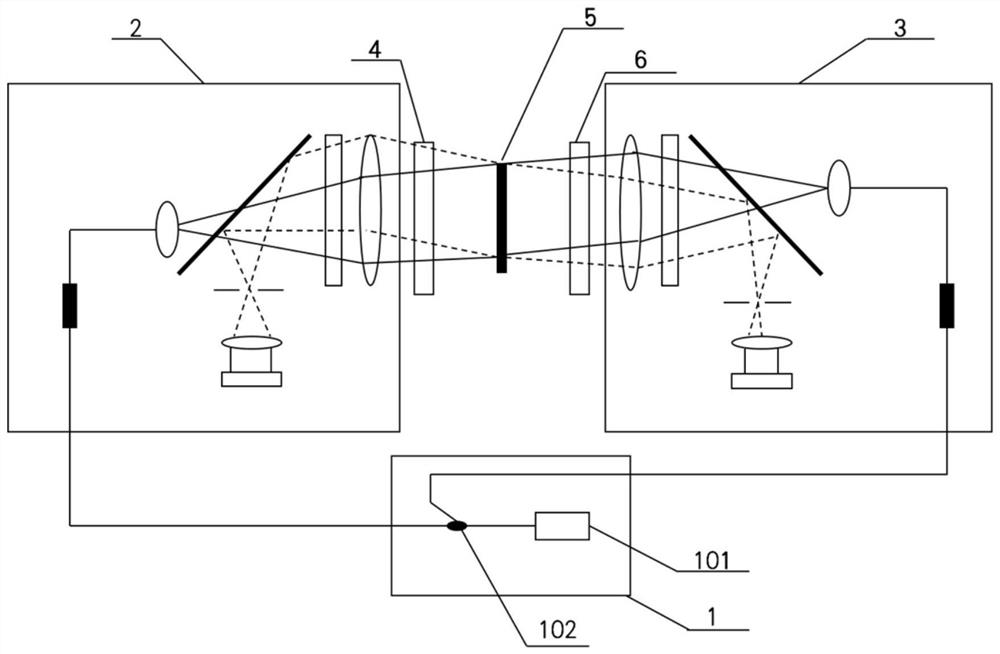
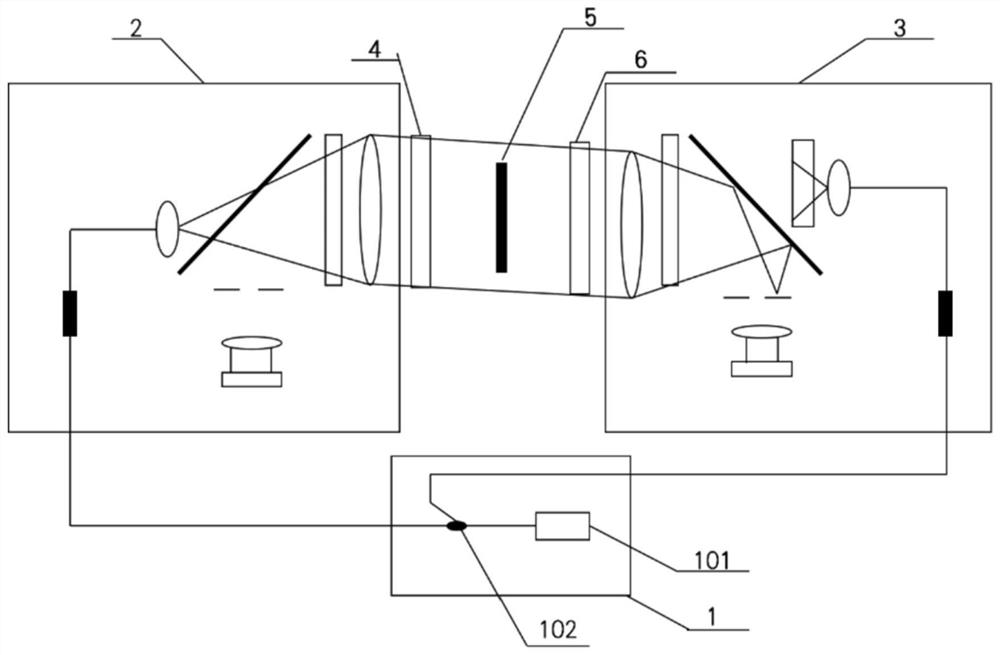
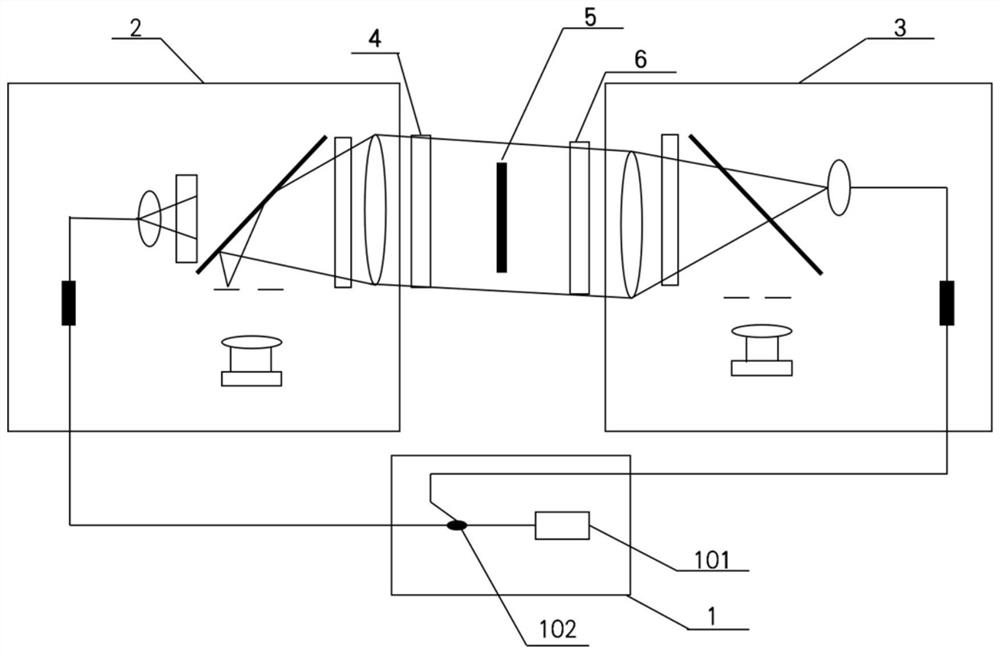
A bilateral Fizeau interferometer detection device comprises a light source module, a first interferometer host, a second interferometer host, a first standard lens, a second standard lens and a detected non-transparent plane. The first interferometer host and the second interferometer host are both Fizeau interferometers. The point light source is located on the focal plane of the collimating mirror but not on the focal point, so that an included angle is formed between the emergent light transmitted by the collimating mirror and the optical axis of the interferometer, and through cooperation with the diaphragm, the emergent light of the interferometer at the opposite side enters the interferometer at the local side and then converges at the shading area of the diaphragm, and the receiving of an interferogram of the interferometer at the local side is not influenced; or the optical switch is used for enabling the first interferometer host and the second interferometer host to work independently. The device effectively improves the quality of an interference pattern, and has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in operation and high measurement precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Interferometer and method for producing an interferometer
PendingCN112313488ARadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionInterferomeElectrode pair
The invention relates to an interferometer (100) consisting of a holding element (106) having an actuation recess (108), a first mirror element (102), which is or can be arranged on the holding element (106) opposite the actuation recess (108), and a second mirror element (104), which is or can be arranged opposite the first mirror element (102) at a mirror distance, to form an optical slit (112),wherein the first mirror element (102) is or can be arranged between the second mirror element (104) and the holding element (106) and the optical slit (112) is spatially separated from the actuationrecess (108) by the first mirror element (102). The interferometer (100) further comprises an electrode pair of a first actuation electrode (114), which is defined, arranged and / or can be arranged onor in one of the mirror elements (102) or (104), and of a second actuation electrode (116), which is defined, arranged and / or can be arranged on a side of the actuation recess (108) opposite the first actuation electrode (114). The mirror distance can be varied by applying an electrical voltage to the electrode pair.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
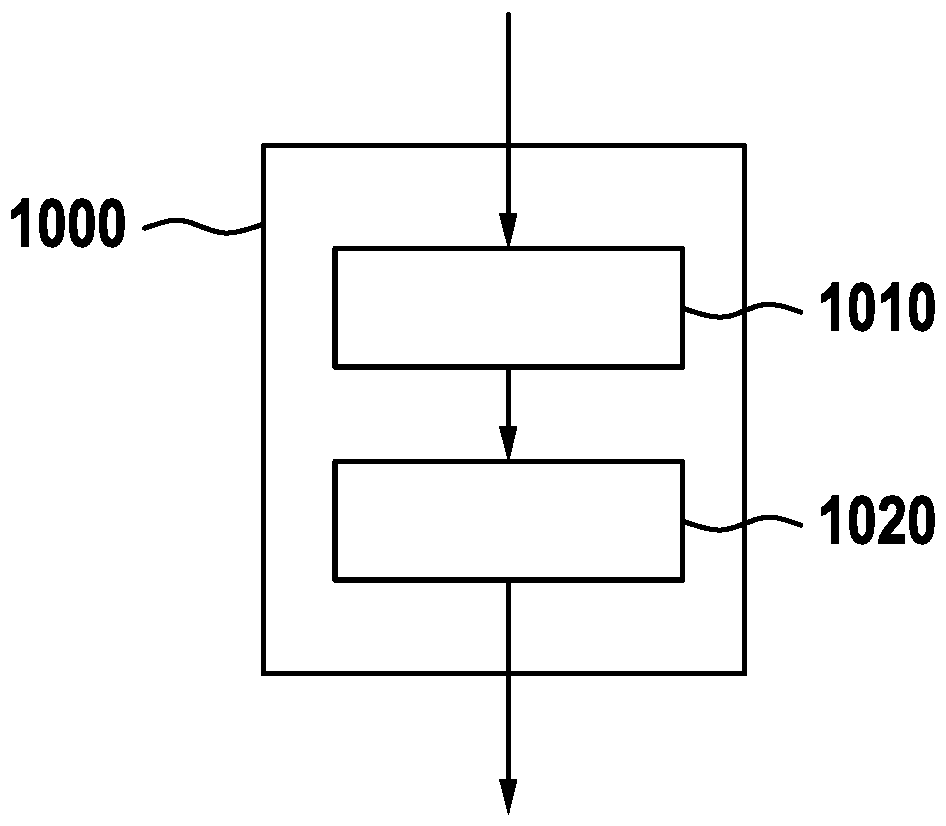
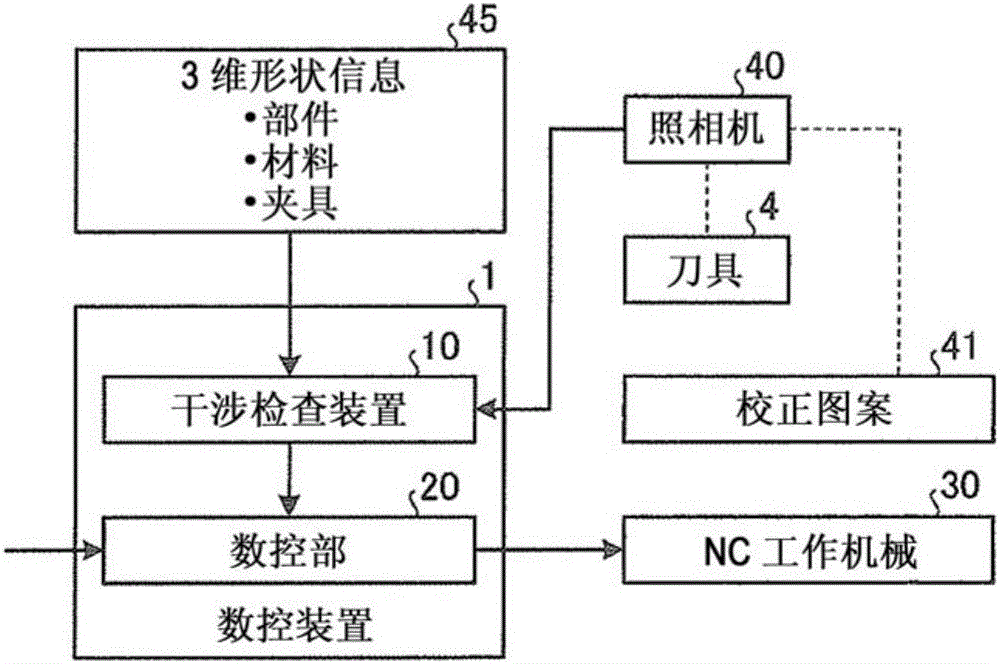
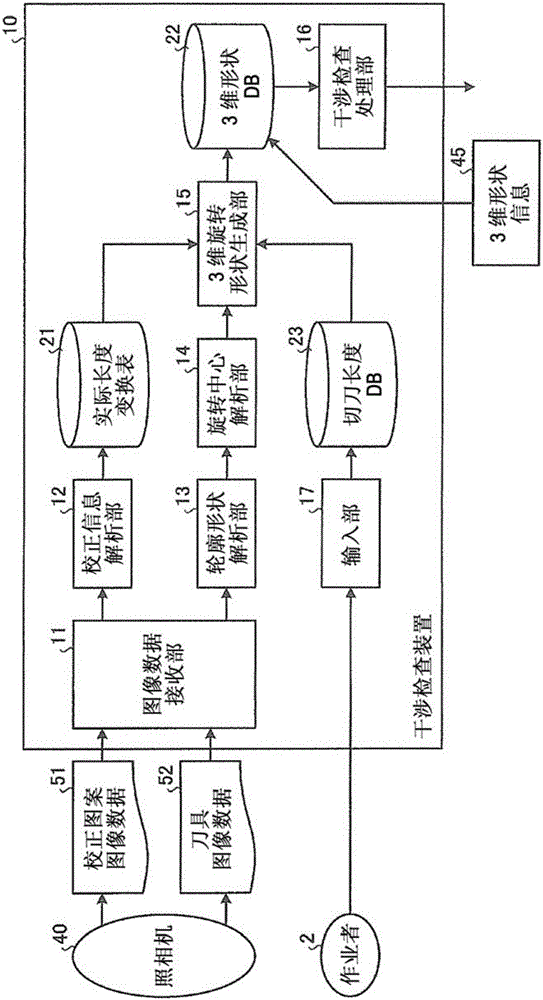
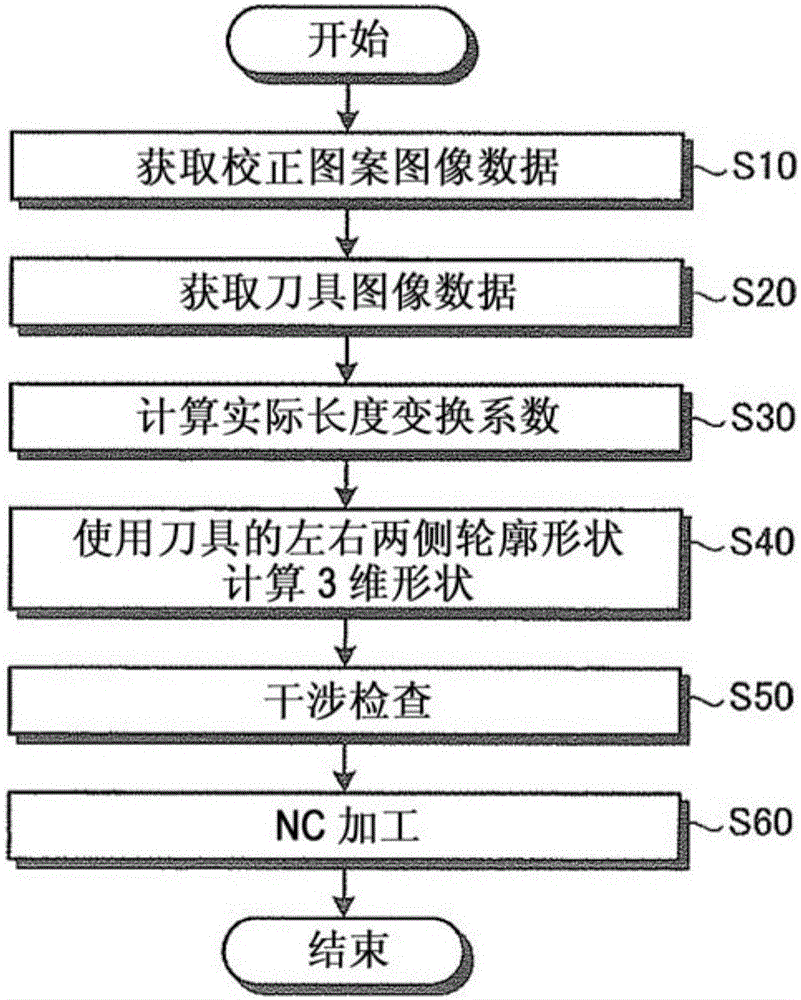
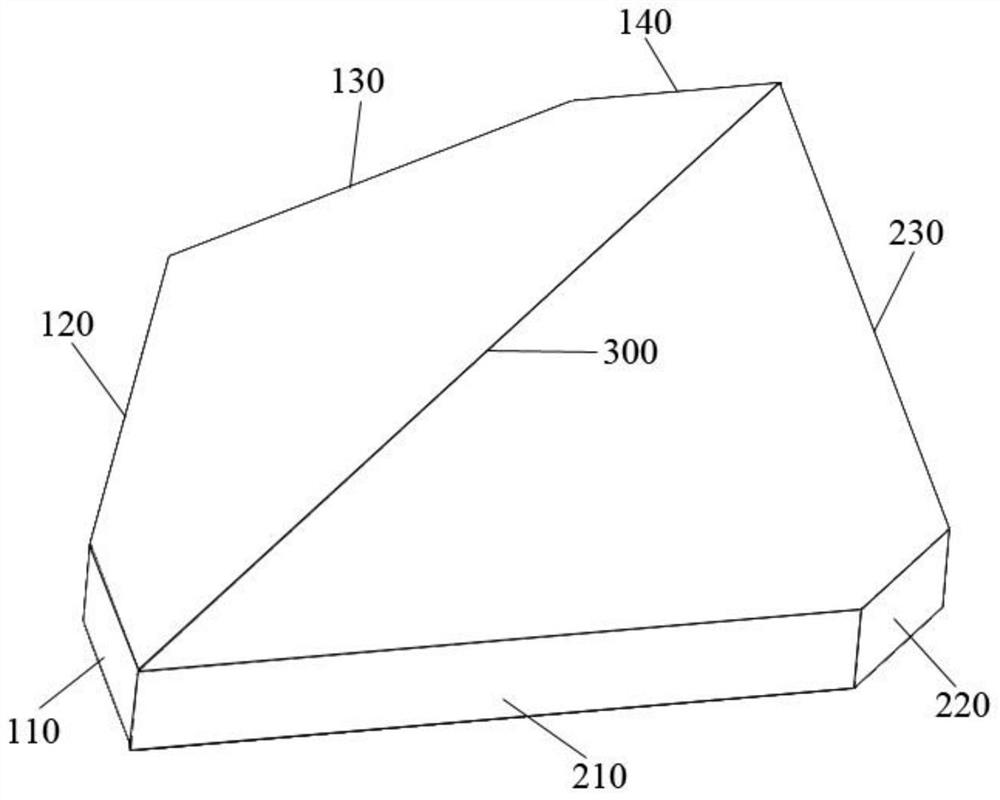
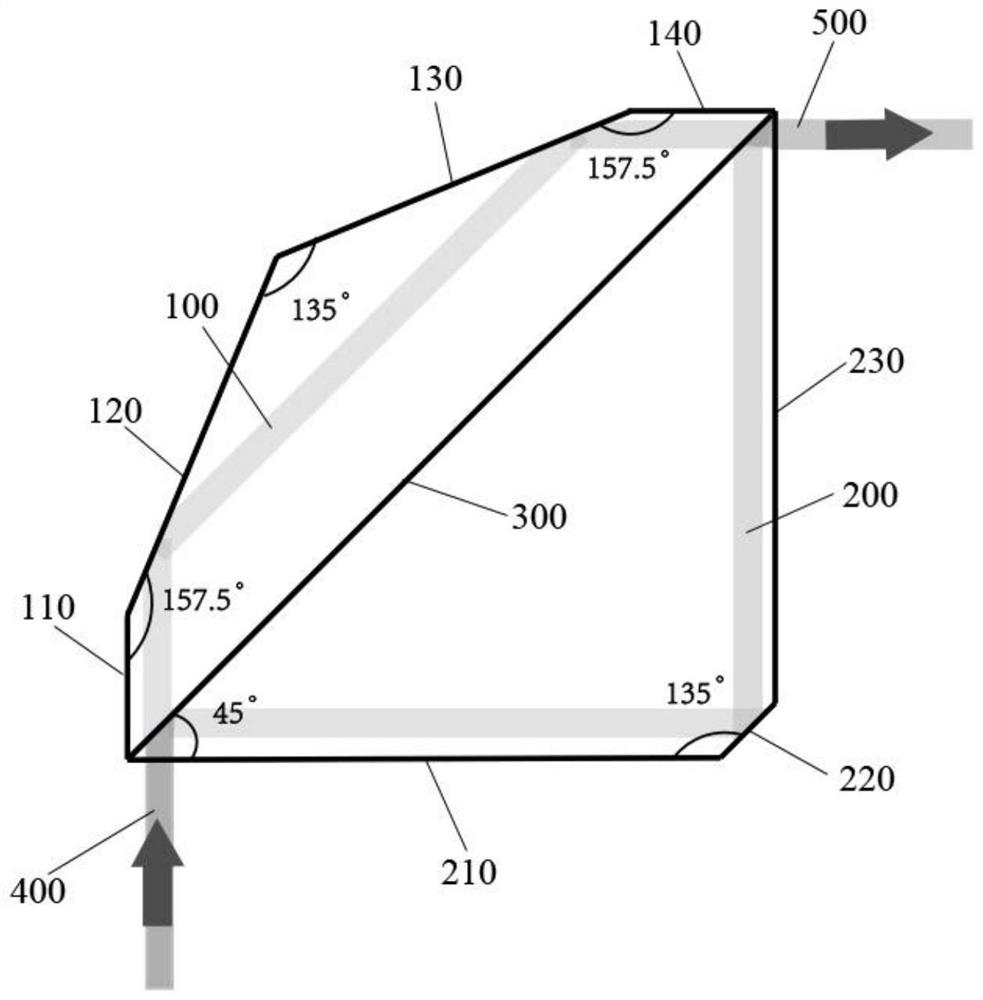
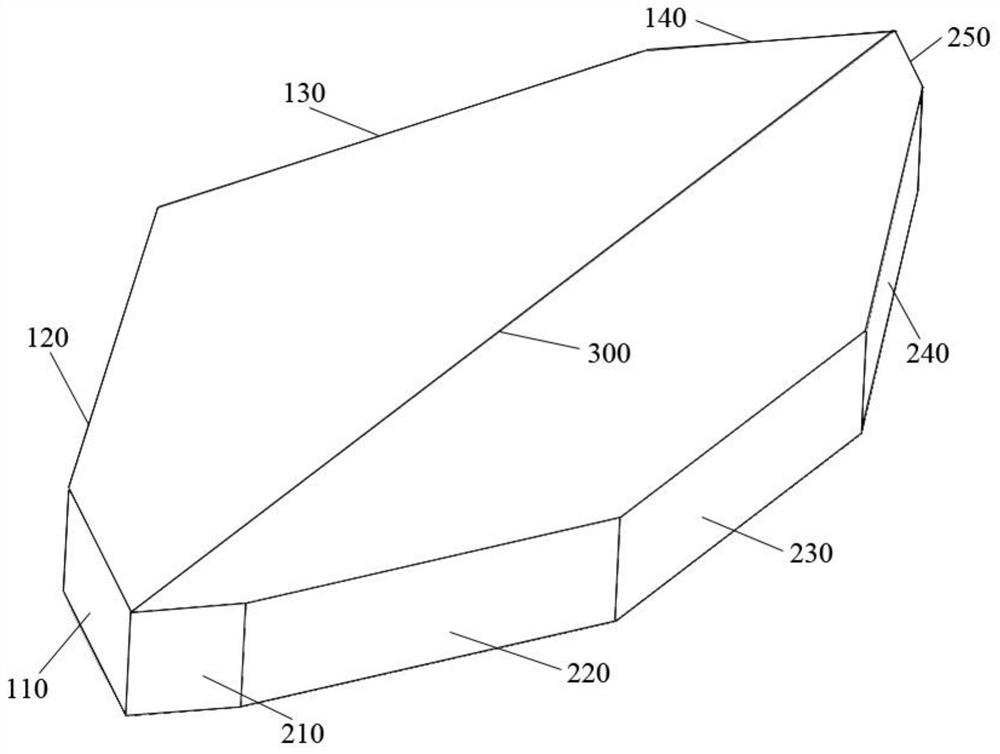
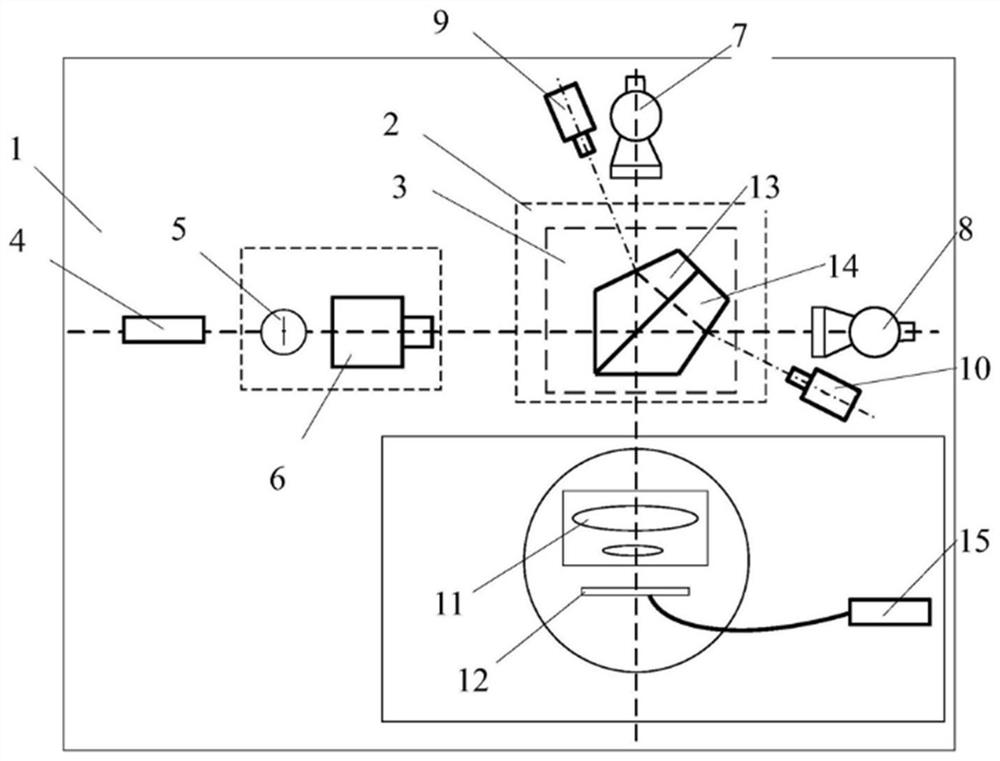
Interference check device and numerical control device
Equipped with: a contour shape analysis unit (13) that analyzes the 2D image of the rotary tool to extract the contour shape and tool length of the tool cross section; a rotation center analysis unit (14) that analyzes the contour shape to obtain the rotary tool the center of rotation; the 3D rotation shape generating part (15), which generates the 3D shape of the rotating tool based on the contour shape, the tool length and the rotation center; and the interference check processing part (16), which uses the 3D shape check in use When the rotary tool performs NC machining on the workpiece, whether the rotary tool interferes with parts other than the rotary tool, the 3D rotary shape generating unit (15) generates the profile of the rotary tool using the left profile shape and the right profile shape The 3-dimensional shape, wherein the left contour shape is the contour shape to the left of the rotation center among the contour shapes, and the right contour shape is the contour shape to the right of the rotation center among the contour shapes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Unit element beam splitting and combining interferometer
The invention relates to a unit element beam splitting and combining interferometer which comprises an element, a light beam enters the element and then is split into two beams of light, namely a first beam of light and a second beam of light, the first beam of light and the second beam of light are respectively reflected for even times and odd times in the element, and the two beams of light arecombined again in the element after being reflected and finally emitted from the element. The problems that an existing interferometer is composed of multiple elements, quite complex, insufficient instability and the like are solved, beam splitting and beam combining can be achieved in the element at the same time through different reflection times and parity, and the interferometer has the advantages of being compact, stable, high in integration degree, high in efficiency, resistant to high power and the like. The interferometer can replace a traditional interferometer composed of multiple elements in many application scenes, for example, but not limited to vector light field generation, vortex beam topological charge measurement, quantum optical logic gates and the like, and has wide potential application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
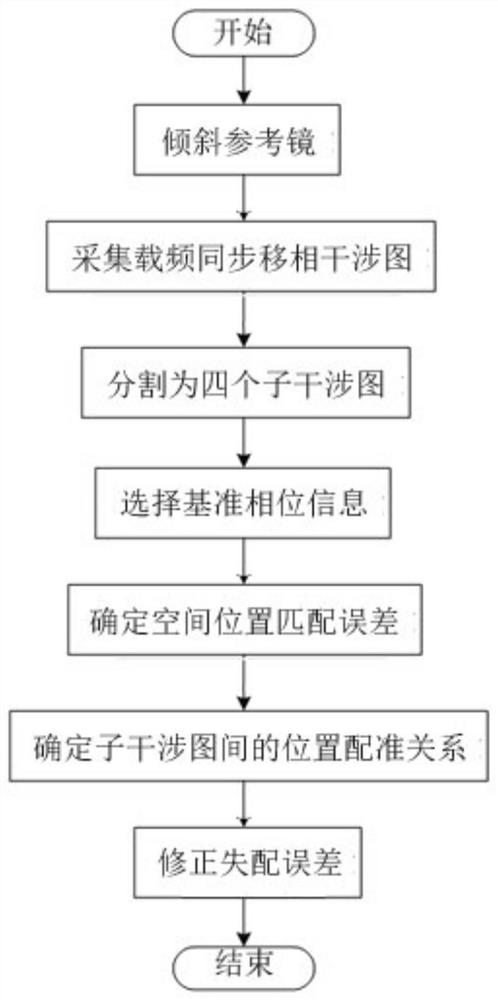
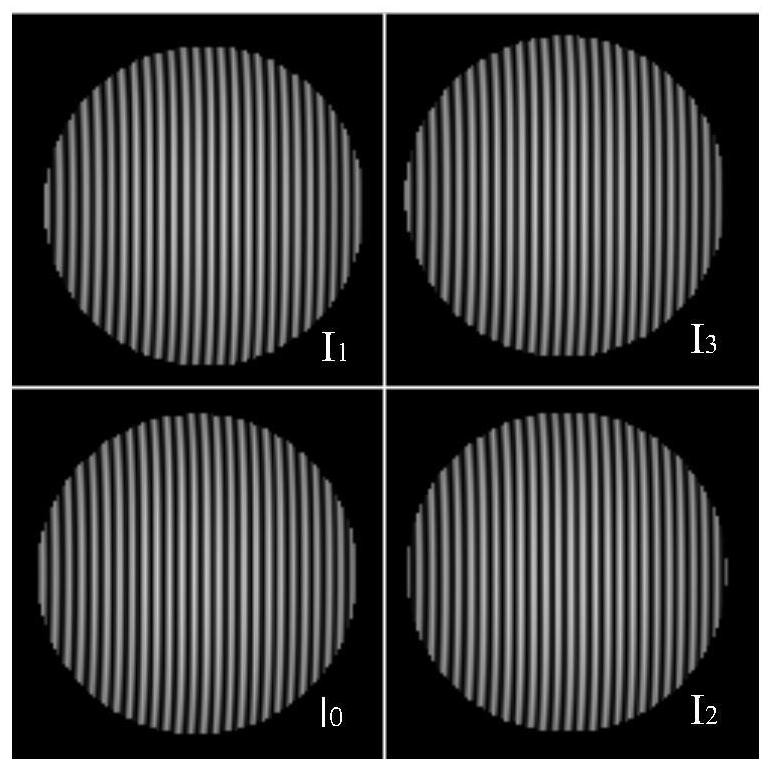
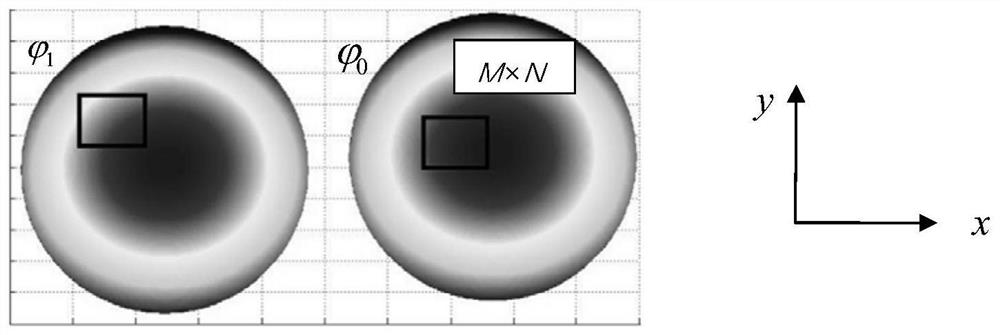
A Method for Spatial Position Registration of Synchronous Phase-shifting Interferogram of Dynamic Interferometer
ActiveCN109632112BHigh degree of automationReduce manual operationsOptical measurementsPhase correlationInterferome
The invention discloses a space location registration method of a synchronous phase-shifted interferogram of a dynamic interferometer. The method comprises the following steps: firstly inclining a reference mirror in the dynamic interferometer, importing linear carrier frequency in the synchronous phase-shifted interferogram, collecting the carrier frequency synchronous phase-shifted interferogram, and dividing the carrier frequency synchronous phase-shifted interferogram into four sub-interferograms; solving phase information of each sub-interferogram by using Fourier filter method, and performing inclination elimination on the phase information to obtain to-be-measured phase information contained in each; and then selecting the phase information contained in one interferogram as standardphase information, determining a space location matching error of the phase information contained in other interferograms and the standard phase information by adopting a quick phase correlation registration method; and finally determining a location registration relation among the sub-interferograms according to the space location matching error of the phase information. The automation degree ofthe space location registration of the dynamic interferometer is improved, the accuracy and the reliability of the space location registration are improved, the method is simple and efficient and theapplicable range is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Interferometer zero path difference online debugging mechanism for VISAR system
PendingCN111521844ARealize online debuggingAvoid uncertaintyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTesting optical propertiesComputational physicsInterferome
The invention discloses an interferometer zero path difference online debugging mechanism for a VISAR system. The objective of the invention is to solve the technical problems of great increase of theoperation complexity of an experimenter, reduction of the experiment efficiency and uncertainty of an experiment result due to judgment of whether an interferometer is in a zero path difference stateor not and a reset process after offline calibration in the prior art. A light source unit, a reflection unit, an adjustment unit and a feedback unit are integrated in the VISAR system; the online debugging of the zero path difference state of the interferometer is realized; the interferometer does not need to be moved out for off-line debugging, the automation level is high, the experiment operation is simplified, and the experiment efficiency is improved; and the zero path difference state of the interferometer can be detected on line, so that the uncertainty of an experimental result is avoided.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
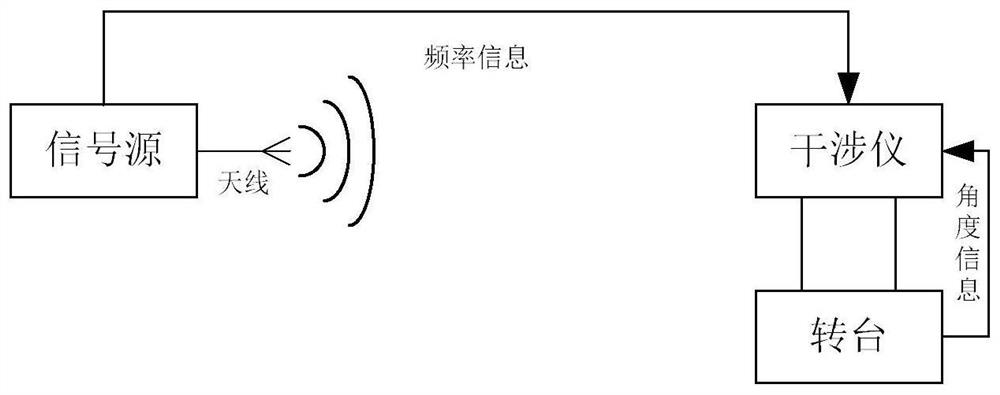
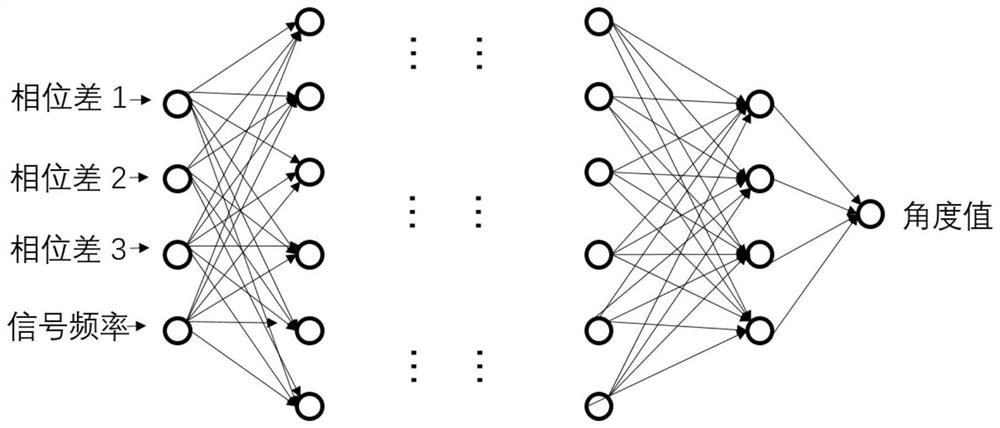
Interferometer angle calculation method based on neural network
ActiveCN111983555ADoes not affect real-time performanceEliminates initial phase correction workNeural architecturesDirection findersAlgorithmInterferome
The invention relates to an interferometer angle calculation method based on a neural network algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: fitting an interferometer angle measurement equation curvethrough a multilayer neural network, and calculating the arrival angle of an incoming wave signal according to the input frequency and phase information. The method can achieve the independent training of a single interferometer, saves the correction process of the interferometer, and can improve the angle measurement precision. The method has the characteristic of being insensitive to the interferometer arraying mode, and can adapt to various different interferometer arraying modes through the same training mode. Meanwhile, the method is not sensitive to the angle range of the incoming wave signal, and can be used for fitting a nonlinear curve under a large-angle condition so that the angle measurement range of the interferometer can be expanded.
Owner:CNGC INST NO 206 OF CHINA ARMS IND GRP
Phase noise compensation for interferometric absolute distance measuring
ActiveCN101128717BLow costReduced Line Width RequirementsInterferometersUsing optical meansPhase noiseEngineering
The invention relates to a method for interferometric absolute distance measuring by a frequency modulation electromagnetic radiation on at least one measurable target and for subsequently receiving aretransmitted radiation with a heterodyne mixture, wherein the radiation is guided in a parallel direction via a reference interferometric length. In such a way, a first digitised interferogram of theradiation retransmitted by the target and a second digitised interferogram of the radiation guided on the reference length are obtainable at a reception. According to phase progression data of the se cond interferogram, a virtual interferogram or a phase progression thereof is synthesised and the distance determination is carried out by comparing the progression face data of the first interferogram with the progression face data of the virtual interferogram.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
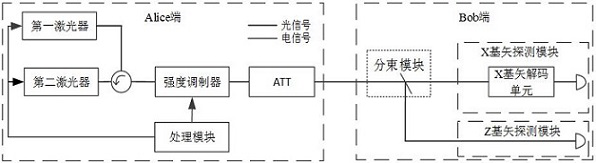
HD-qkd quantum state preparation method, distribution method and device
ActiveCN112511301BReduce in quantityReduce the difficulty of detectionKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The application provides a preparation method, distribution method and device of HD-QKD, wherein in the preparation method of HD-QKD of the present application, when X base vector is selected to prepare a quantum state, only one quantum state |X> is prepared, thus It can be seen that there is only one kind of quantum state prepared by the X base vector of the present application, which is far less than the difficulty of preparing d quantum in the prior art, and the number of photodetectors required is also small, and the number of photodetectors only needs one Therefore, it not only greatly reduces the detection difficulty, but also saves the photodetector and reduces the cost of the equipment. There is only one type of quantum state prepared by the HD-QKD of the present application, so the number of unequal interferometers in the detection module will be greatly reduced, so the error of the arm length difference of the unequal interferometer is easy to control, greatly reducing The manufacturing difficulty of the detection module is reduced, and the volume of the device is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCHUANGWEI NANJING QUANTUM COMM TECH CO LTD
Control method of integrated interferometer
PendingCN105807568ALarge measuring strokeMake a smooth transitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusControl areaComputer science
The invention discloses a control method of an integrated interferometer. The control method comprises 1, arranging at least two interferometers along a first direction, 2, setting control weight of each one of the interferometers, wherein when a work stage or a mask stage moves to a control area of each one of the interferometers, a weight factor is equal to 1, when the work stage or the mask stage moves to a non-control area, the weight factor is equal to 0, and when the work stage or the mask stage moves to a common control area of the two interferometers, the weight factor is a multiple order function, and 3, determining if the interferometer produces light leakage and carrying out dynamic zeroization on the interferometer producing light leakage if the leakage is produced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
A kind of gluing method of solid sagnac interferometer
In order to solve the existing solid sagnac interferometer gluing method, when the large gluing stress in the gluing process causes the deformation of the interferometer reflective surface, the interferometer components cannot be repaired twice, resulting in a decrease in the modulation degree of the interferometer and the adjustment of the gluing process. Complicated technical problems, the present invention proposes a gluing method for a solid sagnac interferometer, by adjusting the coating order of the working surface of the interferometer, and finally cold-coating the internal reflection film, the influence of the gluing process on the internal reflection film can be removed; After curing, the shear amount and orthogonality can be adjusted after the first curing; maintaining a temperature of about 40°C during the second coating can anneal the interferometer prism and eliminate part of the bonding stress; by strictly monitoring the reflection during the bonding process Surface verticality, reduce the rotation and inclination of the two half-pentagonal prisms forming the interferometer, minimize the gluing stress caused by the gluing process, and realize the stress-relief installation and adjustment of the solid sagnac interferometer.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interferometer device and method for producing an interferometer device
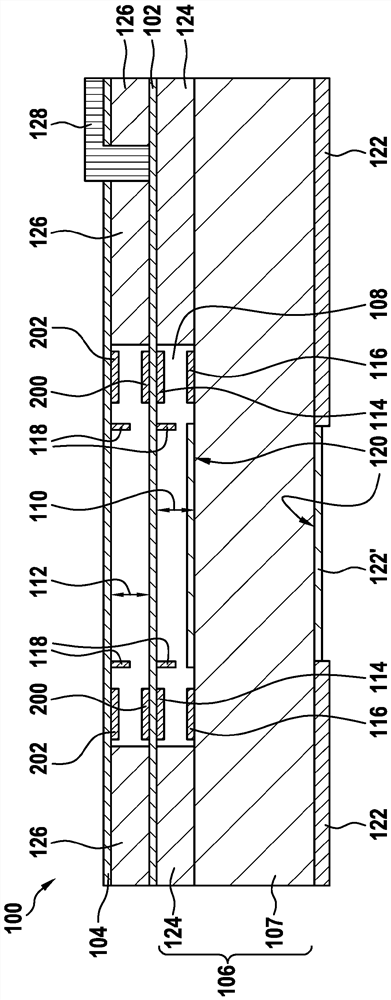
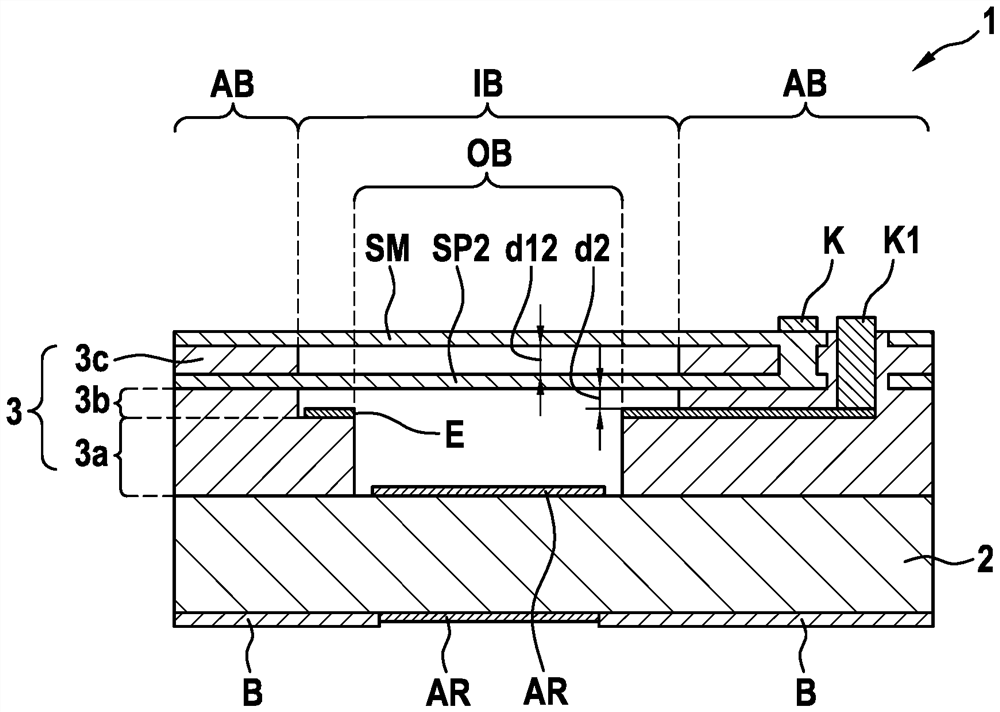
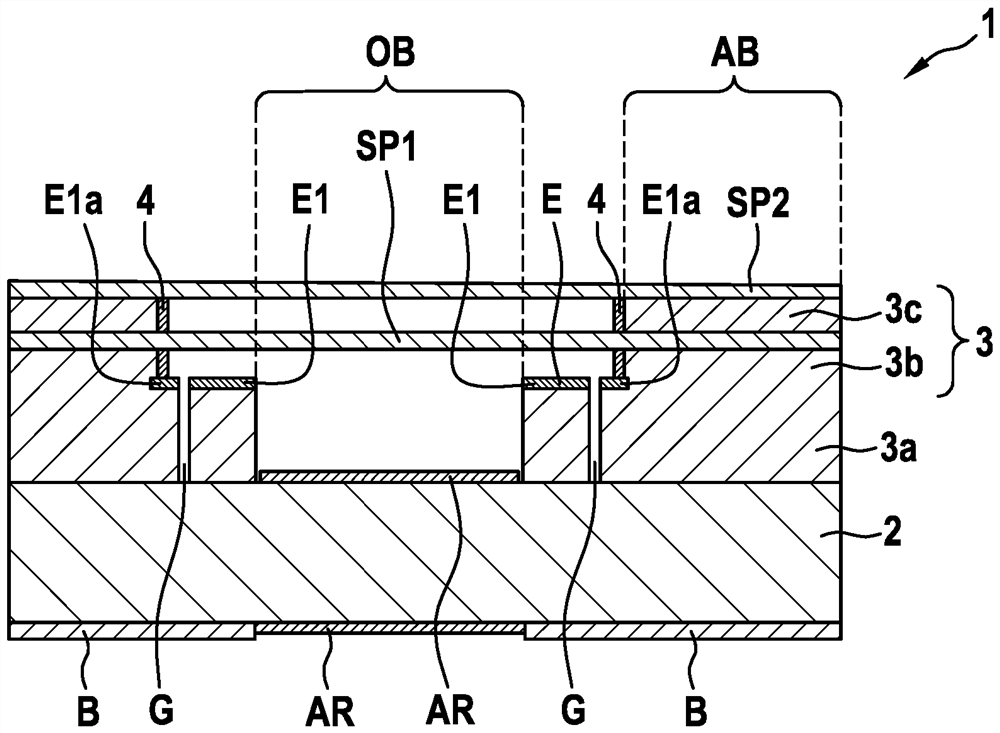
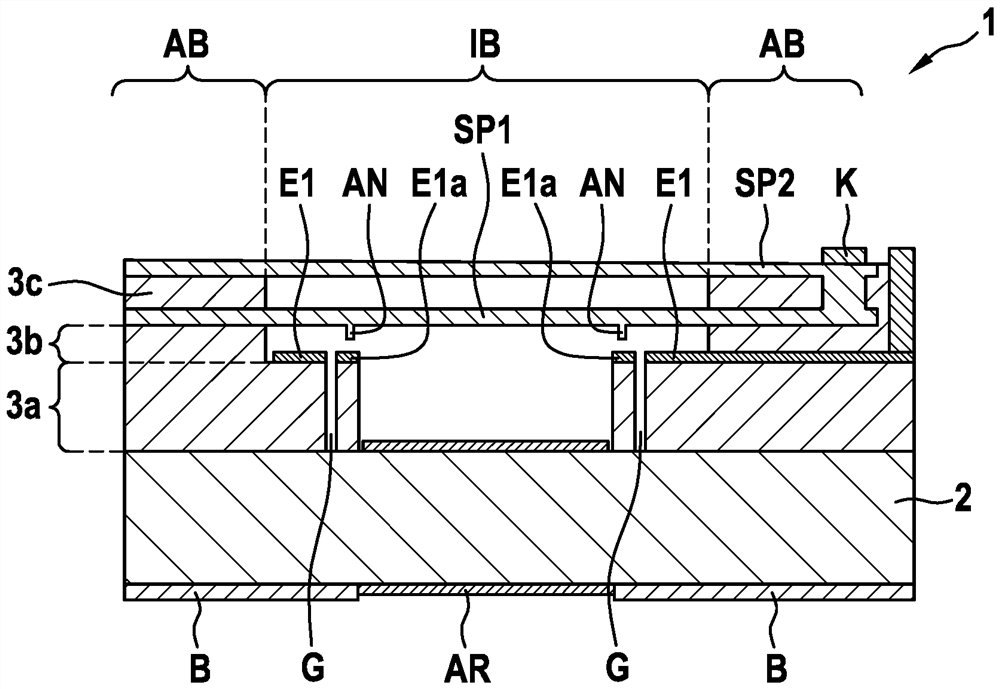
PendingCN113039414AReduce parasitic capacitanceImprove location detectionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationInterferomeMechanical engineering
The invention relates to an interferometer device (1), comprising: a substrate (2); an intermediate layer region (3), which is applied to the substrate (2); a first mirror device (SP1) and a second mirror device (SP2), which are oriented plane-parallel to one another, are spaced apart from one another by a first distance (d12) and are enclosed in or arranged on the intermediate layer region (3), the intermediate layer region (3) being removed below the first mirror device (SP1) and / or below the second mirror device (SP2) in an inner region (IB); and a laterally structured electrode (E), which comprises a first subregion (E1) and at least one second subregion (E2), which is laterally separated from and electrically insulated from the first subregion, which subregions can be connected to different electric potentials, wherein: the electrode (E) is spaced apart from the first or the second mirror device (SP1; SP2) by a second distance (d2); the first subregion (E1) runs in the inner region (IB) and is arranged on the intermediate layer region (3) and the second subregion (E2) runs in an outer region (AB) of the intermediate layer region (3), such that the first mirror device (SP1) and / or the second mirror device (SP2) can be moved electrostatically in the inner region (IB) by means of the first subregion (E1), parallel to the substrate (2), and the first distance (d12) can be varied.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Automatic adjustment method of computer-aided interferometer based on deep learning
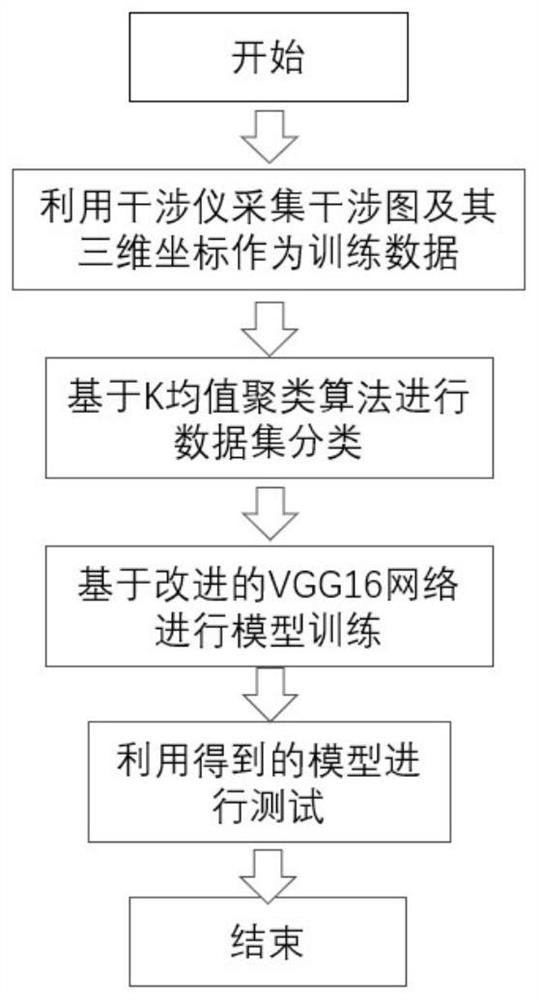
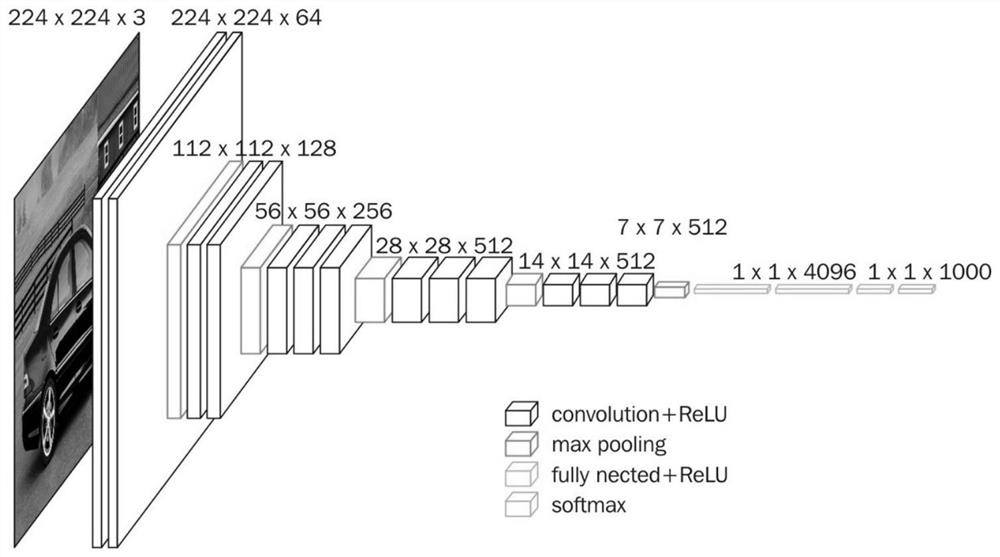
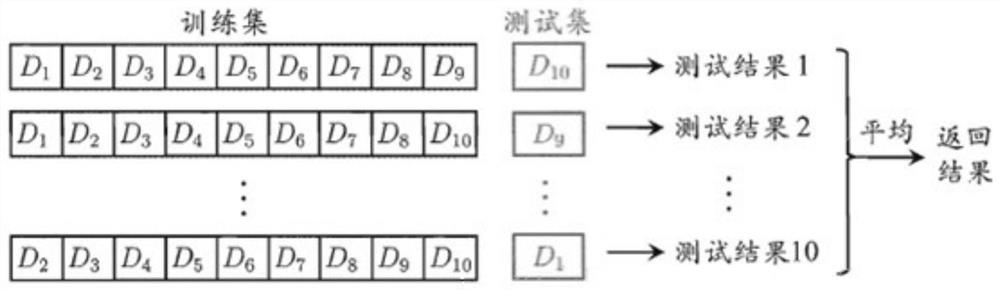
ActiveCN111680741AHigh speedImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses an automatic adjustment method of a computer-aided interferometer based on deep learning. The method comprises steps of collecting an interferogram and three-dimensional coordinates thereof as training data; classifying the expanded training data based on a K-means clustering algorithm to obtain a data set; dividing the data set into a training set and a verification set byadopting a k-fold cross validation method, and training the VGG-16 network model by utilizing the training set and the verification set obtained by each fold; and inputting an interferogram acquiredin real time into the trained VGG-16 network model to obtain the misalignment amount of the interferometer. According to the method, the specific interference pattern deviation value does not need tobe solved; trained network classification data are fully utilized, the coordinates of the position where the interferometer is located are determined by classifying interferograms formed by the interferometer, then the mirror to be measured is controlled to move to the accurate position, the advantages of the deep convolutional network are brought into full play, and the method has the advantagesof being good in robustness and high in accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Interferometer device and method for producing an interferometer device
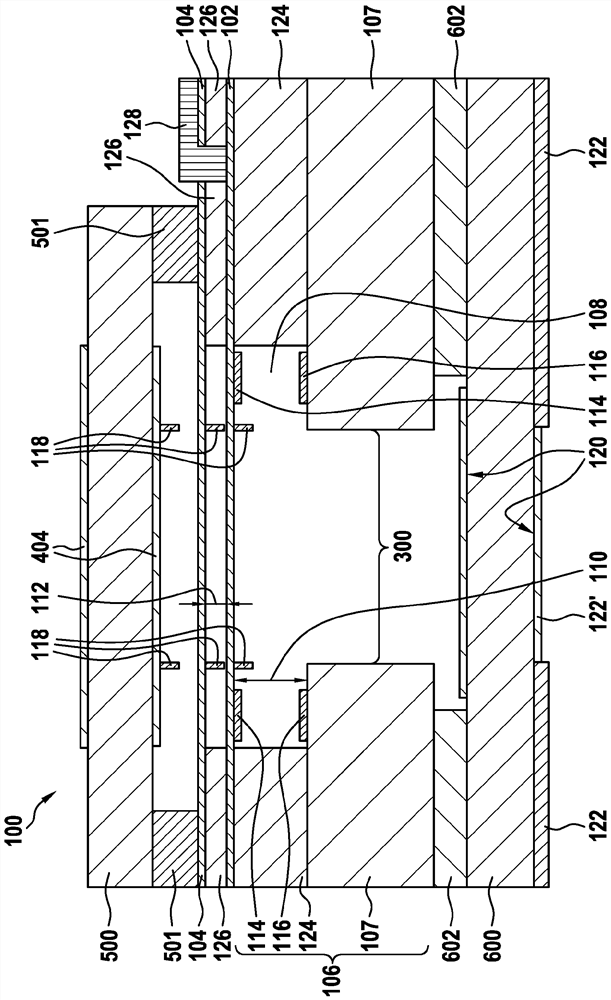
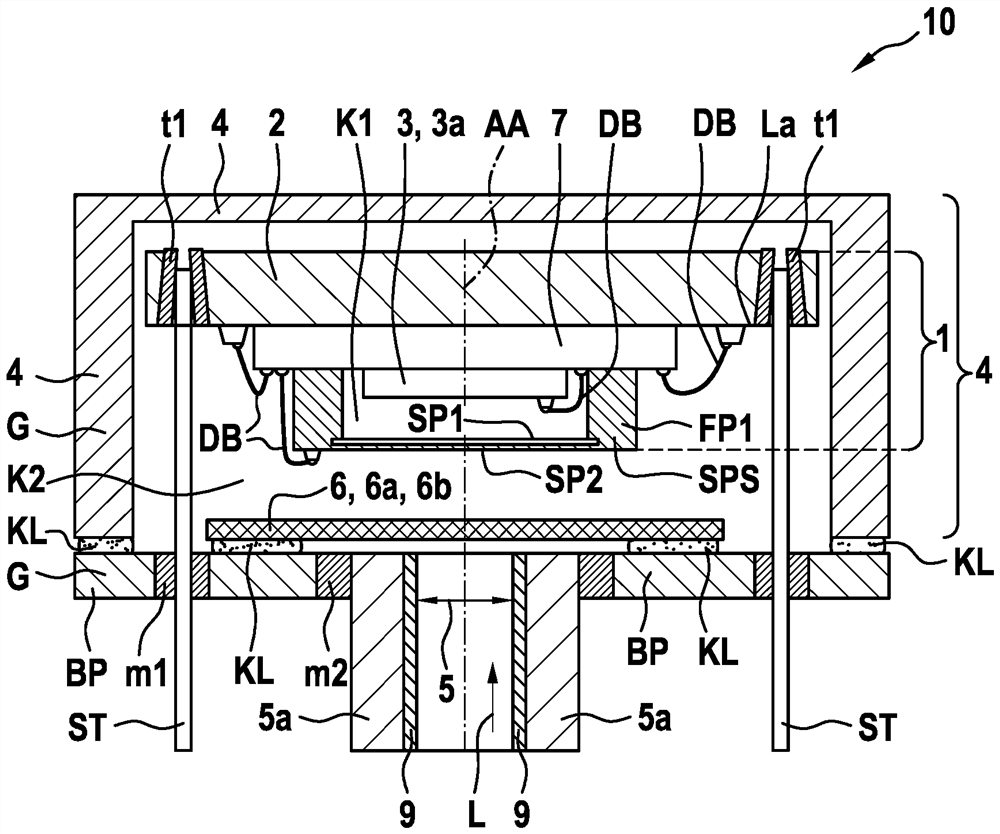
The present invention relates to an interferometer device (10), comprising: an interferometer unit (1), which has a base substrate (2), a Fabry-Perot unit (FPI) and a detector device (3); and a housing (G), which comprises a bottom plate (BP) and a cover structure (4), wherein: the cover structure (4) is arranged on the bottom plate (BP) and encloses a second cavity (K2) between the cover structure (4) and the bottom plate (BP); the bottom plate (BP) or the cover structure (4) comprises an opening (5), which is surrounded by side walls (5a), which extend perpendicularly to a surface of the bottom plate (BP) or the cover structure (4); and the interferometer unit (1) is arranged in the second cavity (K2) and in a light incidence direction (L) through the opening (5) such that the Fabry-Perot unit (FPI) of the interferometer unit (1) faces the opening (5).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com